- 1Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering, College of Engineering, Qatar University, Doha, Qatar
- 2Department of Built Environment, Oslo Metropolitan University, Oslo, Norway
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into structural engineering holds great promise for advancing analysis, design, and maintenance. However, it also raises critical ethical and governance challenges—including bias, lack of transparency, accountability gaps, and equity concerns—which are particularly significant in a discipline where public safety is paramount. This study addresses these issues through eight fictional but realistic case studies that illustrate plausible ethical dilemmas, such as algorithmic bias in predictive models and tensions between AI-generated recommendations and human engineering judgment. In response, the study proposes a structured framework for responsible AI implementation, organized into three key domains: (i) Technical Foundations (focusing on bias mitigation, robust validation, and explainability); (ii) Operational and Governance Considerations (emphasizing industry standards and human-in-the-loop oversight); and (iii) Professional and Societal Responsibilities (advocating for equity, accessibility, and ethical awareness among engineers). The framework offers actionable guidance for engineers, policymakers, and researchers seeking to align AI adoption with ethical principles and regulatory standards. Beyond offering practical tools, the study explores broader theoretical and institutional implications of AI, including risks associated with model drift, the need for lifecycle oversight, and the importance of cultural and geographic adaptability. It also outlines future challenges and opportunities, such as incorporating AI ethics into engineering education and considering the ethical impact of emerging technologies like quantum computing and digital twins. Rather than offering prescriptive answers, the study aims to initiate an essential dialogue on the evolving role of AI in structural engineering, equipping stakeholders to manage its benefits and risks while upholding trust, fairness, and public safety.
1 Literature review
Artificial intelligence (AI) (Sheikh et al., 2023; Xu et al., 2021) is revolutionizing the field of structural engineering by offering powerful tools that enhance traditional methods and introduce innovative approaches (Lagaros and Plevris, 2022; Solorzano and Plevris, 2022b). AI has found applications across a wide range of domains (Mahajan et al., 2024), including enhancements to the Finite Element Method for faster and more accurate simulations (Bolandi et al., 2022; Korzeniowski and Weinberg, 2021; Meethal et al., 2023; Uriarte et al., 2022), surrogate modeling (Liang et al., 2018; Solorzano and Plevris, 2022a; Solorzano and Plevris, 2023; Song and Fu, 2023), structural health monitoring (SHM) (Mondal and Chen, 2022; Plevris and Papazafeiropoulos, 2024) using image processing (Dong and Catbas, 2020; Ehtisham et al., 2024; Ferraris et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2024) and sensor data analysis (Kurian and Liyanapathirana, 2020), and structural optimization (Chamatidis et al., 2023; Solorzano and Plevris, 2020) for achieving efficient, cost-effective and sustainable designs (Lagaros et al., 2008; Plevris et al., 2024). Additionally, AI is being utilized for predictive maintenance (Ghaffari et al., 2024; Scaife, 2024; Ucar et al., 2024), enabling engineers to anticipate and address potential failures before they occur, and load prediction (Zhang et al., 2021), where AI models forecast complex loading scenarios such as wind (Song et al., 2024), earthquake (Hu et al., 2024), and traffic loads (Hussain et al., 2023; Xu, 2024) with greater precision. Other emerging applications include automated design generation using generative algorithms (Liao et al., 2024; Onatayo et al., 2024; Oscar et al., 2023; Ploennigs and Berger, 2024), risk assessment (Wang et al., 2022) and failure prediction through probabilistic AI models (Jia and Wu, 2022), earthquake risk mitigation (Plevris, 2024) and material characterization (Gamil, 2023; Li et al., 2022), where machine learning (ML) aids in predicting material properties and behaviors under various conditions. These advances enable engineers to solve complex problems with improved precision, efficiency, and reliability, marking a transformative shift in the way structures are analyzed, designed, and maintained throughout their lifecycle.
To gain a comprehensive understanding of AI-based methods in structural engineering, we conducted a literature review using the Scopus database. After presenting selected individual examples of AI applications in specific areas of structural engineering in the previous paragraph, our search strategy shifts toward identifying review articles that offer broad perspectives on AI’s role in the field. This approach was adopted to mitigate the fragmentation often encountered in studies focusing on isolated AI applications and to provide a more holistic overview of the discipline. Scopus was the primary database used due to its extensive coverage of engineering literature. Search terms included “artificial intelligence”, “structural engineering”, “machine learning” and “soft computing”. We prioritized peer-reviewed review articles published in reputable journals over the past decade. This timeframe ensures the inclusion of contemporary developments while maintaining relevance.
After establishing a foundational understanding through these review articles, our focus shifted to the ethical considerations surrounding AI adoption in civil and structural engineering, as well as related fields. This involved exploring discussions on governance, transparency, accountability, and fairness in AI-driven engineering applications. Our goal was to identify existing ethical frameworks and guidelines that could be associated with the responsible integration of AI technologies in structural engineering practices. This structured approach allowed us to synthesize current knowledge and identify gaps, thereby informing the development of our approach for ethical AI implementation in structural engineering.
1.1 Review articles on the use of AI in structural engineering
Salehi and Burgueño (2018) review the adoption of emerging AI techniques—ML, pattern recognition, and deep learning (DL)—in structural engineering. These methods improve SHM, damage detection, concrete modeling, and earthquake engineering. The authors highlight the potential for integrating AI with the Internet of Things (IoT) for innovative SHM systems and smart cities. Challenges include data quality, computational efficiency, and method selection, with recommendations for addressing these issues to enhance AI’s impact. Thai (2022) reviews the growing role of ML in structural engineering, emphasizing its potential to address challenges in analyzing nonlinear systems and optimizing performance under extreme conditions. The study outlines core ML techniques, libraries, datasets, and applications, such as structural analysis, health monitoring, fire resistance, and material design. The review serves as a foundational reference for integrating ML into structural engineering.
Focusing on structural wind engineering, the review paper of Mostafa et al. (2022) explores the integration of ML techniques, highlighting their transformative potential in wind load prediction, response analysis, and structural optimization. The study categorizes ML applications into data-driven modeling, aerodynamic shape optimization, and SHM, emphasizing their ability to handle complex, nonlinear interactions inherent in wind engineering. Challenges such as data availability, model interpretability, and computational costs are noted. Recommendations include advancing hybrid models, expanding datasets, and leveraging AI to improve resilience and efficiency in wind-sensitive structural systems.
Tapeh and Naser (2023) present a comprehensive scientometric review of AI, ML, and DL in structural engineering. The study has three objectives: introducing AI techniques relevant to structural engineering, mapping current knowledge through analysis of over 4,000 publications, and reviewing applications in subfields such as earthquake, wind, fire engineering, and SHM. It emphasizes the potential of AI for data-driven solutions in design, monitoring, and optimization while addressing challenges like interpretability, data availability, and adoption barriers. The article by Málaga-Chuquitaype (2022) offers a critical review of ML applications in structural design, exploring its potential to revolutionize traditional approaches. It highlights the integration of ML into conceptual design, optimization, and performance prediction, focusing on its ability to process large datasets and uncover hidden patterns. The authors emphasize challenges, such as data quality, interpretability of models, and integration into existing workflows, while proposing future directions for combining ML with advanced simulation and human-in-the-loop frameworks to enhance design efficiency and innovation.
Harle (2024) reviews advancements in AI within the broader field of civil engineering, emphasizing its transformative potential across domains such as structural design, construction management, geotechnical engineering, transportation, and infrastructure maintenance. AI techniques like ML and genetic algorithms optimize processes, enhance predictions of material behavior, and enable efficient resource management. Applications include soil property estimation, intelligent transportation systems, and defect detection using image analysis. Despite progress, challenges such as data limitations, model reliability, ethical concerns, and interdisciplinary collaboration remain. The study highlights AI’s capacity to improve infrastructure efficiency, safety, and sustainability while proposing directions for future research. The review paper of Chitkeshwar (2024) explores the transformative impact of ML, DL, and AI in structural engineering, highlighting their roles in SHM, optimization, and predictive maintenance. It emphasizes the integration of ML with IoT for real-time monitoring, advancing durability and performance. The study highlights ML-based multi-objective optimization in design, balancing cost and structural integrity, while advocating for algorithm improvements, enhanced data availability, and broader adoption. Challenges and opportunities for revolutionizing structural practices are discussed to inspire further research and application.
The more recent review article of Etim et al. (2024) provides a comprehensive survey of ML applications in structural engineering, emphasizing their transformative potential in modeling, analysis, and design. Key ML techniques are explored for tasks like SHM, damage detection, and material property prediction. The study highlights the ability of ML to address challenges inherent in complex structural systems, offering faster and more accurate solutions compared to traditional methods. The authors identify current limitations, such as data scarcity and model interpretability, and propose strategies for enhancing ML adoption, including better data collection and integration with physics-based models.
1.2 Ethical considerations surrounding AI adoption in structural engineering
As the adoption of AI grows, it brings with it a dual potential: immense benefits alongside ethical risks (Trotta et al., 2023). On the one hand, AI holds the promise of increasing efficiency, reducing human error, and uncovering new design possibilities (Stahl, 2021). On the other hand, its application in critical areas such as structural safety and resilience raises pressing ethical concerns (Dhirani et al., 2023). Issues such as biased algorithms, lack of transparency in AI decision-making, overreliance on automated systems, and the potential for misuse of technology must be carefully addressed. These concerns are particularly significant in structural engineering, where the stakes are high, and decisions directly impact public safety and infrastructure reliability.
While ethics in AI is widely acknowledged as a critically important subject and has been extensively studied across various disciplines (Safdar et al., 2020), there remains a significant gap in research addressing the ethical considerations specific to the application of AI-based methods in structural engineering, as well as in the broader fields of civil engineering and construction. Liang et al. (2024) review ethical considerations surrounding AI and robotics in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry, focusing on issues such as job loss, data privacy, safety, and liability. Through a systematic analysis of recent literature, they identify nine ethical challenges and thirteen research topics tied to these concerns. The authors emphasize the need for greater stakeholder awareness and propose seven future research directions to address gaps, aiming to balance efficiency with ethical responsibility in integrating AI and robotics within AEC practices. Wang (2024) examines the ethical implications of AI in smart city development using actor-network theory. The study analyzes AI applications in smart transportation, water management, healthcare, grids, and city evaluation standards, focusing on interactions among governments, technology developers, and residents. Key challenges include digital ethics, machine ethics, and relational alienation. The article advocates transparent, safe, and accountable AI systems, recognition of nonhuman actors, and the establishment of laws and ethical guidelines to ensure sustainable and inclusive smart city development.
Emaminejad et al. (2022) analyze 490 peer-reviewed articles to explore the role of trust in AI applications within the AEC industry. Their study identifies key sociotechnical factors crucial for building trust, such as system reliability, explainability, and user acceptance, while situating these elements within the distinct characteristics of AEC projects and processes. The authors highlight a significant gap in addressing trust-specific needs within the AEC domain and stress the necessity of aligning AI solutions with both the technical and psychological expectations of industry stakeholders. In a subsequent systematic review (Emaminejad and Akhavian, 2022), the same researchers examine trust in AI and robotics applications in the AEC industry by analyzing 584 publications. This review identifies critical trust dimensions—explainability, reliability, robustness, performance, and safety—and their relevance to current AEC applications. The study underscores the lack of a systematic approach to addressing these trust factors and proposes future research directions aimed at enhancing trustworthiness. The authors emphasize that fostering trust is essential for user acceptance and the successful integration of AI and robotics into AEC workflows.
2 Methodology, objectives and structure of the study
The present study employs an interdisciplinary approach to explore the ethical challenges associated with AI applications in structural engineering and propose strategies for addressing these issues effectively. First, a literature review was conducted to examine existing AI methodologies and their applications in structural engineering, alongside the ethical considerations highlighted in prior research. This review identified key ethical concerns, such as bias, transparency, accountability, and equity, and assessed their implications for engineering workflows. Although the literature provided valuable insights, it became evident that theoretical discussions alone could not fully capture the practical complexities of these ethical challenges.
To bridge this gap, the study developed eight hypothetical case studies designed to illustrate real-world ethical dilemmas that arise in AI applications both today and mainly in the future. These case studies cover a range of critical scenarios, including bias in seismic risk prediction models, accountability in AI-driven SHM, and conflicts between AI-generated recommendations and engineering judgment. Each case study was designed to reflect realistic challenges, emphasizing the high-stakes nature of ethical lapses in structural engineering and their impact on safety, decision-making, and public trust.
Insights from the literature review and case study analysis were synthesized using an iterative approach to develop a structured framework for ethical AI implementation. The literature review provided a view of AI applications in structural engineering and ethical concerns documented in previous studies, while the case studies offered practical scenarios where ethical dilemmas could arise. This dual perspective allowed us to identify recurring challenges and patterns in AI ethics for structural engineering. To ensure that the proposed framework was comprehensive, we drew upon existing AI ethics frameworks from related fields, adapting them to the specific requirements of structural engineering. Additionally, we considered discussions in engineering ethics literature and AI governance frameworks to ensure alignment with existing ethical principles. The resulting framework is structured into three domains: (i) Technical Foundations; (ii) Operational and Governance Frameworks; and (iii) Professional and Societal Responsibilities, each of which encompasses key pillars addressing specific ethical concerns, such as bias mitigation, transparency, and human oversight. The framework does not claim to offer definitive solutions, but it serves as a structured guide to navigating ethical AI adoption in structural engineering. The study also sets out to achieve specific objectives:
1. Identify Ethical Challenges: Examine ethical issues such as bias, transparency, accountability, and reliability that arise in AI-driven structural engineering workflows.
2. Develop Practical Strategies: Formulate actionable approaches for engineers, researchers, and policymakers to effectively address these ethical challenges, ensuring responsible and effective AI deployment.
3. Promote Ethical Practices: Encourage the integration of ethical standards to build trust, ensure safety, and facilitate the seamless incorporation of AI into structural engineering practices.
The methodological structure of the study is presented in Figure 1. Rather than providing definitive answers to the complex and evolving challenges associated with AI adoption in structural engineering, this paper aims to initiate a broader discussion on the risks, uncertainties, and governance issues that will shape the future of AI applications in the field. By integrating technical considerations with ethical foresight, the study underscores the necessity of an interdisciplinary approach to responsible AI implementation. The proposed measures are not presented as absolute solutions, but as guiding principles to help engineers, researchers, and policymakers navigate the ethical landscape of AI adoption. As AI technologies continue to develop, new challenges and unforeseen risks will emerge, requiring continuous reflection, adaptation, and proactive engagement from all stakeholders.
To the best of our knowledge, this study represents the first attempt in the literature to directly address the ethical concerns of AI in structural engineering. Although there has been prior work on AI ethics in a general context and numerous studies on AI applications in structural engineering, no previous research has specifically examined the intersection of AI ethics and structural engineering. Given that this is an emerging and largely unexplored topic, we aim to lay the groundwork for future discussions and research by identifying key ethical challenges and proposing initial directions for responsible AI integration in this field.
The structure of the paper is as follows: Section 1 presents the Literature Review, providing an overview of AI applications in structural engineering and identifying existing gaps in ethical considerations. Section 2 details the Methodology, Objectives, and Structure of the Paper, explaining the research approach, the rationale behind the case studies, and how the ethical AI framework was developed. Section 3 discusses Ethical Challenges in AI Applications, examining key concerns such as bias, transparency, accountability, and equity. Section 4 presents Case Studies of Ethical Dilemmas, illustrating real-world implications of these ethical challenges through hypothetical yet plausible scenarios. Section 5 introduces The Proposed Framework and its Key Pillars, outlining a structured approach to ensuring responsible AI deployment in structural engineering. Section 6 explores Future Directions, focusing on interdisciplinary research opportunities, policy development, and advancements in AI ethics relevant to the field. Finally, Section 7 provides the Conclusions, summarizing the study’s contributions and emphasizing the importance of continued engagement with ethical AI governance in structural engineering.
3 Ethical challenges in AI applications
The integration of AI into structural engineering will open new avenues for innovation, enabling enhanced analysis, design, and monitoring capabilities (Salehi and Burgueño, 2018). However, these advancements also bring significant ethical challenges that must be addressed to ensure responsible and equitable use of AI technologies (Sadek et al., 2024). Ethical decision-making in AI is not simply about fulfilling a set of requirements but about navigating complex, competing principles that often involve careful balancing and trade-offs. In structural engineering, where decisions directly impact public safety, equity, and sustainability, these challenges become even more critical.
AI systems inherently carry limitations and biases, which, if unaddressed, can lead to inequitable or unsafe outcomes. Moreover, the ethical implications of AI applications in structural engineering often require reconciling competing values such as safety vs cost, efficiency vs equity, and innovation vs reliability. These conflicts cannot always be simultaneously satisfied, and decision-makers must evaluate the trade-offs in the context of the engineering project at hand. Frameworks like Beauchamp’s and Childress’ principles of applied ethics (Page 2012)—which include the values of beneficence, non-maleficence, justice and respect for autonomy—offer valuable guidance in addressing such dilemmas.
Although the ethical challenges outlined here—such as bias, transparency, accountability, and equity—are universal across AI applications, Section 4 will provide specific examples and case studies within the context of structural engineering. These fictional scenarios highlight the unique complexities and potential consequences of ethical lapses in this field, where decisions affect technical outcomes and also societal welfare.
The following subsections will go deeper into these ethical challenges, examining issues such as overreliance on AI, data privacy, and the use of experimental technologies. This analysis underscores the importance of establishing frameworks and strategies that ensure the responsible, equitable, and safe application of AI, prioritizing safety, fairness, and transparency in the evolving landscape of structural engineering.
3.1 Bias and fairness
AI models depend heavily on the quality and representativeness of the data they are trained on. In structural engineering, biased datasets can lead to inaccurate predictions and, ultimately, unsafe or inequitable outcomes (Ntoutsi et al., 2020). For example, an ML model trained on data from specific geographic regions or structural types may fail to generalize to other contexts, potentially underestimating vulnerabilities in less-represented scenarios. This can result in unsafe designs, inequities in resource allocation, or prioritization of projects that do not align with broader societal needs. Some may argue that transfer learning (Xing et al., 2024), often employed to enhance AI models using pre-trained knowledge, could offer a solution. However, it may also inherit the same issues. If the original pre-trained model was built on biased or unrepresentative data, those biases can be transferred to the new task. Ensuring fairness requires thorough dataset auditing, inclusion of diverse data sources, and mechanisms to detect and mitigate bias during model training and deployment (Varsha, 2023). It should be noted that biases in AI models will lead to technical inaccuracies as well as compound systemic inequities, as discussed in Section 3.9.
3.2 Transparency and explainability
Explainability refers to the ability of an AI system to provide clear, understandable insights into how it reaches its decisions (Hassija et al., 2024). This concept is particularly crucial in structural engineering, where AI models often influence critical decisions involving public safety. Many AI systems, especially DL algorithms, operate as “black boxes”, offering limited transparency about their internal processes and decision-making pathways (Dobson, 2023).
In structural design and safety assessments, this lack of explainability poses significant challenges (Ali et al., 2023; Hassija et al., 2024). Engineers and stakeholders must be able to understand and evaluate how AI systems arrive at their conclusions, particularly in high-stakes scenarios involving life safety (Balasubramaniam et al., 2023). For instance, if an AI model predicts a reduced risk of structural failure without offering clear reasoning, it can lead to misplaced trust or skepticism. In structural engineering, AI models influencing the design of load-bearing structures or safety assessments must provide clear reasoning to ensure that engineers can validate and trust their outputs, especially when these models inform life-safety decisions.
Developing explainable AI models is crucial for fostering trust, supporting validation processes, and allowing engineers to justify decisions based on AI-generated outputs. These models enhance transparency, making complex algorithms more interpretable and aligning AI-driven insights with accountable engineering practices (Baum et al., 2022).
3.3 Reliability and accuracy
The reliability and accuracy of any AI model are fundamental to its effective deployment, as errors can undermine trust and lead to significant consequences (Scorzato, 2024). This is particularly critical in structural engineering, where inaccuracies can result in major failures or catastrophic outcomes. AI-driven systems may underestimate structural vulnerabilities, overlook damage, or produce overly optimistic predictions during optimization processes. These errors often stem from issues such as overfitting, inadequate training data, or unforeseen operational conditions.
In structural engineering, AI-driven models that optimize structural design or predict maintenance needs must be highly accurate, as errors, such as overlooking critical damage in bridges or underestimating load-bearing limits in skyscrapers, can lead to catastrophic failures, financial losses, and even loss of life in high-stakes scenarios. To mitigate these risks, AI models in structural engineering must undergo rigorous validation and robustness testing (Myllyaho et al., 2021). Additionally, periodic retraining is essential to ensure models remain accurate and adaptable to evolving conditions and environments, safeguarding both public safety and engineering integrity. Although reliability is critical for established AI systems, experimental technologies pose additional ethical concerns, as discussed in Section 3.8.
3.4 Accountability
Accountability refers to the obligation to accept responsibility for actions, decisions, or outcomes. In the context of AI applications in structural engineering, accountability ensures that stakeholders are held answerable for the systems they develop, implement, or use. This principle becomes especially critical when AI-driven designs or recommendations result in errors or failures (Novelli et al., 2024).
Determining accountability in such cases can be highly complex (Buiten et al., 2023). In structural engineering, this challenge arises when an AI system provides recommendations that contribute to a structural failure, such as underestimating a critical load (e.g., wind or earthquake forces) on a bridge. It is crucial to determine whether responsibility falls on the engineers utilizing the AI system, the developers who designed the model, or the organizations that neglected to properly validate its predictions.
Clear accountability frameworks are crucial for ensuring that AI adoption in structural engineering remains transparent and that stakeholders can be held responsible for errors that compromise safety. These frameworks should clearly define roles and responsibilities across the AI lifecycle, from development to deployment and application. This will enhance trust in AI systems and promote their ethical and responsible use.
3.5 Data privacy and security
AI-driven systems in structural engineering increasingly depend on extensive data collection, particularly for real-time structural health monitoring and predictive maintenance (Keshmiry et al., 2024). These systems generate and process vast amounts of data related to infrastructure conditions, including stress levels, material degradation, and environmental impacts. Such data, while essential for enhancing safety and performance, may also contain highly sensitive information about vulnerabilities in critical structures such as bridges, dams, and tunnels. If compromised, this information could pose significant security risks, including the potential for malicious exploitation of structural weaknesses.
Ensuring the protection of this data is paramount, especially in high-risk sectors such as transportation, energy, and public safety, where breaches could lead to serious consequences. Unauthorized access to infrastructure data could facilitate cyberattacks, sabotage, or misuse of critical engineering insights. To mitigate these risks, engineers and organizations must implement robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, multi-factor authentication, and secure cloud-based or on-premise data storage solutions.
Beyond technical protections, compliance with data protection regulations is essential. Frameworks such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) of the EU (Voigt and von dem Bussche, 2024) and other regional standards impose strict requirements for data handling, storage, and sharing. Organizations must establish clear data governance policies, ensuring transparency in data usage while maintaining stakeholder trust. Ethical AI deployment in structural engineering necessitates advanced analytical capabilities and also strong commitments to data privacy, cybersecurity, and regulatory adherence, ensuring that AI-driven insights enhance safety without introducing new security vulnerabilities.
3.6 Overreliance on AI systems
Overreliance on AI systems introduces significant ethical concerns, particularly in high-stakes fields like structural engineering (Klingbeil et al., 2024). Engineers and decision-makers may place undue trust in AI-generated recommendations, neglecting to account for the inherent limitations of the models or failing to critically evaluate their outputs. In structural engineering, overreliance on AI could lead to overlooking site-specific conditions, such as soil type, local climate, or unexpected structural behavior under extreme loads, which can only be adequately evaluated through human expertise. Such overdependence can result in decisions that lack sufficient human judgment, potentially leading to unsafe designs or failure to consider critical factors vital to structural integrity and public safety.
Addressing overreliance involves distinguishing between adequate human judgment and dataset auditing, as discussed earlier in Section 3.1. Dataset auditing is a proactive step focused on building reliable AI models by identifying and mitigating biases in training data, ensuring the quality and representativeness of datasets before the AI model is deployed. In contrast, adequate human judgment serves as a reactive safeguard during the application phase, ensuring that AI outputs are critically reviewed, contextualized, and supplemented with domain expertise to avoid blind trust in automated recommendations.
A well-balanced relationship between AI-driven insights and engineering judgment is critical to ensure that final decisions in areas such as building safety and infrastructure resilience remain well-grounded. Maintaining this equilibrium involves fostering a collaborative relationship between AI systems and human decision-makers, where engineers use AI insights as a starting point but apply their expertise to validate and refine final decisions. This approach minimizes risks while ensuring that AI technologies contribute meaningfully to safe and effective structural engineering practices.
3.7 Misaligned objectives and optimization trade-offs
AI models are typically designed to optimize specific objectives, such as minimizing costs, maximizing efficiency, or enhancing sustainability. However, these objectives can sometimes conflict with broader societal goals, such as promoting equity, ensuring resilience, or maintaining long-term safety (Dung, 2023; Hristova et al., 2024). In structural engineering, optimization models should prioritize long-term safety and sustainability over short-term gains. For example, AI models used for structural optimization should not solely focus on minimizing costs or maximizing efficiency, especially when these objectives may compromise the integrity or resilience of a structure. Reducing material usage in a high-rise building to minimize costs, for instance, may undermine its seismic resilience, posing a safety risk in the event of an earthquake.
Misalignments between AI system objectives and the core responsibilities of engineering pose a significant ethical challenge. In infrastructure projects, where safety, equity, and sustainability are paramount, AI-driven optimization must not prioritize cost efficiency at their expense. However, ensuring AI aligns with these values is highly complex, as ethical principles cannot be easily quantified or translated into mathematical objective functions. While humans intuitively balance safety and long-term impact, AI systems rely on explicit optimization criteria, making it difficult to encode concepts like equity, resilience, or societal welfare in a way machines can process. This challenge underscores the need for multi-objective optimization, ethical constraints, and human oversight to ensure AI-driven decisions uphold public welfare. Even with safeguards, bridging the gap between ethical reasoning and AI logic remains an ongoing challenge.
3.8 Experimental AI technologies
The deployment of experimental or untested AI technologies in structural engineering presents critical ethical challenges. Unlike established systems, these emerging technologies often lack the rigorous validation necessary to ensure safety and reliability. Without adequate testing, they can generate inaccurate predictions or experience system failures, potentially jeopardizing public safety and undermining trust. For example, emerging AI technologies in structural engineering, such as predictive maintenance systems or generative design models, must undergo rigorous validation before deployment in high-risk scenarios. The consequences of faulty AI predictions in critical infrastructure could include building collapse or catastrophic damage to bridges.
High-stakes projects that prioritize innovation over thorough testing risk flawed designs or unforeseen hazards, especially when unique site-specific conditions are not fully accounted for. To address these concerns, organizations should adopt a precautionary approach, which includes phased implementation through pilot testing, robust risk assessments, and iterative validation to identify and mitigate potential issues before full deployment. Collaboration between AI developers and structural engineers is essential to ensure that experimental technologies are both reliable and safe, aligning innovative solutions with the safety and reliability standards expected in structural engineering. For established AI systems, ensuring reliability through rigorous validation and periodic retraining, as discussed in Section 3.3, is equally important.
3.9 Equity and accessibility in AI deployment
AI deployment often depends on financial and technical resources, which can create disparities where wealthier regions gain greater benefits while underserved areas are left behind. This raises ethical concerns about the fair distribution of AI advantages, particularly in structural engineering, where unequal access to AI technologies can deepen disparities in infrastructure development and safety across regions. For example, AI deployment in structural engineering should address the needs of underserved communities, ensuring that rural or economically disadvantaged regions benefit from the safety improvements AI can offer in infrastructure maintenance and disaster resilience.
Equity in deployment also requires tackling technical biases in data and algorithms, as highlighted in Section 3.1. Biased models can perpetuate disadvantages for marginalized communities, amplifying existing inequalities. Ensuring that AI systems are accessible and fair in their application—such as providing equal access to AI-driven structural monitoring systems—is essential to prevent widening gaps between well-resourced and underserved communities. Achieving this involves conducting thorough dataset audits, employing bias mitigation techniques, and incorporating diverse data sources. By addressing both systemic and technical barriers, AI technologies can advance safety and development equitably across all regions.
3.10 Data ownership and consent
In structural engineering, data ownership issues may arise when infrastructure data, collected through SHM systems, is owned by private entities. Ethical concerns regarding data ownership and consent (Beauchamp, 2011) are particularly relevant when monitoring systems are implemented in privately owned structures. Clear guidelines on consent and data usage must be established to ensure that sensitive information, such as weaknesses in private buildings or public infrastructure, is used ethically and in compliance with legal standards (Andreotta et al., 2022).
Addressing these concerns is especially important when AI is applied to private-sector infrastructure projects, where data access and usage might impact stakeholders’ privacy and security. It is essential to ensure that stakeholders are informed about the data collection process, how the data will be used, and their rights to consent or opt-out, thus safeguarding privacy while maintaining transparency and accountability in AI applications.
4 Case studies of ethical dilemmas
The integration of AI into structural engineering workflows introduces complex ethical challenges that demand careful examination. To illustrate these challenges and their potential real-world implications, this section presents eight hypothetical case studies, each addressing a key ethical dilemma associated with AI applications in the field.
Although fictional, the case studies are designed to be both plausible and grounded in emerging trends. They were developed based on several guiding criteria: (i) relevance to the specific ethical concerns identified in the literature review, such as bias, transparency, accountability, and equity; (ii) plausibility based on current and near-future AI capabilities in structural and civil engineering; (iii) diversity across application domains—including design, monitoring, retrofitting, and disaster response—to capture a range of real-world contexts; and (iv) inspiration from analogous precedents, including documented dilemmas and risk patterns observed in related fields such as healthcare, transportation, and smart infrastructure.
These case studies are not modeled on actual incidents but are forward-looking projections that reflect likely scenarios as AI becomes more integrated into structural engineering practice. This speculative yet informed approach allows for exploration of issues that are not yet fully visible in the field due to AI’s still-limited mainstream adoption. By focusing on realistic dilemmas that could plausibly arise, the case studies provide a conceptual testing ground for the ethical framework developed in this study.
To provide an overview of the scenarios and their ethical significance, Table 1 summarizes each case study alongside its primary ethical issue and the corresponding pillars of the proposed framework. This mapping highlights how the fictional dilemmas inform and support the structure of the ethical framework developed in the study.

Table 1. Overview of hypothetical case studies, key ethical challenges, and corresponding pillars of the ethical AI framework for structural engineering.
Following this summary, the detailed case studies are presented individually. Each scenario explores how specific ethical failures—if unaddressed—could compromise safety, equity, and public trust in structural engineering applications of AI. These examples underscore the importance of anticipating and addressing ethical concerns as AI technologies continue to evolve and permeate engineering practice.
4.1 Case study 1: bias in seismic risk prediction models
A city, located in a seismically active region, implemented an AI-based seismic risk prediction system to prioritize retrofitting efforts for its aging infrastructure. The system was trained on a dataset that predominantly featured historical earthquake data and structural information from urban high-rise buildings in the city center. This dataset excluded significant portions of the city’s outskirts, where rural communities and critical infrastructure, such as bridges and small hospitals, are located.
When the AI system was deployed, it prioritized retrofitting urban high-rise buildings, deeming them most at risk based on the training data. However, during a moderate earthquake, a bridge connecting two rural areas and a small hospital on the outskirts suffered severe damage, while the retrofitted urban buildings remained largely unaffected. A post-disaster review revealed that the AI system had underestimated the risks for rural structures because they were poorly represented in the training data. This oversight left vulnerable populations with inadequate protection and disrupted critical access routes, compounding the disaster’s impact.
This case presents several ethical concerns related to bias, fairness, and justice. The decision to prioritize urban structures based on a biased dataset highlights the competing principles of fairness and beneficence (promoting wellbeing). Justice, according to Beauchamp’s principles (Page, 2012), would advocate for a more equitable allocation of resources that reflects the needs of vulnerable populations in underserved areas. Prioritizing the retrofitting of urban areas over rural communities with critical infrastructure violated the principle of justice, as it failed to address the unequal vulnerability of rural residents.
Furthermore, from a utilitarian perspective, the system’s prioritization of high-value urban areas could be seen as an attempt to maximize benefits. However, the lack of inclusivity in the training data ultimately undermined the greatest good for the greatest number, as it failed to account for the potential catastrophic consequences for rural communities. The principle of non-maleficence (avoiding harm) (Al-Bar and Chamsi-Pasha, 2015) would argue that the failure to protect rural areas from seismic risks resulted in unnecessary harm, exacerbating the disaster’s impact.
Additionally, the lack of oversight in decision-making—relying on the AI’s outputs without questioning the representativeness of the training data—demonstrates the need for greater human judgment. The deontological ethics framework (D’Alessandro, 2024) would emphasize the duty of decision-makers to ensure the fairness and accuracy of the system’s outputs, ensuring that vulnerable populations are not neglected in critical decision-making.
This scenario underscores the importance of ensuring fairness and inclusivity in AI training datasets. Beauchamp’s principle of justice demands that AI systems be designed to reflect the diversity of structural types and geographical contexts, ensuring equitable resource distribution. To address such issues, cities must incorporate diverse data sources and continuously update the AI model to reflect these factors. Mechanisms to audit datasets for bias and implement explainable AI are also essential to prevent similar outcomes in the future, ensuring the responsible and ethical use of AI in critical infrastructure planning.
4.2 Case study 2: accountability in AI-driven structural health monitoring
The deployment of AI systems for Structural Health Monitoring (SHM) introduces significant accountability challenges, particularly when failures result from errors in system performance or recommendations. Consider an AI system monitoring a bridge for structural weaknesses by analyzing real-time sensor data and historical maintenance records. If the system fails to detect critical defects in support beams due to an incomplete or biased training dataset, a catastrophic failure could occur, leading to severe damage and potential loss of life. In such a scenario, determining accountability becomes complex: Should responsibility fall on the engineers who relied on the AI, the developers who designed the system, the organization that failed to validate its accuracy, or the state agency that approved its use? This example underscores the need for rigorous validation, continuous monitoring, and clear accountability structures in AI-driven SHM applications, especially when public safety is at stake.
In another scenario, an AI system successfully detects structural weaknesses in a bridge, identifying signs of fatigue in key load-bearing components. However, it misinterprets the severity of the issue, recommending superficial repairs instead of addressing the underlying structural defects. Engineers, relying on the AI’s assessment, implement the suggested measures, only for the bridge to eventually collapse due to the unresolved weaknesses. This raises a deeper accountability dilemma: Should responsibility fall on the engineers for not critically evaluating the AI’s recommendations, the developers for designing a flawed decision-making algorithm, or the organization for deploying the system without proper human oversight safeguards? Unlike traditional engineering workflows, AI introduces a non-human actor into the decision-making process, complicating conventional notions of responsibility and professional liability.
These scenarios highlight the importance of ensuring that AI systems provide clear, interpretable outputs, allowing engineers to make informed decisions. To address these concerns, AI systems for SHM must undergo extensive testing, incorporate mechanisms for explainable outputs, and include robust human oversight protocols.
Furthermore, emerging regulatory frameworks, such as the European Union’s Artificial Intelligence Act (AI Act) (Cancela-Outeda, 2024; Covelo de Abreu, 2024), propose structured approaches to accountability in AI applications. The AI Act classifies AI systems based on risk levels and mandates specific requirements for high-risk systems, including those used in critical infrastructure like bridges. It emphasizes the need for transparency, human oversight, and clear delineation of responsibilities among AI providers, deployers, and users. In the context of structural engineering, adopting such frameworks can support shared accountability models where engineers retain ultimate decision-making authority, while developers and institutions are held responsible for system accuracy, validation, and ethical design. Establishing clear accountability frameworks is essential to ensure the responsible and ethical use of AI in structural engineering.
4.3 Case study 3: data privacy breaches in structural health monitoring
A city implemented an AI-powered SHM system to enhance the safety and reliability of its infrastructure. The system continuously collected and analyzed data from critical structures, such as bridges and tunnels, using a network of IoT sensors. This data included real-time measurements of structural strain, vibrations, temperature variations, and usage patterns, which were stored in a central database accessible to authorized personnel for analysis and maintenance planning.
Despite the system’s sophisticated functionality, the database was not adequately secured. A vulnerability in the system’s network allowed a malicious actor to gain unauthorized access to the data. The attacker extracted sensitive information about a major suspension bridge’s structural vulnerability, including stress points and areas flagged for urgent maintenance. This information was subsequently misused for financial and criminal purposes. The attacker sold the data to an organized group, which used it to exploit the vulnerabilities during a critical moment, causing partial structural damage and widespread panic.
While the bridge did not completely collapse, the incident forced the authorities to shut it down for emergency inspections and repairs, leading to significant economic losses, disruptions to transportation, and diminished public trust in the city’s infrastructure management. This scenario highlights significant risks and ethical concerns: (i) The stolen data provided detailed insights into the bridge’s weaknesses, which were exploited to cause damage. This underscores the danger of sensitive infrastructure data falling into the wrong hands; (ii) The misuse of SHM data violated the fundamental principle of confidentiality, raising questions about the ethical responsibility of organizations to safeguard critical infrastructure information; (iii) The bridge closure resulted in significant economic losses for businesses relying on the transportation network and caused frustration among commuters, highlighting the cascading effects of a data breach; (iv) The lack of robust security measures and oversight raised ethical questions about who should be held accountable—the system developers for inadequate cybersecurity, the city for failing to enforce proper data protection protocols, or the engineers who managed the system without addressing potential vulnerabilities.
This case study emphasizes the importance of addressing data privacy in SHM systems through robust security protocols, access control mechanisms and data minimization. Through prioritizing cybersecurity and ethical considerations, SHM systems can continue to provide valuable insights without exposing critical infrastructure to undue risks.
4.4 Case study 4: organizational pressures vs engineering judgment in high-rise design
A construction firm in New City implemented an advanced AI system to optimize the structural design of a high-rise residential building. The AI recommended reducing the reinforcement steel in the building’s core structure to cut costs, asserting that the reduced reinforcement still satisfied basic safety margins under normal load conditions. The decision, derived from an AI trained on extensive datasets, was presented as a reliable and efficient solution. However, Alex, a senior structural engineer with extensive experience, raised concerns about the recommendation.
While the design complied with safety codes, Alex argued that the AI’s recommendation might compromise the building’s robustness during rare but critical events, such as seismic activity or unexpected loading scenarios. He pointed out that the AI had likely overlooked site-specific factors, including unique soil conditions and the building’s coastal location, which exposed it to high wind loads. These factors were crucial for the building’s long-term stability and safety.
At the same time, the AI’s recommendation presented a valid ethical consideration—cost reduction. The project management team, constrained by deadlines and budgets, insisted on implementing the AI’s design. The system’s data-driven analysis promised significant cost savings and more efficient use of resources. They argued that cutting costs could make the project more financially viable, benefiting both the firm and its clients, potentially making housing more affordable in an economically challenging environment. However, this pushed the boundaries of ethical trade-offs between financial considerations and safety.
Despite Alex’s objections, the team pressured him to approve the plan, citing the AI’s efficiency and its compliance with safety codes as justifications. Under organizational pressure, Alex reluctantly signed off on the design, facing a moral dilemma between his professional duty to ensure safety and the pressure to meet financial and time constraints. The decision also raised concerns about the role of human judgment in the face of AI-driven solutions—should the decision be based solely on AI’s “data-driven” conclusions, or should there be a more human-centered approach that accounts for the uncertainties AI might overlook?
Months later, a rare but intense windstorm caused noticeable vibrations in the building, alarming residents and requiring costly retrofitting to reinforce its structural integrity. This incident incurred financial losses and led to significant public criticism of the decision-making process. The case raised ethical questions about whether the firm prioritized cost savings at the expense of ensuring the safety and wellbeing of residents and workers, especially in a region prone to extreme weather events.
This scenario underscores the complex nature of ethical decision-making in structural engineering, where multiple valid principles must be weighed. On the one hand, the desire to reduce costs and improve economic viability presents an ethical argument, especially in terms of making housing more affordable and addressing financial constraints. On the other hand, public safety and long-term sustainability must take precedence in design decisions, particularly in regions with unique environmental risks. The dilemma also highlights the importance of human expertise in assessing factors that AI might overlook, such as local site conditions, which are crucial for engineering resilience.
This case study illustrates how ethical decisions in structural engineering must navigate competing imperatives—cost-efficiency vs safety, short-term financial gains vs long-term stability, and AI-driven solutions vs human judgment. It emphasizes the need for organizations to foster an environment where engineers can advocate for safety without undue pressure and where AI serves as a tool to support, not replace, human expertise. The incident also highlights the importance of multi-faceted ethical frameworks that guide decisions when diverse ethical principles are in conflict.
4.5 Case study 5: ethical concerns in retrofitting decisions
A city located in a seismically active region adopted an AI-powered system to prioritize retrofitting efforts for its aging infrastructure. The AI model was designed to analyze structural vulnerability, economic impact, and maintenance history to rank structures based on their need for retrofitting. The city implemented this system to efficiently allocate limited funding for disaster preparedness.
When the AI model’s recommendations were reviewed, it prioritized retrofitting high-value commercial buildings in the downtown area, such as office towers, shopping malls, and luxury apartment complexes. These structures were deemed critical due to their economic contribution and high repair costs in the event of an earthquake. However, older residential buildings in low-income neighborhoods, many of which housed the city’s most vulnerable populations, were ranked much lower on the list. These neighborhoods had limited structural documentation and were often constructed before modern building codes were enforced, making them particularly susceptible to seismic damage.
City officials, following the AI’s recommendations, allocated most of the retrofitting budget to the commercial district, leaving the residential neighborhoods with minimal resources for upgrades. Months later, a moderate earthquake struck Rivertown. While the retrofitted commercial buildings sustained minimal damage, several residential structures in low-income areas collapsed, resulting in casualties and widespread displacement of vulnerable families. Public outrage ensued, with community leaders accusing the city of prioritizing economic interests over human lives.
This case study highlights the following ethical concerns: (i) The AI system’s prioritization disproportionately benefited affluent areas, exacerbating existing social inequalities and neglecting the safety of marginalized communities; (ii) The model was trained to value economic metrics, such as property value and commercial importance, over human-centric factors like population density or vulnerability; (iii) Decision-makers relied heavily on the AI recommendations without critically evaluating whether the algorithm’s priorities aligned with ethical considerations and community needs.
4.6 Case study 6: lack of explainability in AI-Based load prediction for a bridge design
In a growing city, a new suspension bridge was planned to connect two busy districts across a river. To optimize the design and ensure safety, the project team employed an advanced AI system to predict complex loading scenarios, including vehicular traffic, pedestrian usage, and environmental loads such as wind and temperature variations. The AI system, trained on historical data from similar bridges worldwide, provided recommendations for the optimal material selection and load distribution.
During the design phase, the AI system recommended reducing the dimensions of certain load-bearing cables, claiming the adjustments would save costs while maintaining safety margins. When queried, the system provided an output indicating that the reduced dimensions would perform adequately under the forecasted load conditions. However, the AI system, based on a DL model, could not explain how it arrived at this conclusion. The engineers were presented with a probability score indicating safety compliance but were unable to trace the factors influencing this score or the internal logic behind the recommendation.
Senior structural engineer Maria, experienced with suspension bridge designs, expressed concern. She believed the cables might be undersized given the expected traffic growth and unpredictable wind conditions unique to the city’s coastal climate. The project management team, however, insisted on adopting the AI’s cost-saving recommendations, citing budget constraints and confidence in the model’s advanced capabilities.
Two years after construction, the bridge began exhibiting unusual vibrations during high wind events. Further analysis revealed that the cable dimensions were insufficient to dampen these effects, a factor the AI had failed to consider due to the absence of similar coastal conditions in its training data. Although the bridge did not fail, extensive retrofitting was required, leading to additional costs and public criticism of the decision-making process.
The case study highlights the following ethical concerns: (i) The AI system’s inability to provide a transparent rationale for its recommendations left engineers unable to critically assess the model’s reliability, undermining trust in its output; (ii) The project management team’s dependence on AI recommendations, without adequate human evaluation, prioritized cost savings over cautious engineering judgment; (iii) The absence of clear explainability made it difficult to determine responsibility for the misjudgment, shifting blame between the AI developers, the engineers, and the decision-makers.
4.7 Case study 7: ethical implications of AI in post-disaster damage assessment
Following a major earthquake in the metropolitan region of a city, the city government deployed an AI-powered system to perform rapid post-disaster damage assessments of buildings and infrastructure. The system analyzed drone footage and satellite imagery using ML algorithms to categorize structures into three levels of damage: minor, moderate, and severe. The AI system prioritized efficiency, generating results within hours, compared to the days or weeks required for traditional human-led assessments.
During the rebuilding process, several buildings categorized as having “minor damage” by the AI collapsed unexpectedly when subjected to normal use, causing injuries and fatalities. A subsequent investigation revealed that the AI system had struggled to assess certain structural configurations and materials, such as older masonry buildings and hybrid construction methods, due to a lack of training data. This issue had been flagged by developers but overlooked during deployment in the urgency of the disaster response.
This case underscores the need for robust testing and validation of AI systems in disaster response scenarios, as well as clear communication of uncertainties and limitations to ensure their responsible use (Plevris, 2025a). The ethical concerns that this case study highlights are: (i) The prioritization of speed over thoroughness compromised the accuracy of the assessments, resulting in undetected severe damage in some structures; (ii) The system was deployed without sufficient testing in real-world post-disaster conditions, highlighting the risks of using unproven technology in high-stakes scenarios; (iii) The lack of explainable outputs left engineers and officials unable to verify the AI’s conclusions, undermining trust in the system; (iv) The decision to deploy an untested system raises ethical questions about who bears responsibility for the failures—the developers for highlighting the limitations, or the decision-makers who ignored them.
4.8 Case study 8: ethical dilemmas in AI-assisted material selection
To promote sustainability, a city introduced an AI-driven system to assist structural engineers in selecting environmentally friendly materials for large infrastructure projects. The system was designed to balance factors such as cost, environmental impact, and structural performance. When used to plan a new public transportation hub, the AI system recommended a novel composite material that features a low carbon footprint and reduced costs compared to traditional materials.
Although the material passed initial strength tests and met code requirements, several engineers expressed concerns about its long-term durability under local environmental conditions, including high humidity and temperature fluctuations. However, the project managers, under pressure to meet sustainability goals and budgets, chose to follow the AI’s recommendations without conducting extended testing. Five years after the hub was completed, structural degradation in key load-bearing elements was discovered, necessitating extensive repairs and raising questions about the long-term viability of the chosen material.
This case highlights the importance of balancing innovation with caution, ensuring that AI-driven recommendations for sustainability do not compromise structural integrity or public safety. The ethical concerns that this case study highlights are: (i) The AI prioritized sustainability metrics over long-term performance, potentially compromising the structure’s safety and longevity; (ii) The decision to forego extended testing highlights the risks of overreliance on AI without adequate human judgment and verification; (iii) Responsibility for the premature degradation is unclear—does it lie with the AI developers, the engineers who approved the recommendation, or the project managers who prioritized cost and sustainability metrics? (iv) The use of unproven materials raises ethical questions about the risks involved in adopting innovative technologies without comprehensive validation.
5 The proposed framework and its key pillars
The proposed framework for ethical use of AI in structural engineering aims to address the ethical challenges of AI in structural engineering in an organized manner. Through categorizing its seven key pillars into three main domains—(A) Technical Foundations, (B) Operational and Governance Frameworks, and (C) Professional and Societal Responsibilities—the framework ensures a holistic approach to ethical AI integration. This structure balances technical accuracy, organizational oversight, and social responsibility, offering a roadmap for engineers, organizations, and policymakers.
Figure 2 visually summarizes the framework, presenting the seven key pillars within these three domains. Each pillar addresses a critical component of ethical AI implementation, forming an interconnected structure that guides the responsible integration of AI into structural engineering.
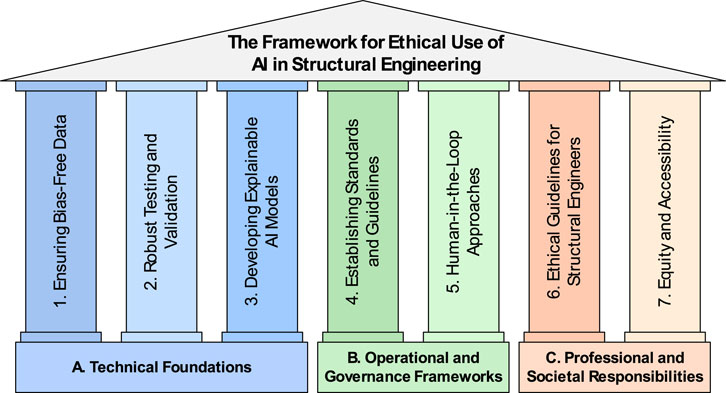
Figure 2. The framework for ethical use of AI in structural engineering: key pillars categorized into technical, operational, and societal domains.
The Technical Foundations domain focuses on the core technical strategies required to ensure that AI systems are reliable, transparent, and fair. These include measures to address data bias, improve validation processes, and enhance explainability, forming the foundation for trustworthy AI applications.
The Operational and Governance Frameworks domain emphasizes the structural and procedural mechanisms needed to guide ethical AI deployment. This includes the establishment of industry standards and guidelines to ensure consistency and accountability, as well as the integration of human-in-the-loop approaches to maintain human oversight in decision-making processes.
The Professional and Societal Responsibilities domain highlights the broader responsibilities of engineers to uphold ethical standards, promote equity, and ensure accessibility. This includes adhering to ethical guidelines and ensuring that AI benefits extend beyond resource-rich areas to underserved communities and smaller organizations.
Although each of the seven key pillars is presented individually for conceptual clarity, they are inherently interdependent and mutually reinforcing. For example, Robust Testing and Validation (Pillar 2) supports Explainability (Pillar 3) by enabling transparent communication of model performance. Similarly, Bias-Free Data (Pillar 1) and Equity and Accessibility (Pillar 7) are deeply connected, as addressing technical bias is a prerequisite for achieving social equity in deployment. Human-in-the-Loop Approaches (Pillar 5) serve as a bridge between technical foundations and professional responsibilities, ensuring that human judgment governs AI decision-making. Thus, the framework should not be viewed as a checklist but as an interconnected system where each pillar supports and amplifies the others to ensure holistic ethical implementation.
The following Subsections 5.1–5.7 provide a detailed exploration of each pillar, outlining specific strategies, principles, and practical applications that support ethical AI use in structural engineering workflows.
5.1 Key pillar 1: ensuring bias-free data
This first pillar is grounded in the ethical principle of justice, which demands fairness and equitable treatment across all populations. In the context of AI, ensuring bias-free data supports distributive justice by avoiding systemic disadvantages for underrepresented communities. It also aligns with non-maleficence, as biased models may cause harm through unequal treatment or unsafe outcomes in marginalized areas. Jobin et al. (2019) highlight that justice and non-maleficence are among the most commonly cited ethical principles in global AI guidelines, underscoring their centrality in responsible AI development. Furthermore, Leavy et al. (2020) discuss how biases in AI training data can perpetuate social injustices, emphasizing the need for data practices that uphold these ethical standards.
The foundation of any AI system lies in the quality and representativeness of the data it is trained on (Ntoutsi et al., 2020). To minimize bias and promote fairness in structural engineering applications, several strategies must be implemented. First, systematic dataset audits are essential (Adams et al., 2023; Li and Goel, 2024). These audits involve a thorough review of training datasets to identify and mitigate biases that could skew AI outputs. For instance, datasets should encompass a diverse range of structural types, materials, and geographic regions to ensure that AI models are applicable across varied contexts and scenarios.
Another effective strategy is data augmentation (Grover et al., 2024), which enhances dataset diversity by generating synthetic data for underrepresented cases. This approach is particularly useful for addressing gaps in scenarios such as rare seismic events or unique structural configurations. By simulating these conditions, data augmentation helps AI systems make more accurate and equitable predictions across a wider spectrum of use cases.
Finally, incorporating fairness metrics into the evaluation of AI model outputs is crucial. These metrics provide quantitative measures of fairness, enabling engineers to assess whether an AI model’s predictions disproportionately favor or disadvantage certain groups or scenarios. By actively monitoring and addressing fairness through such metrics, AI systems can be refined to ensure equitable outcomes in structural engineering applications.
Together, these measures form a robust framework for ensuring bias-free data, enabling AI systems to function more reliably and ethically in diverse structural engineering contexts.
5.2 Key pillar 2: robust testing and validation
Robust validation practices in AI align closely with ethical principles such as beneficence (Thomson, 2023) and non-maleficence (Al-Bar and Chamsi-Pasha, 2015), emphasizing the professional duty to promote safety and prevent harm. From a deontological perspective, engineers are ethically obligated to ensure that the tools they use—especially in safety-critical fields like structural engineering—meet stringent standards for reliability and performance. Utilitarian considerations also support this obligation: maximizing public safety and minimizing risk benefits the greatest number of people. As Floridi and Cowls (2019) note, beneficence and non-maleficence remain among the most foundational principles for ethical AI governance.
In structural engineering, AI tools must be rigorously tested and validated before being trusted in high-stakes decisions. This validation goes beyond initial performance checks and requires structured, transparent methodologies tailored to each application. Challenges include defining clear performance thresholds, interpreting black-box models, and aligning AI predictions with engineering codes and established safety practices (Numan, 2020). Universal validation criteria remain elusive, but context-specific benchmarks must still be developed to ensure AI tools do not undermine structural integrity.
Testing protocols should be diversified to reflect the many potential AI use cases—such as seismic risk assessment, structural health monitoring, and failure prediction. These protocols should include: (i) Stress testing under extreme loading conditions; (ii) Simulation of data incompleteness or noise; (iii) Quantification of model uncertainty; (iv) Performance benchmarking against conventional engineering calculations.
A critical component of robust validation is addressing performance drift—where AI model accuracy degrades over time due to changing structural, environmental, or usage conditions. To mitigate this, validation must extend throughout the entire AI lifecycle. Engineers should implement: (i) Continuous validation procedures that periodically test performance on new data; (ii) Model retraining protocols based on updated infrastructure conditions; (iii) Sunset policies that retire or phase out outdated models before they become unreliable.
These practices transform validation into a dynamic and ongoing responsibility, rather than a one-time event. Lifecycle-aware validation supports beneficence by maintaining performance and non-maleficence by preventing harm due to model obsolescence. It also reflects the engineer’s ethical obligation to monitor and manage tools in use, reinforcing professional accountability and public trust.
While Pillar 5 (Human-in-the-Loop Approaches) focuses on human ethical oversight and decision-making, this pillar centers on the technical integrity and lifecycle governance of AI systems. Feedback loops discussed here serve the engineering validation function, allowing technical recalibration based on evolving system behavior—distinct from human moral oversight loops emphasized in HITL contexts.
Finally, ethical AI governance in structural engineering must embed risk management directly into testing frameworks. This includes tracking unintended biases, auditing prediction stability, and documenting model limitations. Though many of these techniques are still evolving, the responsibility to build, test, and refine robust validation protocols is clear. This framework does not claim to provide prescriptive solutions, but it calls for an industry-wide commitment to advance these practices as AI becomes more deeply integrated into structural engineering workflows.
5.3 Key pillar 3: developing explainable AI models
This pillar aligns strongly with autonomy and respect for persons (Łuków and Różyńska, 2014) from deontological ethics, emphasizing that users and stakeholders have a right to understand how decisions are made. Explainability also supports accountability (Reichborn-Kjennerud, 2018) by making it possible to trace outcomes back to responsible agents. Promoting transparency enhances trust, which is foundational to ethical engineering practice (Visave, 2025).
To foster trust and enhance usability, AI models in structural engineering must provide outputs that are clear and understandable to both engineers and stakeholders. One effective approach to achieving this is through the use of explainable AI techniques (Czerwinska, 2022; Ding et al., 2022). Tools such as SHAP (SHapley Additive exPlanations) (Merrick and Taly, 2020) can quantify the importance of individual features and illustrate how specific inputs influence the model’s predictions. By providing detailed explanations, these techniques enable engineers to validate the AI’s outputs effectively and build confidence in its recommendations.
Another strategy is to employ simpler model architectures for scenarios where transparency is critical (Felzmann et al., 2020). Models such as decision trees, rule-based systems, or linear regression offer inherent interpretability, making it easier for engineers to understand the reasoning behind predictions (Tursunalieva et al., 2024). These models are particularly useful in safety-critical applications, where the ability to trace decision paths is essential for informed decision-making.
Additionally, the development of interactive visualization tools can significantly enhance the interpretability of AI systems (Wang et al., 2023). These tools allow users to visualize the model’s decision-making process in an intuitive manner, such as by highlighting critical structural elements that influence safety predictions. By presenting complex information in a user-friendly format, these visualizations help bridge the gap between advanced AI algorithms and practical engineering applications.
By incorporating these approaches, AI models can become more transparent, enabling engineers and stakeholders to make more informed and confident decisions while addressing ethical concerns related to accountability and trust.
5.4 Key pillar 4: establishing standards and guidelines
Establishing standards reflects deontological ethics by formalizing duties and responsibilities for engineers and institutions. It also supports non-maleficence (Al-Bar and Chamsi-Pasha, 2015) and justice, ensuring that AI applications meet uniform safety and ethical benchmarks across the industry. This pillar contributes to utilitarian outcomes (Kay, 2018) by reducing uncertainty and preventing harm across broad populations.
To ensure the consistent and ethical use of AI in structural engineering, the establishment of formalized standards and guidelines is paramount. One critical step is advocating for the development of industry standards by professional organizations such as the American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) or the European Community on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences (ECCOMAS). These organizations are well-positioned to create standardized frameworks that define best practices for integrating AI into structural engineering workflows. Such standards can help ensure that AI technologies are applied consistently and ethically across the industry, fostering uniformity and accountability.
In addition to industry standards, the publication of best practice guides is vital. These guides should provide detailed instructions on responsibly integrating AI into engineering processes, covering key elements such as protocols for model validation, documentation requirements, and methods for detecting and mitigating bias in AI systems. By offering practical resources for engineers and organizations, these guides can support the responsible adoption of AI while addressing potential ethical challenges.
Furthermore, AI systems must align with existing regulatory frameworks to maintain compliance and uphold safety standards. Aligning AI applications with established engineering codes and safety requirements ensures that AI-generated recommendations meet the same rigorous quality and safety standards as traditional engineering methods. This regulatory alignment fosters trust among engineers, regulators, and the public, providing assurance that AI technologies are deployed responsibly.
Existing regulatory initiatives also highlight the importance of this alignment. For example, the U.S. Department of Homeland Security (DHS) has released a framework to guide the safe and secure deployment of AI in critical infrastructure (U.S. Department of Homeland Security, 2024). This framework emphasizes the necessity of managing a wide range of risks, including misuse and accidents, while underscoring the importance of rigorous testing and validation before integrating AI into essential services. Similarly, the European Parliament has addressed the ethical implications of AI technologies, advocating for comprehensive guidelines to ensure responsible development and implementation (European Parliamentary Research Service, 2020). These guidelines stress the importance of aligning AI applications with ethical standards to mitigate potential risks, particularly those associated with untested or experimental technologies.
Together, these measures—industry standards, best practice guides, and compliance with existing regulations—form a comprehensive approach to ensuring the consistency, reliability, and ethical integrity of AI in structural engineering. By incorporating established frameworks and aligning with evolving regulatory guidelines, the structural engineering field can adopt AI technologies confidently and responsibly.
5.5 Key pillar 5: human-in-the-loop approaches
Human-in-the-Loop (HITL) refers to a collaborative approach where human oversight and input are integral to the functioning of AI systems. HITL approaches emphasize respect for autonomy (Łuków and Różyńska, 2014) and the deontological duty of engineers to make informed and morally responsible decisions (Smith et al., 2014). Rather than replacing human judgment, this pillar supports collaborative decision-making where AI augments but does not override professional expertise. It also reinforces non-maleficence (Al-Bar and Chamsi-Pasha, 2015) by guarding against unchecked automation and unintended consequences.
In structural engineering, HITL approaches are particularly essential in safety-critical applications, where nuanced human judgment is required to assess risks, ensure structural integrity, and interpret complex or uncertain model outputs (Mosqueira-Rey et al., 2023; Wu et al., 2022). Oversight mechanisms must therefore be built into engineering workflows, ensuring that AI recommendations undergo meaningful human evaluation before implementation.
Effective HITL implementation requires formal review protocols and training programs that empower engineers to critically assess AI outputs, understand model limitations, and intervene when necessary. These skills help prevent blind trust in automated systems and ensure engineers retain active control over decision-making.
Importantly, HITL is not limited to initial deployment. Human oversight must persist throughout the AI lifecycle to uphold ethical and professional standards. While Pillar 2 addresses the technical validation of AI models, this pillar emphasizes the moral and professional obligation of engineers to remain engaged post-deployment. This includes periodic reassessment of AI recommendations, reflection on changing infrastructure contexts, and readiness to override the system when warranted. Human oversight must remain dynamic, responsive to new information, and attuned to ethical risk.
By embedding HITL approaches into structural engineering practice, professionals ensure that AI enhances—rather than replaces—human responsibility. This safeguards public welfare, reinforces trust, and preserves ethical integrity in the face of evolving technologies.
5.6 Key pillar 6: ethical guidelines for structural engineers
Ethical guidelines are rooted in virtue ethics (Gustafson and Peterson, 2023) and professional deontology (Poff, 2023), emphasizing the character, responsibility, and moral reasoning of engineers. They also promote beneficence by encouraging continuous education and interdisciplinary collaboration to improve outcomes. Ethical codes help ensure that innovation does not outpace the profession’s ability to manage risk and uphold public trust.
The integration of AI into structural engineering necessitates a unified framework of ethical guidelines to ensure its responsible and effective use. These guidelines emphasize transparency, continuous education, and interdisciplinary collaboration, which collectively uphold public safety, fairness, and accountability. Transparency is fundamental for building trust and ensuring accountability in AI applications. Engineers must understand the capabilities and limitations of AI models, clearly disclose the utilization of AI outputs, and maintain detailed documentation of decisions to provide stakeholders with a clear rationale for critical design and safety choices.
To complement transparency, continuous education equips engineers with the knowledge needed to navigate the evolving landscape of AI technologies and ethical considerations. Professional development programs and the inclusion of AI ethics in engineering education prepare both current and future professionals to address challenges such as explainability, bias mitigation, and reliability testing. Staying informed ensures engineers remain competent and adaptable to advancements.
Interdisciplinary collaboration bridges the gap between AI technology and practical engineering applications. Engineers working alongside AI developers, ethicists, and domain experts can align technical capabilities with real-world requirements while addressing societal and ethical implications. This collaborative approach ensures that AI solutions foster innovation while adhering to ethical standards, creating systems that prioritize public safety, fairness, and accountability. Through these interconnected strategies, the integration of AI into structural engineering can be both innovative and ethically sound. The structural engineering community can effectively integrate AI by adhering to these principles, ensuring its application enhances innovation and public trust while safeguarding ethical standards.
5.7 Key pillar 7: equity and accessibility
This pillar is deeply connected to the principle of justice (Jobin et al., 2019), advocating for fair access to the benefits of AI regardless of geographic or economic disparities. It also supports utilitarianism (Kay, 2018) by aiming to maximize the positive impact of AI on broader society. Ensuring accessibility reflects a commitment to social responsibility and prevents the deepening of existing inequalities.
Equity and accessibility are critical considerations in the ethical implementation of AI in structural engineering. While AI technologies have the potential to revolutionize the field, their benefits are often unevenly distributed, creating disparities between resource-rich and resource-constrained regions or organizations. Smaller municipalities or rural communities may lack the financial resources or technical expertise to implement advanced AI-driven systems for SHM or disaster preparedness. This can exacerbate existing inequalities, leaving underserved areas more vulnerable to structural failures or natural disasters. Ensuring that AI applications are accessible to all communities is essential to bridge this gap and uphold the principles of fairness and social responsibility.
To promote equity, AI systems should be designed and deployed with inclusivity in mind (Zowghi and Bano, 2024). This includes creating cost-effective solutions that can be adopted by smaller organizations and ensuring that training datasets reflect the diverse needs of urban, suburban, and rural environments. Partnerships between governments, academic institutions, and private organizations can help fund and develop AI systems that address the needs of marginalized or under-resourced communities. Moreover, open-source AI models and tools can play a vital role in democratizing access to advanced technologies, enabling wider adoption and reducing the financial barriers for smaller stakeholders.
Accessibility also extends to ensuring that the outputs and recommendations of AI systems are understandable and actionable for all users, regardless of their technical expertise. Providing user-friendly interfaces, intuitive visualizations, and training programs for engineers and decision-makers in under-resourced areas can empower them to effectively utilize AI systems.
The structural engineering community can ensure that the transformative potential of AI benefits society as a whole, rather than deepening existing inequalities, through prioritizing equity and accessibility. This pillar is a vital component of a responsible and ethical AI framework, reinforcing the commitment to fairness and inclusivity in engineering practice.
6 Future directions
The integration of AI into structural engineering holds substantial promise, offering new capabilities in analysis, monitoring, design, and optimization. However, realizing this potential requires long-term foresight and a commitment to addressing the ethical, technical, and regulatory challenges that will continue to emerge as AI becomes more widespread. While the proposed framework provides immediate guidance on responsible AI integration, it is deliberately conceptual. Structural engineering is only beginning to adopt AI in meaningful ways, and the field currently lacks sufficient empirical experience to support rigid checklists or detailed implementation protocols.
Oversimplified or premature standardization may obscure the inherent complexities involved in aligning AI technologies with public safety, engineering integrity, and professional ethics. At this early stage, the value of the framework lies in its ability to raise awareness, guide ethical reflection, and serve as a foundation for ongoing development. As empirical knowledge expands and real-world applications grow, this framework can inform the creation of formal ethical guidelines, educational curricula, lifecycle management strategies, and regulatory systems tailored to structural engineering.
Future progress will require sustained interdisciplinary collaboration, global coordination, and proactive adaptation to technological innovation. The sections that follow outline key directions for research, education, policy, and inclusive development, highlighting how the ethical foundation presented here can evolve to meet emerging needs.
6.1 Expanding interdisciplinary research
The future of ethical AI in structural engineering lies in interdisciplinary collaboration that extends beyond current practices. Research initiatives should deepen partnerships among structural engineers, AI developers, ethicists, social scientists, and policymakers to explore new challenges at the intersection of technology, ethics, and society. Topics such as mitigating unintended consequences of emerging AI technologies, addressing systemic inequalities, and developing scalable AI systems for diverse infrastructure contexts require joint efforts across disciplines.
One of the most pressing areas for interdisciplinary research is the validation and safety assurance of AI-driven structural engineering systems. Unlike conventional engineering models, which rely on deterministic calculations and well-established safety factors, AI introduces probabilistic uncertainty that must be rigorously quantified to ensure reliability in real-world applications. Future efforts should focus on developing systematic AI validation methodologies that align with existing engineering safety frameworks. This includes integrating AI-driven uncertainty quantification into structural safety assessments to ensure that AI-generated predictions remain interpretable and reliable. Additionally, AI models should be subjected to reliability-based stress testing under extreme conditions, such as seismic events, progressive collapse scenarios, and material degradation over time. These validation techniques will be essential to assess the robustness of AI-generated insights and prevent failures that could compromise public safety.
As AI continues to evolve, the need for cross-disciplinary expertise becomes increasingly important. Engineers must work alongside AI researchers and ethicists to ensure that AI models comply with structural safety standards while remaining accountable and transparent. Without such collaborative research, AI-assisted structural decisions may lack the clarity, reliability, and robustness needed for safety-critical applications.
Establishing internationally accepted ethical standards will also require global partnerships that can adapt to regional differences while maintaining a unified framework for responsible AI deployment. Government agencies, academic institutions, and private-sector stakeholders should prioritize funding for interdisciplinary research initiatives that advance AI’s role in structural engineering while addressing its ethical implications. A coordinated effort between technical and non-technical fields will be essential in ensuring that AI applications in structural engineering are innovative and also safe, transparent, and equitable.
In addition to advancing technical validation and collaborative research, it is essential to develop long-term oversight frameworks that ensure AI systems remain reliable, ethical, and safe over time. As AI tools evolve or face new deployment environments, continuous post-deployment monitoring, periodic revalidation, and sunset policies for outdated models must be established. Without such governance mechanisms, even well-validated AI systems risk becoming unreliable as data distributions shift or structural demands change. A robust lifecycle oversight infrastructure is vital to institutionalize accountability and protect public welfare across the lifespan of AI applications.
As AI adoption expands globally, ethical frameworks must be adaptable to differing regional regulatory environments and cultural perspectives on engineering responsibility. Norms related to transparency, autonomy, liability, and public engagement vary considerably across countries, influencing how AI ethics is interpreted and enforced. For instance, the European Union’s AI Act (Cancela-Outeda, 2024; Covelo de Abreu, 2024) emphasizes human oversight and risk-based regulation, while other regions may prioritize innovation or efficiency over formal governance. Therefore, international collaboration is essential not only for technological development but also for aligning ethical standards with local expectations. Future interdisciplinary research must explore how the proposed ethical principles and implementation strategies can be localized to reflect legal systems, cultural values, and professional norms in diverse global contexts. Beyond research, this interdisciplinary spirit must also inform education and professional training, ensuring that ethical literacy evolves alongside technological advancement.
6.2 Transforming engineering education
Preparing future generations of engineers to address the ethical challenges of AI requires a transformative shift in educational approaches. Structural engineering curricula must integrate AI ethics as a core component, moving beyond the technical aspects of AI methods (Plevris, 2025b). This integration should cover ethical theories and provide practical tools and frameworks for navigating real-world dilemmas. Topics such as transparency, accountability, and societal impacts should be framed within structural engineering scenarios, helping students understand how these principles apply to decision-making in practice.
To prepare students for the complex ethical questions they will face, curricula should include specific ethical frameworks such as the four principles of applied ethics of Beauchamp and Childress—autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence and justice (Page 2012)—to guide decisions when multiple ethical principles, such as safety vs cost, public welfare vs efficiency, and equity vs accessibility, come to conflict. Additionally, students should be trained to critically assess these conflicts and make ethically sound decisions in the context of AI-driven engineering systems.
For practicing engineers, lifelong learning initiatives are equally crucial. Professional development programs should include workshops and training sessions that explore the ethical dimensions of AI integration into workflows. These programs must focus on equipping engineers with the tools to critically assess AI systems, identify potential ethical dilemmas, and apply responsible practices in their work. Real-world case studies, role-playing exercises, and simulation-based learning can help engineers develop the skills necessary to weigh competing ethical imperatives in practical scenarios.
Embedding ethics into both foundational education and ongoing professional development ensures that the engineering workforce is prepared to navigate the complexities of a rapidly evolving technological landscape. This approach to AI ethics education will foster technical competence and also the ethical judgment needed to address the challenges posed by AI in structural engineering.
6.3 Adapting to emerging technologies
Emerging technologies such as quantum computing (Hirvensalo, 2004), autonomous systems, and AI-augmented digital twins (DTs) (Al-Sartawi et al., 2024; Hosamo et al., 2022a) are going to transform structural engineering, offering new possibilities for analysis, optimization, and real-time monitoring. However, their adoption also introduces complex ethical and technical challenges that require proactive research and regulatory frameworks. Although these technologies have the potential to improve efficiency and safety, they also present risks related to validation, accountability, and the increasing opacity of AI-driven decision-making processes.
Quantum computing, for example, could revolutionize structural analysis and optimization by solving computationally intensive problems at unprecedented speeds. However, its application raises concerns about data security, model interpretability, and reliability (Boretti, 2024). Unlike classical computing models, quantum-based AI may operate on probabilistic principles that challenge existing verification and validation protocols in structural engineering. Without rigorous validation frameworks, the results produced by quantum-enhanced AI models could be difficult to interpret, leading to potential safety risks.
Similarly, autonomous systems in construction and infrastructure maintenance (Davila Delgado et al., 2019) promise to enhance efficiency and reduce human error, yet they pose significant accountability challenges. Decisions made by AI-driven autonomous agents—such as robotic inspectors or automated reinforcement placement systems—must be traceable, auditable, and aligned with established engineering safety standards. The lack of human oversight in fully autonomous operations could lead to liability issues in the event of structural failures, raising questions about responsibility in AI-assisted decision-making. Ensuring that AI-driven automation adheres to engineering safety protocols will require the development of AI accountability frameworks that clearly define the roles of engineers, AI systems, and regulatory bodies in decision-making processes.
Another critical area of concern is the expanding role of AI-augmented digital twins (DTs) in structural engineering (Hosamo et al., 2022b). Digital twins enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and risk assessment for infrastructure projects, improving the accuracy and efficiency of decision-making. However, they also introduce challenges related to data privacy, system reliability, and the ethical implications of predictive analytics. AI-driven digital twins rely on large-scale data collection and modeling, raising concerns about data ownership, cybersecurity, and the unintended consequences of algorithmic biases. A structured risk assessment approach must be adopted to evaluate the ethical and safety implications of AI-augmented infrastructure monitoring systems, ensuring that these tools enhance, rather than compromise, engineering integrity.
To responsibly harness these technologies, structural engineers must integrate rigorous AI validation protocols into their workflows. Unlike traditional engineering verification methods, AI-based validation requires stress testing, explainability techniques, and benchmarking against industry safety codes such as ASCE 7 (American Society of Civil Engineers, 2016), Eurocode 0 (CEN, 2002), other structural design codes, and ISO/IEC 23894:2023 (AI Guidance on risk management) (International Organization for Standardization, 2023a). AI models used in structural engineering should undergo performance benchmarking, uncertainty quantification, and adversarial stress testing to ensure their reliability in safety-critical applications. Additionally, pilot testing and phased implementation strategies should be prioritized to assess the risks of AI deployment in high-stakes engineering environments before widespread adoption.
6.4 Shaping future policy and regulation
As AI technologies become increasingly integral to structural engineering, it is imperative that policy and regulatory frameworks evolve accordingly. Future regulations should address challenges such as managing the ethical implications of automated decision-making, ensuring accountability in autonomous systems, and safeguarding against AI misuse in critical infrastructure.
To effectively govern AI integration, adopting established standards is essential. For instance, ISO/IEC 23894:2023 (International Organization for Standardization, 2023a) provides comprehensive guidance on AI risk management, offering organizations strategies to identify and mitigate potential risks associated with AI deployment. Similarly, ISO/IEC 42001:2023 (International Organization for Standardization, 2023b) outlines requirements for AI management systems, assisting organizations in implementing, maintaining, and continually improving their AI processes.
Incorporating these standards into regulatory frameworks ensures that AI applications in structural engineering adhere to recognized best practices, thereby enhancing safety and reliability. Moreover, collaboration among industry associations, government bodies, and global organizations is crucial for creating adaptive regulatory mechanisms. These collaborative efforts should focus on defining safety benchmarks, clarifying accountability structures, and establishing enforceable ethical standards that align with rapid technological advancements.
By integrating standardized guidelines and fostering collaborative efforts, the structural engineering field can navigate the complexities introduced by AI technologies, ensuring that their adoption enhances both innovation and public safety.
Importantly, regulatory approaches to AI differ significantly across countries, and a one-size-fits-all model may not be appropriate. Therefore, ethical frameworks for AI in structural engineering should be flexible enough to accommodate various legal traditions, infrastructural needs, and cultural attitudes toward risk and professional responsibility. Regional adaptations may be necessary to ensure that global principles are implemented effectively and respectfully within local governance systems.
To ensure lasting ethical compliance, regulatory strategies should also include long-term lifecycle management plans for AI systems. These plans must outline responsibilities for ongoing performance evaluation, retraining procedures, and criteria for decommissioning outdated or underperforming models. Embedding lifecycle oversight into regulation not only ensures sustained safety but also aligns AI use with evolving legal, technical, and societal expectations. Future policy frameworks should encourage institutions to treat AI governance as a continuous process, not a one-time certification step.
6.5 Promoting inclusive AI and public engagement
The benefits of AI in structural engineering must be accessible to all, not just resource-rich regions or organizations. Future efforts should focus on creating affordable and scalable AI solutions tailored to the needs of under-resourced communities. Open-source initiatives and public-private partnerships can democratize access to advanced AI tools, bridging the gap between urban and rural infrastructure needs.
Engaging the public and diverse stakeholders in discussions about AI’s role in infrastructure projects will be equally critical. Public forums, workshops, and interactive outreach initiatives can foster transparency and build trust, ensuring that AI is implemented with broad societal consensus.
7 Conclusion
The integration of AI into structural engineering presents both extraordinary opportunities and unprecedented ethical challenges. From enhanced predictive modeling and structural monitoring to automated decision-making, AI promises to reshape the field. Yet, in a domain where public safety, reliability, and fairness are non-negotiable, the ethical deployment of such technologies must be deliberate, transparent, and grounded in well-articulated principles.
This study proposes a comprehensive framework for responsible AI in structural engineering, built on a foundation of literature review, hypothetical case studies, and interdisciplinary ethical reasoning. The eight case studies presented illustrate forward-looking ethical dilemmas that engineers and organizations are likely to face as AI becomes more embedded in practice. These scenarios emphasize the need for critical safeguards—particularly in areas of accountability, transparency, and professional judgment—and serve as a conceptual testing ground for the proposed framework.
The framework is structured around three core domains: Technical Foundations; Operational and Governance Frameworks; and Professional and Societal Responsibilities. Within these, seven key pillars address essential ethical imperatives, including bias mitigation, robust validation, explainability, human oversight, professional standards, engineering ethics, and equitable access. Each pillar has been explicitly linked to underlying ethical theories—such as justice, autonomy, non-maleficence, beneficence, utilitarianism, and virtue ethics—enhancing the philosophical rigor and interdisciplinary relevance of the framework.
The framework places particular emphasis on lifecycle management issues—such as model drift, feedback loops, continuous validation, and sunset policies—which are integrated within the pillars on validation and human oversight. It also accounts for geographic and contextual variability, acknowledging that AI ethics must be sensitive to differences in regulatory environments, legal systems, and cultural norms. Rather than prescribing rigid checklists, the framework offers adaptable guiding principles that can be tailored to specific contexts. This flexible approach reflects the evolving nature of AI in structural engineering, a field characterized by ongoing technological innovation and inherent uncertainty.
Responsibility in AI-driven structural engineering must be shared across the AI lifecycle, with clear delineation of roles. Engineers retain the ultimate responsibility for safety-critical decisions, especially where AI outputs influence design or assessment. However, responsibility also extends to developers who build AI models, institutions that deploy them, and regulatory bodies that govern their use. Within Domain C of the framework (Professional and Societal Responsibilities), accountability is embedded through guidelines that emphasize transparency, documentation, and ethical awareness among practitioners. These ensure that ethical duties are not abstract, but actionable and attributable. To avoid diffusion of responsibility, organizations should establish explicit responsibility matrices that assign decision authority, oversight obligations, and liability boundaries across the AI deployment chain.
The study also outlines critical future directions, including the need for interdisciplinary research collaborations, reforms in engineering education to integrate AI ethics, adaptation to emerging technologies such as digital twins and quantum computing, the evolution of regulatory frameworks, and inclusive public engagement. Together, these forward-looking considerations form a roadmap for transforming the ethical foundation proposed in this study into more formalized protocols and governance structures over time.
By aligning ethical frameworks with structural engineering standards and referencing emerging international regulations (e.g., ISO/IEC 23894:2023 (International Organization for Standardization, 2023a) and ISO/IEC 42001:2023 (International Organization for Standardization, 2023b)), this work bridges the gap between abstract ethical guidelines and safety-critical applications. Although the framework is conceptual, it is intended as a living structure—one that supports ethical foresight, provokes professional dialogue, and informs future empirical research and regulatory development.
Ultimately, this work aims to serve as a catalyst for sustained engagement with the ethical dimensions of AI in structural engineering. It invites engineers, researchers, and policymakers to anticipate rather than react, to build ethics into the core of technical systems, and to ensure that AI advances not only engineering efficiency but also societal wellbeing, safety, and trust.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
VP: Conceptualization, Visualization, Investigation, Writing – review and editing, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Validation, Formal Analysis, Methodology. HH: Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Validation
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
The author(s) declared that they were an editorial board member of Frontiers, at the time of submission. This had no impact on the peer review process and the final decision.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors verify and take full responsibility for the use of generative AI in the preparation of this manuscript. Generative AI tools were used in a limited capacity for language refinement and copyediting purposes only. These tools assisted in improving clarity, grammar, and readability, but all content, ideas, analysis, and conclusions presented in the manuscript are the original work of the authors.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
AEC, Architecture, Engineering, and Construction; AI, Artificial Intelligence; ANN, Artificial Neural Network; ASCE, American Society of Civil Engineers; CNN, Convolutional Neural Network; DHS, Department of Homeland Security; DL, Deep Learning; DT, Digital Twin; ECCOMAS, European Community on Computational Methods in Applied Sciences; GDPR, General Data Protection Regulation; HITL, Human-in-the-Loop; IoT, Internet of Things; ML, Machine Learning; NN, Neural Network; OSP, Optimal Sensor Placement; SHAP, SHapley Additive exPlanations; SHM, Structural Health Monitoring; W3C, World Wide Web Consortium; XAI, Explainable Artificial Intelligence
References
Adams, C., Eslamnejad, M., Khadka, A., M’manga, A., Shaw, H., and Zhao, Y. (2023). “Auditing AI systems: a metadata approach,” in Artificial intelligence XL (Cham, Switzerland), 241–246. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-47994-6_22
Al-Bar, M. A., and Chamsi-Pasha, H. (2015). “Nonmaleficence.” in Contemporary bioethics: islamic perspective, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 119–128. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-18428-9_7
Ali, S., Abuhmed, T., El-Sappagh, S., Muhammad, K., Alonso-Moral, J. M., Confalonieri, R., et al. (2023). Explainable artificial intelligence (XAI): what we know and what is left to attain trustworthy artificial intelligence. Inf. Fusion, 99, 101805. doi:10.1016/j.inffus.2023.101805
Al-Sartawi, A. M. A. M., Al-Qudah, A. A., and Shihadeh, F. (2024). Artificial intelligence-augmented digital twins. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-43490-7
American Society of Civil Engineers (2016). Minimum design loads and associated criteria for buildings and other structures. United States: ASCE, Structural Engineering Institute.
Andreotta, A. J., Kirkham, N., and Rizzi, M. (2022). AI, big data, and the future of consent. AI and Soc. 37(4), 1715–1728. doi:10.1007/s00146-021-01262-5
Balasubramaniam, N., Kauppinen, M., Rannisto, A., Hiekkanen, K., and Kujala, S. (2023). Transparency and explainability of AI systems: from ethical guidelines to requirements. Inf. Softw. Technol. 159, 107197. doi:10.1016/j.infsof.2023.107197
Baum, K., Mantel, S., Schmidt, E., and Speith, T. (2022). From responsibility to reason-giving explainable artificial intelligence. Philosophy Technol. 35(1), 12. doi:10.1007/s13347-022-00510-w
Beauchamp, T. L. (2011). Informed consent: its history, meaning, and present challenges. Camb. Q. Healthc. Ethics, 20(4), 515–523. doi:10.1017/S0963180111000259
Bolandi, H., Li, X., Salem, T., Boddeti, V. N., and Lajnef, N. (2022). Bridging finite element and deep learning: high-resolution stress distribution prediction in structural components. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 16(11), 1365–1377. doi:10.1007/s11709-022-0882-5
Boretti, A. (2024). Technical, economic, and societal risks in the progress of artificial intelligence driven quantum technologies. Discov. Artif. Intell. 4(1), 67. doi:10.1007/s44163-024-00171-y
Buiten, M., de Streel, A., and Peitz, M. (2023). The law and economics of AI liability. Comput. Law and Secur. Rev. 48, 105794. doi:10.1016/j.clsr.2023.105794
Cancela-Outeda, C. (2024). The EU's AI act: a framework for collaborative governance. Internet Things, 27, 101291. doi:10.1016/j.iot.2024.101291
CEN (2002). EN 1990. Eurocode: basis of structural design. Cham, Switzerland: European Committee for Standardization CEN.
Chamatidis, I., Stoumpos, M., Kazakis, G., Kallioras, N. A., Triantafyllou, S., Plevris, V., et al. (2023). Overview on machine learning assisted topology optimization methodologies. in Machine learning in modeling and simulation: methods and applications, Editors T. Rabczuk, and K.-J. Bathe, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 373–394. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-36644-4_10
Chitkeshwar, A. (2024). Revolutionizing structural engineering: applications of machine learning for enhanced performance and safety. Archives Comput. Methods Eng. 31, 4617–4632. doi:10.1007/s11831-024-10117-3
Covelo de Abreu, J. (2024). The “artificial intelligence act” proposal on European e-justice domains through the lens of user-focused, user-friendly and effective judicial protection principles. in Multidisciplinary perspectives on artificial intelligence and the law, Editors H. Sousa Antunes, P. M. Freitas, A. L. Oliveira, C. Martins Pereira, E. Vaz de Sequeira, and L. Barreto Xavier, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 397–414. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-41264-6_21
Czerwinska, U. (2022). Interpretability of machine learning models. in Applied data science in tourism: interdisciplinary approaches, methodologies, and applications, Editor R. Egger, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 275–303. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-88389-8_14
D’Alessandro, W. (2024). Deontology and safe artificial intelligence. Philos. Stud. doi:10.1007/s11098-024-02174-y
Davila Delgado, J. M., Oyedele, L., Ajayi, A., Akanbi, L., Akinade, O., Bilal, M., et al. (2019). Robotics and automated systems in construction: understanding industry-specific challenges for adoption. J. Build. Eng. 26, 100868. doi:10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100868
Dhirani, L. L., Mukhtiar, N., Chowdhry, B. S., and Newe, T. (2023). Ethical dilemmas and privacy issues in emerging technologies: a review. Sensors 23 (3), 1151. doi:10.3390/s23031151
Ding, W., Abdel-Basset, M., Hawash, H., and Ali, A. M. (2022). Explainability of artificial intelligence methods, applications and challenges: a comprehensive survey. Inf. Sci.,615, 238–292. doi:10.1016/j.ins.2022.10.013
Dobson, J. E. (2023). On reading and interpreting black box deep neural networks. Int. J. Digital Humanit. 5 (2), 431–449. doi:10.1007/s42803-023-00075-w
Dong, C.-Z., and Catbas, F. N. (2020). A review of computer vision–based structural health monitoring at local and global levels. Struct. Health Monit. 20, 692–743. doi:10.1177/1475921720935585
Dung, L. (2023). Current cases of AI misalignment and their implications for future risks. Synthese 202 (5), 138. doi:10.1007/s11229-023-04367-0
Ehtisham, R., Qayyum, W., Camp, C. V., Plevris, V., Mir, J., Khan, Q.-u. Z., et al. (2024). Computing the characteristics of defects in wooden structures using image processing and CNN. Automation Constr. 158, 105211. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105211
Emaminejad, N., and Akhavian, R. (2022). Trustworthy AI and robotics: implications for the AEC industry. Automation Constr. 139, 104298. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104298
Emaminejad, N., Maria North, A., and Akhavian, R. (2022). Trust in AI and implications for AEC research: a literature analysis. in Computing in civil engineering 2021. American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE), 295–303. doi:10.1061/9780784483893.037
Etim, B., Al-Ghosoun, A., Renno, J., Seaid, M., and Mohamed, M. S. (2024). Machine learning-based modeling for structural engineering: a comprehensive survey and applications overview. Buildings 14 (11), 3515. doi:10.3390/buildings14113515
European Parliamentary Research Service (2020). The ethics of artificial intelligence: issues and initiatives. PE, 634.452. European Parliament.
Felzmann, H., Fosch-Villaronga, E., Lutz, C., and Tamò-Larrieux, A. (2020). Towards transparency by design for artificial intelligence. Sci. Eng. Ethics 26 (6), 3333–3361. doi:10.1007/s11948-020-00276-4
Ferraris, C., Amprimo, G., and Pettiti, G. (2023). Computer vision and image processing in structural health monitoring: overview of recent applications. Signals 4 (3), 539–574. doi:10.3390/signals4030029
Floridi, L., and Cowls, J. (2019). A unified framework of five principles for AI in society. Harv. Data Sci. Rev. 1 (1). doi:10.1162/99608f92.8cd550d1
Gamil, Y. (2023). Machine learning in concrete technology: a review of current researches, trends, and applications. Front. Built Environ. 9. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2023.1145591
Ghaffari, A., Shahbazi, Y., Mokhtari Kashavar, M., Fotouhi, M., and Pedrammehr, S. (2024). Advanced predictive structural health monitoring in high-rise buildings using recurrent neural networks. Buildings 14 (10), 3261. doi:10.3390/buildings14103261
Grover, D. V., Ahmad, N., Fatima, M. I., Alam, M., and Khan, D. I. R. (2024). “Real-world applications of generative AI for data augmentation,” in Blockchain, IoT, and AI technologies for supply chain management: apply emerging technologies to address and improve supply chain management, Editors D. V. Grover, D. B. B. Balusamy, D. M. Milanova, and D. A. Y. Felix, Berkeley, CA: Apress, 383–412. doi:10.1007/979-8-8688-0315-4_15
Gustafson, A., and Peterson, E. (2023). “Virtue ethics,” in Encyclopedia of business and professional ethics, Editors D. C. Poff, and A. C. Michalos, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1856–1859. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-22767-8_398
Harle, S. M. (2024). Advancements and challenges in the application of artificial intelligence in civil engineering: a comprehensive review. Asian J. Civ. Eng. 25 (1), 1061–1078. doi:10.1007/s42107-023-00760-9
Hassija, V., Chamola, V., Mahapatra, A., Singal, A., Goel, D., Huang, K., et al. (2024). Interpreting black-box models: a review on explainable artificial intelligence. Cogn. Comput. 16 (1), 45–74. doi:10.1007/s12559-023-10179-8
Hosamo, H. H., Imran, A., Cardenas-Cartagena, J., Svennevig, P. R., Svidt, K., and Nielsen, H. K. (2022a). A review of the digital twin technology in the AEC-FM industry. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2022(1), 2185170. doi:10.1155/2022/2185170
Hosamo, H. H., Svennevig, P. R., Svidt, K., Han, D., and Nielsen, H. K. (2022b). A Digital Twin predictive maintenance framework of air handling units based on automatic fault detection and diagnostics. Energy Build. 261, 111988. doi:10.1016/j.enbuild.2022.111988
Hristova, T., Magee, L., and Soldatic, K. (2024). The problem of alignment. AI and SOCIETY. doi:10.1007/s00146-024-02039-2
Hu, Y., Wang, W., Li, L., and Wang, F. (2024). Applying machine learning to earthquake engineering: a scientometric analysis of world research. Buildings 14 (5), 1393. doi:10.3390/buildings14051393
Hussain, S., Hussain, S. M., Xin, Y., and Wang, Z.-C. (2023). Vehicle load identification based on bridge response using deep convolutional neural network. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 24, 1235–1252. doi:10.1080/13467581.2024.2328634
International Organization for Standardization (2023a). ISO/IEC 23894:2023 Information technology — artificial intelligence — guidance on risk management.
International Organization for Standardization (2023b). ISO/IEC 42001:2023 Information technology — artificial intelligence — management system.
Jia, D.-W., and Wu, Z.-Y. (2022). Structural probabilistic seismic risk analysis and damage prediction based on artificial neural network. Structures 41, 982–996. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2022.05.056
Jobin, A., Ienca, M., and Vayena, E. (2019). The global landscape of AI ethics guidelines. Nat. Mach. Intell. 1 (9), 389–399. doi:10.1038/s42256-019-0088-2
Kay, C. D. (2018). “Utilitarianism,” in Global encyclopedia of public administration, public policy, and governance, Editor A. Farazmand, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 6086–6091. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-20928-9_2399
Keshmiry, A., Hassani, S., and Dackermann, U. (2024). “5 - AI-based structural health monitoring systems,” in Artificial intelligence applications for sustainable construction, Editors M. L. Nehdi, H. C. Arora, K. Kumar, R. Damaševičius, and A. Kumar (Woodhead Publishing), 151–170. doi:10.1016/B978-0-443-13191-2.00008-0
Kim, J.-W., Choi, H.-W., Kim, S.-K., and Na, W. S. (2024). Review of image-processing-based technology for structural health monitoring of civil infrastructures. J. Imaging 10 (4), 93. doi:10.3390/jimaging10040093
Klingbeil, A., Grützner, C., and Schreck, P. (2024). Trust and reliance on AI — an experimental study on the extent and costs of overreliance on AI. Comput. Hum. Behav. 160, 108352. doi:10.1016/j.chb.2024.108352
Korzeniowski, T. F., and Weinberg, K. (2021). A multi-level method for data-driven finite element computations. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 379, 113740. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2021.113740
Kurian, B., and Liyanapathirana, R. (2020). “Machine learning techniques for structural health monitoring,” Proceedings of the 13th international conference on damage assessment of structures, Singapore: Springer, 3–24. doi:10.1007/978-981-13-8331-1_1
Lagaros, N. D., and Plevris, V. (2022). Artificial intelligence (AI) applied in civil engineering. Appl. Sci. 12, 7595(15). doi:10.3390/app12157595
Lagaros, N. D., Tsompanakis, Y., Fragiadakis, M., Plevris, V., and Papadrakakis, M. (2008). “Metamodel-based computational techniques for solving structural optimization problems considering uncertainties,” in Structural design optimization considering uncertainties. Editors Y. Tsompanakis, N. D. Lagaros, and M. Papadrakakis (London: CRC Press), 567–597.
Leavy, S., O’Sullivan, B., and Siapera, E. (2020). Data, power and bias in artificial intelligence. ArXiv e-prints(arXiv:2008.07341). doi:10.48550/arXiv.2008.07341
Li, Y., and Goel, S. (2024). Making it possible for the auditing of AI: a systematic review of AI audits and AI auditability. Inf. Syst. Front. doi:10.1007/s10796-024-10508-8
Li, Z., Yoon, J., Zhang, R., Rajabipour, F., Srubar Iii, W. V., Dabo, I., et al. (2022). Machine learning in concrete science: applications, challenges, and best practices. npj Comput. Mater. 8 (1), 127. doi:10.1038/s41524-022-00810-x
Liang, C.-J., Le, T.-H., Ham, Y., Mantha, B. R. K., Cheng, M. H., and Lin, J. J. (2024). Ethics of artificial intelligence and robotics in the architecture, engineering, and construction industry. Automation Constr. 162, 105369. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2024.105369
Liang, L., Liu, M., Martin, C., and Sun, W. (2018). A deep learning approach to estimate stress distribution: a fast and accurate surrogate of finite-element analysis. J. R. Soc. Interface 15 (138), 20170844. doi:10.1098/rsif.2017.0844
Liao, W., Lu, X., Fei, Y., Gu, Y., and Huang, Y. (2024). Generative AI design for building structures. Automation Constr. 157, 105187. doi:10.1016/j.autcon.2023.105187
Łuków, P., and Różyńska, J. (2014). “Respect for autonomy,” in Encyclopedia of global bioethics, Editor H. ten Have (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 1–12. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-05544-2_380-1
Mahajan, L. S., Kirange, M., and Suryawanshi, G. (2024). An artificial intelligence applications in structural engineering. Innovation Smart Sustain. Infrastructure 2, 215–227. doi:10.1007/978-981-97-3994-3_15
Málaga-Chuquitaype, C. (2022). Machine learning in structural design: an opinionated review. Front. Built Environ. 8. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2022.815717
Meethal, R. E., Kodakkal, A., Khalil, M., Ghantasala, A., Obst, B., Bletzinger, K.-U., et al. (2023). Finite element method-enhanced neural network for forward and inverse problems. Adv. Model. Simul. Eng. Sci. 10 (1), 6. doi:10.1186/s40323-023-00243-1
Merrick, L., and Taly, A. (2020). “The explanation game: explaining machine learning models using shapley values,”in Machine learning and knowledge extraction. (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 17–38. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-57321-8_2
Mondal, T. G., and Chen, G. (2022). Artificial intelligence in civil infrastructure health monitoring—historical perspectives, current trends, and future visions. Front. Built Environ. 8. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2022.1007886
Mosqueira-Rey, E., Hernández-Pereira, E., Alonso-Ríos, D., Bobes-Bascarán, J., and Fernández-Leal, Á. (2023). Human-in-the-loop machine learning: a state of the art. Artif. Intell. Rev. 56 (4), 3005–3054. doi:10.1007/s10462-022-10246-w
Mostafa, K., Zisis, I., and Moustafa, M. A. (2022). Machine learning techniques in structural wind engineering: a state-of-the-art review. Appl. Sci. 12 (10), 5232. doi:10.3390/app12105232
Myllyaho, L., Raatikainen, M., Männistö, T., Mikkonen, T., and Nurminen, J. K. (2021). Systematic literature review of validation methods for AI systems. J. Syst. Softw. 181, 111050. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2021.111050
Novelli, C., Taddeo, M., and Floridi, L. (2024). Accountability in artificial intelligence: what it is and how it works. AI Soc. 39 (4), 1871–1882. doi:10.1007/s00146-023-01635-y
Ntoutsi, E., Fafalios, P., Gadiraju, U., Iosifidis, V., Nejdl, W., Vidal, M.-E., et al. (2020). Bias in data-driven artificial intelligence systems—an introductory survey. WIREs Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 10 (3), e1356. doi:10.1002/widm.1356
Numan, G. (2020). Testing artificial intelligence. in The future of software quality assurance, Editor S. Goericke, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 123–136. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-29509-7_10
Onatayo, D., Onososen, A., Oyediran, A. O., Oyediran, H., Arowoiya, V., and Onatayo, E. (2024). Generative AI applications in architecture, engineering, and construction: trends, implications for practice, education and imperatives for upskilling—a review. Architecture 4 (4), 877–902. doi:10.3390/architecture4040046
Oscar, L. H., Cerqueira, L. C., Cunha, P. H., and Qualharini, E. L. (2023). Generative design in civil construction: a case study in Brazil. Front. Built Environ. 9. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2023.1150767
Page, K. (2012). The four principles: can they be measured and do they predict ethical decision making? BMC Med. Ethics 13, 10. doi:10.1186/1472-6939-13-10
Plevris, V. (2024). AI-driven innovations in earthquake risk mitigation: a future-focused perspective. Geosciences 14 (9), 244. doi:10.3390/geosciences14090244
Plevris, V. (2025a). Assessing uncertainty in image-based monitoring: addressing false positives, false negatives, and base rate bias in structural health evaluation. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 39, 959–972. doi:10.1007/s00477-024-02898-7
Plevris, V. (2025b). A glimpse into the future of civil engineering education: the new era of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and large language models. J. Civ. Eng. Educ. 151 (2), 02525001. doi:10.1061/JCEECD.EIENG-2193
Plevris, V., Almutairi, A., and Jiménez Rios, A. (2024). Advancing sustainability through structural optimization: innovations in material efficiency and environmental impact reduction. The 1st international conference on net-zero built environment: innovations in materials, structures, and management practices (Net-Zero Future 2024), Oslo, Norway, 19–21 June 2024, 1611–1623. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-69626-8_134
Plevris, V., and Papazafeiropoulos, G. (2024). AI in structural health monitoring for infrastructure maintenance and safety. Infrastructures 9 (12), 225. doi:10.3390/infrastructures9120225
Ploennigs, J., and Berger, M. (2024). Automating computational design with generative AI. Civ. Eng. Des. 6 (2), 41–52. doi:10.1002/cend.202400006
Poff, D. C. (2023). “Deontology,” in Encyclopedia of business and professional ethics, Editors D. C. Poff, and A. C. Michalos, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 538–540. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-22767-8_399
Reichborn-Kjennerud, K. (2018). “Accountability and ethics,” in Global encyclopedia of public administration, public policy, and governance, Editor A. Farazmand, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 42–49. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-20928-9_2465
Sadek, M., Kallina, E., Bohné, T., Mougenot, C., Calvo, R. A., and Cave, S. (2024). Challenges of responsible AI in practice: scoping review and recommended actions. AI and SOCIETY. doi:10.1007/s00146-024-01880-9
Safdar, N. M., Banja, J. D., and Meltzer, C. C. (2020). Ethical considerations in artificial intelligence. Eur. J. Radiology 122, 108768. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.108768
Salehi, H., and Burgueño, R. (2018). Emerging artificial intelligence methods in structural engineering. Eng. Struct. 171, 170–189. doi:10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.05.084
Scaife, A. D. (2024). Improve predictive maintenance through the application of artificial intelligence: a systematic review. Results Eng. 21, 101645. doi:10.1016/j.rineng.2023.101645
Scorzato, L. (2024). Reliability and interpretability in science and deep learning. Minds Mach. 34 (3), 27. doi:10.1007/s11023-024-09682-0
Sheikh, H., Prins, C., and Schrijvers, E. (2023). “Artificial intelligence: definition and background,” in Mission AI: the new system technology, Editors H. Sheikh, C. Prins, and E. Schrijvers, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 15–41. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-21448-6_2
Smith, J., Gardoni, P., and Murphy, C. (2014). The responsibilities of engineers. Sci. Eng. Ethics 20 (2), 519–538. doi:10.1007/s11948-013-9463-2
Solorzano, G., and Plevris, V. (2020). Optimum design of RC footings with genetic algorithms according to ACI 318-19. Buildings 10 (6), 110–117. doi:10.3390/buildings10060110
Solorzano, G., and Plevris, V. (2022a). ANN-based surrogate model for predicting the lateral load capacity of RC shear walls. 8th European congress on computational methods in applied Sciences and engineering (ECCOMAS 2022), Oslo, Norway, 5–9 June 2022. doi:10.23967/eccomas.2022.050
Solorzano, G., and Plevris, V. (2022b). Computational intelligence methods in simulation and modeling of structures: a state-of-the-art review using bibliometric maps. Front. Built Environ. 8. doi:10.3389/fbuil.2022.1049616
Solorzano, G., and Plevris, V. (2023). DNN-MLVEM: a data-driven macromodel for rc shear walls based on deep neural networks. Mathematics 11 (10), 2347. doi:10.3390/math11102347
Song, D., Tan, X., Huang, Q., Wang, L., Dong, M., Yang, J., et al. (2024). Review of AI-based wind prediction within recent three years: 2021–2023. Energies 17 (6), 1270. doi:10.3390/en17061270
Song, J., and Fu, T. (2023). “Deep learning based structural reliability finite element analysis surrogate for hydro-generator lower frame,” in 2023 5th asia energy and electrical engineering symposium (AEEES)23-26 March 2023 (IEEE), 150–154. doi:10.1109/AEEES56888.2023.10114264
Stahl, B. C. (2021). “Ethical issues of AI,” in Artificial intelligence for a better future: an ecosystem perspective on the ethics of AI and emerging digital technologies, Editor B. C. Stahl, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 35–53. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-69978-9_4
Tapeh, A. T. G., and Naser, M. Z. (2023). Artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning in structural engineering: a scientometrics review of trends and best practices. Archives Comput. Methods Eng. 30 (1), 115–159. doi:10.1007/s11831-022-09793-w
Thai, H.-T. (2022). Machine learning for structural engineering: a state-of-the-art review. Structures 38, 448–491. doi:10.1016/j.istruc.2022.02.003
Thomson, C. J. H. (2023). “Beneficence,” in Encyclopedia of business and professional ethics, Editors D. C. Poff, and A. C. Michalos, (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 198–200. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-22767-8_44
Trotta, A., Ziosi, M., and Lomonaco, V. (2023). The future of ethics in AI: challenges and opportunities. AI and Soc. 38 (2), 439–441. doi:10.1007/s00146-023-01644-x
Tursunalieva, A., Alexander, D. L. J., Dunne, R., Li, J., Riera, L., and Zhao, Y. (2024). Making sense of machine learning: a review of interpretation techniques and their applications. Appl. Sci. 14 (2), 496. doi:10.3390/app14020496
Ucar, A., Karakose, M., and Kırımça, N. (2024). Artificial intelligence for predictive maintenance applications: key components, trustworthiness, and future trends. Appl. Sci. 14 (2), 898. doi:10.3390/app14020898
Uriarte, C., Pardo, D., and Omella, Á. J. (2022). A finite element based deep learning solver for parametric PDEs. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Engrg. 391, 114562. doi:10.1016/j.cma.2021.114562
U.S. Department of Homeland Security (2024). Groundbreaking framework for the safe and secure deployment of AI in critical infrastructure unveiled. United States: Department of Homeland Security.
Varsha, P. S. (2023). How can we manage biases in artificial intelligence systems – a systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 3 (1), 100165. doi:10.1016/j.jjimei.2023.100165
Visave, J. (2025). Transparency in AI for emergency management: building trust and accountability. AI and Ethics. doi:10.1007/s43681-025-00692-x
Voigt, P., and von dem Bussche, A. (2024). The EU general data protection regulation (GDPR). A practical guide. Cham: Springer doi:10.1007/978-3-031-62328-8
Wang, B. (2024). Ethical reflections on the application of artificial intelligence in the construction of smart cities. J. Eng. 2024 (1), 8207822. doi:10.1155/2024/8207822
Wang, X., Mazumder, R. K., Salarieh, B., Salman, A. M., Shafieezadeh, A., and Li, Y. (2022). Machine learning for risk and resilience assessment in structural engineering: progress and future trends. J. Struct. Eng. 148 (8), 03122003. doi:10.1061/(ASCE)ST.1943-541X.0003392
Wang, X., Wu, Z., Huang, W., Wei, Y., Huang, Z., Xu, M., et al. (2023). VIS+AI: integrating visualization with artificial intelligence for efficient data analysis. Front. Comput. Sci. 17 (6), 176709. doi:10.1007/s11704-023-2691-y
Wu, X., Xiao, L., Sun, Y., Zhang, J., Ma, T., and He, L. (2022). A survey of human-in-the-loop for machine learning. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 135, 364–381. doi:10.1016/j.future.2022.05.014
Xing, Z., Pan, Y., Yang, Y., Yuan, X., Liang, Y., and Huang, Z. (2024). Transfer learning integrating similarity analysis for short-term and long-term building energy consumption prediction. Appl. Energy 365, 123276. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123276
Xu, W. (2024). Vehicle load identification using machine vision and displacement influence lines. Buildings 14 (2), 392. doi:10.3390/buildings14020392
Xu, Y., Liu, X., Cao, X., Huang, C., Liu, E., Qian, S., et al. (2021). Artificial intelligence: a powerful paradigm for scientific research. Innovation 2 (4), 100179. doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100179
Zhang, L., Wen, J., Li, Y., Chen, J., Ye, Y., Fu, Y., et al. (2021). A review of machine learning in building load prediction. Appl. Energy 285, 116452. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116452
Keywords: responsible AI, AI governance, AI ethics, accountability, transparency and explainability, AI risk management, AI framework for structural engineering
Citation: Plevris V and Hosamo H (2025) Responsible AI in structural engineering: a framework for ethical use. Front. Built Environ. 11:1612575. doi: 10.3389/fbuil.2025.1612575
Received: 15 April 2025; Accepted: 30 June 2025;
Published: 11 July 2025.
Edited by:
Tadesse Gemeda Wakjira, University of British Columbia, CanadaReviewed by:
Themistoklis Tsalkatidis, Norwegian University of Life Sciences, NorwayIda Mascolo, University of Naples Federico II, Italy
Amir Ali Shahmansouri, Washington State University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Plevris and Hosamo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Vagelis Plevris, dnBsZXZyaXNAcXUuZWR1LnFh
 Vagelis Plevris
Vagelis Plevris Haidar Hosamo
Haidar Hosamo