- Department of Neurosurgery, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hainan Medical University, Haikou, China
Ferroptosis, an iron-dependent form of cell death, has emerged as a critical factor in the pathogenesis of central nervous system (CNS) injuries, including neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, and traumatic brain injury. This review highlights disrupted iron metabolism, glutathione depletion, and antioxidant system impairment as core mechanisms, alongside polyunsaturated fatty acid oxidation contributing to neuronal damage. Diagnostic advancements, such as MRI-based iron quantification and lipid ROS detection, offer clinical potential but require validation. Therapeutic strategies, including iron chelators, antioxidants, and lipid metabolism modulators, demonstrate efficacy in preclinical models by attenuating ferroptosis. Translational challenges persist due to incomplete mechanistic insights, tissue-specific iron dynamics, and delivery limitations. The dual role of iron in CNS physiology and pathology underscores the need for interdisciplinary research to refine diagnostics and therapies. Emphasizing ferroptosis as a therapeutic target, this work advocates for a deeper exploration of immune interactions and combinatorial approaches to improve outcomes in CNS injuries.
1 Introduction
Central nervous system (CNS) injuries, including neurodegenerative diseases and stroke, pose a significant global health burden as the leading cause of disability and the second most common cause of death globally (Chin and Vora, 2014). The pathological basis of these conditions involves aberrant neuronal death, exacerbated by neurons’ limited capacity for regeneration through cellular division. Neuronal death occurs through multiple pathways including apoptosis, necrosis, pyroptosis, parthanatos, and the recently discovered ferroptosis (Fricker et al., 2018). While these pathways share some common features, ferroptosis displays distinct morphological and biochemical characteristics that differentiate it from other forms of cell death.
Ferroptosis, first described in 2012, is an iron-dependent form of regulated cell death characterized by: (1) accumulation of lipid peroxides and reactive oxygen species (ROS), (2) distinct mitochondrial morphology including shrinkage and cristae reduction, and (3) dependence on iron metabolism (Dixon et al., 2012; Yao et al., 2021). Ferroptosis is mostly caused by glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPX4) failure and consequent lipid peroxidation (LP), as opposed to apoptosis, which requires caspase activation, or necrosis, which results in cell death. Ferroptosis, a novel form of cell death in CNS injuries, has garnered increasing attention due to its underlying mechanism and role (Dixon et al., 2012; Dixon, 2017). The pathological basis of CNS injuries lies in aberrant neuronal death, which is compounded by neurons’ inability to divide, thus preventing the replacement of damaged neurons through standard cellular renewal mechanisms. Notably, the brain, the most oxygen-consuming organ in the human body, has relatively weak antioxidant defense mechanisms and is rich in polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) (Kagan et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2019). This makes the brain especially vulnerable to ferroptosis and more susceptible to its damaging effects. Increasing evidence indicates a strong association between ferroptosis and CNS injuries, particularly in crucial CNS regions such as the cerebral cortex, hippocampus, striatum, and spinal cord (Dixon et al., 2012; Skouta et al., 2014; Chen et al., 2015; Martinez et al., 2019). Therefore, studying ferroptosis is crucial for advancing the treatment and rehabilitation of CNS injuries.
Iron, a vital trace element, is essential for the proper functioning of the CNS (Thirupathi and Chang, 2019). However, excessive iron accumulation can lead to neuronal death through ferroptosis and exacerbated inflammation (Xiong et al., 2019). Abnormal iron accumulation is closely associated with the progression of various CNS injuries, including Parkinson’s disease (PD) (Xiong et al., 2019) and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (Peng et al., 2021), stroke, and traumatic brain injury (TBI). Consequently, understanding the mechanism and role of ferroptosis in CNS injuries is vital to developing new diagnostic methods and therapeutic strategies, potentially offering significant clinical value for improving the prognosis and outcomes.
While the role of ferroptosis in CNS injuries has been initially recognized, the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely understood (Goldsteins et al., 2022; David et al., 2023). Moreover, many studies are limited to animal models and in vitro experiments. To comprehensively analyze existing evidence, we systematically searched PubMed and Web of Science using the following keyword combinations: ferroptosis AND (central nervous system injury)/ferroptosis AND (central nervous system damage)/ferroptosis AND (central nervous system disease)/ferroptosis AND (neurodegenerative diseases)/ferroptosis AND [(Parkinson’s disease) OR (Alzheimer’s disease) OR (Huntington’s disease) OR (multiple sclerosis)]/ferroptosis AND [(subarachnoid hemorrhage) OR (SAH)]/ferroptosis AND [(traumatic brain injury) OR TBI OR (head injury)]/ferroptosis AND [stroke OR (cerebral hemorrhage)]/ferroptosis AND (spinal cord injury). However, the papers that were not reviews or research articles were not included. This article summarizes the mechanisms, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies for ferroptosis in CNS injuries. We conduct a comprehensive review of recent studies on ferroptosis and CNS injuries, aiming to enhance our understanding of the underlying mechanisms and to refine therapeutic strategies for treating CNS injuries.
2 Ferroptosis
2.1 Definition and characteristics of ferroptosis
In Dolma et al. (2003) discovered that erastin could effectively induce tumor cell death in RAS-mutant tumors. They found that this process did not involve traditional cell death pathways (Dolma et al., 2003). Iron chelators could suppress this death process, accompanied by increased intracellular lipid ROS levels (Yagoda et al., 2007; Yang and Stockwell, 2008). The term “ferroptosis” was introduced by Dixon et al. (2012) to describe a distinctive form of cell death that is iron-dependent and non-apoptotic. This process is characterized by the buildup of intracellular lipid ROS (Dixon et al., 2012). These findings suggest that ferroptosis may represent a novel mechanism of cell death. Cell death is a complex and diverse process, and ferroptosis, as a unique mode of cell death, differs significantly from necrosis, apoptosis, and autophagy in terms of morphology, biochemical characteristics, and gene expression (Stockwell et al., 2017; Wu et al., 2018). Ferroptosis is defined by the preservation of functional cytoplasmic membranes, increased mitochondrial membrane density, decreased or absent cristae, increased release of oxidized PUFAs, elevated cytoplasmic levels of lipid ROS, and the process can be inhibited by iron chelators (Yang and Stockwell, 2008; Dixon et al., 2012).
2.2 Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis
2.2.1 Iron metabolism
Iron is an essential physiological element, and its distribution and levels can significantly impact physiological processes (Yan and Zhang, 2019). Iron overload plays a critical factor in ferroptosis. Iron (Fe2+) generates large amounts of hydroxyl radicals through Fenton and iron-catalyzed Haber-Weiss reactions, catalyzing the generation of ROS, which in turn leads to the development of LP (MacKenzie et al., 2008; Bogdan et al., 2016). Fe2+ is produced through intestinal absorption or erythrocyte degradation and then oxidizes to iron (Fe3+). Fe3+ binds to transferrin and enters cells via transferrin receptor (TFR) mediated endocytosis (Frazer and Anderson, 2014). Within endosomes, Fe3+ is reduced back to Fe2+ primarily by six-transmembrane epithelial antigen of prostate 3 (STEAP3) in vivo (Ohgami et al., 2006; Bogdan et al., 2016), with significant contribution from superoxide anion (O2•–) generated through NADPH oxidase activity. This reduction is critical for Fenton reactions: Fe2+ reacts with H2O2 to generate hydroxyl radicals (•OH) via the iron-catalyzed Haber-Weiss reaction (Liochev and Fridovich, 1999). Iron can be stored in the labile iron pool or transported via divalent metal transporter 1 (DMT1) or Zinc-Iron regulatory protein family 8/14. Excessive Fe2+ is oxidized to Fe3+ by ferroportin (FPN) to maintain intracellular iron homeostasis (Bogdan et al., 2016). Silencing TFR can inhibit erastin-induced ferroptosis (Gao et al., 2015), while heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) supplementation accelerates erastin-induced ferroptosis (Kwon et al., 2015). Heat shock protein beta-1 reduced intracellular iron by suppressing telomeric repeat factor 1, further inhibiting ferroptosis (Sun et al., 2015). Ferritin, a 24-subunit nanocage complex comprising ferritin light chain (FTL) and ferritin heavy chain 1 (FTH) polypeptides, functions as the primary intracellular iron storage protein to inhibit ferroptosis at the cellular level through two key mechanisms: (1) iron sequestration: the ferroxidase activity of FTH causes up to 4,500 iron atoms to mineralize within its cavity and oxidize Fe2+ to Fe3+. This lowers the pool of labile iron that is accessible for Fenton reactions (Arosio et al., 2017). (2) antioxidant protection: Ferritin inhibits iron-catalyzed lipid peroxidation by separating redox-active iron. FTH1 overexpression gives resistance to erastin-induced ferroptosis, whereas genetic ablation of FTH1 increases cellular vulnerability (Alvarez et al., 2017). Systemically, serum ferritin represents the body’s iron storage, but because it is largely an iron buffer and cannot release iron, it does not directly control ferroptosis (Wang et al., 2010). The ferroptosis-inhibitory function is thus confined to the intracellular compartment. Fe2+ is transported to Fe3+ for storage in ferritin through FPN or poly(rC)-binding protein 1/2, depending on the formation of heteropolymers by FTH and FTL.
Iron homeostasis begins with dietary absorption in the duodenum, where Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ by duodenal cytochrome B and transported via DMT1 into enterocytes. Systemic iron is oxidized to Fe3+ by hephaestin, bound to transferrin, and circulated in plasma. Excess iron is stored in hepatocytes or macrophages via ferritin, while systemic efflux is regulated by ferroportin (FPN) and hepcidin (Frazer and Anderson, 2014). Endosomal Fe3+ is reduced to Fe2+ by STEAP3 and exported to the cytosol via DMT1. Excess Fe2+ is exported by FPN or oxidized by ceruloplasmin. Disruption of these regulatory mechanisms elevates labile iron pools, potentiating Fenton reactions and ferroptosis.
2.2.2 Amino acid metabolism
Mounting studies indicate that cystine uptake via System Xc– is crucial for maintaining glutathione (GSH) levels and inhibiting ferroptosis (Aoyama and Nakaki, 2015). Inhibiting GSH synthesis can induce ferroptosis (Yang et al., 2014). System Xc– (a special cystine/glutamate transporter) exchanges intracellular glutamate for extracellular cystine in a 1:1 ratio (Dixon et al., 2012), driven by the high intracellular glutamate concentration rather than adenosine triphosphate (Bridges et al., 2012; Friedmann Angeli et al., 2014). The System Xc– transport may be inhibited by elevated extracellular glutamate levels. Following cellular uptake, cystine undergoes reduction to cysteine, primarily mediated by thioredoxin-related protein 14 (TRP14) through the dithiol-disulfide exchange (Martí-Andrés et al., 2024). This cysteine then reacts with glutamate, forming γ-glutamylcysteine, a process catalyzed by glutamylcysteine ligase. Finally, glycine combines with γ-glutamylcysteine to produce GSH, facilitated by the enzyme GSH synthetase (Philpott and Ryu, 2014). The function of the anti-LP enzyme GPX4 can be directly inhibited, through covalent modification by compounds like RSL3 (RAS-selective lethal 3), or indirectly through GSH depletion, leading to the generation of excessive lipid peroxides, causing ferroptosis (Cui et al., 2022; Weaver and Skouta, 2022). This process is the critical factor in ferroptosis. GPX4 consumes GSH to reduce lipid hydroperoxides (L-OOH) to lipid alcohols. At the same time, GSH is oxidized to GSH disulfide, which is then decreased back to GSH by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH)-dependent on GSH reductase to enter the next cycle.
Additionally, L-OOH is oxidized by Fe2+ to generate tremendously reactive lipid alkoxyl radicals (LO•), which destroy PUFAs through a chain reaction, leading to membrane injury and cell death (Gaschler and Stockwell, 2017). GSH can also act as a binding ligand for Fe2+ in the unstable iron pool, preventing the formation of hydroxyl radicals from its reaction with H2O2 (Philpott and Ryu, 2014). GPX4 utilizes GSH to reduce lipid peroxides of PUFAs to lipids, maintaining the balance between lipid peroxides and lipids.
2.2.3 Lipid metabolism
Fatty acids are essential molecular constituents of the brain, comprising over 50% of its dry weight, with PUFAs representing approximately 40% of the total FAs (Lauritzen et al., 2001; Yao et al., 2021). PUFAs are integral components of neuronal membrane phospholipids, playing a crucial role in sustaining essential membrane functions, including signal transduction, regulation of ion channels, and the activity of membrane-associated proteins (Wainwright, 2002; Haag, 2003). By modulating synaptic activity, neurotransmitter levels, and receptor distribution and activity, PUFAs directly impact cognitive function, learning, and memory in the brain (Chalon, 2006; Weiser et al., 2016).
Omega-3 PUFAs possess distinct anti-inflammatory and metabolic characteristics, suggesting their significant potential for treating PD and AD (Cunnane et al., 2009; Weiser et al., 2016), and multiple sclerosis (MS) (Siegert et al., 2017). Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), an Omega-3 PUFA, has been proven to effectively inhibit abnormal neuronal firing in epilepsy by regulating voltage-gated potassium channels (Börjesson and Elinder, 2011). PUFAs are essential for neurological maturation during early development, especially in infancy; a deficiency of DHA precursors has been associated with occipital cortex dysfunction and peripheral neuropathy (Uauy et al., 2000). However, the high reactivity of PUFA makes them vulnerable to free radical attack and LP, resulting in a high risk of OS on brain tissue. Particularly vulnerable are PUFAs containing allyl carbon, such as arachidonic acid and DHA, which are easily oxidized to harmful LP products (Uauy et al., 2000). Under pathological conditions, phosphatidylethanolamine, derivatives of PUFAs, may undergo oxidation mediated by lipoxygenases, resulting in the formation of lipid peroxides, which can trigger ferroptosis (Uauy et al., 2000). The disruption of cellular membrane integrity, particularly in neuronal cell membranes and organelles such as mitochondria and the endoplasmic reticulum (Gaschler and Stockwell, 2017; Kagan et al., 2017; Zou et al., 2020), adversely impacts neural functions by altering membrane potential and disrupting ion homeostasis. This ultimately adds to neuronal dysfunction and death by causing abnormal synaptic activity and reduced neurotransmitter release. In particular, Omega-3 PUFAs such as DHA, by altering cell membrane fluidity, may directly influence cellular sensitivity to oxidative stress and thus the process of ferroptosis. The cellular metabolic mechanisms of ferroptosis are illustrated in Figure 1.
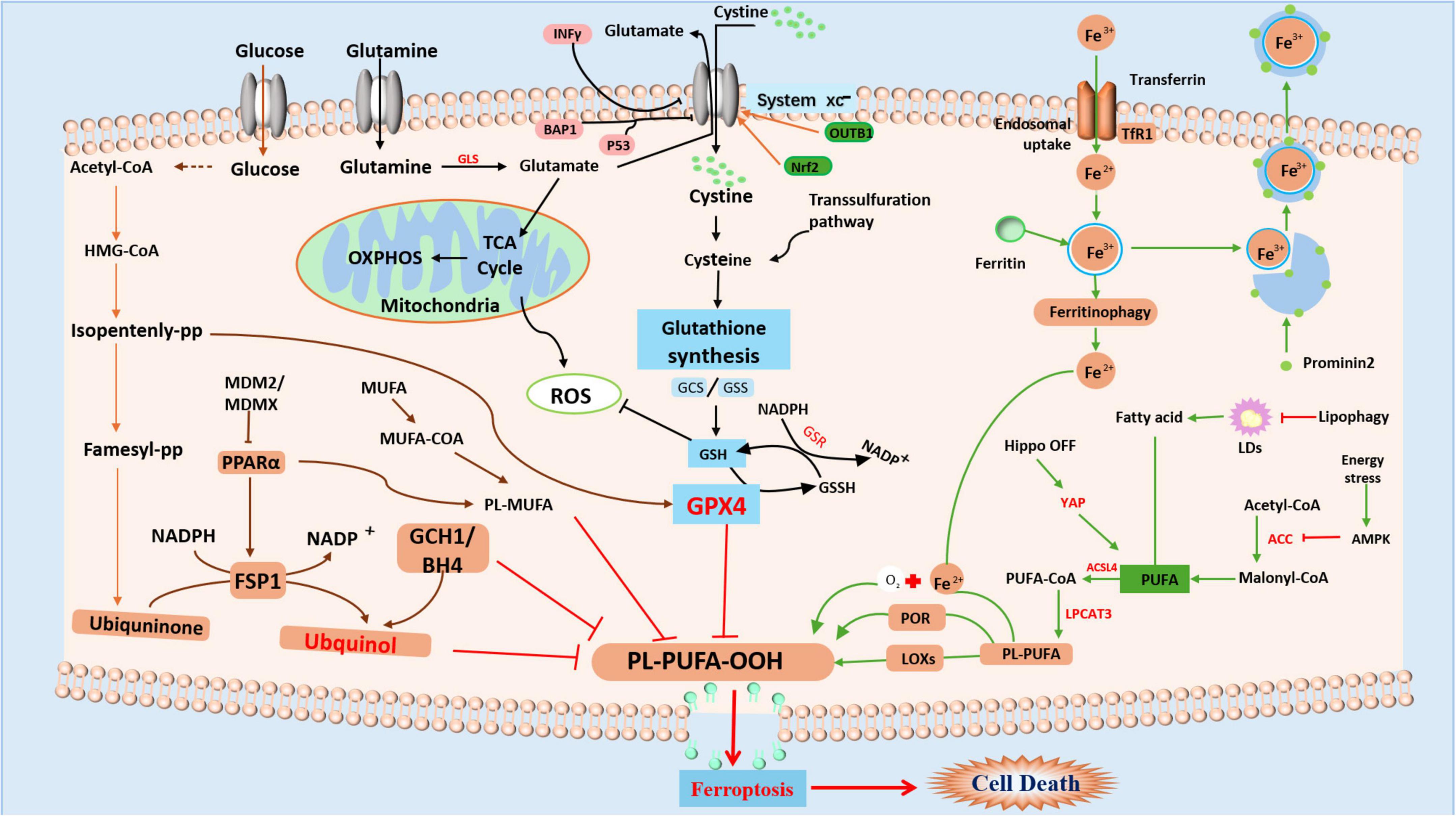
Figure 1. Summary of the mechanism of ferroptosis Ferroptosis is mainly caused by the GSH-dependent enzyme GPX4, which inhibits the production of Fe2+dependent lipid ROS by converting cytotoxic lipid hydroperoxides (L-OOH) to non-toxic alcohols (L-OH). Controlled by the cystine/glutamate antiporter (System Xc–), GSH functions as a cofactor for GPX4. Ferroptosis is brought on by depleting GSH, inactivating GPX4, and raising lipid peroxides when System Xc–, GSH production, or GPX4 itself are inhibited. Iron overload results from a disturbance of iron homeostasis, which includes ferritinophagy-mediated breakdown, absorption, export, and storage. Through the Fenton reaction, excess iron catalyzes the production of harmful lipid ROS. Furthermore, PUFAs are changed into peroxidation-susceptible PUFA phospholipids by enzymes (such as COXs and LOXs).
2.2.4 Other metabolic pathways
Mitochondria play an essential role in the advancement and development of ferroptosis (Gao et al., 2019). The mevalonate pathway affects the production of CoQ10, an endogenous antioxidant involved in regulating iron metabolism. Levels of NADPH and selenium also influence the development of ferroptosis. NAD PH has a reducing effect, while selenium promotes the biosynthesis of GPX4, which enhances resistance to iron-induced damage. Glutamine metabolic pathways are crucial for the formation of intracellular iron ions and ROS, thereby regulating iron metabolism. Glutaminase transforms glutamine, a key substrate for the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA), into α-ketoglutarate (α-KG). In addition to improving mitochondrial respiration and electron transport chain activity, α-KG replenishes TCA cycle intermediates, which raises the production of ROS (Martínez-Reyes and Chandel, 2020; Zhang et al., 2021). In addition, α-KG can be utilized via malic enzyme to generate NADPH, a process that supports glutathione regeneration (Cluntun et al., 2017). α-KG activates prolyl hydroxylases (PHDs) that stabilize hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) (Martínez-Reyes and Chandel, 2020). HIF-1α transcriptionally upregulates TfR1, leading to increased iron uptake (Yang et al., 2018). Additionally, HIF-1α increases ceruloplasmin, which promotes the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, facilitating the efflux of iron from cells (Yang et al., 2025). Glutamine provides carbon skeletons for the manufacture of glutathione through the enzyme glutamate-cysteine ligase and selenocysteine biosynthesis, which is essential for GPX4 action (Ingold et al., 2018). Thus, glutamine metabolism serves as a metabolic rheostat for ferroptosis sensitivity by coordinately regulating iron homeostasis and oxidative stress.
2.3 Ferroptosis and other cell death pathways
Ferroptosis differs from other cell death modalities in both molecular mechanisms and morphological characteristics, since it is a unique iron-dependent type of controlled cell death triggered by LP and GPX4 inactivation (Table 1).
2.3.1 Ferroptosis and necroptosis
The process of necroptosis is governed by the activation of receptor-interacting protein kinases (RIPK) 1/3, along with mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL) (Conrad et al., 2016). Müller et al. (2017) found in a mouse model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury that the absence of ACSL4, a factor associated with ferroptosis, rendered cells more vulnerable to necroptosis over time. In contrast, cells lacking in MLKL protein were more prone to ferroptosis. Additionally, aberrant RIPK3, p-MLKL, FTL, and LP expression were observed in mouse hippocampal tissues in a chronic mild unpredictable stress model (Cao et al., 2021). However, further research is essential to clarify the regulatory interactions between necroptosis and ferroptosis.
2.3.2 Ferroptosis and autophagy
Autophagy is a cellular process characterized by the formation of autophagosomes, which are double-membrane structures that encapsulate cytoplasmic constituents and organelles for degradation. These autophagosomes subsequently fuse with lysosomes to form autolysosomes, where the sequestered contents are degraded to meet cellular metabolic needs and facilitate organelle turnover (Luo and Tao, 2020). Recent studies have demonstrated that heat shock protein 90, a critical molecular chaperone, regulates Lamp-2a expression in the autophagic pathway and regulates ferroptosis (Zhang C. et al., 2024). Nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA 4) serves as a selective cargo receptor that targets ferritin to autophagosomes (Le et al., 2024). This NCOA4-mediated degradation releases iron stores, increasing labile iron pools (Hoelzgen et al., 2024; Zhu et al., 2024). Silencing NCOA4 reduces iron-mediated neuronal death in TBI models (Li et al., 2021; Bengson et al., 2023). Another study found that autophagy promoted the degradation of neuronal ferritin in a mouse model of SAH, leading to elevated free iron levels and ultimately promoting ferritin deposition (Liang et al., 2022). These results deepen our insight into the interplay between autophagy and ferroptosis. However, additional investigation is necessary to clarify the regulatory mechanisms that connect these two processes.
2.3.3 Ferroptosis and apoptosis
Apoptosis is a common mechanism of programmed cell death, which can be initiated by external or internal pathways. It has been found that the ferroptosis inducer, erastin, irreversibly activates CHOP/PUMA within the p53 signaling pathway, thereby enhancing the sensitivity of tumor cells to apoptosis inducers and facilitating apoptosis (Hong et al., 2017). These findings provide important clues for exploring the interaction between ferroptosis and apoptosis. This process is characterized by several distinct features: nuclear condensation, cell swelling, and the emergence of lipid membrane vesicles on the plasma membrane, ultimately resulting in cell lysis, all occurring without fragmentation of nuclear DNA (Hu et al., 2020).
2.3.4 Ferroptosis and pyroptosis
Pyroptosis is a form of inflammatory cell death that is typically triggered by pathogen-associated molecular patterns or damage-associated molecular patterns. It is characterized by cell swelling, plasma membrane rupture, and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-1β and interleukin-18 (Bergsbaken et al., 2009; Broz, 2025). Pyroptosis is caused by the activation of inflammasomes, which then trigger caspase-1, cleaving gasdermin D and creating membrane holes. These pores allow the discharge of intracellular chemicals, like ROS, which can worsen lipid peroxidation and oxidative stress (Bergsbaken et al., 2009). Recent studies have indicated that there may be crosstalk between pyroptosis and ferroptosis (Cao et al., 2022; Eskander et al., 2025). Mitochondrial dysfunction links ferroptotic lipid peroxidation to pyroptotic NLRP3 activation (Chen et al., 2023; Lyamzaev et al., 2023; Tian et al., 2023). Ferroptosis may be facilitated by a pro-oxidant environment created by the generation of ROS and the loss of cellular membrane integrity during pyroptosis. Ferroptosis may also be further promoted by the release of iron from injured cells during pyroptosis, which may worsen iron excess in the surrounding tissue. However, further research is needed to determine the precise molecular processes and signaling pathways that underlie the connection between these two types of cell death.
3 Role of ferroptosis in CNS injuries
Ferroptosis is closely related to CNS injuries, with current research focusing mainly on neurodegenerative diseases, stroke, TBI, and similar conditions (Figure 2).
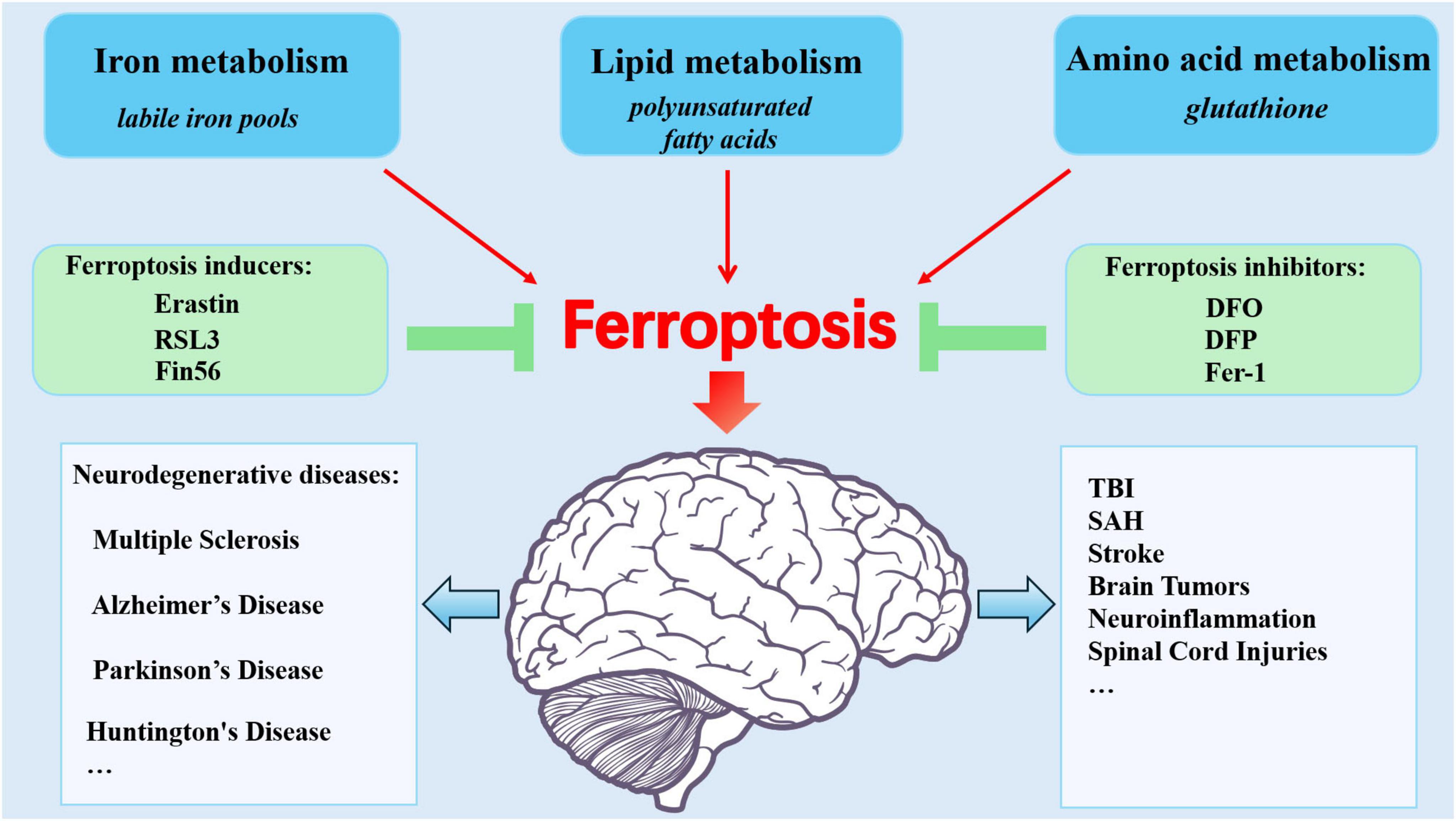
Figure 2. Ferroptosis: Metabolic Pathways, Modulators, and CNS injury diseases. Ferroptosis stems from dysregulated iron metabolism, lipid metabolism, and amino acid metabolism. The inhibitors and inducers are involved in ferroptosis. Brain iron overload contributes to CNS injuries including stroke, TBI, SAH, tumors, neuroinflammation, spinal cord injuries, and neurodegenerative diseases.
3.1 Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is mainly defined by the gradual degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons located in the iron-rich substantia nigra. Mitochondrial and lysosomal dysfunction, dysregulated iron metabolism, and accumulation of ROS are considered to be pivotal elements in the pathogenesis of PD, ultimately leading to neuronal degeneration and death (Matak et al., 2016; Burbulla et al., 2017). Epidemiological studies show that high dietary iron intake may increase the risk of PD. Ferroptosis, a novel form of cell death regulated by protein kinase C (PKC), plays a critical role in PD pathogenesis. PKC activation increases the catalytic activity of 12/15-lipoxygenase toward PUFAs in neuronal membranes by phosphorylating it. This encourages ferroptotic death and lipid peroxidation (Choudhary et al., 2022; Pratt, 2023). Overexpression of the PKCδ isoform increases the susceptibility of substantia nigra neurons, but PKC inhibitors such as chelerythrine decrease the α-synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic cells caused by rotenone (Kabiraj et al., 2015). Recent studies have highlighted the significant role of glial cells, including microglia and astrocytes, in the progression of PD (Wang et al., 2023; Brash-Arias et al., 2024). Studies have identified excessive iron accumulation, alongside activated microglia and immunoreactive astrocytes, in the brains of individuals with PD (Lee and Lee, 2019; Foley et al., 2022; López-Aguirre et al., 2025). This glia can induce neuronal death by triggering OS and releasing proinflammatory factors (Braak et al., 2007). Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) exploits magnetic susceptibility differences between tissues to quantify non-heme iron. SWI has been used to assess iron deposition in the basal ganglia of PD patients, with findings indicating a progressive increase as the disease advances (Mohammadi and Ghaderi, 2024; He et al., 2025; Lancione et al., 2025). Ferrostatin-1 (Fer-1) analogs and PKC inhibitors have proven effective in mitigating neuronal injury caused by ferroptosis. Deferoxamine (DFO) alleviates PD symptoms, especially in patients with reduced plasma ceruloplasmin (Kosyakovsky et al., 2021). Ceruloplasmin, a ferroxidase enzyme, is a significant blood protein that carries copper and contributes to iron metabolism by promoting the oxidation of Fe2+ to Fe3+, which is necessary for iron storage and transportation (Roeser et al., 1970; Liu et al., 2022). DFO improves motor symptoms in PD patients with low ceruloplasmin levels by lowering oxidative stress and iron overload (Grolez et al., 2015; Lin et al., 2022). DFO effectively reduces iron content in the dentate nucleus regions without adversely affecting cognition or mood (Martin-Bastida et al., 2017). However, the overall efficacy of DFO in PD remains uncertain, highlighting the need for more extensive clinical trials to explore the potential benefits of iron chelation therapy. Fer-1 has also been found to inhibit ROS/RNS, attenuating rotenone-induced α-synuclein aggregation in dopaminergic SH-SY5Y cells (Kabiraj et al., 2015), thereby reversing MPTP-triggered behavioral deficits in a mouse model of PD and protecting the neurons (Do Van et al., 2016). Aggregation of alpha-synuclein in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neurons promotes calcium influx and LP, thereby triggering ferroptosis (Angelova et al., 2020). Notably, three distinct inhibitors of ferroptosis, including PUFAs, DFO, and Fer-1, effectively impede this process, thus creating new therapeutic possibilities for PD treatment.
3.2 Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is marked by the gradual deterioration of neurons within the CNS. Accumulating evidence indicates that iron imbalance triggers OS and the overproduction of ROS, subsequently leading to cell death—a process indicative of the involvement of ferroptosis in AD progression (Raven et al., 2013). The reduction of GPX4 severely impairs neuronal defenses against OS and increases the risk of ferroptosis. In GPX4 brain-inducible knockout mouse models, vitamin E deficiency accelerated hippocampal neuronal degeneration and behavioral decline (Wortmann et al., 2013). At the same time, inhibition of ferroptosis with Liproxstatin-1 (Lip-1) slowed this process, highlighting the effect of ferroptosis in AD and suggesting novel therapeutic avenues (Hambright et al., 2017). Molecules with anti-ferroptosis properties significantly protect the CNS, providing a new perspective for AD administration. Many studies have focused on α-lipoic acid (LA), a small molecule with antioxidant and iron-chelating properties. LA inhibits Tau-mediated imbalances in iron metabolism, LP, and inflammatory responses in P301S tau transgenic mice (Zhang Y. H. et al., 2018). It also activates the mitogen-activated protein kinases signaling pathway and promotes GPX4 expression, enhancing resistance to ferroptosis and decreasing the accumulation of neurofibrillary tangles. Chalcone derivatives, particularly compounds 14a-c, have demonstrated protective solid effects against Aβ1-42-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cell models by inhibiting LP and preventing ferroptosis (Cong et al., 2019). Additionally, GSH deficiency may exacerbate OS, which in turn affects AD development. Studies have found that iron accumulation can exacerbate GSH loss, leading to increased ROS production (Núñez et al., 2004; Belaidi and Bush, 2016; Li et al., 2020). MRI testing has revealed raised iron levels in the hippocampus of AD patients (van Bergen et al., 2016). Another study has demonstrated that astrocytes and neurons mediate the interaction between ferroptosis and AD progression (Fan et al., 2024; Li et al., 2024). Hepcidin expression in astrocytes regulates iron intake, which helps mitigate neuronal loss in the cortex and hippocampus of amyloid precursor protein/presenilin-1 (APP/PS1) mice (Xu et al., 2020; Li et al., 2024). Activation of microglia and iron accumulation in APP/PS1 mice has been associated with neuroinflammation and Aβ aggregation (McIntosh et al., 2019). Thus, astrocyte-regulated iron efflux impairment, microglial iron buildup, and iron-mediated GSH depletion create a self-reinforcing cycle that propels ferroptosis in AD. This triad may be the focus of early therapies that delay neurodegeneration.
3.3 Huntington’s disease
Huntington’s disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. Research indicates that superfluous iron accumulation in the brain’s basal ganglia may accelerate disease progression (Sánchez-Castañeda et al., 2013; Domínguez et al., 2016; Niu et al., 2018; Abdelfattah et al., 2020). Iron accumulation, LP, and GSH dysregulation are directly linked to ferroptosis. A study demonstrates that iron induces microglial activation in HD mice, suggesting a synergistic interaction between iron and HD in promoting this activation (Donley et al., 2021). Research has shown that HD patients’ striatal synaptosomes exhibit higher levels of 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE), a hallmark of LP (Lee et al., 2011; Lee et al., 2025). The striatum’s GPX4 activity is decreased in the R6/2 mouse model of HD (Chen et al., 2015). The loss of GPX4, an essential enzyme that shields cells from LP, would make neurons more vulnerable to ferroptosis (Bellinger et al., 2011; Hambright et al., 2017). Research indicates that mitochondrial GPX4 depletion increases ROS, further contributing to cellular damage and ferroptosis (Agrawal et al., 2018). Mounting studies have revealed that cell injury in HD primarily involves the loss of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and neurons, potentially affecting the cerebral cortex and striatum (Yu et al., 2003; Tydlacka et al., 2008; Crotti et al., 2014). The main therapeutic agents targeting HD-associated ferroptosis include DFO and Fer-1. DFO can alleviate excessive iron accumulation in the brain’s basal ganglia, while Fer-1, a ferroptosis inhibitor, prevents oxidative lipid injury and cell death in HD models (Skouta et al., 2014). These findings offer a promising new therapeutic strategy for HD.
3.4 Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic inflammatory condition of CNS marked by demyelination, neuronal injury, and associated neurological dysfunction. Recent studies have highlighted the critical role of iron metabolism imbalance in the pathogenesis of MS. Ferroptosis may be a major pathogenic process in MS, as evidenced by studies showing raised iron levels and increased LP in lesion regions and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of MS patients, associated with impaired iron homeostasis (Zivadinov et al., 2018; Van San et al., 2023; Zhang X. et al., 2024). In mouse models of MS, decreased expression of GPX4 and SLC7A11, along with elevated LP, has been observed in gray matter and spinal cord tissues (Hu et al., 2019; Moezzi et al., 2022). These models exhibit abnormal mitochondrial morphology in neurons, consistent with features of ferroptosis. Inhibition of ferroptosis or downregulation of ACSL4 expression significantly improves clinical symptoms, reduces neuronal death, and alleviates neuroinflammation (Van San et al., 2023). Further research indicates that ferroptosis can foster T-cell activation and the development of autoimmune responses (Luoqian et al., 2022). These findings suggest that developing targeted therapies to inhibit T-cell activation mediated by ferroptosis could assist in suppressing CNS inflammation and treat MS, offering new hope for patients with this debilitating condition. Furthermore, brain organoids and three-dimensional culture models are employed for high-throughput drug screening because they can replicate the networks involved in iron metabolism in the human brain (Aldewachi et al., 2021).
3.5 Stroke
3.5.1 Ischemic stroke
Mounting studies have revealed that ischemic stroke increases iron deposition, mitochondrial dysfunction, LP, and iron overload. Ischemia-reperfusion injury suppresses the expression of tau protein, triggers iron accumulation in neurons, and promotes ferroptosis (Tuo et al., 2017). Inhibitors of ferroptosis have the potential to improve outcomes in patients with ischemic stroke. N-acetylcysteine (NAC) protects neurons from iron-induced ferroptosis by reducing free radical production, thereby reducing neuronal mortality (Kamel et al., 2024). NAC treatment decreased the initiation of cascades of neuronal death, including lipid peroxidation, after experimental cerebral ischemia (Hong et al., 2020). A clinical trial study suggests that NAC promotes early neurological recovery in patients with ischemic stroke (Komakula et al., 2024). Carvacrol has been found to protect Gerbil hippocampal neurons from ischemia-reperfusion injury by impeding ferroptosis by increased GPX4 expression (Guan et al., 2019).
3.5.2 Hemorrhagic stroke
Research has investigated that ferroptosis occurs in experimental cerebral hemorrhage (CH) models and brain tissues of patients affected by CH (Li et al., 2017; Zille et al., 2017; Chen et al., 2019). In a CH rat model, GPX4 levels gradually decreased, reaching a low point at 24 h after CH (Zhang Z. et al., 2018). After CH, free iron is released from the hemoglobin degradation products, leading to excessive iron accumulation in brain tissue. This generates high ROS, LP, and OS levels, ultimately resulting in cell death. The iron chelator DFO has been shown to decrease ROS production, mitigate hemoglobin-induced neurotoxicity, reduce brain edema, and enhance functional outcomes in both in vivo and in vitro models of CH (Regan and Panter, 1996; Nakamura et al., 2004; Okauchi et al., 2009). Additionally, Fer-1 significantly reduces secondary brain injury following CH. Potential therapeutic targets for ferroptosis after CH include selenium supplementation, iron chelators, lipoxygenase inhibitors, and DMT1 inhibitors. These studies provide valuable insight into the mechanisms underlying ferroptosis in strokes and identify potential therapeutic targets.
3.6 Traumatic brain injury
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) is followed by a cascade of secondary injuries, including the release of excitatory neurotransmitters and Fe2+, OS, LP, and the accumulation of ROS, all of which induce ferroptosis (Anthonymuthu et al., 2018). Iron levels in the brain significantly increased after TBI, likely due to hemorrhage-induced iron deposition in the brain parenchyma. Chronic brain injury may occur in a region of iron deposition and is associated with tissue loss. Studies have indicated that iron and ROS accumulation, increased transferrin levels, decreased GPX activity, and mitochondrial dysfunction can induce ferroptosis after TBI. Fer-1 reduces tissue damage and improves outcomes in a TBI mouse model (Xie et al., 2019). Controlled cortical impact leads to the accumulation of oxidized PE, upregulated expression of 15-lipoxygenase and ACSL4, and reduced GSH (Kenny et al., 2019). TBI research in animals mostly uses the controlled cortical impact (CCI) approach. But when it comes to mimicking secondary damage pathways and reproducing the pathological variety of genuine TBI, this model shows serious shortcomings. Accordingly, future research should concentrate on creating clinically appropriate multimodal models in order to more accurately replicate the course of disease.
Additionally, miR-212-5p regulates prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase-2 to reduce ferroptosis-induced neuronal death (Xiao et al., 2019). In TBI mice, alterations in iron regulatory proteins (GPX4, SLC7A11, ACSL4) are evident in the brain cortex. TBI activates ferroptosis, inflammation, and immune responses, mainly through microglia and macrophages, influencing TBI outcomes and offering therapeutic targets (Li and Jia, 2023). Cells undergoing ferroptosis release pro-inflammatory damage-associated molecular patterns which activate the innate immune response. This activation disrupts the equilibrium between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory processes, particularly within brain tissues (Proneth and Conrad, 2019). This disruption may exacerbate the initial injury and contribute to the progression of neurological damage. Understanding ferroptosis’s role in neuronal death post-TBI offers new avenues for therapy, highlighting the importance of researching optimal timing for anti-ferroptosis treatments and drug development.
3.7 Spinal cord injuries
Spinal cord injuries (SCI), known for causing severe disability and mortality, present significant medical challenges worldwide. The pathogenesis of SCI is intricate and not yet fully understood, with current treatment options being limited. Recent research suggests that activated microglia in SCI can release substantial amounts of nitric oxide, which in turn decreases ferritin levels while upregulating the expression of TFR, DMT1, and iron regulatory protein 1 in motor neurons (Feng et al., 2021). Research has revealed that iron chelators and specific inhibitors may have therapeutic potential for SCI. DFO upregulates GPX4, xCT, and GSH, curbs gliocyte overgrowth, enhances long-term motor function, and mitigates iron overload (Yao et al., 2019). SRS16-86, a new ferroptosis inhibitor, significantly elevates GPX4, GSH, and xCT levels, decreases LP, restrains glial cell activation, and reduces neuronal injury in SCI models (Zhang et al., 2019). Anthocyanin and grape seed-derived proanthocyanidins improve motor function in SCI mice by decreasing iron and TBARS levels, downregulating ALOX15 and ACSL4 while upregulating HO-1, GSH, and GPX4 (Zhou et al., 2020). Fer-1 reverses mitochondrial irregularities and inflammation after SCI by inhibiting glial cell activity, reducing iron accumulation, and downregulating the expression of ferroptosis-related genes. Zinc ions prevent ferroptosis after SCI by enhancing Nrf2/HO-1 activity and reducing ferroptosis products such as GSH, GPX4, and ROS (Ge et al., 2021). Lipoxin A4, an anti-inflammatory lipid mediator, promotes neuroprotection and recovery after SCI by influencing the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway (Lu et al., 2018; Wei et al., 2021). Edaravone is a free radical scavenger that enhances GPX4 and xCT while reducing ACSL4 and ROS, suggesting it may inhibit ferroptosis in the acute phase SCI. These compounds intervene in ferroptosis through multiple mechanisms, opening new therapeutic avenues for SCI. Ongoing studies aim to validate their clinical safety and efficacy, striving to enhance treatment options for patients with SCI.
3.8 Shared molecular drivers of ferroptosis in CNS injuries
Ferroptosis is a major pathogenic process in CNS injuries, such as stroke, TBI, and neurodegenerative disorders. Although there are triggers unique to each disease, the fundamental molecular processes causing ferroptosis show notable commonalities, providing a single target for treatment. We summarize these common mechanisms and how disease-specific factors affect them below.
(1) Core pathways
Excessive iron accumulation in CNS injuries drives divergent mechanisms: nigral iron excess in PD promotes LP via Fenton reactions (Ayton and Lei, 2014; You et al., 2015), while AD demonstrates co-localized hippocampal iron deposition with tau/Aβ pathology (Van San et al., 2023; Zhou et al., 2024), and stroke or TBI liberates free iron to amplify oxidative stress (Toro-Urrego et al., 2019; Liu D. et al., 2024). These processes synergize with GPX4 suppression, a critical antioxidant enzyme whose downregulation exacerbates neuronal damage by impairing lipid peroxide neutralization in AD, stroke, and TBI models (Yoo et al., 2010; Hambright et al., 2017; Weaver and Skouta, 2022). Furthermore, ACSL4-mediated esterification of PUFAs into peroxidation-vulnerable membrane domains establishes a self-reinforcing pathway, with elevated ACSL4 expression in stroke, AD, and PD intensifying lipid oxidative damage (Zheng et al., 2024), collectively forming an iron-dependent oxidative injury axis.
(2) Disease-specific modulation
Iron-bound α-synuclein oligomers in PD produce redox-active substances that hasten dopaminergic degradation and LP (Calabresi et al., 2023). While hyperphosphorylated tau interferes with mitochondrial iron export, increasing neuronal iron retention and lipid ROS through GPX4 depletion, Aβ plaques in AD trap iron to produce oxidative hotspots (Liu D. et al., 2024). Microglial cytokine-driven inhibition of System Xc– and GSH depletion, in conjunction with hemorrhagic heme iron excess and blood-brain barrier (BBB) rupture, prime neurons for ferroptosis in stroke/TBI (Tang et al., 2020; Guo et al., 2023; Wei, 2024).
4 Diagnostic approaches for ferroptosis in CNS injuries
Ferroptosis is characterized by iron buildup, which can be measured in a number of ways. Ferroptosis diagnosis necessitates a multimodal evaluation of antioxidant failure, lipid peroxidation, and iron dysregulation. Neuroimaging, biofluid analysis, and histopathology methods can all be used to accomplish this thorough assessment.
4.1 Neuroimaging biomarkers
MRI has become a useful technique for evaluating brain iron buildup. The substantia nigra of PD patients and the hippocampus of AD patients can both have iron accumulation that SWI can identify (Raven et al., 2013; Xu et al., 2020). The more accurate measurement of brain iron concentration is provided by quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM), which has shown notable specificity in determining iron content in TBI lesions and neurodegenerative patterns (Gozt et al., 2021; Koch et al., 2021; Ravanfar et al., 2021). However, these techniques have limitations, such as the inability to distinguish ferroptosis-specific iron from other forms of iron deposition, underscoring the need for further standardization.
4.2 Biofluid biomarkers
Ferroptosis can be diagnosed minimally invasively with biofluid analysis. When compared to controls, AD patients have greater levels of lipid peroxides in their CSF (Mizoi et al., 2014; Bradley-Whitman and Lovell, 2015; Plascencia-Villa and Perry, 2023). After TBI, GPX4 activity is significantly decreased in serum and CSF (Cheng et al., 2023; Fang et al., 2023). Free iron levels in CSF correlate with the severity of SCI (Kwon et al., 2017). These biomarkers are at various stages of validation, with some undergoing Phase II validation and others being verified across multiple centers.
4.3 Histopathological techniques
Histopathological techniques offer a direct assessment of ferroptosis in tissue samples. The semi-quantitative identification of iron in post-mortem tissue is frequently accomplished using Prussian blue staining. The ACSL4/GPX4 ratio has been shown to predict ferroptosis in MS lesions, and 4-HNE adducts indicate lipid peroxidation in the AD hippocampus (Butterfield et al., 2010; Luoqian et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2023). The C11-BODIPY test, which uses a fluorescent probe to selectively sensitize lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis, is one of the emerging techniques in this field (Dai et al., 2023).
4.4 Challenges and future directions
Ferroptosis diagnosis still faces a number of difficulties despite tremendous advancements. Clinical interpretation is made more difficult by the absence of established reference ranges for biofluid indicators such as lipid peroxides and CSF iron. Furthermore, it is still unclear how these biomarkers change over time in acute vs. chronic damage phases. It is imperative to build multiplex point-of-care platforms that can concurrently evaluate oxidative stress, inflammation, and iron status in order to address these issues. There is potential for these combined techniques to increase the precision and effectiveness of ferroptosis diagnosis in clinical settings.
5 Therapeutic strategies in CNS injuries: preclinical evidence and clinical translation
Targeting ferroptosis therapeutically shows promise for treating CNS injuries. Clinical translation is made more difficult by the fact that intervention efficacy differs greatly between experimental models and disease situations. Preclinical information from in vitro and in vivo studies of acute injuries and neurodegenerative disorders, as well as clinical practice concerns, are reviewed in conjunction with ferroptosis-targeted therapies. Key agents are summarized in Table 2.
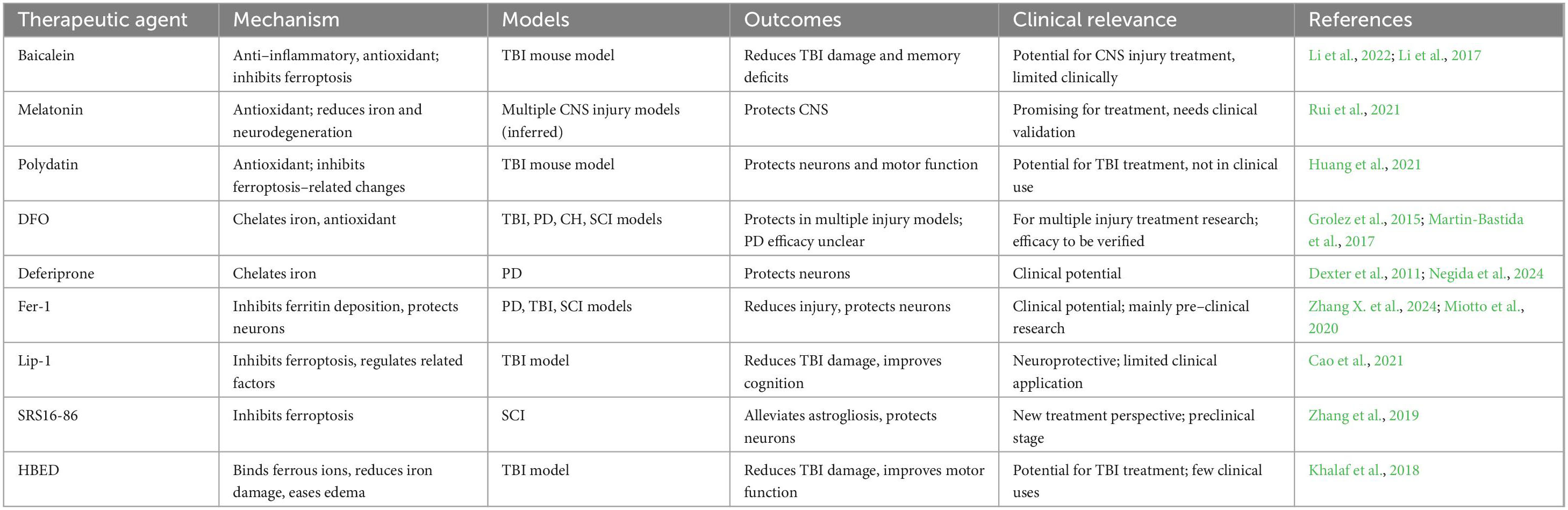
Table 2. Therapeutic agents inhibiting ferroptosis: mechanisms and clinical advances in CNS injuries.
5.1 Interventions validated in cellular models
Several therapies have demonstrated proof-of-concept in vitro using glial and neuronal cells. Iron chelators such as DFO (100 μM) have been shown to downregulate TFR1 and reduce erastin-induced ferroptosis in SH-SY5Y dopaminergic neurons (Hadzhieva et al., 2013; Kabiraj et al., 2015). Similarly, GPX4 activity is restored by Lip-1 (0.5 μM), saving HT22 hippocampal neurons treated with RSL3 (Friedmann Angeli et al., 2014). These in vitro models yield promising results, but they lack the neuroimmune interaction, systemic metabolic effects, and BBB dynamics necessary to fully understand the therapeutic potential of the medications.
5.2 Therapeutic efficacy in animal models
5.2.1 Neurodegenerative disorders
Several compounds have demonstrated significant therapeutic potential in animal models of neurodegenerative diseases, such as AD and PD (Carrera and Cacabelos, 2019). Fer-1, administered intraperitoneally at a dose of 2.5 mg/kg, decreased neuronal loss in the substantia nigra pars compacta and improved rotarod test performance in a mouse model of MPTP-induced PD (Wang et al., 2022). Deferiprone (10 mg/kg) dramatically reduced the loss of dopaminergic neurons and striatal dopamine content in the 6-OHDA rat model of PD (Dexter et al., 2011). Lip-1 given intraperitoneally (10 mg/kg) reduced hippocampus iron and restored impairments in the Morris water maze test in an APP/PS1 mouse model of AD (Hambright et al., 2017). Vitamin E/Lip-1 rescues cognitive decline in AD mice (Hambright et al., 2017). Selenium supplementation increases GPX4 activity, reducing ferroptosis in MS models (Van San et al., 2023). Inhibition of ACSL4 such as thiazolidinediones and rosiglitazone facilitates neurological recovery by regulation of ferroptosis after stroke and TBI (Yang et al., 2023).
5.2.2 Acute CNS injuries
Promising outcomes have also been noted in models of acute CNS injuries, including CH and SCI. After CH, DFO was administered to a rat model, which resulted in improved limb symmetry and a statistically significant decrease in edema (Okauchi et al., 2009). Ferroptosis inhibitor SRS16-86 improved the Basso, Beattie, and Bresnahan locomotor scores and increased GPX4 expression in a rat model of contusion SCI (Zhang et al., 2019). Fer-1 improves SCI recovery compared to the free drug (Liu S. et al., 2024). Nanoparticles co-loaded with DFO and antioxidants show synergistic effects in TBI (Huang et al., 2024).
5.3 Clinical translation status
There are various obstacles to overcome while moving from preclinical success to clinical application. Among the trials that have been finished is the use of DFO in PD (Phase II), which appeared to reduce nigral iron on MRI but had no effect on the Unified PD Rating Scale (Martin-Bastida et al., 2017). Deferiprone decreased iron in the substantia nigra and raised striatal dopamine levels when given orally at 30 mg/kg in a phase 2 randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial in PD (Martin-Bastida et al., 2017). The N, N′-Di(2-hydroxybenzyl) ethylenediamine-N, N′-diacetic acid monohydrochloride (HBED), an iron chelator, mitigates iron-related damage by binding ferrous ions, facilitating their transport across BBB, and converting them to ferric ions. With a higher iron affinity and fewer adverse effects than DFO, HBED has demonstrated benefits in TBI models (Khalaf et al., 2018). Moreover, HBED has passed Phase I in clinical trials and is shown to be safe to administer to humans (Grady et al., 1994; Chang et al., 2005). Lip-1 for TBI has finished Phase I safety investigations (Mohammed et al., 2023). A trial (NCT04566991) will evaluate the safety and efficacy of clinical DFO for the treatment of SAH in patients. However, the narrow therapeutic window and BBB penetration are significant translation challenges.
5.4 Comparative therapeutic efficacy
The translation of therapeutic agents from animal models to clinical trials faces significant barriers. Although iron chelators have demonstrated neuroprotection in animal models, their use in human trials has been constrained by insufficient CNS biodistribution. Because of pharmacokinetic instability, GPX4 activators remain in the preclinical stage even though they significantly reduce the extent of lesions in TBI mice (Liu J. et al., 2024; Qian et al., 2025). ACSL4 inhibitors have decreased ferroptosis in AD mice, but their poor target selectivity makes them unsuitable for human trials (Jia et al., 2023; Zha et al., 2025).
5.5 Future directions
Future studies should concentrate on combinatorial regimens to improve therapy efficacy, such as combining immunomodulators and ferroptosis inhibitors. Novel delivery methods, such as nanoparticles, which boost brain bioavailability in primates, present encouraging paths around BBB restrictions (Pinheiro et al., 2021). Additionally, increasing the success rate of therapeutic interventions will require the use of biomarker-guided therapy, such as QSM-MRI for patient stratification in clinical trials.
6 Conclusion and perspectives
Ferroptosis, a form of programmed cell death characterized by iron-dependent LP, has emerged as a critical factor in CNS injuries. While iron is essential for neurological function, excessive iron accumulation can lead to cellular damage and death. Ferroptosis involves various mechanisms, including iron metabolism, amino acid, lipid metabolisms, and immune responses.
However, the current understanding of the mechanisms of ferroptosis remains incomplete, especially within the complex neurological environment. It is yet unclear how ferroptosis and other cell death mechanisms interact, and research is needed to understand their cross-regulatory networks utilizing genetic engineering models like GPX4/ACSL4 double knockout systems. Additionally, ferroptosis activates immune cells, particularly macrophages and microglia, by inducing inflammatory responses, playing a significant role in CNS pathology. Future studies should focus on exploring the specific mechanisms of immunomodulation during ferroptosis, including how ferroptosis activates microglia and macrophages and promotes inflammatory responses. The development of novel treatments for CNS injury may be facilitated by these investigations. Next-generation ferroptosis treatments should either have better BBB permeability or use delivery systems based on nanoparticles for accurate CNS targeting to improve therapeutic approaches. Ferroptosis biomarkers, such as LP products, should also be included in clinical trial designs to precisely evaluate the therapeutic effects of anti-ferroptosis medication. By gaining a deeper insight into ferroptosis and its associated immune mechanisms, we can potentially uncover more effective treatments for CNS injuries and other conditions linked to ferroptosis.
Author contributions
QH: Supervision, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Funding acquisition. HZ: Methodology, Writing – review and editing, Visualization, Data curation. SC: Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis. YW: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Data curation. JZ: Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft, Supervision.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Hainan Provincial Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 821RC697 and 822RC833) and the Science and Technology Special Fund of Hainan Province (ZDYF2024SHFZ133).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abdelfattah, M. S., Badr, S. E. A., Lotfy, S. A., Attia, G. H., Aref, A. M., Abdel Moneim, A. E., et al. (2020). Rutin and selenium co-administration reverse 3-Nitropropionic acid-induced neurochemical and molecular impairments in a mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Neurotox Res. 37, 77–92. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00086-y
Agrawal, S., Fox, J., Thyagarajan, B., and Fox, J. H. (2018). Brain mitochondrial iron accumulates in Huntington’s disease, mediates mitochondrial dysfunction, and can be removed pharmacologically. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 120:317329.
Aldewachi, H., Al-Zidan, R. N., Conner, M. T., and Salman, M. M. (2021). High-Throughput screening platforms in the discovery of novel drugs for neurodegenerative diseases. Bioengineering (Basel) 8:30. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering8020030
Alvarez, S. W., Sviderskiy, V. O., Terzi, E. M., Papagiannakopoulos, T., Moreira, A. L., Adams, S., et al. (2017). NFS1 undergoes positive selection in lung tumours and protects cells from ferroptosis. Nature 551, 639–643. doi: 10.1038/nature24637
Angelova, P. R., Choi, M. L., Berezhnov, A. V., Horrocks, M. H., Hughes, C. D., De, S., et al. (2020). Alpha synuclein aggregation drives ferroptosis: An interplay of iron, calcium and lipid peroxidation. Cell Death Differ. 27, 2781–2796. doi: 10.1038/s41418-020-0542-z
Anthonymuthu, T. S., Kenny, E. M., Lamade, A. M., Kagan, V. E., and Bayır, H. (2018). Oxidized phospholipid signaling in traumatic brain injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 124, 493–503. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.06.031
Aoyama, K., and Nakaki, T. (2015). Glutathione in cellular redox homeostasis: Association with the excitatory amino acid carrier 1 (EAAC1). Molecules 20, 8742–8758. doi: 10.3390/molecules20058742
Arosio, P., Elia, L., and Poli, M. (2017). Ferritin, cellular iron storage and regulation. IUBMB Life 69, 414–422. doi: 10.1002/iub.1621
Ayton, S., and Lei, P. (2014). Nigral iron elevation is an invariable feature of Parkinson’s disease and is a sufficient cause of neurodegeneration. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014:581256. doi: 10.1155/2014/581256
Belaidi, A. A., and Bush, A. I. (2016). Iron neurochemistry in Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: Targets for therapeutics. J. Neurochem. 139(Suppl. 1), 179–197. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13425
Bellinger, F. P., Bellinger, M. T., Seale, L. A., Takemoto, A. S., Raman, A. V., Miki, T., et al. (2011). Glutathione peroxidase 4 is associated with neuromelanin in substantia nigra and dystrophic axons in putamen of Parkinson’s brain. Mol. Neurodegener. 6:8. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-8
Bengson, E. F., Guggisberg, C. A., Bastian, T. W., Georgieff, M. K., and Ryu, M. S. (2023). Quantitative omics analyses of NCOA4 deficiency reveal an integral role of ferritinophagy in iron homeostasis of hippocampal neuronal HT22 cells. Front. Nutr. 10:1054852. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2023.1054852
Bergsbaken, T., Fink, S. L., and Cookson, B. T. (2009). Pyroptosis: Host cell death and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 7, 99–109. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2070
Bogdan, A. R., Miyazawa, M., Hashimoto, K., and Tsuji, Y. (2016). Regulators of iron homeostasis: New players in metabolism, cell death, and disease. Trends Biochem. Sci. 41, 274–286. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2015.11.012
Börjesson, S. I., and Elinder, F. (2011). An electrostatic potassium channel opener targeting the final voltage sensor transition. J. Gen. Physiol. 137, 563–577. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201110599
Braak, H., Sastre, M., and Del Tredici, K. (2007). Development of alpha-synuclein immunoreactive astrocytes in the forebrain parallels stages of intraneuronal pathology in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 114, 231–241. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0244-3
Bradley-Whitman, M. A., and Lovell, M. A. (2015). Biomarkers of lipid peroxidation in Alzheimer disease (AD): An update. Arch. Toxicol. 89, 1035–1044. doi: 10.1007/s00204-015-1517-6
Brash-Arias, D., García, L. I., Pérez-Estudillo, C. A., Rojas-Durán, F., Aranda-Abreu, G. E., Herrera-Covarrubias, D., et al. (2024). The role of astrocytes and alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: A review. NeuroScience 5, 71–86. doi: 10.3390/neurosci5010005
Bridges, R., Lutgen, V., Lobner, D., and Baker, D. A. (2012). Thinking outside the cleft to understand synaptic activity: Contribution of the cystine-glutamate antiporter (System xc-) to normal and pathological glutamatergic signaling. Pharmacol. Rev. 64, 780–802. doi: 10.1124/pr.110.003889
Broz, P. (2025). Pyroptosis: Molecular mechanisms and roles in disease. Cell Res. 35, 334–344. doi: 10.1038/s41422-025-01107-6
Burbulla, L. F., Song, P., Mazzulli, J. R., Zampese, E., Wong, Y. C., Jeon, S., et al. (2017). Dopamine oxidation mediates mitochondrial and lysosomal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Science 357, 1255–1261. doi: 10.1126/science.aam9080
Butterfield, D. A., Bader Lange, M. L., and Sultana, R. (2010). Involvements of the lipid peroxidation product, HNE, in the pathogenesis and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1801, 924–929. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2010.02.005
Calabresi, P., Mechelli, A., Natale, G., Volpicelli-Daley, L., Di Lazzaro, G., and Ghiglieri, V. (2023). Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies: From overt neurodegeneration back to early synaptic dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 14:176. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05672-9
Cao, H., Zuo, C., Huang, Y., Zhu, L., Zhao, J., Yang, Y., et al. (2021). Hippocampal proteomic analysis reveals activation of necroptosis and ferroptosis in a mouse model of chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression. Behav. Brain Res. 407:113261. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2021.113261
Cao, Z., Qin, H., Huang, Y., Zhao, Y., Chen, Z., Hu, J., et al. (2022). Crosstalk of pyroptosis, ferroptosis, and mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2-related mechanisms in sepsis-induced lung injury in a mouse model. Bioengineered 13, 4810–4820. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2033381
Carrera, I., and Cacabelos, R. (2019). Current drugs and potential future neuroprotective compounds for Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 17, 295–306. doi: 10.2174/1570159X17666181127125704
Chalon, S. (2006). Omega-3 fatty acids and monoamine neurotransmission. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 75, 259–269. doi: 10.1016/j.plefa.2006.07.005
Chang, E. F., Claus, C. P., Vreman, H. J., Wong, R. J., and Noble-Haeusslein, L. J. (2005). Heme regulation in traumatic brain injury: Relevance to the adult and developing brain. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 25, 1401–1417. doi: 10.1038/sj.jcbfm.9600147
Chen, B., Chen, Z., Liu, M., Gao, X., Cheng, Y., Wei, Y., et al. (2019). Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis in the acute phase of intracerebral hemorrhage shows long-term cerebroprotective effects. Brain Res. Bull. 153, 122–132. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.08.013
Chen, L., Hambright, W. S., Na, R., and Ran, Q. (2015). Ablation of the ferroptosis inhibitor glutathione peroxidase 4 in neurons results in rapid motor neuron degeneration and paralysis. J. Biol. Chem. 290, 28097–28106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.680090
Chen, Y., Fang, Z. M., Yi, X., Wei, X., and Jiang, D. S. (2023). The interaction between ferroptosis and inflammatory signaling pathways. Cell Death Dis. 14:205. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05716-0
Cheng, H., Wang, P., Wang, N., Dong, W., Chen, Z., Wu, M., et al. (2023). Neuroprotection of NRF2 against ferroptosis after traumatic brain injury in mice. Antioxidants (Basel) 12:731. doi: 10.3390/antiox12030731
Chin, J. H., and Vora, N. (2014). The global burden of neurologic diseases. Neurology 83, 349–351. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000000610
Choudhary, R., Kumar, M., and Katyal, A. (2022). 12/15-Lipoxygenase debilitates mitochondrial health in intermittent hypobaric hypoxia induced neuronal damage: An in vivo study. Redox Biol. 49:102228. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.102228
Cluntun, A. A., Lukey, M. J., Cerione, R. A., and Locasale, J. W. (2017). Glutamine metabolism in Cancer: Understanding the heterogeneity. Trends Cancer 3, 169–180. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2017.01.005
Cong, L., Dong, X., Wang, Y., Deng, Y., Li, B., and Dai, R. (2019). On the role of synthesized hydroxylated chalcones as dual functional amyloid-β aggregation and ferroptosis inhibitors for potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 166, 11–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.01.039
Conrad, M., Angeli, J. P., Vandenabeele, P., and Stockwell, B. R. (2016). Regulated necrosis: Disease relevance and therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15, 348–366. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.6
Crotti, A., Benner, C., Kerman, B. E., Gosselin, D., Lagier-Tourenne, C., Zuccato, C., et al. (2014). Mutant Huntingtin promotes autonomous microglia activation via myeloid lineage-determining factors. Nat. Neurosci. 17, 513–521.
Cui, C., Yang, F., and Li, Q. (2022). Post-Translational modification of GPX4 is a promising target for treating ferroptosis-related diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 9:901565. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.901565
Cunnane, S. C., Plourde, M., Pifferi, F., Bégin, M., Féart, C., and Barberger-Gateau, P. (2009). Fish, docosahexaenoic acid and Alzheimer’s disease. Prog. Lipid Res. 48, 239–256. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2009.04.001
Dai, Z., Zhang, W., Zhou, L., and Huang, J. (2023). Probing lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis: Emphasizing the utilization of C11-BODIPY-Based protocols. Methods Mol. Biol. 2712, 61–72. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3433-2_6
David, S., Ryan, F., Jhelum, P., and Kroner, A. (2023). Ferroptosis in neurological disease. Neuroscientist 29, 591–615. doi: 10.1177/10738584221100183
Dexter, D. T., Statton, S. A., Whitmore, C., Freinbichler, W., Weinberger, P., Tipton, K. F., et al. (2011). Clinically available iron chelators induce neuroprotection in the 6-OHDA model of Parkinson’s disease after peripheral administration. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 118, 223–231. doi: 10.1007/s00702-010-0531-3
Dixon, S. J. (2017). Ferroptosis: Bug or feature? Immunol. Rev. 277, 150–157. doi: 10.1111/imr.12533
Dixon, S. J., Lemberg, K. M., Lamprecht, M. R., Skouta, R., Zaitsev, E. M., Gleason, C. E., et al. (2012). Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149, 1060–1072. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Do Van, B., Gouel, F., Jonneaux, A., Timmerman, K., Gelé, P., Pétrault, M., et al. (2016). Ferroptosis, a newly characterized form of cell death in Parkinson’s disease that is regulated by PKC. Neurobiol. Dis. 94, 169–178. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.05.011
Dolma, S., Lessnick, S. L., Hahn, W. C., and Stockwell, B. R. (2003). Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell 3, 285–296. doi: 10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00050-3
Domínguez, J. F., Ng, A. C., Poudel, G., Stout, J. C., Churchyard, A., Chua, P., et al. (2016). Iron accumulation in the basal ganglia in Huntington’s disease: Cross-sectional data from the IMAGE-HD study. J. Neurol Neurosurg. Psychiatry 87, 545–549. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-310183
Donley, D. W., Realing, M., Gigley, J. P., and Fox, J. H. (2021). Iron activates microglia and directly stimulates indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase activity in the N171-82Q mouse model of Huntington’s disease. PLoS One 16:e0250606.
Eskander, G., Abdelhamid, S. G., Wahdan, S. A., and Radwan, S. M. (2025). Insights on the crosstalk among different cell death mechanisms. Cell Death Discov. 11:56. doi: 10.1038/s41420-025-02328-9
Fan, Y. G., Ge, R. L., Ren, H., Jia, R. J., Wu, T. Y., Lei, X. F., et al. (2024). Astrocyte-derived lactoferrin inhibits neuronal ferroptosis by reducing iron content and GPX4 degradation in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Pharmacol. Res. 209:107404. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2024.107404
Fang, J., Yuan, Q., Du, Z., Zhang, Q., Yang, L., Wang, M., et al. (2023). Overexpression of GPX4 attenuates cognitive dysfunction through inhibiting hippocampus ferroptosis and neuroinflammation after traumatic brain injury. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 204, 68–81. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2023.04.014
Feng, Z., Min, L., Chen, H., Deng, W., Tan, M., Liu, H., et al. (2021). Iron overload in the motor cortex induces neuronal ferroptosis following spinal cord injury. Redox Biol. 43:101984. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101984
Foley, P. B., Hare, D. J., and Double, K. L. (2022). A brief history of brain iron accumulation in Parkinson disease and related disorders. J. Neural Transm. (Vienna) 129, 505–520. doi: 10.1007/s00702-022-02505-5
Frazer, D. M., and Anderson, G. J. (2014). The regulation of iron transport. Biofactors 40, 206–214. doi: 10.1002/biof.1148
Fricker, M., Tolkovsky, A. M., Borutaite, V., Coleman, M., and Brown, G. C. (2018). Neuronal cell death. Physiol. Rev. 98, 813–880. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00011.2017
Friedmann Angeli, J. P., Schneider, M., Proneth, B., Tyurina, Y. Y., Tyurin, V. A., Hammond, V. J., et al. (2014). Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 16, 1180–1191. doi: 10.1038/ncb3064
Gao, M., Monian, P., Quadri, N., Ramasamy, R., and Jiang, X. (2015). Glutaminolysis and transferrin regulate ferroptosis. Mol. Cell 59, 298–308. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.06.011
Gao, M., Yi, J., Zhu, J., Minikes, A. M., Monian, P., Thompson, C. B., et al. (2019). Role of mitochondria in ferroptosis. Mol. Cell 73, 354–363.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.10.042.
Gaschler, M. M., and Stockwell, B. R. (2017). Lipid peroxidation in cell death. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 482, 419–425. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.10.086
Ge, M. H., Tian, H., Mao, L., Li, D. Y., Lin, J. Q., Hu, H. S., et al. (2021). Zinc attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury by activating Nrf2/GPX4 defense pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 27, 1023–1040. doi: 10.1111/cns.13657
Goldsteins, G., Hakosalo, V., Jaronen, M., Keuters, M. H., and Lehtonen, Š, andKoistinaho, J. (2022). CNS redox homeostasis and dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. Antioxidants (Basel) 11:405. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020405
Gozt, A., Hellewell, S., Ward, P. G. D., Bynevelt, M., and Fitzgerald, M. (2021). Emerging applications for quantitative susceptibility mapping in the detection of traumatic brain injury pathology. Neuroscience 467, 218–236. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2021.05.030
Grady, R. W., Salbe, A. D., Hilgartner, M. W., and Giardina, P. J. (1994). Results from a phase I clinical trial of HBED. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 356, 351–359. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-2554-7_37
Grolez, G., Moreau, C., Sablonnière, B., Garçon, G., Devedjian, J. C., Meguig, S., et al. (2015). Ceruloplasmin activity and iron chelation treatment of patients with Parkinson’s disease. BMC Neurol. 15:74. doi: 10.1186/s12883-015-0331-3
Guan, X., Li, X., Yang, X., Yan, J., Shi, P., Ba, L., et al. (2019). The neuroprotective effects of carvacrol on ischemia/reperfusion-induced hippocampal neuronal impairment by ferroptosis mitigation. Life Sci. 235:116795. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2019.116795
Guo, J., Tuo, Q. Z., and Lei, P. (2023). Iron, ferroptosis, and ischemic stroke. J. Neurochem. 165, 487–520. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15807
Haag, M. (2003). Essential fatty acids and the brain. Can. J. Psychiatry 48, 195–203. doi: 10.1177/070674370304800308
Hadzhieva, M., Kirches, E., Wilisch-Neumann, A., Pachow, D., Wallesch, M., Schoenfeld, P., et al. (2013). Dysregulation of iron protein expression in the G93A model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroscience 230, 94–101. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2012.11.021
Hambright, W. S., Fonseca, R. S., Chen, L., Na, R., and Ran, Q. (2017). Ablation of ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4 in forebrain neurons promotes cognitive impairment and neurodegeneration. Redox Biol. 12, 8–17. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.01.021
He, Z., Yang, C., Zhou, L., and Li, S. (2025). The combination of the 18F-FDG PET and susceptibility-weighted imaging for diagnosis of cerebral glucose metabolism and iron deposition in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 15:20029. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-02672-x
Hoelzgen, F., Nguyen, T. T. P., Klukin, E., Boumaiza, M., Srivastava, A. K., Kim, E. Y., et al. (2024). Structural basis for the intracellular regulation of ferritin degradation. Nat. Commun. 15:3802. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48151-1
Hong, D. K., Kho, A. R., Lee, S. H., Jeong, J. H., Kang, B. S., Kang, D. H., et al. (2020). Transient receptor potential melastatin 2 (TRPM2) inhibition by antioxidant, N-Acetyl-l-Cysteine, reduces global cerebral ischemia-induced neuronal death. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:6026. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176026
Hong, S. H., Lee, D. H., Lee, Y. S., Jo, M. J., Jeong, Y. A., Kwon, W. T., et al. (2017). Molecular crosstalk between ferroptosis and apoptosis: Emerging role of ER stress-induced p53-independent PUMA expression. Oncotarget 8, 115164–115178. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23046
Hu, C. L., Nydes, M., Shanley, K. L., Morales Pantoja, I. E., Howard, T. A., and Bizzozero, O. A. (2019). Reduced expression of the ferroptosis inhibitor glutathione peroxidase-4 in multiple sclerosis and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Neurochem. 148, 426–439. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14604
Hu, X., Chen, H., Xu, H., Wu, Y., Wu, C., Jia, C., et al. (2020). Role of pyroptosis in traumatic brain and spinal cord injuries. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 16, 2042–2050. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.45467
Huang, L., He, S., Cai, Q., Li, F., Wang, S., Tao, K., et al. (2021). Polydatin alleviates traumatic brain injury: Role of inhibiting ferroptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commu.556:149155.
Huang, Y., Wang, X., Li, W., Yue, F., Wang, M., and Zhou, F. (2024). Exenatide-Modified deferoxamine-based nanoparticles ameliorates neurological deficits in Parkinson’s disease mice. Int. J. Nanomed. 19, 10401–10414. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S479670
Ingold, I., Berndt, C., Schmitt, S., Doll, S., Poschmann, G., Buday, K., et al. (2018). Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis. Cell 172, 409–422.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.048.
Jia, B., Li, J., Song, Y., and Luo, C. (2023). ACSL4-Mediated ferroptosis and its potential role in central nervous system diseases and injuries. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:10021. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210021
Kabiraj, P., Valenzuela, C. A., Marin, J. E., Ramirez, D. A., Mendez, L., Hwang, M. S., et al. (2015). The neuroprotective role of ferrostatin-1 under rotenone-induced oxidative stress in dopaminergic neuroblastoma cells. Protein J. 34, 349–358. doi: 10.1007/s10930-015-9629-7
Kagan, V. E., Mao, G., Qu, F., Angeli, J. P., Doll, S., Croix, C. S., et al. (2017). Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 13, 81–90. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2238
Kamel, A. A., Nassar, A. Y., Meligy, F. Y., Omar, Y. A., Nassar, G. A. Y., and Ezzat, G. M. (2024). Acetylated oligopeptide and N-acetylcysteine protect against iron overload-induced dentate gyrus hippocampal degeneration through upregulation of Nestin and Nrf2/HO-1 and downregulation of MMP-9/TIMP-1 and GFAP. Cell Biochem. Funct. 42:e3958. doi: 10.1002/cbf.3958
Kenny, E. M., Fidan, E., Yang, Q., Anthonymuthu, T. S., New, L. A., Meyer, E. A., et al. (2019). Ferroptosis contributes to neuronal death and functional outcome after traumatic brain injury. Crit. Care Med. 47, 410–418. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003555
Khalaf, S., Ahmad, A. S., Chamara, K. V. D. R., and Doré, S. (2018). Unique properties associated with the brain penetrant iron chelator HBED reveal remarkable beneficial effects after brain trauma. J. Neurotrauma 36, 43–53. doi: 10.1089/neu.2017.5617
Koch, K. M., Nencka, A. S., Swearingen, B., Bauer, A., Meier, T. B., and McCrea, M. (2021). Acute post-concussive assessments of brain tissue magnetism using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Neurotrauma 38, 848–857. doi: 10.1089/neu.2020.7322
Komakula, S., Bhatia, R., Sahib, A., Upadhyay, A., Leve Joseph, S., Garg, A., et al. (2024). Safety and efficacy of N-acetylcysteine (NAC) as an adjunct to standard treatment in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A randomized controlled pilot trial (NACTLYS). Sci. Rep. 14:1103. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-49054-9
Kosyakovsky, J., Fine, J. M., Frey, W. H., and Hanson, L. R. (2021). Mechanisms of intranasal deferoxamine in neurodegenerative and neurovascular disease. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 14:95. doi: 10.3390/ph14020095
Kwon, B. K., Streijger, F., Fallah, N., Noonan, V. K., Bélanger, L. M., Ritchie, L., et al. (2017). Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers to stratify injury severity and predict outcome in human traumatic spinal cord injury. J. Neurotrauma 34, 567–580. doi: 10.1089/neu.2016.4435
Kwon, M. Y., Park, E., Lee, S. J., and Chung, S. W. (2015). Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget 6, 24393–24403. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5162
Lancione, M., Donatelli, G., Migaleddu, G., Cencini, M., Bosco, P., Costagli, M., et al. (2025). High resolution multi-parametric probabilistic in vivo atlas of dorsolateral nigral hyperintensity via 7 T MRI. Sci. Data 12:958. doi: 10.1038/s41597-025-05325-w
Lauritzen, L., Hansen, H. S., Jørgensen, M. H., and Michaelsen, K. F. (2001). The essentiality of long chain n-3 fatty acids in relation to development and function of the brain and retina. Prog. Lipid Res. 40, 1–94. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7827(00)00017-5
Le, Y., Liu, Q., Yang, Y., and Wu, J. (2024). The emerging role of nuclear receptor coactivator 4 in health and disease: A novel bridge between iron metabolism and immunity. Cell Death Discov. 10:312. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02075-3
Lee, J., Kosaras, B., Del Signore, S. J., Cormier, K., McKee, A., Ratan, R. R., et al. (2011). Modulation of lipid peroxidation and mitochondrial function improves neuropathology in Huntington’s disease mice. Acta Neuropathol. 121, 487–498. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0788-5
Lee, J. H., and Lee, M. S. (2019). Brain iron accumulation in atypical parkinsonian syndromes: In vivo MRI evidences for distinctive patterns. Front. Neurol. 10:74. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00074
Lee, J.-M., McLean, Z. L., Correia, K., Shin, J. W., Lee, S., Jang, J.-H., et al. (2025). Genetic modifiers of somatic expansion and clinical phenotypes in Huntington’s disease highlight shared and tissue-specific effects. Nat. Genet. 57, 1426–1436. doi: 10.1038/s41588-025-02191-5
Li, C., Sun, G., Chen, B., Xu, L., Ye, Y., He, J., et al. (2021). Nuclear receptor coactivator 4-mediated ferritinophagy contributes to cerebral ischemia-induced ferroptosis in ischemic stroke. Pharmacol. Res. 174:105933. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105933
Li, J., Cao, F., Yin, H. L., Huang, Z. J., Lin, Z. T., Mao, N., et al. (2020). Ferroptosis: Past, present and future. Cell Death Dis. 11:88. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
Li, M., Meng, Z., Yu, S., Li, J., Wang, Y., Yang, W., et al. (2022). Baicalein ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting ferroptosis via regulating GPX4/ACSL4/ACSL3 axis. Chem. Biol. Interact. 366:110137.
Li, Q., Han, X., Lan, X., Gao, Y., Wan, J., Durham, F., et al. (2017). Inhibition of neuronal ferroptosis protects hemorrhagic brain. JCI Insight 2:e90777. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.90777
Li, Q. S., and Jia, Y. J. (2023). Ferroptosis: A critical player and potential therapeutic target in traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury. Neural Regen. Res. 18, 506–512. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.350187
Li, Z., Zhang, Y., Ji, M., Wu, C., Zhang, Y., and Ji, S. (2024). Targeting ferroptosis in neuroimmune and neurodegenerative disorders for the development of novel therapeutics. Biomed. Pharmacother. 176:116777. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116777
Liang, Y., Deng, Y., Zhao, J., Liu, L., Wang, J., Chen, P., et al. (2022). Ferritinophagy is involved in experimental subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced neuronal ferroptosis. Neurochem. Res. 47, 692–700. doi: 10.1007/s11064-021-03477-w
Lin, K. J., Chen, S. D., Lin, K. L., Liou, C. W., Lan, M. Y., Chuang, Y. C., et al. (2022). Iron Brain menace: The involvement of ferroptosis in Parkinson disease. Cells 11:3829. doi: 10.3390/cells11233829
Liochev, S. I., and Fridovich, I. (1999). Superoxide and iron: Partners in crime. IUBMB Life 48, 157–161. doi: 10.1080/713803492
Liu, D., Yang, S., and Yu, S. (2024). Interactions between ferroptosis and oxidative stress in ischemic stroke. Antioxidants (Basel) 13:1329. doi: 10.3390/antiox13111329
Liu, J., Tang, D., and Kang, R. (2024). Targeting GPX4 in ferroptosis and cancer: Chemical strategies and challenges. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 45, 666–670. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2024.05.006
Liu, S., Chen, F., Han, J., Wang, L., and Dong, Y. (2024). Ferrostatin-1 improves neurological impairment induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury in the spinal cord through ERK1/2/SP1/GPX4. Exp. Neurol. 373:114659. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2023.114659
Liu, Z., Wang, M., Zhang, C., Zhou, S., and Ji, G. (2022). Molecular functions of ceruloplasmin in metabolic disease pathology. Diab. Metab. Syndr. Obes. 15, 695–711. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S346648
López-Aguirre, M., Balzano, T., Monje, M. H. G., Esteban-García, N., Martínez-Fernández, R., Del Rey, N. L., et al. (2025). Nigrostriatal iron accumulation in the progression of Parkinson’s disease. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 11:72. doi: 10.1038/s41531-025-00911-6
Lu, T., Wu, X., Wei, N., Liu, X., Zhou, Y., Shang, C., et al. (2018). Lipoxin A4 protects against spinal cord injury via regulating Akt/nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2/heme oxygenase-1 signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 97, 905–910. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.10.092
Luo, C., and Tao, L. (2020). The function and mechanisms of autophagy in traumatic brain injury. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1207, 635–648. doi: 10.1007/978-981-15-4272-5_46
Luoqian, J., Yang, W., Ding, X., Tuo, Q. Z., Xiang, Z., Zheng, Z., et al. (2022). Ferroptosis promotes T-cell activation-induced neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Cell Mol. Immunol. 19, 913–924. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00883-0
Lyamzaev, K. G., Panteleeva, A. A., Simonyan, R. A., Avetisyan, A. V., and Chernyak, B. V. (2023). The critical role of mitochondrial lipid peroxidation in ferroptosis: Insights from recent studies. Biophys. Rev. 15, 875–885. doi: 10.1007/s12551-023-01126-w
MacKenzie, E. L., Iwasaki, K., and Tsuji, Y. (2008). Intracellular iron transport and storage: From molecular mechanisms to health implications. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 10, 997–1030. doi: 10.1089/ars.2007.1893
Martí-Andrés, P., Finamor, I., Torres-Cuevas, I., Pérez, S., Rius-Pérez, S., Colino-Lage, H., et al. (2024). TRP14 is the rate-limiting enzyme for intracellular cystine reduction and regulates proteome cysteinylation. EMBO J. 43, 2789–2812. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00117-1
Martin-Bastida, A., Ward, R. J., Newbould, R., Piccini, P., Sharp, D., Kabba, C., et al. (2017). Brain iron chelation by deferiprone in a phase 2 randomised double-blinded placebo controlled clinical trial in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 7:1398. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-01402-2
Martinez, A. M., Mirkovic, J., Stanisz, Z. A., Patwari, F. S., and Yang, W. S. (2019). NSC-34 motor neuron-like cells are sensitized to ferroptosis upon differentiation. FEBS Open Bio 9, 582–593. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12577
Martínez-Reyes, I., and Chandel, N. S. (2020). Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control physiology and disease. Nat. Commun. 11:102. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13668-3
Matak, P., Matak, A., Moustafa, S., Aryal, D. K., Benner, E. J., Wetsel, W., et al. (2016). Disrupted iron homeostasis causes dopaminergic neurodegeneration in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 113, 3428–3435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1519473113
McIntosh, A., Mela, V., Harty, C., Minogue, A. M., Costello, D. A., Kerskens, C., et al. (2019). Iron accumulation in microglia triggers a cascade of events that leads to altered metabolism and compromised function in APP/PS1 mice. Brain Pathol. 29, 606–621. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12704
Miotto, G., Rossetto, M., Di Paolo, M. L., Orian, L., Venerando, R., Roveri, A., et al. (2020). Insight into the mechanism of ferroptosis inhibition by ferrostatin-1. Redox Biol. 28:101328.
Mizoi, M., Yoshida, M., Saiki, R., Waragai, M., Uemura, K., Akatsu, H., et al. (2014). Distinction between mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease by CSF amyloid β40 and β42, and protein-conjugated acrolein. Clin. Chim. Acta 430, 150–155. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.01.007
Moezzi, D., Dong, Y., Jain, R. W., Lozinski, B. M., Ghorbani, S., D’Mello, C., et al. (2022). Expression of antioxidant enzymes in lesions of multiple sclerosis and its models. Sci. Rep. 12:12761. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-16840-w
Mohammadi, S., and Ghaderi, S. (2024). Parkinson’s disease and Parkinsonism syndromes: Evaluating iron deposition in the putamen using magnetic susceptibility MRI techniques - A systematic review and literature analysis. Heliyon 10:e27950. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27950
Mohammed, F. S., Omay, S. B., Sheth, K. N., and Zhou, J. (2023). Nanoparticle-based drug delivery for the treatment of traumatic brain injury. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 20, 55–73. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2023.2152001
Müller, T., Dewitz, C., Schmitz, J., Schröder, A. S., Bräsen, J. H., Stockwell, B. R., et al. (2017). Necroptosis and ferroptosis are alternative cell death pathways that operate in acute kidney failure. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 74, 3631–3645. doi: 10.1007/s00018-017-2547-4
Nakamura, T., Keep, R. F., Hua, Y., Schallert, T., Hoff, J. T., and Xi, G. (2004). Deferoxamine-induced attenuation of brain edema and neurological deficits in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. J. Neurosurg. 100, 672–678. doi: 10.3171/jns.2004.100.4.0672
Negida, A., Hassan, N. M., Aboeldahab, H., Zain, Y. E., Negida, Y., Cadri, S., et al. (2024). Efficacy of the iron-chelating agent, deferiprone, in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 30:e14607.
Niu, L., Ye, C., Sun, Y., Peng, T., Yang, S., Wang, W., et al. (2018). Mutant huntingtin induces iron overload via up-regulating IRP1 in Huntington’s disease. Cell Biosci. 8:41. doi: 10.1186/s13578-018-0239-x
Núñez, M. T., Gallardo, V., Muñoz, P., Tapia, V., Esparza, A., Salazar, J., et al. (2004). Progressive iron accumulation induces a biphasic change in the glutathione content of neuroblastoma cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 37, 953–960. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.06.005
Ohgami, R. S., Campagna, D. R., McDonald, A., and Fleming, M. D. (2006). The Steap proteins are metalloreductases. Blood 108, 1388–1394. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-02-003681
Okauchi, M., Hua, Y., Keep, R. F., Morgenstern, L. B., and Xi, G. (2009). Effects of deferoxamine on intracerebral hemorrhage-induced brain injury in aged rats. Stroke 40, 1858–1863. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.535765
Peng, Y., Chang, X., and Lang, M. (2021). Iron homeostasis disorder and Alzheimer’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:12442. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212442
Philpott, C. C., and Ryu, M. S. (2014). Special delivery: Distributing iron in the cytosol of mammalian cells. Front. Pharmacol. 5:173. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2014.00173
Pinheiro, R. G. R., Coutinho, A. J., Pinheiro, M., and Neves, A. R. (2021). Nanoparticles for targeted brain drug delivery: What do we know? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:11654. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111654
Plascencia-Villa, G., and Perry, G. (2023). Roles of oxidative stress in synaptic dysfunction and neuronal cell death in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxidants (Basel) 12:1628. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081628
Pratt, D. A. (2023). Targeting lipoxygenases to suppress ferroptotic cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 120:e2309317120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309317120
Proneth, B., and Conrad, M. (2019). Ferroptosis and necroinflammation, a yet poorly explored link. Cell Death Differ. 26, 14–24. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0173-9
Qian, J. Y., Lou, C. Y., Chen, Y. L., Ma, L. F., Hou, W., and Zhan, Z. J. (2025). A prospective therapeutic strategy: Gpx4-targeted ferroptosis mediators. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 281:117015. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2024.117015
Ravanfar, P., Loi, S. M., Syeda, W. T., Van Rheenen, T. E., Bush, A. I., Desmond, P., et al. (2021). Systematic review: Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping (QSM) of brain iron profile in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 15:618435. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.618435
Raven, E. P., Lu, P. H., Tishler, T. A., Heydari, P., and Bartzokis, G. (2013). Increased iron levels and decreased tissue integrity in hippocampus of Alzheimer’s disease detected in vivo with magnetic resonance imaging. J. Alzheimers Dis. 37, 127–136. doi: 10.3233/JAD-130209
Regan, R. F., and Panter, S. S. (1996). Hemoglobin potentiates excitotoxic injury in cortical cell culture. J. Neurotrauma 13, 223–231. doi: 10.1089/neu.1996.13.223
Roeser, H. P., Lee, G. R., Nacht, S., and Cartwright, G. E. (1970). The role of ceruloplasmin in iron metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 49, 2408–2417. doi: 10.1172/JCI106460
Rui, T., Wang, H., Li, Q., Cheng, Y., Gao, Y., Fang, X., et al. (2021). Deletion of ferritin H in neurons counteracts the protective effect of melatonin against traumatic brain injury-induced ferroptosis. J. Pineal Res. 70:e12704.
Sánchez-Castañeda, C., Cherubini, A., Elifani, F., Péran, P., Orobello, S., Capelli, G., et al. (2013). Seeking Huntington disease biomarkers by multimodal, cross-sectional basal ganglia imaging. Hum. Brain Mapp. 34, 1625–1635. doi: 10.1002/hbm.22019
Siegert, E., Paul, F., Rothe, M., and Weylandt, K. H. (2017). The effect of omega-3 fatty acids on central nervous system remyelination in fat-1 mice. BMC Neurosci. 18:19. doi: 10.1186/s12868-016-0312-5
Skouta, R., Dixon, S. J., Wang, J., Dunn, D. E., Orman, M., Shimada, K., et al. (2014). Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 4551–4556. doi: 10.1021/ja411006a
Stockwell, B. R., Friedmann Angeli, J. P., Bayir, H., Bush, A. I., Conrad, M., Dixon, S. J., et al. (2017). Ferroptosis: A regulated cell death nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 171, 273–285. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
Sun, X., Ou, Z., Xie, M., Kang, R., Fan, Y., Niu, X., et al. (2015). HSPB1 as a novel regulator of ferroptotic cancer cell death. Oncogene 34, 5617–5625. doi: 10.1038/onc.2015.32
Tang, S., Gao, P., Chen, H., Zhou, X., Ou, Y., and He, Y. (2020). The role of iron, its metabolism and ferroptosis in traumatic brain injury. Front. Cell Neurosci. 14:590789. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.590789
Thirupathi, A., and Chang, Y. Z. (2019). Brain iron metabolism and CNS diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1173, 1–19. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9589-5_1
Tian, H. Y., Huang, B. Y., Nie, H. F., Chen, X. Y., Zhou, Y., Yang, T., et al. (2023). The interplay between mitochondrial dysfunction and ferroptosis during ischemia-associated central nervous system diseases. Brain Sci. 13:1367. doi: 10.3390/brainsci13101367
Toro-Urrego, N., Turner, L. F., and Avila-Rodriguez, M. F. (2019). New insights into oxidative damage and iron associated impairment in traumatic brain injury. Curr. Pharm. Des. 25, 4737–4746. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666191111153802
Tuo, Q. Z., Lei, P., Jackman, K. A., Li, X. L., Xiong, H., Li, X. L., et al. (2017). Tau-mediated iron export prevents ferroptotic damage after ischemic stroke. Mol. Psychiatry 22, 1520–1530. doi: 10.1038/mp.2017.171
Tydlacka, S., Wang, C. E., Wang, X., Li, S., and Li, X. J. (2008). Differential activities of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in neurons versus glia may account for the preferential accumulation of misfolded proteins in neurons. J. Neurosci. 28, 13285–13295.
Uauy, R., Mena, P., and Rojas, C. (2000). Essential fatty acids in early life: Structural and functional role. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 59, 3–15. doi: 10.1017/s0029665100000021
van Bergen, J. M., Hua, J., Unschuld, P. G., Lim, I. A., Jones, C. K., Margolis, R. L., et al. (2016). Quantitative susceptibility mapping suggests altered brain iron in premanifest Huntington disease. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 37, 789–796. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A4617
Van San, E., Debruyne, A. C., Veeckmans, G., Tyurina, Y. Y., Tyurin, V. A., Zheng, H., et al. (2023). Ferroptosis contributes to multiple sclerosis and its pharmacological targeting suppresses experimental disease progression. Cell Death Differ. 30, 2092–2103. doi: 10.1038/s41418-023-01195-0
Wainwright, P. E. (2002). Dietary essential fatty acids and brain function: A developmental perspective on mechanisms. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 61, 61–69. doi: 10.1079/pns2001130
Wang, T., Sun, Y., and Dettmer, U. (2023). Astrocytes in Parkinson’s disease: From role to possible intervention. Cells 12:2336. doi: 10.3390/cells12192336
Wang, W., Knovich, M. A., Coffman, L. G., Torti, F. M., and Torti, S. V. (2010). Serum ferritin: Past, present and future. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1800, 760–769. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2010.03.011
Wang, Z.-L., Yuan, L., Li, W., and Li, J.-Y. (2022). Ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease: Glia-neuron crosstalk. Trends Mol. Med. 28, 258–269. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.02.003
Weaver, K., and Skouta, R. (2022). The selenoprotein glutathione peroxidase 4: From molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Biomedicines 10:891. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10040891
Wei, C. (2024). The role of glutathione peroxidase 4 in neuronal ferroptosis and its therapeutic potential in ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Brain Res. Bull. 217:111065. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2024.111065
Wei, N., Lu, T., Yang, L., Dong, Y., and Liu, X. (2021). Lipoxin A4 protects primary spinal cord neurons from Erastin-induced ferroptosis by activating the Akt/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. FEBS Open Bio 11, 2118–2126. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13203
Weiser, M. J., Butt, C. M., and Mohajeri, M. H. (2016). Docosahexaenoic acid and cognition throughout the lifespan. Nutrients 8:99. doi: 10.3390/nu8020099
Wortmann, M., Schneider, M., Pircher, J., Hellfritsch, J., Aichler, M., Vegi, N., et al. (2013). Combined deficiency in glutathione peroxidase 4 and vitamin E causes multiorgan thrombus formation and early death in mice. Circ. Res. 113, 408–417. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.279984
Wu, J. R., Tuo, Q. Z., and Lei, P. (2018). Ferroptosis, a recent defined form of critical cell death in neurological disorders. J. Mol. Neurosci. 66, 197–206. doi: 10.1007/s12031-018-1155-6
Wu, Y., Song, J., Wang, Y., Wang, X., Culmsee, C., and Zhu, C. (2019). The potential role of ferroptosis in neonatal brain injury. Front. Neurosci. 13:115. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00115
Xiao, X., Jiang, Y., Liang, W., Wang, Y., Cao, S., Yan, H., et al. (2019). miR-212-5p attenuates ferroptotic neuronal death after traumatic brain injury by targeting Ptgs2. Mol. Brain 12:78. doi: 10.1186/s13041-019-0501-0
Xie, B. S., Wang, Y. Q., Lin, Y., Mao, Q., Feng, J. F., Gao, G. Y., et al. (2019). Inhibition of ferroptosis attenuates tissue damage and improves long-term outcomes after traumatic brain injury in mice. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 25, 465–475. doi: 10.1111/cns.13069
Xiong, H., Tuo, Q. Z., Guo, Y. J., and Lei, P. (2019). Diagnostics and treatments of iron-related CNS diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1173, 179–194. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-9589-5_10
Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., Zhang, J. H., Han, K., Zhang, X., Bai, X., et al. (2020). Astrocyte hepcidin ameliorates neuronal loss through attenuating brain iron deposition and oxidative stress in APP/PS1 mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 158, 84–95. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.07.012
Yagoda, N., von Rechenberg, M., Zaganjor, E., Bauer, A. J., Yang, W. S., Fridman, D. J., et al. (2007). RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 447, 864–868. doi: 10.1038/nature05859
Yan, N., and Zhang, J. (2019). Iron metabolism, ferroptosis, and the links with Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 13:1443. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01443
Yang, J., Shi, X., Wang, Y., Ma, M., Liu, H., Wang, J., et al. (2023). Multi-Target neuroprotection of thiazolidinediones on Alzheimer’s disease via neuroinflammation and ferroptosis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 96, 927–945. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230593
Yang, L., Wang, D., Wang, X. T., Lu, Y. P., and Zhu, L. (2018). The roles of hypoxia-inducible Factor-1 and iron regulatory protein 1 in iron uptake induced by acute hypoxia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 507, 128–135. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.10.185
Yang, W. S., SriRamaratnam, R., Welsch, M. E., Shimada, K., Skouta, R., Viswanathan, V. S., et al. (2014). Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156, 317–331.
Yang, W. S., and Stockwell, B. R. (2008). Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem. Biol. 15, 234–245. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2008.02.010
Yang, Z., Su, W., Wei, X., Pan, Y., Xing, M., Niu, L., et al. (2025). Hypoxia inducible factor-1α drives cancer resistance to cuproptosis. Cancer Cell 43, 937–954.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2025.02.015.
Yao, M. Y., Liu, T., Zhang, L., Wang, M. J., Yang, Y., and Gao, J. (2021). Role of ferroptosis in neurological diseases. Neurosci. Lett. 747:135614. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2020.135614
Yao, X., Zhang, Y., Hao, J., Duan, H. Q., Zhao, C. X., Sun, C., et al. (2019). Deferoxamine promotes recovery of traumatic spinal cord injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. Neural Regen. Res. 14, 532–541. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.245480
Yoo, M. H., Gu, X., Xu, X. M., Kim, J. Y., Carlson, B. A., Patterson, A. D., et al. (2010). Delineating the role of glutathione peroxidase 4 in protecting cells against lipid hydroperoxide damage and in Alzheimer’s disease. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 12, 819–827. doi: 10.1089/ars.2009.2891
You, L. H., Li, F., Wang, L., Zhao, S. E., Wang, S. M., Zhang, L. L., et al. (2015). Brain iron accumulation exacerbates the pathogenesis of MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 284, 234–246. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.09.071
Yu, Z. X., Li, S. H., Evans, J., Pillarisetti, A., Li, H., and Li, X. J. (2003). Mutant huntingtin causes context-dependent neurodegeneration in mice with Huntington’s disease. J. Neurosci. 23, 2193–2202.
Zha, X., Liu, X., Wei, M., Huang, H., Cao, J., Liu, S., et al. (2025). Microbiota-derived lysophosphatidylcholine alleviates Alzheimer’s disease pathology via suppressing ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 37, 169–186.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.10.006.
Zhang, C., Chen, X., Liu, R., and Zhao, G. (2024). HSP90 inhibition attenuated isoflurane-induced neurotoxicity in mice and human neuroglioma cells. Neurochem. Res. 49, 706–717. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04060-1
Zhang, J. Y., Zhou, B., Sun, R. Y., Ai, Y. L., Cheng, K., Li, F. N., et al. (2021). The metabolite α-KG induces GSDMC-dependent pyroptosis through death receptor 6-activated caspase-8. Cell Res. 31, 980–997. doi: 10.1038/s41422-021-00506-9
Zhang, X., Hu, Y., Wang, B., and Yang, S. (2024). Ferroptosis: Iron-mediated cell death linked to disease pathogenesis. J. Biomed. Res. 38, 413–435. doi: 10.7555/JBR.37.20230224
Zhang, Y., Sun, C., Zhao, C., Hao, J., Zhang, Y., Fan, B., et al. (2019). Ferroptosis inhibitor SRS 16-86 attenuates ferroptosis and promotes functional recovery in contusion spinal cord injury. Brain Res. 1706, 48–57. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.10.023
Zhang, Y. H., Wang, D. W., Xu, S. F., Zhang, S., Fan, Y. G., Yang, Y. Y., et al. (2018). α-Lipoic acid improves abnormal behavior by mitigation of oxidative stress, inflammation, ferroptosis, and tauopathy in P301S Tau transgenic mice. Redox Biol. 14, 535–548. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2017.11.001
Zhang, Z., Wu, Y., Yuan, S., Zhang, P., Zhang, J., Li, H., et al. (2018). Glutathione peroxidase 4 participates in secondary brain injury through mediating ferroptosis in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Brain Res. 1701, 112–125. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.012
Zheng, Y., Sun, J., Luo, Z., Li, Y., and Huang, Y. (2024). Emerging mechanisms of lipid peroxidation in regulated cell death and its physiological implications. Cell Death Dis. 15:859. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07244-x
Zhou, H., Yin, C., Zhang, Z., Tang, H., Shen, W., Zha, X., et al. (2020). Proanthocyanidin promotes functional recovery of spinal cord injury via inhibiting ferroptosis. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 107:101807. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101807
Zhou, J., Wearn, A., Huck, J., Hughes, C., Baracchini, G., Tremblay-Mercier, J., et al. (2024). Iron deposition and distribution across the hippocampus is associated with pattern separation and pattern completion in older adults at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 44:e1973232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1973-23.2024
Zhu, Q., Zhai, J., Chen, Z., Guo, Z., Wang, N., Zhang, C., et al. (2024). Ferritinophagy: Molecular mechanisms and role in disease. Pathol. Res. Pract. 262:155553. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2024.155553
Zille, M., Karuppagounder, S. S., Chen, Y., Gough, P. J., Bertin, J., Finger, J., et al. (2017). Neuronal death after hemorrhagic stroke in vitro and in vivo shares features of ferroptosis and necroptosis. Stroke 48, 1033–1043. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015609
Zivadinov, R., Tavazzi, E., Bergsland, N., Hagemeier, J., Lin, F., Dwyer, M. G., et al. (2018). Brain iron at quantitative MRI is associated with disability in multiple sclerosis. Radiology 289, 487–496. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2018180136
Keywords: neurological injuries, ferroptosis, iron, lipid peroxidation, central nervous system
Citation: Huang Q, Zhang H, Chen S, Wang Y and Zhou J (2025) Ferroptosis in central nervous system injuries: molecular mechanisms, diagnostic approaches, and therapeutic strategies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 19:1593963. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1593963
Received: 15 March 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 22 July 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Tozzi, University of Perugia, ItalyReviewed by:
Antonio Martínez-Ruiz, Princess University Hospital, SpainMingzi Zhang, University of Southern California, United States
Walter Moos, University of California, San Francisco, United States
Copyright © 2025 Huang, Zhang, Chen, Wang and Zhou. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jian Zhou, emoxMzcwNUAxNjMuY29t
 Qiuhu Huang
Qiuhu Huang Jian Zhou
Jian Zhou