- 1Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yueyang Hospital of Integrated Traditional Chinese and Western Medicine, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2School of Rehabilitation Science, Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 3Engineering Research Center of Traditional Chinese Medicine Intelligent Rehabilitation, Ministry of Education, Shanghai, China
State dependent memory (SDM) occurs when memory retrieval varies with the individual's psychological and physiological state at encoding and recall. Growing evidence shows that internal states shape memory performance across all phases of memory. Examples include affective and physiological conditions, medication effects, and disease states. This review examines how these states affect encoding, storage, and retrieval. We argue that internal states modulate activity in brain regions involved in memory by altering neurotransmitter signaling and by inducing plastic organization of neural circuits and networks. We believe this perspective can guide personalized electrical neuromodulation and multimodal intervention strategies for memory disorders.
1 Introduction
State dependent memory (SDM) refers to better performance in memory retrieval when a person is in a similar state as when the memory was initially encoded (Bower, 1981). SDM often occurs under specific internal conditions, including anxiety, fear, depression, sleep, and states induced by alcohol or drugs (Ebrahimi-Ghiri et al., 2019). For example, when information is encoded in a state of depression, individuals more readily access memories congruent with that mood than unrelated memories (Ellwart et al., 2003; Everaert et al., 2022). Similarly, individuals with alcohol dependence may have difficulty recalling events learned while sober when intoxicated (Miller et al., 1978).
Memory is a dynamic cognitive process supported by neural circuits composed of excitatory and inhibitory neurons (Nelson and Valakh, 2015; Vogels et al., 2011). The balance between excitation and inhibition (E/I balance) within these circuits is tightly regulated by neurotransmitter systems, including glutamate, dopamine, noradrenaline, and others, and is critical for memory and cognitive function (Ghatak et al., 2021; Han et al., 2020; Takahashi, 2011; Parsaei et al., 2011). Emotional states can modulate this balance by influencing synaptic plasticity, thereby shaping memory processes (Han et al., 2020; Turkileri and Sakaki, 2017; Tanaka et al., 2000). For example, acute stress can disrupt the E/I balance, offering a circuit-level explanation for how internal states affect memory (Han et al., 2020).
Neural networks across brain regions govern memory and contribute to SDM. Key structures, including the hippocampal complex (Sumadevi, 2024), the amygdalar complex (McDonald, 2014), and the prefrontal cortex (PFC; Chafee and Heilbronner, 2022), play central roles in this process (Zarrindast and Khakpai, 2020). Memory emerges from widespread interactions among multiple regions that are coordinated through complex networks. In the fear-related network of mice, certain hub regions exhibit strong connectivity with other areas, and the strength of these connections can be dynamically modulated, affecting the functional state of the network (Vetere et al., 2017). The influence of internal states on memory depends on both circuit plasticity and mechanisms that reorganize networks, which in turn alter processing pathways and memory performance (Yang et al., 2006; Mohr et al., 2016; Hennings et al., 2019; Wen et al., 2021; Shine et al., 2016). Recent studies using a brain-wide neuron quantification toolkit have revealed different neuronal patterns across phases of aversive memory in males and females, although these differences were not reflected in behavior (Franceschini et al., 2023).
SDM may provide new insights for circuit-based therapeutic approaches, such as neurostimulation, in treating memory-related disorders. Neurodegenerative and psychiatric conditions, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), major depressive disorder (MDD), and anxiety disorders (ANX), frequently involve memory dysfunction (Demic and Cheng, 2014; Mioni et al., 2015; Lee and Fernandes, 2017; Vetere et al., 2025). Patients often exhibit memory deficits that are influenced by physiological or psychological states (Bronnick et al., 2007; Gisquet-Verrier et al., 2015; Radulovic et al., 2017; Huang and Li, 2021). For instance, individuals with PD commonly experience anxiety and depression, which can bias attention, impair working-memory updating and task-relevant encoding, and disrupt hippocampal-dependent retrieval, leading to difficulties in prospective memory such as remembering medication schedules (Yang et al., 2018; Hammarlund et al., 2024; Sumbul-Sekerci et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2018). These state-dependent effects have important implications for designing electrical neurostimulation protocols aimed at enhancing memory. Therefore, neurostimulation to enhance memory should be tailored to both the patients internal state and the targeted memory phase. While electrical neurostimulation is increasingly applied to memory disorders, evidence for its efficacy in improving memory or regulating internal states remains variable. Current interventions rely primarily on open-loop transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) and deep brain stimulation (DBS) targeting specific regions or networks (R. Rezai and Sharma, 2014; Marder et al., 2022). Neural responses to such stimulation show considerable variability across individuals (Wansbrough et al., 2024). Given that memory dysfunction in different disorders may be influenced by distinct internal states, there is a need for more precise, state-aware stimulation protocols.
In this review, we synthesize evidence for state dependence across encoding, storage, and retrieval and address the following: (i) state-dependent effects across these memory stages; (ii) supporting mechanisms within neural circuits and network plasticity; (iii) behavioral signatures and methods for assessing SDM; (iv) SDM manifestations in pathological conditions; and (v) circuit-based neuromodulation and intervention strategies for SDM. We argue that state-dependent mechanisms offer a promising framework for developing more precise and effective interventions to enhance memory and treat memory-related disorders.
2 State dependency in memory encoding, storage, and retrieval
This section reviews how internal physiological and emotional states influence memory across the phases of encoding, storage, and retrieval. Anxiety and acute stress can disrupt encoding by impairing attentional allocation and working-memory processes. Conditions such as sleep and stress modulate storage and consolidation, and they shape the durability and transformation of memory traces over time. Retrieval is particularly sensitive to the alignment between the emotional state at retrieval and that at encoding. Greater state congruence is typically associated with higher neural pattern similarity across phases and improved recall accuracy. To make phase boundaries explicit and to consolidate the physiological-process basis for our subsequent circuit-level discussion, we summarize state-dependent influences by memory phase in Table 1.
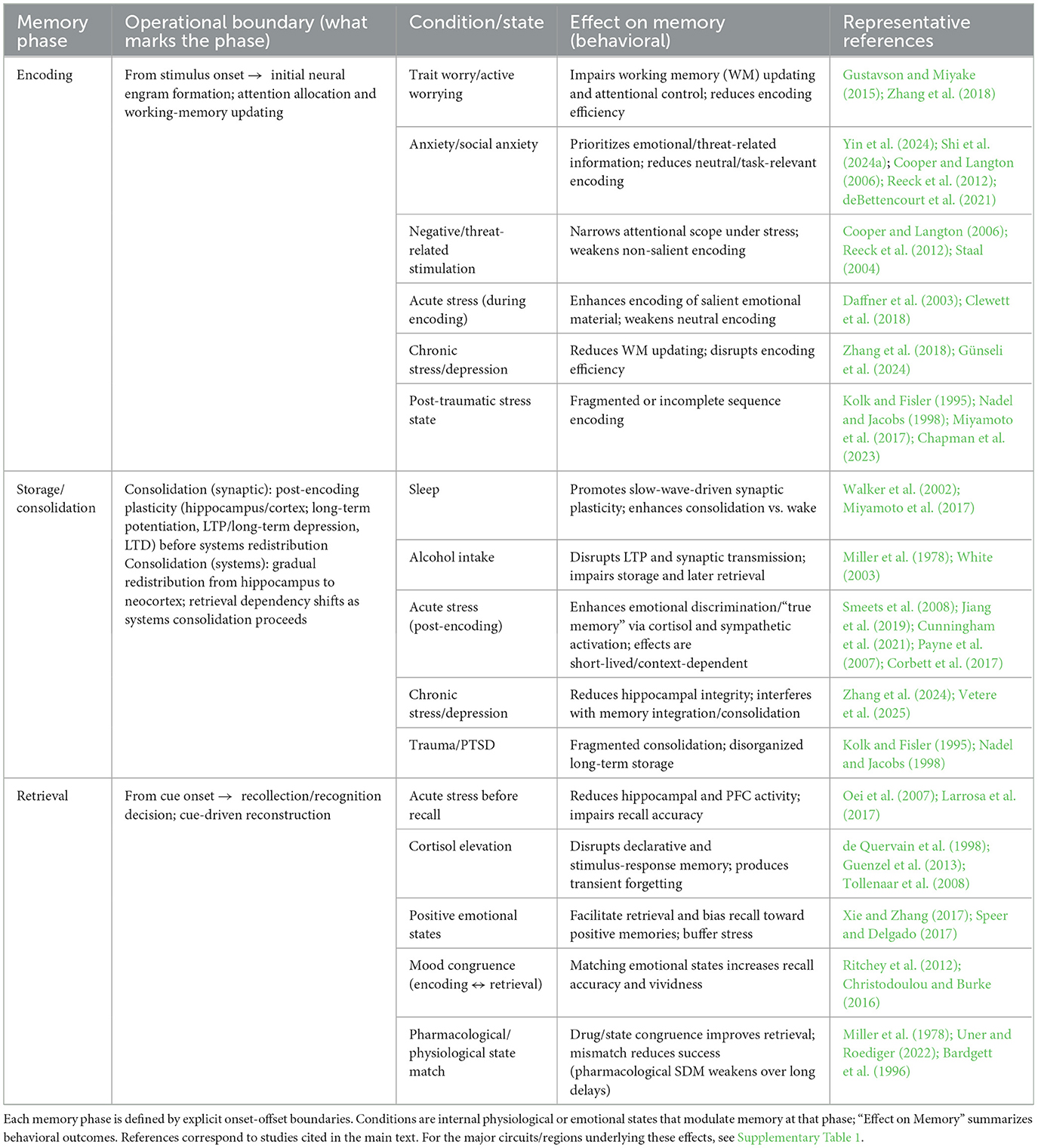
Table 1. State-dependent effects across memory phases: conditions, behavioral outcomes, and clarified onset-offset boundaries.
2.1 State dependence in memory encoding
Memory encoding is the first stage of memory formation, during which information, such as sounds, images, or smells, is transformed into neural representations that can be processed and stored in long-term memory, often as sequential patterns of activity in the hippocampus (Levy and Wu, 1996; Lisman and Jensen, 2013; Kesner and Rolls, 2015). Memory encoding involves both the reception and the initial interpretation of information. The initial processing stage under negative emotional states is often fragile. For example, active worrying, a core component of anxiety, reduces working memory (WM) capacity, compromising the ability to handle multiple tasks or streams of information simultaneously (Sari et al., 2017).
Working memory is particularly critical during the early processing stage of encoding, as newly encoded information is retained for varying durations depending on processing depth. Sensory information is typically retained only briefly, with most dissipating during the sensory memory stage (Wang et al., 2016). Only a subset of information receives attention and is transferred to short-term or working memory, where it guides decision-making over minutes (Wang et al., 2016). During this stage, working memory plays an “updating” role, selecting and maintaining relevant information while removing outdated or irrelevant content (Ecker et al., 2010; Mastrangelo, 2024; Taylor et al., 2022).
Impaired working memory updating is observed in mood disorders and is associated with disruptions during the encoding phase, further reducing encoding efficiency (Zhang et al., 2018; Günseli et al., 2024). Research indicates that trait worry is linked to difficulties in updating working memory, even in non-threatening contexts (Gustavson and Miyake, 2015).
Anxious states prioritize threat-related information during early encoding, reallocating attention toward emotionally salient cues at the expense of other information, thereby reducing encoding efficiency (Yin et al., 2024; Shi et al., 2024a; deBettencourt et al., 2021). Selective attention shifts depending on task demands and emotional states, and studies of visual search demonstrate emotion-driven prioritization and stress-induced narrowing of attentional scope (Cooper and Langton, 2006; Reeck et al., 2012; Staal, 2004). This attentional bias can weaken the processing of task-relevant information, impairing memory encoding (Nie et al., 2024). Conversely, acute stress can enhance the encoding of salient material, highlighting state-dependent effects (Daffner et al., 2003; Clewett et al., 2018).
Fragmented sequence encoding has been observed in post-traumatic stress states (Kolk and Fisler, 1995; Nadel and Jacobs, 1998). Typically, theta (θ) oscillations coordinate neuronal activity to regulate memory formation, but extreme inhibitory states, such as during trauma, can weaken these oscillations, causing newly encoded information to enter subsequent stages in a fragmented form (Ji et al., 2024; Miyamoto et al., 2017; Chapman et al., 2023).
2.2 State dependence in memory storage
Following encoding, newly formed memories exist in a labile, temporary state, making them vulnerable to interference (Mosha and Robertson, 2016). Proactive interference occurs when previously learned information disrupts the learning of new, related material, while retroactive interference arises when new learning impairs retrieval of existing memories (Mercer and Fisher, 2022; Schubert, 2023). Consolidation transforms these fragile memory representations into stable long-term storage.
Physiological conditions, such as sleep, can significantly affect consolidation and memory storage (Xin and Yuan, 2015). For instance, Walker et al. (2002) found that sleep enhances learning compared with wakefulness over the same interval, a phenomenon known as sleep-dependent memory consolidation. During sleep, synchronized neuronal oscillations, including slow waves (0.5–4 Hz), regulate synaptic strength and facilitate memory consolidation (Miyamoto et al., 2017).
Alcohol can disrupt memory storage by affecting synaptic plasticity, causing neuronal hyperpolarization, impaired signal transmission, and reduced long-term synaptic connectivity, which together interfere with proper memory storage and retrieval (Miller et al., 1978; White, 2003).
Stress effects on memory storage are not uniformly negative. Acute stress can enhance discrimination of related memories and improve true memory performance during consolidation, effects that are closely linked to stress-induced cortisol and sympathetic activity (Smeets et al., 2008; Jiang et al., 2019; Cunningham et al., 2021). However, these enhancements are often short-lived or context-dependent, for example, favoring emotional over neutral memory during early consolidation (Payne et al., 2007; Corbett et al., 2017). Additionally, hippocampal dysfunction in depression and trauma-related memory fragmentation in PTSD can disrupt consolidation and memory organization, discussed further in Section 5.
2.3 State dependence in memory retrieval
Memory retrieval involves recalling stored information and accessing established memory traces (Savarimuthu and Ponniah, 2023). Successful retrieval depends on the fidelity of neuronal discharge sequences formed during encoding (Vaz et al., 2020), with greater similarity between encoding and retrieval activity facilitating recall (Ritchey et al., 2012). When emotional states during retrieval match those during encoding, information is more readily accessed, whereas state-inconsistent memories may be overlooked or forgotten (Christodoulou and Burke, 2016).
Acute stress prior to retrieval typically impairs memory, as demonstrated by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies showing reduced hippocampal and PFC activity when stress occurs after encoding but before retrieval (Oei et al., 2007; Larrosa et al., 2017). Stress can also alter synaptic plasticity by inducing long-term depression (LTD) and disrupting hippocampal circuit interactions, leading to transient or persistent forgetting (Diamond et al., 2005; Yang et al., 2006). Cortisol elevations further impact both hippocampus-dependent declarative and striatum-dependent stimulus-response memory, potentially compromising long-term memory (de Quervain et al., 1998; Tollenaar et al., 2008; Guenzel et al., 2013).
Emotional memory retrieval is particularly relevant for affective disorders, which are often characterized by biases toward negative memories (Paunovic et al., 2002; Buchanan, 2007; Cohen and Kahana, 2022). Individuals with depression or in irrelevant contexts may ruminate on negative memories, limiting their ability to respond to current challenges (Gotlib et al., 2004; Leyman et al., 2006; Alipour et al., 2025). Conversely, strategies that promote retrieval of positive emotional memories can buffer stress and modulate affective states (Speer and Delgado, 2017).
3 The role of circuits and networks in SDM
This section outlines how neural circuits and large-scale networks support SDM. At the circuit level, interactions among the hippocampus, PFC, amygdala, and other interconnected regions shape state-dependent encoding, storage, and retrieval. At the systems level, large-scale networks organize attention, control, and internal mentation, and shifts in arousal and affect can rebalance these networks and change memory performance. Supplementary Table 1 summarizes phase-specific neural substrates, highlighting representative circuits and networks implicated in SDM.
3.1 Dynamic regulation of brain areas and circuits in SDM
During memory encoding, the bidirectional functional connectivity between the hippocampus and PFC is a key neural circuit (Das and Menon, 2024; Su et al., 2024). The hippocampus is responsible for integrating information from different brain regions into a complete memory representation (Marr, 1971; Eichenbaum, 2004), whereas the PFC is involved in memory encoding (Fletcher, 1998) and can influence the computations of the hippocampus during memory encoding by providing top-down state signals (Nyberg et al., 2019). The hippocampus interacts with the PFC to integrate old and new knowledge, guiding the encoding of new memories (Preston and Eichenbaum, 2013; Sekeres et al., 2024). During encoding, the amygdala supports state-dependent processing of emotional information (LaBar and Cabeza, 2006). The basolateral amygdala (BLA; Patel et al., 2016) contributes to encoding of salient negative information across internal states, especially in the recognition and response to emotions such as fear and anxiety (LeDoux, 2003). During this process, the hippocampal complex contributes contextual representations and interpretive frameworks, thereby modulating the amygdala's response to emotionally salient stimuli (Phelps, 2004). However, the amygdala and hippocampus do not synergize in all types of memory. During the encoding of associative memory, an increase in amygdala activity, does not disrupt hippocampal association-memory processes, although it impairs emotional associative memory (Madan et al., 2017). This indicates that under negative emotions, the amygdala does not inhibit the associative encoding function of the hippocampus.
During memory storage and consolidation, the PFC supports retention by regulating posterior sensory representations rather than storing content itself (Lara and Wallis, 2015). It monitors and organizes memory and, together with the hippocampus, forms a schema network that integrates new information into existing knowledge (Simons and Spiers, 2003; Maviel et al., 2004; Frankland and Bontempi, 2005; Khan et al., 2024). The central amygdala (CeA) contributes to early consolidation of fear memory and is not merely a downstream relay of the basolateral complex (Pitts and Takahashi, 2011; Kim et al., 2017). In mice, fear learning and consolidation involve engagement of a distributed thalamic-hippocampal-cortical network, which shows small-world organization and supports long-term stability (Wheeler et al., 2013). In humans, fear-memory storage is associated with increased connectivity between the amygdala and dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and between the hippocampus and insula, together with decreased connectivity between the amygdala and medial PFC (mPFC; Feng et al., 2013). Stressful states can compromise the transfer of information into long-term memory, and chronic stress can inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation (LTP; Lynch, 2004; Schwabe et al., 2009; Zerbes and Schwabe, 2019).
Interactions among the amygdala, hippocampus, and mPFC support memory retrieval, especially for emotional memories (Buchanan, 2007; Daselaar et al., 2008; Oztekin et al., 2009; Murty et al., 2010). Human studies show that the amygdala participates in emotional arousal. Arousal increases retrieval-related activity in the amygdala and the medial temporal lobe (MTL; Squire and Zola-Morgan, 1991) during long-term memory (Dolcos et al., 2005; Madan et al., 2017). Retrieval engages multiple circuits, including interactions between the postsubiculum and the hippocampus and between the amygdala and the hippocampus via the lateral amygdala (Richter-Levin, 2004; Sotres-Bayon et al., 2012; Wang et al., 2023). In conditioned fear, inputs from the BLA and the ventral hippocampus (vHPC) oppositely modulate the prelimbic (PL) cortical circuitry and shape fear expression (Sierra-Mercado et al., 2011; Sotres-Bayon et al., 2012). The anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) participates in remote contextual fear retrieval, although its dynamic links to other circuits remain unclear (Frankland et al., 2004). Successful retrieval of extinction memory suppresses the original fear response, yet stress impairs extinction learning (Akirav and Maroun, 2007). During extinction, the infralimbic (IL) cortex to BLA pathway inhibits fear expression, and an IL to thalamic nucleus reuniens (Re) to BLA pathway is engaged (Silva et al., 2021; Vafaei et al., 2022; Li et al., 2025). Re links the mPFC and the hippocampus, supports spatial working memory and executive functions, and may be a target for DBS in AD (Viena et al., 2018; Shoob et al., 2023).
Multiple neurotransmitters that participate in signal transmission in memory-related brain regions can also modulate memory and states, including the predominantly excitatory glutamatergic system, the dopaminergic system (Kong et al., 2024), the noradrenergic system (Downs and McElligott, 2022), and the predominantly inhibitory GABAergic system (Russek, 2006). Earlier works showed that these neurotransmitter systems can alter the balance of excitation and inhibition (E/I balance) in neurons during information transmission (Ghatak et al., 2021), which can affect memory performance under certain conditions, such as acute stress (Han et al., 2020). The E/I balance is crucial for maintaining neuronal stability and normal brain function and disruptions in this balance are associated with various neuropsychological disorders (Yizhar et al., 2011; Duma et al., 2024; Racz et al., 2025).
Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) is an important inhibitory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system (CNS; Russek, 2006) that plays a role in maintaining the order of information transmission in the E/I balance (Rideaux et al., 2022). GABA-A receptors in the dorsal hippocampus (Wang et al., 2015) are implicated in various neurodegeneration diseases (Rissman and Mobley, 2011) and participate in Lithium-induced SDM in mice (Parsaei et al., 2011). Lithium is a commonly used mood stabilizer for treating human bipolar disorder (Rybakowski, 2014). In addition, GABA receptors are also believed to play a role in the acquisition, consolidation, and extinction of fear memory (Dubrovina, 2017).
The glutamatergic system, through α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptors, is involved in enhancing synaptic plasticity that underlies fear memory formation (Gonzalez and Jayaraman, 2024). This process may help explain how the hippocampus encodes and stores memories related to fear and avoidance. The N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, another key component of the glutamatergic system, plays a crucial role in the reconsolidation of aversive memories within the amygdala complex (Garcia-delaTorre et al., 2014). Another important neurotransmitter related to aversive memory is histamine (Fabbri et al., 2016). Specifically, it has been shown that depletion of histamine impairs the retrieval of inhibitory avoidance memory in rats (Fabbri et al., 2016), especially when the depletion occurs in the hippocampus or BLA, which damages long-term memory (Benetti et al., 2015). However, when the hippocampus is damaged, restoration of histamine signaling in the BLA can improve memory recovery, suggesting that in damaged brain structures, the histaminergic system's regulation of aversive memory can be compensated through other pathways.
Emotional experiences may be better remembered, partly because adrenergic receptors also influence synaptic plasticity (Katsuki et al., 1997) and enhance memory consolidation (Roozendaal and Hermans, 2017). However, this process is complex, as emotions do not always enhance memory (Madan et al., 2017; Turkileri and Sakaki, 2017). Under acute stress, the noradrenergic system is widely activated, which enhances emotional memories (e.g., fear) and is implicated in anxiety-related arousal (Goddard et al., 2010; Tanaka et al., 2000). In other laboratory studies, chronic stress was found to significantly increase the norepinephrine (NE) transporter and tyrosine hydroxylase, both of which are involved in the synthesis and release of noradrenaline, impairing working memory (Miner et al., 2006; Lee and Goto, 2015). Repeated stress in rats can lead to impairments in spatial and emotional memory due to activation of α1 adrenergic receptors (Faraji et al., 2023).
Dopamine (DA) plays a crucial role in anxiety and fear (de la Mora et al., 2010; El Mansari et al., 2010; Bannon et al., 2020). DA regulates the formation of memories by affecting synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus (Jay, 2003), specifically by enhancing or inhibiting hippocampal LTP and LTD (Tsetsenis et al., 2023). There are five subtypes of dopamine receptors, D1–D5 (Bannon et al., 2020). Among them, the D1 family (D1/D5 receptors), when activated, plays a crucial role in long-term synaptic plasticity in various regions of the hippocampus (Hansen and Manahan-Vaughan, 2012) and may support the dopaminergic modulation of persistent memory (Nagai et al., 2007). Hagena and Manahan-Vaughan (2016) found that the use of D1/D5 receptor antagonists in the hippocampus of laboratory rats significantly impaired LTP and LTD induced by patterned incoming stimuli or new spatial learning. This finding suggests that D1/D5 receptors play an important role in either enhancing or suppressing synaptic plasticity (Lemon and Manahan-Vaughan, 2006). In specific circumstances, the activation of these receptors can trigger the release of DA in the hippocampus, which promotes experience-dependent memory encoding (Hagena and Manahan-Vaughan, 2016) and consolidation of different tasks (Furini et al., 2014). The D1/D5 receptors-induced release of DA in the PFC further promotes long-term retention of recognition memory (Nagai et al., 2007).
3.2 Plasticity of neural networks and SDM
Shi et al. (2024b) demonstrated that whole-brain integration during the memory encoding phase is positively correlated with memory performance, whereas during retrieval, cross-module recruitment of visual and somatomotor networks contributes to memory performance. These findings suggest that different memory stages rely on distinct patterns of network reorganization to meet task demands, highlighting the inherent plasticity of neural networks.
The brain is capable of rapidly reorganizing neural circuits through synaptic modifications occurring within hours, allowing swift adaptation to new experiences and the formation of novel functional subnetworks (Glasser et al., 2011). Such structural changes not only modify local circuits but also enhance global efficiency, particularly within prefrontal cortical networks, thereby reconstructing retrieval pathways for memories (Le Bé and Markram, 2006; Mohr et al., 2016).
Neural circuits flexibly reconfigure according to task demands across different contexts (Trambaiolli et al., 2024). Human fear-extinction studies reveal cross-regional connectivity that extends beyond “classical fear-related” areas, encompassing large-scale networks such as the Default Mode Network (DMN), Ventral Attention Network (VAN), and Frontoparietal Network (FPN), whose functional connectivity dynamically changes during extinction (Wen et al., 2021). Rodent studies show that recall of fears of varying intensity triggers marked changes in circuit coupling (Haubrich and Nader, 2023). Under mild fear, the amygdala (BLA/CeA) acts as a central hub, with the infralimbic cortex (IL) bridging the amygdalar module to the retrosplenial cortex (RSC) and hippocampus. Under severe fear, the network fragments, with the amygdala becoming disconnected from other regions, illustrating state-dependent plasticity. Recall networks are integrated under mild fear but fragment under severe fear, providing a network-level perspective that contextualizes disorders of fear dysregulation such as PTSD and social anxiety disorder.
Anxiety also induces plastic changes in coupling among large-scale systems. fMRI studies report altered connectivity between the DMN and the salience network (SN; Li et al., 2023; Willinger et al., 2024), as well as between the DMN and the dorsal attention network (DAN; De la Peña-Arteaga et al., 2024). DMN dysfunction can contribute to emotional disorders such as anxiety (Zhao et al., 2007). The SN identifies and highlights salient stimuli in the environment, and its overactivation can lead to excessive vigilance and heightened attention to threat (Han et al., 2023). The DAN demonstrates increased sensitivity to threatening stimuli in anxiety, influencing memory performance on attention-dependent tasks (Gao et al., 2023).
Anxious states may lead to excessive processing of threatening information and overemphasis on errors, increasing the likelihood that negative information enters working memory (Grant and White, 2016; Bar-Haim et al., 2007). These network-level shifts are associated with reduced perceptual efficiency and impaired control of worry, and can influence memory across multiple stages (Kim, 2010; Yuan et al., 2021; Xiong et al., 2020; Mallas et al., 2020). Studies on trait anxiety indicate that current emotional states modify the network expression of the trait (De la Peña-Arteaga et al., 2024). When state anxiety is regulated, trait-related associations are focal within the DAN, ventral DMN (vDMN), and auditory network (AN); without such regulation, additional clusters appear in other networks. These patterns reflect a reconfigurable network architecture rather than isolated regional effects, linking SDM to large-scale network plasticity.
4 Understand SDM at the behavioral level
Behavioral assessment of SDM involves three complementary approaches. Task paradigms quantify working and prospective memory under varying cognitive loads, emotion-memory paradigms examine how affect influences memory control and retention, and clinical scales capture state-related changes in cognitive function. Together, these methods provide a comprehensive picture of how internal states shape memory accuracy, accessibility, and overall availability.
4.1 Behavioral differences in SDM
Emotional states act as internal contexts that can strongly influence memory retrieval (Madan et al., 2017). Reinstating negative emotional contexts during retrieval often enhances memory accuracy, while reinstating positive contexts increases the likelihood of successful recall (Xie and Zhang, 2017). This demonstrates that emotional states affect both the accessibility and quality of retrieved memories. These findings align with recent research on emotional dynamics and temporal memory (Wang and Lapate, 2025), showing that shifts from neutral to negative emotions can produce a perceived expansion of time. This “time expansion effect” may serve an adaptive function by enhancing the encoding and retention of emotionally significant events.
Beyond emotional states, physiological factors such as fatigue also impact memory. Fatigue is associated with reduced accuracy and impaired retrieval (Fan et al., 2017), which can lead to information loss and retrieval bias. Such impairments may result from reduced attentional resources under fatigue or high stress, ultimately diminishing cognitive efficiency and memory quality (Stephenson et al., 2019; Kayvani et al., 2023).
4.2 Behavioral methods for assessing SDM
Several behavioral tasks have been developed to evaluate memory performance under different internal states. The n-back test, for example, measures working memory capacity and efficiency (Jaeggi et al., 2010) and can track performance changes under varying cognitive loads (Frost et al., 2021). Under high stress or anxiety, recall of neutral information often declines, while memory for emotional material may improve. Fatigue can make “remember” cues harder to execute and increase sensitivity to “forget” cues.
Prospective memory (PM) tasks provide another approach to assessing SDM. PM refers to the ability to remember and carry out intended actions in the future (Arnold et al., 2014; de Mendonça et al., 2018). By manipulating the relationship between PM goals and ongoing tasks, studies have shown interactions between cognitive load and attentional focus, with the longest response times occurring under conditions of both high load and strong focus (Cantarella et al., 2023). In clinical settings, PM failures, such as missed medication in PD, illustrate the impact of internal states on memory under varying cognitive demands.
Emotion-memory paradigms are central to SDM assessment because emotional states influence both encoding and retrieval. The directed forgetting paradigm, for instance, evaluates how state interference affects memory control by comparing forgetting for emotional vs. neutral materials (Wierzba et al., 2018). Emotional induction tasks, using visual images or music, test how affective cues modulate memory performance (Diener et al., 2023). Emotional working memory tasks, such as the two-back emotional working memory task, assess how affective content influences the maintenance and updating of information (Zhang et al., 2022; Yavas, 2024).
Clinical scales complement laboratory tasks by capturing broader cognitive and emotional effects on memory. The Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAS) includes cognitive items that reflect attention, memory, tension, worry, fatigue, and somatic symptoms (Gjerris et al., 1983). Although the scale does not directly measure emotion-memory interactions, anxiety as a state can disrupt memory processing, leading to reduced performance on cognitive tests that depend on attention and executive function (Isakulyan and Marachev, 2024). Broader assessments, such as the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), measure attention, executive function, and memory. Combined with behavioral tasks, these scales provide multi-dimensional, indirect measures of how emotional states influence cognition. For example, patients with anxiety often score lower on the MoCA compared with non-anxious controls, suggesting that heightened anxiety can impair attention, executive function, and memory (Liu et al., 2016; Li et al., 2017).
5 SDM regulation in pathological conditions
Neurodegenerative and psychiatric disorders show memory impairments that depend on internal states. These impairments involve alterations in key brain regions, circuits, neurotransmitter systems, and network connectivity. This section discusses how internal states influence memory in each condition and how these insights can guide targeted interventions and treatment strategies.
5.1 State-dependent changes in neurodegenerative diseases
AD involves progressive decline in contextual, spatial, working, and semantic memory (Arlt, 2013). Patients often struggle to recall recent experiences, complete complex tasks, understand certain vocabulary and concepts, and navigate their environment (Arlt, 2013). Multiple brain regions, particularly the hippocampus and cortex, degenerate, impairing structures, function, and neural circuits (Vetere et al., 2025). Early hippocampal atrophy may heighten sensitivity to stress, accelerating memory decline (Bierman et al., 2009). Patients also often show difficulties in recognizing and regulating emotions, including impaired emotional discernment, anxiety, and depressive symptoms (Sinclair et al., 2023). These neuropsychiatric signs may signal early social behavior problems (Strijkert et al., 2023) and affect quality of life (Martinez et al., 2018). Stress can further disrupt emotional processing, related to anxiety and cortisol levels (Gómez-Gallego and Gómez-García, 2018). Sleep disturbances, including fragmented nighttime sleep, excessive napping, and disrupted sleep-wake cycles, are common (Peter-Derex et al., 2015) and can worsen cognitive and emotional deficits (Cui et al., 2025). Environmental factors, such as pollutants, lifestyle, and diet, also contribute to AD risk (Saragea, 2024). These state-dependent effects, where impaired connectivity impacts both new memory encoding and retrieval, are especially evident with hippocampal and cortical decline (Dufort-Gervais et al., 2019; Silva and Martínez, 2023).
PD is another prevalent neurodegenerative disorder (Jagadeesan et al., 2017). Its pathology is mainly linked to dopaminergic neuron loss in the substantia nigra pars compacta, resulting in dopamine depletion in basal ganglia circuits (Jagadeesan et al., 2017; Latif et al., 2021). Working memory deficits are common in PD, manifesting as difficulty maintaining and manipulating information (Muslimovic et al., 2005; Giehl et al., 2020), linked to prefrontal-striatal circuit dysfunction (Gruber et al., 2006; Fallon et al., 2017; Lee et al., 2025). Unlike AD, where integrating new information is the main issue, short-term memory problems in PD often present as increased random guessing, attentional fluctuations, and executive dysfunction (Zokaei et al., 2020). Memory consolidation and attentional filtering can also be impaired (Lee, 2023). Cognitive deficits extend to decision-making, executive control, and cognitive flexibility (Pagonabarraga and Kulisevsky, 2012; Smith et al., 2020). In PD with mild cognitive impairment, widespread deficits can impair prospective memory, such as remembering medication schedules, raising adherence risks (Sumbul-Sekerci et al., 2022; Jia et al., 2018). Functional connectivity of basal ganglia-thalamocortical structures, including the dorsomedial thalamus, caudate, and putamen, declines as cognitive status worsens (Owens-Walton et al., 2021). Emotional changes, including depression, anxiety, and apathy, also significantly impact memory (Boller et al., 1998; Broen et al., 2016; Yang et al., 2018; Weintraub et al., 2022; Hammarlund et al., 2024). Anxiety in PD engages fear-related and limbic cortico-striato-thalamo-cortical circuits, with circuitry differing from healthy populations (Carey et al., 2020). These cross-network reorganizations may reshape memory in a state-dependent manner, requiring further study (Wang et al., 2025; Longo et al., 2024).
5.2 State-dependent memory regulation in mental disorders
Individuals with anxiety disorders exhibit attentional biases during encoding, showing heightened vigilance to emotional cues and prioritizing negative or threatening information (Wabnitz et al., 2015; Mogg and Bradley, 2016). Encoding under threat engages the ACC more strongly, which reduces later recognition (Garibbo et al., 2019). Early biases toward negative material have been observed during encoding (Shi et al., 2024a). Anxiety also increases rumination and the retrieval of threat-related memories, sometimes promoting re-experiencing similar to PTSD (Coles and Heimberg, 2002; Lee and Fernandes, 2017; Bolton and Robinson, 2017). Neuroimaging shows that state anxiety modulates amygdala-prefrontal cortex coupling, favoring retrieval of memories congruent with the current emotional state (Garcia et al., 1999; Ganella et al., 2017). In trait anxiety, cross-network coupling varies with internal state, providing a network-level basis for SDM variability (see Subsection 3.2).
Patients with depression tend to recall more negative events, reinforcing their depressive state and creating a vicious cycle (Ellwart et al., 2003; Everaert et al., 2022). Chronic negative stress in depression is linked to disrupted hippocampal structure and functional connectivity (Zhang et al., 2024), hindering the integration of new information into existing knowledge (Sekeres et al., 2024). Memory consolidation in this context relies on reactivation of original traces (Heinbockel et al., 2024), reducing stability and weakening coherence and accuracy. Even when memories are formed, patients may not retain them long. Functional and structural changes in the hippocampus and PFC are common (Gallassi et al., 2006; Sałaciak et al., 2023). Evidence also shows network reorganization in depression, affecting systems such as the central executive network (CEN; Ho et al., 2017), anterior DMN-right FPN interaction, DMN-SN interaction (Cao et al., 2020), and emotion-related networks (Li et al., 2021). These connectivity alterations are state-dependent (Leistedt et al., 2009; Rosenbaum et al., 2015). Considering frequent selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) non-response (Li, 2023), understanding SDM may guide more effective treatment. NE and DA systems contribute to MDD pathophysiology (El Mansari et al., 2010), suggesting that multitarget or non-serotonergic agents may improve outcomes (Stahl et al., 2004; Daniels et al., 2024; Álvarez-Silva et al., 2024; Iqbal et al., 2024). Cognitive behavioral therapy can also improve attention and memory across emotional states by addressing negative thinking patterns (Moorey and Hollon, 2021; Bernhardt et al., 2021).
Memory impairments in PTSD include uncontrollable recollections of traumatic events, such as flashbacks, or the inability to recall certain experiences, known as dissociative amnesia (Boysan, 2016). After trauma, neuronal activity sequences often become fragmented and fail to integrate effectively into storage circuits (Kolk and Fisler, 1995; Nadel and Jacobs, 1998), leading to insufficient encoding and making the retrieval of memories difficult (Bedard-Gilligan and Zoellner, 2012). Hippocampal dysfunction contributes to these difficulties, affecting the organization and recall of traumatic event details (Acheson et al., 2012). Trauma also alters the function and structure of the amygdala in PTSD (Zhang et al., 2019; Ousdal et al., 2020). Encoding of negative information preferentially recruits the BLA (Patel et al., 2016). At the same time, reduced activity in both the hippocampus and amygdala may exacerbate trauma-related memory distortions under high stress and arousal (Hayes et al., 2011). Studies also indicate that GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in the amygdala display distinct activation patterns (Fang et al., 2018; Zhang et al., 2019). The interplay between these regions, circuits, and neurotransmitter systems is critical for understanding PTSD-related memory impairments. Network-based analyses reveal decreased connectivity between the amygdala and PFC, supporting disrupted fronto-limbic circuits, as well as reduced connectivity within hippocampal-PFC networks (Admon et al., 2013; Spielberg et al., 2015). These network deficits can impair extinction-memory retrieval and maintenance, exacerbating intrusive recollections. PTSD is also associated with a decline in global network efficiency, particularly involving the DMN and imbalances in connectivity between the DMN and SN. These network-level disruptions contribute to fragmented memories, difficulties in memory maintenance and retrieval, and increased likelihood of intrusive re-experiencing. Considering the DMN's role in self-referential processing and recollection, and the SN's role in dynamically switching between DMN and CEN during cognitive tasks, these alterations provide a framework for testing hypotheses about memory processes in PTSD, including extinction learning, intrusive recollection, and dissociation.
5.3 SDM in schizophrenia
Memory impairments in schizophrenia primarily appear as deficits in memory encoding and retrieval, which may be linked to impaired novelty detection in mesolimbic circuits and reduced prefrontal and temporal lobe function (Schiltz et al., 2010). During episodic memory tasks (Ragland et al., 2009), individuals with schizophrenia show reduced PFC activation, which compromises executive function, memory encoding and retrieval efficiency, and overall information processing speed (Nathaniel-James et al., 1996). These impairments are influenced by emotional instability and high cognitive load. Emotional regulation significantly affects memory in schizophrenia, as emotional instability interferes with both encoding and retrieval through complex interactions between emotion-processing and memory systems (Herbener et al., 2007; Dieleman and Röder, 2012). Patients often show heightened sensitivity to negative emotional stimuli, which can reduce memory accuracy and introduce bias, causing inconsistencies in recalling emotional information (Sergerie et al., 2009; Walsh-Messinger et al., 2014). High cognitive load further depletes memory resources, lowering the efficiency of both encoding and retrieval (Granholm et al., 1997). During complex tasks requiring sustained attention, patients frequently struggle to allocate working memory effectively, resulting in impaired performance (Becerril and Barch, 2010; Grimes et al., 2017). Nevertheless, variations in emotional regulation and cognitive load management can partially improve memory performance. Interventions such as cognitive behavioral therapy and targeted memory training have been shown to enhance memory organization and retrieval, thereby improving memory function in schizophrenia (Bonner-Jackson and Barch, 2011; Jantzi et al., 2019).
6 Circuit-based neuromodulation and intervention strategies for SDM
Building on the neural circuit mechanisms of SDM described in the preceding sections, this part focuses on circuit-based neuromodulation and related intervention strategies. Electrical and non-invasive stimulation techniques such as TMS and DBS provide important tools for modulating memory-related networks, and newer approaches including transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) are expanding the range of possible applications. At the same time, closed-loop stimulation, neurofeedback, and brain-computer interface (BCI) paradigms illustrate how interventions can be tailored to ongoing brain states. Integrating neuromodulation with pharmacological and psychological treatments highlights future opportunities for multimodal and individualized therapies targeting SDM-related memory dysfunction.
6.1 Applications of neurostimulation technologies in memory regulation
Electrical neurostimulation technology, particularly personalized neurostimulation, is becoming important in treating neuropsychiatric disorders. However, evidence of its effectiveness in memory and state regulation varies significantly, and its safety and efficacy in human trials have not been fully validated. Further investigations are needed to deepen our understanding of its mechanisms of action, optimize stimulation protocols, and assess long-term effects of these treatments to enhance their precision and effectiveness.
To modulate brain activity and alleviate memory disorders, two widely used electrical neurostimulation techniques are TMS and DBS. TMS is a non-invasive electrical stimulation method (Roth et al., 2007; Marder et al., 2022) that can directly regulate the excitatory activity and plasticity of specific brain regions (Thomson et al., 2020; Marder et al., 2022). Multiple studies have shown that repetitive TMS (rTMS) influences memory across various states by modulating neural activity in specific brain areas (Coughlan et al., 2022), neurotransmitter levels (Claverie et al., 2024), and the functional connectivity of neural networks (Mottaghy et al., 2000). Unlike non-invasive techniques, DBS delivers continuous electrical stimulation to deep brain structures by means of implanted electrodes targeting specific regions (R. Rezai and Sharma, 2014). This technique has been used to treat various diseases, including PD, epilepsy, and mental disorders (Degirmenci, 2024). Although the mechanisms and targets of stimulation methods are different, they ultimately converge on a common brain network (Obeso et al., 2011; Siddiqi and Fox, 2022). In recent years, researchers have found that DBS can significantly improve memory-related functions by stimulating specific areas within the memory formation network, such as the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex (Khan et al., 2019).
Notably, both rTMS and DBS are influenced by the functional state of the targeted brain region, which shapes their effects on memory. rTMS may enhance or suppress memory depending on whether the cortex is in a high or low activation state, and entorhinal DBS has been observed to improve recall only when applied during neural activity patterns conducive to effective memory encoding (Silvanto and Pascual-Leone, 2008; Ezzyat et al., 2018). These findings suggest that aligning stimulation with the brain's ongoing functional state is critical for achieving consistent and effective neuromodulation outcomes. Nevertheless, rTMS and DBS do not encompass the full spectrum of circuit-based neuromodulation techniques currently under development (Chan et al., 2009; Fang et al., 2024; Wansbrough et al., 2024; Najera et al., 2025). the safety and efficacy of emerging neurostimulation paradigms still require further research (Rossi et al., 2009; Taylor et al., 2018). To better understand their potential in memory regulation and align with SDM mechanisms, it is also important to examine additional techniques that target memory-related neural networks.
6.2 Other circuit-based neuromodulation approaches
Beyond rTMS and DBS, several additional neuromodulation techniques have shown potential in modulating memory-related circuits and networks (Keeser et al., 2011; Antonenko et al., 2019; Mezger et al., 2020; Abellaneda-Pérez et al., 2020). tDCS (Woods et al., 2016) delivers weak electrical currents to the cortex and can alter cortical excitability (Polizzotto et al., 2020). This method has been associated with improvements in working memory, attention and executive function in conditions such as AD (Gangemi et al., 2020; Tariq et al., 2023), PD (Boggio et al., 2006) and MDD (Wolkenstein and Plewnia, 2013; Oliveira et al., 2013). Yet, clinical outcomes of tDCS remain inconsistent across studies (Suemoto et al., 2014; Bystad et al., 2016). Recent studies have employed high-definition tDCS in order to achieve more precise targeting and to monitor activity in specific circuits and networks (Rasmussen et al., 2021; He et al., 2025).
tACS applies oscillatory currents at defined frequencies and can entrain endogenous neural rhythms such as theta-gamma coupling (Diedrich et al., 2024). This mechanism has been linked to improvements in working memory (Mirjalili et al., 2025). By applying frequency-specific stimulation, tACS can modulate neural oscillations that are critical for memory formation (Shtoots et al., 2024; Paßmann et al., 2024; Zhang et al., 2025). Recent findings suggest that the after-effects of tACS depend on the ongoing state of brain activity, indicating that state-dependent plasticity may be one of the neural mechanisms influencing its efficacy (Agboada et al., 2025).
Although challenges remain in translating these novel techniques into widespread human applications (Martinez-Nunez et al., 2024), they broaden the range of circuit-based neuromodulation and provide additional avenues for interventions tailored to internal state in memory disorders.
6.3 Personalized neuralstimulation strategies based on neural networks
Some specially designed neurostimulation studies (Hubbard et al., 2021; Soleimani et al., 2023) have proposed that insights into the relationship between memory disorders and network imbalances may enable the development of tailored stimulation patterns that align with individual neural network patterns and physiological-psychological states. While TMS is typically designed in an open-loop mode (Marder et al., 2022), closed-loop stimulation paradigms are increasingly being investigated. These approaches integrate electroencephalography (EEG) or other neural readouts to allow for real-time adjustment of parameters based on changes in brain activity, and can therefore more precisely optimize the memory encoding process in specific brain regions (Wischnewski et al., 2024).
Recent work combining closed-loop stimulation with neurofeedback or BCI technology illustrates the potential of state-informed modulation strategies. For example, stimulation of the lateral temporal cortex guided by neural activity patterns has been shown to enhance subsequent recall ability (Ezzyat et al., 2018; Kahana et al., 2023). Adaptive methods that incorporate psychological states into stimulation protocols may improve treatment outcomes and reduce side effects (Fedotchev, 2023). At the same time, neural network models and machine learning algorithms are increasingly used to simulate and predict the dynamic behavior of the brain (Mill et al., 2022; Kurtin et al., 2023), enabling more individualized and precise regulation of memory-related processes. Together, these developments suggest that circuit-based neuromodulation, including methods described in Section 6.2, can evolve toward genuinely personalized and state-dependent interventions.
6.4 Future perspectives: toward multimodal and integrative therapies
While circuit-based neuromodulation has shown considerable promise in treating memory disorders, its effectiveness as a standalone intervention appears limited (Wu et al., 2025). Pharmacological treatments therefore remain indispensable, as they target neurotransmitter systems such as dopamine, norepinephrine, and GABA, which critically shape SDM processes (Bairy and Kumar, 2019; Akyuz et al., 2024). For instance, dopaminergic agents have been shown to improve executive and working memory functions through corticostriatal circuits in PD (Simioni et al., 2017). Fluctuations in dopamine activity influence whether memories are successfully encoded and retrieved under specific brain states, suggesting that pharmacological modulation can help align neural conditions with optimal memory performance (MacDonald et al., 2013).
Psychological interventions are also highly relevant, as they can reshape maladaptive emotional states and cognitive patterns, directly influencing memory encoding and retrieval biases (Hayes et al., 2023). Techniques such as cognitive behavioral therapy (Curtiss et al., 2021), mindfulness training (Hofmann and Gómez, 2017), and exposure-based therapies (Hedman et al., 2017) have been shown to enhance memory performance and emotional regulation in disorders ranging from depression and anxiety to schizophrenia. When combined with neurostimulation, these approaches may act synergistically, aligning neural modulation with cognitive and emotional states to maximize therapeutic effects (Dedoncker et al., 2021; Zhantleuova et al., 2025; Saccenti and Koster, 2024).
Integrating these pharmacological, psychological, and lifestyle approaches with neurostimulation offers a multimodal framework that targets multiple levels of neural function and behavior, creating opportunities for more precise, individualized interventions in memory disorders.
7 Conclusions
State dependence reveals the complexity of memory across physiological and pathological conditions and is evident at both neural and behavioral levels. In neuropsychiatric disorders, internal and external conditions such as emotional state, substance use, sleep quality, stress, and fatigue can shape each phase of memory and may exacerbate cognitive deficits.
Although SDM appears robust across many situations, several boundary conditions limit how broadly it applies. When strong external retrieval support is provided, such as in recognition tests or heavily cued recall, the reliance on internal states is reduced, and SDM effects are smaller compared with free recall (Uner and Roediger, 2022). The strength of the memory trace also plays a significant role, as SDM effects tend to weaken when memories are either highly overlearned, reaching a performance ceiling, or very weak, approaching a floor level (Petzka et al., 2021; Guskjolen and Cembrowski, 2023; Tomé et al., 2024). Additionally, time and systems-level reorganization can diminish SDM effects. Over longer delays, especially across weeks, pharmacologically induced SDM often weakens (Bardgett et al., 1996), in line with the process of systems consolidation (Dudai, 2004), which reduces the dependency of memory retrieval on encoding-state features. The specificity of the internal state is another crucial factor. When the affective/arousal state at encoding is not well-differentiated, or when mood is reinstated despite environmental changes, the apparent place-dependent effects may disappear (Corson and Verrier, 2007; Robinson and Rollings, 2010; Van Damme, 2013). Finally, task and memory-system differences indicate that SDM is not expressed uniformly across all paradigms, with some showing little or no state dependence (Radulovic et al., 2017).
Across the evidence reviewed, interactions among hippocampal, prefrontal, and amygdalar circuits, together with the organization of large-scale networks and neuromodulatory influences from DA, NE, and GABA, help explain why memory performance varies with internal state and point to interventions that are tailored to the patient's state and to the memory phase being targeted. These insights widen the range of neuromodulation approaches that act on circuits and networks in memory disorders. Although challenges remain, including individual variability and the limited translation of newer techniques into routine care, SDM provides a practical framework for designing and evaluating modulation that takes both state and phase into account. As neuroscience and artificial intelligence advance, strategies that align stimulation with a person's current state and the relevant memory phase may enable more personalized and effective treatment.
Author contributions
YL: Writing – original draft. GZ: Writing – review & editing. RQ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. JM: Writing – review & editing, Investigation. JX: Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 82302870; 82472589); Shanghai Rising-Star Program (Grant No. 24QA2709300); Shanghai Leading Talent Program of Eastern Talent Plan (Grant No. QNJY2024077); Science & Technology Development Fund of Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Grant No. 23KFL112); High-level Chinese Medicine Key Discipline Construction Project (Integrative Chinese and Western Medicine Clinic) of National Administration of TCM (zyyzdxk-2023065); Shanghai Hospital Development Center Foundation-Shanghai Municipal Hospital Rehabilitation Medicine Specialty Alliance (SHDC22023304).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fncel.2025.1629796/full#supplementary-material
References
Abellaneda-Pérez, K., Vaqué-Alcázar, L., Perellón-Alfonso, R., Bargalló, N., Kuo, M.-F., Pascual-Leone, A., et al. (2020). Differential tDCS and tACS effects on working memory-related neural activity and resting-state connectivity. Front. Neurosci. 13:1440. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.01440
Acheson, D. T., Gresack, J. E., and Risbrough, V. B. (2012). Hippocampal dysfunction effects on context memory: possible etiology for posttraumatic stress disorder. Neuropharmacology 62, 674–685. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2011.04.029
Admon, R., Milad, M. R., and Hendler, T. (2013). A causal model of post-traumatic stress disorder: disentangling predisposed from acquired neural abnormalities. Trends Cogn. Sci. 17, 337–347. doi: 10.1016/j.tics.2013.05.005
Agboada, D., Zhao, Z., and Wischnewski, M. (2025). Neuroplastic effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS): from mechanisms to clinical trials. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 19:1548478. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2025.1548478
Akirav, I., and Maroun, M. (2007). The role of the medial prefrontal cortex-amygdala circuit in stress effects on the extinction of fear. Neural Plast. 2007, 1–11. doi: 10.1155/2007/30873
Akyuz, E., Arulsamy, A., Aslan, F. S., Sarisözen, B., Guney, B., Hekimoglu, A., et al. (2024). An expanded narrative review of neurotransmitters on Alzheimer's disease: the role of therapeutic interventions on neurotransmission. Mol. Neurobiol. 62, 1631–1674. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04333-y
Alipour, A., Rahimi, A., Shadnia, S., Rahimi, M., Erfan Talab Evini, P., Hosseini, S. M., et al. (2025). Investigating the relationship between automatic negative thoughts and experiential avoidance with psychological distress and the mediating role of cognitive emotion regulation in patients with a history of suicide attempt. Iran. J. Psychiatry 20, 12–21. doi: 10.18502/ijps.v20i1.17397
Álvarez-Silva, A., Rodríguez-Manzo, G., Reyes, R., and Fernández-Guasti, A. (2024). Combination of low doses of mirtazapine plus venlafaxine produces antidepressant-like effects in rats, without affecting male or female sexual behavior. Psychopharmacology 242, 189–204. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06661-2
Antonenko, D., Hayek, D., Netzband, J., Grittner, U., and Flöel, A. (2019). tDCS-induced episodic memory enhancement and its association with functional network coupling in older adults. Sci. Rep. 9:2273. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-38630-7
Arlt, S. (2013). Non-Alzheimer's disease-related memory impairment and dementia. Dial. Clin. Neurosci. 15, 465–473. doi: 10.31887/DCNS.2013.15.4/sarlt
Arnold, N. R., Bayen, U. J., and Böhm, M. F. (2014). Is prospective memory related to depression and anxiety? A hierarchical MPT modelling approach. Memory 23, 1215–1228. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2014.969276
Bairy, L. K., and Kumar, S. (2019). Neurotransmitters and neuromodulators involved in learning and memory. Int. J. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. 8:2777. doi: 10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20195296
Bannon, M. J., Bannon, E. E., and Bannon, K. T. (2020). “Dopamine,” in eLS: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences [Internet] (Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd). doi: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0000279.pub4
Bardgett, M. E., Newcomer, J. W., and Taylor, G. T. (1996). The effects of chronic corticosterone on memory performance in the platform maze task. Physiol. Behav. 59, 1111–1115. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(95)02172-8
Bar-Haim, Y., Lamy, D., Pergamin, L., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M. J., and van IJzendoorn, M. H. (2007). Threat-related attentional bias in anxious and nonanxious individuals: a meta-analytic study. Psychol. Bull. 133, 1–24. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.1.1
Becerril, K., and Barch, D. (2010). Influence of emotional processing on working memory in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 37, 1027–1038. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbq009
Bedard-Gilligan, M., and Zoellner, L. A. (2012). Dissociation and memory fragmentation in post-traumatic stress disorder: an evaluation of the dissociative encoding hypothesis. Memory 20, 277–299. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2012.655747
Benetti, F., Furini, C. R. G., de Carvalho Myskiw, J., Provensi, G., Passani, M. B., Baldi, E., et al. (2015). Histamine in the basolateral amygdala promotes inhibitory avoidance learning independently of hippocampus. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, E2536–E2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1506109112
Bernhardt, M., Schwert, C., Aschenbrenner, S., Weisbrod, M., and Schröder, A. (2021). Longitudinal changes of cognitive deficits and treatment outcome of cognitive behavioral therapy for major depression. J. Nervous Mental Dis. 209, 336–342. doi: 10.1097/NMD.0000000000001301
Bierman, E. J. M., Comijs, H. C., Jonker, C., Scheltens, P., and Beekman, A. T. F. (2009). The effect of anxiety and depression on decline of memory function in Alzheimer's disease. Int. Psychogeriatr. 21, 1142–1147. doi: 10.1017/S1041610209990512
Boggio, P. S., Ferrucci, R., Rigonatti, S. P., Covre, P., Nitsche, M., Pascual-Leone, A., et al. (2006). Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on working memory in patients with Parkinson's disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 249, 31–38. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2006.05.062
Boller, F., Marcie, P., Starkstein, S., and Traykov, L. (1998). Memory and depression in Parkinson's disease. Euro. J. Neurol. 5, 291–295. doi: 10.1046/j.1468-1331.1998.530291.x
Bolton, S., and Robinson, O. J. (2017). The impact of threat of shock-induced anxiety on memory encoding and retrieval. Learn. Memory 24, 532–542. doi: 10.1101/lm.045187.117
Bonner-Jackson, A., and Barch, D. M. (2011). Strategic manipulations for associative memory and the role of verbal processing abilities in schizophrenia. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 17, 796–806. doi: 10.1017/S1355617711000749
Boysan, M. (2016). “Associations between dissociation and post-traumatic stress response,” in Comprehensive Guide to Post-Traumatic Stress Disorders, eds. C. R. Martin, V. R. Preedy, and V. B. Patel (Cham: Springer International Publishing), 831–849. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-08359-9_13
Broen, M. P. G., Narayen, N. E., Kuijf, M. L., Dissanayaka, N. N. W., and Leentjens, A. F. G. (2016). Prevalence of anxiety in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Mov. Disord. 31, 1125–1133. doi: 10.1002/mds.26643
Bronnick, K., Emre, M., Lane, R., Tekin, S., and Aarsland, D. (2007). Profile of cognitive impairment in dementia associated with Parkinson's disease compared with Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. 78, 1064–1068. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.2006.108076
Buchanan, T. W. (2007). Retrieval of emotional memories. Psychol. Bull. 133, 761–779. doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.133.5.761
Bystad, M., Grønli, O., Rasmussen, I. D., Gundersen, N., Nordvang, L., Wang-Iversen, H., et al. (2016). Transcranial direct current stimulation as a memory enhancer in patients with Alzheimer's disease: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Alzheimer. Res. Ther. 8:13. doi: 10.1186/s13195-016-0180-3
Cantarella, G., Mastroberardino, S., Bisiacchi, P., and Macaluso, E. (2023). Prospective memory: the combined impact of cognitive load and task focality. Brain Struct. Func. 228, 1425–1441. doi: 10.1007/s00429-023-02658-3
Cao, J., Ai, M., Chen, X., Chen, J., Wang, W., and Kuang, L. (2020). Altered resting-state functional network connectivity is associated with suicide attempt in young depressed patients. Psychiatry Res. 285:112713. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2019.112713
Carey, G., Görmezoglu, M., de Jong, J. J. A., Hofman, P. A. M., Backes, W. H., Dujardin, K., et al. (2020). Neuroimaging of anxiety in Parkinson's disease: a systematic review. Mov. Disord. 36, 327–339. doi: 10.1002/mds.28404
Chafee, M. V., and Heilbronner, S. R. (2022). Prefrontal cortex. Curr. Biol. 32, R346–R351. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2022.02.071
Chan, D. T. M., Zhu, X. L., Yeung, J. H. M., Mok, V. C. T., Wong, E., Lau, C., et al. (2009). Complications of deep brain stimulation: a collective review. Asian J. Surg. 32, 258–263. doi: 10.1016/S1015-9584(09)60404-8
Chapman, J., Kao, T., Teh, J., Haroutonian, C., Grunstein, R., Naismith, S., et al. (2023). P047 slow wave dynamics in mild cognitive impairment compared with age matched controls: a high density EEG study. Sleep Adv. 4, A51–A52. doi: 10.1093/sleepadvances/zpad035.132
Christodoulou, J., and Burke, D. M. (2016). Mood congruity and episodic memory in young children. J. Exp. Child. Psychol. 142, 221–229. doi: 10.1016/j.jecp.2015.09.019
Claverie, D., Cressant, A., Thomasson, J., Castellarin, C., Grandperret, V., Barbier, L., et al. (2024). rTMS mechanisms for posttraumatic stress disorder treatment in a mouse model. J. Psychiatr. Res. 179, 33–43. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2024.08.041
Clewett, D. V., Huang, R., Velasco, R., Lee, T. H., and Mather, M. (2018). Locus coeruleus activity strengthens prioritized memories under arousal. J. Neurosci. 38, 1558–1574. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2097-17.2017
Cohen, R. T., and Kahana, M. J. (2022). A memory-based theory of emotional disorders. Psychol. Rev. 129, 742–776. doi: 10.1037/rev0000334
Coles, M. E., and Heimberg, R. G. (2002). Memory biases in the anxiety disorders. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 22, 587–627. doi: 10.1016/S0272-7358(01)00113-1
Cooper, R. M., and Langton, S. R. (2006). Attentional bias to angry faces using the dot-probe task? It depends when you look for it. Behav. Res Ther. 44, 1321–1329. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2005.10.004
Corbett, B., Weinberg, L., and Duarte, A. (2017). The effect of mild acute stress during memory consolidation on emotional recognition memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 145, 34–44. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.08.005
Corson, Y., and Verrier, N. (2007). Emotions and false memories: valence or arousal? Psychol. Sci. 18, 208–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9280.2007.01874.x
Coughlan, G., Bouffard, N. R., Golestani, A., Thakral, P. P., Schacter, D. L., Grady, C., et al. (2022). Transcranial magnetic stimulation to the angular gyrus modulates the temporal dynamics of the hippocampus and entorhinal cortex. Cereb. Cortex 33, 3255–3264. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac273
Cui, L., Wan, Y., Lu, Y., Meng, M., and Zhang, N. (2025). Sleep disturbances and their correlation with memory impairment in patients with Alzheimer's disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment. J. Alzheimer. Dis. Rep. 9:25424823241309063. doi: 10.1177/25424823241309063
Cunningham, T. J., Mattingly, S. M., Tlatenchi, A., Wirth, M. M., Alger, S. E., Kensinger, E. A., et al. (2021). Higher post-encoding cortisol benefits the selective consolidation of emotional aspects of memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 180:107411. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2021.107411
Curtiss, J. E., Levine, D. S., Ander, I., and Baker, A. W. (2021). Cognitive-behavioral treatments for anxiety and stress-related disorders. Focus 19, 184–189. doi: 10.1176/appi.focus.20200045
Daffner, K. R., Scinto, L. F. M., Weitzman, A. M., Faust, R., Rentz, D. M., Budson, A. E., et al. (2003). Frontal and parietal components of a cerebral network mediating voluntary attention to novel events. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 15, 294–313. doi: 10.1162/089892903321208213
Daniels, S., El Mansari, M., and Blier, P. (2024). AMPA receptors modulate enhanced dopamine neuronal activity induced by the combined administration of venlafaxine and brexpiprazole. Neuropsychopharmacology 49, 2042–2051. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01958-4
Das, A., and Menon, V. (2024). Frequency-specific directed connectivity between the hippocampus and parietal cortex during verbal and spatial episodic memory: an intracranial EEG replication. Cereb. Cortex 34:bhae287. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhae287
Daselaar, S. M., Rice, H. J., Greenberg, D. L., Cabeza, R., LaBar, K. S., and Rubin, D. C. (2008). The spatiotemporal dynamics of autobiographical memory: neural correlates of recall, emotional intensity, and reliving. Cereb. Cortex 18, 217–229. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhm048
de la Mora, M. P., Gallegos-Cari, A., Arizmendi-García, Y., Marcellino, D., and Fuxe, K. (2010). Role of dopamine receptor mechanisms in the amygdaloid modulation of fear and anxiety: structural and functional analysis. Prog. Neurobiol. 90, 198–216. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.10.010
De la Peña-Arteaga, V., Chavarría-Elizondo, P., Juaneda-Seguí, A., Martínez-Zalacaín, I., Morgado, P., Menchón, J. M., et al. (2024). Trait anxiety is associated with attentional brain networks. Euro. Neuropsychopharmacol. 83, 19–26. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2024.02.013
de Mendonça, A., Felgueiras, H., Verdelho, A., Câmara, S., Grilo, C., Maroco, J., et al. (2018). Memory complaints in amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment: more prospective or retrospective? Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 33, 1011–1018. doi: 10.1002/gps.4886
de Quervain, D. J.-F., Roozendaal, B., and McGaugh, J. L. (1998). Stress and glucocorticoids impair retrieval of long-term spatial memory. Nature 394, 787–790. doi: 10.1038/29542
deBettencourt, M. T., Williams, S. D., Vogel, E. K., and Awh, E. (2021). Sustained attention and spatial attention distinctly influence long-term memory encoding. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 33, 2132–2148. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_01748
Dedoncker, J., Baeken, C., De Raedt, R., and Vanderhasselt, M.-A. (2021). Combined transcranial direct current stimulation and psychological interventions: state of the art and promising perspectives for clinical psychology. Biol. Psychol. 158:107991. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2020.107991
Degirmenci, Y. (2024). Current DBS programming. Deep Brain Stimul. 4, 29–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jdbs.2023.12.002
Demic, S., and Cheng, S. (2014). Modeling the dynamics of disease states in depression. PLoS ONE 9:e110358. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0110358
Diamond, D. M., Park, C. R., Campbell, A. M., and Woodson, J. C. (2005). Competitive interactions between endogenous LTD and LTP in the hippocampus underlie the storage of emotional memories and stress-induced amnesia. Hippocampus 15, 1006–1025. doi: 10.1002/hipo.20107
Diedrich, L., Kolhoff, H. I., Bergmann, C., Bähr, M., and Antal, A. (2024). Boosting working memory in the elderly: driving prefrontal theta-gamma coupling via repeated neuromodulation. GeroScience 47, 1425–1440. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01272-3
Dieleman, S., and Röder, C. H. (2012). Emotional memory modulation in schizophrenia: an overview. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 127, 183–194. doi: 10.1111/acps.12047
Diener, E., Cha, Y., and Oishi, S. (2023). Reinterpreting mood induction experiments. J. Posit. Psychol. 18, 339–349. doi: 10.1080/17439760.2022.2036799
Dolcos, F., LaBar, K. S., and Cabeza, R. (2005). Remembering one year later: role of the amygdala and the medial temporal lobe memory system in retrieving emotional memories. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 102, 2626–2631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0409848102
Downs, A. M., and McElligott, Z. A. (2022). Noradrenergic circuits and signaling in substance use disorders. Neuropharmacology 208:108997. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.108997
Dubrovina, N. I. (2017). GABA receptors in the modulation of fear memory extinction. Neurosci. Behav. Physiol. 47, 573–584. doi: 10.1007/s11055-017-0438-7
Dudai, Y. (2004). The neurobiology of consolidations, or, how stable is the engram?. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 55, 51–86. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.55.090902.142050
Dufort-Gervais, J., Mongrain, V., and Brouillette, J. (2019). Bidirectional relationships between sleep and amyloid-beta in the hippocampus. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 160, 108–117. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2018.06.009
Duma, G. M., Cuozzo, S., Wilson, L., Danieli, A., Bonanni, P., and Pellegrino, G. (2024). Excitation/inhibition balance relates to cognitive function and gene expression in temporal lobe epilepsy: a high density EEG assessment with aperiodic exponent. Brain Commun. 6:fcae231. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae231
Ebrahimi-Ghiri, M., Khakpai, F., and Zarrindast, M.-R. (2019). Cross state-dependent memory retrieval between morphine and norharmane in the mouse dorsal hippocampus. Brain Res. Bull. 153, 24–29. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2019.08.003
Ecker, U. K., Lewandowsky, S., Oberauer, K., and Chee, A. E. (2010). The components of working memory updating: an experimental decomposition and individual differences. J. Exp. Psychol. Learn. 36:170. doi: 10.1037/a0017891
Eichenbaum, H. (2004). Hippocampus: cognitive processes and neural representations that underlie declarative memory. Neuron 44, 109–120. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2004.08.028
El Mansari, M., Guiard, B. P., Chernoloz, O., Ghanbari, R., Katz, N., and Blier, P. (2010). Relevance of norepinephrine-dopamine interactions in the treatment of major depressive disorder. CNS Neurosci. Therap. 16, e1–e17. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2010.00146.x
Ellwart, T., Rinck, M., and Becker, E. S. (2003). Selective memory and memory deficits in depressed inpatients. Depress. Anxiety 17, 197–206. doi: 10.1002/da.10102
Everaert, J., Vrijsen, J. N., Martin-Willett, R., van de Kraats, L., and Joormann, J. (2022). A meta-analytic review of the relationship between explicit memory bias and depression: depression features an explicit memory bias that persists beyond a depressive episode. Psychol. Bull. 148, 435–463. doi: 10.1037/bul0000367
Ezzyat, Y., Wanda, P. A., Levy, D. F., Kadel, A., Aka, A., Pedisich, I., et al. (2018). Closed-loop stimulation of temporal cortex rescues functional networks and improves memory. Nat. Commun. 9:365. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02753-0
Fabbri, R., Furini, C. R. G., Passani, M. B., Provensi, G., Baldi, E., Bucherelli, C., et al. (2016). Memory retrieval of inhibitory avoidance requires histamine H1 receptor activation in the hippocampus. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, E2714–E2720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1604841113
Fallon, S. J., Mattiesing, R. M., Muhammed, K., Manohar, S., and Husain, M. (2017). Fractionating the neurocognitive mechanisms underlying working memory: independent effects of dopamine and Parkinson's disease. Cereb. Cortex 27, 5727–5738. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhx242
Fan, J., Yang, K., Wang, H., Li, J., and Wen, Z. (2017). Progress of cognitive impairment induced by mental fatigue. Progress Modern Biomed. 17, 7179–7182. doi: 10.13241/j.cnki.pmb.2017.36.042
Fang, Q., Li, Z., Huang, G.-D., Zhang, H.-H., Chen, Y.-Y., Zhang, L.-B., et al. (2018). Traumatic stress produces distinct activations of GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons in amygdala. Front. Neurosci. 12:387. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00387
Fang, X., Wang, S., Luo, Y., Lin, Y., Yang, W., and Zhang, T. (2024). Deep brain temporally interfering magnetic stimulation via parametric characterized spatial array. AIP Adv. 14:085201. doi: 10.1063/5.0219428
Faraji, N., Meftahi, G. H., Shiravi, A., and Bahari, Z. (2023). Evaluation of the effects of phenylephrine and prazosin injection into basolateral amygdala on the post-stress experience of memory retrieval in rats. Learn. Motiv. 81:101868. doi: 10.1016/j.lmot.2022.101868
Fedotchev, A. (2023). Methods of closed-loop adaptive neurostimulation: features, achievements and prospects for development. Ross. Fiziol. Zh. Im. I. M. Sechenova 109, 1151–1166. doi: 10.31857/S0869813923090030
Feng, P., Feng, T., Chen, Z., and Lei, X. (2013). Memory consolidation of fear conditioning: bi-stable amygdala connectivity with dorsal anterior cingulate and medial prefrontal cortex. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 9, 1730–1737. doi: 10.1093/scan/nst170
Fletcher, P. (1998). The functional roles of prefrontal cortex in episodic memory. I. Encoding. Brain 121, 1239–1248. doi: 10.1093/brain/121.7.1239
Franceschini, A., Mazzamuto, G., Checcucci, C., Chicchi, L., Fanelli, D., Costantini, I., et al. (2023). Brain-wide neuron quantification toolkit reveals strong sexual dimorphism in the evolution of fear memory. Cell Rep. 42:112908. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112908
Frankland, P. W., and Bontempi, B. (2005). The organization of recent and remote memories. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6, 119–130. doi: 10.1038/nrn1607
Frankland, P. W., Bontempi, B., Talton, L. E., Kaczmarek, L., and Silva, A. J. (2004). The involvement of the anterior cingulate cortex in remote contextual fear memory. Science 304, 881–883. doi: 10.1126/science.1094804
Frost, A., Moussaoui, S., Kaur, J., Aziz, S., Fukuda, K., and Niemeier, M. (2021). Is the n-back task a measure of unstructured working memory capacity? Towards understanding its connection to other working memory tasks. Acta Psychol. 219:103398. doi: 10.1016/j.actpsy.2021.103398
Furini, C. R. G., Myskiw, J. C., Schmidt, B. E., Marcondes, L. A., and Izquierdo, I. (2014). D1 and D5 dopamine receptors participate on the consolidation of two different memories. Behav. Brain Res. 271, 212–217. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2014.06.027
Gallassi, R., Di Sarro, R., Morreale, A., and Amore, M. (2006). Memory impairment in patients with late-onset major depression: the effect of antidepressant therapy. J. Affect. Disord. 91, 243–250. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2006.01.018
Ganella, D. E., Barendse, M. E. A., Kim, J. H., and Whittle, S. (2017). Prefrontal-amygdala connectivity and state anxiety during fear extinction recall in adolescents. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 11:587. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2017.00587
Gangemi, A., Colombo, B., and Fabio, R. A. (2020). Effects of short- and long-term neurostimulation (tDCS) on Alzheimer's disease patients: two randomized studies. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 33, 383–390. doi: 10.1007/s40520-020-01546-8
Gao, Y., Guo, X., Zhong, Y., Liu, X., Tian, S., Deng, J., et al. (2023). Decreased dorsal attention network homogeneity as a potential neuroimaging biomarker for major depressive disorder. J. Affect. Disord. 332, 136–142. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2023.03.080
Garcia, R., Vouimba, R.-M., Baudry, M., and Thompson, R. F. (1999). The amygdala modulates prefrontal cortex activity relative to conditioned fear. Nature 402, 294–296. doi: 10.1038/46286
Garcia-delaTorre, P., Pérez-Sánchez, C., Guzmán-Ramos, K., and Bermúdez-Rattoni, F. (2014). Role of glutamate receptors of central and basolateral amygdala nuclei on retrieval and reconsolidation of taste aversive memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 111, 35–40. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.03.003
Garibbo, M., Aylward, J., and Robinson, O. J. (2019). The impact of threat of shock-induced anxiety on the neural substrates of memory encoding and retrieval. Soc. Cogn. Affect. Neurosci. 14, 1087–1096. doi: 10.1093/scan/nsz080
Ghatak, S., Talantova, M., McKercher, S. R., and Lipton, S. A. (2021). Novel therapeutic approach for excitatory/inhibitory imbalance in neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative diseases. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 61, 701–721. doi: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-032320-015420
Giehl, K., Ophey, A., Hammes, J., Rehberg, S., Lichtenstein, T., Reker, P., et al. (2020). Working memory training increases neural efficiency in Parkinson's disease: a randomized controlled trial. Brain Commun. 2:fcaa115. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaa115
Gisquet-Verrier, P., Lynch, J. F., Cutolo, P., Toledano, D., Ulmen, A., Jasnow, A. M., et al. (2015). Integration of new information with active memory accounts for retrograde amnesia: a challenge to the consolidation/reconsolidation hypothesis? J. Neurosci. 35, 11623–11633. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1386-15.2015
Gjerris, A., Bech, P., Bøjholm, S., Bolwig, T. G., Kramp, P., Clemmesen, L., et al. (1983). The hamilton anxiety scale. J. Affect. Disord. 5, 163–170. doi: 10.1016/0165-0327(83)90009-5
Glasser, D. M., Tsui, J. M. G., Pack, C. C., and Tadin, D. (2011). Perceptual and neural consequences of rapid motion adaptation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 108, E1080–E1088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1101141108
Goddard, A. W., Ball, S. G., Martinez, J., Robinson, M. J., Yang, C. R., Russell, J. M., et al. (2010). Current perspectives of the roles of the central norepinephrine system in anxiety and depression. Depress. Anxiety 27, 339–350. doi: 10.1002/da.20642
Gómez-Gallego, M., and Gómez-García, J. (2018). Effects of stress on emotional memory in patients with Alzheimer's disease and in healthy elderly. Int. Psychogeriatr. 30, 1199–1209. doi: 10.1017/S1041610217002642
Gonzalez, C. U., and Jayaraman, V. (2024). Structural dynamics in α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid receptor gating. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 87:102833. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2024.102833
Gotlib, I. H., Krasnoperova, E., Yue, D. N., and Joormann, J. (2004). Attentional biases for negative interpersonal stimuli in clinical depression. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 113, 127–135. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.113.1.121
Granholm, E., Morris, S. K., Sarkin, A. J., Asarnow, R. F., and Jeste, D. V. (1997). Pupillary responses index overload of working memory resources in schizophrenia. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 106, 458–467. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.106.3.458
Grant, D. M., and White, E. J. (2016). “Influence of anxiety on cognitive control processes,” in Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Psychology [Internet], ed. O. J. Braddick (Oxford: Oxford University Press). doi: 10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.74
Grimes, K. M., Zanjani, A., and Zakzanis, K. K. (2017). Memory impairment and the mediating role of task difficulty in patients with schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 71, 600–611. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12520
Gruber, A. J., Dayan, P., Gutkin, B. S., and Solla, S. A. (2006). Dopamine modulation in the basal ganglia locks the gate to working memory. J. Comput. Neurosci. 20, 153–166. doi: 10.1007/s10827-005-5705-x
Guenzel, F. M., Wolf, O. T., and Schwabe, L. (2013). Stress disrupts response memory retrieval. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38, 1460–1465. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2012.12.010
Günseli, E., Foster, J. J., Sutterer, D. W., Todorova, L., Vogel, E. K., and Awh, E. (2024). Encoded and updated spatial working memories share a common representational format in alpha activity. iScience 27:108963. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108963
Guskjolen, A., and Cembrowski, M. S. (2023). Engram neurons: encoding, consolidation, retrieval, and forgetting of memory. Mol. Psychiatry 28, 3207–3219. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02137-5
Gustavson, D. E., and Miyake, A. (2015). Trait worry is associated with difficulties in working memory updating. Cogn. Emot. 30, 1289–1303. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2015.1060194
Hagena, H., and Manahan-Vaughan, D. (2016). Dopamine D1/D5, but not D2/D3, receptor dependency of synaptic plasticity at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses that is enabled by patterned afferent stimulation, or spatial learning. Front. Synaptic Neurosci. 8:31. doi: 10.3389/fnsyn.2016.00031
Hammarlund, C. S., Khalaf, A., Westergren, A., Hagell, P. L., and Hagell, P. (2024). Facing and dealing with emotional turbulence: living with newly diagnosed Parkinson's disease. Scand. J. Caring Sci. 38, 701–710. doi: 10.1111/scs.13258
Han, K., Lee, M., Lim, H.-K., Jang, M. W., Kwon, J., Lee, C. J., et al. (2020). Excitation-inhibition imbalance leads to alteration of neuronal coherence and neurovascular coupling under acute stress. J. Neurosci. 40, 9148–9162. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1553-20.2020
Han, S., Gao, J., Hu, J., Ye, Y., Huang, H., Liu, J., et al. (2023). Disruptions of salience network during uncertain anticipation of conflict control in anxiety. Asian J. Psychiatr. 88:103721. doi: 10.1016/j.ajp.2023.103721
Hansen, N., and Manahan-Vaughan, D. (2012). Dopamine D1/D5 receptors mediate informational saliency that promotes persistent hippocampal long-term plasticity. Cereb. Cortex 24, 845–858. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs362
Haubrich, J., and Nader, K. (2023). Network-level changes in the brain underlie fear memory strength. Elife 12:RP88172. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88172.3
Hayes, B. K., Harikumar, A., Ferguson, L. A., Dicker, E. E., Denny, B. T., and Leal, S. L. (2023). Emotion regulation during encoding reduces negative and enhances neutral mnemonic discrimination in individuals with depressive symptoms. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 205:107824. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2023.107824
Hayes, J. P., LaBar, K. S., McCarthy, G., Selgrade, E., Nasser, J., Dolcos, F., et al. (2011). Reduced hippocampal and amygdala activity predicts memory distortions for trauma reminders in combat-related PTSD. J. Psychiatr. Res. 45, 660–669. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.10.007
He, F., Wang, L., Yang, Q., and Wang, J. (2025). High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation modulation of brain network connectivity in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Neuroreport 36, 767–776. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000002199
Hedman, E., Hesser, H., Andersson, E., Axelsson, E., and Ljótsson, B. (2017). The mediating effect of mindful non-reactivity in exposure-based cognitive behavior therapy for severe health anxiety. J. Anxiety Disord. 50, 15–22. doi: 10.1016/j.janxdis.2017.04.007
Heinbockel, H., Wagner, A. D., and Schwabe, L. (2024). Post-retrieval stress impairs subsequent memory depending on hippocampal memory trace reinstatement during reactivation. Sci. Adv. 10:eadm7504. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adm7504
Hennings, A. C., McClay, M., Lewis-Peacock, J. A., and Dunsmoor, J. E. (2019). Neural reinstatement guides context-dependent emotional memory retrieval. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/785899
Herbener, E. S., Rosen, C., Khine, T., and Sweeney, J. A. (2007). Failure of positive but not negative emotional valence to enhance memory in schizophrenia. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 116, 43–55. doi: 10.1037/0021-843X.116.1.43
Ho, T. C., Sacchet, M. D., Connolly, C. G., Margulies, D. S., Tymofiyeva, O., Paulus, M. P., et al. (2017). Inflexible functional connectivity of the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex in adolescent major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 42, 2434–2445. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.103
Hofmann, S. G., and Gómez, A. F. (2017). Mindfulness-based interventions for anxiety and depression. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 40, 739–749. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2017.08.008
Huang, Z., and Li, X. (2021). Processing of emotional information in working memory in major depressive disorder. Xin Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan 29:252. doi: 10.3724/sp.j.1042.2021.00252
Hubbard, R. J., Zadeh, I., Jones, A. P., Robert, B., Bryant, N. B., Clark, V. P., et al. (2021). Brain connectivity alterations during sleep by closed-loop transcranial neurostimulation predict metamemory sensitivity. Netw. Neurosci. 5, 734–756. doi: 10.1162/netn_a_00201
Iqbal, S. Z., Saxena, K., Lateef, A., Khan, S., Blassingame, J., and Shah, A. A. (2024). Treatment-resistant depression and medications. Psychiatr. Ann. 54, e177–e181. doi: 10.3928/00485713-20240618-04
Isakulyan, E. L., and Marachev, M. P. (2024). Features of cognitive functions in generalized anxiety disorder: narrative review. Euro. Psychiatry 67, S424–S425. doi: 10.1192/j.eurpsy.2024.879
Jaeggi, S. M., Buschkuehl, M., Perrig, W. J., and Meier, B. (2010). The concurrent validity of the N-back task as a working memory measure. Memory 18, 394–412. doi: 10.1080/09658211003702171
Jagadeesan, A. J., Murugesan, R., Vimala Devi, S., Meera, M., Madhumala, G., Vishwanathan Padmaja, M., et al. (2017). Current trends in etiology, prognosis and therapeutic aspects of Parkinson's disease: a review. Acta Biomed. 88, 249–262. doi: 10.23750/abm.v88i3.6063
Jantzi, C., Mengin, A. C., Serfaty, D., Bacon, E., Elowe, J., Severac, F., et al. (2019). Retrieval practice improves memory in patients with schizophrenia: new perspectives for cognitive remediation. BMC Psychiatry 19:355. doi: 10.1186/s12888-019-2341-y
Jay, T. M. (2003). Dopamine: a potential substrate for synaptic plasticity and memory mechanisms. Prog. Neurobiol. 69, 375–390. doi: 10.1016/S0301-0082(03)00085-6
Ji, Z., Chu, T., Dong, X., Yu, C., Bush, D., Burgess, N., et al. (2024). Dynamical modulation of hippocampal replay sequences through firing rate adaptation. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.13.612895
Jia, S.-H., Li, K., Su, W., Li, S.-H., and Chen, H.-B. (2018). Impairment in the intention formation and execution phases of prospective memory in Parkinson's disease. Front. Neurosci. 12:98. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00098
Jiang, A., Tran, T. T., Madison, F. N., and Bakker, A. (2019). Acute stress-induced cortisol elevation during memory consolidation enhances pattern separation. Learn. Mem. 26, 121–127. doi: 10.1101/lm.048546.118
Kahana, M. J., Ezzyat, Y., Wanda, P. A., Solomon, E. A., Adamovich-Zeitlin, R., Lega, B. C., et al. (2023). Biomarker-guided neuromodulation aids memory in traumatic brain injury. Brain Stimul. 16, 1086–1093. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2023.07.002
Katsuki, H., Izumi, Y., and Zorumski, C. F. (1997). Noradrenergic regulation of synaptic plasticity in the hippocampal CA1 region. J. Neurophysiol. 77, 3013–3020. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.77.6.3013
Kayvani, M., Kavyani, A., and Soltani, S. (2023). The induced fatigue on attention networks of active and inactive individuals: effect of exercise. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/2023.08.14.553215
Keeser, D., Meindl, T., Bor, J., Palm, U., Pogarell, O., Mulert, C., et al. (2011). Prefrontal transcranial direct current stimulation changes connectivity of resting-state networks during fMRI. J. Neurosci. 31, 15284–15293. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0542-11.2011
Kesner, R. P., and Rolls, E. T. (2015). A computational theory of hippocampal function and tests of the theory: new developments. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 48, 92–147. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.11.009
Khan, A., Eden Ti, C. H., Yuan, K., Garcia, M. C., Anderson, M. C., and Tong, R. K.-Y. (2024). Stimulating the medial prefrontal cortex disrupts inhibitory control over memory by modulating frontal and parietal brain regions. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.30.577598
Khan, I. S., D.' Agostino, E. N., Calnan, D. R., Lee, J. E., and Aronson, J. P. (2019). Deep brain stimulation for memory modulation: a new Frontier. World Neurosurg. 126, 638–646. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.12.184
Kim, H. (2010). Dissociating the roles of the default-mode, dorsal, and ventral networks in episodic memory retrieval. Neuroimage 50, 1648–1657. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2010.01.051
Kim, J., Zhang, X., Muralidhar, S., LeBlanc, S. A., and Tonegawa, S. (2017). Basolateral to central amygdala neural circuits for appetitive behaviors. Neuron 93, 1464–1479.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.02.034
Kolk, B. A., and Fisler, R. (1995). Dissociation and the fragmentary nature of traumatic memories: overview and exploratory study. J. Trauma. Stress 8, 505–525. doi: 10.1007/BF02102887
Kong, M.-S., Jo, Y. S., Sethi, E., Pyeon, G. H., and Zweifel, L. S. (2024). A dopamine-dependent mechanism for reward-induced modification of fear memories. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.05.611495
Kurtin, D. L., Giunchiglia, V., Vohryzek, J., Cabral, J., Skeldon, A. C., and Violante, I. R. (2023). Moving from phenomenological to predictive modelling: progress and pitfalls of modelling brain stimulation in-silico. Neuroimage 272:120042. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2023.120042
LaBar, K. S., and Cabeza, R. (2006). Cognitive neuroscience of emotional memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 7, 54–64. doi: 10.1038/nrn1825
Lara, A. H., and Wallis, J. D. (2015). The role of prefrontal cortex in working memory: a mini review. Front. Syst. Neurosci. 9:173. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2015.00173
Larrosa, P. N. F., Ojea, A., Ojea, I., Molina, V. A., Zorrilla-Zubilete, M. A., and Delorenzi, A. (2017). Retrieval under stress decreases the long-term expression of a human declarative memory via reconsolidation. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 142, 135–145. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.03.005
Latif, S., Jahangeer, M., Maknoon Razia, D., Ashiq, M., Ghaffar, A., Akram, M., et al. (2021). Dopamine in Parkinson's disease. Clin. Chim. Acta 522, 114–126. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2021.08.009
Le Bé, J. V., and Markram, H. (2006). Spontaneous and evoked synaptic rewiring in the neonatal neocortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. USA. 103, 13214–13219. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604691103
LeDoux, J. (2003). The emotional brain, fear, and the amygdala. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 23, 727–738. doi: 10.1023/A:1025048802629
Lee, B., Young, C. B., Cai, W., Yuan, R., Ryman, S., Kim, J., et al. (2025). Dopaminergic modulation and dosage effects on brain state dynamics and working memory component processes in Parkinson's disease. Nat. Commun. 16:2433. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-56660-w
Lee, C., and Fernandes, M. (2017). Emotional encoding context leads to memory bias in individuals with high anxiety. Brain Sci. 8:6. doi: 10.3390/brainsci8010006
Lee, E.-Y. (2023). Memory deficits in Parkinson's disease are associated with impaired attentional filtering and memory consolidation processes. J. Clin. Med. 12:4594. doi: 10.3390/jcm12144594
Lee, Y.-A., and Goto, Y. (2015). Chronic stress effects on working memory: association with prefrontal cortical tyrosine hydroxylase. Behav. Brain Res. 286, 122–127. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2015.03.007
Leistedt, S. J., Coumans, N., Dumont, M., Lanquart, J. P., Stam, C. J., and Linkowski, P. (2009). Altered sleep brain functional connectivity in acutely depressed patients. Hum. Brain Mapp. 30, 2207–2219. doi: 10.1002/hbm.20662
Lemon, N., and Manahan-Vaughan, D. (2006). Dopamine D1/D5 receptors gate the acquisition of novel information through hippocampal long-term potentiation and long-term depression. J. Neurosci. 26, 7723–7729. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1454-06.2006
Levy, W. B., and Wu, X. (1996). The relationship of local context codes to sequence length memory capacity. Network 7, 371–384. doi: 10.1088/0954-898X/7/2/019
Leyman, L., De Raedt, R., Schacht, R., and Koster, E. H. (2006). Attentional biases for angry faces in unipolar depression. Psychol. Med. 37, 393–402. doi: 10.1017/S003329170600910X
Li, C.-T. (2023). “Overview of treatment-resistant depression,” in Progress in Brain Research, Vol. 278, eds. C.-T. Li and C.-M. Cheng (Amsterdam: Elsevier), 1–23. doi: 10.1016/bs.pbr.2023.03.007
Li, H., Bai, C., Wang, R., Zheng, T., and Sun, H. (2017). Correlation between negative emotions and cognitive function impairment in patients with anxiety disorder. J. Int. Psychiatry 44, 68–71.
Li, R., Shen, F., Sun, X., Zou, T., Li, L., Wang, X., et al. (2023). Dissociable salience and default mode network modulation in generalized anxiety disorder: a connectome-wide association study. Cereb. Cortex 33, 6354–6365. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhac509
Li, W., Lei, D., Tallman, M. J., Patino, L. R., Gong, Q., Strawn, J. R., et al. (2021). Emotion-related network reorganization following fish oil supplementation in depressed bipolar offspring: an fMRI graph-based connectome analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 292, 319–327. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2021.05.086
Li, Z., Qu, Y., Wu, Q.-L., Tang, L., Dong, Y., and Xu, X.-F. (2025). Input-output organization of the mouse BLA-projecting IL neurons. Front. Neurosci. 19:1532078. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1532078
Lisman, J. E., and Jensen, O. (2013). The theta-gamma neural code. Neuron 77, 1002–1016. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2013.03.007
Liu, H., Li, D., Qiu, F., Dong, C., Zhang, Y., Han, R., et al. (2016). Effects of emotion on cognitive function in patients with mild to moderate Parkinson's disease. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 16, 92–97.
Longo, C., Romano, D. L., Malaguti, M. C., Bacchin, R., and Papagno, C. (2024). Cognitive reorganization in patients with Parkinson's disease and mild cognitive Impairment: a neuropsychological network approach. Sci. Rep. 14:28482. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79303-4
Lynch, M. A. (2004). Long-term potentiation and memory. Physiol. Rev. 84, 87–136. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00014.2003
MacDonald, A. A., Seergobin, K. N., Owen, A. M., Tamjeedi, R., Monchi, O., Ganjavi, H., et al. (2013). Differential effects of Parkinson's disease and dopamine replacement on memory encoding and retrieval. PLoS ONE 8:e74044. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074044
Madan, C. R., Fujiwara, E., Caplan, J. B., and Sommer, T. (2017). Emotional arousal impairs association-memory: roles of amygdala and hippocampus. Neuroimage 156, 14–28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.04.065
Mallas, E.-J., De Simoni, S., Scott, G., Jolly, A. E., Hampshire, A., Li, L. M., et al. (2020). Abnormal dorsal attention network activation in memory impairment after traumatic brain injury. Brain 144, 114–127. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa380
Marder, K. G., Barbour, T., Ferber, S., Idowu, O., and Itzkoff, A. (2022). Psychiatric applications of repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Focus 20, 8–18. doi: 10.1176/appi.focus.20210021
Marr, D. (1971). Simple memory: a theory for archicortex. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 262, 23–81. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1971.0078
Martinez, M., Multani, N., Anor, C. J., Misquitta, K., Tang-Wai, D. F., Keren, R., et al. (2018). Emotion detection deficits and decreased empathy in patients with Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease affect caregiver mood and burden. Front. Aging Neurosci. 10:120. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2018.00120
Martinez-Nunez, A. E., Justich, M. B., Okun, M. S., and Fasano, A. (2024). Emerging therapies for neuromodulation in Parkinson's disease. Neurotherapeutics 21:e00310. doi: 10.1016/j.neurot.2023.e00310
Mastrangelo, A. L. (2024). The effect of state anxiety on working memory updating (PCOM psychology dissertations). Pacheco-Unguetti, 658. https://digitalcommons.pcom.edu/psychology_dissertations/658
Maviel, T., Durkin, T. P., Menzaghi, F., and Bontempi, B. (2004). Sites of neocortical reorganization critical for remote spatial memory. Science 305, 96–99. doi: 10.1126/science.1098180
McDonald, A. J. (2014). “Amygdala,” in Encyclopedia of the Neurological Sciences, 2nd Edn. eds. R. B. Daroff and M. J. Aminoff (Waltham, MA: Academic Press; Elsevier), 153−156. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-385157-4.01113-1
Mercer, T., and Fisher, L. P. (2022). Magnitude and sources of proactive interference in visual memory. Memory 30, 591–609. doi: 10.1080/09658211.2022.2032179
Mezger, E., Rauchmann, B.-S., Brunoni, A. R., Bulubas, L., Thielscher, A., Werle, J., et al. (2020). Effects of bifrontal transcranial direct current stimulation on brain glutamate levels and resting state connectivity: multimodal MRI data for the cathodal stimulation site. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 271, 111–122. doi: 10.1007/s00406-020-01177-0
Mill, R. D., Hamilton, J. L., Winfield, E. C., Lalta, N., Chen, R. H., and Cole, M. W. (2022). Network modeling of dynamic brain interactions predicts emergence of neural information that supports human cognitive behavior. PLoS Biol. 20:e3001686. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3001686
Miller, M., Adesso, V., Fleming, J., Gino, A., and Lauerman, R. (1978). Effects of alcohol on the storage and retrieval processes of heavy social drinkers. J. Exp. Psychol. Hum. Learn. 4, 246–255. doi: 10.1037/0278-7393.4.3.246
Miner, L. H., Jedema, H. P., Moore, F. W., Blakely, R. D., Grace, A. A., and Sesack, S. R. (2006). Chronic stress increases the plasmalemmal distribution of the norepinephrine transporter and the coexpression of tyrosine hydroxylase in norepinephrine axons in the prefrontal cortex. J. Neurosci. 26, 1571–1578. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4450-05.2006
Mioni, G., Meligrana, L., Rendell, P. G., Bartolomei, L., Perini, F., and Stablum, F. (2015). Event-based prospective memory in patients with Parkinson's disease: the effect of emotional valence. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 9:427. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2015.00427
Mirjalili, M., Palamarchuk, I. S., Brooks, H., Zomorrodi, R., Melichercik, A., Wang, W., et al. (2025). Individualized frequency and montage tACS to engage theta-gamma coupling and enhance working memory in mild cognitive impairment. Front. Psychiatry 16:1565881. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2025.1565881
Miyamoto, D., Hirai, D., and Murayama, M. (2017). The roles of cortical slow waves in synaptic plasticity and memory consolidation. Front. Neural Circuits 11:92. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2017.00092
Mogg, K., and Bradley, B. P. (2016). Anxiety and attention to threat: cognitive mechanisms and treatment with attention bias modification. Behav. Res. Ther. 87, 76–108. doi: 10.1016/j.brat.2016.08.001
Mohr, H., Wolfensteller, U., Betzel, R. F., Mišić, B., Sporns, O., Richiardi, J., et al. (2016). Integration and segregation of large-scale brain networks during short-term task automatization. Nat. Commun. 7:13217. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13217
Moorey, S., and Hollon, S. D. (2021). “Cognitive behavioral therapy for depression,” in Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Psychology [Internet], ed. O. J. Braddick (Oxford: Oxford University Press). doi: 10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.837
Mosha, N., and Robertson, E. M. (2016). Unstable memories create a high-level representation that enables learning transfer. Curr. Biol. 26, 100–105. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.11.035
Mottaghy, F. M., Krause, B. J., Kemna, L. J., Töpper, R., Tellmann, L., Beu, M., et al. (2000). Modulation of the neuronal circuitry subserving working memory in healthy human subjects by repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurosci. Lett. 280, 167–170. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(00)00798-9
Murty, V. P., Ritchey, M., Adcock, R. A., and LaBar, K. S. (2010). fMRI studies of successful emotional memory encoding: a quantitative meta-analysis. Neuropsychologia 48, 3459–3469. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2010.07.030
Muslimovic, D., Post, B., Speelman, J. D., and Schmand, B. (2005). Cognitive profile of patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson disease. Neurology 65, 1239–1245. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000180516.69442.95
Nadel, L., and Jacobs, W. J. (1998). Traumatic memory is special. Curr. Dir. Psychol. Sci. 7, 154–157. doi: 10.1111/1467-8721.ep10836842
Nagai, T., Takuma, K., Kamei, H., Ito, Y., Nakamichi, N., Ibi, D., et al. (2007). Dopamine D1 receptors regulate protein synthesis-dependent long-term recognition memory via extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 in the prefrontal cortex. Learn. Mem. 14, 117–125. doi: 10.1101/lm.461407
Najera, R. A., Kabotyanski, K. E., McLaughlin, N. C., Gregory, S. T., Anand, A., Shofty, B., et al. (2025). Cost-effectiveness analysis of deep brain stimulation versus treatment as usual for treatment-resistant obsessive-compulsive disorder. J. Neurosurg. 142, 1225–1234. doi: 10.3171/2024.7.JNS232642
Nathaniel-James, D. A., Brown, R., and Ron, M. A. (1996). Memory impairment in schizophrenia: its' relationship to executive function. Schizophr. Res. 18:211. doi: 10.1016/0920-9964(96)85651-9
Nelson, S. B., and Valakh, V. (2015). Excitatory/inhibitory balance and circuit homeostasis in autism spectrum disorders. Neuron 87, 684–698. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.07.033
Nie, C., Zhao, X., and Gao, Z. (2024). Influence of different attention load on framing effect of risk decision-making. Adv. Psychol. 14, 654–660. doi: 10.12677/ap.2024.144263
Nyberg, L., Andersson, M., Lundquist, A., Salami, A., and Wåhlin, A. (2019). Frontal contribution to hippocampal hyperactivity during memory encoding in aging. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 12:229. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00229
Obeso, I., Ray, N. J., Antonelli, F., Cho, S. S., and Strafella, A. P. (2011). Combining functional imaging with brain stimulation in Parkinson's disease. Int. Rev. Psychiatr. 23, 467–475. doi: 10.3109/09540261.2011.621414
Oei, N. Y. L., Elzinga, B. M., Wolf, O. T., de Ruiter, M. B., Damoiseaux, J. S., Kuijer, J. P. A., et al. (2007). Glucocorticoids decrease hippocampal and prefrontal activation during declarative memory retrieval in young men. Brain Imag. Behav. 1, 31–41. doi: 10.1007/s11682-007-9003-2
Oliveira, J. F., Zanão, T. A., Valiengo, L., Lotufo, P. A., Benseñor, I. M., Fregni, F., et al. (2013). Acute working memory improvement after tDCS in antidepressant-free patients with major depressive disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 537, 60–64. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2013.01.023
Ousdal, O. T., Milde, A. M., Hafstad, G. S., Hodneland, E., Dyb, G., Craven, A. R., et al. (2020). The association of PTSD symptom severity with amygdala nuclei volumes in traumatized youths. Transl. Psychiatry 10:288. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-00974-4
Owens-Walton, C., Jakabek, D., Power, B. D., Walterfang, M., Hall, S., van Westen, D., et al. (2021). Structural and functional neuroimaging changes associated with cognitive impairment and dementia in Parkinson's disease. Psychiatry Res. Neuroimag. 312:111273. doi: 10.1016/j.pscychresns.2021.111273
Oztekin, I., McElree, B., Staresina, B. P., and Davachi, L. (2009). Working memory retrieval: contributions of the left prefrontal cortex, the left posterior parietal cortex, and the hippocampus. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 21, 581–593. doi: 10.1162/jocn.2008.21016
Pagonabarraga, J., and Kulisevsky, J. (2012). Cognitive impairment and dementia in Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 46, 590–596. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2012.03.029
Parsaei, L., Rangchiyan, M., Ahmadi, S., and Zarrindast, M. R. (2011). GABA A receptors in the dorsal hippocampus are involved in sate-dependent learning induced by lithium in mice. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 10, 127–134.
Paßmann, S., Baselgia, S., Kasten, F. H., Herrmann, C. S., and Rasch, B. (2024). Differential online and offline effects of theta-tACS on memory encoding and retrieval. Cogn. Affect. Behav. Neurosci. 24, 894–911. doi: 10.3758/s13415-024-01204-w
Patel, R., Girard, T. A., Pukay-Martin, N., and Monson, C. (2016). Preferential recruitment of the basolateral amygdala during memory encoding of negative scenes in posttraumatic stress disorder. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 130, 170–176. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2016.02.003
Paunovic, N., Lundh, L.-G., and Öst, L.-G. (2002). Attentional and memory bias for emotional information in crime victims with acute posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). J. Anxiety Disord. 16, 675–692. doi: 10.1016/S0887-6185(02)00136-6
Payne, J. D., Jackson, E. D., Hoscheidt, S., Ryan, L., Jacobs, W. J., and Nadel, L. (2007). Stress administered prior to encoding impairs neutral but enhances emotional long-term episodic memories. Learn. Mem. 14, 861–868. doi: 10.1101/lm.743507
Peter-Derex, L., Yammine, P., Bastuji, H., and Croisile, B. (2015). Sleep and Alzheimer's disease. Sleep Med. Rev. 19, 29–38. doi: 10.1016/j.smrv.2014.03.007
Petzka, M., Charest, I., Balanos, G. M., and Staresina, B. P. (2021). Does sleep-dependent consolidation favour weak memories? Cortex 134, 65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2020.10.005
Phelps, E. A. (2004). Human emotion and memory: interactions of the amygdala and hippocampal complex. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 14, 198–202. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2004.03.015
Pitts, M. W., and Takahashi, L. K. (2011). The central amygdala nucleus via corticotropin-releasing factor is necessary for time-limited consolidation processing but not storage of contextual fear memory. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 95, 86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2010.11.006
Polizzotto, N. R., Ramakrishnan, N., and Cho, R. Y. (2020). Is it possible to improve working memory with prefrontal tDCS? Bridging currents to working memory models. Front. Psychol. 11:939. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2020.00939
Preston, A. R., and Eichenbaum, H. (2013). Interplay of hippocampus and prefrontal cortex in memory. Curr. Biol. 23, R764–R,773. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.05.041
Racz, F. S., Farkas, K., Becske, M., Molnar, H., Fodor, Z., Mukli, P., et al. (2025). Reduced temporal variability of cortical excitation/inhibition ratio in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia 11:20. doi: 10.1038/s41537-025-00568-3
Radulovic, J., Jovasevic, V., and Meyer, M. A. (2017). Neurobiological mechanisms of state-dependent learning. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 45, 92–98. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2017.05.013
Ragland, J. D., Laird, A. R., Ranganath, C., Blumenfeld, R. S., Gonzales, S. M., and Glahn, D. C. (2009). Prefrontal activation deficits during episodic memory in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 166, 863–874. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2009.08091307
Rasmussen, I. D., Boayue, N. M., Mittner, M., Bystad, M., Grønli, O. K., Vangberg, T. R., et al. (2021). High-definition transcranial direct current stimulation improves delayed memory in Alzheimer's disease patients: a pilot study using computational modeling to optimize electrode position. J. Alzheimers Dis. 83, 753–769. doi: 10.3233/JAD-210378
Reeck, C., LaBar, K., and Egner, T. (2012). Neural mechanisms mediating contingent capture of attention by affective stimuli. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 24, 1113–1126. doi: 10.1162/jocn_a_00211
Rezai, A. R., and Sharma, M. (2014). Deep brain stimulation (DBS): current and emerging applications. Japan. J. Neurosurg. 23, 648–660. doi: 10.7887/jcns.23.648
Richter-Levin, G. (2004). The amygdala, the hippocampus, and emotional modulation of memory. Neuroscientist 10, 31–39. doi: 10.1177/1073858403259955
Rideaux, R., Ehrhardt, S. E., Wards, Y., Filmer, H. L., Jin, J., Deelchand, D. K., et al. (2022). On the relationship between GABA+ and glutamate across the brain. Neuroimage 257:119273. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2022.119273
Rissman, R. A., and Mobley, W. C. (2011). Implications for treatment: GABAA receptors in aging, Down syndrome and Alzheimer's disease. J. Neurochem. 117, 613–622. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07237.x
Ritchey, M., Wing, E. A., LaBar, K. S., and Cabeza, R. (2012). Neural similarity between encoding and retrieval is related to memory via hippocampal interactions. Cereb. Cortex 23, 2818–2828. doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhs258
Robinson, S. J., and Rollings, L. J. L. (2010). The effect of mood-context on visual recognition and recall memory. J. Gen. Psychol. 138, 66–79. doi: 10.1080/00221309.2010.534405
Roozendaal, B., and Hermans, E. J. (2017). Norepinephrine effects on the encoding and consolidation of emotional memory: improving synergy between animal and human studies. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 14, 115–122. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2017.02.001
Rosenbaum, D., Hagen, K., Deppermann, S., Kroczek, A. M., Haeussinger, F. B., Heinzel, S., et al. (2015). State-dependent altered connectivity in late-life depression: a functional near-infrared spectroscopy study. Neurobiol. Aging 39, 57–68. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.11.022
Rossi, S., Hallett, M., Rossini, P. M., and Pascual-Leone, A. (2009). Safety, ethical considerations, and application guidelines for the use of transcranial magnetic stimulation in clinical practice and research. Clin. Neurophysiol. 120, 2008–2039. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2009.08.016
Roth, Y., Padberg, F., and Zangen, A. (2007). “Transcranial magnetic stimulation of deep brain regions: principles and methods,” in Advances in Biological Psychiatry, Vol. 23, eds. M. A. Marcolin and F. Padberg (Basel: Karger), 204–224. doi: 10.1159/000101039
Russek, S. J. (2006). “Aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors,” in eLS: Encyclopedia of Life Sciences [Internet] (Chichester: John Wiley and Sons, Ltd). doi: 10.1002/9780470015902.a0005907
Rybakowski, J. K. (2014). Response to lithium in bipolar disorder: clinical and genetic findings. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 5, 413–421. doi: 10.1021/cn5000277
Saccenti, D., and Koster, E. H. W. (2024). Boosting psychotherapy with noninvasive brain stimulation: the whys and wherefores of modulating neural plasticity to promote therapeutic change. Neural Plast. 2024:7853199. doi: 10.1155/np/7853199
Sałaciak, K., Koszałka, A., Lustyk, K., Żmudzka, E., Jagielska, A., and Pytka, K. (2023). Memory impairments in rodent depression models: a link with depression theories. Progress Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 125:110774. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2023.110774
Saragea, P. D. (2024). The genetic landscape of early and late-onset Alzheimer's disease: a review. Acta Marisiensis Seria Medica 70, 205–215. doi: 10.2478/amma-2024-0030
Sari, B. A., Koster, E. H. W., and Derakshan, N. (2017). The effects of active worrying on working memory capacity. Cogn. Emot. 31, 995–1003. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2016.1170668
Savarimuthu, A., and Ponniah, R. J. (2023). Receive, retain and retrieve: psychological and neurobiological perspectives on memory retrieval. Integr. Psychol. Behav. Sci. 58, 303–318. doi: 10.1007/s12124-023-09752-5
Schiltz, K., Zierhut, K. C., and Bogerts, B. (2010). P03-125 - memory dysfunction and defective novelty detection in schizophrenia. Euro. Psychiatry 25:1105. doi: 10.1016/S0924-9338(10)71094-4
Schubert, T. (2023). Retroactive interference arises from semantic similarity. Nat. Rev. Psychol. 2, 71–71. doi: 10.1038/s44159-023-00154-3
Schwabe, L., Böhringer, A., and Wolf, O. T. (2009). Stress disrupts context-dependent memory. Learn. Mem. 16, 110–113. doi: 10.1101/lm.1257509
Sekeres, M. J., Schomaker, J., Nadel, L., and Tse, D. (2024). To update or to create? The influence of novelty and prior knowledge on memory networks. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 379:20230238. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0238
Sergerie, K., Armony, J. L., Menear, M., Sutton, H., and Lepage, M. (2009). Influence of emotional expression on memory recognition bias in schizophrenia as revealed by fMRI. Schizophr. Bull. 36, 800–810. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbn172
Shi, G., Wang, C., Cui, L., Zhang, Q., and Guo, C. (2024a). The memory bias toward negative context in episodic memory in anxiety individuals-an exploratory study through ERPs. Int. J. Psychol. Sci. 4, 57–64. doi: 10.11648/j.ijps.20240403.12
Shi, Y., Yang, L., Lu, J., Yan, T., Ding, Y., and Wang, B. (2024b). The dynamic reconfiguration of the functional network during episodic memory task predicts the memory performance. Sci. Rep. 14:20527. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-71295-5
Shine, J. M., Bissett, P. G., Bell, P. T., Koyejo, O., Balsters, J. H., Gorgolewski, K. J., et al. (2016). The dynamics of functional brain networks: integrated network states during cognitive task performance. Neuron 92, 544–554. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.018
Shoob, S., Buchbinder, N., Shinikamin, O., Gold, O., Baeloha, H., Langberg, T., et al. (2023). Deep brain stimulation of thalamic nucleus reuniens promotes neuronal and cognitive resilience in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. Nat. Commun. 14:7002. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-42721-5
Shtoots, L., Nadler, A., Partouche, R., Sharir, D., Rothstein, A., Shati, L., et al. (2024). Frontal midline theta transcranial alternating current stimulation enhances early consolidation of episodic memory. NPJ Sci. Learn. 9:8. doi: 10.1038/s41539-024-00222-0
Siddiqi, S. H., and Fox, M. D. (2022). “Combining invasive and noninvasive brain stimulation,” in Connectomic Deep Brain Stimulation, ed. A. Horn (London: Academic Press; Elsevier), 505–523. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-821861-7.00024-5
Sierra-Mercado, D., Padilla-Coreano, N., and Quirk, G. J. (2011). Dissociable roles of prelimbic and infralimbic cortices, ventral hippocampus, and basolateral amygdala in the expression and extinction of conditioned fear. Neuropsychopharmacology 36, 529–538. doi: 10.1038/npp.2010.184
Silva, A., and Martínez, M. C. (2023). Spatial memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease and their connection to cognitive maps' formation by place cells and grid cells. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 16:1082158. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1082158
Silva, B. A., Astori, S., Burns, A. M., Heiser, H., van den Heuvel, L., Santoni, G., et al. (2021). A thalamo-amygdalar circuit underlying the extinction of remote fear memories. Nat. Neurosci. 24, 964–974. doi: 10.1038/s41593-021-00856-y
Silvanto, J., and Pascual-Leone, A. (2008). State-dependency of transcranial magnetic stimulation. Brain Topogr. 21, 1–10. doi: 10.1007/s10548-008-0067-0
Simioni, A. C., Dagher, A., and Fellows, L. K. (2017). Effects of levodopa on corticostriatal circuits supporting working memory in Parkinson's disease. Cortex 93, 193–205. doi: 10.1016/j.cortex.2017.05.021
Simons, J. S., and Spiers, H. J. (2003). Prefrontal and medial temporal lobe interactions in long-term memory. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 4, 637–648. doi: 10.1038/nrn1178
Sinclair, L. I., Lawton, M., Palmer, J., and Ballard, C. G. (2023). Is depression in those with Alzheimer's disease different to depression in those without dementia? Alzheimer. Dementia 19:e066500. doi: 10.1002/alz.066500
Smeets, T., Otgaar, H., Candel, I., and Wolf, O. T. (2008). True or false? Memory is differentially affected by stress-induced cortisol elevations and sympathetic activity at consolidation and retrieval. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33, 1378–1386. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2008.07.009
Smith, C. R., Cullen, B., Sheridan, M. P., Cavanagh, J., Grosset, K. A., and Grosset, D. G. (2020). Cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease is multifactorial: a neuropsychological study. Acta Neurol. Scand. 141, 500–508. doi: 10.1111/ane.13226
Soleimani, G., Nitsche, M. A., Bergmann, T. O., Towhidkhah, F., Violante, I. R., Lorenz, R., et al. (2023). Closing the loop between brain and electrical stimulation: towards precision neuromodulation treatments. Transl. Psychiatry 13:279. doi: 10.1038/s41398-023-02565-5
Sotres-Bayon, F., Sierra-Mercado, D., Pardilla-Delgado, E., and Quirk, G. J. (2012). Gating of fear in prelimbic cortex by hippocampal and amygdala inputs. Neuron 76, 804–812. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.09.028
Speer, M. E., and Delgado, M. R. (2017). Reminiscing about positive memories buffers acute stress responses. Nat. Hum. Behav. 1:93. doi: 10.1038/s41562-017-0093
Spielberg, J. M., McGlinchey, R. E., Milberg, W. P., and Salat, D. H. (2015). Brain network disturbance related to posttraumatic stress and traumatic brain injury in veterans. Biol. Psychiatry 78, 210–216. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.013
Squire, L. R., and Zola-Morgan, S. (1991). The medial temporal lobe memory system. Science 253, 1380–1386. doi: 10.1126/science.1896849
Staal, M. A. (2004). Stress, Cognition, and Human Performance: A Literature Review and Conceptual Framework. NASA Technical Memorandum NASA/TM-2004-212824. Moffett Field, CA: NASA Ames Research Center. Available at: https://ntrs.nasa.gov/ (Accessed June 20, 2025).
Stahl, S. M., Pradko, J., Haight, B. R., Modell, J. G., Rockett, C. B., and Learned-Coughlin, S. (2004). A review of the neuropharmacology of bupropion, a dual norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake inhibitor. Primary Care Companion CNS Disord. 6:159. doi: 10.4088/PCC.v06n0403
Stephenson, M. L., Ostrander, A. G., Norasi, H., and Dorneich, M. C. (2019). Shoulder muscular fatigue from static posture concurrently reduces cognitive attentional resources. Hum. Factors 62, 589–602. doi: 10.1177/0018720819852509
Strijkert, F., Huitema, R. B., van Munster, B. C., and Spikman, J. M. (2023). Impaired emotion recognition: a potential marker for social behavioral problems in patients with amnestic mild cognitive impairment and early Alzheimer disease? Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 37, 189–194. doi: 10.1097/WAD.0000000000000567
Su, M., Hu, K., Liu, W., Wu, Y., Wang, T., Cao, C., et al. (2024). Theta oscillations support prefrontal-hippocampal interactions in sequential working memory. Neurosci. Bull. 40, 147–156. doi: 10.1007/s12264-023-01134-6
Suemoto, C. K., Apolinario, D., Nakamura-Palacios, E. M., Lopes, L., Paraizo Leite, R. E., Sales, M. C., et al. (2014). Effects of a non-focal plasticity protocol on apathy in moderate Alzheimer's disease: a randomized, double-blind, sham-controlled trial. Brain Stimul. 7, 308–313. doi: 10.1016/j.brs.2013.10.003
Sumadevi, K. T. (2024). The hippocampus: anatomy, function and clinical correlation. Sri Lanka Anatomy J. 8, 6–20. doi: 10.4038/slaj.v8i1.220
Sumbul-Sekerci, B., Hanagasi, H. A., Bilgic, B., Tufekcioglu, Z., Gurvit, H., and Emre, M. (2022). Medication management and treatment adherence in Parkinson's disease patients with mild cognitive impairment. Acta Neurol. Belg. 123, 823–829. doi: 10.1007/s13760-022-01916-1
Takahashi, T. (2011). Mechanisms underlying contextual fear learning. Commun. Integr. Biol. 4, 726–727. doi: 10.4161/cib.17505
Tanaka, M., Yoshida, M., Emoto, H., and Ishii, H. (2000). Noradrenaline systems in the hypothalamus, amygdala and locus coeruleus are involved in the provocation of anxiety: basic studies. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 405, 397–406. doi: 10.1016/S0014-2999(00)00569-0
Tariq, R., Kansal, B., Shaikh, R., Datta, S., Anadkat, H., and Bista, S. (2023). Outcomes and factors affecting transcranial direct current stimulation in Alzheimer's disease patients: a systematic review. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 20, 250–266. doi: 10.2174/1567205020666230601095957
Taylor, R., Galvez, V., and Loo, C. (2018). Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) safety: a practical guide for psychiatrists. Austral. Psychiatry 26, 189–192. doi: 10.1177/1039856217748249
Taylor, R., Tomić, I., Aagten-Murphy, D., and Bays, P. M. (2022). Working memory is updated by reallocation of resources from obsolete to new items. Attention Percept. Psychophys. 85, 1437–1451. doi: 10.3758/s13414-022-02584-2
Thomson, A. C., Kenis, G., Tielens, S., de Graaf, T. A., Schuhmann, T., Rutten, B. P. F., et al. (2020). Transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced plasticity mechanisms: TMS-related gene expression and morphology changes in a human neuron-like cell model. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 13:528396. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.528396
Tollenaar, M. S., Elzinga, B. M., Spinhoven, P., and Everaerd, W. (2008). Long-term outcomes of memory retrieval under stress. Behav. Neurosci. 122, 697–703. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.122.3.697
Tomé, D. F., Zhang, Y., Aida, T., Mosto, O., Lu, Y., Chen, M., et al. (2024). Dynamic and selective engrams emerge with memory consolidation. Nat. Neurosci. 27, 561–572. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01551-w
Trambaiolli, L., Maffei, C., Dann, E., Biazoli Jr, C., Bezgin, G., Yendiki, A., et al. (2024). Translation of monosynaptic circuits underlying amygdala fMRI neurofeedback training. Neuropsychopharmacology 49, 1839–1850. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01944-w
Tsetsenis, T., Broussard, J. I., and Dani, J. A. (2023). Dopaminergic regulation of hippocampal plasticity, learning, and memory. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 16:1092420. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1092420
Turkileri, N., and Sakaki, M. (2017). “Neural mechanisms underlying the effects of emotional arousal on memory,” in Memory in a Social Context: Brain, Mind, and Society, eds. T. Tsukiura and S. Umeda (Tokyo: Springer), 43–55. doi: 10.1007/978-4-431-56591-8_4
Uner, O., and Roediger, H. (2022). Do recall and recognition lead to different retrieval experiences? Am. J. Psychol. 135, 33–43. doi: 10.5406/19398298.135.1.03
Vafaei, A. A., Rashidy-Pour, A., Trahomi, P., Omoumi, S., and Dadkhah, M. (2022). Role of amygdala-infralimbic cortex circuitry in glucocorticoid-induced facilitation of auditory fear memory extinction. Basic Clin. Neurosci. J. 13, 193–206. doi: 10.32598/bcn.2021.2161.1
Van Damme, I. (2013). Mood and the DRM paradigm: an investigation of the effects of valence and arousal on false memory. Q. J. Exp. Psychol. 66, 1060–1081. doi: 10.1080/17470218.2012.727837
Vaz, A. P., Wittig, J. H. Jr., Inati, S. K., and Zaghloul, K. A. (2020). Replay of cortical spiking sequences during human memory retrieval. Science 367, 1131–1134. doi: 10.1126/science.aba0672
Vetere, G., Kenney, J. W., Tran, L. M., Xia, F., Steadman, P. E., Parkinson, J., et al. (2017). Chemogenetic interrogation of a brain-wide fear memory network in mice. Neuron 94, 363–374.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.03.037
Vetere, L. M., Galas, A. M., Vaughan, N., Feng, Y., Christenson Wick, Z., Philipsberg, P. A., et al. (2025). Medial entorhinal-hippocampal desynchronization parallels the emergence of memory impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease pathology. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.15.633171
Viena, T. D., Linley, S. B., and Vertes, R. P. (2018). Inactivation of nucleus reuniens impairs spatial working memory and behavioral flexibility in the rat. Hippocampus 28, 297–311. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22831
Vogels, T. P., Sprekeler, H., Zenke, F., Clopath, C., and Gerstner, W. (2011). Inhibitory plasticity balances excitation and inhibition in sensory pathways and memory networks. Science 334, 1569–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.1211095
Wabnitz, P., Martens, U., and Neuner, F. (2015). Written threat: electrophysiological evidence for an attention bias to affective words in social anxiety disorder. Cogn. Emot. 30, 516–538. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2015.1019837
Walker, M. P., Brakefield, T., Morgan, A., Hobson, J. A., and Stickgold, R. (2002). Practice with sleep makes perfect: sleep-dependent motor skill learning. Neuron 35, 205–211. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(02)00746-8
Walsh-Messinger, J., Ramirez, P. M., Wong, P., Antonius, D., Aujero, N., McMahon, K., et al. (2014). Impairment in emotional modulation of attention and memory in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 157, 63–69. doi: 10.1016/j.schres.2014.05.014
Wang, F., Chen, X., Bo, B., Zhang, T., Liu, K., Jiang, J., et al. (2023). State-dependent memory retrieval: insights from neural dynamics and behavioral perspectives. Learn. Mem. 30, 325–337. doi: 10.1101/lm.053893.123
Wang, J., and Lapate, R. C. (2025). Emotional state dynamics impacts temporal memory. Cogn. Emot. 39, 136–155. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2024.2349326
Wang, P., Eshaq, R. S., Meshul, C. K., Moore, C., Hood, R. L., and Leidenheimer, N. J. (2015). Neuronal gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) type A receptors undergo cognate ligand chaperoning in the endoplasmic reticulum by endogenous GABA. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 9:188. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2015.00188
Wang, Y. Y., Zhu, Z. J., and Wu, Y. H. (2016). The dynamic memory system: the encoding, consolidation and forgetting process of memory (in Chinese). Chin. Sci. Bull. 61, 12–19. doi: 10.1360/N972015-00653
Wang, Z., Jakowec, M. W., Petzinger, G. M., and Holschneider, D. P. (2025). Functional remapping in networks of the Parkinsonian brain: a preclinical neuroimaging perspective with clinical correlates. Transl. Neurosci. 16:20250374. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2025-0374
Wansbrough, K., Tan, J., Vallence, A.-M., and Fujiyama, H. (2024). Recent advancements in optimising transcranial electrical stimulation: reducing response variability through individualised stimulation. Curr. Opin. Behav. Sci. 56:101360. doi: 10.1016/j.cobeha.2024.101360
Weintraub, D., Aarsland, D., Chaudhuri, K. R., Dobkin, R. D., Leentjens, A. F., Rodriguez-Violante, M., et al. (2022). The neuropsychiatry of Parkinson's disease: advances and challenges. Lancet Neurol. 21, 89–102. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(21)00330-6
Wen, Z., Chen, Z. S., and Milad, M. R. (2021). Fear extinction learning modulates large-scale brain connectivity. Neuroimage 238:118261. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118261
Wheeler, A. L., Teixeira, C. M., Wang, A. H., Xiong, X., Kovacevic, N., Lerch, J. P., et al. (2013). Identification of a functional connectome for long-term fear memory in mice. PLoS Comput. Biol. 9:e1002853. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002853
White, A. M. (2003). What happened? Alcohol, memory blackouts, and the brain. Alcohol. Res. Curr. Rev. 27, 186–196.
Wierzba, M., Riegel, M., Wypych, M., Jednoróg, K., Grabowska, A., and Marchewka, A. (2018). Cognitive control over memory - individual differences in memory performance for emotional and neutral material. Sci. Rep. 8:3808. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-21857-1
Willinger, D., Häberling, I., Ilioska, I., Berger, G., Walitza, S., and Brem, S. (2024). Weakened effective connectivity between salience network and default mode network during resting state in adolescent depression. Front. Psychiatry 15:1386984. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1386984
Wischnewski, M., Shirinpour, S., Alekseichuk, I., Lapid, M. I., Nahas, Z., Lim, K. O., et al. (2024). Real-time TMS-EEG for brain state-controlled research and precision treatment: a narrative review and guide. J. Neural Eng. 21:061001. doi: 10.1088/1741-2552/ad8a8e
Wolkenstein, L., and Plewnia, C. (2013). Amelioration of cognitive control in depression by transcranial direct current stimulation. Biol. Psychiatry 73, 646–651. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2012.10.010
Woods, A. J., Antal, A., Bikson, M., Boggio, P. S., Brunoni, A. R., Celnik, P., et al. (2016). A technical guide to tDCS, and related non-invasive brain stimulation tools. Clin. Neurophysiol. 127, 1031–1048. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2015.11.012
Wu, M., Song, W., Wang, X., Teng, L., Li, J., Zhang, J., et al. (2025). Efficacy of non-invasive brain stimulation interventions on cognitive impairment: an umbrella review of meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 22:22. doi: 10.1186/s12984-025-01566-3
Xie, W., and Zhang, W. (2017). Mood-dependent retrieval in visual long-term memory: dissociable effects on retrieval probability and mnemonic precision. Cogn. Emot. 32, 674–690. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2017.1340261
Xin, F., and Yuan, H. (2015). The memory consolidation function of sleep. Adv. Psychol. 5, 199–206. doi: 10.12677/ap.2015.54028
Xiong, H., Guo, R. J., and Shi, H. W. (2020). Altered default mode network and salience network functional connectivity in patients with generalized anxiety disorders: an ICA-based resting-state fMRI study. Evid. Based Complement. Alternative Med. 2020:4048916. doi: 10.1155/2020/4048916
Yang, J., Han, H., Cui, M., Wang, L., Cao, J., Li, L., et al. (2006). Acute behavioural stress facilitates long-term depression in temporoammonic-CA1 pathway. Neuroreport 17, 753–757. doi: 10.1097/01.wnr.0000209044.66482.c5
Yang, J., Wang, G., and Tang, Q. (2018). A study of prospective memory in patients with Parkinson's disease and emotional apathy. Chine. J. Neuromed. 17, 376–380.
Yavas, E. (2024). Differential effects of anxiety levels on dorsolateral prefrontal cortex-mediated emotional working memory. Curr. Psychol. 43, 36897–36910. doi: 10.1007/s12144-024-07129-4
Yin, F., Si, F., Huo, S., Wang, Z., Yang, H., Zhao, X., et al. (2024). Social anxiety modulating early processing for social threat words: an ERP study. Cogn. Emot. 39, 603–613. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2024.2381660
Yizhar, O., Fenno, L. E., Prigge, M., Schneider, F., Davidson, T. J., O'Shea, D. J., et al. (2011). Neocortical excitation/inhibition balance in information processing and social dysfunction. Nature 477, 171–178. doi: 10.1038/nature10360
Yuan, Y., Pan, X., and Wang, R. (2021). Biophysical mechanism of the interaction between default mode network and working memory network. Cogn. Neurodyn. 15, 1101–1124. doi: 10.1007/s11571-021-09674-1
Zarrindast, M. R., and Khakpai, F. (2020). State-dependent memory and its modulation by different brain areas and neurotransmitters. EXCLI J. 19, 1081–1099. doi: 10.17179/excli2020-2612
Zerbes, G., and Schwabe, L. (2019). Across time and space: spatial-temporal binding under stress. Learn. Mem. 26, 473–484. doi: 10.1101/lm.050237.119
Zhang, D., Xie, H., He, Z., Wei, Z., and Gu, R. (2018). Impaired working memory updating for emotional stimuli in depressed patients. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 12:65. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2018.00065
Zhang, H.-H., Meng, S.-Q., Guo, X.-Y., Zhang, J.-L., Zhang, W., Chen, Y.-Y., et al. (2019). Traumatic stress produces delayed alterations of synaptic plasticity in basolateral amygdala. Front. Psychol. 10:2394. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02394
Zhang, J., Ouyang, J., Liu, T., Wang, X., Gao, B., Zhang, J., et al. (2025). Triangular wave tACS improves working memory performance by enhancing brain activity in the early stage of encoding. Neurosci. Bull. 41, 1213–1228. doi: 10.1007/s12264-025-01413-4
Zhang, L., Zhang, Y., Guo, W., Ma, Q., Zhang, F., Li, K., et al. (2024). An effect of chronic negative stress on hippocampal structures and functional connectivity in patients with depressive disorder. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 20, 1011–1024. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S460429
Zhang, M., Li, P., Yu, L., Ren, J., Jia, S., Wang, C., et al. (2022). Emotional body expressions facilitate working memory: evidence from the n-back task. PsyCh. J. 12, 178–184. doi: 10.1002/pchj.616
Zhantleuova, A., Karimova, A., Andreou, A. P., Kustubayeva, A. M., Giniatullin, R., and Davletov, B. (2025). Focused modulation of brain activity: a narrative review. Biomedicines 13:1889. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13081889
Zhao, X.-H., Wang, P.-J., Li, C.-B., Hu, Z.-H., Xi, Q., Wu, W.-Y., et al. (2007). Altered default mode network activity in patient with anxiety disorders: an fMRI study. Eur. J. Radiol. 63, 373–378. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.02.006
Keywords: state-dependent memory (SDM), memory retrieval, memory encoding, memory storage, neural circuits
Citation: Liu Y, Zhang G, Qi R, Ma J and Xu J (2025) State-dependent memory mechanisms insights from neural circuits and clinical implications. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 19:1629796. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1629796
Received: 16 May 2025; Accepted: 09 October 2025;
Published: 30 October 2025.
Edited by:
Magdalena Pereyra, Institut de l'Audition, Institut Pasteur, FranceReviewed by:
Ludovico Silvestri, University of Florence, ItalyJuan Facundo Morici, Institut National de la Santé et de la Recherche Médicale (INSERM), France
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Zhang, Qi, Ma and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianguang Xu, eGlnQHNodXRjbS5lZHUuY24=; Jie Ma, ZHJtYWppZUAxMjYuY29t; Rui Qi, cWlydWkzNkAxMjYuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Yang Liu
Yang Liu Guohui Zhang
Guohui Zhang Rui Qi
Rui Qi Jie Ma
Jie Ma Jianguang Xu
Jianguang Xu