- 1Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, United States
- 2Center for Neurotherapeutics, University of South Carolina, Columbia, SC, United States
Microtubule-associated protein (MAP) tau stabilizes neuronal microtubules in axonal transport and contributes to healthy synapses. In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), tau proteins become hyperphosphorylated, reduce microtubule binding, and aggregate into paired helical filaments (PHFs) in neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs). Although the steps of this dysregulation of tau are well established, the mechanisms by which each step is regulated remain incompletely understood. Misfolded protein aggregates, such as amyloid β-peptides (Aβ), are degraded by autophagy and lysosomal pathways, in which small GTPases play essential roles. However, how tau aggregates and spreads from nerve cells and whether small GTPases similarly play pivotal roles are not as clear. Here we review the recent evidence to propose that small GTPases are important in tau protein posttranslational phosphorylation, aggregation, and clearance. As such, small GTPases may prove to be important therapeutic targets that can reduce the AD tau burden.
1 Physiological roles of amyloid precursor proteins (APPs) and microtubule-associated protein (MAP) tau
Intracellular neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) and extracellular amyloid plaques (or senile plaques, SPs) are the two most prominent hallmark pathologies of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (Plascencia-Villa and Perry, 2022). SP consists of a core structure of Aβs, which are derived from the much larger amyloid precursor protein (APP) (Zheng and Koo, 2011). While APP plays important roles in normal physiology (Zheng et al., 1995), the overburden of Aβ deposition in brain tissue elicits a cascade of events that are harmful for the brain (Jagust, 2016).
On the other hand, microtubule-associated protein (MAP) tau is the major component of NFTs (Grundke-Iqbal et al., 1986; Ihara et al., 1986; Kosik et al., 1986; Wood et al., 1986). Tau proteins are the integral component of neuronal microtubules where proteins synthesized in the neuronal perikaryon are transported using microtubules as a “railroad” track to the distant synapses. Under physiological conditions, tau proteins localize selectively to axons and stabilize axonal microtubules, whereas other MAPs, such as MAP2, are localized predominantly to the dendrites (Binder et al., 1986). In addition to the role of tau protein as a stabilizer of microtubules, tau has demonstrated involvement in a collection of other cellular processes. Several studies have demonstrated tau interactions with NMDA receptors can regulate NMDA receptor activity, indicating a possible role in synaptic plasticity (Sinsky et al., 2021; Mondragón-Rodríguez et al., 2012). Furthermore, tau has exhibited the ability to bind to nucleic acids to prevent oxidative damage, as well as regulate axonal myelination (Kent et al., 2020; Sinsky et al., 2021).
While Aβ peptides are linked to AD pathologies, it is now postulated that they may also play important roles in protecting brain functions. For example, studies suggest that Aβ may be a response to pathogen-induced neuroinflammation (Wozniak et al., 2009; Eimer et al., 2018; Itzhaki et al., 2016; Jorfi et al., 2023). Similarly, the hyperphosphorylation of tau proteins is integral in AD pathologies but is increased during normal development and is involved in regulating neurite outgrowth (Stoothoff and Johnson, 2005). There is also evidence that tau displays a transient protective effect against Aβ-induced cognitive impairments in animal models (Emmerson et al., 2024).
2 AD tau proteins and their roles in disease progression
In AD, earlier investigations discovered that NFTs consist of, almost exclusively, hyperphosphorylated tau proteins (Grundke-Iqbal et al., 1986; Wood et al., 1986; Ihara et al., 1986). The follow up studies showed that AD brain lysates enriched with tau proteins displayed a reduced taxol-stabilized microtubule binding capability (Nieto et al., 1991; Bramblett et al., 1992). Lu and Wood (1993) provided direct evidence in a binary interaction study that tau proteins isolated from AD brain are defective at promoting tubulin assembly. The observation was further supported by Yoshida and Ihara (1993) that tau in PHF is almost assembly-incompetent. These studies thus validated the hypothesis that AD tau is compromised in its functions to nucleate, bundle, and stabilize microtubules.
On the other hand, it is hypothesized that hyperphosphorylated AD tau proteins are more readily detached from microtubules and form aggregates to spread from one brain region to another (Miao et al., 2019; Wegmann et al., 2021). The tau aggregates are likely to induce the increased detachment of microtubule-bound tau proteins and thus further destabilize axonal microtubule systems, leading to synaptic loss and dementia. However, the molecular mechanisms by which the tau aggregates form and spread are not completely understood. Recent studies suggest that in addition to abnormal phosphorylation, other factors like polyanions can influence tau aggregation (Fichou et al., 2018). RNA, the most potent polyanion trigger of tau aggregation in vitro (Kampers et al., 1996), appears to be the most abundant in the neuronal cytoplasm (McMillan et al., 2023). It is likely that a disrupted nuclear-to-cytoplasmic transport can lead to nuclear RNAs mis-localizing to the cytoplasm where they bind to tau proteins to promote tau aggregation. Studies have shown that tau aggregates released from the neurons can spread to other neurons by macropinocytosis (Wu et al., 2013; Wu et al., 2016; Evans et al., 2018). In this regard, defective intracellular trafficking and vesicular transport are also a likely culprit of AD tau pathogenesis.
3 Small GTPases: their physiological roles in cell signaling
It is important to note that the defective intracellular transport underlies the formation of many neuropathological inclusions such as Aβ and TDP-43 (Chou et al., 2018; Zhuravleva et al., 2021). The potential links between mis-localized RNAs and tau aggregation suggest that this crucial dysregulation occurs at intracellular trafficking and transport of cellular organelles and proteins, where small GTPases play a pivotal role.
Small GTPases of Ras superfamily are 21 kDa enzymes that bind and hydrolyze guanosine triphosphate (GTP). They are molecular switches that activate and regulate downstream signaling pathways (Dautt-Castro et al., 2024). Small GTPases have two states: an active GTP-bound state and an inactive GDP-bound state (Figure 1). Guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs) can remove GDP from a small GTPase in exchange for GTP, activating the complex. GTPase activating proteins (GAPs) inactivate GTP-bound small GTPases by accelerating the hydrolysis of the bound GTP to GDP. GDP dissociation inhibitors, or GDI, bind to small GTPases and prevent the dissociation of GDP that keeps the enzymes in an inactive state (Aguilar et al., 2017). GDI proteins also prevent small GTPases from interacting with organelle membranes to activate further signaling.

Figure 1. Small GTPases cycle between a GDP-bound/inactive state through GAP activity and a GTP-bound/active state through GEF activity.
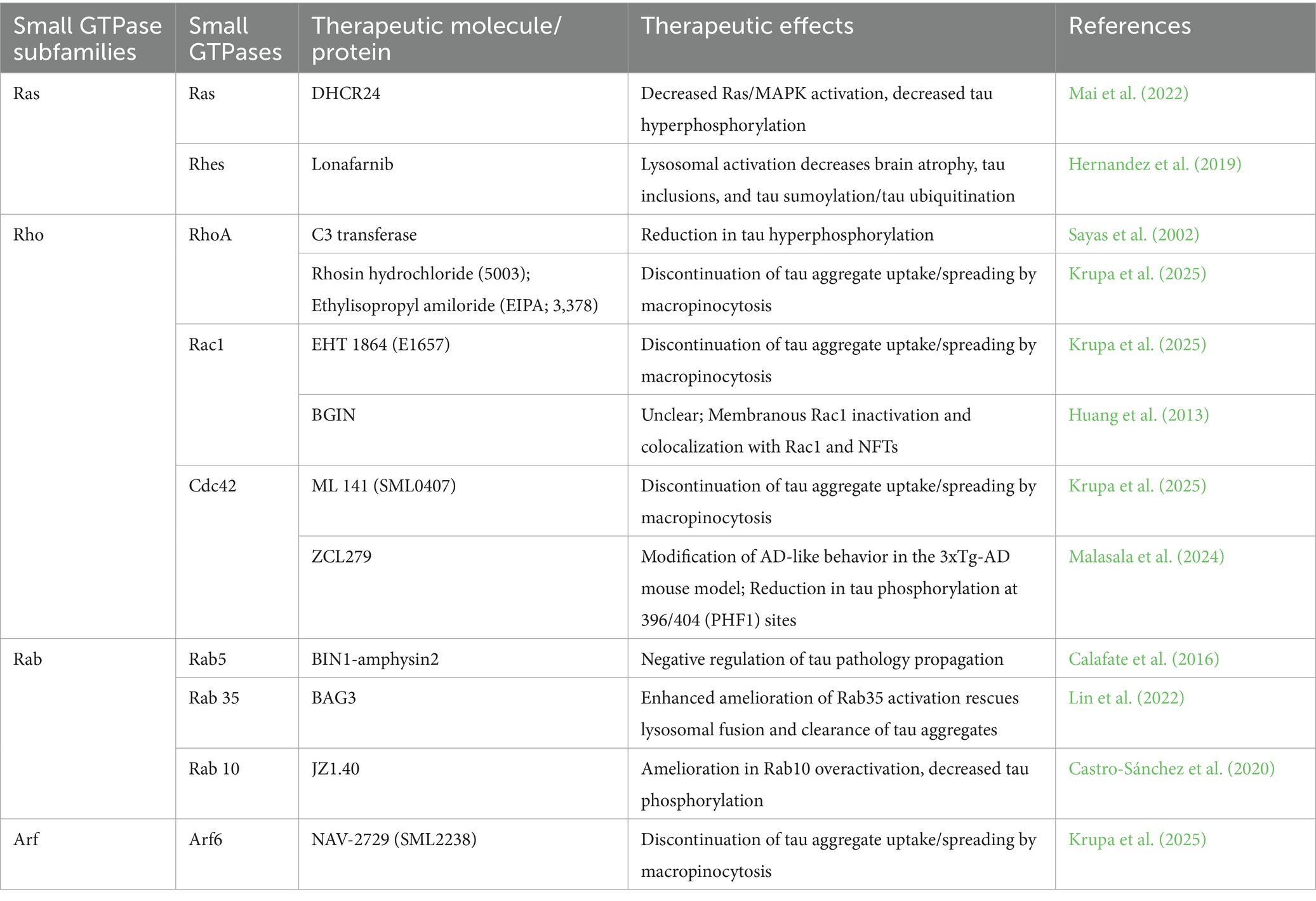
Members of the Ras superfamily regulate signaling pathways involved in many cellular processes. The most prominent small GTPase subfamilies include Ras, Ran, Rho, Rab, Arf, and Miro, which control proliferation, nuclear transport, cytoskeletal regulation/dynamics, membrane trafficking, vesicular transport, and mitochondrial transport, respectively (Kay et al., 2018; Jeong et al., 2022; Arrazola Sastre et al., 2020) (Figure 2). The Ras superfamily also extends to more than 170 small GTPases that include GEM and RRAG involved in autophagy and lysosomal functions (Colicelli, 2004). While many of these cellular functions are dysregulated in AD and related dementias (ADRDs), impaired intracellular protein transport and trafficking are among the earliest neuropathogenic events, including defective protein processing and phosphorylation, as well as misfolding and aggregation (Ferreira et al., 1997; Cataldo et al., 2000; Hunter et al., 2013; Wegmann et al., 2021). As we review the evidence, we hypothesize that small GTPases are important in tau protein posttranslational phosphorylation and distribution, aggregation and propagation, and clearance.
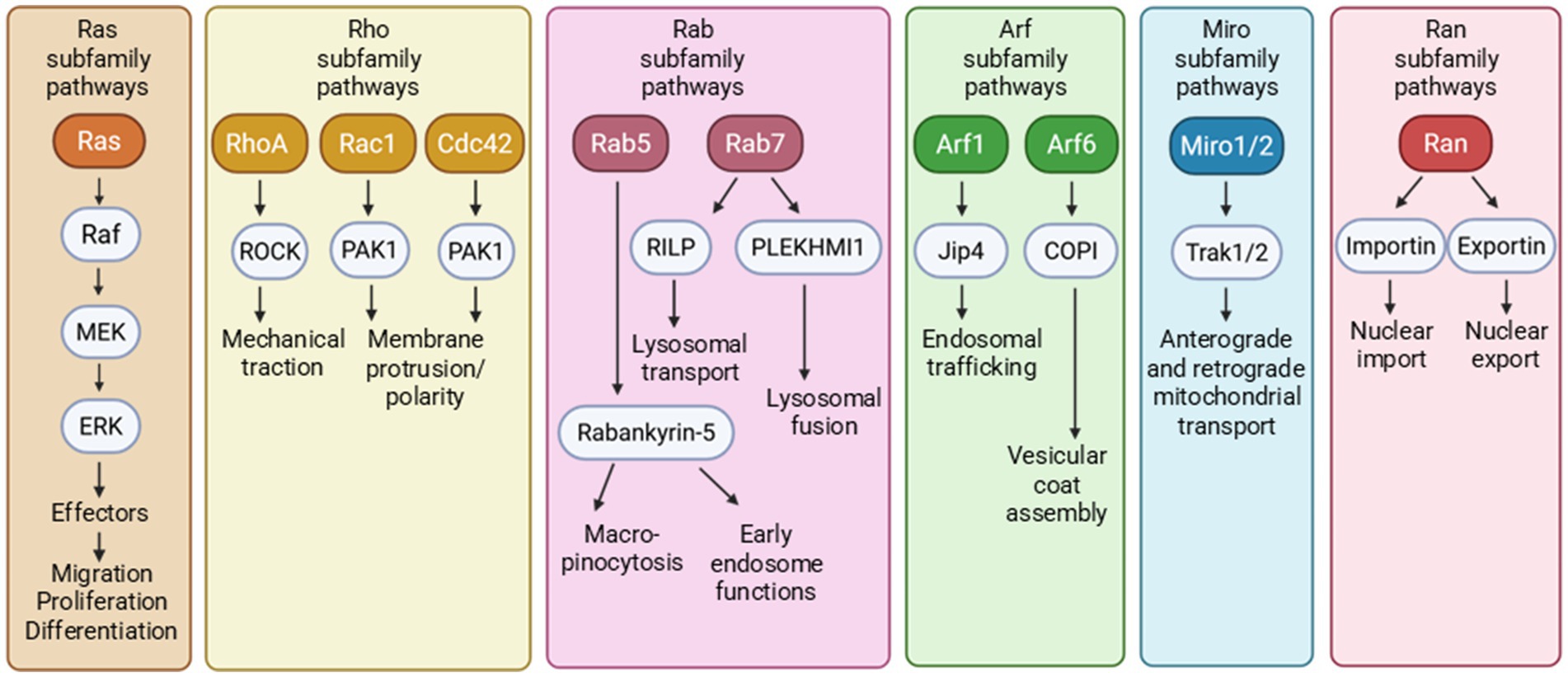
Figure 2. The small GTPases of Ras superfamily encompass multiple small GTPase subfamilies that affect numerous downstream cellular functions.
4 The roles of small GTPases in tau hyperphosphorylation
The hyperphosphorylation of tau is an important step in AD tau pathogenesis. Evidence suggests that small GTPases and related signaling networks play a role in tau hyperphosphorylation (Figure 3).
Figure 3. Small GTPase pathways, particularly those of the Ras, Rho, and Rab subfamilies appear to indirectly and directly induce changes in tau phosphorylation. More specifically, the dysregulation/overactivation of small GTPases and their pathways often contribute to tau hyperphosphorylation. Solid arrowheads indicate observed or reported connections that activate/upregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process; dotted arrowheads indicate unknown or hypothetical/indirect connections that activate/upregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process. Solid flathead arrows indicate observed or reported connections that inhibit/downregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process; dotted flathead arrows indicate unknown or hypothetical/indirect connections that inhibit/downregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process.
In AD disease models, the Rab, Rho, and Ras small GTPase subfamilies are implicated in tau phosphorylation through APP exposure. For instance, one study demonstrated that Rab5 was overactivated in AD and was typically mediated by APP-β secretase cleaved C-terminal fragment (APP-βCTF) (Pensalfini et al., 2020). However, Rab5 could also be activated independently of APP-βCTF in the PA-Rab5 mouse model, causing increased glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) activity to promote tau hyperphosphorylation. A classical member of the Rho GTPase subfamily, Rac1 additionally exhibited abnormal activation, as seen in the hippocampus of 6-week-old 3xTg-AD mouse model (Borin et al., 2018). The in vitro investigation of Rac1-specific signaling demonstrated that Rac1 activation induces tau hyperphosphorylation at residue pT181 through the increased processing of APP.
Other studies demonstrate that with elevated APP exposure, Ras signaling is similarly increased, causing various downstream effects. In PC12 cells, secreted APP stimulates MAPK or ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase), an effector of the Ras pathway (Greenberg et al., 1994). Further, a PC12 dominant inhibitory Ras cell line prevented secreted APP from stimulating MAPK/ERK, impeding tau phosphorylation, while the opposite effect was observed in cell lines without Ras inhibition. Likewise, APP knockdown (KD) in B103 rat neuroblastoma cells inhibited Ras–ERK activity. Finally, primary rat neurons treated with Aβ produced selective phosphorylation of adult tau isoforms (Ferreira et al., 1997) and increased Ras–ERK signaling and GSK-3 activation along with phosphorylated tau (Kirouac et al., 2017).
Interestingly, in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease (PD), overexpressed α-synuclein in E18 cortical neurons induced a notable increase in the activation of small GTPases Rab5 and Rab7 (Fang et al., 2017). This increased Rab subfamily activation did not coincide with abnormal tau phosphorylation, suggesting that alternative pathways may induce tau hyperphosphorylation in PD tauopathies.
In addition to APP playing a role in small GTPase-induced tau hyperphosphorylation, the related GSK-3 pathway is involved in modulating tau phosphorylation. Namely, the Rab and Ras subfamilies have been implicated in regulating the GSK-3 pathway that leads to an increase in phosphorylated tau in murine models (Kirouac et al., 2017; Pensalfini et al., 2020). Along with these subfamilies, Rho subfamily small GTPases appear to have a connection with GSK-3 and tau hyperphosphorylation as well. This relation was exemplified in rat cerebellar granule neurons, in which lysophosphatidic acid (LPS) induced G protein subunit Gα13 to interact with RhoA (Sayas et al., 2002). This interaction activated GSK-3β to induce tau hyperphosphorylation and could be blocked by RhoA inhibition with C3 transferase.
Related to the GSK-3 signaling pathways are the MAPK/ERK signaling pathways associated with Ras, which may likewise induce tau hyperphosphorylation. MAPK/ERK is a downstream effector of the Ras/Raf cascade which can regulate and be regulated by GSK-3 (Ding et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2006). Expanding upon the studies described above, increased MAPK/ERK activity can led to increased tau phosphorylation (Greenberg et al., 1994; Kirouac et al., 2017). In fact, MAPK/ERK can convert wildtype tau to hyperphosphorylated tau and reduce its ability to promote microtubule assembly. Additionally, microinjected MAPK/ERK can result in AD-like tau phosphorylation at serine 396/404 (PHF-1) residues in cultured hippocampal neurons (Lu et al., 1993).
Additional literature supports this evidence. In one study, treating human wild-type tau-expressing SH-SY5Y cells with zinc increased the phosphorylation of serine 214 in tau, whereas suppression of the Ras–Raf-MAPK pathway inhibited this phosphorylation (Kim et al., 2011). Conversely, synthetase 3β-hydroxysterol-Δ24 reductase (DHCR24) KD in C8D1A astrocytes activated the rafts/caveolae-dependent Ras–MEK–ERK signaling pathway to induce tau hyperphosphorylation (Mai et al., 2022). Furthermore, DHCR24 overexpression prevented Ras–MEK–ERK overactivation, decreasing tau hyperphosphorylation.
Alternatively, Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), a protein prevalent in PD, may play a role in tauopathy development. LRRK2 mutations are among the most common genetic causes of PD, both in familial and sporadic cases. LRRK2 provides an interesting link on small GTPases targeting different neurodegenerative diseases such as AD and PD. Although LRRK2 mutations are not common in AD, it is associated with the downstream kinase substrate Rab subfamily proteins including Rab10 (Liu et al., 2020).
A study analyzing LRRK2-mediated Rab10 phosphorylation in AD patient hippocampal tissues revealed that the pRab10-T73 epitope was associated with NFTs (Yan et al., 2018). Rab10 was similarly found to be highly co-localized with hyperphosphorylated tau. Rab10 was further demonstrated to associate with tau phosphorylation when tauopathy mice treated with LRRK2 inhibitor JZ1.40 exhibited a reversal of Rab10 overactivation and tau hyperphosphorylation (Castro-Sánchez et al., 2020). Besides LRRK2 affecting Rab activity and tau phosphorylation, LRRK2 may achieve similar results through activating MAPK/ERK pathways. Evidence demonstrates that LRRK2 can bind to small GTPases and act as a scaffold to facilitate MAPK/ERK activation (Boon et al., 2014). If LRRK2 mediates tau phosphorylation through the MAPK/ERK pathway, this would corroborate similar instances of small GTPase regulation of tau hyperphosphorylation by MAPK/ERK activity (Lu et al., 1993; Greenberg et al., 1994; Kim et al., 2011; Kirouac et al., 2017; Mai et al., 2022).
Equally important, the Rho GTPase subfamily may regulate tau phosphorylation through means other than APP, MAPK/ERK, and GSK-3 interactions. Rho GTPases can affect tau hyperphosphorylation through direct GAP, GEF, GDI, or effector modulation. For example, Cdc42, a classical Rho subfamily member and crucial regulator of synaptic plasticity, is inactivated by Cdc42GAP. The analysis of a heterozygous Cdc42GAP mouse model with elevated Cdc42 activity suggested that the Cdc42GAP deficiency induced and accelerated AD-like phenotypes while overexpression of dominant-negative Cdc42 reversed synaptic loss and tau hyperphosphorylation (Zhu et al., 2023). The importance of Cdc42 regulation in AD can be further implicated in a recent study in which the modulation of Cdc42 interaction with its selective GEF, intersectin 1 (ITSN1), attenuated AD-like behavior and reduced the hyperphosphorylation of tau at serine 396/404 (or PHF-1) site in the 3xTg-AD mouse model (Malasala et al., 2024).
In another study, RhoGDIα, an inhibitor of Rho activity, was shown to interact with and directly bind to tau (Zhang et al., 2023). Forced expression of RhoGDIα in Aβ25-35- and H/R-induced PC12 cells reduced tau hyperphosphorylation and inhibited Caspase-3 activity. In addition, forced RhoGDIα expression in AD and vascular dementia mouse models ameliorated associated pathological symptoms.
A different study revealed that CDK5 could regulate tau phosphorylation via Rac1. In 24-month-old 3xTg-AD mice, CDK5 dysregulation led to tau hyperphosphorylation, whereas CDK5 KD with RNAi reduced hyperphosphorylated tau and NFTs (Posada-Duque et al., 2015). Along with CDK5 KD, p35 over-expression, and constitutively active Rac1 in primary hippocampal neurons could induce similar neuroprotective effects. These findings appear to be at odds with a study that found a correlation between Rac1 activation and tau hyperphosphorylation in 6-week-old 3xTg-AD mice (Borin et al., 2018). These data suggest that the Rac1 associated manifestation of AD tau pathogenesis may depend on the disease stage, and the different upstream targeting of Rac1 regulation may prove valuable in preventing tau hyperphosphorylation.
Likewise, dysregulation of the downstream effectors of Rho GTPase, for example, Rho kinases (ROCK1 and ROCK2), may play a role in pathways associated with tau hyperphosphorylation. Specifically, studies showed that ROCK1 could phosphorylate the Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) to promote tau dephosphorylation (Wang et al., 2016). Furthermore, ROCK1 KD by microRNA-146a induced abnormal tau hyperphosphorylation, and supplemental analysis of AD patient brain tissue revealed ROCK colocalization with hyperphosphorylated tau in early NFTs. In addition, Caspase-2, an activator of ROCK2, was required for cognitive decline in human-APP transgenic mice (Pozueta et al., 2013). This was also demonstrated by decreased tau phosphorylation levels in J20 mice with Caspase-2 KO. On the other hand, ROCK2 inhibition by fasudil in mouse hippocampal neurons reduced tau phosphorylation (Gao et al., 2019). These findings suggest that significant ROCK dysregulation, whether regulated by Rho or other proteins, can lead to tau hyperphosphorylation.
While a large number of studies focus on tau phosphorylation, it is critical to consider other post-translational modifications (PTMs) that may contribute to tauopathy (Avila et al., 2004). Similarly to how small GTPases are implicated in tau phosphorylation, small GTPases may play a role in other potentially pathogenic tau PTMs. A reduction in Rhes via lonafarnib coincided with a similar decrease in tau SUMOylation and ubiquitination (Hernandez et al., 2019). Other evidence suggests that Rho and ROCK may activate Caspase 3 in a positive-feedback loop-like manner (Shi and Wei, 2007). Consequently, Rho activity may create tau PTMs downstream, as Caspase 3 demonstrates the ability to generate tau truncations commonly seen in AD brain tissues (Gu et al., 2020). Ras may play a part in its acetylation. According to Alquezar et al. (2021), CREB-binding protein, a histone acetyltransferase, appears to induce tau acetylation and shows altered levels in AD patients and an AD mouse model. Another study demonstrated the ability of the Ras/MAPK pathway to recruit CREB-binding protein (Foulds et al., 2004), suggesting that the Ras small GTPase pathway may potentially trigger tau PTMs through acetylation.
5 The roles of small GTPase in tau aggregation
In addition to small GTPase activity affecting tau hyperphosphorylation, small GTPases and their associated pathways may further play a part in the propagation and formation of tau aggregates and NFTs (Figure 4).
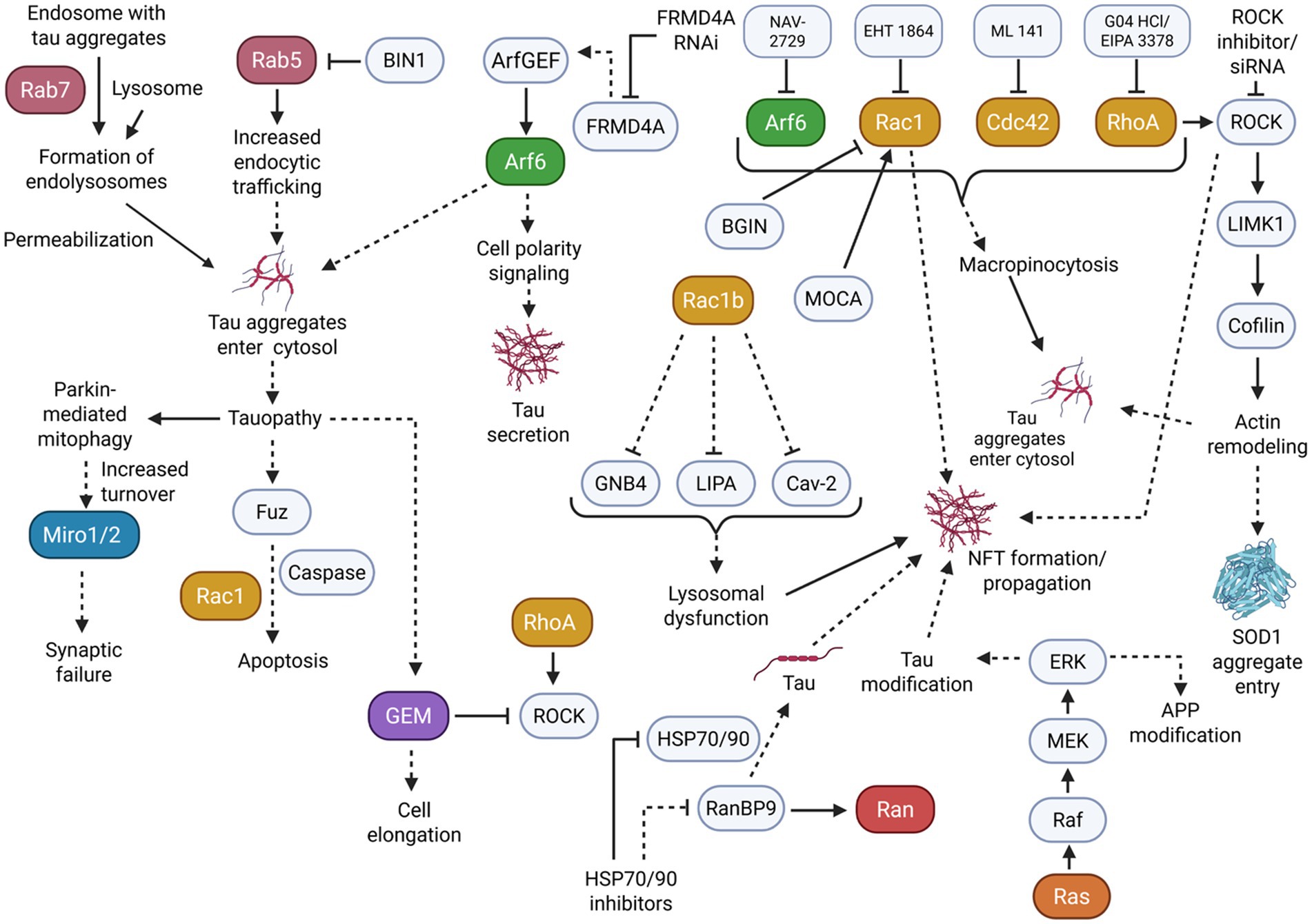
Figure 4. Many small GTPase subfamilies play a role in the propagation of tauopathy. Mainly, dysregulation in vesicular trafficking and membrane dynamics resulting from small GTPase activity can induce an increased entrance/secretion of tau aggregates and the formation of NFTs to further burden cells. Solid arrowheads indicate observed or reported connections that activate/upregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process; dotted arrowheads indicate unknown or hypothetical/indirect connections that activate/upregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process. Solid flathead arrows indicate observed or reported connections that inhibit/downregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process; dotted flathead arrows indicate unknown or hypothetical/indirect connections that inhibit/downregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process. Curly brackets represent multiple molecules or proteins involved in one of the previously described connections.
The Rab small GTPase subfamily, which plays a key role in membrane trafficking, may become dysregulated and promote the subsequent propagation of tauopathy. This dysregulation can be demonstrated in HEK 293T cells and tau transgenic rTg4510 mice. For example, Rab7 overexpression substantially increased tau aggregation through membrane permeabilization of endolysosomes (Polanco et al., 2021). These effects were remediated by Rab7 KD to modify lysosomal function. Studies using rat neurons showed that Rab5 was overactivated due to low BIN1-amphiphysin2 (BIN1), which displayed tau pathology propagation (Calafate et al., 2016). Notably, low BIN1 expression increased the internalization of aggregates, whereas BIN1 overexpression prevented these effects. These findings indicate that excessive Rab activity could promote the beginnings of tau pathology.
As seen with Rab GTPase dysregulation, dysregulation in Arf GTPase can also affect vesicular transport pathways to contribute to elevated tau aggregation. To demonstrate, in another study using HEK293T cells, Arf activity was necessary for tau secretion (Yan et al., 2016). More specifically, tau secretion induced by FRMD4A only occurred in the presence of Arf GEF interactors, while Arf6 and cell polarity signaling stimulated tau secretion. This secretion was effectively blocked by FRMD4A RNAi in mature cortical neurons. On the other hand, in human iPSC (induced pluripotent stem cell) neurons, Arf6 also appears to positively regulate tau aggregate entry by macropinocytosis, as the uptake and propagation of tau aggregates was attenuated by Arf6 inhibition (Krupa et al., 2025).
Further evidence implicates the Rho small GTPase family in tau pathology propagation by affecting the cytoskeletal system. This was seen in a study using the SOD1G93A transgenic mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Rho GTPase, ROCK1, and LIMK1 kinases activity induced cortical actin remodeling for the cell entry of tau aggregates (Zhong et al., 2018). Particularly, inhibiting Rho and ROCK increased cofilin-1 activity to change actin dynamics and elevate aggregate entry. Rho family members also regulate tau aggregate entry through macropinocytosis, similarly to Arf6, in iPSC neurons. Rac1, Cdc42, and RhoA inhibition were able to reduce the uptake of tau aggregates by macropinocytosis (Krupa et al., 2025).
As opposed to secreting or taking in aggregates, Rho-related tau propagation also appears to occur through inducing the formation of NFTs and aggregates. For example, Rac1b, a constitutively active splice variant of Rac1 GTPase, colocalized significantly with tau in AD human brain tissues (Perez et al., 2012). Further single-cell gene expression profiling showed down-regulation of caveolin 2, GNB4, and lipase A in AD Rac1b-positive/p75NTR-labeled cholinergic neurons compared with Rac1b-negative/p75NTR-labeled neurons, implicating Rac1b as a modulator of NFT formation and membrane dysfunction in AD.
As previously described, ROCK may also play a role in tau pathology. ROCK inhibitor Y27632 treatment on ischemic rats reduced PHF immunoreactivity, demonstrating a potential for the positive regulation of ROCK on NFT formation (Castro-Alvarez et al., 2011).
Similarly, in another study, Rac1 signaling in HeLa cells was affected by BARGIN (BGIN), a brain-specific RhoGAP variant (Huang et al., 2013). BGIN activity caused membranous Rac1 inactivation, while AD brain tissues revealed a colocalization of BGIN and Rac1 with NFTs. However, studies using APP-expressing cell models have shown that increased levels of Aβ correlate with increased BGIN/poly-Ubiquitination interactions. This suggests that BGIN may be involved in Rac1 inactivation in response to proteotoxicity in AD. Alternatively, the loss of Modifier of cell adhesion (MOCA), a GEF of Rac1 typically found in NFTs, decreases cofilin inactivation and alters LIMK activity (Chen et al., 2009). These changes resulted in axonal degeneration and sensorimotor impairments in mice. Considering the complex roles of Rac1 in modulating tau phosphorylation, the close association of Rac1 and its regulators in NFTs may implicate a regulatory role of Rac1 in NFT formation and propagation.
In addition to Rho GTPases affecting tau aggregation, tauopathy models may have a reciprocal effect on Rho and Rho-related proteins. In particular, Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1 (Miro1) experienced an increased turnover in tauopathy mouse neurons as a result of an extensive activation of Parkin-mediated mitophagy (Jeong et al., 2022). Overexpressing Miro1 levels rescued mitochondrial anterograde movement, reversing the effects of synaptic failure induced by tau accumulation. In another study, a Drosophila model expressing excessive tau induced the upregulation of Fuz, a protein involved in planar cell polarity signaling (Chen et al., 2018). This upregulation triggered neuronal apoptosis through the Rac1 GTPase/Caspase signaling pathways, consequently indicating that Rac1 downstream targeting may also relieve neurodegeneration as a result of tauopathy.
Further evidence demonstrates that Gem GTPase, an extended Ras superfamily member in the RGK subfamily and a negative regulator of the Rho-ROCK pathway, is also affected by tau interactions. Gem was significantly elevated in the brains of tau-deficient mice. Overexpressed Gem induced cell elongation in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells that do not express tau (Oyama et al., 2004). Co-expression of tau led to anti-elongation activity in CHO cells.
Separate evidence suggests that small GTPases other than Rho, Arf, and Rab may be involved in tau aggregation. This is seen in part through a study that demonstrated activating the Ras-dependent MAPK/ERK cascade in AD patient brain samples allowed the mediation of post-transcription modification of APP and tau (Gärtner et al., 1999). Notably, Ras was significantly elevated in the initial stages of AD before SP and NFT formation. These results could potentially implicate the Ras pathway activity as either an initiator of tau propagation or a consequence of other neurodegenerative pathways. Similarly to Ras, Ran-binding protein 9 (RanBP9), a regulator of the Ran GTPase, was found to be highly elevated in AD patient brains and AD mouse models (Woo et al., 2017). Inducing overexpression or KD of RanBP9 caused changes in tau levels, and RanBP9 diminished the anti-tau potency of heat shock protein (HSP70/90) inhibitors.
Literature suggests that the misfolded and aggregated tau can further induce the development of tauopathy via prion-like replication mechanisms. Notably, accelerated misfolding of tau can occur through interactions between misfolded/aggregated tau and native tau, which is further exacerbated through seeding and spread to other cells (Ayers et al., 2018; Jackson et al., 2022). As previously elaborated upon, small GTPases, particularly those of the Rab, Rho, and Arf subfamilies, demonstrated the ability to induce tau aggregation, tau seeding, and secretion. By altering membrane dynamics and vesicular transport pathways, the dysregulation of small GTPases appears to contribute to the prion-like pathogenesis of tau.
6 The roles of small GTPase in tau clearance
As well as small GTPases regulating tau aggregation, literature suggests that small GTPases play a role in the clearance of tau aggregates. This clearance is particularly demonstrated through lysosomal pathways. Careful regulation of these small GTPase pathways appears to be critical to clearance, as their dysregulation may promote further tau aggregation (Figure 5).
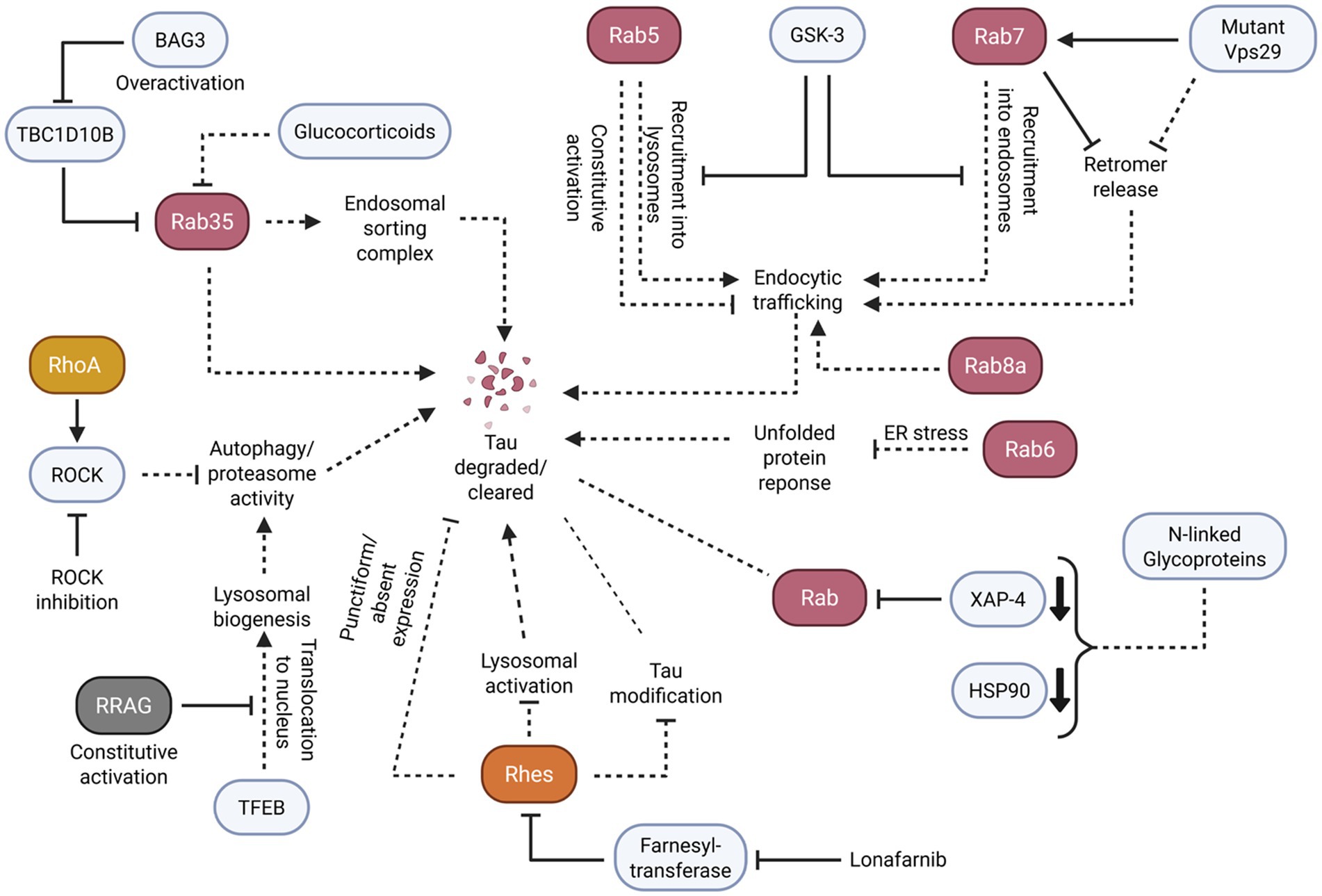
Figure 5. Small GTPases facilitate the proper clearance of tau and tau aggregates through the careful regulation of endosomal/lysosomal trafficking and activation of autophagy responses. Solid arrowheads indicate observed or reported connections that activate/upregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process; dotted arrowheads indicate unknown or hypothetical/indirect connections that activate/upregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process. Solid flathead arrows indicate observed or reported connections that inhibit/downregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process; dotted flathead arrows indicate unknown or hypothetical/indirect connections that inhibit/downregulate a protein, signaling molecule, or cellular process. Dotted lines without arrowheads or flathead arrows represent an unknown or hypothetical/indirect connection between proteins, signaling molecules, and/or cellular processes. Curly brackets represent multiple molecules or proteins involved in one of the previously described connections. Small bold, downturned arrowheads represent a decrease in protein levels.
In particular, the Rab small GTPase subfamily demonstrated potential key roles in tau clearance through lysosomal and endolysosomal processing. Active Rab35 appears to facilitate the proper functioning of the endosomal sorting complex to mitigate tau aggregation. For example, in human AD brains and P301S tau transgenic mice, BAG3 overexpression rescued TBC1D10B-induced Rab35 inactivation (Lin et al., 2022). Conversely, Rab35 inactivation yielded impairment in the downstream endosomal sorting complex, impeding lysosomal fusion. This outcome consequently led to a failure of tau clearance. Likewise, Rab35 inactivation induced by glucocorticoids in N2a cells impaired tau degradation, while restoring Rab35 activity ameliorated the effects of glucocorticoid-induced tau accumulation (Vaz-Silva et al., 2018).
Like Rab35, Rab5 and Rab7 regulate endosomal function, particularly in early and late endosomes, which is crucial to cellular clearance. To illustrate these functions, GSK-3 inhibition in MEF cells increased the recruitment of Rab5 into endosomes and the clustering of Rab7/RILP into lysosomes (Avrahami et al., 2020). Further results revealed that constitutively active Rab5 caused the dysfunction of endocytic traffic despite GSK-3 inhibition, preventing a restoration of lysosomal acidification. Alternatively, in Drosophila neurons, Rab7 facilitated the endosomal binding and release of retromer, a protein-recycling complex part of the endolysosomal pathway (Ye et al., 2020). Prolonged Rab7 activation and retromer binding caused by a mutant retromer Vps29 subunit led to lysosomal stress and impaired clearance. In addition, reducing the amount of Rab7 rescued clearance by autophagy in Vps29 mutant brains. As a result, Rab5 and Rab7 regulation of endocytic traffic appears to be crucial to clearance pathways, supporting its potential role in tau clearance.
Rab8a, another protein involved in protein transport, appears to have a comparable role in aggregate clearance. For example, one study that used H4 cells with induced Rab8a overexpression resulted in a reduction in total tau and phosphorylated tau (Parmar, 2024). In comparison, with mutant, non-functioning Rab8a, no reduction in tau was observed. It is important to note that Rab8a has already been demonstrated to accelerate endocytosed Aβ trafficking to lysosome expression, suggesting that Rab8a can also regulate tau clearance through similar means.
Outside of the Rab subfamily, the Rho and RRAG GTPases may also regulate tau clearance pathways through lysosomes and autophagy. For instance, one study that inhibited ROCK in tau-expressing M1C cells and primary cultured mouse neurons reduced the total and phosphorylated tau protein (Hamano et al., 2020). In addition, ROCK inhibition activated the autophagy and proteasome pathways for the degradation of tau protein. Another study that used cultured primary mouse neurons demonstrated that the nuclear translocation of transcription factor EB (TFEB) mediated lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy to clear aggregated tau (Akwa et al., 2023). On the contrary, neurons with constitutively active RRAG GTPases sequestered TFEB in the cytosol, preventing tau clearance.
In addition to small GTPases managing tau clearance through lysosomal/endosomal pathways, small GTPases may facilitate tau clearance through post-translational control and modification pathways. An example of this is seen in a study examining the brains of AD and control patients. Analysis revealed that there was Rab6 upregulation in the AD temporal cortex during the same stage as unfolded protein response (UPR) activation (Scheper et al., 2007). Notably, there was some colocalization of Rab6 and hyperphosphorylated tau, and there was a strong correlation between Rab6 and BiP, a protein involved in protein processing. Additional evidence supports this association between Rab6 and the UPR, as Rab6 activity was shown to modulate the UPR after prolonged ER stress (Elfrink et al., 2012). These studies suggest that Rab6 may play a role in redirecting proteins, including tau, to the ER for subsequent degradation.
In a separate study, AD brains exhibited altered levels of concanavalin-A (Con-A), a protein involved in N-linked-glycoprotein binding (Owen et al., 2009). AD hippocampus contained decreased Con-A-associated protein levels of Rab GDI XAP-4 and HSP90, which are notably involved in regulating membrane trafficking and tau association. The data of this study may further support Rab dysregulation as a contributor of tau clearance failure.
Similarly, Rhes, a Ras subfamily-related small GTPase, appears to manage tau clearance with post-translational control and modification pathways. To demonstrate, inhibiting farnesyltransferase with lonafarnib in a mouse model of tauopathy exhibited a reduction in Rhes and a decrease in brain atrophy, tau inclusions, tau sumoylation, and tau ubiquitination (Hernandez et al., 2019). Furthermore, the reduction of tau pathology through Rhes inactivation was operated through lysosomal activation. In another study, histological examination of human tauopathy brains revealed that neurons with punctiform or absent patterns of Rhes tended to include elevated levels of tau aggregates while neurons with diffuse Rhes distribution had lower tau (Ehrenberg et al., 2021). Likewise, these Rhes distributions also affected the frequency of post-translational tau modifications.
Here, a summary table is presented to illustrate the functional relationship between small GTPases and tau protein posttranslational phosphorylation and distribution, aggregation and propagation, and clearance (Table 1).
7 Targeting small GTPases as a treatment option to clear tau pathologies
The important modulatory roles of small GTPases in AD tau pathogenesis, such as hyperphosphorylation, aggregation, and propagation, suggest that this large Ras superfamily of signaling proteins may be a therapeutic target for AD and ADRD. They are particularly suitable for drug development in chronic diseases like neurodegenerative disorders because they are molecular switches, and their activation and inactivation can be controlled by GEFs, GAPs and GDIs to achieve tissue and cell selectivity.
Over the past decades, many small GTPase modulators have been developed. They are being applied widely in investigations of cardiovascular disorders and stroke, stem cell functions, infectious and inflammatory diseases, neurological disorders, and cancer. However, there are very few clinical applications of small GTPase modulators for neurodegenerative diseases (Table 2).
Targeting the RhoA downstream effector ROCK is among the most notable therapeutic approaches reviewed in neurodegenerative disease research (Zheng et al., 2025; Weber and Herskowitz, 2021). Fasudil and its derivatives were approved in the 1990’s for clinical treatment of vasospasm. But they have also inhibited ROCK and decreased phosphorylated tau in AD neuro-spheroids (Giunti et al., 2023) and in primary neurons (Hamano et al., 2020). They are currently in clinical trials for tauopathies of progressive supranuclear Palsy-Richardson syndrome and corticobasal syndrome in the US (NCT04734379). Fasudil is also under compassionate use for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis in the US (NCT03792490) and Europe (2017-003676-31) (Zheng et al., 2025).
Evidence also shows that other classical Rho GTPases, such as Rac1 and Cdc42, are dysregulated in AD. Like RhoA signaling, there were conflicting studies about the overactivation or inactivation in Rac1 and Cdc42 associated with AD (Huesa et al., 2010; Nik Akhtar and Lu, 2023; Nik Akhtar et al., 2024). Nevertheless, NSC23766, a Rac1 selective inhibitor that interferes with the interactions of Rac1 and its GEF Tiam, decreased Aβ levels and prevented Aβ42 peptide-induced cell death (Aguilar et al., 2017). ZCL279, which interferes with the interactions of Cdc42 with its selective GEF, ITSN1, modified AD-like behavior in the 3xTg-AD mouse model and reduced tau phosphorylation at 396/404 (PHF1) sites (Malasala et al., 2024).
Several other small GTPase modulators described here may suggest their targeting potential in AD. Lonafarnib is the first FDA-approved drug for Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome and some types of progeroid laminopathies. It inhibits farnesyltransferase, an enzyme involved in the farnesylation of some small GTPases. The reduction of Ras family protein Rhes and the decreased tau pathologies following lonafarnib treatment (Hernandez et al., 2019) raised the possibility of potential benefits of inhibition of various farnesylated small GTPases in AD.
Finally, LRRK2 inhibitor JZ1.40 reduced Rab10 overactivation and tau hyperphosphorylation in tauopathy mice (Castro-Sánchez et al., 2020). Currently, there are multiple ongoing clinical trials utilizing LRRK2 inhibitors, like BIIB122, DNL201, and DNL151 (Jennings et al., 2023; Hyderi et al., 2025). It remains to be seen whether these LRRK2 inhibitors inhibit PD through Rab subfamily small GTPases and whether the same strategy can apply to AD treatment.
8 Summary
Literature survey revealed many small GTPases involved in AD tau pathogenesis. This included all subfamilies in the Ras superfamily of small GTPases, namely, Ras, Ran, Rho, Rab, Arf, and Miro.
Specifically, small GTPases of the different subfamilies can regulate the different phases of AD tau pathogenesis from hyperphosphorylation, to aggregation and propagation. These findings support targeting small GTPases as a potential AD therapeutic strategy.
It is also important to note that for some small GTPases, such as Rac1, evidence demonstrates that both stimulation and inhibition can lead to the attenuation of some aspects of AD pathogenesis. The context-dependent functions of small GTPases suggest that a minimum level of their activity may be important in physiological functions (Socodato et al., 2023). Alternatively, different small GTPases may exert their effects at different stages of AD pathogenesis in a cell- and region-selective manner.
Author contributions
PH: Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft, Investigation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Methodology. Y-HC: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Conceptualization, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Investigation. QL: Investigation, Resources, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Supervision, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Project administration, Visualization, Validation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported in part by NIH Director’s Transformative Research Award R01 GM146257 and the SC SmartState Center for Economic Excellence.
Acknowledgments
We wish to express deep gratitude to many of our colleagues who have contributed to this ever-developing field which we may have omitted citing their studies in this article. We also acknowledge the use of BioRender software for generating illustrations.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aguilar, B. J., Zhu, Y., and Lu, Q. (2017). Rho GTPases as therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's Res. Ther. 9:97. doi: 10.1186/s13195-017-0320-4
Akhtar, S. N., Tran, T. D., Chen, Y. H., and Lu, Q. (2024). Spatial and planar profiling of Rac1/Cdc42 signaling in Alzheimer's disease brain. J. Alzheimers Dis. 102, 670–682. doi: 10.1177/13872877241291076
Akwa, Y., Di Malta, C., Zallo, F., Gondard, E., Lunati, A., Diaz-de-Grenu, L. Z., et al. (2023). Stimulation of synaptic activity promotes TFEB-mediated clearance of pathological MAPT/tau in cellular and mouse models of tauopathies. Autophagy 19, 660–677. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2022.2095791
Alquezar, C., Arya, S., and Kao, A. W. (2021). Tau post-translational modifications: dynamic transformers of tau function, degradation, and aggregation. Front. Neurol. 11:595532. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.595532
Arrazola Sastre, A., Luque Montoro, M., Gálvez-Martín, P., Lacerda, H. M., Lucia, A. M., Llavero, F., et al. (2020). Small GTPases of the Ras and rho families switch on/off Signaling pathways in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21:6312. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176312
Avila, J., Lucas, J. J., Perez, M., and Hernandez, F. (2004). Role of tau protein in both physiological and pathological conditions. Physiol. Rev. 84, 361–384. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00024.2003
Avrahami, L., Paz, R., Dominko, K., Hecimovic, S., Bucci, C., and Eldar-Finkelman, H. (2020). GSK-3-TSC axis governs lysosomal acidification through autophagy and endocytic pathways. Cell. Signal. 71:109597. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109597
Ayers, J. I., Giasson, B. I., and Borchelt, D. R. (2018). Prion-like spreading in Tauopathies. Biol. Psychiatry 83, 337–346. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2017.04.003
Binder, L. I., Frankfurter, A., and Rebhun, L. I. (1986). Differential localization of MAP-2 and tau in mammalian neurons in situ. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 466, 145–166. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1986.tb38392.x
Boon, J. Y., Dusonchet, J., Trengrove, C., and Wolozin, B. (2014). Interaction of LRRK2 with kinase and GTPase signaling cascades. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 7:64. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2014.00064
Borin, M., Saraceno, C., Catania, M., Lorenzetto, E., Pontelli, V., Paterlini, A., et al. (2018). Rac1 activation links tau hyperphosphorylation and aβ dysmetabolism in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 6:61. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0567-4
Bramblett, G. T., Trojanowski, J. Q., and Lee, V. M. (1992). Regions with abundant neurofibrillary pathology in human brain exhibit a selective reduction in levels of binding-competent tau and accumulation of abnormal tau-isoforms (A68 proteins). Lab. Investig. 66, 212–222
Calafate, S., Flavin, W., Verstreken, P., and Moechars, D. (2016). Loss of Bin1 promotes the propagation of tau pathology. Cell Rep. 17, 931–940. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.063
Castro-Alvarez, J. F., Gutierrez-Vargas, J., Darnaudéry, M., and Cardona-Gómez, G. P. (2011). ROCK inhibition prevents tau hyperphosphorylation and p25/CDK5 increase after global cerebral ischemia. Behav. Neurosci. 125, 465–472. doi: 10.1037/a0023167
Castro-Sánchez, S., Zaldivar-Diez, J., Luengo, E., López, M. G., Gil, C., Martínez, A., et al. (2020). Cognitive enhancement, TAU phosphorylation reduction, and neuronal protection by the treatment of an LRRK2 inhibitor in a tauopathy mouse model. Neurobiol. Aging 96, 148–154. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2020.09.006
Cataldo, A. M., Peterhoff, C. M., Troncoso, J. C., Gomez-Isla, T., Hyman, B. T., and Nixon, R. A. (2000). Endocytic pathway abnormalities precede amyloid beta deposition in sporadic Alzheimer's disease and down syndrome: differential effects of APOE genotype and presenilin mutations. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 277–286. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9440(10)64538-5
Chen, Z. S., Li, L., Peng, S., Chen, F. M., Zhang, Q., An, Y., et al. (2018). Planar cell polarity gene Fuz triggers apoptosis in neurodegenerative disease models. EMBO Rep. 19:e45409. doi: 10.15252/embr.201745409
Chen, Q., Peto, C. A., Shelton, G. D., Mizisin, A., Sawchenko, P. E., and Schubert, D. (2009). Loss of modifier of cell adhesion reveals a pathway leading to axonal degeneration. J. Neurosci. 29, 118–130. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3985-08.2009
Chou, C. C., Zhang, Y., Umoh, M. E., Vaughan, S. W., Lorenzini, I., Liu, F., et al. (2018). TDP-43 pathology disrupts nuclear pore complexes and nucleocytoplasmic transport in ALS/FTD. Nat. Neurosci. 21, 228–239. doi: 10.1038/s41593-017-0047-3
Colicelli, J. (2004). Human RAS superfamily proteins and related GTPases. Sci. STKE 2004:RE13. doi: 10.1126/stke.2502004re13
Dautt-Castro, M., Rebolledo-Prudencio, O. G., Estrada-Rivera, M., Islas-Osuna, M. A., Jijón-Moreno, S., and Casas-Flores, S. (2024). Trichoderma virens big Ras GTPase-1, a molecular switch for transforming a mutualistic fungus to plants in a deleterious microbe. Microbiol. Res. 278:127508. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2023.127508
Ding, Q., Xia, W., Liu, J. C., Yang, J. Y., Lee, D. F., Xia, J., et al. (2005). Erk associates with and primes GSK-3beta for its inactivation resulting in upregulation of beta-catenin. Mol. Cell 19, 159–170. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2005.06.009
Ehrenberg, A. J., Leng, K., Letourneau, K. N., Hernandez, I., Lew, C., Seeley, W. W., et al. (2021). Patterns of neuronal Rhes as a novel hallmark of tauopathies. Acta Neuropathol. 141, 651–666. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02279-2
Eimer, W. A., Vijaya Kumar, D. K., Navalpur Shanmugam, N. K., Rodriguez, A. S., Mitchell, T., Washicosky, K. J., et al. (2018). Alzheimer's disease-associated β-amyloid is rapidly seeded by Herpesviridae to protect against brain infection. Neuron 99, 56–63.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.06.030
Elfrink, H. L., Zwart, R., Cavanillas, M. L., Schindler, A. J., Baas, F., and Scheper, W. (2012). Rab6 is a modulator of the unfolded protein response: implications for Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 28, 917–929. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110971
Emmerson, J. T., Do Carmo, S., Lavagna, A., Huang, C., Wong, T. P., Martinez-Trujillo, J. C., et al. (2024). Paradoxical attenuation of early amyloid-induced cognitive impairment and synaptic plasticity in an aged APP/tau bigenic rat model. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 12:193. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01901-0
Evans, L. D., Wassmer, T., Fraser, G., Smith, J., Perkinton, M., Billinton, A., et al. (2018). Extracellular monomeric and aggregated tau efficiently enter human neurons through overlapping but distinct pathways. Cell Rep. 22, 3612–3624. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.021
Fang, F., Yang, W., Florio, J. B., Rockenstein, E., Spencer, B., Orain, X. M., et al. (2017). Synuclein impairs trafficking and signaling of BDNF in a mouse model of Parkinson's disease. Sci. Rep. 7:3868. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-04232-4
Ferreira, A., Lu, Q., Orecchio, L., and Kosik, K. S. (1997). Selective phosphorylation of adult tau isoforms in mature hippocampal neurons exposed to fibrillar a beta. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 9, 220–234. doi: 10.1006/mcne.1997.0615
Fichou, Y., Lin, Y., Rauch, J. N., Vigers, M., Zeng, Z., Srivastava, M., et al. (2018). Cofactors are essential constituents of stable and seeding-active tau fibrils. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 115, 13234–13239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1810058115
Foulds, C. E., Nelson, M. L., Blaszczak, A. G., and Graves, B. J. (2004). Ras/mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling activates Ets-1 and Ets-2 by CBP/p300 recruitment. Mol. Cell. Biol. 24, 10954–10964. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.24.10954-10964.2004
Gao, Y., Yan, Y., Fang, Q., Zhang, N., Kumar, G., Zhang, J., et al. (2019). The rho kinase inhibitor fasudil attenuates Aβ1-42-induced apoptosis via the ASK1/JNK signal pathway in primary cultures of hippocampal neurons. Metab. Brain Dis. 34, 1787–1801. doi: 10.1007/s11011-019-00487-0
Gärtner, U., Holzer, M., and Arendt, T. (1999). Elevated expression of p21ras is an early event in Alzheimer's disease and precedes neurofibrillary degeneration. Neuroscience 91, 1–5. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00059-7
Giunti, E., Collu, R., Daley, S., Querfurth, H., Morin, P., Killick, R., et al. (2023). Reduction of phosphorylated tau in Alzheimer's disease induced pluripotent stem cell-derived neuro-spheroids by rho-associated coiled-coil kinase inhibitor Fasudil. J. Alzheimers Dis. 96, 1695–1709. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230551
Greenberg, S. M., Koo, E. H., Selkoe, D. J., Qiu, W. Q., and Kosik, K. S. (1994). Secreted beta-amyloid precursor protein stimulates mitogen-activated protein kinase and enhances tau phosphorylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 7104–7108. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.15.7104
Grundke-Iqbal, I., Iqbal, K., Tung, Y. C., Quinlan, M., Wisniewski, H. M., and Binder, L. I. (1986). Abnormal phosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau in Alzheimer cytoskeletal pathology. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 4913–4917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4913
Gu, J., Xu, W., Jin, N., Li, L., Zhou, Y., Chu, D., et al. (2020). Truncation of tau selectively facilitates its pathological activities. J. Biol. Chem. 295, 13812–13828. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.012587
Hamano, T., Shirafuji, N., Yen, S. H., Yoshida, H., Kanaan, N. M., Hayashi, K., et al. (2020). Rho-kinase ROCK inhibitors reduce oligomeric tau protein. Neurobiol. Aging 89, 41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2019.12.009
Hernandez, I., Luna, G., Rauch, J. N., Reis, S. A., Giroux, M., Karch, C. M., et al. (2019). A farnesyltransferase inhibitor activates lysosomes and reduces tau pathology in mice with tauopathy. Sci. Transl. Med. 11:eaat3005. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aat3005
Huang, T. Y., Michael, S., Xu, T., Sarkeshik, A., Moresco, J. J., Yates, J. R. 3rd, et al. (2013). A novel Rac1 GAP splice variant relays poly-Ub accumulation signals to mediate Rac1 inactivation. Mol. Biol. Cell 24, 194–209. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E12-07-0565
Huesa, G., Baltrons, M. A., Gómez-Ramos, P., Morán, A., García, A., Hidalgo, J., et al. (2010). Altered distribution of RhoA in Alzheimer's disease and AbetaPP overexpressing mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 19, 37–56. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2010-1203
Hunter, M. P., Russo, A., and O'Bryan, J. P. (2013). Emerging roles for intersectin (ITSN) in regulating signaling and disease pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 14, 7829–7852. doi: 10.3390/ijms14047829
Hyderi, Z., Farhana, M. S., Singh, T. P., and Ravi, A. V. (2025). Therapeutic targeting of autosomal Parkinson's disease by modulation of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein. Brain Res. 1860:149674. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2025.149674
Ihara, Y., Nukina, N., Miura, R., and Ogawara, M. (1986). Phosphorylated tau protein is integrated into paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J. Biochem. 99, 1807–1810. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135662
Itzhaki, R. F., Lathe, R., Balin, B. J., Ball, M. J., Bearer, E. L., Braak, H., et al. (2016). Microbes and Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 51, 979–984. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160152
Jackson, N. A., Guerrero-Muñoz, M. J., and Castillo-Carranza, D. L. (2022). The prion-like transmission of tau oligomers via exosomes. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:974414. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.974414
Jagust, W. (2016). Is amyloid-β harmful to the brain? Insights from human imaging studies. Brain 139, 23–30. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv326
Jennings, D., Huntwork-Rodriguez, S., Vissers, M. F. J. M., Daryani, V. M., Diaz, D., Goo, M. S., et al. (2023). LRRK2 inhibition by BIIB122 in healthy participants and patients with Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 38, 386–398. doi: 10.1002/mds.29297
Jeong, Y. Y., Han, S., Jia, N., Zhang, M., Sheshadri, P., Tammineni, P., et al. (2022). Broad activation of the parkin pathway induces synaptic mitochondrial deficits in early tauopathy. Brain 145, 305–323. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab243
Jorfi, M., Park, J., Hall, C. K., Lin, C. J., Chen, M., von Maydell, D., et al. (2023). Infiltrating CD8+ T cells exacerbate Alzheimer's disease pathology in a 3D human neuroimmune axis model. Nat. Neurosci. 26, 1489–1504. doi: 10.1038/s41593-023-01415-3
Kampers, T., Friedhoff, P., Biernat, J., Mandelkow, E. M., and Mandelkow, E. (1996). RNA stimulates aggregation of microtubule-associated protein tau into Alzheimer-like paired helical filaments. FEBS Lett. 399, 344–349. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(96)01386-5
Kay, L., Pienaar, I. S., Cooray, R., Black, G., and Soundararajan, M. (2018). Understanding Miro GTPases: implications in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 55, 7352–7365. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-0927-x
Kent, S. A., Spires-Jones, T. L., and Durrant, C. S. (2020). The physiological roles of tau and aβ: implications for Alzheimer's disease pathology and therapeutics. Acta Neuropathol. 140, 417–447. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02196-w
Kim, I., Park, E. J., Seo, J., Ko, S. J., Lee, J., and Kim, C. H. (2011). Zinc stimulates tau S214 phosphorylation by the activation of Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase-kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway. Neuroreport 22, 839–844. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0b013e32834c0a2d
Kirouac, L., Rajic, A. J., Cribbs, D. H., and Padmanabhan, J. (2017). Activation of Ras-ERK Signaling and GSK-3 by amyloid precursor protein and amyloid Beta facilitates neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's disease. eNeuro 4:ENEURO.0149-16.2017. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0149-16.2017
Kosik, K. S., Joachim, C. L., and Selkoe, D. J. (1986). Microtubule-associated protein tau (tau) is a major antigenic component of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 4044–4048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4044
Krupa, J., Medapati, M., Tsang, A., Seah, C., and Pasternak, S. (2025). Macropinocytosis of aggregated amyloid-beta and tau requires Arf6 and the RhoGTPases Rac1, Cdc42 and RhoA. bioRxiv 2025.03.02.641073; doi: 10.1101/2025.03.02.641073
Lin, H., Tang, M., Ji, C., Girardi, P., Cvetojevic, G., Chen, D., et al. (2022). BAG3 regulation of RAB35 mediates the endosomal sorting complexes required for transport/Endolysosome pathway and tau clearance. Biol. Psychiatry 92, 10–24. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2021.10.024
Liu, Z., Xu, E., Zhao, H. T., Cole, T., and West, A. B. (2020). LRRK2 and Rab10 coordinate macropinocytosis to mediate immunological responses in phagocytes. EMBO J. 39:e104862. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020104862
Lu, Q., Soria, J. P., and Wood, J. G. (1993). p44mpk MAP kinase induces Alzheimer type alterations in tau function and in primary hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 35, 439–444. doi: 10.1002/jnr.490350411
Lu, Q., and Wood, J. G. (1993). Functional studies of Alzheimer's disease tau protein. J. Neurosci. 13, 508–515. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00508.1993
Mai, M., Guo, X., Huang, Y., Zhang, W., Xu, Y., Zhang, Y., et al. (2022). DHCR24 knockdown induces tau hyperphosphorylation at Thr181, Ser199, Ser262, and Ser396 sites via activation of the lipid raft-dependent Ras/MEK/ERK Signaling pathway in C8D1A astrocytes. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 5856–5873. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02945-w
Malasala, S., Azimian, F., Chen, Y. H., Twiss, J. L., Boykin, C., Akhtar, S. N., et al. (2024). Enabling systemic identification and functionality profiling for Cdc42 homeostatic modulators. Commun. Chem. 7:271. doi: 10.1038/s42004-024-01352-7
McMillan, P. J., Benbow, S. J., Uhrich, R., Saxton, A., Baum, M., Strovas, T., et al. (2023). Tau-RNA complexes inhibit microtubule polymerization and drive disease-relevant conformation change. Brain 146, 3206–3220. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad032
Miao, J., Shi, R., Li, L., Chen, F., Zhou, Y., Tung, Y. C., et al. (2019). Pathological tau from Alzheimer's brain induces site-specific hyperphosphorylation and SDS- and reducing agent-resistant aggregation of tau in vivo. Front. Aging Neurosci. 11:34. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2019.00034
Mondragón-Rodríguez, S., Trillaud-Doppia, E., Dudilot, A., Bourgeois, C., Lauzon, M., Leclerc, N., et al. (2012). Interaction of endogenous tau protein with synaptic proteins is regulated by N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent tau phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 32040–32053. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.401240
Nieto, A., Correas, I., López-Otín, C., and Avila, J. (1991). Tau-related protein present in paired helical filaments has a decreased tubulin binding capacity as compared with microtubule-associated protein tau. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1096, 197–204. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90005-t
Nik Akhtar, S., and Lu, Q. (2023). RhoA-LIMK Signaling Axis reveals rostral-caudal plane and spatial dysregulation in the brain of Alzheimer's disease mouse models. J. Alzheimers Dis. 95, 1643–1656. doi: 10.3233/JAD-230408
Owen, J. B., Di Domenico, F., Sultana, R., Perluigi, M., Cini, C., Pierce, W. M., et al. (2009). Proteomics-determined differences in the concanavalin-A-fractionated proteome of hippocampus and inferior parietal lobule in subjects with Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment: implications for progression of AD. J. Proteome Res. 8, 471–482. doi: 10.1021/pr800667a
Oyama, F., Kotliarova, S., Harada, A., Ito, M., Miyazaki, H., Ueyama, Y., et al. (2004). Gem GTPase and tau: morphological changes induced by gem GTpase in CHO cells are antagonized by tau. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 27272–27277. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M401634200
Parmar, M. (2024). Exploring the therapeutic role of Rab8a in 4R-Tauopathy. Alzheimers Dement. 20:e092498. doi: 10.1002/alz.092498
Pensalfini, A., Kim, S., Subbanna, S., Bleiwas, C., Goulbourne, C. N., Stavrides, P. H., et al. (2020). Endosomal dysfunction induced by directly Overactivating Rab5 recapitulates prodromal and neurodegenerative features of Alzheimer's disease. Cell Rep. 33:108420. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108420
Perez, S. E., Getova, D. P., He, B., Counts, S. E., Geula, C., Desire, L., et al. (2012). Rac1b increases with progressive tau pathology within cholinergic nucleus basalis neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Am. J. Pathol. 180, 526–540. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.027
Plascencia-Villa, G., and Perry, G. (2022). Neuropathologic changes provide insights into key mechanisms of Alzheimer disease and related dementia. Am. J. Pathol. 192, 1340–1346. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2022.07.002
Polanco, J. C., Hand, G. R., Briner, A., Li, C., and Götz, J. (2021). Exosomes induce endolysosomal permeabilization as a gateway by which exosomal tau seeds escape into the cytosol. Acta Neuropathol. 141, 235–256. doi: 10.1007/s00401-020-02254-3
Posada-Duque, R. A., López-Tobón, A., Piedrahita, D., González-Billault, C., and Cardona-Gomez, G. P. (2015). p35 and Rac1 underlie the neuroprotection and cognitive improvement induced by CDK5 silencing. J. Neurochem. 134, 354–370. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13127
Pozueta, J., Lefort, R., Ribe, E. M., Troy, C. M., Arancio, O., and Shelanski, M. (2013). Caspase-2 is required for dendritic spine and behavioural alterations in J20 APP transgenic mice. Nat. Commun. 4:1939. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2927
Sayas, C. L., Avila, J., and Wandosell, F. (2002). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is activated in neuronal cells by Galpha12 and Galpha13 by rho-independent and rho-dependent mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 22, 6863–6875. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-16-06863.2002
Scheper, W., Hoozemans, J. J., Hoogenraad, C. C., Rozemuller, A. J., Eikelenboom, P., and Baas, F. (2007). Rab6 is increased in Alzheimer's disease brain and correlates with endoplasmic reticulum stress. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 33, 523–532. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2007.00846.x
Shi, J., and Wei, L. (2007). Rho kinase in the regulation of cell death and survival. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 55, 61–75. doi: 10.1007/s00005-007-0009-7
Sinsky, J., Pichlerova, K., and Hanes, J. (2021). Tau protein interaction partners and their roles in Alzheimer's disease and other Tauopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:9207. doi: 10.3390/ijms22179207
Socodato, R., Almeida, T. O., Portugal, C. C., Santos, E. C. S., Tedim-Moreira, J., Galvão-Ferreira, J., et al. (2023). Microglial Rac1 is essential for experience-dependent brain plasticity and cognitive performance. Cell Rep. 42:113447. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113447
Stoothoff, W. H., and Johnson, G. V. (2005). Tau phosphorylation: physiological and pathological consequences. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1739, 280–297. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2004.06.017
Vaz-Silva, J., Gomes, P., Jin, Q., Zhu, M., Zhuravleva, V., Quintremil, S., et al. (2018). Endolysosomal degradation of tau and its role in glucocorticoid-driven hippocampal malfunction. EMBO J. 37:e99084. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899084
Wang, G., Huang, Y., Wang, L. L., Zhang, Y. F., Xu, J., Zhou, Y., et al. (2016). MicroRNA-146a suppresses ROCK1 allowing hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease. Sci. Rep. 6:26697. doi: 10.1038/srep26697
Wang, Q., Zhou, Y., Wang, X., and Evers, B. M. (2006). Glycogen synthase kinase-3 is a negative regulator of extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Oncogene 25, 43–50. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1209004
Weber, A. J., and Herskowitz, J. H. (2021). Perspectives on ROCK2 as a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15:636017. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.636017
Wegmann, S., Biernat, J., and Mandelkow, E. (2021). A current view on tau protein phosphorylation in Alzheimer's disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 69, 131–138. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2021.03.003
Woo, J. A., Liu, T., Zhao, X., Trotter, C., Yrigoin, K., Cazzaro, S., et al. (2017). Enhanced tau pathology via RanBP9 and Hsp90/Hsc70 chaperone complexes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 26, 3973–3988. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx284
Wood, J. G., Mirra, S. S., Pollock, N. J., and Binder, L. I. (1986). Neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer disease share antigenic determinants with the axonal microtubule-associated protein tau (tau). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 4040–4043. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4040
Wozniak, M. A., Mee, A. P., and Itzhaki, R. F. (2009). Herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA is located within Alzheimer's disease amyloid plaques. J. Pathol. 217, 131–138. doi: 10.1002/path.2449
Wu, J. W., Herman, M., Liu, L., Simoes, S., Acker, C. M., Figueroa, H., et al. (2013). Small misfolded tau species are internalized via bulk endocytosis and anterogradely and retrogradely transported in neurons. J. Biol. Chem. 288, 1856–1870. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.394528
Wu, J. W., Hussaini, S. A., Bastille, I. M., Rodriguez, G. A., Mrejeru, A., Rilett, K., et al. (2016). Neuronal activity enhances tau propagation and tau pathology in vivo. Nat. Neurosci. 19, 1085–1092. doi: 10.1038/nn.4328
Yan, X., Nykänen, N. P., Brunello, C. A., Haapasalo, A., Hiltunen, M., Uronen, R. L., et al. (2016). FRMD4A-cytohesin signaling modulates the cellular release of tau. J. Cell Sci. 129, 2003–2015. doi: 10.1242/jcs.180745
Yan, T., Wang, L., Gao, J., Siedlak, S. L., Huntley, M. L., Termsarasab, P., et al. (2018). Rab10 phosphorylation is a prominent pathological feature in Alzheimer's disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 63, 157–165. doi: 10.3233/JAD-180023
Ye, H., Ojelade, S. A., Li-Kroeger, D., Zuo, Z., Wang, L., Li, Y., et al. (2020). Retromer subunit, VPS29, regulates synaptic transmission and is required for endolysosomal function in the aging brain. eLife 9:e51977. doi: 10.7554/eLife.51977
Yoshida, H., and Ihara, Y. (1993). Tau in paired helical filaments is functionally distinct from fetal tau: assembly incompetence of paired helical filament-tau. J. Neurochem. 61, 1183–1186. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1993.tb03642.x
Zhang, H., Lu, F., Liu, P., Qiu, Z., Li, J., Wang, X., et al. (2023). A direct interaction between RhoGDIα/tau alleviates hyperphosphorylation of tau in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 18, 58–71. doi: 10.1007/s11481-021-10049-w
Zheng, H., Jiang, M., Trumbauer, M. E., Sirinathsinghji, D. J., Hopkins, R., Smith, D. W., et al. (1995). beta-Amyloid precursor protein-deficient mice show reactive gliosis and decreased locomotor activity. Cell 81, 525–531. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90073-x
Zheng, H., and Koo, E. H. (2011). Biology and pathophysiology of the amyloid precursor protein. Mol. Neurodegener. 6:27. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-27
Zheng, C., Xia, W., and Zhang, J. (2025). Rock inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Front. Aging 6:1547883. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2025.1547883
Zhong, Z., Grasso, L., Sibilla, C., Stevens, T. J., Barry, N., and Bertolotti, A. (2018). Prion-like protein aggregates exploit the RHO GTPase to cofilin-1 signaling pathway to enter cells. EMBO J. 37:e97822. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797822
Zhu, M., Xiao, B., Xue, T., Qin, S., Ding, J., Wu, Y., et al. (2023). Cdc42GAP deficiency contributes to the Alzheimer's disease phenotype. Brain 146, 4350–4365. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad184
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease, small GTPases, microtubule-associated protein tau, hyperphosphorylation, aggregation, propagation, clearance, neurofibrillary tangles
Citation: Hoegy P, Chen Y-H and Lu Q (2025) The role of small GTPases in Alzheimer’s disease tau pathologies. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 19:1650400. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1650400
Edited by:
Robert M. Hughes, East Carolina University, United StatesReviewed by:
Alessandro Didonna, East Carolina University, United StatesColin OBanion, TorqueBio, United States
Copyright © 2025 Hoegy, Chen and Lu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qun Lu, cXVuQG1haWxib3guc2MuZWR1
 Peter Hoegy
Peter Hoegy Yan-Hua Chen1,2
Yan-Hua Chen1,2 Qun Lu
Qun Lu