- Behavioral Neurology Division, Department of Neurology, Oklahoma University Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK, United States
Though usually described as isolated models, neurodegenerative diseases exist in a significant proportion of cases as mixed pathologies, particularly in older adults. The presence of co-pathologies may influence phenotypes and progression, and the correct classification in vivo has proven to be challenging, particularly without proper biomarker panels. Recent breakthroughs in biomarkers, enabling earlier detection in Alzheimer’s disease and, more recently, in synuclein-related diseases, are promising as a first step toward the wider detection of all other abnormal proteins involved in neurodegenerative diseases. Over the past decade, the growing body of research on TDP-43 pathology has led to considering TDP-43 as a potential major contributor to the neurodegenerative process. TDP-43’s normal function is essential for neuronal survival and the regulation of RNA processing and cellular stress response; abnormal TDP-43 protein leads to altered cell function and survival. TDP-43 is notably the neuropathological hallmark of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) as well as some form of frontotemporolobar degeneration (FTLD). Tauopathies, divided in primary or secondary tauopathies cover other forms of FTLD including Pick disease (PiD), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) but also non-FTLD diseases like Alzheimer’s disease (AD) which can be classified as secondary tauopathy. As the importance of copathology is more and more recognized, TDP-43 is also frequently observed in conjunction with other proteinopathies, possibly with a synergistic or additive effect, although the exact mechanism is still unclear. In Alzheimer’s disease, the limbic predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathologic change (LATE-NC) co-occurrence with Alzheimer’s disease neuropathologic changes (ADNC) lead to a more rapid course. Although there are currently no approved and validated biomarkers for its early detection, several promising tools, including neuroimaging and biofluid biomarkers, are under development, offering hope for the earlier detection of TDP-43 pathology in vivo. Accurate identification of the underlying proteinopathies and pathological processes could lead to better diagnosis and classification, more precise selection of clinical trial candidates, and ultimately, disease-specific tailored treatments.
Introduction
Many neurodegenerative diseases are proteinopathies, characterized by the abnormal aggregation and accumulation of one or more misfolded proteins, which are thought to play a crucial role in their pathophysiology. With the advancement of biomarkers and the progress in understanding abnormal brain aging over recent years, multiple studies have demonstrated that most neurogenerative diseases involve more than one protein in complex interactions that contribute to neurodegeneration and symptoms (Rahimi and Kovacs, 2014). Since its first description in 2006 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and over the past decade, the transactive response DNA binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) has been identified as one of the key proteins associated with neurodegenerative diseases, along with amyloid, various strains of tau, and alpha-synuclein, among others (Neumann et al., 2006; Vanden Broeck et al., 2014). TDP-43 is a highly conserved and ubiquitously expressed RNA/DNA binding protein belonging to the hnRNP family of heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP) (Shenouda et al., 2022). It is an intranuclear protein encoded by the TARDBP gene, located on chromosome 1 (1p36.22), that can also shuttle to the cytoplasm depending on transcriptional needs. TDP-43 plays an important role in the functions of many cells, including RNA metabolism, mRNA transport, microRNA maturation, and cellular stress response (Prasad et al., 2019; de Boer et al., 2020). TDP-43 regulates its own expression via a complex mechanism and direct action on the TARDBP gene. Altered regulation or misdistribution of the protein will lead to altered cell function and survival, but the exact process is still poorly understood (Koyama et al., 2016).
Tau is another key protein whose dysfunction can lead to neurodegeneration. It is a microtubule-associated protein that stabilizes the neuronal cytoskeleton through this association and regulates axonal transport. It also plays a role in synaptic signaling and synaptic plasticity, as well as in axonal elongation and maturation, and is involved in RNA processing. Both TDP-43 and tau are RNA-binding proteins (RBP), involved in RNA regulation and mediating stress granule formation. Abnormal tau, including that caused by gene mutations or aberrant post-translational modifications— for example, hyperphosphorylation or N-glycosylation —is associated with a higher tendency to aggregate. These aggregates will form in the cytoplasm and alter normal neuronal function, while the absence of tau in the nucleus will, in turn, affect DNA and RNA processing and the maintenance of their integrity (Wang and Mandelkow, 2016; Koren et al., 2020; Samudra et al., 2023).
Abnormal conformation in TDP-43 can be observed in several neurodegenerative diseases, such as FTLD and ALS, where hyperphosphorylated and ubiquitinated TDP-43 accumulate as neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions identified during neuropathological examination (Neumann et al., 2007; Rutherford et al., 2008; Meneses et al., 2021), but also in Limbic-predominant Age-related TDP-43 Encephalopathy (LATE), an entity often found in the brains of older adults and present on average in approximately one-third of autopsies of individuals above 85 years old (Wilson et al., 2013; Nelson et al., 2022). The latter is defined by neuropathological changes in a limbic distribution with misfolded TDP-43 aggregates, referred to as LATE neuropathological change (LATE-NC). Misfolded proteins, including tau, are thought to be able to spread in a “prion-like” manner following the neuronal network, and TDP-43 is no exception either (Dugger and Dickson, 2017; Jo et al., 2020). TDP-43 pathology can co-occur in other proteinopathies, and with increasing interest in its possible role in tauopathies. Recent research suggests a potential interaction between both and possible synergistic effects; some studies suggest that TDP-43 pathology can exacerbate tau aggregation and seeding (Riku et al., 2022; Tomé et al., 2023; Tomé et al., 2024). In this review, we will examine the interaction between TDP-43 and tau and how this affects clinical assessment and diagnostics. We will discuss the ongoing development of TDP-43 biomarkers to facilitate a more precise identification of underlying pathology in vivo, which in turn will help optimize the development of therapeutic interventions.
TDP-43 pathology
TDP-43 is a 414 amino acid protein with four domains, including a N-terminal domain, two RNA recognition motif domains (RRM1 and RRM2), and a C-terminal low-complexity domain (LCD) (Jiang et al., 2017). It also contains a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and a nuclear export signal (NES) that shuttles TDP-43 between the nucleus and the cytoplasm (Winton et al., 2008). The N-terminal domain mediates the formation of homodimers and oligomers (Chang et al., 2012) that participate in TDP-43’s physiological functioning and contains a sequence important for its transportation to the nucleus. The N-terminal domain may participate in TDP-43’s splicing function and protect it from forming cytoplasmic inclusions (Jiang et al., 2017). The RRMs are critical for its binding to RNA/DNA and exerting its role on mRNA, as well as forming ribonucleotide granules. The C-terminal low-complexity domain contains a glycine-rich region and a Glutamine/Asparagine (Q/N)-rich domain (Carrasco et al., 2023). This LCD prion-like domain (PrLD) mediates protein-protein interaction with other splicing factors, including heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1), hnRNPA2B1, and fused in sarcoma (FUS) and is essential to regulate the splicing of some mRNA transcripts (Harrison and Shorter, 2017). PrLD is also important to the recruitment of TDP-43 into the formation of stress granules which are cytosolic structures that form transiently after cells are exposed to an environmental stress (Bentmann et al., 2012). C-terminal glycine-rich region regulates protein solubility. Most disease-related TDP-43 mutations are found in the LCD (Johnson et al., 2008; Corbet et al., 2021). PrLD seems to be participating in the aggregation process, and its deletion could suppress neurotoxicity (Ash et al., 2010). The LCD domain participates in the process of forming TDP-43 lipid droplets, known as liquid-liquid phase separation (LLPS), and perturbation of this phase formation may lead to pathological aggregation and dysfunction. However, this is still largely poorly understood (Babinchak et al., 2019; Corbet et al., 2021; Babinchak and Surewicz, 2023).
TDP-43 is an essential, highly conserved, and ubiquitously expressed RNA-binding protein involved in multiple steps of RNA processing, including transcription, translation, splicing, and stabilization and is encoded by the TARDBP gene on chromosome 1 (Ou et al., 1995; Cohen et al., 2011). It is a nuclear transcription factor regulating numerous genes (Buratti and Baralle, 2010). TDP-43 in physiological context is mostly present in the nucleus of the neurons but can also be found in oligomeric state in the cytoplasm (Kellett et al., 2025). The processus leading to mislocalization remains unclear. Mislocalized TDP-43 forms misfolded insoluble aggregates, some hyperphosphorylated and ubiquitinated, called “inclusion bodies” in the neuronal cytoplasm, as well as in nuclei and cell processes (neurites) of neurons and in oligodendroglia and astrocytes (de Boer et al., 2020). In 2006, TDP-43 was discovered as the major protein present in the ubiquitinated inclusions found in ALS (Lou Gehrig’s disease) (Arai et al., 2006) and has since lead to the discovery of its association with many neurodegenerative diseases and trial to understand it’s place in the degeneration cascade.
TDP-43 proteinopathy refers to a broad group of neurodegenerative processes in which one of the primary types of misfolded protein accumulation leading to typical inclusions found on neuropathological examination is TDP-43 (Liao et al., 2022). It can be divided into primary TDP-43 proteinopathies, referring to the disease driven primarily by TDP-43, which include FTLD-TDP, FTLD-ALS, for which TDP-43 is a pathological hallmark (Neumann et al., 2006; Kabashi et al., 2008; Sreedharan et al., 2008), and the Limbic-predominant Age-related TDP-43 Encephalopathy (LATE), which will be reviewed further later in this review. Perry syndrome is another rare form of TDP-43 proteinopathy, highlighting the broad spectrum of disorders associated with this proteinopathy (Wider et al., 2009; Mishima et al., 2018), and is an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease caused by a mutation in the dynactin 1 (DCTN1) gene on chromosome 2p13.1 that results in TDP-43 pathology (Ueda et al., 2024). It is clinically defined by neuropsychiatric features, including apathy that can be the initial symptom, severe depression, a symmetrical Parkinsonism usually poorly or transiently responsive to L-DOPA, significant weight loss, and central hypoventilation with respiratory failure being the most frequent cause of death (Perry et al., 1975; Dulski et al., 2021; Tsuboi et al., 2021). Mutation or downregulation of dynactin 1 has also been associated with sporadic or familial ALS (Laird et al., 2008). Perturbation of the microtubule-associated motor protein complex dynactin leads to dysfunction and dysregulation in stress granule disassembly in stressed cells, resulting in TDP-43 cytoplasmic accumulation (Ueda et al., 2024). Interestingly, tau and dynactin interact with each other, and the attachment of the dynactin complex to the microtubule is strengthened by tau, showing another connection between TDP-43 pathways and tau pathways (Magnani et al., 2007; Ueda et al., 2024).
Secondary TDP-43 proteinopathies refer to neurodegenerative diseases or non-neurodegenerative diseases in which TDP-43 plays a role and can be found associated with other proteins or pathological processes. This broader group include neurodegenerative diseases including Alzheimer’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), corticobasal degeneration (CBD), Parkinson’s disease (PD) (Chanson et al., 2010), multiple system atrophy (MSA) (Koga et al., 2018), Lewy body disease (Uchino et al., 2015), Huntington’s disease (HD) (Davidson et al., 2009), Primary age related tauopathy (PART) but also non-neurodegenerative disease like chronic traumatic encephalopathy (CTE) (McKee et al., 2010; McKee et al., 2015; Heyburn et al., 2019a; Heyburn et al., 2019b), brain tumors (Lin et al., 2017), or post-infectious or post-toxin exposure like in Parkinson-Guam dementia syndrome (Hasegawa et al., 2007; Kawakami et al., 2019; Ke et al., 2023; Rahic et al., 2023).
Cellular stress, including that related to toxin exposure, dysimmunity, and inflammation, may lead to TDP-43 dysfunctions and aggregation (Thammisetty et al., 2018; Bright et al., 2021; Masrori et al., 2022; Garamszegi et al., 2024). Genetic mutations beyond those in the TARDBP gene have also been linked to TDP-43 pathology, particularly C9Orf72 and GNR, and can serve as a common ground for some of these processes (Pickford et al., 2011; O’Rourke et al., 2016; Pottier et al., 2019; Kahriman et al., 2023). Both C9Orf72 and GNR genes are also associated with tauopathies.
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD) refers to a clinicopathologic and genetically heterogeneous group of pathologies manifested by several and sometimes overlapping clinical syndromes that span from cognitive and behavioral symptoms like in Pick’s disease and behavioral variant FTD (bvFTD), to more language predominant symptoms in semantic primary progressive aphasia (svPPA) and nonfluent variant primary progressive aphasia (nfPPA) to include motor and movement symptoms in corticobasal degeneration (CBD), progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) (Forman et al., 2007; Rabinovici et al., 2010; Younes and Miller, 2020; Neumann et al., 2021). At the neuropathological level, FTLD-TDP represents the most frequent underlying pathology in 45%–50% of cases, followed closely by FTLD-tau (40%–45%), then FTLD-FUS (5%–10%), and finally by other pathologies (Mackenzie et al., 2010). FTLD-TDP underlying pathology is widespread in the neocortex, hippocampus, and subcortical areas (Neumann et al., 2021). FTLD-TDP is itself divided into five major histological subtypes, categorized by the type of inclusions (designated as A to E), morphology, anatomical distribution, and cellular location. FTLD-tau is itself sub-classified according to the underlying strain of tau, which includes 3-repeat (3R) tau inclusion like found in Pick’s disease (PiD), 4-repeat (4R) tau pathologies-[CBD, PSP, aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG), Argyrophilic grain disease (AGD), and globular glial tauopathy (GGT)- or with both three and 4-repeat tau forms (3R/4R) as in PART and tangle only dementia (ToD) (Mackenzie et al., 2011; Neumann et al., 2021; Nilaver and Urbanski, 2023).
ALS is the most common adult-onset motoneuron disease characterized by an upper and lower motoneuron degeneration, leading to rapidly progressive paresis, which can lead to death in 2–4 years on average (Hobson and McDermott, 2016). Some behavioral and cognitive changes are frequent in as many as 50% of patients, while 5%–25% may meet criteria for clinical frontotemporal dementia (FTD). Up to 35% FTLD pathology is found in ALS autopsy series (Cividini et al., 2022). Upon neuropathological examination at autopsy, the pathognomonic finding of abnormal inclusion bodies is found in the cytoplasm of motor neurons. These inclusions are made up in more than 90% of cases of mislocalized and aggregated TDP-43 (Suk and Rousseaux, 2020). FTD-ALS cognitive symptoms can be similar to the behavioral variant FTD (BvFTD), while it can also present with a language variant, semantic variant in one third of FTD-ALS (Tan et al., 2019). Several other processes can be associated with TDP-43, including Hippocampal sclerosis (HS) of aging (Nelson et al., 2013; Nag et al., 2015; Nho et al., 2016; Cykowski et al., 2017; Nelson et al., 2019; Nelson et al., 2024).
All these neurodegenerative diseases are associated with the abnormal neuronal and glial accumulation of misfolded proteins; however, it remains unclear whether the pathological process results from a gain-of-function, loss-of-function, or both (Gendron and Petrucelli, 2009; Polymenidou et al., 2011; Wang and Mandelkow, 2016; de Boer et al., 2020; Ezzat et al., 2023). In the case of TDP-43, the abnormal trafficking of endogenous TDP-43 between the nucleus and the cytoplasm appears to lead to the formation of aggregates, including neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions (NCIs), neuronal intranuclear inclusions (NIIs), and/or dystrophic neurites (DNs), which collectively represent TDP-43 pathology (McAleese et al., 2017). As TDP-43 proteinopathy can be associated with many other neurodegenerative diseases, particularly tauopathies, considerable interest has grown in recent years to understand its role better, develop biomarkers to help recognize it outside of neuropathology/autopsy contexts, and ultimately provide future therapeutic approaches and clinical trials (Latimer and Liachko, 2021; Riku et al., 2022; VandeVrede et al., 2023).
TDP-43 in mixte pathology with tau
Combined pathologies are increasingly recognized as an important field of investigation, as longitudinal studies have reported the co-occurrence of TDP-43 and tau. It becomes crucial to understand the various interactions at play in order to develop targeted therapies (Latimer and Liachko, 2021). TDP-43 has been shown to influence tau expression and protein levels, worsening tau aggregation and propagation (Gu et al., 2017; Riku et al., 2022; Tomé et al., 2023). However, as mentioned above, there is still considerable uncertainty regarding whether this is due to a loss of function, a gain of function, or both (Nelson et al., 2019; Wisse et al., 2025).
In the case of the primary TDP-43 proteinopathy LATE, LATE-NC can be found in one third of older adults above 85 years old and present with an amnestic syndrome like Alzheimer’s disease that is clinically indistinguishable from AD. It can cohabitate with other neurodegenerative diseases, and is very frequently found concomitantly with ADNC, with as many as up to 50% of cases in copathology in older adults (Nelson et al., 2019; Katsumata et al., 2022; Nelson et al., 2022). The presence of both pathologies, ADNC and LATE-NC, has been shown to worsen cognitive decline (Montine et al., 2022). When isolated, its course is usually slower, more limited to episodic memory, with some reports of behavioral manifestations that could be part of its picture (Brenowitz et al., 2014; Nag et al., 2018; Nelson et al., 2019; Liu et al., 2020; Ono et al., 2025). Neuropathology staging based on the anatomical progression of LATE-NC pathology was proposed by Nelson et al. (2019). Stage 1 involves TDP-43 pathology distribution limited to the amygdala, stage 2 involves the hippocampus, and stage 3 affects the amygdala, hippocampus, and the middle frontal gyrus (Nelson et al., 2019; Nelson et al., 2022). This is the most commonly used staging system, though a more detailed 5-stage system has been utilized for research purposes in some studies like the Religious Orders Study and Memory and Aging project (ROSMAP) (Nag and Schneider, 2023). More recently, Wolk et al. (2025) proposed criteria for the clinical diagnosis of LATE, distinguishing LATE-NC as a primary process not or minimally associated with ADNC and classifying it as possible or probable LATE, or when LATE-NC is found in a mixed pathology with AD. They defined core clinical criteria, including a primary amnestic syndrome with temporal-limbic memory loss and most other cognitive domains mostly spared. However, use of biomarkers remain critical and are required to help better distinguish both process, with the use of the MRI brain showing disproportional hippocampal atrophy as a marker of LATE-NC, as well as the presence or absence of AD biomarkers to classify the underlying pathology better and assess for AD; in case of positive AD biomarkers, additional testing is required using PET scan (tau PET and FDG-PET scan) (Wolk et al., 2025). The type of interaction between these two proteinopathies remains a subject of debate and research. Some hypotheses suggest a synergistic or additive effect, while others lean more toward a role in the timing of neurodegeneration progression. A concurrent progression between TDP-43 and AD stages, and particularly between tau and higher Braak stages, supports some interaction or synergy between the two. Moreover, the association extends beyond a parallel progression: the absence of TDP-43, even for the same burden of AD pathology, correlates with normal cognition, as noted in Josephs et al.’s (2014) study. Colocalization of both pathologies in the same neurons could support a common pathophysiological process (Montalbano et al., 2020). Tomé et al. (2021) also demonstrated that in AD, LATE-NC pathology was associated with an increased presence of NFT and phosphorylated tau (p-tau), as well as TDP-43, which increased p-tau aggregation and seeding (Nelson et al., 2022). APOE E4 is associated with both an increased risk for AD and LATE-NC, suggesting some common pathophysiological pathways (de Flores et al., 2020; Dugan et al., 2021). TDP-43 pathology can also localize to the striatonigral system and present with parkinsonism and/or PSP-like syndrome (Murakami, 1999; Ono et al., 2025). In AD, it can be misinterpreted clinically for presence of Lewy Body copathology (Ono et al., 2025). In Ono et al.’s (2025) study, TDP-43 pathology correlated with reduced pigmented neuron density. As they used an antibody recognizing earlier stages of tau (pretangle and tangle), they found an association between tau and non-pigmented neuron density. Early tau pathology has been reported in the elderly above 90 years with Parkinsonism, even in the absence of AD or Lewy body pathology, which reinforces the importance of using markers for early tau to ensure that we capture the full spectrum of tau-related disease and co-pathology (Chu et al., 2024).
HS of aging (HS-aging) is frequently found in older adults as well, is associated with cognitive decline and dementia, and can present with an amnestic syndrome mimicking AD. It is defined by its neuropathological criteria with neuronal loss and gliosis in the hippocampi, out of proportion for an AD-only pathology. It is also frequently associated with ADNC, LATE-NC, and FTLD (Anderson et al., 2025). HS-aging is very frequently associated with TDP-43 pathology, leading to worse cognitive functioning and decline when they cohabitate (Nelson et al., 2013; Nag et al., 2015). Its diagnosis is mostly postmortem, with the typical neuropathological findings of neuronal loss and gliosis affecting principally the CA1 hippocampal subfield and subiculum. The cause of this selective vulnerability remains unclear, ranging from hypoxia, atherosclerotic disease, and being in a watershed area, to inflammatory, hyperexcitability, and excitotoxicity (Cole, 2007; Hatanpaa et al., 2014; Walker, 2015). TDP-43 presence was found to be associated with an increased likelihood of HS of aging, and inflammation may contribute (Nag et al., 2015).
In FTLD, the concomitant presence of TDP-43 and tau was previously considered rare, mainly due to an independent process or contextual circumstances, such as genetics or age (Robinson et al., 2014). However, mixed pathology is now being reported more frequently. Some limitations in sampling or the type of markers used may have prevented the identification of TDP-43 (Amador-Ortiz et al., 2007; Robinson et al., 2014; Kim et al., 2018; Koga et al., 2022). The choice of markers targeting the advanced, mature stage of tau in neurofibrillary tangles, such as the ghost tangle, may miss earlier and less mature stages of tau (Ono et al., 2025). In a neuropathology series of 201 autopsy-confirmed FTLD-TDP by Koga et al. (2022), 42% had concomitant ARTAG, 36% had PART, 22% had concurrent AGD, and finally 1% had pathology CBD. FTLD-TDP type A seems particularly at risk of being combined with tau pathology, and as much as in 50% of cases (Gefen et al., 2018). Interestingly, this group appeared to have a longer duration of disease and a longer lifespan, challenging the classic understanding that copathology accelerates the disease process and severity of symptoms. For FTLD driven by tau, the 4R tauopathy CBD appears to be the one showing the most frequent participation of TDP-43 in ∼16% of neuropathological cases in some series (Uryu et al., 2008; Uryu et al., 2008; Kim et al., 2018). In the Uryu et al. (2008) case series, which included 39 CBD pathological cases, 15.4% of the CBD cases exhibited some TDP-43 pathology, with 2 cases showing limited deposition in the dentate granule cells of the hippocampus, as well as in the entorhinal cortex. Four other cases had more diffuse aggregates observed in the temporal and frontal cortex, as well as the basal ganglia. There were no significant differences in age at death or disease duration between the TDP-43-positive and TDP-43-negative CBD groups in this specific study, although some other studies suggested that co-pathology could affect survival and disease duration (Uryu et al., 2008; Yamashita et al., 2014). TDP-43 and tau were sometimes colocalized, particularly in the frontal gray matter (Uryu et al., 2008). The distribution of TDP-43 pathology in the case by Kouri et al. (2013) was more unusual, differing from other previously reported cases of co-pathology in CBD, and was associated with both TDP-43 and tau pathology in the olivopontocerebellar system, suggesting a role in phenotypic presentation (Kouri et al., 2013). In FTLD-PSP, reports of the contribution of TDP-43 are more limited. Although initially thought to be more dependent on other pathologies like HS and AD, as cases with co-pathology were older in age and had higher Braak Neurofibrillary and Thal phases, some regions of vulnerability to PSP could also be affected by TDP-43. FTLD-PSP with concomitant tau and TDP-43 pathologies tend to have higher regional tau burden compared to TDP-43-negative ones, and a significant correlation between tau and TDP-43 burden was noted in the occipitotemporal gyrus, suggesting a potential interactive effect in this region (Yokota et al., 2010). TDP-43 and tau were frequently colocalized in the limbic system, particularly in the amygdala, where colocalization in the same neurons was observed (Kim et al., 2018). However, colocalization in the same neurons was not observed in some other regions, such as the hippocampal dentate gyrus, suggesting possible regional differences in pathophysiological mechanisms, as well as both independent and overlapping pathways (Yokota et al., 2010; Koga et al., 2017; Storey et al., 2017). Association could also be genetically predetermined, as it has been shown that PSP with TDP-43 had decreased expression of the TMEM106b homozygous minor allele gene, thought to be protective of TDP-43, compared to PSP without TDP-43 (Koga et al., 2017).
PART, previously called “Senile dementia of neurofibrillary type” or “tangle-predominant dementia,” is very frequently found in older brains, can mimic clinically amnestic AD but usually with milder symptoms that can still progress to dementia, and the progression is usually related to the tauopathic burden (Noda et al., 2006; Jellinger and Attems, 2007; Crary et al., 2014). Histologically, PART presents the same neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) as in AD, but without the presence of amyloid (Aβ) protein (“NFT+/Aβ-” brains) and with no involvement of the neocortex. The hippocampal tau burden also differs from that of classical AD, with the CA2 subsection being more involved than the CA1 subsection (Besser et al., 2017; Hickman et al., 2020). TDP-43 co-pathology in PART is usually less severe than in AD and may not significantly affect the clinical presentation (Josephs et al., 2017). Zhang et al. (2019) developed a staging system based on the TDP-43 dissemination sequence in PART, which is relatively similar to the one seen in AD, though more limited to the limbic system. Stage I has TDP-43 limited to the amygdala, spreading to the hippocampus in stage II, the neocortex in stage III, and finally to the putamen, pallidum, insular cortex, and the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus in stage IV (Zhang et al., 2019; Nag and Schneider, 2023).
We would like to include to this review the currently rarer but intriguing entities represented by the Guam Parkinsonism-Dementia Complex (G-PDC) and the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-Parkinsonism-Dementia Complex (ALS-PDC), which may represent the same neurodegenerative disease with varying phenotypes. This now rare neurodegenerative disease endemic in Guam among the Chamorro people is characterized clinically by either primarily a Parkinsonian syndrome with dementia in G-PDC or a primarily motor presentation similar to classic sporadic ALS, sometimes associated with features of G-PDC either in the same individual or in the same family (Oyanagi, 2005; Verheijen et al., 2018). It was found to be secondary to exposure to a toxin from the seeds of cycad plants, which are used as food and in traditional medicine. The toxin may also precipitate genetic mutations, possibly via exposure during the prenatal or perinatal period (Spencer, 2022). It is characterized neuropathologically by both TDP-43 and tau copathology, and both pathologies are thought to contribute to the mechanisms of neurodegeneration (Geser et al., 2008). Other aggregates have been described associated with them, including Amyloid-β (Aβ) protein and alpha-synuclein (Condello et al., 2023). An inflammatory process resulting from exposure to the neurotoxin could be the primary basis for a common pathway leading to both TDP-43 and tau dysfunction. Several studies demonstrated a relationship between TDP-43 and immune-inflammatory pathways (Bright et al., 2021). Other studies have found a link between immunity and inflammation in the initiation of tau pathology and its progression (Johnson and Lukens, 2025). Cytoplasmic TDP-43 inclusions may be associated with defective RNA processing and other cellular disruptions, including mitochondrial dysfunction, nucleocytoplasmic transport, impaired endocytosis, and protein dysfunction (Verheijen et al., 2018). Glial cells can contain abnormal aggregates and may play a role in the pathophysiological process, as well as in the extracellular tau deposits, which increase microglial reactivity, a phenomenon also observed in other neurodegenerative diseases (Schwab et al., 1996; McGeer et al., 1997; Verheijen et al., 2018). The innate immune system and inflammation represent potential therapeutic targets; however, further research is needed to understand their relationship with neurodegenerative processes better (Bright et al., 2021). Similarly, TDP-43 can coexist with tau in Anti-IgLON5 disease, a neuroimmune disorder characterized by secondary tauopathy and neurodegeneration. TDP-43 and tau can either coexist or be found in distinct locations (Gelpi et al., 2016; Cagnin et al., 2017). One hypothesis is that the proinflammatory environment in neurons affected by the anti-IgLON5 antibody facilitates protein misfolding and neurodegeneration, which may lead to the accumulation of tau and secondary TDP-43; however, a synergy between both proteins is also a possibility (Gelpi et al., 2016). Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is associated with local inflammation in the area of the trauma, which can disseminate to other brain areas according to recent studies (Shi et al., 2019). Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a mixed 3R/4R tauopathy that mainly happens in the context of repeated head impacts (Cherry et al., 2020). Abnormal TDP-43 pathology is often observed on neuropathology and appears to progress with the stages of CTE and as tau pathology becomes more widespread, which suggests an association between the two processes (McKee et al., 2015; McKee et al., 2016; Heyburn et al., 2019b; Nicks et al., 2023; van Amerongen et al., 2023). A common denominator could potentially be a primary inflammation pathway leading to TDP-43 and tau dysregulation (Bright et al., 2021).
The amygdala: a possible pivotal role in neurodegeneration
The frequent and early involvement of the amygdala in diverse proteinopathies raises the possibility of pathological synergies starting in the amygdala (Gonzalez-Rodriguez et al., 2023; Villar-Conde et al., 2023). The amygdala is a crucial brain structure in the anterior medial temporal lobe involved not only in emotions and behaviors, but also in memory and cognition (Avecillas-Chasin et al., 2023). A recent review from Stouffer et al. (2024) emphasizes the importance of the amygdala as an early involvement in AD, supported by early neuropsychiatric symptoms in some patients. The amygdala was also one of the sites with the earliest positivity on tau-PET in the Insel et al. (2020) study on AD, sometimes as early as 10 years prior to AD diagnosis. MRI brain and volumetric analysis studies have shown a relationship between areas, including amygdala atrophy, and neuropsychiatric symptoms in early disease, or as a predictor of AD diagnosis and dementia (Liu et al., 2010; Trzepacz et al., 2013). Amygdala subnuclei are also involved in FTLD to a diverse degree, depending on the underlying pathology (Bocchetta et al., 2019). The most affected are those with FTLD due to MAPT mutation carriers and in FTLD-TDP-43 type C (Bocchetta et al., 2021). It is also recognized in FTLD-ALS (Kawashima et al., 2001; Takeda et al., 2017). A recent study in ALS showed that intra-neuronal accumulation of TDP-43 in the amygdala correlated with behavioral changes in sporadic ALS (Rifai et al., 2024). Connectomics identifies the amygdala as a key hub in most neurodegenerative diseases. The propagation, also known as seeding of proteinopathies, typically spreads through a connected network, and the amygdala is a highly interconnected center, including the hippocampus and the prefrontal cortex (Ubeda-Bañon et al., 2020). Abnormal connectivity in the amygdala circuitry is happening early in AD and is identified as a possible marker of early disease (Kicik et al., 2025). Amygdala changes were also reported in cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD), with associated disrupted connectivity (Cheng et al., 2024). This association between vascular impairment, endothelial dysfunction and disruption of the amygdala-hippocampal circuitry may play a key role in neurodegeneration, as vascular disease is very frequently found on autopsy in neurodegenerative diseases (Cheng et al., 2024). Impaired perfusion, as well as local inflammation and metabolic dysfunction, could potentially drive or at least participate in triggering the neurodegenerative process in this location. Imaging studies looking at iron deposits as a marker of early neuronal damage found an association between iron deposition in the amygdala and vascular cognitive impairment (Cheng et al., 2024). The relationship could be bi-directional, and a recent study by Arribas et al. (2024) demonstrated the importance of endothelial TDP-43 for vascular integrity, highlighting that abnormal TDP-43 can also potentially lead to disruption of the blood-brain barrier and contribute to neuroinflammation. Its close anatomical proximity to the ependymal lining as well as the pia mater, particularly the ventromedial part, could play a role, as suggested by the presence of subependymal and subpial TDP-43 or tau. Atypical star-shaped TDP-43 inclusions have been recently identified, primarily in the subpial medial region of the amygdala, and they colocalize with tau in superagers (Geser et al., 2010; Kovacs et al., 2016; Nelson et al., 2018; Carlos et al., 2023a). It is hypothesized that this anatomical location close to the vasculature and CSF could increase exposure to extravasated plasma protein due to defects in blood-brain-barrier permeability, triggering pathways associated with neurodegeneration and proteinopathies. More research is needed to understand the mechanisms and timing better (Schultz et al., 2004; Lace et al., 2012). Appropriate sampling, including the amygdala, during neuropathology examinations, as well as the use of markers that allow the detection of tau at different stages of maturity (such as CP13 or PHF-1), and assessing for atypical TDP-43 inclusions, appears important to better assess the whole spectrum of co-pathology in the brain (Carlos et al., 2023a; Chu et al., 2024; Ono et al., 2025).
Toward biomarkers for TDP-43
The important role of TDP-43 in copathology and its potential synergistic effect on neurodegeneration, as reviewed above, raises the urgent need for biomarkers to facilitate more precise clinical diagnosis, which will help guide therapeutic approaches tailored to each underlying pathology and mechanism. Failing to identify copathology appropriately may lead to inappropriately interpreting clinical trial results, resulting in delays and setbacks (Figure 1).
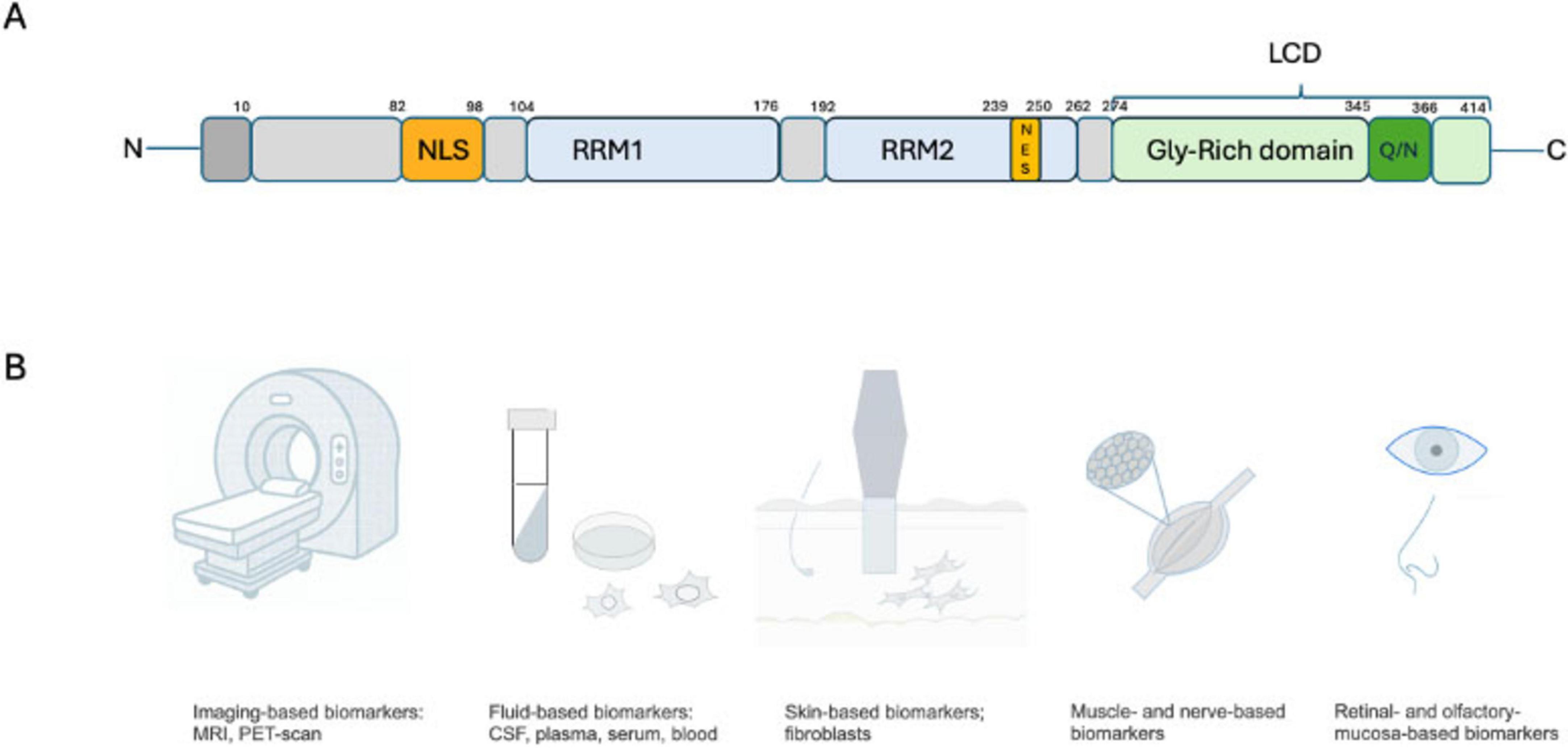
Figure 1. (A) TDP-43 protein contain a N-terminal domain, a nuclear localization sequence (NLS), two RNA recognition motifs (RRM1 and RRM2), a nuclear export sequence (NES), then the C-terminal domain/low complexity domain (LCD)/ prion-like domain with a glycine-rich domain and containing the Glutamine/Asparagine (Q/N) domain. (B) Potential target for biomarkers development, with most data coming from the neuroimaging field at that time, but with some promising development as well in biofluids and tissue-based markers.
MRI brain imaging
Neuroimaging is one of the most promising tools currently available to help identify TDP-43, either indirectly or directly. MRI can be used to assess neurodegeneration (N), and although it is not necessarily an early marker or a direct one, it still plays a key role in identifying atrophy patterns and neurodegeneration progression, helping with the diagnosis and staging process, and as a cue to assess for co-pathology (Jack et al., 2024; Youssef et al., 2025). Due to the lack of readily available in vivo molecular biomarkers for TDP-43 at this time, most data come from clinical-radiological and histological correlations, as cortical atrophy patterns seen on MRI correlate with progression and staging of TDP-43 pathology (Bejanin et al., 2019; Nelson et al., 2019). In all tauopathies, a greater volume loss is seen in the presence of co-pathology. In AD, the mesial temporal lobe (MTL) is usually the first affected. The presence of TDP-43 and HS coexisting with AD corresponds to additional disproportionate hippocampal volume loss on MRI brain compared to AD alone, which is a clue pointing toward multiple underlying proteinopathies (de Flores et al., 2020; Yu et al., 2020; Lyu et al., 2024; Wisse et al., 2025). Some previous longitudinal volumetric analyses have failed to correlate MTL volume with either amyloid or tau pathology, suggesting the presence of an additional factor. TDP-43 has been suggested here as a potential key actor in the potentiation of observed neurodegeneration. TDP-43 is thought to be associated with a greater degree of volume loss in AD, particularly when localized in the hippocampus, more so than when localized in the amygdala alone, and this independently of the presence of HS. The discrepancies between the amount of tau (for example, evaluated with tau-PET scan) compared to the degree of neurodegeneration are called the T-N mismatch (Carlos et al., 2023b), which correlated with non-AD pathology and particularly TDP-43 copathology as proven on neuropathology studies after autopsy (Josephs et al., 2017; Woodworth et al., 2022; Lyu et al., 2024). Tau was shown to correlate with a faster rate of atrophy early in the disease stage of AD, but had a lesser effect in the later stages of the disease (Josephs et al., 2017). Woodworth et al. (2022) also found a strong association between HS and hippocampal volume. Hippocampal subfield studies demonstrated a unique effect of TDP-43 with smaller CA1 and subiculum as well as inward deformation in bilateral CA1 and subiculum, and the most anterior portion of the left hippocampus. This deformation correlated with cognitive scores (Vos de Wael et al., 2018; Heywood et al., 2022). Pattern of MTL atrophy may differentiate AD with versus without TDP-43 pathology. de Flores et al. (2020) found a strong association between the anterior region of the MTL and TDP-43 (particularly in the entorhinal cortex and anterior hippocampus volumes). At the same time, tau was more associated with the posterior part of the hippocampus, and suggested using the ratio between the anterior hippocampus and the parahippocampal cortex that would serve as an early marker of TDP 43 beyond amygdala-only pathology in AD copathology (de Flores et al., 2020).
MRI brain scans enable volumetric analysis of other areas of interest, as well as the assessment of other possible confounders and co-pathologies. In one longitudinal MRI study, AD neuropathology was more closely associated with changes in ventricular volume than with hippocampal volumes, with CAA and vascular co-pathology also being potential contributors (Erten-Lyons et al., 2013). A more recent study with 3D-T1 3T-MRI showed that excessive amygdala volume loss could serve as a clinical biomarker for underlying TDP-43/LATE copathology (Wesseling et al., 2025). In Kim et al. (2018)’s study comparing the clinical and pathological presentations between the different subtypes of FTLD-TDP and FTLD-tau, the MRI brain showed that in FTLD-TDP as a primary disease with additional concurrent tau, there was more widespread atrophy compared to FTLD-TDP alone. Additionally, for primary FTLD-tau (CBD) with concomitant TDP-43, there was significant left asymmetrical atrophy, particularly in frontoparietal, hippocampal, striatum, and amygdala, when pure FTLD-tau (CBD) was associated with bilateral frontoparietal and basal ganglia atrophy, sparing the MTL (Kim et al., 2018; Buciuc et al., 2020; de Boer et al., 2020). More specific techniques, such as diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), are being studied. White matter (WM) changes are an important feature associated with the process of neurodegeneration and axonal loss. Structural MRI, as well as DTI, may allow for the identification of patterns that help distinguish them from what is usually attributed to small vessel disease. In ALS, Cheng et al. (2020) demonstrated macro and microstructural WM changes with alteration of the corticospinal tract and corpus callosum with increased mean diffusivity and decreased fractional anisotropy (FA), as well as decreased fiber density and bundle cross-section on Fixel-based analysis (FBA). A study by Maj et al. (2022) also suggested that using FA at the brainstem level and particularly in the pons could be a valuable biomarker for distinguishing ALS patients from healthy controls. Cortical tau load in AD has shown to be associated with worse WM burden (Brun and Englund, 1986; McAleese et al., 2015; Kantarci et al., 2017). Regional differences have been identified in AD, with temporal and parietal WM changes reported as correlating with the cortical axonal loss in AD, while frontal changes are a result of both small vessel disease and the AD degenerative process (Brun and Englund, 1986; McAleese et al., 2015). Patterns of atrophy have also been characterized in CBD and particularly in the premotor and supplemental areas (SMA) (Constantinides et al., 2019; Di Stasio et al., 2019). In PSP, the gray matter of the midbrain is involved, leading to the description of the “hummingbird sign” and “Mickey-mouse sign”; however, other regions can also be affected, including the superior cerebellar peduncles (SCP), the thalamus, and the frontal and motor areas (Albrecht et al., 2019; Lupascu et al., 2023). WM changes are also a key feature in PSP and CBD. FBA studies showed a specific pattern of bundle atrophy following axonal degeneration by quantifying fiber density and fiber bundle cross-section in 4R tauopathy and have been suggested as a better tool than DTI to assess in vivo, disease-specific, WM changes correlating with neuropathology findings associated with 4R tau spread and clinical symptoms, which could help monitor for disease progression. In PSP, involvement of the corpus callosum, as well as descending tracts from the primary motor cortex to the corona radiata, the internal capsule, thalamic radiation, and midbrain, is observed (Nguyen et al., 2021; Sakamoto et al., 2021; Uchida et al., 2023). FBA has also been used more recently in semantic variant dementia and is able to show a more comprehensive and specific map of WM changes than DTI, revealing early disruption in the anterior commissure, projections to the parahippocampal gyrus and amygdala, as well as parietal connection pathways in semantic dementia (Mandelli et al., 2025). FBA appears also able to differentiate changes due to presumed LATE from changes due to amnestic AD, and with alterations in the callosal fibers connecting the middle frontal gyri and of the cerebello-thalamo-cortical tracts in LATE, while involving more the callosal fibers connecting the superior frontal gyrus as well as temporo-limbic tracts in amnestic AD (Ahmadi et al., 2024; Lebrun et al., 2024; Vanderlinden et al., 2025). More studies will likely be conducted to expand our knowledge and the use of FBA in the future, enabling better assessment of TDP-43 copathology, not only in LATE and AD, but also in other tauopathies (Table 1).
Positron emission tomography scan (PET-scan) imaging
FDG-PET is a non-specific neuroimaging test used to assess patterns of glucose metabolism in the brain. Beyond initial visual assessment, a quantitative analysis using software enables a comparison of the subject to the brain atlas of normal controls, utilizing a z-score. This approach ultimately allows for assessing whether the area of hypometabolism matches a specific pattern described in a particular pathology, thereby increasing confidence in diagnosis and accuracy (Na et al., 2024). However, this is not a specific test and should always be integrated into the broader clinical and imaging context. A hypometabolism pattern affecting the posterior parietal and temporal lobes, including the posterior cingulate, is suggestive of AD pathology (Jagust et al., 2007). Stage et al. (2020) showed that, however, in late-onset non-AD dementia, both pronounced atrophy and hypometabolism predominate for the bilateral temporal and prefrontal cortices, extending to the parietal lobes in more advanced disease, which was concordant with the pattern seen in LATE, or TDP-43-HS. The lack of tau binding in the medial temporal lobes seemed to exclude PART (Stage et al., 2020). A temporolimbic FDG-PET pattern, thought to correlate with LATE-NC staging, was also reported in other studies, including the one by Grothe et al. (2023). A pattern of hypometabolism in the MTL and the orbitofrontal cortex with preserved inferior temporal cortex metabolism leading to a high inferior temporal/MTL ratio is suggestive of LATE-NC underlying pathology (Botha et al., 2018; Grothe et al., 2023; Corriveau-Lecavalier et al., 2024). An amyloid-positive PET scan is a useful tool to rule in the presence of Alzheimer’s pathology. In contrast, a negative amyloid PET scan can help rule it out, which can help assess or rule out co-pathology (Matsuda et al., 2022; Wolk et al., 2025).
Tau-PET is currently not widely available in clinics and is primarily used in research. It could play a role not only from a diagnosis standpoint and identifying tau pathology, but also for staging purposes. The diversity and multiple strains of tau, which are also broadly divided into AD-tau and non-AD-tau, make finding tau ligands challenging (Choi et al., 2018; Schöll et al., 2019; Buchholz and Zempel, 2024). Moreover, tau is located both extra- and intracellularly, adding to the challenge in the development of a proper molecule. First-generation Tau ligand Flortaucipir shows strong affinity for AD tau but low affinity and off-target binding for other tauopathies (Ossenkoppele et al., 2018). Several second-generation ligands are currently promising and have less off-target binding (Smith et al., 2020). [18F]-MK-6240 has higher selectivity and is specific mainly for tau associated with Alzheimer’s disease, and with less to no binding in non-AD tau (Malarte et al., 2021). [18F]PI-2620 has shown promise as a candidate for use in non-AD pathologies (Tezuka et al., 2021; Cassinelli Petersen et al., 2022). It revealed a distinct pattern of binding in amyloid and non-amyloid corticobasal syndrome, which could aid in differential diagnosis and the identification of 4R tauopathies (Palleis et al., 2021). Brendel et al.’s (2020) study, which used a dynamic acquisition protocol, showed moderate-to-high discriminative performance between PSP and controls with [(18)F]PI-2620, characterized by increased uptake in the globus pallidus and subcortical regions associated with PSP (Yap et al., 2021). [18F]PI-2620 is currently in phase 3 of clinical development for the detection of tau in AD, as well as in 4R tauopathy like PSP and CBD, and received a fast track designation from the FDA. The study will evaluate cognitively normal seniors, as well as their ability to distinguish AD or FTLD-tau from FTLD-TDP, and assess their association with phenotypical features.1 [18F]OXD-2314 is another ligand showing promise in non-AD tau, pending further evaluation in patient populations of non-AD tauopathies (Lindberg et al., 2024). A negative tau PET scan, combined with suggestive FDG-PET findings for temporal-limbic hypometabolism, can suggest TDP-43 pathology (Botha et al., 2018; Stage et al., 2020).
Direct detection of TDP-43 aggregates by PET holds promises for a more accurate diagnosis, patient stratification, and assessment of therapeutic efficacy in clinical trials. Current research to identify the best candidate is ongoing. Some promising candidates have been reported, particularly the [18F]ACI-19278 tracer, which could become the first TDP-43 PET scan tracer in the future. This tracer showed high affinity for human brain-derived TDP-43 and appeared to be able to differentiate FTLD-TDP type A and B from controls in samples. It did not show off-target binding and was highly selective for TDP-43 (Seredenina et al., 2023). Seredenina et al. (2023) also reported that it quickly and efficiently crossed the blood-brain barrier and had a fast and complete washout, which limits the risk for a non-specific background signal. All these characteristics are promising, and the product is currently in an early-phase 1 clinical trial, with study completion estimated for late 2026.
TDP-43 biomarkers beyond neuroimaging
The development of fluid biomarkers for TDP-43 is ongoing, but has proved to be challenging; however, recent advancements using either antibody-based approach or proteomics show promise. Several issues remain, including the risk of binding to both the pathological and physiological forms of TDP-43, as well as variations in detected levels depending on solubility and sample origin. TDP-43 is a widely expressed protein, and its levels may not be explicitly related to CNS damage, but rather to damage in other organs (Cordts et al., 2023; López-Carbonero et al., 2024). Katisko et al. (2022)’s study utilized the Simoa® sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit for TDP-43 to measure soluble TDP-43 in serum. Their study revealed a significant difference, with slightly decreased TDP-43 levels in FTD-TDP compared to FTD-tau and healthy controls (Katisko et al., 2022). Ren et al. (2021) also used a sandwich ELISA kit for TDP-43 and measured plasma and CSF TDP-43 levels, as well as phosphorylated TDP-43 (pTDP-43) levels, in ALS compared to healthy controls. The results showed that both TDP-43 and pTDP-43 were elevated in ALS and correlated well with CSF levels. The use of pTDP-43/TDP-43 in plasma helped differentiate between healthy controls and the ALS group and could be a good candidate as a biomarker in this context (Ren et al., 2021). The Multimer Detection System (MDS) platform, an atypical sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), was utilized by Jamerlan et al., (2023; 2025) and enabled the detection of increased oligomeric TDP-43 in the plasma of a small cohort of FTLD-semantic dementia. Another promising new technique is the proteomic platform using the Nucleic-Acid-Linked Immuno-Sandwich Assay (NULISA™), which utilizes oligonucleotide-conjugated antibodies to amplify signals from neurodegeneration-associated proteins, including those related to TDP-43 pathologies. Several studies have demonstrated its potential in detecting TDP-43 and pTDP-43 in plasma, suggesting its potential as a diagnostic tool in ALS and other TDP-43-related pathologies, including LATE-NC. However, the detection sensitivity remains suboptimal, and further studies are currently underway (Zeng et al., 2024; Thomas et al., 2025; Wang et al., 2025).
Another method currently evaluated uses the measurement of extracellular vesicles (EVs) in biofluids. EVs are cell-derived lipid nanoparticles that are released by cells into the extracellular environment, serving as transport vesicles that traffic macromolecules from the CNS to the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) and blood. In LATE, EVs-TDP-43 derived from astrocyte-derived extracellular vesicles (ADEVs) was shown to be significantly increased in the plasma of individuals. This finding suggests that EVs-TDP-43 derived from neuronal and glial cells may serve as valuable diagnostic biomarkers in neurodegeneration, including LATE and potentially other TDP-43 proteinopathies. However, several questions and challenges remain, including the replicability and consistency of findings, the risk of potential artifacts from the EV enrichment material, and the time-consuming and often poorly reproducible methods of EV purification (Thompson et al., 2016; Sproviero et al., 2019; Pasetto et al., 2021; Winston et al., 2022; Dellar et al., 2025).
Another growing field of research for TDP-43 biomarkers focuses on the study of cryptic peptides. Abnormal TDP-43 affects its normal splicing function, leading to the inclusion of cryptic exons during transcription. This results in cryptic peptides from altered transcripts, which subsequently impair functions when not degraded by regulatory and monitoring pathways. Transcriptomic and proteomic approaches are currently being investigated to develop validated assays that assess cryptic peptides in biospecimens, thereby facilitating the detection of TDP-43 pathology, including co-pathology (Irwin et al., 2024; Seddighi et al., 2024).
Recent findings of high concentrations of TDP-43 in the cytosol of platelets have sparked interest in utilizing platelets as a potential biomarker (Wilhite et al., 2017; Luthi-Carter et al., 2024). Research focusing on ALS demonstrated increased levels of abnormal TDP-43 in platelets in the ALS group compared to healthy controls, and increased with disease duration (Hishizawa et al., 2019). It is hypothesized that abnormal TDP-43 could make its way from astrocytes to platelets via a permeable blood-brain barrier (Fang et al., 2014; Kopeikina and Ponomarev, 2021) or via platelet activation and release of platelet-activating factor (PAF) at the choroid plexus-blood-CSF barrier due to inflammation and leading to a leaky barrier (Čarna et al., 2023). However, much remains to be learned about utilizing platelets as a biomarker in copathology. Another approach by Quek et al. (2020) used ALS patient’s blood to generate monocyte-derived microglia (MDMi), which allowed the detection of TDP-43 and pTDP-43 cytoplasmic inclusions in ALS patients compared to healthy control. This model also helped demonstrating the mislocalization of TDP-43 in microglia in ALS patients (Quek et al., 2020; Quek et al., 2022). MDMi allows an easy sampling using blood collection, and shows promise as a screening tool in neurodegeneration and dementia beyond ALS (Banerjee et al., 2021; Quek and White, 2023).
The skin and the nervous system share the same ectodermal origin, leading to the concept of the skin-brain axis (Jameson et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2024), making skin an attractive candidate for assessing abnormal proteins and biomarkers in neurodegenerative diseases (Suzuki et al., 2010; Paré et al., 2015). There is already a fair amount of published work supporting the skin as a potentially accessible tissue for evaluating TDP-43 pathology (Sabatelli et al., 2015; Wang et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2015). Most studies comes from the ALS research and have shown a significant association between a higher amount of TDP-43 inclusion in ALS patients and a significantly higher amount of TDP-43 in the epidermis and dermis, as well as a higher amount of TDP-43 in the cytoplasm of dermal fibroblasts (Riancho et al., 2020; Romano et al., 2020; Rubio et al., 2022). Epidermal TDP-43 mRMA expression appears reduced in ALS patients, particularly in those with upper-limb onset (Abe et al., 2017). Ren et al. (2018) demonstrated the involvement of the peripheral and autonomic nervous systems in ALS patients, characterized by reduced intraepidermal nerve fiber density, as well as the deposition of TDP-43 and phosphorylated TDP-43 around autonomic nerve fibers. One study in a small cohort of sporadic ALS failed to demonstrate any specific changes in fibroblasts however (Codron et al., 2018), and more data remain needed in larger cohorts at different stages of the disease and particularly at an early stage as the amount of TDP-43 positive cells has been shown to be positively associated with the duration of the disease in ALS patients (Suzuki et al., 2010). Besides ALS, skin biopsy and fibroblast use have limited evidence in FTLD, which may be related to culture conditions and other limitations. However, fibroblasts may exhibit other markers of cellular stress that could be useful in identifying FTLD patients, and further research is ongoing (Riancho et al., 2020; Leskelä et al., 2021; Hoffmann and Haapasalo, 2022). Skin biopsy studies have shown promise in detecting tau using a tau seeding activity assay (tau-SAA), which exhibits a greater affinity for 4R tau than 3R tau, and notably demonstrates better accuracy in PSP (Vacchi et al., 2022; Dellarole et al., 2024; Martinez-Valbuena et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024). Beyond the skin, muscle has also been investigated, mainly in neuromuscular diseases such as ALS. However, physiologically, TDP-43 is involved in the muscular regeneration process, and deposits are hypothesized to be more closely related to this process; further research is required (Ishikawa et al., 2012; Paré et al., 2015; Vogler et al., 2018; Liu et al., 2022). The olfactory mucosa is also studied, and TDP-43 aggregates using the TDP-43 seeding amplification assay (TDP43-SAA) have been shown to accurately distinguish TDP-43 pathology, pending further validation on a larger cohort (Fontana et al., 2024; Vizziello et al., 2025). Tau-SAA on the olfactory mucosa also has some limited positive data, but is considered invasive, increasing the risk of infections, and overall a less preferable option (Vacchi et al., 2025).
Retinal-based TDP-43 biomarkers are also being investigated, as some recent animal studies suggest early retinal changes in TDP-43 proteinopathies (Gao et al., 2024). However, there is still limited data in humans, primarily from autopsy reports (Glashutter et al., 2025). A small molecule tracer selectively binding TDP-43 in the retina is being evaluated through a phase 1/2 trial, the PROBE-trial, though no final results have been published yet, and research is ongoing (Glashutter et al., 2025). The use of nanotechnology, like the tau-fluorophore BT-1, a BODIPY-based probe and highly specific fluorescent ligand, is another promising technique that may expand our ability to evaluate for tau in the human retina and our ability for early detection of tauopathies (Soloperto et al., 2022; Barolo et al., 2024). The same techniques could potentially be used to develop TDP-43 probes.
In summary, the development of valid tools for the detection of TDP-43 in biofluids or other tissues proves to be challenging and is currently ongoing, including several other targets beyond plasma and CSF, with some data in skin and fibroblasts and pending larger studies, while retinal-based biomarkers using nanotechnology and TDP-43 or tau-probes may be promising, though also in need of further research and validation (Table 2).
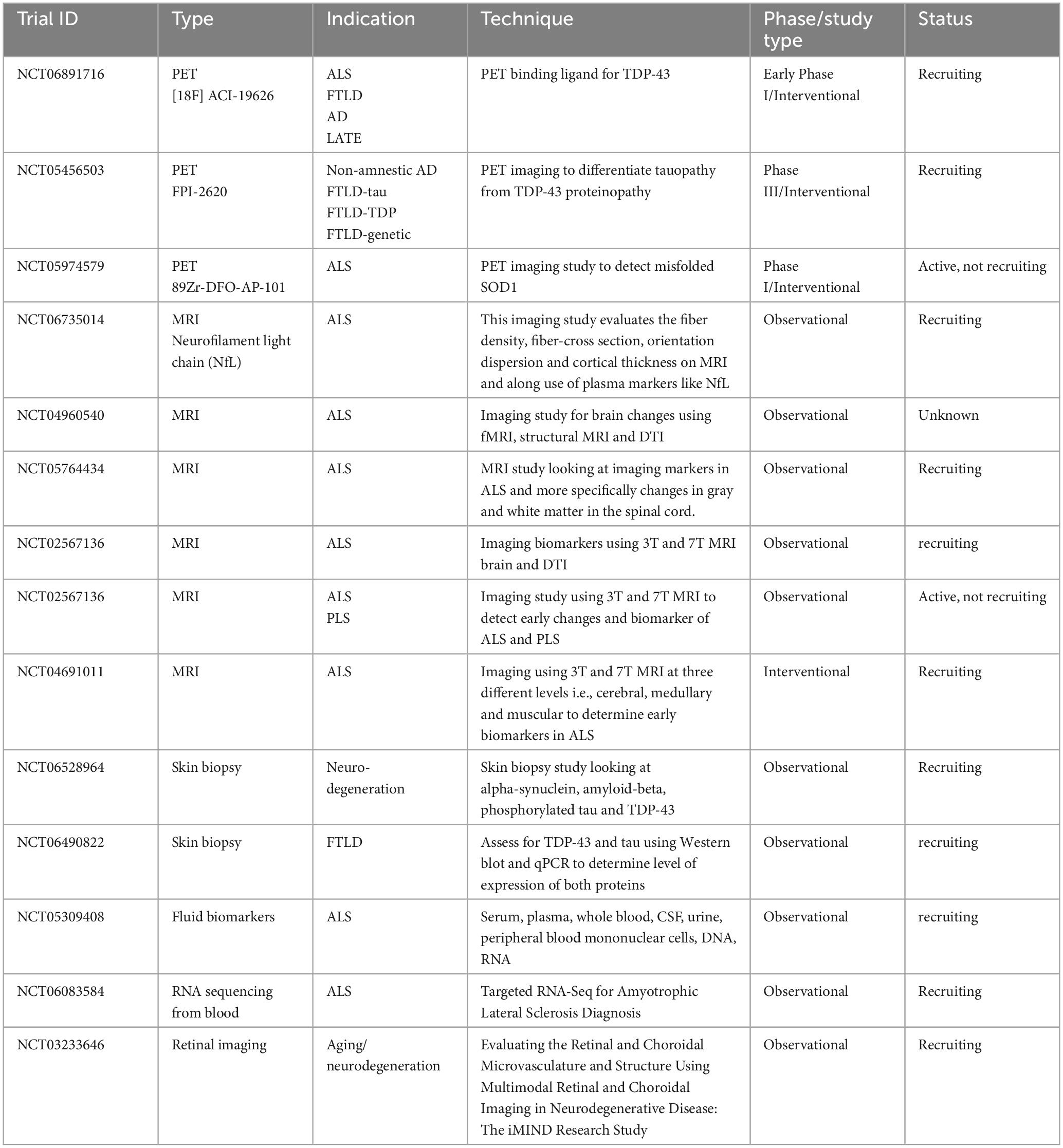
Table 2. Summary of clinical trials on TDP-43 proteinopathy and biomarkers currently listed as recruiting/active in clinicaltrials.gov.
Conclusion
TDP-43 frequently cohabits, though to varying degrees, with other neurodegenerative diseases, including tauopathies, and is suspected to be a major contributor to the neurodegenerative process. Several arguments suggest potential additive or synergistic effects with other proteins, particularly with tau, although common pathways and pathophysiological processes leading to multiple proteinopathies are also considered. The development of accurate and validated neuroimaging and fluid or tissue biomarkers is ongoing and will be crucial in identifying TDP-43 pathology and co-pathology, which will enable more precise diagnosis and in vivo pathology classification, facilitating the more accurate selection of candidates for clinical trials and allowing for future targeted and tailored treatments.
Author contributions
AN: Writing – original draft, Resources, Investigation. CD: Project administration, Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Resources.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
Abe, K., Ohkubo, T., and Yokota, T. (2017). <Original Article> TDP-43 in the skin of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. J. Med. Dent. Sci. 64, 9–17. doi: 10.11480/jmds.640102
Ahmadi, K., Pereira, J., van Westen, D., Pasternak, O., Zhang, F., Nilsson, M., et al. (2024). Fixel-based analysis reveals tau-related white matter changes in early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 44:e0538232024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0538-23.2024
Albrecht, F., Bisenius, S., Neumann, J., Whitwell, J., and Schroeter, M. (2019). Atrophy in midbrain & cerebral/cerebellar pedunculi is characteristic for progressive supranuclear palsy – A double-validation whole-brain meta-analysis. Neuroimage Clin. 22:101722. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2019.101722
Amador-Ortiz, C., Lin, W., Ahmed, Z., Personett, D., Davies, P., Duara, R., et al. (2007). TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 61, 435–445. doi: 10.1002/ana.21154
Anderson, A., Dopler, M., Arezoumandan, S., Osei-Kankam, D., Davis, S., Ajroud, K., et al. (2025). Cytoplasmic expression of trans-active response DNA-binding protein-43 in aged mice display hippocampal sclerosis-like degeneration and neuronal loss with reduced lifespan. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 84, 293–304. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlae137
Arai, T., Hasegawa, M., Akiyama, H., Ikeda, K., Nonaka, T., Mori, H., et al. (2006). TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 351, 602–611. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.10.093
Arribas, V., Onetti, Y., Ramiro-Pareta, M., Villacampa, P., Beck, H., Alberola, M., et al. (2024). Endothelial TDP-43 controls sprouting angiogenesis and vascular barrier integrity, and its deletion triggers neuroinflammation. JCI Insight 9:e177819. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.177819
Ash, P., Zhang, Y., Roberts, C., Saldi, T., Hutter, H., Buratti, E., et al. (2010). Neurotoxic effects of TDP-43 overexpression in C. elegans. Hum. Mol. Genet. 19, 3206–3218. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddq230
Avecillas-Chasin, J., Levinson, S., Kuhn, T., Omidbeigi, M., Langevin, J., Pouratian, N., et al. (2023). Connectivity-based parcellation of the amygdala and identification of its main white matter connections. Sci. Rep. 13:1305. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28100-6
Babinchak, W., and Surewicz, W. (2023). Biophysical Studies of LLPS and Aggregation of TDP-43 LCD. Methods Mol. Biol. 2551, 497–513. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2597-2_31
Babinchak, W., Haider, R., Dumm, B., Sarkar, P., Surewicz, K., Choi, J., et al. (2019). The role of liquid-liquid phase separation in aggregation of the TDP-43 low-complexity domain. J. Biol. Chem. 294, 6306–6317. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.007222
Banerjee, A., Lu, Y., Do, K., Mize, T., Wu, X., Chen, X., et al. (2021). Validation of induced microglia-like cells (iMG Cells) for future studies of brain diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15:629279. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.629279
Barolo, L., Gigante, Y., Mautone, L., Ghirga, S., Soloperto, A., Giorgi, A., et al. (2024). Ferritin nanocage-enabled detection of pathological tau in living human retinal cells. Sci. Rep. 14:11533. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-62188-8
Bejanin, A., Murray, M., Martin, P., Botha, H., Tosakulwong, N., Schwarz, C., et al. (2019). Antemortem volume loss mirrors TDP-43 staging in older adults with non-frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Brain 142, 3621–3635. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz277
Bentmann, E., Neumann, M., Tahirovic, S., Rodde, R., Dormann, D., and Haass, C. (2012). Requirements for stress granule recruitment of fused in sarcoma (FUS) and TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43). J. Biol. Chem. 287, 23079–23094. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.328757
Besser, L., Crary, J., Mock, C., and Kukull, W. (2017). Comparison of symptomatic and asymptomatic persons with primary age-related tauopathy. Neurology 89, 1707–1715. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000004521
Bocchetta, M., Iglesias, J., Cash, D., Warren, J., and Rohrer, J. (2019). Amygdala subnuclei are differentially affected in the different genetic and pathological forms of frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 11, 136–141. doi: 10.1016/j.dadm.2018.12.006
Bocchetta, M., Malpetti, M., Todd, E., Rowe, J., and Rohrer, J. (2021). Looking beneath the surface: The importance of subcortical structures in frontotemporal dementia. Brain Commun. 3:fcab158. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcab158
Botha, H., Mantyh, W., Murray, M., Knopman, D., Przybelski, S., Wiste, H., et al. (2018). FDG-PET in tau-negative amnestic dementia resembles that of autopsy-proven hippocampal sclerosis. Brain 141, 1201–1217. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy049
Brendel, M., Barthel, H., van Eimeren, T., Marek, K., Beyer, L., Song, M., et al. (2020). Assessment of 18F-PI-2620 as a biomarker in progressive supranuclear palsy. JAMA Neurol. 77, 1408–1419. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.2526
Brenowitz, W., Monsell, S., Schmitt, F., Kukull, W., and Nelson, P. (2014). Hippocampal sclerosis of aging is a key Alzheimer’s disease mimic: Clinical-pathologic correlations and comparisons with both alzheimer’s disease and non-tauopathic frontotemporal lobar degeneration. J. Alzheimers Dis. 39, 691–702. doi: 10.3233/JAD-131880
Bright, F., Chan, G., van Hummel, A., Ittner, L., and Ke, Y. D. (2021). TDP-43 and inflammation: Implications for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22:7781. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157781
Brun, A., and Englund, E. (1986). A white matter disorder in dementia of the Alzheimer type: A pathoanatomical study. Ann. Neurol. 19, 253–262. doi: 10.1002/ana.410190306
Buchholz, S., and Zempel, H. (2024). The six brain-specific TAU isoforms and their role in Alzheimer’s disease and related neurodegenerative dementia syndromes. Alzheimers Dement. 20, 3606–3628. doi: 10.1002/alz.13784
Buciuc, M., Botha, H., Murray, M., Schwarz, C., Senjem, M., Jones, D., et al. (2020). Utility of FDG-PET in diagnosis of Alzheimer-related TDP-43 proteinopathy. Neurology 95, e23–e34. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000009722
Buratti, E., and Baralle, F. (2010). The multiple roles of TDP-43 in pre-mRNA processing and gene expression regulation. RNA Biol. 7, 420–429. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.4.12205
Cagnin, A., Mariotto, S., Fiorini, M., Gaule, M., Bonetto, N., Tagliapietra, M., et al. (2017). Microglial and neuronal TDP-43 pathology in anti-IgLON5-related tauopathy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 59, 13–20. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170189
Carlos, A., Sekiya, H., Koga, S., Gatto, R., Casey, M., Pham, N., et al. (2023a). Clinicopathologic features of a novel star-shaped transactive response DNA-binding protein 43 (TDP-43) pathology in the oldest old. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 83, 36–52. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlad105
Carlos, A., Tosakulwong, N., Weigand, S., Senjem, M., Schwarz, C., Knopman, D., et al. (2023b). TDP-43 pathology effect on volume and flortaucipir uptake in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 2343–2354. doi: 10.1002/alz.12878
Čarna, M., Onyango, I. G., Katina, S., Holub, D., Novotny, J. S., Nezvedova, M., et al. (2023). Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease: Involvement of the choroid plexus. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 3537–3554. doi: 10.1002/alz.12970
Carrasco, J., Antón, R., Valbuena, A., Pantoja-Uceda, D., Mukhi, M., Hervás, R., et al. (2023). Metamorphism in TDP-43 prion-like domain determines chaperone recognition. Nat. Commun. 14:466. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36023-z
Cassinelli Petersen, G., Roytman, M., Chiang, G., Li, Y., Gordon, M., and Franceschi, A. (2022). Overview of tau PET molecular imaging. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 35, 230–239. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000001035
Chang, C., Wu, T., Wu, C., Chiang, M., Toh, E., Hsu, Y., et al. (2012). The N-terminus of TDP-43 promotes its oligomerization and enhances DNA binding affinity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 425, 219–224. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2012.07.071
Chanson, J., Echaniz-Laguna, A., Vogel, T., Mohr, M., Benoilid, A., Kaltenbach, G., et al. (2010). TDP43-positive intraneuronal inclusions in a patient with motor neuron disease and Parkinson’s disease. Neurodegener. Dis. 7, 260–264. doi: 10.1159/000273591
Cheng, L., Tang, X., Luo, C., Liu, D., Zhang, Y., and Zhang, J. (2020). Fiber-specific white matter reductions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neuroimage Clin. 28:102516. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2020.102516
Cheng, Z., Nie, W., Leng, J., Yang, L., Wang, Y., Li, X., et al. (2024). Amygdala and cognitive impairment in cerebral small vessel disease: Structural, functional, and metabolic changes. Front. Neurol. 15:1398009. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1398009
Cherry, J., Kim, S., Stein, T., Pothast, M., Nicks, R., Meng, G., et al. (2020). Evolution of neuronal and glial tau isoforms in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Pathol. 30, 913–925. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12867
Choi, Y., Ha, S., Lee, Y., Kim, Y., Lee, D., and Kim, D. (2018). Development of tau PET imaging ligands and their utility in preclinical and clinical studies. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 52, 24–30. doi: 10.1007/s13139-017-0484-7
Chu, Y., Hirst, W., Federoff, H., Harms, A., Stoessl, A., and Kordower, J. (2024). Nigrostriatal tau pathology in parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 147, 444–457. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad388
Cividini, C., Basaia, S., Spinelli, E., Canu, E., Castelnovo, V., Riva, N., et al. (2022). Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia: Shared and divergent neural correlates across the clinical spectrum. Neurology 98, e402–e415. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000013123
Codron, P., Cassereau, J., Vourc’h, P., Veyrat-Durebex, C., Blasco, H., Kane, S., et al. (2018). Primary fibroblasts derived from sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients do not show ALS cytological lesions. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. Frontotemporal Degener. 19, 446–456. doi: 10.1080/21678421.2018.1431787
Cohen, T., Lee, V., and Trojanowski, J. Q. (2011). TDP-43 functions and pathogenic mechanisms implicated in TDP-43 proteinopathies. Trends Mol. Med. 17, 659–667. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2011.06.004
Cole, A. (2007). Hippocampal sclerosis: An inflammatory hypothesis. Neurology 69, 1204–1205. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000279585.36404.d0
Condello, C., Ayers, J., Dalgard, C., Garcia Garcia, M., Rivera, B., Seeley, W., et al. (2023). Guam ALS-PDC is a distinct double-prion disorder featuring both tau and Aβ prions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 120:e2220984120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2220984120
Constantinides, V., Paraskevas, G., Paraskevas, P., Stefanis, L., and Kapaki, E. (2019). Corticobasal degeneration and corticobasal syndrome: A review. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 1, 66–71. doi: 10.1016/j.prdoa.2019.08.005
Corbet, G., Wheeler, J., Parker, R., and Weskamp, K. (2021). TDP43 ribonucleoprotein granules: Physiologic function to pathologic aggregates. RNA Biol. 18, 128–138. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2021.1963099
Cordts, I., Wachinger, A., Scialo, C., Lingor, P., Polymenidou, M., Buratti, E., et al. (2023). TDP-43 proteinopathy specific biomarker development. Cells 12:597. doi: 10.3390/cells12040597
Corriveau-Lecavalier, N., Botha, H., Graff-Radford, J., Switzer, A., Przybelski, S., Wiste, H., et al. (2024). Clinical criteria for a limbic-predominant amnestic neurodegenerative syndrome. Brain Commun. 6:fcae183. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae183
Crary, J., Trojanowski, J., Schneider, J., Abisambra, J., Abner, E., Alafuzoff, I., et al. (2014). Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): A common pathology associated with human aging. Acta Neuropathol. 128, 755–766. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1349-0
Cykowski, M., Powell, S., Schulz, P., Takei, H., Rivera, A., Jackson, R., et al. (2017). Hippocampal sclerosis in older patients: Practical examples and guidance with a focus on cerebral age-related TDP-43 with sclerosis. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 141, 1113–1126. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0469-SA
Davidson, Y., Amin, H., Kelley, T., Shi, J., Tian, J., Kumaran, R., et al. (2009). TDP-43 in ubiquitinated inclusions in the inferior olives in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and in other neurodegenerative diseases: A degenerative process distinct from normal ageing. Acta Neuropathol. 118, 359–369. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0526-z
de Boer, E., Orie, V., Williams, T., Baker, M., De Oliveira, H., Polvikoski, T., et al. (2020). TDP-43 proteinopathies: A new wave of neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 92, 86–95. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2020-322983
de Flores, R., Wisse, L., Das, S., Xie, L., McMillan, C., Trojanowski, J., et al. (2020). Contribution of mixed pathology to medial temporal lobe atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 16, 843–852. doi: 10.1002/alz.12079
Dellar, E., Nikel, L., Fowler, S., Vahsen, B., Dafinca, R., Feneberg, E., et al. (2025). Extracellular vesicles in TDP-43 proteinopathies: Pathogenesis and biomarker potential. Mol. Neurodegener. 20:68. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00859-4
Dellarole, I., Vacchi, E., Ruiz-Barrio, I., Pinton, S., Raimondi, A., Rossi, S., et al. (2024). Tau seeding activity in skin biopsy differentiates tauopathies from synucleinopathies. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 10:116. doi: 10.1038/s41531-024-00728-9
Di Stasio, F., Suppa, A., Marsili, L., Upadhyay, N., Asci, F., Bologna, M., et al. (2019). Corticobasal syndrome: Neuroimaging and neurophysiological advances. Eur. J. Neurol. 26, 701–e52. doi: 10.1111/ene.13928
Dugan, A., Nelson, P., Katsumata, Y., Shade, L., Boehme, K., Teylan, M., et al. (2021). Analysis of genes (TMEM106B, GRN, ABCC9, KCNMB2, and APOE) implicated in risk for LATE-NC and hippocampal sclerosis provides pathogenetic insights: A retrospective genetic association study. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 9:152. doi: 10.1186/s40478-021-01250-2
Dugger, B., and Dickson, D. (2017). Pathology of neurodegenerative diseases. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 9:a028035. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a028035
Dulski, J., Cerquera-Cleves, C., Milanowski, L., Kidd, A., Sitek, E., Strongosky, A., et al. (2021). Clinical, pathological and genetic characteristics of Perry disease-new cases and literature review. Eur. J. Neurol. 28, 4010–4021. doi: 10.1111/ene.15048
Erten-Lyons, D., Dodge, H. H., Woltjer, R., Silbert, L. C., Howieson, D. B., Kramer, P., et al. (2013). Neuropathologic basis of age-associated brain atrophy. JAMA Neurol. 70, 616–622. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.1957
Ezzat, K., Sturchio, A., and Espay, A. (2023). The shift to a proteinopenia paradigm in neurodegeneration. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 193, 23–32. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-323-85555-6.00001-1
Fang, W., Zhang, R., Sha, L., Lv, P., Shang, E., Han, D., et al. (2014). Platelet activating factor induces transient blood-brain barrier opening to facilitate edaravone penetration into the brain. J. Neurochem. 128, 662–671. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12507
Fontana, E., Bongianni, M., Benussi, A., Bronzato, E., Scialo, C., Sacchetto, L., et al. (2024). Detection of TDP-43 seeding activity in the olfactory mucosa from patients with frontotemporal dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 20, 1156–1165. doi: 10.1002/alz.13541
Forman, E., Herbert, J., Moitra, E., Yeomans, P., and Geller, P. A. A. (2007). randomized controlled effectiveness trial of acceptance and commitment therapy and cognitive therapy for anxiety and depression. Behav. Modif. 31, 772–799. doi: 10.1177/0145445507302202
Gao, J., Leinonen, H., Wang, E., Ding, M., Perry, G., Palczewski, K., et al. (2024). Sex-specific early retinal dysfunction in mutant TDP-43 transgenic mice. J. Alzheimers Dis. 97, 927–937. doi: 10.3233/JAD-231102
Garamszegi, S., Brzostowicki, D., Coyne, T., Vontell, R., and Davis, D. A. (2024). TDP-43 and Alzheimer’s disease pathology in the brain of a harbor porpoise exposed to the cyanobacterial toxin BMAA. Toxins 16:42. doi: 10.3390/toxins16010042
Gefen, T., Ahmadian, S., Mao, Q., Kim, G., Seckin, M., Bonakdarpour, B., et al. (2018). Combined pathologies in FTLD-TDP types A and C. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 77, 405–412. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nly018
Gelpi, E., Höftberger, R., Graus, F., Ling, H., Holton, J., Dawson, T., et al. (2016). Neuropathological criteria of anti-IgLON5-related tauopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 132, 531–543. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1591-8
Gendron, T., and Petrucelli, L. (2009). The role of tau in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 4:13. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-4-13
Geser, F., Robinson, J., Malunda, J., Xie, S., Clark, C., Kwong, L., et al. (2010). Pathological 43-kDa transactivation response DNA-binding protein in older adults with and without severe mental illness. Arch. Neurol. 67, 1238–1250. doi: 10.1001/archneurol.2010.254
Geser, F., Winton, M., Kwong, L., Xu, Y., Xie, S., Igaz, L., et al. (2008). Pathological TDP-43 in parkinsonism-dementia complex and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of Guam. Acta Neuropathol. 115, 133–145. doi: 10.1007/s00401-007-0257-y
Glashutter, M., Wijesinghe, P., and Matsubara, J. A. (2025). TDP-43 as a potential retinal biomarker for neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Neurosci. 19:1533045. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1533045
Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M., Villar-Conde, S., Astillero-Lopez, V., Villanueva-Anguita, P., Ubeda-Banon, I., Flores-Cuadrado, A., et al. (2023). Human amygdala involvement in Alzheimer’s disease revealed by stereological and dia-PASEF analysis. Brain Pathol. 33:e13180. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13180
Grothe, M., Moscoso, A., Silva-Rodríguez, J., Lange, C., Nho, K., Saykin, A., et al. (2023). Differential diagnosis of amnestic dementia patients based on an FDG-PET signature of autopsy-confirmed LATE-NC. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 1234–1244. doi: 10.1002/alz.12763
Gu, J., Wu, F., Xu, W., Shi, J., Hu, W., Jin, N., et al. (2017). TDP-43 suppresses tau expression via promoting its mRNA instability. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, 6177–6193. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx175
Harrison, A., and Shorter, J. (2017). RNA-binding proteins with prion-like domains in health and disease. Biochem. J. 474, 1417–1438. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20160499
Hasegawa, M., Arai, T., Akiyama, H., Nonaka, T., Mori, H., Hashimoto, T., et al. (2007). TDP-43 is deposited in the Guam parkinsonism-dementia complex brains. Brain 130, 1386–1394. doi: 10.1093/brain/awm065
Hatanpaa, K., Raisanen, J., Herndon, E., Burns, D., Foong, C., Habib, A., et al. (2014). Hippocampal sclerosis in dementia, epilepsy, and ischemic injury: Differential vulnerability of hippocampal subfields. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 73, 136–142. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000000170
Heyburn, L., Abutarboush, R., Goodrich, S., Urioste, R., Batuure, A., Statz, J., et al. (2019a). repeated low-level blast overpressure leads to endovascular disruption and alterations in TDP-43 and Piezo2 in a rat model of blast TBI. Front. Neurol. 10:766. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00766
Heyburn, L., Sajja, V., and Long, J. (2019b). The role of TDP-43 in military-relevant TBI and chronic neurodegeneration. Front. Neurol. 10:680. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2019.00680
Heywood, A., Stocks, J., Schneider, J., Arfanakis, K., Bennett, D., Beg, M., et al. (2022). The unique effect of TDP-43 on hippocampal subfield morphometry and cognition. Neuroimage Clin. 35:103125. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103125
Hickman, R., Flowers, X., and Wisniewski, T. (2020). Primary age-related tauopathy (PART): Addressing the spectrum of neuronal tauopathic changes in the aging brain. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 20:39. doi: 10.1007/s11910-020-01063-1
Hishizawa, M., Yamashita, H., Akizuki, M., Urushitani, M., and Takahashi, R. (2019). TDP-43 levels are higher in platelets from patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis than in healthy controls. Neurochem. Int. 124, 41–45. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2018.12.009
Hobson, E., and McDermott, C. (2016). Supportive and symptomatic management of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 12, 526–538. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.111
Hoffmann, D., and Haapasalo, A. (2022). Patient-derived skin fibroblasts as a model to study frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 17, 2669–2671. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.335814
Insel, P., Mormino, E., Aisen, P., Thompson, W., and Donohue, M. (2020). Neuroanatomical spread of amyloid β and tau in Alzheimer’s disease: Implications for primary prevention. Brain Commun. 2:fcaa007. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcaa007
Irwin, K., Jasin, P., Braunstein, K., Sinha, I., Garret, M., Bowden, K., et al. (2024). A fluid biomarker reveals loss of TDP-43 splicing repression in presymptomatic ALS-FTD. Nat. Med. 30, 382–393. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02788-5
Ishikawa, H., Yasui, K., Oketa, Y., Suzuki, M., and Ono, S. (2012). Increased expression of valosin-containing protein in the skin of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Clin. Neurosci. 19, 522–526. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2011.05.044
Jack, C., Andrews, J., Beach, T., Buracchio, T., Dunn, B., Graf, A., et al. (2024). Revised criteria for diagnosis and staging of Alzheimer’s disease: Alzheimer’s Association Workgroup. Alzheimers Dement. 20, 5143–5169. doi: 10.1002/alz.13859
Jagust, W., Reed, B., Mungas, D., Ellis, W., and Decarli, C. (2007). What does fluorodeoxyglucose PET imaging add to a clinical diagnosis of dementia? Neurology 69, 871–877. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000269790.05105.16
Jamerlan, A., Shim, K., Sharma, N., and An, S. (2025). Multimer detection system: A universal assay system for differentiating protein oligomers from monomers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26:1199. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031199
Jamerlan, A., Shim, K., Youn, Y., Teunissen, C., An, S., Scheltens, P., et al. (2023). Increased oligomeric TDP-43 in the plasma of Korean frontotemporal dementia patients with semantic dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 19, 4020–4027. doi: 10.1002/alz.13127
Jameson, C., Boulton, K., Silove, N., Nanan, R., and Guastella, A. (2023). Ectodermal origins of the skin-brain axis: A novel model for the developing brain, inflammation, and neurodevelopmental conditions. Mol. Psychiatry 28, 108–117. doi: 10.1038/s41380-022-01829-8
Jellinger, K., and Attems, J. (2007). Neurofibrillary tangle-predominant dementia: Comparison with classical Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. 113, 107–117. doi: 10.1007/s00401-006-0156-7
Jiang, L., Xue, W., Hong, J., Zhang, J., Li, M., Yu, S., et al. (2017). The N-terminal dimerization is required for TDP-43 splicing activity. Sci. Rep. 7:6196. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-06263-3
Jo, M., Lee, S., Jeon, Y., Kim, S., Kwon, Y., and Kim, H. (2020). The role of TDP-43 propagation in neurodegenerative diseases: Integrating insights from clinical and experimental studies. Exp. Mol. Med. 52, 1652–1662. doi: 10.1038/s12276-020-00513-7
Johnson, A., and Lukens, J. (2025). Emerging roles for innate and adaptive immunity in tauopathies. Cell Rep. 44:116232. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2025.116232
Johnson, B., McCaffery, J., Lindquist, S., and Gitler, A. D. (2008). A yeast TDP-43 proteinopathy model: Exploring the molecular determinants of TDP-43 aggregation and cellular toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 105, 6439–6444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802082105
Josephs, K., Murray, M., Tosakulwong, N., Whitwell, J., Knopman, D., Machulda, M., et al. (2017). Tau aggregation influences cognition and hippocampal atrophy in the absence of beta-amyloid: A clinico-imaging-pathological study of primary age-related tauopathy (PART). Acta Neuropathol. 133, 705–715. doi: 10.1007/s00401-017-1681-2
Josephs, K., Whitwell, J., Weigand, S., Murray, M., Tosakulwong, N., Liesinger, A., et al. (2014). TDP-43 is a key player in the clinical features associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 127, 811–824. doi: 10.1007/s00401-014-1269-z
Kabashi, E., Valdmanis, P., Dion, P., Spiegelman, D., McConkey, B., Vande Velde, C., et al. (2008). TARDBP mutations in individuals with sporadic and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Nat. Genet. 40, 572–574. doi: 10.1038/ng.132
Kahriman, A., Bouley, J., Tuncali, I., Dogan, E., Pereira, M., Luu, T., et al. (2023). Repeated mild traumatic brain injury triggers pathology in asymptomatic C9ORF72 transgenic mice. Brain 146, 5139–5152. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad264
Kantarci, K., Murray, M., Schwarz, C., Reid, R., Przybelski, S., Lesnick, T., et al. (2017). White-matter integrity on DTI and the pathologic staging of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 56, 172–179. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.04.024
Katisko, K., Huber, N., Kokkola, T., Hartikainen, P., Krüger, J., Heikkinen, A., et al. (2022). Serum total TDP-43 levels are decreased in frontotemporal dementia patients with C9orf72 repeat expansion or concomitant motoneuron disease phenotype. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 14:151. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-01091-8
Katsumata, Y., Shade, L., Hohman, T., Schneider, J., Bennett, D., Farfel, J., et al. (2022). Multiple gene variants linked to Alzheimer’s-type clinical dementia via GWAS are also associated with non-Alzheimer’s neuropathologic entities. Neurobiol Dis. 174:105880. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105880
Kawakami, I., Arai, T., and Hasegawa, M. (2019). The basis of clinicopathological heterogeneity in TDP-43 proteinopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 138, 751–770. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02077-x
Kawashima, T., Doh-ura, K., Kikuchi, H., and Iwaki, T. (2001). Cognitive dysfunction in patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis is associated with spherical or crescent-shaped ubiquitinated intraneuronal inclusions in the parahippocampal gyrus and amygdala, but not in the neostriatum. Acta Neuropathol. 102, 467–472. doi: 10.1007/s004010100398
Ke, H., Liu, K., Jiao, B., and Zhao, L. (2023). Implications of TDP-43 in non-neuronal systems. Cell Commun. Signal. 21:338. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01336-5
Kellett, E., Bademosi, A., and Walker, A. (2025). Molecular mechanisms and consequences of TDP-43 phosphorylation in neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 20:53. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00839-8
Kicik, A., Kurt, E., Hari, E., Ulasoglu-Yildiz, Ç,Gurvit, H., and Demiralp, T. (2025). Impact of amygdala functional connectivity on cognitive impairment in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol. Sci. 46, 2601–2610. doi: 10.1007/s10072-025-08091-0
Kim, E., Brown, J., Deng, J., Hwang, J., Spina, S., Miller, Z., et al. (2018). Mixed TDP-43 proteinopathy and tauopathy in frontotemporal lobar degeneration: Nine case series. J. Neurol. 265, 2960–2971. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-9086-2
Kim, H., Jung, H., Park, Y., Heo, S., Kim, S., and Moon, M. (2024). Skin-brain axis in Alzheimer’s disease - Pathologic, diagnostic, and therapeutic implications: A hypothetical review. Aging Dis. 16, 901–916. doi: 10.14336/AD.2024.0406
Koga, S., Lin, W., Walton, R., Ross, O., and Dickson, D. W. (2018). TDP-43 pathology in multiple system atrophy: Colocalization of TDP-43 and α-synuclein in glial cytoplasmic inclusions. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 44, 707–721. doi: 10.1111/nan.12485
Koga, S., Sanchez-Contreras, M., Josephs, K., Uitti, R., Graff-Radford, N., van Gerpen, J., et al. (2017). Distribution and characteristics of transactive response DNA binding protein 43 kDa pathology in progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov. Disord. 32, 246–255. doi: 10.1002/mds.26809
Koga, S., Zhou, X., Murakami, A., Fernandez De Castro, C., Baker, M. C., Rademakers, R., et al. (2022). Concurrent tau pathologies in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with TDP-43 pathology. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 48:e12778. doi: 10.1111/nan.12778
Kopeikina, E., and Ponomarev, E. D. (2021). The role of platelets in the stimulation of neuronal synaptic plasticity, electric activity, and oxidative phosphorylation: Possibilities for new therapy of neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 15:680126. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.680126
Koren, S., Galvis-Escobar, S., and Abisambra, J. (2020). Tau-mediated dysregulation of RNA: Evidence for a common molecular mechanism of toxicity in frontotemporal dementia and other tauopathies. Neurobiol. Dis. 141:104939. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104939
Kouri, N., Oshima, K., Takahashi, M., Murray, M., Ahmed, Z., Parisi, J., et al. (2013). Corticobasal degeneration with olivopontocerebellar atrophy and TDP-43 pathology: An unusual clinicopathologic variant of CBD. Acta Neuropathol. 125, 741–752. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1087-8
Kovacs, G. G., Ferrer, I., Grinberg, L. T., Alafuzoff, I., Attems, J., Budka, H., et al. (2016). Aging-related tau astrogliopathy (ARTAG): Harmonized evaluation strategy. Acta Neuropathol. 131, 87–102. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1509-x
Koyama, A., Sugai, A., Kato, T., Ishihara, T., Shiga, A., Toyoshima, Y., et al. (2016). Increased cytoplasmic TARDBP mRNA in affected spinal motor neurons in ALS caused by abnormal autoregulation of TDP-43. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 5820–5836. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw499
Lace, G., Ince, P., Brayne, C., Savva, G., Matthews, F., de Silva, R., et al. (2012). Mesial temporal astrocyte tau pathology in the MRC-CFAS ageing brain cohort. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 34, 15–24. doi: 10.1159/000341581
Laird, F., Farah, M., Ackerley, S., Hoke, A., Maragakis, N., Rothstein, J., et al. (2008). Motor neuron disease occurring in a mutant dynactin mouse model is characterized by defects in vesicular trafficking. J. Neurosci. 28, 1997–2005. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4231-07.2008
Latimer, C., and Liachko, N. (2021). Tau and TDP-43 synergy: A novel therapeutic target for sporadic late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Geroscience 43, 1627–1634. doi: 10.1007/s11357-021-00407-0
Lebrun, A., Leprince, Y., Lagarde, J., Olivieri, P., Moussion, M., Noiray, C., et al. (2024). How fiber bundle alterations differ in presumed LATE and amnestic Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 20, 6922–6934. doi: 10.1002/alz.14156
Leskelä, S., Hoffmann, D., Rostalski, H., Huber, N., Wittrahm, R., Hartikainen, P., et al. (2021). FTLD patient-derived fibroblasts show defective mitochondrial function and accumulation of p62. Mol. Neurobiol. 58, 5438–5458. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02475-x
Liao, Y., Ma, J., and Dou, J. (2022). The role of TDP-43 in neurodegenerative disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 59, 4223–4241. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02847-x
Lin, T., Chen, M., Lin, L., Huang, P., Lo, W., Yang, Y., et al. (2017). TDP-43/HDAC6 axis promoted tumor progression and regulated nutrient deprivation-induced autophagy in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 8, 56612–56625. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17979
Lindberg, A., Murrell, E., Tong, J., Mason, N., Sohn, D., Sandell, J., et al. (2024). Ligand-based design of [18F]OXD-2314 for PET imaging in non-Alzheimer’s disease tauopathies. Nat. Commun. 15:5109. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49258-1
Liu, T., Zhu, B., Liu, Y., Zhang, X., Yin, J., Li, X., et al. (2020). Multi-omic comparison of Alzheimer’s variants in human ESC-derived microglia reveals convergence at APOE. J. Exp. Med. 217:e20200474. doi: 10.1084/jem.20200474
Liu, Y., Paajanen, T., Zhang, Y., Westman, E., Wahlund, L., Simmons, A., et al. (2010). Analysis of regional MRI volumes and thicknesses as predictors of conversion from mild cognitive impairment to Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 31, 1375–1385. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.01.022
Liu, Z., Guo, X., Guo, H., Luo, J., and Xiao, F. (2022). Muscle and skin fibroblast TDP-43 expression, dynamic mutation analysis of NOTCH2NLC and C9orf72 in patients with FOSMN. Neurol. Sci. 43, 6505–6510. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06339-7
López-Carbonero, J., García-Toledo, I., Fernández-Hernández, L., Bascuñana, P., Gil-Moreno, M., Matías-Guiu, J., et al. (2024). In vivo diagnosis of TDP-43 proteinopathies: In search of biomarkers of clinical use. Transl. Neurodegener. 13:29. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00419-8
Lupascu, N., Lupescu, I., Caloianu, I., Naftanaila, F., Glogojeanu, R., Sirbu, C., et al. (2023). Imaging criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy: Supportive or mandatory? Diagnostics 13:1967. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13111967
Luthi-Carter, R., Cappelli, S., Le Roux-Bourdieu, M., Tentillier, N., Quinn, J. P., Petrozziello, T., et al. (2024). Location and function of TDP-43 in platelets, alterations in neurodegenerative diseases and arising considerations for current plasma biobank protocols. Sci. Rep. 14:21837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-70822-8
Lyu, X., Duong, M., Xie, L., de Flores, R., Richardson, H., Hwang, G., et al. (2024). Tau-neurodegeneration mismatch reveals vulnerability and resilience to comorbidities in Alzheimer’s continuum. Alzheimers Dement. 20, 1586–1600. doi: 10.1002/alz.13559
Mackenzie, I., Neumann, M., Baborie, A., Sampathu, D., Du Plessis, D., Jaros, E., et al. (2011). A harmonized classification system for FTLD-TDP pathology. Acta Neuropathol. 122, 111–113. doi: 10.1007/s00401-011-0845-8
Mackenzie, I., Neumann, M., Bigio, E., Cairns, N., Alafuzoff, I., Kril, J., et al. (2010). Nomenclature and nosology for neuropathologic subtypes of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: An update. Acta Neuropathol. 119, 1–4. doi: 10.1007/s00401-009-0612-2
Magnani, E., Fan, J., Gasparini, L., Golding, M., Williams, M., Schiavo, G., et al. (2007). Interaction of tau protein with the dynactin complex. EMBO J. 26, 4546–4554. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601878
Maj, E., Jamroży, M., Bielecki, M., Bartoszek, M., Gołȩbiowski, M., Wojtaszek, M., et al. (2022). Role of DTI-MRI parameters in diagnosis of ALS: Useful biomarkers for daily practice? Tertiary centre experience and literature review. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 56, 490–498. doi: 10.5603/PJNNS.a2022.0070
Malarte, M., Nordberg, A., and Lemoine, L. (2021). Characterization of MK6240, a tau PET tracer, in autopsy brain tissue from Alzheimer’s disease cases. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol Imaging 48, 1093–1102. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-05035-y
Mandelli, M. L., Cobigo, Y., Perretti, I., Leichter, D., Alba, C., Bogley, R., et al. (2025). Fixel-based analysis reveals detailed white matter changes in semantic dementia. Res Sq [Preprint]. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6874132/v1
Martinez-Valbuena, I., Tartaglia, M., Fox, S., Lang, A., and Kovacs, G. (2024). Four-repeat tau seeding in the skin of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. JAMA Neurol. 81, 1228–1230. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2024.3162
Masrori, P., Beckers, J., Gossye, H., and Van Damme, P. (2022). The role of inflammation in neurodegeneration: Novel insights into the role of the immune system in C9orf72 HRE-mediated ALS/FTD. Mol. Neurodegener. 17:22. doi: 10.1186/s13024-022-00525-z
Matsuda, H., Okita, K., Motoi, Y., Mizuno, T., Ikeda, M., Sanjo, N., et al. (2022). Clinical impact of amyloid PET using 18F-florbetapir in patients with cognitive impairment and suspected Alzheimer’s disease: A multicenter study. Ann. Nucl. Med. 36, 1039–1049. doi: 10.1007/s12149-022-01792-y
McAleese, K., Firbank, M., Dey, M., Colloby, S., Walker, L., Johnson, M., et al. (2015). Cortical tau load is associated with white matter hyperintensities. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 3:60. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0240-0
McAleese, K., Walker, L., Erskine, D., Thomas, A., McKeith, I., and Attems, J. (2017). TDP-43 pathology in Alzheimer’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies and ageing. Brain Pathol. 27, 472–479. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12424
McGeer, P., Schwab, C., McGeer, E., Haddock, R., and Steele, J. (1997). Familial nature and continuing morbidity of the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism dementia complex of Guam. Neurology 49, 400–409. doi: 10.1212/wnl.49.2.400
McKee, A., Cairns, N., Dickson, D., Folkerth, R., Keene, C., Litvan, I., et al. (2016). The first NINDS/NIBIB consensus meeting to define neuropathological criteria for the diagnosis of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Acta Neuropathol. 131, 75–86. doi: 10.1007/s00401-015-1515-z
McKee, A., Gavett, B., Stern, R., Nowinski, C., Cantu, R., Kowall, N., et al. (2010). TDP-43 proteinopathy and motor neuron disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 69, 918–929. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e3181ee7d85
McKee, A., Stein, T., Kiernan, P., and Alvarez, V. (2015). The neuropathology of chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain Pathol. 25, 350–364. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12248
Meneses, A., Koga, S., O’Leary, J., Dickson, D., Bu, G., and Zhao, N. (2021). TDP-43 pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 16:84. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00503-x
Mishima, T., Fujioka, S., Tomiyama, H., Yabe, I., Kurisaki, R., Fujii, N., et al. (2018). Establishing diagnostic criteria for Perry syndrome. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 89, 482–487. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2017-316864
Montalbano, M., McAllen, S., Cascio, F., Sengupta, U., Garcia, S., Bhatt, N., et al. (2020). TDP-43 and Tau oligomers in Alzheimer’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and frontotemporal dementia. Neurobiol. Dis. 146:105130. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105130
Montine, T., Corrada, M., Kawas, C., Bukhari, S., White, L., Tian, L., et al. (2022). Association of cognition and dementia with neuropathologic changes of Alzheimer disease and other conditions in the oldest old. Neurology 99, e1067–e1078. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000200832
Murakami, N. (1999). Parkinsonism-dementia complex on Guam - overview of clinical aspects. J. Neurol. 246, II16–II18. doi: 10.1007/BF03161077
Na, S., Kang, D., Kim, G., Kim, K., Kim, Y., Kim, H., et al. (2024). The usefulness of 18F-FDG PET to differentiate subtypes of dementia: The systematic review and meta-analysis. Dement. Neurocogn. Disord. 23, 54–66. doi: 10.12779/dnd.2024.23.1.54
Nag, S., and Schneider, J. (2023). Limbic-predominant age-related TDP43 encephalopathy (LATE) neuropathological change in neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 19, 525–541. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00846-7
Nag, S., Yu, L., Boyle, P., Leurgans, S., Bennett, D., and Schneider, J. A. (2018). TDP-43 pathology in anterior temporal pole cortex in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 6:33. doi: 10.1186/s40478-018-0531-3
Nag, S., Yu, L., Capuano, A., Wilson, R., Leurgans, S., Bennett, D., et al. (2015). Hippocampal sclerosis and TDP-43 pathology in aging and Alzheimer disease. Ann. Neurol. 77, 942–952. doi: 10.1002/ana.24388
Nelson, P., Abner, E., Patel, E., Anderson, S., Wilcock, D., Kryscio, R., et al. (2018). The amygdala as a locus of pathologic misfolding in neurodegenerative diseases. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 77, 2–20. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlx099
Nelson, P., Brayne, C., Flanagan, M., Abner, E., Agrawal, S., Attems, J., et al. (2022). Frequency of LATE neuropathologic change across the spectrum of Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology: Combined data from 13 community-based or population-based autopsy cohorts. Acta Neuropathol. 144, 27–44. doi: 10.1007/s00401-022-02444-1
Nelson, P., Dickson, D., Trojanowski, J., Jack, C., Boyle, P., Arfanakis, K., et al. (2019). Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): Consensus working group report. Brain 142, 1503–1527. doi: 10.1093/brain/awz099
Nelson, P., Fardo, D., Wu, X., Aung, K., Cykowski, M., and Katsumata, Y. (2024). Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE-NC): Co-pathologies and genetic risk factors provide clues about pathogenesis. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 83, 396–415. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlae032
Nelson, P., Smith, C., Abner, E., Wilfred, B., Wang, W., Neltner, J., et al. (2013). Hippocampal sclerosis of aging, a prevalent and high-morbidity brain disease. Acta Neuropathol. 126, 161–177. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1154-1
Neumann, M., Kwong, L., Sampathu, D., Trojanowski, J., and Lee, V. M. (2007). TDP-43 proteinopathy in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: Protein misfolding diseases without amyloidosis. Arch. Neurol. 64, 1388–1394. doi: 10.1001/archneur.64.10.1388
Neumann, M., Lee, E., and Mackenzie, I. (2021). Frontotemporal lobar degeneration TDP-43-immunoreactive pathological subtypes: Clinical and mechanistic significance. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1281, 201–217. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-51140-1_13
Neumann, M., Sampathu, D., Kwong, L., Truax, A., Micsenyi, M., Chou, T., et al. (2006). Ubiquitinated TDP-43 in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 314, 130–133. doi: 10.1126/science.1134108
Nguyen, T., Cheng, J., Chen, Y., Lin, Y., Tsai, C., Lu, C., et al. (2021). Fixel-based analysis of white matter degeneration in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy or multiple system atrophy, as compared to Parkinson’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 13:625874. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2021.625874
Nho, K., Saykin, A., and Nelson, P. (2016). Hippocampal sclerosis of aging, a common Alzheimer’s disease ‘mimic’: Risk genotypes are associated with brain atrophy outside the temporal lobe. J. Alzheimers Dis. 52, 373–383. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160077
Nicks, R., Clement, N., Alvarez, V., Tripodis, Y., Baucom, Z., Huber, B., et al. (2023). Repetitive head impacts and chronic traumatic encephalopathy are associated with TDP-43 inclusions and hippocampal sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. 145, 395–408. doi: 10.1007/s00401-023-02539-3
Nilaver, B., and Urbanski, H. (2023). Mechanisms underlying TDP-43 pathology and neurodegeneration: An updated Mini-Review. Front. Aging Neurosci. 15:1142617. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2023.1142617
Noda, K., Sasaki, K., Fujimi, K., Wakisaka, Y., Tanizaki, Y., Wakugawa, Y., et al. (2006). Quantitative analysis of neurofibrillary pathology in a general population to reappraise neuropathological criteria for senile dementia of the neurofibrillary tangle type (tangle-only dementia): The Hisayama Study. Neuropathology 26, 508–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2006.00722.x
Ono, D., Sekiya, H., Maier, A., Murray, M., Koga, S., and Dickson, D. (2025). Parkinsonism in Alzheimer’s disease without Lewy bodies in association with nigral neuron loss: A data-driven clinicopathologic study. Alzheimers Dement. 21:e14628. doi: 10.1002/alz.14628
O’Rourke, J., Bogdanik, L., Yáñez, A., Lall, D., Wolf, A., Muhammad, A., et al. (2016). C9orf72 is required for proper macrophage and microglial function in mice. Science 351, 1324–1329. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf1064
Ossenkoppele, R., Rabinovici, G. D., Smith, R., Cho, H., Schöll, M., Strandberg, O., et al. (2018). Discriminative accuracy of [18F]flortaucipir positron emission tomography for alzheimer disease vs other neurodegenerative disorders. JAMA 320, 1151–1162. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.12917
Ou, S., Wu, F., Harrich, D., García-Martínez, L., and Gaynor, R. (1995). Cloning and characterization of a novel cellular protein, TDP-43, that binds to human immunodeficiency virus type 1 TAR DNA sequence motifs. J. Virol. 69, 3584–3596. doi: 10.1128/JVI.69.6.3584-3596.1995
Oyanagi, K. (2005). The nature of the parkinsonism-dementia complex and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of Guam and magnesium deficiency. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 11, S17–S23. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2005.02.010
Palleis, C., Brendel, M., Finze, A., Weidinger, E., Bötzel, K., Danek, A., et al. (2021). Cortical [(18) F]PI-2620 binding differentiates corticobasal syndrome subtypes. Mov. Disord. 36, 2104–2115. doi: 10.1002/mds.28624
Paré, B., Touzel-Deschênes, L., Lamontagne, R., Lamarre, M., Scott, F., Khuong, H., et al. (2015). Early detection of structural abnormalities and cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in tissue-engineered skins derived from ALS patients. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 3:5. doi: 10.1186/s40478-014-0181-z
Pasetto, L., Callegaro, S., Corbelli, A., Fiordaliso, F., Ferrara, D., Brunelli, L., et al. (2021). Decoding distinctive features of plasma extracellular vesicles in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol. Neurodegener. 16:52. doi: 10.1186/s13024-021-00470-3
Perry, T., Bratty, P., Hansen, S., Kennedy, J., Urquhart, N., and Dolman, C. (1975). Hereditary mental depression and Parkinsonism with taurine deficiency. Arch. Neurol. 32, 108–113. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1975.00490440058009
Pickford, F., Marcus, J., Camargo, L., Xiao, Q., Graham, D., Mo, J., et al. (2011). Progranulin is a chemoattractant for microglia and stimulates their endocytic activity. Am. J. Pathol. 178, 284–295. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.002
Polymenidou, M., Lagier-Tourenne, C., Hutt, K., Huelga, S., Moran, J., Liang, T., et al. (2011). Long pre-mRNA depletion and RNA missplicing contribute to neuronal vulnerability from loss of TDP-43. Nat. Neurosci. 14, 459–468. doi: 10.1038/nn.2779
Pottier, C., Ren, Y., Perkerson, R. B., Baker, M., Jenkins, G. D., van Blitterswijk, M., et al. (2019). Genome-wide analyses as part of the international FTLD-TDP whole-genome sequencing consortium reveals novel disease risk factors and increases support for immune dysfunction in FTLD. Acta Neuropathol. 137, 879–899. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-01962-9
Prasad, A., Bharathi, V., Sivalingam, V., Girdhar, A., and Patel, B. (2019). Molecular mechanisms of TDP-43 misfolding and pathology in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 12:25. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00025
Quek, H., and White, A. (2023). Patient-specific monocyte-derived microglia as a screening tool for neurodegenerative diseases. Neural Regen. Res. 18, 955–958. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.355740
Quek, H., Cuní-López, C., Stewart, R., Colletti, T., Notaro, A., Nguyen, T., et al. (2022). ALS monocyte-derived microglia-like cells reveal cytoplasmic TDP-43 accumulation, DNA damage, and cell-specific impairment of phagocytosis associated with disease progression. J. Neuroinflamm. 19:58. doi: 10.1186/s12974-022-02421-1
Quek, H., Cuní-López, C., Stewart, R., Colletti, T., Notaro, A., Sun, Y., et al. (2020). ALS monocyte-derived microglia reveal cytoplasmic TDP-43 accumulation, DNA damage, and cell-specific impairment of phagocytosis associated with disease progression. bioRxiv [Preprint]. bioRxiv:2020.2010.2025.354399.
Rabinovici, G., Furst, A., Alkalay, A., Racine, C., O’Neil, J., Janabi, M., et al. (2010). Increased metabolic vulnerability in early-onset Alzheimer’s disease is not related to amyloid burden. Brain 133, 512–528. doi: 10.1093/brain/awp326
Rahic, Z., Buratti, E., and Cappelli, S. (2023). Reviewing the potential links between viral infections and TDP-43 proteinopathies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 24:1581. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021581
Rahimi, J., and Kovacs, G. (2014). Prevalence of mixed pathologies in the aging brain. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 6:82. doi: 10.1186/s13195-014-0082-1
Ren, Y., Li, S., Chen, S., Sun, X., Yang, F., Wang, H., et al. (2021). TDP-43 and phosphorylated TDP-43 levels in paired plasma and CSF samples in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 12:663637. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.663637
Ren, Y., Liu, W., Li, Y., Sun, B., Li, Y., Yang, F., et al. (2018). Cutaneous somatic and autonomic nerve TDP-43 deposition in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Neurol. 265, 1753–1763. doi: 10.1007/s00415-018-8897-5
Riancho, J., Castanedo-Vázquez, D., Gil-Bea, F., Tapia, O., Arozamena, J., Durán-Vían, C., et al. (2020). ALS-derived fibroblasts exhibit reduced proliferation rate, cytoplasmic TDP-43 aggregation and a higher susceptibility to DNA damage. J. Neurol. 267, 1291–1299. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09704-8
Rifai, O. M., Waldron, F. M., O’Shaughnessy, J., Read, F. L., Gilodi, M., Pastore, A., et al. (2024). Amygdala TDP-43 pathology is associated with behavioural dysfunction and ferritin accumulation in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. bioRxiv [Preprint]. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.01.596819
Riku, Y., Yoshida, M., Iwasaki, Y., Sobue, G., Katsuno, M., and Ishigaki, S. (2022). TDP-43 proteinopathy and tauopathy: Do they have pathomechanistic links? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23:15755. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415755
Robinson, A., Thompson, J., Weedon, L., Rollinson, S., Pickering-Brown, S., Snowden, J., et al. (2014). No interaction between tau and TDP-43 pathologies in either frontotemporal lobar degeneration or motor neurone disease. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 40, 844–854. doi: 10.1111/nan.12155
Romano, N., Catalani, A., Lattante, S., Belardo, A., Proietti, S., Bertini, L., et al. (2020). ALS skin fibroblasts reveal oxidative stress and ERK1/2-mediated cytoplasmic localization of TDP-43. Cell Signal 70:109591. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109591
Rubio, M., Herrando-Grabulosa, M., Velasco, R., Blasco, I., Povedano, M., and Navarro, X. (2022). TDP-43 cytoplasmic translocation in the skin fibroblasts of ALS patients. Cells 11:209. doi: 10.3390/cells11020209
Rutherford, N., Zhang, Y., Baker, M., Gass, J., Finch, N., Xu, Y., et al. (2008). Novel mutations in TARDBP (TDP-43) in patients with familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS Genet. 4:e1000193. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000193
Sabatelli, M., Zollino, M., Conte, A., Del Grande, A., Marangi, G., Lucchini, M., et al. (2015). Primary fibroblasts cultures reveal TDP-43 abnormalities in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients with and without SOD1 mutations. Neurobiol. Aging 36:2005.e5–2005.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.02.009
Sakamoto, S., Kimura, T., Kajiyama, K., Ando, K., Takeda, M., and Yoshikawa, H. (2021). Dentatorubrothalamic tract reduction using fixel-based analysis in corticobasal syndrome. Neuroradiology 63, 529–538. doi: 10.1007/s00234-020-02559-w
Samudra, N., Lane-Donovan, C., VandeVrede, L., and Boxer, A. (2023). Tau pathology in neurodegenerative disease: Disease mechanisms and therapeutic avenues. J. Clin. Invest. 133:e168553. doi: 10.1172/JCI168553
Schöll, M., Maass, A., Mattsson, N., Ashton, N., Blennow, K., Zetterberg, H., et al. (2019). Biomarkers for tau pathology. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 97, 18–33. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2018.12.001
Schultz, C., Ghebremedhin, E., Del Tredici, K., Rüb, U., and Braak, H. (2004). High prevalence of thorn-shaped astrocytes in the aged human medial temporal lobe. Neurobiol. Aging 25, 397–405. doi: 10.1016/S0197-4580(03)00113-1
Schwab, C., Steele, J., and McGeer, P. (1996). Neurofibrillary tangles of Guam Parkinson-dementia are associated with reactive microglia and complement proteins. Brain Res. 707, 196–205. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(95)01257-5
Seddighi, S., Qi, Y., Brown, A., Wilkins, O., Bereda, C., Belair, C., et al. (2024). Mis-spliced transcripts generate de novo proteins in TDP-43-related ALS/FTD. Sci. Transl. Med. 16:eadg7162. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adg7162
Seredenina, T., Vokali, E., Dreyfus, N., Chevallier, E., Afroz, T., Jaquier, T., et al. (2023). Discovery and optimization of the first-in-class TDP-43 PET tracer. Alzheimers Dement. 19:e075525. doi: 10.1002/alz.083411
Shenouda, M., Xiao, S., MacNair, L., Lau, A., and Robertson, J. (2022). A C-terminally truncated TDP-43 Splice isoform exhibits neuronal specific cytoplasmic aggregation and contributes to TDP-43 pathology in ALS. Front. Neurosci. 16:868556. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.868556
Shi, K., Zhang, J., Dong, J., and Shi, F. (2019). Dissemination of brain inflammation in traumatic brain injury. Cell Mol. Immunol. 16, 523–530. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0213-5
Smith, R., Schöll, M., Leuzy, A., Jögi, J., Ohlsson, T., Strandberg, O., et al. (2020). Head-to-head comparison of tau positron emission tomography tracers [18F]flortaucipir and [18F]RO948. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 47, 342–354. doi: 10.1007/s00259-019-04496-0
Soloperto, A., Quaglio, D., Baiocco, P., Romeo, I., Mori, M., Ardini, M., et al. (2022). Rational design and synthesis of a novel BODIPY-based probe for selective imaging of tau tangles in human iPSC-derived cortical neurons. Sci. Rep. 12:5257. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-09016-z
Spencer, P. (2022). Parkinsonism and motor neuron disorders: Lessons from Western Pacific ALS/PDC. J. Neurol. Sci. 433:20021. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2021.120021
Sproviero, D., La Salvia, S., Colombo, F., Zucca, S., Pansarasa, O., Diamanti, L., et al. (2019). Leukocyte derived microvesicles as disease progression biomarkers in slow progressing amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients. Front. Neurosci. 13:344. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00344
Sreedharan, J., Blair, I., Tripathi, V., Hu, X., Vance, C., Rogelj, B., et al. (2008). TDP-43 mutations in familial and sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Science 319, 1668–1672. doi: 10.1126/science.1154584
Stage, E., Svaldi, D., Phillips, M., Canela, V., Duran, T., Goukasian, N., et al. (2020). Neurodegenerative changes in early- and late-onset cognitive impairment with and without brain amyloidosis. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 12:93. doi: 10.1186/s13195-020-00647-w
Storey, K., Johanidesová, S., Matěj, R., Keller, J., Rohan, Z., and Rusina, R. (2017). FTLD-TDP and progressive supranuclear palsy in comorbidity-a report of two cases with different clinical presentations. Neurocase 23, 5–11. doi: 10.1080/13554794.2016.1264058
Stouffer, K., Grande, X., Düzel, E., Johansson, M., Creese, B., Witter, M., et al. (2024). Amidst an amygdala renaissance in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 147, 816–829. doi: 10.1093/brain/awad411
Suk, T., and Rousseaux, M. (2020). The role of TDP-43 mislocalization in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol. Neurodegener. 15:45. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00397-1
Suzuki, M., Mikami, H., Watanabe, T., Yamano, T., Yamazaki, T., Nomura, M., et al. (2010). Increased expression of TDP-43 in the skin of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol. Scand. 122, 367–372. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2010.01321.x
Takeda, T., Seilhean, D., Le Ber, I., Millecamps, S., Sazdovitch, V., Kitagawa, K., et al. (2017). Amygdala TDP-43 pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and motor neuron disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 76, 800–812. doi: 10.1093/jnen/nlx063
Tan, R., Guennewig, B., Dobson-Stone, C., Kwok, J., Kril, J., Kiernan, M., et al. (2019). The underacknowledged PPA-ALS: A unique clinicopathologic subtype with strong heritability. Neurology 92, e1354–e1366. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000007146
Tezuka, T., Takahata, K., Seki, M., Tabuchi, H., Momota, Y., Shiraiwa, M., et al. (2021). Evaluation of [(18)F]PI-2620, a second-generation selective tau tracer, for assessing four-repeat tauopathies. Brain Commun. 3:fcab190. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcab190
Thammisetty, S., Pedragosa, J., Weng, Y., Calon, F., Planas, A., and Kriz, J. (2018). Age-related deregulation of TDP-43 after stroke enhances NF-κB-mediated inflammation and neuronal damage. J. Neuroinflamm. 15:312. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1350-y
Thomas, E., Han, C., Kim, W., Asress, S., Li, Y., Taylor, J., et al. (2025). ALS plasma biomarkers reveal neurofilament and pTau correlate with disease onset and progression. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 12, 714–723. doi: 10.1002/acn3.70001
Thompson, A., Gray, E., Heman-Ackah, S., Mäger, I., Talbot, K., Andaloussi, S., et al. (2016). Extracellular vesicles in neurodegenerative disease - pathogenesis to biomarkers. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 12, 346–357. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2016.68
Tomé, S., Gawor, K., and Thal, D. R. (2024). LATE-NC in Alzheimer’s disease: Molecular aspects and synergies. Brain Pathol. 34:e13213. doi: 10.1111/bpa.13213
Tomé, S., Gomes, L., Li, X., Vandenberghe, R., Tousseyn, T., and Thal, D. R. (2021). TDP-43 interacts with pathological τ protein in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 141, 795–799. doi: 10.1007/s00401-021-02295-2
Tomé, S., Tsaka, G., Ronisz, A., Ospitalieri, S., Gawor, K., Gomes, L., et al. (2023). TDP-43 pathology is associated with increased tau burdens and seeding. Mol. Neurodegener. 18:71. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00653-0
Trzepacz, P., Yu, P., Bhamidipati, P., Willis, B., Forrester, T., Tabas, L., et al. (2013). Frontolimbic atrophy is associated with agitation and aggression in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 9:S95–S104.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2012.10.005
Tsuboi, Y., Mishima, T., and Fujioka, S. (2021). Perry disease: Concept of a new disease and clinical diagnostic criteria. J. Mov. Disord. 14, 1–9. doi: 10.14802/jmd.20060
Ubeda-Bañon, I., Saiz-Sanchez, D., Flores-Cuadrado, A., Rioja-Corroto, E., Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M., Villar-Conde, S., et al. (2020). The human olfactory system in two proteinopathies: Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. Transl. Neurodegener. 9:22. doi: 10.1186/s40035-020-00200-7
Uchida, W., Kamagata, K., Andica, C., Takabayashi, K., Saito, Y., Owaki, M., et al. (2023). Fiber-specific micro- and macroscopic white matter alterations in progressive supranuclear palsy and corticobasal syndrome. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 9:122. doi: 10.1038/s41531-023-00565-2
Uchino, A., Takao, M., Hatsuta, H., Sumikura, H., Nakano, Y., Nogami, A., et al. (2015). Incidence and extent of TDP-43 accumulation in aging human brain. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 3:35. doi: 10.1186/s40478-015-0215-1
Ueda, T., Takeuchi, T., Fujikake, N., Suzuki, M., Minakawa, E., Ueyama, M., et al. (2024). Dysregulation of stress granule dynamics by DCTN1 deficiency exacerbates TDP-43 pathology in Drosophila models of ALS/FTD. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 12:20. doi: 10.1186/s40478-024-01729-8
Uryu, K., Nakashima-Yasuda, H., Forman, M., Kwong, L., Clark, C., Grossman, M., et al. (2008). Concomitant TAR-DNA-binding protein 43 pathology is present in Alzheimer disease and corticobasal degeneration but not in other tauopathies. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 67, 555–564. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e31817713b5
Vacchi, E., Lazzarini, E., Pinton, S., Chiaro, G., Disanto, G., Marchi, F., et al. (2022). Tau protein quantification in skin biopsies differentiates tauopathies from alpha-synucleinopathies. Brain 145, 2755–2768. doi: 10.1093/brain/awac161
Vacchi, E., Ruiz-Barrio, I., and Melli, G. (2025). Tau biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases: Current state and perspectives. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 134:107772. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2025.107772
van Amerongen, S., Kamps, S., Kaijser, K., Pijnenburg, Y., Scheltens, P., Teunissen, C., et al. (2023). Severe CTE and TDP-43 pathology in a former professional soccer player with dementia: A clinicopathological case report and review of the literature. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 11:77. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01572-3
Vanden Broeck, L., Callaerts, P., and Dermaut, B. (2014). TDP-43-mediated neurodegeneration: Towards a loss-of-function hypothesis? Trends Mol. Med. 20, 66–71. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2013.11.003
Vanderlinden, G., Radwan, A., Christiaens, D., Blommaert, J., Sunaert, S., Vandenbulcke, M., et al. (2025). Fibre density and cross-section associate with hallmark pathology in early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 17:73. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01710-0
VandeVrede, L., La Joie, R., Horiki, S., Mundada, N., Koestler, M., Hwang, J., et al. (2023). Co-pathology may impact outcomes of amyloid-targeting treatments: Clinicopathological results from two patients treated with aducanumab. Acta Neuropathol. 146, 777–781. doi: 10.1007/s00401-023-02631-8
Verheijen, B., Oyanagi, K., and van Leeuwen, F. (2018). Dysfunction of protein quality control in parkinsonism-dementia complex of guam. Front. Neurol. 9:173. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00173
Villar-Conde, S., Astillero-Lopez, V., Gonzalez-Rodriguez, M., Saiz-Sanchez, D., Martinez-Marcos, A., Ubeda-Banon, I., et al. (2023). Synaptic involvement of the human amygdala in Parkinson’s disease. Mol. Cell Proteomics 22:100673. doi: 10.1016/j.mcpro.2023.100673
Vizziello, M., Dellarole, I., Ciullini, A., Pascuzzo, R., Lombardo, A., Bellandi, F., et al. (2025). TDP-43 seeding activity in the olfactory mucosa of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Mol. Neurodegener. 20:49. doi: 10.1186/s13024-025-00833-0
Vogler, T., Wheeler, J., Nguyen, E. D., Hughes, M., Britson, K., Lester, E., et al. (2018). TDP-43 and RNA form amyloid-like myo-granules in regenerating muscle. Nature 563, 508–513. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0665-2
Vos de Wael, R., Larivière, S., Caldairou, B., Hong, S. J., Margulies, D. S., Jefferies, E., et al. (2018). Anatomical and microstructural determinants of hippocampal subfield functional connectome embedding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 115, 10154–10159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803667115
Walker, M. (2015). Hippocampal sclerosis: Causes and prevention. Semin. Neurol. 35, 193–200. doi: 10.1055/s-0035-1552618
Wang, J., Schneider, J. A., Bennett, D. A., Seyfried, N. T., Young-Pearse, T. L., and Yang, H.-S. (2025). Plasma TDP-43 is a potential biomarker for advanced limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy neuropathologic change. medRxiv [Preprint]. medRxiv: 2025.2007.2009.25331146.
Wang, X., Zhou, S., Ding, X., Ma, M., Zhang, J., Zhou, Y., et al. (2015). Activation of ER stress and autophagy induced by TDP-43 A315T as pathogenic mechanism and the corresponding histological changes in skin as potential biomarker for ALS with the mutation. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 11, 1140–1149. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.12657
Wang, Y., and Mandelkow, E. (2016). Tau in physiology and pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 5–21. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2015.1
Wang, Z., Wu, L., Gerasimenko, M., Gilliland, T., Shah, Z., Lomax, E., et al. (2024). Seeding activity of skin misfolded tau as a biomarker for tauopathies. Mol. Neurodegener. 19:92. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00781-1
Wesseling, A., Calandri, I., Bouwman, M., Reijner, N., Deshayes, N., Barkhof, F., et al. (2025). Amygdalar and hippocampal volume loss in limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy. Brain 25:awaf201. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaf201
Wider, C., Dickson, D., Stoessl, A., Tsuboi, Y., Chapon, F., Gutmann, L., et al. (2009). Pallidonigral TDP-43 pathology in Perry syndrome. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 15, 281–286. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2008.07.005
Wilhite, R., Sage, J., Bouzid, A., Primavera, T., and Agbas, A. (2017). Platelet phosphorylated TDP-43: An exploratory study for a peripheral surrogate biomarker development for Alzheimer’s disease. Future Sci. OA 3:FSO238. doi: 10.4155/fsoa-2017-0090
Wilson, R., Yu, L., Trojanowski, J., Chen, E., Boyle, P., Bennett, D., et al. (2013). TDP-43 pathology, cognitive decline, and dementia in old age. JAMA Neurol. 70, 1418–1424. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.3961
Winston, C., Sukreet, S., Lynch, H., Lee, V., Wilcock, D., Nelson, P., et al. (2022). Evaluation of blood-based, extracellular vesicles as biomarkers for aging-related TDP-43 pathology. Alzheimers Dement. 14:e12365. doi: 10.1002/dad2.12365
Winton, M., Igaz, L., Wong, M., Kwong, L., Trojanowski, J., and Lee, V. (2008). Disturbance of nuclear and cytoplasmic TAR DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) induces disease-like redistribution, sequestration, and aggregate formation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 13302–13309. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M800342200
Wisse, L., Wuestefeld, A., Murray, M., Jagust, W., and La Joie, R. (2025). Role of tau versus TDP-43 pathology on medial temporal lobe atrophy in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 21:e14582. doi: 10.1002/alz.14582
Wolk, D., Nelson, P., Apostolova, L., Arfanakis, K., Boyle, P., Carlsson, C., et al. (2025). Clinical criteria for limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy. Alzheimers Dement. 21:e14202. doi: 10.1002/alz.14202
Woodworth, D., Sheikh-Bahaei, N., Scambray, K., Phelan, M., Perez-Rosendahl, M., Corrada, M., et al. (2022). Dementia is associated with medial temporal atrophy even after accounting for neuropathologies. Brain Commun. 4:fcac052. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac052
Yamashita, S., Sakashita, N., Yamashita, T., Tawara, N., Tasaki, M., Kawakami, K., et al. (2014). Concomitant accumulation of α-synuclein and TDP-43 in a patient with corticobasal degeneration. J. Neurol. 261, 2209–2217. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7491-8
Yang, S., Zhang, K., Kariawasam, R., Bax, M., Fifita, J., Ooi, L., et al. (2015). Evaluation of skin fibroblasts from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients for the rapid study of pathological features. Neurotox. Res. 28, 138–146. doi: 10.1007/s12640-015-9532-1
Yap, S., Frias, B., Wren, M., Schöll, M., Fox, N., Årstad, E., et al. (2021). Discriminatory ability of next-generation tau PET tracers for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 144, 2284–2290. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab120
Yokota, O., Davidson, Y., Bigio, E., Ishizu, H., Terada, S., Arai, T., et al. (2010). Phosphorylated TDP-43 pathology and hippocampal sclerosis in progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol. 120, 55–66. doi: 10.1007/s00401-010-0702-1
Younes, K., and Miller, B. (2020). Frontotemporal dementia: Neuropathology, genetics, neuroimaging, and treatments. Psychiatr. Clin. North Am. 43, 331–344. doi: 10.1016/j.psc.2020.02.006
Youssef, H., Weissmann, C., Uruk, G., and Gatto, R. (2025). Looking into abnormal co-expressions of tau and TDP-43 in the realm of mixed dementia types: A double-punch scenario. Brain Sci. 15:716. doi: 10.3390/brainsci15070716
Yu, L., Boyle, P., Dawe, R., Bennett, D., Arfanakis, K., and Schneider, J. (2020). Contribution of TDP and hippocampal sclerosis to hippocampal volume loss in older-old persons. Neurology 94, e142–e152. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008679
Zeng, X., Lafferty, T., Sehrawat, A., Chen, Y., Ferreira, P., Bellaver, B., et al. (2024). Multi-analyte proteomic analysis identifies blood-based neuroinflammation, cerebrovascular and synaptic biomarkers in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Neurodegener. 19:68. doi: 10.1186/s13024-024-00753-5
Keywords: copathology, TDP-43, tauopathies, neuroimaging, biomarkers
Citation: Nasir AR and Delpirou Nouh C (2025) TDP-43-proteinopathy at the crossroads of tauopathy: on copathology and current and prospective biomarkers. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 19:1671419. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2025.1671419
Received: 24 July 2025; Accepted: 06 October 2025;
Published: 28 October 2025.
Edited by:
Rodolfo Gabriel Gatto, Mayo Clinic, United StatesReviewed by:
Albert Acewicz, Institute of Psychiatry and Neurology (IPIN), PolandJuan Ignacio López-Carbonero, San Carlos University Clinical Hospital, Spain
Copyright © 2025 Nasir and Delpirou Nouh. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Claire Delpirou Nouh, Q2xhaXJlLURlbHBpcm91Tm91aEBvdS5lZHU=
 Abdul R. Nasir
Abdul R. Nasir Claire Delpirou Nouh
Claire Delpirou Nouh