- 1Department of General Surgery, Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
- 2Department of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Affiliated Hospital of Hebei University, Baoding, Hebei, China
- 3Department of General Surgery, Peoples Hospital of Linxi County, Xingtai, Hebei, China
- 4Department of General Surgery, Zhangjiakou First Hospital, Zhangjiakou, Hebei, China
- 5Department of Endocrinology, Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei, China
Background: Genetic polymorphisms in the nonmetastatic cell 1 gene (NME1) are reportedly associated with the risk of various tumors and the prognoses of cancer patients. The aims of this study were to evaluate the contribution of two polymorphisms of NME1 to the risk of colorectal cancer (CRC) development and the clinical outcomes of CRC patients in a northern Chinese population.
Methods: This study included 453 CRC patients and 464 controls. Genotyping of two polymorphisms (rs2302254 and rs16949649) in the promoter region of NME1 was performed using the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method.
Results: The results revealed that the rs2302254 and rs16949649 polymorphisms were not associated with the risk of CRC. However, the rs2302254 TT mutant genotype was associated with an increased risk for advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis. Moreover, survival analysis revealed that patients with the homozygous mutant TT genotype of rs2302254 had significantly shorter disease-free survival (DFS) and overall survival (OS) times than patients with the homozygous wild-type CC genotype.
Conclusion: The rs2302254 polymorphism might function as a potential molecular marker for predicting the progression and prognosis of CRC.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common malignant tumors, estimated with 152,810 new cases and 53,010 mortalities occurring in the United States in 2024 (Siegel et al., 2024). Recent years, the incidence rate of CRC has also increased in China (Xu et al., 2023). Despite the high therapeutic success rate for CRC patients with early-stage disease, most patients are diagnosed at clinically intermediate to advanced stages, and the five-year survival rate of CRC patients is only approximately 60% (Cardoso et al., 2022). Metastasis and disease relapse are the major causes of a poor prognosis in CRC patients (Swartjes et al., 2024). Currently, CRC screening methods mainly include colonoscopy and histopathology tests, which exhibit low sensitivity and poor specificity (Onyoh et al., 2019). Therefore, the identification of reliable biomarkers that could help to predict the risk of CRC and monitor the prognosis of CRC patients is essential.
The nonmetastatic cell 1 gene (NME1) was first known as a metastasis suppressor gene and was first isolated from murine K-1735 melanoma cell lines (Steeg et al., 1988). This gene product NME1 is the “A” subunit of nucleoside diphosphate (NDP) kinase. Apart from catalyzing the conversion of ADP to ATP in the presence of GTP, NME1 possesses other enzymatic activities, such as histidine protein kinase, serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, and 3′-5′ exonuclease (Roymans et al., 2002; Steeg et al., 2003; Zhang et al., 2011). In addition, NME1 also plays an important role in cell proliferation, differentiation and development, signal transduction, and gene expression (Yu et al., 2021). The reduced expression of NME1 was found to be associated with increased metastatic behavior in various tumors, including breast carcinoma and lung cancer (Zhang et al., 2023; Lu et al., 2024). However, the opposite trend was observed in some other cancers, such as gastric cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and neuroblastoma (Xie et al., 2023; Yang et al., 2022; Chicco et al., 2023). Thus, NME1 might play different roles in carcinomas of different origins. In colorectal tumor tissues, the expression of NME1 was shown to be low, and reduced NME1 was associated with higher Dukes stages, poorer differentiation, and positive lymph node metastases in CRC patients (Yang et al., 2016; Lin et al., 2011). Furthermore, CRC patients with NME1-negative tumors had a poorer prognosis than those with NME1-positive tumors (Fu and Chu, 2015). These findings indicate that NME1 might be involved in the formation and progression of CRC.
The human NME1 lies on chromosome 17q21, and several single nucleotide polymorphisms have been identified within this gene. Among them, two functional polymorphisms, rs2302254 and rs16949649, have been reported to be associated with the risk of developing various tumors and the prognosis of cancer patients. For example, Rajagopal et al. (2020) revealed that the CC genotype frequency of rs16949649 was 13.2% in the breast cancer patients and 8.4% in the control group, and the rs16949649 CC genotype was associated with a significantly increased risk of breast cancer. Li et al. (2012) showed that the rs2302254 TT mutation genotype frequency was 9.3% in the ovarian cancer patients, and the ovarian cancer patients with rs2302254 T/T genotype had a shorter survival time. However, little is known regarding the effects of NME1 genetic variants on CRC. In this study, we evaluated the contribution of the two polymorphisms of NME1 to the risk of CRC development and the clinical outcomes of CRC patients in a northern Chinese population.
Materials and methods
Study subjects
In this case‒control study, a total of 917 peripheral blood samples from 453 CRC patients and 464 controls were collected consecutively from May 2016 to December 2021 at the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University. All CRC patients were diagnosed via pathology. Patients who had any other previous malignant tumors or who received adjuvant chemotherapy or preoperative radiotherapy were excluded from this study. The controls were recruited from healthy volunteers who participated in general health checks at the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University during the same time-period of case collection. The exclusion criterion for the control subjects was no personal or family history of malignant disease.
After patients underwent surgical treatment for CRC, follow-up was performed from July 2016 to January 2024. The clinical symptoms, serum carcinoembryonic antigen levels, and computed tomography scans were obtained to assess potential relapse of CRC. The survival data of CRC patients were also evaluated. Disease-free survival (DFS) was defined as the time interval between the date of surgery and the date of first disease relapse. Overall survival (OS) was defined as the time interval from the date of study entry to the date of death from any cause.
All study participants were unrelated Han Chinese people who resided in Shijiazhuang and the surrounding areas. Written informed consent was provided by all the recruited subjects according to the Helsinki declaration. This case‒control study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University.
DNA extraction and genotyping
Genomic DNA was extracted from the collected peripheral blood within 1 week using the salting-out method. Genotyping of the two NME1 polymorphisms was performed with the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) method. The primers for PCR amplification of rs2302254 were 5′-CGC GAA CGA AGG AAG TGA GTC A-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCC GCC AGC ACC CGA AAC-3′ (reverse). The primers for rs16949649 were 5′-CGG CTC CTG ATT CCA TTT TTG TAC-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCT TCT GGG AGG GAT GGG AGT ATA-3′ (reverse). PCR was conducted in a 20 μL volume including 100 ng of DNA template, 200 nM of each primer, 2 μL of 10XPCR buffer, 1 unit of Taq DNA polymerase (TiangeBjotech, Beijing, China), 0.4 μL of 10 mM dNTPs, and nuclease-free water. The cycling conditions for PCR were 94°C for 5 min, followed by 35 cycles of 94°C for 45 s, 63°C for 45 s for rs2302254, 62°C for 45 s for rs16949649, and 72°C for 45 s, with a final elongation at 72°C for 7 min. The amplified PCR products were digested overnight at 37°C with the 5 U restriction enzyme BanII (Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) for rs2302254 and HinfI (Sangon Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China) for the rs16949649 polymorphism. The digested products were separated on a 4% agarose gel and visualized under ultraviolet light. In addition, to validate the results of PCR-RFLP, the genotypes in approximately 10% of the samples were detected with direct sequencing method, and the results were 100% concordant.
Statistical analysis
All the data analyses were performed with SPSS 22.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, United States). The fitness of the genotype frequencies to Hardy–Weinberg equilibrium (HWE) was analyzed with a chi-squared test. Comparisons of clinical data between the case and control groups were conducted with Student's t-test or a chi-squared test. Differences in genotype distribution between CRC patients and controls were compared with a chi-squared test and Bonferroni’s correction. An unconditional logistic regression model was applied to calculate the odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Survival analyses were evaluated with the Kaplan‒Meier (K–M) method, and differences among genotypes were estimated with a log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were conducted with the Cox proportional hazards regression model. A P value less than 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Characteristics of the study subjects
The mean ages of the CRC patients and controls were 61.53 ± 12.48 years (range 26–86) and 60.91 ± 11.50 years (range 29–81), respectively. There was no significant difference between the two groups with respect to age (P = 0.437). In addition, the sex distribution was also similar between the cases and controls (P = 0.277). The genotype distributions of rs2302254 and rs16949649 were in line with Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in the control group (P = 0.681 and 0.974, respectively).
The genotypic frequencies of rs2302254 and rs16949649 polymophisms in patients with CRC and controls
Table 1 summarizes the genotype frequencies of rs2302254 and rs16949649. The frequencies of the rs2302254 CC, CT, and TT genotypes were 54.3%, 36.2%, and 9.5%, respectively, in patients with CRC and 58.0%, 35.3%, and 6.7%, respectively, in controls. No significant difference was detected in the genotype frequencies of rs2302254 between the case and control groups (Table 1). Similarly, the genotype frequencies of the rs16949649 polymorphism did not vary significantly between patients with CRC and controls (Table 1).
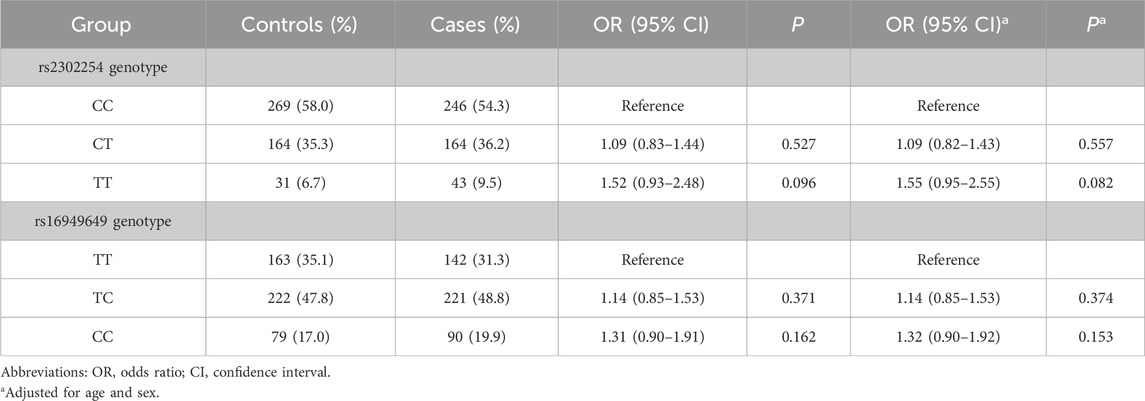
Table 1. The genotypic frequencies of rs2302254 and rs16949649 polymophisms in patients with colorectal cancer and controls.
Associations of rs2302254 and rs16949649 with the clinicopathological characteristics of CRC patients
Results of the stratified analysis of NME1 polymorphisms and clinicopathological features of CRC patients are listed in Table 2. The rs2302254 and rs16949649 polymorphisms were not associated with age, sex, or histological grade of CRC patients. However, patients with the rs2302254 TT genotype were at significantly greater risk of having advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis than those with the rs2302254 CC genotype (Table 2; P = 0.023 and 0.026, respectively).
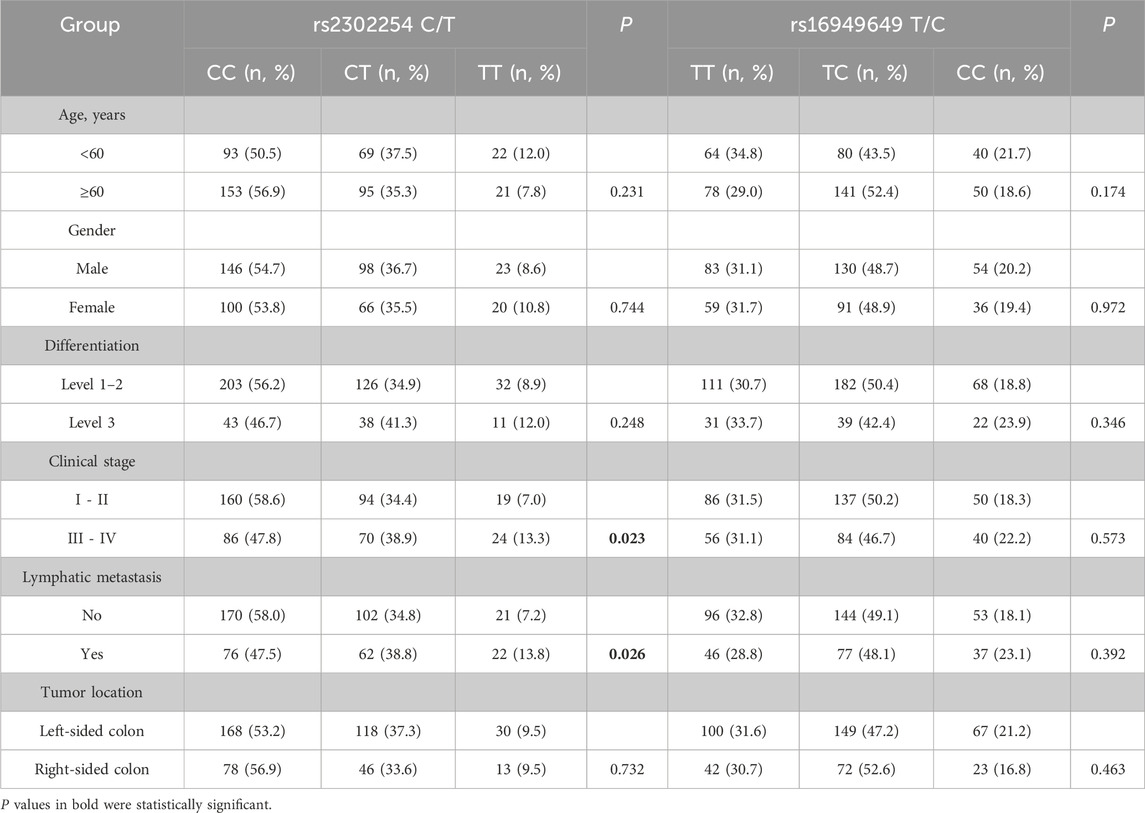
Table 2. Association of rs2302254 and rs16949649 with the clinical characteristics of colorectal cancer patients.
Associations of rs2302254 and rs16949649 with the prognosis of CRC patients
Among the 453 CRC patients, 293 were followed for more than 5 years. Kaplan–Meier plots revealed that the rs2302254 polymorphism was significantly associated with the clinical outcomes of CRC patients (Figures 1A,B). Patients with the homozygous mutant TT genotype of rs2302254 had significantly shorter DFS and OS times than patients with the homozygous wild-type CC genotype according to univariate analysis (Tables 3, 4; HR = 2.22, 95% CI = 1.36–3.63, P = 0.001; HR = 2.25, 95% CI = 1.30–3.69, P = 0.004). The significant association between rs2302254 and CRC patient prognosis was maintained according to a multivariate analysis (Tables 3, 4; HR = 2.09, 95% CI = 1.27–3.46, P = 0.004; HR = 2.02, 95% CI = 1.16–3.54, P = 0.014). Considering the rs16949649 polymorphism, survival analysis suggested that this genetic variant was not related to the DFS or OS of CRC patients (Figures 1C,D; Tables 3, 4).
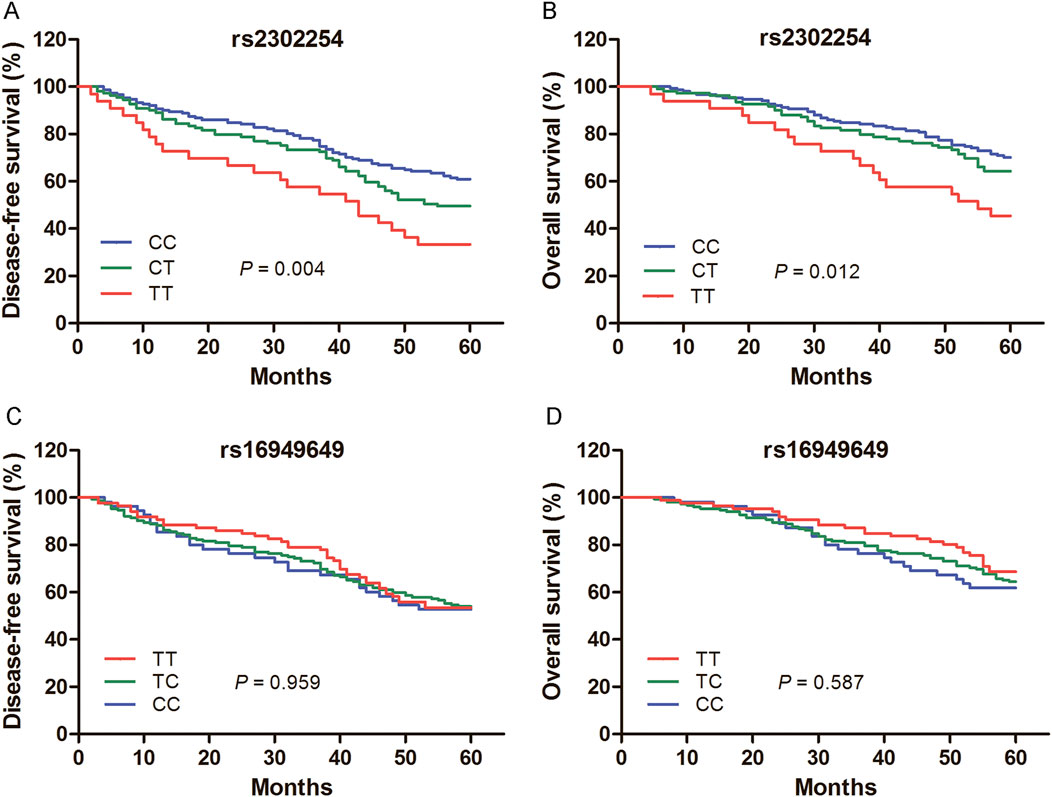
Figure 1. Kaplan–Meier evaluates for the prognosis of colorectal cancer (CRC) patients according to the genotypes of rs2302254 and rs16949649. (A) Mean disease-free survival times of CRC patients carrying the rs2302254 CC, CT, and TT genotypes were 48.0, 44.5 and 37.0 months, respectively (P = 0.004). (B) Mean overall survival times of CRC patients carrying the rs2302254 CC, CT, and TT genotypes were 52.8, 51.1 and 44.9 months, respectively (P = 0.012). (C) Mean disease-free survival times of CRC patients carrying the rs16949649 TT, TC, and CC genotypes were 46.7, 45.2 and 44.2 months, respectively (P = 0.959). (D) Mean overall survival times of CRC patients carrying the rs16949649 TT, TC, and CC genotypes were 53.2, 50.8 and 49.7 months, respectively (P = 0.587).
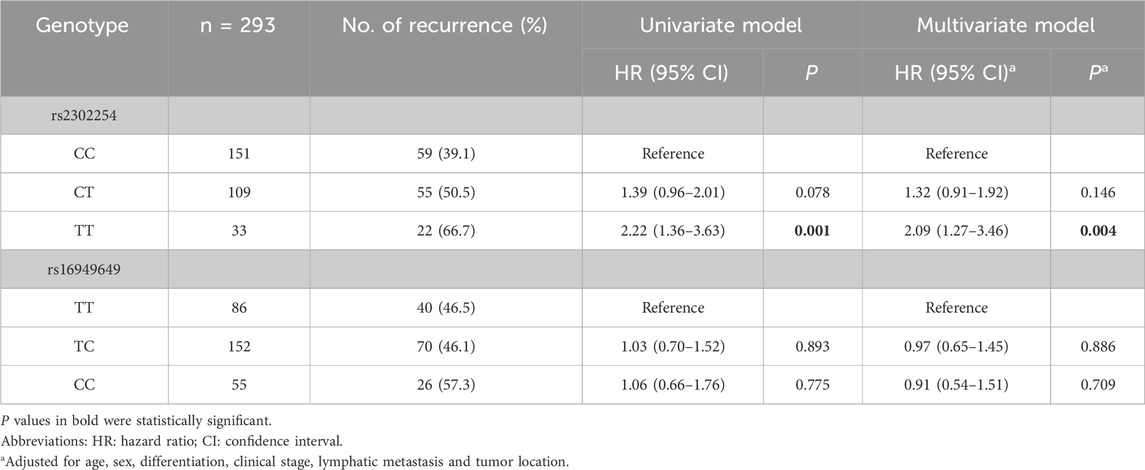
Table 3. Association between NME1 polymorphisms and the 5-year disease-free survival of colorectal cancer patients.
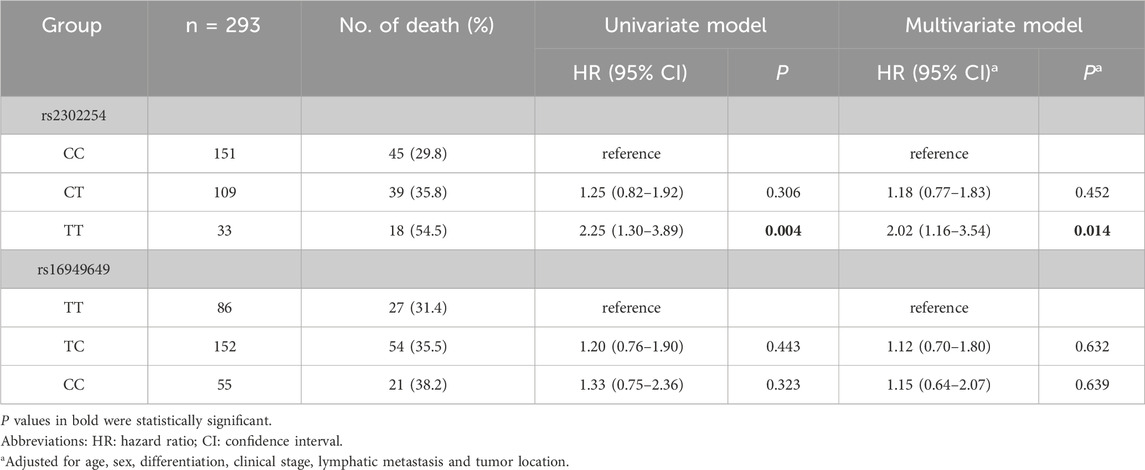
Table 4. Association between NME1 polymorphisms and the 5-year overall survival of colorectal cancer patients.
Discussion
In this study, we assessed the role of rs2302254 and rs16949649 polymorphisms in the risk of developing CRC and the prognoses of CRC patients. The results indicated that the two genetic variants of NME1 were not associated with susceptibility to CRC but may be associated with the clinical outcomes of CRC patients. Patients with the rs2302254 TT genotype had a significantly worse prognosis than those with the CC genotype.
Expression of NME1 was shown to be aberrant in a variety of solid tumors (Zhang et al., 2023b; Guo et al., 2022; Bao et al., 2022). However, the underlying mechanism of the regulation of NME1 expression remains poorly understood. Ouatas et al. (2002) reported that three regions within the NME1 promoter are involved in differential NME1 expression in breast cancer cells: i.e., a 544 bp AvrII fragment, which consists of an inhibitory element; a 248 bp AvrII–Nhel fragment, which results in increased NME1 expression; and a 195 bp NheI-XbaI fragment, which is responsible for the basal expression level of NME1. Deletion of the 544 bp AvrII fragment, which includes the rs16949649, rs3760468, and rs3760469 polymorphisms, contributes to a 20% increase in NME1 promoter activity in MCF7 cells, and deletion of the 195 bp NheI-XbaI fragment, which includes the rs2302254 polymorphism, abolishes the promoter activity of NME1. In addition, a study of breast cancer cells revealed that minor alleles of the rs2302254 and rs3760468 polymorphisms decreased NME1 activity (Qu et al., 2008). These data indicated that single nucleotide polymorphisms (rs2302254 and rs16949649) in the promoter region of NME1 may regulate the expression of NME1 protein.
The association between rs2302254 and risk of cancer has been investigated in many studies. A meta-analysis revealed that this genetic variant was linked to the risk of gastric cancer (Shi et al., 2018). However, no significant relationship was found between the rs2302254 polymorphism and susceptibility to epithelial ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer or breast cancer (Rajagopal et al., 2020; Li et al., 2012; Márquez-González et al., 2024). Similarly, our results also revealed that there was no significant difference in the genotype or allele frequencies of rs2302254 between CRC patients and controls. However, the rs2302254 TT mutant genotype was associated with an increased risk for advanced clinical stage and lymph node metastasis. Furthermore, CRC patients with the homozygous mutant TT genotype of rs2302254 had significantly shorter DFS and OS times than those with the homozygous wild-type CC genotype. This finding was similar to the results of Li et al. (2012), who reported that the rs2302254 TT genotype was related to poor clinical outcomes in ovarian cancer patients. It has been reported that decreased NME1 was associated with higher clinical stage and worse prognosis in patients with CRC (Fu and Chu, 2015). Thus, we speculated that the rs2302254 polymorphism may impact the progression and survival of patients with CRC by reducing the expression of NME1.
Rs16949649 is one of the most heavily studied genetic variants located in the NME1 promoter region. A previous study revealed that this polymorphism was associated with the incidence and recurrence of invasive pituitary adenoma (Wang and Sang, 2020). Qu et al. (2008) reported that breast cancer patients carrying the rs16949649 C allele had higher cancer-specific mortality than those carrying the wild-type allele. To date, there have been no reports regarding the role of the rs16949649 polymorphism in CRC. Our study suggested that rs16949649 was not associated with susceptibility to CRC or the prognosis of CRC patients. The reason for the discrepancy in these findings may be different effects of rs16949649 on different cancer types. Therefore, further evidence from well-designed studies is needed to clarify the contribution of this NME1 genetic variant to the risk and survival of patients with carcinomas.
Two main limitations exist in this study. First, the sample size, especially the number of CRC patients followed for more than 5 years, was relatively small. Moreover, the frequency of rs2302254 T/T genotype is very low in the CRC patients. Thus, our findings on the associations of rs2302254 with the clinicopathological characteristics and prognosis of CRC patients should be interpreted with caution. Second, all study participants were recruited from the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University. Therefore, there may be systematic error and selection bias in this study.
In conclusion, our study suggests that the TT mutation genotype of rs2302254 was related to advanced clinical stage, positive lymph node metastasis, and poor clinical outcomes in CRC patients. The rs2302254 polymorphism in the NME1 promoter might function as a potential molecular marker for predicting the progression and prognosis of CRC. However, larger-scale and multiethnic studies are needed to confirm our conclusions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YL: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. TB: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Visualization. ZZ: Data curation, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. YX: Investigation, Software, Writing – review and editing. DK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing, Formal Analysis, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Resources, Validation, Visualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the S&T program of Hebei (Grant number: 22377759D), Hebei Natural Science Foundation (Grant number: H2021206177), and the Medical Science Research Project of Hebei (Grant numbers: 20180558 and 20221233).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the doctors in the Department of the Fourth Hospital of Hebei Medical University for their help in recruiting study participants.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bao, Z., Zhu, R., Fan, H., Ye, Y., Li, T., and Chai, D. (2022). Aberrant expression of Spag6 and Nm23 predicts poor prognosis of human osteosarcoma. Front. Genet. 13, 1012548. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.1012548
Cardoso, R., Guo, F., Heisser, T., De Schutter, H., Van Damme, N., Nilbert, M. C., et al. (2022). Overall and stage-specific survival of patients with screen-detected colorectal cancer in European countries: a population-based study in 9 countries. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 21, 100458. doi:10.1016/j.lanepe.2022.100458
Chicco, D., Sanavia, T., and Jurman, G. (2023). Signature literature review reveals ahcy, Dpysl3, and Nme1 as the most recurrent prognostic genes for neuroblastoma. BioData Min. 16 (1), 7. doi:10.1186/s13040-023-00325-1
Fu, J. W., and Chu, X. Q. (2015). Correlation between non-metastatic protein 23 expression and clinicopathological features of colorectal cancer in asians. Genet. Mol. Res. 14 (4), 15597–15608. doi:10.4238/2015.December.1.11
Guo, S., Liu, L., Li, Y., Shi, H., and Cong, A. N. (2022). Correlation between Nm23-H_1 expression and transvaginal color Doppler ultrasound performance after radiotherapy for cervical cancer. Transl. Cancer Res. 11 (5), 1354–1361. doi:10.21037/tcr-22-1114
Li, Y., Kang, S., Qin, J. J., Wang, N., Zhou, R. M., and Sun, H. Y. (2012). Nm23 gene polymorphisms are associated with survival of patients with epithelial ovarian cancer but not with susceptibility to disease. Gynecol. Oncol. 126 (3), 455–459. doi:10.1016/j.ygyno.2012.06.004
Lin, M. S., Chen, W. C., Huang, J. X., Gao, H. J., Zhang, B. F., Fang, J., et al. (2011). Tissue microarrays in Chinese human rectal cancer: study of expressions of the tumor-associated genes. Hepatogastroenterology 58 (112), 1937–1942. doi:10.5754/hge11262
Lu, Z., Liu, B., Kong, D., Zhou, X., Pei, D., and Liu, D. (2024). Nsun6 regulates Nm23-H1 expression in an M5c manner to affect epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer. Med. Princ. Pract. 33 (1), 56–65. doi:10.1159/000535479
Márquez-González, R. M., Saucedo-Sariñana, A. M., de Jesús Tovar-Jacome, C., Barros-Núñez, P., Gallegos-Arreola, M. P., Orozco-Gutiérrez, M. H., et al. (2024). Nme1 and dcc variants are associated with susceptibility and tumor characteristics in Mexican patients with colorectal cancer. J. Egypt. Natl. Canc. Inst. 36 (1), 10. doi:10.1186/s43046-024-00213-7
Onyoh, E. F., Hsu, W. F., Chang, L. C., Lee, Y. C., Wu, M. S., and Chiu, H. M. (2019). The rise of colorectal cancer in asia: epidemiology, screening, and management. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 21 (8), 36. doi:10.1007/s11894-019-0703-8
Ouatas, T., Clare, S. E., Hartsough, M. T., De La, R. A., and Steeg, P. S. (2002). Mmtv-associated transcription factor binding sites increase Nm23-H1 metastasis suppressor gene expression in human breast carcinoma cell lines. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 19 (1), 35–42. doi:10.1023/a:1013897022827
Qu, S., Long, J., Cai, Q., Shu, X. O., Cai, H., Gao, Y. T., et al. (2008). Genetic polymorphisms of metastasis suppressor gene Nme1 and breast cancer survival. Clin. Cancer Res. 14 (15), 4787–4793. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0083
Rajagopal, T., Seshachalam, A., Akshaya, R. L., Rathnam, K. K., Talluri, S., Jothi, A., et al. (2020). Association of hotair (Rs920778 and Rs1899663) and Nme1 (Rs16949649 and Rs2302254) gene polymorphisms with breast cancer risk in India. Gene 762, 145033. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2020.145033
Roymans, D., Willems, R., Van Blockstaele, D. R., and Slegers, H. (2002). Nucleoside diphosphate kinase (Ndpk/Nm23) and the waltz with multiple partners: possible consequences in tumor metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 19 (6), 465–476. doi:10.1023/a:1020396722860
Shi, X., Jin, H., Peng, M., Li, B., She, M., Zhu, T., et al. (2018). Association between Nme1 polymorphisms and cancer susceptibility: a meta-analysis based on 1644 cases and 2038 controls. Pathol. Res. Pract. 214 (4), 467–474. doi:10.1016/j.prp.2018.02.020
Siegel, R. L., Giaquinto, A. N., and Jemal, A. (2024). Cancer statistics, 2024. Ca. Cancer J. Clin. 74 (1), 12–49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
Steeg, P. S., Bevilacqua, G., Kopper, L., Thorgeirsson, U. P., Talmadge, J. E., Liotta, L. A., et al. (1988). Evidence for a novel gene associated with low tumor metastatic potential. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 80 (3), 200–204. doi:10.1093/jnci/80.3.200
Steeg, P. S., Palmieri, D., Ouatas, T., and Salerno, M. (2003). Histidine kinases and histidine phosphorylated proteins in mammalian cell biology, signal transduction and cancer. Signal Transduct. Cancer. Cancer Lett. 190 (1), 1–12. doi:10.1016/s0304-3835(02)00499-8
Swartjes, H., Sijtsma, F. P. C., Elferink, M. A. G., van Erning, F. N., Moons, L. M. G., Verheul, H. M. W., et al. (2024). Trends in incidence, treatment, and relative survival of colorectal cancer in The Netherlands between 2000 and 2021. Eur. J. Cancer 205, 114104. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2024.114104
Wang, H., and Sang, W. (2020). Association of Nm23 polymorphisms and clinicopathological features and recurrence of invasive pituitary adenomas. Pituitary 23 (2), 113–119. doi:10.1007/s11102-019-01006-1
Xie, M., Zhang, L., Han, L., Huang, L., Huang, Y., Yang, M., et al. (2023). The ash1l-as1-ash1l Axis controls nme1-mediated activation of the ras signaling in gastric cancer. Oncogene 42 (46), 3435–3445. doi:10.1038/s41388-023-02855-8
Xu, L., Zhao, J., Li, Z., Sun, J., Lu, Y., Zhang, R., et al. (2023). National and subnational incidence, mortality and associated factors of colorectal cancer in China: a systematic analysis and modelling study. J. Glob. Health 13, 04096. doi:10.7189/jogh.13.04096
Yang, J., Li, Z., Pang, Y., Zhou, T., Sun, J., Cheng, X. Y., et al. (2022). Microrna-139-5p negatively regulates Nme1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 31 (6), 655–670. doi:10.17219/acem/146579
Yang, T., Chen, B. Z., Li, D. F., Wang, H. M., Lin, X. S., Wei, H. F., et al. (2016). Reduced Nm23 protein level correlates with worse clinicopathologic features in colorectal cancers: a meta-analysis of pooled data. Medicine 95 (4), e2589. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000002589
Yu, L., Wang, X., Zhang, W., Khan, E., Lin, C., and Guo, C. (2021). The multiple regulation of metastasis suppressor Nm23-H1 in cancer. Life Sci. 268, 118995. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118995
Zhang, J., Gelman, I. H., Qu, J., and Hochwald, S. N. (2023b). Phosphohistidine signaling promotes fak-Rb1 interaction and growth factor-independent proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 42 (6), 449–460. doi:10.1038/s41388-022-02568-4
Zhang, Q., McCorkle, J. R., Novak, M., Yang, M., and Kaetzel, D. M. (2011). Metastasis suppressor function of Nm23-H1 requires its 3'-5' exonuclease activity. Int. J. Cancer 128 (1), 40–50. doi:10.1002/ijc.25307
Keywords: NME1, polymorphism, colorectal cancer, risk, prognosis
Citation: Liu Y, Bai T, Zhang Z, Xu Y and Kong D (2025) Nonmetastatic cell 1 gene polymorphisms are associated with the clinical progression and prognoses of patients with colorectal cancer. Front. Genet. 16:1485855. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1485855
Received: 25 August 2024; Accepted: 28 April 2025;
Published: 09 May 2025.
Edited by:
M. Geoffrey Hayes, Northwestern University, United StatesReviewed by:
Lizbeth Gonzalez-Herrera, Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán, MexicoShing Cheng Tan, National University of Malaysia, Malaysia
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Bai, Zhang, Xu and Kong. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Dexian Kong, a29uZ2RleGlhbjA0QDE2My5jb20=
 Yabin Liu
Yabin Liu Tianliang Bai2
Tianliang Bai2 Dexian Kong
Dexian Kong