- 1Department of Ophthalmology, Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Hubei Province Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
- 2The First Clinical Medical School of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan, China
- 3Hubei Key Laboratory of Agricultural Bioinformatics, College of Informatics, Huazhong Agricultural University, Wuhan, China
- 4Department of Medicine, Wuhan Primbio Medical Laboratory, Wuhan, China
Introduction: The diversity of phenotypes, ranging from inherited retinal dystrophies (such as Stargardt disease 1, cone–rod dystrophy 3, and retinitis pigmentosa 19) to late-onset age-related macular degeneration 2, has been attributed to loss-of-function variants in the ABCA4 gene. In this study, we aimed to identify and analyze potential pathogenic ABCA4 variants in patients with Stargardt disease or retinitis pigmentosa and to explore the impact of an intronic variant (NM_000350.3:c.6386 + 4A>G) on mRNA splicing.
Methods: We enrolled three patients from unrelated families with Stargardt disease or retinitis pigmentosa after comprehensive ophthalmological evaluations were performed. Whole-exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing were applied for mutation screening, focusing on inherited retinal dystrophy-related genes. Additionally, the splicing alteration caused by c.6386 + 4A>G was functionally characterized by a minigene splicing assay.
Results: Five ABCA4 germline variants were detected in three patients: one frameshift, one nonsense, one splicing, and two missense variants. Furthermore, two pathogenic and two likely pathogenic variants and one variant of uncertain significance were determined according to ACMG/AMP and ClinGen sequence variant interpretation (SVI) guidelines. The minigene splicing assay result proved that c.6386 + 4A>G affected the wild-type donor splice-site recognition of intron 46 and yielded a truncated transcript with a 47-bp deletion in exon 46.
Discussion: Our study identified two novel ABCA4 variants, expanding the mutational spectrum of the ABCA4 gene in Stargardt disease and retinitis pigmentosa while providing new insights into the molecular pathology of ABCA4 splicing defects.
Introduction
Inherited retinal dystrophies (IRDs) are a group of hereditary diseases that cause severe vision loss due to photoreceptor degeneration or dysfunction (Blackshaw et al., 2001; Karali and Banfi, 2015; Verbakel et al., 2018). They affect approximately 1 in 2,000–3,000 individuals worldwide (Olivares-Gonzalez et al., 2021). IRDs are extremely heterogeneous in terms of genotype and phenotype. One phenotype could result from variants in multiple genes, and diverse variants in the same gene may lead to different phenotypic characteristics (Jaffal et al., 2023; Manley et al., 2023). A total of 306 identified genes have been documented in the Retinal Information Network (RetNet, https://web.sph.uth.edu/RetNet/; accessed October 2024). ABCA4 is one of the most prevalent IRD-causing genes across populations, with its variants accounting for 2%–5% of non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa (RP) cases (Fahim et al., 1993; Bouzidi et al., 2022). For instance, Haer-Wigman et al. reported that approximately 7% of the causative variants in 266 Dutch patients with visual impairment were detected in the ABCA4 gene (Haer-Wigman et al., 2017). Bernardis et al. found that the most recurrent pathogenic mutations in 109 IRD-affected patients were in the ABCA4 and USH2A genes (Bernardis et al., 2016). Perea-Romero et al. identified ABCA4 as the most prevalent gene in autosomal recessive nonsyndromic RP families among 6089 IRD-affected cases (Perea-Romero et al., 2021).
The human ABCA4 gene (OMIM: 601691) is located on chromosome 1p22.1, spans more than 128 kb, and contains 50 exons (Allikmets et al., 1998). The protein encoded by this gene, ATP-binding cassette superfamily transmembrane protein, is primarily expressed in retinal photoreceptors. The ABCA4 protein transports N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine (NrPE) from the lumen to the cytoplasmic leaflet of rod and cone disc membranes by utilizing the energy derived from adenosine triphosphate (ATP) binding and hydrolysis (Beharry et al., 2004). If the ABCA4 protein is dysfunctional, NrPE and all-trans-retinal (ATR) accumulate and condense into N-retinylidene-N-retinylphosphatidylethanolamine (A2PE) in the photoreceptor outer segments. Subsequently, the shed photoreceptor outer segments are phagocytosed by retinal pigment epithelial (RPE) cells, which hydrolyze A2PE via lysosomal enzymes to form N-retinylidene-N-retinylethanolamine (A2E) (Al-Khuzaei et al., 2021; Molday et al., 2022). Consequently, A2E that cannot be further metabolized accumulates within the RPE, forming the main component of lipofuscin, a substance toxic to the RPE, leading to degeneration of RPE and loss of photoreceptor cells (Tsybovsky et al., 2010). Clinically, this process manifests as a reduction or loss of visual acuity.
Functional impairment of the ABCA4 protein is responsible for a wide range of retinal degeneration phenotypes, including Stargardt disease 1 (STGD1), cone–rod dystrophy 3 (CRD3), retinitis pigmentosa 19 (RP19), and other conditions collectively referred to as ABCA4-associated retinopathies (Sheremet et al., 2018; Cremers et al., 2020). Among these, RP19 is characterized by the progressive degeneration and death of rod photoreceptors, resulting in night blindness, decay of visual acuity, and concentric constriction of the visual field (Rudolph et al., 2002; Zhu et al., 2021). In RP19 patients, fundus examinations reveal bone spicule-like pigmentation, peripheral scattered pigmentation, or severe atrophy of the RPE, while the electroretinogram (ERG) shows abolished rod responses and markedly diminished cone responses (Mullins et al., 2012). The main clinical manifestation of STGD1 is progressive bilateral centrifugal vision loss caused by macular atrophy and subretinal deposition of lipofuscin-like substances, typically occurring in childhood or early adolescence (Tsang and Sharma, 2018; Cremers et al., 2020). It is crucial to report and functionally characterize novel potentially pathogenic ABCA4 sequence variants to enable precise diagnosis and therapy of ABCA4-related IRDs.
We hereby describe three unrelated patients who were clinically diagnosed with RP or STGD1. We analyzed the mutational spectrum of ABCA4 in the patients using whole-exome sequencing (WES) and explored the pathogenesis of the novel splicing variant by an in vitro minigene assay.
Materials and methods
Clinical examination
This study was conducted in accordance with guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki. Ethical approval was obtained from the Human Research Ethics Committee of Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (Wuhan, China). Each proband underwent a detailed clinical history review and comprehensive ophthalmological evaluation by a retina specialist. Age at onset and disease progression was determined by patients’ self-reported history of visual loss. The following examinations were performed: fundus photography (Canon CF-1, Tokyo, Japan), visual field examination (AP-7000 automatic perimeter, Kowa, Japan), spectral domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT; Heidelberg Engineering GmbH 69121, Heidelberg, Germany), and fluorescein fundus angiography (Canon, Tokyo, Japan). The patients’ parents denied any family history of ocular disease.
DNA isolation and next-generation sequencing
Three milliliters of peripheral blood was collected from the three patients and their available family members. Genomic DNA (gDNA) was isolated from peripheral blood leukocytes using the magnetic bead method blood gDNA extraction kit (Tiangen Biotech, Beijing, China). The gDNA concentration was quantified using a Qubit 3.0 fluorometer (Qubit double-stranded DNA detection kit, Invitrogen, USA), while integrity was assessed by 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. Qualified gDNA samples were fragmented using the VAHTS® Universal Plus DNA Library Prep Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China) and processed with the xGen® Exome Research Panel v2.0 (Integrated DNA Technologies, USA) for liquid-phase capture to build a library targeting the human whole-exome region. The prepared DNA library was then used to perform 150-bp paired-end sequencing of the whole exome on the MGISEQ-T7 sequencing platform (Mgi Tech Co., Ltd., China).
Bioinformatics analysis
Bioinformatics analysis revealed that each sample yielded over 10 Gb of sequencing data, with coverage over 20× at more than 99% and an average read depth exceeding 120× across all analyzed genomic regions. Sequencing reads were aligned to the GRCh38 human reference genome using Burrows–Wheeler Aligner (BWA, v0.7.16a, http://bio-bwa.sourceforge.net/). To ensure alignment accuracy, low-quality reads and adapter sequences were removed using fastp (fastp v0.21.0). Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) duplicates were eliminated with sambamba (sambamba 0.8.0). Variant calling was performed on the generated BAM file using the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK, v4.0.8.1, https://gatk.broadinstitute.org/). Detected variants included single-nucleotide variants (SNVs) and small insertions/deletions (Indels) less than 50 bp in length. Variants were filtered based on sequencing depth (>20X) and variant quality (QualByDepth>2). ANNOVAR (v20200608, https://annovar.openbioinformatics.org/) was utilized for variant annotation. Annotated variants were further filtered and prioritized by minor allele frequency (ExAC, gnomAD, 1000 Genomes, and in-house variant frequency database), protein effect (missense, synonymous, frameshift, in-frame indel, and splicing variants), various in silico prediction scores (e.g., CADD_PHRED, REVEL, SIFT, Polyphen-2, MutationTaster, and SpliceAI), inheritance pattern of related disease (autosomal dominant, autosomal recessive, or X-linked), and clinical phenotype concordance. Exonic copy number variants (CNVs) were calculated using an in-house algorithm by analyzing target region read depths relative to an internal control dataset. Cryptic splice sites were predicted using Human Splice Finder (HSF, v3.1, http://www.umd.be/HSF3/HSF.shtml), VarSEAK (https://varseak.bio/index.php), and SpliceAI (https://spliceailookup.broadinstitute.org/). The pathogenicity of candidate variants was interpreted according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics/Association for Molecular Pathology (ACMG/AMP) (Tavtigian et al., 2018; Harrison et al., 2019) and ClinGen sequence variant interpretation (SVI) guidelines (https://clinicalgenome.org/working-groups/sequence-variant-interpretation/). The structural domain annotation of identified variants was performed using InterPro (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro). Variants were mapped to functional domains based on the InterPro and classified according to their positions within key domains. To assess the evolutionary conservation of amino acid residues affected by missense variants, multiple sequence alignment was performed using ClustalW (https://www.genome.jp/tools-bin/clustalw).
Sanger sequencing
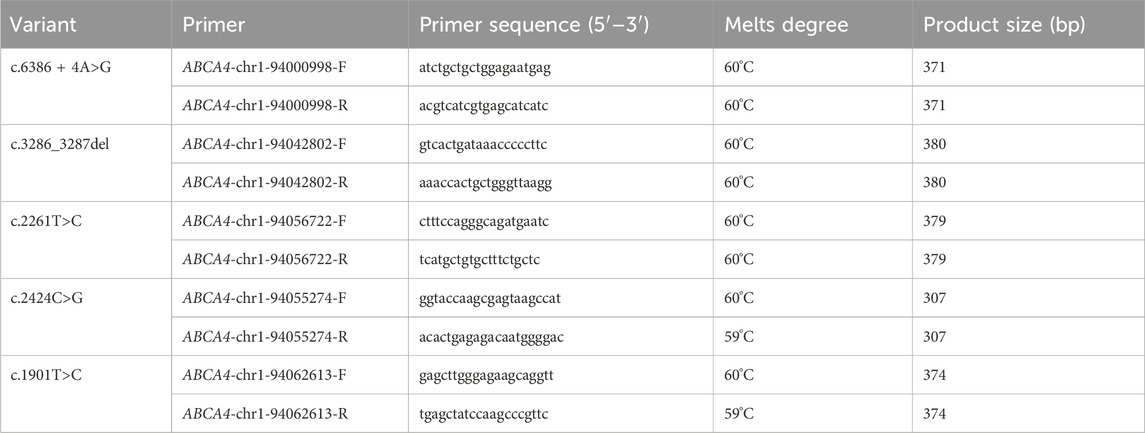
Specific primer pairs for the candidate variants were designed using the Primer3 algorithm (Primer3web version 4.1.0, https://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3/). The designed primers were used to amplify regions of DNA sequence containing the variants by PCR. The PCR amplicons were purified, and then Sanger sequencing was performed for PCR products on the ABI 3730XL DNA analyzer platform (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, United States). The nucleotide primer sequences of candidate variants are listed in Table 1.
Minigene splicing assay
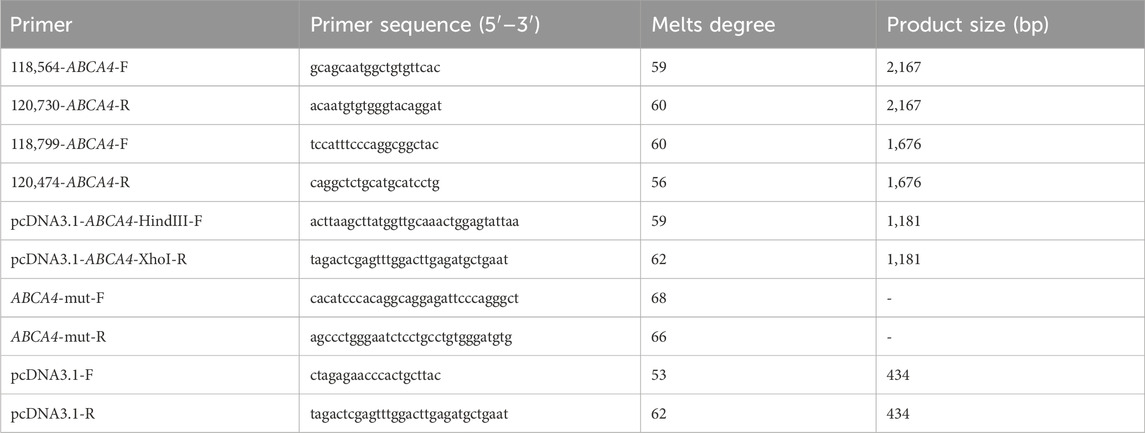
The c.3286_3287del variant has been previously reported; therefore, functional studies were not conducted on it. We utilized a minigene splicing assay to assess the impact of a novel intronic ABCA4 variant (c.6386 + 4A>G) on mRNA splicing. In vitro minigene functional verification was performed by Bioeagle Biotech Co., Ltd. (Wuhan, China). Wild-type and mutant-type ABCA4 genomic segments encompassing exons 45 to 47 were cloned and inserted into the splicing pcDNA3.1 vector to construct pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-wt and pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-mut minigenes, respectively. First, two pairs of nested primers (118564-ABCA4-F/120474-ABCA4-R and 118799-ABCA4-F/120730-ABCA4-R) were designed to PCR amplify the ABCA4 genomic region encompassing exons 45–47. The 1181-bp wild-type fragment was amplified from the nested PCR product using primers pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-HindIII-F and pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-XhoI-R. The anterior and posterior segments of the mutant fragment were separately amplified using the primers pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-HindⅢ-F ABCA4-mut-R and pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-XhoI-R ABCA4-mut-F, respectively, followed by equimolar mixing of the products. The full-length 1181-bp mutant fragment was PCR-amplified from this mixture using the primers pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-HindIII-F and pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-XhoI-R. The wild-type and mutant fragments were cloned and inserted into the empty pcDNA3.1 vector (Figure 1). MCF-7 and HEK293T cells were transfected with the minigene constructs using Hieff Trans liposomal transfection reagent (Yeasen Biotechnology Shanghai Co., Ltd., Cat. China) per the manufacturer’s protocol. After 48-h incubation, total cellular RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent and reverse-transcribed. The cDNA was PCR-amplified with vector primers pcDNA3.1-F and pcDNA3.1-R. Sanger sequencing was used to analyze the splicing pattern of the wild-type and mutant minigene vectors (with parallel validation in the pcMINI-N vector; see Supplementary Figure S1). The primer sequences are listed in Table 2.
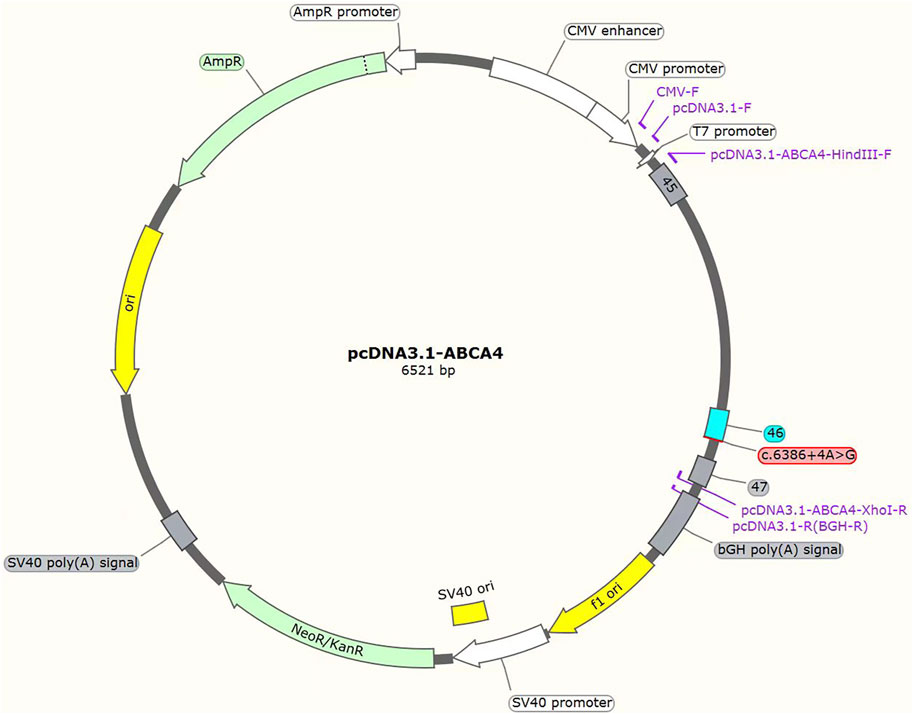
Figure 1. Structures of the splicing vector pcDNA3.1-ABCA4 and minigene pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-wt/pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-mut (c.6386 + 4A>G).
Results
Clinical features
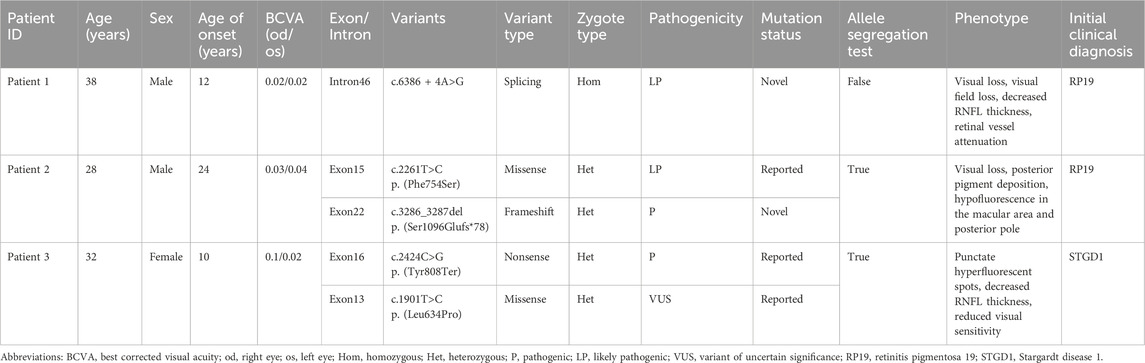
Three unrelated Han Chinese patients (two males and one female) with RP or Stargardt Disease. underwent WES. The basic clinical phenotypic features and molecular diagnoses of these three patients are shown in Table 3. Bilateral visual acuity in each patient showed a progressive decline. No family history of RP, macular degeneration, or other retinal dystrophies was reported in any of the patients.
Patient 1
Fundus photography of Patient 1, performed in another hospital, showed attenuated blood vessels, bone spicule-shaped pigment deposits, and optic disc pallor. Visual field perimetry disclosed significant peripheral visual field loss in both eyes. High-resolution SD-OCT of the retinal nerve fiber layer (RNFL) showed a decrease in the nasal inner retinal thickness (Figure 2).
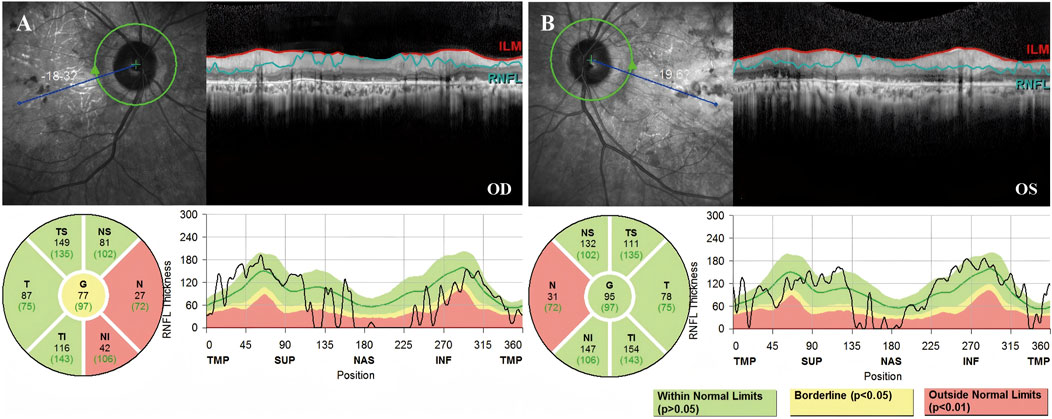
Figure 2. High-resolution SD-OCT of Patient 1 demonstrated decreased inner retinal thickness in specific regions. RNFL is the abbreviation for the retinal nerve fiber layer. The global (G), temporal-inferior (TI, 270°–315°), temporal (T, 315°–45°), temporal-superior (TS, 45°–90°), nasal-superior (NS, 90°–135°), nasal (N, 135°–225°), and nasal-inferior (NI, 225°–270°) RNFL thickness measurements were recorded separately for each sector in micrometers (μm). The measured RNFL thickness of each sector (black numbers) and the age-correlated 50% percentile (green numbers) are illustrated in the pie charts. (A) The nasal RNFL and nasal-inferior RNFL around the optic disk in the right eye showed abnormal thinning. (B) The nasal RNFL around the optic disc in the left eye showed abnormal thinning.
Patient 2
Fundus photography of Patient 2 showed normal-appearing optic disks and hyperpigmentation in the macula in both eyes. Fluorescein fundus angiography (FFA) demonstrated diffuse hypofluorescence in the macular area and posterior pole bilaterally. Macular OCT revealed degeneration and thickening of the outer retina (Figure 3).
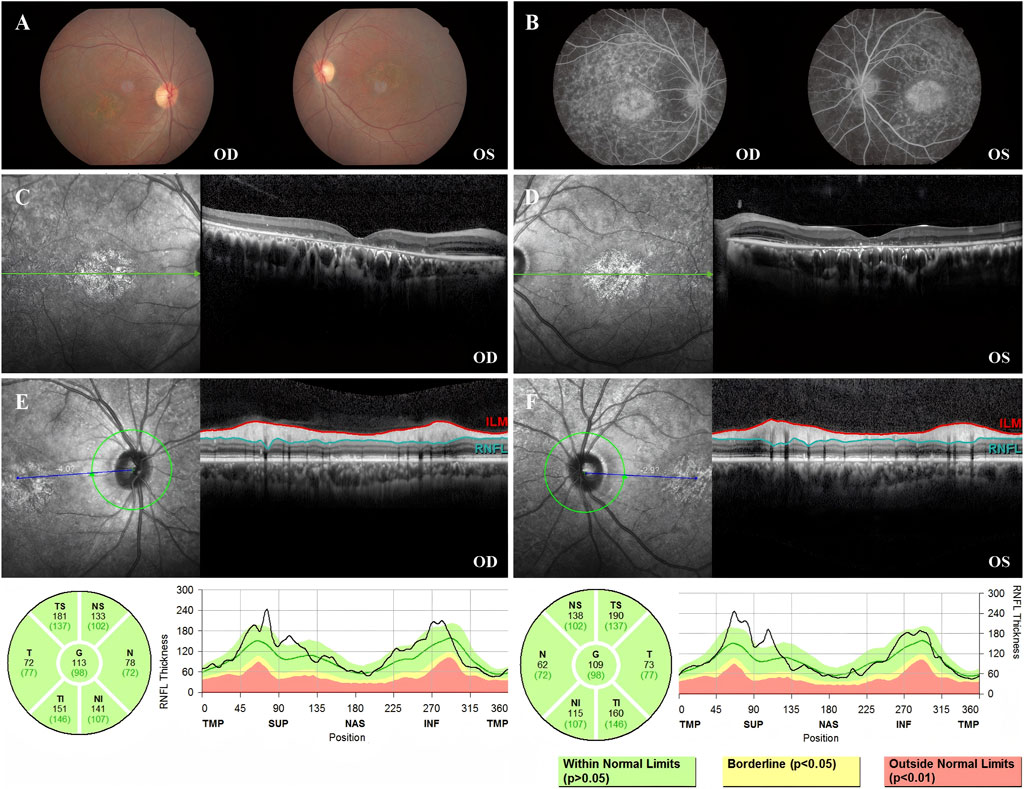
Figure 3. Color fundus photography, FFA, macular OCT, and RNFL of Patient 2. (A) Color fundus photographs of both eyes showing normal optic disk appearance bilaterally. Notably, patchy hyperpigmentation and retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) changes are present in the macular area of both eyes, more prominent in the right eye (OD). (B) FFA image showing abundant diffuse hypofluorescence in the macular area and posterior pole bilaterally. (C) Macular OCT of the right eye, demonstrating the degeneration of the outer retina. (D) Macular OCT of the left eye, demonstrating the degeneration of the outer retina. (E) RNFL of the right eye was normal. (F) RNFL of the left eye was normal.
Patient 3
Fundus images of Patient 3 revealed atrophy and pigmentation of the posterior pole of the retina. FFA displayed multiple hyperfluorescent punctate lesions within the macular area. Macular OCT showed a marked decrease in the thickness of the bilateral RPE, retinal neurosensory layer, and choroid layer in the macula. The RNFL showed abnormal thinning in the superotemporal and inferotemporal quadrants around both optic disks. The visual field showed reduced visual sensitivity and defects in the central 30° bilaterally (Figure 4).
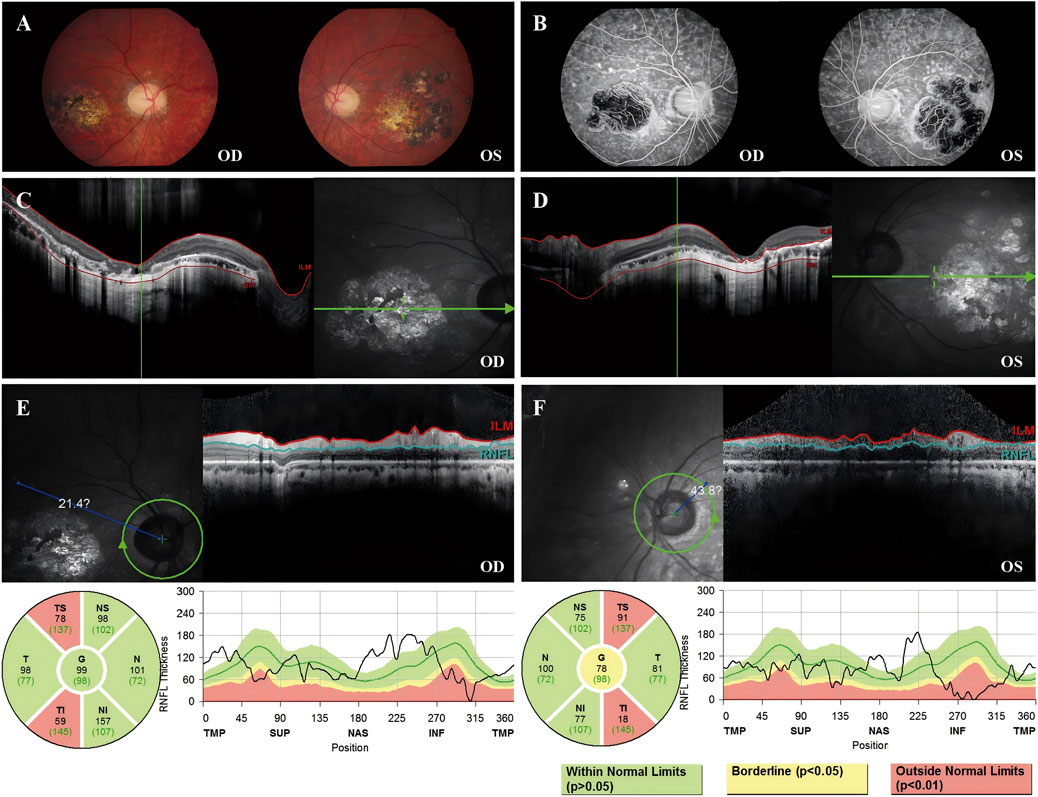
Figure 4. Color fundus photography, FFA, macular OCT, and RNFL image of Patient 3. (A) Color fundus photograph revealing retinal pigmentation and atrophy. (B) FFA image reveals inhomogeneous strong fluorescence in the posterior pole and a large area of fluorescence in the macular area. (C) OCT image of the right eye revealed that the outer retina was thin and atrophied in the macular area. (D) OCT image of the left eye revealed that the outer retina was thin and atrophied in the macular area. (E) The TS sector measures 78 μm (below the 1st percentile, indicated in red), and the TI sector measures 59 μm (also below the 1st percentile), suggesting statistically significant thinning (p < 0.01) in these regions. (F) The TS sector measures 91 μm (below the 1st percentile, indicated in red), and the TI sector measures 18 μm (also below the 1st percentile), suggesting statistically significant thinning (p < 0.01) in these regions.
Molecular analysis and minigene assay
Patient 1 revealed a novel homozygous variant c.6386 + 4A>G in the intron 46 of the ABCA4 gene adjacent to the donor splice site (Figure 5A). This variant was absent from public databases (gnomAD v4.1.0, https://gnomad.broadinstitute.org/) and the literature. In silico analyses using SpliceAI and HSF predicted disruption of the wild-type donor splice site. The minigene splicing assay results showed that both pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-wt and pcDNA3.1-ABCA4-mut plasmids were successfully transfected into MCF-7 and HEK293T cells (Figure 5B). Agarose gel electrophoresis revealed that the mutant type had two bands. One band was the same as the wild-type band in length, and the other band was smaller with faster migration (Figure 5C). Sanger sequencing confirmed that the wild-type minigene transcribed the normal mRNA product composed of exon 45, exon 46, and exon 47. However, the mutant minigene mRNA transcribed product lacked 47 bp of exon 46 (c.6340_6386del), causing a frameshift to p. (Val2114Hisfs*5) (Figure 5D). The transcriptional results of the pc-MINI-N vector are shown in Supplementary Figure S2. The variant was classified as likely pathogenic based on ACMG/AMP and ClinGen SVI guidelines with evidence from a minigene assay (PS3+PM2_Supporting + PM3_Supporting).
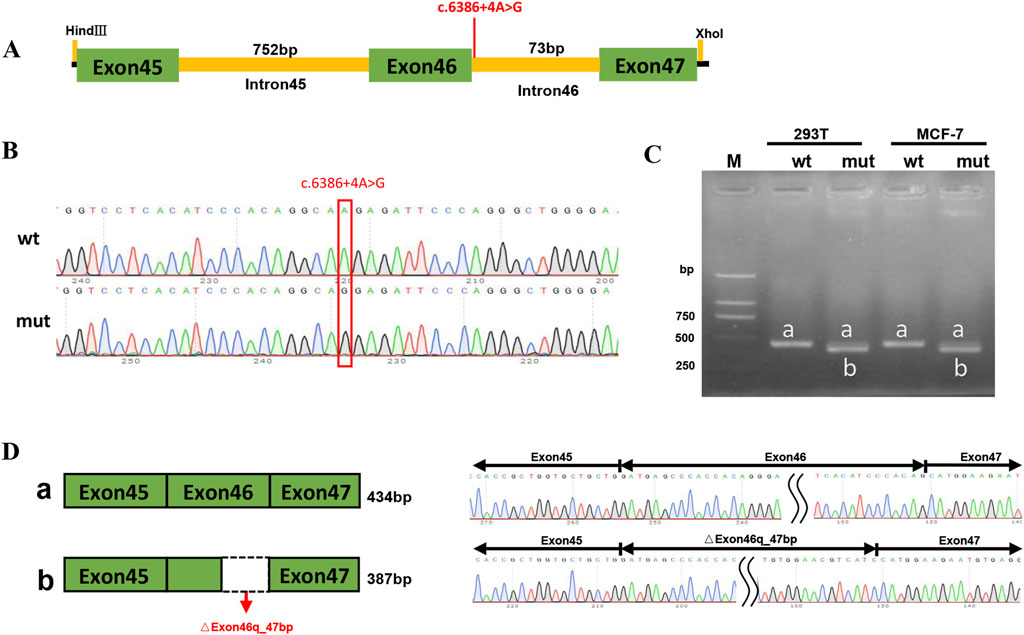
Figure 5. PcDNA3.1 minigene splicing assays. (A) The location of the variant c.6386 + 4A>G in ABCA4 minigene. (B) Sanger sequencing results of the recombinant vector: Top: wt, wild-type, Bottom: mut, mutant. (C) Agarose gel electrophoresis result of transcript PCR product in both MCF-7 and HEK293T cell lines. The wild-type minigene had one band, a (434 bp), and the mutant minigene had two bands: a (434 bp) and b (387 bp). (D) A schematic of cloned vectors and alternative splicing. Sanger sequencing of the PCR products showed that the difference between the two transcripts was based on the absence or presence of 47 bp of exon46.
Patient 2 revealed biallelic ABCA4 variants: c.3286_3287del, p.(Ser1096Glufs*78), and c.2261T>C, p.(Phe754Ser). Segregation analysis confirmed that the c.3286_3287del variant was paternally inherited, and the c.2261T>C variant was maternally inherited (Figures 6A,B). c.2261T>C is a phenylalanine-to-serine missense substitution, predicted to be deleterious by SIFT (https://www.jcvi.org/research/provean) and MutationTaster (https://sites.google.com/site/revelgenomics/). Conservation analysis showed that the mutated phenylalanine residue was conserved across seven species, spanning vertebrates from mammals to amphibians (Figure 7). The variant was previously reported in three Chinese patients with STGD1 or cone–rod dystrophy (Jiang et al., 2016; Hu et al., 2019; Li et al., 2023) and was categorized as likely pathogenic (PM2_Supporting + PM3_Strong + PP3). The c.3286_3287del frameshift variant was predicted to undergo nonsense-mediated mRNA decay by the AutoPVS1 tool (https://autopvs1.genetics.bgi.com). It was classified as pathogenic (PVS1+PM2_Supporting + PM3).
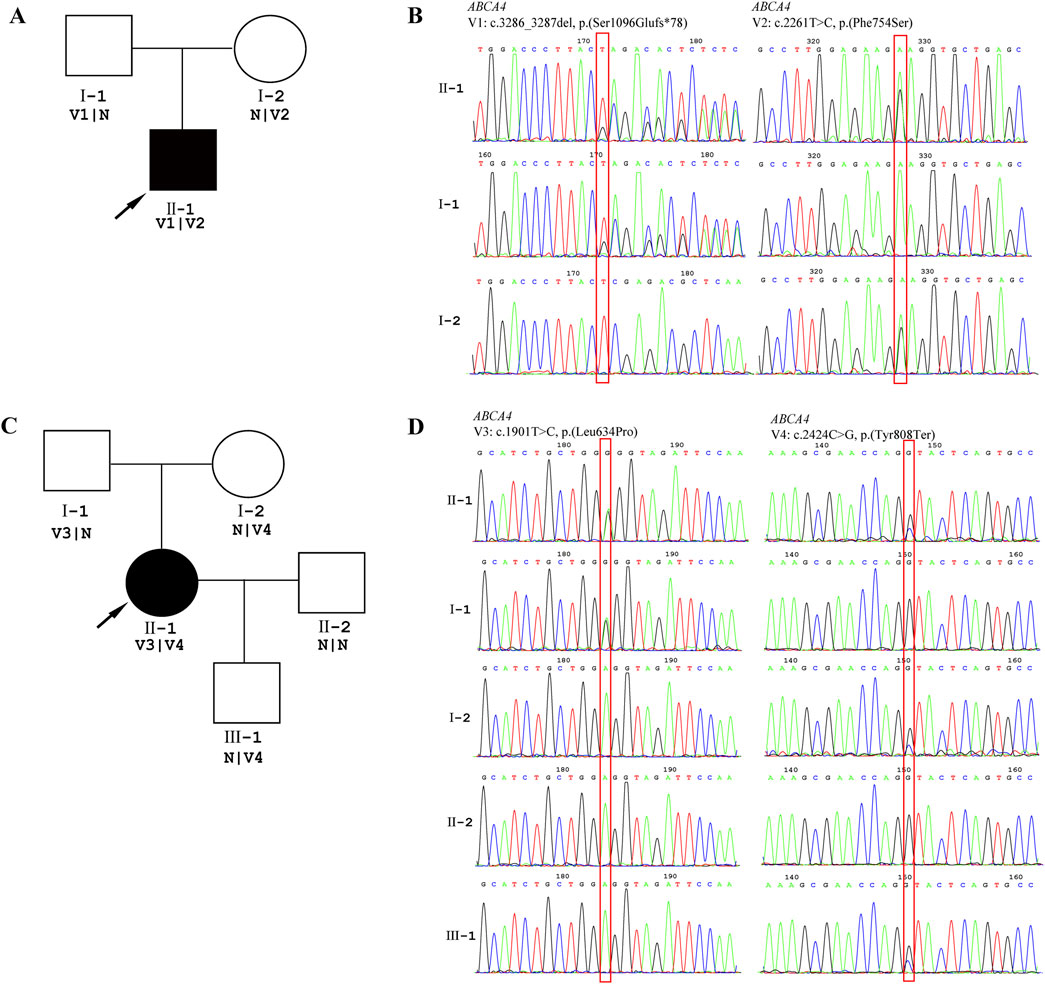
Figure 6. Genetic testing results. DNA samples from patients were subjected to WES, and their family members were recruited for Sanger sequencing. (A) Pedigree of the family of Patient 2. (B) The chromatographs of Sanger sequencing of family members of Patient 2. (C) Pedigree of family of Patient 3. (D) The chromatographs of Sanger sequencing of family members of Patient 3. The red box indicates the location of the variant, and the arrow indicates the proband.
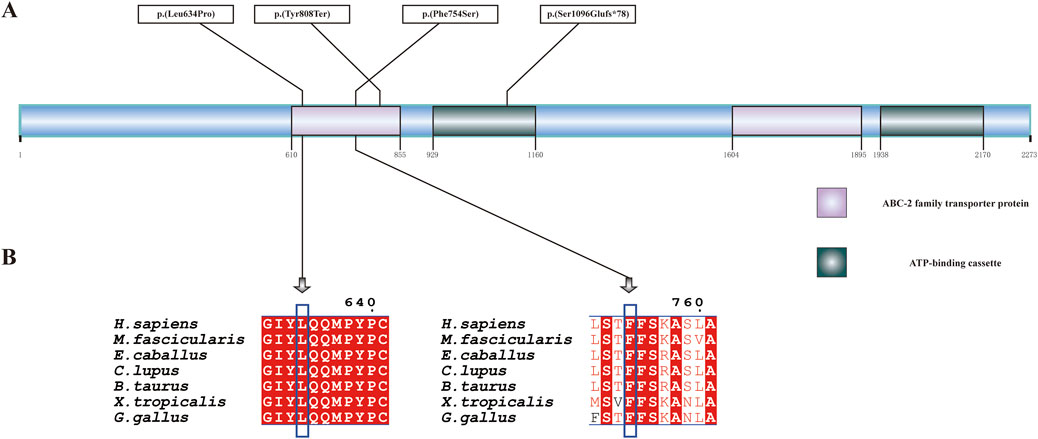
Figure 7. ABCA4 protein structure and conservation analysis. (A) Linear diagram of the wild-type ABCA4 polypeptide. The purple and green boxes denote two representative domains, namely, the ABC-2 family transporter protein domain and the ATP-binding cassette domain. (B) Conservation analysis of p.(Leu634Pro) and p.(Phe754Ser) across seven species by multiple sequence alignment. The blue box indicates the location of the variant. The aligned organisms include Homo sapiens, Macaca fascicularis, Equus caballus, Canis lupus familiaris, Bos taurus, Gallus gallus, and Xenopus tropicalis.
Patient 3 inherited the c.2424C>G, p.(Tyr808Ter) variant from her mother and the c.1901T>C, p.(Leu634Pro) variant from her father (Figures 6C,D). The c.2424C>G variant creates a premature stop codon at position 808. Sanger sequencing confirmed that the nonsense variant was also present in the patient’s unaffected son. This variant was previously reported in over 10 STGD1 or cone-rod dystrophy patients with compound heterozygous genotypes in the ABCA4 gene (Jiang et al., 2016; Qu et al., 2021; Chen et al., 2022; Li et al., 2023). It was classified as a pathogenic variant (PVS1+PM3_Verystrong + PM2_Supporting). The c.1901T>C variant results in a leucine-to-proline missense substitution. Multiple sequence alignment showed that codon 634 was conserved across seven species (Figure 7), although the variant was classified as a variant of uncertain significance (PM2_Supporting + PM3+PP3) based on limited evidence to date. Population frequencies and in silico prediction results of five ABCA4 variants in the three patients are provided in Supplementary Table S1.
Discussion
ABCA4 is associated with STGD1, CORD3, RP19, and AMD2 (Cremers et al., 2020; Al-Khuzaei et al., 2021; Romano et al., 2024). Large cohort studies across diverse ethnic populations have defined the ABCA4 mutational spectrum, associated phenotypes, and genotype–phenotype correlations in these IRDs (Rivera et al., 2000; Fujinami et al., 2013; Jiang et al., 2016; Schulz et al., 2017; Hu et al., 2019; Del Pozo-Valero et al., 2020). Pathogenic variants encompass various types, including missense and nonsense variants, splicing (canonical and non-canonical) variants, deep-intronic variants, in-frame indels, large indels, and complex rearrangements (Human Gene Mutation Database; https://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/search.php). Several pathogenic variants exhibit marked ethnic predilection, with notably elevated frequencies in specific populations: c.5882G>A (20.5% allele frequency in Europeans) (Rivera et al., 2000), c.6320G>A (19.32% in African Americans) (Zernant et al., 2014), and c.2424C>G (5.2% in Chinese) (Sun et al., 2021). Further mechanistic studies of these variants may elucidate the molecular basis of the relationship between genotypic and phenotypic manifestations.
In this study, we describe three middle-aged patients with ABCA4-associated IRDs. Patient 1 had the homozygous c.6386 + 4A>G splicing variant and was born to consanguineous parents. Although parental samples were unavailable, we infer that his father and mother were both heterozygous carriers of this variant. Most disease-causing splicing variants occur at canonical +1/+2 or −1/−2 positions (Krawczak et al., 1992); however, non-canonical splice-site variants can also disrupt mRNA processing and result in a dysfunctional protein. Several studies have reported different intronic variants in the ABCA4 gene associated with retinal degeneration. For example, Cremers et al. reported five cone-rod dystrophy (CRD) patients in a consanguineous family who were compound heterozygotes for the IVS30+1G→T variant and the IVS40+5G→A variant, which would lead to skipping of exon 40 with a reading frame shift in exon 41 (Cremers et al., 1998). Sangermano et al. performed in vitro minigene splice assays to analyze the effect of 47 non-canonical splice-site variants (NCSS) on ABCA4 pre-mRNA splicing. Among these variants, 29 variants (62%) induced single or multi-exon skipping (e.g., c.302 + 4A>C, c.2919-10T>C), eight variants (17%) showed multiple splice defects like skipping/elongation or skipping/retention (e.g., c.160 + 5G>C, c.303-3C>G, and c.5898+5del), six variants (13%) resulted in exon elongation (e.g., c.1937 + 13T>G, c.5313-3C>G) (Sangermano et al., 2018). Fadaie et al. found that deep-intronic variants, such as c.193-619A>G, c.2919-826T>A, and c.3050 + 370C>T, caused significant splicing defects in minigene splice assays. These variants generated pseudoexons containing premature stop codons, leading to predicted truncated ABCA4 proteins (Khan et al., 2019).
The variants c.3286_3287del, p.(Ser1096Glufs*78), and c.2261T>C, p.(Phe754Ser) in trans were identified in Patient 2, while c.2424C>G, p.(Tyr808Ter), and c.1901T>C, p.(Leu634Pro) in trans were identified in Patient 3 in ABCA4. Both patients had a loss-of-function variant that was predicted to cause protein truncation and a missense variant that was predicted to be likely to damage protein function according to sequence conservation analysis. Our structural analysis revealed that p. (Leu634Pro), p.(Phe754Ser), and p.(Tyr808Ter) were located within the ABC-2 family transporter protein domain, while p.(Ser1096Glufs*78) was mapped to the ATP-binding cassette domain.
A genotype-phenotype correlation model elucidated that residual activity of the ABCA4 protein was correlated with the severity of retinal dystrophy (van Driel et al., 1998; Maugeri et al., 1999). According to the activity of the ABCA4 protein, variants in the ABCA4 gene are classified as deleterious (no activity), severe, moderately severe, or mild. Patients harboring two severe variants or null alleles typically present with pan-retinal cone–rod dystrophy (CRD). The combination of a severe variant with a moderately severe variant leads to CRD, while a severe variant with a mild variant or two moderately severe variants results in classic Stargardt disease type 1 (STGD1) (Cremers et al., 2020). In our study cohort, Patient 1, who carried the homozygous c.6386 + 4A>G, p. (Val2114Hisfs*5) variant, presented with retinitis pigmentosa, a type of rod-cone dystrophy. Our minigene assay demonstrated that the variant c.6386 + 4A>G led to disruption of RNA splicing, resulting in a predicted truncated protein. Patient 2, who carried the severe variant c.3286_3287del, p.(Ser1096Glufs*78) and the moderately severe variant c.2261T>C, p.(Phe754Ser), showed a milder phenotype of retinitis pigmentosa. Patient 3, harboring two variants c.2424C>G, p.(Tyr808Ter) and c.1901T>C, p.(Leu634Pro), was diagnosed with STGD1. The variant p.(Tyr808Ter), in combination with one of the missense variants p.(Arg24His), p.(Phe2188Ser), p.(Ser100Tyr), or p.(Asn965Ser) in trans, has been previously associated with more than seven STGD1 patients (Jiang et al., 2016; Li et al., 2023).
WES is a powerful and widely used technique to diagnose genetic abnormalities, yet it has limitations. Because WES primarily targets exonic regions and their immediate flanking sequences, it frequently misses deep-intronic variants that may affect splicing. This is particularly relevant for genes like ABCA4, where numerous pathogenic deep-intronic variants have been identified (Khan et al., 2019; Wang et al., 2025). Furthermore, WES often detects a substantial number of variants of uncertain significance (VUS) during genetic screening of human exons and their flanking regions (Yang et al., 2013; Umair, 2023). To interpret the clinical significance of VUS, further research and evidence are needed. Functional studies play a pivotal role in variant assessment, with minigene assays providing a rapid tool to evaluate effects on splicing compared to wild-type sequences (Abramowicz and Gos, 2018). Minigene assays have been applied across multiple genetic disorders. For example, Valeria et al. demonstrated efficient characterization of NF1 splicing alterations using minigene assays (Morbidoni et al., 2021). María et al. performed functional studies of ALMS1 variants with minigene assays (Alvarez-Satta et al., 2017). Additionally, Ruixiao et al. identified seven exonic variants in SLC4A1, ATP6V1B1, and ATP6V0A4 that altered RNA splicing based on minigene assays (Zhang et al., 2021). Wang et al. proved that ABCA4 deep-intronic variants contributed to nearly half of unsolved Stargardt cases through minigene experiments (Wang et al., 2025). While in silico predictions provide clues, experimental validation is key for the clinical interpretation of VUS (Li et al., 2024). Integrating evidence from sequencing, predictive models, and functional assays will advance the identification of disease-causing variants and elucidate underlying mechanisms of pathogenesis. These findings may contribute to the interpretation of variants of uncertain significance and highlight the potential of functional assays, such as minigene systems, in supporting variant classification. While further validation in larger cohorts is needed, this approach could aid in improving genetic counseling and personalized management.
In summary, we described three patients with ABCA4-related IRD phenotypes harboring five different variants in the ABCA4 gene. The generated data may have implications for genetic counseling, disease management, and support early intervention for a better prognosis in ABCA4-related IRD.
Data availability statement
The whole exome sequencing data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Genome Sequence Archive (Genomics, Proteomics & Bioinformatics 2021) in National Genomics Data Center (Nucleic Acids Res 2022), China National Center for Bioinformation / Beijing Institute of Genomics, Chinese Academy of Sciences (GSA-Human: HRA011833) that are publicly accessible at https://ngdc.cncb.ac.cn/gsa-human. The patients' phenotypes and detected variants have been submitted to ClinVar (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/) under the submission numbers SCV004174835, SCV004174061, SCV004174062, SCV004174063, SCV004174064.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Human Research Ethics Committee of Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
QL: writing – original draft and writing – review and editing. JH: writing – original draft and writing – review and editing. LS: methodology, software, and writing – review and editing. GZ: data curation, investigation, and writing – review and editing. LX: data curation, investigation, and writing – review and editing. KW: formal analysis and writing – review and editing. XL: investigation, software, and writing – review and editing. LY: methodology and writing – review and editing. DL: conceptualization and writing – review and editing. LM: methodology and writing – review and editing. JL: conceptualization, funding acquisition, project administration, resources, supervision, and writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Knowledge Innovation Special Dawn Program Project of the Wuhan Science and Technology Bureau (No. 2022020801020510) and the Science and technology research project of the Hubei Provincial Department of Education (No. B2021108).
Acknowledgments
We would like to express our gratitude to Dr. Guohua Yang of the School of Basic Medical Science of Wuhan University for providing technical support. We also thank the patients for participating in this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2025.1516872/full#supplementary-material
References
Abramowicz, A., and Gos, M. (2018). Splicing mutations in human genetic disorders: examples, detection, and confirmation. J. Appl. Genet. 59 (3), 253–268. doi:10.1007/s13353-018-0444-7
Al-Khuzaei, S., Broadgate, S., Foster, C. R., Shah, M., Yu, J., Downes, S. M., et al. (2021). An overview of the genetics of ABCA4 retinopathies, an evolving story. Genes (Basel) 12 (8), 1241. doi:10.3390/genes12081241
Allikmets, R., Wasserman, W. W., Hutchinson, A., Smallwood, P., Nathans, J., Rogan, P. K., et al. (1998). Organization of the ABCR gene: analysis of promoter and splice junction sequences. Gene 215 (1), 111–122. doi:10.1016/s0378-1119(98)00269-8
Alvarez-Satta, M., Castro-Sanchez, S., Pousada, G., and Valverde, D. (2017). Functional analysis by minigene assay of putative splicing variants found in Bardet-Biedl syndrome patients. J. Cell Mol. Med. 21 (10), 2268–2275. doi:10.1111/jcmm.13147
Beharry, S., Zhong, M., and Molday, R. S. (2004). N-retinylidene-phosphatidylethanolamine is the preferred retinoid substrate for the photoreceptor-specific ABC transporter ABCA4 (ABCR). J. Biol. Chem. 279 (52), 53972–53979. doi:10.1074/jbc.M405216200
Bernardis, I., Chiesi, L., Tenedini, E., Artuso, L., Percesepe, A., Artusi, V., et al. (2016). Unravelling the complexity of inherited retinal dystrophies molecular testing: added value of targeted next-generation sequencing. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 6341870. doi:10.1155/2016/6341870
Blackshaw, S., Fraioli, R. E., Furukawa, T., and Cepko, C. L. (2001). Comprehensive analysis of photoreceptor gene expression and the identification of candidate retinal disease genes. Cell 107 (5), 579–589. doi:10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00574-8
Bouzidi, A., Charoute, H., Charif, M., Amalou, G., Kandil, M., Barakat, A., et al. (2022). Clinical and genetic spectrums of 413 North African families with inherited retinal dystrophies and optic neuropathies. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 17 (1), 197. doi:10.1186/s13023-022-02340-7
Chen, L., Wang, N., Lai, M., Hou, F., He, J., Fan, X., et al. (2022). Clinical and genetic investigations in Chinese families with retinitis pigmentosa. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 247 (12), 1030–1038. doi:10.1177/15353702221085711
Cremers, F. P., van de Pol, D. J., van Driel, M., den Hollander, A. I., van Haren, F. J., Knoers, N. V., et al. (1998). Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa and cone-rod dystrophy caused by splice site mutations in the Stargardt's disease gene ABCR. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7 (3), 355–362. doi:10.1093/hmg/7.3.355
Cremers, F. P. M., Lee, W., Collin, R. W. J., and Allikmets, R. (2020). Clinical spectrum, genetic complexity and therapeutic approaches for retinal disease caused by ABCA4 mutations. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 79, 100861. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100861
Del Pozo-Valero, M., Riveiro-Alvarez, R., Blanco-Kelly, F., Aguirre-Lamban, J., Martin-Merida, I., Iancu, I. F., et al. (2020). Genotype-phenotype correlations in a Spanish cohort of 506 families with biallelic ABCA4 pathogenic variants. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 219, 195–204. doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2020.06.027
Fahim, A. T., Daiger, S. P., and Weleber, R. G. (1993). “Nonsyndromic retinitis pigmentosa overview,” in GeneReviews((R)). Editors M. P. Adam, J. Feldman, G. M. Mirzaa, R. A. Pagon, S. E. Wallace, and A. Amemiya (Seattle (WA)).
Fujinami, K., Zernant, J., Chana, R. K., Wright, G. A., Tsunoda, K., Ozawa, Y., et al. (2013). ABCA4 gene screening by next-generation sequencing in a British cohort. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 54 (10), 6662–6674. doi:10.1167/iovs.13-12570
Haer-Wigman, L., van Zelst-Stams, W. A., Pfundt, R., van den Born, L. I., Klaver, C. C., Verheij, J. B., et al. (2017). Diagnostic exome sequencing in 266 Dutch patients with visual impairment. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 25 (5), 591–599. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2017.9
Harrison, S. M., Biesecker, L. G., and Rehm, H. L. (2019). Overview of specifications to the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines. Curr. Protoc. Hum. Genet. 103 (1), e93. doi:10.1002/cphg.93
Hu, F. Y., Li, J. K., Gao, F. J., Qi, Y. H., Xu, P., Zhang, Y. J., et al. (2019). ABCA4 gene screening in a Chinese cohort with Stargardt disease: identification of 37 novel variants. Front. Genet. 10, 773. doi:10.3389/fgene.2019.00773
Jaffal, L., Joumaa, H., Noureldine, J., Banjak, M., Ibrahim, M., Mrad, Z., et al. (2023). The genetic landscape of inherited retinal dystrophies in Arabs. BMC Med. Genomics 16 (1), 89. doi:10.1186/s12920-023-01518-7
Jiang, F., Pan, Z., Xu, K., Tian, L., Xie, Y., Zhang, X., et al. (2016). Screening of ABCA4 gene in a Chinese cohort with Stargardt disease or cone-rod dystrophy with a report on 85 novel mutations. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 57 (1), 145–152. doi:10.1167/iovs.15-18190
Karali, M., and Banfi, S. (2015). Inherited Retinal Dystrophies: the role of gene expression regulators. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 61, 115–119. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2015.02.007
Khan, M., Cornelis, S. S., Khan, M. I., Elmelik, D., Manders, E., Bakker, S., et al. (2019). Cost-effective molecular inversion probe-based ABCA4 sequencing reveals deep-intronic variants in Stargardt disease. Hum. Mutat. 40 (10), 1749–1759. doi:10.1002/humu.23787
Krawczak, M., Reiss, J., and Cooper, D. N. (1992). The mutational spectrum of single base-pair substitutions in mRNA splice junctions of human genes: causes and consequences. Hum. Genet. 90 (1-2), 41–54. doi:10.1007/BF00210743
Li, C., Luo, Y., Xie, Y., Zhang, Z., Liu, Y., Zou, L., et al. (2024). Structural and functional prediction, evaluation, and validation in the post-sequencing era. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 23, 446–451. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2023.12.031
Li, W., He, X. D., Yang, Z. T., Han, D. M., Sun, Y., Chen, Y. X., et al. (2023). De novo mutations contributes approximately 7% of pathogenicity in inherited eye diseases. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 64 (2), 5. doi:10.1167/iovs.64.2.5
Manley, A., Meshkat, B. I., Jablonski, M. M., and Hollingsworth, T. J. (2023). Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pathogenesis underlying inherited retinal dystrophies. Biomolecules 13 (2), 271. doi:10.3390/biom13020271
Maugeri, A., van Driel, M. A., van de Pol, D. J., Klevering, B. J., van Haren, F. J., Tijmes, N., et al. (1999). The 2588G↠C mutation in the ABCR gene is a mild frequent founder mutation in the Western European population and allows the classification of ABCR mutations in patients with Stargardt disease. Am J Hum Genet. 64 (4), 1024–35. doi:10.1086/302323
Molday, R. S., Garces, F. A., Scortecci, J. F., and Molday, L. L. (2022). Structure and function of ABCA4 and its role in the visual cycle and Stargardt macular degeneration. Prog. Retin Eye Res. 89, 101036. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2021.101036
Morbidoni, V., Baschiera, E., Forzan, M., Fumini, V., Ali, D. S., Giorgi, G., et al. (2021). Hybrid minigene assay: an efficient tool to characterize mRNA splicing profiles of NF1 variants. Cancers (Basel) 13 (5), 999. doi:10.3390/cancers13050999
Mullins, R. F., Kuehn, M. H., Radu, R. A., Enriquez, G. S., East, J. S., Schindler, E. I., et al. (2012). Autosomal recessive retinitis pigmentosa due to ABCA4 mutations: clinical, pathologic, and molecular characterization. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 53 (4), 1883–1894. doi:10.1167/iovs.12-9477
Olivares-Gonzalez, L., Velasco, S., Campillo, I., and Rodrigo, R. (2021). Retinal inflammation, cell death and inherited retinal dystrophies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (4), 2096. doi:10.3390/ijms22042096
Perea-Romero, I., Gordo, G., Iancu, I. F., Del Pozo-Valero, M., Almoguera, B., Blanco-Kelly, F., et al. (2021). Genetic landscape of 6089 inherited retinal dystrophies affected cases in Spain and their therapeutic and extended epidemiological implications. Sci. Rep. 11 (1), 1526. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-81093-y
Qu, L. H., Jin, X., Zeng, C., Zhou, N. G., Liu, Y. H., and Lin, Y. (2021). Targeted next-generation sequencing identifies ABCA4 mutations in Chinese families with childhood-onset and adult-onset Stargardt disease. Biosci. Rep. 41 (6). doi:10.1042/BSR20203497
Rivera, A., White, K., Stohr, H., Steiner, K., Hemmrich, N., Grimm, T., et al. (2000). A comprehensive survey of sequence variation in the ABCA4 (ABCR) gene in Stargardt disease and age-related macular degeneration. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67 (4), 800–813. doi:10.1086/303090
Romano, F., Lamanna, F., Boon, C. J. F., Siligato, A., Kalra, G., Agarwal, A., et al. (2024). Clinical, genotypic, and imaging characterization of the spectrum of ABCA4 retinopathies. Ophthalmol. Retina 8 (5), 509–519. doi:10.1016/j.oret.2023.10.023
Rudolph, G., Kalpadakis, P., Haritoglou, C., Rivera, A., and Weber, B. H. (2002). Mutations in the ABCA4 gene in a family with Stargardt's disease and retinitis pigmentosa (STGD1/RP19). Klin. Monbl Augenheilkd 219 (8), 590–596. doi:10.1055/s-2002-34425
Sangermano, R., Khan, M., Cornelis, S. S., Richelle, V., Albert, S., Garanto, A., et al. (2018). ABCA4 midigenes reveal the full splice spectrum of all reported noncanonical splice site variants in Stargardt disease. Genome Res. 28 (1), 100–110. doi:10.1101/gr.226621.117
Schulz, H. L., Grassmann, F., Kellner, U., Spital, G., Ruther, K., Jagle, H., et al. (2017). Mutation spectrum of the ABCA4 gene in 335 Stargardt disease patients from a multicenter German cohort-impact of selected deep intronic variants and common SNPs. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 58 (1), 394–403. doi:10.1167/iovs.16-19936
Sheremet, N. L., Grushke, I. G., Zhorzholadze, N. V., A S, Tanas, A. S., and Strelnikov, V. V. (2018). Inherited retinal diseases in patients with ABCA4 gene mutations. Inherited retinal diseases in patients with ABCA4 gene mutations. 134(4):68–73. doi:10.17116/oftalma201813404168
Sun, Z., Yang, L., Li, H., Zou, X., Wang, L., Wu, S., et al. (2021). Clinical and genetic analysis of the ABCA4 gene associated retinal dystrophy in a large Chinese cohort. Exp. Eye Res. 202, 108389. doi:10.1016/j.exer.2020.108389
Tavtigian, S. V., Greenblatt, M. S., Harrison, S. M., Nussbaum, R. L., Prabhu, S. A., Boucher, K. M., et al. (2018). Modeling the ACMG/AMP variant classification guidelines as a Bayesian classification framework. Genet. Med. 20 (9), 1054–1060. doi:10.1038/gim.2017.210
Tsang, S. H., and Sharma, T. (2018). Stargardt disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1085, 139–151. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-95046-4_27
Tsybovsky, Y., Molday, R. S., and Palczewski, K. (2010). The ATP-binding cassette transporter ABCA4: structural and functional properties and role in retinal disease. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 703, 105–125. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-5635-4_8
Umair, M. (2023). Rare genetic disorders: beyond whole-exome sequencing. J. Gene Med. 25 (10), e3503. doi:10.1002/jgm.3503
van Driel, M. A., Maugeri, A., Klevering, B. J., Hoyng, C. B., and Cremers, F. P. (1998). ABCR unites what ophthalmologists divide(s). Ophthalmic Genet. 19(3), 117–22. doi:10.1076/opge.19.3.117.2187
Verbakel, S. K., van Huet, R. A. C., Boon, C. J. F., den Hollander, A. I., Collin, R. W. J., Klaver, C. C. W., et al. (2018). Non-syndromic retinitis pigmentosa. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 66, 157–186. doi:10.1016/j.preteyeres.2018.03.005
Wang, Y., Wang, P., Yi, Z., Ouyang, J., Jiang, Y., Li, S., et al. (2025). ABCA4 deep intronic variants contributed to nearly half of unsolved Stargardt cases with a milder phenotype. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 66 (1), 65. doi:10.1167/iovs.66.1.65
Yang, Y., Muzny, D. M., Reid, J. G., Bainbridge, M. N., Willis, A., Ward, P. A., et al. (2013). Clinical whole-exome sequencing for the diagnosis of mendelian disorders. N. Engl. J. Med. 369 (16), 1502–1511. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1306555
Zernant, J., Collison, F. T., Lee, W., Fishman, G. A., Noupuu, K., Yuan, B., et al. (2014). Genetic and clinical analysis of ABCA4-associated disease in African American patients. Hum. Mutat. 35 (10), 1187–1194. doi:10.1002/humu.22626
Zhang, R., Chen, Z., Song, Q., Wang, S., Liu, Z., Zhao, X., et al. (2021). Identification of seven exonic variants in the SLC4A1, ATP6V1B1, and ATP6V0A4 genes that alter RNA splicing by minigene assay. Hum. Mutat. 42 (9), 1153–1164. doi:10.1002/humu.24246
Keywords: ABCA4 gene, inherited retinal dystrophy, whole-exome sequencing, minigene assay, Stargardt disease, retinitis pigmentosa
Citation: Luo Q, Huang J, Shi L, Zhang G, Xue L, Wu K, Li X, Yang L, Li D, Mao L and Luo J (2025) Identification and functional characterization of ABCA4 gene variants in three patients with Stargardt disease or retinitis pigmentosa. Front. Genet. 16:1516872. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1516872
Received: 25 October 2024; Accepted: 13 May 2025;
Published: 18 June 2025.
Edited by:
Akio Oishi, Nagasaki University, JapanReviewed by:
Ivana Mihalek, University of Rijeka, CroatiaZelia Corradi, Radboud University Medical Centre, Netherlands
Copyright © 2025 Luo, Huang, Shi, Zhang, Xue, Wu, Li, Yang, Li, Mao and Luo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jihong Luo, MTg2Mjc3MjE4NjVAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors share first authorship
 Qi Luo1†
Qi Luo1† Liangwei Mao
Liangwei Mao Jihong Luo
Jihong Luo