- Department of Clinical Laboratory, The Second Hospital of Jiaxing, Zhejiang, China
Background: Mitochondrial acetaldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) plays a critical role in the metabolism of ethanol and nitroglycerin. Mutations in ALDH2 reduce enzymatic activity, impairing nitroglycerin metabolism. ALDH2 genetic polymorphisms exhibit significant regional variations across China. This study investigates the distribution of ALDH2 allelic and genotypic frequencies in patients with angina pectoris across northern (Luoyang, Henan), eastern (Jiaxing, Zhejiang), and southern (Guilin, Guangxi) China, and explores the relationship between ALDH2 genotypes and selected clinical characteristics.
Materials and Methods: A total of 1,084 angina pectoris patients were recruited from the three aforementioned regions. ALDH2 genotyping was performed using fluorescence quantitative PCR, and associations between genotypes and clinical characteristics, such as smoking and alcohol consumption histories, were analyzed.
Results: The geographical distribution of the ALDH2 rs671 G→A mutation showed a significant increase in mutation frequency from northern to southern China. Genotypic distributions differed significantly across regions, with GG being predominant in northern China and higher frequencies of GA and AA observed in southern regions. Additionally, lifestyle factors such as smoking and alcohol consumption were significantly associated with the presence of the A allele, reflecting the interplay between genetics and environmental influences.
Conclusion: This study reveals significant regional differences in ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism and its association with lifestyle factors in angina pectoris patients across China. Since the ALDH2*2 variant markedly reduces the metabolic activation of nitroglycerin, these findings have important clinical implications: in regions with a higher prevalence of the A allele, patients may exhibit reduced therapeutic response to nitroglycerin. This highlights the need for region-specific and genotype-informed strategies in the management of angina pectoris.
Introduction
ALDH2 is localized within the mitochondria, which are situated on chromosome 12 (12q24.4). It consists of 13 exons and 12 introns, encoding a protein of 500 amino acids (Li et al., 2006). ALDH2 exhibits both aldehyde dehydrogenase and esterase activities, playing a pivotal role as a key enzyme in the metabolic pathways of ethanol and nitroglycerin drugs (Luo, 2022; Cai et al., 2023). Moreover, it possesses cardioprotective properties by reducing myocardial cell apoptosis (Pan et al., 2021; Mizuno et al., 2016a; Xia et al., 2020). Studies investigating the genetic polymorphism of ALDH2 have elucidated that the predominant genotype at locus ra671 is GG (wild-type ALDH2). However, when carrying the mutant allele ALDH2*2 polymorphism, there occurs a substitution from glutamic acid (Glu) to lysine (Lys) at position 504 (rs671, ALDH2*2 or Glu504Lys) (Crabb et al., 1989; Zhao, 2019; Yoshida et al., 1995). This mutation impairs the cofactor binding ability of ALDH2, leading to decreased enzymatic activity. Heterozygous individuals retain only about 10% of the enzyme activity compared to wild-type individuals, while homozygous mutants completely lack enzymatic activity (Lai et al., 2014).
The mutation of ALDH2 results in a reduction in enzyme activity, leading to impaired alcohol breakdown and the development of alcohol metabolism-related diseases such as liver damage (Bosron et al., 1988) and various types of cancer (Zhang and Fu, 2021; Wang et al., 2020). Moreover, polymorphisms in the ALDH2 gene are associated with the occurrence and progression of coronary artery disease (Tang, 2024). The ALDH2 variant reduces enzymatic activation of nitroglycerin, a key drug used for angina symptom relief, leading to decreased vasodilatory effects. For instance, Zhang et al. demonstrated that patients with mutant ALDH2 alleles had significantly lower changes in coronary artery diameter and systolic blood pressure after nitroglycerin administration compared to wild-type individuals (Zhang, 2025). Moreover, the East Asian-specific ALDH22 genotype has been repeatedly associated with increased risk of coronary spastic angina, a subtype of angina pectoris, and diminished therapeutic response to nitrate-based therapy (Mizuno et al., 2015). Additionally, among patients with coronary spastic angina, those with the ALDH22 genotype had markedly reduced nitroglycerin-mediated dilation and increased nitrate tolerance following continuous glyceryl trinitrate administration, compared to ALDH21 homozygote (Mizuno et al., 2020). Finally, Miura et al. conducted a randomized crossover trial in Japanese volunteers with different ALDH2 genotypes and found that individuals carrying the mutant ALDH2*2 allele exhibited approximately 40% less vasodilatory response to nitroglycerin compared to wild-type controls, reinforcing the genotype-dependent variation in nitrate efficacy (Xia et al., 2015).
These pharmacogenetic findings underscore the importance of considering ALDH2 genotype when prescribing nitrate therapy for angina pectoris. Given the clear clinical consequences of the ALDH2*2 allele on nitroglycerin metabolism and response (Min and Kitakaze, 2020), it becomes crucial to investigate not only its presence but also its regional distribution among patient populations. Understanding such geographical patterns may help optimize individualized treatment strategies across different regions of China. Previous studies have identified significant ethnic and geographic differences in the distribution of ALDH2 gene polymorphisms (Cook, 2021; Tokiya, 2023; Chen et al., 2022; Li et al., 2009). However, the geographical distribution of ALDH2 polymorphisms in Chinese patients with cardiovascular diseases remains largely unexplored.
This study aims to fill this gap by examining the genotypic and allelic frequencies of ALDH2 in angina pectoris patients from three geographically distinct regions—northern, eastern, and southern China. Our findings reveal a clear geographical trend, with a higher frequency of the G→A mutation observed in the southern regions compared to the north. These regional variations have important clinical implications, as they may affect the metabolism of nitroglycerin and other drugs that rely on ALDH2 activity, making it essential to consider these genetic differences when prescribing treatment.
In addition to examining the geographical distribution of ALDH2 polymorphisms, it is essential to explore how these genetic variations interact with clinical and lifestyle factors in angina pectoris patients. Previous studies have highlighted the potential influence of lifestyle behaviors, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, on the prevalence of ALDH2 mutations (Chen et al., 2022; Ma et al., 2017). To better understand these interactions, this study also analyzed the relationship between ALDH2 genotypes and selected clinical characteristics, including patient histories of smoking, alcohol consumption, and hypertension, as well as laboratory indicators. These findings provide valuable insights into the interplay between genetic predisposition and environmental factors, which could have significant implications for personalized treatment strategies in angina pectoris patients.
Materials and methods
Study participants
Patients diagnosed with angina pectoris and admitted to the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Jiaxing University, and Guilin Medical College Second Affiliated Hospital between 1 September 2021, and 31 August 2023 were included in this study. We included all clinically classified angina pectoris patients, including those with stable, unstable, and variant angina pectoris, without distinguishing between specific subtypes or imposing comorbidity restrictions. There were no restrictions based on gender, age, or ethnicity. A total of 1,084 patients residing in local counties or cities were screened; among them were 359 from Luoyang, 352 from Jiaxing, and 373 from Guilin. The cohort consisted of 650 male patients and 434 female patients overall. Specifically, for Luoyang, there were 214 males and 145 females with an average age of 65.05 years; for Jiaxing, there were 189 males and 163 females with an average age of 64.94 years; for Guilin there were 247 males and 126 females with an average age of 67.51 years. Although the ages ranged from 29 to 97 years old among angina pectoris patients, the majority belonged to middle-aged and elderly individuals.
Definition of variables
The primary outcome of this study was the distribution of ALDH2 rs671 genotypes (GG, GA, AA) across different geographic regions and their associations with selected clinical characteristics. Exposure variables included geographic region (northern, eastern, and southern China) and patient lifestyle factors, such as smoking and alcohol consumption. Clinical predictors analyzed in relation to ALDH2 genotypes included history of hypertension, diabetes, and several laboratory parameters. Potential confounders, including age and gender, were recorded but not adjusted for in the statistical analysis. The diagnosis of angina pectoris was based on clinical symptoms, electrocardiogram (ECG) findings, and/or coronary angiography results, according to standard cardiology guidelines at the respective institutions.
Detection of ALDH2 gene polymorphism
Peripheral blood samples from angina pectoris patients were promptly processed for ALDH2 gene polymorphism detection upon collection. Genomic DNA was extracted from whole blood using a commercially available kit (Beijing Tiangen Biochemical Technology Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China). The ALDH2 rs671 gene polymorphism was determined using a human-specific detection kit (Wuhan Kanglu Biotechnology Co., Ltd., Wuhan, China) based on the PCR-fluorescent probe method, following the manufacturer’s instructions.
Detection of clinical observation indicators
During hospitalization, comprehensive clinical information of patients with ALDH2 gene polymorphism was collected, including gender, smoking history, drinking history, hypertension history, diabetes history, as well as laboratory indicators such as hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP), total bilirubin (TBIL), direct bilirubin (DBIL), alkaline phosphatase (ALT), triglyceride (TG), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and homocysteine (HCY). Furthermore, the study compared the differences in laboratory indicators between patients with angina pectoris and other patients in the cardiovascular department or undergoing routine physical examinations.
Bias control
To minimize potential sources of bias, we used the same standardized PCR-fluorescent probe method for ALDH2 genotyping across all three centers. Clinical and laboratory data were extracted from hospital electronic medical records using predefined criteria, reducing information bias. Patients were consecutively enrolled during the study period to mitigate selection bias. Furthermore, all three hospitals followed national laboratory protocols, ensuring consistency and comparability of biochemical measurements. Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium analysis was conducted to confirm the representativeness of the genotypic distribution within each regional population.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 25.0 (IBM, Armonk, NY, United States). The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to assess the normality of quantitative variables. Normally distributed data were expressed as mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA. Non-normally distributed data were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test or Kruskal–Wallis test. Categorical variables were analyzed using the Chi-square test. A significance level of P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
No multivariable regression or confounder-adjusted analyses were conducted. No subgroup or interaction analyses were performed. Complete case analysis was used, and no missing data imputation was necessary. Patients were enrolled consecutively without sampling randomization. No sensitivity analyses were performed in this study.
Results
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium analysis of ALDH2 genotypes in angina pectoris patients across three Chinese regions
A total of 1,084 patients diagnosed with angina pectoris were consecutively recruited from three hospitals between September 2021 and August 2023. All patients who met the inclusion criteria were included in the final analysis. There were no dropouts or exclusions during the study period. Therefore, no formal flow diagram was used.
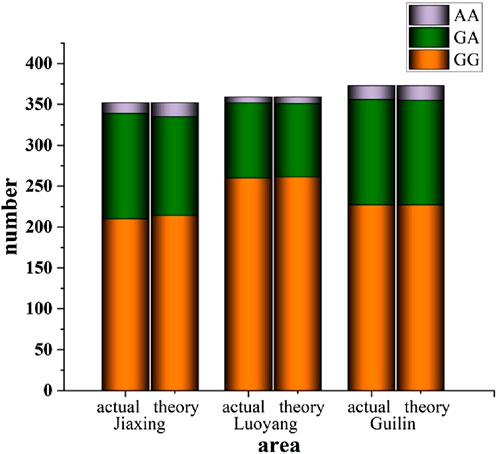
The ALDH2 loci data from populations in Jiaxing, Luoyang, and Guilin were subjected to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium analysis. For instance, in the Jiaxing region, the observed genotype counts were 210 for GG, 129 for GA, and 13 for AA. Consequently, the observed genotype frequencies were 59.66% for GG, 36.65% for GA, and 3.69% for AA, with corresponding allele frequencies of 77.99% for G and 22.01% for A. According to Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium expectations, the theoretical genotype counts would be 214 for GG, 121 for GA, and 17 for AA. A comparison between the observed and expected genotype counts is presented in Table 1 and illustrated in Figure 1. The χ2 value of 0.827 and P-value of 0.661 (P > 0.05) suggest that the sample from Jiaxing adheres to the Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, indicating that it is representative of the population in this region. Similar findings were observed in the Luoyang (P = 0.956) and Guilin (P = 0.984) regions, where both P-values also exceeded the significance level of α = 0.1, further supporting the representativeness of these samples.
Regional variations in ALDH2 polymorphism among angina pectoris patients in China
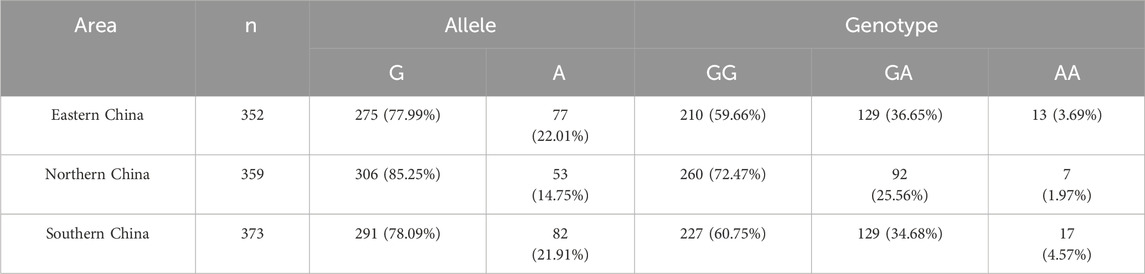
This study detected the ALDH2 gene polymorphism in 352 angina pectoris patients treated at the Second Hospital of Jiaxing, 359 angina pectoris patients treated at the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Science and Technology, and 373 angina pectoris patients treated at the Second Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University from September 2021 to August 2023. In eastern China (Jiaxing), the G and A allele frequencies were 77.99% and 22.01%, respectively, with the wild-type GG genotype occurring in 59.66% of cases, the heterozygous GA genotype in 36.65%, and the homozygous AA genotype in 3.69%. In northern China (Luoyang), the G and A allele frequencies were 85.25% and 14.75%, respectively, with GG, GA, and AA genotype frequencies of 72.47%, 25.56%, and 1.97%. In southern China (Guilin), the G and A allele frequencies were 78.09% and 21.91%, respectively, with corresponding GG, GA, and AA genotype frequencies of 60.75%, 34.68%, and 4.57% (Table 2). Figure 2 provides a visual representation of these disparities.
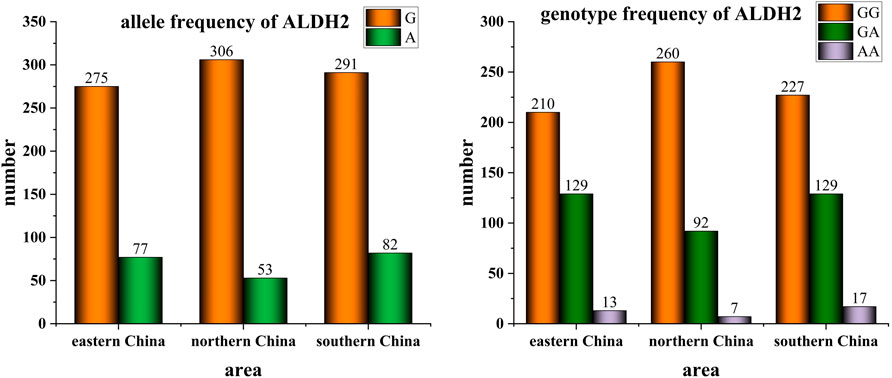
Figure 2. Allele and genotype frequency of ALDH2 in individuals with angina pectoris from different geographical regions of China.
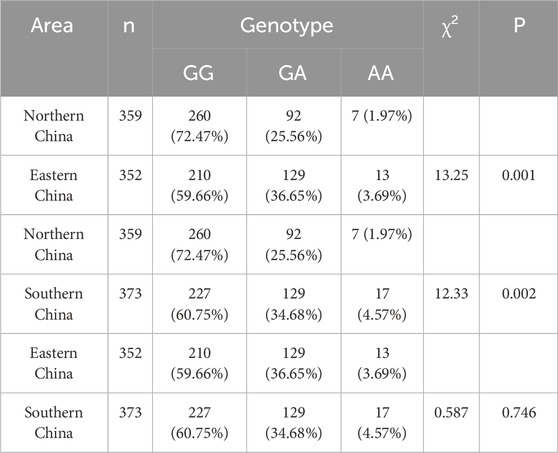
Comparing the detection results from the three regions (Table 3), statistically significant differences were observed in the ALDH2 genotypes among populations in northern, eastern, and southern China. Consequently, a gradual increasing trend was observed in the proportion of G→A mutations from north to south. The G→A mutation at the ALDH2 rs671 locus leads to a reduction in ALDH2 activity, with heterozygous individuals exhibiting only approximately 10% of the enzyme activity seen in wild-type individuals, while homozygous mutant individuals completely lack enzymatic activity. Therefore, individuals carrying the A allele have diminished capacity for alcohol metabolism and experience discomfort such as flushing and accelerated heartbeat even with minimal alcohol consumption. The geographical variations in gene polymorphism at the ALDH2 rs671 locus align with current observations that people residing in northern China tend to exhibit greater tolerance towards alcohol compared to those living in southern regions.
The relationship between ALDH2 genotype and clinical parameters
The geographical distribution of ALDH2 polymorphisms among angina pectoris patients in three regions of China has been the focus of our research, While these variations offer valuable insights into regional genetic disparities, understanding how these polymorphisms relate to specific clinical characteristics is crucial for assessing their broader implications. Identifying these associations can shed light on the role of ALDH2 genotypes in influencing lifestyle-related risk factors, metabolic profiles, and disease progression, ultimately guiding more targeted and effective treatment strategies.
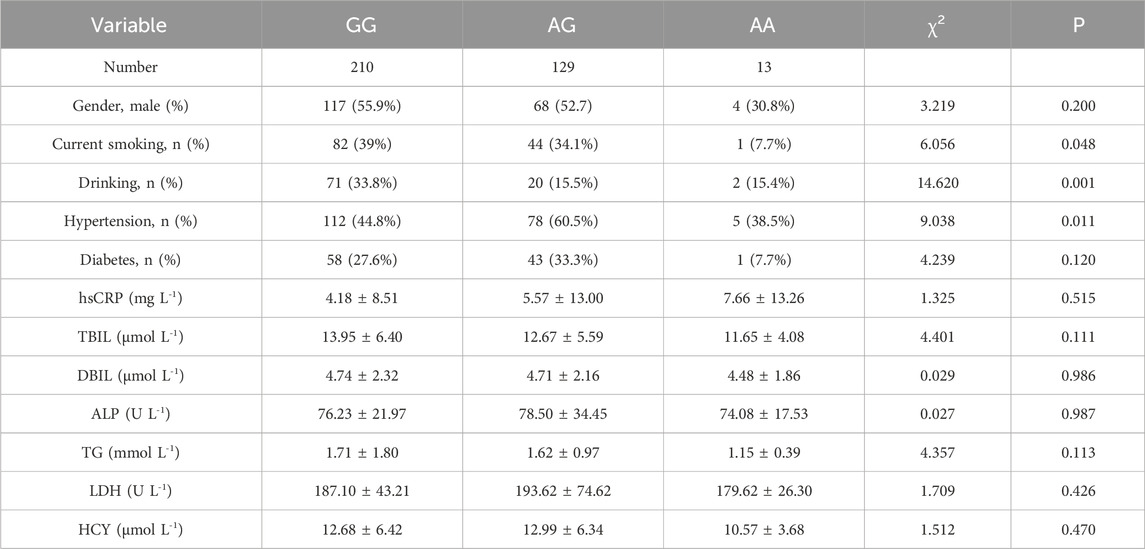
To further explore the relationship between ALDH2 genotypes and clinical characteristics, we conducted a comparative analysis of various factors among ALDH2-mutated patients in East China. These factors included gender, smoking history, alcohol consumption, hypertension, diabetes, and laboratory indicators such as hsCRP, total TBIL, DBIL, ALT, TG, LDH, and HCY. As summarized in Table 4, individuals with a smoking habit, alcohol consumption, or a history of hypertension were more likely to carry genetic mutations, and these differences were statistically significant. However, no significant associations were observed between gender or laboratory indicators and genotype. This lack of significance may be attributed to the higher proportion of male participants in our sample, as well as notable variations in participant distribution across the different genotypes.
Discussion
ALDH2 plays a crucial role in the bioactivation of nitroglycerin by catalyzing its conversion to nitric oxide (NO), a potent vasodilator that alleviates myocardial ischemia. This mitochondrial dehydrogenase reduces organic nitrates to NO, which activates soluble guanylate cyclase in vascular smooth muscle (Opelt et al., 2016). However, the ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism (Glu504Lys) markedly impairs this enzymatic activity—heterozygotes retain only ∼10% of wild-type function, while homozygous mutants lose nearly all activity—leading to reduced nitroglycerin bioactivation and diminished vasodilatory response. Moreover, a 2022 study showed that continuous nitroglycerin use in ALDH2 variant carriers exacerbates nitrate tolerance and vascular dysregulation (Maiuolo, 2022), highlighting the clinical implications of this pharmacogenetic interaction.
Previous studies have established that there are significant regional differences in the distribution of the ALDH2 G-to-A mutation between northern and southern China among the general population (Zhang et al., 2021). Pecifically, a higher proportion of individuals in southern China carry the A allele, leading to reduced ALDH2 enzyme activity. This geographical variation has been linked to differences in alcohol tolerance across these regions, with northern populations exhibiting greater tolerance (Cao, 2020). Despite this known variation in the general population, the distribution of ALDH2 genotypes among patients with angina pectoris had not been thoroughly investigated before this study. This gap in research is particularly important because ALDH2 plays a crucial role in the metabolism of nitroglycerin, a key medication used to relieve angina symptoms. The G-to-A mutation at the ALDH2 rs671 locus results in reduced or absent enzyme activity, significantly impairing the conversion of nitroglycerin into nitric oxide, which is necessary for vasodilation and pain relief in angina patients.
Our study found that the distribution of the ALDH2 G-to-A mutation in patients with coronary heart disease varies significantly between northern and southern China, as well as between eastern and northern China. Specifically, the chi-square test revealed significant differences between eastern and northern regions (P = 0.001) and between northern and southern regions (P = 0.002), but no significant difference between eastern and southern regions. These findings suggest that the previously observed geographical variations in the general population extend to patients with coronary heart disease, potentially affecting the efficacy of nitroglycerin treatment across different regions.
Our study also revealed significant associations between ALDH2 genotypes and lifestyle factors, as shown in Table 4. Individuals with a history of smoking, alcohol consumption, or hypertension were more likely to carry the A allele, highlighting the influence of environmental factors on the prevalence of ALDH2 mutations. Notably, previous studies have indicated that the ALDH2 A allele may not only be more prevalent among individuals with certain lifestyle habits, but may also amplify the biological effects of exposures such as smoking and alcohol, further contributing to cardiovascular risk. ALDH2 deficiency leads to accumulation of toxic aldehydes like acetaldehyde and 4-HNE, which are normally cleared by the wild-type enzyme. In individuals who consume alcohol, especially those carrying the A allele, acetaldehyde accumulates and induces oxidative stress, endothelial dysfunction, and sympathetic activation, which can exacerbate cardiac ischemia (Chen et al., 2010; Zhang, 2023). Similarly, smoking generates reactive aldehydes and ROS, and the lack of effective detoxification in ALDH22 carriers may potentiate inflammation and vascular injury (Tsai et al., 2020; Mizuno et al., 2016b). Therefore, beyond pharmacogenetics, the A allele may influence angina risk and disease progression through impaired detoxification and greater vulnerability to environmental toxins. These findings underscore the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in angina pectoris patients and highlight the need for further research to refine treatment strategies based on these interactions. However, the relatively small number of AA genotype carriers (n = 13) limits the statistical power of subgroup comparisons and raises the possibility of false-negative or unstable estimates. Therefore, these associations should be interpreted with caution. Further large-scale, multi-center studies are needed to confirm these preliminary findings and to better understand how genetic and environmental factors jointly influence angina risk and treatment response.
Given these findings, it is essential to consider regional and lifestyle differences in ALDH2 polymorphism when prescribing nitroglycerin for angina pectoris. In areas where the A allele is more prevalent, such as southern China, clinicians may need to monitor patients more closely for nitroglycerin efficacy and explore alternative treatments if standard doses prove insufficient. This study underscores the importance of personalized medicine and highlights the need for further research into the impact of ALDH2 polymorphisms on the treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Limitations
This study has several limitations. First, the cohort was restricted to three regions in China—Jiaxing, Luoyang, and Guilin—which may not capture the full genetic diversity of the broader Chinese or global populations. Second, although the overall sample size was reasonable, subgroup analyses (particularly for the AA genotype) were limited by small numbers, which may affect the reliability of certain associations. Third, we did not adjust for potential confounders such as age and gender, nor did we apply corrections for multiple statistical comparisons, which increases the risk of false-positive findings. Lastly, the cross-sectional design limits causal interpretation, and future longitudinal studies are needed to validate these findings and assess their clinical implications.
Data availability statement
The aggregate data (Geographical Distribution of ALDH2 rs671 Polymorphism in Chinese angina pectoris Patients), supporting the findings of this study, are available within this article. The original individual-level genotype datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available at this time due to patient privacy and ethical considerations, but are available upon reasonable request from the corresponding author (Siqi Xu, eHVzaXFpMDk2N0B6anh1LmVkdS5jbg==).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Institutional Review Committee of Jiaxing Second Hospital (2024-036-01). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participant’s; legal guardians/next of kin.
Author contributions
WD: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. JY: Writing – original draft. SX: Data curation, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. HL: Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This project was financially supported by the Jiaxing Science and Technology Plan Projects (2024AD30077, 2024AY40034 and 2025CGW105).
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our sincere appreciation to the diligent data collection teams and dedicated participants from Guangxi, Henan, and Jiaxing whose invaluable contributions have made this study possible.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Bosron, W. F., Lumeng, L., and Li, T.-K. (1988). Genetic polymorphism of enzymes of alcohol metabolism and susceptibility to alcoholic liver disease. Mol. Aspects Med. 10 (2), 147–158. doi:10.1016/0098-2997(88)90019-2
Cai, N., Li, C., Gu, X., Zeng, W., Liu, J., Zeng, G., et al. (2023). ALDH2 rs671 and MTHFR rs1801133 polymorphisms are risk factors for arteriosclerosis in multiple arteries. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 23 (1), 319. doi:10.1186/s12872-023-03354-0
Cao, Y., Li, L., Xu, M., Feng, Z., Sun, X., Lu, J., et al. (2020). The ChinaMAP analytics of deep whole genome sequences in 10,588 individuals. Cell Res. 30 (9), 717–731. doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0322-9
Chen, C. H., Sun, L., and Mochly-Rosen, D. (2010). Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase and cardiac diseases. Cardiovasc Res. 88 (1), 51–57. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq192
Chen, C.-H., Kraemer, B. R., and Mochly-Rosen, D. (2022). ALDH2 variance in disease and populations. DMM Dis. Model. Mech. 15 (6), dmm049601. doi:10.1242/DMM.049601
Cook, W. K., Tam, C. C., Luczak, S. E., Kerr, W. C., Mulia, N., and Lui, C. (2021). Alcohol consumption, cardiovascular-related conditions, and ALDH2* 2 ethnic group prevalence in Asian Americans. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 45 (2), 418–428. doi:10.1111/acer.14539
Crabb, D. W., Edenberg, H. J., Bosron, W. F., and Li, T. K. (1989). Genotypes for aldehyde dehydrogenase deficiency and alcohol sensitivity. The inactive ALDH2 (2) allele is dominant. J. Clin. investigation 83 (1), 314–316. doi:10.1172/JCI113875
Lai, C. L., Yao, C. T., Chau, G. Y., Yang, L. F., Kuo, T. Y., Chiang, C. P., et al. (2014). Dominance of the inactive Asian variant over activity and protein contents of mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in human liver. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 38 (1), 44–50. doi:10.1111/acer.12215
Li, Y., Zhang, D., Jin, W., Shao, C., Yan, P., Xu, C., et al. (2006). Mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 (ALDH2) Glu504Lys polymorphism contributes to the variation in efficacy of sublingual nitroglycerin. J. Clin. investigation 116 (2), 506–511. doi:10.1172/JCI26564
Li, H., Borinskaya, S., Yoshimura, K., Kal'ina, N., Marusin, A., Stepanov, V. A., et al. (2009). Refined geographic distribution of the oriental ALDH2* 504Lys (nee 487Lys) variant. Ann. Hum. Genet. 73 (3), 335–345. doi:10.1111/j.1469-1809.2009.00517.x
Luo, C., Zhou, B., Cui, Y., Liu, Z., and Wang, S. (2022). ALDH2 knockout protects against aortic dissection. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 22 (1), 443. 1–10. doi:10.1186/s12872-022-02874-5
Ma, C., Yu, B., Zhang, W., Wang, W., Zhang, L., and Zeng, Q. (2017). Associations between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) rs671 genetic polymorphisms, lifestyles and hypertension risk in Chinese Han people. Sci. Rep. 7 (1), 11136. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11071-w
Maiuolo, J., Oppedisano, F., Carresi, C., Gliozzi, M., Musolino, V., Macrì, R., et al. (2022). The generation of nitric oxide from aldehyde dehydrogenase-2: the role of dietary nitrates and their implication in cardiovascular disease management. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 23 (24), 15454. doi:10.3390/ijms232415454
Min, K.-D., and Kitakaze, M. (2020). Nitroglycerin tolerance in patients with ALDH2 variant. Circulation J. 84 (3), 384–385. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-20-0049
Mizuno, Y., Harada, E., Morita, S., Kinoshita, K., Hayashida, M., Shono, M., et al. (2015). East asian variant of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 is associated with coronary spastic angina: possible roles of reactive aldehydes and implications of alcohol flushing syndrome. Circulation 131 (19), 1665–1673. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.013120
Mizuno, Y., Hokimoto, S., Harada, E., Kinoshita, K., Nakagawa, K., Yoshimura, M., et al. (2016a). Variant aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH 2* 2) is a risk factor for coronary spasm and ST Segment Elevation myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 5 (5), e003247. doi:10.1161/JAHA.116.003247
Mizuno, Y., Hokimoto, S., Harada, E., Kinoshita, K., Yoshimura, M., and Yasue, H. (2016b). Variant aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2*2) in East asians interactively exacerbates Tobacco smoking risk for coronary spasm - possible role of reactive aldehydes. Circ. J. 81 (1), 96–102. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-16-0969
Mizuno, Y., Harada, E., Kugimiya, F., Shono, M., Kusumegi, I., Yoshimura, M., et al. (2020). East asians variant mitochondrial aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 genotype exacerbates nitrate tolerance in patients with coronary spastic angina. Circ. J. 84 (3), 479–486. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-19-0989
Opelt, M., Eroglu, E., Waldeck-Weiermair, M., Russwurm, M., Koesling, D., Malli, R., et al. (2016). Formation of nitric oxide by aldehyde dehydrogenase-2 is necessary and sufficient for vascular bioactivation of nitroglycerin. J. Biol. Chem. 291 (46), 24076–24084. doi:10.1074/jbc.M116.752071
Pan, G., Roy, B., and Palaniyandi, S. S. (2021). Diabetic aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 mutant (ALDH2*2) mice are more susceptible to cardiac ischemic-reperfusion injury due to 4-Hydroxy-2-Nonenal induced coronary endothelial cell damage. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 10 (18), e021140. doi:10.1161/JAHA.121.021140
Tang, C., Shi, F., Ji, Y., Zhu, J., and Gu, X. (2024). Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 (ALDH2) rs671 polymorphism is a predictor of pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease. Hear. Lung Circ. 33 (2), 230–239. doi:10.1016/j.hlc.2023.11.012
Tokiya, M., Kobayashi, T., Kido, M. A., and Matsumoto, A. (2023). ALDH2 polymorphism rs671 and alcohol consumption: possible explanatory factors for race/ethnic differences in bone density. Osteoporos. Int. 34 (12), 2133–2135. doi:10.1007/s00198-023-06909-1
Tsai, S. H., Hsu, L. A., Tsai, H. Y., Yeh, Y. H., Lu, C. Y., Chen, P. C., et al. (2020). Aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 protects against abdominal aortic aneurysm formation by reducing reactive oxygen species, vascular inflammation, and apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells. Faseb J. 34 (7), 9498–9511. doi:10.1096/fj.201902550RRR
Wang, W., Wang, C., Xu, H., and Gao, Y. (2020). Aldehyde dehydrogenase, liver disease and cancer. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 16 (6), 921–934. doi:10.7150/ijbs.42300
Xia, J. Q., Song, J., Zhang, Y., An, N. N., Ding, L., and Zhang, Z. (2015). Effect of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene polymorphism on hemodynamics after nitroglycerin intervention in Northern Chinese Han population. Chin. Med. J. Engl. 128 (2), 180–185. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.149192
Xia, C.-L., Chu, P., Liu, Y. X., Qu, X. L., Gao, X. F., Wang, Z. M., et al. (2020). ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism and the risk of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) in patients with cardiovascular diseases. J. Hum. Hypertens. 34 (1), 16–23. doi:10.1038/s41371-019-0182-2
Yoshida, A., Twele, T. W., Davé, V., and Beutler, E. (1995). Molecular abnormality of a phosphoglycerate kinase variant (PGK-Alabama). Mol. Dis. 21 (3), 179–181. doi:10.1006/bcmd.1995.0020
Zhang, H., and Fu, L. (2021). The role of ALDH2 in tumorigenesis and tumor progression: targeting ALDH2 as a potential cancer treatment. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 11 (6), 1400–1411. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.02.008
Zhang, X., Sun, A., and Ge, J. (2021). Origin and spread of the ALDH2 Glu504Lys allele. Phenomics 1, 222–228. doi:10.1007/s43657-021-00017-y
Zhang, J., Guo, Y., Zhao, X., Pang, J., Pan, C., Wang, J., et al. (2023). The role of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 in cardiovascular disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 20 (7), 495–509. doi:10.1038/s41569-023-00839-5
Zhang, K., He, C., Tong, Y., and He, Y. (2025). Relationship between aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 gene polymorphism and vasodilative effect of nitroglycerin on coronary arteries. J. Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 85 (5), 358–363. doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000001682
Keywords: ALDH2 polymorphism, angina pectoris, regional variation, clinical characteristics, nitroglycerin
Citation: Dong W, Yu J, Xu S and Li H (2025) Geographical distribution of ALDH2 rs671 polymorphism in Chinese angina pectoris patients. Front. Genet. 16:1543963. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1543963
Received: 12 December 2024; Accepted: 18 August 2025;
Published: 05 September 2025.
Edited by:
Chunheng Mo, Sichuan University, ChinaReviewed by:
Hongbin Lv, Southwest Medical University, ChinaYongliang Jia, Zhengzhou University, China
Copyright © 2025 Dong, Yu, Xu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Siqi Xu, eHVzaXFpMDk2N0B6anh1LmVkdS5jbg==; Hongsheng Li, anhsaHM3NkB6anh1LmVkdS5jbg==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Wenjia Dong
Wenjia Dong Junjie Yu†
Junjie Yu† Siqi Xu
Siqi Xu