- 1Department of Medical Oncology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China
- 2Shenzhen University, Shenzhen, China
Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusion, an oncogenic driver alteration, accounts for 5%–6% of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) provide significant clinical benefit in advanced ALK-rearranged NSCLC. However, acquired resistance to ALK TKIs inevitably arises, and the underlying mechanisms remain incompletely elucidated. This report describes a stage IV lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patient with ALK-rearranged who developed KIF5B-RET fusion-mediated resistance following second-line alectinib therapy. The patient achieved a partial response (PR) to third-line pralsetinib, sustained for 4 months. This case highlights KIF5B-RET fusion as a potential resistance mechanism post alectinib treatment and suggested = pralsetinib, a RET inhibitor, as a viable therapeutic option in this context. These findings contribute to the evolving understanding of resistance management strategies in ALK-rearranged NSCLC.
Introduction
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) accounts for 80%–85% of lung cancer cases and remains a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide (Siegel et al., 2022). Advances in next-generation sequencing (NGS) technology and precision oncology have revolutionized therapeutic strategies, enabling targeted therapies to become a cornerstone of NSCLC management (Tan and Tan, 2022). Among oncogenic driver alterations, anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) fusions are identified in 5%–6% of NSCLC patients and serve as critical therapeutic targets (Yang et al., 2023). Multiple ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) with excellent efficacy, including first-generation crizotinib, second-generation ceritinib, alectinib, and brigatinib, and third-generation lorlatinib, have been approved for treating ALK-rearranged NSCLC patients. Despite their clinical success, the long-term efficacy of these agents is frequently hindered by the inevitable development of resistance, the mechanisms of which remain incompletely characterized. This case report describes a stage IV ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) patient who developed KIF5B-RET fusion-mediated resistance to second-line alectinib therapy. Notably, the patient achieved a partial response third-line pralsetinib, a selective RET inhibitor, with a duration of 4 months, provide novel insights into resistance mechanisms and salvage therapeutic options.
Case description
In September 2020, a 50-year-old male presented to his local hospital with persistent cough. Initial chest computed tomography (CT) imagine identified a nodule in the dorsal segment of the left lower lung lobe. Subsequent followed-up scans performed due to progressive symptoms revealed a 11 mm × 10 mm lesion in the left lower lung and enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes. A lymph node biopsy at this stage confirmed poorly differentiated LUAD with genetic testing demonstrating wild-type EGFR exons (18-21) and ALK. Notably, the local hospital omitted tumor marker assessment (e.g., carcinoembryonic antigen) and immunohistochemical analysis of biopsy specimens.
In February 2021, the patient was referred to our institution with worsening tracheophonia. Repeat chest CT scans showed a left lower lung lesion, enlarged right supraclavicular and mediastinal lymph nodes, and a new in the right lower lung nodule. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and bone emission computed tomography scan revealed no evidence of brain or bone metastases. NGS (11- gene panel covering 11 oncogenic driver genes recommended by the NCCN guidelines) of the biopsy tissue from the 4L lymph node biopsy tissue identified an echinoderm microtubule-associated protein-like 4 (EML4)-ALK- rearranged (allele frequency: 16%). The patient was diagnosed with stage IVa (cT1N3M1a) ALK rearranged LUAD. The treatment timeline is summarized in Figure 1.
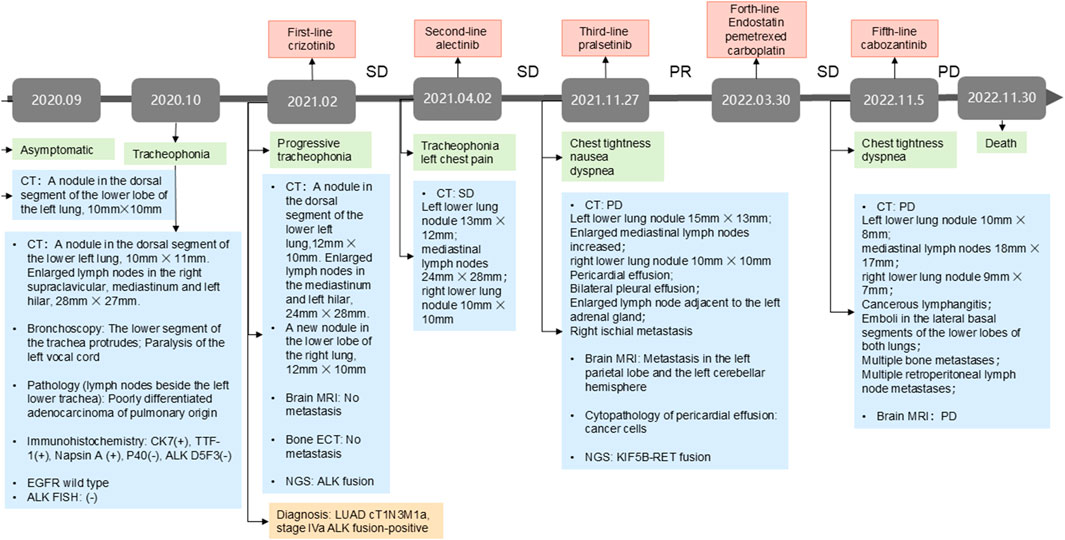
Figure 1. The treatment milestone of the patient. NGS, next-generation sequencing; PR, partial response; SD, stable disease; PD, progressive disease; TMB, tumor mutational burden; LUAD, lung adenocarcinoma. CT, computed tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging.
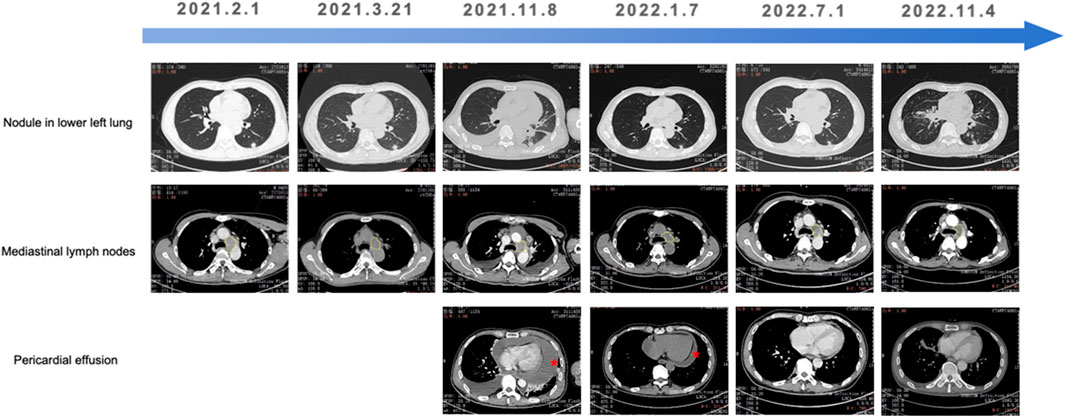
Owing to financial constraints, the patient received first-line crizotinib (250 mg twice daily) from February to March 2021. While imaging indicated stable disease, his clinical symptoms, including tracheophonia and left chest pain, progressively deteriorated. Second-line therapy with alectinib (600 mg twice daily) was initiated, achieving stable disease until November 2021, when the patient developed chest tightness, nausea, and dyspnea. Chest CT at progression demonstrated significant mediastinal lymphadenopathy, pericardial effusion and bilateral pleural effusions. Brain MRI confirmed new metastasis lesion. Concurrently, the primary left lower lung lesion and right lung metastatic nodule exhibited slight enlargement. Laboratory findings revealed severe transaminitis (ALT and AST >1000 U/L) and jaundice.
Alectinib was discontinued due to hepatotoxicity, and the patient received glutathione and polyene phosphatidylcholine for transaminase reduction. Pericardiocentesis yielded 200–300 mL of hemorrhagic pericardial effusion daily, with cytopathology confirmed malignant cell. NGS of the pericardial effusion (520-gene panel, Burning Rock Biotech, Guangzhou, China)detected the original ALK rearrangement, and a novel KIF5B-RET fusion (K15:R12 allele frequency AF: 31.86%, tumor mutation burden:4.99 mutations/Mb).
Given pralsetinib’s approval for RET-fusion-positive NSCLC, third-line pralsetinib (400 mg daily) was administered from November 2021, to March 2022, achieving partial response (RECIST 1.1). Treatment was discontinued due to financial constraints, and subsequent therapy include Endostar (recombinant human endostatin injection) combined with pemetrexed-carboplatin chemotherapy. During chemotherapy, the patient required hospitalization for zoledronic acid (bone metastasis management) and intrathoracic cisplatin (pleural effusion control). Disease progression (PD) occurred after five chemotherapy cycles. Cabozantinib (140 mg daily) was initiated on November 2022, but was discontinue due to severe adverse reactions. Palliative care was initiated following confirmed progression on chest CT, and the patient succumbed to the disease in late November 2022. Longitudinal CT imaging of the patient’s thoracic lesions are shown in Figure 2.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this represents the first documented case of KIF5B-RET fusion as a resistance mechanism to alectinib in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. Alectinib, a second-generation ALK TKI has been widely used in patients progressing on crizotinib, supported by its robust efficacy reported in the phase III clinical trial ALUR study (Novello et al., 2018). In this case, the patient derived a progression-free survival (PFS) of 7 months from alectinib after failing first-line crizotinib.
While first- and next-generation ALK inhibitors prolong survival in ALK rearrangements NSCLC, resistance remains inevitably (Okada et al., 2019). Prior studies indicate that over 50% of alectinib-resistant tumors harbor secondary ALK mutations, with ALK G1202R (29% prevalence), ALK I1171T/N/S, ALK V1180L, and ALK L1196M (Gainor et al., 2016; Haratake et al., 2021). Additionally, MET overexpression or amplification contributes to acquired resistance alectinib through bypass signaling activation (Haratake et al., 2021). In NSCLC after multi-line targeted therapy, there is often activation of multiple driver genes and more potential treatment targets. Therefore, NGS using a broader gene panel has potential benefits for these patients. In this case, the patient progressing on alectinib underwent NGS on pericardial effusion, which revealed the presence of KIF5B-RET fusion without secondary ALK mutation or MET amplification. RET rearrangement, observed in 1%–3% of treatment-naïve NSCLCs (Tan and Tan, 2022), have been reported in EGFR-TKIs such as osimertinib (Leonett et al., 2019; Offin et al., 2018). However, reports linking RET fusions to ALK TKI resistance are scarce. Yan et al. reported a case of NCOA4-RET fusion mutation occurring after acquired resistance to alectinib (Yan et al., 2024). Both previous studies and our case suggest that KIF5B-RET fusion could contribute to resistance to the second-generation ALK TKI alectinib. The patient was observed to benefit from third-line pralsetinib.
Liquid biopsy has emerged as a minimally invasive tool for molecular profiling in NSCLC, utilizing peripheral blood, pleural effusion, and cerebrospinal fluid to circumvent tumor heterogeneity (Ye et al., 2019; He et al., 2022). Multiple retrospective analyses have demonstrated that NGS performed on body fluids, including pericardial effusion, exhibits high concordance with tissue-based testing in detecting driver gene alterations (Wei et al., 2016; Zhang et al., 2019). While pericardial effusion analysis in this case successfully identified KIF5B-RET fusion, its utility is constrained by limited availability and potential sampling bias. Future studies should validate the concordance between pericardial effusion and tissue-based genomic profiles in larger cohorts.
The next-generation sequencing (NGS) performed in this study was DNA-based, utilizing a panel covering 11 oncogenic driver genes recommended by the NCCN guidelines for lung cancer, which includes RET fusion detection. While the KIF5B-RET fusion was identified at disease progression (allele frequency: 31.86%), baseline NGS analysis of the initial lymph node biopsy (February 2021) confirmed wild-type ALK and EGFR but did not detect RET alterations. Notably, RNA-based NGS, which offers higher sensitivity for fusion detection, was not performed due to insufficient tissue availability.
It is important to acknowledge that discordance between DNA- and RNA-based NGS has been reported in prior studies, primarily due to differences in genomic breakpoints or low tumor content in samples (Li et al., 2020). Thus, while our findings strongly suggest KIF5B-RET fusion as an acquired resistance mechanism post-alectinib, the possibility of a pre-existing subclonal RET fusion below the detection threshold of DNA-NGS at baseline cannot be entirely excluded. Future studies incorporating paired RNA sequencing or more sensitive assays (e.g., digital PCR) in longitudinal samples would help clarify the origin of this alteration.
There are some limitations associated with this study. Firstly, it just a case report involves only one patient. More evidence is needed to investigate whether the presence of KIF5B-RET is one of the mechanisms underlying resistance to alectinib. Secondly, the concordance of genomic profiling between pericardial effusion and paired tissue samples derived from NSCLC patients should be investigated in a large cohort study.
The emergence of KIF5B-RET fusion as a resistance mechanism in this case underscores the complexity of bypass signaling in ALK-rearranged NSCLC. Beyond genomic alterations, epigenetic dysregulation—including DNA methylation, histone modifications, and chromatin remodeling—has been increasingly recognized as a driver of therapeutic resistance and tumor evolution (Jones and Baylin, 2007; Sharma et al., 2010). For instance, hypermethylation of tumor suppressor genes (e.g., CDKN2A) or hypomethylation of oncogenic promoters (e.g., RET) may synergize with fusion events to sustain proliferative signaling (Heller et al., 2013). Recent studies suggest that ALK fusions themselves can modulate the epigenetic landscape by recruiting histone acetyltransferases (HATs) or methyltransferases (e.g., EZH2), thereby promoting oncogene addiction and resistance to TKIs (Lovly and Shaw, 2014). In RET-rearranged tumors, aberrant DNA methylation patterns have been linked to enhanced RET transcription and pathway activation, independent of fusion allele frequency (Gautschi et al., 2017). These findings highlight the potential interplay between genetic and epigenetic mechanisms in mediating resistance.
Notably, RET fusions may exploit epigenetic machinery to amplify downstream signaling. Preclinical models demonstrate that RET fusion proteins recruit histone deacetylases (HDACs) to repress negative regulators of the MAPK pathway, such as DUSP6, fostering sustained ERK activation (Drilon et al., 2018). Similarly, ALK fusions have been shown to induce global DNA hypomethylation via downregulation of DNMT3A, facilitating the expression of pro-metastatic genes (Wata et al., 2015). In this patient, while RNA-based epigenetic profiling was not performed, the high allele frequency of KIF5B-RET (31.86%) and its temporal association with alectinib resistance suggest that epigenetic co-drivers—if present—could have amplified RET-dependent survival signals.
Targeting epigenetic modifiers represents a promising avenue to overcome resistance in ALK/RET-altered NSCLC. HDAC inhibitors (e.g., panobinostat) and DNA hypomethylating agents (e.g., azacitidine) have shown preclinical efficacy in restoring TKI sensitivity by re-sensitizing resistant clones to apoptosis (Topper et al., 2017). For example, targeting the menin-PRC2 complex (which includes EZH2) suppresses lung adenocarcinoma growth by mediating H3K27me3-dependent silencing of the oncogenic growth factor pleiotrophin (PTN) (Gao et al 2009). This highlights the therapeutic potential of disrupting PRC2-mediated epigenetic silencing in this context. In RET-fusion-positive cancers, BET inhibitors (e.g., JQ1) disrupt BRD4-mediated transcriptional elongation of RET, potentiating the effects of RET TKIs (Puissant et al., 2013). Future studies should explore whether adjunct epigenetic therapy could extend the durability of pralsetinib in patients with RET-mediated resistance.
This case highlights KIF5B-RET fusion as a putative resistance mechanism to alectinib, while underscoring the need to investigate epigenetic contributors to ALK/RET pathway dysregulation. The integration of pharmacoepigenetic approaches—such as DNA methylation profiling or HDAC inhibition—into resistance management strategies may uncover novel therapeutic vulnerabilities. We propose that longitudinal epigenetic profiling of liquid biopsy samples (e.g., cfDNA or pericardial effusion) could identify dynamic changes in chromatin modifiers or methylation patterns associated with resistance. Furthermore, clinical trials evaluating combinations of RET/ALK inhibitors with epigenetic agents (e.g., HDAC or EZH2 inhibitors) are warranted to determine whether such strategies can delay or reverse resistance in molecularly defined subsets.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital (No. 2023051). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
FJ: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft. CW: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Formal Analysis. FY: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Resources, Software. SW: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Validation, Visualization. FW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study funded by Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation of Guangdong Province, Enterprise Joint Fund (2021A1515220143), Guangzhou Life Oasis Public Service Center Dayi Lung Cancer Research Project for Young and Middle-aged scholars (1-24), and 2022 Clinical Research Project of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital (No. 23).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Drilon, A., Hu, Z. I., Lai, G. G. Y., and Tan, D. S. W. (2018). Targeting RET-driven cancers: lessons from evolving preclinical and clinical landscapes. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 15 (3), 150–167. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.188
Gainor, J. F., Dardaei, L., Yoda, S., Friboulet, L., Leshchiner, I., Katayama, R., et al. (2016). Molecular mechanisms of resistance to first- and second-generation ALK inhibitors in ALK-rearranged lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 6 (10), 1118–1133. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0596
Gao, S. B., Feng, Z. J., Xu, B., Wu, Y., Yin, P., Yang, Y., et al. (2009). Suppression of lung adenocarcinoma through menin and polycomb gene-mediated repression of growth factor pleiotrophin. Oncogene. Cancer Sci. 28 (46), 4095–104. doi:10.1038/onc.2009.273
Gautschi, O., Milia, J., Filleron, T., Wolf, J., Carbone, D. P., Owen, D., et al. (2017). Targeting RET in patients with RET-rearranged lung cancers: results from the global, multicenter RET registry. J. Clin. Oncol. 35 (13), 1403–1410. doi:10.1200/JCO.2016.70.9352
Haratake, N., Toyokawa, G., Seto, T., Tagawa, T., Okamoto, T., Yamazaki, K., et al. (2021). The mechanisms of resistance to second- and third-generation ALK inhibitors and strategies to overcome such resistance. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 21 (9), 975–988. doi:10.1080/14737140.2021.1940964
He, J., Hu, X., Chen, L., Liu, Q., and Jiang, Y. (2022). Characteristics of genomic alterations in pericardial effusion of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Front. Genet. 13, 850290. doi:10.3389/fgene.2022.850290
Heller, G., Zielinski, C. C., and Zöchbauer-Müller, S. (2013). Lung cancer epigenetics: emerging biomarkers. Biomark. Med. 7 (1), 49–58. doi:10.2217/bmm.12.111
Jones, P. A., and Baylin, S. B. (2007). The epigenomics of cancer. Cell 128 (4), 683–692. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.01.029
Leonetti, A., Sharma, S., Minari, R., Perego, P., Giovannetti, E., and Tiseo, M. (2019). Resistance mechanisms to osimertinib in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 121 (9), 725–737. doi:10.1038/s41416-019-0573-8
Li, W., Liu, Y., Li, W., Chen, L., and Ying, J. (2020). Intergenic breakpoints identified by DNA sequencing confound targetable kinase fusion detection in NSCLC. J. Thorac. Oncol. 15 (7), 1223–1231. doi:10.1016/j.jtho.2020.02.023
Lovly, C. M., and Shaw, A. T. (2014). Molecular pathways: resistance to kinase inhibitors and implications for therapeutic strategies. Clin. Cancer Res. 20 (9), 2249–2256. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-13-1610
Novello, S., Mazières, J., Oh, I. J., de Castro, J., Migliorino, M. R., Helland, Å., et al. (2018). Alectinib versus chemotherapy in crizotinib-pretreated anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-positive non-small-cell lung cancer: results from the phase III ALUR study. Ann. Oncol. 29 (6), 1409–1416. doi:10.1093/annonc/mdy121
Offin, M., Somwar, R., Rekhtman, N., Benayed, R., Chang, J. C., Plodkowski, A., et al. (2018). Acquired ALK and RET gene fusions as mechanisms of resistance to osimertinib in EGFR-mutant lung cancers. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2, 1–12. doi:10.1200/PO.18.00126
Okada, K., Araki, M., Sakashita, T., Ma, B., Kanada, R., Yanagitani, N., et al. (2019). Prediction of ALK mutations mediating ALK-TKIs resistance and drug re-purposing to overcome the resistance. EBioMedicine 41, 105–119. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.01.019
Puissant, A., Frumm, S. M., Alexe, G., Bassil, C. F., Qi, J., Chanthery, Y. H., et al. (2013). Targeting MYCN in neuroblastoma by BET bromodomain inhibition. Cancer Discov. 3 (3), 308–323. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0418
Sharma, S. V., Lee, D. Y., Li, B., Quinlan, M. P., Takahashi, F., Maheswaran, S., et al. (2010). A chromatin-mediated reversible drug-tolerant state in cancer cell subpopulations. Cell 141 (1), 69–80. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.02.027
Siegel, R. L., Miller, K. D., Fuchs, H. E., and Jemal, A. (2022). Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72 (1), 7–33. doi:10.3322/caac.21708
Tan, A. C., and Tan, D. S. W. (2022). Targeted therapies for lung cancer patients with oncogenic driver molecular alterations. J. Clin. Oncol. 40 (6), 611–625. doi:10.1200/JCO.21.01626
Topper, M. J., Vaz, M., Chiappinelli, K. B., DeStefano Shields, C. E., Niknafs, N., Yen, R. W. C., et al. (2017). Epigenetic therapy ties MYC depletion to reversing immune evasion and treating lung cancer. Cell 171 (6), 1284–1300.e21. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.022
Watanabe, T., Miura, T., and Deguchi, Y. (2015). DNA methylation at hepatitis B viral integration sites is associated with methylation at flanking genomic regions. BMC Genomics 16, 642. doi:10.1101/gr.175240.114
Wei, S., Lieberman, D., Morrissette, J. J., Baloch, Z. W., Roth, D. B., and McGrath, C. (2016). Using “residual” FNA rinse and body fluid specimens for next-generation sequencing: an institutional experience. Cancer Cytopathol. 124 (5), 324–329. doi:10.1002/cncy.21666
Yan, H., Zeng, L., and Zhang, Y. (2024). RET rearrangement as a mechanism of resistance to ALK-TKI in non-small cell lung cancer patient with EML4-ALK fusion: a case report. Heliyon 10 (9), e29928. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29928
Yang, Y., Min, J., Yang, N., Yu, Q., Cheng, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2023). Envonalkib versus crizotinib for treatment-naive ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer: a randomized, multicenter, open-label, phase III trial. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8 (1), 301. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01538-w
Ye, Q., Ling, S., Zheng, S., and Xu, X. (2019). Liquid biopsy in hepatocellular carcinoma: circulating tumor cells and circulating tumor DNA. Mol. Cancer 18 (1), 114. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1043-x
Keywords: lung adenocarcinoma, KIF5B-RET, alectinib, pralsetinib, case report, ALK-rearranged
Citation: Jin F, Wang C, Yang F, Wang S and Wang F (2025) Case Report: Successful late-line pralsetinib treatment in an ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma patient with KIF5B-RET fusion resistant to alectinib. Front. Genet. 16:1569912. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1569912
Received: 02 February 2025; Accepted: 02 June 2025;
Published: 17 June 2025.
Edited by:
Andrés López-Cortés, Universidad de Las Américas, EcuadorReviewed by:
Umamaheswaran Gurusamy, Nationwide Children’s Hospital, United StatesSantosh Anand, University of Missouri, United States
Copyright © 2025 Jin, Wang, Yang, Wang and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Fen Wang, ZmluYV93YW5nQDE2My5jb20=
‡Present Address: Chenyang Wang, Department of Medical Oncology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China
§These authors have contributed equally to this work
†ORCID: Shubin Wang, orcid.org/0000-0002-8641-8488
 Feng Jin
Feng Jin Chenyang Wang
Chenyang Wang Fang Yang
Fang Yang Shubin Wang1†
Shubin Wang1† Fen Wang
Fen Wang