- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China
Stem cell research has significantly transformed regenerative medicine, with pluripotent stem cells (PSCs) serving as the cornerstone for disease modeling, drug screening, and therapeutic applications. Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) exhibit unparalleled self-renewal and tri-lineage differentiation, while induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) bypass ethical constraints through somatic cell reprogramming. Clinical trials highlight the potential of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in osteoarthritis and graft-versus-host disease, which leverage their immunomodulatory and paracrine effects. Despite advancements, challenges persist: iPSCs face epigenetic instability and tumorigenic risks, and adult stem cells struggle with inefficient differentiation. This paper systematically reviews stem cell source classification, differentiation regulatory mechanisms, cutting-edge technologies such as CRISPR/Cas9, and explores field-specific controversies (e.g., epigenetic stability of iPSCs) and future directions (e.g., integration of organoids and biomaterials). By analyzing current progress and challenges, it provides a multidimensional perspective for stem cell research.
1 Introduction
The emergence of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in 2006 marked a paradigm shift, allowing patients to receive specific treatments without damage to embryos. However, some critical debates still persist, including the following: (1) Source-specific regulation: How do transcriptional networks differ between ESCs, iPSCs, and adult stem cells? (2) Ethical dilemmas: While iPSCs circumvent the use of embryos, chimeric models and germline editing remain contentious. (3) Standardization gaps: Heterogeneity in MSC batches and variability in iPSC differentiation protocols hinder their clinical scalability. This article integrates research findings and focuses on three major directions: the classification and characteristics of stem cells, cutting-edge technologies for differentiation regulation, and bottlenecks in clinical translation. This study aims to provide a systematic analysis for the development of this field.
2 Types and sources of stem cells
2.1 Embryonic stem cells
Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) are pluripotent cells derived from the inner cell mass of blastocyst-stage embryos obtained from mice or humans. They possess pluripotency and can be infinitely expanded in vitro without undergoing replicative senescence or aging (Lorzadeh and Kazemirad, 2018; Zhang et al., 2025). Building upon prolonged in vitro culture techniques for human embryos, researchers have systematically characterized the developmental dynamics and molecular signatures of distinct cell lineages. A recent study revealed critical functional roles of FGF, Wnt, and BMP signaling pathways in lineage specification and further elucidated potential mechanisms underlying the aberrant development of aneuploid embryos (Shahbazi et al., 2020; Molè et al., 2021; Ai et al., 2023). However, the application of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) raises some ethical issues, including the following: 1) the vague definition of the moral status of embryos. Although embryos within 14 days can be used to save patients, their biological life needs to be respected; 2) undesirable practices in informed consent, such as inducing participants to sign documents and concealing intended uses; 3) risks of harm, including patient health issues caused by defects in cloning technology, as well as risks to gamete providers in underground markets; 4) ethical concerns regarding the dignity and safety of chimeric embryos; and 5) challenges in benefit distribution, including result-sharing, interest allocation, and conflicts between embryos and patients—ultimately requiring a balance of interests (Mountford, 2008; Bhartiya et al., 2013; Luk et al., 2017). Therefore, current related research is mainly limited to animal experimentation, and clinical translation still lacks sufficient data to support its safety and efficacy.
2.2 Adult stem cells
Adult stem cells (ASCs) are present in various tissues and organs of adults, such as the bone marrow, skin, brain, and intestine. Under normal circumstances, they remain in a quiescent state but are activated to participate in tissue repair in the presence of tissue damage. They include hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), and so on. Although their differentiation potential is limited, they have a relatively high level of safety. In the future, through the integration of single-cell sequencing and organoid technologies, adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) are likely to become the core tools for personalized medicine and disease modeling, bridging the gap between safety and functionality in precision medicine.
2.2.1 Hematopoietic stem cells
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are pluripotent stem cells that possess the abilities of self-renewal, proliferation, and pluripotent differentiation (Laurenti and Göttgens, 2018; Calvanese et al., 2022). Most HSCs remain stationary in the body, which is an important mechanism for maintaining HSC numbers and hematopoietic balance. Additionally, HSCs maintain a stable state to preserve their self-renewal capacity and protect themselves from genetic damage and excessive stress, thus ensuring their long-term survival and normal function (Chen et al., 2021). Under stressful conditions such as tissue damage and inflammation, HSCs can be activated and enter the cell cycle to begin self-renewal and differentiation in response to these emergencies (Dzierzak and Bigas, 2018). Due to their unique hematopoietic reconstitution ability, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) has become an important method for treating various hematological diseases, including malignant tumors of hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow and immunodeficiency diseases (Demirci et al., 2020). However, the insufficient number of donor cells remains the main bottleneck limiting its clinical application (Domingues et al., 2017; Okeke et al., 2021). In the future, with breakthroughs in gene editing technologies (such as CRISPR) and in vitro amplification technologies, it is expected that these advancements will reduce the shortage of donor cells, improve transplantation efficiency and safety, and provide more treatment options for patients.
2.2.2 Mesenchymal stem cells
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are a type of adult stem cell derived from the mesoderm. They primarily reside in the bone marrow and account for 0.001%–0.01% of the total nucleated cell population. MSCs exhibit characteristics such as self-renewal capacity, chemotactic migration properties, and transdifferentiation potential, making them ideal seed cells for tissue engineering (García-Pagán et al., 2012; Drela et al., 2020). Their unique immunomodulatory function modulates the body’s inflammatory response through the expression of immunosuppressive factors. For instance, MSCs can promote angiogenesis and re-epithelialization, regulate immune activity, reduce inflammation, and ultimately facilitate the repair of diabetic foot ulcers (Yu et al., 2023). A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study investigated the efficacy of a single intraarticular (IA) injection of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) in patients with knee osteoarthritis (OA). The results demonstrated that a single administration of allogeneic BM-MSCs via IA injection significantly alleviated pain at 9 months compared to the control group. Furthermore, quantitative T2 MRI cartilage mapping revealed that IA BM-MSCs inhibited OA progression over a 12-month period (Lee et al., 2024). In studies on graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), human placental mesenchymal stem cells (hPMSCs) were shown to mitigate GVHD-induced liver injury by reducing the proportion of CD8+PD-1+ T cells via the CD73/ADO/Nrf2 signaling pathway (Yan et al., 2025). Although extensive research supports the role of MSCs in liver regeneration and functional recovery, the therapeutic application of MSC transplantation for liver injuries remains contentious (He et al., 2024; Mincheva et al., 2025; Tian et al., 2025). A critical challenge lies in the in vivo microenvironment’s propensity to drive aberrant MSC differentiation into myofibroblasts, promoting fibrotic scar formation instead of functional hepatocyte differentiation (Ichim et al., 2018). This uncontrolled differentiation represents the primary obstacle to achieving therapeutic efficacy.
2.3 Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)
iPSCs are pluripotent cells that are artificially generated through genetic reprogramming of mature somatic cells. Their discovery has overcome some ethical limitations associated with embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and has demonstrated unique advantages (Takahashi and Yamanaka, 2006). Similar to ESCs, iPSCs express pluripotency markers, possess unlimited proliferative capacity, and can differentiate into ectodermal, mesodermal, and endodermal cells (Shi et al., 2017; Omole and Fakoya, 2018). Furthermore, iPSCs can be generated through autologous cell reprogramming or customized generation of cells with specific genetic backgrounds, providing opportunities for personalized medicine (Mianné et al., 2018; Stoddard-Bennett and Reijo Pera, 2019). Unlike ESCs, iPSCs circumvent the need to destroy human embryos and offer flexible applications, enabling non-invasive collection from patients with rare diseases. iPSCs have been widely used to model heart diseases, study hereditary arrhythmias, and investigate neurological disorders (including Alzheimer’s disease), liver diseases, and spinal cord injuries. The discovery of iPSCs has significantly advanced regenerative medicine, unlocking new avenues for harnessing pluripotent cells’ potential (Aboul-Soud et al., 2021). Table 1 summarizes the sources, key characteristics, clinical applications, and major challenges of ESCs, HSCs, MSCs, and iPSCs. Careful comparisons show that stem cells from different sources exhibit significant differences in differentiation potential, ethical constraints, and clinical translation potential.
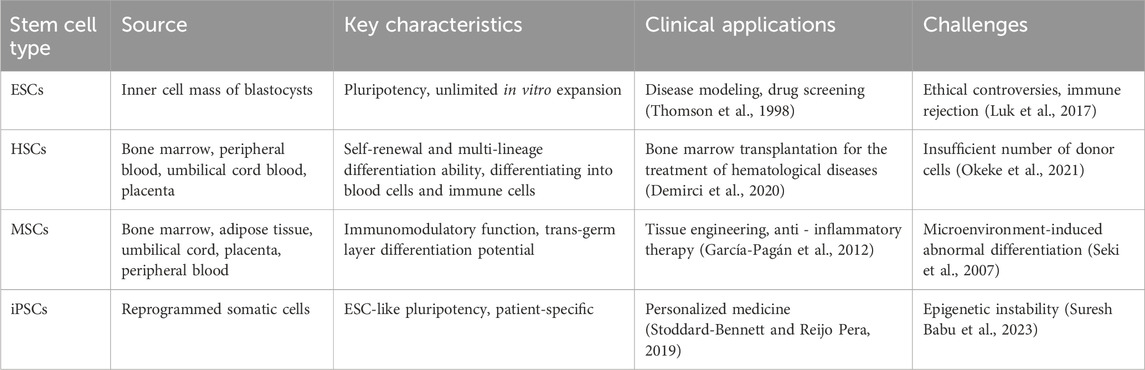
Table 1. Classification, source, key characteristics, clinical applications and challenges of stem cells.
3 Regulatory mechanisms of stem cell differentiation
3.1 Intrinsic regulatory mechanisms
3.1.1 Transcription factor network
Specific transcription factors maintain the self-renewal ability of stem cells or initiate the differentiation program through synergistic effects. For example, inhibition of the transcription regulator NF-kB (nuclear factor kappa B) impedes the differentiation of the mesoderm and neuroectoderm in mouse and human embryonic stem cells (Kaltschmidt et al., 2021). Furthermore, transcription factor CEBPD-mediated Wilms tumor 1-associated protein (WTAP) promotes the stemness, growth, migration and glycolysis of glioblastoma stem cell-like cells (GSCs) and reduces their tumorigenicity in vivo (Geng et al., 2025).
3.1.2 Epigenetic modifications
Epigenetic modifications determine the differentiation fate of stem cells by dynamically regulating gene expression. For example, in clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats/CRISPR-associated protein 9 (CRISPR/Cas9)-mediated ING5 knockout mice, the absence of ING5 leads to low fertility and depletion of stem cell pools in multiple tissues, although it does not reduce lifespan or impair wound healing ability (Al Shueili et al., 2025). Both drug inhibition and siRNA-mediated EZH2 knockout can reduce the level of H3K27me3 near the transcription initiation region, thereby stimulating the expression of related bone genes and promoting the osteogenic differentiation of MSCs (Dudakovic et al., 2018). Patient-derived primary glioblastoma stem cell lines, astrocyte cell lines, and primary fibroblast cell lines were treated with epigenetic drugs and found to produce human leukocyte antigen class I-presenting antigens while minimizing the potential side effects of activating unwanted genomic regions (Jang et al., 2024).
3.1.3 Metabolic regulation
The metabolic state of stem cells is closely related to their differentiation ability. For example, MFN2 and the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway co-regulate the glycolysis of iPSC-MSCs. The deficiency of MFN2 promotes aerobic glycolysis and osteogenic differentiation (Deng et al., 2022). During the differentiation of stem cells into astrocytes, GLUT1 expression is reduced, with neural progenitor cells showing the lowest expression levels. Truncated GLUT1 did not affect the differentiation of stem cells into astrocytes. However, astrocytes in GLUT1 deficiency syndrome (GLUT1DS) failed to express full-length GLUT1 at the protein level. Furthermore, glucose uptake, lactate production, glycolysis, mitochondrial activity, ATP levels, and extracellular glutamate release were all reduced (Pervaiz et al., 2025). In an animal model of Werner syndrome accompanied by severe osteoporosis, the restoration of NAD+ alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction and extends the lifespan of cells (Oshima et al., 2017; Fang et al., 2019).
3.2 Extrinsic regulatory mechanisms
3.2.1 Microenvironment (niche) signals
The microenvironment in which stem cells reside regulates their behavior through mechanical forces and biochemical signals. For example, the extracellular matrix (ECM) enhances mitochondrial fusion by upregulating fusion-related protein expression and suppressing associated inhibitory protein activity, thereby promoting osteogenesis. YAP affects glycolysis, glutamine metabolism, and other metabolic processes; regulates stiffness-mediated osteogenic differentiation; and acts as a mechanical sensor integrating ECM mechanical signals with energy metabolism signals. Additionally, glycolysis regulates YAP activity through cytoskeletal tension-mediated nuclear deformation (Na et al., 2024). Non-selective NO inhibitors inhibit methotrexate-induced Wnt/β-catenin target genes and Lgr5+ cell activity but also enhance sFRP-1 expression. Thus, methotrexate partially mediates intestinal stem cell integrity through NO-dependent Wnt/β-catenin signaling and may enhance tolerance to methotrexate-induced injury (Machida et al., 2022).
3.2.2 Cell interactions
Cytokines such as VEGF and FGF secreted by neighboring cells, as well as miRNAs carried by exosomes, can regulate the differentiation of stem cells. Differentiation signals can also be transmitted through intercellular junctions, such as gap junctions, or through adhesion molecules, such as cadherins. For example, a study confirmed that mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) promote intestinal mucosal repair by regulating fibroblast-epithelial cell interactions. In the in vitro co-culture model, fibroblasts treated with MSC-CM (CCD-18Co) promoted intestinal epithelial cell (Caco-2) proliferation by increasing the positive rate of EdU and accelerated wound healing by enhancing cell migration (Huang et al., 2025). Embryonic stem cells (ESCs) co-cultured with neural stem cells (NSCs) express higher levels of the ectodermal markers PAX6 and SOX1 under two co-culture conditions; however, the differentiation efficiency of the conditioned medium (CM) was lower than that of the non-conditioned medium. The results indicate that co-culture with NSCs promotes the differentiation of ESCs into the ectoderm (Kim et al., 2022).
4 Cutting-edge technologies and applications
4.1 Gene editing technology
The combination of CRISPR-Cas9 technology and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) provides a new strategy for the treatment of genetic diseases. For example, Mazzarino et al. used iPSCs and CRISPR-Cas9 technology to establish Alzheimer’s disease brain tissue models derived from both the wild-type and homozygous mutant variants of APOE3Ch. They found that the homozygous mutation of APOE3Ch can resist neurodegeneration and delay disease progression (Mazzarino et al., 2023). The Itoh team discovered that CRISPR-Cas9 technology can correct pathogenic mutations in iPSCs specific to recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB), achieving residue-free gene editing via the piggyBac transposon system (Itoh et al., 2020).
4.2 Organoid construction
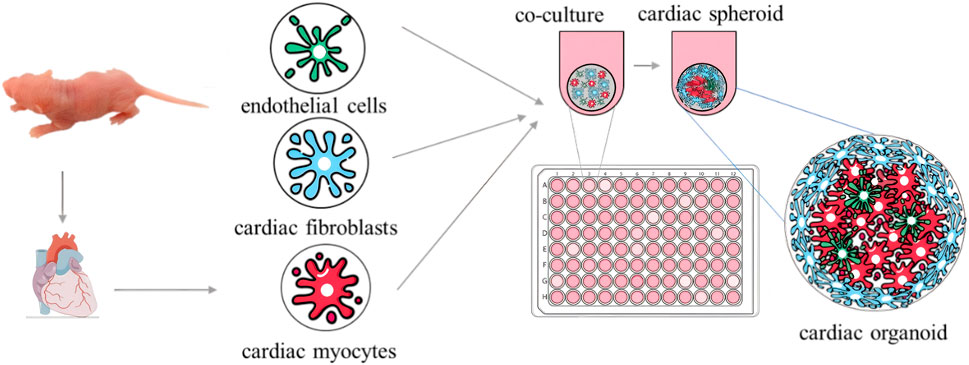
Breakthroughs have been made in organoid model construction technology, with the research field trending toward the coordinated development of multi-organ systems. In terms of basic model construction, researchers have successively overcome the challenge of simulating multiple organs in vitro, such as using 3D retinal pigment epithelial cell models derived from patients (Manian et al., 2021); brain organoids with complex neural activity and optic cup fine structures (Gabriel et al., 2021); patient-derived cervical cancer organoid models (Kutle et al., 2023); 3D pancreatic organoid models (Darrigrand et al., 2024); cardiac organoids characterized by cardiac microsphere formation through 3D co-culture (Figure 1) (Fan et al., 2023); and spontaneous beating scaffold-free human cardiac organoids (Xia et al., 2025). These milestones collectively drive organoid technology from single-organ simulation to the construction of complex physiological environments with multi-system interactions.
4.3 3D bioprinting
Using 3D bioprinting promotes the development of personalized medicine through the customization of organs and medical devices. This technology enables precise printing of tissues and organs, such as cardiac tissues, skin, and bones (Omondi et al., 2024), and offers novel approaches for personalized drug manufacturing (Ullah et al., 2023). It has the potential to revolutionize medical device manufacturing by enhancing precision and targeting in tissue engineering and drug delivery (Dedeloudi et al., 2025). The customized bioprinting process not only improves transplantation success rates but also mitigates immune rejection. Additionally, material optimization facilitates achieving a balance between the mechanical properties of the devices and patients’ comfort.
5 Clinical transformation bottlenecks and future directions
5.1 Technical bottlenecks
The clinical application of stem cells poses significant challenges. The engraftment and survival of transplanted stem cells in myocardial tissue represent the most critical barrier in cell therapy. Preclinical studies (Hou et al., 2005) and clinical trials (Blocklet et al., 2010) demonstrate that cell retention rates fall below 10% within 24 h post-transplantation, with only ∼1% remaining after 4 weeks (Terrovitis et al., 2009). This rapid attrition primarily results from blood flow shear stress, extravasation at injection sites, and cell death. More critically, undifferentiated iPSCs exhibit inherent tumorigenic potential, potentially leading to teratoma formation and genetic aberrations (Sato et al., 2019; Lemmens et al., 2023). Additional risks emerge during reprogramming and in vitro culture/expansion, including genomic instability (e.g., chromosomal amplifications and copy-number variations), reactivation of pluripotency transgenes, and mutations in proto-oncogenes/tumor suppressor genes (Sato et al., 2019; Stoddard-Bennett and Pera, 2020; Suresh Babu et al., 2023). These safety concerns collectively constitute major obstacles to stem cell clinical translation.
5.2 Future strategies
Artificial intelligence (AI) technology has become an emerging trend. In liver regeneration, AI can automatically segment the liver parenchyma from imaging data such as CT and MRI through upgraded algorithms, achieving “millimeter-level” accurate calculation of the liver volume, which far surpasses traditional manual measurement methods. When combined with imaging tracking technology, it can dynamically generate the regeneration curve after liver resection and identify the inflection point of the regeneration rate, providing an accurate basis for perioperative nutritional intervention (Lau et al., 2017; Sabanayagam et al., 2020; Maheshwari et al., 2023). In the future, by constructing an interdisciplinary AI platform that integrates global stem cell research data, clinical cases, and patient information using natural language processing technology to standardize unstructured data; and mining potential associations through machine learning, this system will provide multi-dimensional data support for optimizing liver regeneration treatment strategies.
6 Discussion
The rapid development of stem cell research provides unprecedented opportunities for regenerative medicine and disease treatment; however, its clinical translation still faces multiple challenges. First, although iPSC technology has successfully avoided the ethical controversies of ESCs, its epigenetic instability and potential tumorigenicity remain the core issues restricting its widespread application (Sato et al., 2019). For example, residual pluripotency genes (such as c-Myc) during the reprogramming process may cause genomic abnormalities and lead to the formation of teratomas (Lemmens et al., 2023). Secondly, the insufficient differentiation efficiency and functional maturity of stem cells limit their therapeutic efficacy in tissue repair. Taking mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) as an example, they are prone to differentiate into fibroblasts instead of functional hepatocytes in the liver injury microenvironment, further exacerbating fibrosis (Ichim et al., 2018), which indicates that the microenvironment regulation strategies need to be further optimized.
The integration of cutting-edge technologies provides new ideas for breaking through these bottlenecks. The combination of gene editing technology (such as CRISPR-Cas9) and iPSCs has successfully corrected mutations related to genetic diseases (Itoh et al., 2020). For example, the use of CRISPR/Cas9 technology to introduce heterozygous point mutations in the PRPF8 gene of normal induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) lines and establish PRPF8 gene mutant cell lines (CSUASOi012-A-2) has provided valuable cellular resources for studying the pathogenesis of retinitis pigmentosa (Chen et al., 2025). However, the off-target effects of gene editing still need to be strictly evaluated. Organoid technology studies the efficacy of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived lung organoids (hiLOs) derived from NKX2.1+ lung progenitor cells and airway basal cells (hiBCs) as a 3D model by simulating the 3D structure of organ development. For instance, targeting the most common mutation, F508del, researchers have assessed CFTR modulator response through forskolin-induced swelling assay. ROC analysis of FIS assay results showed an optimal cutoff value of 1.21, a sensitivity of 65.9%, a specificity of 71.8%, and a prediction accuracy of 76.4% for the model. The results demonstrated that hiLOs can effectively model CF pathology and predict patient-specific responses to modulators (Demchenko et al., 2025), providing a more accurate model for disease mechanism research and drug screening (Hofbauer et al., 2021). Furthermore, 3D bioprinting technology can achieve personalized tissue construction (Omondi et al., 2024); however, these technical methods still have certain limitations. For example, although CRISPR-Cas9/iPSC can accurately correct genetic defects, they still face differences in gene correction efficiency and the possibility of off-target effects in different iPSC cell lines (Walsh and Jin, 2024). Although 3D bioprinting could facilitate personalized tissue manufacturing some material limitations persist. For instance, synthetic polymers implanted in the body could trigger immune responses and induce inflammation (Wang et al., 2024). Biomaterials have better biological activity, but cytotoxic products may be released during degradation, and challenges persist in large-scale production and consistent control of biomaterials (Yuan et al., 2024). Organoid models are able to generalize disease pathology but lack vascularization and immune components, thereby limiting translational relevance (Wen et al., 2024).
Future research should focus on interdisciplinary innovation. AI has great potential in stem cell research. For example, machine learning can predict differentiation pathways and optimize culture conditions by analyzing single-cell sequencing data (Sabanayagam et al., 2020). Additionally, combining biomaterials science with stem cell biology to develop bioengineered microenvironment scaffolds may enhance the directed differentiation and functional integration of stem cells. Furthermore, standardizing the stem cell preparation process and establishing a long-term safety evaluation system are the key to promoting clinical translation.
In conclusion, the success of stem cell research requires both in-depth exploration of basic mechanisms and precise application of technological advancements. Through interdisciplinary cooperation and technological innovation, it is expected to break through existing bottlenecks and achieve clinical translation of regenerative medicine.
Author contributions
ZS: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. HuD: Writing – review and editing. XF: Writing – review and editing. WZ: Writing – review and editing. HoD: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aboul-Soud, M. A. M., Alzahrani, A. J., and Mahmoud, A. (2021). Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs)—roles in regenerative therapies, disease modelling and drug screening. Cells 10, 2319. doi:10.3390/cells10092319
Ai, Z., Niu, B., Yin, Y., Xiang, L., Shi, G., Duan, K., et al. (2023). Dissecting peri-implantation development using cultured human embryos and embryo-like assembloids. Cell Res. 33, 661–678. doi:10.1038/s41422-023-00846-8
Al Shueili, B., Dantas, A., Mahe, E., Chu, T. H., Yang, Y., Labit, E., et al. (2025). Knockout of the ING5 epigenetic regulator confirms roles in stem cell maintenance and tumor suppression in vivo. PLoS ONE 20, e0313255. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0313255
Bhartiya, D., Nagvenkar, P., Sriraman, K., and Shaikh, A. (2013). An overview of pluripotent stem cells. Pluripot. Stem Cells. doi:10.5772/55130
Blocklet, D., Toungouz, M., Berkenboom, G., Lambermont, M., Unger, P., Preumont, N., et al. (2010). Myocardial homing of nonmobilized peripheral-blood CD34+ cells after intracoronary injection. Stem Cells 24, 333–336. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2005-0201
Calvanese, V., Capellera-Garcia, S., Ma, F., Fares, I., Liebscher, S., Ng, E. S., et al. (2022). Mapping human haematopoietic stem cells from haemogenic endothelium to birth. Nature 604, 534–540. doi:10.1038/s41586-022-04571-x
Chen, H., Liang, Y., Chen, Y., Liang, Y., Li, X., Duan, C., et al. (2025). Generation of a human iPSC line with heterozygous PRPF8 c.5792C > T, p. T1931M mutation to model retinitis pigmentosa using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. Stem Cell Res. 84, 103689. doi:10.1016/j.scr.2025.103689
Chen, Z., Huo, D., Li, L., Liu, Z., Li, Z., Xu, S., et al. (2021). Nuclear DEK preserves hematopoietic stem cells potential via NCoR1/HDAC3-Akt1/2-mTOR axis. J. Exp. Med. 218, e20201974. doi:10.1084/jem.20201974
Darrigrand, J.-F., Isaacson, A., and Spagnoli, F. M. (2024). Generation of human iPSC-derived pancreatic organoids to study pancreas development and disease. BioRxiv. doi:10.1101/2024.10.24.620102
Dedeloudi, A., Farzeen, F., Lesutan, V.-N., Irwin, R., Wylie, M. P., Andersen, S., et al. (2025). Biopolymeric 3D printed scaffolds as a versatile tissue engineering treatment for congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Int. J. Pharm. 672, 125313. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2025.125313
Demchenko, A., Balyasin, M., Nazarova, A., Grigorieva, O., Panchuk, I., Kondrateva, E., et al. (2025). Human induced lung organoids: a promising tool for cystic fibrosis drug screening. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 26, 437. doi:10.3390/ijms26020437
Demirci, S., Leonard, A., and Tisdale, J. F. (2020). Hematopoietic stem cells from pluripotent stem cells: clinical potential, challenges, and future perspectives. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 9, 1549–1557. doi:10.1002/sctm.20-0247
Deng, L., Yi, S., Yin, X., Li, Y., and Luan, Q. (2022). MFN2 knockdown promotes osteogenic differentiation of iPSC-MSCs through aerobic glycolysis mediated by the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 13, 162. doi:10.1186/s13287-022-02836-w
Domingues, M. J., Nilsson, S. K., and Cao, B. (2017). New agents in HSC mobilization. Int. J. Hematol. 105, 141–152. doi:10.1007/s12185-016-2156-2
Drela, K., Stanaszek, L., Snioch, K., Kuczynska, Z., Wrobel, M., Sarzynska, S., et al. (2020). Bone marrow-derived from the human femoral shaft as a new source of mesenchymal stem/stromal cells: an alternative cell material for banking and clinical transplantation. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 11, 262. doi:10.1186/s13287-020-01697-5
Dudakovic, A., Camilleri, E. T., Paradise, C. R., Samsonraj, R. M., Gluscevic, M., Paggi, C. A., et al. (2018). Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (Ezh2) controls bone formation and cell cycle progression during osteogenesis in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 293, 12894–12907. doi:10.1074/jbc.ra118.002983
Dzierzak, E., and Bigas, A. (2018). Blood development: hematopoietic stem cell dependence and independence. Cell Stem Cell 22, 639–651. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2018.04.015
Fan, S., Xiao, G., Ni, J., Zhao, Y., Du, H., Liang, Y., et al. (2023). Guanxinning injection ameliorates cardiac remodeling in HF mouse and 3D heart spheroid models via p38/FOS/MMP1-mediated inhibition of myocardial hypertrophy and fibrosis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 162, 114642. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.114642
Fang, E. F., Hou, Y., Lautrup, S., Jensen, M. B., Yang, B., SenGupta, T., et al. (2019). NAD+ augmentation restores mitophagy and limits accelerated aging in Werner syndrome. Nat. Commun. 10, 5284. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13172-8
Gabriel, E., Albanna, W., Pasquini, G., Ramani, A., Josipovic, N., Mariappan, A., et al. (2021). Human brain organoids assemble functionally integrated bilateral optic vesicles. Cell Stem Cell 28, 1740–1757.e8. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2021.07.010
García-Pagán, J.-C., Gracia-Sancho, J., and Bosch, J. (2012). Functional aspects on the pathophysiology of portal hypertension in cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 57, 458–461. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.03.007
Geng, J., Shao, Y., Pu, Y., Wu, Y., and Yang, Z. (2025). Transcription factor CEBPD-mediated WTAP facilitates the stemness, growth, migration and glycolysis of glioblastoma stem like cells. Neurochem. Res. 50, 100. doi:10.1007/s11064-024-04321-7
He, L., Xu, J., Huang, P., Bai, Y., Chen, H., Xu, X., et al. (2024). miR-9-5p and miR-221-3p promote human mesenchymal stem cells to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury by enhancing human mesenchymal stem cell engraftment and inhibiting hepatic stellate cell activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 7235. doi:10.3390/ijms25137235
Hofbauer, P., Jahnel, S. M., Papai, N., Giesshammer, M., Deyett, A., Schmidt, C., et al. (2021). Cardioids reveal self-organizing principles of human cardiogenesis. Cell 184, 3299–3317.e22. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.04.034
Hou, D., Youssef, E.A.-S., Brinton, T. J., Zhang, P., Rogers, P., Price, E. T., et al. (2005). Radiolabeled cell distribution after intramyocardial, intracoronary, and interstitial retrograde coronary venous delivery: implications for current clinical trials. Circulation 112, 150–156. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.104.526749
Huang, Z., Yang, H., Chao, K., and Gao, X. (2025). P0134 Human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote intestinal mucosal repair by activating fibroblasts-epithelial interactions. J. Crohns Colitis 19, i521. doi:10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjae190.0308
Ichim, T. E., O’Heeron, P., and Kesari, S. (2018). Fibroblasts as a practical alternative to mesenchymal stem cells. J. Transl. Med. 16, 212. doi:10.1186/s12967-018-1536-1
Itoh, M., Kawagoe, S., Tamai, K., Nakagawa, H., Asahina, A., and Okano, H. J. (2020). Footprint-free gene mutation correction in induced pluripotent stem cell (iPSC) derived from recessive dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa (RDEB) using the CRISPR/Cas9 and piggyBac transposon system. J. Dermatol. Sci. 98, 163–172. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2020.04.004
Jang, H. J., Shah, N. M., Maeng, J. H., Liang, Y., Basri, N. L., Ge, J., et al. (2024). Epigenetic therapy potentiates transposable element transcription to create tumor-enriched antigens in glioblastoma cells. Nat. Genet. 56, 1903–1913. doi:10.1038/s41588-024-01880-x
Kaltschmidt, C., Greiner, J. F. W., and Kaltschmidt, B. (2021). The transcription factor NF-κB in stem cells and development. Cells 10, 2042. doi:10.3390/cells10082042
Kim, Y. R., Jang, S. W., Han, J. H., Na, G. R., Jang, H., and Choi, H. W. (2022). The effects of co-culture of embryonic stem cells with neural stem cells on differentiation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 44, 6104–6116. doi:10.3390/cimb44120416
Kutle, I., Polten, R., Hachenberg, J., Klapdor, R., Morgan, M., and Schambach, A. (2023). Tumor organoid and spheroid models for cervical cancer. Cancers 15, 2518. doi:10.3390/cancers15092518
Lau, L., Kankanige, Y., Rubinstein, B., Jones, R., Christophi, C., Muralidharan, V., et al. (2017). Machine-learning algorithms predict graft failure after liver transplantation. Transplantation 101, e125–e132. doi:10.1097/tp.0000000000001600
Laurenti, E., and Göttgens, B. (2018). From haematopoietic stem cells to complex differentiation landscapes. Nature 553, 418–426. doi:10.1038/nature25022
Lee, B.-W., Lee, J. J., Jung, J.-Y., and Ju, J. H. (2024). Intra-articular injection of human bone marrow–derived mesenchymal stem cells in knee osteoarthritis: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Cell Transpl. 34, 9636897241303275. doi:10.1177/09636897241303275
Lemmens, M., Perner, J., Potgeter, L., Zogg, M., Thiruchelvam, S., Müller, M., et al. (2023). Identification of marker genes to monitor residual iPSCs in iPSC-derived products. Cytotherapy 25, 59–67. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2022.09.010
Lorzadeh, N., and Kazemirad, N. (2018). Embryonic stem cells and infertility. Am. J. Perinat. 35, 925–930. doi:10.1055/s-0038-1632367
Luk, F., Eggenhofer, E., Dahlke, M. H., and Hoogduijn, M. J. (2017). The use of stem cells for treatment of diseases. Front. Young Minds. 5, 9. doi:10.3389/frym.2017.00009
Machida, M., Machida, T., Kikuchi, M., Shimizu, A., Ida, S., Tawaraya, Y., et al. (2022). Methotrexate mediates the integrity of intestinal stem cells partly through nitric oxide-dependent Wnt/β-catenin signaling in methotrexate-induced rat ileal mucositis. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 148, 281–285. doi:10.1016/j.jphs.2022.01.002
Maheshwari, K., Cywinski, J. B., Papay, F., Khanna, A. K., and Mathur, P. (2023). Artificial intelligence for perioperative medicine: perioperative intelligence. Anesth. Analg. 136, 637–645. doi:10.1213/ane.0000000000005952
Manian, K. V., Galloway, C. A., Dalvi, S., Emanuel, A. A., Mereness, J. A., Black, W., et al. (2021). 3D iPSC modeling of the retinal pigment epithelium-choriocapillaris complex identifies factors involved in the pathology of macular degeneration. Cell Stem Cell 28, 978. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2021.03.024
Mazzarino, R., Perez-Corredor, P., Vanderleest, T., Vacano, G., Sanchez, J., Villalba-Moreno, N., et al. (2023). APOE3Christchurch modulates tau phosphorylation and β-catenin/Wnt/cadherin signaling in induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cerebral organoids from Alzheimer’s cases. BioRxiv 17. doi:10.1101/2023.01.11.523290
Mianné, J., Ahmed, E., Bourguignon, C., Fieldes, M., Vachier, I., Bourdin, A., et al. (2018). Induced pluripotent stem cells for primary ciliary dyskinesia modeling and personalized medicine. Am. J. Resp. Cell Mol. Biol. 59, 672–683. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2018-0213TR
Mincheva, G., Moreno-Manzano, V., Felipo, V., and Llansola, M. (2025). Extracellular vesicles from mesenchymal stem cells improve liver injury in rats with mild liver damage. Underlying mechanisms and role of TGFβ. Life Sci. 364, 123429. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2025.123429
Molè, M. A., Coorens, T. H. H., Shahbazi, M. N., Weberling, A., Weatherbee, B. A. T., Gantner, C. W., et al. (2021). A single cell characterisation of human embryogenesis identifies pluripotency transitions and putative anterior hypoblast centre. Nat. Commun. 12, 3679. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23758-w
Mountford, J. C. (2008). Human embryonic stem cells: origins, characteristics and potential for regenerative therapy. Beitr. Infus. 18, 1–12. doi:10.1111/j.1365-3148.2007.00807.x
Na, J., Yang, Z., Shi, Q., Li, C., Liu, Y., Song, Y., et al. (2024). Extracellular matrix stiffness as an energy metabolism regulator drives osteogenic differentiation in mesenchymal stem cells. Bioact. Mater. 35, 549–563. doi:10.1016/j.bioactmat.2024.02.003
Okeke, C., Silas, U., Okeke, C., and Chikwendu, C. (2021). Current trends on hemopoietic stem cells. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 16, 199–208. doi:10.2174/1574888x15999200729162021
Omole, A. E., and Fakoya, A. O. J. (2018). Ten years of progress and promise of induced pluripotent stem cells: historical origins, characteristics, mechanisms, limitations, and potential applications. PeerJ 6, e4370. doi:10.7717/peerj.4370
Omondi, O. B., Arroyan, Y. N., Onyango, B., Kong, L., Wang, G., and Ye, Z. (2024). Revolutionizing healthcare: emerging frontiers in 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Eur. Polym. J. 217, 113210. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2024.113210
Oshima, J., Sidorova, J. M., and Monnat, R. J. (2017). Werner syndrome: clinical features, pathogenesis and potential therapeutic interventions. Ageing Res. Rev. 33, 105–114. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2016.03.002
Pervaiz, I., Mehta, Y., and Al-Ahmad, A. J. (2025). Glucose transporter 1 deficiency impairs glucose metabolism and barrier induction in human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived astrocytes. J. Cell. Physiol. 240, 31523. doi:10.1002/jcp.31523
Sabanayagam, C., Xu, D., Ting, D. S. W., Nusinovici, S., Banu, R., Hamzah, H., et al. (2020). A deep learning algorithm to detect chronic kidney disease from retinal photographs in community-based populations. Lancet Digit. Health 2, e295–e302. doi:10.1016/s2589-7500(20)30063-7
Sato, Y., Bando, H., Di Piazza, M., Gowing, G., Herberts, C., Jackman, S., et al. (2019). Tumorigenicity assessment of cell therapy products: the need for global consensus and points to consider. Cytotherapy 21, 1095–1111. doi:10.1016/j.jcyt.2019.10.001
Seki, E., De Minicis, S., Österreicher, C. H., Kluwe, J., Osawa, Y., Brenner, D. A., et al. (2007). TLR4 enhances TGF-β signaling and hepatic fibrosis. Nat. Med. 13, 1324–1332. doi:10.1038/nm1663
Shahbazi, M. N., Wang, T., Tao, X., Weatherbee, B. A. T., Sun, L., Zhan, Y., et al. (2020). Developmental potential of aneuploid human embryos cultured beyond implantation. Nat. Commun. 11, 3987. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17764-7
Shi, Y., Inoue, H., Wu, J. C., and Yamanaka, S. (2017). Induced pluripotent stem cell technology: a decade of progress. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 16, 115–130. doi:10.1038/nrd.2016.245
Stoddard-Bennett, T., and Pera, R. (2020). Stem cell therapy for Parkinson’s disease: safety and modeling. Neural Regen. Res. 15, 36–40. doi:10.4103/1673-5374.264446
Stoddard-Bennett, T., and Reijo Pera, R. (2019). Treatment of Parkinson’s disease through personalized medicine and induced pluripotent stem cells. Cells 8, 26. doi:10.3390/cells8010026
Suresh Babu, S., Duvvuru, H., Baker, J., Switalski, S., Shafa, M., Panchalingam, K. M., et al. (2023). Characterization of human induced pluripotent stems cells: current approaches, challenges, and future solutions. Biotechnol. Rep. 37, e00784. doi:10.1016/j.btre.2023.e00784
Takahashi, K., and Yamanaka, S. (2006). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024
Terrovitis, J., Lautamäki, R., Bonios, M., Fox, J., Engles, J. M., Yu, J., et al. (2009). Noninvasive quantification and optimization of acute cell retention by in vivo positron emission tomography after intramyocardial cardiac-derived stem cell delivery. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 54, 1619–1626. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2009.04.097
Thomson, J. A., Itskovitz-Eldor, J., Shapiro, S. S., Waknitz, M. A., Swiergiel, J. J., Marshall, V. S., et al. (1998). Embryonic stem cell lines derived from human blastocysts. Science 282, 1145–1147. doi:10.1126/science.282.5391.1145
Tian, Y., Jin, M., Ye, N., Gao, Z., Jiang, Y., and Yan, S. (2025). Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes attenuate mouse non-heart-beating liver transplantation through Mir-17-5p-regulated Kupffer cell pyroptosis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 16, 57. doi:10.1186/s13287-025-04169-w
Ullah, M., Wahab, A., Khan, S. U., Naeem, M., Rehman, K., Ali, H., et al. (2023). 3D printing technology: a new approach for the fabrication of personalized and customized pharmaceuticals. Eur. Polym. J. 195, 112240. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.112240
Walsh, C., and Jin, S. (2024). Induced pluripotent stem cells and CRISPR-Cas9 innovations for treating alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency and glycogen storage diseases. Cells 13, 1052. doi:10.3390/cells13121052
Wang, Z., Sun, Y., and Li, C. (2024). Advances in 3D printing technology for preparing bone tissue engineering scaffolds from biodegradable materials. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 12, 1483547. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2024.1483547
Wen, Z., Orduno, M., Liang, Z., Gong, X., and Mak, M. (2024). Optimization of vascularized intestinal organoid model. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 13, 2400977. doi:10.1002/adhm.202400977
Xia, X., Hu, M., Zhou, W., Jin, Y., and Yao, X. (2025). Engineering cardiology with miniature hearts. Mater. Today Bio 31, 101505. doi:10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101505
Yan, W., Zhang, H., Zhang, J., Zhao, Y., Wu, Y., Ma, X., et al. (2025). Human placental mesenchymal stem cells regulate the antioxidant capacity of CD8+PD-1+ T cells through the CD73/ADO/Nrf2 pathway to protect against liver damage in mice with acute graft-versus-host disease. Mol. Immunol. 179, 71–83. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2025.01.016
Yu, X., Liu, P., Li, Z., and Zhang, Z. (2023). Function and mechanism of mesenchymal stem cells in the healing of diabetic foot wounds. Front. Endocrinol. 14, 1099310. doi:10.3389/fendo.2023.1099310
Yuan, X., Zhu, W., Yang, Z., He, N., Chen, F., Han, X., et al. (2024). Recent advances in 3D printing of smart scaffolds for bone tissue engineering and regeneration. Adv. Mater. 36, 2403641. doi:10.1002/adma.202403641
Keywords: pluripotent stem cells, regenerative medicine, stem cell differentiation, disease modeling, stem cell therapy
Citation: Su Z, Dong H, Fang X, Zhang W and Duan H (2025) Frontier progress and translational challenges of pluripotent differentiation of stem cells. Front. Genet. 16:1583391. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1583391
Received: 25 February 2025; Accepted: 16 April 2025;
Published: 28 April 2025.
Edited by:
Zhengdong Zhang, First Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu Medical College, ChinaReviewed by:
Tong Li, Chongqing Medical University, ChinaShenghuishang Shang, Shandong University, China
Copyright © 2025 Su, Dong, Fang, Zhang and Duan. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong Duan, ZHVhbmhvbmcxOTcwQDEyNi5jb20=
 Zhengbing Su
Zhengbing Su Hui Dong
Hui Dong Wenli Zhang
Wenli Zhang Hong Duan
Hong Duan