- Department of Medical Genetics and Prenatal Screening, Taiyuan Maternal and Child Health Hospital, Taiyuan, China
Introduction: Pathogenic variants in NR4A2 are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders including intellectual developmental disorder with language impairment and early-onset dopa-responsive dystonia-parkinsonism (IDLDP). Here we report two pediatric NR4A2-related cases presenting with global developmental delay, speech impairment, and intellectual disability.
Methods: Comprehensive genetic investigations including whole-exome sequencing revealed a de novo missense variant (c.994G>C, p.Val332Leu) in NR4A2 and a 2q23.3-q24.2 deletion encompassing NR4A2. Functional validation via RNA sequencing revealed that the missense variant induces pathogenic exon 4 skipping through aberrant splicing. Both patients exhibited marked clinical improvements in linguistic competence and motor function following levodopa therapy, initiated after confirmation of dopaminergic responsiveness. A systematic review of 19 reported NR4A2-related cases revealed substantial phenotypic heterogeneity, with three of them demonstrating favorable responses to dopaminergic treatment.
Results: Our findings underscore the diagnostic value of integrating molecular profiling with functional RNA analysis to resolve complex neurogenetic disorders. Levodopa therapy shows therapeutic potential for NR4A2-deficient patients with dopa-responsive features, especially in linguistic improvement. This study expands the understanding of NR4A2-associated pathogenesis and provides insights for the precision management of related neurodevelopmental conditions.
1 Introduction
NR4A2 gene (MIM *601828), also known as NURR1, encodes nuclear receptor subfamily 4 group A member 2, a member of the steroid–thyroid hormone–retinoid receptor superfamily, which is a conserved transcription factor implicated in the development and maintenance of dopamine-synthesizing cells. By regulating gene expression in the human brain, NR4A2 specifically influences the maturation and development of neurons, particularly dopaminergic neurons (Lévy et al., 2018). Structural and sequence variants in NR4A2 leading to haploinsufficiency have been identified in patients with intellectual developmental disorder characterized by language impairment and early-onset dopa-responsive dystonia-parkinsonism (IDLDP), with the first reports published in 2017 (Reuter et al., 2017). Phenotypic heterogeneity exists and the severity is highly variable, but core symptom of patients is developmental delay affecting motor, cognitive, and speech, with half of patients develop various types of seizures (Gabaldon-Albero et al., 2024). Since NR4A2 plays a role in maintenance of adult midbrain dopaminergic neuron, it is also associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s disease, schizophrenia, and manic depression (Le et al., 2003; Buervenich et al., 2000).
Following comprehensive clinical evaluations of two pediatric cases (an 8-year-old and a 6-year-old) presenting with global developmental delay with predominant language impairment and intellectual disability, whole-exome sequencing (WES) revealed a missense variant and a microdeletion involving NR4A2 gene. The patient with the missense variant underwent further functional validation through RNA sequencing of peripheral blood specimens, which demonstrated the missense variant’s disruptive effect on splicing fidelity, culminating in a definitive molecular diagnosis. Both patients demonstrated marked improvement in linguistic competence and motor function following initiation of levodopa therapy, which was instituted after confirming dopaminergic responsiveness through clinical trials.
In-depth phenotypic characterization, detailed treatment protocols, and a comprehensive review of published NR4A2 cases offer a thorough understanding of patients afflicted with intellectual developmental disorder with language impairment and early-onset DOPA-responsive dystonia-parkinsonism. Furthermore, exploration of the molecular mechanisms underlying NR4A2-associated intellectual developmental disorder with language impairment and early-onset DOPA-responsive dystonia-parkinsonism is imperative for the development of efficacious therapies and enhanced clinical outcomes.
2 Methods
2.1 Clinical evaluation of the patient
The evaluation of two pediatric patients with intellectual disability and language delay involved a multidisciplinary approach, including medical history review, clinical examination, and neurodevelopmental assessments. A comprehensive medical history was obtained for both patients, focusing on developmental milestones (motor, cognitive, and language domains), family history of neurodevelopmental disorders, and prenatal/perinatal complications. A detailed physical examination was conducted to assess anthropometric measurements and identify dysmorphic features. Intellectual functioning was measured using the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC-V), while language abilities were evaluated with International Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health (ICF) Speech Function Assessment Criteria. Dopamine and homovanillic acid levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) was measured for prediction of dopa-responsive.
2.2 Whole exome sequencing and analysis
Trio-based whole-exome sequencing (WES) was conducted to identify any underlying genetic causes. In brief, genomic DNA was extracted from the patient’s peripheral blood and fragmented into 150–200 bp fragments. Sequencing libraries were constructed utilizing the SureSelect XT Human All Exon V6 kit from Agilent Technologies (Santa Clara, CA, United States), and sequencing was carried out on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 System (Illumina, San Diego, CA, United States). Data quality control and adaptor sequence removal were performed using Fastqc (Babraham Research Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom) and Fastp (Visible Genetics, Inc., Toronto, Canada) tools, respectively. Alignment with the reference genome was conducted utilizing SpeedSeq (Ira Hall Lab, St. Louis, MO, United States). The Genome Analysis Toolkit (Broad Institute, Cambridge, MA, United States) was employed to identify variations in the BAM file meeting quality control criteria, generating a VCF format file. Annotation of variations in VCF files was carried out using the Ingenuity Variant Analysis (Ingenuity Systems, Redwood City, CA, United States) and Translational Genomics Expert platforms. All potential variants were confirmed through Sanger sequencing and validated using parental test results. Copy number variants were detected using the CNVkit open-source software (Larsen et al., 2016). Pathogenicity classification performed according to the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines. Sanger sequencing was used to confirm any identified variants. The clinical findings were correlated with genetic data to form a comprehensive diagnostic profile.
2.3 RNA-sequencing and data analysis
The patient’s peripheral blood was drawn and total RNA was extracted by using the RNeasy Kits (Qiagen). Poly(A) mRNA was selected and the complementary DNA (cDNA) libraries were prepared with the Illumina TruSeq Stranded mRNA Library Prep kit (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, United States) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The cDNA libraries were sequenced on an Illumina NovaSeq 6000 System (Illumina, Inc., San Diego, CA, United States) using 150 bp paired-end reads.
The generated FASTQ files underwent quality control and adapter sequence removal using Fastqc v.0.11.9 (Babraham Research Institute, Cambridge, United Kingdom) and Fastp v.0.20.1 (Visible Genetics, Inc., Toronto, Canada), respectively. To detect gene fusions and enhance the sensitivity of novel splice junction detection, clean data were aligned to the reference human genome (hg19) using STAR v.2.7.8a (Cold Spring Harbor, New York, United States) with the parameters twopassMode and chimeric output function (chimSegmentMin = 12, twopassMode = ‘Basic’). Gene-level quantifications were performed using RSEM (v1.2.28). Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified compared to controls with an adjusted p value <0.05 cutoff (q-value) using DESeq2 (v.1.26.0). LeafCutter was employed to assess the statistical significance of differences in the quantity of each splicing event (minclureads = 30; maxintronlen = 500,000; mincluratio = 1e-5). Specifically, each patient was compared against all other controls for differential splicing analysis (min_samples_per_group = 1; min_samples_per_intron = 1). The resulting P values were subjected to correction for multiple testing using a family-wise error rate approach. Additionally, aberrant splicing events were visualized using Sashimi plots generated with MISO (v.0.5.4) and Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV). STAR-Fusion utilized chimeric and discordant read alignments identified by the STAR aligner to predict fusion events.
3 Result
3.1 Clinical manifestation
Patient 1, an 8-year-old male, was born at full-term via spontaneous vaginal delivery, with no complications noted during the labor examination. He has a 22-year-old sister who is developing normally. At 19 months of age, the patient was first referred for medical evaluation due to concurrent delays in language and motor development. When assessed using the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-Fourth Edition (WISC-IV) at the age of 8, his Full Scale IQ (FSIQ) score was 65, which is indicative of a significant intellectual development disorder. The assessment based on the International Classification of Functioning (ICF) revealed mild impairments in speech and language development.
Patient 2, a 7-year-old female, was born at full-term via cesarean section. Prenatal ultrasound revealed oligohydramnios (amniotic fluid index [AFI] <5 cm). She has a 12-year-old brother with normal development. Her FSIQ score on the WISC-IV was 57. Developmental assessments further indicated overall delays in language, gross motor skills, fine motor skills, and social skills.
In order to evaluate dopaminergic dysfunction, the levels of dopamine and homovanillic acid in cerebrospinal fluid were measured. For Patient 1, the dopamine level in the CSF was 10.5 ng/mL (normal range: 20–30 ng/mL), and the HVA level was 180 ng/mL (normal range: 300–600 ng/mL), indicating a significant reduction in dopaminergic activity. For Patient 2, the dopamine level was 15 ng/mL (normal range: 20–30 ng/mL), and the HVA level was 220 ng/mL (normal range: 300–600 ng/mL), also suggesting dopaminergic dysfunction. Based on these findings, L-DOPA therapy was initiated at 8.5 years for Patient 1 and at 7.75 years for Patient 2, respectively.
The therapeutic regimen strictly adhered to the guidelines for children with dopa-responsive dystonia. The initial dose was set at 0.5 mg/kg per day, divided evenly into four doses, and was gradually increased to 2 mg/kg per day.
After 6 months of continuous treatment, remarkable improvements were observed in the language and motor development of both patients. Moreover, as evaluated by the WISC-IV, the Full Scale IQ of Patient 1 and Patient 2 increased by 10 and 12 points, respectively. Additionally, parental feedback indicated substantial enhancements in the patients’ verbal and physical abilities (Supplementary Video S1).
3.2 Review of reported NR4A2 cases
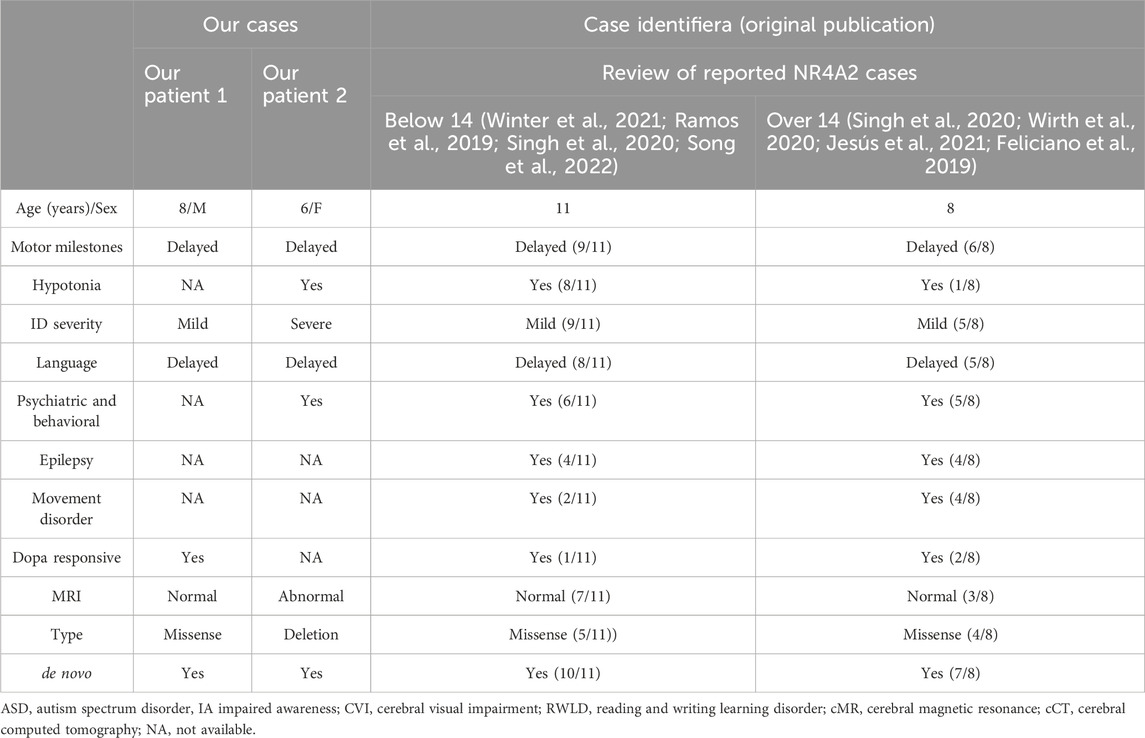
In this study, we performed a systematic review of the pathogenic variants in the NR4A2 gene reported in pediatric patients and collected their detailed clinical information. As of December 2023, a comprehensive literature search of PubMed, Embase, and Web of Science databases identified 10 studies documenting 19 pediatric cases with NR4A2 gene variants, encompassing 21 unique pathogenic variants (Table 1). Among the reported pathogenic variants within the NR4A2 gene, nine were missense variants, six were frameshift variants, two were nonsense variants, and two were splicing variants (see Table 1).
In this study, we conducted an in-depth analysis of three patient cases characterized by suboptimal overall development. Following the administration of dopamine therapy, these patients exhibited notable improvements across multiple metrics (see Table 2).
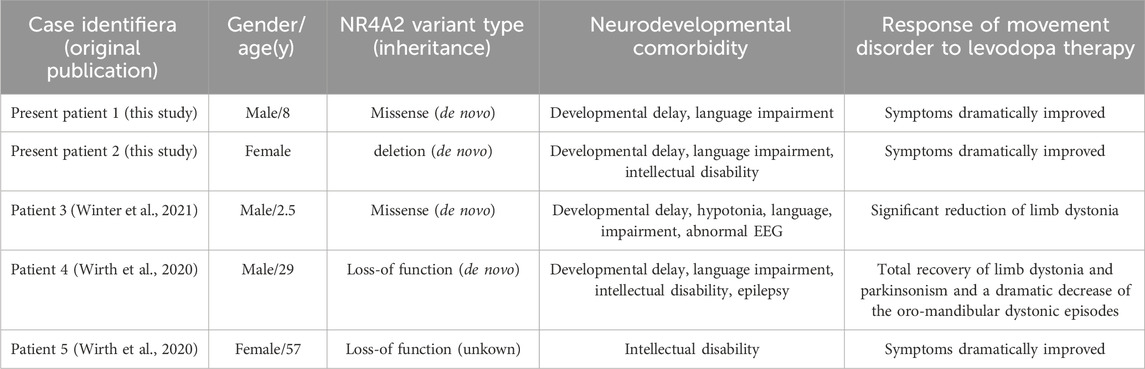
Table 2. Patients with NR4A2 (likely) pathogenic variants and movement disorder symptoms reported to date.
3.3 Identification of genomic variants in NR4A2 gene and aberrant splicing event revealed by RNA-sequencing
Patient 1: Exome sequencing identified a missense variant, c.994G>C (p.Val332Leu) based on the reference sequence NM_006186.4 for the NR4A2 gene. Subsequently, Sanger sequencing was performed on the proband and his parents to validate the variant. The results of Sanger sequencing confirmed the de novo nature of this variant (Figure 1A). It was not observed in population databases (gnomAD, in-house exomes). Significantly, the SpliceAI software was employed to predict the impact of the variant carried by the patient on mRNA splicing. The predictions indicated a high level of deleteriousness, with a score of 0.9 for the c.994G>C variant. Furthermore, an aberrant splicing event associated with the missense variant within the NR4A2 gene was detected by RNA sequencing analysis. This event led to the production of an aberrant transcript characterized by the skipping of exon 4 of the NR4A2 gene (Figure 1B). In line with the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines for the interpretation of genetic variants, this variant was categorized as ‘likely pathogenic’ (PS2+PM2_supporting + PP3).
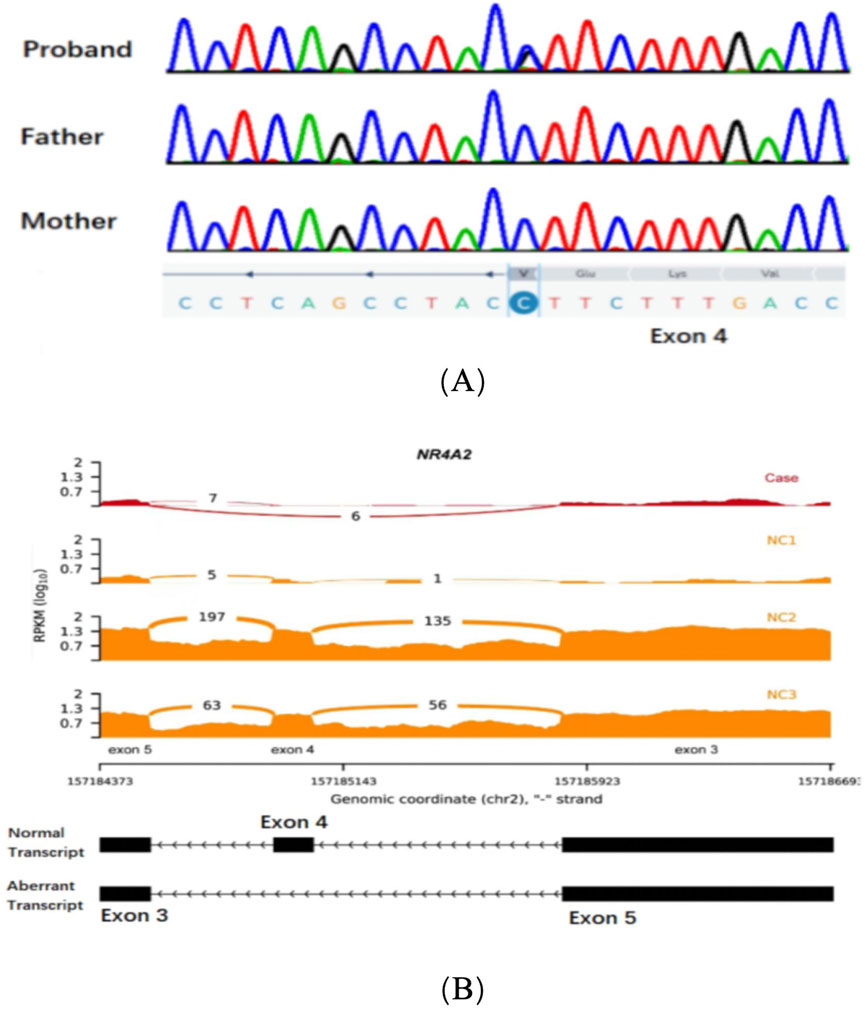
Figure 1. (A) Sanger sequencing chromatograms of exon 4 in the NR4A2 gene for the proband, father, and mother. (B) RNA sequencing data showing NR4A2 exon coverage. The reads per kilobase per million mapped reads (RPKM) values are plotted for three normal controls (NC1, NC2, and NC3) and the case (Case). The case shows an abnormal splicing pattern with a significant additional exon 4 skipping transcript compared to the normal controls.
Patient 2: Copy number analysis based on WES data revealed the presence of a 9.2 Mb deletion, spanning from q23.3 to the q24.2 region on the chromosome 2. According to the ACMG guidelines, this deletion was classified pathogenic. It is worth noting that this deleted region encompasses the haploinsufficient gene NR4A2 (Figure 2).
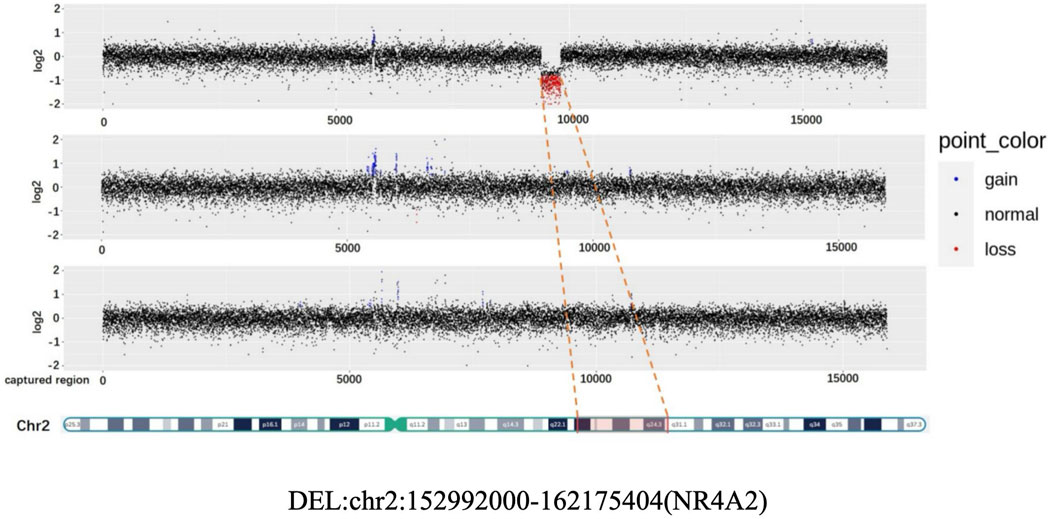
Figure 2. CNV (Copy Number variation) map depicting the deletion in chromosome 2 for the proband, father, and mother.
4 Discussion
In the present study, exome sequencing and genome-wide copy number variation analysis were employed to identify a missense variant and a microdeletion involving the NR4A2 gene in two patients who exhibited global developmental delay and speech deficits. Subsequent RNA sequencing analysis was carried out to decipher the pathogenesis underlying the missense variant. According to metrics in Decipher databases (pHaplo = 0.98, pLI = 1) and clincal cases encompassing only NR4A2 gene published by Lévy J, Grotto Set al (Lévy et al., 2018), NR4A2 haploinsufficiency is associated with related neurological disorders. Thus transcriptional alteration derived from the novel missense variants in our patient supported its haploinsufficiency consequence, while the 9.2 Mb deletion encompassing 2q23.3 to q24.2 will inevitably lead to haploinsufficiency of NR4A2. The results of this analysis demonstrated abnormal splicing of the transcript, thereby shedding light on the molecular mechanism. After a comprehensive and detailed clinical evaluation of both patients, levodopa therapy was administered with the aim of addressing potential alterations in dopamine response. Remarkably, this treatment regimen resulted in substantial improvements in both language development and neurophysiological function.
NR4A2 plays a pivotal role in the development of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons and is therefore implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases linked to the midbrain dopamine system (Larsen et al., 2016). This gene, which is actively expressed during embryogenesis, plays a critical role not only in the early differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons but also in the long-term maintenance of these neurons throughout adulthood. Genetic variants within this gene have been reported in patients suffering from intellectual developmental disorder characterized by language impairment, as well as early - onset DOPA - responsive dystonia - parkinsonism.
Dysfunction of the NR4A2 gene has been linked to a wide range of disorders associated with dopaminergic impairment, encompassing Parkinson’s disease (PD), schizophrenia, and manic depression (Bannon et al., 2002). In PD, the progressive degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra leads to a significant reduction in dopamine synthesis and release (Surmeier et al., 2017). This dopaminergic deficit is a key pathological feature of the disease and contributes to the characteristic motor and non-motor symptoms observed in PD patients. The dopaminergic system’s dysregulation affects the basal ganglia circuitry, disrupting the balance between direct and indirect pathways (Gerfen and Surmeier, 2011). L-DOPA, a well-recognized dopamine precursor, is capable of efficiently alleviating symptoms by restoring dopamine levels. Its efficacy has been demonstrated across a variety of diseases related with altered dopa-responsiveness (Chase, 1998).
Therefore, we have summarized here the clinical characteristics based on a total of 19 cases (Table 1). At the last clinical assessment, patient ages ranged from 2 to 32 years. No abnormalities in prenatal or perinatal history were detected in any case; growth parameters were normal. Developmental delay and/or intellectual disability was the characteristic shared by all the patients, ranging from mild to severe. Language disorder was the second most frequent, being reported in 14 patients. In one case, expressive language was absent at 6 years (Shimojima et al., 2017), while in eight patients, a moderate to severe disorder of the expressive and receptive language was noted; information on this issue was unavailable in five cases. Learning disabilities were reported in six cases, most frequently related to the acquisition of reading and writing. Neuropsychiatric issues were described in 10 patients and included aggressive behavior, anxiety, ADHD, and autism. In terms of motor development, delays were observed in nine cases, along with reports of hypotonia. Nevertheless, there were no reports of any patients being unable to achieve independent walking. In one particular case, the patient was only able to walk independently after receiving treatment with L-dopa (Winter et al., 2021).
Movement disorders were reported in seven patients. Among them, symptoms manifested during childhood in only one case, with the most common onset period occurring between late adolescence and young adulthood. The reported phenotypes included adult-onset dystonia-parkinsonism (3/19), isolated dystonia (2/19), dystonia accompanied by chorea (1/19), ataxia associated with motor tics (1 out of 19), and isolated ataxia (1/19). It is noteworthy to mention the evolutionary nature of the semiology depicted in certain of these cases. The symptoms may initiate as tics, progress to focal dystonia, and subsequently develop into dystonia-parkinsonism (Albanese et al., 2013). In one particular case, focal dystonia in the form of oculogyric crises emerged during the course of treatment with olanzapine, a dopaminergic antagonist (Haggstrom et al., 2017; Friedman, 2016). This occurrence could potentially be attributed to an augmented susceptibility to extrapyramidal symptoms associated with the utilization of such drugs. Epilepsy is also a frequent sign, reported in 42% (8/19) patients. Almost half of the patients present epilepsy, which may initiate at any age and in a diverse semiology, accompanied by the aforementioned complex and in many occasions severe neurodevelopmental disorder.
After detecting the missense variant in the NR4A2 gene through WES, according to the ACMG variant classification guidelines, were categorized as variants of Variant of Uncertain Significance (VUS). However, considering the highly concordant disease phenotype caused by this gene with the patient’s current phenotype, the variant was still considered as potential genetic etiologies. Combining the predictive results of from SpliceAI software does not rule out the possibility of this rare variants affecting mRNA splicing. The peripheral blood sample was collected as an actionable sample for RNA sequencing, given that the expression of the NR4A2 gene was regarded as abundant. Subsequently, via RNA sequencing analysis, it was successfully determined that this rare variant directly influenced splicing, ultimately leading to an outcome analogous to that of loss-of-function variants. The variant’s pathogenicity classification was reclassified from VUS to LP following RNA-seq validation of aberrant splicing patterns, aligning with ACMG guidelines for functional evidence integration. Complementary to DNA sequencing, RNA-seq has recently been utilized to detect abnormalities in the transcriptome, such as aberrant expression, splicing, and monoallelic gene expression (MAE), thereby increasing the molecular diagnostic yield by approximately 7.5%–36% (Li et al., 2024). RNA-seq can effectively detect abnormal splicing and related variations, which can help improve the diagnosis rate of most previously undiagnosed neuromuscular diseases (Cummings et al., 2017).
Congenital dopa-responsive disorders are a group of heterogeneous conditions. Their hallmark is the alleviation of clinical symptoms upon the administration of levodopa and/or dopaminergic agents. Among the reported patients with NR4A2 variants, levodopa was prescribed to three of them for symptom management. Patient 1 presented at the age of 29 with early-onset dystonia-parkinsonism, intellectual disability (ID), and epilepsy. When his intelligence quotient was assessed at 37 years old, it was found to be 56. Levodopa treatment led to a complete recovery from limb dystonia and parkinsonism, along with a remarkable reduction in oro-mandibular dystonic episodes. Throughout the course of the disease, the daily levodopa doses required to control his symptoms gradually increased (Friedman, 2016). Patient 2 was referred at the age of 57 for a genetic diagnosis due to a phenotype characterized by a combination of dystonia, parkinsonism, and mild intellectual disability (ID). After commencing a dopaminergic treatment regimen that combined levodopa/carbidopa and bromocriptine, these symptoms showed a dramatic improvement. The third patient was a boy of German descent who presented with global developmental delay and limb dystonia that onset in infancy. When administered levodopa at a dosage of 75 mg per day, the child experienced a substantial reduction in involuntary movements. During the period when he continued to receive levodopa treatment, a trend towards accelerated motor development was noted (Friedman, 2016).
In our case, after comprehensively evaluating the severity of the patient’s clinical manifestations and the parents’ treatment preferences, we measured the levels of dopamine and homovanillic acid in the patient’s cerebrospinal fluid to assess dopamine responsiveness. Since the initiation of levodopa therapy, we have regularly monitored the patient’s intellectual function and language ability. After 6 months of treatment, the assessment revealed a five - point increase in the patient’s overall intelligence quotient. Additionally, parental reports indicated remarkable improvements in the child’s language skills and physical capabilities. Therefore, for children with similar genetic variants, when there is significant dopamine responsiveness impairment, levodopa treatment may be a viable option. However, the dosage, regimen, expected response and need for additional treatment depend on the underlying aetiology, disease severity, and adverse effects (Connolly and Lang, 2014; Hechtner et al., 2014; Gc et al., 1969; Warren Ola et al., 2013). Treatment must be tailored to the individual in collaboration with a doctor with experience in the field. The recommended starting dose of levodopa is 0.5–1 mg/kg/day. If no response is seen but the diagnosis is still suspected, the dose should be gradually increased (Connolly and Lang, 2014; Hechtner et al., 2014; Gc et al., 1969; Warren Ola et al., 2013; Willemsen et al., 2010; Echenne et al., 2006).
In conclusion, through the combined application of whole - exome sequencing and RNA sequencing, we precisely diagnosed two children carrying NR4A2 gene variants. Moreover, we pinpointed abnormal splicing transcripts as the underlying pathogenic mechanism. Following a comprehensive clinical assessment of the patients, a trial treatment with levodopa led to substantial enhancements in their overall intellectual development and language proficiency. Our experience in diagnosing and treating these cases serves as a significant addition to the existing knowledge of dopa-responsive diseases. It also offers valuable insights for the diagnosis and treatment of related neurological disorders.
Our study has several notable limitations. Enrolling only two patients significantly compromised the statistical power and generalizability of the findings for this disease cohort. Although preliminary observations of treatment response were made, large-scale multicenter cohort studies are urgently needed to validate therapeutic efficacy and elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms. Current assessments of neurologic function recovery predominantly based on parental reports and subjective scales should be supplemented with long-term objective metrics (e.g., quantitative motor testing or neuroimaging biomarkers). A standardized long-term follow-up protocol integrating serial clinical evaluations is planned to monitor treatment durability and disease progression, with a specific focus on incorporating longitudinal data to refine prognostic models.
Data availability statement
All data analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author (YD) on reasonable request.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the Taiyuan Maternal and Child Healthcare Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
NL: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Writing – review and editing. TL: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YD: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Project administration, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Shanxi Provincial Health Commission (grant 2024189).
Acknowledgments
We would like to extend our sincere gratitude to the two patients and their families for their invaluable cooperation. We also wish to acknowledge the assistance provided by Yao Ruen.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2025.1590292/full#supplementary-material
References
Albanese, A., Bhatia, K., Bressman, S. B., Delong, M. R., Fahn, S., Fung, V. S. C., et al. (2013). Phenomenology and classification of dystonia: a consensus update. Mov. Disord. 28 (7), 863–873. doi:10.1002/mds.25475
Bannon, M. J., Pruetz, B., Manning-Bog, A. B., Whitty, C. J., Michelhaugh, S. K., Sacchetti, P., et al. (2002). Decreased expression of the transcription factor NURR1 in dopamine neurons of cocaine abusers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99 (9), 6382–6385. doi:10.1073/pnas.092654299
Buervenich, S., Carmine, A., Arvidsson, M., Xiang, F., Zhang, Z., Sydow, O., et al. (2000). NURR1 mutations in cases of schizophrenia and manic-depressive disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. 96 (6), 808–813. doi:10.1002/1096-8628(20001204)96:6<808::aid-ajmg23>3.0.co;2-e
Chase, T. N. (1998). The significance of continuous dopaminergic stimulation in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Drugs 55 (Supplement 1), 1-9. doi:10.2165/00003495-199855001-00001
Connolly, B. S., and Lang, A. E. (2014). Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 311, 1670–1683. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.3654
Cummings, B. B., Marshall, J. L., Tukiainen, T., Lek, M., Donkervoort, S., Foley, A. R., et al. (2017). Improving genetic diagnosis in Mendelian disease with transcriptome sequencing. Sci. Transl. Med. 9 (386), eaal5209. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal5209
Echenne, B., Roubertie, A., Assmann, B., Lutz, T., Penzien, J. M., Thöny, B., et al. (2006). Sepiapterin reductase deficiency: clinical presentation and evaluation of long-term therapy. Pediatr. Neurol. 35, 308–313. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2006.05.006
Feliciano, P., Zhou, X., Astrovskaya, I., Turner, T. N., Wang, T., Brueggeman, L., et al. (2019). Exome sequencing of 457 autism families recruited online provides evidence for autism risk genes. Med 4, 19. doi:10.1038/s41525-019-0093-8
Friedman, J. R. (2016). What is not in the name? Dopa-responsive dystonia may respond to more than L-dopa. Pediatr. Neurol. 59, 76–80. doi:10.1016/j.pediatrneurol.2015.12.016
Gabaldon-Albero, A., Mayo, S., and Martinez, F. (2024). NR4A2 as a novel target gene for developmental and epileptic encephalopathy: a systematic review of related disorders and therapeutic strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (10), 5198. doi:10.3390/ijms25105198
Gc, C., Papavasiliou, P. S., and Gellene, R. (1969). Modification of parkinsonism-chronic treatment with L-dopa. N. Engl. J. Med. 280, 337–345. doi:10.1056/nejm196902132800701
Gerfen, C. R., and Surmeier, D. J. (2011). Modulation of striatal projection systems by dopamine. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 34 (1), 441–466. doi:10.1146/annurev-neuro-061010-113641
Haggstrom, L., Darveniza, P., and Tisch, S. (2017). Mild parkinsonian features in dystonia: literature review, mechanisms and clinical perspectives. Park. Relat. Disord. 35, 1–7. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.10.022
Hechtner, M. C., Vogt, T., Zöllner, Y., Schröder, S., Sauer, J. B., Binder, H., et al. (2014). Quality of life in Parkinson's disease patients with motor fluctuations and dyskinesias in five European countries. Park. and Relat. Disord. 20 (9), 969–974. doi:10.1016/j.parkreldis.2014.06.001
Jesús, S., Hinarejos, I., Carrillo, F., Martínez-Rubio, D., Macías-García, D., Sánchez-Monteagudo, A., et al. (2021). NR4A2 mutations can cause intellectual disability and language impairment with persistent dystonia-parkinsonism. Neurol. Genet. 7, e543. doi:10.1212/NXG.0000000000000543
Larsen, K., Momeni, J., Farajzadeh, L., Callesen, H., and Bendixen, C. (2016). Molecular characterization and analysis of the porcine NURR1 gene. Biochim. Open 3, 26–39. doi:10.1016/j.biopen.2016.07.001
Le, W., Xu, P., Jankovic, J., Jiang, H., Appel, S. H., Smith, R. G., et al. (2003). Mutations in NR4A2 associated with familial Parkinson disease. Nat. Genet. 33 (1), 85–89. doi:10.1038/ng1066
Lévy, J., Grotto, S., Mignot, C., Maruani, A., Delahaye-Duriez, A., Benzacken, B., et al. (2018). NR4A2 haploinsufficiency is associated with intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorder. Clin. Genet. 94 (2), 264–268. doi:10.1111/cge.13383
Li, S., Zhao, S., Sinson, J. C., Bajic, A., Rosenfeld, J. A., Neeley, M. B., et al. (2024). The clinical utility and diagnostic implementation of human subject cell transdifferentiation followed by RNA sequencing. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 111 (5), 841–862. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.03.007
Ramos, L. L. P., Monteiro, F. P., Sampaio, L. P. B., Costa, L. A., Ribeiro, M. D. O., Freitas, E. L., et al. (2019). Heterozygous loss of function of NR4A2 is associated with intellectual deficiency, Rolandic epilepsy, and language impairment. Clin. Case Rep. 7, 1582–1584. doi:10.1002/ccr3.2260
Reuter, M. S., Krumbiegel, M., Schlüter, G., Ekici, A. B., Reis, A., and Zweier, C. (2017). Haploinsufficiency of NR4A2 is associated with a neurodevelopmental phenotype with prominent language impairment. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 173 (8), 2231–2234. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.38288
Shimojima, K., Okamoto, N., and Yamamoto, T. (2017). Possible genes responsible for developmental delay observed in patients with rare 2q23q24 microdeletion syndrome: literature review and description of an additional patient. Congenit. Anom. Kyoto 57, 109–113. doi:10.1111/cga.12205
Singh, S., Gupta, A., Zech, M., Sigafoos, A. N., Clark, K. J., Dincer, Y., et al. (2020). De novo variants of NR4A2 are associated with neurodevelopmental disorder and epilepsy. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 22, 1413–1417. doi:10.1038/s41436-020-0815-4
Song, X., Xu, W., Xiao, M., Lu, Y., Lan, X., Tang, X., et al. (2022). Two novel heterozygous truncating variants in NR4A2 identified in patients with neurodevelopmental disorder and brief literature review. Front. Neurosci. 16, 956429. doi:10.3389/fnins.2022.956429
Surmeier, D., Obeso, J., and Halliday, G. (2017). Selective neuronal vulnerability in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 18, 101–113. doi:10.1038/nrn.2016.178
Warren Olanow, C., Kieburtz, K., Rascol, O., Poewe, W., Schapira, A. H., Emre, M., et al. (2013). Factors predictive of the development of Levodopa-induced dyskinesia and wearing-off in Parkinson's disease. Mov. Disord. 28 (8), 1064–1071. doi:10.1002/mds.25364
Willemsen, M. A., Verbeek, M. M., Kamsteeg, E. J., de Rijk-van Andel, J. F., Aeby, A., Blau, N., et al. (2010). Tyrosine hydroxylase deficiency: a treatable disorder of brain catecholamine biosynthesis. Brain 133, 1810–1822. doi:10.1093/brain/awq087
Winter, B., Krämer, J., Meinhardt, T., Berner, D., Alt, K., Wenzel, M., et al. (2021). NR4A2 and dystonia with dopa responsiveness. Mov. Disord. 36, 2203–2204. doi:10.1002/mds.28701
Keywords: NR4A2 gene, intellectual developmental disorder, dopa-responsive dystonia-parkinsonism, whole-exome sequencing, RNA sequencing, L-DOPA treatment
Citation: Liang N, Li T and Deng Y (2025) Combined molecular characterization and dopa-responsive treatment in two patients with NR4A2-associated intellectual developmental disorder. Front. Genet. 16:1590292. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1590292
Received: 09 March 2025; Accepted: 28 August 2025;
Published: 11 September 2025.
Edited by:
Alessandro Fiorenzano, Lund University, SwedenReviewed by:
Kartik Singhai, National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences (NIMHANS), IndiaSheng Luo, The Second Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liang, Li and Deng. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Deng, ZGVuZ3lhbmcwNzE3QDE2My5jb20=
 Na Liang
Na Liang Ting Li
Ting Li