- 1Puai Medical College, Shaoyang University, Shaoyang, China
- 2Department of Nephrology and Rheumatism Immunity, The First Affiliated Hospital of Hunan University of Medicine, Huaihua, China
Amino acid transporters (AATs) allow the transport of amino acids and play important roles in the various physiological processes and environmental responses of plants. The lysine and histidine transporter (LHT) subfamily is an important type of AAT. However, a genome-wide overview of the LHT gene family has not been conducted in L. macranthoides Hand.-mazz. In this study, 11 LHT genes were identified in the Lonicera macranthoides genome. To further understand the functions of LmLHT genes, the gene and protein characteristics, transmembrane helices, evolutionary relationships, chromosomal distribution, cis-acting elements of promoters, and expression patterns were systematically analyzed. According to the results, LmLHT genes were divided into two groups based on the phylogenetic analysis. Transmembrane helices of LmLHT proteins ranged from seven to 16. Gene structure and conserved motif analysis revealed that exon-intron structures and motifs were relatively conserved in the LmLHT family. LmLHT genes were distributed on six of the nine chromosomes and had the most collinear gene pairs with NtLHT genes. Additionally, phytohormones, low-temperature, drought-inducibility, defense and stress related cis-acting elements were enriched in the promoters of LmLHT genes. LmLHT genes showed distinct or preferential expression patterns in various tissues, signifying their potential roles in plant growth and development. We also found that some LmLHT genes were responsive to cold and drought stresses, indicating their roles in abiotic stress adaptation. Overall, our results provided comprehensive insight into the LmLHT gene family and will be useful for future functional analyses.
Introduction
Nitrogen (N) is the major nutrient factor for plant growth and development, and plants can absorb and utilize inorganic and organic N in soil. Organic N includes amino acids, peptides and proteins (Cai and Aharoni, 2022). Approximately 40% of organic N in soil comprises peptides and proteins, and 45%–50% of soil organic N comprises amino acids (Cao et al., 2016). The concentrations of total amino acids in soil may be as high as 150 μmol/L (Weigelt et al., 2005). Amino acids and their derivatives not only participate in N fluxes both in poor and fertile soils, but also play an important role in the N cycle in plant organs (Inselsbacher and Näsholm, 2012). For plants, amino acids are essential for the activities of enzymes and proteins. Moreover, amino acids are important components of chlorophyll, polyamines, phytohormones, creatinine and nucleotides (Dong et al., 2020; Yahyaoui and Pérez-Frías, 2020). Therefore, these acids play important roles in the entire life cycle of plants, including regulating the defense response and N utilization efficiency, affecting the quality and biomass, changing the root or shoot morphology, and act as precursors of secondary metabolites (Perchlik and Tegeder, 2017; Guo et al., 2020b; Guo et al., 2021).
Generally, proteins and peptides in organic N cannot be directly absorbed by plant roots, while amino acids can be obtained by roots and transported to shoots or leaves through xylem and phloem (Näsholm et al., 2009; Tegeder and Masclaux-Daubresse, 2018). As the level of amino acids in the soil is significantly lower than that of root cells, membrane localized amino acid transporters (AATs) are necessary for the uptake of amino acids from soil (Tegeder, 2014). Currently, plant AATs are divided into three main families: the amino acid/auxin permease (AAAP) family, the amino acid polyamine and choline (APC) transporter family, and the usually multiple amino acids move in and out transporter (UMAMIT) family (Cao et al., 2024). The AAAP family contains eight subfamilies: proline transporters (ProTs), amino acid permeases (AAPs), auxin transporters (AUXs), lysine and histidine transporters (LHTs), aromatic and neutral amino-acid transporters (ANTs), γ-aminobutyric acid transporters (GATs), amino acid transporter-like proteins (ATLs), and vesicular aminergic-associated transporters (VATs) (Yang et al., 2020). The APC family contains three subfamilies: cationic amino acid transporters (CATs), L-type amino acid transporters (LATs), and polyamine H+-symporters (PHSs) (Saha and Gupta, 2022; Du et al., 2024). Among these families, AAP, LHT, and ProT are the most studied AATs in plants (Fan et al., 2023).
AtAAP1 was the first identified amino acid transporter in plants and mediates the transport of neutral and charged amino acids (Perchlik et al., 2014). Overexpression of AtAAP1 significantly increases the transport of chlorantraniliprole–alanine conjugate (Ren et al., 2019). AtAAP2 functions in the long distance transfer of amino acids, and the growth and development of leaves are enhanced in the atapp2 mutant, which in turn increases seed yield and oil content (Elashry et al., 2013). AtAAP3 is mainly expressed in the roots and can transport basic amino acids, such as lysine, histidine, and arginine (Okumoto et al., 2004). The root-knot nematode (RKN) infestation levels and egg mass number in the atapp3 mutant were notably decreased, indicating that AtAAP3 may act as a positive regulator for plants against RKN invasion (Marella et al., 2012). In total, 19 OsAAP genes have been identified in the rice genome. OsAAP1 is located in plasma and nuclear membranes, its overexpression increases tiller numbers and fills grains, while the osaap1 mutant presents the opposite phenotype (Ji et al., 2020). Lysine and arginine can be transported by OsAAP3, overexpression of OsAAP3 increases the accumulation of these amino acids, but reduces the number of tillers and fills grains in transgenic plants (Wei et al., 2021). OsAAP12 is located in the plasma membrane, the number of tillers is decreased in OsAAP12 overexpression plants but increased in osaap12 mutant lines (Jin et al., 2024).
AtLHT1 was the first identified transporter of the lysine and histidine transporter family. AtLHT1 exhibits high expression in roots, flowers, and siliques. Overexpression of AtLHT1 improves N efficiency and promotes plant growth, whereas disruption of AtLHT1 affects amino acid uptake and inhibits plant growth (Hirner et al., 2006). In addition, AtLHT1 is associated with the transport of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid, an important precursor of ethylene (Shin et al., 2015). AtLHT4 has strong expression in anthers, which suggests that AtLHT4 may be involved in anther and pollen development (Rabby et al., 2022). There are six OsLHT genes (OsLHT1-OsLHT6) in the rice genome, and the most studied member is OsLHT1. OsLHT1 is strictly located in the plasma membrane and participates in the transport of Asparagine (Guo et al., 2020b). Knockout of OsLHT1 decreases the concentration of amino acid in xylem sap, and the translocation of amino acid in the shoot is restricted, resulting in reduced plant height, stem length, and grain yield (Guo et al., 2020a). Notably, loss of function of OsLHT1 increases the expression of defense-responsive genes and produces more salicylic acid and jasmonic acid. Therefore, rice blast disease resistance is improved in OsLHT1 mutants (Guo et al., 2023). OsLHT5 was localized in the cytosol and plasma membrane. The expression of OsLHT5 was downregulated when treated with PEG and NaCl, which suggests that OsLHT5 may play a role in abiotic stress response in rice (Fan et al., 2023). There were 23 NtLHT genes (NtLHT1-NtLHT23) in tobacco, and the overexpression of NtLHT1 accelerated leaf senescence and affected leaf morphology. Moreover, the expression of NtLHT1 was increased under abiotic stress, and the germination rate in NtLHT1-overexpressing plants was significantly higher than in ntlht1 mutants, which suggests that NtLHT1 may be involved in abiotic stress tolerance in tobacco (Xing et al., 2024). NtLHT22 was localized in the plasma membrane. The amino acid content was significantly altered in NtLHT22-overexpressing plants and ntlht22 mutants, which implies that NtLHT22 participates in amino acid homeostasis in tobacco (Li Z. et al., 2022).
Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-Mazz. is a species of the Caprifoliaceae family, also known as “shanyinhua” or “mountain honeysuckle” (Liu et al., 2024). It is widely planted in Southwestern China, including Hunan Province, Guizhou Province, and Chongqing City. The fresh and dried flower buds of Lonicera macranthoides are used as important ingredients in traditional Chinese medicine to treat and prevent fever, furuncles, inflammation, and cardiovascular diseases (Pan et al., 2021). The LHT gene family is important for plant growth, development, and quality. In this study, we have systematically and comprehensively identified the LHT gene family in L. macranthoides. The physicochemical characteristics, phylogenetic evolutions, gene architecture, chromosomal localization, gene collinearity, and cis-acting elements in the LmLHT gene family were analyzed. Additionally, the expression patterns of LmLHT genes in different tissues and abiotic stresses were examined using quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR). Our research provides useful insights for future functional analysis of LmLHT.
Materials and methods
Plant materials
L. macranthoides Hand.-mazz plants were cultured in a greenhouse with a cycle of 16 h of light, 8 h of darkness, 22°C–24 °C. Different tissues (root, stem, leaf, white flower, and yellow flower) were collected at 6 months to analyze the expression of LmLHT. For cold stress treatment, four-week-old seedlings were exposed in a growth chamber at 4 °C for 5 h. For drought stress treatment, four-week-old seedlings were not watered until the leaves were completely wilted (Xie et al., 2021). The leaves of six sample plants were mixed, frozen with liquid nitrogen and then stored at −80 °C for future use.
Identification of LmLHT gene family
The AtLHT genes retrieved from TAIR (http://www.arabidopsis.org) were used as a query to search in the L. macranthoides genome with an E-value cutoff ≤0.01 (Rhee et al., 2003; Yin et al., 2023). Subsequently, the Hidden Markov Model profile of the LHT domain (PF01490) was obtained from the Pfam database, and the candidate LmLHT protein sequences were confirmed on the Conserved Domain Database (CDD) of the NCBI (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/) (Sonnhammer et al., 1997; Marchler-Bauer et al., 2015). The identified LmLHT protein sequences were renamed according to their chromosomal locations. Moreover, the basic information and chemical parameters of the LmLHT proteins were analyzed with the online tool ExPASy (http://web.expasy.org/protparam/).
Transmembrane, protein structure and phylogenetic analysis
The transmembrane domain and protein structure of the LmLHTs were analyzed with the online tool PROTTER (http://wlab.ethz.ch/protter/start/) and PHYRE server v2.0 (http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index), respectively. The protein sequences of 11 LmLHTs, 6 OsLHTs, 10 AtLHTs, and 23 NtLHTs were aligned using ClustalX software (version 2.1). Subsequently, a neighbor-joining (NJ) phylogenetic tree was built using MEGA X software (version 10.1.8) with 2000 bootstraps.
Gene structure and conserved motif analysis
The coding sequence and genomic sequence of each LmLHT genes were submitted to the GSDS tool (http://gsds.cbi.pku.edu.cn) to analyze the gene structure. The conserved motifs of the LmLHT proteins were identified using the MEME tool (http://meme-suite.org/tools/meme).
Chromosomal distribution and collinearity analysis
The chromosomal distribution of the LmLHT genes was mapped and annotated using the MG2C tool (http://mg2c.iask.in/mg2c_v2.0/). Collinear gene pairs between L. macranthoides, tobacco, rice, and Arabidopsis were investigated with the MCScanX tool (Wang et al., 2012). Subsequently, the results were drawn using Circos (Krzywinski et al., 2009).
Promoter analysis of LmLHT genes
The promoter sequences about 2,000 bp upstream of the start site of the LmLHT genes were obtained from the L. macranthoides genome (Yin et al., 2023), and the obtained sequences were submitted to PlantCARE (http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/webtools/plantcare/html/) to analyze the cis-regulatory elements, and the results were displayed using TBtools (Chen et al., 2020).
Total RNA isolation and qRT-PCR
Total RNA was isolated from frozen samples with a FastPure Plant RNA Isolate Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). The quality of total RNA was detected using NanoDrop One (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). The first strand cDNA was generated from 1 μg of total RNA with a cDNA Synthesis Kit (Vazyme, Nanjing, China). qRT-PCR was carried out using an ABI QuantStudio 3 system with SYBR Green (TIANGEN, Beijing, China), and PCR reactions were 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 56 °C for 30 s. The 18S rRNA gene was adopted as the internal control, and the gene expression level was analyzed using the 2−ΔΔCT method (Schmittgen and Livak, 2008; Chen et al., 2023). The primers used for qRT-PCR are provided in Supplementary Table S1.
Results
Genome-wide identification and basic information analysis of LmLHT
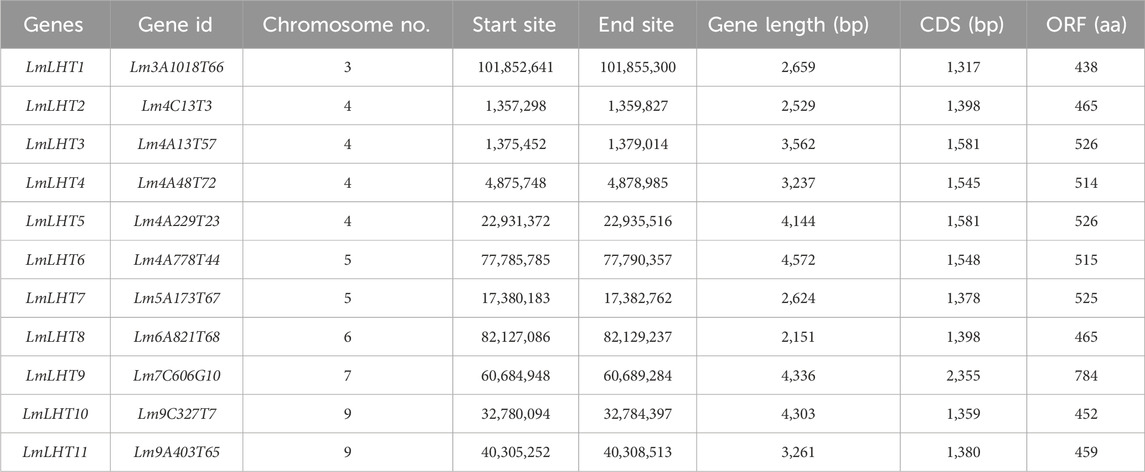
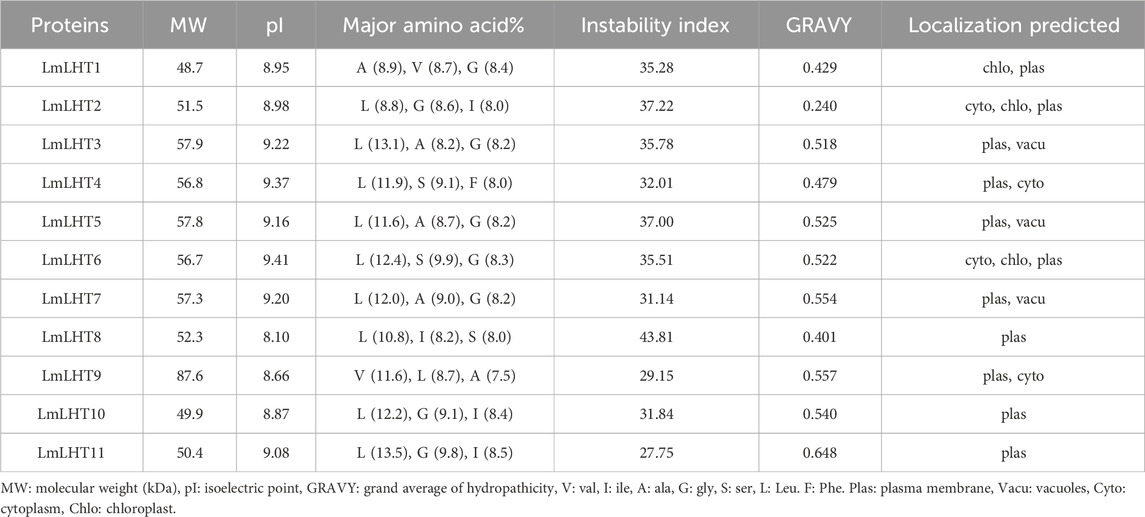
In this study, Arabidopsis LHT proteins retrieved from TAIR were used to identify candidate LHT genes in L. macranthoides. As a result, 11 LHT genes were identified in the L. macranthoides genome. To facilitate further research, we renamed the LmLHT genes from LmLHT1 to LmLHT11 in the order of their physical chromosome locations. The genomic and coding sequences of the LmLHTs varied from 2,151 to 4,336 bp and 1,317 to 2,355 bp, respectively. The protein length of the LmLHTs varied from 438 aa to 784 aa (Table 1). Their deduced molecular weight varied from 48.7 to 87.6 kDa, and their isoelectric point varied from 8.10 to 9.41. The major amino acids in the LmLHT proteins were leucine, glycine, and alanine, and most LmLHT proteins (except LmLHT8) were stable (instability index <40). The GRAVY values indicated that all of the LmLHT proteins were hydrophobic (GRAVY index >0). Furthermore, most of the proteins were localized in the plasma membrane (Table 2).
We also analyzed the transmembrane regions of the LmLHT proteins with the online tool PROTTER. These proteins contained 7 to 16 transmembrane domains, and most of them (91%) varied from 7 to 11 (Supplementary Figure S1). Protein structure analysis indicated that the LmLHT proteins were composed of α helices, β turns, random coils, and extended strands and had similar structures. Among these structures, α helices were the most abundant, while β turns were uncommon (Supplementary Figure S2).
Evolutionary relationship of LHT genes in Lonicera macranthoides, tobacco, rice, and arabidopsis
To explore the evolutionary relationships of the LHT gene family in L. macranthoides, tobacco, rice, and Arabidopsis, a phylogenetic tree was constructed with the neighbor-joining method for 11 LHT proteins from L. macranthoides, 23 LHT proteins from tobacco, 6 LHT proteins from rice, and 10 LHT proteins from Arabidopsis. As shown in Figure 1, the LHT proteins were classified into two subfamilies, which was consistent with the results of a previous study (Wang et al., 2019). Subfamily Ⅰ contained 8 LmLHT members (LmLHT2/5/6/7/8/9/10/11), 13 NtLHT members (NtLHT3/5/6/7/11/12/13/15/16/17/18/22/23), 2 OsLHT members (OsLHT3/5), and 4 AtLHT members (AtLHT2/5/7/10). Subfamily II contained 3 LmLHT members (LmLHT1/3/4), 10 NtLHT members (NtLHT1/2/4/8/9/10/14/19/20/21), 4 OsLHT members (OsLHT1/2/4/6), and 6 AtLHT members (AtLHT1/3/4/6/8/9). These results indicated that subfamily I contained more LmLHT members than subfamily II, and the members in the same subfamily may have closer evolutionary relationships.
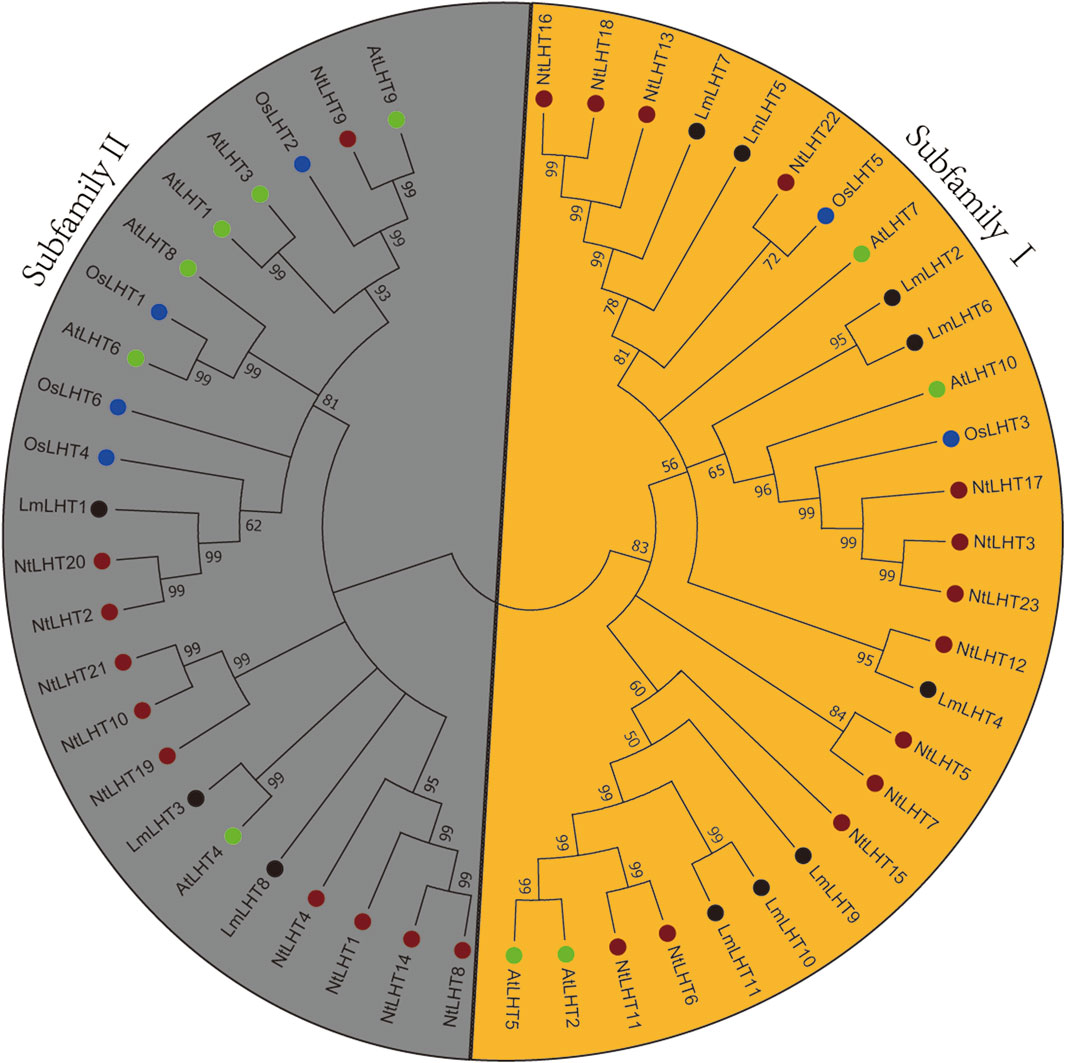
Figure 1. Phylogenetic analysis of LHT proteins in Lonicera macranthoides, tobacco, rice and Arabidopsis. The tree divides 11 LHT proteins from Lonicera macranthoides, 23 LHT proteins from tobacco, 6 LHT proteins from rice, and 10 LHT proteins from Arabidopsis into two subgroups. Black, red, blue, and green colors represent Lonicera macranthoides, tobacco, rice and Arabidopsis, respectively.
Gene structure and motif analysis of LmLHT family members
To better understand the evolution of LmLHT family members, a neighbor-joining tree was reconstructed between the LmLHT genes. The LmLHT genes were divided into two subfamilies; these results are consistent with previous research on tobacco (Li Z. et al., 2022). The gene structure and protein motifs could also provide evolutionary information. Gene structure analysis showed that all of the LmLHT genes had five exons and four introns, with the exception of LmLHT1, which had eight exons and seven introns. Furthermore, we performed a conserved motif analysis of the LmLHT proteins with MEME. It was observed that LmLHT3/4/5/6/7 contained 14 motifs, excluding motif 15, which we found to exist only in LmLHT8/9/10/11. In addition, LmLHT2 only had nine conserved motifs, which is less than the other LmLHT members, implying that some motifs were lost or degenerated during the process of evolution. It is worth noting that although LmLHT1 has the largest number of exons, it does not contain the largest number of conserved motifs. Therefore, the increased exons in LmLHT1 may act as regulatory exons rather than encoding protein motifs (Figure 2; Supplementary Figure S3). These results suggested that the conserved motifs in LmLHT family members may have undergone loss or gain during evolution.
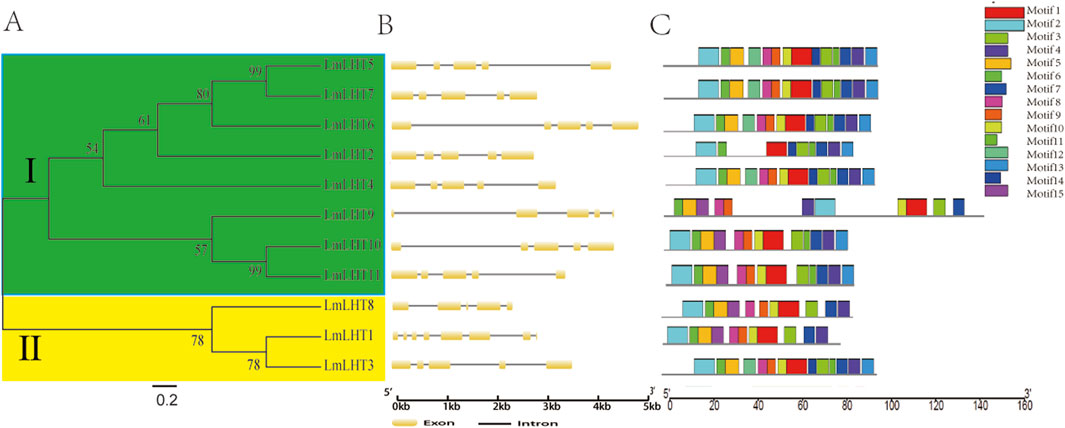
Figure 2. Evolutionary relationship, gene structure and motif analysis of LmLHT family members. (A) The phylogenetic tree was built from LmLHT proteins. The LmLHT protein sequences were divided into two subfamilies: green and yellow colors indicate subfamily Ⅰ and subfamily Ⅱ, respectively. (B) Exon–intron organization of LmLHT genes. Brown boxes represent exons, and block lines represent introns. (C) Conserved motifs of LmLHT proteins. The motifs are displayed in different colored boxes.
Chromosomal distribution and collinear analysis of LmLHT genes
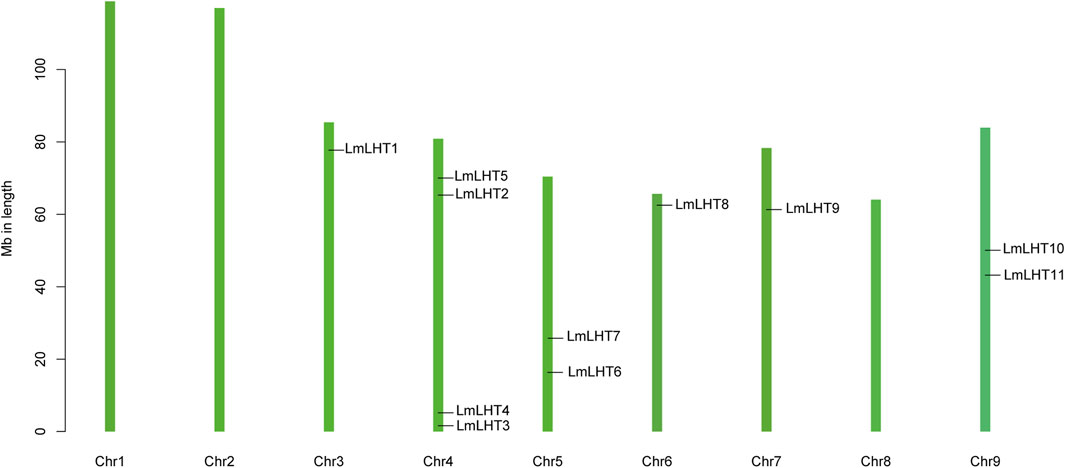
The localization of the LmLHT genes on chromosomes was identified, and it was found that they were randomly distributed on six out of nine chromosomes. Chromosome 4 contained four LmLHT genes, and chromosomes 5 and 9 contained two LmLHT genes. Only a single LmLHT gene was distributed on each of chromosomes 3, 6, and 7 (Figure 3).
Previous studies indicated that tandem, segmental, transposition, and whole genome duplication play an important role in gene duplication events (Zhang et al., 2020; Li H. et al., 2022). As shown in Figure 4, two genes (LmLHT3 and LmLHT4) were tandemly duplicated on chromosome 4, and one gene pairs (LmLHT8 and LmLHT9) was likely segmentally duplicated. These results suggested that tandem and segmental duplication play a crucial role in the expansion of the LmLHT gene family. To further investigate the evolutionary relationship between LHT genes, we conducted a collinearity analysis for L. macranthoides, tobacco, rice, and Arabidopsis. Collinear gene pairs between 12 of the LmLHT genes with LHT genes in tobacco were identified, followed by 6 LmLHT gene pairs with Arabidopsis, and 2 LmLHT gene pairs with rice. In addition, most collinear relationships between these species were one-to-one matches (Figure 4).
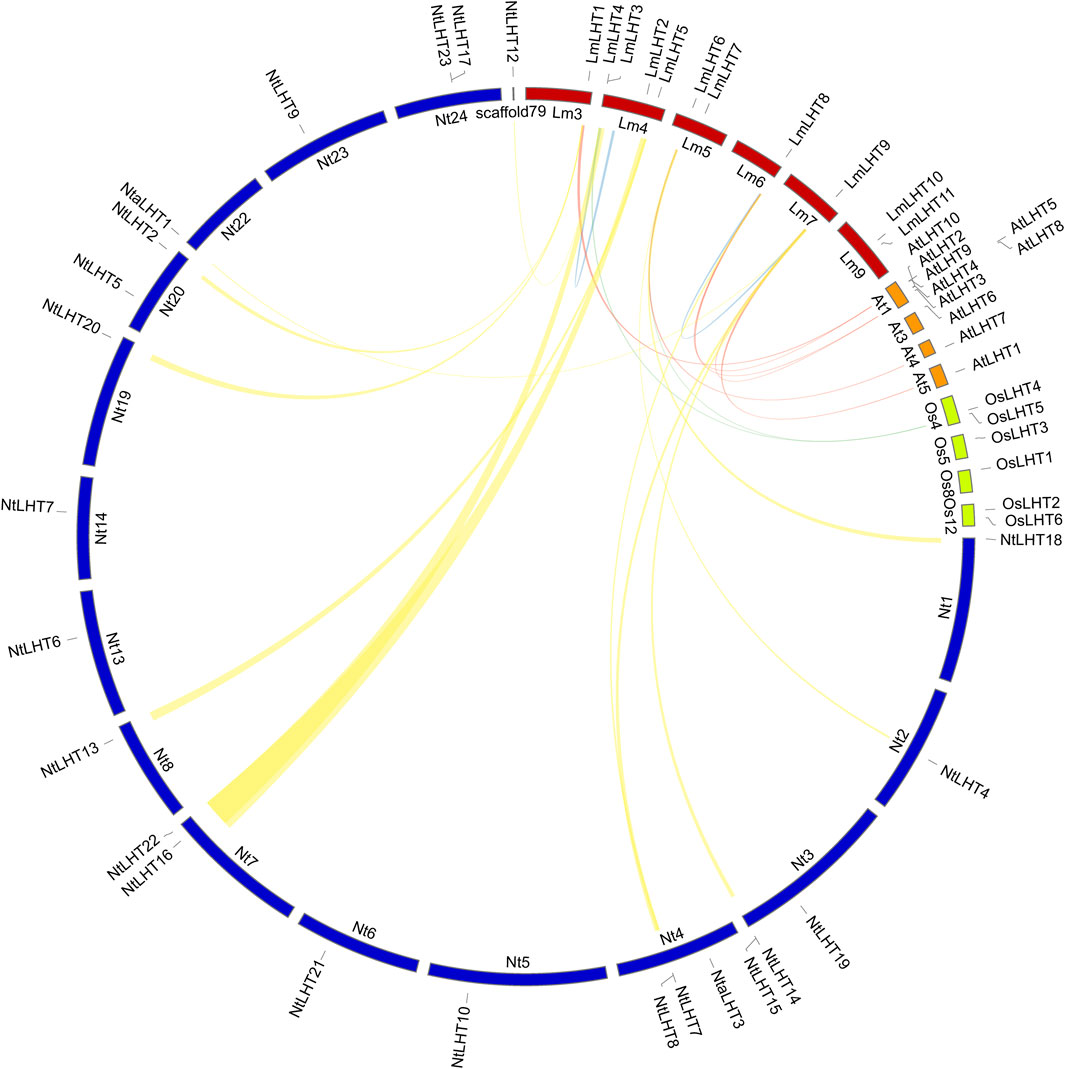
Figure 4. Collinearity analysis of LHT family members between Lonicera macranthoides (Lm), tobacco (Nt), rice (Os), and Arabidopsis (At). The yellow lines represent the collinear gene pairs between Lonicera macranthoides and tobacco, the red lines represent the collinear gene pairs between Lonicera macranthoides and Arabidopsis, the green lines represent the collinear gene pairs between Lonicera macranthoides and rice, and the blue lines represent the duplicated LmLHT genes.
Cis-acting element analysis of LmLHT genes
To better understand the regulatory mechanisms of the LmLHT genes, 2,000 bp upstream sequences of these genes were used for cis-acting element analysis. The cis-acting elements in LmLHT promoters were diverse. As shown in Figure 5, light-responsive elements were the most abundant cis-acting elements in LmLHT promoters, indicating that these elements had indispensable roles. Cis-acting elements involved in anaerobic induction were identified in most LmLHT promoters. Moreover, most of the LmLHT promoters contained stress (e.g., low temperature and drought inducibility)-response elements. Apart from these, cis-acting elements involved in hormone response, such as abscisic acid, auxin, MeJA, salicylic acid, and gibberellin, were also distributed in the promoters of the LmLHT genes. These results suggested that the LmLHT genes may exhibit different regulation features and perform different functions in various biological processes.
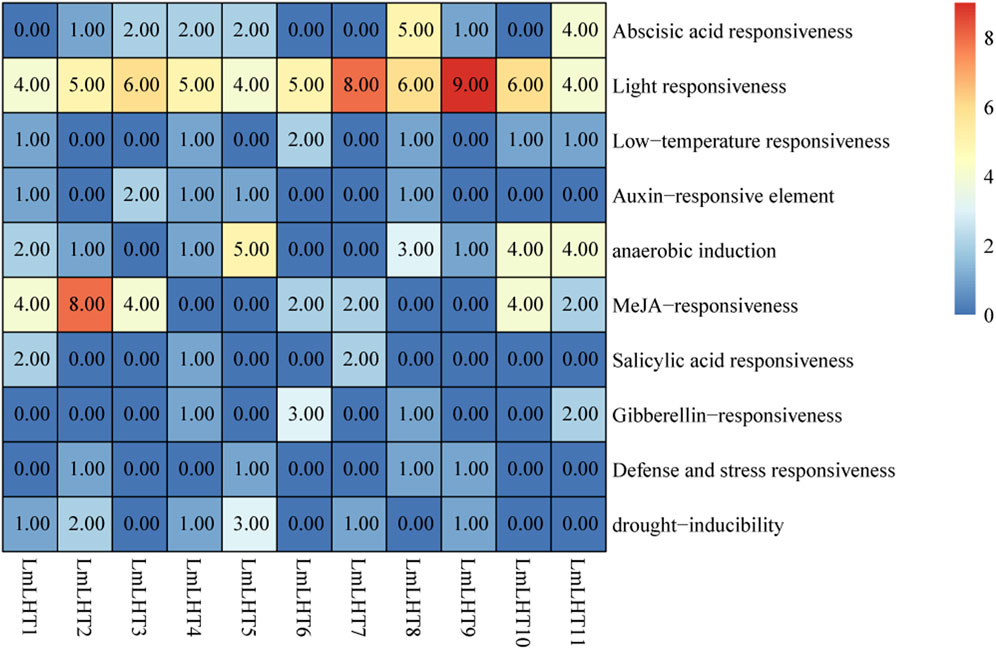
Figure 5. Cis-acting element analysis in the promoter region of LmLHT genes. The numbers and colors in the box represent different elements.
Expression patterns of LmLHT genes in different tissues
To explore the expression patterns of the LmLHT genes, five tissues were selected for analysis: leaf (L), root (R), stem (S), white flower (WF), and yellow flower (YF). As shown in Figure 6, nearly half of the LmLHT genes, namely, LmLHT1, LmLHT2, LmLHT4, LmLHT7, and LmLHT9, were highly expressed in the root, white flower, and yellow flower, implying that these genes may function primarily there. In particular, the expression of LmLHT2 in the white flower and yellow flower was significantly higher than in the other tissues, implying that it may be involved in flower development. LmLHT11 was expressed in all the tested tissues, showing constitutive expression patterns. Furthermore, LmLHT3 was highly expressed in the root, while LmLHT6 and LmLHT10 were highly expressed in the leaf. Interestingly, LmLHT8 showed low expression in the white flower and yellow flower, LmLHT5 showed no expression in the yellow flower, and LmLHT6 showed no expression in the white flower and the yellow flower. In general, most of the LmLHT genes were preferentially expressed in vegetative tissues (root and leaf) rather than in the reproductive organ (flower).
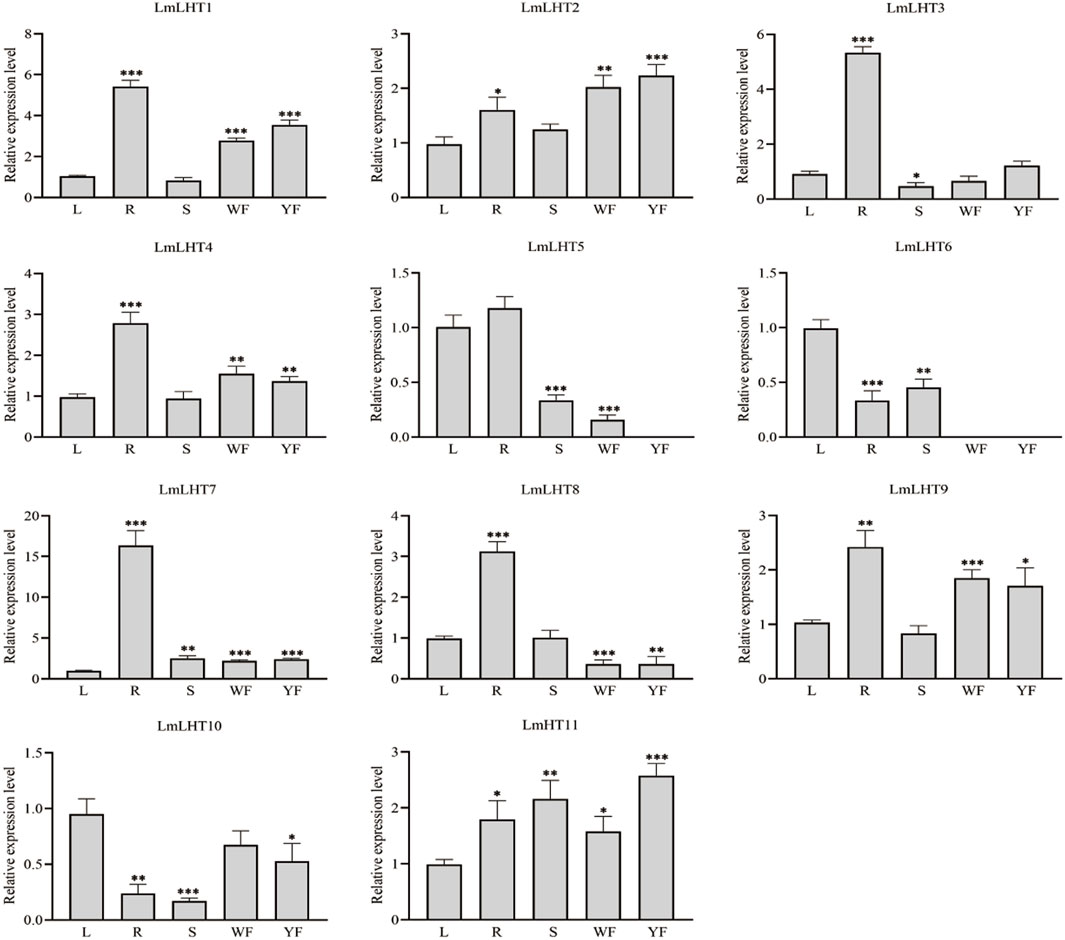
Figure 6. Expression levels of LmLHT in selected tissues. L: leaf, R: root, S: stem, WF: white flower, YF: yellow flower. Expression levels of LmLHT in leaves were set to one. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3).
Expression patterns of LmLHT genes in response to cold and drought stresses
Abiotic stresses often adversely affect the growth and development of plants, and previous studies have shown that LHT genes are responsive to various abiotic stresses (Fan et al., 2023). In this study, the expression patterns of LmLHT genes were investigated in response to cold and drought stresses. We found that the expression level of most of the LmLHT genes presented noticeable changes under cold or drought treatments (Figure 7). Under cold stress, the expression level of LmLHT1 and LmLHT11 was upregulated, while the expression level of LmLHT3 and LmLHT8 were significantly downregulated. After drought treatment, the expression level of seven genes (LmLHT1/LmLHT2/LmLHT4/LmLHT5/LmLHT7/LmLHT9/LmLHT11) was upregulated. By contrast, the expression of LmLHT3 was downregulated. These results indicated that different LmLHT genes may have distinctive roles in response to cold and drought stresses.
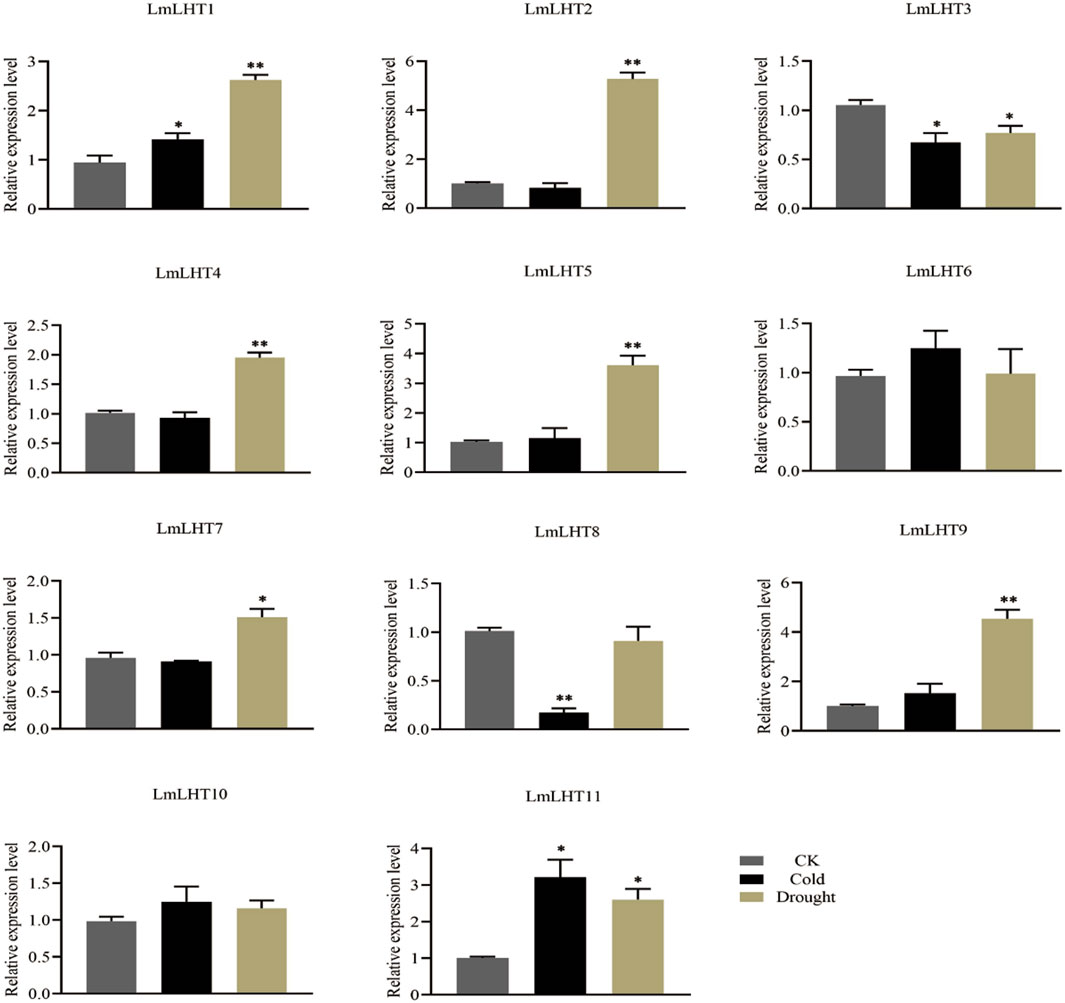
Figure 7. Expression levels of LmLHT under cold and drought stresses, seedlings under normal conditions were used as controls. Data are mean ± SD (n = 3).
Discussion
N, including organic N and inorganic N, is a core factor in determining plant yield and quality. In most plants, N is exchanged and transported primarily in the form of amino acids. For this reason, amino acids have multiple functions in plant growth and development and are involved in various biological processes. These functions include regulating N metabolism and protein synthesis, altering root and shoot architecture, and acting as signal molecules to defend against biotic and abiotic stresses (Dong et al., 2024). AATs mediate the transport of amino acids from soil and the translocation to different tissues in plants. The AAAP superfamily is an important part of AATs, and the LHT subfamily is widely studied and functionally characterized by AAAP (Wang et al., 2019). Based on the whole genome sequencing and bioinformatics analysis, LHTs were identified in many species, including Arabidopsis (10 genes), rice (6 genes), tobacco (23 genes), and maize (15 genes) (Li Z. et al., 2022; Rabby et al., 2022), while the members and functions of LHTs are much less known in medicinal plants.
L. macranthoides is a famous traditional medicinal plant that is widely cultivated in Southwestern China. It has been reported that L. macranthoides plays a unique role in defending against animal and human viruses, such as the H1N1 flu virus, SARS coronavirus, and COVID-19. L. macranthoides contains a variety of biologically active compounds, including chlorogenic acid, phenolic acids, flavonoids, and organic acids (Tang et al., 2021). Increasing evidence suggests that amino acids and their derivatives possess antioxidant capacity, and the content of amino acids may provide an important contribution to the pharmacological effects of L. macranthoides (Long et al., 2024). The homeostasis and metabolism of amino acids are closely associated with AATs. However, AATs have yet to be isolated and characterized in L. macranthoides. In this study, we conducted a comprehensive identification and classification of the LHT subfamily of AATs in L. macranthoides.
We identified 11 LHT genes in the L. macranthoides genome, more than the number previously found in rice and Arabidopsis but less than that in tobacco and maize. The difference in the number of LmLHTs compared to other plants may be related to genome size, gene duplication, polyploidization events, and evolutionary history (Chen et al., 2025). Physiochemical properties, such as molecular weight, isoelectric point, amino acid composition, instability index, GRAVY index, and predicted subcellular localization were similar in LmLHT proteins (Table 2), which suggested that LmLHT proteins were relatively conserved during evolution. However, there are also some subtle differences. For example, the number of transmembrane helices in LmLHT proteins varied greatly (Supplementary Figure S1). Phylogenetic analysis of LHT proteins from L. macranthoides, tobacco, rice, and Arabidopsis indicated that these family members were categorized into two subgroups, and subgroup I possesses more LHT proteins than subgroup II (Figure 1), which is consistent with previous studies on tobacco regarding the LHT family (Li Z. et al., 2022). We also found that the distribution of OsLHTs and AtLHTs in the subgroups differs from previous studies, which may be attributed to the differences in bootstrap parameters (Wang et al., 2019). The exon–intron organization in most LmLHT family members was similar (Figure 2B), while the number of motifs in the LmLHT family members were ranged from 9 to 14 (Figure 2C). Therefore, these results imply that the number and type of motifs in LmLHT family members may be closely related with function conservation and diversification.
Gene family expansion is a common event during plant evolution, which in turn increases the gene copies for plants. Therefore, the diversity and quantity of gene families were more complex through gene duplication (Hong et al., 2024). Gene duplication events are well documented in legumes (Chen et al., 2025), grapes (Guo et al., 2025), Arabidopsis (Cheng et al., 2016), etc. Chromosome localization analysis showed that chromosome 4 contained more LmLHT genes (Figure 3), and this distribution pattern may be related to gene duplication. Moreover, we found that tandem and segmental duplication events occurred in the L. macranthoides genome. In addition, 12 gene pairs between L. macranthoides and tobacco, and 6 gene pairs between L. macranthoides and Arabidopsis were observed in the multi-collinearity analysis, while only 2 gene pairs were observed in L. macranthoides and rice (Figure 4). Thus, we speculated that the collinearity gene pairs between L. macranthoides and other plant species were mainly established after the differentiation of monocotyledonous and dicotyledonous plants.
Cis-acting elements are the non-coding DNA sequences identified in the promoter of genes, the types and number of cis-acting elements are closely related to gene function (Li et al., 2021). Promoter analysis of the LmLHT genes revealed that the most abundant cis-acting elements were associated with light response, suggesting that the expression of these genes might be regulated by light stimuli. Phytohormones play multiple roles in various biological processes and signal transduction, and cis-acting elements involved in various phytohormone responses were found in the LmLHT genes. At the same time, biotic and abiotic stress-related cis-acting elements also exist in the promoter of the LmLHT genes (Figure 5). Therefore, the abundant of cis-acting elements in the LmLHT genes promotor may contribute significantly to their functional diversity.
The expression patterns of genes in different plant tissues are helpful for their functional characterization. We analyzed the expression levels of the LmLHT genes in different parts and organs. More than half of the LmLHT genes showed high expression levels in the root. LmLHT6/LmLHT10 are highly expressed in the leaf and LmLHT2/LmLHT11 exhibited constitutive expression in the tested tissues. In addition, the expression level of LmLHT5/LmLHT6/LmLHT8 in the flower is lower than in other tissues (Figure 6). These findings indicated that different LmLHT genes may have identical or reverse functions during growth and development. The expression of AATs in plants could be significantly influenced by abiotic stresses (Tian et al., 2020). In the present study, we found that four and eight LmLHT genes responded to cold and drought stresses, respectively. Cis-acting elements related to cold stress response were not detected in the promoters of LmLHT3/LmLHT9, and a drought-inducibility element was not identified in the promoter of LmLHT11. However, the expression of LmLHT9 and LmLHT11 was increased under cold and drought treatments. In addition, the expression of LmLHT3 was decreased with cold and drought stresses (Figure 7). These results indicate that the expression of LmLHT3/LmLHT9/LmLHT11 under cold or drought stresses may not been directly related to the cis-acting elements on their promoters. Instead, it may be indirectly influenced by transcription factors or epigenetic regulation. Previous studies indicated that overexpression of the light-responsive transcript factor SlBBX20 increased the expression of low-temperature responsive genes in tomato (Ma et al., 2025). The bHLH transcript factor MYC2 is a core regulator of the JA signal pathway, which participates in repeat dehydration stress in Arabidopsis (Liu et al., 2016). The exogenous application of ABA altered DNA methylation and stress-related gene expression in grape, thereby affecting fruit ripening (Li et al., 2024). Therefore, the complex expression patterns of the LmLHT genes indicate that L. macranthoides might have developed specialized regulatory mechanisms to adapt to environmental stresses.
Conclusion
In summary, a systematic study was performed to identify and characterize the LHT family genes in L. macranthoides. The LmLHT genes were studied in terms of their physicochemical characteristics, evolutionary relationships, gene structure, conserved motif, chromosomal locations, collinearity, and cis-acting elements, which provide insights into the evolutionary history of this family in L. macranthoides. The expression patterns of LmLHT genes in different tissues and under cold and drought stresses were complex, suggesting that LmLHT genes play important roles in various biological processes. Overall, this study not only provides useful information for a comprehensive understanding of LmLHT genes, but also lays a solid foundation for the further application of these genes.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
ZL: Formal Analysis, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YuH: Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Data curation, Methodology. CL: Investigation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft, Methodology. LC: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft. YaH: Methodology, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Writing – original draft, Validation, Conceptualization, Data curation. XC: Supervision, Writing – review and editing, Conceptualization, Validation.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Excellent Youthful Scientific Research Project, Department of Education of Hunan Province (24B0691), The Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2024JJ9593 and 2025JJ70194), and the National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (S202310547024).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2025.1614541/full#supplementary-material
References
Cai, J., and Aharoni, A. (2022). Amino acids and their derivatives mediating defense priming and growth tradeoff. Curr. Opin. Plant. Biol. 69, 102288. doi:10.1016/j.pbi.2022.102288
Cao, C., Qiu, X., Yang, Z., and Jin, Y. (2024). New insights into the evolution and function of the UMAMIT (USUALLY MULTIPLE ACIDS MOVE IN AND OUT TRANSPORTER) gene family. J. Plant Res. 138, 3–17. doi:10.1007/s10265-024-01596-3
Cao, X., Ma, Q., Zhong, C., Yang, X., Zhu, L., Zhang, J., et al. (2016). Elevational variation in soil amino acid and inorganic nitrogen concentrations in taibai Mountain, China. Plos One 11, e0157979. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0157979
Chen, C., Chen, H., Zhang, Y., Thomas, H. R., Frank, M. H., He, Y., et al. (2020). TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 13, 1194–1202. doi:10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chen, N., Wang, S., Yin, Y., Ren, G., Zhang, Y., Qu, L., et al. (2025). Genome-wide identification of the AAAP gene family and expression analysis under tissue-specific expression in five legumes. BMC Genomics 26, 173. doi:10.1186/s12864-025-11224-6
Chen, Y., Xu, N., Du, L., Zhang, J., Chen, R., Zhu, Q., et al. (2023). Light plays a critical role in the accumulation of chlorogenic acid in Lonicera macranthoides hand.-mazz. Plant Physiol. biochem. 196, 793–806. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2023.02.016
Cheng, L., Yuan, H. Y., Ren, R., Zhao, S. Q., Han, Y. P., Zhou, Q. Y., et al. (2016). Genome-wide identification, classification, and expression analysis of amino acid transporter gene family in glycine max. Front. Plant Sci. 7, 515. doi:10.3389/fpls.2016.00515
Dong, C., Li, F., Yang, T., Feng, L., Zhang, S., Li, F., et al. (2020). Theanine transporters identified in tea plants (Camellia sinensis L.). Plant J. 101, 57–70. doi:10.1111/tpj.14517
Dong, K., Ye, Z., Hu, F., Shan, C., Wen, D., and Cao, J. (2024). Improvement of plant quality by amino acid transporters: a comprehensive review. Plant Physiol. biochem. 215, 109084. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.109084
Du, X.-Q., Sun, S.-S., Zhou, T., Zhang, L., Feng, Y.-N., Zhang, K.-L., et al. (2024). Genome-wide identification of the CAT genes and molecular characterization of their transcriptional responses to various nutrient stresses in allotetraploid rapeseed. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25, 12658. doi:10.3390/ijms252312658
Elashry, A., Okumoto, S., Siddique, S., Koch, W., Kreil, D. P., and Bohlmann, H. (2013). The AAP gene family for amino acid permeases contributes to development of the cyst nematode Heterodera schachtii in roots of arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 70, 379–386. doi:10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.016
Fan, T., Wu, C., Yang, W., Lv, T., Zhou, Y., and Tian, C. (2023). The LHT gene family in rice: molecular characterization, transport functions and expression analysis. Plants (Basel) 12, 817. doi:10.3390/plants12040817
Guo, N., Gu, M., Hu, J., Qu, H., and Xu, G. (2020a). Rice OsLHT1 functions in leaf-to-panicle nitrogen allocation for grain yield and quality. Front. Plant Sci. 11, 1150. doi:10.3389/fpls.2020.01150
Guo, N., Hu, J., Yan, M., Qu, H., Luo, L., Tegeder, M., et al. (2020b). Oryza sativa lysine-histidine-type transporter 1 functions in root uptake and root-to-shoot allocation of amino acids in rice. Plant J. 103, 395–411. doi:10.1111/tpj.14742
Guo, N., Qu, H., Zhi, Y., Zhang, Y., Cheng, S., Chu, J., et al. (2023). Knock out of amino acid transporter gene OsLHT1 accelerates leaf senescence and enhances resistance to rice blast fungus. J. Exp. Bot. 74, 4143–4157. doi:10.1093/jxb/erad125
Guo, N., Zhang, S., Gu, M., and Xu, G. (2021). Function, transport, and regulation of amino acids: what is missing in rice? Crop J. 9, 530–542. doi:10.1016/j.cj.2021.04.002
Guo, X., He, N., Huang, B., Chen, C., Zhang, Y., Yang, X., et al. (2025). Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of amino acid/auxin permease (AAAP) genes in grapes (Vitis vinifera L.) under abiotic stress and during development. Plants (Basel) 14, 128. doi:10.3390/plants14010128
Hirner, A., Ladwig, F., Stransky, H., Okumoto, S., Keinath, M., Harms, A., et al. (2006). Arabidopsis LHT1 is a high-affinity transporter for cellular amino acid uptake in both root epidermis and leaf mesophyll. Plant Cell 18, 1931–1946. doi:10.1105/tpc.106.041012
Hong, Z., Zhu, L., Liu, C., Wang, K., Rao, Y., and Lu, H. (2024). Genome-wide identification and evolutionary analysis of functional BBM-Like genes in plant species. Genes (Basel) 15, 1614. doi:10.3390/genes15121614
Inselsbacher, E., and Näsholm, T. (2012). The below-ground perspective of forest plants: soil provides mainly organic nitrogen for plants and mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 195, 329–334. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04169.x
Ji, Y., Huang, W., Wu, B., Fang, Z., and Wang, X. (2020). The amino acid transporter AAP1 mediates growth and grain yield by regulating neutral amino acid uptake and reallocation in Oryza sativa. J. Exp. Bot. 71, 4763–4777. doi:10.1093/jxb/eraa256
Jin, F., Huang, W., Xie, P., Wu, B., Zhao, Q., and Fang, Z. (2024). Amino acid permease OsAAP12 negatively regulates rice tillers and grain yield by transporting specific amino acids to affect nitrogen and cytokinin pathways. Plant Sci. 347, 112202. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2024.112202
Krzywinski, M., Schein, J., Birol, I., Connors, J., Gascoyne, R., Horsman, D., et al. (2009). Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 19, 1639–1645. doi:10.1101/gr.092759.109
Li, H., Wen, X., Huang, X., Wei, M., Chen, H., Yu, Y., et al. (2022a). Genome-wide identification and characterization of TCP gene family members in Melastoma candidum. Molecules 27, 9036. doi:10.3390/molecules27249036
Li, Y.-M., Zhang, H.-X., Tang, X.-S., Wang, Y., Cai, Z.-H., Li, B., et al. (2024). Abscisic acid induces DNA methylation alteration in genes related to berry ripening and stress response in grape (Vitis vinifera L). J. Agr. Food. Chem. 72, 15027–15039. doi:10.1021/acs.jafc.4c02303
Li, Z., Gao, J., Wang, G., Wang, S., Chen, K., Pu, W., et al. (2021). Genome-wide identification and characterization of GASA gene family in Nicotiana tabacum. Front. Genet. 12, 768942. doi:10.3389/fgene.2021.768942
Li, Z., Gao, J., Wang, S., Xie, X., Wang, Z., Peng, Y., et al. (2022b). Comprehensive analysis of the LHT gene family in tobacco and functional characterization of NtLHT22 involvement in amino acids homeostasis. Front. Plant Sci. 13, 927844. doi:10.3389/fpls.2022.927844
Liu, N., Staswick, P. E., and Avramova, Z. (2016). Memory responses of Jasmonic acid-associated Arabidopsis genes to a repeated dehydration stress. Plant, Cell Environ. 39, 2515–2529. doi:10.1111/pce.12806
Liu, Q., Yu, H., Dong, Y., Quan, W., Su, Z., and Li, L. (2024). Quality evaluation of lonicerae flos produced in southwest China based on HPLC analysis and antioxidant activity. Molecules 29, 2560. doi:10.3390/molecules29112560
Long, Y., Zeng, J., Liu, X., Wang, Z., Tong, Q., Zhou, R., et al. (2024). Transcriptomic and metabolomic profiling reveals molecular regulatory network involved in flower development and phenotypic changes in two Lonicera macranthoides varieties. 3 Biotech. 14, 174. doi:10.1007/s13205-024-04019-1
Ma, Y., Chen, M., Xing, Y., Li, Z., Zhou, T., Yan, H., et al. (2025). The light-responsive transcription factor SlBBX20 improves low-temperature resistance of Solanum lycopersicum by affecting photosynthetic capacity, antioxidant capacity, and osmotic adjustment. Plant Cell Rep. 44, 97. doi:10.1007/s00299-025-03480-3
Marchler-Bauer, A., Derbyshire, M. K., Gonzales, N. R., Lu, S., Chitsaz, F., Geer, L. Y., et al. (2015). CDD: ncbi's conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D222–D226. doi:10.1093/nar/gku1221
Marella, H. H., Nielsen, E., Schachtman, D. P., and Taylor, C. G. (2012). The amino acid permeases AAP3 and AAP6 are involved in root-knot nematode parasitism of arabidopsis. Mol. Plant-Microbe Int. 26, 44–54. doi:10.1094/MPMI-05-12-0123-FI
Näsholm, T., Kielland, K., and Ganeteg, U. (2009). Uptake of organic nitrogen by plants. New Phytol. 182, 31–48. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8137.2008.02751.x
Okumoto, S., Koch, W., Tegeder, M., Fischer, W. N., Biehl, A., Leister, D., et al. (2004). Root phloem-specific expression of the plasma membrane amino acid proton co-transporter AAP3. J. Exp. Bot. 55, 2155–2168. doi:10.1093/jxb/erh233
Pan, Y., Zhao, X., Wu, X. L., Wang, Y., Tan, J., and Chen, D. X. (2021). Transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses provide insights into the biosynthesis of chlorogenic acids in Lonicera macranthoides hand.-mazz. Plos One 16, e0251390. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0251390
Perchlik, M., Foster, J., and Tegeder, M. (2014). Different and overlapping functions of arabidopsis LHT6 and AAP1 transporters in root amino acid uptake. J. Exp. Bot. 65, 5193–5204. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru278
Perchlik, M., and Tegeder, M. (2017). Improving plant nitrogen use efficiency through alteration of amino acid transport processes. Plant Physiol. 175, 235–247. doi:10.1104/pp.17.00608
Rabby, M. G., Hossen, M. M., Kamal, M. M., and Islam, M. N. (2022). Genome-wide identification and functional analysis of lysine histidine transporter (LHT) gene families in maize. Genet. Res. 2022, 2673748. doi:10.1155/2022/2673748
Ren, Z., Chen, Z., Luo, X., Su, J., Yao, G., Xu, H., et al. (2019). Overexpression of AtAAP1 increased the uptake of an alanine-chlorantraniliprole conjugate in Arabidopsis thaliana. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 26, 36680–36687. doi:10.1007/s11356-019-06671-0
Rhee, S. Y., Beavis, W., Berardini, T. Z., Chen, G., Dixon, D., Doyle, A., et al. (2003). The arabidopsis information resource (TAIR): a model organism database providing a centralized, curated gateway to arabidopsis biology, research materials and community. Nucleic Acids Res. 31, 224–228. doi:10.1093/nar/gkg076
Saha, J., and Gupta, S. (2022). Molecular characterization, evolutionary and phylogenetic analyses of rice ACT/BAT-type amino acid transporters. Comput. Biol. Chem. 100, 107745. doi:10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2022.107745
Schmittgen, T. D., and Livak, K. J. (2008). Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative CT method. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1101–1108. doi:10.1038/nprot.2008.73
Shin, K., Lee, S., Song, W.-Y., Lee, R.-A., Lee, I., Ha, K., et al. (2015). Genetic identification of ACC-RESISTANT2 reveals involvement of LYSINE HISTIDINE TRANSPORTER1 in the uptake of 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-Carboxylic acid in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell Physiol. 56, 572–582. doi:10.1093/pcp/pcu201
Sonnhammer, E. L. L., Eddy, S. R., and Durbin, R. (1997). Pfam: a comprehensive database of protein domain families based on seed alignments. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinforma. 28, 405–420. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0134(199707)28:3<405::AID-PROT10>3.0.CO;2-L
Tang, N., Cao, Z., Yang, C., Ran, D., Wu, P., Gao, H., et al. (2021). A R2R3-MYB transcriptional activator LmMYB15 regulates chlorogenic acid biosynthesis and phenylpropanoid metabolism in Lonicera macranthoides. Plant Sci. 308, 110924. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2021.110924
Tegeder, M. (2014). Transporters involved in source to sink partitioning of amino acids and ureides: opportunities for crop improvement. J. Exp. Bot. 65, 1865–1878. doi:10.1093/jxb/eru012
Tegeder, M., and Masclaux-Daubresse, C. (2018). Source and sink mechanisms of nitrogen transport and use. New Phytol. 217, 35–53. doi:10.1111/nph.14876
Tian, R., Yang, Y., and Chen, M. (2020). Genome-wide survey of the amino acid transporter gene family in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.): identification, expression analysis and response to abiotic stress. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 162, 1372–1387. doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.302
Wang, X., Yang, G., Shi, M., Hao, D., Wei, Q., Wang, Z., et al. (2019). Disruption of an amino acid transporter LHT1 leads to growth inhibition and low yields in rice. BMC Plant Biol. 19, 268. doi:10.1186/s12870-019-1885-9
Wang, Y., Tang, H., DeBarry, J. D., Tan, X., Li, J., Wang, X., et al. (2012). MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 40, e49. doi:10.1093/nar/gkr1293
Wei, Q., Yan, Z., Xiong, Y., and Fang, Z. (2021). Altered expression of OsAAP3 influences rice lesion mimic and leaf senescence by regulating arginine transport and nitric oxide pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 22 (4), 2181. doi:10.3390/ijms22042181
Weigelt, A., Bol, R., and Bardgett, R. D. (2005). Preferential uptake of soil nitrogen forms by grassland plant species. Oecologia 142, 627–635. doi:10.1007/s00442-004-1765-2
Xie, X., Cao, P., Wang, Z., Gao, J., Wu, M., Li, X., et al. (2021). Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of the PDR gene family in tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Gene 788, 145637. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2021.145637
Xing, J., Yang, W., Xu, L., Zhang, J., Yang, Y., Jiang, J., et al. (2024). Overexpression of NtLHT1 affects the development of leaf morphology and abiotic tolerance in tobacco. Plant Sci. 339, 111961. doi:10.1016/j.plantsci.2023.111961
Yahyaoui, R., and Pérez-Frías, J. (2020). Amino acid transport defects in human inherited metabolic disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21 (1). doi:10.3390/ijms21010119
Yang, G., Wei, Q., Huang, H., and Xia, J. (2020). Amino acid transporters in plant cells: a brief review. Plants 9 (8), 967. doi:10.3390/plants9080967
Yin, X., Xiang, Y., Huang, F.-Q., Chen, Y., Ding, H., Du, J., et al. (2023). Comparative genomics of the medicinal plants Lonicera macranthoides and L. japonica provides insight into genus genome evolution and hederagenin-based saponin biosynthesis. Plant Biotechnol. J. 21, 2209–2223. doi:10.1111/pbi.14123
Keywords: Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-mazz, AAT, LHT, genome-wide, abiotic stresses
Citation: Li Z, Hu Y, Liang C, Chen L, Hu Y, Wu X and Chen X (2025) Genome-wide identification of LHT gene family in Lonicera macranthoides Hand.-Mazz and their responses to abiotic stresses. Front. Genet. 16:1614541. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1614541
Received: 19 April 2025; Accepted: 23 June 2025;
Published: 01 July 2025.
Edited by:
Hongjian Wan, Zhejiang Academy of Agricultural Sciences, ChinaReviewed by:
Swarup Roy Choudhury, Indian Institute of Science Education and Research, Tirupati, IndiaAduragbemi Emmanuel Amo, Texas A and M University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Li, Hu, Liang, Chen, Hu, Wu and Chen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaoqiu Wu, eGlhb3FpdXd1aEAxNjMuY29t; Xia Chen, Y3gxNTI3QDE2My5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Zhaowu Li
Zhaowu Li Yue Hu1†
Yue Hu1†