- 1School of Electronic Information, Xijing University, Xi’an, China
- 2Guangxi Key Lab of Human-Machine Interaction and Intelligent Decision, Guangxi Academy of Sciences, Nanning, China
- 3School of Computer Science and Technology, China University of Mining and Technology, Xuzhou, China
- 4College of Big Data and Internet, Shenzhen Technology University, Shenzhen, China
- 5School of Computer Science, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi’an, China
Introduction: Predicting interactions between microRNAs (miRNAs) and messenger RNAs (mRNAs) is crucial for understanding gene expression regulation mechanisms and their roles in diseases. Existing prediction methods face significant limitations in simultaneously handling RNA sequence complexity and graph structural information.
Methods: We propose GRMMI, a framework that effectively leverages both sequence and node features by combining FastText-pretrained sequence embeddings with GraRep graph embeddings to capture semantic and topological information. The method introduces antisense-aware sequence processing that reverses mRNA orientation to better simulate the natural miRNA-mRNA complementary binding mechanism. Additionally, GRMMI employs cross-sequence mutual attention architecture that enables deep exploration of inter-RNA dependencies beyond traditional single-sequence analysis limitations. Unlike existing approaches that rely primarily on sequence-based features, GRMMI achieves multi-dimensional information fusion by integrating CNN-BiLSTM architecture with mutual attention mechanisms.
Results: Evaluation on the MTIS-9214 dataset shows that GRMMI achieves an AUC of 0.9347 and accuracy of 86.65%.
Discussion: Case studies confirm the practical utility of GRMMI in identifying biologically significant RNA interactions, providing valuable insights for disease mechanism research and therapeutic target discovery.
Highlights
• This study introduces a mutual attention mechanism, enabling the model to effectively capture the complex interaction features between miRNAs and mRNAs, thereby uncovering additional latent associative information.
• The mRNA sequence is inputted in reverse order into the model, taking into account the biological characteristics of miRNA and mRNA binding.
• An improved FastText method is used as the pre-training model for RNA sequences, allowing for the generation of feature embeddings more aligned with the experimental objectives during deep mining.
Introduction
Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) are RNA molecules that regulate gene expression at the post-transcriptional level and lack protein-coding potential. They interact with other biomolecules as functional macromolecules to modulate various cellular processes. With the growing body of research on the ncRNAs, it has been established that both microRNAs, referred to as miRNAs, and messenger RNAs referred to as mRNAs are central to numerous biological processes. MiRNAs, approximately 22 nucleotides in length, were first discovered in Caenorhabditis elegans in 1993. They regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally in plants and animals by binding to specific mRNA sequences through complementary base pairing, influencing translation efficiency or promoting mRNA degradation, ultimately resulting in the suppression of protein synthesis (Kim and Croce, 2023; Walgrave et al., 2021).
MiRNA genes are transcribed into pri-miRNAs in the nucleus, processed by the Drosha enzyme to form pre-miRNAs, and then transported to the cytoplasm, where the Dicer enzyme produces mature miRNAs (Wei et al., 2024; Wang et al., 2024; Peng et al., 2024a). One strand integrates into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) to silence target mRNAs. MiRNAs play a crucial role in disease processes, including immune responses (Taganov et al., 2006; Peng et al., 2022), cell cycle regulation (Carleton et al., 2007), and tumor invasion (Hussen et al., 2021; Jiang et al., 2024). Abnormal miRNA expression or impairment is linked to various diseases, particularly cancers like breast, pancreatic (Fathi et al., 2021), and lung cancer (Ni et al., 2021). For instance, certain miRNAs are overexpressed in cancer and inhibit the activity of specific tumor suppressor genes, leading to cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. Differential expression of other miRNAs fails to suppress oncogenes, thus making them prime targets for the possible diagnosis and therapeutic interventions in the cancer progression. miRNA-based treatment strategies, such as miRNA mimics and ASOs (Baker et al., 2024), hold significant promise in advancing medical research.
MRNAs, on the other hand, are transcribed from DNA to carry genetic information for protein synthesis in a process called transcription. During this process, RNA polymerase synthesizes mRNA using a DNA template in the nucleus (Qin et al., 2022). The mRNA is subsequently transported to the cytoplasm, where ribosomes translate it into proteins. Beyond protein synthesis, mRNAs play a key role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and facilitating rapid responses to environmental changes (Das et al., 2021), such as stress or nutrient deprivation, by regulating their own synthesis. These dynamic adjustments enable mRNAs to precisely regulate gene expression in changing conditions (Zhao et al., 2021). However, mRNA regulation is not solely intrinsic. Small non-coding RNAs, such as miRNAs, function as sequence-specific inhibitors of mRNA activity, modulating post-transcriptional processes and influencing both mRNA stability and translation efficiency.
The regulation of gene expression by miRNAs and mRNAs is mediated through highly specific and dynamic interactions. A single miRNA can target multiple mRNAs, while a single mRNA may be regulated by multiple miRNAs. In most cases, miRNA binding sites are located in the 3′untranslated region (3′UTR) of mRNAs (Griesemer et al., 2021). In certain instances, miRNA binding sites may also be found within the coding sequence (CDS) or the 5′untranslated region (5′UTR) (Chekulaeva, 2023). The interaction between miRNAs and their target mRNAs results in either translational inhibition or mRNA degradation, thereby modulating specific protein expression levels. Studies indicate that miRNA-mRNA interactions play a critical role in physiological processes such as cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis, as well as in the initiation and progression of diseases (Laggerbauer and Engelhardt, 2022; Peng et al., 2024b). For instance, aberrant miRNA expression has been implicated in cancer, neurological disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. Understanding miRNA-mRNA interactions provides insight into the underlying molecular mechanisms of these disorders and facilitates the identification of novel therapeutic targets in precision medicine.
Although traditional wet lab methods (e.g., RNA immunoprecipitation, reporter gene assay, and quantitative PCR) have advanced the understanding of miRNA-mRNA interactions, they face several limitations, such as long experimental cycles, high labor costs, and limited scalability for large-scale miRNA-mRNA pair screening. These limitations arise from the inherent characteristics of wet lab methods, rendering them less capable of addressing the intricate regulatory relationships between miRNAs and mRNAs arising in complex biological systems. These challenges have been addressed by machine learning-based computational methods in the study of miRNA-target mRNA interactions. Such approaches have since been integrated with multidimensional biological data that allow high-throughput prediction and analysis. For example, traditional tools, such as TargetScan (McGeary et al., 2019) and miRDB (Chen and Wang, 2020), are based on seed sequence matching and conservation analysis in identifying potential targets, which limits their ability to integrate complex biological features.
Several models like deepTarget (Lee et al., 2016) integrate sequence-based features and nonlinear learning to achieve better model performance. The capabilities of deep learning to process large-scale data have proven successful across various fields. For example, a deep graph convolutional network (DGCN) was developed by Chen et al. to predict the miRNA-disease associations by constructing a unified graph structure, which takes into account potential nonlinear associations among miRNAs and diseases, leading to significant improvements in prediction performance (Zheng et al., 2021; Peng et al., 2021a). Liu et al. proposed the MPCLCDA model for circRNA-disease association prediction, in which heterogeneous networks are created from automatic meta-path selection and contrastive learning, thus effectively predicting circRNA-disease associations using graph convolutional techniques (Liu et al., 2023). Likewise, Guo et al. proposed employing structural deep neural network embedding models to predict circRNA-miRNA interactions, this model combines structural and sequence features to achieve high predictive performance by reconstructing the association matrix (Guo et al., 2022; Peng et al., 2021b). All these works validate significant advantages of deep learning in handling complex biological networks, incorporate multidimensional features, and optimize prediction accuracy, offering methodological insights for miRNA-target mRNA prediction.
Although deep learning has advanced miRNA-target mRNA prediction, current methods have notable limitations in feature integration and attention mechanisms. Existing approaches like miTAR primarily rely on CNN-BiLSTM hybrid architectures to capture spatial and sequential features but lack sophisticated attention mechanisms to dynamically prioritize important features during prediction (Gu et al., 2021). Methods such as miGAP (Yoon et al., 2023) and AEmiGAP (Yoon et al., 2024), while achieving high performance through advanced embedding techniques and autoencoder-based feature extraction, still focus predominantly on sequence-level information without incorporating structural node attributes or topological relationships. These approaches treat miRNA and gene sequences as isolated entities, missing the opportunity to leverage graph-based representations that can capture the inherent network structure of molecular interactions. Furthermore, current methods do not employ attention mechanisms to adaptively weight different feature components, limiting their ability to focus on the most relevant sequence patterns and structural characteristics for specific miRNA-mRNA pairs.
To address these limitations, we propose the GRMMI model, which combines graph structures and attention mechanisms to provide a more comprehensive approach. Unlike existing sequence-only methods, GRMMI integrates both RNA sequence features and node attributes within a unified framework, using CNN-BiLSTM to extract sequence features—CNN captures local patterns and BiLSTM captures extended dependencies. The key innovation lies in the mutual attention mechanism that assigns dynamic importance to features, enabling the model to better capture miRNA-mRNA interactions compared to static feature weighting in current approaches. GRMMI also reverses the mRNA sequence to align with the antisense strand pairing mechanism of miRNAs, enhancing understanding of their complementary binding. Graph embedding techniques represent RNA node features and topological structures, improving the ability of the model to capture RNA interactions beyond pure sequence information. The joint representation of sequence and graph-based features is then used for prediction output.
Materials and methods
Data description
MiRTarBase is a widely used bioinformatics database that curates experimentally validated miRNA-mRNA interactions (Huang et al., 2022). It integrates data from experimental techniques like reporter assays, RNA immunoprecipitation, and microarray analyses, ensuring high quality and reliability of miRNA-target gene relationships. From the miRTarBase database, we extracted a dataset of 9,214 experimentally validated miRNA-mRNA interaction pairs, comprising 3,069 mRNAs and 861 miRNAs. We refer to this dataset as MTIS-9214, and the relationships among some of the data are illustrated in Figure 1. The miRNA sequence information was retrieved from miRBase (Kozomara et al., 2019), while the mRNA sequences were obtained from GENCODE-v38 (GRCh38. p14).
To construct a comprehensive dataset for model training and evaluation, we also generated an equal-sized negative sample dataset. The negative samples were created by randomly pairing miRNAs with mRNAs, ensuring that these pairings were not present in the experimentally validated dataset. In other words, these miRNA-mRNA pairs lacked any known experimental evidence. The inclusion of negative samples facilitates the ability of the model to effectively distinguish between true positive interactions and non-functional pairings, which is crucial for reducing false positives and improving predictive accuracy. Ultimately, the size of the negative sample dataset was matched to the positive dataset, with both containing 9,214 interaction pairs. This balanced dataset design eliminates the issue of class imbalance during model training, enhancing the performance of the model and its ability to predict real-world biological interactions.
Method architecture
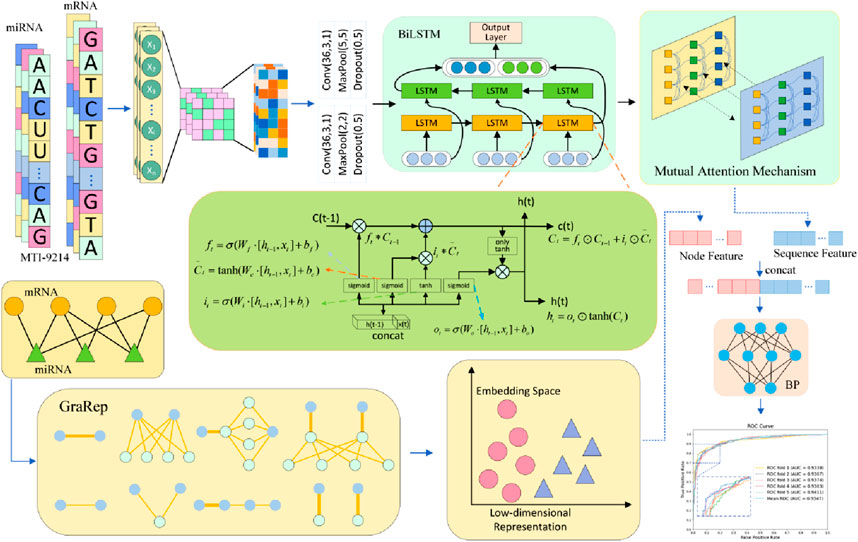
In this study, we propose a computational framework for GRMMI, aiming to enhance the prediction performance of miRNA-mRNA interaction pairs by extracting and integrating RNA sequence and node features. As illustrated in Figure 2, we first utilize the miRNA sequences from the miRBase database and the mRNA sequences from GRCh38. p14 for pretraining using the FastText model to obtain the initial sequence embedding weights of RNA sequences. Subsequently, the sequence feature extraction module of the GRMMI framework is applied to the data from the MTIS-9214 dataset to extract sequence features. Meanwhile, we employ the GraRep graph embedding method to extract the node features of miRNA-mRNA interaction pairs. Finally, a BP neural network is utilized to fuse the sequence and node features. Based on the extracted features, the model is applied to interaction prediction.
Pretrained RNA sequence embedding weights extraction
The development of NLP has advanced from rule-based methods to deep learning models. Traditional approaches like bag-of-words (BoW) struggled to capture sequential and semantic relationships. With the introduction of word embedding techniques such as Word2Vec, GloVe (Pennington et al., 2014), and FastText (Joulin et al., 2016), NLP models gained the ability to capture semantic information more effectively. These advancements have been applied to bioinformatics, where RNA sequences, akin to a “language” with nucleotides as “words,” can be analyzed using NLP. Word embeddings represent biological sequences as low-dimensional vectors, capturing complex patterns for prediction and analysis.
In this study, we used FastText as the embedding extraction tool to represent features of miRNA and mRNA sequences. This model leverages subword information of words using subword information. FastText provides word embedding combined with n-gram subword modeling, which makes it suitable for biological sequences with local structural features. The detailed structure and results are shown in Figure 3.
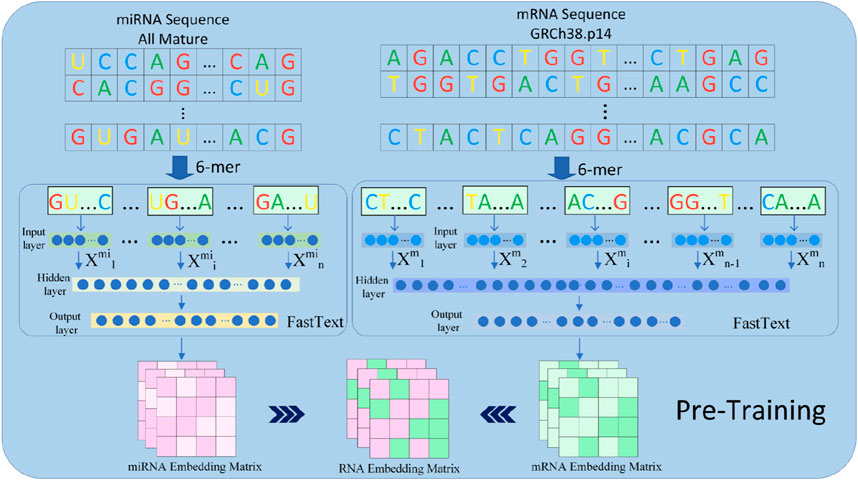
Figure 3. The pretraining component in the GRMMI model. In the process of deriving pre-trained weights for the model, miRNA sequences are utilized in their entirety, whereas mRNA sequences are randomly segmented into fragments ranging from 200 to 400 nucleotides using a sliding window approach. These sequences and fragments are then tokenized into k-mers, which are treated as words. The FastText algorithm is employed to extract sequence weights from the RNA corpus, and these weights are subsequently utilized as the weights for the downstream embedding layer in the model.
The fundamental idea behind FastText is an extension of the Skip-gram model, representing RNA sequences using n-gram subwords. In the experiment, FastText was employed to pretrain miRNA and mRNA sequences and extract the embedding weights of RNA sequences for downstream embedding layers. Given the relatively long lengths of mRNA sequences, we employed a sliding window approach to segment each mRNA sequence into 200–400 nucleotide fragments with overlapping regions between windows to preserve potential binding site integrity, while miRNA sequences were left unsegmented due to their shorter lengths. Subsequently, each fragment was passed through FastText to generate k-mer embeddings, where k = 6 For an miRNA or mRNA sequence
where k-mer refers to a sub-sequence of length k = 6 each
For pretraining k-mer embeddings with FastText, the skip-gram method is employed. The objective is to maximize the co-occurrence probability between the center k-mer and its surrounding k-mers in the sequence. The objective function is defined as shown in Equation 2:
Let
The co-occurrence probability
Extraction of RNA sequence embeddings using the GRMMI
Since RNA sequences consist of discrete bases (A, U, C, G/T) as symbolic data, directly inputting them into deep learning models to capture semantic and structural features is challenging. To address this, the GRMMI framework incorporates a sequence feature extraction module designed with an embedding layer, a convolutional neural network (CNN) layer, a bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) layer, and a mutual attention mechanism layer employing a multi-head attention mechanism. As part of preprocessing, mRNA sequences were reversed from their original 5′to 3′orientation to a 3′to 5′direction, aligning with the antisense strand pairing mechanism of miRNAs. T This adjustment enhances the ability of the model to learn features critical for predicting miRNA-mRNA interactions by simulating complementary base-pairing interactions, ensuring the processed sequence data accurately represents their functional relationships.
Within the GRMMI framework, the sequence feature extraction module first employs an embedding layer to map these discrete symbols into low-dimensional dense vector representations, capturing latent relationships and contextual information between bases. The embedding weights are initialized with pre-trained FastText vectors, leveraging semantic features from large-scale RNA datasets. Next, the model uses a CNN layer to extract local RNA sequence features. This layer identifies significant base patterns for functional inference and, through convolution and pooling, efficiently processes local features, enhances computational efficiency, and reduces data dimensionality. After processing by the CNN layer, the RNA sequence features are represented as shown in Equations 4, 5:
Here,
BiLSTM, an extension of LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory network) (Nguyen et al., 2021), addresses the vanishing and exploding gradient problems in standard RNNs through its gating mechanisms and processes input sequences in both forward and backward directions, enabling it to effectively model long-range dependencies (Aslan et al., 2021). For an input sequence
The forget gate
where
The input gate
The candidate cell state
The cell state update
where
The output gate
The hidden state
For a BiLSTM, it consists of two LSTM layers: the forward LSTM processes the sequence
The final hidden state
After being processed by the CNN, the sequence is further modeled by a BiLSTM layer to capture global contextual information. BiLSTM captures both forward and backward dependencies between bases, which is suitable for RNA sequences due to their bidirectional structures and long-range dependencies. This enables a comprehensive representation of the structural and functional features of RNA (Zhang et al., 2022).
The addition of BiLSTM overcomes the limitation of CNN in only capturing local patterns, enhancing feature representation. The sequence data is then processed by a mutual attention mechanism, which captures the interactions between miRNA and mRNA sequences and emphasizes their global dependencies, focusing on the dynamic relationships between the features of both input sequences (Yang et al., 2021).
The miRNA and mRNA feature representations obtained from the BiLSTM layer serve as the inputs to the mutual attention mechanism, as defined in Equations 15, 16:
Here,
The mutual attention mechanism is implemented using multi-head attention. In multi-head attention, each head applies independent weight matrices to linearly transform the input features into Query
Here,
The core of the mutual attention mechanism is to compute the attention scores between miRNA and mRNA sequences to capture their mutual dependencies. Specifically, the similarity score matrix
The similarity score matrix
In this formula,
Next, for the similarity score matrix
Here,
Finally, after obtaining the attention weight matrix
Here,
where
Through the above operations, the attention mechanism dynamically aggregates key-value information related to the query, thereby generating feature representations that effectively capture the interaction relationships between miRNA and mRNA sequences (Wang et al., 2023).
RNA node feature extraction
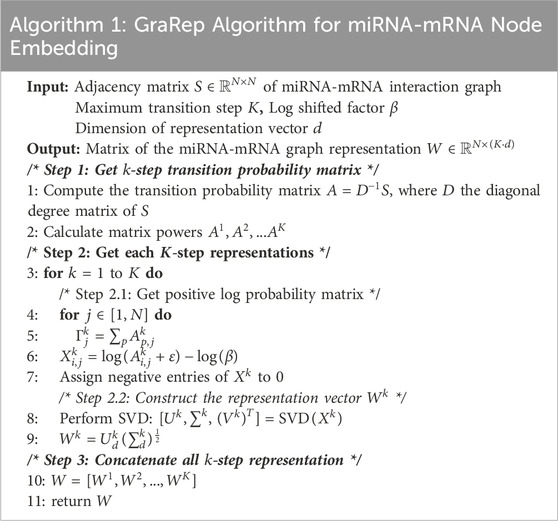
Since miRNA and mRNA are distinct nodes with complex functional associations, and their interaction relationships are sparse (each miRNA is associated with only a limited number of mRNAs), miRNA can indirectly influence other miRNAs through multiple steps. To capture RNA node features, we use the GraRep method, which embeds graph nodes into a low-dimensional vector space while preserving structural information. By applying matrix factorization, GraRep captures both local and global relationships between nodes, revealing multi-order adjacency relationships (Cao et al., 2015). The first-order adjacency matrix captures direct miRNA-mRNA relationships, while higher-order matrices uncover indirect ones. The embeddings of GraRep provide a unified feature space for miRNA and mRNA, reflecting their complex interactions. The process is detailed in Table 1.
Step-1 Get
First, the adjacency matrix
The matrix
Step-2 Get each
The embeddings
Singular value decomposition (SVD) is then performed on
Step-3 Concatenate all
By concatenating the embeddings from all orders, the final node feature matrix
Experiments and results
Evaluation criteria
In the experiments, the model performance was evaluated using the following eight metrics: Accuracy (Acc), F1-score (F1), Area Under the ROC Curve (AUC), Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve (AUPR), Matthews Correlation Coefficient (MCC), Sensitivity (SEN), Precision (PPV), and Specificity (TNR). The formulas for these metrics are shown in Equations 22–27:
Here, TP (True Positives) refers to the number of samples correctly predicted as positive, TN (True Negatives) refers to the number of samples correctly predicted as negative, FP (False Positives) refers to the number of samples incorrectly predicted as positive, and FN (False Negatives) refers to the number of samples incorrectly predicted as negative.
Results
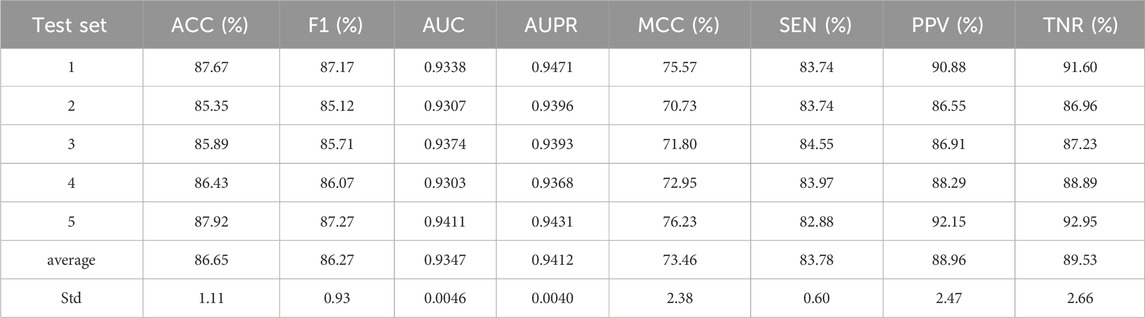
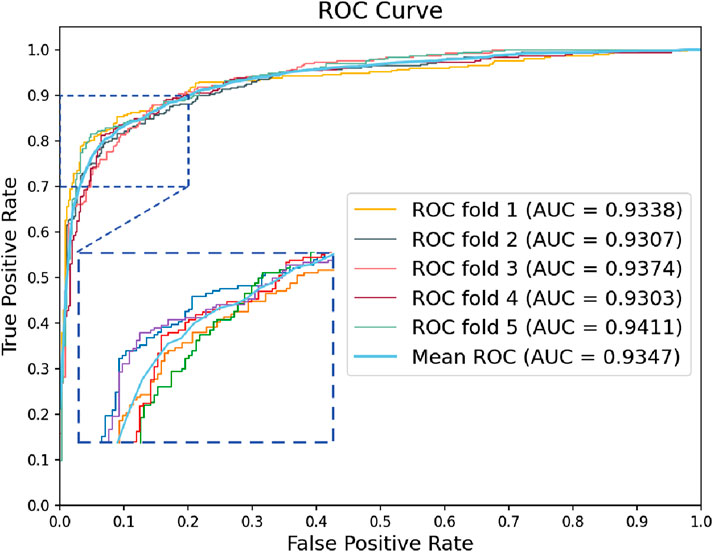
We used GRMMI to perform 5-fold cross-validation on the MTIS-9214 dataset to comprehensively evaluate the performance of the model. Additionally, we replaced different components of the model to analyze their impact on overall performance, thereby investigating the contribution of each component to the specific task. Specifically, we replaced the BiLSTM, attention mechanism, feature extraction module, and fusion strategy with other commonly used methods for comparative experiments. Performance changes were analyzed using metrics such as ACC and F1-score calculated with a fixed classification threshold of 0.5 to validate the advantages and robustness of GRMMI in predicting miRNA-mRNA interaction pairs. The detailed results for each fold are shown in Table 2 and Figure 4.
Comparison of different pretraining methods
In the GRMMI model, we used FastText for RNA pretraining to obtain sequence weights suitable for the embedding layer in downstream tasks. To verify the effectiveness of FastText in RNA sequence feature pretraining, we conducted a comparative experiment where Word2Vec was used as an alternative pretraining method. The RNA sequences were pretrained using Word2Vec, and the resulting embedding weights were applied to the GRMMI model for performance evaluation.
Figure 5 compares Word2Vec and FastText across six performance metrics, with pink bars representing Word2Vec and blue bars representing FastText. The results show mixed performance between the two models across different evaluation metrics. FastText achieves higher scores in Accuracy (86.65% vs. 85.31%), F1 Score (86.27% vs. 84.59%), and AUC (93.06% vs. 92.47%). However, the differences are relatively modest, with AUPR showing only a marginal advantage for FastText (94.12% vs. 93.78%). Conversely, Word2Vec demonstrates better performance in PPV (91.75% vs. 88.96%) and TNR (89.53% vs. 88.96%). The shaded regions highlight these performance differences between the two models. While the ability of FastText to decompose words into subwords enables it to capture character-level features and local patterns in RNA sequences, the overall performance comparison suggests that FastText is more suitable for this study, as it shows advantages in key comprehensive metrics that are important for the overall model evaluation.
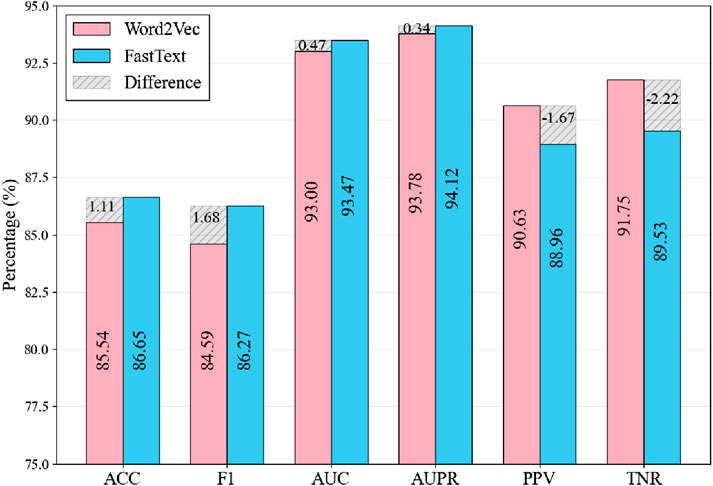
Figure 5. Comparison of Results Using Different Word Embedding Methods. The shaded regions indicate the metric differences between FastText and Word2Vec, calculated as FastText values minus Word2Vec values.
Sequence feature extraction using different deep learning frameworks
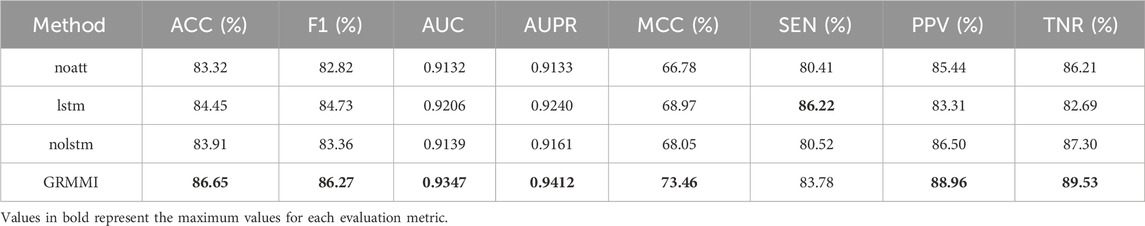
For RNA sequence embedding extraction, the GRMMI framework employs a sequence feature extraction module designed with an embedding layer, followed by CNN, BiLSTM, and mutual attention mechanisms. To analyze the contribution of the mutual attention mechanism and BiLSTM, we conducted ablation experiments while keeping the embedding extraction and fusion methods unchanged. GRMMI-noatt removes the mutual attention mechanism, retaining CNN and BiLSTM. GRMMI-lstm replaces BiLSTM with a unidirectional LSTM. GRMMI-nolstm removes the BiLSTM layer entirely, using CNN and the mutual attention mechanism after the embedding layer.
Through the results in Table 3, we see that removing the mutual attention mechanism causes the biggest drop in performance, especially in F1 and MCC, highlighting its role in capturing dependencies between sequences. Replacing BiLSTM with unidirectional LSTM reduces performance but remains better than having no LSTM, demonstrating the importance of BiLSTM for context and sequence modeling. Overall, modular synergies ensure strong RNA sequence feature extraction by integrating various facets of GRMMI.
Feature extraction using different graph embedding methods
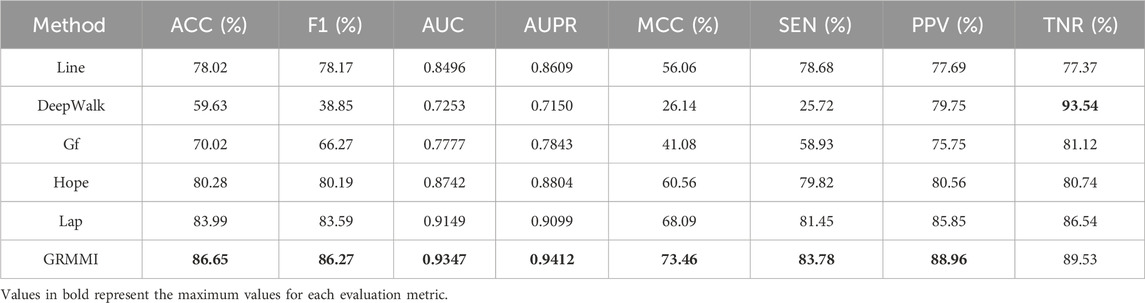
For node feature extraction, we observed favorable results using the GraRep graph embedding method. To evaluate the performance of other mainstream methods, we conducted a comparative experiment using various graph embedding approaches, including LINE, DeepWalk, Graph Factorization (GF), HOPE, and Laplacian Eigenmaps (LAP).
Through the results in Table 4, we see that GRMMI achieves the best performance across nearly all metrics, followed by Lap, while DeepWalk demonstrates the worst performance. This may be attributed to the reliance of DeepWalk on the random walk mechanism, which primarily captures local node relationships. However, the miRNA-mRNA network exhibits a complex global topology that cannot be adequately represented by only considering local information. The performance of GRMMI can be attributed to its use of the GraRep method, which captures the structural characteristics and higher-order relationships within the miRNA-mRNA network. This result supports the applicability of the GraRep method in modeling complex miRNA-mRNA networks.
Comparison of different embedding dimensions
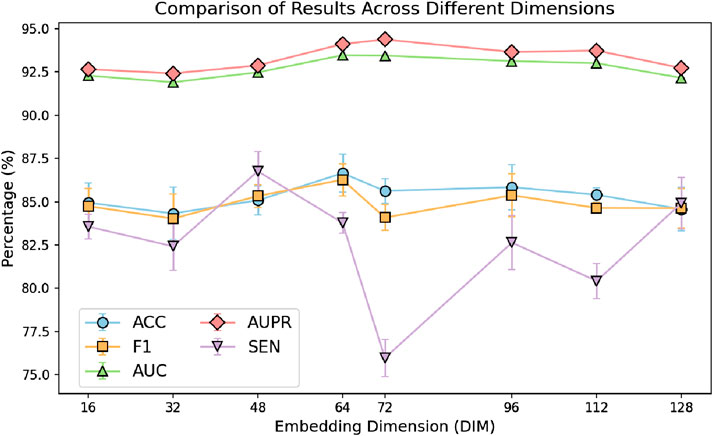
In the GRMMI method, the embedding dimension for both sequence features and node features was set to 64. To verify whether 64 is the optimal embedding dimension, we conducted a comparative experiment by varying the embedding dimensions. The dimensions were divided into eight intervals: 16, 32, 48, 64, 72, 96, 112, and 128.
From the analysis of the results in Figure 6, it can be observed that changes in embedding dimensions significantly affect the performance of the model. As the embedding dimension increases, the model demonstrates improvement in certain metrics; however, after surpassing 64 dimensions, the performance gains begin to diminish slightly. This could be attributed to the fact that lower-dimensional embeddings are insufficient to fully represent the complex miRNA-mRNA network structure. On the other hand, excessively high dimensions may introduce redundant information, leading to increased noise, which ultimately affects the generalization ability of the model.
Comparison of different fusion methods
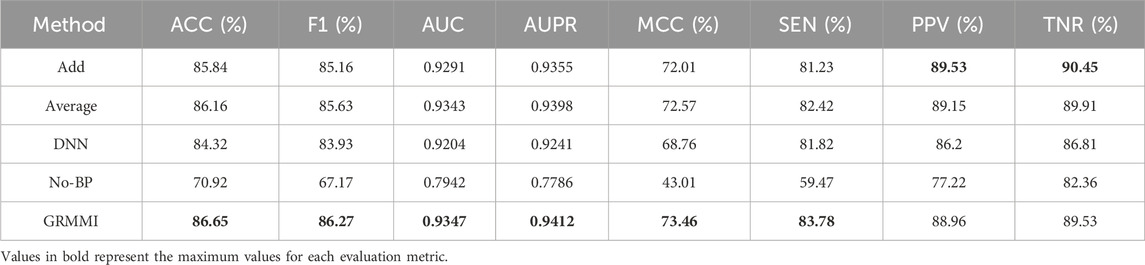
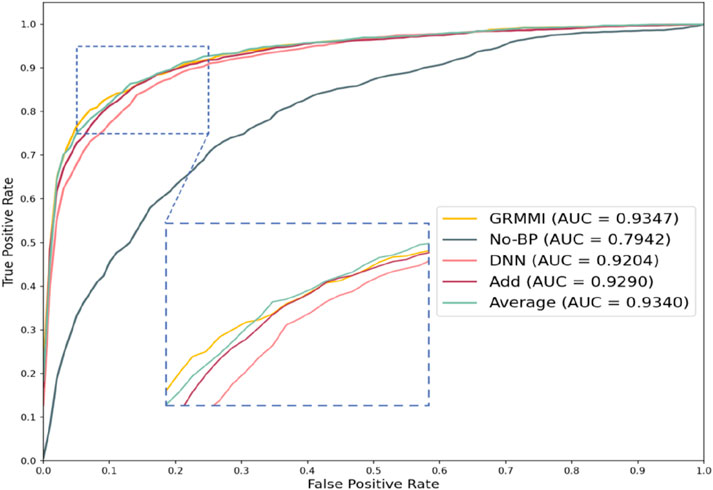
To evaluate the impact of different feature fusion methods on predicting miRNA-mRNA interactions, ablation experiments were designed focusing solely on the feature fusion stage while keeping the sequence and node feature extraction methods unchanged. The GRMMI method fuses sequence and node features using the Concatenate method, followed by nonlinear processing. Variations tested include replacing the Concatenate method with additive or average fusion, using a deep neural network (DNN) instead of the original fusion method while retaining Concatenate, and bypassing the additional processing layer entirely by directly inputting the features into the prediction layer after Concatenate. Table 5 presents the evaluation metrics of GRMMI and its variant models under 5-fold cross-validation, showing the average results across folds with the highest values for each metric highlighted in bold. The ROC curves for different fusion methods are illustrated in Figure 7.
The results show that the No-BP method, which directly inputs concatenated features into the prediction layer without nonlinear processing, performs significantly worse than methods with nonlinear processing (e.g., BP or DNN). This highlights the importance of nonlinear transformations in capturing complex feature relationships. Nonlinear processing is critical for miRNA-mRNA interaction prediction, as it captures feature interdependencies, while the No-BP method fails to express these patterns, leading to a decline in metrics like AUC and F1-score. The BP method demonstrates stable performance by efficiently mining fused features through fully connected layers and activation functions. Although DNN theoretically captures more complex patterns, it underperforms due to the current data scale, suggesting that moderately complex models like BP are more advantageous for tasks with complex feature relationships, while overly complex models like DNN may be limited by data volume or computational resources.
Comparison of different classifiers
To evaluate the classification performance of different classifiers on fused features, we designed a comparative experiment using various classifiers. In the original experiment, a fully connected layer was used to output classification results. To further investigate, we introduced multiple traditional machine learning classifiers for comparison and evaluated their performance.
In the experiments, other settings were kept unchanged, and the fused features from the BP neural network were used as input. Six traditional machine learning classifiers were tested, including SVM, Random Forest, AdaBoost, Gradient Boosting, KNN, and Logistic Regression. The results were evaluated using 5-fold cross-validation and are presented in Figure 8.
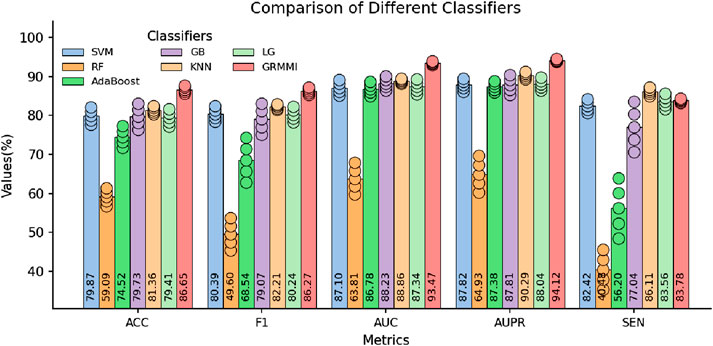
Figure 8. Comparison of Selected Metrics Across Different Classifiers. The circles represent the standard deviation range from 5-fold cross-validation, indicating performance variability for each classifier.
The results show that while traditional classifiers can perform classification, their performance, especially in metrics like AUC, AUPR, and MCC, is inferior to GRMMI. GRMMI achieves an MCC of 73.46%, outperforming KNN (63.03%) and other classifiers, most of which fall below 60%. Notably, Random Forest performs poorly, with an MCC of only 19.7%. These findings highlight the ability of GRMMI to deliver balanced and consistent results, capturing complex nonlinear feature relationships that traditional classifiers struggle to model.
Comparison with mainstream prediction algorithms
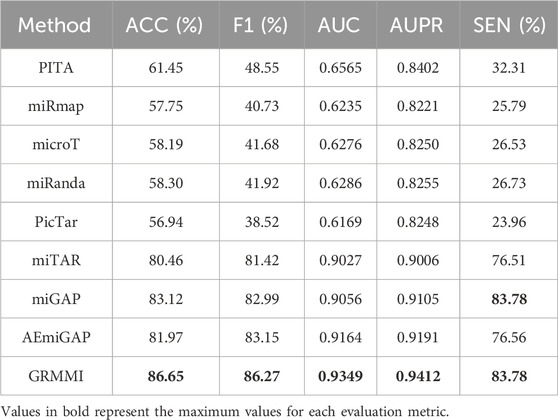
We compared GRMMI with several mainstream miRNA-mRNA prediction algorithms and state-of-the-art deep learning methods. The traditional algorithms include PITA (based on binding energy changes and target site accessibility) (Kertesz et al., 2007), miRmap (integrating multiple parameters to evaluate miRNA-mediated gene repression) (Vejnar and Zdobnov, 2012), microT (based on seed region matching rules combined with conservation information) (Maragkakis et al., 2009), miRanda (combining base pairing and binding energy calculation for initial screening) (Betel et al., 2010), and PicTar (leveraging multi-species conservation for joint prediction) (Chen and Rajewsky, 2006). Additionally, we compared against three representative deep learning baseline methods: miTAR, a hybrid deep learning approach that integrates CNN and bidirectional RNN layers to learn both spatial and sequential features from raw miRNA and target sequences (Gu et al., 2021). miGAP, a deep learning method that leverages protein2Vec embedding and LSTM-based architecture for miRNA-gene association prediction (Yoon et al., 2023); and AEmiGAP, an advanced deep learning model that integrates autoencoders with LSTM networks to capture latent relationships between miRNAs and genes (Yoon et al., 2024).
Through the results in Table 6, GRMMI shows improved performance compared to both traditional miRNA-mRNA prediction algorithms and other deep learning methods across evaluated metrics. Compared to traditional methods, this performance can be attributed to the integration by GRMMI of diverse RNA sequence and structural features combined with deep learning techniques, which enables more comprehensive capture of the complex regulatory relationships between miRNAs and mRNAs. The nonlinear fitting capability of deep learning models allows GRMMI to extract latent biological information from high-dimensional features while reducing the reliance on specific rules, such as seed region matching or evolutionary conservation, that is common in traditional algorithms. When compared to other deep learning approaches, GRMMI demonstrates advantages in capturing both local and global sequence patterns through its graph-based architecture.
Case studies
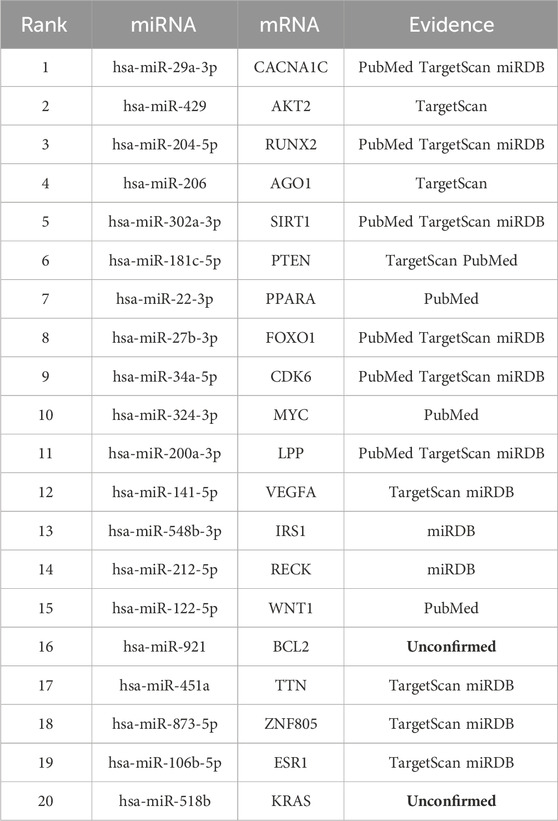
In this section, we performed case studies to demonstrate the capability of the GRMMI model in predicting potential miRNA-mRNA interaction pairs. All experimentally validated miRNA-mRNA pairs were used to train the GRMMI model, which was then applied to predict unknown interactions. The model assigned probability scores to each unknown interaction, ranked in descending order. The top 20 predicted interactions were selected for further analysis and inputted for queries in the miRWalk database.
The results of the miRWalk queries are shown in the table below (Dweep and Gretz, 2015). In this table: PubMed indicates interactions that have been experimentally validated and documented in PubMed. TargetScan indicates interactions that were also predicted by the TargetScan tool. miRDB indicates interactions that were predicted by the miRDB database. Unconfirmed indicates interactions that have not yet been experimentally validated or predicted by any of these tools. The detailed results are as shown in Table 7.
The relationships between miRNA and mRNA are crucial for understanding disease mechanisms and developing therapeutic strategies. Exploring these interactions can provide new insights and potential targets for molecular diagnostics, drug development, and precision medicine.
For example, hsa-miR-29a-3p targets CACNA1C, playing a key role in atrial fibrillation by disrupting calcium homeostasis in cardiomyocytes. This discovery offers a new target for intervention (Zhao et al., 2016). Similarly, hsa-miR-204-5p targets RUNX2, regulating vascular smooth muscle cell calcification. By inhibiting RUNX2 expression, it reduces vascular calcification (Cui et al., 2012), providing a basis for developing miRNA-based therapies for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases.
Conclusion
The identification of miRNA-mRNA interactions is crucial for understanding disease mechanisms and developing therapeutic interventions. These regulatory relationships significantly influence gene expression and play essential roles in the onset and progression of various diseases, including cancer and cardiovascular disorders. This study proposed an innovative deep learning model, GRMMI, to enhance the accuracy of miRNA-mRNA interaction predictions.
The GRMMI model integrates sequence features and node features using a CNN-BiLSTM architecture combined with mutual attention mechanisms and graph embedding techniques. During data preprocessing, to better reflect the complementary pairing mechanism between miRNA and mRNA, the mRNA sequences were reversed from their original 3′to 5′orientation to a 5′to 3′orientation. This adjustment aligns the direction of mRNA sequences with that of miRNA, enabling the model to more accurately learn the pairing relationships and regulatory effects between the two. By effectively fusing these features through a backpropagation neural network, the model demonstrates significant advantages in predictive performance compared to traditional and alternative methods. Case studies further validated the effectiveness of the GRMMI model in identifying potential miRNA-mRNA interactions and demonstrated its practical significance in biological research.
Despite its promising predictive performance, the GRMMI model has some limitations. For example, there is room for improvement in the integration of multi-dimensional features, and its adaptability to larger-scale real-world biological datasets requires further validation. Additionally, the complexity of the model may impose higher computational resource requirements, which could be a limitation for large-scale applications. Future research will focus on optimizing feature extraction and fusion strategies to reduce the introduction of redundant information, improving the adaptability of the model to sparse data, and integrating more biological information into the model.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author contributions
T-LS: Writing – original draft. LWa: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Investigation. LWo. Z-HY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing – review and editing. C-QY: Writing – review and editing, Software. CJ: Writing – review and editing, Validation. S-ZL: Writing – review and editing, Software.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi (Grants 2023GXNSFDA026031, 2024GXNSFAA010283); Guangxi Science and Technology Program (Grant 2024-102-3); Natural Science Foundation of Shandong (Grant ZR2022LZL003); National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grants 62172355, 61702444, 62273284); National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars of China (Grant 62325308); General Science Research Project of Shaanxi Provincial Department of Education (Grant 24JK0693).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aslan, M. F., Unlersen, M. F., Sabanci, K., and Durdu, A. (2021). CNN-Based transfer learning–BiLSTM network: a novel approach for COVID-19 infection detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 98, 106912. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106912
Baker, A. H., Giacca, M., and Thum, T. (2024). miRNA discovery to therapy: the field is sufficiently mature to assess the value of miRNA-based therapeutics. Mol. Ther. 33, 3–4. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2024.12.024
Betel, D., Koppal, A., Agius, P., Sander, C., and Leslie, C. (2010). Comprehensive modeling of microRNA targets predicts functional non-conserved and non-canonical sites. Genome Biol. 11, R90–14. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-8-r90
Cao, S., Lu, W., and Xu, Q. (2015). “Grarep: learning graph representations with global structural information,” in Proceedings of the 24th ACM international on conference on information and knowledge management, 891–900.
Carleton, M., Cleary, M. A., and Linsley, P. S. (2007). MicroRNAs and cell cycle regulation. Cell cycle 6 (17), 2127–2132. doi:10.4161/cc.6.17.4641
Chekulaeva, M. (2023). First demonstration of miRNA-dependent mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 24 (3), 164. doi:10.1038/s41580-022-00557-9
Chen, K., and Rajewsky, N. (2006). Natural selection on human microRNA binding sites inferred from SNP data. Nat. Genet. 38 (12), 1452–1456. doi:10.1038/ng1910
Chen, Y., and Wang, X. (2020). miRDB: an online database for prediction of functional microRNA targets. Nucleic acids Res. 48 (D1), D127–D131. doi:10.1093/nar/gkz757
Cui, R.-R., Li, S.-J., Liu, L.-J., Yi, L., Liang, Q.-H., Zhu, X., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-204 regulates vascular smooth muscle cell calcification in vitro and in vivo. Cardiovasc. Res. 96 (2), 320–329. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvs258
Das, S., Vera, M., Gandin, V., Singer, R. H., and Tutucci, E. (2021). Intracellular mRNA transport and localized translation. Nat. Rev. Mol. cell Biol. 22 (7), 483–504. doi:10.1038/s41580-021-00356-8
Dweep, H., and Gretz, N. (2015). miRWalk2. 0: a comprehensive atlas of microRNA-target interactions. Nat. methods 12 (8), 697. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3485
Fathi, M., Ghafouri-Fard, S., Abak, A., and Taheri, M. (2021). Emerging roles of miRNAs in the development of pancreatic cancer. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 141, 111914. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111914
Griesemer, D., Xue, J. R., Reilly, S. K., Ulirsch, J. C., Kukreja, K., Davis, J. R., et al. (2021). Genome-wide functional screen of 3′ UTR variants uncovers causal variants for human disease and evolution. Cell 184 (20), 5247–5260. e19. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.08.025
Gu, T., Zhao, X., Barbazuk, W. B., and Lee, J.-H. (2021). miTAR: a hybrid deep learning-based approach for predicting miRNA targets. BMC Bioinforma. 22, 96–16. doi:10.1186/s12859-021-04026-6
Guo, L.-X., You, Z.-H., Wang, L., Yu, C.-Q., Zhao, B.-W., Ren, Z.-H., et al. (2022). A novel circRNA-miRNA association prediction model based on structural deep neural network embedding. Briefings Bioinforma. 23 (5), bbac391. doi:10.1093/bib/bbac391
Huang, H.-Y., Lin, Y.-C.-D., Cui, S., Huang, Y., Tang, Y., Xu, J., et al. (2022). miRTarBase update 2022: an informative resource for experimentally validated miRNA–target interactions. Nucleic acids Res. 50 (D1), D222–D230. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab1079
Hussen, B. M., Hidayat, H. J., Salihi, A., Sabir, D. K., Taheri, M., and Ghafouri-Fard, S. (2021). MicroRNA: a signature for cancer progression. Biomed. and Pharmacother. 138, 111528. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111528
Jiang, C., Wang, L., Yu, C.-Q., You, Z.-H., Wang, X.-F., Wei, M.-M., et al. (2024). Hither-CMI: prediction of circRNA-miRNA interactions based on a hybrid multimodal network and higher-order neighborhood information via a graph convolutional network. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 65, 446–459. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.4c01991
Joulin, A., Grave, E., Bojanowski, P., and Mikolov, T. (2016). Bag of tricks for efficient text classification. arXiv Prepr. arXiv:1607.01759. doi:10.48550/arXiv.1607.01759
Kertesz, M., Iovino, N., Unnerstall, U., Gaul, U., and Segal, E. (2007). The role of site accessibility in microRNA target recognition. Nat. Genet. 39 (10), 1278–1284. doi:10.1038/ng2135
Kim, T., and Croce, C. M. (2023). MicroRNA: trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies. Exp. and Mol. Med. 55 (7), 1314–1321. doi:10.1038/s12276-023-01050-9
Kozomara, A., Birgaoanu, M., and Griffiths-Jones, S. (2019). miRBase: from microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic acids Res. 47 (D1), D155–D162. doi:10.1093/nar/gky1141
Laggerbauer, B., and Engelhardt, S. (2022). MicroRNAs as therapeutic targets in cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. investigation 132 (11), e159179. doi:10.1172/JCI159179
Lee, B., Baek, J., Park, S., and Yoon, S. (2016). “deepTarget: End-To-End learning framework for microRNA target prediction using deep recurrent neural networks,” in Proceedings of the 7th ACM international conference on bioinformatics, computational biology, and health informatics, 434–442.
Liu, W., Tang, T., Lu, X., Fu, X., Yang, Y., and Peng, L. (2023). MPCLCDA: predicting circRNA–disease associations by using automatically selected meta-path and contrastive learning. Briefings Bioinforma. 24 (4), bbad227. doi:10.1093/bib/bbad227
Maragkakis, M., Reczko, M., Simossis, V. A., Alexiou, P., Papadopoulos, G. L., Dalamagas, T., et al. (2009). DIANA-MicroT web server: elucidating microRNA functions through target prediction. Nucleic acids Res. 37 (Suppl. l_2), W273–W276. doi:10.1093/nar/gkp292
McGeary, S. E., Lin, K. S., Shi, C. Y., Pham, T. M., Bisaria, N., Kelley, G. M., et al. (2019). The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy. Science 366 (6472), eaav1741. doi:10.1126/science.aav1741
Nguyen, H. D., Tran, K. P., Thomassey, S., and Hamad, M. (2021). Forecasting and anomaly detection approaches using LSTM and LSTM autoencoder techniques with the applications in supply chain management. Int. J. Inf. Manag. 57, 102282. doi:10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2020.102282
Ni, J., Zhang, X., Li, J., Zheng, Z., Zhang, J., Zhao, W., et al. (2021). Tumour-derived exosomal lncRNA-SOX2OT promotes bone metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting the miRNA-194-5p/RAC1 signalling axis in osteoclasts. Cell death and Dis. 12 (7), 662. doi:10.1038/s41419-021-03928-w
Peng, W., Che, Z., Dai, W., Wei, S., and Lan, W. (2022). Predicting miRNA-disease associations from miRNA-gene-disease heterogeneous network with multi-relational graph convolutional network model. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinforma. 20 (6), 3363–3375. doi:10.1109/TCBB.2022.3187739
Peng, W., Du, J., Dai, W., and Lan, W. (2021a). Predicting miRNA-disease association based on modularity preserving heterogeneous network embedding. Front. cell Dev. Biol. 9, 603758. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.603758
Peng, W., He, Z., Dai, W., and Lan, W. (2024a). MHCLMDA: multihypergraph contrastive learning for miRNA–disease association prediction. Briefings Bioinforma. 25 (1), bbad524. doi:10.1093/bib/bbad524
Peng, W., Yi, S., Dai, W., and Wang, J. (2021b). Identifying and ranking potential cancer drivers using representation learning on attributed network. Methods 192, 13–24. doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2020.07.013
Peng, W., Zhou, Z., Dai, W., Yu, N., and Wang, J. (2024b). Multi-network graph contrastive learning for cancer driver gene identification. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 11, 3430–3440. doi:10.1109/tnse.2024.3373652
Pennington, J., Socher, R., and Manning, C. D. (2014). “Glove: global vectors for word representation,” in Proceedings of the 2014 conference on empirical methods in natural language processing (EMNLP), 1532–1543.
Qin, S., Tang, X., Chen, Y., Chen, K., Fan, N., Xiao, W., et al. (2022). mRNA-based therapeutics: powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 7 (1), 166. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01007-w
Taganov, K. D., Boldin, M. P., Chang, K.-J., and Baltimore, D. (2006). NF-kappaB-dependent induction of microRNA miR-146, an inhibitor targeted to signaling proteins of innate immune responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103 (33), 12481–12486. doi:10.1073/pnas.0605298103
Vejnar, C. E., and Zdobnov, E. M. (2012). MiRmap: comprehensive prediction of microRNA target repression strength. Nucleic acids Res. 40 (22), 11673–11683. doi:10.1093/nar/gks901
Walgrave, H., Zhou, L., De Strooper, B., and Salta, E. (2021). The promise of microRNA-based therapies in Alzheimer’s disease: challenges and perspectives. Mol. Neurodegener. 16, 76–16. doi:10.1186/s13024-021-00496-7
Wang, L., Li, Z.-W., Hu, J., Wong, L., Zhao, B.-W., and You, Z.-H. (2024). A PiRNA-disease association model incorporating sequence multi-source information with graph convolutional networks. Appl. Soft Comput. 157, 111523. doi:10.1016/j.asoc.2024.111523
Wang, L., Wong, L., You, Z.-H., and Huang, D.-S. (2023). AMDECDA: attention mechanism combined with data ensemble strategy for predicting CircRNA-disease association. IEEE Trans. Big Data 10, 320–329. doi:10.1109/tbdata.2023.3334673
Wei, M., Wang, L., Li, Y., Li, Z., Zhao, B., Su, X., et al. (2024). BioKG-CMI: a multi-source feature fusion model based on biological knowledge graph for predicting circRNA-miRNA interactions. Sci. China Inf. Sci. 67 (8), 189104. doi:10.1007/s11432-024-4098-3
Yang, Z., Zhong, W., Zhao, L., and Chen, C. Y.-C. (2021). ML-DTI: mutual learning mechanism for interpretable drug–target interaction prediction. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12 (17), 4247–4261. doi:10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c00867
Yoon, S., Hwang, I., Cho, J., Yoon, H., and Lee, K. (2023). Migap: Mirna–Gene association prediction method based on deep learning model. Appl. Sci. 13 (22), 12349. doi:10.3390/app132212349
Yoon, S., Yoon, H., Cho, J., and Lee, K. (2024). AEmiGAP: autoencoder-based miRNA–Gene association prediction using deep learning method. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 25 (23), 13075. doi:10.3390/ijms252313075
Zhang, Z.-Y., Ning, L., Ye, X., Yang, Y.-H., Futamura, Y., Sakurai, T., et al. (2022). iLoc-miRNA: extracellular/intracellular miRNA prediction using deep BiLSTM with attention mechanism. Briefings Bioinforma. 23 (5), bbac395. doi:10.1093/bib/bbac395
Zhao, F., Zhou, Z., Dang, Y., Na, H., Adam, C., Lipzen, A., et al. (2021). Genome-wide role of codon usage on transcription and identification of potential regulators. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 118 (6), e2022590118. doi:10.1073/pnas.2022590118
Zhao, Y., Yuan, Y., and Qiu, C. (2016). Underexpression of CACNA1C caused by overexpression of microRNA-29a underlies the pathogenesis of atrial fibrillation. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 22, 2175–2181. doi:10.12659/msm.896191
Keywords: miRNA-Target mRNA interactions, mutual attention mechanisms, BiLSTM, fastText, GraRep
Citation: Shi T-L, Wang L, Wong L, You Z-H, Yu C-Q, Jiang C and Liang S-Z (2025) Incorporating graph representation and mutual attention mechanism for MiRNA-MRNA interaction prediction. Front. Genet. 16:1637427. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1637427
Received: 29 May 2025; Accepted: 27 June 2025;
Published: 17 July 2025.
Edited by:
Juexin Wang, Purdue University Indianapolis, United StatesReviewed by:
Wei Peng, Kunming University of Science and Technology, ChinaHang Wei, Xidian University, China
Copyright © 2025 Shi, Wang, Wong, You, Yu, Jiang and Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Lei Wang, bGVpd2FuZ0BjdW10LmVkdS5jbg==; Zhu-Hong You, emh1aG9uZ3lvdUBud3B1LmVkdS5jbg==; Chang-Qing Yu, eGF5Y3FAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†ORCID: Leon Wong, orcid.org/0000-0002-6864-991X
 Tai-Long Shi
Tai-Long Shi Lei Wang
Lei Wang Leon Wong
Leon Wong Zhu-Hong You
Zhu-Hong You Chang-Qing Yu
Chang-Qing Yu Chen Jiang
Chen Jiang Si-Zhe Liang
Si-Zhe Liang