- 1Department of Pediatrics, Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
- 2Guizhou Children’s Hospital, Zunyi, China
- 3Collaborative Innovation Center for Tissue Injury Repair and Regenerative Medicine of Zunyi Medical University, Zunyi, China
Objective: The study aims to describe the clinical manifestations, immunophenotype, and gene mutation characteristics of a child with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID) caused by an IL2RG mutation (NM_000206.3; exon 2 c.216C > A, p.Cys72*), and to contextualize these findings through a review of reported cases of X-SCID associated with Talaromyces marneffei (T. marneffei) infection, highlighting the immunological and diagnostic relevance of the mutation.
Methods: The clinical data of a child with X-SCID caused by an IL2RG mutation were retrospectively analyzed. Whole-exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing were used to identify the mutation, and flow cytometry was employed for immunophenotypic analysis to assess the impact of the mutation on immune function. A literature review was performed on reported cases of X-SCID associated with T. marneffei infection identified in PubMed and Scopus.
Results: The patient was a 4-month-old male infant presenting with chronic diarrhea, recurrent fever, and anemia, with poor response to antibiotic treatment. Laboratory tests indicated T. marneffei infection, significantly reduced T lymphocytes and NK cells, and decreased levels of immunoglobulins (IgG, IgA, IgE). Genetic testing revealed a de novo hemizygous mutation in the IL2RG gene (NM_000206.3; exon2 c.216C > A, p.Cys72*), which has not been previously reported. Flow cytometric analysis showed a severe reduction in T lymphocytes, absence of CD8 + T cells, reduced NK cells, and a normal number of B lymphocytes. Six cases of IL2RG gene mutation combined with T. marneffei infection were identified in the literature, most showing fever, hepatosplenomegaly and respiratory tract infection.
Conclusion: This case of X-SCID caused by a novel de novo IL2RG mutation expands the known mutation spectrum and highlights its immunological and diagnostic relevance. The review of reported cases of X-SCID with T. marneffei infection further clarifies genotype–phenotype correlations and supports improved recognition of such rare presentations.
1 Introduction
Inborn Errors of Immunity (IEI), historically referred to as Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases (PIDs), are a group of genetically heterogeneous disorders caused by defects in the immune system, leading to increased susceptibility to infections. Since 1970, the World Health Organization (WHO) has organized meetings and established the International Union of Immunological Societies (IUIS), which defined and classified “Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases.” Initially, 16 distinct immunodeficiencies were identified. Approximately every 2 years, the IUIS releases updated reports, refining the classification of IEI. In 2022, the IUIS updated its classification, maintaining the 10 major categories of IEI established in 2019 and incorporating 55 new monogenic defects along with one autoantibody phenotype, detailing their key clinical and laboratory features (Tangye et al., 2022). Given the involvement of hundreds of genes in IEI, clinical phenotypes are often not highly specific, making diagnosis based solely on phenotypes challenging. Consequently, most novel variants are identified through next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, with whole-exome sequencing (WES) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS) now considered the standard for identifying new pathogenic gene variants (Seleman et al., 2017; Meyts et al., 2016).
Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID), one of the most devastating forms of IEI, is a genetically heterogeneous disorder characterized by arrested T lymphocyte development, accompanied by varying degrees of functional abnormalities in B cells and NK cells, leading to severe impairment of both cellular and humoral immunity (Al Sukaiti et al., 2021). Infants with SCID typically present with respiratory symptoms, chronic diarrhea, failure to thrive, and recurrent opportunistic infections within the first 2–6 months of life (Aluri et al., 2019). The incidence of SCID varies geographically. Epidemiological data indicate an estimated prevalence of 1.7 per 100,000 live births in the Greece-Turkey region (Michos et al., 2011). In Germany, a comprehensive analysis of SCID cases diagnosed in pediatric hospitals between 2014 and 2015, using stringent inclusion and exclusion criteria, estimated an annual incidence of 1.6 per 100,000 live births (Shai et al., 2020). In Israel, neonatal screening for SCID revealed a higher incidence of 1 in 29,000 live births (Lev et al., 2022). These findings highlight the importance of region-specific epidemiological studies and early diagnostic interventions for SCID.
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency (X-SCID), caused by mutations in the interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain (IL2RG) gene, is one of the most common forms of SCID, accounting for approximately 50%–60% of cases (Mahdavi et al., 2021). Infants with X-SCID typically present with clinical symptoms within the first 2–5 months of life, characterized by recurrent opportunistic infections and reduced numbers and impaired function of T cells and/or B cells. Without treatment, most X-SCID patients succumb to infections within the first year of life (Jiang et al., 2024). Current therapeutic strategies for X-SCID include infection prophylaxis, immune replacement therapy, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), and certain gene therapies (Aranda et al., 2024). Although molecular genetic methods such as quantitative detection of T-cell receptor excision circles (TRECs) (Currier and Puck, 2021) and kappa-deleting recombination excision circles (KRECs) (Nakagawa et al., 2011) are available for SCID screening, clinical implementation of SCID screening and genetic testing remains limited (Boyarchuk et al., 2022). Additionally, due to the early onset and nonspecific clinical manifestations of X-SCID, clinicians often face challenges in accurately diagnosing immunodeficiency disorders at an early stage.
In this study, we describe the clinical manifestations, immunophenotypic characteristics, and diagnostic and therapeutic management of a patient with X-SCID harboring a novel de novo IL2RG mutation. We also provide a comprehensive review of all reported X-SCID cases combined with Talaromyces marneffei (T. marneffei) infection in the literature. The aim of this study is to describe the clinical and immunophenotypic features of a patient with X-SCID harboring a novel de novo IL2RG mutation, review all reported cases of X-SCID associated with T. marneffei infection, and provide insights to support early diagnosis, treatment, and screening in at-risk families.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patient
The subject of this study was a 4-month-old male infant. Clinical data were collected after obtaining informed consent from his legal guardian. This study was conducted in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University.
2.2 Genetic sequencing analysis
Peripheral blood samples were collected from the patient and both parents for DNA extraction. Whole-exome sequencing was performed using NGS technology and Sanger sequencing (MyGenostics, Beijing, China) was applied for variant validation. Databases such as HGMD, ClinVar, PubMed, and Scopus were searched, and relevant literature was reviewed. Variants were classified according to the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG).
2.3 Flow cytometry
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) of the patient were isolated and counted. The following fluorescently labeled antibodies were used for surface staining of T and B cells: anti-TCRαβ-PE (306708; BioLegend), anti-TCRγδ-Brilliant Violet 421 (331218; BioLegend), anti-CD3-PerCP (300326; BioLegend), anti-CD4-FITC (300506; BioLegend), anti-CD8a-Brilliant Violet 510 (301048; BioLegend), anti-CD27-APC (356410; BioLegend), anti-CD45RA-PE-Cy7 (304126; BioLegend), anti-CD19-APC (302212; BioLegend), anti-CD27-PB (302822; BioLegend), anti-IgD-AF488 (348216; BioLegend), anti-CD38-PerCP (303520; BioLegend), and anti-CD24-PE (311106; BioLegend). Stained cells were analyzed using a FACS Canto Plus flow cytometry (BD, United States) and data were processed using FlowJo software.
3 Results
3.1 Case presentation
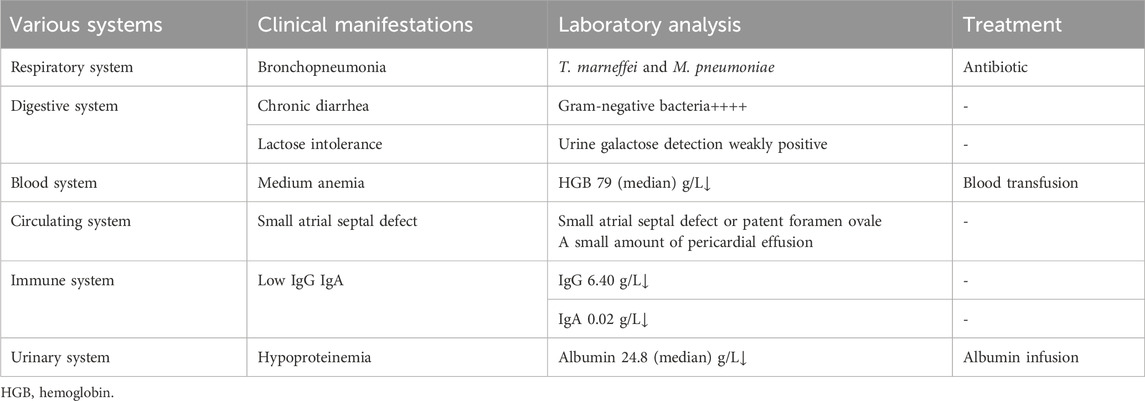
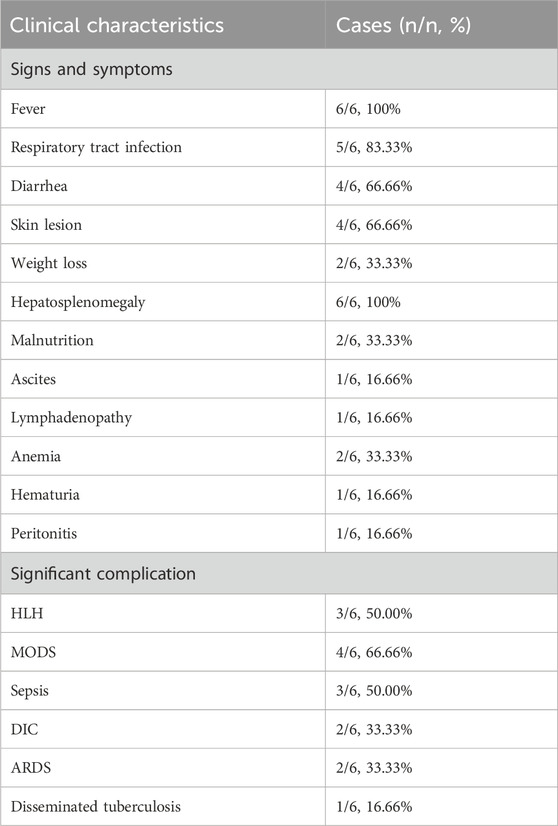
A 4-month-old male infant with no family history of immunodeficiency was born via full-term cesarean section to healthy, non-consanguineous parents (G1P1). Birth history indicated nuchal cord and meconium-stained amniotic fluid, with a history of neonatal transfusion. Postnatal feeding involved a combination of breast milk and formula. At 3 months of age, the infant developed recurrent diarrhea (7–8 episodes daily), characterized by yellow-green loose stools with mucus. Symptomatic treatment reduced stool frequency but did not improve stool consistency. By 4 months of age, he exhibited recurrent fever and persistent diarrhea. Laboratory tests revealed anemia with a hemoglobin level of 85 g/L (reference range, 100–140 g/L). During hospitalization, anti-infective and supportive therapies were ineffective. After referral, due to the complexity of the condition, the family ultimately opted to discontinue treatment. Key clinical features throughout the disease course included recurrent fever, diarrhea, cough, progressive anemia, hepatosplenomegaly and generalized edema (Table 1).
3.2 Laboratory examination and inspection
Continuous monitoring of routine blood parameters after admission revealed the following: although the white blood cell count remained within normal range, lymphocyte counts were markedly reduced (0.17–1.15 × 109/L, reference 0.8–4.0 × 109/L) (Figures 1A,B). Hemoglobin levels remained persistently below normal despite multiple erythrocyte transfusions (56–94 g/L, reference 100–140 g/L) (Figure 1C). A markedly elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) level suggested an ongoing infectious process. The observed decline in hs-CRP at 4 months and 27 days of age was attributed to a 3-day course of glucocorticoid therapy. Notably, the hs-CRP subsequently increased following discontinuation of corticosteroid treatment (Figure 1D).
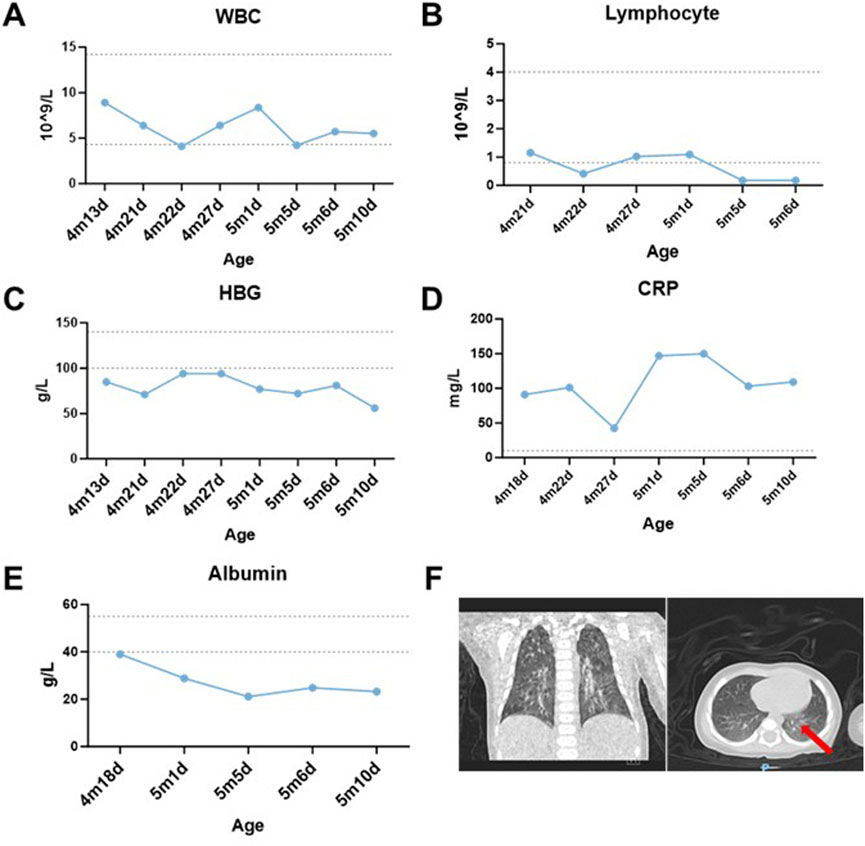
Figure 1. Laboratory examinations and results. (A,B) Dynamic changes of white blood cell (WBC) and lymphocyte counts in the patient over time. (C) Post-transfusion hemoglobin (HGB) levels failed to normalize despite red blood cell transfusions on 4m21d, 4m22d, and 5m5d. (D) Hypersensitive C-reactive protein (hs-CRP) fluctuated repeatedly during hospitalization, remaining around 100 mg/L except on 4m27d. (E) Temporal changes in serum albumin levels. (F) Coronal chest CT demonstrating scattered inflammatory infiltrates in bilateral lungs (red arrow). The ‘m’ indicates months, while the ‘d’ signifies day.
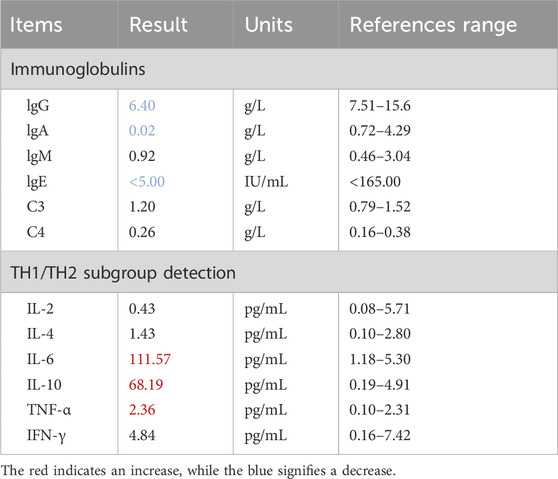
The patient developed generalized edema accompanied by progressive hypoalbuminemia during hospitalization (21.1–39 g/L, reference 40–55 g/L) (Figure 1E). Imaging studies revealed bilateral bronchopneumonia on Chest CT (Figure 1F) and a small atrial septal defect or patent foramen ovale with left-to-right atrial shunt and minimal pericardial effusion on cardiac ultrasound. Immunoglobulin assays showed significantly decreased IgA (0.02 g/L, reference 0.72–4.29 g/L) and IgE (<5 IU/mL, reference <165 IU/mL), with IgG also below the normal range. Inflammatory factors, such as IL-6 (111.57 pg/mL, reference 1.18–5.30 pg/mL), were significantly elevated (Table 2). Urinalysis demonstrated weakly positive galactose. The patient presented with co-infection of Mycoplasma pneumoniae and T. marneffei.
During comprehensive anti-infective therapy, sequential administration of third-generation cephalosporins, carbapenem antibiotics (imipenem), and antifungal agents (voriconazole and amphotericin B lipid complex) was initiated. Supportive treatments included packed red blood cell transfusions for severe anemia, human albumin supplementation to correct hypoalbuminemia-associated edema, and intravenous immunoglobulin for immunomodulation. Post-transfer, the antimicrobial regimen was augmented with linezolid and levofloxacin, alongside invasive mechanical ventilation and continuous blood purification therapy. Despite multidisciplinary intensive care, the child exhibited persistent multi-organ dysfunction with no resolution of inflammatory markers or radiographic abnormalities. Due to progression to end-stage disease, the family elected to withdraw life-sustaining therapies.
3.3 Genetic testing and analysis
Based on the patient’s postnatal history of recurrent bacterial infections, chronic diarrhea, and persistent hypoalbuminemia, an IEI was strongly suspected. Given the absence of similar clinical manifestations in either parent, the mutation was hypothesized to be de novo. WES of peripheral blood samples from the patient and both parents identified a nonsense variant in IL2RG (NM_000206.3, exon 2, c.216C > A, p.Cys72*). According to the ACMG/AMP variant interpretation guidelines, this variant met criteria for classification as pathogenic (PVS1 [predicted loss-of-function variant] + PS2 [de novo origin] + PM2 [absent in population databases]). Family pedigree analysis confirmed no familial recurrence (Figure 2A). The ClinVar database contained no prior reports associating this variant with disease. Sanger sequencing further confirmed its de novo origin (Figure 2B).
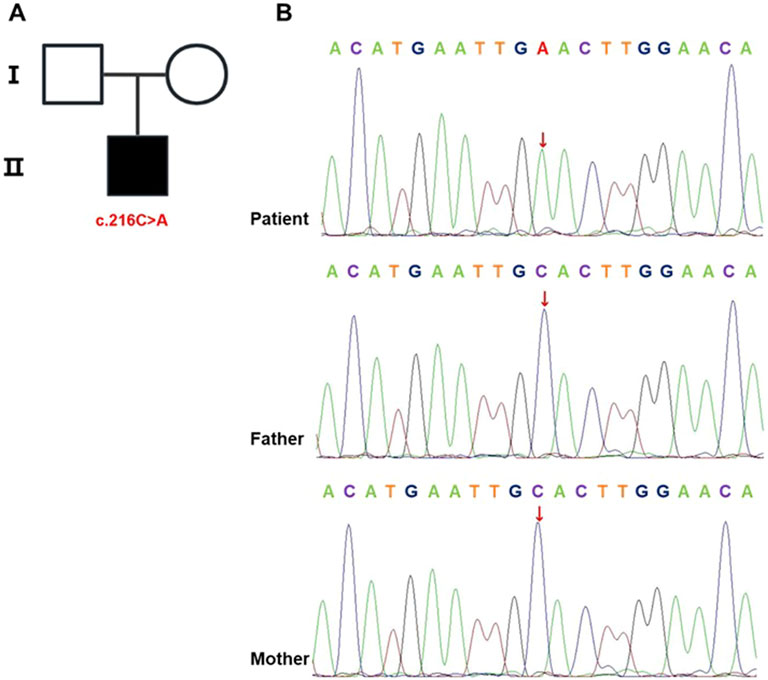
Figure 2. IL2RG mutation identified in the proband. (A) Pedigree chart. Males are represented by squares and females by circles, with the black-shaded square denoting the affected male carrying the mutation. (B) Sanger sequencing of IL2RG in the proband and his parents. The analysis identified a c.216C > A mutation in the proband, while this variant was absent in both parental samples.
3.4 Immune function evaluation
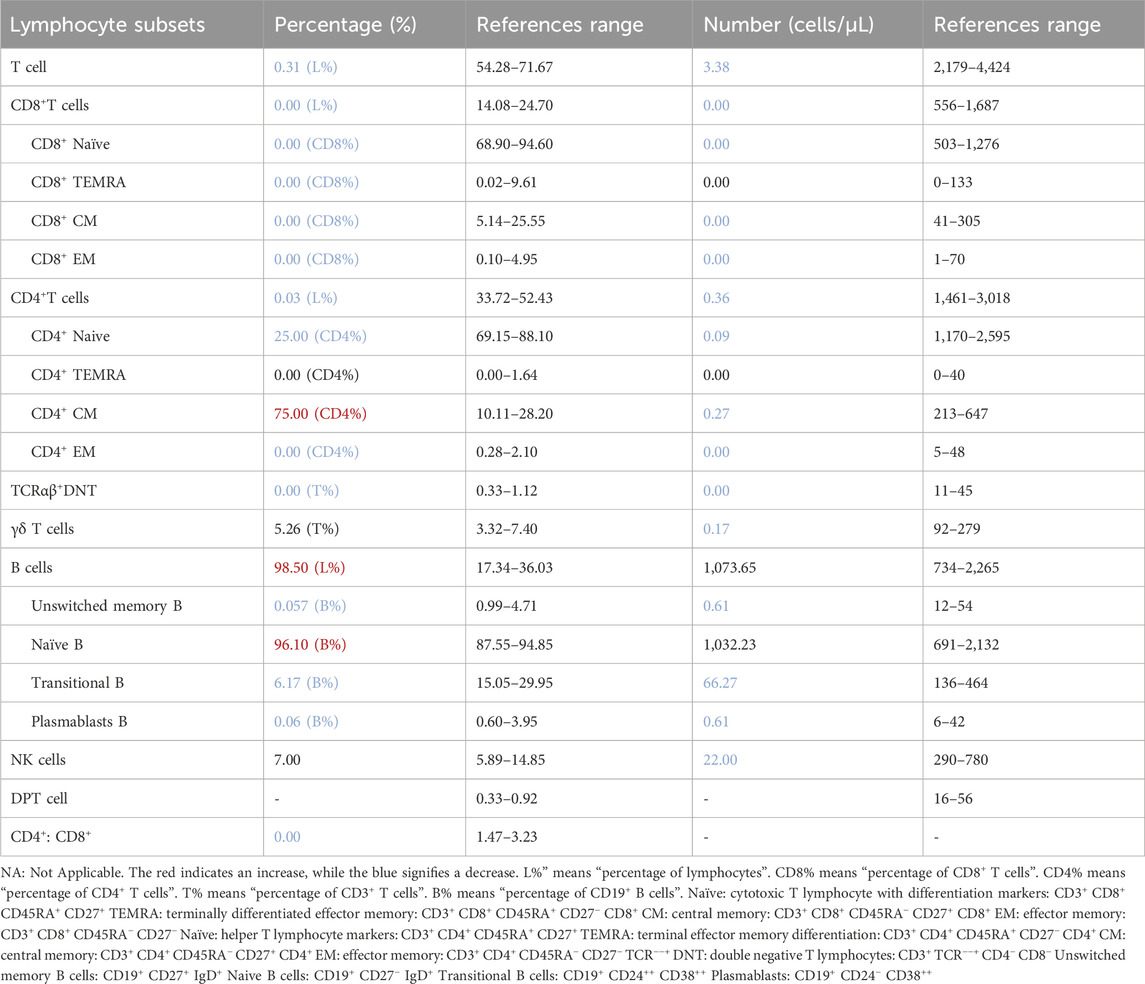
Previous studies have shown that X-SCID caused by IL2RG mutations results in defective T lymphocyte development. We performed flow cytometry to quantify lymphocyte subsets in the patient’s PBMCs (Table 3). Results showed a markedly reduced total T cell count, with undetectable CD8+ T cells and an extremely low proportion of CD4+ T cells; residual T cells were predominantly naive and central memory. B lymphocytes showed an increased total count but were composed mainly of immature B cells, accounting for 96.10% of the population. The nonsense mutation in IL2RG caused severe T cell depletion, impairing T-B cell collaboration and leading to B cell differentiation arrest. Persistent bacterial and viral infections likely further contributed to B cell dysfunction.
3.5 Summary of X-SCID cases combined with T. marneffei infection in the literature
In this case, T. marneffei was isolated from both bone marrow and peripheral blood cultures, with serological testing confirming of HIV seronegativity. An initial keyword search in PubMed and Scopus retrieved six articles. After applying predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria, five eligible patients were ultimately identified from 4 included studies (Figure 3). Clinical data from these five patients, together with the present case, were extracted and systematically analyzed with respect to demographic characteristics, clinical manifestations, genetic mutation profiles, and therapeutic management strategies (Tables 4 and 5). One case was not included in the table because the mutation site was not specified (Xie et al., 2022).
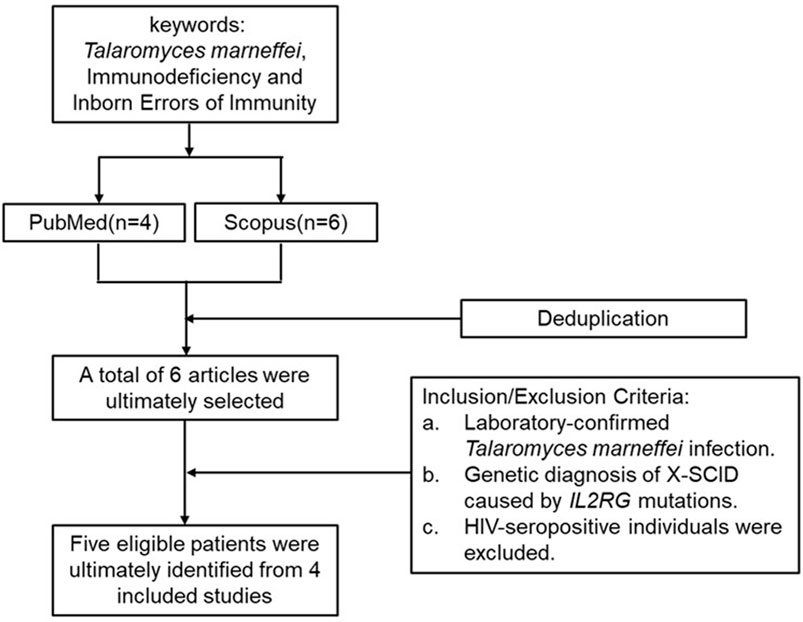
Figure 3. Literature search and selection process for reported cases of IL2RG mutation with T. marneffei infection.
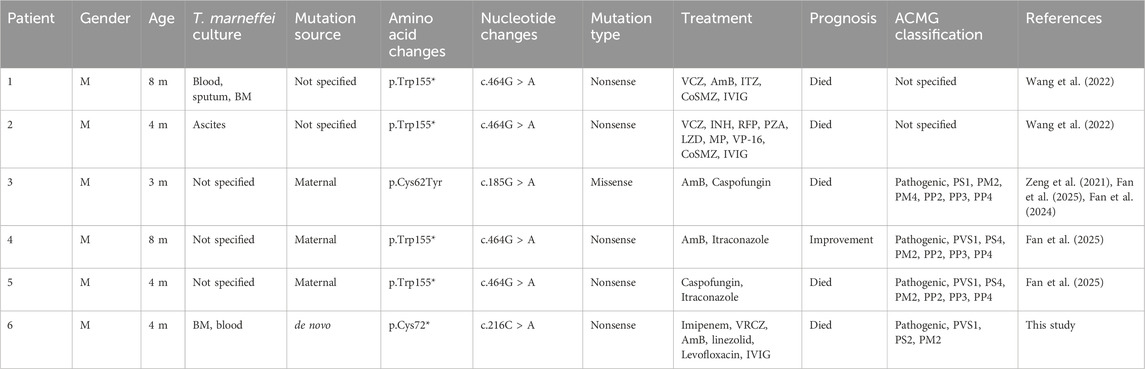
Table 4. Summary of previously reported cases of IL2RG mutation combined with T. marneffei infection.
Most cases exhibited persistent fever, recurrent respiratory infections, hepatosplenomegaly and chronic diarrhea (Table 5). Genetic analysis revealed that 83.33% harbored nonsense mutations in the IL2RG gene, with 66.67% carrying the c.464G > A (p.Trp155*) variant. Notably, both this study and recent literature suggest a significantly increased incidence of T. marneffei co-infection in patients with X-SCID. Therefore, detection of this pathogen should prompt clinicians to consider underlying immunodeficiency, enabling earlier diagnosis and timely intervention.
4 Discussion
This study reports a 4-month-old male infant with chronic diarrhea, recurrent fever, and invasive pulmonary infection. Laboratory investigations revealed profound T-cell deficiency, markedly reduced IgA, IgG, and IgE levels, and co-infections with M. pneumoniae and disseminated T. marneffei. WES identified a novel IL2RG nonsense mutation (c.216C > A, p.Cys72*), producing a hemizygous variant that prematurely truncates the γ-common chain (γc) at cysteine 72. Classified as pathogenic according to ACMG guidelines, family testing confirmed its de novo origin. To our knowledge, this is the first global report of this variant. Despite antifungal therapy and immunologic support, the patient showed no improvement, and treatment was withdrawn, leading to death.
According to the HGMD (Pro 2024.4), 278 pathogenic IL2RG variants have been reported, including missense, frameshift, nonsense, and splice-site mutations, with missence/nonsence mutations being the most common. The interleukin receptor γc chain is a shared signaling subunit of the IL-2, IL-4, IL-7, IL-9, IL-15, and IL-21 receptor complexes, regulating T, B, and NK cells development and function via the JAK-STAT pathway (Leonard et al., 2019; Habib et al., 2002). In this case, the IL2RG mutation likely caused complete structural loss of γc, resulting in classic X-SCID with a T−B+NK− immunophenotype. Functional assays were not performed due to limited sample availability.
A subset of missense mutations (e.g., exon 8 c.982C > T) (Lim et al., 2019) may partially retain γc-JAK3 binding capacity, presenting as atypical X-SCID with delayed onset or milder infections, but still progressing to immune failure. Our review of reported X-SCID cases with T. marneffei co-infection shows that most involve nonsense mutations with rapid clinical deterioration. Therefore, detection of T. marneffei in pediatric patients, particularly those with severe or recurrent infections, should prompt early investigation for underlying inborn errors of immunity.
T. marneffei is a dimorphic pathogenic fungus endemic to Southeast Asia, which can cause disseminated disease in both immunocompetent and immunocompromised individuals, particularly those with CD4+ T cell depletion (Wang et al., 2023; Pruksaphon et al., 2022). It spreads hematogenously and via the lymphatic system, leading to multi-organ abscesses involving the liver, spleen, bone marrow, and skin. Disseminated T. marneffei infection occurs predominantly in patients with acquired immunodeficiency, such as HIV/AIDS, but its incidence is also rising among non-HIV immunocompromised populations in parallel with increased use of organ transplantation, immunosuppressants, and targeted therapies (Vanittanakom et al., 2006; Chan et al., 2016). Previous reports have documented concomitant lymphocytopenia and T/NK-cell dysfunction in non-HIV patients with T. marneffei infection, all of whom had preexisting immune impairment (Hu et al., 2021).
In this pediatric case, genetically confirmed X-SCID established profound T-cell deficiency as the permissive state for disseminated fungal infection. The child’s progressive anemia and hypodense hepatic lesion were consistent with invasive fungal complications, highlighting the essential role of T-cell-mediated immunity in controlling deep-seated mycoses. Thus, lymphocytopenia in this patient was mechanistically rooted in the IL2RG mutation, with T. marneffei infection representing a consequence rather than the cause of immune dysregulation.
Flow cytometric immunophenotyping revealed a classic T−B+NK− immunophenotype, characteristic of X-SCID. Although B lymphocyte counts were elevated, dysfunction of the interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain (γc) disrupted intracellular signaling during T cell development, resulting in T cell developmental arrest and subsequent B-cell functional impairment (Cao et al., 2024). Functional assays could not be performed due to limited blood samples, as the family opted for palliative care following secondary multi-organ failure and disseminated intravascular coagulation.
Mutations in IL2RG are the most common genetic cause of X-SCID. Although current reports suggest that the incidence of X-SCID in China is lower than in Western countries; this cannot yet be considered accurate due to the incomplete implementation of newborn screening and limited clinician awareness of IEI manifestations (Puck, 2019; Chen et al., 2024; Kwan et al., 2014). To improve early diagnosis, it is recommended to combine TREC and KREC assays with NGS in newborns from high-risk families. Early genetic analysis diagnosis and timely interventions are crucial, as HSCT performed within 3.5 months of birth yields an 8-year Kaplan-Meier survival rate of 96%, compared with 70% for later transplantation (Railey et al., 2009). Reducing X-SCID mortality in China will require nationwide newborn screening coverage, the establishment of regional IEI referral networks, and individualized treatment pathways guided by ACMG variant interpretation criteria.
5 Conclusion
In summary, we report a novel IL2RG mutation (NM_000206.3, exon 2, c.216C > A, p.Cys72*) in a patient with a classic X-SCID phenotype. This finding expands the known pathogenic spectrum of IL2RG and may improve clinical recognition of related disorders. The patient’s presentation, laboratory data, and co-infection with T. marneffei highlight the diagnostic value of integrating phenotypic and molecular analyses in suspected IEI. Review of reported cases indicates that T. marneffei infection may serve as an early warning sign of underlying immunodeficiency, warranting prompt evaluation for IEI in affected patients.
Data availability statement
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Affiliated Hospital of Zunyi Medical University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s), and minor(s)’ legal guardian/next of kin, for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
LiW: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AR: Formal analysis, Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. YH: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. LuW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. SW: Investigation, Validation, Writing – review and editing. XX: Writing – review and editing. MT: Supervision, Writing – review and editing. YC: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review and editing. PH: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing - original draft, Writing – review and editing. ZD: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing - original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Guizhou Provincial Program on Commercialization of Scientific and Technological Achievements (QKHCG [2024]ZD012), the Medical Research Union Fund for High-quality Health Development of Guizhou Province (2024GZYXKYJJXM0062, 2024GZYXKYJJXM0061), Guizhou Association for Science and Technology Youth Talent Lifting Project (ZD), and the Key Advantageous Discipline Construction Project of Guizhou Provincial Health Commission in 2023.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank the patient’s family for their participation and all contributors for their valuable support to this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. DeepSeek was utilized exclusively for article polishing purposes.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
IEI, Inborn Errors of Immunity; PIDs, Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases; WHO, World Health Organization; IUIS, International Union of Immunological Societies; NGS, next-generation sequencing; WES, whole-exome sequencing; WGS, whole-genome sequencing; SCID, Severe Combined Immunodeficiency; X-SCID, X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency; IL2RG, interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain; HSCT, hematopoietic stem cell transplantation; TRECs, T-cell receptor excision circles; KRECs, kappa-deleting recombination excision circles; ACMG, American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics; PBMCs, Peripheral blood mononuclear cells; HGMD, Human Gene Mutation Database; BM, Bone Marrow; HLH, Hemophagocytic Syndromes; MODS, Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome; VCZ, Voriconazole; AmB, Bmphotericin b; ITZ, Itraconazole; CoSMZ, Compound Sulfamethoxazole Tablets; IVIG, Intravenous Immunoglobulin; INH, Isoniazid; RFP, Rifampicin; PZA, Pyrazinamide; LZD, Linezolid; MP, Methylprednisolone; VP-16, Etoposide; ARDS, Respiratory Distress Syndrome; DIC, Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation; VRCZ, Voriconazole; WBC, white blood cell.
References
Al Sukaiti, N., Ahmed, K., Alshekaili, J., Al Kindi, M., Cook, M. C., and Farsi, T. A. (2021). A Decade Experience on Severe Combined Immunodeficiency Phenotype in Oman, Bridging to Newborn Screening. Front. Immunol.11, 623199. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.623199
Aluri, J., Desai, M., Gupta, M., Dalvi, A., Terance, A., Rosenzweig, S. D., et al. (2019). Clinical, Immunological, and Molecular Findings in 57 Patients With Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID) From India. Front. Immunol., 10–23. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.00023
Aranda, C. S., Gouveia-Pereira, M. P., da Silva, C. J. M., Rizzo, M. C. F. V., Ishizuka, E., de Oliveira, E. B., et al. (2024). Severe combined immunodeficiency diagnosis and genetic defects. Immunol. Rev. 322 (1), 138–147. doi:10.1111/imr.13310
Boyarchuk, O., Yarema, N., Kravets, V., Shulhai, O., Shymanska, I., Chornomydz, I., et al. (2022). Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency: the results of the first pilot TREC and KREC study in Ukraine with involving of 10,350 neonates. Front. Immunol. 13, 999664. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.999664
Cao, F., Shi, Y., Deng, F., and Yan, Y. (2024). Novel IL2RG gene mutation causing primary combined immunodeficiency disease: a case report and literature review. Central-European J. Immunol. 49 (3), 300–307. doi:10.5114/ceji.2024.142340
Chan, J. F., Lau, S. K., Yuen, K. Y., and Woo, P. C. Y. (2016). Talaromyces (penicillium) marneffei infection in non-HIV-infected patients. Emerg. Microbes and Infect. 5 (3), e19. doi:10.1038/emi.2016.18
Chen, C., Zhang, C., Wu, D. W., Wang, B. Y., Xiao, R., Huang, X. L., et al. (2024). Comprehensive newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency, X-linked agammaglobulinemia, and spinal muscular atrophy: the Chinese experience. World J. Pediatr. 20 (12), 1270–1282. doi:10.1007/s12519-024-00846-7
Currier, R., and Puck, J. M. (2021). SCID newborn screening: what we’ve learned. J. allergy Clin. Immunol. 147 (2), 417–426. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.020
Fan, H. F., Zeng, S. Q., and Huang, L. (2024). Peripheral immune profile and gene variations of 11 immunodeficiency virus-negative children with Talaromyces marneffei infection. Chin. J. Appl. Clin. Pediatr. 39 (01), 44–48. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn101070-20230629-00544
Fan, H., Yang, Z., Wu, Y., Lu, X., Li, T., Lu, X., et al. (2025). Human inborn errors of immunity underlying Talaromyces marneffei infections: a multicenter, retrospective cohort study. Front. Immunol. 16, 1492000. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2025.1492000
Habib, T., Senadheera, S., Weinberg, K., and Kaushansky, K. (2002). The common gamma chain (gamma c) is a required signaling component of the IL-21 receptor and supports IL-21-induced cell proliferation via JAK3. Biochemistry 41 (27), 8725–8731. doi:10.1021/bi0202023
Hu, F., Liu, S., Liu, Y., Li, X., Pang, R., and Wang, F. (2021). The decreased number and function of lymphocytes is associated with Penicillium marneffei infection in HIV-negative patients. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 54 (3), 457–465. doi:10.1016/j.jmii.2020.02.007
Jiang, C., He, Y., Chen, X., Xia, F., Shi, F., Xu, X., et al. (2024). X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency complicated by disseminated bacillus calmette-Guérin disease caused by a novel pathogenic mutation in exon 3 of the IL2RG gene: a case report and literature review. Front. Immunol. 15, 1453046. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1453046
Kwan, A., Abraham, R. S., Currier, R., Brower, A., Andruszewski, K., Abbott, J. K., et al. (2014). Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency in 11 screening programs in the United States. JAMA 312 (7), 729–738. doi:10.1001/jama.2014.9132
Leonard, W. J., Lin, J. X., and O’Shea, J. J. (2019). The γc family of cytokines: basic biology to therapeutic ramifications. Immunity 50 (4), 832–850. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.028
Lev, A., Sharir, I., Simon, A. J., Levy, S., Lee, Y. N., Frizinsky, S., et al. (2022). Lessons learned from five years of newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency in Israel. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 10 (10), 2722–2731.e9. doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2022.04.013
Lim, C. K., Abolhassani, H., Appelberg, S. K., Sundin, M., and Hammarström, L. (2019). IL2RG hypomorphic mutation: identification of a novel pathogenic mutation in exon 8 and a review of the literature. Allergy, Asthma and Clin. Immunol. 15 (1), 2. doi:10.1186/s13223-018-0317-y
Mahdavi, F. S., Keramatipour, M., Ansari, S., Sharafian, S., Karamzade, A., and Tavakol, M. (2021). X-linked SCID with a rare mutation. Allergy, Asthma, Clin. Immunol. Official J. Can. Soc. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 17, 107. doi:10.1186/s13223-021-00605-7
Meyts, I., Bosch, B., Bolze, A., Boisson, B., Itan, Y., Belkadi, A., et al. (2016). Exome and genome sequencing for inborn errors of immunity. J. allergy Clin. Immunol. 138 (4), 957–969. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2016.08.003
Michos, A., Tzanoudaki, M., Villa, A., Giliani, S., Chrousos, G., and Kanariou, M. (2011). Severe combined immunodeficiency in Greek children over a 20-year period: rarity of γc-chain deficiency (X-linked) type. J. Clin. Immunol. 31 (5), 778–783. doi:10.1007/s10875-011-9564-0
Nakagawa, N., Imai, K., Kanegane, H., Sato, H., Yamada, M., Kondoh, K., et al. (2011). Quantification of κ-deleting recombination excision circles in Guthrie cards for the identification of early B-cell maturation defects. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 128 (1), 223–225. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2011.01.052
Pruksaphon, K., Nosanchuk, J. D., Ratanabanangkoon, K., and Youngchim, S. (2022). Talaromyces marneffei infection: virulence, intracellular lifestyle and host defense mechanisms. J. Fungi 8 (2), 200. doi:10.3390/jof8020200
Puck, J. M. (2019). Newborn screening for severe combined immunodeficiency and T-cell lymphopenia. Immunol. Rev. 287 (1), 241–252. doi:10.1111/imr.12729
Railey, M. D., Lokhnygina, Y., and Buckley, R. H. (2009). Long term clinical outcome of patients with severe combined immunodeficiency who received related donor bone marrow transplants without pre-transplant chemotherapy or post-transplant GVHD prophylaxis. J. Pediatr. 155 (6), 834–840. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.07.049
Seleman, M., Hoyos-Bachiloglu, R., Geha, R. S., and Chou, J. (2017). Uses of next-generation sequencing technologies for the diagnosis of primary immunodeficiencies. Front. Immunol. 8, 847. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2017.00847
Shai, S., Perez-Becker, R., Andres, O., Bakhtiar, S., Bauman, U., von Bernuth, H., et al. (2020). Incidence of SCID in Germany from 2014 to 2015 an ESPED* Survey on Behalf of the API*** Erhebungseinheit für Seltene Pädiatrische Erkrankungen in Deutschland (German Paediatric Surveillance Unit)** Arbeitsgemeinschaft Pädiatrische Immunologie. J. Clin. Immunol. 40 (5), 708–717. doi:10.1007/s10875-020-00782-x
Tangye, S. G., Al-Herz, W., Bousfiha, A., Cunningham-Rundles, C., Franco, J. L., Holland, S. M., et al. (2022). Human inborn errors of immunity: 2022 update on the classification from the international union of immunological societies expert Committee. J. Clin. Immunol. 42 (7), 1473–1507. doi:10.1007/s10875-022-01289-3
Vanittanakom, N., Cooper, C. R., Fisher, M. C., and Sirisanthana, T. (2006). Penicillium marneffei infection and recent advances in the epidemiology and molecular biology aspects. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 19 (1), 95–110. doi:10.1128/CMR.19.1.95-110.2006
Wang, L., Luo, Y., Li, X., Xia, Y., He, T., et al. (2022). Talaromyces marneffei infections in 8 Chinese children with inborn errors of immunity. Mycopathologia 187 (5-6), 455–467. doi:10.1007/s11046-022-00659-0
Wang, F., Han, R., and Chen, S. (2023). An overlooked and underrated endemic mycosis—talaromycosis and the pathogenic fungus Talaromyces marneffei. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 36 (1), e0005122. doi:10.1128/cmr.00051-22
Xie, G., Chen, J. H., Sun, L. F., Wang, W., Li, Z. C., and Wang, W. J. (2022). Clinical analysis of 7 children infected with Talaromyces marneffei. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi = Chin. J. Pediatr. 60 (9), 925–929. doi:10.3760/cma.j.cn112140-20220331-00260
Keywords: IL2RG, X-SCID, lymphocyte, Talaromyces marneffei, T cell
Citation: Wang L, Ren A, He Y, Wang L, Wang S, Xie X, Tan M, Chen Y, Huang P and Du Z (2025) A novel de novo IL2RG nonsense mutation in a pediatric patient with X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency. Front. Genet. 16:1641956. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1641956
Received: 05 June 2025; Accepted: 09 September 2025;
Published: 07 October 2025.
Edited by:
Sara Manti, University of Messina, ItalyReviewed by:
David Cruz Robles, National Cardiology Institute Ignacio Chavez, MexicoPatricia Jeanne De Souza Mendonça-Mattos, Hemopa Foundation- Center of Hemotherapy and Hematology of Pará, Brazil
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Ren, He, Wang, Wang, Xie, Tan, Chen, Huang and Du. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zuochen Du, ZHpjOTAzNkAxMjYuY29t; Pei Huang, ZmVuZ2xpbjQ2MjBAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Lin Wang1,2
Lin Wang1,2 Yan Chen
Yan Chen Pei Huang
Pei Huang Zuochen Du
Zuochen Du