- 1Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 3Department of Oncology, Affiliated Hospital of Chengdu University, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Department of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, First People’s Hospital of Neijiang, Neijiang, Sichuan, China
- 5Department of General Surgery (Hepatopancreatobiliary Surgery), Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 6Department of Interventional & Vascular, Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Cancer vaccines represent a promising therapeutic modality in immuno-oncology, yet their efficacy is severely constrained within the immunosuppressive microenvironment of lung tumors. Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic dysregulation are now understood as critical, interconnected determinants that orchestrate tumor microenvironment (TME) immunosuppression and fundamentally shape anti-tumor immune responses. This review comprehensively examines the mechanistic interplay between metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic regulation, and how nanoplatform technologies can be engineered to modulate these axes to augment cancer vaccine efficacy. We analyze advanced nano-delivery system design strategies, the synergistic effects of combining metabolic intervention with epigenetic modification, and their application in overcoming the formidable barriers of the lung TME. By integrating recent advances in nanotechnology, epigenetics, and tumor immunometabolism, we provide critical insights into the development of next-generation cancer vaccines. Furthermore, we propose a novel conceptual framework—The Epi-Met-Immune Synergistic Network—to dissect these interactions and identify key nodes for rational therapeutic intervention, aiming to enhance and sustain durable anti-tumor immunity.
Introduction
The landscape of cancer immunotherapy has been revolutionized by the advent of cancer vaccines, which harness the host immune system’s capacity to mount specific anti-tumor responses (Sharma et al., 2017). Despite remarkable clinical successes in certain malignancies, lung tumors present formidable challenges due to their profoundly immunosuppressive microenvironment (Looi et al., 2019). The intricate interplay between metabolic dysregulation and epigenetic alterations within the tumor microenvironment (TME) orchestrates a complex network of immunosuppressive mechanisms that severely compromise vaccine efficacy (Bader et al., 2020).
At its core, cancer is a disease of dysregulated gene expression, driven not only by genetic mutations but also by profound epigenetic alterations. Epigenetic reprogramming—encompassing DNA methylation, histone modifications, and chromatin remodeling—serves as a fundamental mechanism by which tumor cells evade immune surveillance and sustain proliferation across a wide spectrum of malignancies. During the escape phase of cancer immunoediting, genetic and epigenetic alterations in tumor cells—reversible through nanomaterial interventions—result in tumor antigen deficiency and impaired antigen-presenting machinery. These changes also foster the development of an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, characterized by expanded populations of immunosuppressive cells and accumulated immunosuppressive molecules, which collectively inactivate cytotoxic immune cells such as cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs) (Liu et al., 2024). The strategic reversal of these epigenetic aberrations has thus emerged as a promising therapeutic avenue in oncology, aiming to restore antitumor immunity and sensitize tumors to various immunotherapies.
This promise, however, remains largely unrealized specifically in lung cancer, where the therapeutic vaccines have consistently faltered against a profoundly immunosuppressive microenvironment (Lahiri et al., 2023). Here, the intricate interplay between metabolic dysregulation and the aforementioned epigenetic alterations within the TME orchestrates a complex network of immunosuppressive mechanisms that severely compromise vaccine efficacy (Giaccone et al., 2015). Landmark trials underscore this difficulty: the MAGE-A3 protein vaccine, despite successfully inducing antigen-specific T-cell responses, failed to improve overall or disease-free survival and the L-BLP25 vaccine similarly did not show significant difference in overall survival in Phase III studies (Batchu et al., 2014; Butts et al., 2014). These data highlight a critical challenge: the TME orchestrates a complex network of immunosuppressive mechanisms, driven by factors such as the accumulation of regulatory T cells, that actively subverts vaccine-induced immunity and severely compromises therapeutic efficacy.
Metabolic reprogramming in lung tumors encompasses a spectrum of alterations, including enhanced glycolysis, aberrant amino acid metabolism, and lipid metabolic rewiring, collectively creating a hostile metabolic milieu that impairs immune cell function (Arner and Rathmell, 2023). Concurrently, epigenetic modifications—including DNA methylation patterns, histone post-translational modifications, and chromatin remodeling—fundamentally alter gene expression programs that govern immune recognition and response (Dai et al., 2021). These epigenetic changes not only affect tumor cells but also reprogram infiltrating immune cells, establishing durable immunosuppressive phenotypes (Cao and Yan, 2020).
The emergence of nanotechnology has opened unprecedented opportunities for precision medicine approaches that simultaneously target metabolic and epigenetic abnormalities (Zhang et al., 2023). Nanoplatforms offer unique advantages including enhanced drug stability, targeted delivery, controlled release kinetics, and the capacity for multi-drug co-delivery (Zhang et al., 2021). By integrating metabolic modulators with epigenetic therapeutics within sophisticated nanocarriers, it becomes possible to synergistically reprogram the TME and potentiate cancer vaccine responses (Ren et al., 2023).
This review provides a comprehensive analysis of how epigenetic-regulated nanoplatforms influence metabolic reprogramming to enhance cancer vaccine efficacy. We examine the molecular mechanisms underlying TME immunosuppression, evaluate current nanoplatform design strategies, and discuss emerging therapeutic approaches. Critically, we introduce the Epi-Met-Immune Synergistic Network as a conceptual model to deconstruct the complex feedback loops that drive therapeutic resistance, thereby providing a rational basis for designing multi-targeted nanoplatforms to overcome these barriers.
Characteristics of the immunosuppressive lung TME and challenges for cancer vaccines
Immunosuppressive mechanisms in the lung tumor microenvironment
The lung tumor microenvironment represents a paradigm of immune dysfunction, characterized by multiple interconnected immunosuppressive mechanisms (Altorki et al., 2019). Regulatory T cells (Tregs) accumulate within lung tumors through chemokine-mediated recruitment and local expansion, establishing dominant immunosuppressive networks (Togashi et al., 2019). These Tregs express high levels of checkpoint molecules including CTLA-4 and PD-1, while secreting immunosuppressive cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β (Zhang et al., 2024). The functional stability of intratumoral Tregs is maintained through specific metabolic adaptations, including enhanced fatty acid oxidation and resistance to lactate-induced suppression (Zhou L. et al., 2024).
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) represent another critical component of lung tumor immunosuppression (He et al., 2025). These heterogeneous populations of immature myeloid cells accumulate in response to tumor-derived factors including GM-CSF, VEGF, and prostaglandins (Li K. et al., 2021). MDSCs employ multiple mechanisms to suppress anti-tumor immunity, including arginine depletion through arginase-1 expression (Bronte et al., 2003), production of reactive oxygen species, and induction of Treg differentiation (Groth et al., 2019; Serafini et al., 2006). The metabolic profile of MDSCs is characterized by enhanced glycolysis and altered lipid metabolism, which not only supports their immunosuppressive functions but also renders them resistant to metabolic stress within the TME (Jin et al., 2023; Yan et al., 2019).
The expression of immune checkpoint molecules extends beyond infiltrating immune cells to encompass tumor cells and stromal components. Lung tumors frequently upregulate PD-L1 expression through various mechanisms including oncogenic signaling, inflammatory cytokines, and hypoxia-inducible factors (Yamaguchi et al., 2022). Additionally, alternative checkpoint pathways such as TIM-3, LAG-3, and TIGIT create redundant immunosuppressive networks that limit vaccine-induced immune responses (Cai et al., 2023) (Figure 1).
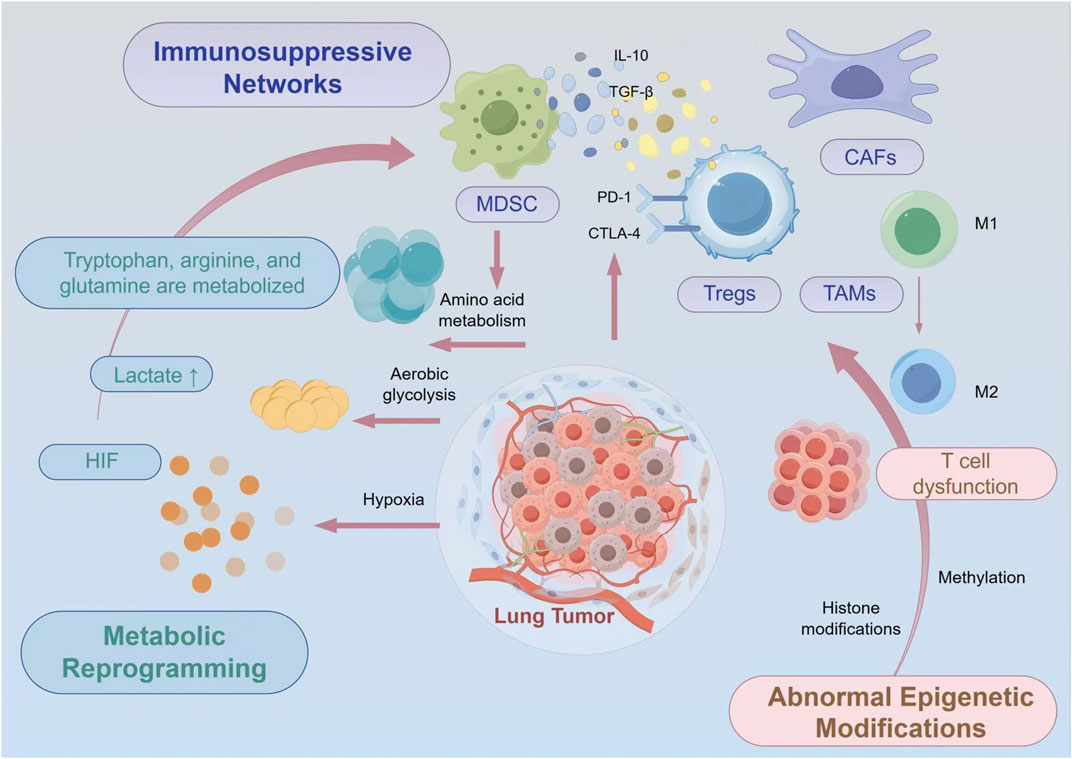
Figure 1. Comprehensive Schematic Illustration of the Immunosuppressive Lung Tumor Microenvironment. The lung tumor microenvironment exhibits pronounced immunosuppressive characteristics, including the accumulation and functional activation of immunosuppressive cells such as Tregs and MDSCs, alongside aberrant expression of immune checkpoint molecules including PD-L1. Concurrently, metabolic abnormalities (lactate accumulation, hypoxia, amino acid depletion) and epigenetic dysregulation (T cell exhaustion, immune cell epigenetic reprogramming) further reinforce these immunosuppressive networks. These multifaceted mechanisms collectively present significant challenges for the application of cancer vaccines, necessitating integrated therapeutic approaches that simultaneously address these interconnected immunosuppressive pathways.
Metabolic abnormalities and their impact on immune cell function
The metabolic landscape of lung tumors profoundly shapes immune cell function and fate. Aerobic glycolysis in tumor cells leads to excessive lactate production, creating an acidic microenvironment that impairs T cell proliferation and cytotoxic function (Wu et al., 2023). Lactate acts as both a metabolic substrate and signaling molecule, promoting regulatory T cell differentiation while suppressing effector T cell responses (Llibre et al., 2025). The acidic pH also interferes with antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity and reduces the efficacy of therapeutic antibodies (Liu Y. et al., 2022).
Hypoxia represents another hallmark of the lung tumor metabolic environment. Regions of severe hypoxia stabilize hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs), which orchestrate transcriptional programs that promote immunosuppression (Lee et al., 2020). HIF-1α drives the expression of checkpoint ligands, enhances MDSC recruitment, and promotes the differentiation of tumor-associated macrophages toward immunosuppressive phenotypes (Luo et al., 2022). Moreover, hypoxia impairs dendritic cell maturation and antigen presentation, critical processes for effective cancer vaccine responses (Kheshtchin et al., 2016).
Amino acid metabolism within lung tumors creates additional immunosuppressive barriers (Chen et al., 2024). Tumor cells and immunosuppressive myeloid cells deplete essential amino acids including tryptophan, arginine, and glutamine from the microenvironment (Kheshtchin et al., 2016). Tryptophan catabolism through indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) produces kynurenine metabolites that directly suppress T cell proliferation and promote Treg differentiation (Munn et al., 1998; Fallarino et al., 2006). Arginine depletion by arginase-expressing MDSCs impairs T cell receptor signaling and memory formation, while glutamine restriction compromises T cell activation and effector function (Crump et al., 2021).
Epigenetic determinants of T cell exhaustion in the lung tumor microenvironment
T cell exhaustion in lung tumors represents a paradigmatic example of epigenetically-encoded immune dysfunction that profoundly limits cancer vaccine efficacy (Pan and Zheng, 2020). This functionally impaired state is not merely transient but is stabilized through comprehensive epigenetic reprogramming, establishing a self-reinforcing gene expression program resistant to conventional immunotherapeutic interventions (Belk et al., 2022a). Genome-wide epigenetic profiling has revealed distinctive chromatin accessibility landscapes in exhausted tumor-infiltrating T cells, characterized by inaccessible chromatin at effector gene loci juxtaposed with enhanced accessibility at inhibitory receptor genes (Belk et al., 2022b). These alterations are accompanied by region-specific DNA methylation patterns, including hypermethylation at cytokine promoters (IFN-γ, TNF-α) and hypomethylation at immune checkpoint loci (PD-1, CTLA-4), collectively restricting T cell functional plasticity (Smith et al., 2020).
The epigenetic architecture of exhausted T cells is further sculpted by a characteristic histone modification signature. Enhancer regions of effector genes display reduced H3K27ac and H3K4me1, while inhibitory receptor loci exhibit enrichment of these activation-associated marks. Concurrently, the repressive H3K27me3 mark, catalyzed by the PRC2 complex via EZH2, accumulates at critical effector gene promoters, silencing cytotoxic programs while sparing checkpoint receptor expression. This role of EZH2 as a key enforcer of immunosuppression is not limited to exhausted T cells; forryptophan catabolism through indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) produces kynurenine metabolites that directly suppress T cell proliferation and promote Treg differentiation instance, recent work demonstrates that its hyperactivation in regulatory T cells also enhances their suppressive capacity and stability (Peeters et al., 2024). This epigenetic imbalance is perpetuated by increased HDAC activity, which depletes activating acetylation marks at key effector loci, diminishing both their transcriptional potential and functional capacity (Ibrahim et al., 2024). Recent analyses have further revealed that these modifications are progressively established during tumor progression, creating increasingly fixed states of dysfunction that correspond with resistance to checkpoint blockade therapy (Perrier et al., 2020).
The architecture of immunosuppression in the lung TME is fortified by the epigenetic reprogramming of multiple immune lineages, creating formidable barriers to cancer vaccine efficacy. Beyond the tumor cells themselves, key innate immune cells are functionally subverted; TAMs are skewed towards an M2-like phenotype through alterations in their enhancer landscapes, while MDSCs are locked into an immature, suppressive state by stable epigenetic modifications (Niu et al., 2022). This intricate cellular network, however, exposes critical gaps in our fundamental understanding. For instance, the precise molecular pathways through which tumor-derived metabolites like adenosine and reactive oxygen species (ROS) drive epigenetic silencing in effector CD8+ T cells remain to be fully elucidated (Yerinde et al., 2019). Furthermore, it is unclear how distinct inhibitory axes—such as immune checkpoint over-activation, HLA-I downregulation, and metabolic hostility—synergize to create a composite barrier that is impenetrable to single-antigen vaccines (Yi et al., 2019). Finally, the dynamic interplay between evolving tumor antigen heterogeneity and the progressive exhaustion of immune cells represents a core clinical bottleneck, and whether personalized antigen design can reverse this tolerance to establish long-term memory remains a pivotal unanswered question (Jia et al., 2022). Herein lies the central challenge and opportunity: because these immunosuppressive states are epigenetically encoded, targeting the epigenetic machinery itself offers a foundational strategy to dismantle the entire network and overcome the core barriers limiting cancer vaccine efficacy.
The role of epigenetic regulation in reversing lung cancer immunosuppression
DNA methyltransferase inhibitors promoting lung cancer antigen expression
DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi) have emerged as powerful tools for reversing epigenetic silencing in lung tumors (Goyal et al., 2023; Vendetti and Rudin, 2013). Aberrant DNA hypermethylation silences numerous tumor antigens, including cancer-testis antigens (CTAs), neoantigens, and MHC class I molecules, thereby limiting tumor immunogenicity (Geissler et al., 2024). DNMTi treatment induces global DNA hypomethylation, reactivating silenced tumor antigens and enhancing immune recognition.
The mechanisms of DNMTi-mediated immune activation extend beyond simple antigen re-expression (Huang et al., 2021). DNMTi treatment activates endogenous retroviral elements and repetitive sequences, triggering viral mimicry responses. This phenomenon induces type I interferon signaling through activation of cytosolic nucleic acid sensors, creating an inflammatory milieu that enhances dendritic cell activation and T cell priming (Chiappinelli et al., 2015). Furthermore, DNMTi treatment upregulates antigen processing and presentation machinery, including TAP transporters, immunoproteasome subunits, and MHC molecules (Ignatz-Hoover et al., 2022).
Recent studies have demonstrated that DNMTi can reprogram the metabolic landscape of lung tumors. By altering the methylation status of metabolic gene promoters, DNMTi treatment reduces glycolytic flux and lactate production, partially alleviating metabolic immunosuppression (Xu et al., 2023). Additionally, DNMTi-induced changes in tumor cell metabolism can enhance their susceptibility to immune-mediated killing through metabolic checkpoint mechanisms (Wang et al., 2025).
Histone deacetylase inhibitors enhancing T cell memory responses
HDAC inhibitors represent another class of epigenetic modulators with significant immunomodulatory potential (Hicks et al., 2020). In the context of lung cancer immunotherapy, HDAC inhibitors exert pleiotropic effects that enhance vaccine-induced immune responses (Li X. et al., 2021). By increasing histone acetylation at memory-associated gene loci, HDAC inhibitors promote the differentiation and maintenance of memory T cells, crucial for durable anti-tumor immunity (Ellmeier and Seiser, 2018).
HDAC inhibition in T cells enhances the expression of transcription factors associated with memory formation (Ibrahim et al., 2024; Montacchiesi and Pace, 2022). These transcriptional changes are accompanied by metabolic reprogramming toward oxidative phosphorylation, a metabolic profile that supports memory T cell survival and function. Moreover, HDAC inhibitors reduce the expression of inhibitory receptors on T cells, potentially reversing exhaustion phenotypes and restoring effector function.
The effects of HDAC inhibitors extend to antigen-presenting cells, where they enhance costimulatory molecule expression and cytokine production. Dendritic cells treated with HDAC inhibitors show improved antigen presentation capacity and increased production of T cell-polarizing cytokines (De Sa Fernandes et al., 2024). In tumor-associated macrophages, HDAC inhibition can shift polarization away from immunosuppressive M2-like phenotypes toward inflammatory M1-like states (Yang et al., 2025).
Non-coding RNAs in immune regulation
The landscape of non-coding RNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), represents an emerging frontier in epigenetic immunomodulation. In lung tumors, specific miRNA signatures regulate key aspects of immune function (Zhu et al., 2021; Iqbal et al., 2019). Tumor-derived exosomes carrying immunosuppressive miRNAs, such as miR-21 and miR-155, can reprogram immune cells toward tolerogenic phenotypes (Shokati and Safari, 2023; Yang et al., 2013). Conversely, certain miRNAs function as tumor suppressors and immune activators, suggesting therapeutic potential for miRNA-based interventions (Kim and Croce, 2023).
LncRNAs orchestrate complex regulatory networks that influence immune responses at multiple levels. The lncRNA NEAT1 promotes MDSC expansion and function, while MALAT1 regulates dendritic cell differentiation and antigen presentation (Wu et al., 2018). Targeting these lncRNAs through antisense oligonucleotides or CRISPR-based approaches offers novel strategies for modulating tumor immunity (Arun et al., 2018).
Recent advances in understanding circular RNAs (circRNAs) have revealed their roles in immune regulation. CircRNAs can function as miRNA sponges, modulating the availability of miRNAs that regulate immune checkpoints and inflammatory responses (Meng et al., 2024). The stability and tissue-specific expression of circRNAs make them attractive targets for immunomodulatory interventions (Misir et al., 2022).
While these epigenetic modulators—DNMT inhibitors, HDAC inhibitors, and non-coding RNA-based therapeutics—offer powerful, mechanistically distinct avenues to reverse immunosuppression, their translation into effective clinical strategies for lung cancer is hampered by a series of profound and interconnected challenges. The suppressive TME, densely populated by Tregs and MDSCs, remains a formidable barrier that can neutralize the benefits of vaccine-induced T cells (Munn and Bronte, 2016). Furthermore, the technical hurdles in developing truly personalized neoantigen vaccines, from prediction accuracy to overcoming tumor heterogeneity, limit broad applicability (Wu et al., 2024). Finally, the systemic delivery of these potent agents raises significant concerns regarding off-target effects and toxicity, highlighting a critical need for delivery systems that can precisely target tumor tissue while protecting the payload (Manzari et al., 2021). Therefore, simply possessing these epigenetic tools is not enough; the central challenge lies in deploying them effectively within the complex biological landscape of the tumor. This necessitates the development of advanced delivery platforms capable of integrating multiple therapeutic strategies to dismantle the immunosuppressive network at its core (Figure 2).
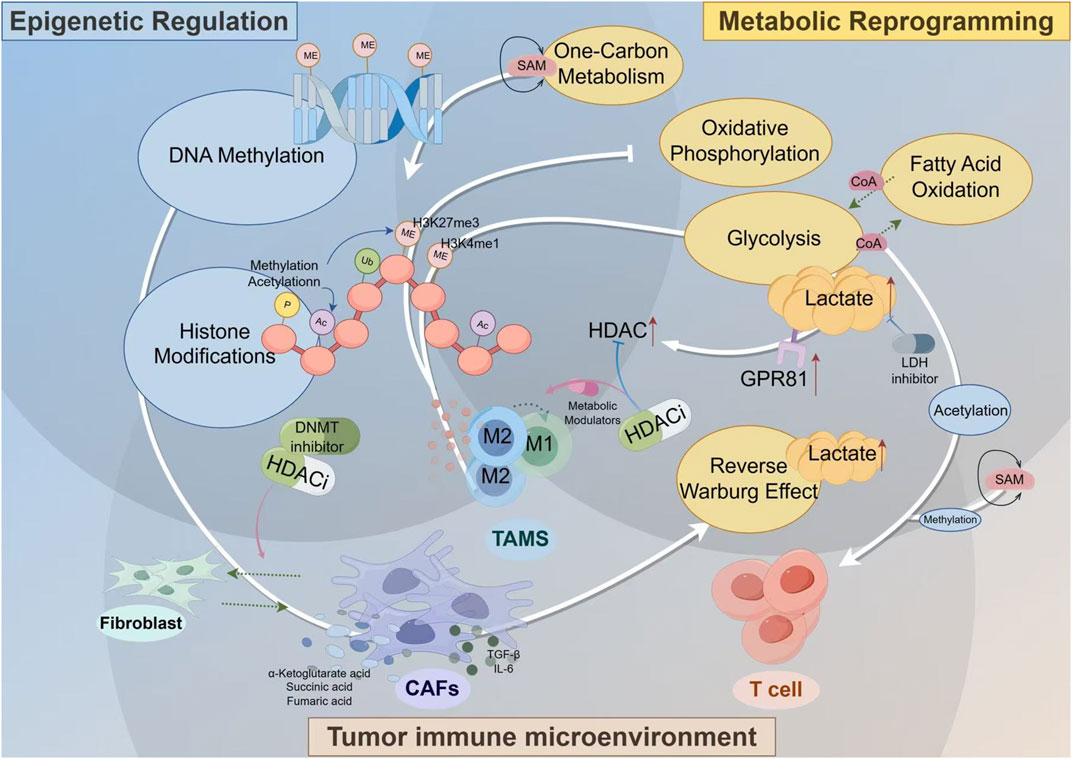
Figure 2. The Interplay of Metabolic Reprogramming and Epigenetic Regulation in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. Key stromal cells, such as CAFs and TAMs, adopt altered metabolic programs like the Reverse Warburg Effect, producing an abundance of metabolites including lactate, SAM, and Acetyl-CoA. These molecules are not merely metabolic byproducts but act as critical signaling molecules (for example lactate via its GPR81 receptor to upregulate HDAC) and essential substrates for epigenetic enzymes that control DNA methylation and histone modifications. This direct metabolic-epigenetic link ultimately dictates the functional phenotype of immune cells, crucially promoting the polarization of TAMs towards an immunosuppressive M2 state. The diagram highlights how this self-reinforcing cycle can be therapeutically targeted with inhibitors for key nodes like HDAC, DNMT, and LDH, offering a strategy to break the cycle and reprogram the TME towards an anti-tumor state.
The Epi-Met-Immune synergistic network: a framework for therapeutic design
Beyond linear pathways: the need for an integrated network model
Designing therapies for the lung TME demands a departure from linear thinking. The intertwined challenges of epigenetic silencing and metabolic hostility are not independent pathways but are locked in a profound bidirectional interplay, creating pathological feedback loops that establish and maintain a remarkably stable immunosuppressive state. A metabolic alteration, for example, can drive an epigenetic change that, in turn, transcriptionally reinforces the aberrant metabolic phenotype and its downstream immunological consequences (Lu and Thompson, 2012). To deconstruct this complexity and move beyond empirical drug combinations, we propose the Epi-Met-Immune Synergistic Network, a multi-layered framework designed to map the key molecular and cellular players, their dynamic interactions, and the critical nodes for rational therapeutic intervention.
Layers and nodes of the network
The network is conceptualized as three interconnected, interdependent layers. The foundational Epigenetic Layer comprises the architects of the chromatin landscape—the enzymatic machinery that writes, erases, and reads epigenetic marks. Key nodes here include DNMTs, HDACs, and histone methyltransferases like EZH2. This epigenetic control directly governs the Metabolic Layer, which comprises core metabolic pathways whose effector metabolites function dually as cellular fuel and potent signaling molecules (Keating and El-Osta, 2015). Critical nodes include glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS), while metabolites such as lactate, succinate, and α-ketoglutarate directly influence epigenetic enzyme activity, and the availability of universal donors like S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) and Acetyl-CoA links metabolic status directly back to epigenetic potential (Yu and Li, 2024; Yellen, 2018). Ultimately, the functional output of this intricate epi-metabolic crosstalk manifests in the Immune Layer, which encompasses the primary cellular actors of the anti-tumor response, including cytotoxic effector cells (CD8+ T cells, NK cells), immunosuppressive populations (Tregs, MDSCs, M2-polarized TAMs), and professional antigen-presenting cells (DCs).
Dynamic interactions and paradigmatic feedback loops
The true power of this framework lies in mapping the self-perpetuating circuits that drive therapeutic resistance. A paradigmatic example is the Warburg effect, which results in a lactate-rich TME (Lane et al., 2020). Lactate, now understood to be a potent oncometabolite, acts as a competitive inhibitor of α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, including TET enzymes and certain histone demethylases (Faubert et al., 2017). This epigenetic reprogramming cripples the expression of key effector cytokines like IFN-γ and granzyme B in infiltrating CD8+ T cells, thus directly linking a metabolic byproduct to profound immune dysfunction via an epigenetic mechanism (Zebley et al., 2020). This crosstalk is profoundly bidirectional. Conversely, epigenetic programs can dictate metabolic fate, as seen in a T cell destined for exhaustion. Here, key epigenetic writers like EZH2 actively enforce a repressive transcriptional program, silencing entire gene networks required for T-cell proliferation, survival, and metabolic fitness (Zhao et al., 2016). This entire pathological loop is stabilized by the hypoxic, nutrient-poor conditions of the TME, creating a state of immune paralysis that is remarkably resistant to reversal (Figure 3).
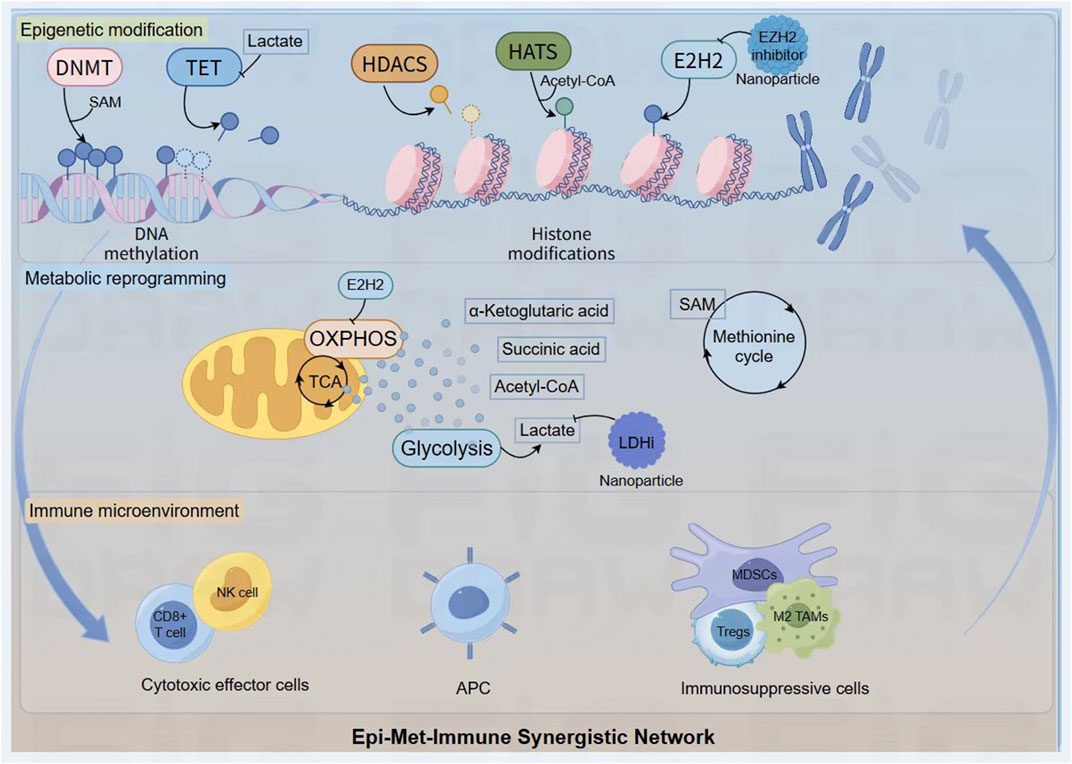
Figure 3. The Epi-Met-Immune Synergistic Network. Key metabolites generated from pathways like glycolysis and the methionine cycle (for example lactate, Acetyl-CoA, SAM) act as critical cofactors or inhibitors for epigenetic enzymes (DNMT, TET, HATs), directly linking the cell’s metabolic state to the regulation of DNA and histone modifications. This interplay is bidirectional, as epigenetic regulators like EZH2 can in turn control metabolic programs such as OXPHOS. This self-reinforcing feedback loop ultimately shapes the immune landscape, promoting a shift from cytotoxic effector cells to a dominant population of immunosuppressive cells (Tregs, MDSCs, M2 TAMs). The network serves as a rational blueprint for therapeutic intervention, where nanoplatforms are designed to deliver inhibitors against key nodes (for example EZH2i, LDHi) to simultaneously disrupt these pathological circuits and dismantle the foundations of tumor immunosuppression.
Network plasticity and therapeutic sequencing
Crucially, the Epi-Met-Immune Network is not a static entity but a dynamic system that evolves under selective pressure. In nascent tumors, the network’s connections may be highly plastic and malleable, representing a state of reversible immunosuppression. However, under the relentless pressure of tumor progression and therapy, these connections can become progressively hardwired or canalized. This is exemplified by T-cell exhaustion, where initial, reversible dysfunction (plasticity) transitions into a deeply entrenched epigenetic state (fixation) that is profoundly resistant to reversal by conventional immunotherapies (Blank et al., 2019).
This temporal evolution is not merely a challenge; it presents a critical, yet largely unexplored, therapeutic opportunity: the strategic sequencing of interventions. The concept of a fixed immunosuppressive state raises pivotal questions for clinical trial design. Can epigenetic modulators be deployed as priming agents to reverse epigenetic fixation and reopen a window of vulnerability to subsequent cancer vaccines or ICIs? What is the optimal duration and timing of this window before the network re-establishes its resilient, immunosuppressive state? Therefore, understanding the network’s temporal dynamics is paramount for designing therapies that are not only potent but also precisely timed to exploit moments of maximum vulnerability, a concept we term chronotherapy in this context.
A rational map for nanotherapeutic intervention
Crucially, the Epi-Met-Immune Network serves as a rational map for a paradigm shift in therapeutic design—from single-agent targeting to multi-pronged, systems-level disruption. By visualizing the interconnected nodes, we can identify strategic points for intervention. A nanoplatform delivering an EZH2 inhibitor targets a key node in the Epigenetic Layer, while another carrying a lactate dehydrogenase inhibitor (LDHi) severs a critical link in the Metabolic Layer.
The ultimate goal, uniquely enabled by advanced nanoplatforms, is to co-deliver multiple agents that simultaneously attack different pathological connections within this network. This represents a move towards the controlled demolition of the entire immunosuppressive architecture. Nanocarriers are the essential enabling technology for this strategy, as they can ensure that distinct therapeutic agents arrive at the same tumor site at the same time, a prerequisite for disrupting a tightly regulated biological network. This systems-level approach offers a far more robust strategy to dismantle the foundations of immunosuppression and unlock the full potential of cancer vaccines.
Epigenetic influence on metabolic reprogramming in enhancing lung cancer vaccine response
The functional manifestation of the Epi-Met-Immune Network is profoundly governed by its spatial organization within the tumor architecture. The TME is not a homogenous mixture of cells and metabolites; rather, it is a structured landscape with distinct ecological niches that dictate the network’s local topology. In the tumor’s hypoxic core, for instance, the network is dominated by metabolic suppression, where HIF-1α activation drives intense glycolysis, lactate accumulation, and subsequent epigenetic silencing of T-cell effector programs. In stark contrast, at the invasive front or proliferative margin, where immune infiltration is more active, the network may be rewired to favor adaptive resistance mechanisms, such as IFN-γ-driven PD-L1 expression and T-cell exhaustion mediated by direct cell-cell contact.
Unveiling this spatial heterogeneity is no longer a theoretical exercise but a tangible goal, enabled by the advent of Spatial Omics. Technologies like spatial transcriptomics and metabolomics are beginning to provide high-resolution maps of the network’s activity, moving our understanding from bulk analysis to a spatially resolved atlas. This granular view is critical, as it provides the ultimate rationale for developing “smart” nanoplatforms capable of navigating to and responding within specific microenvironmental niches (for example hypoxia, acidity). Therefore, the following analysis of individual cell populations must be interpreted through this spatial lens, recognizing that their epigenetic and metabolic states are fundamentally shaped by their precise location within the tumor ecosystem.
Epigenetic regulation of lung cancer-associated macrophages
TAMs in lung cancer undergo extensive epigenetic reprogramming that shapes their metabolic and functional phenotypes (Morrissey et al., 2021). The transcription factor landscape of TAMs is fundamentally altered through changes in enhancer accessibility and promoter methylation (Larionova et al., 2020). Key metabolic genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are epigenetically silenced in M2-like TAMs, while glycolytic genes show increased accessibility and expression (Jiang et al., 2024). This metabolic shift reflects a distinct epigenetic program orchestrated by specific histone modifications, including H3K4me1 marks at glycolytic gene enhancers and H3K27me3 marks at oxidative metabolism gene promoters (Saeed et al., 2014).
The metabolic reprogramming of TAMs creates a self-reinforcing loop that maintains their immunosuppressive phenotype. Enhanced glycolysis in TAMs leads to lactate production, which acts through GPR81 receptors to induce further epigenetic changes, including increased expression of HDAC enzymes (Zhang et al., 2022). These HDACs deacetylate histones at pro-inflammatory gene loci, suppressing the production of anti-tumor cytokines and chemokines. Additionally, metabolite-sensitive epigenetic enzymes, such as α-ketoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases, are influenced by the altered metabolic state of TAMs, affecting DNA and histone demethylation processes (Yu and Li, 2024; Lin et al., 2015).
Targeting the epigenetic-metabolic axis in TAMs offers promising strategies for enhancing vaccine responses. Combination approaches using HDAC inhibitors with metabolic modulators can reprogram TAMs toward anti-tumor phenotypes. For instance, inhibiting glycolysis while simultaneously modulating epigenetic enzymes can break the immunosuppressive feedback loop, restoring TAM inflammatory functions and enhancing their capacity to support vaccine-induced T cell responses (Jeong et al., 2019).
Epigenetic regulation of T lymphocytes
The epigenetic landscape of tumor-infiltrating T lymphocytes profoundly influences their metabolic programming and functional capacity (Liu X. et al., 2022). Effector T cells require robust glycolytic metabolism to support their proliferation and cytotoxic functions, yet the lung tumor microenvironment imposes metabolic restrictions that are reinforced by epigenetic modifications (Beckermann et al., 2017). Exhausted T cells exhibit specific methylation patterns at metabolic gene loci, with hypermethylation of glycolytic enzyme promoters and altered chromatin accessibility at mitochondrial biogenesis genes (Franco et al., 2020).
The metabolic-epigenetic interplay in T cells is mediated by metabolite availability and enzymatic activity. S-adenosylmethionine (SAM), the universal methyl donor, links one-carbon metabolism to DNA and histone methylation (Lee et al., 2023). In the nutrient-depleted tumor microenvironment, altered SAM availability affects methylation patterns, influencing T cell differentiation and function. Similarly, acetyl-CoA levels, determined by the balance between glycolysis and fatty acid oxidation, regulate histone acetylation and gene expression programs in T cells (Soriano-Baguet and Brenner, 2023).
Recent studies have revealed that metabolic interventions can reverse epigenetic T cell dysfunction (Liu et al., 2025a; Han et al., 2023). Supplementation with specific metabolites or use of metabolic pathway inhibitors can restore epigenetic marks associated with effector function. For example, inhibiting lactate dehydrogenase not only reduces lactate production but also alters the NAD+/NADH ratio, affecting the activity of sirtuins and other NAD+-dependent epigenetic enzymes (Anderson et al., 2017; Xie et al., 2020). This metabolic-epigenetic reprogramming can enhance T cell responses to cancer vaccines by restoring effector functions and preventing exhaustion.
Epigenetic regulation of cancer-associated fibroblasts
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) represent a critical stromal component that undergoes significant epigenetic reprogramming in lung tumors (Raaijmakers et al., 2024). The transformation of normal fibroblasts to CAFs involves widespread changes in DNA methylation and histone modifications that lock in their activated, pro-tumorigenic phenotype (Yang et al., 2023). These epigenetic changes directly influence CAF metabolism, shifting them toward glycolytic metabolism and enhanced production of metabolites that support tumor growth and immunosuppression.
CAFs exhibit unique metabolic features, including reverse Warburg metabolism, where they provide lactate and other metabolites to fuel tumor cells (Liang et al., 2022). This metabolic phenotype is maintained by epigenetic modifications at key metabolic gene loci. Hypomethylation of glycolytic enzyme promoters and altered histone acetylation patterns at oxidative metabolism genes create a stable metabolic program (Kim et al., 2022). Additionally, CAFs produce metabolites that function as epigenetic modifiers, including α-ketoglutarate, succinate, and fumarate, which influence the activity of demethylases in neighboring cells (Mishra et al., 2019).
The secretome of epigenetically reprogrammed CAFs profoundly impacts vaccine responses. CAF-derived factors, including TGF-β, IL-6, and various chemokines, create physical and chemical barriers to T cell infiltration and function (Wu et al., 2021). Epigenetic targeting of CAFs, particularly through DNMT or HDAC inhibition, can normalize their phenotype and reduce their immunosuppressive effects (Ramaiah et al., 2021). Combined with metabolic interventions, epigenetic CAF reprogramming represents a promising strategy for improving vaccine efficacy in lung tumors.
Nanoplatforms: overcoming the pharmacological barriers of epigenetic therapy
Epigenetic regulation in lung cancer therapy
Despite the significant potential of epigenetic therapies such as DNMTi and HDACi in lung cancer immunotherapy—including mechanisms like inducing viral mimicry and enhancing antigen presentation—their clinical translation faces considerable pharmacological challenges. These challenges primarily involve severe off-target effects and dose-limiting toxicities (for example myelosuppression) due to their broad mechanisms of action, as well as suboptimal pharmacokinetic properties such as rapid systemic clearance and poor penetration into deep tumor tissues. Furthermore, significant inter- and intratumoral heterogeneity in epigenetic states and immune microenvironments in lung cancer leads to unpredictable and inconsistent treatment responses. These fundamental pharmacological and biological barriers collectively prevent free drugs from achieving and sustaining therapeutically effective concentrations within tumors, thereby hindering durable remodeling of the epigenetic landscape and ultimately limiting the clinical efficacy of both monotherapy and combination strategies with immune checkpoint inhibitors.
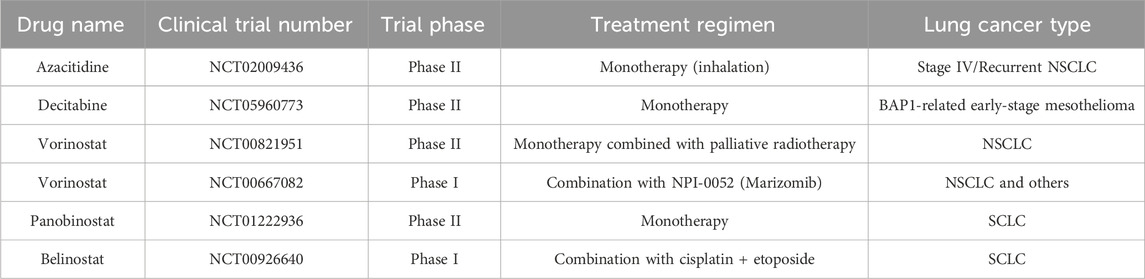
Epigenetic therapies have emerged as promising approaches for reversing the profound immune dysregulation in lung tumors. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors (DNMTi) and histone deacetylase inhibitors (HDACi) demonstrate multifaceted mechanisms of action that extend beyond direct cytotoxicity to include robust immunomodulatory effects (Luszczek et al., 2010; Blagitko-Dorfs et al., 2019; Huang et al., 2024). Notably, azacitidine and decitabine induce viral mimicry responses through endogenous retroviral element reactivation, enhancing type I interferon signaling and antigen presentation machinery (Table 1).
Yet, the clinical translation of these agents has been tempered by significant clinical hurdles, starkly illustrating the discrepancy between preclinical potential and clinical reality. The trials of epigenetic monotherapies are paradigmatic. For instance, the phase II study of systemically administered Vorinostat with radiotherapy (NCT00821951) failed to yield breakthroughs in NSCLC. This outcome is largely attributed to its narrow therapeutic window; the doses required to avoid systemic toxicities like fatigue and thrombocytopenia are likely insufficient to achieve the sustained, biologically effective concentrations needed within the TME to durably remodel the epigenetic landscape and reverse T-cell exhaustion. This limitation persists even when attempting to bypass systemic routes. An innovative trial exploring inhaled Azacitidine (NCT02009436) also met with limited success, suggesting that overcoming systemic toxicity is only half the battle. The trial’s failure underscores that free drugs, even when delivered locally, face formidable intratumoral barriers, including rapid clearance and poor penetration through dense stromal architecture.
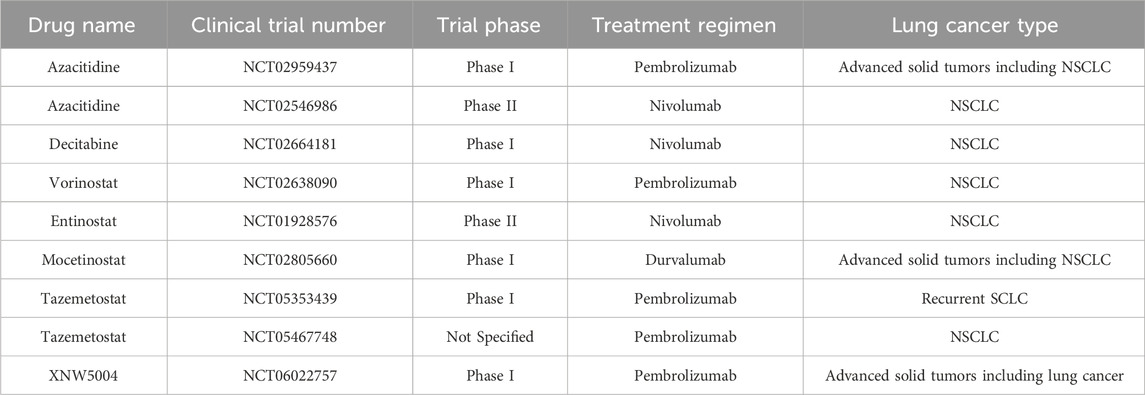
The strategy of combining epigenetic agents with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has yielded encouraging signals (Table 2), yet the clinical trials themselves have uncovered profound, unresolved complexities that temper enthusiasm and guide future research. For example, the phase II study of Azacitidine plus Nivolumab (NCT02546986), while demonstrating some clinical activity, produced a modest objective response rate (ORR). A crucial lesson from this trial is the decisive role of patient heterogeneity. The study did not employ biomarker-based patient stratification, such as pre-treatment DNA methylation profiles or baseline immune infiltration status, leaving a critical question unanswered: which patient subgroups are most likely to benefit from this dual strategy of ‘epigenetic reprogramming’ and ‘immune checkpoint liberation’? This highlights the paramount urgency for developing robust predictive biomarkers.
Complementing the challenge of patient selection is the equally critical issue of therapeutic scheduling and dynamics. While the combination of Entinostat and Nivolumab (NCT01928576) produced encouraging results, the dosing and timing regimens were largely empirical. We lack a fundamental understanding of the optimal ‘time window’ for epigenetic-drug-induced antigen expression and immune cell reprogramming. Should treatment involve a prolonged, low-dose ‘epigenetic priming’ to ‘warm up’ the TME before ICI administration, or is a concurrent, high-dose pulse more effective? This challenge of dynamic therapeutic optimization represents a significant, yet largely overlooked, scientific frontier that current clinical trial designs have not systematically addressed.
Collectively, these trials underscore that the next-generation of combination therapies must evolve beyond simply mixing active agents and towards a sophisticated, biomarker-guided approach that personalizes treatment to both the patient and the dynamic temporal evolution of the tumor-immune dialogue. The clinical setbacks are rooted in a confluence of fundamental pharmacological and biological barriers (Zhou et al., 2023). The non-specific mechanism of action of current epigenetic drugs results in substantial off-target effects and dose-limiting toxicities like myelosuppression, while their suboptimal pharmacokinetic properties are characterized by rapid clearance and poor tissue penetration (Xu et al., 2023). Compounding these issues is the profound epigenetic and immunological heterogeneity across lung tumors, which dictates differential therapeutic responses. It is precisely this multifaceted challenge—requiring therapies that can navigate systemic toxicities, breach physical tumor barriers, and be deployed with precise temporal control—that nanoplatform-based delivery systems are poised to address. Advanced nanocarriers offer the potential to resolve these limitations by simultaneously widening the therapeutic window, overcoming delivery barriers, and enabling the spatiotemporal control required to orchestrate a productive anti-tumor immune response.
Cancer vaccination in lung tumors depends on a functional cancer-immunity cycle (CI cycle), which requires robust antigenicity and adjuvanticity to sustain antitumor immunity. The cycle involves seven steps: antigen release and capture, processing and presentation, T-cell priming, trafficking, infiltration, tumor recognition, and killing. However, epigenetic and metabolic dysregulation disrupts multiple stages beyond adjuvanticity. For example, DNMT-mediated hypermethylation silences tumor antigens (for example MAGE-A3), while lactate accumulation in the TME inhibits TET demethylases in dendritic cells, impairing antigen presentation. IDO-driven tryptophan catabolism enhances EZH2 activity in T cells, repressing effector genes via H3K27me3 and promoting T-cell anergy. CAFs further disrupt T-cell trafficking through epigenetic silencing of chemokines like CXCL10. Nanomaterials can simultaneously target these barriers: pH-responsive nanoparticles co-delivering DNMT and LDHi restore antigen expression, improve DC function, and enhance T-cell activation, as shown by increased CD8+ T-cell infiltration and tumor control in preclinical models. A broader CI cycle-focused approach is essential to improve response rates in lung cancer vaccines (Liu et al., 2024).
Targeted nano-delivery systems
The integration of epigenetic modulators into nanoplatform designs could potentially revolutionize approaches to lung cancer therapy. Nanocarriers offer unique advantages for delivering epigenetic drugs, including protection from degradation, enhanced tumor accumulation, and controlled release kinetics. Lipid-based nanoparticles have shown particular promise for delivering DNMTi and HDAC inhibitors, with modifications such as PEGylation extending circulation time and reducing immunogenicity (Sukocheva et al., 2022) (Figure 4).
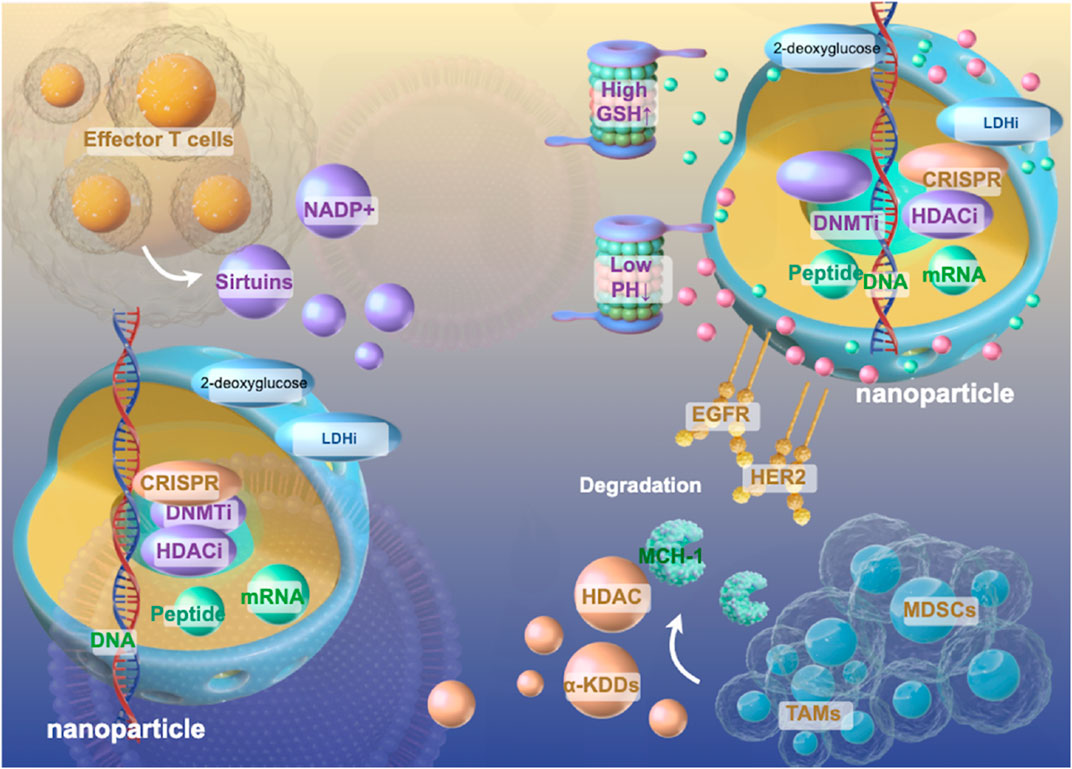
Figure 4. Schematic Diagram of Epigenetics-Centered Multifunctional Nanoplatform Design. Multifunctional nanoplatforms integrating epigenetic therapeutics (DNMTi, HDACi, CRISPR components) with metabolic modulators (2-deoxyglucose, LDHi) to synergistically reprogram the immunosuppressive lung tumor microenvironment as described in sections 5.2–5.3. These sophisticated delivery systems incorporate tumor-targeting ligands (EGFR, HER2) and stimuli-responsive elements (pH, GSH-sensitive) that enable precise spatiotemporal control of drug release within the complex immunosuppressive cellular architecture comprising effector T cells, MDSCs, and TAMs. By simultaneously disrupting the self-reinforcing epigenetic-metabolic feedback loops that maintain immunosuppressive phenotypes while enhancing antigen presentation machinery, these nanoplatforms represent a promising strategy to overcome the formidable barriers to cancer vaccine efficacy in lung tumors through comprehensive reprogramming of the tumor immune landscape.
Advanced nanoplatform designs incorporate stimuli-responsive elements that enable precise spatiotemporal control of epigenetic drug release. pH-responsive nanocarriers exploit the acidic tumor microenvironment to trigger drug release specifically within tumors (Chen et al., 2023). Redox-responsive systems utilize the elevated glutathione levels in cancer cells to achieve intracellular drug release (Raza et al., 2018). These smart delivery systems minimize off-target effects while maximizing therapeutic efficacy.
Cell-specific delivery to immune populations within the tumor microenvironment requires sophisticated targeting approaches (Lei et al., 2020). Nanoparticles decorated with antibodies against immune cell markers can selectively deliver cargo to specific immune subsets (Kimmel et al., 2025; Jain et al., 2024). For instance, CD3e f (ab)2 fragment nanoparticles can deliver metabolic modulators specifically to cytotoxic T cells (Kim et al., 2021), while anti-F4/80 targeting enables macrophage-specific delivery (Terry et al., 2015). This precision targeting minimizes systemic effects while maximizing local immunomodulation.
The tumor microenvironment presents unique opportunities for environmental targeting. Enzyme-cleavable linkers responsive to matrix metalloproteinases enable selective drug release in the tumor stroma (Li et al., 2020; Iaccarino et al., 2019). Hypoxia-responsive nanocarriers utilize the low oxygen tension in tumors to trigger drug release through reduction of azobenzene or nitroimidazole groups (Thambi et al., 2014). These environmental targeting strategies complement receptor-based approaches to achieve optimal drug delivery.
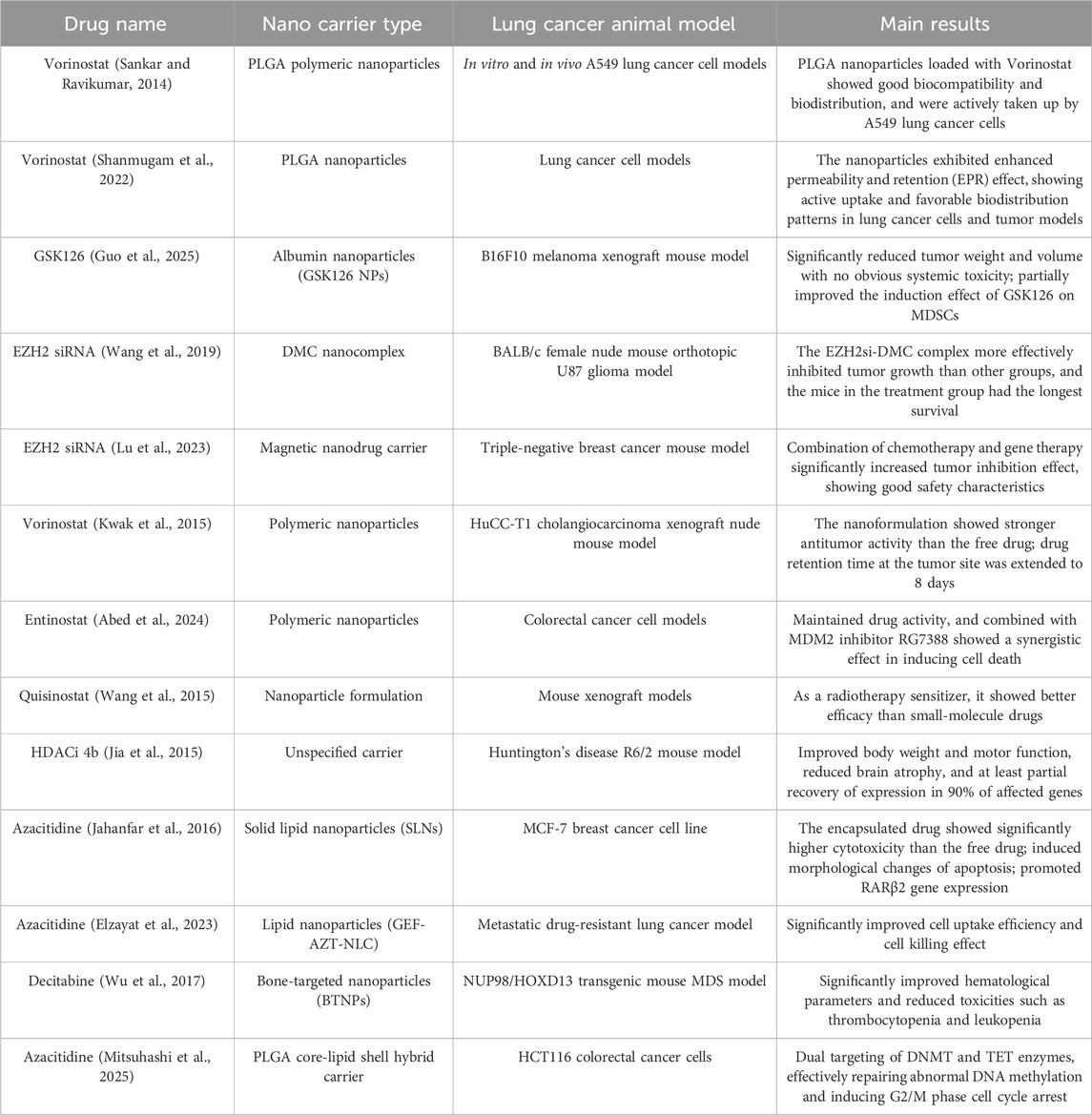
Preclinical studies investigating epigenetic modulator-loaded nanoplatforms have established compelling proof-of-concept, as summarized in Table 3. Lipid-based nanoformulations, for example, have shown considerable promise by enabling the co-delivery of synergistic epigenetic agents, such as decitabine and panobinostat, to enhance anti-tumor efficacy in preclinical models (Rehman et al., 2024). These advances, marked by favorable biodistribution and enhanced anti-tumor immune responses, are certainly encouraging. However, these promising findings must be interpreted with caution, as a critical appraisal reveals significant translational challenges embedded within the study designs.
To begin with, the choice of animal model often inflates therapeutic expectations. The success of nanoparticles in an immunologically favorable model, which is inherently sensitive to immunotherapy, cannot be directly extrapolated to the profoundly immunosuppressive microenvironment of primary lung cancer (Wang et al., 2024). To generate more predictive data, future preclinical validation must pivot towards more clinically relevant systems, such as Kras/p53 genetically engineered mouse models or patient-derived xenografts (PDX) (Nakahata et al., 2022). Furthermore, the concept of ‘targeted delivery’ itself warrants critical scrutiny. Despite reports of sophisticated targeting strategies, the unavoidable reality is that a majority of nanoparticles are sequestered by the reticuloendothelial system (RES) (Tang et al., 2019). This ‘off-target’ accumulation is not merely a loss of payload but a potentially potent immunomodulatory event—for instance, by altering Kupffer cell function or systemic T-cell priming—a “double-edged sword” effect that remains a largely unexplored dimension of nanomedicine. Finally, the very elegance of these nanoplatforms often conceals their greatest translational barrier: manufacturing complexity (Feng et al., 2024). The chemistry, manufacturing, and controls (CMC) for multi-component systems are exceptionally demanding (O'Brien Laramy et al., 2025). A forward-looking perspective must therefore recognize that the next breakthrough in this field may lie not in increasing design complexity, but in mastering the manufacturability and scalability required for clinical translation.
Synergistic effects of co-loading metabolic regulators and epigenetic nanomedicine
The co-encapsulation of metabolic regulators and epigenetic drugs within nanoplatforms may generates synergistic effects that extend far beyond simple additive responses (Liu S. et al., 2025; Zhou Y. et al., 2024). This synergy arises from the fundamental interconnection between cellular metabolism and epigenetic regulation, where metabolites serve as essential cofactors for epigenetic enzymes while epigenetic modifications control the expression of metabolic genes (Thakur and Chen, 2019). The simultaneous modulation of both systems creates a powerful positive feedback loop that amplifies therapeutic efficacy.
The powerful synergy generated by co-encapsulating metabolic regulators and epigenetic drugs can be understood rationally through the lens of the Epi-Met-Immune Network. Rather than being a simple additive effect, this strategy represents a concerted attack on the feedback loops that maintain immunosuppression. For example, by simultaneously delivering a glycolytic inhibitor and an HDACi, a nanoplatform can disrupt both a key node in the Metabolic Layer (lactate production) and another in the Epigenetic Layer (histone acetylation), effectively dismantling the self-reinforcing circuit that connects metabolic hostility to T-cell epigenetic silencing.
At the molecular level, metabolic inhibitors such as 2-deoxyglucose or lactate dehydrogenase inhibitors reduce the production of oncometabolites that normally inhibit epigenetic enzymes (Wong et al., 2017). For instance, decreased lactate production enhances the activity of histone deacetylases by altering the NAD+/NADH ratio, while reduced 2-hydroxyglutarate levels restore the function of TET enzymes and histone demethylases (An et al., 2023). When combined with direct epigenetic modulators like HDAC inhibitors or DNA methyltransferase inhibitors, this metabolic reprogramming synergistically enhances chromatin remodeling and gene expression changes (Ramaiah et al., 2021). Studies have demonstrated that this combination achieves greater changes in immune-related gene expression compared to either treatment alone (Liang et al., 2023; Fang et al., 2021).
This combination effect may have a significant impact on immune cell function within the tumor microenvironment. Co-delivery of glycolytic inhibitors with epigenetic drugs not only reduces metabolic competition between tumor cells and T cells but also prevents the epigenetic imprinting of exhaustion programs (Geng et al., 2023). This action results in a enhancement in T cell cytotoxicity compared to monotherapy approaches.
The temporal dynamics of synergistic effects reveal another layer of complexity. Metabolic reprogramming can sensitize cells to subsequent epigenetic interventions by altering the availability of metabolic cofactors (Sun et al., 2022). S-adenosylmethionine levels, modulated by methionine metabolism inhibitors, directly influence DNA and histone methylation patterns (Pascale et al., 2022). When combined with DNMT inhibitors, this metabolic priming enhances demethylation efficiency (Blagitko-Dorfs et al., 2019). Conversely, epigenetic drugs can reprogram metabolic gene expression, creating sustained metabolic changes that persist beyond drug clearance (Peng and Zhong, 2015). This bidirectional enhancement creates durable therapeutic effects that extend the duration of immune activation.
The synergy extends to overcoming drug resistance mechanisms. Tumor cells often develop resistance to metabolic inhibitors through compensatory metabolic pathways, but co-delivered epigenetic drugs can silence these escape routes by modulating the expression of alternative metabolic enzymes (Park et al., 2020; Scumaci and Zheng, 2023). Similarly, epigenetic drug resistance mediated by drug efflux pumps or metabolic inactivation can be circumvented by metabolic modulators that alter cellular energy states and transporter function (Ingelman-Sundberg et al., 2013). This reciprocal resistance prevention has been demonstrated to maintain drug sensitivity longer than single-agent treatments in preclinical models (Singh and Yeh, 2017).
Immune adjuvant functions of epigenetic nano-vaccines
Beyond drug delivery, nanoplatforms themselves can function as immune adjuvants, enhancing vaccine responses through multiple mechanisms (Zhao T. et al., 2023). The physicochemical properties of nanoparticles, including size, shape, and surface chemistry, influence their immunogenicity (David et al., 2016; Lin et al., 2020). Nanoparticles in the 20–200 nm range are efficiently taken up by dendritic cells and transported to lymph nodes, optimal for initiating immune responses (Manolova et al., 2008; Zhao H. et al., 2023). Surface modifications with pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) further enhance their adjuvant activity (Ben-Akiva et al., 2025).
Inorganic nanoparticles, particularly those based on gold, silica, or iron oxide, can activate innate immune responses through multiple pathways (Palomino-Cano et al., 2024). These materials can trigger inflammasome activation, leading to IL-1β production and enhanced antigen presentation (van de Veerdonk et al., 2011). The controlled release of ions from degradable inorganic nanoparticles provides sustained immune stimulation (Liu et al., 2025c). Additionally, the photothermal properties of certain nanoparticles enable combination with thermal ablation therapies, releasing tumor antigens while providing adjuvant signals (Ashikbayeva et al., 2019).
Biomimetic nanoplatforms represent an emerging frontier in vaccine design (Liu J. et al., 2022). Cell membrane-coated nanoparticles combine the drug delivery capabilities of synthetic carriers with the biological functions of cell membranes (Xu et al., 2020). Tumor cell membrane-coated particles present a full array of tumor antigens while protecting encapsulated drugs (Jiang et al., 2020). Dendritic cell membrane coatings provide natural targeting to lymph nodes and enhanced T cell activation (Cao et al., 2023). These biomimetic approaches blur the lines between drug delivery vehicles and vaccines themselves.
Future directions and clinical translation challenges
From single-node targeting to rational network disruption
The future of epigenetic nanomedicine lies not in simply improving the delivery of single agents, but in rationally designing platforms that can overcome the TME’s most formidable property: its capacity for adaptive resistance. This requires elevating our view of the Epi-Met-Immune Synergistic Network from a static map of immunosuppression to a dynamic engine of therapeutic failure. When a single node is targeted with a monotherapy, such as an EZH2 inhibitor, the network often responds not by collapsing, but by adaptively rewiring itself. The system compensates by upregulating alternative metabolic pathways or engaging different epigenetic silencing mechanisms, effectively circumventing the therapeutic blockade and driving resistance.
This inherent resilience renders single-agent strategies fundamentally inadequate and reframes the mission of nanomedicine: the goal is not merely to achieve synergy, but to preemptively dismantle the network’s capacity for adaptive resistance. This is the ultimate rationale for multi-pronged, systems-level disruption. The next paradigm shift will involve leveraging patient-specific data to guide these attacks. For instance, emerging liquid biopsy technologies that map circulating tumor DNA methylation patterns will not only serve as diagnostic biomarkers but will also reveal the network’s active pathways and predict its likely escape routes (Luo et al., 2021). This information, when processed by AI-driven algorithms, can guide the selection or even de novo design of a nanoplatform co-delivering a specific combination of agents—such as an EZH2 inhibitor and a lactate dehydrogenase inhibitor—to sever not only the primary driver pathways but also the anticipated resistance circuits (Wei et al., 2021; Zhang et al., 2017). This represents the ultimate goal of precision medicine: moving from pathway-level intervention to patient-specific network demolition.
A clinical roadmap: from network theory to precision intervention
Operationalizing the Epi-Met-Immune Network concept requires a closed-loop, four-stage clinical paradigm. The process initiates with a high-resolution diagnosis, using liquid biopsies to map the patient-specific network topology and identify its dominant immunosuppressive circuits. This functional map then guides the rigorous ex vivo validation of a rationally selected multi-component nanoplatform in patient-derived models, such as tumor organoids, to confirm its ability to dismantle the target pathways. Only upon this personalized confirmation of efficacy is the synergistic therapy administered, initiating a continuous feedback loop where serial monitoring tracks the network’s adaptive rewiring in real-time. This final stage enables dynamic therapeutic steering, allowing for the adjustment of treatment to preemptively counter resistance and ensure durable clinical benefit (Figure 5).
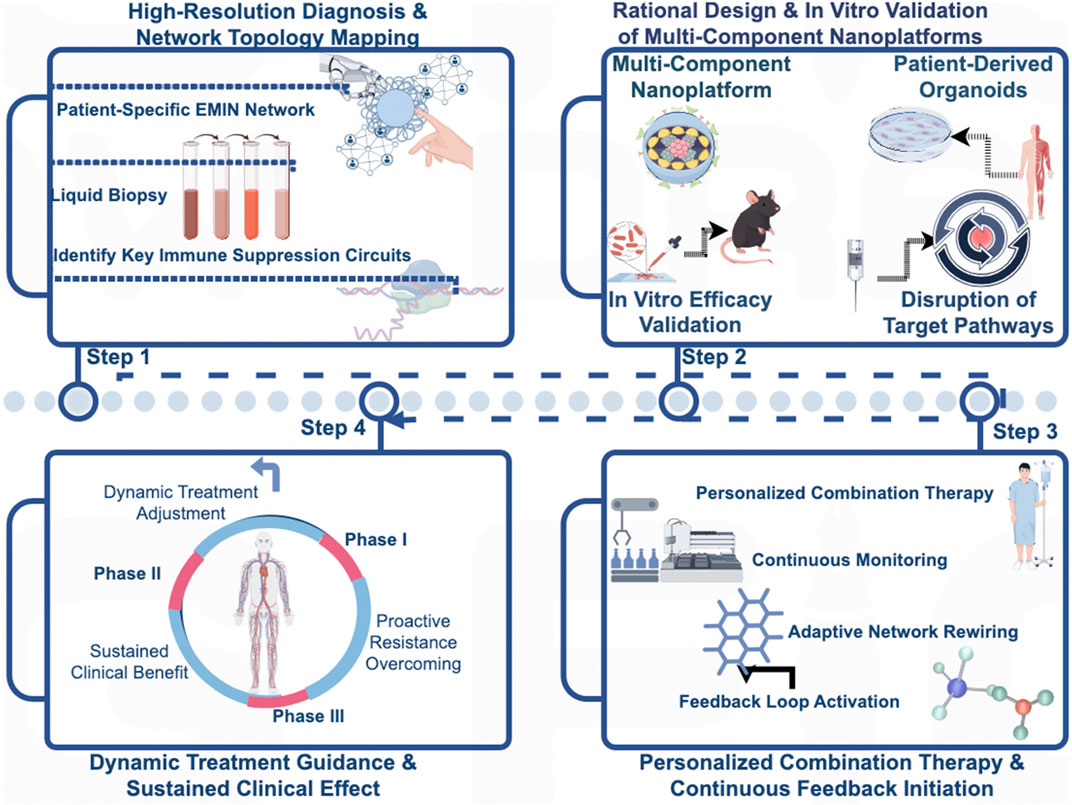
Figure 5. A Closed-Loop Clinical Paradigm for Precision Intervention Based on the Epi-Met-Immune Network. This figure illustrates a proposed closed-loop, four-stage clinical paradigm for operationalizing the Epi-Met-Immune Network concept to guide personalized cancer therapy. (Stage 1: High-Resolution Diagnosis) The process begins with a high-resolution diagnosis, utilizing technologies such as liquid biopsy to map the patient-specific network topology and identify the dominant immunosuppressive circuits. (Stage 2: Ex Vivo Validation) Based on this functional map, a rationally selected multi-component nanoplatform is subjected to rigorous ex vivo validation in patient-derived models, such as tumor organoids, to confirm its ability to dismantle the identified target pathways. (Stage 3: Personalized Administration) Only after this personalized confirmation of efficacy is the synergistic therapy administered to the patient, initiating a continuous feedback loop. (Stage 4: Dynamic Monitoring and Steering) Finally, serial monitoring is employed to track the network’s adaptive rewiring in real-time, enabling dynamic therapeutic steering to preemptively counter resistance and ensure durable clinical benefit.
Overcoming the physical and manufacturing barriers
Despite promising preclinical results, the translation of these sophisticated network-disrupting therapies faces two intertwined engineering challenges: manufacturing scalability and penetrating the tumor microenvironment (Metselaar and Lammers, 2020). The clinical translation of multi-component nanotherapeutics is critically bottlenecked by challenges in CMC, where establishing standardized, scalable processes that ensure batch-to-batch consistency and long-term stability is paramount (Gawne et al., 2023). This complexity is mirrored by regulatory hurdles, as agencies like the FDA and EMA require stringent characterization and safety assessments, making early and continuous engagement essential. Once successfully manufactured, these nanoparticles confront the second challenge: the profound heterogeneity of the TME, which severely limits the universal applicability of passive targeting via the EPR effect (Du et al., 2015). Successfully delivering a network-disrupting payload requires overcoming formidable physical barriers—including anomalous vasculature and a rigid extracellular matrix—and hostile chemical gradients like hypoxia and acidity (Ross et al., 2015). Therefore, future strategies must evolve beyond passive accumulation to include active targeting ligands, biomimetic coatings that use immune cells as Trojan horses, and intelligent, stimuli-responsive systems designed to trigger drug release only upon reaching the specific metabolic or pH conditions of the deep tumor core.
Ensuring clinical viability and economic accessibility
Ultimately, the success of these transformative therapies will be determined by their real-world clinical viability and economic sustainability. While the initial investment for advanced nanomedicines is substantial, their potential to offer durable responses or even cures provides considerable long-term economic value by reducing downstream healthcare costs and enhancing patient productivity (Bosetti and Jones, 2019). However, realizing this potential requires a paradigm shift in implementation. This includes adopting value-based pricing models that link payment to clinical outcomes, exploring innovative financing mechanisms, and integrating cost-effectiveness analyses early in the development process. Ensuring equitable access to these technologies will require a comprehensive framework that balances immediate budgetary constraints with long-term societal benefit, making these powerful network-disrupting therapies a reality for patients (Toro et al., 2025).
Conclusion
The convergence of nanotechnology with epigenetic and metabolic modulation represents a transformative frontier in cancer immunotherapy. This review has advanced the concept that durable anti-tumor immunity is hindered not by isolated pathways but by a resilient, interconnected network of epi-metabolic feedback loops. By proposing the Epi-Met-Immune Synergistic Network as a conceptual framework, we provide a rational basis for designing sophisticated nanoplatforms capable of systems-level intervention—co-delivering synergistic agents to dismantle the very foundations of immunosuppression. While overcoming translational hurdles in manufacturing and delivery remains critical, this network-guided approach promises to fundamentally reshape cancer vaccine development, transforming immunologically “cold” tumors into responsive malignancies amenable to precision therapy.
Author contributions
MX: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Writing – original draft. XZ: Conceptualization, Formal Analysis, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. XY: Data curation, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. CM: Data curation, Investigation, Supervision, Writing – review and editing. XL: Project administration, Resources, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. GCh: Data curation, Formal Analysis, Project administration, Writing – review and editing. GYu: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review and editing. SL: Writing – review and editing, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision. RC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grant 2024ZYD0334 from Special Project for Central Government-Guided Local Sci-Tech Development in Sichuan Province and grant No. 2022-JYJ-153 from the Luzhou Science and Technology Plan Project.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the assistance of DeepL in improving the grammar, word choice, and writing of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Abed, A., Greene, M. K., Lees, A., Hindley, A., Longley, D. B., McDade, S. S., et al. (2024). Nanoencapsulation of MDM2 inhibitor RG7388 and Class-I HDAC inhibitor entinostat enhances their therapeutic potential through synergistic antitumor effects and reduction of systemic toxicity. Mol. Pharm. 21, 1246–1255. doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.3c00926
Altorki, N. K., Markowitz, G. J., Gao, D., Port, J. L., Saxena, A., Stiles, B., et al. (2019). The lung microenvironment: an important regulator of tumour growth and metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 19, 9–31. doi:10.1038/s41568-018-0081-9
An, Y. J., Jo, S., Kim, J. M., Kim, H. S., Kim, H. Y., Jeon, S. M., et al. (2023). Lactate as a major epigenetic carbon source for histone acetylation via nuclear LDH metabolism. Exp. Mol. Med. 55, 2238–2247. doi:10.1038/s12276-023-01095-w
Anderson, K. A., Madsen, A. S., Olsen, C. A., and Hirschey, M. D. (2017). Metabolic control by sirtuins and other enzymes that sense NAD(+), NADH, or their ratio. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Bioenerg. 1858, 991–998. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2017.09.005
Arner, E. N., and Rathmell, J. C. (2023). Metabolic programming and immune suppression in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 41, 421–433. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2023.01.009
Arun, G., Diermeier, S. D., and Spector, D. L. (2018). Therapeutic targeting of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 24, 257–277. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2018.01.001
Ashikbayeva, Z., Tosi, D., Balmassov, D., Schena, E., Saccomandi, P., and Inglezakis, V. (2019). Application of nanoparticles and nanomaterials in thermal ablation therapy of cancer. Nanomater. (Basel) 9, 1195. doi:10.3390/nano9091195
Bader, J. E., Voss, K., and Rathmell, J. C. (2020). Targeting metabolism to improve the tumor microenvironment for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cell 78, 1019–1033. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.05.034
Batchu, R. B., Gruzdyn, O., Potti, R. B., Weaver, D. W., and Gruber, S. A. (2014). MAGE-A3 with cell-penetrating domain as an efficient therapeutic cancer vaccine. JAMA Surg. 149, 451–457. doi:10.1001/jamasurg.2013.4113
Beckermann, K. E., Dudzinski, S. O., and Rathmell, J. C. (2017). Dysfunctional T cell metabolism in the tumor microenvironment. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 35, 7–14. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2017.04.003
Belk, J. A., Daniel, B., and Satpathy, A. T. (2022a). Epigenetic regulation of T cell exhaustion. Nat. Immunol. 23, 848–860. doi:10.1038/s41590-022-01224-z
Belk, J. A., Yao, W., Ly, N., Freitas, K. A., Chen, Y. T., Shi, Q., et al. (2022b). Genome-wide CRISPR screens of T cell exhaustion identify chromatin remodeling factors that limit T cell persistence. Cancer Cell 40, 768–786.e7. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2022.06.001
Ben-Akiva, E., Chapman, A., Mao, T., and Irvine, D. J. (2025). Linking vaccine adjuvant mechanisms of action to function. Sci. Immunol. 10, eado5937. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.ado5937
Blagitko-Dorfs, N., Schlosser, P., Greve, G., Pfeifer, D., Meier, R., Baude, A., et al. (2019). Combination treatment of acute myeloid leukemia cells with DNMT and HDAC inhibitors: predominant synergistic gene downregulation associated with gene body demethylation. Leukemia 33, 945–956. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0293-8
Blank, C. U., Haining, W. N., Held, W., Hogan, P. G., Kallies, A., Lugli, E., et al. (2019). Defining 'T cell exhaustion. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 19, 665–674. doi:10.1038/s41577-019-0221-9
Bosetti, R., and Jones, S. L. (2019). Cost-effectiveness of nanomedicine: estimating the real size of nano-costs. Nanomedicine (Lond). 14, 1367–1370. doi:10.2217/nnm-2019-0130
Bronte, V., Serafini, P., De Santo, C., Marigo, I., Tosello, V., Mazzoni, A., et al. (2003). IL-4-induced arginase 1 suppresses alloreactive T cells in tumor-bearing mice. J. Immunol. 170, 270–278. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.170.1.270
Butts, C., Socinski, M. A., Mitchell, P. L., Thatcher, N., Havel, L., Krzakowski, M., et al. (2014). Tecemotide (L-BLP25) versus placebo after chemoradiotherapy for stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (START): a randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 15, 59–68. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70510-2
Cai, L., Li, Y., Tan, J., Xu, L., and Li, Y. (2023). Targeting LAG-3, TIM-3, and TIGIT for cancer immunotherapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 16, 101. doi:10.1186/s13045-023-01499-1
Cao, J., and Yan, Q. (2020). Cancer epigenetics, tumor immunity, and immunotherapy. Trends Cancer 6, 580–592. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2020.02.003
Cao, Y., Long, J., Sun, H., Miao, Y., Sang, Y., Lu, H., et al. (2023). Dendritic cell-mimicking nanoparticles promote mRNA delivery to lymphoid organs. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10, e2302423. doi:10.1002/advs.202302423
Chen, Z., Wang, X., Zhao, N., Chen, H., and Guo, G. (2023). Advancements in pH-responsive nanocarriers: enhancing drug delivery for tumor therapy. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 20, 1623–1642. doi:10.1080/17425247.2023.2292678
Chen, J., Cui, L., Lu, S., and Xu, S. (2024). Amino acid metabolism in tumor biology and therapy. Cell Death Dis. 15, 42. doi:10.1038/s41419-024-06435-w
Chiappinelli, K. B., Strissel, P. L., Desrichard, A., Li, H., Henke, C., Akman, B., et al. (2015). Inhibiting DNA methylation causes an interferon response in cancer via dsRNA including endogenous retroviruses. Cell 162, 974–986. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.07.011
Crump, N. T., Hadjinicolaou, A. V., Xia, M., Walsby-Tickle, J., Gileadi, U., Chen, J. L., et al. (2021). Chromatin accessibility governs the differential response of cancer and T cells to arginine starvation. Cell Rep. 35, 109101. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109101
Dai, E., Zhu, Z., Wahed, S., Qu, Z., Storkus, W. J., and Guo, Z. S. (2021). Epigenetic modulation of antitumor immunity for improved cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 20, 171. doi:10.1186/s12943-021-01464-x
David, C. A., Owen, A., and Liptrott, N. J. (2016). Determining the relationship between nanoparticle characteristics and immunotoxicity: key challenges and approaches. Nanomedicine (Lond) 11, 1447–1464. doi:10.2217/nnm-2016-0017
De Sa Fernandes, C., Novoszel, P., Gastaldi, T., Krauss, D., Lang, M., Rica, R., et al. (2024). The histone deacetylase HDAC1 controls dendritic cell development and anti-tumor immunity. Cell Rep. 43, 114308. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114308
Du, J., Lane, L. A., and Nie, S. (2015). Stimuli-responsive nanoparticles for targeting the tumor microenvironment. J. Control Release 219, 205–214. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.08.050
Ellmeier, W., and Seiser, C. (2018). Histone deacetylase function in CD4(+) T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 18, 617–634. doi:10.1038/s41577-018-0037-z
Elzayat, E. M., Sherif, A. Y., Nasr, F. A., Attwa, M. W., Alshora, D. H., Ahmad, S. F., et al. (2023). Enhanced codelivery of gefitinib and azacitidine for treatment of metastatic-resistant lung cancer using biodegradable lipid nanoparticles. Mater. (Basel) 16, 5364. doi:10.3390/ma16155364
Fallarino, F., Grohmann, U., You, S., McGrath, B. C., Cavener, D. R., Vacca, C., et al. (2006). The combined effects of tryptophan starvation and tryptophan catabolites down-regulate T cell receptor zeta-chain and induce a regulatory phenotype in naive T cells. J. Immunol. 176, 6752–6761. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.176.11.6752
Fang, H., Guo, Z., Chen, J., Lin, L., Hu, Y., Li, Y., et al. (2021). Combination of epigenetic regulation with gene therapy-mediated immune checkpoint blockade induces anti-tumour effects and immune response in vivo. Nat. Commun. 12, 6742. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-27078-x
Faubert, B., Li, K. Y., Cai, L., Hensley, C. T., Kim, J., Zacharias, L. G., et al. (2017). Lactate metabolism in human lung tumors. Cell 171, 358–371.e9. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.019
Feng, Y., Wang, J., Cao, J., Cao, F., and Chen, X. (2024). Manipulating calcium homeostasis with nanoplatforms for enhanced cancer therapy. Explor. (Beijing) 4, 20230019. doi:10.1002/EXP.20230019
Franco, F., Jaccard, A., Romero, P., Yu, Y. R., and Ho, P. C. (2020). Metabolic and epigenetic regulation of T-cell exhaustion. Nat. Metab. 2, 1001–1012. doi:10.1038/s42255-020-00280-9
Gawne, P. J., Ferreira, M., Papaluca, M., Grimm, J., and Decuzzi, P. (2023). New opportunities and old challenges in the clinical translation of nanotheranostics. Nat. Rev. Mater 8, 783–798. doi:10.1038/s41578-023-00581-x
Geissler, F., Nesic, K., Kondrashova, O., Dobrovic, A., Swisher, E. M., Scott, C. L., et al. (2024). The role of aberrant DNA methylation in cancer initiation and clinical impacts. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 16, 17588359231220511. doi:10.1177/17588359231220511
Geng, C., Pang, S., Ye, R., Shi, J., Yang, Q., Chen, C., et al. (2023). Glycolysis-based drug delivery nanosystems for therapeutic use in tumors and applications. Biomed. Pharmacother. 165, 115009. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115009
Giaccone, G., Bazhenova, L. A., Nemunaitis, J., Tan, M., Juhasz, E., Ramlau, R., et al. (2015). A phase III study of belagenpumatucel-L, an allogeneic tumour cell vaccine, as maintenance therapy for non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 51, 2321–2329. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2015.07.035
Goyal, A., Bauer, J., Hey, J., Papageorgiou, D. N., Stepanova, E., Daskalakis, M., et al. (2023). DNMT and HDAC inhibition induces immunogenic neoantigens from human endogenous retroviral element-derived transcripts. Nat. Commun. 14, 6731. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-42417-w
Groth, C., Hu, X., Weber, R., Fleming, V., Altevogt, P., Utikal, J., et al. (2019). Immunosuppression mediated by myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) during tumour progression. Br. J. Cancer 120, 16–25. doi:10.1038/s41416-018-0333-1
Guo, Y., Huang, J., Lin, M., Yin, Q., Zhang, T., Guo, Z., et al. (2025). Nano particle loaded EZH2 inhibitors: increased efficiency and reduced toxicity for malignant solid tumors. J. Transl. Int. Med. 13, 156–169. doi:10.1515/jtim-2025-0020
Han, S., Georgiev, P., Ringel, A. E., Sharpe, A. H., and Haigis, M. C. (2023). Age-associated remodeling of T cell immunity and metabolism. Cell Metab. 35, 36–55. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2022.11.005
He, S., Zheng, L., and Qi, C. (2025). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in the tumor microenvironment and their targeting in cancer therapy. Mol. Cancer 24, 5. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02208-3
Hicks, K. C., Knudson, K. M., Lee, K. L., Hamilton, D. H., Hodge, J. W., Figg, W. D., et al. (2020). Cooperative immune-mediated mechanisms of the HDAC inhibitor entinostat, an IL15 superagonist, and a cancer vaccine effectively synergize as a novel cancer therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 26, 704–716. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-19-0727
Huang, K. C., Chiang, S. F., Ke, T. W., Chen, T. W., Hu, C. H., Yang, P. C., et al. (2021). DNMT1 constrains IFNβ-mediated anti-tumor immunity and PD-L1 expression to reduce the efficacy of radiotherapy and immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 10, 1989790. doi:10.1080/2162402X.2021.1989790
Huang, W., Zhu, Q., Shi, Z., Tu, Y., Li, Q., Zheng, W., et al. (2024). Dual inhibitors of DNMT and HDAC induce viral mimicry to induce antitumour immunity in breast cancer. Cell Death Discov. 10, 143. doi:10.1038/s41420-024-01895-7
Iaccarino, G., Profeta, M., Vecchione, R., and Netti, P. A. (2019). Matrix metalloproteinase-cleavable nanocapsules for tumor-activated drug release. Acta Biomater. 89, 265–278. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.043
Ibrahim, M. L., Zheng, H., Barlow, M. L., Latif, Y., Chen, Z., Yu, X., et al. (2024). Histone deacetylase inhibitors directly modulate T cell gene expression and signaling and promote development of effector-exhausted T cells in murine tumors. J. Immunol. 212, 737–747. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.2300475
Ignatz-Hoover, J. J., Murphy, E. V., and Driscoll, J. J. (2022). Targeting proteasomes in cancer and infectious disease: a parallel strategy to treat malignancies and microbes. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 12, 925804. doi:10.3389/fcimb.2022.925804
Ingelman-Sundberg, M., Zhong, X. B., Hankinson, O., Beedanagari, S., Yu, A. M., Peng, L., et al. (2013). Potential role of epigenetic mechanisms in the regulation of drug metabolism and transport. Drug Metab. Dispos. 41, 1725–1731. doi:10.1124/dmd.113.053157
Iqbal, M. A., Arora, S., Prakasam, G., Calin, G. A., and Syed, M. A. (2019). MicroRNA in lung cancer: role, mechanisms, pathways and therapeutic relevance. Mol. Asp. Med. 70, 3–20. doi:10.1016/j.mam.2018.07.003
Jahanfar, F., Hasani, A., Shanebandi, D., Rahmati, M., and Hamishehkar, H. (2016). Enhanced in Vitro anti-tumor activity of 5-Azacytidine by entrapment into solid lipid nanoparticles. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 6, 367–375. doi:10.15171/apb.2016.048
Jain, M., Yu, X., Schneck, J. P., and Green, J. J. (2024). Nanoparticle targeting strategies for lipid and polymer-based gene delivery to immune cells In Vivo. Small Sci. 4, 2400248. doi:10.1002/smsc.202400248
Jeong, H., Kim, S., Hong, B. J., Lee, C. J., Kim, Y. E., Bok, S., et al. (2019). Tumor-associated macrophages enhance tumor hypoxia and aerobic glycolysis. Cancer Res. 79, 795–806. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2545
Jia, H., Morris, C. D., Williams, R. M., Loring, J. F., and Thomas, E. A. (2015). HDAC inhibition imparts beneficial transgenerational effects in huntington's disease mice via altered DNA and histone methylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 112, E56–E64. doi:10.1073/pnas.1415195112
Jia, Q., Wang, A., Yuan, Y., Zhu, B., and Long, H. (2022). Heterogeneity of the tumor immune microenvironment and its clinical relevance. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 11, 24. doi:10.1186/s40164-022-00277-y
Jiang, Y., Krishnan, N., Zhou, J., Chekuri, S., Wei, X., Kroll, A. V., et al. (2020). Engineered cell-membrane-coated nanoparticles directly present tumor antigens to promote anticancer immunity. Adv. Mat. 32, e2001808. doi:10.1002/adma.202001808
Jiang, G., Hong, J., Sun, L., Wei, H., Gong, W., Wang, S., et al. (2024). Glycolysis regulation in tumor-associated macrophages: its role in tumor development and cancer treatment. Int. J. Cancer 154, 412–424. doi:10.1002/ijc.34711
Jin, J., Zhao, Q., Wei, Z., Chen, K., Su, Y., Hu, X., et al. (2023). Glycolysis-cholesterol metabolic axis in immuno-oncology microenvironment: emerging role in immune cells and immunosuppressive signaling. Cell Biosci. 13, 189. doi:10.1186/s13578-023-01138-9
Keating, S. T., and El-Osta, A. (2015). Epigenetics and metabolism. Circ. Res. 116, 715–736. doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303936
Kheshtchin, N., Arab, S., Ajami, M., Mirzaei, R., Ashourpour, M., Mousavi, N., et al. (2016). Inhibition of HIF-1α enhances anti-tumor effects of dendritic cell-based vaccination in a mouse model of breast cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 65, 1159–1167. doi:10.1007/s00262-016-1879-5
Kim, T., and Croce, C. M. (2023). MicroRNA: trends in clinical trials of cancer diagnosis and therapy strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 55, 1314–1321. doi:10.1038/s12276-023-01050-9
Kim, D., Wu, Y., Li, Q., and Oh, Y. K. (2021). Nanoparticle-mediated lipid metabolic reprogramming of T cells in tumor microenvironments for immunometabolic therapy. Nanomicro Lett. 13, 31. doi:10.1007/s40820-020-00555-6
Kim, J., Lee, H., Yi, S. J., and Kim, K. (2022). Gene regulation by histone-modifying enzymes under hypoxic conditions: a focus on histone methylation and acetylation. Exp. Mol. Med. 54, 878–889. doi:10.1038/s12276-022-00812-1
Kimmel, B. R., Arora, K., Chada, N. C., Bharti, V., Kwiatkowski, A. J., Finkelstein, J. E., et al. (2025). Potentiating cancer immunotherapies with modular albumin-hitchhiking nanobody-STING agonist conjugates. Nat. Biomed. Eng. doi:10.1038/s41551-025-01400-0
Kwak, T. W., Kim, D. H., Jeong, Y. I., and Kang, D. H. (2015). Antitumor activity of vorinostat-incorporated nanoparticles against human cholangiocarcinoma cells. J. Nanobiotechnology 13, 60. doi:10.1186/s12951-015-0122-4
Lahiri, A., Maji, A., Potdar, P. D., Singh, N., Parikh, P., Bisht, B., et al. (2023). Lung cancer immunotherapy: progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 22, 40. doi:10.1186/s12943-023-01740-y
Lane, A. N., Higashi, R. M., and Fan, T. W. (2020). Metabolic reprogramming in tumors: contributions of the tumor microenvironment. Genes Dis. 7, 185–198. doi:10.1016/j.gendis.2019.10.007
Larionova, I., Kazakova, E., Patysheva, M., and Kzhyshkowska, J. (2020). Transcriptional, epigenetic and metabolic programming of tumor-associated macrophages. Cancers (Basel) 12, 1411. doi:10.3390/cancers12061411
Lee, P., Chandel, N. S., and Simon, M. C. (2020). Cellular adaptation to hypoxia through hypoxia inducible factors and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 21, 268–283. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-0227-y
Lee, Y. H., Ren, D., Jeon, B., and Liu, H. W. (2023). S-Adenosylmethionine: more than just a methyl donor. Nat. Prod. Rep. 40, 1521–1549. doi:10.1039/d2np00086e
Lei, X., Lei, Y., Li, J. K., Du, W. X., Li, R. G., Yang, J., et al. (2020). Immune cells within the tumor microenvironment: biological functions and roles in cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Lett. 470, 126–133. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.009
Li, M., Zhao, G., Su, W. K., and Shuai, Q. (2020). Enzyme-responsive nanoparticles for anti-tumor drug delivery. Front. Chem. 8, 647. doi:10.3389/fchem.2020.00647
Li, K., Shi, H., Zhang, B., Ou, X., Ma, Q., Chen, Y., et al. (2021a). Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as immunosuppressive regulators and therapeutic targets in cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6, 362. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00670-9
Li, X., Su, X., Liu, R., Pan, Y., Fang, J., Cao, L., et al. (2021b). HDAC inhibition potentiates anti-tumor activity of macrophages and enhances anti-PD-L1-mediated tumor suppression. Oncogene 40, 1836–1850. doi:10.1038/s41388-020-01636-x
Liang, L., Li, W., Li, X., Jin, X., Liao, Q., Li, Y., et al. (2022). 'Reverse Warburg effect' of cancer‑associated fibroblasts (review). Int. J. Oncol. 60, 67. doi:10.3892/ijo.2022.5357
Liang, Y., Wang, L., Ma, P., Ju, D., Zhao, M., and Shi, Y. (2023). Enhancing anti-tumor immune responses through combination therapies: epigenetic drugs and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Front. Immunol. 14, 1308264. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1308264
Lin, A. P., Abbas, S., Kim, S. W., Ortega, M., Bouamar, H., Escobedo, Y., et al. (2015). D2HGDH regulates alpha-ketoglutarate levels and dioxygenase function by modulating IDH2. Nat. Commun. 6, 7768. doi:10.1038/ncomms8768
Lin, J., Miao, L., Zhong, G., Lin, C. H., Dargazangy, R., and Alexander-Katz, A. (2020). Understanding the synergistic effect of physicochemical properties of nanoparticles and their cellular entry pathways. Commun. Biol. 3, 205. doi:10.1038/s42003-020-0917-1
Liu, Y., Lee, A. G., Nguyen, A. W., and Maynard, J. A. (2022a). An antibody Fc engineered for conditional antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity at the low tumor microenvironment pH. J. Biol. Chem. 298, 101798. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101798
Liu, X., Hoft, D. F., and Peng, G. (2022b). Tumor microenvironment metabolites directing T cell differentiation and function. Trends Immunol. 43, 132–147. doi:10.1016/j.it.2021.12.004
Liu, J., Liew, S. S., Wang, J., and Pu, K. (2022c). Bioinspired and biomimetic delivery platforms for cancer vaccines. Adv. Mat. 34, e2103790. doi:10.1002/adma.202103790
Liu, J., Li, B., Li, L., Ming, X., and Xu, Z. P. (2024). Advances in nanomaterials for immunotherapeutic improvement of cancer chemotherapy. Small 20, e2403024. doi:10.1002/smll.202403024
Liu, L., Hao, Z., Yang, X., Li, Y., Wang, S., and Li, L. (2025a). Metabolic reprogramming in T cell senescence: a novel strategy for cancer immunotherapy. Cell Death Discov. 11, 161. doi:10.1038/s41420-025-02468-y
Liu, S., Liu, Z., Lei, H., Miao, Y. B., and Chen, J. (2025b). Programmable nanomodulators for precision therapy, engineering tumor metabolism to enhance therapeutic efficacy. Adv. Healthc. Mater 14, e2403019. doi:10.1002/adhm.202403019
Liu, L., Huang, K., Sun, X., Shi, J., Yin, X., Zhao, W., et al. (2025c). Tunable ion-release biodegradable nanoparticles enhanced pyroptosis for tumor immunotherapy. Biomaterials 317, 123111. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2025.123111
Llibre, A., Kucuk, S., Gope, A., Certo, M., and Mauro, C. (2025). Lactate: a key regulator of the immune response. Immunity 58 (58), 535–554. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2025.02.008
Looi, C. K., Chung, F. F., Leong, C. O., Wong, S. F., Rosli, R., and Mai, C. W. (2019). Therapeutic challenges and current immunomodulatory strategies in targeting the immunosuppressive pancreatic tumor microenvironment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 38, 162. doi:10.1186/s13046-019-1153-8
Lu, C., and Thompson, C. B. (2012). Metabolic regulation of epigenetics. Cell Metab. 16, 9–17. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2012.06.001
Lu, Y., Gu, F., Ma, Y., Li, R., Luo, Y., Da, X., et al. (2023). Simultaneous delivery of doxorubicin and EZH2-Targeting siRNA by vortex magnetic nanorods synergistically improved anti-tumor efficacy in triple-negative breast cancer. Small 19, e2301307. doi:10.1002/smll.202301307
Luo, H., Wei, W., Ye, Z., Zheng, J., and Xu, R. H. (2021). Liquid biopsy of methylation biomarkers in cell-free DNA. Trends Mol. Med. 27, 482–500. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2020.12.011
Luo, F., Lu, F. T., Cao, J. X., Ma, W. J., Xia, Z. F., Zhan, J. H., et al. (2022). HIF-1α inhibition promotes the efficacy of immune checkpoint blockade in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Lett. 531, 39–56. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2022.01.027
Luszczek, W., Cheriyath, V., Mekhail, T. M., and Borden, E. C. (2010). Combinations of DNA methyltransferase and histone deacetylase inhibitors induce DNA damage in small cell lung cancer cells: correlation of resistance with IFN-Stimulated gene expression. Mol. Cancer Ther. 9, 2309–2321. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-10-0309
Manolova, V., Flace, A., Bauer, M., Schwarz, K., Saudan, P., and Bachmann, M. F. (2008). Nanoparticles target distinct dendritic cell populations according to their size. Eur. J. Immunol. 38, 1404–1413. doi:10.1002/eji.200737984
Manzari, M. T., Shamay, Y., Kiguchi, H., Rosen, N., Scaltriti, M., and Heller, D. A. (2021). Targeted drug delivery strategies for precision medicines. Nat. Rev. Mater 6, 351–370. doi:10.1038/s41578-020-00269-6
Meng, L., Wu, H., Wu, J., Ding, P., He, J., Sang, M., et al. (2024). Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors: insights into the regulation of circular RNAS involved in cancer hallmarks. Cell Death Dis. 15, 3. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06389-5
Metselaar, J. M., and Lammers, T. (2020). Challenges in nanomedicine clinical translation. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 10, 721–725. doi:10.1007/s13346-020-00740-5
Mishra, R., Haldar, S., Suchanti, S., and Bhowmick, N. A. (2019). Epigenetic changes in fibroblasts drive cancer metabolism and differentiation. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 26, R673–R688. doi:10.1530/ERC-19-0347
Misir, S., Wu, N., and Yang, B. B. (2022). Specific expression and functions of circular RNAs. Cell Death Differ. 29, 481–491. doi:10.1038/s41418-022-00948-7
Mitsuhashi, R., Sato, K., and Kawakami, H. (2025). Novel epigenetics control (EpC) nanocarrier for cancer therapy through dual-targeting approach to DNA methyltransferase and ten-eleven translocation enzymes. Epigenomes. 9, 6. doi:10.3390/epigenomes9010006
Montacchiesi, G., and Pace, L. (2022). Epigenetics and CD8(+) T cell memory. Immunol. Rev. 305, 77–89. doi:10.1111/imr.13057
Morrissey, S. M., Zhang, F., Ding, C., Montoya-Durango, D. E., Hu, X., Yang, C., et al. (2021). Tumor-derived exosomes drive immunosuppressive macrophages in a pre-metastatic niche through glycolytic dominant metabolic reprogramming. Cell Metab. 33, 2040–2058.e10. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2021.09.002
Munn, D. H., and Bronte, V. (2016). Immune suppressive mechanisms in the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 39, 1–6. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2015.10.009
Munn, D. H., Zhou, M., Attwood, J. T., Bondarev, I., Conway, S. J., Marshall, B., et al. (1998). Prevention of allogeneic fetal rejection by tryptophan catabolism. Science 281, 1191–1193. doi:10.1126/science.281.5380.1191
Nakahata, K., Simons, B. W., Pozzo, E., Shuck, R., Kurenbekova, L., Prudowsky, Z., et al. (2022). K-Ras and p53 mouse model with molecular characteristics of human rhabdomyosarcoma and translational applications. Dis. Model Mech. 15, dmm049004. doi:10.1242/dmm.049004
Niu, Y., Chen, J., and Qiao, Y. (2022). Epigenetic modifications in tumor-associated macrophages: a new perspective for an old foe. Front. Immunol. 13, 836223. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2022.836223
O'Brien Laramy, M., Foley, D. A., Pak, R. H., Lewis, J. A., McKinney, E., Egan, P. M., et al. (2025). Chemistry, manufacturing and controls strategies for using novel excipients in lipid nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 20, 331–344. doi:10.1038/s41565-024-01833-9
Palomino-Cano, C., Moreno, E., Irache, J. M., and Espuelas, S. (2024). Targeting and activation of macrophages in leishmaniasis. A focus on iron oxide nanoparticles. Front. Immunol. 15, 1437430. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1437430
Pan, X., and Zheng, L. (2020). Epigenetics in modulating immune functions of stromal and immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol. Immunol. 17, 940–953. doi:10.1038/s41423-020-0505-9
Park, J. H., Pyun, W. Y., and Park, H. W. (2020). Cancer metabolism: phenotype, signaling and therapeutic targets. Cells 9, 2308. doi:10.3390/cells9102308
Pascale, R. M., Simile, M. M., Calvisi, D. F., Feo, C. F., and Feo, F. (2022). S-Adenosylmethionine: from the discovery of its inhibition of tumorigenesis to its use as a therapeutic agent. Cells 11, 409. doi:10.3390/cells11030409
Peeters, J. G. C., Silveria, S., Ozdemir, M., Ramachandran, S., and DuPage, M. (2024). Hyperactivating EZH2 to augment H3K27me3 levels in regulatory T cells enhances immune suppression by driving early effector differentiation. Cell Rep. 43, 114724. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2024.114724
Peng, L., and Zhong, X. (2015). Epigenetic regulation of drug metabolism and transport. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 5, 106–112. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.007
Perrier, A., Didelot, A., Laurent-Puig, P., Blons, H., and Garinet, S. (2020). Epigenetic mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors. Biomolecules 10, 1061. doi:10.3390/biom10071061
Raaijmakers, K., Adema, G. J., Bussink, J., and Ansems, M. (2024). Cancer-associated fibroblasts, tumor and radiotherapy: interactions in the tumor micro-environment. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 43, 323. doi:10.1186/s13046-024-03251-0
Ramaiah, M. J., Tangutur, A. D., and Manyam, R. R. (2021). Epigenetic modulation and understanding of HDAC inhibitors in cancer therapy. Life Sci. 277, 119504. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119504
Raza, A., Hayat, U., Rasheed, T., Bilal, M., and Iqbal, H. M. N. (2018). Redox-responsive nano-carriers as tumor-targeted drug delivery systems. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 157, 705–715. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.08.034
Rehman, M., Tahir, N., Sohail, M. F., Qadri, M. U., Duarte, S. O. D., Brandao, P., et al. (2024). Lipid-based nanoformulations for drug delivery: an ongoing perspective. Pharmaceutics 16, 1376. doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16111376
Ren, H., Jia, W., Xie, Y., Yu, M., and Chen, Y. (2023). Adjuvant physiochemistry and advanced nanotechnology for vaccine development. Chem. Soc. Rev. 52, 5172–5254. doi:10.1039/d2cs00848c
Ross, K. A., Brenza, T. M., Binnebose, A. M., Phanse, Y., Kanthasamy, A. G., Gendelman, H. E., et al. (2015). Nano-enabled delivery of diverse payloads across complex biological barriers. J. Control Release 219, 548–559. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.08.039
Saeed, S., Quintin, J., Kerstens, H. H., Rao, N. A., Aghajanirefah, A., Matarese, F., et al. (2014). Epigenetic programming of monocyte-to-macrophage differentiation and trained innate immunity. Science. 345, 1251086. doi:10.1126/science.1251086
Sankar, R., and Ravikumar, V. (2014). Biocompatibility and biodistribution of suberoylanilide hydroxamic acid loaded poly (DL-lactide-co-glycolide) nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery in cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 68, 865–871. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2014.07.015
Scumaci, D., and Zheng, Q. (2023). Epigenetic meets metabolism: novel vulnerabilities to fight cancer. Cell Commun. Signal 21, 249. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01253-7
Serafini, P., Borrello, I., and Bronte, V. (2006). Myeloid suppressor cells in cancer: recruitment, phenotype, properties, and mechanisms of immune suppression. Semin. Cancer Biol. 16, 53–65. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2005.07.005
Shanmugam, G., Rakshit, S., and Sarkar, K. (2022). HDAC inhibitors: targets for tumor therapy, immune modulation and lung diseases. Transl. Oncol. 16, 101312. doi:10.1016/j.tranon.2021.101312
Sharma, P., Hu-Lieskovan, S., Wargo, J. A., and Ribas, A. (2017). Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168, 707–723. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.017
Shokati, E., and Safari, E. (2023). The immunomodulatory role of exosomal microRNA networks in the crosstalk between tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tumor cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 120, 110267. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110267
Singh, N., and Yeh, P. J. (2017). Suppressive drug combinations and their potential to combat antibiotic resistance. J. Antibiot. (Tokyo) 70, 1033–1042. doi:10.1038/ja.2017.102
Smith, J., Sen, S., Weeks, R. J., Eccles, M. R., and Chatterjee, A. (2020). Promoter DNA hypermethylation and paradoxical gene activation. Trends Cancer 6, 392–406. doi:10.1016/j.trecan.2020.02.007
Soriano-Baguet, L., and Brenner, D. (2023). Metabolism and epigenetics at the heart of T cell function. Trends Immunol. 44, 231–244. doi:10.1016/j.it.2023.01.002
Sukocheva, O. A., Liu, J., Neganova, M. E., Beeraka, N. M., Aleksandrova, Y. R., Manogaran, P., et al. (2022). Perspectives of using microRNA-loaded nanocarriers for epigenetic reprogramming of drug resistant colorectal cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 86, 358–375. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2022.05.012
Sun, L., Zhang, H., and Gao, P. (2022). Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer. Protein Cell 13, 877–919. doi:10.1007/s13238-021-00846-7
Tang, Y., Wang, X., Li, J., Nie, Y., Liao, G., Yu, Y., et al. (2019). Overcoming the reticuloendothelial system barrier to drug delivery with a “Don't-Eat-Us” strategy. ACS Nano 13, 13015–13026. doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b05679
Terry, S. Y., Boerman, O. C., Gerrits, D., Franssen, G. M., Metselaar, J. M., Lehmann, S., et al. (2015). ¹¹¹In-anti-F4/80-A3-1 antibody: a novel tracer to image macrophages. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 42, 1430–1438. doi:10.1007/s00259-015-3084-8
Thakur, C., and Chen, F. (2019). Connections between metabolism and epigenetics in cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 57, 52–58. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.06.006
Thambi, T., Deepagan, V. G., Yoon, H. Y., Han, H. S., Kim, S. H., Son, S., et al. (2014). Hypoxia-responsive polymeric nanoparticles for tumor-targeted drug delivery. Biomaterials 35, 1735–1743. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.11.022
Togashi, Y., Shitara, K., and Nishikawa, H. (2019). Regulatory T cells in cancer immunosuppression - implications for anticancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 16, 356–371. doi:10.1038/s41571-019-0175-7
Toro, W., Yang, M., Patel, A., Zhang, S., Dabbous, O., and Garrison, L. P. (2025). Evolving concept of value in health economics and outcomes research: emerging tools for innovation and access to cell and gene therapies for rare diseases. Value Health 28, 686–691. doi:10.1016/j.jval.2024.12.006
van de Veerdonk, F. L., Netea, M. G., Dinarello, C. A., and Joosten, L. A. (2011). Inflammasome activation and IL-1β and IL-18 processing during infection. Trends Immunol. 32, 110–116. doi:10.1016/j.it.2011.01.003
Vendetti, F. P., and Rudin, C. M. (2013). Epigenetic therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: targeting DNA methyltransferases and histone deacetylases. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 13, 1273–1285. doi:10.1517/14712598.2013.819337
Wang, E. C., Min, Y., Palm, R. C., Fiordalisi, J. J., Wagner, K. T., Hyder, N., et al. (2015). Nanoparticle formulations of histone deacetylase inhibitors for effective chemoradiotherapy in solid tumors. Biomaterials 51, 208–215. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.02.015
Wang, X., Hua, Y., Xu, G., Deng, S., Yang, D., and Gao, X. (2019). Targeting EZH2 for glioma therapy with a novel nanoparticle-siRNA complex. Int. J. Nanomedicine 14, 2637–2653. doi:10.2147/ijn.S189871
Wang, J., Wang, Y., and Jiang, X. (2024). Targeting anticancer immunity in melanoma tumour microenvironment: unleashing the potential of adjuvants, drugs, and phytochemicals. J. Drug Target 32, 1052–1072. doi:10.1080/1061186X.2024.2384071
Wang, H., Zhou, F., Qin, W., Yang, Y., Li, X., and Liu, R. (2025). Metabolic regulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor immune microenvironment: targets and therapeutic strategies. Theranostics 15, 2159–2184. doi:10.7150/thno.105276
Wei, X., Song, M., Li, W., Huang, J., Yang, G., and Wang, Y. (2021). Multifunctional nanoplatforms co-delivering combinatorial dual-drug for eliminating cancer multidrug resistance. Theranostics 11, 6334–6354. doi:10.7150/thno.59342
Wong, C. C., Qian, Y., and Yu, J. (2017). Interplay between epigenetics and metabolism in oncogenesis: mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Oncogene 36, 3359–3374. doi:10.1038/onc.2016.485
Wu, X., Hu, Z., Nizzero, S., Zhang, G., Ramirez, M. R., Shi, C., et al. (2017). Bone-targeting nanoparticle to co-deliver decitabine and arsenic trioxide for effective therapy of myelodysplastic syndrome with low systemic toxicity. J. Control Release 268, 92–101. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2017.10.012
Wu, J., Zhang, H., Zheng, Y., Jin, X., Liu, M., Li, S., et al. (2018). The long noncoding RNA MALAT1 induces tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells via miR155/Dendritic cell-specific intercellular adhesion Molecule-3 grabbing Nonintegrin/IL10 axis. Front. Immunol. 9, 1847. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.01847
Wu, F., Yang, J., Liu, J., Wang, Y., Mu, J., Zeng, Q., et al. (2021). Signaling pathways in cancer-associated fibroblasts and targeted therapy for cancer. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6, 218. doi:10.1038/s41392-021-00641-0
Wu, L., Jin, Y., Zhao, X., Tang, K., Zhao, Y., Tong, L., et al. (2023). Tumor aerobic glycolysis confers immune evasion through modulating sensitivity to T cell-mediated bystander killing via TNF-Alpha. Cell Metab. 35, 1580–1596 e1589. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2023.07.001
Wu, D. W., Jia, S. P., Xing, S. J., Ma, H. L., Wang, X., Tang, Q. Y., et al. (2024). Personalized neoantigen cancer vaccines: current progression, challenges and a bright future. Clin. Exp. Med. 24, 229. doi:10.1007/s10238-024-01436-7
Xie, N., Zhang, L., Gao, W., Huang, C., Huber, P. E., Zhou, X., et al. (2020). NAD(+) metabolism: pathophysiologic mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 5, 227. doi:10.1038/s41392-020-00311-7
Xu, C. H., Ye, P. J., Zhou, Y. C., He, D. X., Wei, H., and Yu, C. Y. (2020). Cell membrane-camouflaged nanoparticles as drug carriers for cancer therapy. Acta Biomater. 105, 1–14. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2020.01.036
Xu, X., Peng, Q., Jiang, X., Tan, S., Yang, Y., Yang, W., et al. (2023). Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications in cancer: from the impacts and mechanisms to the treatment potential. Exp. Mol. Med. 55, 1357–1370. doi:10.1038/s12276-023-01020-1
Yamaguchi, H., Hsu, J. M., Yang, W. H., and Hung, M. C. (2022). Mechanisms regulating PD-L1 expression in cancers and associated opportunities for novel small-molecule therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 19, 287–305. doi:10.1038/s41571-022-00601-9
Yan, D., Adeshakin, A. O., Xu, M., Afolabi, L. O., Zhang, G., Chen, Y. H., et al. (2019). Lipid metabolic pathways confer the immunosuppressive function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor. Front. Immunol. 10, 1399. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.01399
Yang, M., Shen, H., Qiu, C., Ni, Y., Wang, L., Dong, W., et al. (2013). High expression of miR-21 and miR-155 predicts recurrence and unfavourable survival in non-small cell lung cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 49, 604–615. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2012.09.031
Yang, D., Liu, J., Qian, H., and Zhuang, Q. (2023). Cancer-associated fibroblasts: from basic science to anticancer therapy. Exp. Mol. Med. 55, 1322–1332. doi:10.1038/s12276-023-01013-0
Yang, Y., Li, S., To, K. K. W., Zhu, S., Wang, F., and Fu, L. (2025). Tumor-associated macrophages remodel the suppressive tumor immune microenvironment and targeted therapy for immunotherapy. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 44, 145. doi:10.1186/s13046-025-03377-9
Yellen, G. (2018). Fueling thought: management of glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation in neuronal metabolism. J. Cell Biol. 217, 2235–2246. doi:10.1083/jcb.201803152
Yerinde, C., Siegmund, B., Glauben, R., and Weidinger, C. (2019). Metabolic control of epigenetics and its role in CD8(+) T cell differentiation and function. Front. Immunol. 10, 2718. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2019.02718
Yi, M., Jiao, D., Qin, S., Chu, Q., Wu, K., and Li, A. (2019). Synergistic effect of immune checkpoint blockade and anti-angiogenesis in cancer treatment. Mol. Cancer 18, 60. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0974-6
Yu, X., and Li, S. (2024). Specific regulation of epigenome landscape by metabolic enzymes and metabolites. Biol. Rev. Camb Philos. Soc. 99, 878–900. doi:10.1111/brv.13049
Zebley, C. C., Gottschalk, S., and Youngblood, B. (2020). Rewriting history: epigenetic reprogramming of CD8(+) T cell differentiation to enhance immunotherapy. Trends Immunol. 41, 665–675. doi:10.1016/j.it.2020.06.008
Zhang, M., Liu, E., Cui, Y., and Huang, Y. (2017). Nanotechnology-based combination therapy for overcoming multidrug-resistant cancer. Cancer Biol. Med. 14, 212–227. doi:10.20892/j.issn.2095-3941.2017.0054
Zhang, P., Meng, J., Li, Y., Yang, C., Hou, Y., Tang, W., et al. (2021). Nanotechnology-enhanced immunotherapy for metastatic cancer. Innov. (Camb) 2, 100174. doi:10.1016/j.xinn.2021.100174
Zhang, Y., Zhang, X., Meng, Y., Xu, X., and Zuo, D. (2022). The role of glycolysis and lactate in the induction of tumor-associated macrophages immunosuppressive phenotype. Int. Immunopharmacol. 110, 108994. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108994
Zhang, J., Huang, L., Ge, G., and Hu, K. (2023). Emerging epigenetic-based nanotechnology for cancer therapy: modulating the tumor microenvironment. Adv. Sci. (Weinh) 10, e2206169. doi:10.1002/advs.202206169
Zhang, A., Fan, T., Liu, Y., Yu, G., Li, C., and Jiang, Z. (2024). Regulatory T cells in immune checkpoint blockade antitumor therapy. Mol. Cancer 23, 251. doi:10.1186/s12943-024-02156-y
Zhao, E., Maj, T., Kryczek, I., Li, W., Wu, K., Zhao, L., et al. (2016). Cancer mediates effector T cell dysfunction by targeting microRNAs and EZH2 via glycolysis restriction. Nat. Immunol. 17, 95–103. doi:10.1038/ni.3313
Zhao, T., Cai, Y., Jiang, Y., He, X., Wei, Y., Yu, Y., et al. (2023a). Vaccine adjuvants: mechanisms and platforms. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 8, 283. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01557-7
Zhao, H., Li, Y., Zhao, B., Zheng, C., Niu, M., Song, Q., et al. (2023b). Orchestrating antigen delivery and presentation efficiency in lymph node by nanoparticle shape for immune response. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 13, 3892–3905. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.02.003
Zhou, P., Chen, L., Wu, Z., Wang, E., Yan, Y., Guan, X., et al. (2023). The barriers and facilitators for the implementation of clinical practice guidelines in healthcare: an umbrella review of qualitative and quantitative literature. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 162, 169–181. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2023.08.017
Zhou, L., Velegraki, M., Wang, Y., Mandula, J. K., Chang, Y., Liu, W., et al. (2024a). Spatial and functional targeting of intratumoral tregs reverses CD8+ T cell exhaustion and promotes cancer immunotherapy. J. Clin. Invest. 134, e180080. doi:10.1172/JCI180080
Zhou, Y., Yuan, J., Xu, K., Li, S., and Liu, Y. (2024b). Nanotechnology reprogramming metabolism for enhanced tumor immunotherapy. ACS Nano 18, 1846–1864. doi:10.1021/acsnano.3c11260
Keywords: metabolic reprogramming, epigenetic regulation, nanoplatforms, cancer vaccines, immunosuppression, lung tumors
Citation: Xu M, Zhang X, Yu X, Ma C, Li X, Chen G, Yuan G, Lin S and Cui R (2025) Epigenetic and metabolic reprogramming via nanotechnology: a synergistic approach to cancer vaccination in lung tumors. Front. Genet. 16:1666561. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1666561
Received: 21 August 2025; Accepted: 16 September 2025;
Published: 08 October 2025.
Edited by:
Johannes Fahrmann, University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Dhiraj Bhatia, Indian Institute of Technology Gandhinagar, IndiaJie Liu, Hong Kong Baptist University, Hong Kong SAR, China
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Zhang, Yu, Ma, Li, Chen, Yuan, Lin and Cui. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng Lin, bHNsaW5zaGVuZ0AxNjMuY29t; Ran Cui, Y3IxMDA0OTJAZ21haWwuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Min Xu
Min Xu Xialin Zhang2†
Xialin Zhang2† Gang Yuan
Gang Yuan Sheng Lin
Sheng Lin Ran Cui
Ran Cui