- 1Research Centre for Medical Genetics, Moscow, Russia
- 2Veltischev Research and Clinical Institute for Pediatrics and Pediatric Surgery of the Pirogov Russian National Research Medical University, Moscow, Russia
- 3Genomed, Moscow, Russia
- 4FSBEI FPE RMACPE MOH, Moscow, Russia
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency (ALD) is a rare neurometabolic disorder caused by biallelic loss-of-function variants in the ADSL gene. We report a severe type I ALD case involving a 2-year-old boy presenting with early-onset polymorphic seizures (clonic/myoclonic), developmental delay, and progressive neurological deterioration. Seizures were temporarily controlled with ethosuximide and vigabatrin, though neurodegeneration progressed. Analysis of whole-exome sequencing data revealed compound-heterozygous variants in the ADSL gene: the known pathogenic missense variant c.340T>C (p.Tyr114His) and a novel variant c.859A>G (p.Ile287Val). Although p.Ile287Val is predicted to be benign at the protein level, RNA analysis demonstrated that c.859A>G activates a cryptic splice site in exon 8, resulting in aberrant transcripts (64%, 4-bp deletion, targeted by nonsense-mediated decay) and a smaller proportion of normal transcripts (36%) encoding the p.Ile287Val protein. This case highlights splicing disruption as a novel pathogenic mechanism in ALD and expands the mutational spectrum associated with the disease. This case also underscores the importance of integrating RNA analysis with genomic data to uncover cryptic splicing defects, especially when protein-level predictions suggest benignity.
1 Introduction
Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency (ALD; OMIM 103050) is a rare autosomal recessive disorder caused by the accumulation of neurotoxic metabolites (S-Ado and SAICAr), impairing early development (Spiegel et al., 2006; Dutto et al., 2022). ALD is commonly classified into type I (severe, early-onset form), type II (moderate form with developmental delay and seizures), and a rare, fatal neonatal form, with severity generally correlating with residual enzymatic activity (Kmoch et al., 2000; Jurecka et al., 2008). While the majority of previously reported ADSL variants are missense mutations studied primarily for their protein-level effects (Kmoch et al., 2000; Jurecka et al., 2008; Zikanova et al., 2010), we identified the first disease-associated variant, c.859A>G (p.Ile287Val) [Clinvar ID: 1437877], that exerts pathogenicity through splicing disruption and nonsense-mediated decay (NMD), revealing an alternative disease mechanism in ALD.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Molecular genetic diagnostics
Blood samples were collected from the proband and his unaffected parents. Genomic DNA was extracted using standard methods. DNA diagnosis in the proband was carried out by targeted high-throughput sequencing (HTS) of clinically relevant genes (clinical exome sequencing, CES). CES was performed on an Illumina NextSeq 500 instrument in the 2 × 151 bp paired-end mode. A total of 13.7 million reads were obtained, corresponding to a 99.9× on-target average sequencing depth, based on the TruSight One Sequencing Panel target region list. The raw sequencing data have been processed with a previously published custom pipeline (Marakhonov et al., 2018). The mapped reads were visualized using the Integrative Genomics Viewer (IGV) software (https://www.igv.org/, accessed on 20 November 2023; © 2013–2018 Broad Institute, Boston, MA, United States, and the Regents of the University of California, San Diego, CA, United States). Variant filtering was based on their frequency, with variants having a frequency of less than 1% in the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD v.2.1.1) and coding region sequence effects such as missense, nonsense, coding indels, and splice sites being considered. The clinical significance of the variants was evaluated using the ACMG criteria for variant interpretation. All variants are reported according to the NM_000026.4 transcript of the ADSL gene.
2.2 RT-PCR analysis
To obtain mRNA, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were separated from the whole blood by a density gradient centrifugation method using Ficoll. Then, cells were lysed in ExtractRNA buffer (Eurogen, Russia), аnd total RNA was prepared by phenol-chloroform extraction. For purification from genomic DNA, the RNA was treated with DNase I (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, United States). cDNA was obtained using a reverse transcription system (Dialat Ltd., Moscow, Russia). To assess the quality of the cDNA, qPCR was performed with primers for the B2M housekeeping gene. PCR amplification was performed with the following primers: ADSL Ex5F (5′-ATCTCCAGAACTTGAAGCGTG) and ADSL Ex9R (5′-TGGGATTCCGCTTATATGGCA). The PCR product was analyzed on a 2% agarose gel with subsequent Sanger sequencing. To assess the ratio of mRNA isoforms, fragment analysis with a FAM-6-tagged forward primer was performed.
2.3 NMD inhibition
In order to inhibit the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay, patient PBMCs were obtained under sterile conditions and treated with 300 μM cycloheximide. After a 6-h incubation, mRNA was isolated and processed as described above.
2.4 In vitro splicing analysis
In vitro splicing analysis was performed using the minigene expression system as described by Davydenko et al. (2024). For minigene construction, the region encompassing exons 8 and 9 of the ADSL was amplified from the genomic DNA of the heterozygous carrier with the following primers: EcoRI-ADSL Ex8F (5′-AAAAGAATTCTTCTTTCCATGATGCCTTAAGC) and XhoI-ADSL Ex9R (5′-AAAACTCGAGAACTCCCTCAAGTGTGTTTTCT). The obtained wild-type and mutant PCR products were cloned into the pSPL3-Flu2 plasmid vector. The structure of minigenes was confirmed by sequencing.
The vectors were then transfected into HEK293T cells by calcium phosphate transfection. The cells were harvested after 48 h, and total RNA and cDNA were obtained in the same way for the mRNA analysis. To detect the splicing products, a plasmid-specific primer, TurboFP-F (5′-ACAAAGAGACCTACGTCGAGCA), and an ADSL gene-specific primer, Ex9R (5′-TGGGATTCCGCTTATATGGCA), were used. The PCR product was analyzed in a urea polyacrylamide gel with urea and further Sanger sequencing. The ratio of mRNA isoforms was calculated by fragment analysis.
2.5 3D Modeling of protein structure
Structural assessment and visualization of the ADSL protein, including wild-type and mutant forms, were performed using the SWISS-MODEL structure assessment web server (https://swissmodel.expasy.org/assess) (Waterhouse et al., 2024). Mol* viewer (https://molstar.org/viewer) was used for 3D visualization and alignment of wild-type and mutant proteins (Sehnal et al., 2021).
3 Results
3.1 Clinical presentation
The proband was a 2-year-old boy (the first known affected family member) with a history of clonic, myoclonic, and generalized seizures. He was born at term following his mother’s first pregnancy, with a birth weight of 3,500 g, a body length of 52 cm, and Apgar scores of 8 and 9 at 1 min and 5 min, respectively. By the end of the first month, he exhibited poor sucking reflexes and minimal weight gain (only 90 g). Seizures began at 1 month of age, characterized by clonic, myoclonic, and generalized seizures, occurring up to five times daily. During the first 2 years of life, the patient experienced asymmetric tonic seizures, spasms, and eyelid myoclonias. At 2 years of age, the proband’s developmental milestones remained below normal (height: 79 cm [−2.35 SD], weight: 9.5 kg [−2.60 SD], head circumference: 45 cm [−2.56 SD]). A clinical examination showed muscular dystonia, hyperreflexia in both upper and lower limbs, and hypersalivation.
Video electroencephalography (EEG) at 1 month of age showed the absence of a posterior dominant rhythm, but alpha and theta waves were dominant in the background. Physiological sleep patterns were formed and stable. Low-index, multiregional epileptiform activity was recorded in the left temporal and frontal areas and in the right central area (F7, T3, F7-T3, C4). The ictal EEG recorded an asymmetric tonic seizure with a right-sided emphasis and clonic movements in the right leg. The EEG showed regional slowing in the left fronto-central region, with the appearance of repetitive fast activity in the left frontal area (F3). Subsequent EEGs demonstrated a progressive increase in epileptiform activity.
Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed twice. The first MRI, performed at 1 month of age, showed increased MR signals and volume in the putamen and thalamus bilaterally. The second MRI, performed at 2 years and 1 month of age, revealed atrophy of the cerebral cortex and corpus callosum, a persistent lack of myelination, and periventricular leukopathy, hypomyelination of the deep white matter, and symmetrical enlargement of the putamen, thalamus, and red nucleus (Figure 1). A comparison of the two scans showed mild progression of cerebral atrophy and hypoplasia of the corpus callosum.
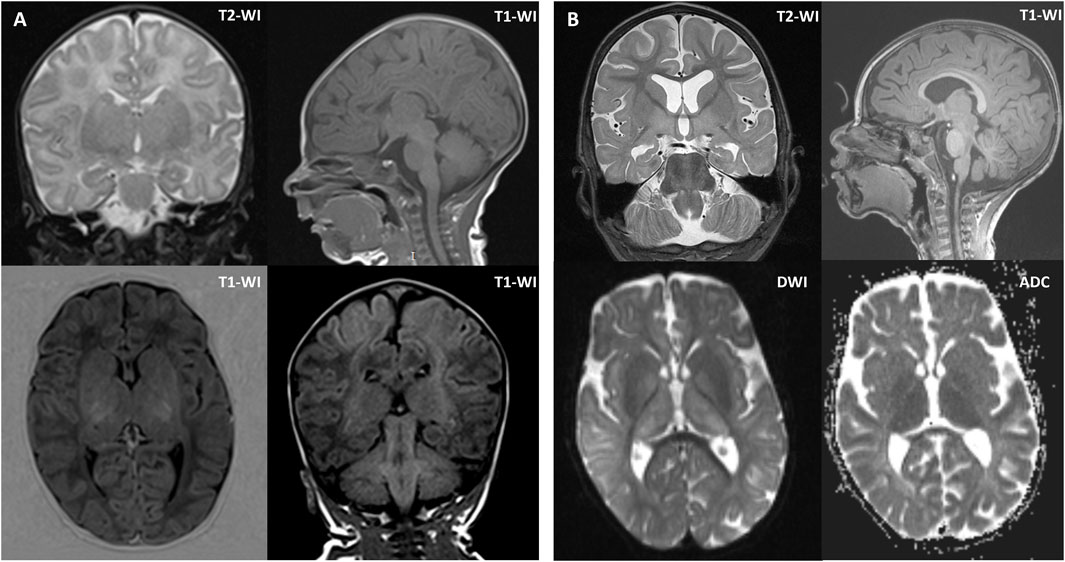
Figure 1. Brain MRI of the proband at 1 month of age (A) and 2 years and 1 month of age (B). (A) Brain MRI at 1 month of age showed symmetrically increased MR signal and volume of the putamen and thalamus. (B) Brain MRI at 2 years and 1 month of age showed mild diffuse cerebral atrophy without cortical architectural disruption, except for hypoplasia of the corpus callosum, periventricular white matter alterations, hypomyelination of the deep white matter, and symmetrical enlargement of the putamen, thalamus, and red nucleus. Axial diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) images showed restricted diffusion in the basal ganglia. Coronal T2-weighted images (T2-WI) at 1 month of age and 2 years and 1 month of age revealed mild progression of cerebral atrophy. Sagittal T1-weighted images (T1-WI) at 1 month of age and 2 years and 1 month of age showed mild progression of hypoplasia of the corpus callosum.
A positive clinical response was observed with ethosuximide therapy, which provided 9 months of remission. Vigabatrin led to 1 month of remission, followed by a reduction in seizure frequency.
3.2 Genetic and functional studies
Gene panel sequencing identified two heterozygous missense variants in the ADSL gene, confirmed by segregation analysis to be in trans position. The first variant, c.340T>C (p.Tyr114His) [Clinvar ID:204807], is a previously described variant with functional studies indicating no residual enzyme activity in the mutant protein (Kmoch et al., 2000; Zikanova et al., 2010). The second, a novel missense variant c.859A>G (p.Ile287Val) [Clinvar ID:1437877], is found in the gnomAD v.4.1 database with a low frequency (0.000004337, 7 heterozygous alleles) (Chen et al., 2024). The majority of in silico programs classify this missense variant as benign or of uncertain significance. However, according to spliceAI predictions, the c.859A>G variant could create a new donor splice site (Donor Gain 0.98) (Jaganathan et al., 2019).
To investigate the possible impact of the variant on splicing, we performed RT-PCR analysis of the patient’s mRNA, extracted from blood. Sequencing of the RT-PCR product of the proband revealed two isoforms: a major one corresponding to the wild type, and a minor one with exon 8 shortened by 4 bp. Fragment analysis showed that the expression of the wild-type ADSL mRNA isoform was 85%, while the expression of the aberrant isoform was 15% (Figure 2A). The same allelic imbalance was observed in the mRNA sample from the patient’s mother. Because the proband had a different single-nucleotide variant (SNV) in the trans position, we sequenced the locus containing the c.340T>C variant in both the proband and the proband’s carrier father. Sequencing showed that the father is fully heterozygous for this variant, while the proband exhibited a reduced level of the wild-type allele by approximately 50%.
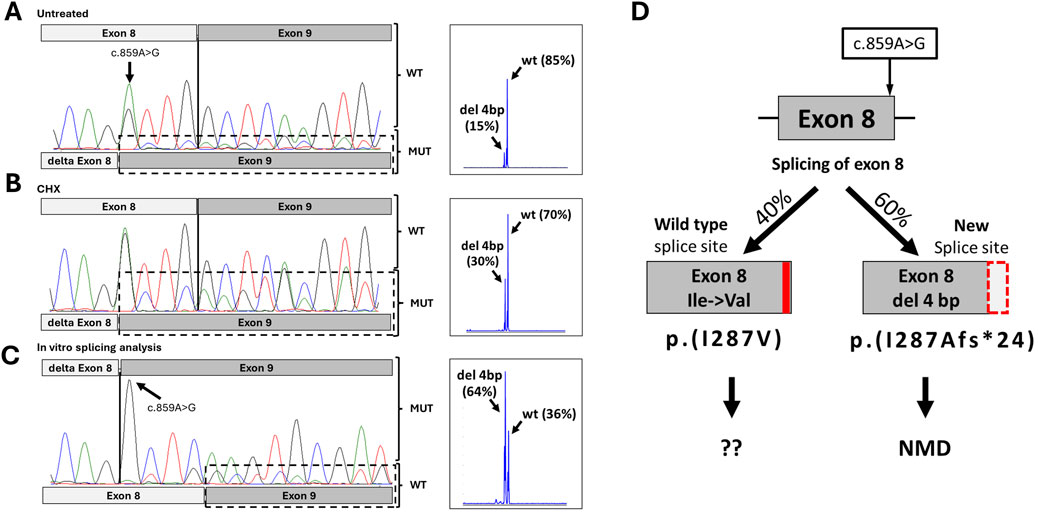
Figure 2. Results of functional studies for c.859A>G. (A) Sanger chromatogram and fragment analysis results from the proband’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells. (B) Sanger chromatogram and fragment analysis results from the proband’s peripheral blood mononuclear cells after inhibition of NMD. (C) Sanger chromatogram and fragment analysis results from minigen construction with variant c.859A>G. (D) Schematic representation of the possible splicing effects caused by the c.859A>G variant, based on splicing analysis results.
Given that the mutant isoform with the 4-nucleotide deletion is expected to result in a frameshift and a premature stop codon, we hypothesized that the mutant isoform carrying the c.859A>G variant undergoes nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD). To test this, we inhibited NMD by treating the patient’s PBMCs with cycloheximide for 6 h. Sequencing of RT-PCR products following NMD inhibition revealed an increase in the mutant isoform peaks to approximately 30%, achieving complete heterozygosity at position c.859 (Figure 2B). Subsequent fragment analysis confirmed that expression of the mutant isoform rose to 30% (Figure 2B). This observed signal change after NMD inhibition suggests that the newly formed donor splicing site is not utilized in 100% of cases, allowing some transcripts to be synthesized using the wild-type donor site.
To verify this, we conducted an in vitro splicing assay. HEK293T cells were transfected with plasmids containing the ADSL gene region surrounding exons 8 and 9, with or without the c.859A>G variant. After 48 h, total RNA was isolated, cDNA was synthesized, and RT-PCR with sequencing was performed. The results showed that the c.859A>G variant leads to the creation of a new donor splice site and a 4-bp deletion in exon 8, as predicted. However, the wild-type isoform was also present. Fragment analysis indicated that in a monoallelic expression system, the wild-type and mutant isoforms comprised approximately 36% and 64%, respectively (Figure 2C).
In summary, the c.859A>G variant leads to the production of two types of transcripts. The primary event (∼60%) is the formation of a new splicing donor site with a 4-bp deletion in exon 8, causing a frameshift and premature stop codon (p.Ile287Alafs*24). This transcript undergoes NMD and does not contribute to protein synthesis (Figure 2D). However, in approximately 40% of cases, the spliceosome utilizes the wild-type donor site, resulting in full-length mRNA with the missense variant Ile287Val.
4 Discussion
Here, we reported a clinical case of ALD type I with two pathogenic variants (p.Ile287Val and p.Tyr114His) in the ADSL gene. The variant c.859A>G (p.Ile287Val) was predicted to create a new donor splice site. Because the second variant, c.340T>C (p.Tyr114His), is located in the enzyme’s active site and has no residual enzyme activity, and biallelic loss-of-function variants are typically lethal, we suggested that the c.859A>G (p.Ile287Val) variant retains some residual enzyme function. Our study demonstrates that this variant produces two types of mutant transcripts. The primary effect is the activation of a new donor splice site in 64% of transcripts, which undergo NMD. The remaining 40% of transcripts produce a mutant ADSL protein isoform with the Ile287Val substitution.
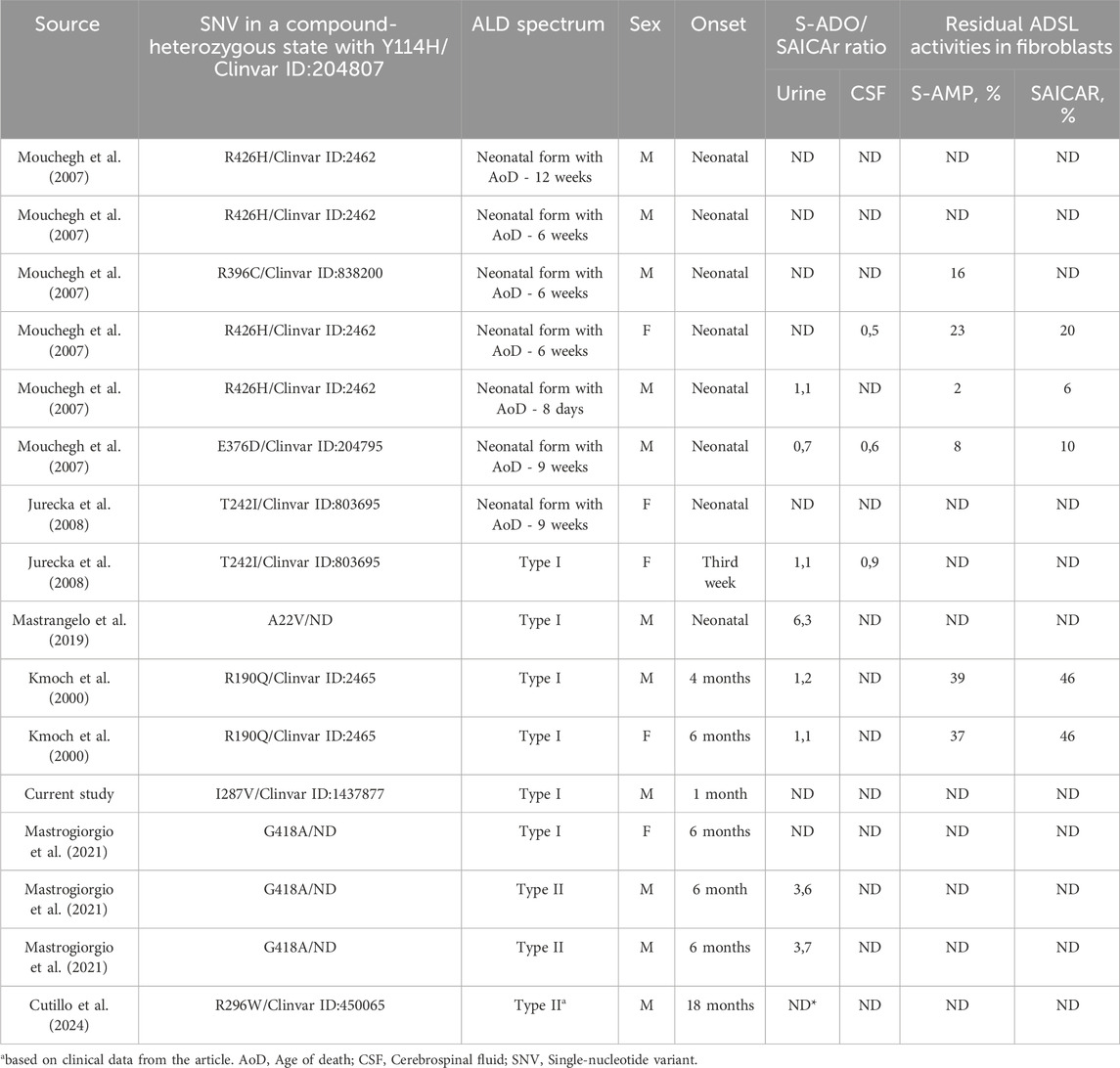
In previous studies, the p.Tyr114His variant had been identified in 14 patients with clinical data (Kmoch et al., 2000; Mouchegh et al., 2007; Jurecka et al., 2008; Mastrangelo et al., 2019; Mastrogiorgio et al., 2021; Cutillo et al., 2024). Of these patients, seven were diagnosed with the neonatal form of ALD, with age of death under 4 months; six were diagnosed with ALD type I; and only two patients with compound-heterozygous Gly418Ala had type II ALD (Table 1). In two studies, residual ADSL activity in fibroblasts was measured, showing 2%–23% S-AMP and 6%–20% SAICAr metabolism for patients with the neonatal form and 37%–39% S-AMP and 46% SAICAr metabolism for those with ALD type I (Kmoch et al., 2000; Mouchegh et al., 2007).
Our proband presented with symptoms consistent with type I ALD and had approximately 40% of transcripts containing the Ile287Val variant from the mutant allele, while the other allele carried the p.Tyr114His variant, which is known to have zero residual enzyme activity (Kmoch et al., 2000; Zikanova et al., 2010). Previous studies have shown that some residual ADSL activity is essential for non-lethal phenotypes (Dutto et al., 2022). According to AlphaMissense predictions, substitutions at codon 287 could most likely disrupt the ADSL wild-type structure (Figure 3A). However, the substitution to valine (Ile287Val) had the lowest pathogenicity score (0.16) in this position, according to AlphaMissense (Figure 3A), and other in silico predictions classified it as likely benign (Jumper et al., 2021).
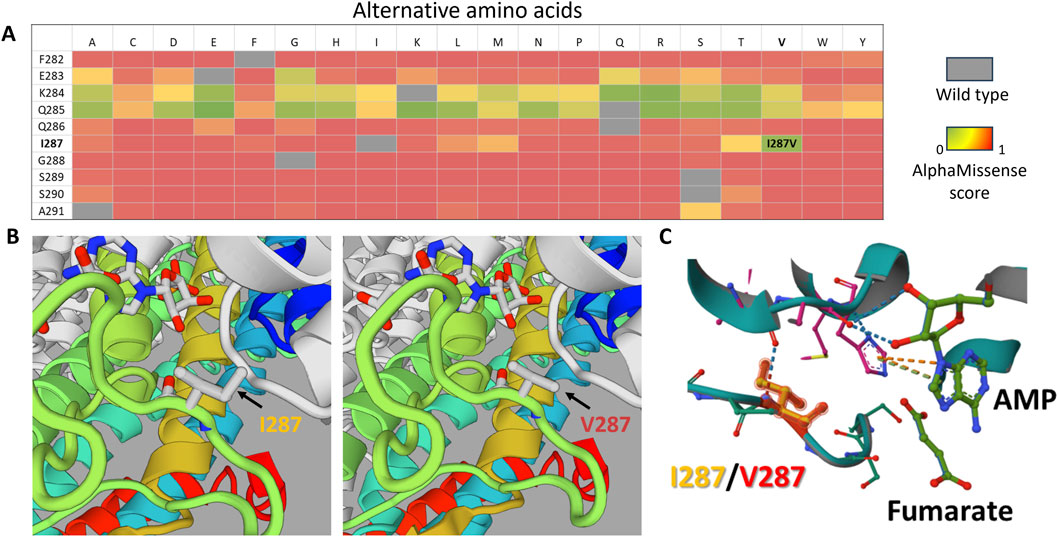
Figure 3. In silico analysis of the p.Ile287Val substitution. (A) Heatmap based on AlphaMissense scores for all possible amino acid substitutions in the F282–A291 region of the ADSL protein. Scores close to 0 (green) indicate substitutions with minimal predicted impact on protein structure, whereas higher scores indicate potential structural effects. (B) 3D model comparison of the wild-type protein (left) and the mutant protein (right), highlighting the region surrounding position 287. (C) Structural alignment of the mutant (turquoise) and wild-type (gray) protein models, demonstrating that position 287 is close to the enzyme’s active site, which is potentially important for enzyme function.
Through 3D modeling of the Ile287Val isoform, we found no significant structural differences compared to the wild type (Figures 3B,C). However, based on in silico predictions alone, we cannot rule out the possibility that Ile287Val may have reduced activity compared to the wild-type isoform. If the Ile287Val variant functions similarly to the wild type in terms of enzymatic activity, then the question arises as to whether it could cause any diseases within the ALD phenotype spectrum in a homozygous state.
One limitation of our study is the lack of enzyme activity testing, which could provide more insight into pathogenicity and its impact on succinylaminoimidazolecarboxamide ribose-5′-phosphate (SAICAR) or S-AMP enzymatic activity. Testing could also clarify whether certain variants contribute to increased SAICAR or S-AMP production compared to the wild type. Additionally, we examined other genes known to be involved in de novo purine synthesis using an MAF <0.5% filter. Although we did not measure the S-Ado/SAICAR ratio, we believe that the clinical presentation, combined with our genetic findings, is sufficient to diagnose the proband with ADSL deficiency.
5 Conclusion
Our case involved a type I ALD patient with two pathogenic variants in the ADSL gene: p.Ile287Val and p.Tyr114His. The c.859A>G (p.Ile287Val) variant leads to abnormal splicing, resulting in transcripts that undergo NMD, while others produce a potentially functional protein with the p.Ile287Val variant. Although enzyme activity testing was not performed, the clinical presentation and genetic findings strongly support the diagnosis of ALD type I.
Data availability statement
The data generated and analyzed in this study are not publicly available due to ethical restrictions and institutional policies regarding patient confidentiality. The informed consent obtained from participants does not allow for public data sharing, in compliance with the approved protocol by the ethics committee. However, the data may be made available to qualified researchers upon reasonable request and with appropriate ethical approvals.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of the Research Centre for Medical Genetics. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation in this study was provided by the participant’s legal guardians/next of kin. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
AB: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. KD: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AM: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AS: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. IK: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. AF: Formal Analysis, Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. MS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (project No 25-65-00031).
Conflict of interest
Authors AS and IK were employed by Genomed.
The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2025.1670299/full#supplementary-material
References
Chen, S., Francioli, L. C., Goodrich, J. K., Collins, R. L., Kanai, M., Wang, Q., et al. (2024). A genomic mutational constraint map using variation in 76,156 human genomes. Nature 625, 92–100. doi:10.1038/s41586-023-06045-0
Cutillo, G., Masnada, S., Lesca, G., Ville, D., Accorsi, P., Giordano, L., et al. (2024). Electroclinical features and phenotypic differences in adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency: long-term follow-up of seven patients from four families and appraisal of the literature. Epilepsia Open 9, 106–121. doi:10.1002/epi4.12837
Davydenko, K., Filatova, A., and Skoblov, M. (2024). Revision of splicing variants in the DMD gene. doi:10.1101/2024.01.31.578175
Dutto, I., Gerhards, J., Herrera, A., Souckova, O., Škopová, V., Smak, J. A., et al. (2022). Pathway-specific effects of ADSL deficiency on neurodevelopment. eLife 11, e70518. doi:10.7554/eLife.70518
Jaganathan, K., Kyriazopoulou Panagiotopoulou, S., McRae, J. F., Darbandi, S. F., Knowles, D., Li, Y. I., et al. (2019). Predicting splicing from primary sequence with deep learning. Cell 176, 535–548. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.12.015
Jumper, J., Evans, R., Pritzel, A., Green, T., Figurnov, M., Ronneberger, O., et al. (2021). Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 596, 583–589. doi:10.1038/s41586-021-03819-2
Jurecka, A., Zikanova, M., Tylki-Szymanska, A., Krijt, J., Bogdanska, A., Gradowska, W., et al. (2008). Clinical, biochemical and molecular findings in seven Polish patients with adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metabolism 94, 435–442. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.04.013
Kmoch, S., Hartmannová, H., Stibůrková, B., Krijt, J., Zikánová, M., and Sebesta, I. (2000). Human adenylosuccinate lyase (ADSL), cloning and characterization of full-length cDNA and its isoform, gene structure and molecular basis for ADSL deficiency in six patients. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 1501–1513. doi:10.1093/HMG/9.10.1501
Marakhonov, A. V., Konovalov, F. A., Makaov, A. K., Vasilyeva, T. A., Kadyshev, V. V., Galkina, V. A., et al. (2018). Primary microcephaly case from the Karachay-cherkess republic poses an additional support for microcephaly and Seckel syndrome spectrum disorders. BMC Med. genomics 11, 8. doi:10.1186/S12920-018-0326-1
Mastrangelo, M., Alfonsi, C., Screpanti, I., Masuelli, L., Tavazzi, B., Mei, D., et al. (2019). Broadening phenotype of adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency: a novel clinical pattern resembling neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Mol. Genet. Metab. Rep. 21, 100502. doi:10.1016/j.ymgmr.2019.100502
Mastrogiorgio, G., Macchiaiolo, M., Buonuomo, P. S., Bellacchio, E., Bordi, M., Vecchio, D., et al. (2021). Clinical and molecular characterization of patients with adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 16, 112. doi:10.1186/s13023-021-01731-6
Mouchegh, K., Zikánová, M., Hoffmann, G. F., Kretzschmar, B., Kühn, T., Mildenberger, E., et al. (2007). Lethal fetal and early neonatal presentation of adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency: observation of 6 patients in 4 families. J. Pediatr. 150, 57–61.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2006.09.027
Sehnal, D., Bittrich, S., Deshpande, M., Svobodová, R., Berka, K., Bazgier, V., et al. (2021). Mol* viewer: modern web app for 3D visualization and analysis of large biomolecular structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, W431–W437. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab314
Spiegel, E. K., Colman, R. F., and Patterson, D. (2006). Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency. Mol. Genet. Metabolism 89, 19–31. doi:10.1016/j.ymgme.2006.04.018
Waterhouse, A. M., Studer, G., Robin, X., Bienert, S., Tauriello, G., and Schwede, T. (2024). The structure assessment web server: for proteins, complexes and more. Nucleic Acids Res. 52, W318–W323. doi:10.1093/nar/gkae270
Keywords: ADSL, ALD, adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency, case report, splicing
Citation: Borovikov A, Davydenko K, Murtazina A, Sharkov A, Kanivets I, Filatova A and Skoblov M (2025) Case Report: Adenylosuccinate lyase deficiency type I caused by splicing disruption due to a novel missense variant in the ADSL gene. Front. Genet. 16:1670299. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1670299
Received: 21 July 2025; Accepted: 01 October 2025;
Published: 24 October 2025.
Edited by:
Zheng Jin Tu, Cleveland Clinic, United StatesReviewed by:
Xiang-Chun Ju, Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology Graduate University, JapanGianni Cutillo, Vita-Salute San Raffaele University, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Borovikov, Davydenko, Murtazina, Sharkov, Kanivets, Filatova and Skoblov. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Artem Borovikov, Ym9yb3Zpa292MzNAZ21haWwuY29t
 Artem Borovikov
Artem Borovikov Ksenia Davydenko1
Ksenia Davydenko1 Aysylu Murtazina
Aysylu Murtazina Ilya Kanivets
Ilya Kanivets Alexandra Filatova
Alexandra Filatova Mikhail Skoblov
Mikhail Skoblov