- 1College of Animal Science, Xinjiang Agricultural University, Urumqi, China
- 2Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Equine Breeding and Exercise Physiology, Urumqi, China
Equine athletic performance is modulated by both genetic and epigenetic mechanisms. As dynamic regulators of gene expression, MicroRNAs (miRNAs) play a central role in the physiological response to exercise-induced stress18. This study focused on the top three elite Yili horses from a 5000-m race, collecting peripheral blood samples pre-race (group B) and post-race (group A). A longitudinal comparative analysis integrating miRNA omics profiling and target gene functional enrichment was performed. Nineteen miRNAs exhibited significant differential expression (10 upregulated, 9 downregulated), with their associated genes primarily implicated in small GTPase-mediated signal transduction, supramolecular complex, and molecular function regulator. Pathway enrichment analysis identified significant associations with Rap1, Ras, and Phospholipase D signaling pathways. These findings suggest that miRNA-mediated regulation may contribute to exercise adaptation by modulating cytoskeletal remodeling and metabolic reprogramming. The study elucidates epigenetic regulatory features underpinning the 5000-m race stress response in Yili horses via omics technology, offering novel insights into the molecular basis of exercise adaptation and establishing quantifiable miRNA markers to inform early-stage equine breeding strategies.
1 Introduction
The Yili horse, originating from the Yili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture in the Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region of China, was developed during the last century by crossing native Kazakh mares with stallions of Orlov, Budyonny, and Russian Don (Wang et al., 2024). The speed of the Yili horse is among the best of Chinese horse breeds, yet there remains a gap compared to major international racing breeds such as the Thoroughbred. Therefore, analyzing the exercise regulation mechanisms of the Yili horse to improve its racing performance is of great significance for enhancing the overall level of horse racing in China. Genetic factors constitute primary regulators of equine athletic traits, and elucidating their molecular basis is essential for precision breeding. Conventional genetic analyses have established moderate to high heritability for exercise-related phenotypes, alongside marked genetic divergence across breeds (Wang C. K. et al., 2025; Welker et al., 2018). Existing studies have identified some molecular markers related to horse movement or speed, such as GSDMC gene (Liu et al., 2025). Nonetheless, the observed phenotypic plasticity implies a substantial contribution from epigenetic modulation.
Emerging evidence highlights the capacity of epigenetic processes-specifically DNA methylation, histone modification, and non-coding RNAs-to respond dynamically to environmental inputs such as training, thereby fine-tuning gene expression in support of exercise adaptation (Cappelli et al., 2024). Among these regulators, miRNAs have garnered significant attention for their role in post-transcriptional gene regulation within exercise-induced stress responses (Li et al., 2025; Zhang et al., 2025).
miRNA is a class of endogenous non-coding small RNAs approximately 22 nucleotides in length, exhibiting high sequence conservation and widespread presence in eukaryotic cells (Wang C. et al., 2025). Its biogenesis initiates with RNA polymerase II-mediated transcription of precursor genes, yielding pri-miRNA, which is subsequently processed by the Drosha-DGCR8 complex into pre-miRNA with a hairpin structure. This intermediate is then exported to the cytoplasm via Exportin-5 and further cleaved by Dicer to generate a mature miRNA duplex. The mature strand associates with the RNA-induced silencing complex and binds to the 3′UTR of target mRNAs through sequence complementarity, resulting in either mRNA degradation or translational repression, thereby negatively regulating gene expression (Hussein, 2012). Accumulating evidence indicates that miRNA participates in the regulation of cellular processes including proliferation, apoptosis, energy metabolism, immune modulation, and tissue repair, and mediates molecular adaptations in response to exercise stimuli (Wilczynska and Bushell, 2015). At the same time, miRNAs are ideal non-invasive biomarkers for motor adaptation monitoring due to their stability in body fluids, tissue-specific expression patterns, and dynamic response to stimuli. In a study on horses (Herkenhoff, 2025), miRNAs are deeply involved in the adaptive regulation of athletic performance, such as muscle development, energy metabolism, and post-exercise inflammatory responses, by regulating gene expression (Bou et al., 2022; Wang T. L. et al., 2025). In terms of diseases, specific miRNA expression profiles are closely related to the occurrence and development of various common diseases such as osteoarthritis, respiratory diseases, and laminitis, making them promising new diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. However, there is a serious lack of research on the mechanism of exercise adaptation, especially the lack of data on local varieties in China, which restricts the application breakthrough of exercise epigenetics.
As a key modulator of gene expression, miRNA exhibits dynamic responsiveness to exercise-induced physiological stress. Acute physical activity rapidly alters the expression of myogenic miRNAs (myomiRs), including miR-1 and miR-133 families, which regulate mitochondrial biogenesis and muscle remodeling by targeting genes such as HDAC4 and NRF1 (Safdar et al., 2009; Zacharewicz et al., 2013). Endurance exercise downregulates miR-23, thereby lifting repression on PGC-1α (Safdar et al., 2009), and enhancing oxidative metabolic adaptation. Expression of miR-206, miR-133a, and miR-133b contributes to skeletal muscle differentiation and may influence muscle growth (Kirby and McCarthy, 2013). miR-146a-5p is upregulated by inflammatory stimuli and attenuates the NF-κB pathway by targeting proinflammatory transcripts such as IRAK1 and TRAF6, thus modulating cytokine signaling and nociceptive processes (Li et al., 2011; Iyer et al., 2012; Roos et al., 2016). Collectively, current evidence suggests that miRNAs act as molecular regulators of exercise adaptation; however, research in this area remains relatively limited in horses (Ding et al., 2025; Yuan et al., 2025), and the mechanisms through which miRNAs regulate exercise responses in equines are still not fully unclear. By integrating whole-transcriptomic profiling with functional enrichment analysis, the present study delineates the exercise-responsive miRNA dynamics in Yili horses, advancing the understanding of epigenetic regulation in equine exercise physiology and informing the development of early-stage, quantifiable markers for breeding selection.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Horse blood collection
We organized a 5000-m race with 24 Yili horses (Figure 1A), all of which were over 3 years old. At 20:00 on the day before the race, jugular venous blood samples were collected from all participating horses. Within 5 min after the race, samples were obtained from the top three performers. Examination revealed that these three horses were all four-year-old stallions. The pre-race blood samples of these horses were retrieved and paired with their post-race samples for subsequent analysis. The race times of these three horses ranged from 5′23″704 to 5′41″339. All samples were preserved in liquid nitrogen. Prior to the race, horses underwent conditioning regimens consistent with those used for thoroughbreds, Horses are subjected to similar basic endurance training (3-4 times a week, 5–10 km cantering) as well as speed training (1-2 times a week, 800–1000 m intermittent sprints) at the owner’s place. The race track is a standard sand track, and all horses are placed in the same stable environment and fed a standard ration 48 h before the race. Pedigree verification and health assessments, including lameness examinations, were conducted by veterinarians in accordance with pre-race protocols. All blood samples from the horses were collected by the same skilled veterinarian using vacuum tubes. To minimize stress on the animals, each sample did not exceed 5 mL, and the entire collection process was completed within 1 min.
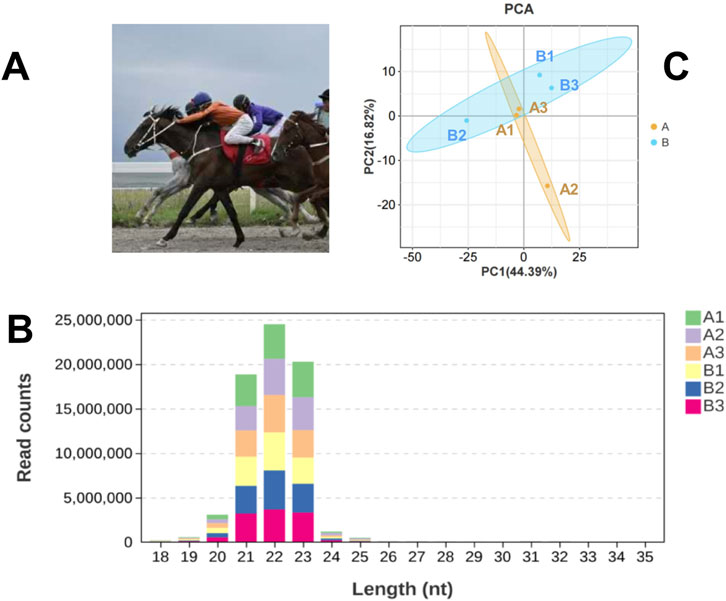
Figure 1. Basic Information of the Experiment. (A) Yili horses in competition; (B) Statistical Analysis of miRNA Length Distribution in Groups A and B Libraries; (C) Principal component analysis (PCA) of samples.
2.2 RNA extraction and quality analysis
Total RNA was isolated from the blood samples of groups A and B using the TRIzol kit (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, United States). RNA degradation and contamination were assessed via 1% agarose gel electrophoresis. RNA yield and purity were quantified using a NanoPhotometer® spectrophotometer, while concentrations were determined with the Qubit® RNA Assay Kit on a Qubit® 2.0 Fluorometer (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, United States). RNA integrity was evaluated with the Nano 6000 Assay Kit on the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2,100 system (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, United States), and samples with RIN values exceeding 7.0 were considered suitable. Small RNA fractions were subsequently utilized for RNA-seq and qRT-PCR analyses.
2.3 Small RNA sequencing and data analysis
2.3.1 Library preparation and small RNA sequencing
Total RNA was subjected to library construction in accordance with the NEB Next Ultra Small RNA Sample Library Preparation Kit protocol (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, United States) designed for Illumina sequencing. Only libraries meeting quality standards proceeded to high-throughput sequencing. PCR-amplified products were separated and purified via 8% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (100 V, 80 min), and 140–160 bp DNA fragments were recovered using 8 μL elution buffer. Library quality was assessed with the Agilent Bioanalyzer 2,100 system employing a DNA high sensitivity chip. Sequencing was performed on the Illumina HiSeq X Ten platform (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, United States), generating 50-nucleotide single-end (SE) read.
2.3.2 Data processing
Cutadapt (v1.2.2) (http://code.google.com/p/cutadapt/) was employed to remove the 3′adapter sequences, followed by selection of small RNAs (sRNAs) ranging from 18 to 30 nt for subsequent analysis. Low-quality reads (Phred score <30) were excluded using the FASTQ quality filter provided by the FASTX-Toolkit v0.0.13.2 (http://hannonlab.cshl.edu/fastx_toolkit/). High-quality reads were then aligned to the EquCab 3.0 horse genome using Bowtie v1.0.1. Known miRNAs were annotated based on miREvo (v1.1), while novel miRNA candidates were identified via miRDeep2 (v0.0.5).
Expression levels of both annotated and novel miRNAs were quantified using TPM (transcripts per million), with normalization calculated as:
2.3.3 Identification of differentially expressed miRNAs and functional enrichment
We employed DESeq2 (v1.24.0) to conduct the differential expression analysis between the two groups of samples (group A post-race and group B pre-race), with key parameters rigorously applied to ensure robust results: the adjusted P-value threshold was set to<0.05 using the Benjamini-Hochberg method. For target gene prediction of the identified miRNAs, we utilized two complementary computational tools-miRanda (v3.3a) with stringent thresholds of score≥140 and binding energy ≤ −10 kcal/mol to prioritize high-affinity interactions, and RNAhybrid (v2.0) requiring P-value ≤0.05 and minimum free energy ≤ −10 kcal/mol to validate thermodynamic stability-adhering to a strict selection criterion where only genes predicted by both algorithms (intersecting results) were retained for subsequent functional analysis.
Gene Ontology (GO) annotation and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analysis of the target genes were performed using the ClusterProfiler (v3.8.1). Statistical significance for enriched functional categories and pathways was determined by a corrected P-value threshold of padj< 0.05, as indicated in the bioinformatics workflow parameters.
2.4 Validation of miRNA expression by qRT-PCR
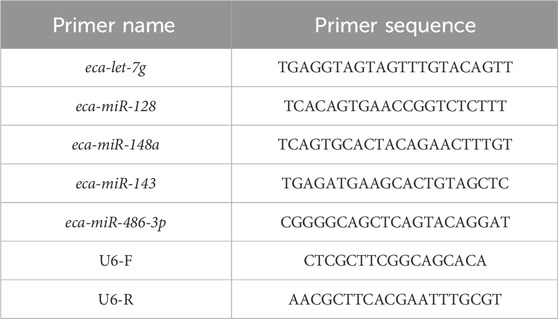
Total RNA was isolated from blood samples collected from Yili horses pre-race (Group B) and post-race (Group A) using standard extraction procedures, followed by reverse transcription with the ReverTra Ace® qPCR RT Kit (TOYOBO, FSQ-101). The 20 μL reverse transcription reaction included 4 μL of 5×RT Buffer, 1 μL Enzyme Mix, 0.5 μL Primer Mix, 2 μg total RNA, and RNase-free water. The reaction was conducted at 37 °C for 15 min and 98 °C for 5 min using a Thermo Veriti PCR instrument. Differentially expressed miRNAs (miR-128, miR-143, miR-148a, miR-486-3p, and let-7g) were randomly selected for analysis, with specific forward primers designed accordingly (primer sequences provided in Table 1). U6 snRNA served as the internal control, using forward primer CTCGCTTCGGCAGCACA and reverse primer AACGCTCACGAATTTGCGT. qPCR amplification was carried out in a 10 μL system comprising 5 μL SYBR® Green Realtime PCR Master Mix (TOYOBO, QPK-201), 0.4 μL of each forward and reverse primer (10 μM), 0.8 μL cDNA template, and Nuclease-Free Water. The amplification was performed using a TL-988 fluorescence qPCR instrument (Tianlong, Xi’an, China) under the following cycling conditions: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of denaturation under 95 °C for 15 s and annealing/extension under 60 °C for 30 s, and a final melting curve analysis from 65 °C to 95 °C. Relative expression levels were determined using the 2-△△Ct method, and statistical comparisons were performed using a paired t-test in SPSS 26, with P < 0.05 indicating significance. Each sample was processed in triplicate, and Ct value variation remained below 5%.
3 Results
3.1 Transcriptome sequencing
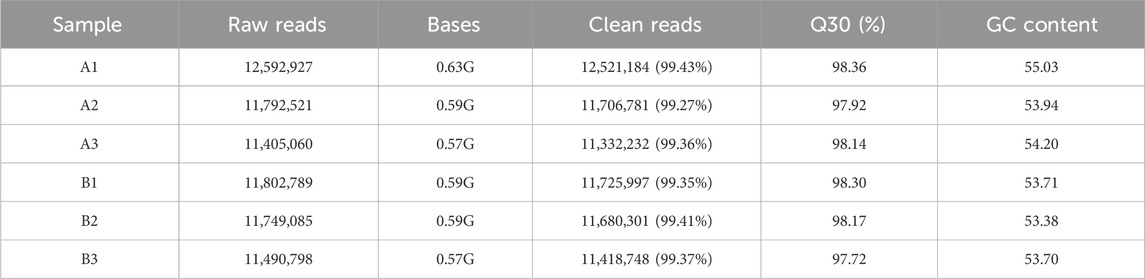
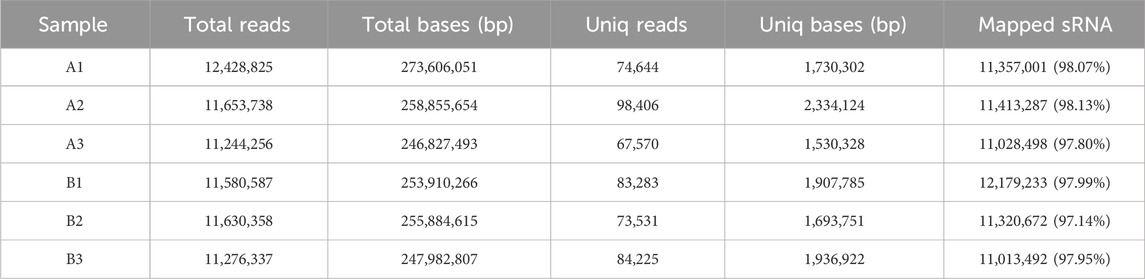
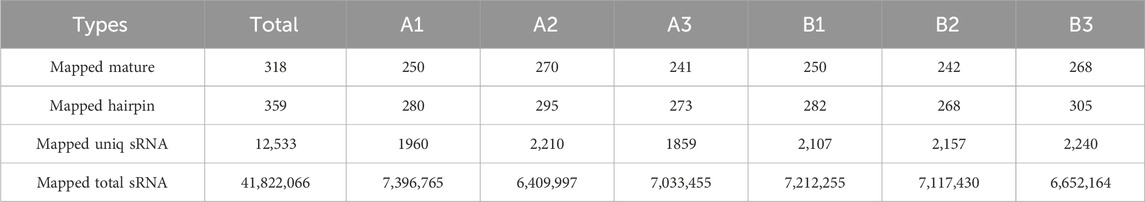
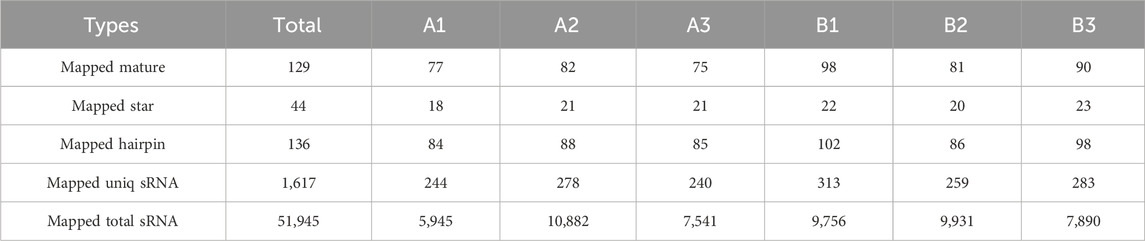
An average of 0.59 G of sequencing data was generated per sample, with Q30 values exceeding 97.72% and GC content ranging from 53% to 55%. Following quality filtering, over 99.27% of raw reads were retained. Clean reads were predominantly distributed between 18 and 30 nt, consistent with the size profile of animal sRNAs. Notably, miRNAs were mainly concentrated within the 21-24 nt range (Figure 1B). Approximately 98% of sRNAs were successfully aligned to the reference genome. Analysis of known miRNAs using the miRBase database identified 318 miRNAs, while novel miRNA prediction yielded an additional 129 candidates (detailed in Table 2–5).
Principal component analysis (PCA) (Figure 1C) revealed partial overlap between group A (orange) and group B (blue), with a discernible directional shift—samples in group A trending leftward and those in group B trending rightward. Although inter-group distinctions were present, complete separation was not achieved. The presence of broadly distributed non-differential miRNAs likely attenuated group-level divergence.
3.2 Differential miRNAs
A total of 19 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified under the criteria of P-value <0.05 and |log2FC| > 0. According to the volcano plot (Figure 2A), comparison between group A and group B revealed 10 upregulated and 9 downregulated miRNAs. Integrated with the clustering analysis shown in the heat map (Figure 2B), the upregulated miRNAs included miR-1, miR-122, miR-128, miR-143, miR-148a, miR-486-3p, miR-486-5p, miR-542-3p, miR-92b, and miR-9a, while the downregulated miRNAs comprised let-7g, miR-21, miR-27b, miR-28-5p, miR-29b, miR-29c, miR-350, miR-432, and miR-872.
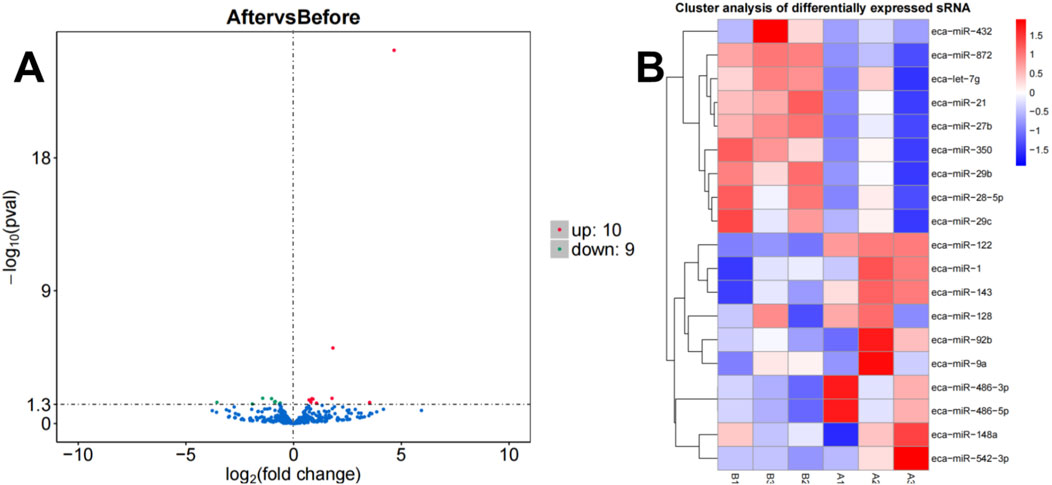
Figure 2. Volcano plot (A) and heatmap (B) illustrating miRNA expression differences between group B and group A.
3.3 Enrichment analysis
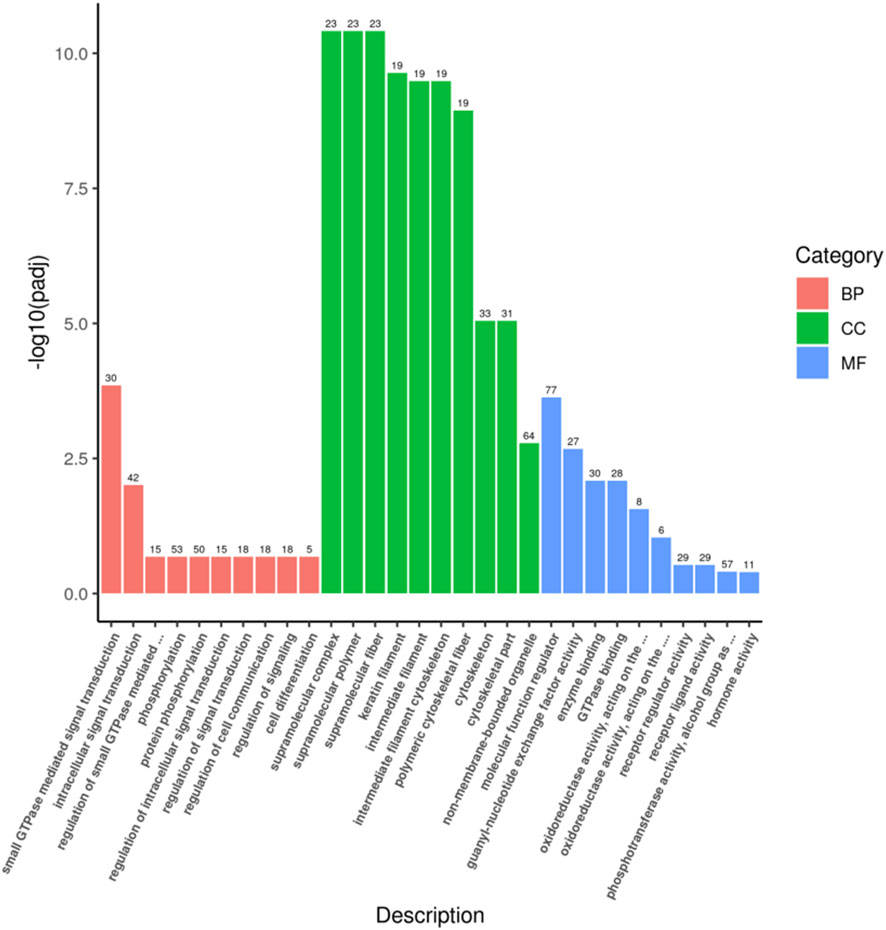
A total of 165 target genes were covered by GO functional annotations, and the classification results showed that the 30 GO terms in which the candidate target genes were mainly involved are shown in Figure 3, including 10 terms each for biological processes (BP), cellular components (CC), and molecular functions (MF), as depicted in Figure 3. Within the BP category, the candidate genes were predominantly involved in small GTPase-mediated signal transduction (GO:0007264) and intracellular signal transduction (GO:0035556). Regarding CC, enrichment was observed in supramolecular complex (GO:0099080) and supramolecular polymer (GO:0099081). For MF, molecular function regulator (GO:0098772) and guanyl-nucleotide exchange factor activity (GO:0005085) were most represented, reflecting roles in transcriptional regulation, enzymatic activity modulation, organelle dynamics, and cellular stress responses.
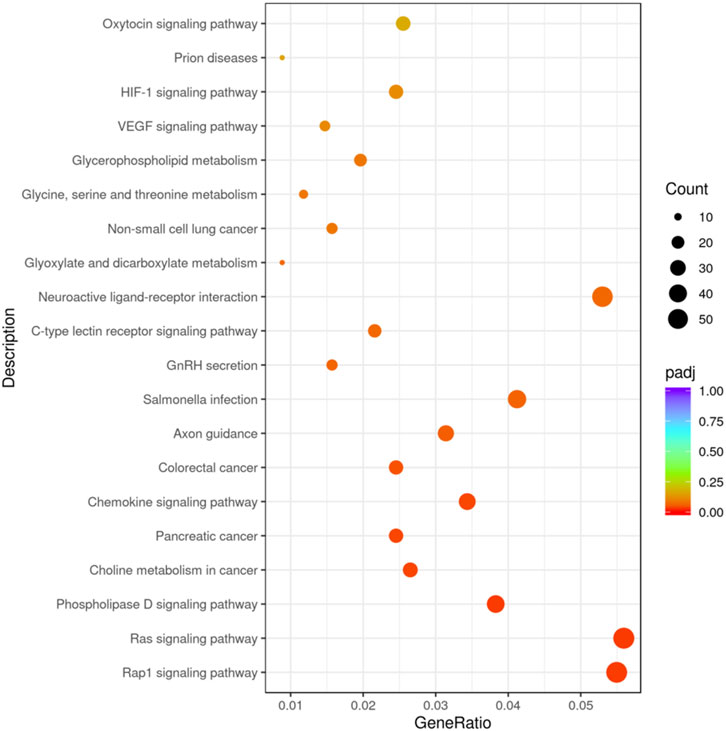
The KEGG pathway covers a total of 117 target genes, and the results show that the candidate target genes are mainly involved in 20 pathways, combined with Figure 4, indicating that these candidate target genes are mainly involved in biological processes such as Rap1 signaling pathway, Ras signaling pathway, and Phospholipase D signaling pathway.
3.4 miRNA-qPCR assay
To evaluate the consistency between transcriptomic profiling and experimental validation, miR-128, miR-143, miR-148a, miR-486-3p, and let-7g were randomly selected for qRT-PCR analysis. As illustrated in Figure 5, expression patterns derived from qPCR closely mirrored those obtained from RNA-seq, thereby confirming the robustness of the sequencing dataset and reinforcing its reliability for further analyses.
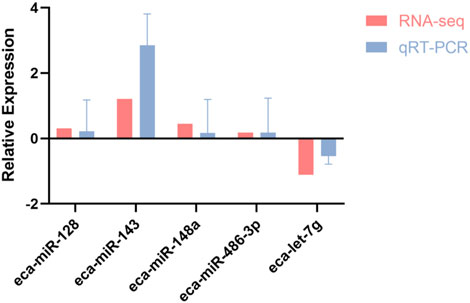
Figure 5. Correlation of RNA-seq and qRT-PCR expression profiles for five differentially expressed miRNAs in racing horses.
4 Discussion
Exercise can induce gene expression modulation through epigenetic mechanisms, with miRNAs serving as key regulatory elements in this process (Grazioli et al., 2017). A total of 19 differentially expressed miRNAs were identified in this study. Existing research indicates that some of these are associated with exercise adaptation. However, their target genes and regulatory mechanisms remain computationally predicted and require experimental validation. Our bioinformatics analysis predicts multiple target genes that have been confirmed by previous studies to be strongly related to athletic performance and muscle adaptation.
Some researchers suggest that miR-1 serves as a biomarker for aerobic activity, with its plasma levels significantly increasing after exercise (Andrea et al., 2019). This is primarily because during physical activity, mechanical overload stimulates skeletal muscles to secrete extracellular vesicles (EVs) enriched with miR-1 (Vechetti et al., 2021). These EVs deliver miR-1 to adipose tissue and promote lipolysis by targeting the Adrb1 and Hsl genes, thereby providing energy for exercise. This process may facilitate the mobilization of energy substrates (such as free fatty acids), thus supporting prolonged physical activity and post-exercise recovery. The upregulation of plasma miR-1 observed in Yili horses after racing in our study is consistent with this systemic adaptive mechanism. This may be mediated by its coordinated regulation of energy metabolism, particularly fatty acid metabolism, to enhance energy supply during racing. Similar results have been found in studies of human marathon runners, suggesting a possible association between miR-1 and exercise (Eyileten et al., 2022; Chalchat et al., 2021). However, our findings lack more direct mechanistic confirmation.
Notably, miR-486-3p was predicted to target several key genes, including CDKN1A and TMSB4X. CDKN1A, implicated in muscle fiber composition, exhibits elevated expression following strength or sprint training (Semenova et al., 2022). TMSB4X functions as a movement- and growth-related factor and chemoattractant released in response to muscle injury, and its plasma levels increase irrespective of exercise modality (Gonzalez-Franquesa et al., 2021). These findings from other researchers are highly consistent with our own results, Upregulation of miR-486-3p may contribute to accelerated muscle fiber repair in Yili horses, mitigate micro-lesion accumulation, and support ongoing cytoskeletal remodeling (Fan, 2020). The findings from studies on endurance racehorses also support our conclusions (de Oliveira et al., 2021), suggesting that miR-486 may be associated with the exercise performance of Yili horses. Additionally, acute high-intensity exercise induces inflammatory responses in equine subjects, and sustained exposure may contribute to the development of degenerative joint conditions (MacNicol et al., 2018). miR-128 suppresses the expression of its target gene TAB2, thereby attenuating TAB2-mediated activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway, which limits inflammation and prevents excessive immune activation (Ren et al., 2021). Therefore, the upregulation of miR-128 in this study may contribute to post-exercise recovery in Yili horses, supporting physiological homeostasis and mitigating inflammatory damage. Furthermore, miR-128 is associated with myogenic processes such as myoblast proliferation and differentiation (Grieb et al., 2023), which may explain why it is affected by exercise in Yili horses. However, further validation with larger sample sizes and more direct evidence is still required.
Under exercise stress, miR-143 coordinately regulates cellular remodeling and inflammatory repair processes by targeting multiple genes, including AKAP13 and STAT4. Specifically, miR-143 modulates the AKAP13-mediated RhoA signaling pathway to optimize cytoskeletal reorganization and adaptive remodeling of myocytes (Langeberg and Scott, 2015), while simultaneously alleviating excessive post-exercise inflammatory responses by suppressing STAT4 (Watfo et al., 2004). We hypothesize that post-exercise upregulation of miR-143 in Yili horses may mediate the following physiological adaptations: these effects significantly enhance the structural integrity of muscle fibers and accelerate inflammation resolution and tissue repair, thereby collectively improving exercise endurance, improve muscle microcirculation, alleviate post-exercise ischemia, protect vascular endothelium from oxidative damage, and enhance osteoblast differentiation-thereby reducing the risk of stress fractures while improving bone elasticity, exercise tolerance, and recovery capacity.
High-intensity exercise imposes substantial energy demands on horses, predisposing them to rapid glycogen depletion, lactate accumulation, and metabolic dysregulation (Jose-Cunilleras, 2024). miR-148a suppress PTEN expression, thereby activating lipogenic signaling pathways such as PPARγ and FASN, ultimately promoting lipid deposition within intramuscular and subcutaneous adipocytes. This modulation of lipid storage is accompanied by enhanced insulin sensitivity and elevated glucose uptake (Jin et al., 2021), The upregulation of miR-148a may activate this coordination mechanism, attenuating lactate accumulation, delaying fatigue onset, and enhancing both racing and post-exercise recovery capacity in Yili horses.
Let-7g modulates glucose metabolism through interaction with the KRAS-PI3K-Rac1-Akt signaling axis, relieving suppression of KRAS-driven pathways and thereby enhancing mitochondrial OXPHOS and glycolytic activity (Hung et al., 2023), the downregulation of let-7g observed in our study may release suppression of this metabolic axis, potentially optimizing energy substrate turnover during high-intensity racing in Yili horses. The core differential miRNAs found in this study are closely associated with the exercise adaptation phenotype, and their feasibility as biomarkers is supported by other studies. These molecules can provide quantitative indicators for early breeding of Yili horses (Herkenhoff, 2025).
GO enrichment analysis in this study revealed that candidate target genes are primarily associated with CC (cellular components) and are highly enriched in terms related to cytoskeletal structure and mechanical strength. This suggests that differentially expressed miRNAs may mediate exercise adaptation in Yili horses by regulating cytoskeletal assembly and organization (Mandal et al., 2022). We therefore hypothesize that these miRNAs potentially enhance structural integrity, force transmission efficiency, and resistance to damage in muscle fibers through promoting cytoskeletal remodeling and reinforcement (Herkenhoff, 2025). This mechanism may constitute an important molecular basis for the exceptional racing observed in Yili horses.
KEGG enrichment analysis of predicted candidate target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs indicated significant involvement in signal transduction pathways. Members of the Ras superfamily, particularly Rap1, were implicated in enriched pathways such as the Rap1 and Ras signaling pathways. Activation of RhoGAP enhances the hydrolysis of RhoA-GTP to its inactive GDP-bound form, thereby attenuating ROCK-dependent myosin phosphorylation (Rajagopal et al., 2013; Heron-Milhavet and Djiane, 2022). Concurrently, Ras signaling promotes plasma membrane localization of glucose transporters and upregulates the expression of glycolytic enzymes via B-Raf/MEK/ERK activation (Vojtek and Der, 1998; Koh et al., 2002). Differentially expressed miRNAs may modulate these signaling pathways to improve muscle contraction efficiency, enhance mobilization and utilization of energy substrates during exercise, and reduce exercise-induced muscle damage in Yili horses.
In conclusion, the 19 differentially expressed miRNAs in Yili horses post-race are unlikely to function in isolation. Instead, they potentially form a coordinated regulatory network that synergistically governs the complex physiological adaptations to endurance exercise by co-targeting central signaling pathways and biological processes. Future studies, such as constructing a comprehensive miRNA interaction network or experimental validation using dual-luciferase assays, are warranted to decipher the precise nature of these interactions.
It must be acknowledged that in order to investigate the pre- and post-race miRNA transcriptome profiles of elite Yili horses while accounting for competition performance, only the top three winning horses were selected for this study. This limited sample size may introduce certain limitations to the accuracy and generalizability of the findings. Furthermore, since the enrichment analysis results were consistent with the regulatory pathways of the identified miRNAs, functional validation of target genes—such as knockdown or overexpression experiments—was not conducted. Additionally, this study included only male Yili horses, all 4 years of age, reflecting the typical age at which racehorses achieve competitive success. While this approach helped control for variations in age, sex, and breed, the influence of these factors warrants further investigation in future studies.
5 Conclusion
This study characterized the dynamic miRNA expression profile associated with exercise-induced stress in Yili horses during a 5000-m race, identifying specific miRNAs—such as miR-1 and miR-486-3p—as potential biomarkers for breeding selection. Corresponding target genes and regulatory pathways involved in the physiological response to exercise were also delineated. Future efforts may focus on functional validation of key miRNAs to support the establishment of an miRNA-based early-stage breeding assessment framework.
Data availability statement
The data presented in the study are deposited in the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) repository, accession number PRJNA1303378.
Ethics statement
The animal studies were approved by Animal Ethics Committee of Xinjiang Agricultural University (approval number: 2024003). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was obtained from the owners for the participation of their animals in this study.
Author contributions
SM: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. WR: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. ZL: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. LL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. RW: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. YS: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. QH: Writing – original draft, Writing – review and editing. SD: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft. JW: Writing – review and editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (32302735), Central Guidance for Local Science and Technology Development Fund (ZYYD2025JD02), Major Science and Technology Special Project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region (2022A02013-1), and Basic Research Funding Projects for Scientific Research in Xinjiang Universities (XJEDU2025J057).
Acknowledgments
The authors express their gratitude to the Xinjiang Key Laboratory of Equine Breeding and Exercise Physiology for their generous support.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fgene.2025.1676558/full#supplementary-material
References
Andrea, G., Ján, K., Simona, V., Andrea, R., Erika, Z., Jana, L., et al. (2019). Selective muscle microRNAs as novel biomarkers of aerobic or anaerobic exercise capacity. Gazz. Med. Ital. Arch. S 178, 245–248. doi:10.23736/S0393-3660.18.03840-8
Bou, T. G. Q., Han, H. G., Mongke, T., Zhao, R. Y., La, X. M., Ding, W. Q., et al. (2022). Fast and slow myofiber-specific expression profiles are affected by noncoding RNAs in Mongolian horses. Comp. Biochem. Phys. 41, 100942. doi:10.1016/j.cbd.2021.100942
Cappelli, K., Mecocci, S., Porceddu, A., Albertini, E., Giontella, A., Miglio, A., et al. (2024). Genome-wide epigenetic modifications in sports horses during training as an adaptation phenomenon. Sci. Rep. 13, 18786. doi:10.1038/s41598-023-46043-w
Chalchat, E., Charlot, K., Garcia-Vicencio, S., Hertert, P., Baugé, S., Bourdon, S., et al. (2021). Circulating microRNAs after a 24-h ultramarathon run in relation to muscle damage markers in elite athletes. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Spor 31, 1782–1795. doi:10.1111/sms.14000
de Oliveira, G. P., Porto, W. F., Palu, C. C., Pereira, L. M., Reis, E. M. M., Marçola, T. G., et al. (2021). Effects of endurance racing on horse plasma extracellular particle miRNA. Equine Vet. J. 53, 618–627. doi:10.1111/evj.13300
Ding, W. Q., Gong, W. D., Bou, T., Shi, L., Lin, Y. A., Wu, H. Z., et al. (2025). Pilot study on the profiling and functional analysis of mRNA, miRNA, and lncRNA in the skeletal muscle of Mongolian horses, xilingol horses, and grassland-Thoroughbreds. Animals 15, 1123. doi:10.3390/ani15081123
Eyileten, C., Wicik, Z., Fitas, A., Marszalek, M., Simon, J. E., De Rosa, S., et al. (2022). Altered circulating MicroRNA profiles after endurance training: a cohort study of ultramarathon runners. Front. Physiol. 12, 792931. doi:10.3389/fphys.2021.792931
Fan, C. Y. (2020). Role of miR-128, Sp1 and CDKN1A mRNA in repairing muscle injury in a rat skeletal muscle injury model. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 82, 58–64. doi:10.36468/pharmaceutical-sciences.spl.124
Gonzalez-Franquesa, A., Stocks, B., Borg, M. L., Kuefner, M., Dalbram, E., Nielsen, T. S., et al. (2021). Discovery of thymosin β4 as a human exerkine and growth factor. Am. J. Physiol-Cell P. H. 321, C770–C778. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00263.2021
Grazioli, E., Dimauro, I., Mercatelli, N., Wang, G., Pitsiladis, Y., Di Luigi, L., et al. (2017). Physical activity in the prevention of human diseases: role of epigenetic modifications. Bmc Genomics 18, 802. doi:10.1186/s12864-017-4193-5
Grieb, A., Schmitt, A., Fragasso, A., Widmann, M., Maturana, F. M., Burgstahler, C., et al. (2023). Skeletal muscle mMicroRNA patterns in response to a single bout of exercise in females: biomarkers for subsequent training adaptation? Biomolecules 13, 884. doi:10.3390/biom13060884
Herkenhoff, M. E. (2025). Equine microRNAs: performance, reproduction, and disease. Microrna 14. doi:10.2174/0122115366369721250606113102
Heron-Milhavet, L., and Djiane, A. (2022). MAGIs: junctional scaffolds linking inter-cellular junction architecture, actin cytoskeleton dynamics, and signaling pathways. J. Cell Signal 3, 141–147. doi:10.33696/Signaling.3.076
Hung, K. C., Tien, N., Bau, D., Yao, C. H., Chen, C. H., Yang, J. L., et al. (2023). Let-7g upregulation attenuated the KRAS-PI3K-Rac1-Akt axis-mediated bioenergetic functions. Cells 12, 2313. doi:10.3390/cells12182313
Hussein, K. (2012). Pathobiology of the microRNA system. Pathologe 33, 70–78. doi:10.1007/s00292-011-1469-4
Iyer, A., Zurolo, E., Prabowo, A., Fluiter, K., Spliet, W. G. M., van Rijen, P. C., et al. (2012). MicroRNA-146a: a key regulator of astrocyte-mediated inflammatory response. PLos One 7, e44789. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044789
Jin, X. Y., Hao, Z. Y., Zhao, M. L., Shen, J. Y., Ke, N., Song, Y. Z., et al. (2021). MicroRNA-148a regulates the proliferation and differentiation of ovine preadipocytes by targeting PTEN. Animals 11, 820. doi:10.3390/ani11030820
Jose-Cunilleras, E. (2024). Abnormalities of body fluids and electrolytes in athletic horses. Equine Sports Med. And Surg. Third Ed., 1003–1030. doi:10.1016/B978-0-7020-8370-9.00044-8
Kirby, T. J., and McCarthy, J. J. (2013). MicroRNAs in skeletal muscle biology and exercise adaptation. Free Radic. Bio Med. 64, 95–105. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.07.004
Koh, Y. H., Ruiz-Canada, C., Gorczyca, M., and Budnik, V. (2002). The Ras1-mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathway regulates synaptic plasticity through fasciclin II-mediated cell adhesion. J. Neurosci. 22, 2496–2504. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-07-02496.2002
Langeberg, L. K., and Scott, J. D. (2015). Signalling scaffolds and local organization of cellular behaviour. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 232–244. doi:10.1038/nrm3966
Li, X., Gibson, G., Kim, J. S., Kroin, J., Xu, S. B., van Wijnen, A. J., et al. (2011). MicroRNA-146a is linked to pain-related pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Gene 480, 34–41. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2011.03.003
Li, H., Liu, G., Wang, B., and Moneni, M. R. (2025). Exosomes and microRNAs as mediators of the exercise. Eur. J. Med. Res. 30, 38. doi:10.1186/s40001-025-02273-4
Liu, X. X., Jia, Y. Z., Pan, J. F., Zhang, Y. L., Gong, Y., Wang, X. T., et al. (2025). Selection at the GSDMC locus in horses and its implications for human mobility. Science. 389, 925–930. doi:10.1126/science.adp4581
MacNicol, J. L., Lindinger, M. I., and Pearson, W. (2018). A time-course evaluation of inflammatory and oxidative markers following high-intensity exercise in horses: a pilot study. J. Appl. Physiol. 124, 860–865. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00461.2017
Mandal, S., Denham, M. M., Spencer, S. J., and Denham, J. (2022). Exercise regulates shelterin genes and microRNAs implicated in ageing in thoroughbred horses. Pflug Arch. Eur. J. Phy 474, 1159–1169. doi:10.1007/s00424-022-02745-0
Rajagopal, S., Kumar, D. P., Mahavadi, S., Bhattacharya, S., Zhou, R. Z., Corvera, C. U., et al. (2013). Activation of G protein-coupled bile acid receptor, TGR5, induces smooth muscle relaxation via both Epac- and PKA-mediated inhibition of RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Am. J. Physiol-Gastr L. 304, G527–G535. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00388.2012
Ren, X. M., Cui, J. X., Xu, T. J., and Sun, Y. N. (2021). microRNA-128 inhibits the inflammatory responses by targeting TAB2 in miiuy croaker, Miichthysmiiuy. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 117, 103976. doi:10.1016/j.dci.2020.103976
Roos, J., Enlund, E., Funcke, J. B., Tews, D., Holzmann, K., Debatin, K. M., et al. (2016). miR-146a-mediated suppression of the inflammatory response in human adipocytes. Sci. Rep. 6, 38339. doi:10.1038/srep38339
Safdar, A., Abadi, A., Akhtar, M., Hettinga, B. P., and Tarnopolsky, M. A. (2009). miRNA in the regulation of skeletal muscle adaptation to acute endurance exercise in C57Bl/6J male mice. PLoS One 4, e5610. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005610
Semenova, E. A., Zempo, H., Miyamoto-Mikami, E., Kumagai, H., Larin, A. K., Sultanov, R. I., et al. (2022). Genome-wide association study identifies CDKN1A as a novel locus associated with muscle fiber composition. Cells 11, 3910. doi:10.3390/cells11233910
Vechetti, I. J., Peck, B. D., Wen, Y., Walton, R. G., Valentino, T. R., Alimov, A. P., et al. (2021). Mechanical overload-induced muscle-derived extracellular vesicles promote adipose tissue lipolysis. Faseb J. 35, e21644. doi:10.1096/fj.202100242R
Vojtek, A. B., and Der, C. J. (1998). Increasing complexity of the ras signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 19925–19928. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.32.19925
Wang, C. K., Zeng, Y. Q., Wang, J. W., Wang, T. L., Li, X. Y., Shen, Z. H., et al. (2024). A genome-wide association study of the racing performance traits in Yili horses based on blink and FarmCPU models. Sci. Rep. 14, 27648. doi:10.1038/s41598-024-79014-w
Wang C. K., C. K., Zeng, Y. Q., Wang, J. W., Wang, T. L., Li, X. Y., Shen, Z. H., et al. (2025). Estimation of genetic parameters of body conformation and racing performance traits in Yili horses. J. Equine Vet. Sci. 146, 105378. doi:10.1016/j.jevs.2025.105378
Wang C., C., Jia, Q. J., Guo, X. J., Li, K., Chen, W. J., Shen, Q., et al. (2025). microRNA-34 family: from mechanism to potential applications. Int. J. Biochem. Cell B 144, 106168. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2022.106168
Wang T. L., T. L., Meng, J., Peng, X., Huang, J. L., Huang, Y. J., Yuan, X. X., et al. (2025). Metabolomics analysis and mRNA/miRNA profiling reveal potential cardiac regulatory mechanisms in Yili racehorses under different training regimens. PLos ONE 20, e0322468. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0322468
Watford, W. T., Hissong, B. D., Bream, J. H., Kanno, Y., Muul, L., and O’Shea, J. J. (2004). Signaling by IL-12 and IL-23 and the immunoregulatory roles of STAT4. Immunol. Rev. 202, 139–156. doi:10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00211.x
Welker, V., Stock, K. F., Schöpke, K., and Swalve, H. H. (2018). Genetic parameters of new comprehensive performance traits for dressage and show jumping competitions performance of German riding horses. Livest. Sci. 212, 93–98. doi:10.1016/j.livsci.2018.04.002
Wilczynska, A., and Bushell, M. (2015). The complexity of miRNA-mediated repression. Cell Death Differ. 22, 22–33. doi:10.1038/cdd.2014.112
Yuan, X. X., Yao, X. K., Zeng, Y. Q., Wang, J. W., Ren, W. L., Wang, T. L., et al. (2025). The impact of the competition on miRNA, proteins, and metabolites in the blood exosomes of the Yili Horse. Genes 16, 224. doi:10.3390/genes16020224
Zacharewicz, E., Lamon, S., and Russell, A. P. (2013). MicroRNAs in skeletal muscle and their regulation with exercise, ageing, and disease. Front. Physiol. 4, 00266. doi:10.3389/fphys.2013.00266
Keywords: Yili horse, athletic performance, epigenetics, miRNA, candidatetarget gene, signal transduction pathway
Citation: Ma S, Ren W, Li Z, Li L, Wang R, Su Y, Huang Q, Dehaxi S and Wang J (2025) Comparative analysis of miRNA expression in Yili horses pre- and post-5000-m race. Front. Genet. 16:1676558. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1676558
Received: 30 July 2025; Accepted: 17 September 2025;
Published: 01 October 2025.
Edited by:
Xuexue Liu, UMR5288 Anthropologie Moleculaire et Imagerie de Synthese (AMIS), FranceReviewed by:
Marcos Edgar Herkenhoff, Santa Catarina State University, BrazilDongyi Bai, Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, China
Copyright © 2025 Ma, Ren, Li, Li, Wang, Su, Huang, Dehaxi and Wang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianwen Wang, ZGt3andAeGphdS5lZHUuY24=
 Shikun Ma
Shikun Ma Wanlu Ren
Wanlu Ren Zexu Li1
Zexu Li1 Luling Li
Luling Li Yi Su
Yi Su Jianwen Wang
Jianwen Wang