- College of Economics, Management and Law, Changchun Normal University, Changchun, China
Introduction: Social reading, which integrates the benefits of social interaction and value co-creation, has gained significant popularity among adolescents.
Methods: This study collected 2,347 valid survey responses from middle school students across Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou and Shenzhen. Based on this dataset, we developed and empirically validated a social reading behavior model featuring a mediating relationship.
Results: The research specifically addressed the relative importance of digital reading literacy and social reading motivation in influencing social reading behavior. Our analysis revealed that when accounting for the mediating effect of social reading motivation, digital reading literacy demonstrates a stronger total effect on social reading behavior compared to the direct influence of social reading motivation. This finding suggested that digital reading literacy plays a pivotal role in shaping adolescents’ social reading practices, highlighting the need for focused attention on developing this competency to enhance overall reading quality.
Discussion: The implications of this study were twofold: theoretically, it contributed to our understanding of how to improve reading quality and cultivate positive digital reading habits among middle school students; practically, it offered valuable insights for educational institutions, policymakers, and social reading platform developers to optimize their approaches to adolescent literacy development.
1 Introduction
Social reading behavior (abbreviated as SRB throughout this study), as a distinctive manifestation of digital reading characterized by interactive collaboration and co-creation, constitutes the primary research focus of this investigation. The present study operationalizes social reading as a novel reading paradigm arising from the convergence of traditional print-based and digital reading practices. Characterized by its reader-centered approach, this paradigm fundamentally relies on social connections, exhibiting key features including content sharing, interactive engagement, user generated content (UGC), and collaborative communication. (He, 2023) Concurrent with the rapid development and pervasive adoption of digital technologies, contemporary reading practices have experienced substantial transformation (China Academy of Press and Publication, 2022). Among contemporary youth populations, SRB—encompassing both interpersonal and humanistic interaction—has demonstrated significant prevalence and growing sociocultural influence (Li and Wu, 2017; Zhao and Hou, 2023). This socialized reading paradigm carries considerable implications for adolescents’ academic achievement trajectories and broader societal development processes (Sun, 2023; Song et al., 2024). It facilitates adolescents’ social integration processes and enhances their interpersonal competence development. Moreover, systematic engagement with discipline-specific knowledge and literary works through socialized reading practices demonstrates significant positive correlations with reading literacy enhancement and language acquisition proficiency. Longitudinal exposure to high-quality reading materials has been shown to reinforce national identity formation, cognitive schema development, and personal growth (Xu et al., 2024).
The pervasive implementation of SRB among secondary school students has uncovered several problematic manifestations, including disproportionate socialization tendencies, attentional diversion, excessive internet engagement, and inadequate supervisory mechanisms (Teng, 2015; Yin, 2017). Empirical investigations by these scholars have established significant correlations between these behavioral patterns and individuals’ deficient digital reading literacy (hereafter abbreviated as DRL). The systematic development of DRL through structured pedagogical interventions, external regulatory frameworks, and evidence-based instructional strategies focusing on critical analysis can effectively equip contemporary readers with the necessary competencies to adapt to dynamic digital environments. This multifaceted approach demonstrates significant potential for enhancing reading efficacy, cultivating responsible “digital citizenship” (Yan and Yang, 2023), and facilitating progressive acculturation to predominant social reading paradigms. Given the need to optimize students’ SRB, improving their DRL is imperative. Currently, it is urgent to explore the role of DRL in the development of SRB and relationship, in order to explain the root cause of the unsatisfactory SRB of students on the surface. At the same time, Social Reading Motivation (hereafter abbreviated as SRM) has always been closely linked to SRB and is an indispensable factor in the study of SRB. Therefore, when the data showed good results, SRM was also included in the research scope and model planning of the research.
Scholars have increasingly explored the factors influencing SRB, with extant literature predominantly focusing on endogenous factors including motivational constructs and metacognitive awareness. Illustratively, Yi (2022) empirical study established intrinsic motivation and reflexive self-awareness as pivotal individual-level predictors of collegiate social reading engagement. The research landscape has subsequently evolved to adopt more holistic analytical frameworks that integrate both endogenous psychological factors and exogenous environmental influences in explaining SRB phenomena. Existing research has identified distinct motivational influences on adolescent SRB, as evidenced by Li and Wu (2017) finding that temporal diversion and self-improvement motives significantly predict reading engagement whereas social interaction and recognition needs primarily drive participatory dimensions. The current literature, however, demonstrates a paucity of empirical investigations examining DRL’s role, with Cho et al. (2017) seminal work constituting a notable exception by establishing that metacognitive strategies (including meaning construction, self-regulation, and source evaluation) significantly enhance secondary students’ critical inquiry competencies following reading activities. The investigation additionally demonstrated that source evaluation serves as a significant moderating variable that enhances the efficacy of both information navigation and textual comprehension strategies. Emerging scholarship, though limited in scope, has progressively examined the DRL-SRB relationship through theoretical and qualitative lenses. He’s (2020) conceptual model positions DRL as an indispensable multidimensional competency in digital environments, comprising behavioral engagement, cognitive processing, and critical evaluation components. This theoretical framework postulates that differential DRL proficiency levels produce observable variations in digital reading practices, thereby establishing literacy as a fundamental determinant of SRB manifestation patterns.
Existing scholarship has yielded significant advancements in SRB research, establishing several well-defined research domains. However, investigations of the DRL-SRB relationship remain largely confined to theoretical conceptualizations, with a marked paucity of empirical quantitative validation. The current literature particularly lacks systematic examination of the mediating mechanisms underlying DRL’s influence on SRB, as noted by Wang et al. (2022a) and Wang et al. (2022b), representing a critical gap requiring rigorous quantitative verification through methodologically sound research designs. Existing research lacks robust investigations into the multivariate influences on SRB, failing to establish a comprehensive theoretical framework that accurately captures the complex, multifaceted nature of this phenomenon (Xu and Zhou, 2021). Moreover, while developmental differences across age groups result in distinct patterns of SRB among minors, existing research has largely overlooked specific demographic cohorts - particularly Chinese students - in its investigations (Xu and Zhou, 2021). Current scholarship demonstrates significant limitations in examining the multivariate determinants of SRB, the current theoretical frameworks and research perspectives concerning student populations in this domain remain insufficiently comprehensive (Xu and Zhou, 2021), consequently yielding underdeveloped tiered SRB theories and suboptimal policy interventions. The present study addresses these limitations by examining DRL and its underlying mechanisms, empirically investigating DRL’s influence on SRB as the primary outcome variable, and ultimately constructing a comprehensive mechanistic model of student SRB patterns. This investigation yields dual substantive contributions to the field: theoretically, it pioneers the application of structural equation modeling to novel pedagogical contexts, providing innovative empirical insights for regulating student SRB patterns; practically, it establishes an evidence-based intervention framework through systematic deconstruction of SRB’s adverse mechanisms, generating actionable policy recommendations for both educational systems and industry practitioners (Song et al., 2024). These multidimensional solutions are designed to simultaneously: (a) foster adolescent development through scientifically-grounded approaches, and (b) drive sustainable advancement in the digital reading sector.
2 Theoretical basis and research hypotheses
Bandura’s Social Learning Theory (alternatively termed Social Cognitive Theory or Triadic Reciprocal Determinism), initially conceptualized in 1952, constitutes a fundamental psychological framework that underscores observational learning as a core mechanism in human behavioral development. This theoretical paradigm maintains that behavioral acquisition occurs not merely through direct reinforcement but predominantly via observation and modeling of others’ actions, with subsequent behavioral modification being mediated by cognitive processing of observed consequences (Bandura, 2018). In examining students’ SRB, extant research has incorporated both social support variables and individual cognitive factors—particularly DRL and reading motivation—into behavioral models (Bandura, 2018). While environmental determinants like social support merit deeper examination, the present investigation prioritizes personal cognitive dimensions given current methodological considerations. Anchored in Social Learning Theory and related conceptual frameworks, this study employs systematic empirical methods to verify the structural relationships underlying SRB phenomena.
2.1 Digital reading literacy and social reading behavior
Drawing on existing research, this investigation hypothesizes a significant positive correlation between students’ DRL and their SRB. As emerging adults in critical developmental transitions, students’ DRL competence serves as a crucial determinant of both academic achievement and psychosocial maturation. Within this conceptual framework, DRL encompasses multidimensional cognitive capabilities including but not limited to: information acquisition, textual integration, critical comprehension, evaluative judgment, metacognitive reflection, and self-regulatory monitoring of linguistically-mediated digital content - all fundamental competencies for attaining personal goals and participating effectively in technology-mediated social practices. This skill represents an essential literacy requirement for effective participation in contemporary digital ecosystems. The cultivation of students’ digital competencies and advanced reading proficiency is crucial for optimizing their engagement with digital reading platforms (Cen, 2020; Zhou et al., 2024), consequently facilitating more sophisticated and socially-embedded digital reading practices characterized by enhanced interaction frequency and operational efficiency. Empirical evidence demonstrates that among the four digital reading strategies (namely acquisition positioning, integrated understanding, evaluation reflection, and monitoring communication) constituting DRL competencies in secondary education contexts, the synergistic application of the latter three strategies (excluding basic information acquisition) significantly enhances the quality of student-generated questioning during digital reading activities (Cho et al., 2017). This strategic competence directly influences both the attainment of digital reading objectives and the cultivation of SRB as a key developmental outcome. These research findings collectively substantiate that DRL proficiency serves as a significant positive predictor of students’ SRB development (Zhou et al., 2024; Cho et al., 2017). Based on the above analysis, this paper proposed the following research hypothesis:
H1: students' DRL has a positive impact on SRB
2.2 The mediating role of social reading motivation
Current empirical studies establish a significant positive correlation between students’ DRL and their SRM. Advanced DRL proficiency enhances readers’ critical capacities in textual analysis, source evaluation, and content selection, thereby optimizing reading goal attainment. This enhanced competency subsequently strengthens SRM through dual mechanisms of self-actualization and informational fulfillment (Zhou et al., 2024; Li et al., 2021). Additionally, advanced DRL proficiency reflects sophisticated information processing capabilities and technical mastery, which serve to significantly enhance SRM. Contemporary research has empirically validated that the dynamic interaction between information literacy competencies and motivational factors synergistically promotes reading performance outcomes in student populations (Li et al., 2021). Based on the above analysis, this paper proposed the following research hypothesis:
H2: students' DRL has a positive impact on their SRM
Empirical evidence substantiates a significant positive relationship between students’ SRM and their subsequent SRB. Functioning as a crucial psychological determinant, SRM operates as the fundamental driving mechanism underlying individuals’ engagement in social reading practices. Research findings indicate that adolescent reading motivation serves as a robust predictor of prosocial behavioral engagement across multiple domains, including moral, communicative, and educational contexts, with behavioral motivation demonstrating particularly strong predictive validity (Li et al., 2021). This relationship has been particularly well-documented in empirical investigations of Shanghai’s urban and rural student cohorts, where SRM demonstrated significant explanatory power and predictive validity for associated reading behaviors (Li et al., 2014). Based on these findings, the current study employed a more geographically diverse sample of students to further verify and extend this proposition. Through comprehensive analysis, we aimed to develop a robust structural equation model that fully captures these behavioral relationships. Therefore, it proposes:
H3: students' SRM has a positive impact on their SRB
Extant empirical studies consistently demonstrate that both DRL and SRM exert significant positive effects on students’ SRB as the dependent variable, with these relationships maintaining statistical significance in multivariate regression analyses. This well-established empirical evidence provides the foundation for H4 in the current investigation. The existing study indicated that intrinsic reading motivation demonstrates a significant positive effect on interest-based reading volume—a key metric of reading engagement (Schiefele et al., 2012). These empirical observations corroborate Wang (2022) findings that revealed significant behavioral divergences in collegiate SRB patterns while specifically establishing the causal effects of reading motivation, multisensory engagement, and associated cognitive factors on reading behavior outcomes. Grounded in these validated relationships and the theoretical foundations supporting H1, we developed an initial multivariate regression framework to rigorously investigate these complex interactions. In summary, it can be inferred that the hypothesis is:
H4: The SRB of students is significantly positively influenced by both their DRL and SRM
Current empirical evidence identifies SRM as a crucial mediating mechanism in the DRL-SRB relationship among student populations. Consistent with prior theoretical development, students’ DRL exhibits a significant positive influence on SRM development. Moreover, as empirically validated through H3 testing, SRM subsequently exerts a substantial facilitative effect on associated reading behaviors. These consistent findings provide empirical support for the proposed mediation model. To further clarify and verify the role of DRL in students, the following research hypothesis was proposed:
H5: students' DRL has a positive impact on SRB as the dependent variable through SRM
3 Research design
3.1 Sample collection
This investigation implemented a hybrid data collection methodology incorporating both digital and paper-based self-report questionnaires, with modality selection determined by participant accessibility and response preferences to maximize engagement. The research instrument was specifically designed to operationalize four latent constructs through psychometrically validated items, with particular emphasis on three principal reading-related dimensions: DRL, SRM, and SRB. These theoretical constructs were systematically operationalized into quantifiable measures using psychometrically validated scale items specifically developed for this investigation. Each measurement instrument was meticulously designed to comprehensively assess the core dimensions of their respective constructs, with participants’ aggregated responses serving as empirical proxies for the underlying theoretical variables. The study targeted four premier Chinese metropolitan regions—Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen—selected as primary research sites based on their established preeminence in global urban development indices and comprehensive socioeconomic advancement. These cities have persistently demonstrated global leadership in educational innovation and cultural transformation, rendering them ideal research contexts for examining modern reading patterns and behavioral dynamics (Liu et al., 2024). Investigating social reading phenomena within these metropolises yields particularly representative data on China’s cutting-edge developments in this domain, while simultaneously generating transferable insights that may inform policy and practice across diverse regional and international contexts. This study employed a multi-modal data collection strategy across China’s four most economically advanced metropolitan areas (Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen) during December 2023–February 2024. The research methodology incorporated both digital (Wenjuanxing platform) and traditional paper-based administration channels, yielding 2,046 online responses complemented by 327 physical questionnaires, ultimately producing a robust final dataset comprising 2,360 validated surveys. Following comprehensive data cleansing procedures for both digital and hardcopy questionnaires, we systematically eliminated invalid responses based on the following exclusion criteria: (a) responses exhibiting discernible patterns or mechanical answering behavior; (b) questionnaires with excessive missing values (exceeding 15% of total items); (c) responses containing significant internal inconsistencies; and (d) submissions completed in implausibly short time frames indicative of inattentive responding. Following rigorous data validation, we retained 2,033 valid online questionnaires and 314 valid paper-based questionnaires, yielding a final sample of 2,347 qualified responses. This represents an exceptional validity rate of 99.45%. The sample size substantially exceeds psychometric requirements, with an observation-to-variable ratio of 26.67: 1, ensuring robust statistical power for subsequent analyses.
3.2 Variable design
The study focused on three principal theoretical constructs: SRB, DRL, and SRM. Within the analytical model, SRB was operationalized as the criterion variable, DRL as the key predictor variable, and SRM as the proposed mediating variable. For construct measurement, the study adapted validated scales from existing literature, with contextual modifications to ensure appropriateness for social reading research and adolescent populations, ultimately comprising 73 scale items across all measures. The readers can find all the relevant parts of the questionnaire used in Appendix.
The assessment of students’ DRL utilized the Reading Literacy Prediction Index Scale, originally validated in the OECD’s PISA 2009 framework (OECD, 2024), which has demonstrated robust psychometric properties in prior DRL research by Zhu and Li (2018). For measuring SRB, the study incorporated adapted versions of established instruments from Li and Wu (2017) work and Li et al. (2015) Online Social Behavior Scale, ensuring measurement validity while maintaining contextual relevance. The selection of these measurement instruments was based on their established theoretical congruence with the current investigation’s framework and empirically demonstrated validity within Chinese educational settings. Their operational feasibility and demonstrated capacity to capture authentic behavioral manifestations among Chinese student populations further substantiated their methodological appropriateness. For assessing SRM, the study employed psychometrically validated instruments from Li (2014) and Li and Wu (2017), applying identical rigorous selection criteria as with the aforementioned scales. All measurement instruments in this study adopted a standardized five-point Likert scale to maintain response consistency and enhance metric precision. For the two newly adapted scales measuring SRB and motivation in student populations, 236 valid responses were obtained through convenience sampling procedures. Psychometric analyses revealed excellent scale reliability, with Cronbach’s α coefficients reaching 0.83 and 0.90, respectively. The KMO measure of sampling adequacy produced values of 0.912 and 0.93, while Bartlett’s test of sphericity showed statistically significant results (p < 0.001) for both constructs, collectively verifying the dataset’s suitability for factor analysis.
3.3 Data analysis methods
The research implemented a tripartite analytical framework to ensure methodological robustness. Initial analyses encompassed comprehensive reliability and validity examinations conducted in SPSS 27.0 and AMOS 28.0, augmented by common method variance evaluation to control for potential measurement biases. The second stage involved testing the mediation model through an integrated approach combining structural equation modeling with the Bootstrap resampling method. Subsequently, a comprehensive structural equation model was developed using AMOS 28.0, followed by rigorous model fit evaluation. In the final stage, to enhance the precision and robustness of the findings, multiple pathways influencing students’ SRB were systematically examined. The Bootstrap procedure in AMOS 28.0 was then implemented to empirically validate the hypothesized relationships.
3.4 Descriptive statistics analysis
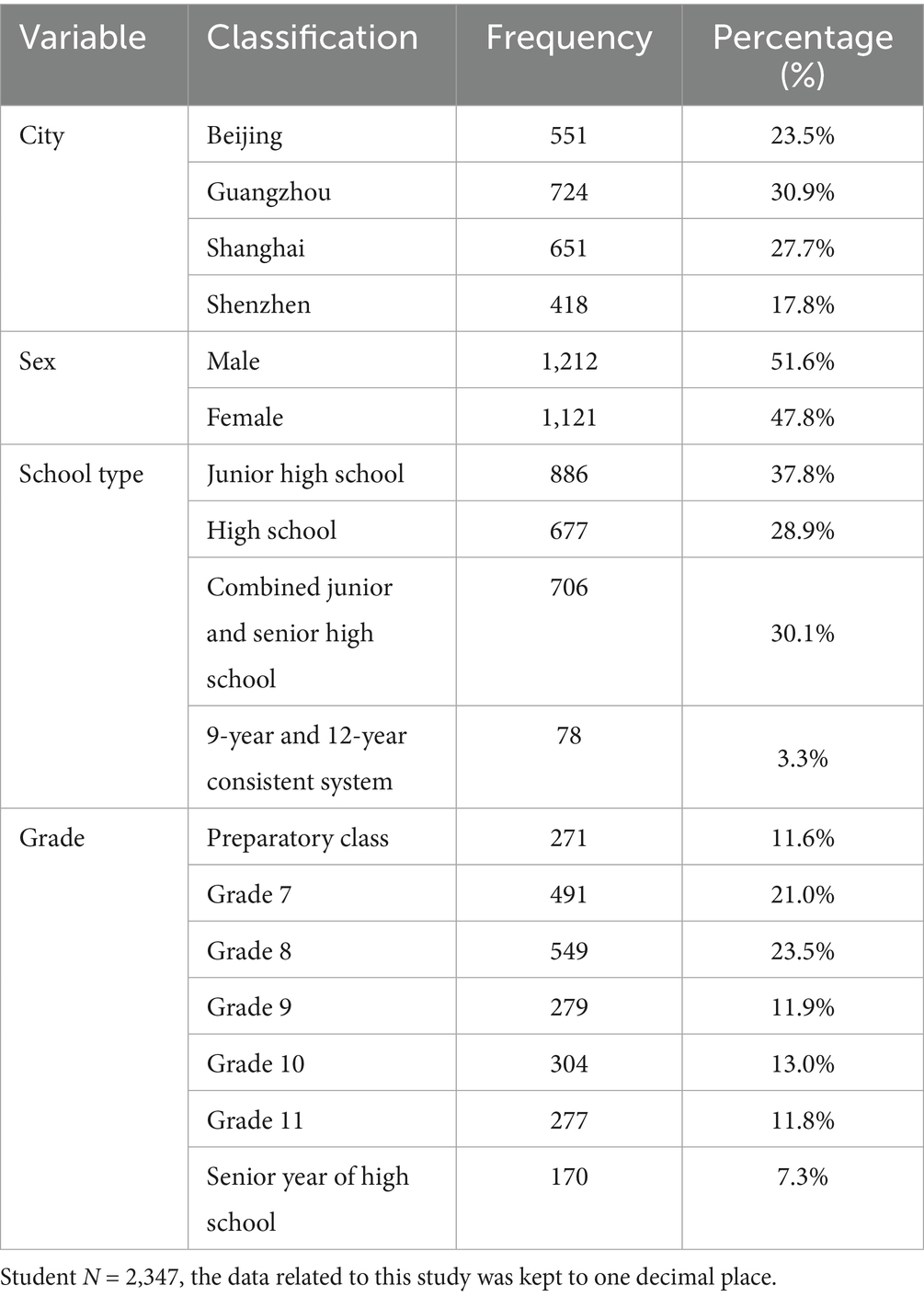
Table 1 presents the descriptive statistics for the study’s final sample (N = 2,347), comprising exclusively urban respondents distributed across four major Chinese metropolitan areas: Beijing (23.5%, n = 551), Guangzhou (30.9%, n = 724), Shanghai (27.7%, n = 651), and Shenzhen (17.8%, n = 418). The geographical distribution demonstrates balanced representation across research sites, with no statistically significant disproportionality observed in regional sample composition. Gender composition was nearly equivalent, comprising 1,212 males (51.6%) and 1,121 females (47.8%). School type distribution included: 886 students (aged 12/13–15/16) from Junior high school (37.8%), 677 high school students (28.9%, aged 15/16–18/19), 706 complete students (30.1%, aged 12/13–18/19), and 78 students in 9–12 continuous education programs (3.3%, aged 12/13–18/19). The sample distribution revealed predominant representation from the three primary educational categories. Grade-level composition included: preparatory class students (a Shanghai-specific program; 11.6%, n = 271), junior high school grades 1–3 (21.0%, n = 491; 23.5%, n = 549; 11.9%, n = 279 respectively), and senior high school grades 1–3 (13.0%, n = 304; 11.8%, n = 277; 7.3%, n = 170 correspondingly). The observed underrepresentation of senior secondary students in the sample may reflect reduced survey participation rates attributable to intensified academic demands characteristic of this pivotal educational transition period. The descriptive statistics of sample characteristics demonstrate that the study achieved reasonably balanced and representative population coverage.
4 Research result
4.1 Scale testing
4.1.1 Common method deviation test
Common method variance was evaluated through Harman’s single-factor test in SPSS 27.0. Principal component analysis extracted seven factors with eigenvalues exceeding 1.0, cumulatively accounting for 68.51% of total variance. The initial factor explained 17.78% of variance, significantly below the 40% critical threshold, thereby confirming the absence of substantial common method bias in the dataset.
4.1.2 Reliability and validity testing
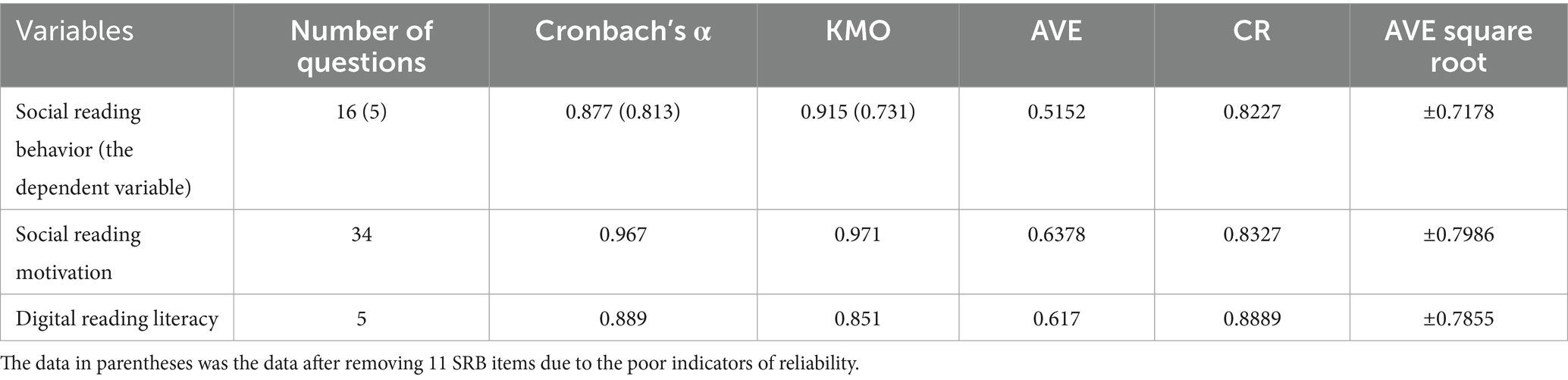
The statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 27.0. As demonstrated in Table 2, all Corrected Item-Total Correlation (CITC) coefficients for SRB and its corresponding observed variables surpassed the psychometric threshold of 0.4, while Cronbach’s α values exceeded the conventional 0.7 reliability benchmark, indicating strong internal consistency. This pattern was replicated for both SRM and DRL constructs, with all CITC values maintaining >0.4 correlations and Cronbach’s α coefficients consistently above 0.7, thereby robustly validating the measurement reliability across all theoretical constructs under investigation.
Content validity assessment confirmed robust psychometric properties for the SRB, SRM, and DRL measurement scales, establishing their appropriateness for subsequent factor analysis. The KMO measure of sampling adequacy and Bartlett’s test of sphericity were systematically computed for each latent construct. Analytical results demonstrated KMO values of 0.915 (post-adjustment: 0.731), 0.971, and 0.851 for SRB, SRM, and DRL, respectively—each surpassing the conventional 0.7 benchmark for factor analytic suitability. Bartlett’s test yielded a significance level of p = 0.000, well below the 0.05 cutoff, confirming excellent suitability for factor analysis (detailed in Table 2).
The convergent validity of the three constructs (SRM, DRL, and SRB) was empirically verified through rigorous testing. Exploratory factor analysis was employed to examine construct validity and factor loading patterns, resulting in the elimination of select SRB items to enhance measurement model specification (see Table 2 for complete results). The analysis yielded the following psychometric indices: SRB AVE = 0.5152, square root 0.7178, combined reliability CR = 0.8227, SRM AVE = 0.6378, square root 0.7986, CR = 0.8327, DRL AVE = 0.617, square root 0.7855, CR = 0.8889 > 0.7. All constructs met established validity criteria, with standardized factor loadings >0.5, composite reliability (CR) values >0.7, and average variance extracted (AVE) estimates >0.5, collectively demonstrating robust measurement properties. These results collectively provide strong evidence for the convergent validity of each construct.
4.1.3 Correlation statistical analysis
Discriminant validity assessment was conducted using Amos 28.0 and SPSS 27.0, revealing significant positive interconstruct correlations: SRB-SRM (r = 0.756, p < 0.01), SRB-DRL (r = 0.661, p < 0.01), and SRM-DRL (r = 0.707, p < 0.01). These statistically robust relationships, detailed in Table 3, demonstrated adequate discriminant validity while simultaneously providing empirical support for the theoretical linkages essential to subsequent hypothesis testing.
4.1.4 Confirmatory factor analysis
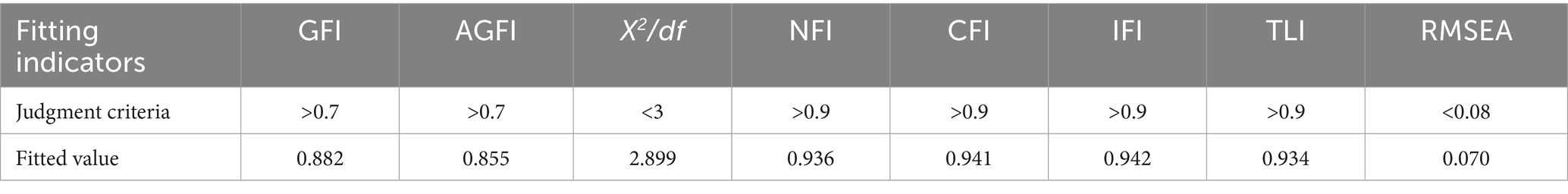
The study conducted comprehensive goodness-of-fit evaluation for the revised theoretical model. Utilizing Amos 28.0 with maximum likelihood estimation, the structural equation modeling analysis yielded the following fit indices: GFI = 0.882, AGFI = 0.855, CMIN/DF = 2.899, NFI = 0.936, CFI = 0.941, IFI = 0.942, TLI = 0.934, and RMSEA = 0.070. Although traditional benchmarks recommend GFI and AGFI values >0.90, contemporary psychometric research (Musa et al., 2021; Anh et al., 2019; Wu, 2009) has established ≥0.70 as acceptable thresholds. As evidenced in Table 4, all model fit indices satisfied these updated criteria, collectively demonstrating that the revised model exhibits statistically adequate fit with the empirical data while maintaining strong explanatory power across eight key fit metrics.
In conclusion, the confirmatory factor analysis conclusively established the measurement model’s psychometric adequacy, with rigorous empirical testing demonstrating excellent scale reliability and construct validity. These results demonstrate that the scales employed exhibit satisfactory stability, strong reliability, and robust effectiveness, thereby ensuring their appropriateness for the current research context.
4.2 Hypothesis testing
4.2.1 Direct effect test
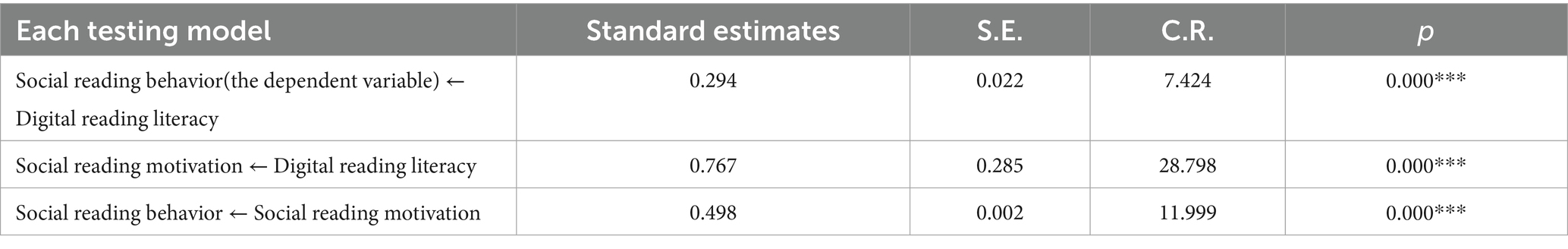
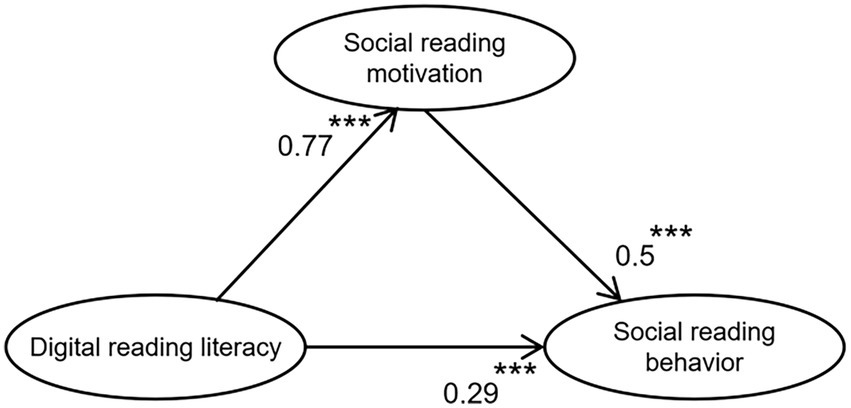
The statistical analyses revealed a significant positive association between students’ DRL and their SRB, thereby confirming H1. The analysis yielded a standardized regression coefficient of β = 0.294 (p < 0.001), indicating a substantial and highly significant relationship between these constructs.
The statistical analyses demonstrated a significant positive association between students’ DRL and SRB, thus empirically validating H2. The DRL of students had a positive impact on their SRM, and the standardized regression coefficient of the impact of DRL on their SRM was 0.767, p < 0.001, passed the significance test (Table 5).
Through conducting a significance test, it was found that the SRM of students had a positive impact on SRB, indicating the validity of H3. The standardized regression coefficient of the influence of high school students’ SRM on their SRB was 0.498, p < 0.001, passed the significance test.
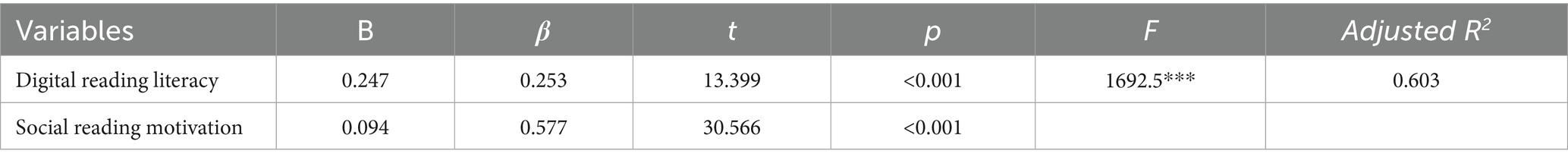
4.2.2 Intermediary effect test
The analytical results provided empirical support for H4, confirming that both DRL and SRM exerted statistically significant effects on students’ SRB. A multiple linear regression analysis was conducted to examine these relationships (see Table 6 for complete results). Diagnostic tests revealed that both independent variables (DRL and SRM) had variance inflation factor (VIF) values of 1.999, well below the threshold of ten, indicating no concerning multicollinearity between predictors. Additionally, the regression diagnostics yielded a Durbin-Watson statistic of 1.944, closely approximating the optimal value of 2.0, thereby confirming observation independence and absence of significant residual autocorrelation. The model exhibited exceptional goodness-of-fit [F(2, df) = 1692.5, p < 0.001], accounting for 60.3% of SRB variance (R2 = 0.603). Both predictors demonstrated significant positive effects: DRL (β = 0.253, p < 0.001) and SRM (β = 0.577, p < 0.001), collectively providing robust empirical support for H4. These results confirm the model’s strong explanatory power and statistical validity in predicting students’ social reading behaviors.
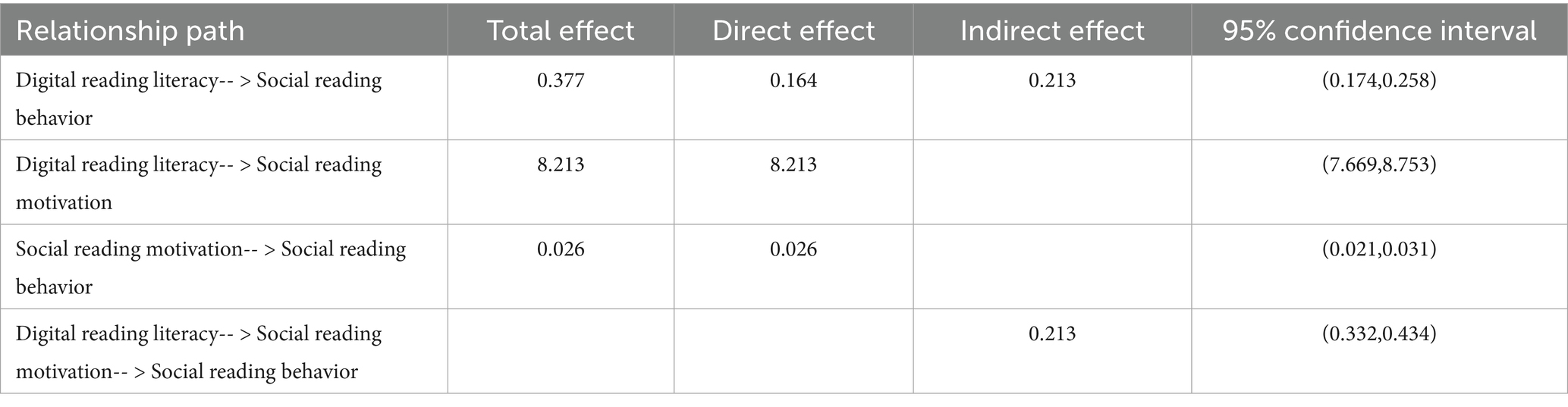
This study confirmed H5, demonstrating that DRL among students positively influenced SRB through the mediating role of SRM, with this indirect effect being statistically significant (see Table 7). To rigorously examine SRM’s mediating effect in the SRB model, we performed a Bootstrap analysis (N = 5,000 iterations) with 95% confidence intervals using Amos 28.0. According to Figure 1 and Table 7, it can be seen that the SRM of students did play a mediating role in the SRB model, with an indirect effect value of 0.213 and a 95% confidence interval of [0.332, 0.434], excluding the 0 value. These findings provide robust support for H5, establishing SRM as a significant mediator in the relationship between DRL and SRB.
5 Conclusion and discussion
5.1 Research conclusion
Drawing upon social learning theory, this study investigated the mechanisms underlying SRB among 2,347 students sampled from four most developed cities in China. Through comprehensive data analysis and hypothesis testing, we identified two distinct pathways of influence: (a) direct effects and (b) mediation effects.
Firstly, structural equation modeling analysis confirmed that both DRL and SRM among students positively influenced their SRB, with DRL additionally exerting a positive effect on SRM. The three principal findings were rigorously validated through comprehensive psychometric analyses. Mediation analysis employing bootstrap resampling methodology (N = 5,000) confirmed SRM’s statistically significant mediating role in the DRL-SRB relationship (β = 0.213, 95% CI [0.187, 0.241], p < 0.001). This mediation effect underscores DRL’s role as a fundamental psychological mechanism underlying SRB formation, demonstrating its broad and substantial influence as a specialized literacy construct in shaping reading-related psychological variables.
5.2 Discussion
The analysis revealed a significant positive direct effect of students’ DRL on their SRB, with higher DRL proficiency consistently predicting more frequent SRB engagement. These findings empirically corroborate prior research (Cho et al., 2017; Zhou et al., 2024) by quantitatively establishing the DRL-SRB relationship while illuminating DRL’s crucial role in modulating observable reading practices. The results highlight the significant role of DRL in shaping external reading behaviors and elucidate the operational mechanism of the DRL blind box phenomenon. This relationship can be explained by several factors. Students with advanced DRL demonstrate superior competencies in digital information retrieval, critical interpretation, and discriminative evaluation, coupled with enhanced self-regulatory capacity. This multifaceted literacy profile enables more effective goal attainment and personal objective fulfillment through social reading platforms. Their sophisticated skill set facilitates proactive risk mitigation and negative outcome reduction in digital environments, thereby significantly increasing both the frequency and quality of their SRB engagement. Conversely, students with underdeveloped DRL encounter significant cognitive and operational challenges in digital reading contexts. These persistent difficulties may initiate a self-perpetuating cycle of negative reinforcement, wherein successive unsuccessful experiences progressively diminish both the frequency and quality of SRB engagement, potentially culminating in reduced participation in or complete avoidance of SRB.
The investigation empirically established a significant positive association between students’ DRL and SRM, with advanced DRL levels consistently predicting stronger motivational engagement. These findings corroborate prior research (Li et al., 2021; Liu et al., 2018) while extending the evidence base through rigorous analysis of empirical data from China’s most technologically advanced urban centers. The results not only confirm DRL’s fundamental role in fostering reading motivation but also provide novel empirical insights for understanding the literacy-motivation-behavior continuum in digital environments (Song et al., 2024). This observed relationship operates through a dual mechanism of benefit realization and Matthew Effect dynamics. Students with superior DRL proficiency demonstrate enhanced capacity to achieve reading objectives and extract maximal utility from social reading platforms, thereby reinforcing their motivational engagement through successful experience accumulation. Conversely, DRL deficiencies disrupt this virtuous cycle, as inadequate literacy skills impede effective platform utilization, potentially triggering a downward spiral of motivational attrition through repeated unsuccessful experiences and diminishing returns.
The analysis revealed a significant positive direct relationship between students’ SRM and their SRB, with increasing motivational levels predicting proportionally higher behavioral engagement. These results substantiate previous findings (Yi, 2022; Li et al., 2014; Rebecca et al., 2022) while addressing a critical geographical limitation in prior research through the inclusion of representative samples from Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, and Shenzhen. By incorporating these technologically advanced urban populations, the current study not only reinforces the SRM-SRB linkage but also extends theoretical understanding of motivation-behavior dynamics in contemporary digital reading contexts. The underlying rationale for this relationship lies in the nature of reading motivation. Although a multifaceted construct, the aggregate level of reading motivation typically influences reading behavior (Lau, 2009). This established principle maintains its explanatory power in social reading contexts, where motivational antecedents systematically precede and shape corresponding behavioral manifestations. Consequently, effective interventions to enhance student engagement in social reading should adopt a motivation-centric approach, specifically targeting four core motivational dimensions: self-development, peer identification, information acquisition, and social interaction.
The study established a significant mediation pathway wherein students’ DRL positively influences SRB through the intermediary role of SRM. This mechanism operates such that elevated DRL levels enhance SRM intensity, which in turn increases SRB frequency. Although prior research has not explicitly verified this complete mediation sequence, our findings conceptually integrate existing evidence documenting: (a) DRL’s positive impact on SRM, and (b) SRM’s behavioral consequences (Li and Wu, 2017; Li et al., 2014; Sun et al., 2019). This mediation mechanism highlights DRL’s crucial and multiple effects in shaping both SRM and behavioral outcomes. The positive influence on behavioral outcomes underscores that DRL has evolved into an essential competency for students operating in digital learning environments (Wang et al., 2022a; Wang et al., 2022b). Enhancing digital reading literacy constitutes a pivotal educational imperative for educators, policymakers, and relevant stakeholders, as it directly contributes to the improvement of both social-based reading and digital reading proficiency among secondary school students. As demonstrated through comprehensive analysis and illustrated in Figure 1, students’ SRB was significantly affected through both direct pathways and mediated mechanisms by DRL, with the magnitude of both direct and total effects exceeding the isolated direct impact of SRM. This comparative empirical finding makes a substantive theoretical contribution to the existing literature, as previous scholarship has failed to systematically establish such differential effect patterns between these critical constructs. This study makes a dual contribution by both advancing the theoretical conceptualization and furnishing robust empirical evidence demonstrating that DRL exerts a substantially greater influence on social SRB than does SRM–the latter having been conventionally considered the most proximal psychological antecedent of behavioral outcomes in prior research (Li and Wu, 2017; Peng and Xiao, 2022; Li et al., 2014; Li, 2014). These findings not only significantly enrich the current theoretical paradigm but also indicate that, in the context of widespread digitalization, fostering digital reading literacy should be prioritized over enhancing reading motivation in educational interventions targeting students’ reading development. Accordingly, both future scholarly investigations and pedagogical practices necessitate a fundamental reconceptualization of their theoretical frameworks and cognitive orientations, with particular emphasis on recognizing DRL’s critical mediating role and strategically harnessing its pivotal function in facilitating SRB enhancement.
5.3 Theoretical value
Firstly, this study makes significant theoretical by constructing a micro-level mechanism model that delineates the causal pathways through which DRL influences SRB. Whereas prior investigations Li and Wu (2017) predominantly focused on examining isolated variables and their direct effects, the current research advances the field by capturing the complex, multi-dimensional mechanisms that underpin SRB formation in social media environments. Through a systematic exploration of both direct and mediated pathways in students’ social reading processes, this study extends the theoretical framework and provides more comprehensive empirical evidence regarding the interconnected variables influencing social reading. The findings not only empirically validate SRB’s mediating role but also offer sophisticated insights into its dual-pathway impact mechanisms.
Secondly, this study broadened the research perspective by expanding the theoretical lens through which SRM is examined. While prior scholarship (Festl, 2021) has predominantly focused on investigating SRM’s direct effects, the present research employs rigorous empirical methods to uncover previously neglected mediation pathways, with particular emphasis on DRL’s pivotal role. Although our analysis confirms SRB’s significant mediating function, the results reveal that DRL exerts a substantially stronger influence on SRB compared to SRM. This critical finding represents a meaningful theoretical advancement in understanding the complex interplay between these key constructs in digital reading contexts.
5.4 Practical logic
For educational stakeholders, particularly students and their guardians, strategic emphasis should be placed on cultivating DRL and associated digital competencies through autonomous learning initiatives. Parental involvement should focus on curating and facilitating access to premium metacognitive resources and digital literacy materials, while actively promoting reflective engagement to enhance metacognitive capabilities. Furthermore, leveraging extended academic breaks presents an optimal opportunity for student participation in rigorously designed hybrid (online-offline) reading literacy enhancement programs. Through these proactive measures, students can consistently maintain and improve their DRL levels while simultaneously developing and sustaining high-quality SRB (Rebecca et al., 2022). For middle schools and district-level administrative bodies must institutionalize the progressive cultivation of students’ DRL as a core educational objective, while simultaneously ensuring the provision of pedagogically sound learning ecosystems and evidence-based instructional resources to facilitate comprehensive literacy development. Educational institutions should systematically cultivate profound reading engagement through a multi-tiered pedagogical framework encompassing structured literacy routines (e.g., morning/evening reading sessions), discipline-specific language instruction, specialized reading curricula, and intensive holiday reading programs. Concurrently, schools must implement strategic behavioral scaffolding through ongoing academic monitoring and differentiated co-curricular interventions to optimize students’ digital reading practices. The systematic development of reading competencies and literacy cultivation should be strategically positioned as a fundamental pillar in institutional academic culture building. Well-equipped educational establishments are recommended to implement innovative pedagogical pilot programs, incorporating rigorous assessment mechanisms to evaluate both the effectiveness and practical implications of these specialized interventions (Pinto and Leite, 2020). These evidence-based initiatives will yield critical empirical data to inform the formulation of future educational policies and the establishment of research-informed instructional benchmarks.
For digital reading platforms targeting educational purposes, the strategic development of developmentally appropriate digital ecosystems-with particular emphasis on adolescent and young adult user groups-represents an effective approach to enhance student engagement and literacy outcomes. Through the implementation of user-centric interface architectures incorporating gamified interactive components, these platforms can optimize user engagement while simultaneously cultivating sustained reading motivation and habitual literacy practices. The interface design must integrate advanced social connectivity features to enable collaborative knowledge construction and participatory community learning. Furthermore, platform administrators should develop hybrid engagement strategies that synergize online and offline interactions, focusing on culturally relevant intellectual properties and contemporary discourse themes. Such initiatives may include the creation of specialized reading communities designed to harness collective intelligence mechanisms, thereby amplifying reading participation and facilitating comprehensive literacy acquisition.
5.5 Research limitations and prospects
This study presents several limitations that must be acknowledged while simultaneously illuminating productive avenues for future investigation. Methodologically, the investigation focused exclusively on students from four metropolitan areas during a fixed time period, consequently limiting our capacity to examine longitudinal developmental trajectories during this crucial period of cognitive and behavioral maturation. This methodological constraint has resulted in an incomplete understanding of the full developmental progression of SRB formation and transformation. Moreover, the current model lacks latent variables, which makes the model relatively simple and can only draws less robust findings. To address these limitations, we strongly advocate for future research employing longitudinal research designs with more geographically diverse sampling frames to more comprehensively capture the dynamic developmental processes underlying SRB evolution.
As a nascent field of inquiry, research on SRB’s impact mechanisms would benefit substantially from incorporating a more comprehensive set of determinants, including both intrinsic psychological constructs (e.g., self-efficacy, personality development) and extrinsic contextual variables (e.g., family socioeconomic status, information and communication technology proficiency). The adoption of interdisciplinary theoretical lenses would facilitate the development of more sophisticated conceptual frameworks, potentially generating dual substantive contributions: (a) practical insights to optimize users’ SRB engagement, and (b) conceptual advances to refresh academic discourse in this field.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements, written informed consent from the participants’ legal guardian/next of kin was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
WZ: Writing – original draft. YW: Writing – review & editing. LJ: Supervision, Project administration, Validation, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This paper is the research findings of the project “Research on Digital Reading Behavior of Adolescents from the Perspective of Social Learning” (encoded 21BTQ027), supported by the 2021 National Social Science Fund of China (NSSFC).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Anh, T. T., Hanb, P. H., Cam, L. N. T., Van, K. P., and Dinh, L. N. (2019). A study of the factors affecting the content created by international travelers in Vietnam. Manag. Sci. Lett. 9, 2051–2062. doi: 10.5267/j.msl.2019.7.001
Bandura, (2018). The social basis of thought and action: Social cognitive theory. Shanghai: East China Normal University Press.
Cen, J. (2020). Xiaoxuesheng shuzihua yuedusuyang diaocha yanjiu [research on digital Reading literacy of primary school students]. PhD diss., Chongqing: Xinan daxue [Chongqing: Southwest University]. doi: 10.27684/d.cnki.gxndx.2020.000596
China Academy of Press and Publication. (2022). Diershiyici quanguo guominyuedu diaocha jieguo fabu [the results of the 21st National Reading Survey Have Been Released]. Available online at: https://www.nppa.gov.cn/xxfb/ywdt/202404/t20240424_844803.html (accessed June 5, 2025).
Cho, B.-Y., Woodward, L., Li, D., and Barlow, W. (2017). Examining adolescents’ strategic processing during online reading with a question-generating task. Am. Educ. Res. J. 54, 691–724. doi: 10.3102/0002831217701694
Festl, R. (2021). Social media literacy & adolescent social online behavior in Germany. J. Child. Media. 15, 249–271. doi: 10.1080/17482798.2020.1770110
He, J. (2020). Jiyu yuedu yingxiang shijiao de duzhe shuziyuedusuyang wenti yanjiu [research on problems of digital Reading literacy of readers from the perspective of Reading influence], vol. 8. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Printing and Technology, 9–10. doi: 10.26968/d.cnki.gbjyc.2020.000086
He, C. (2023). Qingnian shejiaohua yuedu qushi yanjiu [investigating social Reading trends among youth populations]. Renmin Luntan [People's Forum] 5, 104–106.
Lau, K.-L. (2009). Reading motivation, perception of reading instruction and reading amount: a comparison of junior and senior secondary students in Hong Kong. J. Res. Read. 32, 366–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9817.2009.01400.x
Li, W. (2014). Qingshaonian shehuihua yuedu dongji yanjiu [the motivation of adolescents' social Reading: a case study of middle school students' Reading via WeChat in Shanghai]. Zhongguo Tushuguan Xuebao 40, 115–128. doi: 10.13530/j.cnki.jlis.146011
Li, H., Jia, L., and Ye, H. (2021). Xinxi suyang dui xuesheng yu-edu nengli de yingxiang--Jiyu PISA2018 guoji paiming de shizheng fenxi [the effects of information literacy on students' Reading ability: an empirical analysis based on PISA 2018 international ranking]. Guowai Jiaoyu Yanjiu 48, 98–116.
Li, W., and Wu, Y. (2017). Adolescents’ social reading: motivation, behaviour, and their relationship. Electron. Libr. 35, 246–262. doi: 10.1108/EL-12-2015-0239
Li, W., Wu, Y., and Liu, Y. (2014). Qingshaonian shehuihua yuedu dongji yu xingwei zhi guanxi yanjiu [study on relationship between adolescents’ social Reading motivation and their behaviors: a case study of middle school students’ Reading via WeChat in Shanghai]. Tushu Qingbao Yanjiu 58, 61–68. doi: 10.13266/j.issn.0252-3116.2014.23.009
Li, J., Xiao, R., and Wu, L. (2015). Weibo/Weixin wangluo shejiaoxingwei liangbiao bianzhi jiqi zai daxuesheng zhong yingyong de xinxiaodu fenxi [development of the microblog / Wechat Nework social behavior scale and the measurement of its reliability and validity]. Zhongguo Xuexiao Weisheng 36, 1338–1341. doi: 10.16835/j.cnki.1000-9817.2015.09.020
Liu, Kangxia. (2024). The top 100 cities in China for social development (2023) has been released, with Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen ranking among the top three. Available online at: https://news.ecust.edu.cn/2023/1227/c160a177616/page.htm (Accessed June 29, 2025).
Liu, X., Guo, H., and Yue, A. (2018). Qingshaonian jiating yuedu huanjing, yuedu dongji he yuedu suyang de xiangguanxing yanjiu [research on project - based teaching method of document retrieval course]. Hebei Keji Tuyuan 31, 57–60. doi: 10.13897/j.cnki.hbkjty.2018.0030
Liu, S., Guo, L., Zheng, Q., and Wang, H. (2024). Mianxiang shuzi changjing de yuedusuyang ceping:Neihan jieding, yaosu jiegou, gongju shej-i yu sh-uju biaozheng [development and application of an evaluation model for the teaching effectiveness of online courses in universities based on the principles of standardization, precision, and qualitative analysis]. Zhongguo Dianhua Jiaoyu 9, 60–68.
Musa, A. F., Ysin, M. S. M., Simth, J., Yakub, M. A., and Nordin, R. B. (2021). The Malay version of SF-36 health survey instrument: testing data quality, scaling assumptions, reliability and validity in post-coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) surgery patients at the National Heart Institute (Institut Jantung Negara—IJN), Kuala Lumpur. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 19, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12955-020-01658-9
OECD. (2024). PISA 2009 results: what students know and can do: student performance in Reading, mathematics and science (Volumn I). https://www.oecd.org/pisa/pisaproducts/48852548.pdf (Accessed on June 5, 2025).
Peng, S., and Xiao, N. (2022). Zhongxuesheng shuziyuedu dongji ji tuiguang celue yanjiu [research on motivation and promotion strategies of middle school students' digital Reading]. Tushuguan Jianshe. 318, 53–63. doi: 10.19764/j.cnki.tsgjs.20221760
Pinto, M., and Leite, C. (2020). Digital Technologies in Support of students learning in higher education: literature review. Digital Educ. Rev. 37, 343–360. doi: 10.1344/der.2020.37.343-360
Rebecca, J. M. G., Mary, H. I-Y., Emily, G., Luara, R., Saara, M., Ellyn, P., et al. (2022). Becoming literate: educational implications of coordinated neuropsychological development of reading and social-emotional functioning among diverse youth. Literacy Research: Theory, Method, and Practice. 71, 80–132. doi: 10.1177/23813377221120107
Schiefele, U., Schaffner, E., Moller, J., and Wigfield, A. (2012). Dimensions of reading motivation and their relation to reading behavior and competence. Read. Res. Q. 47, 427–463. doi: 10.1002/RRQ.030
Song, J., Feng, Y., and Cheng, J. (2024). Dongji he renzhicelue dui qingshaonian shuziyuedusuyang yingxiang yanjiu [investigating motivational and cognitive influences on adolescent digital Reading literacy: a fuzzy-set qualitative comparative analysis of 510 survey responses]. Tushuguanxue Yanjiu. 45, 96–107. doi: 10.15941/j.cnki.issn1001-0424.2024.05.013
Sun, T. (2023). Jiyu tubianjishufa de shehuihua yuedu xingwei fenxi [analysis of social Reading user behavior based on CPM: a case study of we read]. Qingbao Kexue 41, 148–154. doi: 10.13833/j.issn.1007-7634.2023.10.017
Sun, T., Li, X., and Xu, C. (2019). Shehuihua yuedu yonghu chixu shiyong yiyuan de shejiao yinsuyuan fenxi [Meta-analysis of social factors on continuous use intention of social Reading users]. Shuzi Tushuguan Luntan 11, 21–28.
Teng, Y. (2015). Quanmin yuedu shiyu xia daxuesheng shuziyuedu qingxiang diaocha—yi shanghai xiju xueyuan weili [investigation on the digital Reading tendency of college students in Nationwide Reading: an example of Shanghai theatre academy]. Shuzi Tushuguan Luntan 6, 45–48.
Wang, Y. (2022). Daxuesheng shejiaohua yuedu xingwei leixing jiqi yingxiang yinsu yanjiu--Yi weixin dushu weili [research on social Reading behavior types and influencing factors of college students-taking WeChat Reading as an example]. M.D. thesis. Chengdu: Xin’An jiaotong daxue [Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University].
Wang, Y., Li, N., Xuan, N., Yin, Y., and Liu, C. (2022a). Jiyu cengcifenxifa de shuziyuedusuyang pingce zhibiao tixi jiangou yanjiu [constructing analytic hierarchy process method for digital Reading literacy evaluation index system]. Xiandai Yuanjuli Jiaoyu. 202, 1172–1173. doi: 10.13927/j.cnki.yuan.20220516.005
Wang, Y., Li, N., Yin, Y., and Liu, C. (2022b). Cong zaixian dao yuce: Jiyu BP shenjing wangluo de zhongxiaoxuesheng shuziyuedusuyang pingce tidxi yanjiu [from reproduction to prediction: research on digital Reading literacy evaluation system for primary and secondary school students based on Back-propagation neural network]. Dianhua Jiaoyu Yanjiu 43, 68–76. doi: 10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2022.08.009
Wu, M. (2009). Structural equation modeling-operation and application of AMOS. Chongqing: Chongqing University Press.
Xu, X., Daniel, Z., and Li, Y. (2024). 2023 niandu zhongguo shuziyuedu baogao fabu--shuziyuedu shichang guimo maishang xintaijie [the "2023 China digital Reading report" has been released: The scale of the digital Reading market has reached a new level]. Guangming Ribao. doi: 10.28273/n.cnki.ngmrb.2024.001843
Xu, L., and Zhou, Y. (2021). Woguo shuziyuedu yanjiu zhishitupu fenxi--Jiyu CSSCI qikan lunwen [knowledge map analysis of digital Reading research in China: based on CSSCI journal papers]. Chuban Kexue 29, 84–96. doi: 10.13363/j.publishingjournal.20211117.007
Yan, L., and Yang, X. (2023). Shuzihua yuedu yu yuedusuyang tisheng yanjiu [enhancing Reading literacy through digital Reading: a comprehensive study]. Chuban Guangjiao. 31, 75–79. doi: 10.16491/j.cnki.cn45-1216/g2.2023.22.013
Yi, Y. (2022). Zshidai daxuesheng shehuihuayuedu shejiao xingwei yingxiang yinsu yanjiu [research on influencing factors on the Z-generation college students’ social behaviors]. M.D. thesis, vol. 12. Shanghai: Huadong shifan daxue [Shanghai: East China Normal University], 72–75. doi: 10.27149/d.cnki.ghdsu.2022.003452
Yin, Guoqiang. (2017). Ertong shuzihua yuedu yanjiu--Jiyu ren·jishu·wenhua de tonghe shijiao [research on children's digital Reading-based on the integrated perspective of human, technology, and culture]. PhD diss., Chongqing: Xinan daxu-e [Chongqing: Southwest University]
Zhao, H., and Hou, P. (2023). Chongxin buluohua:Shuzi shidai shehuihua yuedu changjinggoujian ji lujingchongsu [retribalization: the evolution and transformation of social Reading practices in the digital era]. Zhongguo Chuban 24, 3–9.
Zhou, J., Wang, H., and Yang, F. (2024). Mianxiang zhishifuwu de shuziyuedu shengtai xitong de goujian ji yunxing jizhi yanjiu [research on the development and operation mechanism of the digital Reading ecosystem oriented to knowledge service]. Tushuguan. 53, 1231–1233.
Keywords: digital reading literacy, digital social reading behavior, middle school, student mediation effect, behavior driven model
Citation: Zhang W, Wang Y and Jin L (2025) Digital reading literacy, social reading motivation and social reading behavior of middle school students—an analysis based on the mediating effect model. Front. Hum. Dyn. 7:1623865. doi: 10.3389/fhumd.2025.1623865
Edited by:
Cristóbal Fernández Muñoz, Complutense University of Madrid, SpainReviewed by:
Lidia Altamura, University of Valencia, SpainVesna Makitan, University of Novi Sad, Serbia
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang and Jin. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Wenyan Zhang, MjI1NTU2OTBAcXEuY29t
 Wenyan Zhang
Wenyan Zhang Ye Wang
Ye Wang Longyun Jin
Longyun Jin