- School of Liberal Arts, Macau University of Science and Technology, Macau, Macau SAR, China
Against the backdrop of the digital economy profoundly leading the modernization of industrial systems and structures, this study focuses on the impact mechanism of the digital economy on urban insurance demand. Based on panel data from 289 cities in China between 2007 and 2022, a two-way fixed effects model is constructed, and empirical research is conducted using an instrumental variable approach and heterogeneity analysis. The findings are as follows: First, the direct driving effect of the digital economy. The digital economy has a significant positive impact on total insurance demand (TID), property insurance demand (PID), and health insurance demand (HID), with its effect on HID being approximately 1.53 times that on PID, reflecting the more prominent role of health protection demand under the influence of the digital economy. Second, the reinforcing logic of moderating and mediating effects. Economic development level (EDL) significantly strengthens the driving effect of the digital economy on PID by improving digital infrastructure and diversifying demand; human capital level (HCL) comprehensively amplifies the digital driving effect on insurance demand by enhancing the digital adaptation capacity of both supply and demand sides. Meanwhile, the digital economy promotes insurance demand by boosting consumption expenditure (CE). Third, regional heterogeneity characteristics. The impact of the digital economy on insurance demand exhibits a spatial pattern of “stronger in the north than in the south, and stronger in inland areas than in coastal areas.” This study provides mechanistic insights and policy optimization pathways to address the regional disparities in the synergistic development of the digital economy and urban insurance.
1 Introduction
The advent of the digital economy era has profoundly reshaped the landscape and development of industries worldwide. The digital economy is a new economic form characterized by digital knowledge and information as key production factors, modern information networks as the primary carrier, and information and communication technology as the core driving force. Through the deep integration of modern service industries and traditional sectors, it accelerates the restructuring of economic structures and governance models. With its extensive technology spillover effects, it permeates all walks of life, effectively alleviates factor mismatches, and facilitates the transformation and upgrading of traditional industries. According to the “Digital China Development Report,” in 2024, the value-added of core digital economy industries accounted for approximately 10% of China’s GDP, with the scale of these industries steadily expanding. The “China Digital Economy Development Research Report (2024)” indicates that China’s digital economy now constitutes 42.8% of its GDP, further elevating its role in the national economy and solidifying its status as a critical pillar and key driver of economic growth. Digital technologies, represented by artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, and the Internet of Things, are not only transforming various aspects of daily life such as healthcare (Ruiz et al., 2006), communications (Chaintreau et al., 2007), and education (Margaryan et al., 2011) but are also reshaping the design, distribution, and service models of insurance products. Moreover, they have given rise to entirely new risk forms and customer demands, propelling the insurance industry from traditional practices into an accelerated phase of digital transformation. On one hand, digital technologies enable the insurance industry to better respond to customers’ personalized and diverse needs, driving continuous innovation in products and services. On the other hand, digital transformation has intensified market competition, imposing higher requirements on insurance companies’ operational efficiency and risk management capabilities.
Existing literature on the impact of the digital economy on the insurance industry primarily revolves around three dimensions: First, supply-side quality and efficiency improvements, which argue that digital technologies enhance service quality by empowering product design, marketing channels, investment management, and other aspects, though most related studies are qualitative analyses. Second, demand-side stimulation and release, where the development of digital finance significantly increases household participation in commercial insurance and stimulates micro-level demand through mechanisms such as improving consumption environments and alleviating information constraints (Li et al., 2019; Hu et al., 2022; Liang and Yang, 2025). Third, alleviating supply–demand mismatches, as the digital economy is believed to optimize resource allocation by enhancing information symmetry and improving infrastructure (Nourani et al., 2021). However, empirical research directly investigating the relationship between the digital economy and the overall development of the insurance industry remains relatively scarce. Moreover, most studies treat the research period as a homogeneous whole, neglecting phased differences in its impact, such as lag effects, nonlinear characteristics, and significant heterogeneity. Recent research has begun to address these gaps by employing quasi-natural experiments and other methods to verify its promotive effects and dynamic characteristics.
Therefore, analysis at the city level provides a more refined and accurate perspective for examining the intrinsic relationship between the digital economy and insurance demand. This study, based on 16 years of panel data from 289 prefecture-level cities, aims to bridge the aforementioned research gaps. By focusing on urban units, this paper not only more clearly identifies the micro-level driving mechanisms of the digital economy on insurance demand but also examines heterogeneous effects under different city characteristics, thereby providing theoretical foundations and empirical support for local governments and insurance companies to formulate more targeted development strategies. The marginal contributions of this paper are as follows: First, it employs a digital economy indicator system to empirically evaluate the causal relationship between the digital economy and insurance development, expanding the theoretical framework for the insurance industry’s growth. Second, from the perspectives of economic development and human capital, it theoretically analyzes and empirically tests their impact mechanisms on the insurance industry’s development, providing mechanistic evidence for the digital economy’s role in promoting the insurance industry. Third, from a geographical perspective, it explores the heterogeneous characteristics of the digital economy’s impact on the insurance industry, offering references for developing tailored approaches to advance the digital transformation of the insurance sector. Finally, this paper discusses the differential effects of the digital economy on various types of insurance companies and different lines of property insurance, providing insights for optimizing insurance product structures and better leveraging the role of the digital economy in the insurance industry.
2 Literature review
As an emerging economic form, the digital economy utilizes digitalized knowledge and information as key production factors, digital technology as the core driving force, and modern information networks as essential carriers. Through the deep integration of digital technology and the real economy, it enhances the digital, networked, and intelligent levels of the economy and society (Umur, 2006). The core feature of the digital economy lies in restructuring production, distribution, and consumption patterns based on digital technology. Early studies pointed out that the digital economy combines digital information and the internet, representing a form of general-purpose technology that is generating a vast array of new possible combinations (Carlsson, 2004). The core architecture of the digital economy includes three major modules: infrastructure, e-commerce, and electronic business (Mesenbourg, 2001). These modules collectively support the efficient flow and application of data, demonstrating significant advantages especially in areas such as risk management (Krystofik et al., 2020), product development (Zhan et al., 2018), and customer interaction (Sadath, 2013). The deepening application of digital technologies such as mobile payments and inclusive financial development has further driven innovation in the financial sector. These technologies not only enhance economic efficiency but also narrow regional development gaps (Li and Zhang, 2024). In recent times, scholars have conducted in-depth research on the digital economy, exploring its impacts on variables such as carbon emissions (Li et al., 2021), high-quality economic development (Ding et al., 2021; Jiao and Sun, 2021), higher education (Geng et al., 2023), and green economic efficiency (Kong and Li, 2022; Huang et al., 2023; Yang, 2023). At the micro level, the dynamic nature of the digital economy requires enterprises to continuously optimize their data governance capabilities to achieve rapid responses to market changes.
Insurance, as a protective mechanism against risks, essentially transforms individual uncertain losses into quantifiable probabilistic losses for a group through contractual arrangements. Insurance policyholders update their risk perceptions immediately after major disaster losses, and changes in income levels are positively correlated with changes in insurance coverage levels (Mumo and Watt, 2019). Academics generally classify insurance into property insurance and health insurance. At the macro level, increases in per capita disposable income and insurance claims can promote the development of property insurance demand (Chen and Liu, 2017). At the micro level, property and liability insurance companies raise funds to replenish levels depleted by underwriting losses and to finance business growth, and capitalization levels do not constrain insurers’ ability to meet demand during economic downturns (Berry-Stölzle and Esson, 2023). In health insurance, catastrophic insurance plans can reduce spending by 31% compared to zero out-of-pocket costs (Manning et al., 1987), while policies relying on voluntary purchase to reduce the number of uninsured achieve only modest success (Chernew et al., 1997). Additionally, numerous scholars have studied insurance risk assessment models. Hsu et al. (2011) developed a probabilistic model based on historical events through four dimensions, rainfall event module, hydraulic module, vulnerability module, and financial loss module, to assess flood risk in Taiwan. Brown et al. (2015) assessed hail losses using property insurance claims data. Ding et al. (2020) established a risk assessment matrix for major highway structures based on hazard factors, vulnerability carriers, and disaster-predisposing environments, thereby improving risk management levels and insurance benefits. In summary, insurance plays a crucial role in social stability, enhancing national social welfare levels, and promoting regional economic development.
Traditional theory centers on expected utility theory, emphasizing that risk-averse individuals make rational decisions to avoid uncertain losses through insurance. Mossin (1968) groundbreaking research established the foundational model, indicating that individuals determine insurance purchases based on initial wealth and risk exposure. His model shows that insurance demand increases with the degree of risk aversion but is constrained by premium prices and income. Similarly, Yaari (1965), from a consumer theory perspective, incorporated uncertain lifespan into the analysis, demonstrating that life insurance demand stems from utility maximization over the lifecycle, where income levels and expected losses are key drivers. However, these models assume perfect rationality and cannot explain real-world “insurance puzzles.” Although Nyman (2001) reconstructed expected utility theory from a gain perspective, arguing that insurance demand is actually a pursuit of income gains in specific states such as illness rather than mere risk avoidance, this still does not cover all anomalies. Overall, the classical perspective emphasizes the core role of economic variables, but empirical evidence shows its explanatory power is limited, necess supplementation by behavioral theories. Behavioral economics theory compensates for the shortcomings of classical models by introducing cognitive biases to explain insurance demand paradoxes. Pitthan and De Witte's (2021) review systematically points out that prospect theory is the core framework: individuals’ probability weighting function is S-shaped, leading to underestimation of natural disasters and overestimation of medical costs, which contradicts expected utility theory and results in low demand for catastrophe insurance but high demand for small-risk insurance. Schwarcz (2010) further verified that consumers prefer low deductibles and small-risk insurance due to mental accounting and narrow framing biases, decisions are isolated in specific contexts, ignoring the overall risk pool, leading to irrational purchases. Röschmann et al. (2022) used on-demand insurance as an example to illustrate how digital technology can alter risk perception through data capture but is constrained by moral and social factors. These behavioral factors explain why traditional models fail, especially in developing countries or regions.
In the context of digitalization, emerging digital technologies such as mobile money, digital credit scoring, and Earth observation have reshaped rural savings, credit, and insurance service markets (Benami and Carter, 2021), making the upgrading of the traditional insurance industry’s value chain imminent. Unlike the natural evolution in market-based countries, China’s insurance industry has long been directly shaped by industrial policies. Foundational documents such as the “New National Ten Articles” (2014) position insurance as a “social stabilizer,” achieving “supply-led” development through fiscal subsidies, market access restrictions, and state capital dominance (Sutton, 1994). The 2023 inclusive finance strategy further requires insurance companies to penetrate county-level markets, with policy goals taking precedence over commercial logic. Policy dividends have driven the rapid penetration of digital infrastructure. The government-led “Digital China” strategy has enabled the insurance industry to prioritize access to infrastructure support such as 5G and blockchain. State-owned insurance companies’ digital investments account for 8% of revenue, significantly higher than the global average of 3.5% (Shasha, 2023). Liu et al. (2024) constructed the digital transformation of the insurance industry based on three components: digital infrastructure, digital platforms, and digital applications. Pan et al. (2024) explored the impact of digital economy development on social security fund income, finding that for every unit increase in digital economy development, basic pension insurance fund income increased by 0.56%, and basic health insurance fund income increased by 0.33%. It can be seen that existing research on the impact of the digital economy on insurance mostly approaches it from the supply side, demand side, or supply–demand matching perspective, with few studies providing direct empirical evidence of the digital economy’s impact on insurance industry development. Based on this, this paper uses digital economy efficiency measured by principal component analysis as a proxy variable for the digital economy and employs data from 289 cities in China from 2007 to 2022 to empirically study the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand.
3 Research hypotheses and variable explanations
3.1 Influence mechanism of digital economy on urban insurance demand
3.1.1 Direct effect of digital economy on urban insurance demand
As a core driver supporting economic growth, the digital economy exerts a significant impact on urban insurance demand. Big data analytics technology can identify high-risk groups, promoting the expansion of insurance demand into segmented markets. On one hand, digital technology enhances information supervision capabilities, reduces information asymmetry in transaction markets (Grubesic et al., 2019), and increases property insurance demand; on the other hand, it supports home-based elderly care and extends the nursing cycle, thereby boosting long-term health insurance demand. From the perspective of property insurance, digital technology enables precise risk profiling of subjects such as enterprise assets and household properties by constructing dynamic risk assessment models. This not only significantly reduces information asymmetry in traditional insurance markets but also extends insurance products to broader markets. Specifically, Internet of Things (IoT) devices and sensors can monitor property status in real time, enabling dynamic risk assessment and early warning; blockchain technology, through smart contracts, automates, transparentizes, and makes the underwriting and claims processes tamper-proof, greatly enhancing the trust foundation of insurance transactions and directly stimulating the release of property insurance demand. In terms of health insurance, the digital economy demonstrates a dual enabling mechanism of “demand creation and supply optimization.” On one hand, artificial intelligence and medical big data analytics enable precise assessment of individual health risks, shifting insurance pricing from “group averaging” to “individual precision,” and promoting the emergence of innovative products such as long-term care insurance and insurance for individuals with pre-existing conditions (Aimar et al., 2019). On the other hand, digital medical services such as remote consultations, electronic health records, and wearable device monitoring extend the health management cycle for the elderly population. By reducing immediate medical expenditure pressure, these services significantly enhance consumers’ willingness to allocate resources to long-term health insurance. Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H1: The digital economy has a significant positive impact on urban insurance demand.
H2: The digital economy not only affects total insurance demand but also influences property insurance demand and health insurance demand.
3.1.2 Indirect effect of digital economy on urban insurance demand
Economic development level acts as an accelerator for digital economy-enabled insurance demand by enhancing market capacity and demand hierarchy. In cities with high economic development levels, the integration of digital technology and the insurance market is significantly deepened: on one hand, a developed industrial base provides application scenarios for insurance innovation (Liao et al., 2007), with technology parks and advanced manufacturing clusters generating strong demand for new types of property insurance such as technology insurance and cybersecurity insurance, thereby strengthening the impact of the digital economy on property insurance demand; on the other hand, upgrades in residents consumption structure drive the transformation of insurance demand (Zhang and Gao, 2021). Value-added services such as smart health management and pension planning supported by digital technology further amplify the driving effect of the digital economy on the expansion and structural upgrading of the insurance market. Human capital level serves as a catalyst for the digital economy’s promotion of insurance demand by enhancing technological adaptability and market innovation vitality. From a cognitive perspective, residents in cities with high human capital levels have a better understanding and higher acceptance of digital insurance products (Zhang et al., 2006), enabling them to more effectively comprehend and use innovative products such as blockchain-based smart contracts and Usage-Based Insurance (UBI), thereby promoting population welfare (Grigorescu et al., 2021). From an innovation perspective, high-quality talent enhances insurance institutions technology absorption and product development capabilities, accelerating the transformation of digital economy achievements from digitalization to intelligence. For example, through AI actuarial models and personalized insurance plan customization, potential insurance demand is further stimulated. Secondly, the development of the digital economy enhances production efficiency and residents income, broadening consumers budget constraints. Meanwhile, new business models such as e-commerce and digital services stimulate consumption vitality, leading to the expansion and structural upgrading of consumption. Consumption upgrading indicates that households possess more high-value assets and engage in richer consumption scenarios, thereby being exposed to broader risks, which strengthens residents awareness of risk protection. At the same time, improved payment capacity effectively alleviates demand suppression in the insurance market, ultimately converting potential protection needs into actual purchasing behavior for insurance products such as property insurance, health insurance, and liability insurance, driving overall growth in insurance demand. Therefore, the following hypotheses are proposed:
H3: Economic development level plays a moderating role in the relationship between the digital economy and urban insurance demand. The higher the economic development level, the stronger the promoting effect of the digital economy on insurance demand.
H4: Human capital level plays a moderating role in the relationship between the digital economy and urban insurance demand. The higher the human capital level, the more significant the enhancing effect of the digital economy on insurance demand.
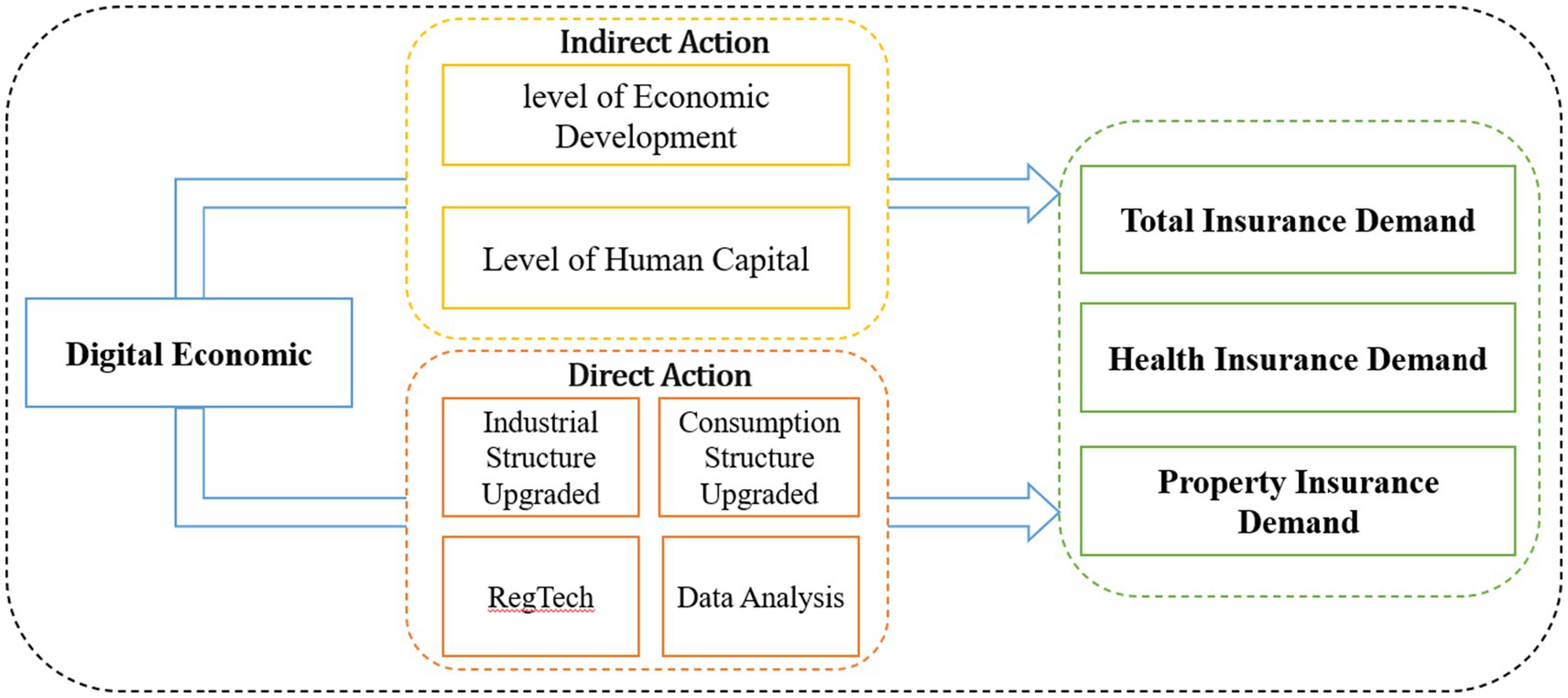
H5: Consumption expenditure plays a mediating role in the relationship between the digital economy and urban insurance demand. The digital economy promotes insurance demand by boosting consumption expenditure. Figure 1 shows the Mechanism Analysis Diagram of Digital Economy and Urban Insurance Demand.
Figure 1
3.2 Data description
The explanatory variable is the Digital Economy Index (DEI). Drawing on the methodology of Zhao et al. (2020), Huang et al. (2019), this study uses four types of indicators: internet penetration rate, employment in related sectors, related output, and mobile phone penetration rate. These indicators, respectively, represent the number of broadband internet subscribers per 100 people, the proportion of employees in computer services and software industries among urban unit employees, per capita telecom business volume, and the number of mobile phone users per 100 people. The original data can all be obtained from the China Urban Statistical Yearbook. The development of digital finance is measured by the China Digital Inclusive Finance Index, jointly compiled by the Digital Finance Research Center of Peking University and Ant Group (Guo et al., 2020). The comprehensive development index of the digital economy is calculated through principal component analysis.
The dependent variable is Insurance Demand. Academically, insurance demand is generally divided into Total Insurance Demand (TID), Property Insurance Demand (PID), and Health Insurance Demand (HID). Premium income is often regarded as one of the important proxy variables for measuring insurance demand, as it reflects the actual sales situation of insurance products in the market. This paper uses urban premium income as a proxy variable for urban insurance demand, and the original data can be obtained from the China Insurance Yearbook. Figure 2 presents the Spatio-Temporal Evolution of Digital Economy and Insurance Demand.
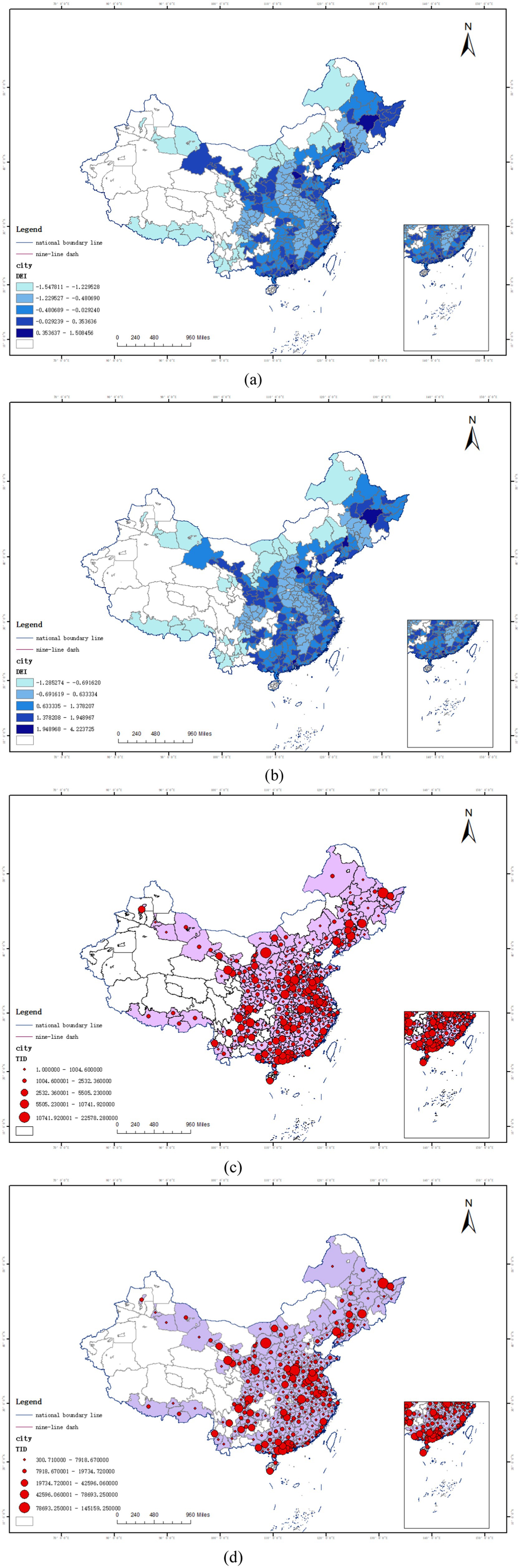
Figure 2. Spatio-temporal evolution of digital economy and insurance demand (a–d). (a) The level of digital technology in 2007. (b) The level of digital technology in 2022. (c) Total insurance demand in 2007. (d) Total insurance demand in 2022. This map is based on the standard map of the Standard map service system of the Ministry of Natural Resources (review number: GS (2022) 1873), and the base map has not been modified.
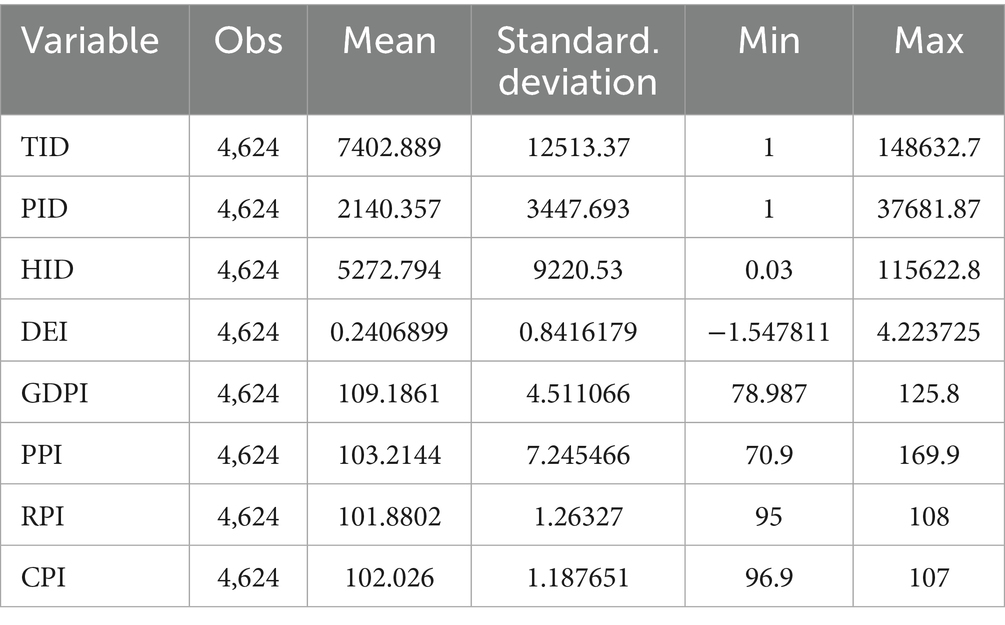
Factors influencing insurance demand are generally categorized into social and economic factors (Yuan and Jiang, 2015). Among the control variables, we select the Gross Domestic Product Index (GDPI) and Producer Price Index (PPI) as economic factors to reflect local economic development. The Retail Price Index (RPI) and Consumer Price Index (CPI) are chosen as social factors to reflect the inflation level of social consumption. The GDP index reflects the regional economic scale, and its growth can drive the upgrading of demand for enterprise property insurance, resident health insurance, and other types (Al-Abd and Mezher, 2014). The PPI is associated with enterprise costs and asset risks, and its fluctuations affect the willingness of manufacturing enterprises to purchase property insurance (Maples et al., 2022). The RPI influences residents’ consumption capacity—short-term inflation may squeeze insurance expenditure, while long-term inflation may boost demand for investment-oriented insurance (Embrey et al., 2021). The CPI affects insurance demand through real income and risk perception effects—short-term inflation may suppress demand for protection-oriented products, whereas long-term inflation expectations may promote the allocation of long-term health insurance (Cogoljević et al., 2018). Collectively, these four indicators systematically cover key factors affecting insurance demand from the dimensions of economic development and social inflation. Furthermore, in the section on moderating effects, this paper uses economic development level and human capital level as proxy variables to deeply explore how economic development and human capital levels influence the correlation between the digital economy and insurance demand. Control variable data are sourced from the official website of the National Bureau of Statistics and the China Economic Data Website. Table 1 Descriptive Statistics displays the descriptive statistics of the above-mentioned variables.
4 Empirical analysis
4.1 Model construction
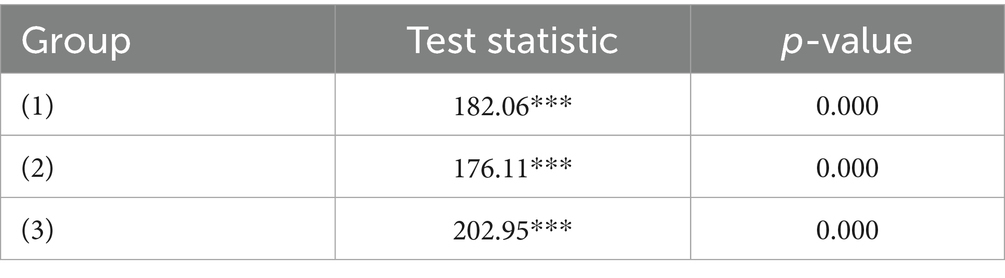
To further examine the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand, this paper establishes a panel regression model. To determine whether a fixed-effects model or random-effects model is appropriate, the Hausman test was employed for analysis. The results indicate that the digital economy shows significant effects on total insurance demand (Group 1), property insurance demand (Group 2), and health insurance demand (Group 3), thus supporting the use of a fixed-effects model (Table 2).
Considering the potential presence of heteroscedasticity, logarithmic transformation was applied to the variables, as shown in Equation 1:
In Equation 1, represents the insurance demand of city in year ; denotes the digital economy index of city in year ; is the intercept term; represents a series of control variables; indicates the individual fixed effect, represents the time fixed effect, and denotes the random disturbance term.
To further test the moderating roles of EDL and HCL in the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand, interaction terms are constructed by multiplying EDL and HCL with DEI, respectively. The coefficients of the interaction terms represent the moderating effects under different levels of economic development and human capital. Based on the above analysis, Equations 2, 3 are constructed:
To examine the mediating role of Consumption Expenditure (CE) in the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand, Equations 4–6 are constructed as follows:
4.2 Impact of digital economy on insurance demand
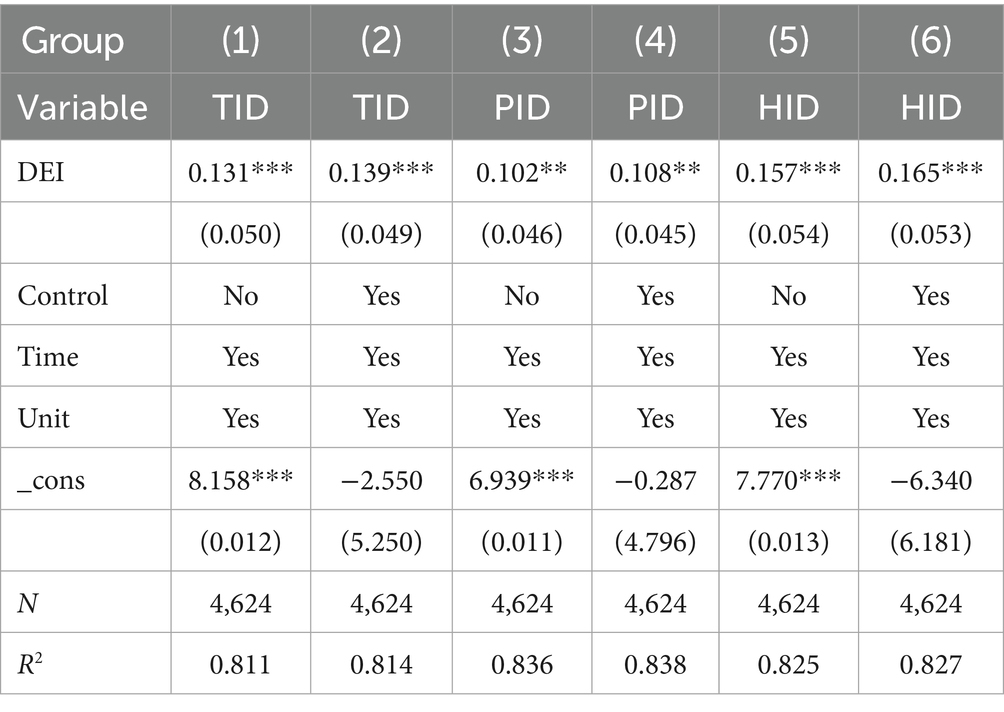
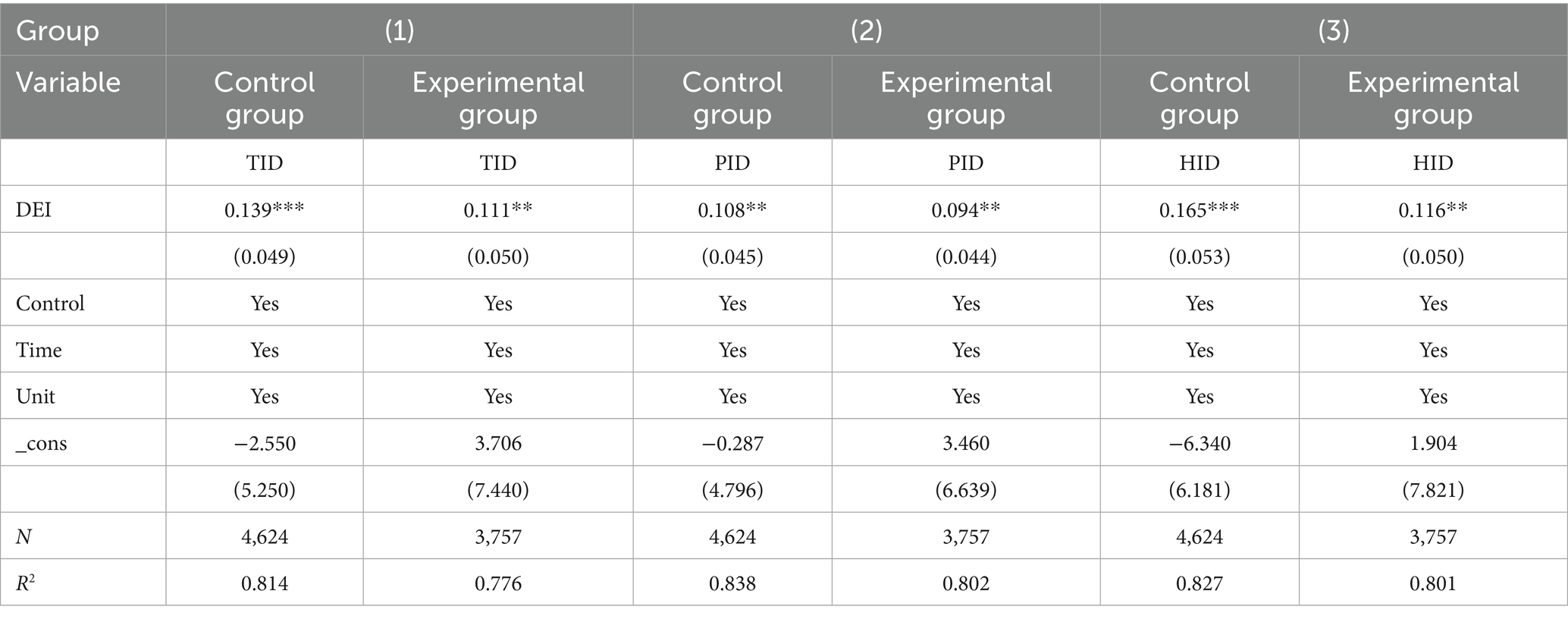
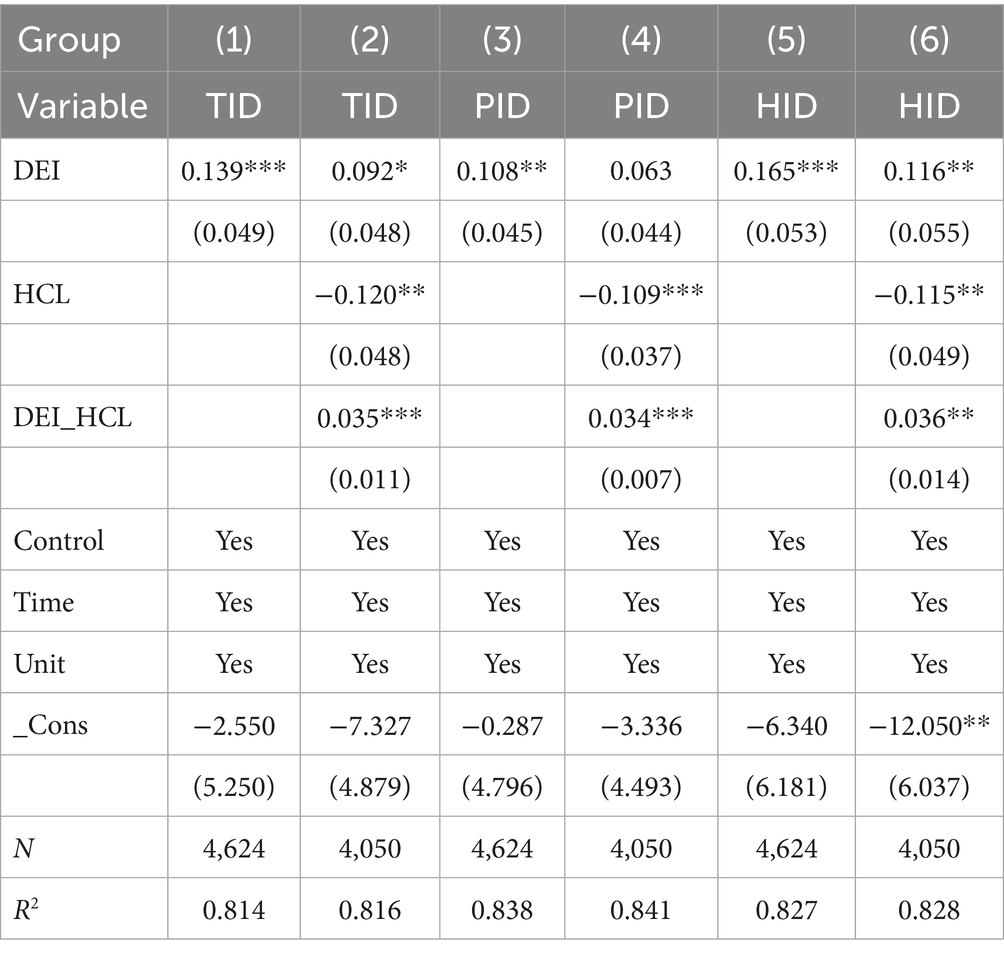
Table 3 Baseline Regression Results examining the impact of the Digital Economy Index (DEI) on insurance demand are reported in the table. The findings indicate that DEI has a statistically significant positive effect on Total Insurance Density (TID), Property Insurance Density (PID), and Health Insurance Density (HID). After controlling for time and individual effects, a 1% increase in DEI leads to an average rise of 0.139% in TID, 0.108% in PID, and 0.165% in HID, with all coefficients significant at the 1% or 5% level. In economic terms, based on the average health insurance density of approximately 1,200 yuan per capita during the sample period, a one-unit increase in the digital economy index corresponds to an average growth of about 198 yuan in health insurance demand. This demonstrates that the enhancing effect of the digital economy on insurance demand is not only statistically significant but also economically substantial. Furthermore, the impact of DEI on health insurance demand is approximately 1.53 times greater than its effect on property insurance, consistent with the theoretical analysis suggesting that digital technology aligns particularly well with the health insurance market through a “demand creation–supply optimization” pathway. This underscores the heightened prominence of health protection demand amid the development of the digital economy. After incorporating control variables, the coefficients of DEI remain stable, and the goodness-of-fit (R2) of the model shows slight improvement, indicating the robustness of the promoting effect of the digital economy on insurance demand.
4.3 Robustness tests
Table 4 presents the results of robustness tests. To begin, it is necessary to exclude the impact of the financial crisis years. The bankruptcy of Lehman Brothers in the United States on September 15, 2008, marked the full escalation of the subprime mortgage crisis into a global financial crisis. By removing data from 2008 and 2009, this study effectively eliminates the distortions in residents’ risk preferences and consumption capacity caused by extreme economic fluctuations during this period. This approach avoids the potential confounding effects of abnormal factors, such as credit contraction and asset depreciation during the crisis, on the assessment of the digital economy’s impact. Through this processing, we can examine whether the promoting effect of the digital economy on insurance demand remains robust under normal economic conditions. The regression results in Table 4 demonstrate that even after controlling for the long-term effects of the 2008 global financial crisis, DEI continues to exhibit a significant positive driving effect on TID, PID, and HID. After including control variables, a 1% increase in extreme temperature risk leads to an average increase of 0.111% in TID, 0.094% in PID, and 0.116% in HID, respectively. The magnitude of these coefficients is similar to the baseline regression results. This outcome confirms that the promoting effect of digital economy development on insurance demand remains robust across different phases of the economic cycle and is not driven by abnormal economic conditions during the financial crisis.
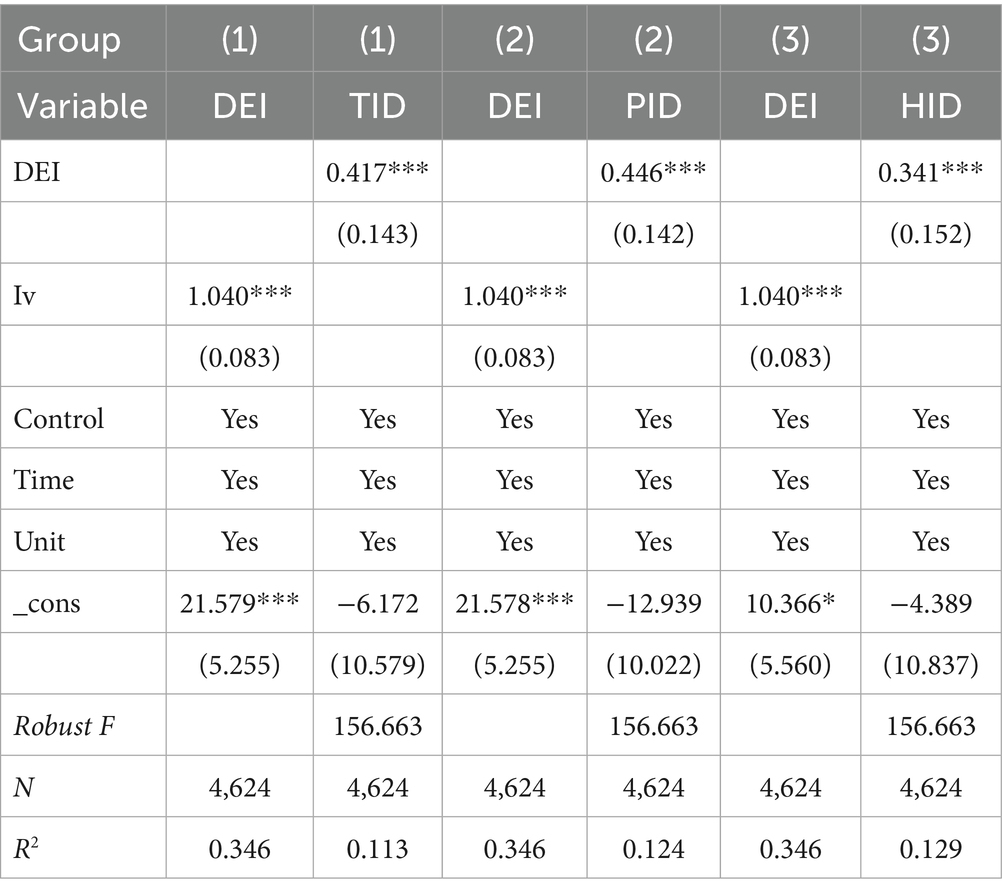
Secondly, Table 5 presents the results of the endogeneity test. Endogeneity issues primarily reflect bidirectional causality between variables, meaning that the development of the digital economy and the level of new urbanization may influence each other. Endogeneity typically arises from correlation between explanatory variables and the error term, which can be caused by omitted key variables, bidirectional causality, or measurement errors, among other factors. To address these potential endogeneity issues, we used river density (IV) across prefecture-level cities as an exogenous instrumental variable for the digital economy. On one hand, key parameters of river systems are determined by the “erosion threshold,” which depends on natural variables such as slope, rainfall intensity, and soil erodibility, rather than economic factors. Erosion rates are related to “distance” and “runoff intensity,” which are purely natural processes (Horton, 1945). Ding and Huang (2023) note that “if river density affects regional economies, it is more likely through influencing the size distribution of regional cities rather than ‘directly impacting’ economic development. Thus, the association between rivers and economic development does not violate the exclusion restriction.” In other words, the historical influence of rivers has been absorbed by the “digital economy” as a mediating variable, while the IV itself is a predetermined natural characteristic. The two-stage least squares (2SLS) method was adopted to test the robustness of the baseline regression results. First, geographical barriers caused by rivers and mountains are important factors influencing economic development. Compared to plain areas, regions with more geographical barriers such as rivers and mountains generally exhibit lower levels of economic development. Areas with higher river and mountain densities were historically more likely to be divided into relatively isolated small regions, leading to segmented local populations. In agricultural societies with limited transportation and geographical barriers, cultural, commercial, and economic exchanges between residents on opposite sides of rivers were significantly reduced, potentially resulting in regional economic disparities over time. Thus, river density is closely related to economic diversity. On the other hand, with advancements in modern transportation and construction technologies, naturally formed rivers are unlikely to directly influence the prosperity of the digital economy in today’s highly connected society, thereby satisfying the exogeneity requirement of the instrumental variable. In the 2SLS regression, the first-stage F-statistic is 156.663, passing the weak instrument test and meeting the requirements for instrument validity. Additionally, since only one instrumental variable is used, the model is exactly identified, and over-identification tests are unnecessary. The results show that the coefficient of the core explanatory variable DEI remains positive and statistically significant at the 1% level, consistent with the baseline regression results.
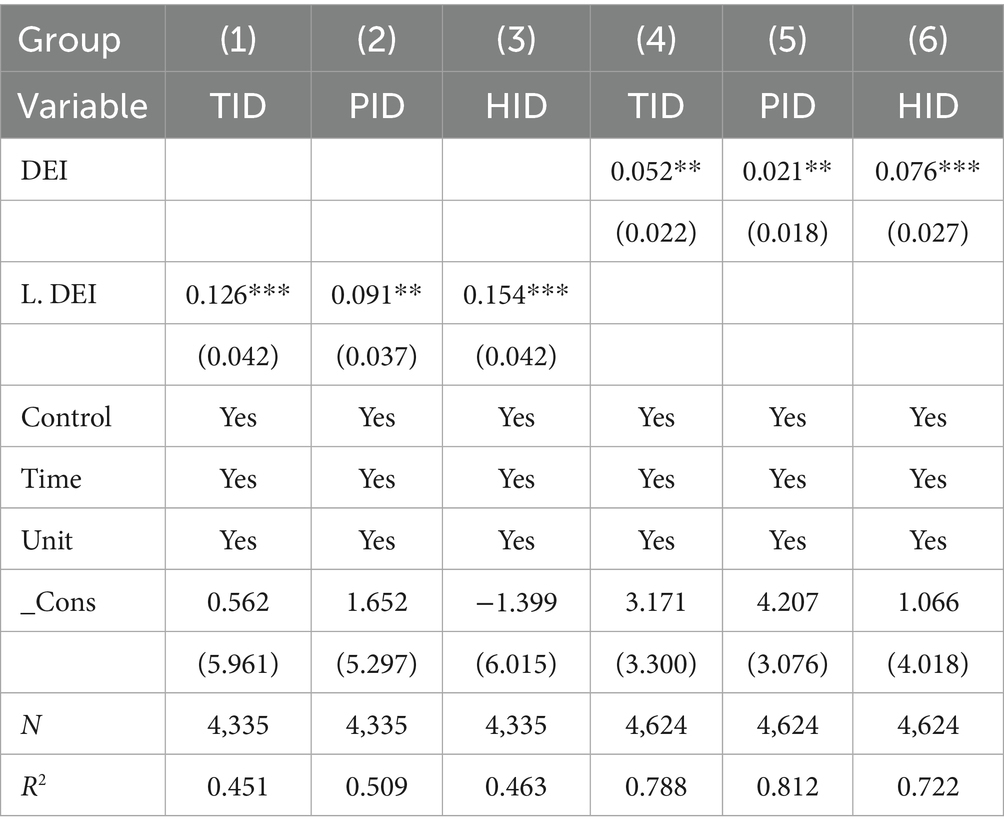
Table 6 presents the results of robustness tests. The robustness test results demonstrate that the promoting effect of the digital economy (DEI) on insurance demand remains statistically significant across different testing methods, further validating the reliability of the baseline regression findings. Specifically, columns (1) to (3) employ alternative core explanatory variables. In the regression using the one period lagged digital economy variable (L. DEI), the coefficients of the core explanatory variable are all significant at the 5% or 1% level, with the direction and magnitude highly consistent with the baseline regression. This confirms that the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand exhibits persistence rather than being a short term shock. Additionally, it effectively mitigates potential reverse causality issues, indicating that prior levels of digital economy development significantly predict current insurance demand. In columns (4) to (6), after winsorizing all variables at the 1% level to exclude the influence of outliers, the coefficients of DEI remain significantly positive. Although the absolute values of the coefficients decrease slightly due to the exclusion of extreme values, the consistency in statistical significance and direction robustly confirms that the baseline regression results are not driven by anomalous observations. The positive correlation between the digital economy and insurance demand holds across different quantiles of the data distribution. Taken together, these two supplementary tests, along with the earlier exclusion of financial crisis years, form a comprehensive robustness analysis framework. They validate the reliability of the core conclusions from three distinct perspectives: time lag effects, outlier interference, and disruptions during specific periods. The results indicate that the promoting effect of the digital economy on insurance demand, including total demand, property insurance demand, and health insurance demand, is not attributable to model specification bias, outliers, or economic fluctuations during exceptional periods. Instead, it represents a robust relationship with universal significance.
4.4 Heterogeneity analysis
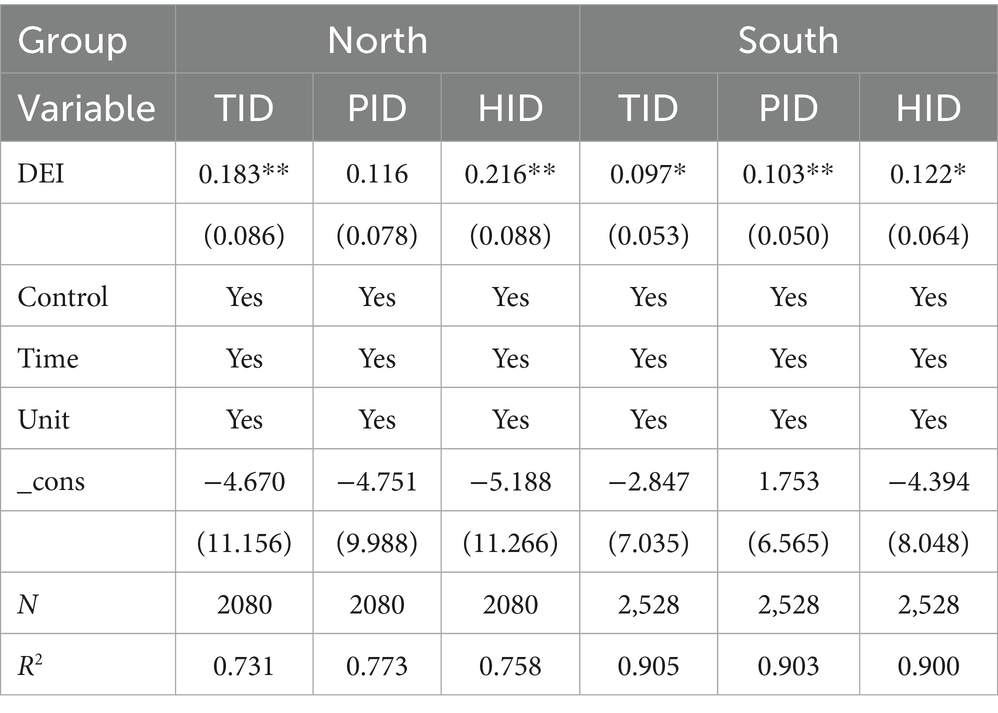
First, based on the north–south city division, there exists significant heterogeneity in the impact of the DEI on insurance demand between northern and southern cities. The coefficients of DEI on TID and HID in northern cities are 0.183 and 0.216, respectively, significantly higher than those in southern cities. In contrast, the effect of DEI on PID in southern cities is only 0.103. This disparity aligns with the moderating effects of economic development level and human capital level proposed in the theoretical section, and can be attributed to multiple reasons. Firstly, industrial structure differences: as a traditional industrial base, northern China has seen strong demand for both property and health insurance driven by the digital transformation of traditional industries, typically manifested in industrial internet-driven safety production insurance demand and the widespread adoption of digital healthcare services. Southern China has a higher proportion of service industries, where earlier penetration of the digital economy has led to diminishing marginal effects. Secondly, policy implementation effects: northern cities have recently benefited from policy support such as the Digital China initiative, with rapid investment growth in digital infrastructure, and local governments’ efforts to promote enterprise digital transformation have simultaneously stimulated insurance demand. Although southern cities face greater climate risks, residents’ risk perception relies on traditional experiences, weakening the driving effect of DEI on HID. Thirdly, human capital distribution: the concentration of universities in northern cities has facilitated the return of digital technology talent, and the rapid development of insurance companies has reinforced the DEI effect. While southern cities exhibit high digital literacy, the insurance industry suffers from a shortage of digital talent. Fourthly, insurance market maturity: the insurance market in southern cities developed earlier, leading to intense competition and severe product homogenization, resulting in a relatively lower marginal contribution of the digital economy. The insurance market in northern cities is in a rapid development phase, where digital innovation has a more pronounced impact on demand stimulation.
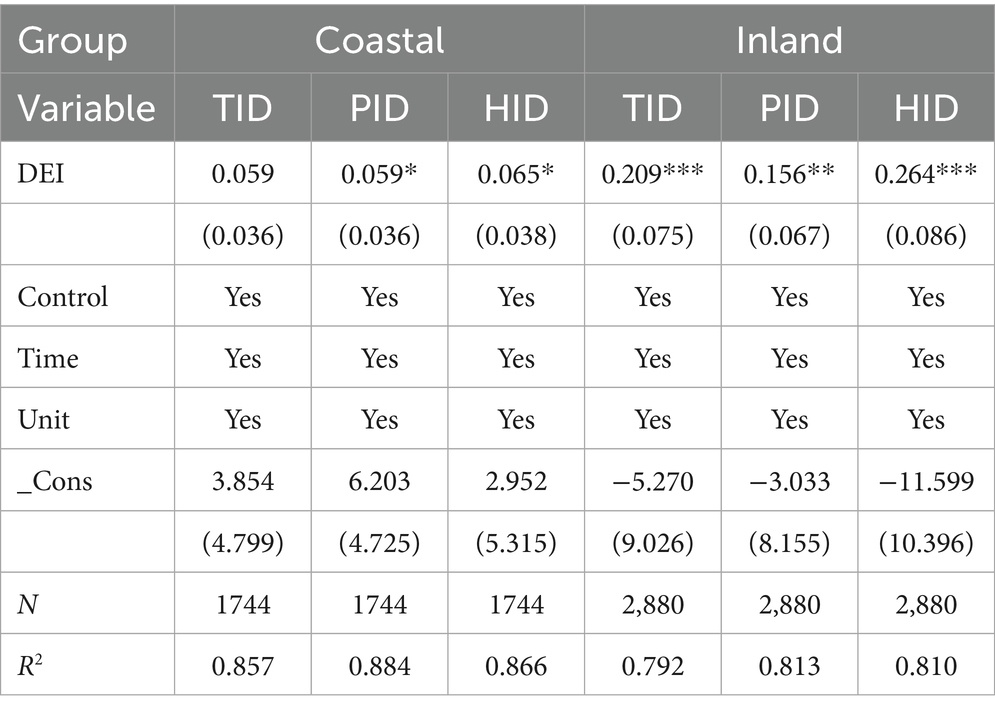
Table 7, Second, the division between coastal and inland cities reveals a significant pattern where the impact of the DEI on insurance demand is stronger in inland areas and weaker in coastal areas. The coefficients of DEI on TID, PID, and HID in inland cities are 0.209, 0.156, and 0.264 respectively, all significantly higher than those in coastal cities, which are 0.059, 0.059, and 0.065. This result further validates the hypothesis regarding the moderating role of economic development level proposed in the theoretical analysis. The underlying reasons include several aspects. First of all, there are differences in development stages. Coastal areas have already achieved relatively high penetration of the digital economy, where the promoting effect of digital technology on the insurance market has entered a phase of diminishing marginal returns. Inland regions are currently in a rapid growth period of digital technology popularization and deepening, where each unit of digital economic growth brings more apparent improvement in protection demand. Second, infrastructure disparities play a role. Inland areas, supported by the new infrastructure policy, are experiencing rapid improvement in digital infrastructure levels, significantly enhancing the accessibility of insurance services. Coastal areas already have relatively well-developed digital infrastructure with limited room for improvement. Third, the pace of industrial transformation differs. Inland areas are undertaking industrial transfer, with digitalization and industrialization progressing simultaneously, generating substantial new property insurance demands stemming from industrial internet and smart manufacturing. Coastal areas shifted earlier toward service-oriented industrial upgrading, where digital technology’s pull on insurance is more reflected in business model innovation rather than scale expansion. Fourth, there are differences in consumer structure. Inland cities have a higher proportion of digital natives among new users, who demonstrate stronger acceptance and trust in internet-based insurance. Coastal insurance markets face intense competition with high customer acquisition costs, leading to diminishing marginal utility from digitalization. Fifth, risk characteristics vary between regions. Coastal areas face higher risks of natural disasters such as typhoons and floods, making property insurance demand relatively inelastic. Inland regions have more diverse risk types, where the risk identification and management functions of digital technology can create new insurance demands.
Tables 8–10 present the results of heterogeneity analysis. First, based on the north–south city division, there exists significant heterogeneity in the impact of the DEI on insurance demand between northern and southern cities. The coefficients of DEI on TID and HID in northern cities are 0.183 and 0.216, respectively, significantly higher than those in southern cities. In contrast, the effect of DEI on PID in southern cities is only 0.103. This disparity aligns with the moderating effects of economic development level and human capital level proposed in the theoretical section, and can be attributed to multiple reasons. Firstly, industrial structure differences: as a traditional industrial base, northern China has seen strong demand for both property and health insurance driven by the digital transformation of traditional industries, typically manifested in industrial internet-driven safety production insurance demand and the widespread adoption of digital healthcare services. Southern China has a higher proportion of service industries, where earlier penetration of the digital economy has led to diminishing marginal effects. Secondly, policy implementation effects: northern cities have recently benefited from policy support such as the Digital China initiative, with rapid investment growth in digital infrastructure, and local governments’ efforts to promote enterprise digital transformation have simultaneously stimulated insurance demand. Although southern cities face greater climate risks, residents’ risk perception relies on traditional experiences, weakening the driving effect of DEI on HID. Thirdly, human capital distribution: the concentration of universities in northern cities has facilitated the return of digital technology talent, and the rapid development of insurance companies has reinforced the DEI effect. While southern cities exhibit high digital literacy, the insurance industry suffers from a shortage of digital talent. Fourthly, insurance market maturity: the insurance market in southern cities developed earlier, leading to intense competition and severe product homogenization, resulting in a relatively lower marginal contribution of the digital economy. The insurance market in northern cities is in a rapid development phase, where digital innovation has a more pronounced impact on demand stimulation.
Second, the division between coastal and inland cities reveals a significant pattern where the impact of the DEI on insurance demand is stronger in inland areas and weaker in coastal areas. The coefficients of DEI on TID, PID, and HID in inland cities are 0.209, 0.156, and 0.264 respectively, all significantly higher than those in coastal cities, which are 0.059, 0.059, and 0.065. This result further validates the hypothesis regarding the moderating role of economic development level proposed in the theoretical analysis. The underlying reasons include several aspects. First of all, there are differences in development stages. Coastal areas have already achieved relatively high penetration of the digital economy, where the promoting effect of digital technology on the insurance market has entered a phase of diminishing marginal returns. Inland regions are currently in a rapid growth period of digital technology popularization and deepening, where each unit of digital economic growth brings more apparent improvement in protection demand. Second, infrastructure disparities play a role. Inland areas, supported by the new infrastructure policy, are experiencing rapid improvement in digital infrastructure levels, significantly enhancing the accessibility of insurance services. Coastal areas already have relatively well-developed digital infrastructure with limited room for improvement. Third, the pace of industrial transformation differs. Inland areas are undertaking industrial transfer, with digitalization and industrialization progressing simultaneously, generating substantial new property insurance demands stemming from industrial internet and smart manufacturing. Coastal areas shifted earlier toward service-oriented industrial upgrading, where digital technology’s pull on insurance is more reflected in business model innovation rather than scale expansion. Fourth, there are differences in consumer structure. Inland cities have a higher proportion of digital natives among new users, who demonstrate stronger acceptance and trust in internet-based insurance. Coastal insurance markets face intense competition with high customer acquisition costs, leading to diminishing marginal utility from digitalization. Fifth, risk characteristics vary between regions. Coastal areas face higher risks of natural disasters such as typhoons and floods, making property insurance demand relatively inelastic. Inland regions have more diverse risk types, where the risk identification and management functions of digital technology can create new insurance demands.
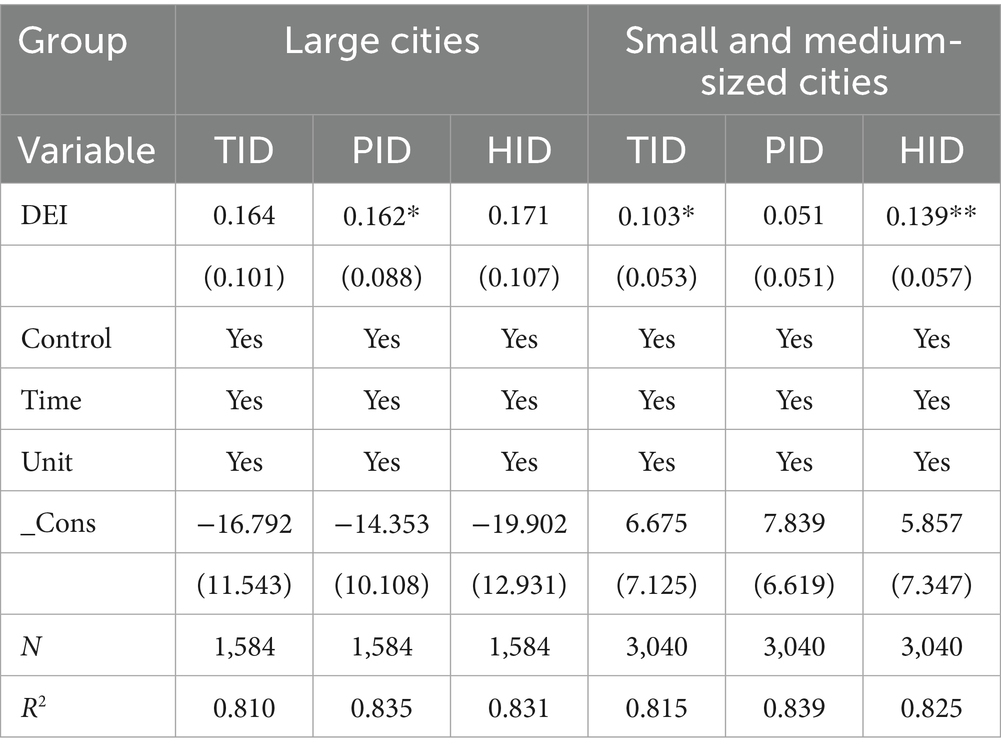
Third, the analysis based on city size classification reveals distinct patterns in the impact of the digital economy index (DEI) on insurance demand. According to the State Council’s “Notice on Adjusting the Standards for Classifying City Sizes,” which categorizes cities based on the permanent resident population in municipal districts, DEI’s influence on insurance demand demonstrates a clear characteristic of “significantly stronger effects in large cities compared to small and medium-sized cities.” As shown in the table, the coefficients of DEI on TID, PID, and HID are substantially higher in large cities than in small and medium-sized cities. Several factors may explain this phenomenon. First, large cities typically possess more advanced digital infrastructure and higher technological capabilities. The coverage of new information infrastructure such as 5G networks and cloud computing centers is significantly greater in large cities than in smaller urban areas, providing a solid foundation for deep integration between the digital economy and the insurance industry. Second, large cities benefit from richer human capital and innovation resources. The concentration of universities, research institutions, and high-tech enterprises not only enhances insurance institutions’ capabilities in developing digital products but also cultivates residents’ awareness and acceptance of digital insurance products. Third, the industrial structure in large cities is more diversified, with well-developed financial, technological, and service sectors. This creates stronger demand for new types of risk protection products (such as cyber security insurance and technology insurance) stimulated by the digital economy. Fourth, residents in large cities generally have higher income levels and more advanced consumption structures, demonstrating greater willingness and ability to pay for high-quality insurance services including health management and retirement planning. Finally, most large insurance institutions headquarters are located in major cities, enabling faster implementation of digital transformation strategies and more prominent scale effects and demonstration effects in digital technology application.
In contrast, the development of the digital economy in small and medium-sized cities relatively lags behind. These cities face certain shortcomings in digital infrastructure construction and talent reserves, traditional insurance sales channels still dominate the market, and residents’ trust and acceptance of internet-based insurance are still in the cultivation stage. These factors result in the pulling effect of the digital economy on insurance demand not being fully realized in smaller urban areas. Notably, DEI still shows a significant promoting effect on health insurance demand in small and medium-sized cities, indicating substantial potential for digital technology in popularizing health protection services.
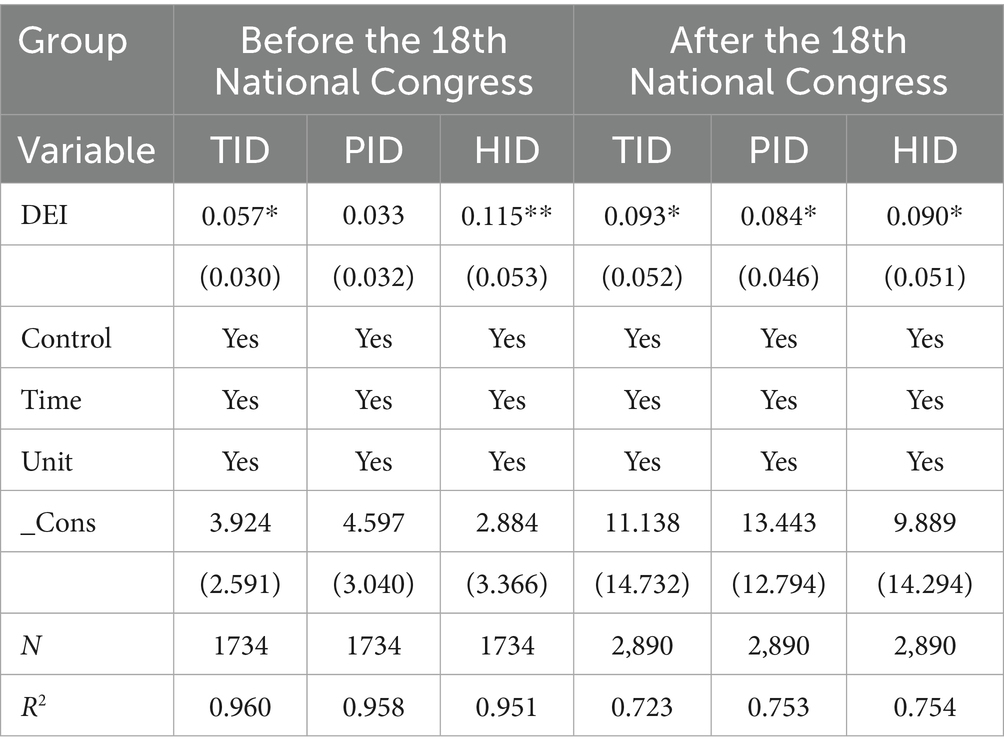
Fourth, subsample regression analysis. Using the year of the 18th National Congress of the Communist Party of China (2012) as the cutoff point, the subsample regression results demonstrate a notable characteristic of “comprehensive enhancement post-18th Congress” in the impact of the Digital Economy Index (DEI) on insurance demand. As shown in the table, the coefficients of DEI on Total Insurance Demand (TID), Property Insurance Demand (PID), and Health Insurance Demand (HID) after the 18th Congress show an overall increasing trend compared to the pre-Congress period. Particularly noteworthy is the transformation of property insurance from statistically insignificant to significantly positive, indicating that the series of major strategic deployments since the 18th National Congress have created more favorable conditions for the deep integration of the digital economy and the insurance industry. This phased difference reflects profound institutional and market transformation factors. First, the 18th National Congress explicitly proposed the “Implementation of Innovation-Driven Development Strategy,” incorporating the digital economy into national strategic emerging industries. Governments at all levels significantly increased investment in digital infrastructure, providing a solid foundation for the application of digital technology in the insurance sector. Second, the policy environment for financial technology continued to optimize after 2013, with the central bank and other departments successively issuing guidelines to promote the healthy development of internet finance, accelerating the digital transformation of the insurance industry. Third, the steady increase in residents’ income levels and consumption structure upgrades, coupled with the implementation of national strategies such as “Healthy China 2030,” enhanced residents’ willingness and ability to purchase property and health insurance. Fourth, breakthrough advancements in digital technologies like big data and artificial intelligence after the 18th National Congress enabled insurance companies to develop more accurate pricing models and more personalized insurance products, significantly improving market supply efficiency. It is worth noting that health insurance already demonstrated relatively high sensitivity before the 18th Congress, possibly due to the relatively simple nature of health insurance products and lower digitalization barriers at that time. However, post-18th Congress, various types of insurance demand have become more balanced, reflecting a more comprehensive and deeper enabling effect of the digital economy on the insurance industry.
5 Mechanism analysis
5.1 Moderating effect analysis
The moderating effect of economic development level (EDL) on the relationship between the digital economy and urban insurance demand exhibits significant differentiation. PID relies more heavily on digital risk control technologies such as IoT and big data for risk assessment and pricing; for instance, smart sensors monitoring asset risks and blockchain enabling automated claims processing. In economically developed regions, higher 5G coverage and advanced enterprise digital transformation, coupled with well-established digital infrastructure, facilitate real-time risk data collection and precise pricing through the DEI. Additionally, enterprises in these regions exhibit more diversified demand for property protection, further amplifying EDL’s moderating effect on PID. From a theoretical perspective, the insurable subjects in property insurance are more objectively quantifiable, making risk pricing and loss assessment more amenable to standardization via digital technologies. Highly developed regions provide the necessary infrastructure and market environment for deep digital technology application. According to information economics theory, this synergy effectively mitigates issues such as adverse selection and moral hazard in insurance markets, significantly enhancing the marginal effects of the digital economy. In contrast, HID is driven more by subjective factors such as residents’ awareness of protection and health concepts. Moreover, health data is constrained by privacy protections and industry barriers, slowing the penetration of digital economy-enabled health insurance technologies in less developed regions. Traditional sales channels for health insurance still dominate in lower-tier markets, weakening the substitution effect of digital channels. More importantly, behavioral insurance theory suggests that mental accounting and ambiguity aversion are more pronounced in health insurance purchasing decisions. These behavioral biases are particularly salient in less developed regions, somewhat undermining the moderating effect of the digital economy and resulting in an insignificant moderating role of EDL on DEI for HID. The moderating effect on TID stems from the combined influence of property and health insurance, with the strong moderating effect of property insurance partially offsetting the weak moderating effect of health insurance.
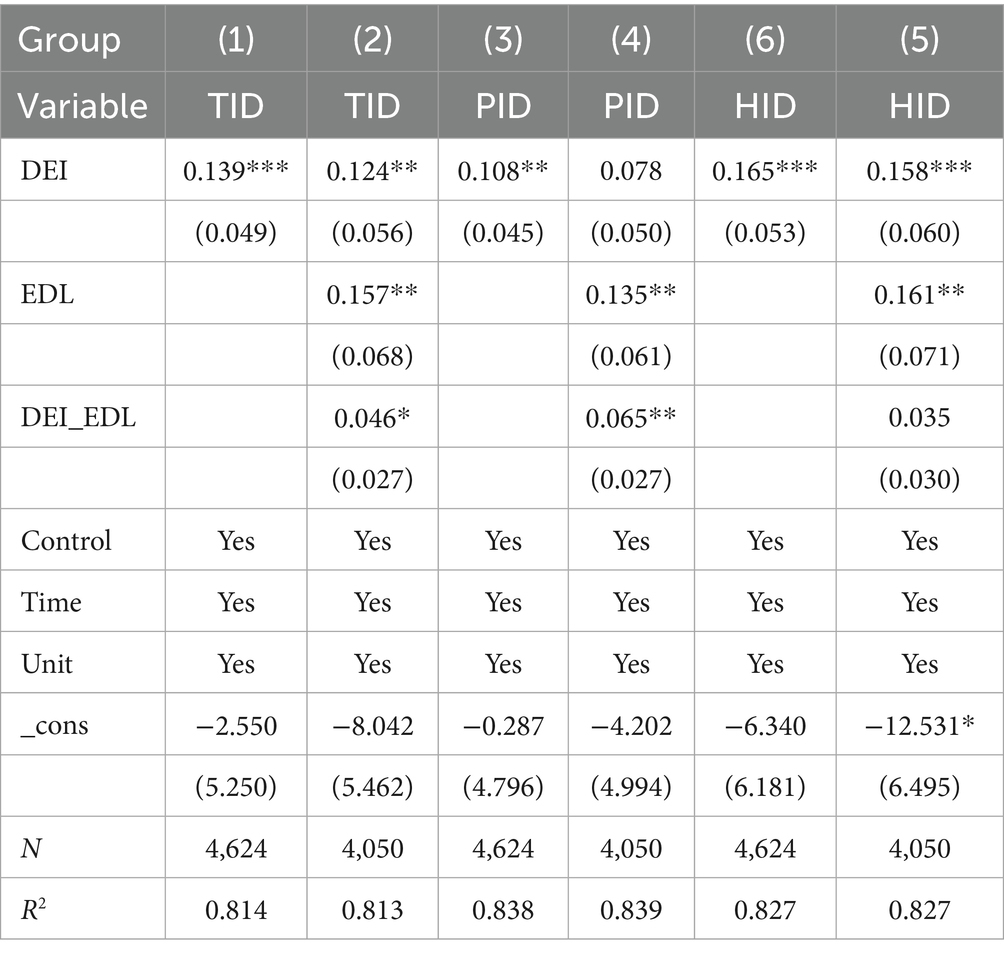
Table 11 and Human capital level (HCL) demonstrates a significant positive moderating effect on the relationship between the DEI and insurance demand. Regression results show that the interaction terms between DEI and HCL are 0.035, 0.034, and 0.036 for TID, PID, and HID, respectively. This indicates that for every 1% increase in HCL, the marginal promoting effect of DEI on insurance density strengthens by 0.035–0.036 units. These findings validate the theoretical hypothesis that human capital acts as a catalyst, with the mechanism aligning with the Technology Acceptance Model and Innovation Diffusion Theory. Populations with high human capital exhibit stronger acceptance of digital technologies, greater understanding of smart insurance products, and higher propensity to purchase insurance through digital channels. Their enhanced risk awareness and protection consciousness further reinforce their insurance purchasing intention in the digital economy context. From the supply perspective, insurance institutions in regions with high human capital levels can more easily attract technological talent to drive digital product innovation. Notably, HCL’s moderating effect on HID is slightly stronger than on PID. This finding corresponds with the experience good characteristic of health insurance, whose value realization depends more heavily on post-purchase claims and service experiences. High human capital groups demonstrate greater trust and proficiency in digital health management, enabling more complete realization of health insurance value perception and thus exhibiting a stronger moderating effect. The negative baseline effect of HCL alone on insurance density can be attributed to the digital economy breaking through the limitations of traditional self-protection patterns among high human capital groups. Digital technologies effectively release their latent insurance demand through technological empowerment (Table 12).
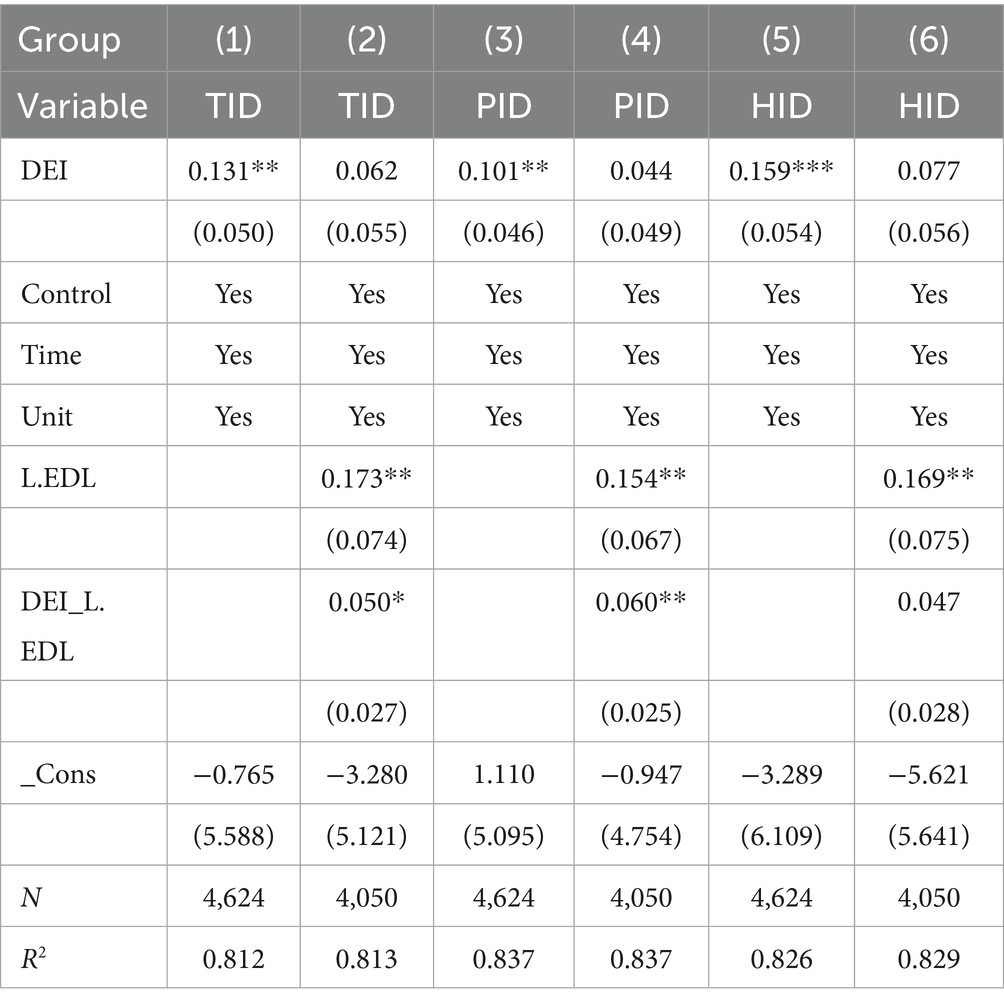
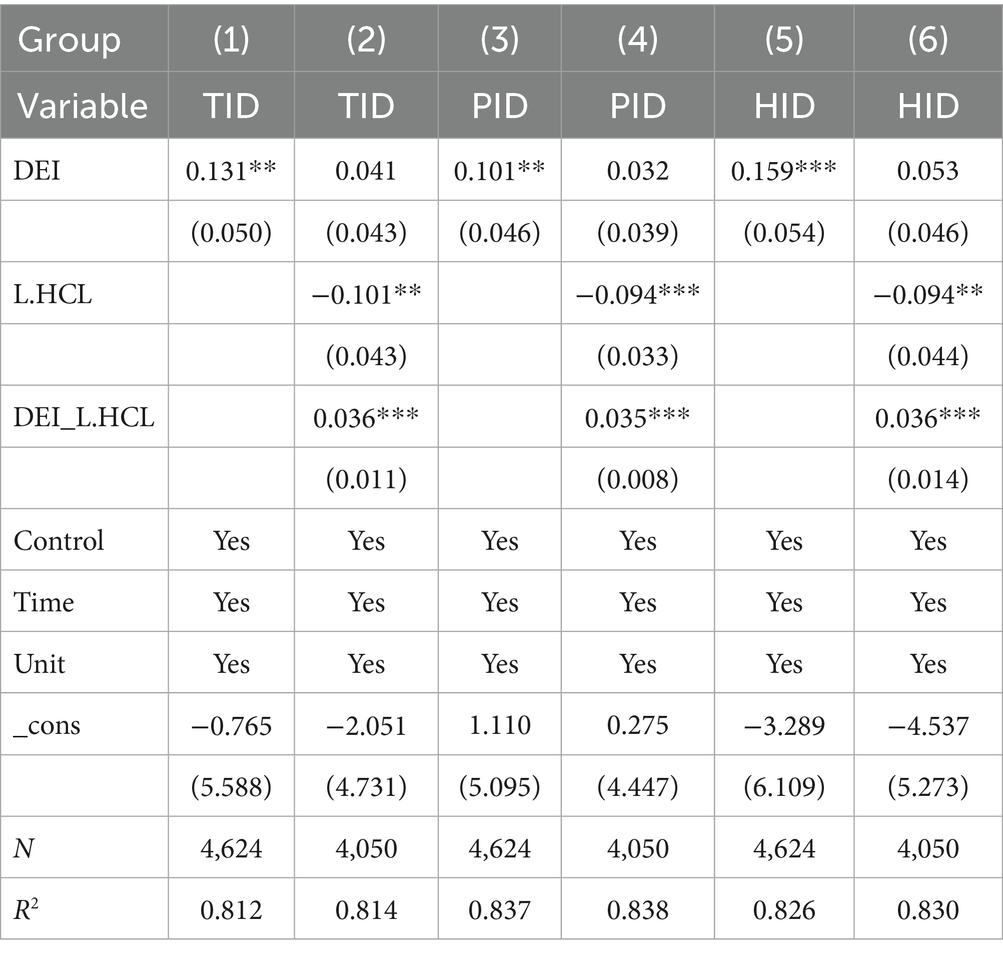
Furthermore, considering that EDL and HCL might themselves be influenced by the development of the digital economy, there exists a potential endogeneity concern regarding these moderating variables due to possible bidirectional causality. To address this issue, we introduced interaction terms between DEI and the lagged values of EDL and HCL into the regression model. Tables 13, 14 present the results of moderating effect. The results indicate that the moderating variables do not exhibit significant endogeneity, confirming the robustness of our findings regarding their moderating effects.
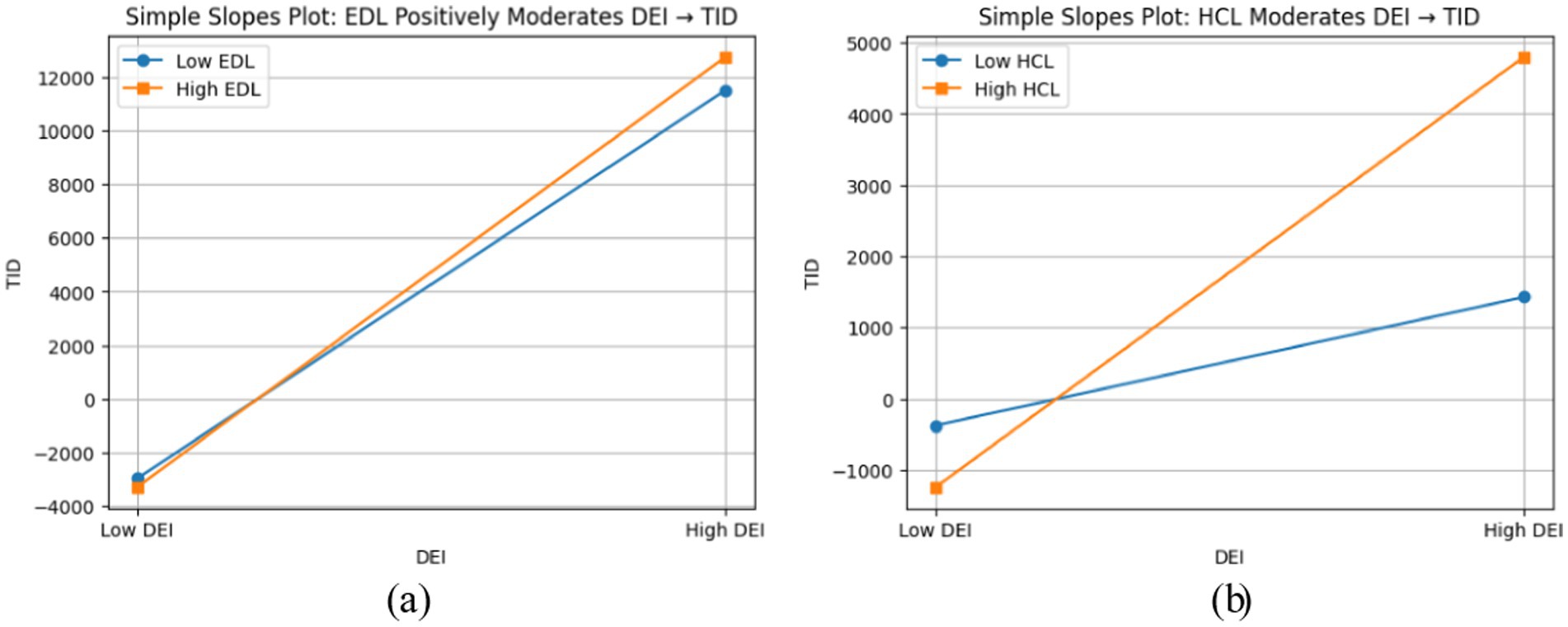
Based on the two simple slope plots presented above, the dual threshold effect of “infrastructure-human capital” in shaping the heterogeneous impact of the digital economy on insurance demand can be clearly observed. In Figure 1, both regression lines show steep upward slopes from “Low DEI” to “High DEI,” with a noticeably steeper slope under high economic development conditions. This visually confirms that economically developed regions, leveraging complete digital infrastructure such as 5G and IoT, significantly amplify the marginal effect of DEI on PID. In contrast, for HID, the lines remain almost parallel between high and low EDL due to data barriers and behavioral biases, indicating an insignificant moderating effect. Figure 3 demonstrates that for both property and health insurance, the slope of the high human capital line is steeper than that of the low human capital line. The slightly larger gap between the lines for health insurance suggests that populations with high human capital are more receptive to digital health management, thereby strengthening the marginal promoting effect of the digital economy on health insurance. The two figures collectively highlight that EDL determines “whether technology can be implemented,” while HCL determines “whether technology can be effectively used.” Together, they form the differentiated pathways through which the digital economy enables insurance demand: property insurance prioritizes “facilities and standardization,” while health insurance emphasizes “experience and individualization.”
5.2 Mediating effect analysis
Table 15 present the results of mediating effect. Consumption expenditure plays a significant mediating role in the process through which the digital economy influences total insurance demand, exhibiting dual characteristics. Empirical analysis demonstrates that the development of the digital economy not only directly drives the growth of insurance demand but also generates indirect effects by enhancing residents’ consumption levels. The digital economy significantly stimulates social consumption vitality, and the expanding scale of consumption further leverages a noticeable increase in protection demand. From a theoretical mechanism perspective, consumption upgrading essentially reflects the concentrated embodiment of residents’ wealth accumulation and the digital transformation of lifestyles. Higher-level consumption implies more diverse property subjects, richer consumption scenarios, and stronger risk protection awareness, thereby creating practical conditions for insurance product penetration. According to neoclassical economic theory, consumption is a function of income. The digital economy promotes residents’ income growth by enhancing production efficiency and creating new business formats, thereby expanding consumers’ budget constraints and purchasing capacity for protection-type products. This effectively alleviates the demand suppression problem in the insurance market caused by insufficient payment capacity. However, the consumption mediation pathway is only one of the mechanisms through which the digital economy affects insurance demand. As a mediating variable, the core significance of consumption expenditure lies in revealing the macro-level path through which the digital economy nourishes the insurance market by expanding the economic and consumption foundation, while the direct driving force of digital technology’s quality and efficiency improvements in the insurance industry itself constitutes a parallel mechanism.
5.3 Mediating effect analysis
Table 15 present the results of mediating effect. Consumption expenditure plays a significant mediating role in the process through which the digital economy influences total insurance demand, exhibiting dual characteristics. Empirical analysis demonstrates that the development of the digital economy not only directly drives the growth of insurance demand but also generates indirect effects by enhancing residents’ consumption levels. The digital economy significantly stimulates social consumption vitality, and the expanding scale of consumption further leverages a noticeable increase in protection demand. From a theoretical mechanism perspective, consumption upgrading essentially reflects the concentrated embodiment of residents’ wealth accumulation and the digital transformation of lifestyles. Higher-level consumption implies more diverse property subjects, richer consumption scenarios, and stronger risk protection awareness, thereby creating practical conditions for insurance product penetration. According to neoclassical economic theory, consumption is a function of income. The digital economy promotes residents’ income growth by enhancing production efficiency and creating new business formats, thereby expanding consumers’ budget constraints and purchasing capacity for protection-type products. This effectively alleviates the demand suppression problem in the insurance market caused by insufficient payment capacity. However, the consumption mediation pathway is only one of the mechanisms through which the digital economy affects insurance demand. As a mediating variable, the core significance of consumption expenditure lies in revealing the macro-level path through which the digital economy nourishes the insurance market by expanding the economic and consumption foundation, while the direct driving force of digital technology’s quality and efficiency improvements in the insurance industry itself constitutes a parallel mechanism.
6 Conclusion and countermeasures
6.1 Research conclusion
First, the digital economy exerts a significant and multi-dimensional positive driving effect on urban insurance demand. Based on panel data from 289 cities in China between 2007 and 2022, this study empirically examines the causal effect of the digital economy on insurance demand using a two-way fixed effects model combined with an instrumental variable approach. The results show that the digital economy not only significantly promotes TID but also positively affects PID and HID. The marginal effect on health insurance is approximately 1.53 times that on property insurance. This finding highlights that, against the backdrop of the digital economy, residents’ preference for health risk management and long-term protection has further intensified, making health insurance the most significantly empowered sector by digital technology.
Second, EDL and HCL play important moderating roles in the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand, while CE serves as a mediating variable. Economic development level significantly enhances the promoting effect of the digital economy on property insurance by improving digital infrastructure, driving enterprise digital transformation, and stimulating diversified demand for property insurance. Human capital level comprehensively strengthens the pulling effect of the digital economy on total insurance demand and its subcategories, particularly exhibiting a more pronounced moderating effect on health insurance, by enhancing residents’ digital literacy and insurance institutions’ innovation capabilities. Simultaneously, the digital economy effectively boosts residents’ income levels by improving production efficiency and fostering emerging business models, thereby enhancing consumers’ budgetary capacity and stimulating their willingness to purchase protection-type products. This, to some extent, alleviates the demand constraints caused by limited payment capacity that hinder the development of the insurance market.
Third, the impact of the digital economy on insurance demand exhibits significant regional heterogeneity. Geographically, northern regions show a stronger promoting effect of the digital economy on insurance compared to southern regions, owing to the digital transformation of traditional industries and greater policy support. Inland areas benefit from accelerated digital infrastructure construction and industrial relocation, resulting in a significantly stronger pulling effect of the digital economy on insurance demand compared to coastal areas. Additionally, large cities, with their concentrated digital resources, abundant human capital, and diverse innovation application scenarios, demonstrate a noticeably higher driving effect of the digital economy on insurance demand than small and medium-sized cities. Heterogeneity analysis further reveals that regional differences in the insurance effects of the digital economy are closely related to local development stages, industrial structures, policy environments, and risk perception patterns.
6.2 Countermeasures and suggestions
First, promote the digital innovation of insurance products with a focus on the health insurance sector. Insurance companies should leverage big data, artificial intelligence, and Internet of Things technologies to prioritize the development of innovative insurance products deeply integrated with digital health management. Examples include dynamically priced health insurance based on wearable device data, medical insurance products combined with telemedicine services, and long-term care insurance tailored for chronic disease patients and the elderly population. The government can establish “Digital Health Insurance Innovation Pilot Zones” to encourage collaboration between insurance companies, technology firms, and medical institutions, building an integrated new model for health insurance and effectively leveraging the digital economy’s stronger role in promoting health insurance demand.
Second, implement regionally differentiated policies to synergize the deep integration of digital infrastructure and insurance development. Given the stronger promoting effect of the digital economy on insurance demand in northern and inland regions, local governments should incorporate digital insurance into their regional digital economy strategies. Northern industrial cities can focus on developing property insurance based on industrial internet, such as smart manufacturing equipment insurance and supply chain disruption insurance. Inland regions should align with the “East Data, West Computing” node construction, deploying digital insurance data centers and disaster recovery systems, and developing insurance products adapted to local characteristic industries like agriculture and energy. Coastal and southern regions should emphasize business model innovation and service upgrades, exploring cross-border digital insurance pilots and developing new types of insurance such as shipping insurance and digital economy platform liability insurance.
Third, strengthen support for key factors and build a policy system that synergizes “economy-human capital-digital” elements. On one hand, continue to enhance digital infrastructure construction, expand 5G and gigabit optical network coverage, and improve computing infrastructure to provide foundational support for insurance digitalization. On the other hand, implement a “Digital Insurance Talent Special Program,” support universities in establishing insurance technology majors, and promote the joint construction of talent training bases by insurance institutions and technology companies to enhance the digital literacy of practitioners. Simultaneously, local governments can use fiscal subsidies, tax incentives, and other means to encourage small and medium-sized enterprises and families to purchase digital insurance products, expanding the market demand base.
Fourth, improve regulatory and risk prevention mechanisms to ensure the stable development of the digital insurance ecosystem. Regulatory authorities should accelerate the establishment of a new regulatory framework adapted to the development of digital insurance, promote the application of regulatory technology, and strengthen the identification and prevention of algorithmic discrimination, data privacy issues, and systemic risks. Encourage insurance companies to establish information disclosure and consumer education systems for digital insurance products to enhance consumer trust. Additionally, set up a digital insurance innovation risk compensation fund to provide risk buffers for innovative products, balancing innovation incentives with risk control.
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this study can be found in online repositories. The names of the repository/repositories and accession number(s) can be found in the article/supplementary material.
Author contributions
ML: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
Aimar, A., Palermo, A., and Innocenti, B. (2019). The role of 3D printing in medical applications: a state of the art. J Healthcare Engineering 2019, 1–10. doi: 10.1155/2019/5340616
Al-Abd, Y., and Mezher, T. (2014). Toward building a national innovation system in UAE. International Journal of Thermal and Environmental Engineering 7, Vancouver. doi: 10.5383/ijtee.07.02.008
Benami, E., and Carter, M. R. (2021). Can digital technologies reshape rural microfinance? Implications for savings, credit, & insurance. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 43, 1196–1220. doi: 10.1002/aepp.13151
Berry-Stölzle, T. R., and Esson, M. I. (2023). Capital issuances and premium growth in the property–liability insurance industry: evidence from the financial crisis and COVID-19 recession. The Geneva Papers on Risk and Insurance Issues and Practice 49, 1–25. doi: 10.1057/s41288-022-00283-5
Brown, T. M., Pogorzelski, W. H., and Giammanco, I. M. (2015). Evaluating hail damage using property insurance claims data. Weather. Clim. Soc. 7, 197–210. doi: 10.1175/WCAS-D-15-0011.1
Carlsson, B. (2004). The digital economy: what is new and what is not? Struct. Chang. Econ. Dyn. 15, 245–264. doi: 10.1016/j.strueco.2004.02.001
Chaintreau, A., Hui, P., Crowcroft, J., Diot, C., Gass, R., and Scott, J. (2007). Impact of human mobility on opportunistic forwarding algorithms. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 6, 606–620. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2007.1060
Chen, G. C., and Liu, Y. Y. (2017). “The empirical analysis on demand of property insurance in Hubei Province based on panel data” in 2017 29th Chinese Control And Decision Conference (CCDC) (IEEE), 6378–6383. doi: 10.1109/ccdc.2017.7978319
Chernew, M., Frick, K., and McLaughlin, C. G. (1997). The demand for health insurance coverage by low-income workers: can reduced premiums achieve full coverage? PubMed 32, 453–470. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9327813
Cogoljević, D., Gavrilović, M., Roganović, M., Matić, I., and Piljan, I. (2018). Analyzing of consumer price index influence on inflation by multiple linear regression. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Appl. 505, 941–944. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2018.04.014
Ding, C., and Huang, W. (2023). City-size distribution and north-south economic differentiation. Finance & Trade Economics 44, 108–125. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-8102.2023.09.007
Ding, C., Liu, C., Zheng, C., and Li, F. (2021). Digital economy, technological innovation and high-quality economic development: based on spatial effect and mediation effect. Sustainability 14:216. doi: 10.3390/su14010216
Ding, Y., Wang, P., Liu, X., Zhang, X., Hong, L., and Cao, Z. (2020). Risk assessment of highway structures in natural disaster for the property insurance. Nat. Hazards 104, 2663–2685. doi: 10.1007/s11069-020-04291-3
Embrey, M., Mbwasi, R., Shekalaghe, E., Liana, J., Kimatta, S., Ignace, G., et al. (2021). National health insurance fund’s relationship to retail drug outlets: a Tanzania case study. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 14:21. doi: 10.1186/s40545-021-00303-0
Geng, Y., Chen, L., Li, J., and Iqbal, K. (2023). Higher education and digital economy: analysis of their coupling coordination with the Yangtze River economic belt in China as the example. Ecol. Indic. 154:110510. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110510
Grigorescu, A., Pelinescu, E., Ion, A. E., and Dutcas, M. F. (2021). Human capital in digital economy: an empirical analysis of central and eastern European countries from the European Union. Sustainability 13:2020. doi: 10.3390/su13042020
Grubesic, T. H., Helderop, E., and Alizadeh, T. (2019). Closing information asymmetries: a scale agnostic approach for exploring equity implications of broadband provision. Telecommun. Policy 43, 50–66. doi: 10.1016/j.telpol.2018.04.002
Guo, F., Wang, J. Y., and Wang, F. (2020). Measuring China’s Digital Financial Inclusion: Index Compilation and Spatial Characteristics [J]. China Economic Quarterly (In Chinese) 19, 1401–1418. doi: 10.13821/j.cnki.ceq.2020.03.12
Horton, R. E. (1945). Erosional development of streams and their drainage basins; hydrophysical approach to quantitative morphology. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 56, 275–370. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1945)56[275:EDOSAT]2.0.CO;2
Hsu, W. K., Huang, P. C., Chang, C. C., Chen, C. W., Hung, D. M., and Chiang, W. L. (2011). An integrated flood risk assessment model for property insurance industry in Taiwan. Nat. Hazards 58, 1295–1309. doi: 10.1007/s11069-011-9732-9
Hu, X., Wang, Z., and Liu, J. (2022). The impact of digital finance on household insurance purchases: evidence from micro data in China. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur. Issues Pract. 47, 538–568. doi: 10.1057/s41288-022-00267-5
Huang, Q. H., Yu, Y. Z., and Zhang, S. L. (2019). Internet Development and Productivity Growth in Manufacturing Industry: Internal Mechanism and China Experiences [J]. China Industrial Economics (In Chinese) 8, 5–23. doi: 10.19581/j.cnki.ciejournal.2019.08.001
Huang, L., Zhang, H., Si, H., and Wang, H. (2023). Can the digital economy promote urban green economic efficiency? Evidence from 273 cities in China. Ecol. Indic. 155:110977. doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2023.110977
Jiao, S., and Sun, Q. (2021). Digital economic development and its impact on econimic growth in China: research based on the prespective of sustainability. Sustainability 13:10245. doi: 10.3390/su131810245
Kong, L., and Li, J. (2022). Digital economy development and green economic efficiency: evidence from province-level empirical data in China. Sustainability 15:3. doi: 10.3390/su15010003
Krystofik, M., Valant, C. J., Archbold, J., Bruessow, P., and Nenadic, N. G. (2020). Risk assessment framework for outbound supply-chain management. Information 11:417. doi: 10.3390/info11090417
Li, J., Wu, Y., and Xiao, J. J. (2019). The impact of digital finance on household consumption: evidence from China. Econ. Model. 86, 317–326. doi: 10.1016/j.econmod.2019.09.027
Li, Y., Yang, X., Ran, Q., Wu, H., Irfan, M., and Ahmad, M. (2021). Energy structure, digital economy, and carbon emissions: evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 28, 64606–64629. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-15304-4
Li, Q., and Zhang, X. (2024). Digital finance development in China: a scientometric review. Heliyon 10:e36107. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36107
Liang, Y., and Yang, Y. (2025). Research on Spatiotemporal Analysis and Prediction of China’s Carbon Emissions Based on LSTM Model. International Theory and Practice in Humanities and Social Sciences 2, 19–32. doi: 10.70693/itphss.v2i9.1347
Liao, S. H., Fei, W. C., and Chen, C. C. (2007). Knowledge sharing, absorptive capacity, and innovation capability: an empirical study of Taiwan's knowledge-intensive industries. J. Inf. Sci. 33, 340–359. doi: 10.1177/0165551506070739
Liu, M., Yang, H., and Zheng, S. (2024). Index construction and application of digital transformation in the insurance industry: evidence from China. PLoS One 19:e0296899. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296899
Manning, W. G., Newhouse, J. P., Duan, N., Keeler, E. B., Leibowitz, A., and Marquis, M. S. (1987). Health insurance and the demand for medical care: evidence from a randomized experiment. PubMed 77, 251–277. Available online at: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10284091
Maples, W. E., Giri, A. K., Coble, K. H., and Subedi, D. (2022). Impact of government programs on producer demand for hedging. Appl. Econ. Perspect. Policy 44, 1126–1138. doi: 10.1002/aepp.13241
Margaryan, A., Littlejohn, A., and Vojt, G. (2011). Are digital natives a myth or reality? University students’ use of digital technologies. Comput. Educ. 56, 429–440. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2010.09.004
Mossin, J. (1968). Aspects of rational insurance purchasing. J. Polit. Econ. 76, 553–568. doi: 10.1086/259427
Mumo, R., and Watt, R. (2019). Residential insurance market responses after earthquake: a survey of Christchurch dwellers. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 40:101166. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdrr.2019.101166
Nourani, M., Kweh, Q. L., Ting, I. W. K., Lu, W., and Strutt, A. (2021). Evaluating traditional, dynamic and network business models: an efficiency-based study of Chinese insurance companies. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur. Issues Pract. 47, 905–943. doi: 10.1057/s41288-021-00246-2
Nyman, J. A. (2001). The demand for insurance: Expected utility theory from a gain perspective, vol. No. 313. Discussion Paper. Minneapolis.
Pan, X., Li, B., and Wu, J. (2024). The effects of digital economy development on social insurance funds revenue: evidence from China. PLoS One 19:e0303897. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0303897
Pitthan, F., and De Witte, K. (2021). Puzzles of insurance demand and its biases: a survey on the role of behavioural biases and financial literacy on insurance demand. J. Behav. Exp. Financ. 30:100471. doi: 10.1016/j.jbef.2021.100471
Röschmann, A. Z., Erny, M., and Wagner, J. (2022). On the (future) role of on-demand insurance: market landscape, business model and customer perception. Geneva Pap. Risk Insur. Issues Pract. 47, 603–642. doi: 10.1057/s41288-022-00265-7
Ruiz, J. G., Mintzer, M. J., and Leipzig, R. M. (2006). The impact of e-learning in medical education. Acad. Med. 81, 207–212. doi: 10.1097/00001888-200603000-00002
Sadath, L. (2013). Data mining in E-Commerce: a CRM platform. International Journal of Computer Applications 68, 32–37. doi: 10.5120/11729-7383
Schwarcz, D. (2010). Regulating consumer demand in insurance markets. Erasmus Law Review 3, 23–45. doi: 10.5553/elr221026712010003001003
Shasha, Z. (2023). The impact of digital transformation on the insurance business model and innovative opportunities. Financial Engineering and Risk Management 6. doi: 10.23977/ferm.2023.061117
Sutton, B. (1994). China's insurance market: an awakening giant in the world's fastest growing region. Assurances 62, 371–390.
Umur, K. (2006). Bankaların internet bankacılığını kullanan müşterilerinin tutumlarına ilişkin değerlendirmeleri ve bir uygulama (Master's thesis). Turkey: Marmara Universitesi.
Yaari, M. E. (1965). Uncertain lifetime, life insurance, and the theory of the consumer. Rev. Econ. Stud. 32:137. doi: 10.2307/2296058
Yang, Y. (2023). Measurement and Analysis of China’s Green Economic Development Level—Evidence from Provincial Panel Data. Academic Journal of Business & Management 5. doi: 10.25236/ajbm.2023.051822
Yuan, C., and Jiang, Y. (2015). Factors affecting the demand for insurance in China. Appl. Econ. 47, 4855–4867. doi: 10.1080/00036846.2015.1037437
Zhan, Y., Tan, K. H., Li, Y., and Tse, Y. K. (2018). Unlocking the power of big data in new product development. Ann. Oper. Res. 270, 577–595. doi: 10.1007/s10479-016-2379-x
Zhang, P., and Gao, J. (2021). Quality of public health insurance and individuals’ consumption structure upgrades: evidence from China. Health Economics Review 11. doi: 10.1186/s13561-021-00343-x
Zhang, L., Wang, H., Wang, L., and Hsiao, W. (2006). Social capital and farmers willingness-to-join a newly established community-based health insurance in rural China. Health Policy 76, 233–242. doi: 10.1016/j.healthpol.2005.06.001
Keywords: digital economy, insurance demand, human capital, economic development, consumption expenditure
Citation: Liang M (2025) Digital economy and urban insurance demand: empirical evidence from 289 cities in China. Front. Hum. Dyn. 7:1669238. doi: 10.3389/fhumd.2025.1669238
Edited by:
Cristóbal Fernández Muñoz, Complutense University of Madrid, SpainReviewed by:
Prasongchai Setthasuravich, The University of Tokyo, JapanXihui Chen, Zhejiang University of Technology, China
Copyright © 2025 Liang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mengyadi Liang, MTIzMDAzNTYxM0BzdHVkZW50Lm11c3QuZWR1Lm1v
 Mengyadi Liang
Mengyadi Liang