- 1First Clinical Medical College, Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 2Gynecology I Department, First Affiliated Hospital Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
- 3Outpatient Department, Second Affiliated Hospital Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine, Harbin, China
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has seen a surge in interest in acupuncture as a treatment for polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition marked by hyperandrogenism, irregular ovulation, and polycystic ovaries. Acupuncture has been shown to dramatically lower androgen levels in PCOS patients; this effect may be achieved by reducing the secretion of neurotransmitters in the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axis and interfering with the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis and its cortisol release. Furthermore, by enhancing glucose metabolism, decreasing inflammation in adipose tissue, and enhancing intercellular communication pathways, acupuncture may indirectly address hyperandrogenemia. Although acupuncture has the potential to treat PCOS, further research is necessary to fully understand its mechanism. It is advised that more clinical research integrating molecular biology and biochemical methods be conducted in the future to determine the precise mechanism of acupuncture's effects on PCOS and to offer new suggestions for managing the condition's symptoms.
1 Introduction
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is a common gynecological endocrine disorder that significantly affects women's health during their reproductive years. Worldwide, PCOS affects 5%−18% of women, and its prevalence is increasing (1, 2). PCOS is a primary cause of metabolic abnormalities and female infertility. Additionally, a substantial proportion of affected individuals exhibit insulin resistance, obesity, acne, and hirsutism. Moreover, patients with PCOS frequently experience anxiety and face an elevated risk of developing long-term comorbidities such as diabetes and cardiovascular diseases (3). The pathogenesis of PCOS remains incompletely understood and involves multiple contributing factors. Contemporary research indicates that factors, including genetic predisposition (4), gut microbiota dysbiosis (5), oxidative stress (6), and unhealthy lifestyles (7), may contribute to PCOS pathogenesis. In addition to hyperandrogenism, abnormal luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone levels are characteristic endocrine manifestations of PCOS (8). Furthermore, adverse emotional states, including stress and anxiety, as well as chronic stress, disrupt normal physiological functions of the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG), and hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axes (9). Consequently, dysregulation of reproductive endocrine axes (e.g., HPG and HPA) induces hormonal disturbances, thereby contributing to the pathogenesis of PCOS.
As a traditional Chinese medical practice, acupuncture stimulates specific acupoints to modulate physiological processes (10). Acupuncture is thought to alleviate PCOS symptoms by regulating qi and blood circulation, enhancing metabolism, and modulating the neuroendocrine system (11). The “Kidney Qi-Tiankui-Chongren-Baogong” mechanism in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) corresponds to the hypothalamus-pituitary-ovary-uterus reproductive axis in modern medicine, providing a theoretical foundation for acupuncture treatment of PCOS. Current pharmacological treatments for PCOS, including hormone therapy and metformin, may cause adverse effects such as chest discomfort, headaches, and fatigue (12). In contrast, acupuncture therapy typically exhibits minimal adverse effects, primarily mild local reactions including redness, swelling, and pain (13). It is widely utilized across multiple medical disciplines, including gynecology and internal medicine, particularly in Asian regions (14). Acupuncture has gained significant research attention recently due to its favorable safety profile and minimal adverse effects, making it a popular alternative to pharmacological therapies for PCOS management. Several clinical studies have investigated potential therapeutic benefits of acupuncture for PCOS, including effects on hyperandrogenism, ovulation induction, menstrual cycle regulation, and insulin sensitivity (15). Although preliminary studies suggest potential benefits of acupuncture for PCOS, its precise mechanisms remain unclear, warranting further investigation to confirm efficacy and elucidate mechanisms of action (16).
This review aims to provide a novel perspective on acupuncture's role in PCOS management by examining its effects on hyperandrogenism and associated endocrine mechanisms. Through systematic analysis of current experimental evidence, we will evaluate the clinical efficacy of acupuncture and identify endocrine-related mechanistic changes. This synthesis will provide substantiated evidence for clinical translation and advance a comprehensive understanding of acupuncture's therapeutic potential in PCOS.
2 Acupuncture treatment for hyperandrogenism in PCOS patients
Clinical studies investigating acupuncture's effects on hyperandrogenism in PCOS have demonstrated positive outcomes. Clinical evidence indicates that PCOS patients undergoing acupuncture therapy exhibit significant reductions in serum testosterone levels following treatment. For instance, Jedel et al. (17) reported that 16 weeks of low-frequency electroacupuncture (EA) significantly reduced testosterone levels and increased estradiol levels in PCOS patients. Furthermore, low-frequency electroacupuncture demonstrated superior efficacy in ameliorating hyperandrogenism compared to exercise interventions. Compared with the exercise group, the low-frequency electroacupuncture (EA) group exhibited a 25% reduction in circulating testosterone (T), along with 30 and 28% decreases in androsterone glucuronide and 3α-androstanediol levels, respectively. Menstrual frequency significantly increased from 0.28 episodes at baseline to 0.69 episodes per month (p < 0.05). The EA intervention induced a 19% decline in dihydrotestosterone (DHT) levels, demonstrating superior efficacy compared to the 2% reduction observed in the exercise group (p < 0.01). Concurrently, acne severity scores showed a 32% improvement in the EA group, with concomitant reductions in estrogen levels: estrone (E1, 19%), estrone sulfate (E1-S, 12%), and estradiol (E2, 3%; all p < 0.05). Similarly, a seminal study by Stener-Victorin et al. (18) demonstrated that EA intervention significantly reduced circulating testosterone (22% reduction) and dihydrotestosterone (DHT, 12% decrease) in obese PCOS patients. Concomitantly, adipose tissue analysis revealed an 18% decline in testosterone concentration along with a 13% reduction in androstenedione levels compared to baseline measurements. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) involving PCOS patients revealed that the Dong's acupuncture (DA) intervention group achieved a more pronounced reduction in total testosterone levels compared with the pharmaceutical group receiving cyproterone acetate/ethinylestradiol (CPA/EE). Quantitative analysis demonstrated significantly greater decreases in the DA group (−0.45 nmol/L, 95% CI −0.52 to −0.38) vs. the CPA/EE group (−0.17 nmol/L, 95% CI −0.24 to −0.10), with the difference between groups reaching statistical significance (p = 0.008) (19). Although limited by a modest sample size (n = 60), the trial demonstrated clinically meaningful superiority of acupuncture therapy over conventional pharmacotherapy in lowering androgen levels. Notably, between-group differences exceeded the minimum clinically important differences for testosterone parameters (Δ = 0.28 nmol/L, ES = 0.62). Concurrently, preliminary evidence from case reports suggested that auricular acupuncture (AA) may ameliorate hyperandrogenemia in infertility management. Of particular mechanistic interest, one observational study (non-PCOS cohort) reported 18%−22% reductions in serum androgens following AA intervention (95% CI −25% to −15%, p = 0.032), though confirmation through powered RCTs remains warranted (20). Clinical randomized controlled trials demonstrate that auricular electroacupuncture effectively ameliorates hyperandrogenism and other PCOS symptoms as adjuvant therapy (21). Furthermore, integrative therapies combining acupuncture with segmental moxibustion and herbal formulations based on TCM syndrome differentiation have significantly reduced hyperandrogenism in PCOS patients with kidney deficiency and phlegm-dampness constitutions (22). Collectively, these findings indicate that acupuncture significantly improves hyperandrogenism in PCOS. Notably, investigators reported concomitant reductions in other PCOS-related symptoms. Park et al. (23) demonstrated that acupuncture intervention significantly improved menstrual cyclicity in PCOS patients. Li et al. (24) reported that electroacupuncture increased ovulation rates and improved live birth rates in PCOS patients following ovulation induction. Additionally, multiple studies document improvements in metabolic parameters, reduced abdominal adiposity, decreased acne severity, and weight reduction (25–27). These clinical findings indicate that acupuncture not only alleviates multiple PCOS-related symptoms but also significantly modulates androgen levels.
Acupuncture therapy for PCOS demonstrates a favorable safety profile, with minimal risk of serious adverse events. Clinical trial participants typically report only mild transient reactions, primarily localized and temporary erythema or bruising at needle insertion sites. These feelings of discomfort are typically mild and transient. As a result, acupuncture is thought to be a rather safe therapeutic choice for PCOS sufferers (28). The selection of acupuncture sites was predominantly concentrated in the lumbosacral region [e.g., Qihai (CV6), Guanyuan (CV4)], lower extremities [e.g., Sanyinjiao (SP6), Yinlingquan (SP9)], and hands (e.g., Dong's acupuncture). Specialized acupuncture was primarily focused on the auricular region (e.g., auricular seed application). These determinations were consistently made based on the practitioner's diagnostic approach and the patient's symptomatic presentation, with no standardized protocols established to date.
3 Acupuncture improves PCOS through the reproductive endocrine axis
3.1 Acupuncture improves PCOS by modulating GnRH pulsatility within the HPG axis
The GnRH pulse generator, located in the arcuate nucleus, is regulated by the interplay of kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin (KNDy) neurons and is finely tuned by steroid feedback (progesterone, estrogen) and metabolic signals such as insulin and leptin (29, 30). In PCOS, reduced progesterone negative feedback combined with elevated ovarian androgen levels accelerates GnRH pulse frequency, leading to excessive LH secretion, an increased LH/FSH ratio, and consequent ovarian hyperandrogenism (31–33).
Li et al. (34) demonstrated that the neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA level in the hypothalamus of adolescent PCOS rats was increased, and electroacupuncture could reverse the NPY level, while the estrous cycle disorder and ovarian morphological abnormalities were significantly improved. Mechanistically, acupuncture downregulates hypothalamic neuropeptide Y while upregulates β-endorphin expression in the arcuate nucleus, thereby stabilizing KNDy neuronal activity and reducing GnRH pulse frequency (35). These neuroendocrine adjustments re-establish a balanced LH/FSH ratio, attenuate ovarian androgen synthesis, and ultimately improve menstrual regularity and ovarian function in PCOS patients (36). In PCOS rat models, acupuncture normalizes the ovarian neuroendocrine milieu by down-regulating nerve growth factor (NGF) and endothelin-1 (ET-1), key mediators of aberrant follicular development and vascular dysregulation, thereby improving folliculogenesis (37). Concurrently, electroacupuncture modulates hypothalamic regulators of GnRH pulsatility by suppressing arcuate-nucleus neuropeptide Y and NGF expression and reducing GnRH mRNA transcription to stabilize KNDy neuronal activity and correct the LH/FSH ratio (38). By rebalancing the HPG axis, acupuncture also mitigates superovulation-induced ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, as demonstrated by reduced serum estradiol, increased pituitary estrogen receptor β expression, and higher counts of healthy antral and mature follicles (39).
In conclusion, current evidence demonstrates that acupuncture modulates the release of neuroendocrine factors, such as NGF, NPY, and ET-1, providing mechanistic insights and future research avenues in treating hyperandrogenism in PCOS.
3.2 Acupuncture improves PCOS by affecting the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis
Controlling stress responses and maintaining internal metabolic balance are the responsibilities of the HPA axis, an essential physiological system. The HPA axis triggers the release of adrenal cortex hormones, mainly cortisol, in response to stress or danger. These hormones help the body release stored energy, improve alertness, and adjust to stressful situations. The immune system and the HPA axis are intimately related; cortisol can regulate immunological balance by reducing inflammation and immune cell activity. Overall, the HPA axis is a critical physiological system responsible for regulating stress responses and maintaining internal metabolic homeostasis. In response to stress or perceived threats, the HPA axis initiates the release of adrenal cortex hormones, primarily cortisol. These hormones facilitate the mobilization of stored energy, enhance alertness, and support the body's adaptation to stressful conditions. The immune system and the HPA axis are closely interconnected; cortisol plays a key role in modulating immune homeostasis by suppressing inflammation and regulating immune cell activity. In pathological conditions, decreased melatonin secretion and new corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor gene mutations (CRHR1 and CRHR2) lead to overactivation of the HPA axis, leading to the risk of developing PCOS (40, 41). Stressful stimuli resulted in elevated salivary cortisol and cortisone levels in PCOS patients, which were positively correlated with circulating androstenedione and DHEA. At the same time, higher HPA-axis activity correlates with higher adrenal androgen output and a worse metabolic profile, circulating androstenedione, salivary cortisol (SalF), and cortisone (SalE) (42). According to previous studies, dysregulation of the HPA axis in patients with PCOS may lead to elevated androgen levels and chronic inflammation (43). Furthermore, HPA axis dysfunction has been implicated in other clinical manifestations of PCOS, such as obesity and hirsutism (42, 44). Increasing attention is being directed toward the role of acupuncture in modulating HPA axis activity, and several mechanisms have been proposed. Evidence suggests that electroacupuncture may alleviate depressive-like behaviors and suppress excessive HPA axis activation in rats subjected to chronic unpredictable mild stress (45). Clinical studies have also demonstrated that acupuncture can significantly reduce generalized anxiety disorder in perimenopausal women by modulating the HPA axis and inhibiting cortisol release (46). Similar findings have been reported in patients with allergic rhinitis and post-stroke anxiety (47, 48). Given the high prevalence of anxiety and depression in patients with PCOS, these findings suggest that electroacupuncture may improve hyperandrogenism by attenuating HPA axis hyperactivity.
In PCOS, HPA axis hyperactivity frequently disrupts endocrine homeostasis. Acupuncture may restore hormonal balance by attenuating HPA axis hyperactivity. We propose that acupuncture ameliorates PCOS symptoms through HPA axis modulation, subsequently regulating neuroendocrine-immune crosstalk. Currently, direct experimental evidence linking acupuncture-mediated HPA axis modulation to hyperandrogenism amelioration remains limited. Future clinical and preclinical studies investigating this pathway would provide stronger mechanistic validation for acupuncture's therapeutic effects (Figure 1).
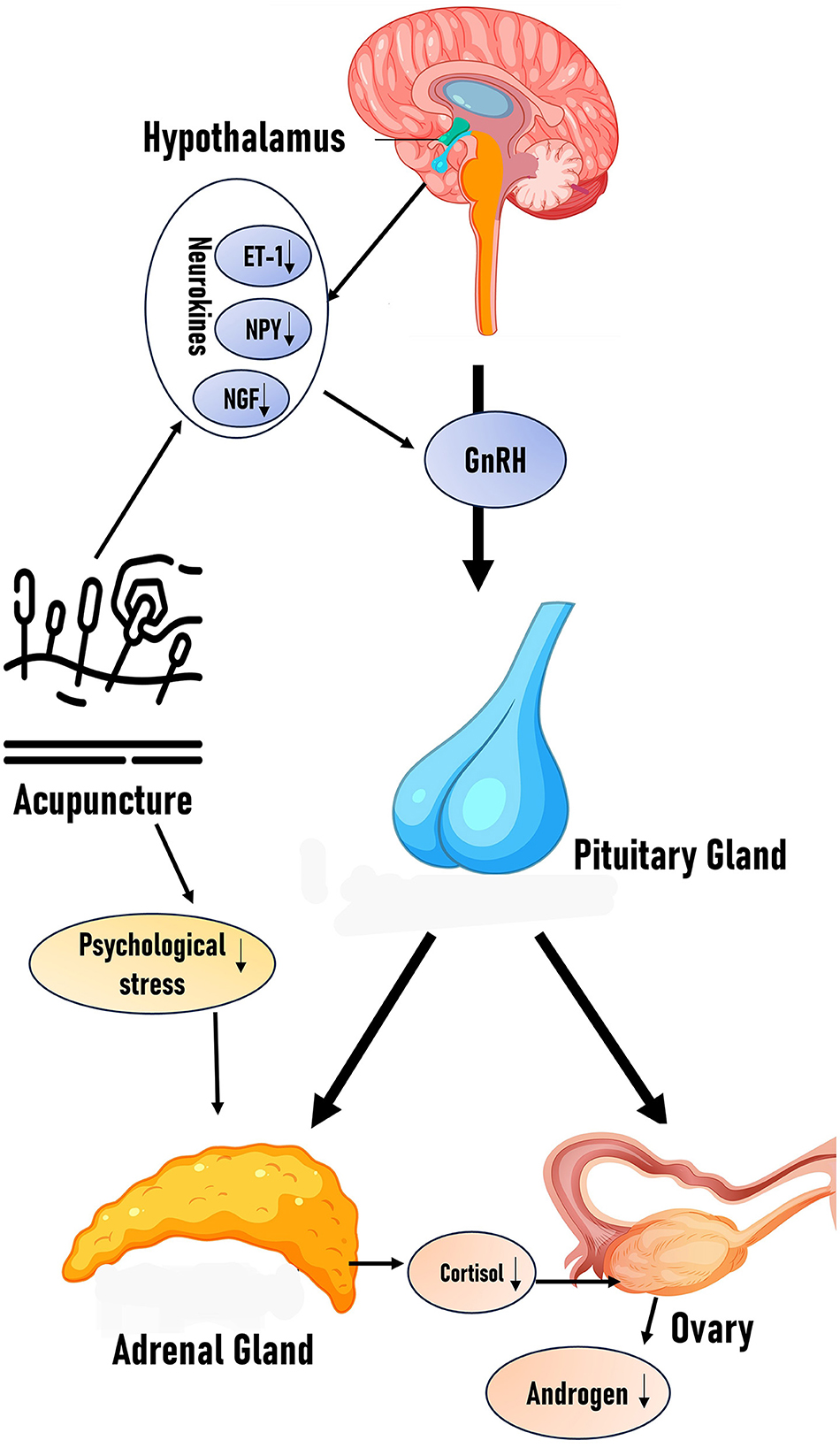
Figure 1. Effects of acupuncture on HPG axis and HPA axis: the figure schematically illustrates how acupuncture modulates the balance of the HPA and HPG axes by reducing neurotransmitters (ET-1, NPY, and NGF) and stressors, along with the proposed hypothesis.
4 Acupuncture improves PCOS by intervening in cellular signaling pathways
4.1 Hypothesis on the mechanisms by which electroacupuncture modulates ovarian-related signaling pathways
To elucidate PCOS pathophysiology and treatment mechanisms, recent research has increasingly focused on signaling molecules, expanding mechanistic investigations to non-pharmacological therapies. Accumulating evidence implicates multiple signaling pathways that are involved in acupuncture's therapeutic actions for PCOS. Primarily, electroacupuncture modulates ovarian signaling pathways to restore ovulatory function in anovulatory PCOS patients. In ovarian granulosa cells, electroacupuncture downregulates chromatin-interacting long non-coding RNA (LncMEG3), PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway components, and autophagy markers (SQSTM1/p62 and LC3II/LC3I ratio). Conversely, it upregulates ovulation-promoting hormone receptors. These findings indicate that electroacupuncture suppresses the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway and attenuates granulosa cell autophagy via LncMEG3 downregulation, thereby promoting ovulation (49). Given that dysregulated granulosa cell autophagy elevates ovarian androgen production (50), we propose that electroacupuncture ameliorates hyperandrogenism through autophagy suppression.
4.2 Hypothesis on the mechanisms by which electroacupuncture modulates signaling pathways related to glucose and lipid metabolism
Furthermore, electroacupuncture stimulation can treat insulin resistance in PCOS by modifying insulin receptor substrate (IRS) signaling pathways and regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Specifically, Xiang et al. (51) demonstrated that electroacupuncture boosts IRS-1 expression in PCOS patients, thereby activating the PI3K/GLUT4 signaling pathway and enhancing insulin signal transduction effectiveness. This improvement in insulin signaling is significant because hyperinsulinemia resulting from insulin resistance is known to enhance ovarian androgen synthesis, a process linked to diminished insulin signaling pathway efficiency (52). Complementing these clinical findings, several animal studies have explored the molecular mechanisms of acupuncture for PCOS from various perspectives. For instance, acupuncture was reported to activate the PI3K/AKT pathway (closely related to the PI3K pathway involved in insulin signaling), enhancing endometrial angiogenesis in PCOS rats. This effect increased the number of implantation sites and improved the rats' reproductive potential (53). This is particularly relevant since hyperandrogenemia, a hallmark of PCOS, often exacerbated by insulin resistance, increases miscarriage risk by impairing endometrial receptivity (54).
4.3 Hypothesis on the mechanisms and gene expression changes induced by electroacupuncture intervention
Furthermore, studies have investigated potential miRNA-mRNA co-expression networks in diabetes and PCOS. Specifically, they discovered that acupuncture significantly increases PLA2G4A expression and decreases miR-32-3p levels. Critically, subsequent research demonstrated that miR-32-3p downregulates PLA2G4A (phospholipase A2, group IVA) expression, and this interaction impacts glucose metabolism in PCOS patients (55). The significance of PLA2G4A dysregulation extends beyond metabolism, as aberrant expression of this gene in PCOS patients' oocytes is also linked to sex hormone receptors (56), highlighting its broader role in PCOS pathophysiology. This illustrates how acupuncture can affect the genetic level by modulating specific gene expression, such as through the miR-32-3p/PLA2G4A axis. Beyond miRNA-mediated mechanisms, acupuncture also directly influences tissue-specific gene expression related to metabolic dysfunction. For instance, manual acupuncture improved glucose clearance and primarily modified gene expression in visceral fat tissue. Experiments by Johansson et al. (57) further demonstrated this in a PCOS rat model: electroacupuncture countered DHT-induced changes by altering gene expression (decreased Tbc1d1 in soleus, increased Nr4a3 in mesenteric fat) and protein expression (increased pAS160/AS160, Nr4a3; decreased GLUT4). These findings on acupuncture's impact on fat tissue gene/protein expression are particularly relevant given clinical observations: studies in women with PCOS show that serum testosterone levels positively correlate with subcutaneous and visceral fat thickness as well as adipocyte size (58), suggesting a link between androgen excess and adipose tissue dysfunction that acupuncture may help modulate.
In conclusion, acupuncture may provide therapeutic effects in PCOS by modulating various signaling pathways involved in adipose tissue, ovarian function, skeletal muscle, the uterus, and insulin regulation. It may also influence gene expression. Despite these promising findings, few studies have specifically investigated the direct mechanisms by which acupuncture alleviates hyperandrogenism. Moreover, further research is needed to elucidate the specific molecular pathways involved and the interactions among these pathways. Currently, little is known about how acupuncture affects molecular expression at the genetic level in patients with PCOS. Continued investigation into the genetic and molecular mechanisms may yield more precise insights and inform the development of targeted acupuncture-based therapies (Figure 2).
5 Acupuncture treats hyperandrogenism by improving blood sugar metabolism in PCOS patients
5.1 How does acupuncture improve glucose metabolism in PCOS
Insulin resistance and glycemic dysregulation are strongly associated with PCOS, leading to elevated circulating insulin levels. Consequently, patients with PCOS have an increased risk of developing diabetes. Studies have shown that glucose intolerance is a common clinical manifestation in women with PCOS (59). It is well-established that insulin primarily promotes androgen production in the ovary, contributing to hyperandrogenism, a hallmark feature of PCOS. However, elevated androgen levels also contribute to the development of insulin resistance, perpetuating a vicious cycle of hyperandrogenism, compensatory hyperinsulinemia, and insulin resistance, ultimately leading to the chronic progression of PCOS (60). Although the precise etiologies of hyperinsulinemia and hyperandrogenemia remain unclear, addressing either condition is essential for the management of metabolic disorders. Numerous studies have demonstrated that acupuncture can modulate glucose metabolism through multiple signaling pathways. Therefore, investigating the effects of acupuncture on blood glucose regulation may help establish its utility in treating hyperglycemia and improving insulin sensitivity in patients with PCOS. Relevant animal studies suggest that electroacupuncture may alleviate insulin resistance in PCOS by modulating insulin signaling pathways. This effect is mediated by upregulating GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle and activating the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in rats (61). Hence, electroacupuncture at ST25 reduced homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance and hemoglobin A1c levels in diabetic model rats. Concurrently, electroacupuncture at ST25 reversed the reductions in adiponectin (Adipo) and AdipoR1 levels in skeletal muscle induced by insulin resistance. Compared with the model group, electroacupuncture further controlled obesity- and inflammation-associated factors [e.g., reduced leptin, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β)]. Relative to the non-EA group, EA reversed alterations in hippocampal mRNA levels of IRS-1, IRS-2, PI3K, Akt, insulin-degrading enzyme, glycogen synthase kinase 3 alpha (GSK3α), and glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β), with higher Akt levels observed in the EA group (62–64). Further studies have demonstrated that acupuncture can significantly improve various PCOS-related symptoms in mice, reduce insulin resistance, and normalize fasting blood glucose levels (65). Clinical studies have shown that individuals with type 2 diabetes experience significant reductions in both average stress scores and fasting blood glucose levels following acupuncture treatment (66). Concurrently, Xu et al. (62) reported that electroacupuncture improves both the morphology and function of pancreatic β-cells in T2DM rats, thereby enhancing overall pancreatic function. These effects are attributed to electroacupuncture-induced suppression of inflammation and modulation of the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system via upregulation of neuropeptide Y and choline acetyltransferase expression.
5.2 Hypothesis on the improvement of hyperandrogenism through acupuncture-mediated modulation of glucose metabolism
In patients with PCOS, elevated blood glucose levels trigger a compensatory increase in insulin secretion due to underlying insulin resistance. This hyperinsulinemia, in turn, contributes to excessive androgen production in the ovaries (67). Furthermore, hyperglycemia may influence androgen levels via metabolic pathways by downregulating insulin-sensitive glucose transporter protein (GLUT4), thereby reducing glucose uptake in ovarian cells (68). Elevated insulin levels can increase IGF-1 expression, which subsequently enhances androgen synthesis in the ovaries, while hyperglycemia may concurrently activate AMPK, further affecting androgen production (69). Emerging evidence suggests that acupuncture may modulate IGF-1 expression (70). This means that by activating particular acupoints (ST29 and SP6 acupuncture points), acupuncture may improve insulin sensitivity and improve cells' ability to absorb glucose. As a result, insulin levels drop, which in turn lessens the signals that cause the ovaries to overproduce androgens. This can be achieved by activating the AMPK pathway since AMPK promotes intracellular glucose metabolism (16). When hyperglycemic, reactive oxygen species (ROS) can rise dramatically. ROS have the ability to directly disrupt the ovaries' androgen synthesis pathways, which can impact the generation of androgens. Based on this study, acupuncture is hypothesized to attenuate oxidative stress by reducing reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation, thereby leading to decreased testosterone levels in PCOS patients, though no experimental evidence supports this mechanism (71). Elevated blood glucose levels can activate nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), thereby promoting the synthesis of pro-inflammatory cytokines. These inflammatory mediators may directly or indirectly impair testosterone synthesis in the ovaries, thereby exacerbating the symptoms of PCOS (72). The anti-inflammatory effects of acupuncture may be mediated by inhibition of the NF-κB signaling pathway, resulting in reduced androgen levels through suppression of inflammatory protein synthesis (73).
In conclusion, studies have suggested that acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medical practice, may offer therapeutic benefits in regulating glucose metabolism. Acupuncture may improve glycemic control through multiple mechanisms, including modulation of insulin sensitivity and secretion, anti-inflammatory effects, and central nervous system regulation. Given the triad of hyperinsulinemia, hyperandrogenemia, and insulin resistance, it is hypothesized that acupuncture may indirectly reduce androgen levels in patients with PCOS by improving pancreatic islet function and glucose metabolism. Additionally, acupuncture has been shown to significantly improve glycemic control in patients with PCOS and may contribute to improved quality of life (74). As research progresses, acupuncture may emerge as an effective adjunctive therapy for managing blood glucose levels in patients with PCOS.
6 PCOS is ameliorated through acupuncture-mediated improvements in adipose tissue functionality and related metabolic parameters
6.1 How does acupuncture improve adipose tissue metabolism in PCOS
Inflammation of adipose tissue is closely associated with PCOS. Beyond serving as an energy storage site, adipose tissue functions as an active endocrine organ, secreting various pro-inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and others (75). In patients with PCOS, adipose tissue inflammation is often markedly elevated, exacerbating clinical symptoms and contributing to abnormal follicular development, hyperandrogenism, and related complications (76). Acupuncture is believed to reduce adipose tissue inflammation, potentially alleviating endocrine disturbances in patients with PCOS. Studies have shown that electroacupuncture can modulate adipose tissue inflammation in obese rats by regulating catecholamine signaling, inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway, and ultimately reducing inflammatory responses (77). Researchers suggest that electroacupuncture may mitigate obesity-related inflammation through these mechanisms. Furthermore, by modulating adipose tissue inflammation, electroacupuncture may contribute to the amelioration of hyperandrogenemia. Women with PCOS are at increased risk of developing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), as elevated androgen levels can induce hepatic steatosis (78). Concurrently, electroacupuncture has demonstrated significant therapeutic effects in rat models of NAFLD characterized by hepatic inflammation. Therefore, by reducing hepatic inflammation, electroacupuncture may also attenuate adipose tissue inflammation and alleviate symptoms of NAFLD (79). Furthermore, the study found that electroacupuncture at Zhongwan (CV12) and Guanyuan (CV4) significantly reduced adiponectin and TNF-α levels in 12–14-week-old obese rats, while increasing leptin levels and significantly decreasing the leptin-to-adiponectin ratio in 3-week-old obese rats (80). Simultaneously, research has demonstrated that intraovarian lipid exposure and the ensuing inflammation and lipotoxicity may be factors in women's elevated testosterone production (81). Therefore, through altering inflammatory lipid metabolism, electroacupuncture may be used to treat hyperandrogenemia. According to Zhang et al's study (82), EA normalized serum dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and progesterone levels in PCOS model rats. Tenericutes at the phylum level and Prevotella_9 at the genus level, which were closely associated with body weight, exhibited significant alterations in the PCOS group before and after EA treatment. Consequently, reductions in visceral and subcutaneous fat content were achieved in PCOS rats. Moreover, an inverse correlation is observed between total testosterone levels and gut microbiota diversity in PCOS patients, while reduced gut microbiota diversity is consistently associated with obesity (83). In addition to modulating the gut microbiota, electroacupuncture may also reduce testosterone levels. Furthermore, acupuncture may improve the metabolic status of obese individuals with PCOS by regulating pathways associated with glucose metabolism (84). These studies offer novel insights into potential therapeutic strategies for managing obesity in PCOS. A randomized controlled clinical trial demonstrated that acupuncture can alter gene expression in adipose tissue of obese women, influencing biological processes including lipid metabolism, olfactory transduction, and gamma-aminobutyric acid signaling pathways (85). This provides important insights into the underlying mechanisms of acupuncture therapy. Multiple studies have proposed diverse mechanisms through which acupuncture regulates fat metabolism. Among these findings, electroacupuncture has been shown to activate the PI3K/Pten/Thbs1 signaling pathway, thereby promoting adipose tissue browning in obese mice. This suggests that electroacupuncture may help alleviate obesity by promoting angiogenesis and adipose tissue browning (86). Alternatively, electroacupuncture may enhance adipose tissue browning through Sirtuin-1–dependent mitochondrial biogenesis and PPARγ deacetylation (87). In addition, individualized acupuncture treatment protocols tailored to patient-specific characteristics and obesity subtypes may be developed.
6.2 Hypothesis on the improvement of hyperandrogenism through acupuncture-mediated regulation of adipose tissue metabolism
Elevated testosterone levels in patients with PCOS are closely associated with impaired lipid metabolism. In patients with PCOS, elevated cholesterol levels may provide increased substrate availability for androgen synthesis, particularly for androgenic steroid hormones, thereby contributing to elevated androgen levels (88). Acupuncture may reduce low-density lipoprotein and total cholesterol levels, thereby decreasing the availability of cholesterol precursors required for testosterone synthesis (89). This effect is likely mediated through the regulation of 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase, a key enzyme in the androgen biosynthesis pathway (90). Inflammatory conditions in adipose tissue are frequently observed in patients with PCOS. Chronic inflammation can lead to the release of various cytokines from adipose tissue, which may disrupt ovarian androgen synthesis pathways and increase androgen levels (91). By reducing adipose tissue inflammation, acupuncture may help regulate testosterone levels. It may suppress the release of inflammatory mediators such as IL-6 and TNF-α from adipose tissue (92). These cytokines are known to influence androgen levels in patients with PCOS (93). Additionally, acupuncture may modulate signaling pathways such as NLRP3, PI3K, and AMPK, thereby improving obesity-related parameters and subsequently reducing testosterone levels (77, 86, 94) (Figure 3).
However, it is important to note that experimental evidence supporting the use of acupuncture for treating hyperandrogenemia remains limited, particularly regarding its effects on the central nervous system, peripheral metabolism, and genetic mechanisms. Although several animal and clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of acupuncture in treating PCOS, the quality of these studies is inconsistent, and the underreporting of negative outcomes may introduce bias. Moreover, there is a continued lack of large-scale systematic reviews and meta-analyses to synthesize and critically assess the current body of research. Therefore, future research should focus on increasing clinical sample sizes and supplementing findings with relevant animal studies, which may yield more robust and reliable outcomes.
7 Acupuncture treatment and quality of life in patients with PCOS
It is well-established that individuals with PCOS frequently experience emotional symptoms, including a diminished health-related quality of life. Among these emotional disturbances, anxiety and depression are particularly prominent. In TCM, liver qi stagnation is commonly considered the underlying cause of anxiety and depression. Consequently, therapeutic strategies focus on alleviating depression and soothing the liver. Acupuncture therapy often involves needle insertion at acupoints along or near the liver meridian. Chang et al. (95) initially demonstrated in a randomized clinical trial that acupuncture had beneficial effects on emotional well being and lipid metabolism in PCOS patients. The present study found that after a 4-month acupuncture intervention, patients exhibited improved lipid metabolism and reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression. These findings support the use of acupuncture as an adjunctive therapy for individuals with PCOS. Another randomized controlled trial investigated the effects of acupuncture on emotional symptoms and quality of life in PCOS patients. Results indicated that the acupuncture group experienced significant improvements in quality of life scores and a marked reduction in anxiety and depression symptoms, further supporting acupuncture as an effective intervention for enhancing psychological well being in PCOS patients (96). Moreover, studies suggest that both standardized and individualized acupuncture treatments significantly improve the quality of life in PCOS patients. Meta-analytic findings highlight the benefits of moxibustion and traditional Chinese medicine in improving the quality of life and alleviating anxiety and depression symptoms in PCOS patients, particularly in the context of fertility-related concerns (97, 98). Finally, researchers observed that acupuncture reduced symptoms of anxiety and depression in PCOS patients. Concurrently, the SF-36 survey revealed improvements in physical functioning, vitality, general health perception, and overall mental health scores. According to this study, acupuncture may alleviate emotional disturbances in PCOS patients, particularly improving physical functioning, vitality, and mental health (99).
Irregular menstruation, acne, and excessive hair growth are common accompanying symptoms in patients with PCOS. An increasing number of studies have shown that acupuncture may be effective in treating hirsutism, acne, and menstrual irregularities in PCOS patients. Zhou et al. (100) investigated the effects of acupuncture on menstrual frequency in patients with PCOS. The study supported acupuncture as an intervention strategy for improving menstrual frequency in PCOS patients, as a significant increase was observed in the true acupuncture group. Another clinical trial (101) confirmed that electroacupuncture significantly improved hirsutism and reproductive function in PCOS patients. Additionally, in obese PCOS patients, abdominal acupuncture has shown significant benefits in improving menstrual frequency, body mass index, and waist-to-hip ratio (102). Furthermore, a randomized controlled trial on auricular acupressure for PCOS patients demonstrated improvement in acne symptoms in the treatment group (27). Moreover, studies investigating the effects of low-frequency electroacupuncture combined with physical activity in PCOS patients have shown significant improvements in menstrual regularity, acne, and hirsutism (17).
In summary, acupuncture is a complementary and alternative therapy that can improve menstrual regularity, reduce hirsutism and acne, enhance quality of life, and support emotional well being and life satisfaction in patients with PCOS. However, there are certain limitations associated with acupuncture. Notably, acupuncture often requires a prolonged course of treatment, which may be challenging for some patients to adhere to. Furthermore, due to individual variability, the effectiveness of acupuncture can vary significantly, resulting in heterogeneous responses among patients. Therefore, more personalized and tailored treatment approaches are warranted. Moreover, many existing studies have limited follow-up durations and lack a comprehensive analysis of long-term treatment outcomes. Encouragingly, most PCOS patients view acupuncture therapy favorably, particularly those seeking to avoid pharmacological treatments and their associated side effects. Many patients consider acupuncture to be a gentle and natural form of therapy.
8 Conclusion
As a safe and cost-effective adjunctive therapy, acupuncture can be integrated with standard pharmacological treatments and lifestyle modifications in PCOS management. While direct evidence from clinical trials or preclinical models demonstrating acupuncture-mediated reduction of circulating androgens remains limited, current clinical and preclinical evidence indicates that acupuncture modulates HPG and HPA axis functions, enhances insulin sensitivity, and attenuates chronic adipose tissue inflammation. These multimodal effects ultimately restore regular menstrual cyclicity, ameliorate hyperandrogenism, and improve psychological well being. Collectively, this evidence supports acupuncture's potential to ameliorate hyperandrogenism.
Mechanistically, acupuncture modulates key pathways regulating steroidogenesis, glucose metabolism, and immune function. Preclinical and clinical studies demonstrate its neuroendocrine regulatory actions through bidirectional modulation of neurotransmitters and hormones. Emerging evidence further indicates that acupuncture alters inflammatory cytokine profiles in adipose tissue, consequently improving metabolic indices.
Future development should focus on personalized acupuncture protocols guided by genetic polymorphisms and validated biomarkers. The identification of reliable biomarkers, including neuroendocrine sensitivity-associated single-nucleotide variants and serum cytokine profiles (103, 104), will enable precise selection of acupoints (e.g., Sanyinjiao [SP6], Qihai [CV6], Guanyuan [CV4], and Zigong [EX-CA1]), optimization of needling parameters, and patient-specific treatment scheduling. Concurrently, rigorously designed multicenter trials with standardized protocols are needed to evaluate long-term safety and therapeutic sustainability.
Establishing internationally standardized guidelines for acupuncture diagnosis, point prescription, and practitioner certification is essential for reproducibility and global implementation. As acupuncture becomes integrated into comprehensive PCOS care pathways, it is poised to evolve as an evidence-based component of personalized medicine, optimizing physiological outcomes and quality of life (Figure 4).
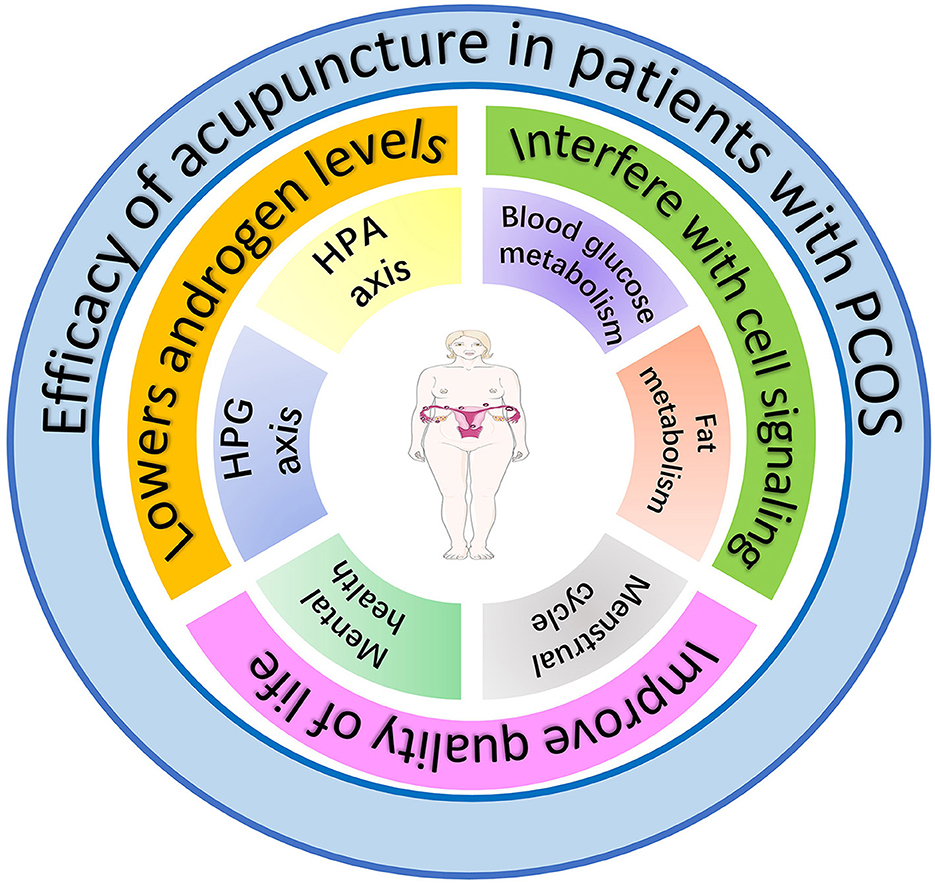
Figure 4. The effects of acupuncture on women with PCOS. The figure hypothesizes that amelioration of PCOS symptoms by acupuncture is achieved through three primary mechanisms: (1) reduction of androgen levels via modulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) and hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal (HPG) axes, (2) improvement of glucose and lipid metabolism through regulation of intercellular signaling pathways, and (3) enhancement of quality of life by ameliorating emotional disturbances and menstrual cyclicity.
Author contributions
Y-XL: Writing – original draft. Y-HH: Writing – review & editing. YJ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. Y-HZ: Funding acquisition, Resources, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 82074259 and 82374286) and Young Qihuang Scholar Developing Program of Heilongjiang Province [Heilongjiang Traditional Chinese Medicine, Letter from the Department of Education (2023), grant no. 36].
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Hoeger KM, Dokras A, Piltonen T. Update on PCOS: consequences, challenges, and guiding treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2021) 106:e1071–83. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa839
2. Joham AE, Norman RJ, Stener-Victorin E, Legro RS, Franks S, Moran LJ, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. (2022) 10:668–80. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00163-2
3. Teede HJ, Misso ML, Costello MF, Dokras A, Laven J, Moran L, et al. Recommendations from the international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. (2018) 110:364–79. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.05.004
4. Zhou J, Liu F, Tian L, Yang M, Tan J, Liu X, et al. Mutational analysis of minichromosome maintenance complex component (MCM) family genes in Chinese Han women with polycystic ovarian syndrome. Gynecol Endocrinol. (2023) 39:2206912. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2023.2206912
5. Liang Y, Zeng W, Hou T, Yang H, Wu B, Pan R, et al. Gut microbiome and reproductive endocrine diseases: a Mendelian randomization study. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1164186. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1164186
6. Kaltsas A, Zikopoulos A, Moustakli E, Zachariou A, Tsirka G, Tsiampali C, et al. The silent threat to women's fertility: uncovering the devastating effects of oxidative stress. Antioxidants. (2023) 12:1490. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081490
7. Teede HJ, Tay CT, Laven J, Dokras A, Moran LJ, Piltonen TT, et al. Recommendations from the 2023 international evidence-based guideline for the assessment and management of polycystic ovary syndrome†. Hum Reprod. (2023) 38:1655–79. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgad463
8. Adams J, Polson D, Abdulwahid N, Morris D, Franks S, Mason H, et al. Multifollicular ovaries: clinical and endocrine features and response to pulsatile gonadotropin releasing hormone. Lancet. (1985) 326:1375–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(85)92552-8
9. Mbiydzenyuy NE, Qulu L-A. Stress, hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, and aggression. Metab Brain Dis. (2024) 39:1613–36. doi: 10.1007/s11011-024-01393-w
10. Kaptchuk TJ. Acupuncture: theory, efficacy, and practice. Ann Intern Med. (2002) 136:374–83. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-136-5-200203050-00010
11. Chen X, He H, Long B, Wei B, Yang P, Huang X, et al. Acupuncture regulates the apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovarian syndrome-related abnormal follicular development through LncMEG3-mediated inhibition of miR-21-3p. Biol Res. (2023) 56:31. doi: 10.1186/s40659-023-00441-6
12. Stańczak NA, Grywalska E. Dudzińska EJ. The latest reports and treatment methods on polycystic ovary syndrome. Ann Med. (2024) 56:2357737. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2024.2357737
13. Xu M, Yang C, Nian T, Tian C, Zhou L, Wu Y, et al. Adverse effects associated with acupuncture therapies: an evidence mapping from 535 systematic reviews. Chin Med. (2023) 18:38. doi: 10.1186/s13020-023-00743-7
14. Park H-L, Lee H-S, Shin B-C, Liu J-P, Shang Q, Yamashita H, et al. Traditional medicine in China, Korea, and Japan: a brief introduction and comparison. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2012) 2012:429103. doi: 10.1155/2012/429103
15. Jo J, Lee YJ, Lee H. Acupuncture for polycystic ovarian syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine. (2017) 96:e7066. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000007066
16. Peng Y, Yang X, Luo X, Liu C, Cao X, Wang H, et al. Novel mechanisms underlying anti-polycystic ovary like syndrome effects of electroacupuncture in rats: suppressing SREBP1 to mitigate insulin resistance, mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress. Biol Res. (2020) 53:50. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00317-z
17. Jedel E, Labrie F, Odén A, Holm G, Nilsson L, Janson PO, et al. Impact of electro-acupuncture and physical exercise on hyperandrogenism and oligo/amenorrhea in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2011) 300:E37–45. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00495.2010
18. Stener-Victorin E, Maliqueo M, Soligo M, Protto V, Manni L, Jerlhag E, et al. Changes in HbA(1c) and circulating and adipose tissue androgen levels in overweight-obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome in response to electroacupuncture. Obes Sci Pract. (2016) 2:426–35. doi: 10.1002/osp4.78
19. Cao Y, Chen H, Zhao D, Zhang L, Yu X, Zhou X, et al. The efficacy of Tung's acupuncture for sex hormones in polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Complement Ther Med. (2019) 44:182–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.04.016
20. Gerhard I, Postneek F. Possibilities of therapy by ear acupuncture in female sterility. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd. (1988) 48:165–71. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1035717
21. Ee C, Smith CA, Costello M, Moran L, Steiner GZ, Stepto N, et al. Acupuncture or auricular electro-acupuncture as adjuncts to lifestyle interventions for weight management in PCOS: protocol for a randomised controlled feasibility study. Pilot Feasibility Stud. (2020) 6:53. doi: 10.1186/s40814-020-00591-4
22. Zhao QY, Sun Y, Zhou J, Gao YL, Ma GZ, Hu ZH, et al. Effectiveness of herb-partitioned moxibustion combined with electroacupuncture on polycystic ovary syndrome in patients with symptom pattern of kidney deficiency and phlegm-dampne. J Tradit Chin Med. (2021) 41:985–93. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2021.06.017
23. Park KS, Gang W, Kim PW, Yang C, Jun P, Jung SY, et al. Efficacy and safety of acupuncture on oligomenorrhea due to polycystic ovary syndrome: an international multicenter, pilot randomized controlled trial. Medicine. (2022) 101:e28674. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028674
24. Li J, Ng EH, Stener-Victorin E, Hu Z, Wu W, Lai M, et al. Comparison of acupuncture pretreatment followed by letrozole versus letrozole alone on live birth in anovulatory infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e010955. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010955
25. Dong H, Wang Q, Cheng L, Wang Z, Wu X, Zhou Z, et al. Effect of low-frequency electro-acupuncture in unmarried women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled study. Altern Ther Health Med. (2022) 28:24–33.
26. Dong HX, Wang Q, Wang Z, Wu XK, Cheng L, Zhou ZM, et al. Impact of low frequency electro-acupuncture on glucose and lipid metabolism in unmarried PCOS women: a randomized controlled trial. Chin J Integr Med. (2021) 27:737–43. doi: 10.1007/s11655-021-3482-z
27. Li Y, Hou L, Wang Y, Xie L, Zhang M, Pan Z, et al. Auricular points acupressure for insulin resistance in overweight/obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome: protocol for a randomised controlled pilot trial. BMJ Open. (2019) 9:e027498. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-027498
28. Li J, Ng EH, Stener-Victorin E, Hu Z, Shao X, Wang H, et al. Acupuncture treatment for insulin sensitivity of women with polycystic ovary syndrome and insulin resistance: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2017) 18:115. doi: 10.1186/s13063-017-1854-2
29. da Costa CS, Oliveira TF, Freitas-Lima LC, Padilha AS, Krause M, Carneiro MTW, et al. Subacute cadmium exposure disrupts the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, leading to polycystic ovarian syndrome and premature ovarian failure features in female rats. Environ Pollut. (2021) 269:116154. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2020.116154
30. Ehrman DA, Barnes RB, Rosenfield RL. Polycystic ovary syndrome as a form of functional ovarian hyperandrogenism due to dysregulation of androgen secretion. Endocr Rev. (1995) 16:322–53. doi: 10.1210/edrv-16-3-322
31. Phumsatitpong C, Wagenmaker ER. Moenter SM. Neuroendocrine interactions of the stress and reproductive axes. Front Neuroendocrinol. (2021) 63:100928. doi: 10.1016/j.yfrne.2021.100928
32. Hakimi O. Cameron L-C. Effect of exercise on ovulation: a systematic review. Sports Med. (2017) 47:1555–67. doi: 10.1007/s40279-016-0669-8
33. Martin B, Golden E, Carlson OD, Egan JM, Mattson MP, Maudsley S. Caloric restriction: impact upon pituitary function and reproduction. Ageing Res Rev. (2008) 7:209–24. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2008.01.002
34. Li Y, Zhi W, Haoxu D, Qing W, Ling C, Ping Y, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on the expression of hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and ghrelin in pubertal rats with polycystic ovary syndrome. PLoS ONE. (2022) 17:e0259609. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0259609
35. Zhaohui Z, Jingzhu Z, Guipeng D, Xuesong W, Yuanming Z, Yinping W, et al. Role of neuropeptide Y in regulating hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad axis in the rats treated with electro-acupuncture. Neuropeptides. (2012) 46:133–9. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2012.03.002
36. Xu G, Zhao X, Li Z, Hu J, Li X, Li J, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on the kisspeptin-gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)/luteinizing hormone (LH) neural circuit abnormalities and androgen receptor expression of kisspeptin/neurokinin B/dynorphin neurons in PCOS rats. J Ovarian Res. (2023) 16:15. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01078-x
37. Stener-Victorin E, Lundeberg T, Cajander S, Aloe L, Manni L, Waldenström U, et al. Steroid-induced polycystic ovaries in rats: effect of electro-acupuncture on concentrations of endothelin-1 and nerve growth factor (NGF), and expression of NGF mRNA in the ovaries, the adrenal glands, and the central nervous system. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. (2003) 1:33. doi: 10.1186/1477-7827-1-33
38. Zhaohui Z, Yugui C, Yuanming Z, Xuesong W, Xiaobing J, Zhice X, et al. Effect of acupuncture on pubertal development of rats and rabbits at different developmental stages. Neuropeptides. (2007) 41:249–61. doi: 10.1016/j.npep.2007.02.003
39. Fu H, Sun J, Tan Y, Zhou H, Xu W, Zhou J, et al. Effects of acupuncture on the levels of serum estradiol and pituitary estrogen receptor beta in a rat model of induced super ovulation. Life Sci. (2018) 197:109–13. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.005
40. Amin M, Horst N, Wu R, Gragnoli C. Novel corticotropin-releasing hormone receptor genes (CRHR1 and CRHR2) linkage to and association with polycystic ovary syndrome. J Ovarian Res. (2023) 16:155. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01159-5
41. Zafari Zangeneh F. Deregulated brain's central clock management on sleep-wake behavior in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: melatonin & sleep pattern. J Family Reprod Health. (2022) 16:229–38. doi: 10.18502/jfrh.v16i4.11348
42. Mezzullo M, Fanelli F, Di Dalmazi G, Fazzini A, Ibarra-Gasparini D, Mastroroberto M, et al. Salivary cortisol and cortisone responses to short-term psychological stress challenge in late adolescent and young women with different hyperandrogenic states. Psychoneuroendocrinology. (2018) 91:31–40. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2018.02.022
43. Gonzalez D, Maidana P, Ibar C, Jamardo J, Jacobsen D, Fritzler A, et al. Hair cortisol in polycystic ovary syndrome. Sci Rep. (2022) 12:10309. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14061-9
44. Pasquali R, Gambineri A. Cortisol and the polycystic ovary syndrome. Expert Rev Endocrinol Metab. (2012) 7:555–66. doi: 10.1586/eem.12.42
45. Chen W, Chen Y, Cheng W, Li P, Shen J, Tong T, et al. Acupuncture exerts preventive effects in rats of chronic unpredictable mild stress: the involvement of inflammation in amygdala and brain-spleen axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2023) 646:86–95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2023.01.046
46. Liu X, Xie X, Li Y, Li M, Wang Y, Wang N, et al. Efficacy of manual acupuncture versus placebo acupuncture for generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) in perimenopause women: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2021) 22:833. doi: 10.1186/s13063-021-05756-x
47. Chen S, Qu SH, Zhang Y, Wen ZH, Guo SN, Zeng WM, et al. Impact of acupuncture for allergic rhinitis on the activity of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Trials. (2019) 20:372. doi: 10.1186/s13063-019-3424-2
48. Li M, Wang Y, Li K, Xu X, Zhuang L. The efficacy and safety of Jin's three-needle therapy vs. placebo acupuncture on anxiety symptoms in patients with post-stroke anxiety: a study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Front Psychiatry. (2022) 13:941566. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.941566
49. Chen X, Tang H, Liang Y, Wu P, Xie L, Ding Y, et al. Acupuncture regulates the autophagy of ovarian granulosa cells in polycystic ovarian syndrome ovulation disorder by inhibiting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through LncMEG3. Biomed Pharmacother. (2021) 144:112288. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2021.112288
50. Kumariya S, Ubba V, Jha RK, Gayen JR. Autophagy in ovary and polycystic ovary syndrome: role, dispute and future perspective. Autophagy. (2021) 17:2706–33. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2021.1938914
51. Xiang S, Xia MF, Song JY, Liu DQ, Lian F. Effect of electro-acupuncture on expression of IRS-1/PI3K/GLUT4 pathway in ovarian granulosa cells of infertile patients with polycystic ovary syndrome-insulin resistance of phlegm-dampness syndrome. Chin J Integr Med. (2021) 27:330–5. doi: 10.1007/s11655-020-3219-z
52. Unluhizarci K, Karaca Z, Kelestimur F. Role of insulin and insulin resistance in androgen excess disorders. World J Diabetes. (2021) 12:616–29. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i5.616
53. Xing L, Chen Y, He Z, He M, Sun Y, Xu J, et al. Acupuncture improves endometrial angiogenesis by activating PI3K/AKT pathway in a rat model with PCOS. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:1790041. doi: 10.1155/2022/1790041
54. Yusuf ANM, Amri MF, Ugusman A, Hamid AA, Wahab NA, Mokhtar MH. Hyperandrogenism and its possible effects on endometrial receptivity: a review. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:12026. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512026
55. Wu J, Chen X. Acupuncture therapy protects PCOS patients with diabetes by regulating miR-32-3p/PLA2G4A pathway. Am J Transl Res. (2021) 13:8819–32.
56. Liu Q, Li Y, Feng Y, Liu C, Ma J, Li Y, et al. Single-cell analysis of differences in transcriptomic profiles of oocytes and cumulus cells at GV, MI, MII stages from PCOS patients. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:39638. doi: 10.1038/srep39638
57. Johansson J, Mannerås-Holm L, Shao R, Olsson A, Lönn M, Billig H, et al. Electrical vs manual acupuncture stimulation in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome: different effects on muscle and fat tissue insulin signaling. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e54357. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054357
58. Echiburú B, Pérez-Bravo F, Galgani JE, Sandoval D, Saldías C, Crisosto N, et al. Enlarged adipocytes in subcutaneous adipose tissue associated to hyperandrogenism and visceral adipose tissue volume in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. (2018) 130:15–21. doi: 10.1016/j.steroids.2017.12.009
59. Ortiz-Flores AE, Luque-Ramírez M, Fernández-Durán E, Alvarez-Blasco F, Escobar-Morreale HF. Diagnosis of disorders of glucose tolerance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) at a tertiary care center: fasting plasma glucose or oral glucose tolerance test? Metabolism. (2019) 93:86–92. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2019.01.015
60. Hernández-Jiménez JL, Barrera D, Espinoza-Simón E, González J, Ortíz-Hernández R, Escobar L, et al. Polycystic ovarian syndrome: signs and feedback effects of hyperandrogenism and insulin resistance. Gynecol Endocrinol. (2022) 38:2–9. doi: 10.1080/09513590.2021.2003326
61. Johansson J, Feng Y, Shao R, Lönn M, Billig H, Stener-Victorin E. Intense electroacupuncture normalizes insulin sensitivity, increases muscle GLUT4 content, and improves lipid profile in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. (2010) 299:E551–9. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00323.2010
62. Xu T, Yu Z, Liu Y, Lu M, Gong M, Li Q, et al. Hypoglycemic effect of electroacupuncture at ST25 through neural regulation of the pancreatic intrinsic nervous system. Mol Neurobiol. (2022) 59:703–16. doi: 10.1007/s12035-021-02609-1
63. Huang X, Huang K, Li Z, Bai D, Hao Y, Wu Q, et al. Electroacupuncture improves cognitive deficits and insulin resistance in an OLETF rat model of Al/D-gal induced aging model via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Brain Res. (2020) 1740:146834. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2020.146834
64. Xu W, Li J, Ji C, Fang D, Yao L, Xu N, et al. Activation of POMC neurons to adiponectin participating in EA-mediated improvement of high-fat diet IR mice. Front Neurosci. (2023) 17:1145079. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1145079
65. Ji C, Xu W, Zhang Z, Cui S, Yi W. Effect of electroacupuncture on reproductive disorders and insulin resistance in a murine polycystic ovary syndrome model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2021) 2021:9968463. doi: 10.1155/2021/9968463
66. Salmani Mood M, Yavari Z, Bahrami Taghanaki H, Mahmoudirad G. The effect of acupressure on fasting blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin and stress in patients with type 2 diabetes. Complement Ther Clin Pract. (2021) 43:101393. doi: 10.1016/j.ctcp.2021.101393
67. Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Dunaif A. Insulin resistance and the polycystic ovary syndrome revisited: an update on mechanisms and implications. Endocr Rev. (2012) 33:981–1030. doi: 10.1210/er.2011-1034
68. Hansen SL, Bojsen-Møller KN, Lundsgaard AM, Hendrich FL, Nilas L, Sjøberg KA, et al. Mechanisms underlying absent training-induced improvement in insulin action in lean, hyperandrogenic women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Diabetes. (2020) 69:2267–80. doi: 10.2337/db20-0062
69. Sanchez-Garrido MA, Tena-Sempere M. Metabolic dysfunction in polycystic ovary syndrome: pathogenic role of androgen excess and potential therapeutic strategies. Mol Metab. (2020) 35:100937. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.01.001
70. Hu T, Lu MN, Chen B, Tong J, Mao R, Li SS, et al. Electro-acupuncture-induced neuroprotection is associated with activation of the IGF-1/PI3K/Akt pathway following adjacent dorsal root ganglionectomies in rats. Int J Mol Med. (2019) 43:807–20. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.4035
71. Ding L, Teng R, Zhu Y, Liu F, Wu L, Qin L, et al. Electroacupuncture treatment ameliorates metabolic disorders in obese ZDF rats by regulating liver energy metabolism and gut microbiota. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1207574. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1207574
72. Tan W, Zhang J, Dai F, Yang D, Gu R, Tang L, et al. Insights on the NF-κB system in polycystic ovary syndrome, attractive therapeutic targets. Mol Cell Biochem. (2024) 479:467–86. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04736-w
73. Li N, Guo Y, Gong Y, Zhang Y, Fan W, Yao K, et al. The anti-inflammatory actions and mechanisms of acupuncture from acupoint to target organs via neuro-immune regulation. J Inflamm Res. (2021) 7191–224. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S341581
74. Liu Y, Fan HY, Hu JQ, Wu TY, Chen J. Effectiveness and safety of acupuncture for insulin resistance in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e13991. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e13991
75. de Medeiros SF, Rodgers RJ, Norman R. Adipocyte and steroidogenic cell cross-talk in polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod Update. (2021) 27:771–96. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmab004
76. Azziz R, Carmina E, Chen Z, Dunaif A, Laven JS, Legro RS, et al. Polycystic ovary syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2016) 2:1–18. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2016.57
77. Lu M, Yu Z, Li Q, Gong M, An L, Xu T, et al. Electroacupuncture stimulation regulates adipose lipolysis via catecholamine signaling mediated by NLRP3 suppression in obese rats. Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12:773127. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.773127
78. Grossmann M, Wierman ME, Angus P, Handelsman D. Reproductive endocrinology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Endocr Rev. (2019) 40:417–46. doi: 10.1210/er.2018-00158
79. Ma B, Li P, An H, Song Z. Electroacupuncture attenuates liver inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease rats. Inflammation. (2020) 43:2372–8. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01306-w
80. Liaw JJ, Peplow PV. Differential effect of electroacupuncture on inflammatory adipokines in two rat models of obesity. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. (2016) 9:183–90. doi: 10.1016/j.jams.2016.02.002
81. Gervais A, Battista M-C, Carranza-Mamane B, Lavoie H, Baillargeon J-P. Follicular fluid concentrations of lipids and their metabolites are associated with intraovarian gonadotropin-stimulated androgen production in women undergoing in vitro fertilization. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2015) 100:1845–54. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-3649
82. Zhang F, Ma T, Tong X, Liu Y, Cui P, Xu X, et al. Electroacupuncture improves metabolic and ovarian function in a rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome by decreasing white adipose tissue, increasing brown adipose tissue, and modulating the gut microbiota. Acupunct Med. (2022) 40:347–59. doi: 10.1177/09645284211056663
83. Torres PJ, Siakowska M, Banaszewska B, Pawelczyk L, Duleba AJ, Kelley ST, et al. Gut microbial diversity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome correlates with hyperandrogenism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. (2018) 103:1502–11. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-02153
84. Yang N, Ma K, Liu W, Zhang N, Shi Z, Ren J, et al. Serum metabolomics probes the molecular mechanism of action of acupuncture on metabolic pathways related to glucose metabolism in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome-related obesity. Biomed Chromatogr. (2023) 37:e5710. doi: 10.1002/bmc.5710
85. Garcia-Vivas JM, Galaviz-Hernandez C, Fernandez-Retana J, Pedroza-Torres A, Perez-Plasencia C, Lopez-Camarillo C, et al. Transcriptomic profiling of adipose tissue in obese women in response to acupuncture catgut embedding therapy with moxibustion. J Altern Complement Med. (2016) 22:658–68. doi: 10.1089/acm.2015.0200
86. Gao H, Li Y, Jin Y, Zhang L, Xia X, Liu J, et al. Electroacupuncture activates angiogenesis by regulating the PI3K/Pten/Thbs1 signaling pathway to promote the browning of adipose tissue in HFD-induced obese mice. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 166:115386. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115386
87. Tang Q, Lu M, Xu B, Wang Y, Lu S, Yu Z, et al. Electroacupuncture regulates inguinal white adipose tissue browning by promoting sirtuin-1-dependent PPARγ deacetylation and mitochondrial biogenesis. Front Endocrinol. (2020) 11:607113. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.607113
88. Kara O, Arsoy HA, Keskin M. Relationship between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hyperandrogenemia in adolescents with polycystic ovary syndrome. Clin Exp Pediatr. (2023) 66:395–402. doi: 10.3345/cep.2023.00353
89. Xu Q, Wu H, Zhu H, Lu C, Tao J, Zhou Z, et al. Grain-sized moxibustion at Zusanli (ST36) promotes hepatic autophagy in rats with hyperlipidemia by regulating the ULK1 and TFEB expression through the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway. Heliyon. (2023) 9:e15316. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15316
90. Takayama K, Fukaya T, Sasano H, Funayama Y, Suzuki T, Takaya R, et al. Immunohistochemical study of steroidogenesis and cell proliferation in polycystic ovarian syndrome. Hum Reprod. (1996) 11:1387–92. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a019405
91. Shabbir S, Khurram E, Moorthi VS, Eissa YTH, Kamal MA. Butler AE. The interplay between androgens and the immune response in polycystic ovary syndrome. J Transl Med. (2023) 21:259. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04116-4
92. He Y, Yang K, Zhang L, Zhan M, Xia XW, Wang HF, et al. Electroacupuncture for weight loss by regulating microglial polarization in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus. Life Sci. (2023) 330:121981. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121981
93. González F, Considine RV, Abdelhadi OA, Acton AJ. Lipid-induced mononuclear cell cytokine secretion in the development of metabolic aberration and androgen excess in polycystic ovary syndrome. Hum Reprod. (2020) 35:1168–77. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deaa056
94. Gong M, Cao C, Chen F, Li Q, Bi X, Sun Y, et al. Electroacupuncture attenuates hepatic lipid accumulation via AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) activation in obese rats. Acupunct Med. (2016) 34:209–14. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2015-010798
95. Chang H, Shi B, Ge H, Liu C, Wang L, Ma C, et al. Acupuncture improves the emotion domain and lipid profiles in women with polycystic ovarian syndrome: a secondary analysis of a randomized clinical trial. Front Endocrinol. (2023) 14:1237260. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1237260
96. Nekooi M, Bazarganipour F, Zoladl M, Heshmat R, Aramesh S, Hosseini N. Effect of acupressure on health-related quality of life in patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome: a randomized clinical trial. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. (2022) 2022:2920132. doi: 10.1155/2022/2920132
97. Huang S, Hu M, Ng EHY, Stener-Victorin E, Zheng Y, Wen Q, et al. A multicenter randomized trial of personalized acupuncture, fixed acupuncture, letrozole, and placebo letrozole on live birth in infertile women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Trials. (2020) 21:239. doi: 10.1186/s13063-020-4154-1
98. Kwon CY, Lee B, Park KS. Oriental herbal medicine and moxibustion for polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis. Medicine. (2018) 97:e12942. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000012942
99. Stener-Victorin E, Holm G, Janson PO, Gustafson D, Waern M. Acupuncture and physical exercise for affective symptoms and health-related quality of life in polycystic ovary syndrome: secondary analysis from a randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2013) 13:131. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-13-131
100. Zhou J, Yang L, Yu J, Wang Y, Liu Z. Efficacy of acupuncture on menstrual frequency in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: protocol for a randomized, controlled trial. Medicine. (2017) 96:e8828. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000008828
101. Wang Z, Dong H, Wang Q, Zhang L, Wu X, Zhou Z, et al. Effects of electroacupuncture on anxiety and depression in unmarried patients with polycystic ovarian syndrome: secondary analysis of a pilot randomised controlled trial. Acupunct Med. (2019) 37:40–6. doi: 10.1136/acupmed-2017-011615
102. Zheng YH, Wang XH, Lai MH, Yao H, Liu H, Ma HX. Effectiveness of abdominal acupuncture for patients with obesity-type polycystic ovary syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. J Altern Complement Med. (2013) 19:740–5. doi: 10.1089/acm.2012.0429
103. Wan K, Jia M, Zhang H, Lan Y, Wang S, Zhang K, et al. Electroacupuncture alleviates neuropathic pain by suppressing ferroptosis in dorsal root ganglion via SAT1/ALOX15 signaling. Mol Neurobiol. (2023) 60:6121–32. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03463-z
Keywords: acupuncture, polycystic ovarian syndrome, hyperandrogenemia, treatment, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM)
Citation: Liu Y-X, Han Y-H, Jiang Y, Zhang J and Zhang Y-H (2025) Experimental analysis of acupuncture's effects on hyperandrogenemia and related symptoms in PCOS patients. Front. Med. 12:1531506. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1531506
Received: 20 November 2024; Accepted: 08 July 2025;
Published: 24 July 2025.
Edited by:
Cristina Secosan, Victor Babes University of Medicine and Pharmacy, RomaniaReviewed by:
Haoxu Dong, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, ChinaTiziana Fidecicchi, University of Pisa, Italy
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Han, Jiang, Zhang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yue-Hui Zhang, Y2hpemlzaHVpLTA0QDE2My5jb20=
 Yu-Xiao Liu
Yu-Xiao Liu Yan-Hua Han1,2
Yan-Hua Han1,2 Yue-Hui Zhang
Yue-Hui Zhang
