Abstract
Background:
Various preparations of tacrolimus have been implemented for patients with vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC). However, there is a lack of evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness of different dosages and forms of tacrolimus for patients with VKC.
Objective:
The present systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the safety and effectiveness of various dosages and forms of tacrolimus for patients with VKC.
Methods:
The literature review was performed through 12 databases on 15 June 2024. All clinical studies comparing the outcomes of different dosages and tacrolimus preparations for VKC were included. Subgroup analysis was performed based on the dosages and formulations of tacrolimus.
Results:
The present meta-analysis included 17 articles, encompassing 832 patients with VKC. Of them, 421 patients received tacrolimus, while 411 patients were in the control group. Of the treated patients with tacrolimus, 66 were treated with tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1%, and 62 were treated with tacrolimus 0.1% ointment. Furthermore, 293 patients were treated with tacrolimus 0.03% ointment. There was a statistically significant (p = 0.02) difference between tacrolimus and the control group regarding the mean score for objective signs with SMD of −0.70 (95%CI:−1.28, −0.13). A statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) was observed between the tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% and the control group with an SMD of −1.09 (95%CI:−1.59, −0.59). There was a significantly lower total subjective symptom score among patients treated with tacrolimus with an SMD of −0.86 (95%CI:−1.44, 0.28) and a probability value of 0.004. A statistically significant lower risk of treatment-related adverse events was revealed among patients treated with tacrolimus 0.03% ointment (p = 0.0002) with an RR of 0.16.
Conclusion:
Tacrolimus is an effective and safe therapeutic intervention for patients with VKC. It remarkably reduced the total score for objective signs and total subjective symptom score of VKC, with a relatively lower risk of treatment-related adverse events. The improvement of clinical manifestations was significantly associated with tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1%, while tacrolimus 0.03% ointment was associated with the lowest risk of treatment-related adverse events.
Introduction
Vernal keratoconjunctivitis (VKC) is a chronic, bilateral yet often asymmetrical progressive disease of the cornea and conjunctiva, whose immuno-allergic etiopathogenesis is still being elucidated. It primarily affects young adults and children living in dry and warm climates, with an overall prevalence of 1% of ocular diseases (1, 2). Two variants of adult VKC have been developed based on the onset of the disease. Early-onset VKC begins in childhood and continues through adulthood, while late-onset VKC emerges after puberty. The hallmarks of VKC are conjunctival papillary inflammation and tissue remodeling (3, 4). The symptoms of the disease frequently occur seasonally and intensely, with the majority of patients experiencing photophobia, hyperemia, tearing, congestion, itching, and burning sensation. Although the disease is self-limiting and resolves around puberty, the worsening of the inflammatory phase of the VKC is bothersome. VKC can lead to sight-threatening sequels if treated inadequately. Blindness may result from corneal-related causes such as scarring, irregular astigmatism, ectasia, and limbal stem cell deficiency, as well as steroid-related side effects like cataract and glaucoma (5–7). The treatment of VKC depends on the frequency and severity of clinical manifestations and the duration of symptoms. The mainstay treatment of VKC is antihistamines, corticosteroids, immunosuppressive agents, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and mast cell stabilizers (8, 9). Local drug administration may control the acute symptoms of VKC; however, the treatment of VKC is challenging, with no gold-standard therapy to control the recurrence and to prevent the progression of the disease (2, 10).
Immunomodulators are alternative therapies with potent anti-inflammatory effects and low adverse events. Tacrolimus is a macrolide immunosuppressant that has been extensively used in tissue transplants. Tacrolimus targets mainly CD4 + T lymphocytes, inhibiting calcineurin and suppressing interleukin 2, T helper 1 (Th1), and Th2 cytokines production. Furthermore, tacrolimus is a mast cell stabilizer, inhibiting histamine release and prostaglandin production (11, 12). The drug has been used in uveitis, corneal transplantation, and graft-versus-host disease. The topical application of tacrolimus significantly reduces the clinical manifestations of chronic allergic eye disorders with higher efficacy and low adverse events relative to corticosteroid therapy (13). The drug replaced corticosteroids for acute episodes and replaced other medications as a maintenance therapy for controlling VKC (11).
Various dosages and forms of tacrolimus have been reported in the literature. The high dosage of topical tacrolimus was associated with irritation, burning sensation, and epithelial keratitis. This may lead to low compliance among the pediatric population (14). There is a lack of evidence regarding the safety and effectiveness of different dosages and forms of tacrolimus for patients with VKC. Previously published reviews have revealed the therapeutic efficacy of tacrolimus for patients with VKC. However, these reviews have several limitations, with a limited number of included studies and heterogeneity due to the use of different preparations and strengths of tacrolimus (15, 16). This highlights the need for a more conclusive review evaluating tacrolimus’s effectiveness based on different dosages and formats. Such knowledge is essential to compel patients to use the most effective tacrolimus protocol to control the VKC course better. Therefore, the present systematic review and meta-analysis evaluated the safety and effectiveness of various dosages and forms of tacrolimus for patients with VKC.
Methodology
The steps of the current systematic review and meta-analysis study followed the guidelines and the recommendations offered through the Cochrane Collaboration and Cochrane Handbook of Systematic Review and Meta-analysis (17) and based on the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) guidelines (18) (Supplementary Table S1) (PROSPERO Number; CRD42024557297).
Search methods
The literature review was performed through 12 databases on 15 June 2024. The following databases were searched using individualized search strings customized for each database: PubMed, ISI, Google Scholar, Scopus, NYAM, SIGLE, VHL, Clinical trials, mRCT, Cochrane Collaboration, EMBASE, and ICTRP. There were no limitations regarding age, gender, publication language, ethnicity, or study region. Citation tracking, cross-referencing, and reviewing the references of the eligible articles and previously published reviews were carried out to retrieve all possible relevant articles. The following keywords were used; “Tacrolimus,” “TCA,” “FK506,” “Vernal keratoconjunctivitis,” “VKC,” “Spring Catarrh.”
Study selection
All clinical studies comparing the outcomes of different dosages and tacrolimus preparations for VKC were included. Non-comparative studies or those that did not report the outcomes of interest were excluded. Furthermore, studies in which data was inaccessible, guidelines, review articles, animal studies, case reports, comments, letters, editorials, posters, and book chapters were excluded. The articles retrieved from the screening process were exported to an Excel sheet after the initial removal of the duplicated reports using EndNote X9 (19). The title, abstract, and full-text screening processes were performed independently to disclose the potentially relevant articles that meet the eligibility criteria. The PRISMA flowchart documented the search process, screening, and the causes of article exclusion at each literature review step.
Data extraction
The data were extracted in a well-organized Microsoft Excel sheet. The source-related data were extracted, including the title, study ID, study regions, study design, registration number, and study period. The methods-related data were extracted, including the eligibility criteria, diagnosis of VKC, previous therapies, dosage and formulations of tacrolimus, the dosages, and formulations of the control arm, grading of VKC, study endpoints, and follow-up periods. Baseline patients’ demographic characteristics were extracted, including sample size, age, body mass index (BMI), comorbidities, co-existing ocular diseases, and smoking history. The disease-related data were extracted, including the duration of the disease, type of VKC, severity of VKC, and symptoms and signs of VKC. The study endpoints were extracted, including total subjective symptom score, total objective symptom score, total objective sign score, and treatment failure. The data were extracted from the reported graphs in the Labcharoenwongs et al. using WebPlotDigitizer software (20).
Study endpoint
Symptoms and signs
Total score for objective signs evaluated the palpebral conjunctiva, bulbar conjunctiva, limbus, and corneal involvement. The signs included hyperemia, edema, follicles, papillae, and giant papillae for the palpebral conjunctiva, hyperemia and chemosis for bulbar conjunctiva, and Trantas’ dot and edema for limbus signs. The corneal involvement was assessed using 4 grades: Normal = 0 Mild = 1+, moderate = 2+, Severe = 3+ (21). The total objective symptom score included hyperemia of bulbar and palpebral conjunctiva, papillae, giant papillae, and corneal infiltration (22). The analyzed articles reported the symptom scores differently for which the standardized mean difference (SMD) was used to standardize the results.
Treatment failure
Persistence of symptoms and signs of inflammation despite medication compliance.
Treatment-related adverse events
Any adverse event related to the medications including minor and major side effects of the medications.
Intraocular pressure
The intraocular pressure (IOP) was measured differently across the studies for which SMD standardize the results. We IOP was measured at the end of the follow-up visit.
Risk of bias and quality assessment
The risk of the bias of the included randomized clinical trials was evaluated based on the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool for assessing the risk of bias. This tool is composed of seven items; random sequence generation, allocation concealment (selection bias), blinding of participants and personnel performance bias, blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias), incomplete outcome data (attrition bias), selective reporting (reporting bias), and other possible causes of bias (23). The quality of the observational studies will be assessed using the National Institute of Health (NIH) quality assessment tool (24). The studies were assorted, based on this quality assessment, into good, fair, and bad when the score was >65%, 30–65, <30%, respectively. If the parameter was controlled, the domain was considered “Yes” and vice versa.
Data analysis
Weighted mean difference (WMD) or standardized mean difference (SMD) was used to analyze the continuous variables. The SMD was used to evaluate the outcomes with different measurements or output values. Data reported in median and range, mean and range, mean and 95%confidence interval (CI) were converted to mean and standard deviation (SD) based on the equations of Hozo et al. (25). The risk ratio (RR) with 95% CI was used for analyzing dichotomous variables. The fixed-effect model was implemented when a fixed population effect size is assumed; otherwise, the random-effects model was used. Statistical heterogeneity was appreciated using Higgins I2 statistic, at the value of > 50%, and the Cochrane Q (Chi2 test), at the value of p < 0.10 (26). The random-effects model was employed to account for this heterogeneity. Publication bias will be assumed in the presence of an asymmetrical funnel plot and based on Egger’s regression test (p-value < 0.10). Subgroup analysis was performed based on the dosages and formulations of tacrolimus. Data analysis was performed using Review Manager version 5.4 and Comprehensive Meta-Analysis v3 software (27, 28). The significant difference was established at the value of p < 0.05.
Results
Systematic searching of the literature revealed a total of 355 articles. Of them, 95 studies were duplicated, resulting in 260 reports included for title and abstract screening. Furthermore, 225 studies were excluded, and 35 were eligible for full-text screening. Sixteen articles were included for data extraction, one of which was excluded, and two were identified through the manual searching process. Seventeen articles were finally included for systematic review and meta-analysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1

PRISMA flow chart showing the process of the literature search, title, abstract, and full text screening, systematic review, and meta-analysis.
Demographic characteristics of the included studies
The present meta-analysis included 17 articles, encompassing 832 patients with VKC (29–45). Of them, 421 patients received tacrolimus, while 411 patients were in the control group. Of the treated patients with tacrolimus, 66 were treated with tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1%, and 62 were treated with tacrolimus 0.1% ointment. Furthermore, 293 patients were treated with tacrolimus 0.03% ointment. There were 12 articles of randomized controlled trials, while there were five observational studies. Nine articles used cyclosporine as the control group, while a placebo was used in two articles. There were 376 females and 96 males. The average age of the included patients ranged from 8 to 17.9 years among the tacrolimus group and from 7.12 to 15.2 years among the control group. There were 69 patients with limbal VKC and 129 patients with tarsal VKC. The average disease duration ranged from 12 months to 3.04 years among the tacrolimus group and 12 months to 3.21 years among the control group (Table 1).
Table 1
| Study ID | Study region | Study design | Study period | Intervention | Treatment protocol | Control | Sample size | Gender | Age (years) | Type of vernal keratoconjunctivitis | Disease duration | Quality assessment | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Females | Males | Limbal | Tarsal | Mixed | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tacrolimus | Control | Tacrolimus | Control | Tacrolimus | Control | Tacrolimus | Control | Tacrolimus | Control | Tacrolimus | Control | ||||||||||||||
| Number | Number | Number | Number | Number | Number | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | Number | Number | Number | Number | Number | Number | Mean ± SD | Mean ± SD | % | Decision | ||||||||
| 1 | Ohashi et al., 2010 (37) | Japan | RCT | February and September 2004 | Tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% | Twice daily for 4 weeks | Placebo | 28 | 28 | 25 | 25 | 3 | 3 | 17.9 ± 9.1 | 15.2 ± 8.1 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | _____ | _____ |
| 2 | Pucci et al., 2015 (38) | Italy | RCT (Cross-over) | March 2008 to August 2010 | Tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% | 1 drop 3 times daily in both eyes for 3 weeks | Cyclosporine eyedrops at 1% | 30 | 30 | 24 | 6 | 9.05 ± 2.12 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 19.13 (7–31)* | _____ | _____ | ||||
| 3 | Labcharoenwongs et al., 2012 (34) | Thailand | RCT | June 2003 to May 2005 | Tacrolimus 0.1% ointment | Twice daily for 12 weeks | 2% cyclosporine eye drops | 12 | 12 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 0 | 10.14 ± 2.60 | 9.07 ± 2.50 | 1 | 4 | 7 | 8 | 4 | 0 | 2.93 ± 2.14 | 3.21 ± 2.51 | _____ | _____ |
| 4 | Nivenius et al., 2007 (36) | Sweden | RCT (Cross-over) | January to April 2004 | Tacrolimus 0.1% ointment | Twice daily for a 3-week period | clobetasone butyrate 0.05% ointment | 20 | 20 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 10.14 ± 2.60 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | _____ | ||
| 5 | Singla et al., 2017 (42) | India | RCT | NR | Tacrolimus 0.1% ointment | Twice daily for 6 weeks | Cyclosporine (2%) | 30 | 26 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 8.33 ± 1.69 | 8.00 ± 1.60 | 23 | 16 | 5 | 8 | 2 | 2 | 16.47 ± 3.08 | 15.81 ± 2.55 | _____ | _____ |
| 6 | Choudhary et al., 2019 (29) | India | RCT | May 2014 to May 2015 | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | NR | Cyclosporine (0.05%) ophthalmic eye drop | 22 | 21 | 8 | 10 | 14 | 11 | 8.00 ± 0.81 | 7.57 ± 0.42 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 1.85 ± 0.20 | 1.71 ± 0.17 | _____ | _____ |
| 7 | Eltagoury et al., 2022 (30) | Egypt | Non-randomized controlled clinical trial | NR | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Twice daily for 2 months | Standard anti-allergic medications | 25 | 25 | 22 | 21 | 3 | 4 | 16.20 ± 5.10 | 16.48 ± 4.19 | 0 | 0 | 21 | 20 | 4 | 5 | NR | NR | _____ | _____ |
| 8 | Gupta et al., 2021 (31) | India | Retrospective | 1 January 2019 to 31 December 2020 | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Three times a day | Interferon α-2b 1 MillionIU/mL | 25 | 25 | 19 | 22 | 6 | 3 | 8.68 ± 2.53 | 7.92 ± 2.33 | 2 | 4 | 15 | 17 | 8 | 4 | 3.04 ± 1.21 | 2.96 ± 1.14 | 70% | Good |
| 9 | Heikal et al., 2020 (32) | Egypt | Prospective | October 2019 to February 2020 | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Every 12 h in both eyes during the 12 weeks | Ciclosporine A eye drop (2%) | 28 | 31 | 23 | 26 | 5 | 5 | 9.96 ± 4.16 | 10.83 ± 4.74 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 70% | Good |
| 10 | Kumari et al., 2018 (33) | India | RCT | March 2015-August 2015 | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Twice daily for 6 weeks | Cyclosporine e/d (0.05%) | 16 | 16 | 15 | 13 | 1 | 3 | 8.06 ± 1.94 | 7.12 ± 1.66 | 3 | 0 | 11 | 13 | 2 | 3 | 14 | 12 | _____ | _____ |
| 11 | Malhotra et al., 2021 (35) | India | Prospective | NR | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Twice daily for 12 weeks | Cyclosporine 0.05% | 19 | 19 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 70% | Good |
| 12 | Padmini et al., 2021 (41) | India | Prospective | December 2017 to February 2021 | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Twice daily for 6 weeks | 0.05% cyclosporin eye drops | 36 | 36 | 30 | 32 | 6 | 4 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 70% | Good |
| 13 | Rathore et al., 2021 (40) | India | Cross-sectional study | February 2019 to July 2019 | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | NR | Olopatadine 0.2% eye drops | 36 | 33 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 12.75 ± 5.54 | 8.88 ± 2.18 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | 70% | Good |
| 14 | Suresha et al., 2023 (43) | India | RCT | NR | Tacrolimus 0.03% Ointment | Twice daily for 8 weeks | 2% cyclosporine eye drops | 29 | 27 | 24 | 14 | 5 | 13 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | _____ | _____ |
| 15 | Qin et al., 2018 (39) | China | RCT | NR | Tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% | One drop/time, twice daily/1 drop/time, 4 times daily | tobramycin dexamethasone | 29 | 27 | NR | NR | NR | NR | 12.56 ± 8.97 | 10 | 6 | 4 | 0 | 15 | 21 | NR | NR | _____ | _____ | |
| 16 | Zanjani et al., 2017 (44) | Iran | RCT | NR | 0.005% tacrolimus | Two drops/time | interferonα-2b + placebo | 28 | 27 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | _____ | _____ |
| 17 | Zhang et al., 2014 (45) | China | RCT | NR | 0.005% tacrolimus | One drop/time, twice daily | placebo | 8 | 8 | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | NR | _____ | _____ |
Demographic characteristics and quality assessment of the included studies.
RCT, Randomized controlled trial; SD, Standard deviation; NR, Non-reported. *Data reported in the form of median and range.
Risk of the bias and quality assessment
Six articles showed a lower risk of random sequence generation bias (33, 34, 36–38, 42). Whereby four articles revealed a low risk of allocation concealment bias (30, 37, 38, 44), two articles showed a high risk of performance bias (29, 39). Eight articles showed a low risk of detection bias (29, 33, 36–42, 45), and three articles showed a high risk of attribution bias (29, 33, 42). Two studies showed unclear risk of reporting bias (39, 44). All the included studies showed good quality based on the NIH tool for quality assessment (Figure 2; Table 1).
Figure 2
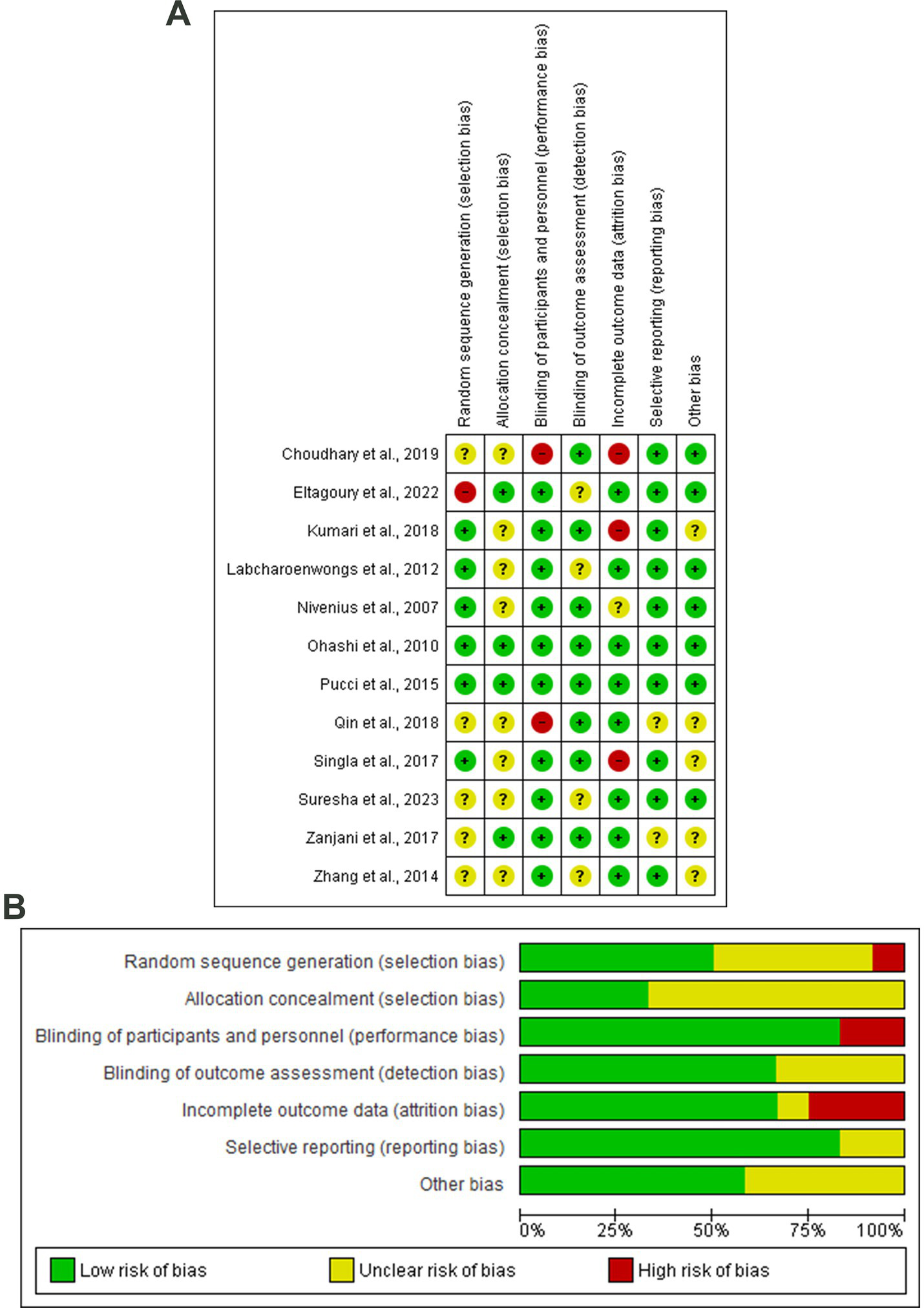
(A) Risk of bias graph, (B) Risk of bias summary: review authors’ judgments about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
Study endpoints
Total score for objective signs
Thirteen articles included 569 patients evaluated the impact of different tacrolimus dosages on the total score for objective signs (29–31, 33, 34, 36, 37, 39–42, 44, 45). There was a statistically significant (p = 0.02) difference between tacrolimus and the control group with SMD of −0.70 (95%CI: −1.28, −0.13) in the random-effects model (I2 = 90%, p < 0.001). Pooling the data in the random-effects model (I2 = 0%, p = 0.92) revealed a statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) between the tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% and control group with an SMD of −1.09 (95%CI: −1.59, −0.59). There was no statistically significant difference between the tacrolimus 0.1% ointment and the control group regarding the mean total score for objective signs (SMD: −0.52, 95%CI: −1.50, 0.46, p = 0.30) in the random-effects model (I2 = 63%, p = 0.007). In this respect, there was no statistically significant difference between tacrolimus 0.03% ointment and the control group with an SMD of −0.03 and 95CI% ranging from −0.65 to 0.59 (p = 0.93). No evidence of publication bias was detected based on the results of Egger’s regression test (Intercept = −3.855, p = 0.4) (Figures 3A,B).
Figure 3
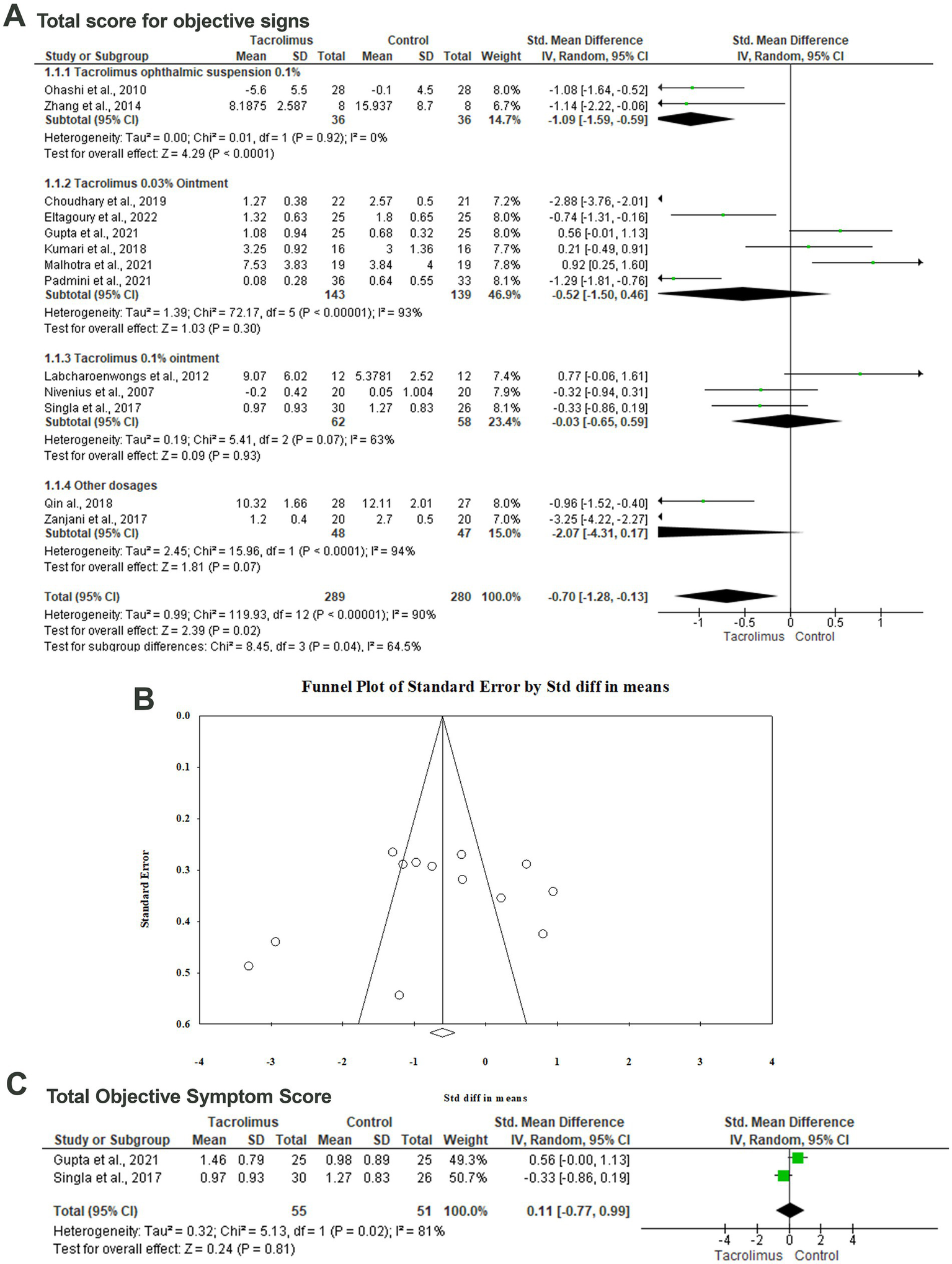
Forest plot of summary analysis of the (A) Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) and 95% CI of mean total score for objective signs between tacrolimus and control groups subgrouped by the dosages and formulations of tacrolimus. (B) Funnel plot showing the symmetrical distribution of the studies along the middle line. (C) Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) and 95% CI of the total objective symptom scores between tacrolimus and control groups. Size of the green squares is proportional to the statistical weight of each trial. The gray diamond represents the pooled point estimate. The positioning of both diamonds and squares (along with 95% CIs) beyond the vertical line (unit value) suggests a significant outcome (IV, inverse variance).
Total objective symptom score
The difference between tacrolimus and control groups regarding the mean total objective symptom scores was reported in two articles among 106 patients (31, 42). Metaanalyzing the data in the random-effects model (I2 = 81%, p = 0.02) revealed no statistically significant difference between both groups with an SMD of 0.11 (95%CI: −0.77, 0.99, p = 0.81) (Figure 3C).
Total subjective symptom score
Fourteen articles included 613 patients evaluated the difference between tacrolimus and control groups regarding the mean total subjective symptom score (29–31, 34–42, 44, 45). In the random-effects model (I2 = 91%, p < 0.001), there was a statistically significant lower total subjective symptom score among patients treated with tacrolimus with an SMD of −0.86 (95%CI: −1.44, 0.28) and probability value of 0.004. Subgroup analysis based on the dosage and form of tacrolimus revealed a statistically significant lower mean total subjective symptom score among patients treated with tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% (SMD; −1.42; 95%CI: −2.34, −0.50; p = 0.002) in the random-effects model (I2 = 69%, p = 0.04). There was no statistically significant difference between tacrolimus 0.1% ointment and the control group regarding the mean total subjective symptom score with an SMD of −0.60 (95%CI: −2.06, 0.87; p = 0.43). In the random-effects model (I2 = 94%, p < 0.001), there was no statistically significant difference between tacrolimus 0.03% ointment and the control group (SMD; −0.55, 95%CI: −1.59, 0.49, p = 0.30) (Figure 4A).
Figure 4
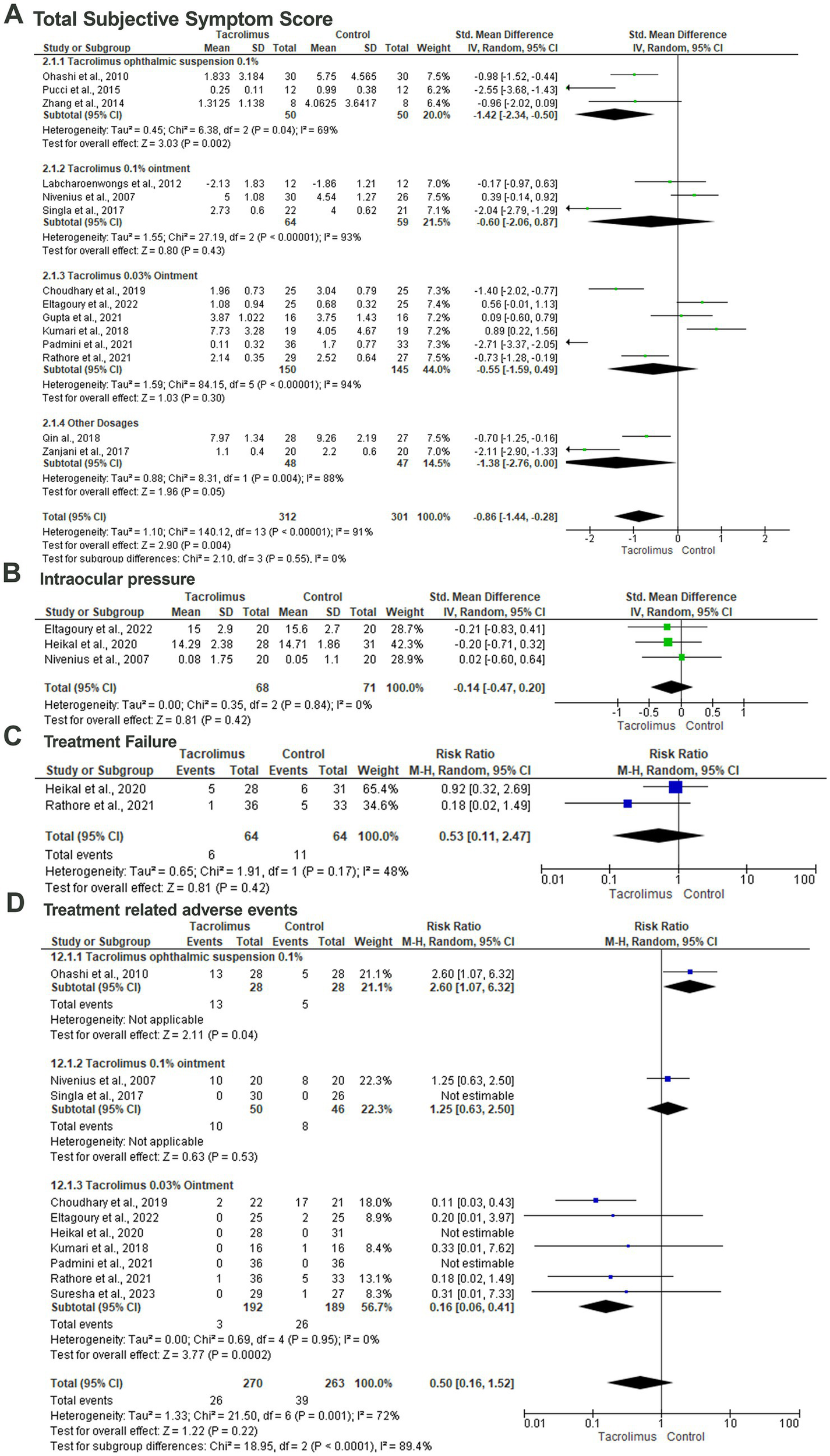
Forest plot of summary analysis of the (A) Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) and 95% CI of mean total subjective symptom score between tacrolimus and control groups subgrouped by the dosages and formulations of tacrolimus. (B) Standardized Mean Difference (SMD) and 95% CI of the mean intraocular pressure between tacrolimus and control groups. (C) Risk ratio and 95% CI of the risk of treatment failure between tacrolimus and control groups. (D) Risk ratio and 95% CI of the risk of treatment-related adverse events between tacrolimus and control groups. Size of the green or blue squares is proportional to the statistical weight of each trial. The gray diamond represents the pooled point estimate. The positioning of both diamonds and squares (along with 95% CIs) beyond the vertical line (unit value) suggests a significant outcome (IV, inverse variance).
Intraocular pressure
Three studies included 139 patients evaluated the difference in intraocular pressure between the tacrolimus and control group within three studies (30, 32, 36). Pooling the data revealed no statistically significant difference between the tacrolimus and the control group with an SMD of −0.14 and 95%CI of −0.47 to 0.20 and probability value of 0.42 in the random-effects model (I2 = 0%, p = 0.48) (Figure 4B).
Treatment failure
The risk of treatment failure was evaluated among 17 patients within two studies (32, 40). In the random-effects model (I2 = 48%, p = 0.17), there was no statistically significant difference between the tacrolimus and control groups with a RR of 0.53 (95%CI: 0.11, 2.47) and probability value of 0.42 (Figure 4C).
Treatment-related adverse events
Ten articles included 533 patients evaluated the treatment-related adverse events with tacrolimus (29, 30, 32, 33, 36, 37, 40–43). Pooling the data in the random-effects model (I2 = 72%, p = 0.001) revealed no statistically significant difference between tacrolimus and control groups with a RR of 0.50 (95%CI: 016, 1.52) and probability value of 0.22. Subgroup analysis based on the dosage of the tacrolimus revealed a statistically significant lower risk of treatment-related adverse events among patients treated with tacrolimus 0.03% ointment (p = 0.0002) with a RR of 0.16 and 95%CI% ranged from 0.06 to 0.41 in the random-effects model (I2 = 0%, p = 0.95) (Figure 4D).
Discussion
VKC is a severe form of ocular allergy which is associated with considerable morbidities. The disease can cause visual loss and primarily begins in children aged between 2 and 10 years old. There has been a controversial result in the literature regarding the impact of different concentrations and tacrolimus preparations on patients with VKC (46). The present meta-analysis revealed the therapeutic efficacy of tacrolimus in treating patients with VKC. Particularly, tacrolimus significantly improved the total score for objective signs and total subjective symptom score with a relatively lower risk of treatment-related adverse events. The tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% achieved statistically significant results compared to the control group, relative to tacrolimus 0.03% ointment and tacrolimus 0.1% ointment. The risk of treatment-related adverse events was reduced by approximately 50% among the tacrolimus group. This risk was reduced more remarkably among patients treated with tacrolimus 0.03% ointment. These findings revealed the excellent efficacy of tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% in treating patients with VKC, promoting the potentiality of using this formulation to enhance local tolerability.
The present meta-analysis revealed a significant reduction in symptoms and signs of VKC among patients treated with tacrolimus, particularly tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1%. These findings were consistent with Zhao et al. (16) who revealed the efficacy of tacrolimus among patients with VKC, reducing congestion, itching, tearing, foreign body sensation, and objective patient signs. Chandra et al. (15) review revealed a significant reduction in symptoms and signs of VKC with topical tacrolimus therapy. Contrary to these findings, Roumeau et al. (47) revealed a similar efficacy of tacrolimus and cyclosporine among patients with severe VKC. Furthermore, they revealed that this efficacy does not differ based on the concentration of tacrolimus, highlighting that a low dosage may be sufficient. The local tolerance of these formulations is mainly concentration-dependent. Fazri et al. (48) revealed that tacrolimus effectively treated patients with VKC, particularly for patients with corticosteroid-refractory VKC.
The present meta-analysis revealed a lower risk of treatment-related adverse events, particularly among patients treated with tacrolimus 0.03% ointment. Tacrolimus is a hydrophobic substance that is unstable at clinically effective concentrations. The aqueous preparation of tacrolimus needed to be prepared in olive oil, castor oil, and dextrin. Conversely, these preparations were associated with redness, burning sensation, itching, and epithelial keratitis. The penetration of the corneal epithelium is difficult due to its unique properties and large molecular size. The dermal ointments were used to attempt such adverse events, which proposed to achieve tolerability and less toxicity (49, 50). Tacrolimus in ointment may have a beneficial effect due to the long-standing effect. Consistent with our findings, Akbari et al. (48) review revealed that topical tacrolimus 0.05% is an effective and safe agent to treat refractory VKC with no systemic or ocular adverse effects.
The present meta-analysis revealed tacrolimus’s functional and safety outcomes among patients with VKC. The study included the largest cohort in the literature, assessing the outcomes of tacrolimus in different dosages and formulations. Conversely, some limitations should be considered while interpreting the resulting evidence. While most eligible studies were randomized controlled trials, some were observational, which confer a substantial risk of information bias. Subsequently, there was significant statistical and methodological heterogeneity between the analyzed articles. This heterogeneity may be attributed to the considerable variation between the analyzed articles regarding the recruitment criteria, sample sizes, follow-up period, treatment protocol, control arm, disease severity, study outcomes, and demographic characteristics of the included patients. The resulting statistical heterogeneity was mitigated by applying the random-effects model and doing subgroup analysis. The wide variations of the control group limited the capability to conduct network meta-analysis. Further randomized controlled trials with adequate samples and prolonged follow-up periods are necessary to mitigate the potential limitations of the analyzed studies.
Conclusion
Tacrolimus is an effective and safe therapeutic intervention for patients with VKC. It remarkably reduced the total score for objective signs and total subjective symptom score of VKC, with a relatively lower risk of treatment-related adverse events. The improvement of clinical manifestations was significantly associated with applying tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1%, while tacrolimus 0.03% ointment was associated with the lowest risk of treatment-related adverse events.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
RA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported and funded by the Deanship of Scientific Research at Imam Mohammad Ibn Saud Islamic University (IMSIU) (grant number IMSIU-DDRSP2501).
Conflict of interest
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author declares that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1542440/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Chigbu DI Labib BA . Immunopharmacology in vernal keratoconjunctivitis: current and future perspectives. Pharm. (2021) 14:658. doi: 10.3390/ph14070658
2.
Brindisi G Cinicola B Anania C De Castro G Nebbioso M Del Giudice MM et al . Vernal keratoconjunctivitis: state of art and update on treatment. Acta Bio Med. (2021) 92:e2021517. doi: 10.23750/abm.v92iS7.12419
3.
Di Zazzo A Micera A De Piano M Coassin M Sharma S Bonini S et al . Adult vernal keratoconjunctivitis: clinical and biochemical profile of a rare disease. Ocul Surf. (2019) 17:737–42. doi: 10.1016/j.jtos.2019.07.004
4.
Leonardi A Lazzarini D Motterle L Bortolotti M Deligianni V Curnow SJ et al . Vernal keratoconjunctivitis-like disease in adults. Am J of Ophthalmol. (2013) 155:796–803. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2012.11.018
5.
Sacchetti M Plateroti R Bruscolini A Giustolisi R Marenco M . Understanding vernal keratoconjunctivitis: beyond allergic mechanisms. Life. (2021) 11:1012. doi: 10.3390/life11101012
6.
Mehta JS Chen W-L Cheng AC Cung LX Dualan IJ Kekunnaya R et al . Diagnosis, management, and treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis in Asia: recommendations from the Management of Vernal Keratoconjunctivitis in Asia expert working group. Front Med. (2022) 9:882240. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.882240
7.
Di Zazzo A Bonini S Fernandes M . Adult vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. (2020) 20:501–6. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000672
8.
Bielory BP O’Brien TP Bielory L . Management of seasonal allergic conjunctivitis: guide to therapy. Acta Ophthalmol. (2012) 90:399–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-3768.2011.02272.x
9.
Irfan S Ahmed A Rasheed F . To assess the efficacy and safety of tacrolimus skin cream, 0.03% in moderate to severe vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Pak J of Ophthalmol. (2015) 31:145. doi: 10.36351/pjo.v31i1.145
10.
Ali A Bielory L Dotchin S Hamel P Strube YNJ Koo EB . Management of vernal keratoconjunctivitis: navigating a changing treatment landscape. Survey Ophthalmol. (2023) 69:265–78. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2023.10.008
11.
Zhai J Gu J Yuan J Chen J . Tacrolimus in the treatment of ocular diseases. BioDrugs. (2011) 25:89–103. doi: 10.2165/11587010-000000000-00000
12.
Gutfreund K Bienias W Szewczyk A Kaszuba A . Topical calcineurin inhibitors in dermatology. Part I: properties, method and effectiveness of drug use. Adv Dermatol Allergol. (2013) 30:165–9. doi: 10.5114/pdia.2013.35619
13.
Kheirkhah A Zavareh M Farzbod F Mahbod M Behrouz M . Topical 0.005% tacrolimus eye drop for refractory vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Eye. (2011) 25:872–80. doi: 10.1038/eye.2011.75
14.
Grubbs JR Jr Tolleson-Rinehart S Huynh K Davis RM . A review of quality of life measures in dry eye questionnaires. Cornea. (2014) 33:215–8. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000000038
15.
Chandra M. Angelina M. , Topical tacrolimus for vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: a systematic review. (2023). doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2664294/v1
16.
Zhao M He F Yang Y Lin W Qiu W Meng Q et al . Therapeutic efficacy of tacrolimus in vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Eur J of Hos Pharm. (2022) 29:129–33. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2020-002447
17.
Higgins J. Thomas J. Chandler J. Cumpston M. Li T. Page M. , Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 6.2 (updated February 2021). (2021). Available online at: www.training.cochrane.org/handbook (Accessed June 3, 2021)
18.
Moher D Liberati A Tetzlaff J Altman DG . Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. BMJ. (2009) 339:b2535. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b2535
19.
Hupe M . EndNote X9. J Electron Resour Med Libr. (2019) 16:117–9. doi: 10.1080/15424065.2019.1691963
20.
WebPlotDigitizer . WebPlotDigitizer, R.A., version 4.3, 2020. Software used for data extraction. (2020)
21.
Uchio E Kimura R Migita H Kozawa M Kadonosono K . Demographic aspects of allergic ocular diseases and evaluation of new criteria for clinical assessment of ocular allergy. Graefe's Archive for Clin and Exp Ophthalmol. (2008) 246:291–6. doi: 10.1007/s00417-007-0697-z
22.
Bleik JH Tabbara KF . Topical cyclosporine in vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Ophthalmology. (1991) 98:1679–84. doi: 10.1016/S0161-6420(91)32069-4
23.
Higgins JPT Altman DG Gøtzsche PC Jüni P Moher D Oxman AD et al . The Cochrane collaboration’s tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2011) 343:d5928. doi: 10.1136/bmj.d5928
24.
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, National Institute of Health . Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross-sectional studies. Bethesda: National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (2014).
25.
Hozo SP Djulbegovic B Hozo I . Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med Res Methdol. (2005) 5:13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-5-13
26.
Higgins JP Thompson SG Deeks JJ Altman DG . Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
27.
Borenstein M Hedges L Higgins J Rothstein HJRJ . Comprehensive meta-analysis V2 [computer software and manual]. software for data analysis (2005) 24:2007.
28.
Cochrane Collaboration Copenhagen, D.T.N.C.C , Cochrane collaboration, review manager (version 5.3)[computer software]. Cochrane Collaboration. (2014)
29.
Choudhary P Singh SP Chaurasia RC Jindal M . A prospective study to compare the efficacy of tacrolimus vs cyclosporine in vernal keratoconjunctivitis in children in India. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol. (2019) 8:1297. doi: 10.18203/2319-2003.ijbcp20192193
30.
Eltagoury M Abou Samra W Ghoneim E . Safety and efficacy of topical tacrolimus 0.03% in the management of vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a non-randomized controlled clinical trial. Med Hypothes Discov Innov Ophthalmol. (2022) 11:52–63. doi: 10.51329/mehdiophthal1446
31.
Gupta S Singh P Singh M Naik M Srivastava K . Is interferon α-2b 1 MillionIU/mL truly better than tacrolimus 0.03% for steroid-resistant VKC?: our 2-year experience at a tertiary health-care Centre. Clin Ophthalmol. (2021) 15:2993–9. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S322378
32.
Heikal MA Soliman TT Abousaif WS Shebl AA . A comparative study between ciclosporine a eye drop (2%) and tacrolimus eye ointment (0.03%) in management of children with refractory vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. (2022) 260:353–61. doi: 10.1007/s00417-021-05356-0
33.
Kumari R Saha BC Sinha BP Mohan N . Tacrolimus versus cyclosporine-comparative evaluation as first line drug in vernal keratoconjuctivitis. Nepal J Ophthalmol. (2017) 9:128–35. doi: 10.3126/nepjoph.v9i2.19257
34.
Labcharoenwongs P Jirapongsananuruk O Visitsunthorn N Kosrirukvongs P Saengin P Vichyanond P . A double-masked comparison of 0.1% tacrolimus ointment and 2% cyclosporine eye drops in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis in children. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol. (2012) 30:177.
35.
Malhotra C Singh H Jain AK Gupta A Ram J . Efficacy of 2% rebamipide suspension for vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a clinical comparison with topical immune modulators cyclosporine and tacrolimus. Ocul Immunol Inflamm. (2022) 30:1083–91. doi: 10.1080/09273948.2020.1867870
36.
Nivenius E Van Der Ploeg I Jung K Chryssanthou E Van Hage M Montan P . Tacrolimus ointment vs steroid ointment for eyelid dermatitis in patients with atopic keratoconjunctivitis. Eye. (2007) 21:968–75. doi: 10.1038/sj.eye.6702367
37.
Ohashi Y Ebihara N Fujishima H Fukushima A Kumagai N Nakagawa Y et al . A randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial of tacrolimus ophthalmic suspension 0.1% in severe allergic conjunctivitis. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. (2010) 26:165–74. doi: 10.1089/jop.2009.0087
38.
Pucci N Caputo R di Grande L de Libero C Mori F Barni S et al . Tacrolimus vs. cyclosporine eyedrops in severe cyclosporine-resistant vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a randomized, comparative, double-blind, crossover study. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. (2015) 26:256–61. doi: 10.1111/pai.12360
39.
Qin X Qin L . Effect comparison of tacrolimus eye drops and tobramycin dexamethasone eye drops in the treatment of catarrh keratoconjunctivitis in spring. Contemporary Med Symp. (2018):35–7.
40.
Rathore HS Saeed S Mukhtar MA Ijaz U Habib A Ghaus I . Comparative evaluation of tacrolimus 0.03% ointment vs olopatadine 0.2% eye drops in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Pak Armed Forces Med J. (2021) 71:34–9. doi: 10.51253/pafmj.v71i1.3251
41.
Padmini S Tasneem I Nayak T Rai S Kumar J Indraja Y . A comparative study of efficacy, tolerability and safety of 0.03% tacrolimus eye ointment and 0.05% cyclosporin eye drops in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Int J Med Ophthalmol. (2021) 3:23–32. doi: 10.33545/26638266.2021.v3.i1a.58
42.
Singla E Singh H Kaur WS Walia S . A double-masked comparison of 0.1% tacrolimus ointment and 2% cyclosporine eye drops as first line drugs in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. IOSR J Dent Med Sci. (2017) 16:30–5. doi: 10.9790/0853-1606023035
43.
Suresha A Shashidhar G Prabhudeva H . Evaluation of tacrolimus and cyclosporine in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis in children. Kerala J Ophthalmol. (2023) 35:155–60. doi: 10.4103/kjo.kjo_46_22
44.
Zanjani H Aminifard MN Ghafourian A Pourazizi M Maleki A Arish M et al . Comparative evaluation of tacrolimus versus interferon alpha-2b eye drops in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a randomized, double-masked study. Cornea. (2017) 36:675–8. doi: 10.1097/ICO.0000000000001200
45.
Zhang X Tang J Wang Q . Analysis on tacrolimus efficacy in the treatment of vernal keratoconjunctivitis. Int Eye Sci. (2014) 14:666–9.
46.
Di Zazzo A Zhu AY Nischal K Fung SS . Vernal keratoconjunctivitis in adults: a narrative review of prevalence, pathogenesis, and management. Front Ophthalmol. (2024) 4:1328953. doi: 10.3389/fopht.2024.1328953
47.
Roumeau I Coutu A Navel V Pereira B Baker JS Chiambaretta F et al . Efficacy of medical treatments for vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. (2021) 148:822–34. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.03.026
48.
Fazri KA Ramadhani F . The analysis study of effectiveness and safety of topical treatment for vernal Keratoconjunctivitis: a comprehensive systematic review. Int J Med Sci Health Res. (2024) 2:30–51. doi: 10.70070/fn3q9p69
49.
Müller GG José NK de Castro RS . Topical tacrolimus 0.03% as sole therapy in vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a randomized double-masked study. Eye Contact Lens. (2014) 40:79–83. doi: 10.1097/ICL.0000000000000001
50.
Kandikattu HK Mishra A . Immunomodulatory effects of tacrolimus (FK506) for the treatment of allergic diseases. Int J Cell Biol Physiol. (2018) 1:5. doi: 10.5281/zenodo.2530969
Summary
Keywords
tacrolimus, vernal keratoconjunctivitis, ointment, suspension, VKC
Citation
AlHuthail R (2025) The impact of tacrolimus therapy on the outcomes of vernal keratoconjunctivitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1542440. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1542440
Received
09 December 2024
Accepted
14 July 2025
Published
30 July 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Daniele Giovanni Ghiglioni, IRCCS Ca ‘Granda Foundation Maggiore Policlinico Hospital, Italy
Reviewed by
Karim Mohamed-Noriega, Autonomous University of Nuevo León, Mexico
Hossein Mostafa Elbadawy, University of Taibah, Saudi Arabia
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 AlHuthail.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Reem AlHuthail, rralhuthail@imamu.edu.sa
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.