Abstract
Purpose:
To compare clinical outcomes between Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation (PFNA) and InterTAN intramedullary nail system in treating unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures (IFF) in elderly patients.
Methods:
A retrospective study of 381 patients with IFF at Tianjin Third Central Hospital compared PFNA (n = 189) and InterTAN (n = 192) surgical treatments. Patient demographics, surgical parameters, postoperative outcomes, Visual Analog Scale (VAS) pain scores, and Harris hip scores were analyzed. Follow-up lasted 6–9 months through outpatient visits and telephone calls.
Results:
Both groups showed comparable baseline characteristics including age, gender, affected side, injury mechanism, comorbidities, and Tronzo-Evans classification (P > 0.05). The PFNA group demonstrated clinically meaningful shorter operation times and reduced blood loss compared to InterTAN (P < 0.05). The InterTAN group achieved earlier postoperative weight-bearing (P < 0.05). No significant differences were found in hospitalization duration or intraoperative blood transfusion rates (P > 0.05). Pain scores were lower in the InterTAN group during the early postoperative period (P < 0.05). Harris hip scores were superior in the InterTAN group during the first week and month post-surgery (P < 0.05), but showed no significant differences at 3 and 6 months (P > 0.05). Postoperative complication rates were similar between groups (P > 0.05).
Conclusion:
While both techniques demonstrated comparable long-term outcomes, PFNA may offer advantages in surgical efficiency and blood loss reduction, whereas InterTAN showed improved early postoperative outcomes regarding weight-bearing and initial pain management. The choice between techniques should consider patient-specific factors and surgical priorities. Further prospective studies are warranted to establish stronger clinical guidance.
Introduction
Intertrochanteric femoral fractures (IFF) occur in the proximal femur between the femoral head and diaphysis, representing a significant clinical challenge in elderly patients over 65 years of age. These fractures account for more than half of all hip fractures in this population (1, 2), with unstable patterns being predominant. The current study aims to compare the clinical efficacy of PFNA and InterTAN systems in treating elderly patients with unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures, with particular emphasis on early functional recovery, inflammatory response, and occult blood loss.
Conservative treatment of elderly patients with unstable IFF has prolonged recovery periods and numerous complications, resulting in high disability and mortality rates (3). Surgical intervention has become the preferred treatment approach due to these limitations of conservative management (4, 5). Currently, two major fixation systems are used clinically: extramedullary and intramedullary systems (6). Intramedullary fixation has gradually replaced extramedullary systems due to advantages including reduced soft tissue trauma, superior fracture fixation, and better biomechanical properties (7, 8). Among intramedullary systems, PFNA (Proximal Femoral Nail Anti-rotation) and InterTAN intramedullary nail systems have gained prominence due to their distinctive designs and biomechanical principles (9, 10).
Despite widespread clinical use of these techniques, comparative studies examining their effects on early functional recovery, inflammatory response, and occult blood loss in elderly patients with unstable intertrochanteric fractures remain limited (11).
Materials and methods
Study design and participants
In this retrospective study, 381 elderly patients with unstable IFF who met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were treated at the Department of Orthopedic Surgery of Tianjin Third Central Hospital from August 2022 to August 2024. Patients were allocated to treatment groups based on the type of internal fixation used: 189 patients received PFNA intramedullary system treatment, and 192 patients received InterTAN intramedullary system treatment. Follow-up assessments were conducted at 1 week, 1 month, 2 months, and 3 months post-surgery through medical records, outpatient visits, and telephone interviews.
Ethical considerations
This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Third Central Hospital (TTC20231STY). All patients provided written informed consent prior to surgical intervention.
The study population consisted of 198 male and 183 female patients, aged 69–80 years with a mean age of (81.78 ± 7.81) years. Detailed surgical techniques for both groups have been standardized and are provided in Supplementary material to maintain narrative focus.
Surgical technique
For PFNA procedures: After anesthesia and positioning on a traction bed, closed reduction was performed under C-arm fluoroscopic guidance. A 3–5 cm longitudinal incision was made above the greater trochanter, followed by guide pin insertion, proximal femur reaming, and nail insertion. The spiral blade was then inserted under fluoroscopic guidance (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1

Intraoperative spiral blade insertion during PFNA procedure. The image demonstrates the proper positioning and insertion technique of the spiral blade component, which is a key distinguishing feature of the PFNA system providing enhanced rotational stability.
For InterTAN procedures: Similar initial preparation was followed, with guide pins inserted into the femoral head and neck under fluoroscopic guidance. After measurement, compression and lag screws were sequentially inserted to achieve fracture compression and fixation. The interlocking compression screw system creates enhanced stability (Figure 2).
FIGURE 2

Intraoperative placement of the dual-screw system during InterTAN procedure. The image shows the characteristic two-screw configuration that provides the InterTAN system’s enhanced rotational control and compression capability.
A representative case from the PFNA group involved a 78-year-old male patient who presented with right hip trauma. Preoperative imaging revealed an unstable intertrochanteric fracture (Figure 3), which was successfully treated with PFNA internal fixation, as demonstrated in the postoperative radiograph (Figure 4).
FIGURE 3

Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph of both hip joints showing unstable right intertrochanteric femoral fracture in a 78-year-old male patient. The fracture pattern demonstrates characteristic features of instability requiring surgical intervention.
FIGURE 4

Postoperative anteroposterior radiograph demonstrating successful PFNA fixation with good fracture reduction and proper implant positioning. The spiral blade is optimally placed in the femoral head with adequate tip-apex distance.
A representative case from the InterTAN group involved an 84-year-old female patient who sustained a left hip injury. The preoperative radiograph revealed an unstable intertrochanteric fracture (Figure 5), which was successfully managed with InterTAN internal fixation as shown in the postoperative imaging (Figure 6).
FIGURE 5
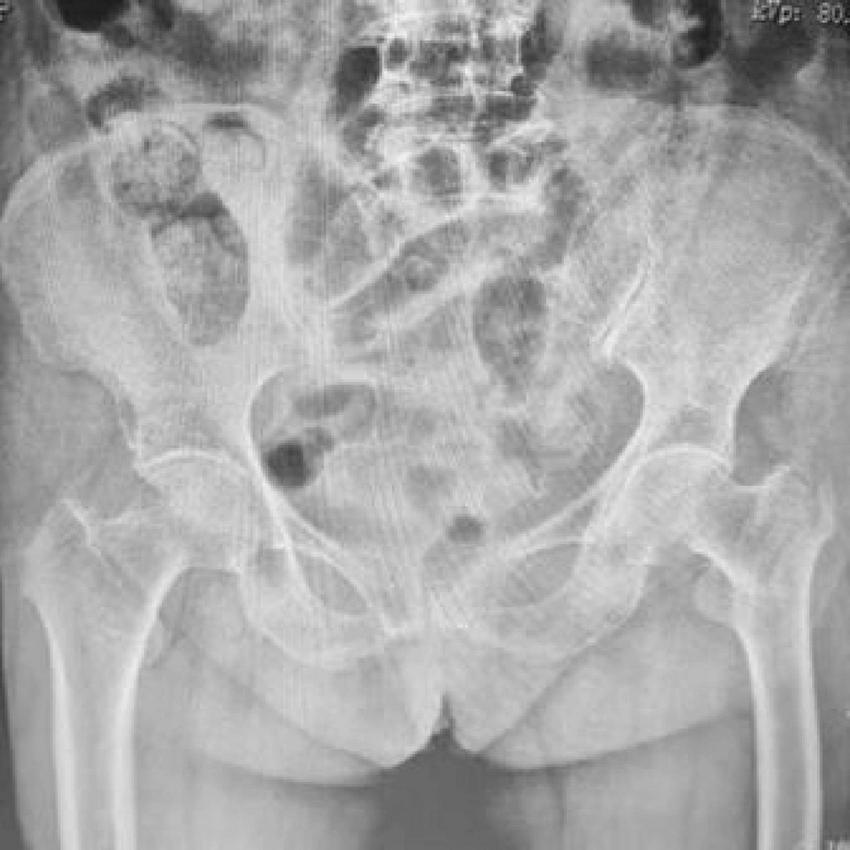
Preoperative anteroposterior radiograph of both hip joints showing unstable left intertrochanteric femoral fracture in an 84-year-old female patient. The fracture configuration demonstrates the complexity typical of unstable patterns requiring advanced fixation techniques.
FIGURE 6

Postoperative anteroposterior radiograph demonstrating successful InterTAN fixation with anatomical fracture reduction and optimal implant positioning. The dual-screw configuration is properly aligned within the femoral head and neck.
Postoperative management
Patients underwent standardized postoperative care protocols including ankle pump exercises, low molecular weight heparin anticoagulation, and calcium supplementation. No drainage systems were employed during surgery for either group.
Inclusion criteria:
-
1.
Unilateral intertrochanteric femoral fracture
-
2.
Age ≥ 65 years
-
3.
Agreement not to remove internal fixation during postoperative follow-up
-
4.
Patients with stable general condition capable of tolerating surgery
-
5.
Pre-fracture ambulatory status
Exclusion criteria:
-
1.
Pathologic fractures
-
2.
Mental illness preventing cooperation with follow-up rehabilitation
-
3.
Patients with poor general condition, severe hepatic and renal insufficiency unable to tolerate surgery
-
4.
Poor coagulation function and high bleeding risk assessed preoperatively
-
5.
Pre-fracture non-ambulatory status
-
6.
Fractures of other parts of the femur on the same side
-
7.
Osteoarthritis of hip, knee, and ankle joints and femoral head necrosis
-
8.
Death during 6-month follow-up period
Outcome measures
Primary outcomes included operative time, intraoperative blood loss, and early postoperative mobility (defined as time to first mobilization from bed as documented in nursing records and standardized mobility assessments). Secondary outcomes encompassed hospitalization duration, blood transfusion requirements, pain scores using the Visual Analog Scale (VAS) derived from standardized pain assessments, Harris hip scores from clinical evaluations, inflammatory markers (hs-CRP and IL-6), and complication rates. All outcomes were extracted from standardized clinical records and assessments.
Statistical analysis
SPSS 26.0 statistical software was used for data analysis. Continuous variables were tested for normality using the Shapiro-Wilk test. For normally distributed data, independent samples t-tests were applied for comparisons between groups, while Mann-Whitney U tests were used for non-normally distributed data. Categorical variables were analyzed using chi-square tests or Fisher’s exact test when appropriate. For multiple group comparisons of inflammatory markers, repeated measures ANOVA was performed. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05. All tests were two-tailed.
Results
Comparison of general basic data between PFNA group and InterTAN group
We analyzed the medical records of 381 patients, with the PFNA Group consisting of 189 cases and the InterTAN Group consisting of 192 cases (Table 1). In the PFNA Group, there were 98 males and 91 females, with an average age of 71.05 ± 9.11 years. The right side was the injury site in 87 cases, while the left side was the injury site in 102 cases. The primary reasons for injury were falls (53 cases), traffic accidents (44 cases), slips (92 cases). Regarding the Tronzo-Evans Classification, there were 102 cases of III, 44 cases of IV, and 43 cases of V. Cardiovascular Disease was present in 104 cases, Diabetes in 112 cases, and Cerebrovascular Disease in 107 cases.
TABLE 1
| Characteristics | PFNA group | InterTAN group | t | χ2 value | p-value | |
| Total cases | 189 | 192 | ||||
| Age (years) | 71.05 ± 9.11 | 69.14 ± 8.54 | 1.13 | 0.65 | ||
| Gender (M/F) | 98/91 | 100/92 | ||||
| Injured side (L/R) | 87/102 | 103/89 | ||||
| Reason for injury | Fall | 53 | 64 | 0.257 | 0.879 | |
| Traffic accident | 44 | 48 | ||||
| Slip | 92 | 80 | ||||
| Tronzo-evans classification | III | 102 | 119 | 0.289 | 0.866 | |
| IV | 44 | 43 | ||||
| V | 43 | 40 | ||||
| Cardiovascular disease | Yes | 104 | 122 | 2.139 | 0.144 | |
| No | 85 | 70 | ||||
| Diabetes | Yes | 112 | 118 | 1.227 | 0.268 | |
| No | 77 | 74 | ||||
| Cerebrovascular disease | Yes | 107 | 121 | 1.083 | 0.298 | |
| No | 82 | 71 |
Comparison of general basic data between PFNA group and InterTAN group.
In the InterTAN Group, there were 100 males and 92 females, with an average age of 69.14 ± 8.54 years. The right side was the injury site in 103 cases, while the left side was the injury site in 89 cases. The primary reasons for injury were falls (64 cases), traffic accidents (48 cases), and slips (80 cases). For the Tronzo-Evans Classification, there were 119 cases of III, 43 cases of IV, and 40 cases of V. Cardiovascular Disease was present in 122 cases, Diabetes in 118 cases, and Cerebrovascular Disease in 121 cases. No significant differences were observed in preoperative baseline characteristics between the two groups, confirming their comparability (P > 0.05).
Comparison of clinical outcomes between PFNA and InterTAN groups
The PFNA group demonstrated significantly shorter surgery time (78.00 ± 19.80 vs. 115.50 ± 30.10 min, t = 6.230, p < 0.001) and reduced intraoperative blood loss (120.00 ± 58.00 vs. 195.00 ± 85.00 mL, t = 4.050, p = 0.001) compared to the InterTAN group (Table 2). The clinical relevance of these differences is substantial, with the 37.5-min reduction in operative time potentially reducing anesthesia-related risks in elderly patients, and the 75 mL reduction in blood loss may decrease transfusion requirements and associated complications. These findings are particularly important for elderly patients with multiple comorbidities who may have limited physiological reserves.
TABLE 2
| Observation indicator | PFNA group | InterTAN group | t | P |
| Surgery time (min) | 78.00 ± 19.800 | 115.50 ± 30.100 | 6.230 | 0.000 |
| Intraoperative blood loss (mL) | 120.00 ± 58.000 | 195.00 ± 85.000 | 4.050 | 0.001 |
| Incision length (cm) | 6.50 ± 1.850 | 7.50 ± 2.400 | 1.580 | 0.110 |
| Early bed activity (d) | 6.80 ± 1.650 | 5.50 ± 1.750 | 3.150 | 0.002 |
| Hospital stay (d) | 15.80 ± 3.100 | 15.50 ± 4.300 | 0.065 | 0.834 |
Comparison of clinical outcomes between PFNA and InterTAN groups.
Regarding early postoperative mobility, the InterTAN group demonstrated significantly earlier bed activity (5.50 ± 1.75 vs. 6.80 ± 1.65 days, t = 3.150, p = 0.002). No significant differences were observed in incision length (7.50 ± 2.40 vs. 6.50 ± 1.85 cm, t = 1.580, p = 0.110) or hospital stay duration (15.50 ± 4.30 vs. 15.80 ± 3.10 days, t = 0.065, p = 0.834) between the groups.
Changes in intraoperative blood transfusion in the PFNA group and the InterTAN group
Although the difference in transfusion rates between groups did not reach statistical significance (PFNA: 47.1% vs. InterTAN: 68.9%, P > 0.05), this 21.8% difference represents a clinically meaningful variation that warrants acknowledgment (Table 3). The higher transfusion rate in the InterTAN group may reflect the increased surgical complexity and longer operative time associated with this technique.
TABLE 3
| Group | Cases (n) | Trans- fusion (n) |
Non-trans- fusion (n) |
Trans- fusion Rate (%) |
χ2 | P-value |
| PFNA group | 189 | 89 | 100 | 47.1% | 1.050 | 0.305 |
| InterTAN group | 192 | 132 | 35 | 68.9% | 1.200 | 0.275 |
Comparison of intraoperative blood transfusion between PFNA group and InterTAN group.
VAS scores in the PFNA group and the InterTAN group
Pain VAS scores revealed consistent pain reduction in both groups following surgery, with the InterTAN group demonstrating more pronounced early pain relief (Table 4). Notably, while the InterTAN group showed significantly lower pain scores at 1 week (6.99 vs. 7.73, p = 0.001), 1 month (4.31 vs. 4.82, p = 0.017), 2 months (3.24 vs. 3.67, p = 0.021), and 3 months (2.09 vs. 2.49, p = 0.034) postoperatively, the absolute differences decreased progressively over time, suggesting convergence of pain outcomes in the longer term.
TABLE 4
| Pain VAS score | PFNA group | InterTAN group | t | P |
| Preoperative | 8.54 | 8.53 | 0.04 | 0.968 |
| 1 week postop | 7.73 | 6.99 | 3.85 | 0.001 |
| 1 month postop | 4.82 | 4.31 | 2.42 | 0.017 |
| 2 months postop | 3.67 | 3.24 | 2.35 | 0.021 |
| 3 months postop | 2.49 | 2.09 | 2.15 | 0.034 |
Analysis of pain VAS scores in two groups.
Harris Scores before and after surgery between two groups
Harris hip scores demonstrated improvement over time in both groups, with the InterTAN group showing superior early recovery (Table 5). The InterTAN group achieved significantly higher Harris scores at 1 week (51.7 ± 2.3 vs. 48.0 ± 2.3, p < 0.001) and 1 month (71.8 ± 2.7 vs. 69.4 ± 3.1, p = 0.001) postoperatively. However, this early advantage disappeared by the 3-month (79.9 ± 2.3 vs. 80.0 ± 2.4, p = 0.761) and 6-month (82.5 ± 2.1 vs. 82.2 ± 2.3, p = 0.564) follow-ups, indicating equivalent long-term functional outcomes.
TABLE 5
| Harris score | PFNA group (mean ± SD) | InterTAN group (mean ± SD) | t | P |
| Preoperative | 15.5 ± 3.2 | 15.5 ± 3.4 | – | – |
| 1 Week Postop | 48.0 ± 2.3 | 51.7 ± 2.3 | 7.2 | 0.000 |
| 1 month postop | 69.4 ± 3.1 | 71.8 ± 2.7 | 3.2 | 0.001 |
| 3 months postop | 80.0 ± 2.4 | 79.9 ± 2.3 | 0.3 | 0.761 |
| 6 months postop | 82.2 ± 2.3 | 82.5 ± 2.1 | 0.6 | 0.564 |
Comparison of Harris Scores before and after surgery between two groups.
Comparison of Inflammatory marker levels between two groups of patients
Both groups demonstrated significant postoperative increases in inflammatory markers compared to baseline values (p < 0.001 for all comparisons). However, the InterTAN group exhibited significantly higher postoperative hs-CRP (39.50 ± 5.84 vs. 34.84 ± 5.17 mg/L, p = 0.002) and IL-6 levels (162.21 ± 19.26 vs. 144.13 ± 17.04 pg/mL, p < 0.001) compared to the PFNA group (Table 6). These elevated inflammatory markers in the InterTAN group likely reflect increased tissue trauma associated with the more complex surgical procedure, including the need for medullary canal expansion and insertion of dual screws. The clinical implications of these differences may include prolonged recovery time, increased postoperative pain, and potentially higher risk of inflammatory-related complications, although further studies are needed to establish direct clinical correlations.
TABLE 6
| Group | Number | White blood cells (× 109/L) | hs-CRP(mg/L) | IL-6(pg/mL) | |||
| Pre-operation | Post-operation | Pre-operation | Post-operation | Pre-operation | Post-operation | ||
| PFNA Group | 189 | 10.85 ± 1.02 | 14.99 ± 3.02a | 27.51 ± 5.20 | 34.84 ± 5.17a | 125.31 ± 15.28 | 144.13 ± 17.04a |
| InterTAN Group | 192 | 10.91 ± 1.12 | 17.26 ± 3.42a | 27.18 ± 5.13 | 39.50 ± 5.84a | 127.30 ± 15.19 | 162.21 ± 19.26a |
| t | 0.216 | 2.716 | 0.244 | 3.261 | 0.499 | 3.838 | |
| p | 0.830 | 0.009 | 0.808 | 0.002 | 0.620 | < 0.001 | |
Comparison of inflammatory index levels between two groups of patients.
Postoperative complication analysis between PFNA group and InterTAN group
Postoperative complications were categorized into infectious complications (lung infections, urinary tract infections), mechanical complications (loosening of tail cap, screw backout, coxa vara, perifixation fractures), and medical complications (bedsores, deep vein thrombosis, new cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases) (Table 7). While overall complication rates showed no statistical difference between groups (χ2 = 3.143, P = 0.765), some notable variations emerged. The InterTAN group demonstrated a higher incidence of lung infections (14.6% vs. 8.5%) and urinary tract infections (15.1% vs. 10.1%), which may be associated with longer operative times leading to prolonged anesthesia exposure and increased physiological stress. These infections, while not statistically significant, could result in extended hospital stays, increased healthcare costs, and delayed functional recovery. Conversely, the PFNA group showed higher rates of mechanical complications including tail cap loosening (12.7% vs. 6.3%) and coxa vara (11.6% vs. 7.8%), which may necessitate revision surgery and impact long-term functional outcomes.
TABLE 7
| Complications | PFNA group | InterTAN group |
| Number of cases (n) | 189 | 192 |
| Bedsores | 32 | 23 |
| Deep vein thrombosis | 33 | 34 |
| Lung infection | 16 | 28 |
| Urinary tract infection | 19 | 29 |
| New cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases | 21 | 26 |
| Loosening of tail cap | 24 | 12 |
| Screw backout | 11 | 11 |
| Coxa vara | 22 | 15 |
| Fracture around internal fixation | 11 | 14 |
Comparison of postoperative complication types between PFNA group and InterTAN group.
Discussion
In this retrospective analysis of 381 elderly patients with unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures, we compared the clinical effects of PFNA and InterTAN intramedullary fixation systems. The study population included 192 cases in the InterTAN group and 189 cases in the PFNA group, with data collected on preoperative characteristics, surgical parameters, and follow-up outcomes.
Our findings demonstrated that the PFNA group achieved superior surgical efficiency with significantly shorter operative times and reduced intraoperative blood loss compared to the InterTAN group. These results align with previous studies by Luo et al., suggesting that the InterTAN system’s more complex design, requiring insertion of two screws and medullary expansion, contributes to increased operative complexity and duration. However, it should be acknowledged that surgical positioning and implant design can significantly influence fracture reduction quality and postoperative rotational alignment in trochanteric femur fractures. Recent studies by Yurteri et al. (12, 13) have demonstrated that operative positioning (lateral decubitus versus traction table) significantly affects intramedullary nailing outcomes in trochanteric fractures. Mercan and Yurteri (14) further compared third-generation intramedullary nails including PFNA and InterTAN in unstable trochanteric fractures, highlighting the importance of surgical technique optimization. Our study did not standardize operative positioning protocols between groups, which represents a potential limitation that may have influenced our outcomes.
The InterTAN group demonstrated advantages in early postoperative recovery, including earlier weight-bearing capability and superior initial pain management. However, the convergence of pain scores and Harris hip scores by the 3-month follow-up suggests that these early benefits may not translate into long-term functional advantages. This temporal pattern emphasizes the importance of considering both short-term and long-term outcomes when selecting treatment approaches.
Recent studies have emphasized the impact of surgical positioning strategies (15–19), such as lateral decubitus versus traction table approaches, on intraoperative visualization and biomechanical outcomes in trochanteric femur fractures. Future studies should consider standardizing these variables to better isolate the effects of implant choice on clinical outcomes.
Conclusion
This retrospective observational study suggests that both PFNA and InterTAN systems provide acceptable clinical outcomes for treating unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in elderly patients. PFNA may be considered for patients with compromised general health status who would benefit from reduced operative time and decreased blood loss. InterTAN might be preferred for patients requiring early mobilization and aggressive rehabilitation protocols. However, these conclusions must be interpreted cautiously given the retrospective nature of this study, potential confounding factors including surgical positioning variations, and the lack of standardization in certain outcome assessments. Prospective randomized controlled trials with standardized surgical protocols and clearly defined outcome measures are necessary to establish definitive treatment guidelines and confirm these preliminary observations.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Tianjin Third Central Hospital (TTC20231STY). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
FF: Intertrochanteric, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XL: Resources, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JL: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. ZC: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. SG: Investigation, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
Thanks to all those who helped with the study but were not listed as co-authors due to insufficient contributions.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1568584/full#supplementary-material
Abbreviations
IFF, Intertrochanteric Femoral Fracture; PFNA, Proximal Femoral Nail Antirotation; InterTAN, InterTAN Hip Fracture Nailing System; MRI, Magentic Resonance Imaging; Harris, Harris hip score; PFN, Proximal Femoral Nail.
References
1.
Ricci W . Stability of intertrochanteric femur fractures.J Orthop Trauma. (2023) 37:S1–4. 10.1097/BOT.0000000000002675
2.
Fischer H Maleitzke T Eder C Ahmad S Stöckle U Braun K . Management of proximal femur fractures in the elderly: Current concepts and treatment options.Eur J Med Res. (2021) 26:86. 10.1186/s40001-021-00556-0
3.
Kiriakopoulos E McCormick F Nwachukwu B Erickson B Caravella J . In-hospital mortality risk of intertrochanteric hip fractures: A comprehensive review of the US Medicare database from 2005 to 2010.Musculoskelet Surg. (2017) 101:213–8. 10.1007/s12306-017-0470-3
4.
Katsuyama Y Okuda Y Kanamura H Sasaki K Saito T Nakamura S . Surgical versus conservative treatment of greater trochanteric fractures with occult intertrochanteric fractures: Retrospective cohort study.Injury. (2023) 54:111055. 10.1016/j.injury.2023.111055
5.
Mascoe J Herickhoff P . Conservative treatment of a nondisplaced intertrochanteric femur fracture: A case report and review of the literature.Iowa Orthop J. (2021) 41:91–4.
6.
Schader J Zderic I Dauwe J Sommer C Gueorguiev B Stoffel K . Biomechanical comparison of intramedullary versus extramedullary implants for fixation of simple pertrochanteric fractures.J Orthop Trauma. (2023) 37:243–8. 10.1097/BOT.0000000000002552
7.
Xie H Xie L Wang J Chen C Zhang C Zheng W . Intramedullary versus extramedullary fixation for the treatment of subtrochanteric fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Int J Surg. (2019) 63:43–57. 10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.01.021
8.
Brewer P Murray J Barr L Headon E Davies H Chadwick C et al Fibula nail fixation in ankle fractures with significant soft tissue compromise: A retrospective cohort study. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. (2022) 32:1257–63. 10.1007/s00590-021-03088-9
9.
Wang W Ni B Shen H Lu H . Meta-analysis of InterTan, PFNA and PFNA-II internal fixation for the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly individuals.Acta Orthop Belg. (2023) 89:51–8. 10.52628/89.1.9923
10.
Li L Fang X Gao J Han W Kong X . Comparison of InterTAN and PFNA internal fixation for elderly patients with intertrochanteric fracture: A retrospective cohort study.Pak J Med Sci. (2024) 40:589–94. 10.12669/pjms.40.4.8794
11.
Harikrishnan P Madivanan I . Supplemental internal wire suspension in orthognathic surgery fixation.J Craniofac Surg. (2019) 30:e97. 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004919
12.
Yurteri A Mercan N Kılıç M Yıldırım A . Comparison of the effects of lateral decubitus position and traction table on intramedullary nailing in trochanteric femur fractures.Cukurova Med J. (2023) 48:1275–81. 10.17826/cumj.1352439
13.
Yurteri A Mercan N Kılıç M Temiz A Dogar F Topak D et al Impact of operative position on rotational alignment after intramedullary nailing of trochanteric fractures: A comparative analysis of lateral decubitus versus supine position. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2024) 25:790. 10.1186/s12891-024-07859-3
14.
Mercan N Yurteri A . Comparative analysis of third-generation intramedullary nails: Retrospective evaluation of PFNA and InterTAN nails in unstable trochanteric fractures.Ann Med Res. (2024) 31:397–403.
15.
Hadar A Mns B Ramdhan A Rahim A Siwendro B Setiadi C . Large primary intradural extramedullary spinal tumors: A case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. (2023) 111:108825. 10.1016/j.ijscr.2023.108825
16.
Poh K Lingaraj K . Complications and their risk factors following hip fracture surgery.J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong). (2013) 21:154–7. 10.1177/230949901302100207
17.
Hu Y Yang MA . predictive scoring system for postoperative delirium in the elderly patients with intertrochanteric fracture.BMC Surg. (2023) 23:154. 10.1186/s12893-023-02065-9
18.
Schroeder J Turner S Buck E . Hip fractures: Diagnosis and management.Am Fam Phys. (2022) 106:675–83.
19.
Li L Wu W . Comparison of clinical effects of PFNA, APFLP and InterTan intramedullary nail in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly patients.Minerva Surg. (2024) 80:97–100. 10.23736/S2724-5691.24.10397-8
Summary
Keywords
intertrochanteric femoral fracture, PFNA, intertan, aging, instability
Citation
Feng F, Li X, Li J, Chen Z and Guo S (2025) Comparison of the efficacy of PFNA and InterTAN intramedullary nail in the treatment of unstable intertrochanteric femoral fractures in the elderly. Front. Med. 12:1568584. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1568584
Received
30 January 2025
Accepted
11 June 2025
Published
01 July 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Yan Press, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Israel
Reviewed by
Yasin Kisioglu, Kocaeli University, Türkiye
Numan Mercan, Ministry of Health, Türkiye
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Feng, Li, Li, Chen and Guo.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Shuzhang Guo, ffhui1234@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.