Abstract
Objective:
The pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases is complex, involving multiple factors, including genetic, environmental, and lifestyle elements. Recent studies have suggested that infectious agents may act as important triggers for neurodegenerative diseases. This study aimed to evaluate the association between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and the risk of neurodegenerative disorders through a systematic review and meta-analysis of existing literature.
Methods:
A systematic search was conducted across the PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Library databases for studies published up to December 2024. The combined effect sizes were expressed as odds ratios (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) and were calculated using a random-effects model. Further exploratory analyses included sensitivity analyses, subgroup analyses, and assessment of publication bias.
Results:
Forty-one studies involving 159,220 participants were selected for the meta-analysis. We found that H. pylori infection was associated with an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease (OR: 1.70; 95% CI: 1.36–2.13; p < 0.001), all-cause dementia (OR: 1.56; 95% CI: 1.24–1.96; p < 0.001), and Alzheimer’s disease (OR: 1.43; 95% CI: 1.01–2.02; p = 0.045). However, H. pylori infection was not associated with the risk of multiple sclerosis (OR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.59–1.11; p = 0.193). Sensitivity analysis suggested that H. pylori infection might play a protective role in the subsequent risk of multiple sclerosis. Subgroup analyses indicated that the association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative disorders may vary based on country, study design, H. pylori detection technique, and study quality.
Conclusion:
This study found that H. pylori infection may be associated with an elevated risk of Parkinson’s disease, all-cause dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease.
Systematic review registration:
INPLASY (INPLASY202510044).
Introduction
Neurodegenerative diseases constitute a heterogeneous set of chronic central nervous system maladies that are marked by progressive neuronal degeneration (1). These disorders exact a substantial toll on society, as they impact millions of people worldwide (2). Given the current lack of a cure and the fatality of some cases, patients necessitate long-term, uninterrupted care. This not only incurs substantial economic expenses but also exerts a heavy burden on social resources. It is estimated that by 2030, the global cost associated with dementia alone will surpass $2 trillion (3). With the global population aging and life expectancy rising, early diagnosis and intervention for neurodegenerative diseases have emerged as pressing public health imperatives.
Although research has indicated that elements like oxidative stress, viral infections, and the natural aging process play a role in the onset of these diseases (4–6), there is still a necessity to delve deeper into their potential risk factors. Pinpointing these risk factors can assist in identifying high-risk groups and enhancing patients’ prognoses and quality of life through early detection. Based on the infection hypothesis associated with neurodegenerative diseases, microorganisms might serve as initiators and/or mediators of these ailments (7). Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection is a prevalent chronic infection that impacts more than 50% of the global population (8). In developing nations, the infection rate is estimated to be between 80 and 90%, whereas in the United States and Europe, it lies between 35 and 40% (9, 10). Research over the past decade has shown that chronic H. pylori infection is associated not only with various extraintestinal manifestations, such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and stroke (11–13), but also with neurocognitive and neuropsychiatric disorders, including all-cause dementia and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) (14–16). H. pylori infection may contribute to these conditions by affecting the brain and vascular systems. These diseases may be triggered by H. pylori infection through mechanisms such as reduced nutrient bioavailability, alterations in gut microbiota, oxidative stress, and metabolic disturbances (17, 18). H. pylori infection may also lead to pathological changes resembling those observed in AD. Consequently, preventing chronic H. pylori infection could have a significant impact on the onset and progression of neurodegenerative diseases.
Recent research has extensively discussed the role of inflammation induced by H. pylori in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease (PD) and AD (19). Additionally, another important article has pointed out that while there is growing interest in the relationship between Helicobacter species and neurological disorders, data on the association with multiple sclerosis (MS) remain limited (20). Previous meta-analyses have also explored the relationship between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases (21–23). Although these studies found H. pylori infection were associated with an increased risk of PD, and all-cause dementia, whereas it did not affect subsequent AD risk (21, 22). Moreover, the study conducted by Yao et al. suggested H. pylori infection was associated with a reduced risk of MS (23). However, there are still some inconsistencies in the results of different meta-analyses. These discrepancies may be due to differences in study populations, inclusion criteria, and the quality of the original studies included in the meta-analyses. Understanding these previous findings is crucial for our current study, as it allows us to build on existing knowledge and further explore the complex relationship between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases such as PD, all-cause dementia, AD, and MS.
Materials and methods
Data sources, search strategy, and selection criteria
This review was carefully designed and reported in accordance with the 2020 updated Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement to ensure the transparency and reliability of the research process (PRISMA Checklist) (24). Our study was registered in INPLASY platform (number: INPLASY202510044). The objective was to comprehensively evaluate existing evidence on the potential association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases. To maximize the dataset, no restrictions were placed on the language or publication status of the included studies.
A systematic search was conducted in PubMed, Embase, and the Cochrane Library for relevant articles published up to December 2024, using the search terms “Helicobacter pylori” AND “neurocognitive disorders.” The detailed search strategy for PubMed is provided in Supplementary Table S1. Additionally, a manual search was performed by reviewing the reference lists of all relevant primary studies and review articles to identify studies that may not have been indexed in the databases but still met the inclusion criteria. This approach helped minimize the risk of missing important studies.
Study relevance was determined by evaluating medical subject headings, research methods, patient populations, study designs, exposure factors, and outcome variables. The literature search was independently conducted by two authors using a standardized method. Any discrepancies that arose during the screening process were resolved through discussion, and if consensus could not be reached, the principal author made the final decision.
Studies were included if they met the following criteria: they used either a case–control or cohort study design, evaluated the association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases, and reported effect estimates with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (95% CI). To ensure accuracy and consistency, the two authors independently reviewed the titles and abstracts of each article to preliminarily select studies that met the inclusion criteria. These selected studies then underwent a full-text review to confirm their compliance with all inclusion criteria. Cross-sectional studies were excluded because they could not establish a causal relationship.
Data collection and quality assessment
Data collected from each study included the first author’s name, publication year, country, study design, sample size, baseline age, percentage of male participants, definition of H. pylori infection, reported endpoints, effect estimates with their 95% confidence intervals, and details of the adjusted models. When dealing with studies that reported outcomes for both all-cause dementia and AD, we implemented a systematic approach to avoid double-counting. For the studies that reported data for both endpoints, we extracted the data separately based on the specific outcome of interest for each meta-analysis. In the meta-analysis of all-cause dementia, we only included the data related to the all-cause dementia outcome from these studies. Similarly, for the meta-analysis of AD, we exclusively used the data specifically reported for AD. This method ensured that each data point was utilized only once, depending on the relevant outcome, and prevented any over- or under-estimation of the associations. The methodological quality of the included studies was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS), a widely validated tool for evaluating observational studies. The NOS consists of three sections: Selection (4 items), Comparability (1 item), and Outcome (3 items), with a total score ranging from 0 to 9. Higher scores indicate better study quality (25). Data extraction and quality assessment were independently conducted by two authors to ensure objectivity and consistency. Both authors thoroughly reviewed each study, extracted the required data, and assessed study quality using the NOS. A third author independently checked the original studies to verify data accuracy and completeness and resolved any discrepancies if necessary.
Statistical analysis
The association between H. pylori infection and the risk of PD, all-cause dementia, AD, and MS was assessed based on the effect estimates and their 95% confidence intervals reported in each study. A random-effects model was used to pool the odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals to account for heterogeneity across studies (26, 27). Heterogeneity among the studies was evaluated using the I2 statistic and Q test. An I2 value greater than 50.0% or a p-value less than 0.10 was considered indicative of significant heterogeneity (28, 29). Sensitivity analyses were conducted to assess the robustness of the pooled results (30). Subgroup analyses were carried out based on country, study design, H. pylori detection methods, reported outcomes, and study quality. Differences between subgroups were compared using the interaction t-test, assuming that the data followed a normal distribution (31). In addition to the subgroup analyses, we performed meta-regression analyses to further explore the sources of heterogeneity (32). Publication bias was visually assessed through funnel plots for PD, all-cause dementia, AD, and MS. Additionally, Egger’s and Begg’s tests were performed to statistically evaluate publication bias (33, 34). All reported p-values were two-sided, and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were conducted using STATA software (version 12.0; StataCorp, College Station, TX, USA).
Results
Literature search
The detailed screening process for the included studies is presented in Figure 1. Initially, 1,341 articles were identified through electronic searches. After removing duplicates, 746 articles remained. Following the screening of titles and abstracts, 659 articles were excluded. The remaining 87 studies underwent a full-text review, resulting in 41 studies that met the inclusion criteria and were included in the meta-analysis (35–75). A manual search of reference lists from these studies identified two additional studies that initially appeared to meet the criteria; however, further screening revealed that these studies were already included in the electronic search results and were therefore excluded.
Figure 1

Flow diagram of the literature search and study selection process.
Study characteristics
Table 1 summarizes the baseline characteristics of the included studies and their participants. Collectively, these studies involved 159,220 participants. Of these, 11 studies employed a cohort design, while the remaining 30 studies used a case–control design. Seventeen studies were conducted in Eastern countries, mainly China, Japan, Iran, India, and Singapore, while the other 24 studies were conducted in Western countries, primarily in Europe and North America. Eighteen studies reported adjusted effect estimates, whereas 23 studies provided unadjusted effect estimates. The quality of the studies, assessed using the NOS, showed that six studies scored 8, twelve studies scored 7, eleven studies scored 6, and the remaining twelve studies scored 5. The inclusion of these lower-quality studies may potentially introduce biases into the meta-analysis results, which will be further discussed in the subsequent sections.
Table 1
| Study | Country | Study design | Sample size | Age (years) | Male (%) | H. pylori infection detection | Reported outcomes | Adjusted | Study quality |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Charlett 1999 (35) | UK | Case-control | 111 | 70.5 | 41.0 | ELISA | PD | Adjusted | 6 |
| Dobbs 2000 (36) | UK | Cohort | 315 | 67.5 | 51.4 | ELISA | PD | Adjusted | 7 |
| Nägga 2003 (37) | Sweden | Case-control | 224 | 71.9 | 44.2 | ELISA | AD, VaD | Adjusted | 5 |
| Kountouras 2006 (38) | Greece | Case-control | 80 | 64.0 | 40.0 | ELISA | AD | Crude | 5 |
| Li 2007 (39) | Japan | Case-control | 190 | 42.2 | 23.7 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Kountouras 2007 (40) | Greece | Case-control | 98 | 67.1 | 39.8 | Biopsy and ELISA | MCI | Crude | 6 |
| Li 2009 (41) | Japan | Case-control | 247 | 39.7 | 25.1 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Charlett 2009 (42) | UK | Case-control | 586 | 59.5 | 50.3 | ELISA | PD | Crude | 7 |
| Kountouras 2009 (43) | Greece | Case-control | 80 | 65.0 | 40.0 | Biopsy and ELISA | AD | Crude | 5 |
| Zarkesh 2009 (44) | Iran | Case-control | 399 | NA | 32.9 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 5 |
| Riskind 2010 (45) | USA | Case-control | 410 | NA | NA | Latex agglutination | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Shiota 2011 (46) | Japan | Case-control | 482 | 75.2 | 27.2 | ELISA | AD | Adjusted | 7 |
| Nielsen 2012 (47) | Denmark | Case-control | 26,900 | 70.8 | 59.7 | ICD-8 and 10 | PD | Adjusted | 8 |
| Ramroodi 2012 (48) | Iran | Case-control | 201 | NA | NA | Western blot | MS | Crude | 5 |
| Mohebi 2013 (49) | Iran | Case-control | 313 | 32.0 | 54.0 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Yoshimura 2013 (50) | Japan | Case-control | 299 | 31.4 | 35.2 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 5 |
| Long 2013 (51) | China | Case-control | 69 | 33.9 | 50.0 | IF | MS | Adjusted | 7 |
| Ram 2013 (52) | Latin America | Case-control | 238 | NA | NA | ICT | MS | Crude | 5 |
| Blaecher 2013 (53) | UK | Case-control | 316 | 52.0 | 48.7 | Biopsy and ELISA | PD | Crude | 6 |
| Baudron 2013 (54) | France | Cohort | 603 | 73.9 | 42.3 | ELISA | All-cause dementia | Adjusted | 8 |
| Nafisah 2013 (55) | USA | Case-control | 52 | 64.1 | NA | ELISA | PD | Crude | 5 |
| Huang 2014 (56) | China | Cohort | 83,965 | 63.3 | 61.6 | ICD-9 | All-cause dementia, AD | Adjusted | 7 |
| Cook 2015 (57) | UK | Case-control | 113 | 51.9 | 31.0 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 5 |
| Pedrini 2015 (58) | Australia | Case-control | 849 | 35.4 | 25.8 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Malli 2015 (59) | India | Case-control | 417 | 36.7 | 33.8 | ELISA | MS | Adjusted | 7 |
| Gavalas 2015 (60) | Greece | Case-control | 64 | 36.7 | 28.1 | Biopsy | MS | Crude | 5 |
| Bu 2015 (61) | China | Case-control | 272 | 67.5 | 52.6 | ELISA | PD | Adjusted | 7 |
| Tsolaki 2015 (62) | Greece | Case-control | 156 | 62.1 | 44.2 | Biopsy | PD, AD | Crude | 5 |
| Bu 2015 (63) | China | Case-control | 263 | 69.5 | 49.8 | ELISA | AD | Adjusted | 7 |
| Deretzi 2016 (64) | Greece | Case-control | 68 | 29.7 | 22.9 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Efthymiou 2017 (65) | Greece | Case-control | 267 | 50.7 | 36.0 | ELISA | MS, PD, AD | Crude | 5 |
| Fani 2018 (66) | Netherlands | Cohort | 4,215 | 68.4 | 45.7 | ELISA | All-cause dementia, AD | Adjusted | 8 |
| Huang 2018 (67) | China | Cohort | 18,210 | 50.9 | 53.3 | ICD-9 | PD | Adjusted | 7 |
| Ranjbar 2019 (68) | Iran | Case-control | 806 | 31.0 | 48.2 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Kiani 2021 (69) | Iran | Case-control | 183 | 35.8 | 16.8 | ELISA | MS | Crude | 6 |
| Zilli 2021 (70) | USA | Cohort | 6,468 | 66.5 | 44.3 | ELISA | All-cause dementia | Adjusted | 8 |
| Fu 2023 (71) | UK | Cohort | 8,144 | 56.5 | 43.7 | ICD-9 | All-cause dementia, AD | Crude | 8 |
| Wang 2023 (72) | China | Cohort | 268 | 70.9 | 46.6 | 14\u00B0C urea breath test | MCI | Adjusted | 7 |
| Davis 2024 (73) | Australia | Cohort | 1,115 | 64.0 | 48.0 | ELISA | All-cause dementia | Adjusted | 7 |
| Hernandez-Ruiz 2024 (74) | France | Cohort | 689 | 75.8 | 62.0 | ELISA | All-cause dementia | Adjusted | 7 |
| Shi 2024 (75) | Singapore | Cohort | 475 | 67.6 | 41.3 | ELISA | All-cause dementia | Adjusted | 8 |
The baseline characteristics of included studies and involved participants.
Parkinson’s disease
A total of 10 studies evaluated the association between H. pylori infection and the risk of PD. The meta-analysis indicated that H. pylori infection was associated with an increased risk of PD (OR: 1.70; 95% CI: 1.36–2.13; p < 0.001; Figure 2), with low heterogeneity observed among the studies (I2 = 35.3%; p = 0.126). Sensitivity analysis demonstrated that the pooled conclusion was robust and remained unchanged when any single study was sequentially removed (Supplementary Figure S1). Subgroup analyses showed that H. pylori infection was associated with an increased risk of PD in most subsets. However, no significant association was observed in studies reporting crude data or those with low quality (Table 2). Meta-regression analyses found the mean age (p = 0.660) and male proportion (p = 0.592) were not significant factors contributing to the association between H. pylori infection and PD (Supplementary Figures S2, S3). There was no significant publication bias concerning the association between H. pylori infection and the risk of PD (Egger’s test: p = 0.272; Begg’s test: p = 0.474; Supplementary Figure S4).
Figure 2

Association between Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection and the risk of Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Table 2
| Outcome | Factors | Subgroups | No of studies | OR and 95%CI | p value | I2 (%) | Q statistic | Interaction test |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PD | Country | Eastern | 2 | 2.04 (1.45–2.88) | < 0.001 | 0.0 | 0.482 | 0.119 |
| Western | 8 | 1.61 (1.22–2.12) | 0.001 | 36.3 | 0.139 | |||
| Study design | Case-control | 8 | 1.59 (1.23–2.05) | < 0.001 | 34.6 | 0.152 | 0.077 | |
| Cohort | 2 | 2.21 (1.50–3.26) | < 0.001 | 0.0 | 0.788 | |||
| Hp detection | ELISA | 7 | 1.70 (1.20–2.39) | 0.003 | 42.2 | 0.109 | 0.706 | |
| Other | 3 | 1.73 (1.22–2.46) | 0.002 | 40.8 | 0.185 | |||
| Outcome | Adjusted | 5 | 1.78 (1.40–2.27) | < 0.001 | 29.0 | 0.228 | 0.523 | |
| Crude | 5 | 1.50 (0.90–2.51) | 0.120 | 49.1 | 0.097 | |||
| Study quality | High | 5 | 1.59 (1.35–1.86) | < 0.001 | 2.6 | 0.392 | 0.685 | |
| Low | 5 | 1.83 (0.94–3.58) | 0.076 | 58.5 | 0.047 | |||
| All-cause dementia | Country | Eastern | 3 | 1.95 (1.29–2.95) | 0.002 | 55.2 | 0.107 | 0.002 |
| Western | 9 | 1.45 (1.11–1.89) | 0.007 | 76.2 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study design | Case–control | 3 | 3.97 (0.81–19.49) | 0.090 | 90.0 | < 0.001 | 0.034 | |
| Cohort | 9 | 1.37 (1.14–1.65) | 0.001 | 65.0 | 0.004 | |||
| Hp detection | ELISA | 9 | 1.60 (1.18–2.17) | 0.002 | 79.2 | < 0.001 | 0.039 | |
| Other | 3 | 1.54 (1.11–2.13) | 0.009 | 55.8 | 0.104 | |||
| Outcome | Adjusted | 9 | 1.37 (1.13–1.66) | 0.001 | 65.7 | 0.003 | 0.068 | |
| Crude | 3 | 4.10 (0.88–19.08) | 0.072 | 90.3 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study quality | High | 9 | 1.37 (1.14–1.65) | 0.001 | 65.0 | 0.004 | 0.034 | |
| Low | 3 | 3.97 (0.81–19.49) | 0.090 | 90.0 | < 0.001 | |||
| AD | Country | Eastern | 3 | 1.01 (0.69–1.49) | 0.941 | 19.9 | 0.287 | 0.305 |
| Western | 6 | 1.83 (1.09–3.08) | 0.023 | 77.5 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study design | Case-control | 5 | 1.70 (0.92–3.14) | 0.090 | 68.6 | 0.013 | 0.265 | |
| Cohort | 4 | 1.27 (0.79–2.06) | 0.326 | 74.5 | 0.008 | |||
| Hp detection | ELISA | 6 | 1.54 (0.98–2.44) | 0.064 | 75.8 | 0.001 | 0.914 | |
| Other | 3 | 1.25 (0.64–2.46) | 0.509 | 61.0 | 0.077 | |||
| Outcome | Adjusted | 5 | 1.22 (0.83–1.80) | 0.303 | 68.6 | 0.013 | 0.078 | |
| Crude | 4 | 2.04 (0.92–4.52) | 0.077 | 69.7 | 0.019 | |||
| Study quality | High | 6 | 1.22 (0.89–1.68) | 0.209 | 61.0 | 0.025 | 0.018 | |
| Low | 3 | 2.63 (0.84–8.18) | 0.096 | 72.6 | 0.026 | |||
| MS | Country | Eastern | 11 | 0.69 (0.50–0.96) | 0.027 | 75.4 | < 0.001 | 0.421 |
| Western | 6 | 1.30 (0.56–3.04) | 0.545 | 86.8 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study design | Case–control | 17 | 0.81 (0.59–1.11) | 0.193 | 79.8 | < 0.001 | – | |
| Cohort | 0 | – | – | – | – | |||
| Hp detection | ELISA | 12 | 0.64 (0.46–0.89) | 0.008 | 78.5 | < 0.001 | < 0.001 | |
| Other | 5 | 1.53 (0.89–2.61) | 0.124 | 48.2 | 0.102 | |||
| Outcome | Adjusted | 2 | 0.77 (0.14–4.20) | 0.759 | 88.5 | 0.003 | 0.278 | |
| Crude | 15 | 0.83 (0.59–1.15) | 0.258 | 79.8 | < 0.001 | |||
| Study quality | High | 2 | 0.77 (0.14–4.20) | 0.759 | 88.5 | 0.003 | 0.278 | |
| Low | 15 | 0.83 (0.59–1.15) | 0.258 | 79.8 | < 0.001 |
Subgroup analyses for neurodegenerative disorders.
All-cause dementia
Twelve studies examined the association between H. pylori infection and the risk of all-cause dementia. The results indicated that H. pylori infection was associated with an increased risk of all-cause dementia (OR: 1.56; 95% CI: 1.24–1.96; p < 0.001; Figure 3), with significant heterogeneity detected among the included studies (I2 = 76.8%; p < 0.001). Sensitivity analysis confirmed that the pooled conclusion was stable and was not altered by the exclusion of any particular study (Supplementary Figure S5). While the significant association persisted in most subgroup analyses, no association was observed when pooling case–control studies, studies reporting crude data, or studies with low quality (Table 2). Meta-regression analyses found the mean age (p = 0.954) and male proportion (p = 0.474) were not significant factors contributing to the association between H. pylori infection and all-cause dementia (Supplementary Figures S6, S7). Significant publication bias was detected for the association between H. pylori infection and the risk of all-cause dementia (Egger’s test: p = 0.009; Begg’s test: p = 0.007; Supplementary Figure S8). However, after adjusting for potential publication bias, the conclusion remained stable.
Figure 3

Association between H. pylori infection and the risk of dementia.
Alzheimer’s disease
Nine studies explored the association between H. pylori infection and the risk of AD. The pooled results showed that H. pylori infection was associated with an increased risk of AD (OR: 1.43; 95% CI: 1.01–2.02; p = 0.045; Figure 4), with significant heterogeneity across studies (I2 = 68.9%; p = 0.001). Sensitivity analysis suggested that the pooled conclusion was not stable due to the marginal confidence interval (Supplementary Figure S9). Subgroup analysis revealed that H. pylori infection was significantly associated with an increased risk of AD in studies conducted in Western countries (Table 2). Meta-regression analyses found the mean age (p = 0.687) and male proportion (p = 0.799) were not significant factors contributing to the association between H. pylori infection and AD (Supplementary Figures S10, S11). No significant publication bias was detected regarding this association (Egger’s test: p = 0.167; Begg’s test: p = 0.076; Supplementary Figure S12).
Figure 4

Association between H. pylori infection and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Multiple sclerosis
Seventeen studies investigated the association between H. pylori infection and the risk of MS. The meta-analysis found no significant association between H. pylori infection and the risk of MS (OR: 0.81; 95% CI: 0.59–1.11; p = 0.193; Figure 5), with significant heterogeneity among studies (I2 = 79.8%; p < 0.001). However, sensitivity analysis, which involved sequentially removing individual studies, revealed a potential inverse association. Specifically, when certain studies were excluded, the pooled odds ratio suggested that H. pylori infection might be associated with a lower risk of MS (Supplementary Figure S13), leading to the hypothesis of a possible “protective role” of H. pylori against MS. Subgroup analyses indicated that H. pylori infection was associated with a reduced risk of MS in studies conducted in Eastern countries and in studies that used ELISA to detect H. pylori infection (Table 2). Meta-regression analyses found the mean age (p = 0.715) and male proportion (p = 0.586) were not significant factors contributing to the association between H. pylori infection and MS (Supplementary Figures S14, S15). Significant publication bias was detected for the association between H. pylori infection and MS risk (Egger’s test: p = 0.001; Begg’s test: p = 0.003; Supplementary Figure S16). However, after adjusting for potential publication bias, the overall conclusion remained unchanged.
Figure 5
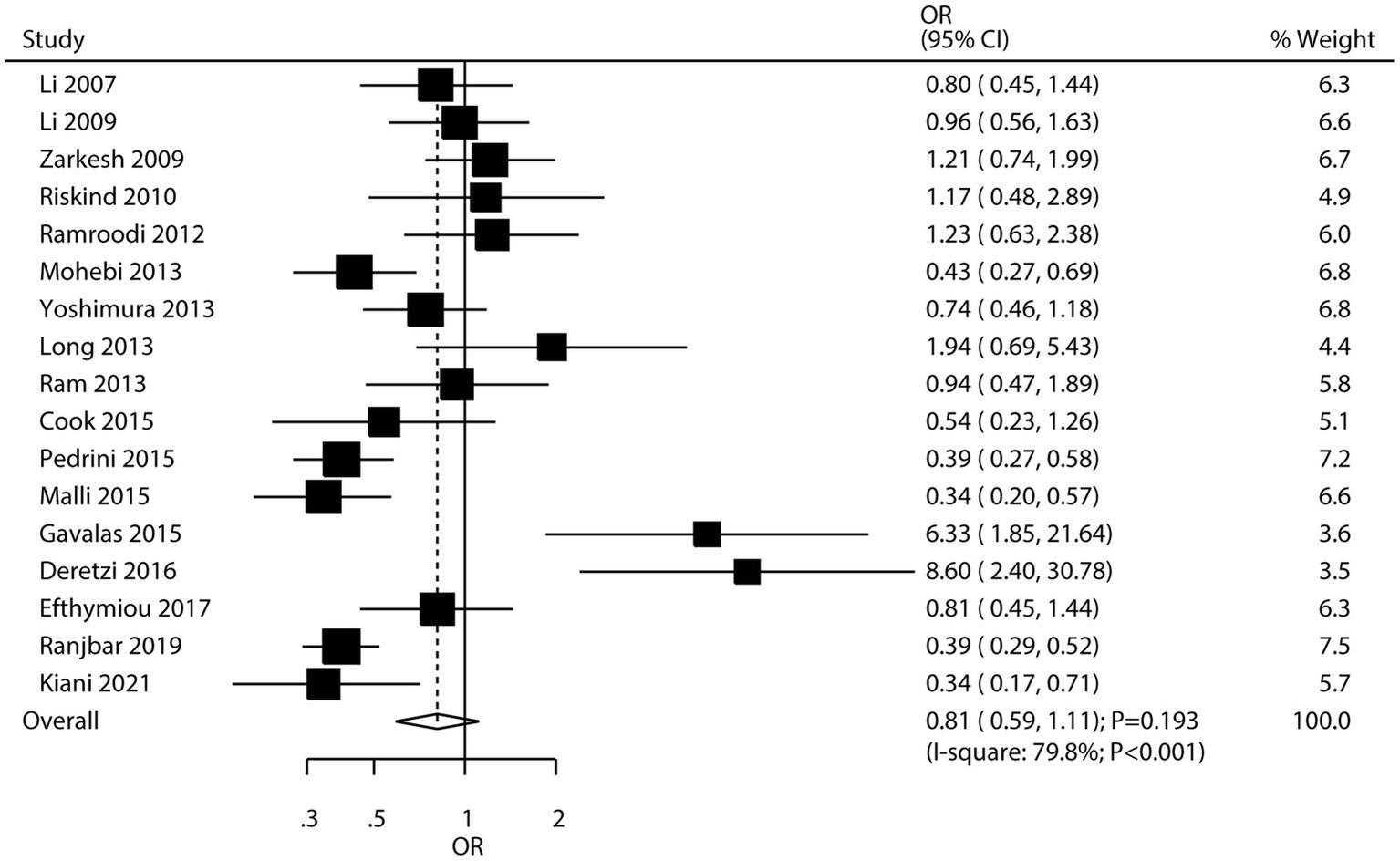
Association between H. pylori infection and the risk of multiple sclerosis (MS).
Discussion
This study, based on epidemiological research, comprehensively explores the possible associations between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases. This large-scale quantitative analysis includes 159,220 individuals from 11 cohort studies and 30 case–control studies, providing broad population representation. The results indicate a significant association between H. pylori infection and an increased risk of PD, all-cause dementia, and AD. However, the association between H. pylori infection and MS was not statistically significant. Sensitivity analysis, however, suggested a significant association between H. pylori infection and a lower risk of MS. Further subgroup analyses offered detailed insights into the risk of H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases across specific populations.
Recent research has emphasized the significance of specific H. pylori virulence factors in its association with neurodegenerative diseases. The cytotoxin-associated gene A (CagA) is one of the most well-studied virulence factors. CagA-positive H. pylori strains have been shown to induce a more robust inflammatory response compared to CagA-negative strains (76). Once injected into host cells, CagA can disrupt cellular signaling pathways, leading to the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and the recruitment of immune cells (77). In the context of AD, CagA may contribute to tau pathology. A recent study demonstrated that CagA can interact with tau proteins, promoting their phosphorylation and aggregation, which are key pathological hallmarks of AD (78). For PD, the chronic inflammation triggered by CagA-positive H. pylori strains may exacerbate the oxidative stress and neuroinflammation associated with the disease, accelerating the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons (79). Microbiota dysbiosis, influenced by H. pylori infection, is another critical aspect that has gained increasing attention. H. pylori colonization of the gastric mucosa can lead to significant alterations in the gut microbiota composition. These changes can disrupt the normal balance of commensal bacteria, affecting the production of short-chain fatty acids and other metabolites with immunomodulatory and neuroprotective properties (80). Moreover, the dysbiotic microbiota may interact with the immune system in ways that promote the development of neurodegenerative diseases, potentially through the activation of pro-inflammatory pathways and the disruption of immune tolerance (81). Molecular mimicry is an emerging mechanism by which H. pylori may contribute to neurodegenerative diseases, particularly in the case of MS. The surface proteins of H. pylori may share sequence or structural similarities with proteins in the central nervous system, leading to an autoimmune response. When the immune system recognizes H. pylori antigens, it may also mistakenly target self-proteins in the brain, triggering the autoimmune attack characteristic of MS (69). In addition, H. pylori-induced vitamin B12 malabsorption is an important factor in the context of neurodegenerative diseases. H. pylori infection can cause atrophic gastritis, which reduces the production of intrinsic factor, essential for vitamin B12 absorption (82). Vitamin B12 deficiency has been linked to cognitive impairment, demyelination, and axonal damage, all of which are relevant to the development of PD and AD (83). Addressing H. pylori-related vitamin B12 malabsorption could potentially be a target for intervention strategies in these neurodegenerative diseases. Finally, the potential role of H. pylori eradication in modulating neurodegenerative risk is an area of growing interest (84).
This study identified a significant association between H. pylori infection and a higher risk of PD, aligning with previous research findings (85). However, our study with a larger sample size and more diverse study populations provides stronger evidence for this association. This may be attributed to our more comprehensive literature search that included studies from both Eastern and Western countries, capturing a broader range of environmental and genetic factors that could influence the relationship. H. pylori infection can cause chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract, leading to systemic inflammatory responses. This persistent inflammation may impact the brain by activating the immune system and releasing inflammatory mediators, thereby promoting neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration (86). Additionally, H. pylori infection can impair the intestinal barrier, increasing gut permeability and allowing harmful substances and bacterial products to enter the bloodstream. This process triggers systemic inflammation and oxidative stress, which can adversely affect the brain and elevate the risk of PD (87). Moreover, H. pylori infection can disrupt the gut microbiota balance, impairing the gut-brain axis and negatively impacting neurological health (88). Finally, the observed increased risk of PD associated with H. pylori infection may be correlated with the duration of infection. It is possible that the longer the body is exposed to H. pylori-induced inflammation, the greater the damage to the nervous system (89). Additionally, although we did not consider the severity of H. pylori infection in our analysis, it is reasonable to hypothesize that a more severe infection may lead to a higher risk. This could be due to a more intense systemic inflammatory response, which may cause greater oxidative stress and damage to neurons in the brain.
We also found a significant association between H. pylori infection and a higher incidence of all-cause dementia, consistent with previous meta-analyses, although the effect size observed in this study was somewhat smaller (21). This difference may be due to variations in study designs, inclusion criteria, and the quality of the original studies included in each meta-analysis. Our study, by including a more recent and extensive range of studies, provides an updated perspective on this association. Additionally, we will discuss how our subgroup analyses based on different factors contribute to a more nuanced understanding compared to previous work. H. pylori infection can disrupt the gut microbiota, leading to the production of harmful metabolites. These metabolites may cross the blood–brain barrier and trigger neuroinflammatory processes (86). We hypothesize that certain bacterial metabolites produced as a result of H. pylori-induced gut microbiota dysbiosis may interact with amyloid-beta and tau proteins in the brain, accelerating the formation of plaques and tangles characteristic of AD. In the case of dementia, the systemic inflammation caused by H. pylori may also lead to cognitive decline by affecting neurotransmitter systems and neuronal plasticity. However, findings regarding the relationship between H. pylori infection and AD remain somewhat inconsistent. This inconsistency may be due to several factors: (1) the specific impact of H. pylori on AD could be influenced by uncontrolled variables, and differences in these variables across studies may lead to varying conclusions; and (2) variations in participant inclusion criteria and the incorporation of more recent literature could contribute to the discrepancies between our findings and those of previous studies (88). Finally, since all-cause dementia encompasses a wide range of etiologies, the association we observed may reflect the cumulative impact of H. pylori infection on various neurodegenerative and vascular processes that contribute to cognitive decline. This highlights the potential importance of considering H. pylori infection as a risk factor across different subtypes of dementia, and further research is needed to explore its specific role in individual dementia etiologies.
The statistically significant ORs for PD and all-cause dementia indicate a notable association between H. pylori infection and these neurodegenerative disorders. These findings may prompt clinicians to consider H. pylori screening and treatment in patients at risk of PD or all-cause dementia, especially in regions with a high prevalence of H. pylori infection. However, it is important to note that while these associations are significant, they should be considered alongside other well-established risk factors for PD and all-cause dementia, such as age, genetic predisposition, and lifestyle factors. From a public health perspective, targeting H. pylori infection could potentially be an additional strategy for reducing the incidence of PD and all-cause dementia. Future studies are needed to explore the cost-effectiveness of such an approach and to determine the optimal timing and method of H. pylori intervention to maximize the potential benefits in preventing these debilitating neurodegenerative diseases.
This study found no statistically significant association between H. pylori infection and the risk of MS, consistent with previous research (90). However, the sensitivity analysis presented an intriguing finding. By sequentially removing individual studies, we observed a potential inverse association, which led us to propose a possible “protective role” of H. pylori against MS. This hypothesis can be partly explained by the “hygiene hypothesis.” According to this theory, early exposure to microorganisms like H. pylori may contribute to the maturation and balance of the immune system (91). In the context of MS, an autoimmune disease characterized by the immune system’s attack on the central nervous system, H. pylori infection might help regulate the immune response. For instance, it could activate regulatory T cells, reducing the overactive immune response that is characteristic of MS. Additionally, H. pylori-induced alterations in the gut microbiota may influence immune function in a way that decreases the likelihood of MS development. However, it is crucial to note that this “protective role” is based on sensitivity analysis results and remains speculative until further research can confirm the association.
Further exploratory analysis suggests that the association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases may be influenced by factors such as country, study design, detection techniques, and study quality. Differences in environmental conditions, lifestyles, and healthcare systems across countries could lead to variations in the prevalence of H. pylori infection and its health impacts. Variations in study designs reflect challenges in establishing causal relationships and increase the potential for bias. Additionally, differences in detection methods for H. pylori infection affect diagnostic accuracy and contribute to inconsistencies in results. As demonstrated by the subgroup analyses, these methodological differences can have a substantial impact on the observed associations between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases. The inconsistent accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of different detection methods, along with potential variations in how they are implemented across studies, can lead to misclassification of H. pylori infection status. This misclassification can either mask true associations or create spurious ones, as seen in the subgroup analysis for MS where the use of ELISA in Eastern studies suggested a protective effect. These findings highlight the need for more standardized and validated H. pylori detection methods in future research on the relationship between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases. Study quality, including sample size, data collection methods, and statistical analysis rigor, also plays a crucial role in the consistency and reliability of findings. Moreover, the presence of 12 studies with a NOS score of ≤5 in our meta-analysis raises concerns about potential biases. Lower-quality studies often lack rigorous control of confounding factors. In particular, studies that reported crude analyses without adjusting for relevant confounders may have introduced significant bias. In crude analyses from low-quality studies, an apparent association between H. pylori and neurodegenerative diseases may be falsely inflated or deflated due to the confounding effects of these unaccounted variables.
It is crucial to acknowledge that the observational nature of the included studies in our meta-analysis inherently limits our ability to establish causal relationships between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases. Although we have observed significant associations, these findings should be interpreted with caution, as they may be influenced by various factors that cannot be fully controlled in observational research. One potential concern is reverse causation. For instance, neurodegenerative diseases may alter the gut microbiota composition, which could, in turn, influence H. pylori colonization. Changes in gastrointestinal motility, immune function, and the production of antimicrobial peptides associated with neurodegenerative diseases might create an environment more or less conducive to H. pylori survival and growth. This could lead to an apparent association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases, where in fact, the disease state is affecting the presence of the bacteria rather than the other way around. Residual confounding is also a significant consideration. Socioeconomic factors can play a major role in both H. pylori exposure and the development of neurodegenerative diseases. Lower socioeconomic status is often associated with higher rates of H. pylori infection due to factors such as poor sanitation, overcrowding, and limited access to healthcare. At the same time, socioeconomic factors can impact lifestyle choices, diet, and access to medical care, all of which are related to the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Even after adjusting for some known confounders in the included studies, residual confounding from unmeasured or inadequately measured socioeconomic factors may still exist, potentially distorting the true association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases.
Several limitations of this study should be acknowledged. First, as this analysis is based on cohort and case–control studies, establishing causality remains challenging. Reverse causation may be a potential issue, as neurodegenerative diseases could influence H. pylori colonization through alterations in the gut microbiota or other physiological changes. Second, considerable heterogeneity exists among some outcome studies, and sensitivity and subgroup analyses cannot fully account for all heterogeneity. Third, the severity of H. pylori infection was not considered, which may influence the strength of its association with neurodegenerative diseases. Fourth, our study is the inclusion of both adjusted and crude ORs in the primary analysis. While this approach allowed us to utilize a larger body of data, it introduced the potential for bias due to unadjusted confounding in studies reporting crude estimates. However, our subgroup analyses based on adjustment status helped to explore the impact of confounding and provided a more nuanced understanding of the associations. Future studies should aim to standardize the reporting of adjusted estimates to reduce heterogeneity and improve the accuracy of meta-analyses in this area. Fifth, the use of various H. pylori detection methods across studies, with their differing accuracies and potential for misclassification, represents a significant source of variability that may have affected the results of our meta-analysis. Sixth, our subgroup analyses for MS is the lack of cohort studies, the absence of cohort studies in our subgroup analyses means that we were unable to fully explore the association between H. pylori infection and MS from a prospective perspective. This may have influenced the stability and generalizability of our subgroup analysis results. Seventh, missing data for age and sex in some studies, indicated as ‘NA’ in Table 1, may have influenced the interpretation of our results. Although we retained these studies to maximize the sample size and noted the missing information, the lack of complete demographic data could potentially introduce bias, especially when exploring subgroup differences or the impact of confounding factors. Future research should prioritize the collection and reporting of comprehensive demographic data to improve the accuracy and reliability of meta-analyses in this field. Eighth, the impact of H. pylori strain virulence, such as the difference between CagA-positive and CagA-negative strains, and the treatment status of the patients were not considered in our analysis. These factors could potentially influence the association between H. pylori infection and neurodegenerative diseases, and may contribute to the observed heterogeneity in outcomes. However, due to the lack of stratified data on these aspects in the included studies, we were unable to explore their effects. Ninth, reliance on published literature introduces inevitable publication bias due to the inaccessibility of unpublished data. Lastly, this analysis is based on aggregated data from the included studies, limiting the depth of exploratory analyses.
This study found that H. pylori infection is associated with an increased risk of PD, all-cause dementia, and AD. Regarding MS, although the primary analysis showed no significant association, sensitivity analysis suggested a potential inverse association, indicating a possible “protective role” of H. pylori. However, this remains to be confirmed by future research. Further large-scale prospective cohort studies are necessary to validate the relationship between H. pylori infection and the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
JD: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft. WS: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. QW: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. ZA: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by grants from the Fifth Batch of National Traditional Chinese Medicine Clinical Excellent Talent Training Project (Chinese Medicine Education Letter [2022] No. 1).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1573299/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Khandia R Gurjar P Priyanka RV Al-Hussain SA Zaki MEA . Recent advances in stem cell therapy: efficacy, ethics, safety concerns, and future directions focusing on neurodegenerative disorders - a review. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:6367–81. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001609
2.
GBD 2017 Inflammatory Bowel Disease Collaborators . The global, regional, and national burden of inflammatory bowel disease in 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 5:17–30. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30333-4
3.
Prince M Wimo A Guerchet M Ali G Wu Y Prina M . The global impact of dementia: an analysis of prevalence, incidence, cost and trends. Alzheimer’s Disease International (2015). Available online at:https://www.alzint.org/u/WorldAlzheimerReport2015.pdf. [Accessed December 30, 2024].
4.
Orfali R Alwatban AZ Orfali RS Lau L Chea N Alotaibi AM et al . Oxidative stress and ion channels in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Physiol. (2024) 15:1320086. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1320086
5.
Gurjar P Khan AA Alanazi AM Vasil'ev VG Zouganelis G Alexiou A . Molecular dissection of herpes simplex virus type 1 to elucidate molecular mechanisms behind latency and comparison of its codon usage patterns with genes modulated during Alzheimer's disease as a part of host-pathogen interaction. J Alzheimers Dis. (2024) 97:1111–23. doi: 10.3233/JAD-231083
6.
Ricci C . Neurodegenerative disease: from molecular basis to therapy. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:967. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020967
7.
Itzhaki RF . Herpes and Alzheimer's disease: subversion in the central nervous system and how it might be halted. J Alzheimers Dis. (2016) 54:1273–81. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160607
8.
Kountouras J Papaefthymiou A Polyzos SA Liatsos C Tzitiridou-Chatzopoulou M Chatzopoulos D et al . Potential impact of Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome-related non-alcoholic fatty liver disease on cardio-cerebrovascular disease. Metabolism. (2022) 135:155276. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2022.155276
9.
Roubaud-Baudron C Krolak-Salmon P Quadrio I Mégraud F Salles N . Impact of chronic Helicobacter pylori infection on Alzheimer's disease: preliminary results. Neurobiol Aging. (2012) 33:1009.e11–9. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.10.021
10.
Lacy BE Rosemore J . Helicobacter pylori: ulcers and more: the beginning of an era. J Nutr. (2001) 131:2789S–93S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.10.2789S
11.
Szwed P Gąsecka A Zawadka M Eyileten C Postuła M Mazurek T et al . Infections as novel risk factors of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: pathophysiological links and therapeutic implications. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:2539. doi: 10.3390/jcm10122539
12.
Yue L Zhang R Chen S Duan G . Relationship between Helicobacter pylori and incident hypertension as well as blood pressure: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Dig Dis. (2023) 41:124–37. doi: 10.1159/000524078
13.
Doheim MF Altaweel AA Elgendy MG Elshanbary AA Dibas M Ali AAHA et al . Association between Helicobacter Pylori infection and stroke: a meta-analysis of 273,135 patients. J Neurol. (2021) 268:3238–48. doi: 10.1007/s00415-020-09933-x
14.
Davidson GL Cooke AC Johnson CN Quinn JL . The gut microbiome as a driver of individual variation in cognition and functional behaviour. Philos Trans R Soc Lond Ser B Biol Sci. (2018) 373:20170286. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2017.0286
15.
Berrett AN Gale SD Erickson LD Brown BL Hedges DW . Helicobacter pylori moderates the association between 5-MTHF concentration and cognitive function in older adults. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0190475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190475
16.
Kountouras J Gavalas E Zavos C Stergiopoulos C Chatzopoulos D Kapetanakis N et al . Alzheimer's disease and Helicobacter pylori infection: defective immune regulation and apoptosis as proposed common links. Med Hypotheses. (2007) 68:378–88. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2006.06.052
17.
Iwasaki T Maruyama A Inui Y Sakurai T Kawano T . In vitro transcytosis of Helicobacter pylori histidine-rich protein through gastric epithelial-like cells and the blood-brain barrier. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. (2022) 86:321–30. doi: 10.1093/bbb/zbab221
18.
Beydoun MA Beydoun HA Hu YH El-Hajj ZW Georgescu MF Noren Hooten N et al . Helicobacter pylori, persistent infection burden and structural brain imaging markers. Brain Commun. (2024) 6:fcae088. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcae088
19.
Alvarez-Arellano L Maldonado-Bernal C . Helicobacter pylori and neurological diseases: married by the laws of inflammation. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. (2014) 5:400–4. doi: 10.4291/wjgp.v5.i4.400 (Accessed December 30, 2024).
20.
Gorlé N Bauwens E Haesebrouck F Smet A Vandenbroucke RE . Helicobacter and the potential role in neurological disorders: there is more than Helicobacter pylori. Front Immunol. (2021) 11:584165. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.584165
21.
Shindler-Itskovitch T Ravona-Springer R Leibovitz A Muhsen K . A systematic review and Meta-analysis of the association between Helicobacterpylori infection and dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. (2016) 52:1431–42. doi: 10.3233/JAD-160132
22.
Shen X Yang H Wu Y Zhang D Jiang H . Meta-analysis: Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with Parkinson's diseases. Helicobacter. (2017) 22:e12398. doi: 10.1111/hel.12398
23.
Yao G Wang P Luo XD Yu TM Harris RA Zhang XM . Meta-analysis of association between Helicobacter pylori infection and multiple sclerosis. Neurosci Lett. (2016) 620:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2016.03.037
24.
Page MJ McKenzie JE Bossuyt PM Boutron I Hoffmann TC Mulrow CD et al . The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
25.
Wells G Shea B O’Connell D . The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa (ON): Ottawa Hospital Research Institute (2009).
26.
DerSimonian R Laird N . Meta-analysis in clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. (1986) 7:177–88. doi: 10.1016/0197-2456(86)90046-2
27.
Ades AE Lu G Higgins JP . The interpretation of random-effects meta-analysis in decision models. Med Decis Mak. (2005) 25:646–54. doi: 10.1177/0272989X05282643
28.
Deeks JJ Higgins JPT Altman DG . Analyzing data and undertaking meta-analyses In: HigginsJGreenS, editors. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions 5.0.1. The Cochrane collaboration. Oxford, UK: John Wiley & Sons (2008)
29.
Higgins JP Thompson SG Deeks JJ Altman DG . Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
30.
Tobias A . Assessing the influence of a single study in meta-analysis. Stata Tech Bull. (1999) 47:15–7.
31.
Altman DG Bland JM . Interaction revisited: the difference between two estimates. BMJ. (2003) 326:219. doi: 10.1136/bmj.326.7382.219
32.
Thompson SG Higgins JP . How should meta-regression analyses be undertaken and interpreted?Stat Med. (2002) 21:1559–73. doi: 10.1002/sim.1187
33.
Egger M Davey Smith G Schneider M Minder C . Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ. (1997) 315:629–34. doi: 10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
34.
Begg CB Mazumdar M . Operating characteristics of a rank correlation test for publication bias. Biometrics. (1994) 50:1088–101. doi: 10.2307/2533446
35.
Charlett A Dobbs RJ Dobbs SM Weller C Brady P Peterson DW . Parkinsonism: siblings share Helicobacter pylori seropositivity and facets of syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. (1999) 99:26–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1999.tb00654.x
36.
Dobbs RJ Charlett A Dobbs SM Weller C Peterson DW . Parkinsonism: differential age-trend in Helicobacter pylori antibody. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2000) 14:1199–205. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00815.x
37.
Nägga K Rajani R Mårdh E Borch K Mårdh S Marcusson J . Cobalamin, folate, methylmalonic acid, homocysteine, and gastritis markers in dementia. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. (2003) 16:269–75. doi: 10.1159/000072812
38.
Kountouras J Tsolaki M Gavalas E Boziki M Zavos C Karatzoglou P et al . Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and Alzheimer disease. Neurology. (2006) 66:938–40. doi: 10.1212/01.wnl.0000203644.68059.5f
39.
Li W Minohara M Su JJ Matsuoka T Osoegawa M Ishizu T et al . Helicobacter pylori infection is a potential protective factor against conventional multiple sclerosis in the Japanese population. J Neuroimmunol. (2007) 184:227–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2006.12.010
40.
Kountouras J Tsolaki M Boziki M Gavalas E Zavos C Stergiopoulos C et al . Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and mild cognitive impairment. Eur J Neurol. (2007) 14:976–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2007.01827.x
41.
Li W Minohara M Piao H Matsushita T Masaki K Matsuoka T et al . Association of anti-Helicobacter pylori neutrophil-activating protein antibody response with anti-aquaporin-4 autoimmunity in Japanese patients with multiple sclerosis and neuromyelitis optica. Mult Scler. (2009) 15:1411–21. doi: 10.1177/1352458509348961
42.
Charlett A Dobbs RJ Dobbs SM Weller C Ibrahim MA Dew T et al . Blood profile holds clues to role of infection in a premonitory state for idiopathic parkinsonism and of gastrointestinal infection in established disease. Gut Pathog. (2009) 1:20. doi: 10.1186/1757-4749-1-20
43.
Kountouras J Boziki M Gavalas E Zavos C Grigoriadis N Deretzi G et al . Eradication of Helicobacter pylori may be beneficial in the management of Alzheimer's disease. J Neurol. (2009) 256:758–67. doi: 10.1007/s00415-009-5011-z
44.
Zarkesh H . The relationship between multiple sclerosis and Helicobacter pylori infection. Mult Scler. (2009) 15:S87.
45.
Riskind PN . Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori seropositivity (HP+) in American patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler. (2010) 16:1008.
46.
Shiota S Murakami K Yoshiiwa A Yamamoto K Ohno S Kuroda A et al . The relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and Alzheimer's disease in Japan. J Neurol. (2011) 258:1460–3. doi: 10.1007/s00415-011-5957-5
47.
Nielsen HH Qiu J Friis S Wermuth L Ritz B . Treatment for Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of Parkinson's disease in Denmark. Eur J Neurol. (2012) 19:864–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03643.x
48.
Ramroodi N Sanadgol N Ghasemi LV Namroodi S . Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and multiple sclerosis (MS) in south-east of Iran. Acad J Org. (2012) 6:5015–9.
49.
Mohebi N Mamarabadi M Moghaddasi M . Relation of helicobacter pylori infection and multiple sclerosis in Iranian patients. Neurol Int. (2013) 5:31–3. doi: 10.4081/ni.2013.e10
50.
Yoshimura S Isobe N Matsushita T Yonekawa T Masaki K Sato S et al . Distinct genetic and infectious profiles in Japanese neuromyelitis optica patients according to anti-aquaporin 4 antibody status. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2013) 84:29–34. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2012-302925
51.
Long Y Gao C Qiu W Hu X Shu Y Peng F et al . Helicobacter pylori infection in Neuromyelitis Optica and multiple sclerosis. Neuroimmunomodulation. (2013) 20:107–12. doi: 10.1159/000345838
52.
Ram M Barzilai O Shapira Y Anaya JM Tincani A Stojanovich L et al . Helicobacter pylori serology in autoimmune diseases - fact or fiction?Clin Chem Lab Med. (2013) 51:1075–82. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0477
53.
Blaecher C Smet A Flahou B Pasmans F Ducatelle R Taylor D et al . Significantly higher frequency of Helicobacter suis in patients with idiopathic parkinsonism than in control patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2013) 38:1347–53. doi: 10.1111/apt.12520
54.
Roubaud Baudron C Letenneur L Langlais A Buissonnière A Mégraud F Dartigues JF et al . Does Helicobacter pylori infection increase incidence of dementia? The Personnes Agées QUID study. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2013) 61:74–8. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12065
55.
Nafisah WY Najman Achok H Hamizah R Azmin S Remli R Shah SA et al . High prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in Malaysian Parkinson's disease patients. J Park Restless Legs Syndrome. (2013) 2013:63–7.
56.
Huang WS Yang TY Shen WC Lin CL Lin MC Kao CH . Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and dementia. J Clin Neurosci. (2014) 21:1355–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2013.11.018
57.
Cook KW Crooks J Hussain K O'Brien K Braitch M Kareem H et al . Helicobacter pylori infection reduces disease severity in an experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Front Microbiol. (2015) 6:52. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00052
58.
Pedrini MJ Seewann A Bennett KA Wood AJ James I Burton J et al . Helicobacter pylori infection as a protective factor against multiple sclerosis risk in females. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. (2015) 86:603–7. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2014-309495
59.
Malli C Pandit L D'Cunha A Mustafa S . Environmental factors related to multiple sclerosis in Indian population. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0124064. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0124064
60.
Gavalas E Kountouras J Boziki M Zavos C Polyzos SA Vlachaki E et al . Relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection and multiple sclerosis. Ann Gastroenterol. (2015) 28:353–6. PMID:
61.
Bu XL Wang X Xiang Y Shen LL Wang QH Liu YH et al . The association between infectious burden and Parkinson's disease: a case-control study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2015) 21:877–81. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.05.015
62.
Tsolaki F Kountouras J Topouzis F Tsolaki M . Helicobacter pylori infection, dementia and primary open-angle glaucoma: are they connected?BMC Ophthalmol. (2015) 15:24. doi: 10.1186/s12886-015-0006-2
63.
Bu XL Yao XQ Jiao SS Zeng F Liu YH Xiang Y et al . A study on the association between infectious burden and Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Neurol. (2015) 22:1519–25. doi: 10.1111/ene.12477
64.
Deretzi G Gavalas E Boziki M Tsiptsios D Polyzos SA Venizelos I et al . Impact of Helicobacter pylori on multiple sclerosis-related clinically isolated syndrome. Acta Neurol Scand. (2016) 133:268–75. doi: 10.1111/ane.12453
65.
Efthymiou G Dardiotis E Liaskos C Marou E Tsimourtou V Rigopoulou EI et al . Immune responses against Helicobacter pylori-specific antigens differentiate relapsing remitting from secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. Sci Rep. (2017) 7:7929. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07801-9
66.
Fani L Wolters FJ Ikram MK Bruno MJ Hofman A Koudstaal PJ et al . Helicobacter pylori and the risk of dementia: a population-based study. Alzheimers Dement. (2018) 14:1377–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.05.005
67.
Huang HK Wang JH Lei WY Chen CL Chang CY Liou LS . Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with an increased risk of Parkinson's disease: a population-based retrospective cohort study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. (2018) 47:26–31. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2017.11.331
68.
Ranjbar R Karampoor S Jalilian FA . The protective effect of Helicobacter Pylori infection on the susceptibility of multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol. (2019) 337:577069. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.577069
69.
Kiani S Vakilian A Kamiab Z Shamsizadeh A . Correlation of dietary intake and Helicobacter pylori infection with multiple sclerosis, a case-control study in Rafsanjan, Iran, 2017-18. Qatar Med J. (2021) 2020:45. doi: 10.5339/qmj.2020.45
70.
Zilli EM O'Donnell A Salinas J Aparicio HJ Gonzales MM Jacob M et al . Herpes Labialis, Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori, and cytomegalovirus infections and risk of dementia: the Framingham heart study. J Alzheimers Dis. (2021) 82:593–605. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200957
71.
Fu J Wei Q Chen X Lai X Shang H . Analysis of the association between pathogen exposure and the risk of dementia. J Alzheimers Dis. (2024) 100:961–72. doi: 10.3233/JAD-240073
72.
Wang J Yu NW Wang DZ Guo L Yang S Zheng B et al . Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with Long-term cognitive decline in older adults: a two-year follow-up study. J Alzheimers Dis. (2023) 91:1351–8. doi: 10.3233/JAD-221112
73.
Davis TME Bruce DG Schimke K Chubb SAP Davis WA . The inter-relationship between Helicobacter pylori infection, dementia and mortality in type 2 diabetes: the Fremantle diabetes study phase I. J Diabetes Complicat. (2024) 38:108854. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2024.108854
74.
Hernández-Ruiz V Roubaud-Baudron C Von Campe H Retuerto N Mégraud F Helmer C et al . Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and incident risk of dementia: the AMI cohort. J Am Geriatr Soc. (2024) 72:1191–8. doi: 10.1111/jgs.18748
75.
Shi R Yu S Larbi A Pin Ng T Lu Y . Specific and cumulative infection burden and mild cognitive impairment and dementia: a population-based study. Brain Behav Immun. (2024) 121:155–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2024.07.026
76.
Saruç M Goksel G Ozkaya S Guclu F Ozbakkaloglu B Yuceyar H . The effect of CagA status on response to Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in Western Turkey. Braz J Med Biol Res. (2001) 34:1435–9. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2001001100010
77.
Chichirau BE Scheidt T Diechler S Neuper T Horejs-Hoeck J Huber CG et al . Dissecting the Helicobacter pylori-regulated transcriptome of B cells. Pathog Dis. (2020) 78:ftaa049. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftaa049
78.
Gu GJ Lund H Wu D Blokzijl A Classon C von Euler G et al . Role of individual MARK isoforms in phosphorylation of tau at Ser262 in Alzheimer's disease. NeuroMolecular Med. (2013) 15:458–69. doi: 10.1007/s12017-013-8232-3
79.
Tse NY Bocchetta M Todd EG Devenney EM Tu S Caga J et al . Distinct hypothalamic involvement in the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-frontotemporal dementia spectrum. Neuroimage Clin. (2023) 37:103281. doi: 10.1016/j.nicl.2022.103281
80.
Liu T Chai S Li M Chen X Xie Y Zhao Z et al . A nanoparticle-based sonodynamic therapy reduces Helicobacter pylori infection in mouse without disrupting gut microbiota. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:844. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-45156-8
81.
Sansores-España LD Melgar-Rodríguez S Olivares-Sagredo K Cafferata EA Martínez-Aguilar VM Vernal R et al . Oral-gut-brain Axis in experimental models of periodontitis: associating gut Dysbiosis with neurodegenerative diseases. Front Aging. (2021) 2:781582. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2021.781582
82.
NICE Guideline . Evidence review for monitoring for gastric cancer in people with vitamin B12 deficiency due to autoimmune gastritis: Vitamin B12 deficiency in over 16s: diagnosis and management: Evidence review G. London: National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) (2024).
83.
Agarwal R . Vitamin B₁₂ deficiency & cognitive impairment in elderly population. Indian J Med Res. (2011) 134:410–2. PMID:
84.
Kang DW Lee JW Park MY Kim SH Um YH Wang SM et al . Impact of Helicobacter pylori eradication on age-specific risk of incident dementia in patients with peptic ulcer disease: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Geroscience. (2025) 47:1161–74. doi: 10.1007/s11357-024-01284-z
85.
Fu P Gao M Yung KKL . Association of Intestinal Disorders with Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. ACS Chem Neurosci. (2020) 11:395–405. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.9b00607
86.
Kountouras J Boziki M Kazakos E Theotokis P Kesidou E Nella M et al . Impact of Helicobacter pylori and metabolic syndrome on mast cell activation-related pathophysiology and neurodegeneration. Neurochem Int. (2024) 175:105724. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105724
87.
Kountouras J Doulberis M Papaefthymiou A Polyzos SA Zavos C Kazakos E et al . Controlling the impact of Helicobacter pylori-related Hyperhomocysteinemia on neurodegeneration. Medicina (Kaunas). (2023) 59:504. doi: 10.3390/medicina59030504
88.
Tohumcu E Kaitsas F Bricca L Ruggeri A Gasbarrini A Cammarota G et al . Helicobacter pylori and the human gastrointestinal microbiota: a multifaceted relationship. Antibiotics (Basel). (2024) 13:584. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13070584
89.
Dardiotis E Tsouris Z Mentis AA Siokas V Michalopoulou A Sokratous M et al . H. Pylori and Parkinson's disease: Meta-analyses including clinical severity. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. (2018) 175:16–24. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.09.039
90.
Thapa S Bhattarai A Shah S Timsina S Chand S Jakimovski D . Helicobacter pylori infection and risk of multiple sclerosis: an updated meta-analysis. Neurol Sci. (2024) 45:2539–48. doi: 10.1007/s10072-024-07328-8
91.
Kira JI Isobe N . Helicobacter pylori infection and demyelinating disease of the central nervous system. J Neuroimmunol. (2019) 329:14–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2018.06.017
Summary
Keywords
Helicobacter pylori infection, Parkinson’s disease, all-cause dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, multiple sclerosis, meta-analysis
Citation
Du J, Shen W, Zhou Z, Wu Q and Ai Z (2025) Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with the risk of neurodegenerative disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1573299. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1573299
Received
08 February 2025
Accepted
15 June 2025
Published
04 July 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Syamal Roy, Indian Institute of Chemical Biology (CSIR), India
Reviewed by
Parvaneh Esmaeilnejad-Ahranjani, Razi Vaccine and Serum Research Institute, Iran
Surajit Bhattacharjee, Tripura University, India
Oindrilla Mukherjee, National Institute of Technology, Durgapur, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Du, Shen, Zhou, Wu and Ai.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zongyao Ai, aizongyao692712@hotmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.