- 1The Department of Nephrology, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 2College of Integrated Chinese and Western Medicine, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
- 3Research Center for Integrative Medicine, The Affiliated Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Background: Kidney Injury Molecule 1 (KIM-1) is a biomarker of proximal tubular injury that can be used for the early detection of acute kidney injury (AKI). This study was designed to systematically review the relevant literature to assess the role of urinary KIM-1 (uKIM-1) and blood KIM-1 (bKIM-1) in diagnosing adult AKI.
Methods: We searched PubMed, Embase, Cochrane, web of science for literature published until 7 August 2024, using the Quality Assessment Tool for Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2). Sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve (AUC) values from the included studies were combined using stata 18.
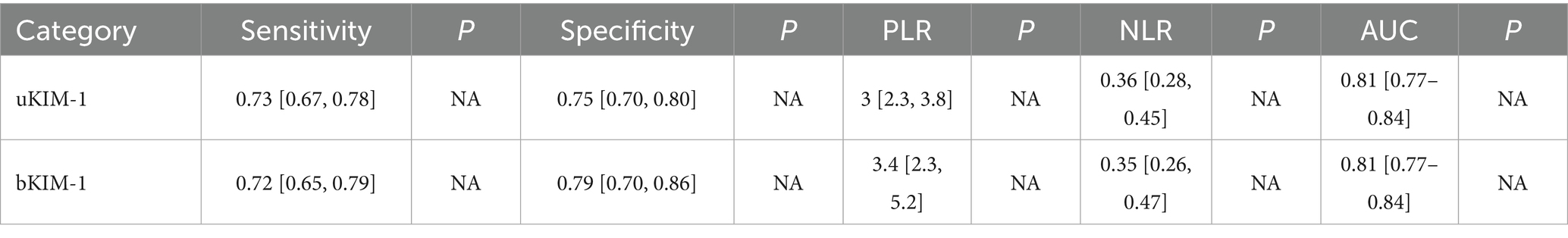
Results: In total, 41 studies involving 1,790 patients were included. The estimated sensitivity of uKIM-1 for diagnosing adult AKI was 0.73 (95% CrI, 0.67–0.78), the specificity was 0.75 (95% CrI, 0.70–0.80), and the AUC was 0.81 (95% CrI 0.77–0.84); while the estimated sensitivity of bKIM-1 for diagnosing AKI was 0.72 (95% CrI 0.65–0.79), specificity was 0.79 (95% CrI, 0.70–0.86), and AUC was 0.81 (95% CrI 0.77–0.84).
Conclusion: uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 show potential as biomarkers for predicting AKI in adult patients, demonstrating relatively high sensitivity and specificity. However, the current meta-analysis does not provide sufficient evidence to make definitive conclusions, and further studies and clinical trials are needed to determine the practical utility of uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 in clinical diagnosis.
1 Introduction
Recognized by almost all medical disciplines, acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common and serious condition. It is characterized by a dramatic decline in kidney function over a period of hours to days and is usually reversible (1). Many patients presenting with AKI have a mixed etiology, often consisting of coexisting sepsis and ischemia-reperfusion injury (2). It affects approximately 25% of hospitalized patients, particularly critically ill patients in intensive care units. It is estimated that AKI affects approximately 20–200 people per million population in the community, accounts for 7–18% of hospitalizations, and occurs in approximately 50% of patients in intensive care units (3, 4). And is associated with cardiovascular disease, end-stage renal disease (ESRD), hypertension, and death (5–7). AKI reportedly causes 2 million deaths worldwide each year, and AKI survivors are at increased risk of chronic kidney disease and ESRD, with significant economic, social, and personal burdens (8, 9). The urgent need for more accurate and effective diagnostic tools for AKI has been highlighted by these studies.
Several new AKI biomarkers have been found and characterized in the last few years. Some are thought to have potential to help diagnose AKI, including neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipid transport protein, interleukin-18, kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (10, 11). Among these various new biomarkers, many researchers have demonstrated that KIM-1 is a significant predictive marker for AKI detection.
KIM-1, as a type I transmembrane protein, was originally hypothesized to be an epithelial cell adhesion molecule, containing a novel immunoglobulin structural domain. In the normal state, this structural domain is typically absent, although its levels are observed to be heightened in proximal tubular parietal cells subsequent to renal tubular damage (12, 13). It has been proposed that uKIM-1 is a sensitive and specific marker of renal injury and can be employed as a prognostic predictor, particularly in the context of AKI in adult patients (14). Despite a substantial body of research, the clinical utility of KIM-1 for the early diagnosis of AKI remains to be established in larger, well-designed studies. Existing evidence is constrained by heterogeneity in patient populations and variability in the timing of biomarker measurement relative to the renal insult. Moreover, few studies have examined how different KIM-1 types in adult populations. Accordingly, this study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic performance of urinary and blood KIM-1 (uKIM-1 and bKIM-1) in adults with AKI.
2 Methods
We followed the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (15). under the registration identifier CRD42024580593.
2.1 Search strategy
Two independent researchers (YS and WWC) searched PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, and the Cochrane Library by searching literature searches up to August 2024. The search included keywords such as “Kidney Injury Molecule 1” or “KIM-1” plus “Acute Kidney Injury” or “Acute Kidney Failure.” In addition, a manual review of references to relevant studies was conducted. There were no language restrictions. In the event of disagreement, the problem was resolved through the involvement of a third researcher (XY). Detailed search formulas for each database are provided in Additional file 1.
2.2 Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Studies that met the following criteria were ultimately retrieved:(1) studies were conducted in patients with AKI, age >18 years; (2) articles with a prospective cohort design, case–control design, or cross-sectional design and explored the performance of uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 in the detection of AKI; and (3) studies that included or allowed for calculation of the estimated sensitivities of uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 in the diagnosis of AKI and the specificity studies.
Criteria for exclusion were: (1) no reported diagnostic accuracy measures for any biomarkers; (2) no reported AKI; and (3) conference abstract, PhD dissertation, review article, or other editorial; (4) pediatric studies.
2.3 Study selection
The retrieved literature was imported into Endnote X9 by two authors (YS and WWC). Duplicates were deleted, and the titles and abstracts of all retrieved articles were screened to exclude non-compliant articles. The final compliant literature was identified based on the inclusion criteria by reading the full text. In the event of disagreement, the problem was resolved through the involvement of a third researcher (XY).
2.4 Data extraction and quality assessment
The following information was extracted from each eligible study: first author, country of origin, year of publication, study design, sample size, patient characteristics (age, sex), and the number of patients who developed AKI. Additionally, data regarding KIM-1 were extracted, including the type of biomarker reported, time of measurement, sensitivity, specificity, true-positive, true-negative, false-positive, and false-negative values for each study.
The Quality Assessment Tool for Diagnostic Accuracy Studies (QUADAS-2) (16) This is a quality assessment tool that has been developed with the specific purpose of enabling the systematic evaluation of diagnostic accuracy studies in order to assess the potential for bias in the studies themselves (17), including 14 questions (each categorized as ‘yes’, ‘no’ or unclear).
The data extraction and quality assessment described above were conducted by two authors (YS and WWC) in an independent manner. In the event of a discrepancy, the matter was settled through the involvement of a third researcher (XY).
2.5 Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using STATA version 18.0 (Stata Corp, College Station, TX), notably with the “midas” commands (18). The bivariate mixed-effects model fits a 2-level model, with independent binomial distributions for the true positives and true negatives conditional on the sensitivity and specificity in each study, and a bivariate normal model for the logit transformations of sensitivity and specificity between studies (18). Based on this model, the pooled sensitivity, pooled specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio, and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) with their 95% CrI were obtained. We also constructed hierarchical summary ROC curves to plot sensitivity versus specificity and calculated the AUC (19). The degree of heterogeneity, which indicates the variation of included studies, was assessed using the I2 statistic (20). I2 describes the percentage of total variation across studies that is attributable to heterogeneity rather than to chance. The value of I2 lies between 0 and 100%, a value of 0% indicates no observed heterogeneity, and values greater than 50% may be considered substantial heterogeneity (18). In addition, we conducted a subgroup analysis according to the detection time, sample size, and presence of chronic kidney disease. Publication bias was evaluated using Deek’s effective sample size funnel plot.
3 Result
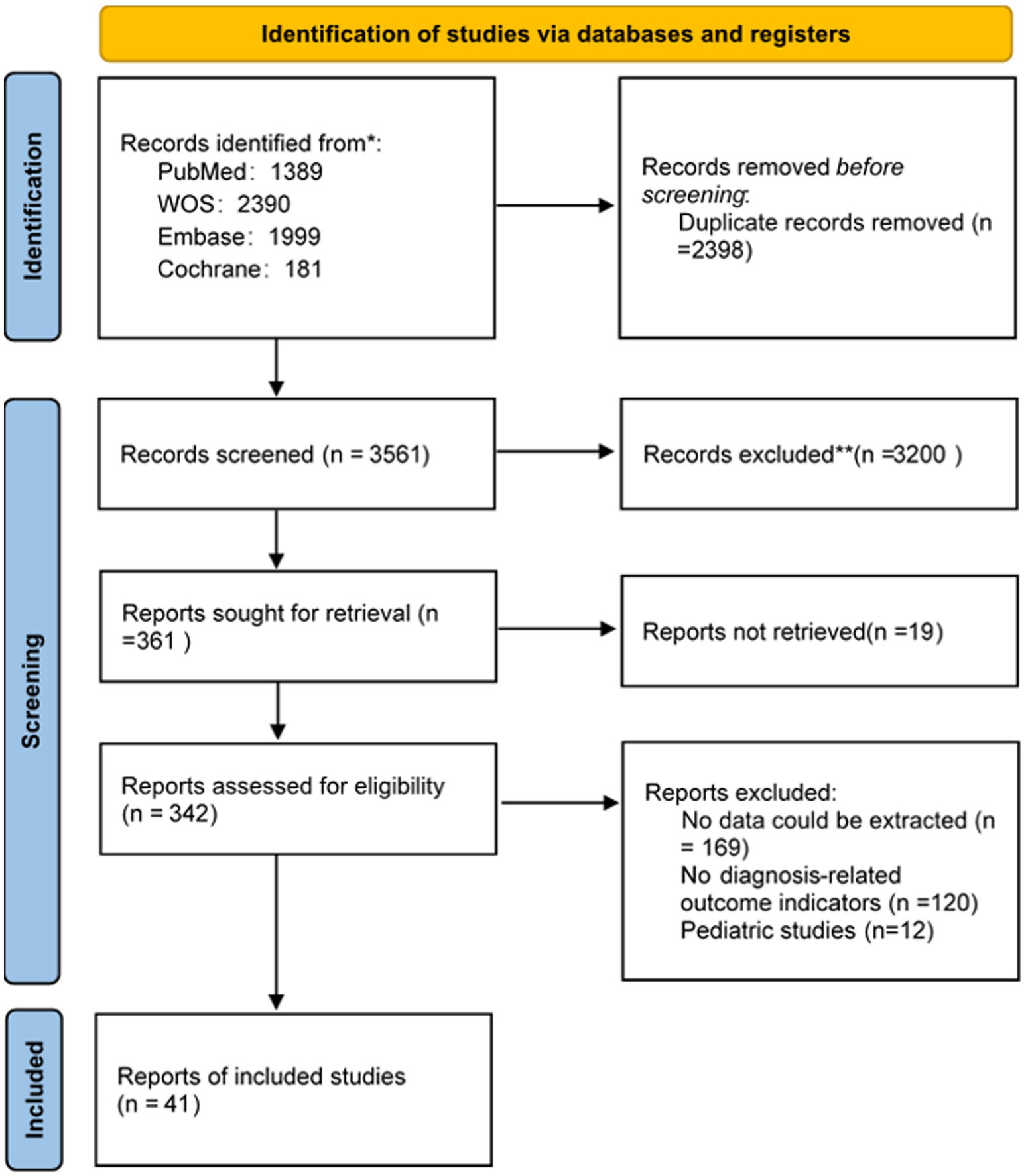
3.1 Selection process
The study selection process is shown in Figure 1. A total of 5,959 publications from different databases were retrieved upon initial search. Of those, 2,398 articles were excluded due to duplication. The remaining studies were screened by title and/or abstract; 3,219 of them were removed because they were reviews, animal research, or conference abstracts. Of the remaining 342 studies (corrected), 301 were excluded due to missing essential data (e.g., sensitivity, specificity, and diagnostic criteria used) and pediatric studies. In summary, 41 original studies (corrected) (21–62) were included in this meta-analysis.
3.2 Study characteristics
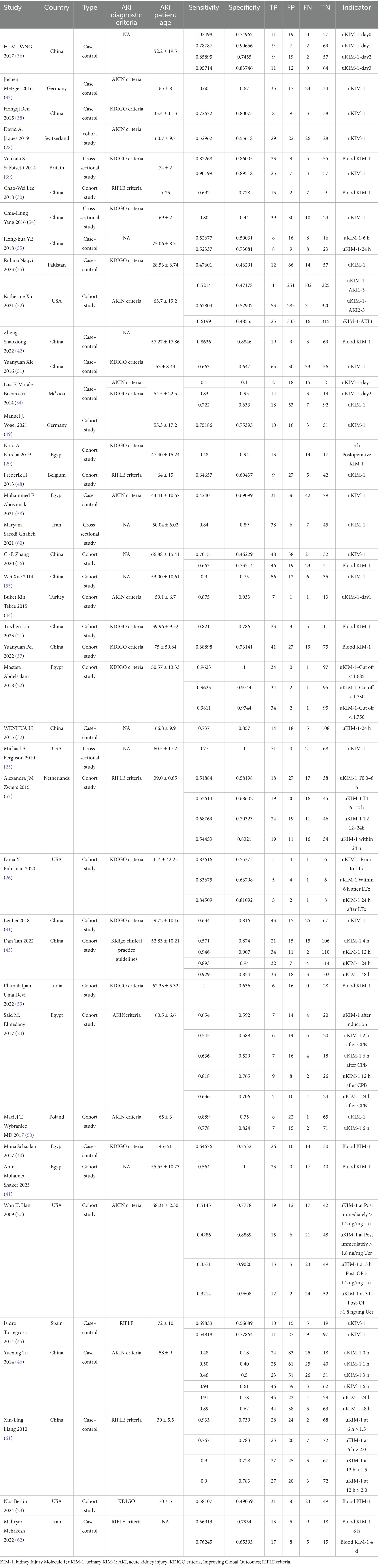
Table 1 summarizes 41 diagnostic studies. Across studies reporting age (n = 38), the study-level, unweighted mean age was 56.9 years, with a median of 58.6 years and an interquartile range (IQR) of 51.0–65.0 years (values outside 0–100 years were excluded as implausible). The median study sample size, estimated from the 2 × 2 data (TP + FP + FN + TN), was 149 patients (IQR 83–225; range 22–2,067).
Regarding design, cohort studies comprised 53.7% (22/41), case–control studies 36.6% (15/41), and cross-sectional studies 9.8% (4/41). AKI diagnostic criteria were most commonly KDIGO (39.0%, 16/41), followed by AKIN (22.0%, 9/41) and RIFLE (14.6%, 6/41); criteria were unreported in 24.4% (10/41). Studies were conducted across 15 countries; the largest contributions came from China (16/41, 39.0%), Egypt (6/41, 14.6%), and the USA (5/41, 12.2%), with additional single- or two-study contributions from Germany, Iran, the Netherlands, Turkey, Switzerland, Belgium, Spain, and others.
Most diagnostic evaluations focused on urinary KIM-1 (uKIM-1) (66 data rows across various time windows), whereas blood/serum KIM-1 (bKIM-1) accounted for 12 evaluations, reflecting a predominance of urinary measurements and multiple predefined sampling time points. Full per-study details, including country, design, AKI criteria, age reporting, and 2 × 2 diagnostic counts, are provided in Table 1.
3.3 Quality assessment
We assessed risk of bias using QUADAS-2 across four domains and evaluated concerns regarding applicability in 41 diagnostic accuracy studies (Figure 2). Domain-level judgments were as follows (n, %):
Patient selection: low 25 (61.0%), high 14 (34.1%), unclear 2 (4.9%).
Index test: low 20 (48.8%), high 8 (19.5%), unclear 13 (31.7%).
Reference standard: low 23 (56.1%), high 0 (0%), unclear 18 (43.9%).
Flow and timing: low 20 (48.8%), high 9 (22.0%), unclear 12 (29.3%).
Concerns regarding applicability (overall): low 25 (61.0%), high 9 (22.0%), unclear 7 (17.1%).
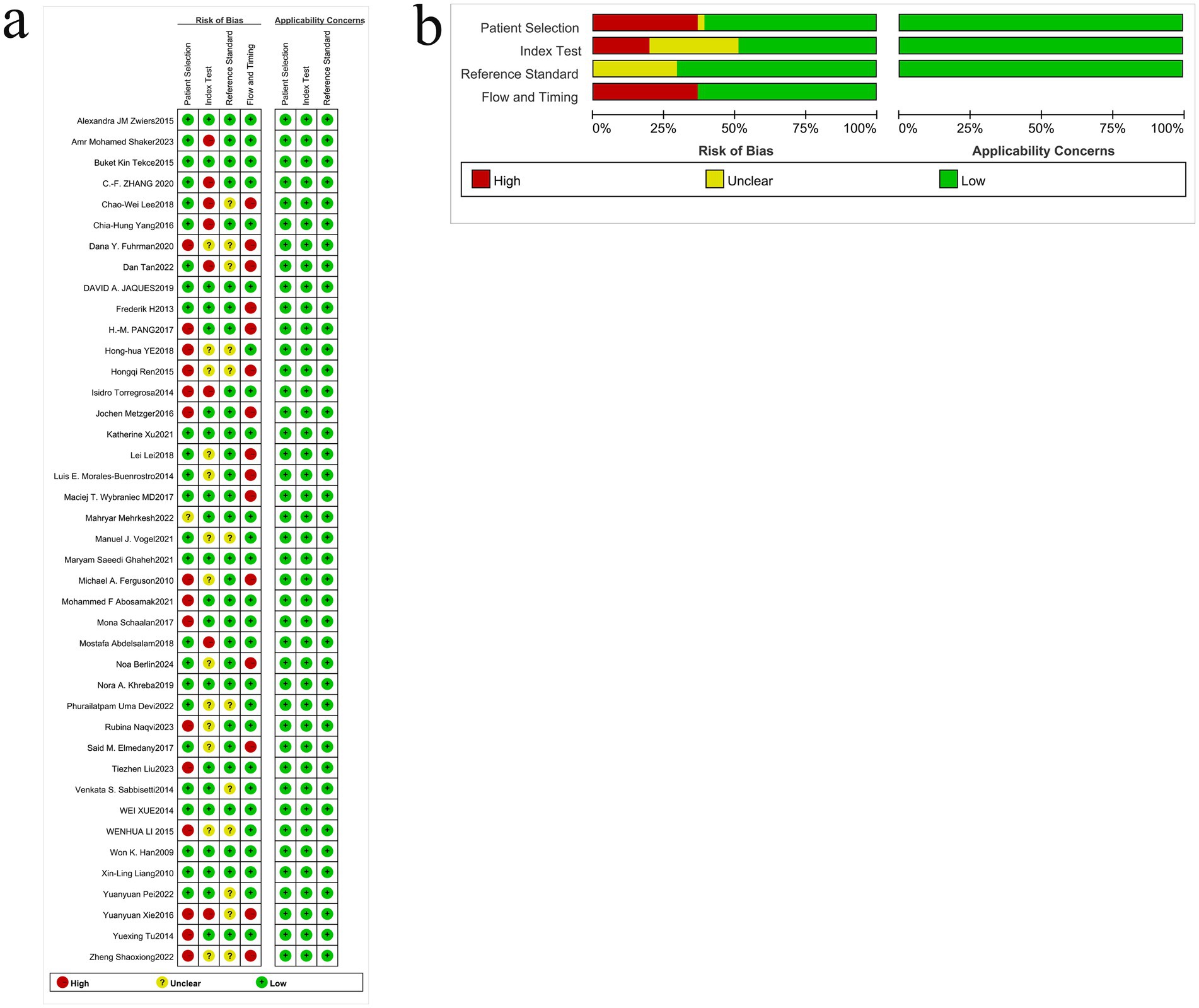
Figure 2. Quality assessment of the included studies. (a) Methodological quality graph. (b) Methodological quality summary.
Common sources of bias included non-consecutive or non-random case inclusion and the use of case–control designs (patient selection), non-blinded interpretation of the index test and post hoc threshold selection (index test), insufficient reporting of blinding or the discriminative capacity of the reference standard (reference standard), and variable/ differential verification, heterogeneous intervals between index and reference tests, or exclusion of participants from the analysis (flow and timing). Applicability concerns mainly reflected mismatches between study populations or testing procedures and routine clinical pathways.
Overall, while over half of the studies were judged at low risk in several domains, the substantial proportions of high or unclear risk—particularly for the index test, reference standard reporting, and flow/timing—underscore the need for future studies with consecutive sampling, prespecified thresholds, blinded interpretation, uniform verification, and complete case inclusion to strengthen internal validity and clinical generalizability.
3.4 Data analysis
3.4.1 uKIM-1
The diagnostic effect of uKIM-1 in patients with AKI was investigated in 32 studies.
The diagnostic effect of uKIM-1 in adult patients with AKI was investigated in 32 of these studies (Figures 3a–c). The results showed that the estimated diagnostic sensitivity of uKIM-1 was 0.73 (95% CrI, 0.67–0.78), the specificity was 0.75 (95% CrI, 0.70–0.80) and the DOR was 8 (95% CrI, 5–13), as shown in Figure 3 and Table 2. The I2 indices were 85.01% (81.96–88.07%) and 94.69% (93.89–95.48%), respectively. The sROC results showed an AUC of 0.81 (95% CrI, 0.77–0.84) for uKIM-1, with substantial heterogeneity in both sensitivity and specificity between studies. The funnel plot showed no significant publication bias (p = 0.1).
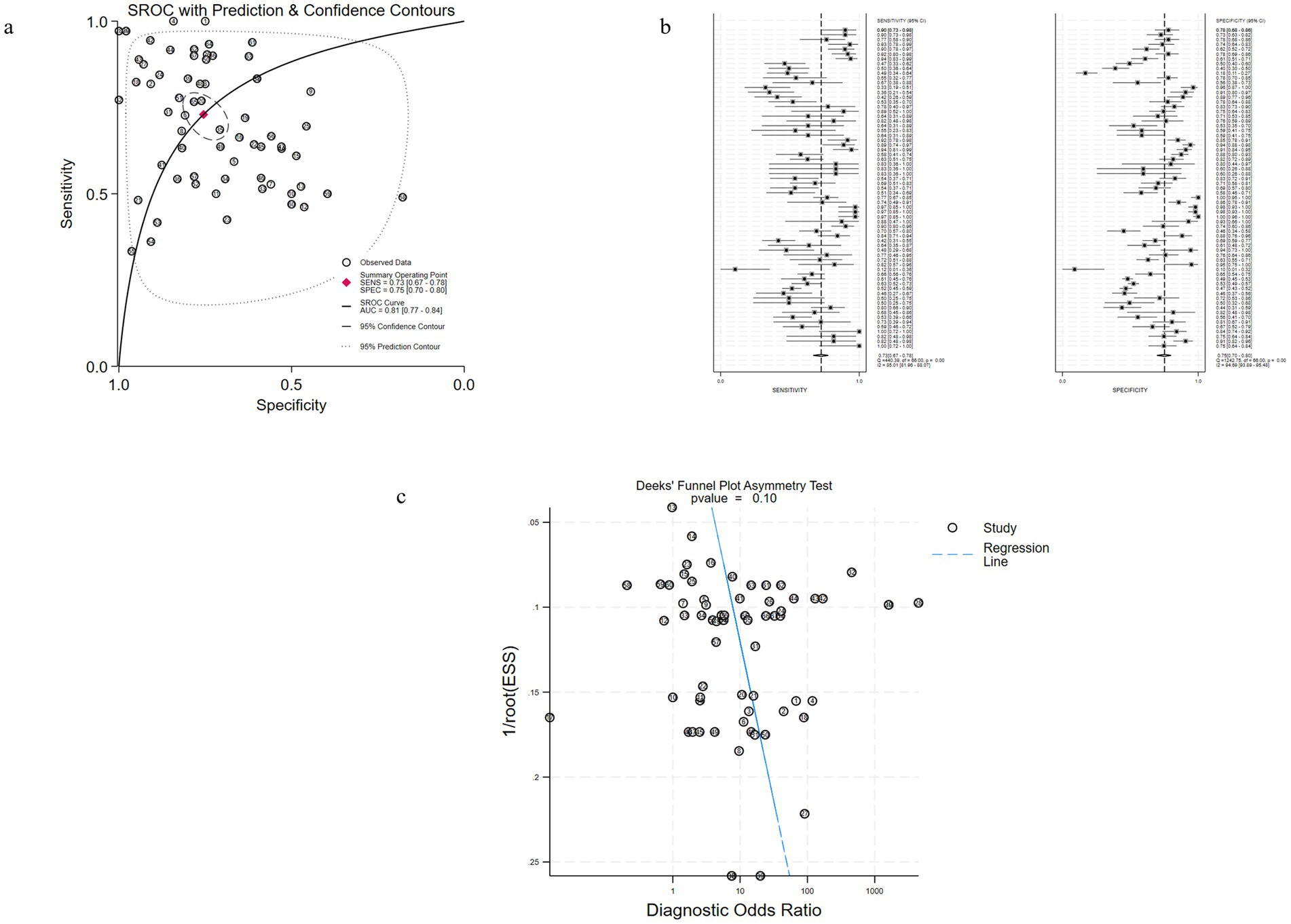
Figure 3. Performance of uKIM-1 for AKI diagnosis in Studies Included in the meta-analysis. (a) SROC plots of uKIM-1 to predict adult AKI. (b) Forest plots of the pooled sensitivity and specificity of uKIM-1 to predict adult AKI. (c) Funnel plot for the evaluation of potential publication bias in diagnosis of uKIM-1 for adult AKI.
The results indicated that the predictive value of uKIM-1 is regarded as the potential biomarker in adult AKI patients.
3.4.2 bKIM-1
Among them, 10 studies involved patients with adult AKI diagnosed by bKIM-1 (Figures 4a–c), and the results showed that the estimated sensitivity of bKIM-1 diagnosis was 0.72 (95% CrI 0.65–0.79) and the specificity was 0.79 (95% CrI, 0.70–0.86). The combined diagnostic ratio (DOR) was 10 (95% CrI, 5–19) and the AUC of bKIM-1 for the diagnosis of AKI was 0.81 (95% CrI 0.70–0.86). The funnel plot showed no significant publication bias (p = 0.20).
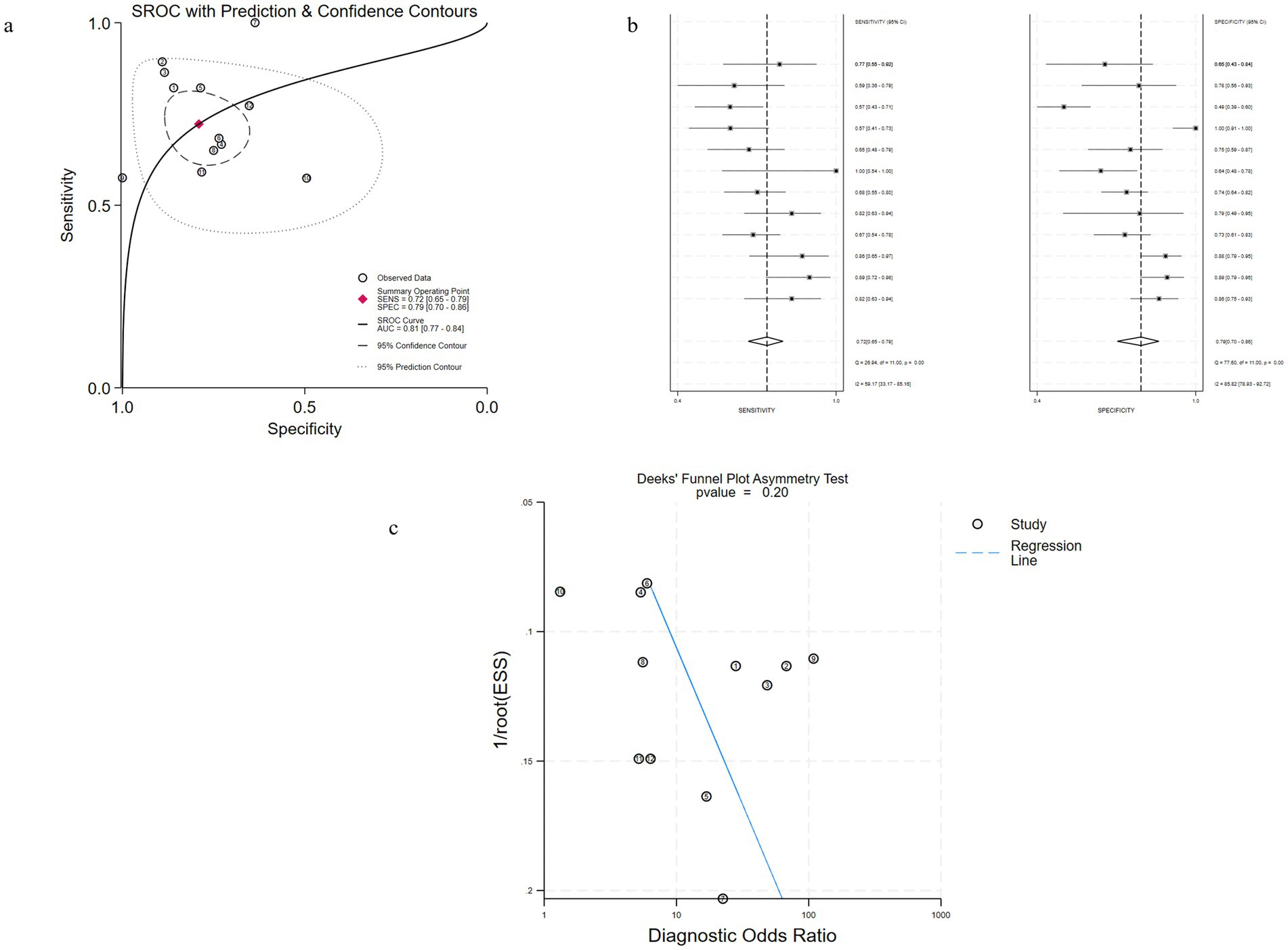
Figure 4. Performance of bKIM-1 for AKI diagnosis in Studies Included in the meta-analysis. (a) Hierarchical summary receiver operating characteristic (SROC) plots of sKIM-1 to predict adult AKI. (b) Forest plots of the pooled sensitivity and specificity of bKIM-1 to predict adult AKI. (c) Funnel plot for the evaluation of potential publication bias in diagnosis of uKIM-1 for adult AKI.
4 Discussion
Early diagnosis of AKI plays an essential role in its treatment and prognosis. Currently, AKI is commonly diagnosed by elevated serum creatinine or decreased urine output. However, Serum creatinine is less useful in AKI since patients are not in a stable condition, causing it to significantly lag behind actual kidney damage (63). It is urgent to find a more effective approach to measuring the diagnosis of AKI. Novel biomarkers have been suggested to have the potential to facilitate early diagnosis of AKI, among which is KIM-1. Previous literature reviews have shown that uKIM-1 levels are linked to the extent of kidney tissue damage and may serve as a dependable predictor of negative renal outcomes in acute tubular injury (64). Additionally, KIM-1 is a sensitive marker for AKI (65). All published studies assessing the diagnostic value of KIM-1 were included in this meta-analysis, and a total of 41 eligible studies were identified and data extracted. In this study, the performance of uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 in predicting AKI was evaluated using sensitivity, specificity, and AUC metrics. The results showed that both uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 were the one of promising predictors. The AUC values of all studies were greater than 0.80, showing a relatively good diagnostic value.
In specific studies, the findings by Geng et al. (14) showed that the AUC of uKIM-1 for diagnosing AKI in adults was 0.62 (95% CrI: 0.41–0.76); the findings by Shao et al. (66) indicated that the AUC of uKIM-1 for diagnosing AKI was 0.86 (95% CrI: 0.83–0.89); and the result from Fazel et al. (67) suggested that the AUC of uKIM-1 for predicting AKI in children was 0.69 (95% CrI: 0.62–0.77). However, in clinical diagnostic studies, bKIM-1 has only been found to have modest results (68). Cai (64) found that uKIM-1 correlates with renal tKIM-1 expression and tubular histologic injury in AKI; in ATI, it may aid prognostication, and combining uKIM-1 with bKIM-1 modestly improves discrimination for severe ATI. The results of our study suggest that uKIM-1 has a better diagnostic value in adults. According to the data of the experimental studies on animals, KIM-1 expression in the epithelial cells of the renal proximal tubules as well as its concentration in urine and blood plasma correlate with the severity of the pathological process in the kidneys (69). Elevation of KIM-1 level in urine (uKIM-1) is a more sensitive indicator of AKI than the reduction of creatinine clearance or albuminuria (70). In addition, it has been suggested that KIM-1 may exert a significant role in renal recovery and tubular regeneration after AKI (71, 72).
The benefits of this study include the first systematic assessment of the diagnostic value of different KIM-1 types in patients with AKI, and a comprehensive analysis of both urine and blood forms of KIM-1 to further clarify the similarities and differences in their diagnostic efficacy. However, there are some limitations to this meta-analysis. Limitations include the limited number of bKIM-1 studies in underage populations, the heterogeneity of sampling windows, and the assay/platform variability and incomplete reporting of normalization (uKIM-1/Cr), which collectively temper the generalizability of pooled estimates. These issues highlight the need for multicenter, platform-harmonized studies with standardized sampling windows and context-specific thresholds across ICU, perioperative, oncology, and pediatric settings.
5 Conclusion
In summary, our study found that uKIM-1 and bKIM-1 are promising predictors of AKI, especially in adult patients, with relatively high sensitivity and specificity. However, further studies and clinical trials are still needed to confirm whether and how KIM-1 is widely used for clinical diagnosis. In the future, we expect KIM-1 or other renal biomarkers to be fully applied in AKI, from clinical detection to treatment and even prevention. Nevertheless, these findings should be interpreted with caution due to heterogeneity in study designs, AKI definitions, sample timing, and assay variability. Further large-scale, high-quality prospective studies are required to validate the clinical utility of KIM-1.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
YS: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. XY: Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft. W-WC: Data curation, Validation, Writing – review & editing. X-MS: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. H-LW: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. H-CS: Funding acquisition, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Sichuan Science and Technology Program (no: 2022YFS0621).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
KIM-1, Kidney Injury Molecule 1; uKIM-1, Urinary KIM-1; QUADAS, Quality Assessment Tool for Diagnostic Accuracy Studies; ESRD, End-stage renal disease; DOR, Diagnostic odds ratio; AKI, Acute kidney injury; bKIM-1, Blood KIM-1; AUC, Area under the curve; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
References
1. Chawla, LS , Bellomo, R , Bihorac, A , Goldstein, SL , Siew, ED , Bagshaw, SM, et al. Acute kidney disease and renal recovery: consensus report of the acute disease quality initiative (ADQI) 16 workgroup. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2017) 13:241–57. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2017.2
2. Andrade, L , Rodrigues, CE , Gomes, SA , and Noronha, IL . Acute kidney injury as a condition of renal senescence. Cell Transplant. (2018) 27:739–53. doi: 10.1177/0963689717743512
3. Lewington, AJ , Cerdá, J , and Mehta, RL . Raising awareness of acute kidney injury: a global perspective of a silent killer. Kidney Int. (2013) 84:457–67. doi: 10.1038/ki.2013.153
4. Hoste, EA , Bagshaw, SM , Bellomo, R , Cely, CM , Colman, R , Cruz, DN, et al. Epidemiology of acute kidney injury in critically ill patients: the multinational AKI-EPI study. Intensive Care Med. (2015) 41:1411–23. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3934-7
5. Ishani, A , Xue, JL , Himmelfarb, J , Eggers, PW , Kimmel, PL , Molitoris, BA, et al. Acute kidney injury increases risk of ESRD among elderly. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 20:223–8. doi: 10.1681/asn.2007080837.;
6. Pechman, KR , De Miguel, C , Lund, H , Leonard, EC , Basile, DP , and Mattson, DL . Recovery from renal ischemia-reperfusion injury is associated with altered renal hemodynamics, blunted pressure natriuresis, and sodium-sensitive hypertension. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. (2009) 297:R1358–63. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.91022.2008
7. James, MT , Ghali, WA , Knudtson, ML , Ravani, P , Tonelli, M , Faris, P, et al. Associations between acute kidney injury and cardiovascular and renal outcomes after coronary angiography. Circulation. (2011) 123:409–16. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.110.970160
8. Tao Li, PK , Burdmann, EA , and Mehta, RL . Acute kidney injury: global health alert. Int J Organ Transplant Med. (2013) 4:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.hkjn.2013.03.001
9. Chawla, LS , Eggers, PW , Star, RA , and Kimmel, PL . Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease as interconnected syndromes. N Engl J Med. (2014) 371:58–66. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1214243
10. Kashani, K , Cheungpasitporn, W , and Ronco, C . Biomarkers of acute kidney injury: the pathway from discovery to clinical adoption. Clin Chem Lab Med. (2017) 55:1074–89. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2016-0973
11. Schrezenmeier, EV , Barasch, J , Budde, K , Westhoff, T , and Schmidt-Ott, KM . Biomarkers in acute kidney injury—pathophysiological basis and clinical performance. Acta Physiol. (2017) 219:554–72. doi: 10.1111/apha.12764.;
12. Han, WK , Bailly, V , Abichandani, R , Thadhani, R , and Bonventre, JV . Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a novel biomarker for human renal proximal tubule injury. Kidney Int. (2002) 62:237–44. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2002.00433.x
13. Waanders, F , van Timmeren, MM , Stegeman, CA , Bakker, SJ , and van Goor, H . Kidney injury molecule-1 in renal disease. J Pathol. (2010) 220:7–16. doi: 10.1002/path.2642
14. Geng, J , Qiu, Y , Qin, Z , and Su, B . The value of kidney injury molecule 1 in predicting acute kidney injury in adult patients: a systematic review and Bayesian meta-analysis. J Transl Med. (2021) 19:105. doi: 10.1186/s12967-021-02776-8
15. Page, MJ , McKenzie, JE , Bossuyt, PM , Boutron, I , Hoffmann, TC , Mulrow, CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
16. Whiting, P , Rutjes, AW , Reitsma, JB , Bossuyt, PM , and Kleijnen, J . The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. (2003) 3:25. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-3-25
17. Whiting, P , Rutjes, AW , Dinnes, J , Reitsma, J , Bossuyt, PM , and Kleijnen, J . Development and validation of methods for assessing the quality of diagnostic accuracy studies. Health Technol Assess. (2004) 8:1–234. doi: 10.3310/hta8250
18. Dwamena, BA . MIDAS: Stata module for meta-analytical integration of diagnostic test accuracy studies [J]. Statistical Software Components (2007).
19. Rosenberger, KJ , Chu, H , and Lin, L . Empirical comparisons of meta-analysis methods for diagnostic studies: a meta-epidemiological study. BMJ Open. (2022) 12:e055336. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2021-055336
20. Chen, B , and Benedetti, A . Quantifying heterogeneity in individual participant data meta-analysis with binary outcomes. Syst Rev. (2017) 6:243. doi: 10.1186/s13643-017-0630-4
21. Liu, TZ , Liu, Q , Qi, HN , Xu, WP , Gao, X , Wang, WZ, et al. Early diagnostic value of KIM-1, NGAL, and NLR in acute kidney injury caused by diquat poisoning. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2023) 2023:247. doi: 10.1155/2023/8213247
22. Abdelsalam, M , Elmorsy, E , Abdelwahab, H , Algohary, O , Naguib, M , El Wahab, AA, et al. Urinary biomarkers for early detection of platinum based drugs induced nephrotoxicity. BMC Nephrol. (2018) 19:219. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-1022-2
23. Berlin, N , Pawar, RD , Liu, X , Balaji, L , Morton, AC , Silverman, J, et al. Kidney-specific biomarkers for predicting acute kidney injury following cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. (2023) 190:109911. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2023.109911
24. Elmedany, SM , Naga, SS , Elsharkawy, R , Mahrous, RS , and Elnaggar, AI . Novel urinary biomarkers and the early detection of acute kidney injury after open cardiac surgeries. J Crit Care. (2017) 40:171–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2017.03.029
25. Ferguson, MA , Vaidya, VS , Waikar, SS , Collings, FB , Sunderland, KE , Gioules, CJ, et al. Urinary liver-type fatty acid-binding protein predicts adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. (2010) 77:708–14. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.422
26. Fuhrman, DY , Kellum, JA , Joyce, EL , Miyashita, Y , Mazariegos, GV , Ganoza, A, et al. The use of urinary biomarkers to predict acute kidney injury in children after liver transplant. Pediatr Transplant. (2020) 24:e13608. doi: 10.1111/petr.13608
27. Han, WK , Wagener, G , Zhu, Y , Wang, S , and Lee, HT . Urinary biomarkers in the early detection of acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2009) 4:873–82. doi: 10.2215/cjn.04810908
28. Jaques, DA , Spahr, L , Berra, G , Poffet, V , Lescuyer, P , Gerstel, E, et al. Biomarkers for acute kidney injury in decompensated cirrhosis: a prospective study. Nephrology. (2019) 24:170–80. doi: 10.1111/nep.13226
29. Khreba, NA , Abdelsalam, M , Wahab, AM , Sanad, M , Elhelaly, R , Adel, M, et al. Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1) as an early predictor for acute kidney injury in post-cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) in open heart surgery patients. Int J Nephrol. (2019) 2019:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2019/6265307
30. Lee, CW , Kou, HW , Chou, HS , Chou, HH , Huang, SF , Chang, CH, et al. A combination of SOFA score and biomarkers gives a better prediction of septic AKI and in-hospital mortality in critically ill surgical patients: a pilot study. World J Emerg Surg. (2018) 13:41. doi: 10.1186/s13017-018-0202-5
31. Lei, L , Li, LP , Zeng, Z , Mu, JX , Yang, X , Zhou, C, et al. Value of urinary KIM-1 and NGAL combined with serum Cys C for predicting acute kidney injury secondary to decompensated cirrhosis. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:7962. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26226-6
32. Li, W , Yu, Y , He, H , Chen, J , and Zhang, D . Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 as an early indicator to predict contrast-induced acute kidney injury in patients with diabetes mellitus undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. Biomed Rep. (2015) 3:509–12. doi: 10.3892/br.2015.449
33. Metzger, J , Mullen, W , Husi, H , Stalmach, A , Herget-Rosenthal, S , Groesdonk, HV, et al. Acute kidney injury prediction in cardiac surgery patients by a urinary peptide pattern: a case-control validation study. Crit Care. (2016) 20:157. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1344-z
34. Morales-Buenrostro, LE , Salas-Nolasco, OI , Barrera-Chimal, J , Casas-Aparicio, G , Irizar-Santana, S , Pérez-Villalva, R, et al. Hsp72 is a novel biomarker to predict acute kidney injury in critically ill patients. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e109407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0109407
35. Naqvi, R , Hossain, N , Butt, S , Bhellar, Z , Fatima, E , Imtiaz, S, et al. Efficacy of multiple biomarkers: NGAL, KIM1, cystatin C and IL18 in predicting pregnancy related acute kidney injury. Pak J Med Sci. (2023) 39:34–40. doi: 10.12669/pjms.39.1.6930
36. Pang, HM , Qin, XL , Liu, TT , Wei, WX , Cheng, DH , Lu, H, et al. Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as early biomarkers for predicting vancomycin-associated acute kidney injury: a prospective study. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2017) 21:4203–13.
37. Pei, Y , Zhou, G , Wang, P , Shi, F , Ma, X , and Zhu, J . Serum cystatin C, kidney injury molecule-1, neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin, klotho and fibroblast growth factor-23 in the early prediction of acute kidney injury associated with sepsis in a Chinese emergency cohort study. Eur J Med Res. (2022) 27:39. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00654-7
38. Ren, H , Zhou, X , Dai, D , Liu, X , Wang, L , Zhou, Y, et al. Assessment of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and interleukin-18 in the early post-burn period to predict acute kidney injury for various degrees of burn injury. BMC Nephrol. (2015) 16:142. doi: 10.1186/s12882-015-0140-3
39. Sabbisetti, VS , Waikar, SS , Antoine, DJ , Smiles, A , Wang, C , Ravisankar, A, et al. Blood kidney injury molecule-1 is a biomarker of acute and chronic kidney injury and predicts progression to ESRD in type I diabetes. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2014) 25:2177–86. doi: 10.1681/asn.2013070758.;
40. Schaalan, M , and Mohamed, W . Predictive ability of circulating osteoprotegerin as a novel biomarker for early detection of acute kidney injury induced by sepsis. Eur Cytokine Netw. (2017) 28:52–62. doi: 10.1684/ecn.2017.0393
41. Shaker, AM , Mohamed, MF , Thabet, KK , Ramzy, T , and Abdelhamid, YM . Serum Interleukin-18, kidney injury Molecule-1, and the renal resistive index for predicating acute kidney injury in critically ill patients with Sepsis. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transplant. (2023) 34:S153–60. doi: 10.4103/sjkdt.sjkdt_56_22
42. Shaoxiong, Z , Zhou, X , Qin, Y , Xiaomei, Y , Lingli, C , Xiaobin, L, et al. Establishment of a time-resolved immunoassay for acute kidney injury based on the detection of Kim-1. J Clin Lab Anal. (2022) 36:e24603. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24603
43. Tan, D , Zhao, L , Peng, W , Wu, FH , Zhang, GB , Yang, B, et al. Value of urine IL-8, NGAL and KIM-1 for the early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in patients with ureteroscopic lithotripsy related urosepsis. Chin J Traumatol. (2022) 25:27–31. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2021.10.001
44. Tekce, BK , Uyeturk, U , Tekce, H , Uyeturk, U , Aktas, G , and Akkaya, A . Does the kidney injury molecule-1 predict cisplatin-induced kidney injury in early stage? Ann Clin Biochem. (2015) 52:88–94. doi: 10.1177/0004563214528312
45. Torregrosa, I , Montoliu, C , Urios, A , Andrés-Costa, MJ , Giménez-Garzó, C , Juan, I, et al. Urinary KIM-1, NGAL and L-FABP for the diagnosis of AKI in patients with acute coronary syndrome or heart failure undergoing coronary angiography. Heart Vessel. (2015) 30:703–11. doi: 10.1007/s00380-014-0538-z
46. Tu, Y , Wang, H , Sun, R , Ni, Y , Ma, L , Xv, F, et al. Urinary netrin-1 and KIM-1 as early biomarkers for septic acute kidney injury. Ren Fail. (2014) 36:1559–63. doi: 10.3109/0886022x.2014.949764
47. Unal, ET , Ozer, EA , Kahramaner, Z , Erdemir, A , Cosar, H , and Sutcuoglu, S . Value of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 levels in predicting acute kidney injury in very low birth weight preterm infants. J Int Med Res. (2020) 48:300060520977442. doi: 10.1177/0300060520977442
48. Verbrugge, FH , Dupont, M , Shao, Z , Shrestha, K , Singh, D , Finucan, M, et al. Novel urinary biomarkers in detecting acute kidney injury, persistent renal impairment, and all-cause mortality following decongestive therapy in acute decompensated heart failure. J Card Fail. (2013) 19:621–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cardfail.2013.07.004
49. Vogel, MJ , Mustroph, J , Staudner, ST , Leininger, SB , Hubauer, U , Wallner, S, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1: potential biomarker of acute kidney injury and disease severity in patients with COVID-19. J Nephrol. (2021) 34:1007–18. doi: 10.1007/s40620-021-01079-x
50. Wybraniec, MT , Chudek, J , Bożentowicz-Wikarek, M , and Mizia-Stec, K . Prediction of contrast-induced acute kidney injury by early post-procedural analysis of urinary biomarkers and intra-renal doppler flow indices in patients undergoing coronary angiography. J Interv Cardiol. (2017) 30:465–72. doi: 10.1111/joic.12404
51. Xie, Y , Wang, Q , Wang, C , Qi, C , Ni, Z , and Mou, S . High urinary excretion of kidney injury molecule-1 predicts adverse outcomes in acute kidney injury: a case control study. Crit Care. (2016) 20:286. doi: 10.1186/s13054-016-1455-6
52. Xu, K , Shang, N , Levitman, A , Corker, A , Kudose, S , Yaeh, A, et al. Elevated neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is associated with the severity of kidney injury and poor prognosis of patients with COVID-19. Kidney Int Rep. (2021) 6:2979–92. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2021.09.005
53. Xue, W , Xie, Y , Wang, Q , Xu, W , Mou, S , and Ni, Z . Diagnostic performance of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin for acute kidney injury in an obstructive nephropathy patient. Nephrology. (2014) 19:186–94. doi: 10.1111/nep.12173
54. Yang, CH , Chang, CH , Chen, TH , Fan, PC , Chang, SW , Chen, CC, et al. Combination of urinary biomarkers improves early detection of acute kidney injury in patients with heart failure. Circul J. (2016) 80:1017–23. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-15-0886
55. Ye, HH , Shen, G , Luo, Q , Zhou, FF , Xie, XL , Wang, CY, et al. Early diagnosis of acute kidney injury in aged patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. (2018) 19:342–8. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1700427
56. Zhang, CF , Wang, HJ , Tong, ZH , Zhang, C , Wang, YS , Yang, HQ, et al. The diagnostic and prognostic values of serum and urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in sepsis induced acute renal injury patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:5604–17. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202005_21346
57. Zwiers, AJ , de Wildt, SN , van Rosmalen, J , de Rijke, YB , Buijs, EA , Tibboel, D, et al. Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin identifies critically ill young children with acute kidney injury following intensive care admission: a prospective cohort study. Crit Care. (2015) 19:181. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0910-0
58. Abosamak, MF , and Alkholy, AF . Urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin are early predictors for acute kidney injury among patients admitted to the surgical ICU. Egypt J Anaesth. (2021) 37:35–42. doi: 10.1080/11101849.2020.1866883
59. Devi, PU , Chanu, LC , Anupama, R , Chongtham, S , and Waikhom, R . Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM 1) and neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin (NGAL) as predictive diagnostic markers of renal dysfunction in patients undergoing major surgery. Int J Acad Med Pharmacy. (2022) 4:77–81. doi: 10.47009/jamp.2022.4.3.17
60. Ghaheh, MS , Mardani, S , Malekpour, A , Elyaderani, FK , Choliche, FS , Mortazavi, N, et al. Comparison of urinary KIM-1 and NGAL and plasma creatinine in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. J Nephropharmacol. (2021) 10:1–6. doi: 10.34172/npj.2021.04
61. Liang, XL , Liu, SX , Chen, YH , Yan, LJ , Li, H , Xuan, HJ, et al. Combination of urinary kidney injury molecule-1 and interleukin-18 as early biomarker for the diagnosis and progressive assessment of acute kidney injury following cardiopulmonary bypass surgery: a prospective nested casecontrol study. Biomarkers. (2010) 15:332–9. doi: 10.3109/13547501003706558
62. Mehrkesh, M , Barekatain, B , Gheisari, A , Ahmadi, M , and Shahsanai, A . Serum KIM-1 and cystatin levels as the predictors of acute kidney injury in asphyxiated neonates. Iran J Neonatol. (2022) 13:6–12. doi: 10.22038/IJN.2021.58428.2126
63. Fry, BC , Edwards, A , and Layton, AT . Impacts of nitric oxide and superoxide on renal medullary oxygen transport and urine concentration. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. (2015) 308:F967–80. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00600.2014
64. Cai, J , Jiao, X , Luo, W , Chen, J , Xu, X , Fang, Y, et al. Kidney injury molecule-1 expression predicts structural damage and outcome in histological acute tubular injury. Ren Fail. (2019) 41:80–7. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2019.1578234
65. Bland, SK , Schmiedt, CW , Clark, ME , DeLay, J , and Bienzle, D . Expression of kidney injury molecule-1 in healthy and diseased feline kidney tissue. Vet Pathol. (2017) 54:490–510. doi: 10.1177/0300985817690213
66. Shao, X , Tian, L , Xu, W , Zhang, Z , Wang, C , Qi, C, et al. Diagnostic value of urinary kidney injury molecule 1 for acute kidney injury: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e84131. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0084131
67. Fazel, M , Sarveazad, A , Mohamed Ali, K , Yousefifard, M , and Hosseini, M . Accuracy of urine kidney injury molecule-1 in predicting acute kidney injury in children; a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Acad Emerg Med. (2020) 8:e44. doi: 10.22037/aaem.v8i1.584
68. Parikh, CR , Thiessen-Philbrook, H , Garg, AX , Kadiyala, D , Shlipak, MG , Koyner, JL, et al. Performance of kidney injury molecule-1 and liver fatty acid-binding protein and combined biomarkers of AKI after cardiac surgery. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2013) 8:1079–88. doi: 10.2215/cjn.10971012
69. Bonventre, JV . Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1): a urinary biomarker and much more. Nephrol Dialys Transplant. (2009) 24:3265–8. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp010
70. Karmakova, Т , Sergeeva, NS , Kanukoev, КY , Alekseev, BY , and Kaprin, АD . Kidney injury molecule 1 (KIM-1): a multifunctional glycoprotein and biological marker (review). Sovrem Tekhnol Med. (2021) 13:64–78. doi: 10.17691/stm2021.13.3.08
71. Alge, JL , and Arthur, JM . Biomarkers of AKI: a review of mechanistic relevance and potential therapeutic implications. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. (2015) 10:147–55. doi: 10.2215/cjn.12191213
Keywords: kidney injury molecule 1, urinary KIM-1, serum KIM-1, acute kidney injury, meta-analysis
Citation: Su Y, Yang X, Cheng W-W, Shang X-M, Wang H-L and Shen H-C (2025) Kidney injury molecule 1 in the early detection of acute kidney injury—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1574945. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1574945
Edited by:
Rajendra Bhimma, University of KwaZulu-Natal, South AfricaReviewed by:
Rimante Cerkauskiene, Vilnius University, LithuaniaSeha Kamil Saygili, Istanbul University-Cerrahpasa, Türkiye
Copyright © 2025 Su, Yang, Cheng, Shang, Wang and Shen. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hong-Chun Shen, c2hlbmhvbmdjaHVuNzlAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Yun Su
Yun Su Xin Yang1
†
Xin Yang1
†
 Hong-Lian Wang
Hong-Lian Wang