- 1Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China
- 2Prenatal Diagnosis Center, Zhongshan Boai Hospital, Zhongshan, Guangdong, China
- 3Department of Ultrasonography, Peking University Shenzhen Hospital, Shenzhen, China
- 4Department of Obstetrics, Zhongshan Boai Hospital, Zhongshan, Guangdong, China
Objective: This research aimed to observe the pregnancy outcomes and early infancy physical growth of fetuses with situs inversus detected during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic at two centers in South China.
Methods: Data were collected from pregnant women with fetal situs inversus between March 2023 and May 2024. Systemic structured ultrasound, clinical manifestations, and genetic tests were conducted. Data on pregnancy outcomes and routine physical examinations of neonates and infants were collected. Statistical analysis was performed to compare the incidence rate of fetal situs inversus in 2023 with the median incidence rate in previous years. Z-scores for head circumference, weight, and length of the infants were calculated using PediTools Electronic Growth Chart Calculators.
Results: A total of 27 patients with fetal situs inversus were detected; situs inversus with dextrocardia was the most common category of all cases (23/27, 85.2%). The incidence rate of fetal situs inversus in Center 1 increased more than sixfold in 2023 compared with the median incidence rate of previous years (1.75‰ vs. 0.25‰, p = 0.000), while in Center 2, the increase was not so obvious (1.22‰ vs. 0.51‰, p = 0.011), both with the peak number of affected fetuses detected mainly in April 2023. In total, 15 newborns with situs inversus totalis (SIT) were delivered (15/27, 55.6%), and the majority were alive and reached their normal growth milestones, except for one infant death. Overall, 11 pregnancies underwent therapeutic abortion, and 1 pregnant woman received twin reduction surgery for one of the cotwins (12/27, 44.4%). Z-score evaluation showed no abnormal early physical growth in weight, head circumference, or length among infants with SIT.
Conclusion: A high incidence of fetal situs inversus during the COVID-19 pandemic was observed in our study. Situs inversus with dextrocardia was associated with relatively good pregnancy outcomes in non-complicated cases. No abnormal early infancy physical growth in weight, head circumference, or length was observed among infants with SIT.
1 Introduction
The normal arrangement of internal organs is known as situs solitus, while situs inversus represents a rare congenital condition in which the major visceral organs are reversed or mirrored from their normal positions (1). Situs inversus totalis (SIT), also known as situs inversus with dextrocardia, is the most common condition and involves the complete transposition of all of the visceral organs, including the heart. The incidence rate is approximately 1 in 8,000 to 1 in 25,000 live births (2). People with SIT have no associated medical symptoms or complications (1), but the condition may cause some confusion in diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, such as in cases of appendicitis or when organ transplantation is required. Rarely, situs inversus with levocardia occurs when the heart remains in its normal position while the other organs are mirrored, and it carries a high risk of severe heart defects. Even rarer forms, such as situs ambiguous or heterotaxy, involve subsets of organs with abnormal positioning or morphology and are more likely to cause medical problems than SIT. Fetal situs inversus has been described since Aristotle’s time, but its precise cause remains undetermined.
In the past 2 years, researchers from different centers in China (3–6) reported an increase in cases of fetal situs inversus in April 2023, after the “Zero-COVID-19” policy was lifted. Our centers also observed this extremely rare phenomenon. This research aimed to observe the pregnancy outcomes and early infancy physical growth of fetal situs inversus in pregnant women during the COVID-19 pandemic, from March 2023 to May 2024, and to discuss the relationship between the abnormality and SARS-CoV-2 infection.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Participants
Pregnant women who were diagnosed with fetal situs inversus during pregnancy and either received routine prenatal care at, or were referred for prenatal diagnosis to, Zhongshan Boai Hospital (Center 1) or Peking University Shenzhen Hospital (Center 2) between March 2023 and May 2024 were included in the study. Those who refused to enroll or could not complete the follow-up visits were excluded from the study. Clinical information such as age, last menstrual period, gravidity and parity history, family history, and teratogenic exposure was collected. Data on fetal situs inversus from 2015 to 2022 at the two centers were retrieved from electronic medical records. The incidence rate of fetal situs inversus in previous years was calculated. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital and Zhongshan Boai Hospital. Written informed consent was obtained from all participating pregnant women for the publication of this study.
2.2 Imaging features
A systematic, structured ultrasound scan, including a double check, was conducted by physicians with specialized training appropriate for diagnostic ultrasound in pregnancy. The scan was conducted between 20 and 24 gestational weeks, or at the time the woman presented to the hospital following referral from another center. The ultrasound instruments used were Voluson E10 systems (GE Healthcare, Zipf, Austria), with probe frequencies of 4~8 MHz. To assess cardiac situs, fetal laterality must first be determined, followed by evaluation of the positions of the stomach and heart. Situs abnormalities should be suspected when the fetal heart and/or stomach are not located on the left side. An abnormal cardiac axis increases the risk of cardiac malformations, especially involving the outflow tracts. A systematic, structured ultrasound examination is then performed. Ultrasound features of the fetus were described following the current clinical guidelines (7, 8).
2.3 COVID-19 diagnosis and clinical manifestations at early gestational age
The clinical manifestations of upper respiratory infection symptoms at early gestational age and their treatments were collected in the medical record system or by asking the pregnant women on the telephone. SARS-CoV-2 infection and reinfection diagnostic criteria followed the Coronavirus Disease-2019 (COVID-19) 2021 Case Definition of the US CDC1 and previous reports (9).
2.4 Genetic tests
Since chromosomal abnormalities and gene mutations are common causes of prenatal fetal malformations, amniocentesis was performed on informed pregnant women under the guidance of B-mode ultrasound, and 30 mL of amniotic fluid was extracted. G-banding fetal chromosome karyotype analysis was performed. Chromosomal microarray analysis (CMA) was performed using Affymetrix CytoScan HD arrays (Affymetrix Inc., Santa Clara, CA, United States) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Data were analyzed using Chromosome Analysis Suite software version 1.2 (Affymetrix Inc., Santa Clara, CA, United States). Trio whole-exome sequencing (trio-WES) was performed using Illumina NextSeq 6,000 (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, United States); all reads were aligned with the human reference genome (hg19). Bioinformatics analysis was performed, and pathogenicity was assessed as per the updated American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) guidelines. Candidate variants were confirmed by Sanger sequencing.
2.5 Follow-up of the pregnancy outcomes
Pregnancy outcomes of all cases were collected from electronic medical records. Management during pregnancy, delivery mode, gestational age at delivery, and information such as gender, weight, and general condition of the newborns after birth were documented.
2.6 Follow-up of early infant physical growth and Z-score evaluation
Early infant physical growth metrics such as head circumference, weight, and length were collected at birth, 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months of age from the participants’ medical files. Z-scores of these growth indicators were calculated using PediTools Electronic Growth Chart Calculators, a widely utilized lambda-mu-sigma-based anthropometric measurement calculation tool, following the operating instructions (10). Z-scores between [−2~2] for head circumference, weight, and length were all indicative of normal growth.
2.7 Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS 25.0 software (IBM, Armonk, NY, United States). The comparison of the incidence rate of fetal situs inversus between the year 2023 and the median incidence rate in the previous years (from 2015 to 2022) was performed using the chi-squared test, and a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Clinical characteristics of the participants
A total of 27 cases of fetal situs inversus were detected at the two centers (Table 1). The ages of the pregnant women ranged from 25 to 39 years. Three women underwent assisted reproductive technology, while the others had natural conception. No obvious family history or teratogenic exposure was reported. Overall, two women with dichorionic diamniotic twins were included in this study; both of whom had one affected fetus. A total of 23 pregnant women (23/27, 85.2%) experienced upper respiratory infection symptoms during early pregnancy. Fever, especially above 38 °C, was the most common clinical characteristic, along with cough, muscle aches, sore throat, headache, fatigue, anorexia, loss of taste, and stuffy nose. A self-testing SARS-CoV-2 Ag rapid test was performed at the time the women were affected. According to clinical criteria and laboratory criteria, 21 pregnant women (77.8%) were confirmed to have SARS-CoV-2 infection, while two others (7.4%) were diagnosed as probable cases.
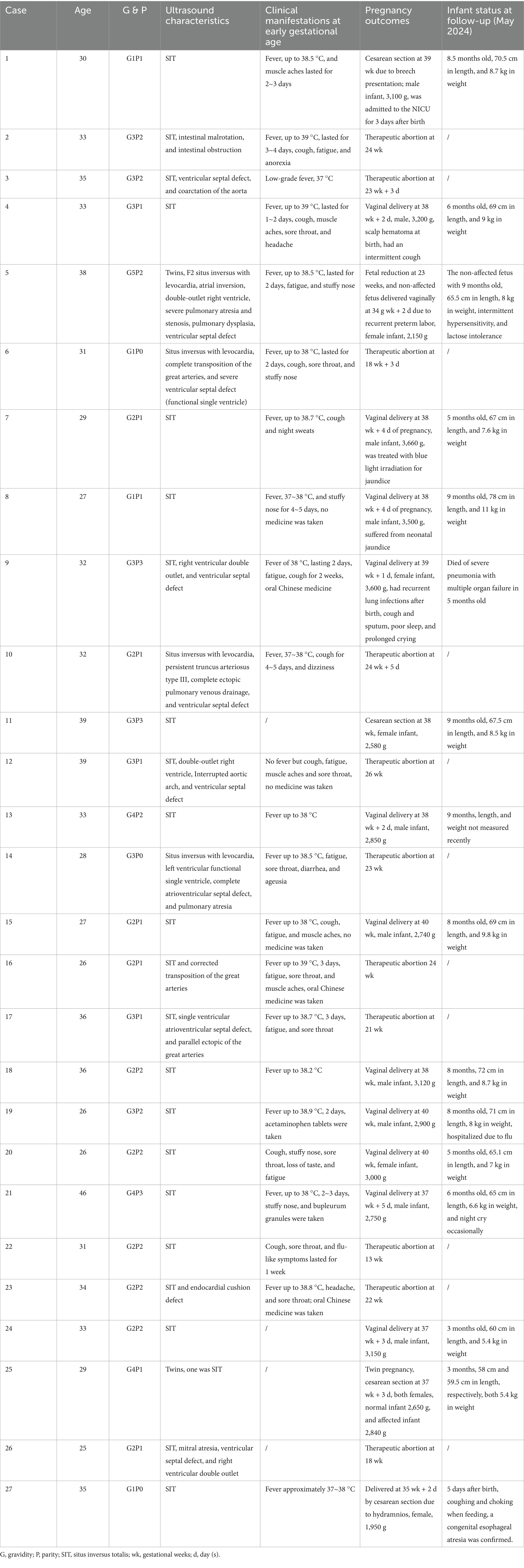
Table 1. Distributions of the ultrasound characteristics, clinical manifestations at early gestational age, pregnancy outcomes, and neonatal information of all the 27 cases of fetal situs inversus.
3.2 Description of the ultrasound characteristics and incidence of fetal situs inversus
Situs inversus with dextrocardia was the most common category among all cases (23/27, 85.2%), including 15 uncomplicated SIT cases (15/27, 55.6%) and 8 cases complicated by heart defects (8/27, 29.6%). Situs inversus with levocardia was found in the remaining 4 cases (4/27, 14.8%), all of which were combined with severe heart defects. Right ventricular double outlet was the most common ultrasound abnormality (4/12, 33.3%) in all the cases. The incidence rate of fetal situs inversus was compared with data from the previous years in the two centers. The results revealed that the incidence rate of fetal situs inversus in Center 1 increased more than sixfold in 2023 compared to the median incidence rate of the previous years (1.75‰ vs. 0.25‰, p = 0.000), while in Center 2, the increase was not so obvious (1.22‰ vs. 0.51‰, p = 0.011) (Table 2), both with the peak number of affected fetuses mainly detected in April 2023, which coincidentally overlaps with the time of early pregnancy infection of SARS-CoV-2.
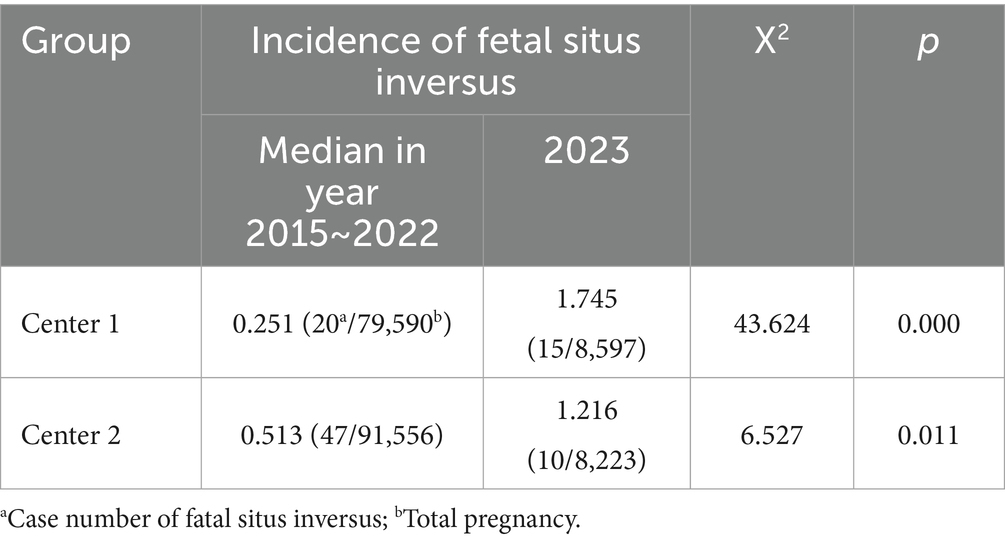
Table 2. Comparison of the incidence rate of fatal situs inversus between the year 2023 and the years from 2015 to 2022.
3.3 Follow-up of pregnancy outcomes
Overall, 15 newborns with situs inversus were delivered (15/27, 55.6%), including 11 male and 4 female newborns. Of these, 11 newborns were delivered vaginally and 4 by cesarean section. Only one pregnancy was delivered by cesarean section at 35 gestational weeks due to hydramnios, and the newborn was diagnosed with esophageal atresia after birth. A total of 14 newborns were stable at birth and thereafter. One infant who had complications such as right ventricular double outlet and ventricular septal defect died of severe pneumonia with multiple organ failure at 5 months of age. In total, 11 pregnancies underwent therapeutic abortion, and 1 pregnant woman received twin reduction surgery for one of the cotwins due to a severe fetal heart defect (12/27, 44.4%). A total of 8 women underwent amniocentesis in the second trimester, but fetal chromosome karyotyping, CMA, and trio-WES did not reveal positive results.
3.4 Early infant physical growth at follow-up
All newborns were rechecked using ultrasound, confirming the prenatal diagnosis of situs inversus. By and large, they reached normal growth milestones at 1 month, 3 months, and 6 months of age during follow-up. No long-term respiratory symptoms were reported during their early lives. Except for one infant with esophageal atresia and another who had intermittent hypersensitivity and lactose intolerance after birth, no other severe or sustained symptoms or diseases were found in the infants during follow-up. Z-score evaluation using anthropometric measurement calculation tools showed that there was no significant abnormal early infancy physical growth in weight, head circumference, and length of the infants with non-complicated situs inversus totalis (Supplementary Table 1). Only one infant (Case 8) had a length Z-score of 2.98 at 6 months of age; all other anthropometric measurements fell into the normal range.
4 Discussion
Studies indicated that motile cilia dysfunction expressed early in development is involved in left–right body axis determination (11, 12). Cilia are hair-like organelles that protrude from the cell surface into the extracellular space and are widely expressed in human tissues, including the respiratory epithelium (13). Primary ciliary dyskinesia (PCD), an autosomal recessive genetic condition, is a disease caused by dysfunction of the cilia that occurs during early embryonic development (14). Normally functioning cilia determine the position of the internal organs during early development, so embryos with PCD have a high risk of developing situs inversus. Cilia are also responsible for clearing mucus from the lungs, and their dysfunction causes increased susceptibility to lung infections, which are often observed in infants shortly after birth or at an early age. Mutations in approximately 50 cilia-related genes are associated with PCD, including DNAI1, DNAH5, and DNAH11 (15). However, in our cases, among those who underwent amniocentesis and trios-WES, no pathogenic gene mutations were detected. Therefore, other factors besides gene mutations must have contributed to the progression of early embryonic developmental abnormalities.
A marked increase in cases was observed several months after the lifting of the “Zero-COVID-19” policy in China (3–6), which coincided with an increase in SARS-CoV-2 infections. SARS-CoV-2 has been observed to cause defects in the ciliated layer of bronchial epithelial cells in deceased COVID-19 patients and animal models (16). This rare clinical evidence suggests a possible link between infection during pregnancy and the development of situs inversus in the fetus, especially during gestational weeks 4 ~ 6, the critical period for organ positioning.
In 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) added SARS-CoV-2 to the list of vertically transmissible infectious agents. The vertical transmission of COVID-19 in the third trimester is approximately 3.2% by infant nasopharyngeal swab testing, with SARS-CoV-2 RNA positivity in 7.7% by placental sample analysis (17). Studies indicate that SARS-CoV-2 can infiltrate the placenta and infect the fetus at different pregnancy stages, but the precise mechanisms of intrauterine transmission remain unclear. An angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2)-associated transmission model may explain the progress of placental translation. ACE2, a placental cell receptor, together with the consistently present neuropilin-1 (NRP-1), can change expression during pregnancy and mediate SARS-CoV-2 infiltration of the placenta, breaching its protective barrier, and infecting the fetus (18). Xiuli Shao et al. confirmed that the expression of ACE2 in ventricular myocytes was upregulated in both fetuses and adults with heart damage (19). If the fetus were infected with the virus, embryopathies and congenital anomalies could result.
However, increased cases of fetal situs inversus after SARS-CoV-2 infection were not seen in the United States (20) and Scandinavian countries (21). The reason for this may be due to the strict lockdown policy by the Chinese government after the outbreak of the pandemic, which protected the majority of Chinese people against infection. The vast majority of people were first infected within a short time window in December 2022. Therefore, China represents a unique model worldwide, making it advantageous for observing complications of the disease. In our study, we observed a significant increase in cases of fetal situs inversus in one prenatal diagnostic center, but data from the other center were not fully consistent with it. This discrepancy was mostly because Center 2 was a regional fetal abnormality referral center, which accepted patients from surrounding cities and thus had a relatively high incidence of fetal situs inversus in the previous years.
A series of structural abnormalities complicated by SIT were detected in our study, such as double-outlet right ventricle, endocardial cushion defect, pulmonary stenosis, pulmonary atresia, single ventricle, transposition of the great arteries, and ventricular septal defect. Early diagnosis and treatment are needed due to the severe complications of specific abnormalities. Situs inversus with levocardia usually carries a high risk of severe heart defects; thus, therapeutic abortion or urgent surgery after birth may be required. In cases of SIT, our study supports that individuals with this abnormality may have no medical symptoms or complications.
Infants of SIT without severe ultrasound abnormalities in our study showed normal physical growth and development at follow-up. The infant of Case 5 had intermittent hypersensitivity and lactose intolerance after delivery, but the syndrome is common in neonates and resolved spontaneously at follow-up visits. Case 8 had a Z-score of 2.98 at 6 months of age, which was outside the normal range; further analysis revealed no other causes, and the deviation was attributed to the parents’ height.
This study only contained a small number of participants, which may make statistical analysis difficult. Clinical information collection was mostly via telephone visits; thus, recall bias was inevitable. Meanwhile, the physiological immunosuppression of pregnant women, the limited transfer of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies from the mother to the fetus, side effects of drugs or vaccines used during the pandemic, and other unknown causes were also indicated as limitations of the study.
5 Conclusion
A high incidence of fetal situs inversus during the COVID-19 pandemic was observed in our study. Situs inversus with dextrocardia was the most common condition of fetal situs inversus and had a relatively good pregnancy outcome in non-complicated cases. Abnormal early infancy physical growth in weight, head circumference, and length of the infants with SIT was not observed in the study.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of Peking University Shenzhen Hospital and Zhongshan Boai Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
YZ: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XD: Data curation, Writing – original draft. HL: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. RC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. FC: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft. DZ: Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was supported by Shenzhen High-level Hospital Construction Fund and Peking University Shenzhen Hospital Scientific Research Fund.
Acknowledgments
We thank all the participants for their cooperation in this study. We thank Dr. Ying Shan for suggestions on study design.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1581322/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1. Eitler, K, Bibok, A, and Telkes, G. Situs inversus totalis: a clinical review. Int J Gen Med. (2022) 15:2437–49. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S295444
2. Devera, J, Licandro, F, Ramos, J, Taymoorian, HT, and Yap, LG. Situs inversus totalis in the neonatal setting. Cureus. (2021) 13:e13516. doi: 10.7759/cureus.13516
3. Guo, Z, Luo, Y, Bi, Y, Liu, L, Qi, Y, Yan, J, et al. Association between situs inversus and maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection at gestational age 4-6 weeks. Med. (2024) 5:1433–41.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2024.07.009
4. Li, Y, Wang, Y, Wu, H, Li, Q, Li, S, Qiu, C, et al. Increased risk of fetal left-right asymmetry disorders associated with maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection during the first trimester. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:11422. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61778-w
5. Qiu, S, Wu, S, Yin, R, Wang, B, and Wu, H. Correlation between COVID-19 infection and fetal situs inversus. Birth Defects Res. (2024) 116:e2324. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.2324
6. Wang, Y, Guo, Z, Ye, B, Liu, L, Mao, X, Luo, Y, et al. Association of SARS-CoV-2 infection during early weeks of gestation with situs inversus. N Engl J Med. (2023) 389:1722–4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2309215
7. International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics and GynecologyCarvalho, JS, Allan, LD, Chaoui, R, Copel, JA, DeVore, GR, et al. ISUOG practice guidelines (updated): sonographic screening examination of the fetal heart. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2013) 41:348–59. doi: 10.1002/uog.12403
8. Salomon, LJ, Alfirevic, Z, Berghella, V, Bilardo, CM, Chalouhi, GE, Da Silva Costa, F, et al. ISUOG practice guidelines (updated): performance of the routine mid-trimester fetal ultrasound scan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. (2022) 59:840–56. doi: 10.1002/uog.24888
9. Cai, C, Li, Y, Hu, T, Liang, R, Wang, K, Guo, C, et al. The associated factors of SARS-CoV-2 reinfection by omicron variant—Guangdong Province, China, December 2022 to January 2023. China CDC Wkly. (2023) 5:391–6. doi: 10.46234/ccdcw2023.075
10. Chou, JH, Roumiantsev, S, and Singh, R. PediTools electronic growth chart calculators: applications in clinical care, research, and quality improvement. J Med Internet Res. (2020) 1:e16204. doi: 10.2196/16204
11. Lowe, LA, Supp, DM, Sampath, K, Yokoyama, T, Wright, CV, Potter, SS, et al. Conserved left-right asymmetry of nodal expression and alterations in murine situs inversus. Nature. (1996) 381:158–61. doi: 10.1038/381158a0
12. Little, RB, and Norris, DP. Right, left and cilia: how asymmetry is established. Semin Cell Dev Biol. (2021) 110:11–8. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.06.003
13. Nonaka, S, Tanaka, Y, Okada, Y, Takeda, S, Harada, A, Kanai, Y, et al. Randomization of left-right asymmetry due to loss of nodal cilia generating leftward flow of extraembryonic fluid in mice lacking KIF3B motor protein. Cell. (1998) 95:829–37. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81705-5
14. Lucas, JS, Davis, SD, Omran, H, and Shoemark, A. Primary ciliary dyskinesia in the genomics age. Lancet Respir Med. (2020) 8:202–16. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(19)30374-1
15. Shoemark, A, Rubbo, B, Legendre, M, Fassad, MR, Haarman, EG, Best, S, et al. Topological data analysis reveals genotype-phenotype relationships in primary ciliary dyskinesia. Eur Respir J. (2021) 58:2002359. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02359-2020
16. Robinot, R, Hubert, M, de Melo, GD, Lazarini, F, Bruel, T, Smith, N, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection induces the dedifferentiation of multiciliated cells and impairs mucociliary clearance. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:4354. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-24521-x
17. Kotlyar, AM, Grechukhina, O, Chen, A, Popkhadze, S, Grimshaw, A, Tal, O, et al. Vertical transmission of coronavirus disease 2019: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol. (2021) 224:35–53.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2020.07.049
18. Gostomczyk, K, Borowczak, J, Siekielska-Domanowska, M, Szczerbowski, K, Maniewski, M, Dubiel, M, et al. Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 placental transmission. Arch Immunol Ther Exp. (2023) 72:1. doi: 10.2478/aite-2024-0001
19. Hao, L, and Feng, R. The atlas of ACE2 expression in fetal and adult human hearts reveals the potential mechanism of heart-injured patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2022) 4:C723–38. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00169.2021
20. Cragan, JD, Cho, SJ, Forestieri, N, Hort, M, Nestoridi, E, Moore, CA, et al. Observed prevalence of congenital situs inversus in the United States before and during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, 2017-2022. Birth Defects Res. (2024) 116:e2424. doi: 10.1002/bdr2.2424
Keywords: pregnancy, situs inversus, dextrocardia, infant, physical growth, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), SARS-CoV-2
Citation: Zhang Y, Dong X, Li H, Chen R, Cai F and Zhang D (2025) Pregnancy outcomes and early infancy physical growth of fetal situs inversus during the COVID-19 pandemic. Front. Med. 12:1581322. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1581322
Edited by:
Depeng Zhao, Shenzhen Maternity and Child Healthcare Hospital, ChinaReviewed by:
Sandra Acevedo Gallegos, Instituto Nacional de Perinatología (INPER), MexicoJia Tang, Guangdong Provincial Family Planning Hospital, China
Wei Shu, Guiling Medical University, China
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Dong, Li, Chen, Cai and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yongke Zhang, eW9uZ2tlZXpoYW5nQGhvdG1haWwuY29t
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡ORCID: Yongke Zhang, orcid.org/0000-0001-8072-4196
 Yongke Zhang
Yongke Zhang Xingsheng Dong2†
Xingsheng Dong2† Haijun Li
Haijun Li Dirong Zhang
Dirong Zhang