Abstract
Gilbert syndrome (GS) is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the UGT1A1 gene. It is characterized by intermittent non-hemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. Herein, we report a patient with GS who presented with chronic hyperbilirubinemia and no other abnormal manifestations. Heterozygous c.1047_1047delG, c.-3279 T>G, and c.-41_-40dupTA mutations were identified in his UGT1A1 gene by using Sanger sequencing. The novel c.1047_1047delG variant was classified as a pathogenic mutation. These findings not only provide a basis for the genetic diagnosis of this GS patient but also expand the variant database of the UGT1A1 gene.
1 Introduction
Gilbert syndrome (GS; OMIM #143500) is an autosomal recessive genetic disorder characterized by intermittent unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in the absence of hemolysis, with no other features of hepatobiliary dysfunction (1). First described in 1901 by Gilbert and Lereboulet (2), its population incidence has been reported to be approximately 3–13% (3, 4). The UGT1A1 gene (OMIM 191740) encodes uridine diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 (UGT1A1), an enzyme primarily localized to the smooth endoplasmic reticulum of hepatocytes. Pathogenic variants in the UGT1A1 gene are the underlying cause of GS. Loss-of-function mutations in this gene reduce UGT1A1 enzyme activity, thereby impairing the conjugation of bilirubin with glucuronic acid. Importantly, GS does not impact life expectancy and typically requires no specific treatment. To date, the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD1) has cataloged 189 mutations in the UGT1A1 gene. In the present study, we report a patient diagnosed with GS and identify novel pathogenic variant in the UGT1A1 gene (NM_000463.3): c.1047_1047delG, g.7652_7652delG, and p.I350Yfs16.
2 Case report and genetic testing
A 17-year-old man had experienced intermittent mild jaundice for more than 8 years. The jaundice was occasionally accompanied by dull pain in the right upper quadrant and was notably triggered by fatigue and fasting. It resolved spontaneously within 1–2 weeks. Throughout the disease course, there was no pruritus, darkening of urine, or clay-colored stools. He had no prior medical history, nor any remarkable personal or family history (Figure 1A). At the time of presentation to our hospital, he exhibited yellowing of the skin and sclera. Laboratory tests revealed a total bilirubin (TBIL) level of 74.2 μmol/L (normal range: 3.4–17.1 μmol/L) and a direct bilirubin (DBIL) level of 68.4 μmol/L (normal range: 0–6 μmol/L); no other significant abnormalities were noted in his liver function tests. Hemolytic tests yielded negative results, and he was also negative for hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection. Ultrasonographic examination of the liver, biliary tract, pancreas, and spleen showed no abnormalities.
Figure 1

Family tree and UGT1A1 genetic analysis. (A) Proband II-1 suffered from GS. (B) Direct sequencing showed heterozygous c.1047_1047delG, c.-3279 T>G, and c.-41_-40dupTA mutations in II-1.
Genomic DNA was isolated from the peripheral blood leukocytes of the patient. The promoter region (encompassing the TATA box), enhancer region [Phenobarbital-responsive enhancer module (PBREM)], coding exons, and splice junctions of the UGT1A1 gene were amplified via polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The primer sequences used are provided in Table 1. PCR products were subjected to Sanger sequencing, and variants in UGT1A1 were identified by aligning the sequencing results with the published reference sequence (GenBank accession no.: NM_000463). The pathogenicity of the identified mutations was interpreted in accordance with the guidelines of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG) (5). The patient provided written informed consent for participation in this study. However, his parents declined to donate their blood samples. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University. Subsequent genetic analysis revealed that the patient carried three heterozygous mutations in UGT1A1: c.1047_1047delG, c.-3279T>G, and c.-41_-40dupTA (corresponding to the UGT1A1*28 allele) (Figure 1B). During telephone follow-up, the patient still reported intermittent jaundice.
Table 1
| UGT1A1 exon | Primer sequence (5′ → 3′) |
|---|---|
| Exon 1–1 | F: TATAAGTAGGAGAGGGCGAACC |
| R: TCAAATTCCAGGCTGCATG | |
| Exon 1–2 | F: GGCCTCCCTGGCAGAAAG |
| R: ATGCCAAAGACAGACTCAAACC | |
| Exon 2 | F: AGGAACCCTTCCTCCTTTAGA |
| R: GAAGCTGGAAGTCTGGGATTAG | |
| Exon 3 | F: CCTCAGAAGCCTTCACAGTTAC |
| R: ATCCAATCCGCCCAACATAC | |
| Exon 4 | F: GTGTCCAGCTGTGAAACTCA |
| R: TGAATGCCATGACCAAAGTATTC | |
| Exon 5 | F: CAACAGGGCAAGACTCTGTATC |
| R: CCTTATTTCCCACCCACTTCTC | |
| Promoter | F: ACAGGTTTCCATGGCGAAAG |
| R: TGTTTTGATCACACGCTGCA | |
| PBREM | F: GGTCACTCAATTCCAAGGGG |
| R: GCATCCAAGCCAGCAAGTAA |
Primers sequences of the UGT1A1 gene.
PBREM, phenobarbital responsive enhancer module; UGT1A1, uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1; F, forward; R, reverse; bp, base pairs.
3 Discussion
The UGT1A1 enzyme is predominantly expressed in the liver, where it localizes to the membrane of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum. Its primary function is to catalyze the conjugation of bilirubin with glucuronic acid. Variations in the UGT1A1 gene can lead to varying degrees of quantitative reduction in UGT1A1 enzyme activity, thereby causing inherited non-hemolytic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (UCH). The classification of Crigler–Najjar syndrome type I (CNS-I, OMIM#218800), Crigler–Najjar syndrome type II (CNS-II, OMIM#606785), and GS subtypes largely relies on serum bilirubin levels (6). However, these conditions are now recognized as representing a continuous clinical spectrum of a single underlying disorder. Specifically, UGT1A1 activity is reduced to approximately 30, 10, and 0% of normal levels in patients with GS, CNS-II, and CNS-I, respectively. Notably, some cases of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and breast milk jaundice may be classified as transient familial neonatal hyperbilirubinemia (OMIM#237900), a condition associated with UGT1A1 gene polymorphisms or mutations (7). The patient’s TBIL levels fall within the range for GS (<100 μmol/L), and the predominance of unconjugated bilirubin is consistent with the pathophysiology of GS. In contrast, CNS-II is characterized by more severe UCH. In CNS-II, TBIL levels are usually 100–400 μmol/L. Additionally, the patient had no history of neonatal jaundice requiring prolonged phototherapy—another key clinical differentiator of CNS-II, which often presents with severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia as a key feature.
The UGT1A1 protein contains several key structural domains that are critical for its enzymatic function in glucuronidation reactions. These domains include: N-terminal substrate-binding domain, C-terminal UDP-glucuronic acid (UDPGA) binding domain, interdomain linker region, transmembrane domain, and cytoplasmic tail. The p.I350Yfs*16 variant in UGT1A1 is a frameshift mutation that introduces a premature termination codon 16 amino acids after the frameshift at position 350. This mutation significantly impacts the protein structure by truncating the C-terminal region, with key effects on critical functional domains. The location of this mutation within UGT1A1 is shown in Figure 2. The variant was evaluated using two widely recognized in silico tools, MutationTaster (8) and PROVEAN (9), both of which consistently predicted pathogenic effects.
Figure 2
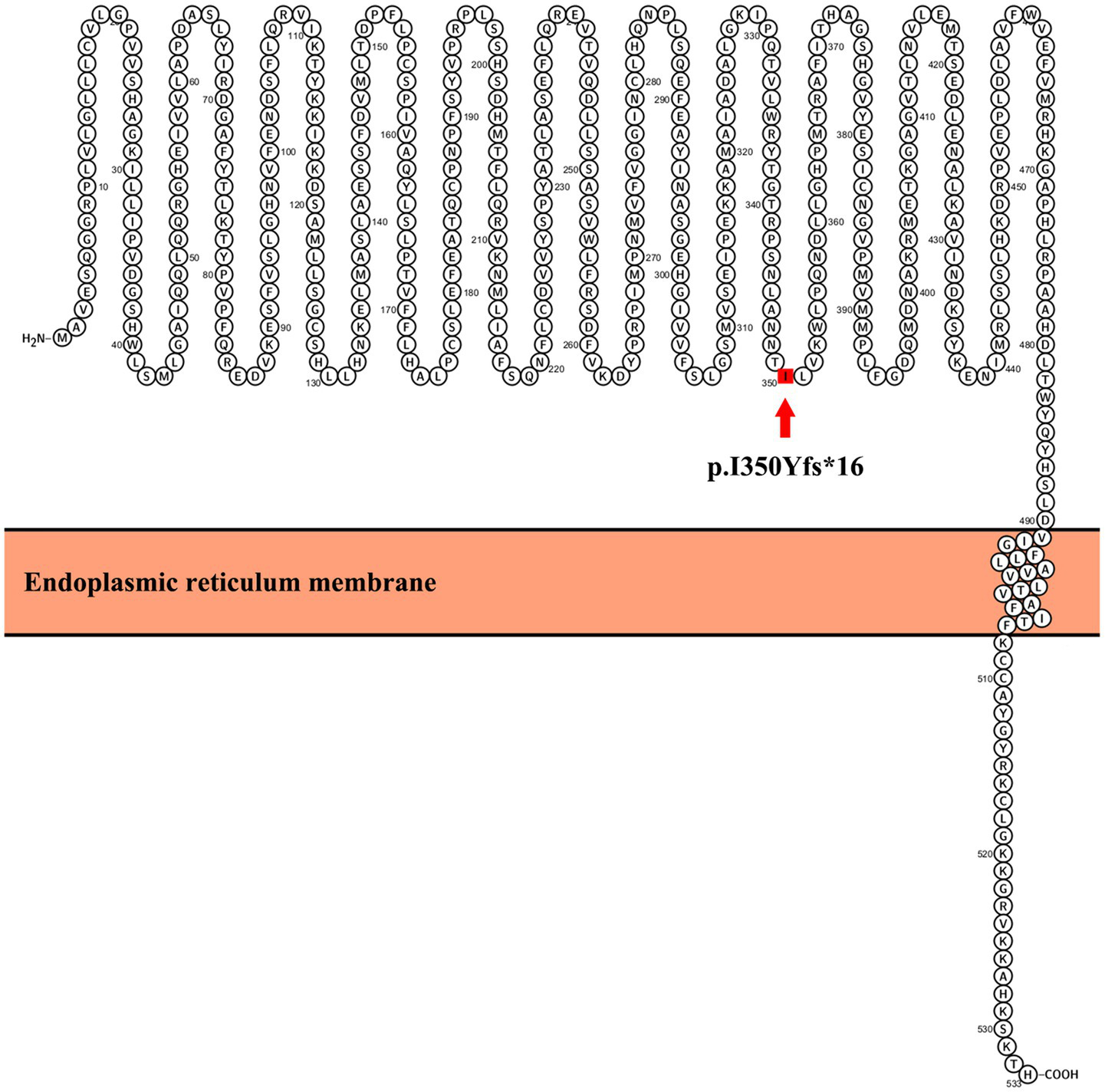
Location of the mutation in UGT1A1. The schematic diagram of UGT1A1 was generated using Protter software (http://wlab.ethz.ch/protter/start/).
The p.I350Yfs*16 variant is a frameshift mutation that disrupts the open reading frame of the UGT1A1 gene, which directly aligns with the “null variant” definition for very strong pathogenic evidence (PVS1). This variant was not detected in large population databases, including the 1000 Genomes Project (1000G), the Exome Aggregation Consortium (ExAC), and the Genome Aggregation Database (gnomAD) (Pathogenic Moderate evidence 2, PM2). Prediction software, MutationTaster and PROVEAN, predicted a deleterious effect of the variant (Pathogenic Supporting evidence 3, PP3). Per ACMG’s variant classification framework, the combination of 1 very strong criterion (PVS1) + 1 moderate criterion (PM2) + 1 supporting criterion (PP3) meets the threshold for pathogenic classification. Additionally, a comprehensive search of the HGMD and a review of previously published literature confirmed that this UGT1A1 variant has not been reported before, thus identifying it as a novel mutation.
Two other known mutations are also associated with GS. The first is a TA insertion in the TATA box of the UGT1A1 promoter, resulting in the [A(TA)₇TAA] genotype. This variant reduces UGT1A1 gene expression by 50–70% (10–12). The second is the c.-3279 T>G variant located in the PBREM, which leads to an approximately 40% decrease in UGT1A1 enzyme activity (13).
The present study is subject to several limitations. The parental sequencing would have further clarified variant inheritance, but it was not feasible due to parental refusal. In addition, we did not perform in vitro functional validation to experimentally confirm the functional impact of the novel c.1047_1047delG variant. However, these limitations do not affect the interpretation of the variant’s pathogenicity, as the variant meets ACMG pathogenic criteria.
4 Conclusion
In conclusion, this study identifies a novel pathogenic mutation in the UGT1A1 gene. These findings not only facilitate the genetic diagnosis of families affected by GS but also expand the known spectrum of UGT1A1 mutations.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets for this article are not publicly available due to concerns regarding participant/patient anonymity. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the ethics committee of the Second Xiangya Hospital of Central South University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
CZ: Investigation, Software, Funding acquisition, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Project administration, Visualization, Data curation, Methodology, Formal Analysis. HH: Investigation, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research was funded by the Department of Science and Technology of Henan Province, China (Grant No. 252300421609) and the Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province, China (Grant No. 2025JJ50515).
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the members of the patients’ families for their participation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1.
Hsu PW Liao PC Kao YH Lin XY Chien RN Yeh CT et al . The mutation hotspots at UGT1A locus may be associated with Gilbert's syndrome affecting the Taiwanese population. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:12709. doi: 10.3390/ijms232012709
2.
Memon N Weinberger BI Hegyi T Aleksunes LM . Inherited disorders of bilirubin clearance. Pediatr Res. (2016) 79:378–86. doi: 10.1038/pr.2015.247
3.
Owens D Evans J . Population studies on Gilbert's syndrome. J Med Genet. (1975) 12:152–6. doi: 10.1136/jmg.12.2.152
4.
Travan L Lega S Crovella S Montico M Panontin E Demarini S . Severe neonatal hyperbilirubinemia and UGT1A1 promoter polymorphism. J Pediatr. (2014) 165:42–5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2014.03.013
5.
Richards S Aziz N Bale S Bick D Das S Gastier-Foster J et al . Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet Med. (2015) 17:405–24. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30
6.
He T Geng X Zhu L Lin X Wang L . Type II Crigler-Najjar syndrome: a case report and literature review. Front Med (Lausanne). (2024) 11:1354514. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1354514
7.
Erlinger S Arias IM Dhumeaux D . Inherited disorders of bilirubin transport and conjugation: new insights into molecular mechanisms and consequences. Gastroenterology. (2014) 146:1625–38. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.03.047
8.
Schwarz JM Cooper DN Schuelke M Seelow D . MutationTaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nat Methods. (2014) 11:361–2. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2890
9.
Choi Y Sims GE Murphy S Miller JR Chan AP . Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e46688. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046688
10.
Gailite L Valenzuela-Palomo A Sanoguera-Miralles L Rots D Kreile M Velasco EA . UGT1A1 variants c.864+5G>T and c.996+2_996+5del of a Crigler-Najjar patient induce aberrant splicing in Minigene assays. Front Genet. (2020) 11:169. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00169
11.
Jirásková A Škrha J Vítek L . Association of low Serum Bilirubin Concentrations and Promoter Variations in the UGT1A1 and HMOX1 genes with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Czech population. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:10614. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310614
12.
Miranda JP Pereira A Corvalán C Miquel JF Alberti G Gana JC et al . Genetic determinants of serum bilirubin using inferred native American gene variants in Chilean adolescents. Front Genet. (2024) 15:1382103. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1382103
13.
Sugatani J Yamakawa K Yoshinari K Machida T Takagi H Mori M et al . Identification of a defect in the UGT1A1 gene promoter and its association with hyperbilirubinemia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2002) 292:492–7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2002.6683
Summary
Keywords
Gilbert syndrome, UGT1A1 , mutation, hyperbilirubinemia, pathogenic
Citation
Zhao C and Huang H (2025) Case Report: Identification of a novel pathogenic UGT1A1 mutation in a Chinese patient with Gilbert syndrome. Front. Med. 12:1581923. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1581923
Received
24 February 2025
Accepted
23 September 2025
Published
15 October 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Shujuan Chen, University of California, San Diego, United States
Reviewed by
Xiaojing Yang, University of California, San Diego, United States
Ching-Shan Huang, Cathay General Hospital, Taiwan
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhao and Huang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Chenyu Zhao, chenyuzhao9305@zzu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.