Abstract
Objectives:
According to the updated Selecting Therapeutic Targets in Inflammatory Bowel Disease (STRIDE-II), mucosal healing (MH) is the long-term therapeutic target for Crohn’s disease (CD). Capsule endoscopy (CE) is effective in evaluating small bowel mucosal inflammation. This research seeks to construct a simple tool for predicting small bowel MH in pediatric CD to aid clinical decision-making.
Methods:
Data from the medical records of patients with CD who underwent CE at the Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center between November 2017 and July 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression algorithm was applied to identify predictive factors for small bowel MH. A nomogram incorporating these factors was constructed to predict the probability of MH in this population.
Results:
In total, 143 CE examinations performed in 91 pediatric CD patients (median age, 11 years) were included. Based on the Lewis scores, the CD patients were divided into “MH” (42 cases) and “non-MH” groups (101 cases). LASSO regression analysis identified erythrocyte sedimentation rate, albumin levels, aspartate transaminase levels, C-reactive protein levels, platelet count, and lymphocyte percentage as the most significant predictors; and thus, these factors were incorporated into the predictive nomogram model. The area under the receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the predictive nomogram model was 0.855 (95% confidence interval, 0.783–0.926), suggesting a high discrimination power.
Conclusion:
A nomogram was constructed to predict small bowel MH in pediatric CD patients. This nomogram model can enable accurate and simple attentive observation of small bowel inflammation in CD patients.
Introduction
Crohn’s disease (CD), a relapsing and remitting inflammatory disease, often requires surgery due to complications, such as strictures, fistulae, and abscesses (1). CD affects the entire gastrointestinal tract from the oral cavity to the anus. Up to 70% of CD patients present with small bowel involvement, and approximately half of the cases involve only the small bowel (2–5). Furthermore, small bowel CD is more refractory and has a higher incidence of intestinal complications than colon CD (6). Nevertheless, assessment of small bowel activity in the CD is relatively more difficult than that of the colon. And it has been reported that small bowel inflammation is considerably underestimated (7).
Mucosal healing (MH) is defined as the resolution of visible inflammation and ulceration during endoscopy, which is an important objective in the disease monitoring of patients with CD. It is widely accepted that MH can reduce the risk of bowel damage, thereby leading to improved long-term outcomes (8–12). Therefore, patients with CD need an evaluation of the entire small intestine, not only to diagnose or assess disease activity before and after treatment but also to confirm the maintenance of MH. Capsule endoscopy (CE) has been utilized to evaluate small bowel pathology in adults and children since 2001 and 2004, respectively (13). In patients with established CD, CE is used for assessing disease activity and extent and monitoring treatment effects and postoperative recurrence (14). CE scores, i.e., Niv and Lewis scores, are effective in predicting clinical outcomes in patients with CD (15–17). Moreover, CE findings can also modify the treatment plan of CD, sometimes avoiding surgery altogether (18).
Nevertheless, despite its obvious advantages, CE has a retention risk, is costly, and requires qualified medical personnel and patient preparation. A meta-analysis reported that CE retention occurred in 3.49% and 1.64% of adult and pediatric CD, respectively (19). The retention rate could be reduced to 1.3% with the use of patency capsule (20). Predicting the rate of small bowel MH can optimize individual treatment strategies timely when CE is unavailable.
Currently, accurate instruments with high sensitivity and specificity that use serological parameters and clinical characteristics to predict MH evaluated by CE in pediatric CD are lacking. Therefore, we aimed to use routine clinical and serological data to construct a nomogram for predicting MH evaluated by CE in pediatric CD.
Materials and methods
Study population
This retrospective study was conducted at the Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center and included consecutive patients aged 1–17 years with established CD who underwent CE between November 2017 and July 2022. Patients without small bowel involvement were excluded from the analysis. The subjects whose CE did not reach the colon during the recording time and those who lacked clinical or laboratory indices were also excluded. The CD diagnosis was retrospectively confirmed based on the Porto criteria defined by the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) (21). Data on patients’ baseline information and that corresponding to the point of CE examination, including age, sex, the Paris Classification (22), weighted Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (wPCDAI) (23), and serological parameters, were collected.
CE procedure
Capsule endoscopy (MiroCam, South Korea) was performed after bowel preparation with polyethylene glycol or mannitol and overnight fasting. If a patient was not able to swallow the CE, a gastroscope was used to deliver the CE. Mucosal inflammation was evaluated using the Lewis scores and MH was defined as a Lewis score of <135 (24).
Construction and evaluation of predictive models
The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression algorithm was applied to identify the most important predictors, minimizing excessive fitting or selection bias in basic features. Subsequently, these variables were used to construct a nomogram. The area under the receiver-operating characteristic curve (AUC) was calculated to assess the nomogram’s discriminative ability, which was then corrected by bootstrapping validation. Furthermore, the calibration curve was presented to illustrate the relationship between predicted probabilities and observed frequencies.
Statistical methods
R 4.2.0 software was used to perform statistical analysis. Normally distributed continuous variables were reported as means ± SD and compared using a 2-sample unpaired t-test. Non-normally distributed continuous variables were presented as medians and interquartile range (IQR) and compared using the Mann–Whitney U test. Categorical variables were summarized as counts and percentages and analyzed by Fisher’s exact test or Chi-squared test. The “glmnet” package was used to select the most significant predictors. The “regplot” and “rms” packages were used to construct the nomogram and presented calibration curves. Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) curves were plotted using the “pROC” package. A P-value of <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Dataset characteristics
Overall, 203 CE examinations were performed in patients with CD at the Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center between November 2017 and July 2022. A total of 12 cases with incompleteness of CE and 48 cases with data defects were excluded from the analysis. Thus, 143 CE examinations performed in 91 patients with CD were included in this study (median age, 11 years). Based on the Lewis scores, the patients with CD were divided into “MH” and “non-MH” groups. A total of 42 cases achieved MH. Table 1 shows the clinical and demographic characteristics of the included cases. The comparison of demographics and laboratory test results between the MH and non-MH groups is presented in Table 2.
TABLE 1
| Characteristics | Median (IQR) or n (%) |
| Male (n, %) | 87 (60.8%) |
| Age, years | 11 (8–13) |
| Disease location | |
| L1 | 3 (2.0%) |
| L1 + L4a | 1 (0.6%) |
| L1 + L4b | 20 (14.0%) |
| L1 + L4a + b | 7 (4.9%) |
| L2 + L4b | 19 (13.3%) |
| L3 | 5 (3.5%) |
| L3 + L4b | 58 (40.6%) |
| L3 + L4a + b | 10 (7.0%) |
| L4b | 14 (9.8%) |
| L4a + b | 6 (4.2%) |
| Behavior | |
| B1 | 139 (97.2%) |
| B2 | 4 (2.8%) |
| B3 | 0 |
| Linear growth failure | 5 (3.5%) |
| Perianal disease | 13 (9.1%) |
| Current treatment | |
| Anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy | 53 (37.1%) |
| Anti-tumor necrosis factor-α therapy + thiopurines | 1 (0.7%) |
| EEN | 20 (14.0%) |
| Corticosteroids | 1 (0.7%) |
| Thiopurines | 1 (0.7%) |
| MTX | 4 (2.8%) |
| Thalidomide | 1 (0.7%) |
| None | 62 (43.4%) |
Characteristics of included cases.
Categorical data were presented as frequency (percentage), continuous data were presented as median (interquartile ranges). EEN, exclusive enteral nutrition; MTX, methotrexate.
TABLE 2
| Characteristics | MH (n = 42) | Non-MH (n = 101) | P-value |
| Sex (M/F) | 28/14 | 59/42 | 0.357 |
| Age (years) | 10.31 (7.40–13.22) | 10.68 (7.65–13.71) | 0.498 |
| wPCDAI | 7.5 (0–14.4) | 27.5 (10.0–47.5) | <0.001 |
| ESR (mm/h) | 20.62 (2.59–38.65) | 44.30 (14.19–74.40) | <0.001 |
| ALB (g/L) | 43.57 (39.50–47.64) | 37.53 (30.22–44.85) | <0.001 |
| GLO (g/L) | 30.04 (24.97–35.11) | 32.31 (27.18–37.44) | 0.017 |
| TBA (μmol/L) | 3.10 (2.55–5.95) | 3.95 (2.20–6.30) | 0.838 |
| TB (μmol/L) | 5.61 (1.45–9.78) | 4.21 (1.41–7.02) | 0.050 |
| DB (μmol/L) | 1.26 (0.20–2.32) | 1.14 (0.40–1.88) | 0.496 |
| IB (μmol/L) | 4.36 (1.03–7.70) | 3.08 (0.85–5.30) | 0.026 |
| ALT (U/L) | 13 (12–18) | 8 (6–13) | <0.001 |
| AST (U/L) | 23 (20–25) | 18 (14–22) | <0.001 |
| GGT (U/L) | 12.45 (7.34–17.56) | 14.22 (6.54–21.89) | 0.111 |
| ALP (U/L) | 209.93 (132.96–286.90) | 168.10 (91.16–245.04) | 0.036 |
| LDH (U/L) | 192.79 (156.42–229.16) | 174.01 (126.67–221.35) | 0.023 |
| Cr (μmol/L) | 40.50 (27.17–53.83) | 40.42 (27.37–53.46) | 0.972 |
| CK (U/L) | 108.00 (81.50–130.75) | 57.00 (34.00–84.00) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 0.92 (0.49–2.75) | 20.75 (2.46–49.46) | <0.001 |
| WBC (109/L) | 6.80 (5.70–8.48) | 8.85 (7.30–11.70) | <0.001 |
| PLT (109/L) | 331.71 (226.70–436.72) | 464.23 (321.25–607.20) | <0.001 |
| HCT (%) | 37.72 (33.80–41.64) | 35.44 (30.83–40.04) | 0.006 |
| Neutrophil (%) | 50.00 (41.25–64.25) | 62.00 (54.00–69.00) | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte (%) | 38.00 (25.25–44.50) | 25.00 (19.00–33.00) | <0.001 |
| Monocyte (%) | 6.00 (6.00–9.00) | 7.00 (6.00–10.00) | 0.009 |
| Eosinophil (%) | 2.00 (1.00–5.00) | 2.00 (1.00–4.00) | 0.518 |
| Basophil (%) | 0.00 (0.00–1.00) | 0.00 (0.00–1.00) | 0.173 |
Differences between small bowel MH and non-MH in pediatric CD patients.
Values are expressed as the mean ± SD or median (IQR). MH, mucosal healing; non-MH, non-mucosal healing; wPCDAI, weighted Pediatric Crohn’s Disease Activity Index; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; ALB, albumin; GLO, globulin; TBA, total bile acid; TB, total bilirubin; DB, direct bilirubin; IB, indirect bilirubin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; GGT, gamma-glutamyltransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; LDH, lactic dehydrogenase; Cr, creatinine; CK, creatine kinase; CRP, C-reactive protein; WBC, white blood cells; PLT, platelet; HCT, hematocrit.
Feature selection
The LASSO logistic regression algorithm was applied to select the most significant predictors. The 10-fold cross-validation method was applied to the iterative analysis, and a model with good performance but minimum number of variables was obtained when λ was 0.043 (Log λ = −3.15) (Figure 1). Among 26 clinical features analyzed in the LASSO logistic regression analysis, 6 features with non-zero coefficients were subsequently selected, including erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), albumin (ALB), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), C-reactive protein (CRP), platelet (PLT), and lymphocyte percentage. The results of multivariate logistic regression analysis of the above features are shown in Table 3.
FIGURE 1

Screening of variables based on LASSO regression. (A) The variation characteristics of the coefficient of variables; (B) the selection process of the optimum value of the parameter λ in the LASSO regression model by 10-fold cross-validation method.
TABLE 3
| Valuables | OR (95% CI) | P-value |
| ESR | 0.991 (0.962–1.017) | 0.516 |
| ALB | 1.068 (0.963–1.170) | 0.163 |
| AST | 1.071 (0.998–1.158) | 0.070 |
| CRP | 0.987 (0.959–1.007) | 0.261 |
| PLT | 0.994 (0.988–0.999) | 0.026 |
| Lymphocyte | 1.012 (0.966–1.060) | 0.623 |
Multivariate logistic regression model for the prediction of small bowel MH in pediatric CD.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; ALB, albumin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CRP, C-reactive protein; PLT, platelet.
Nomogram construction
Based on the β coefficients of the identified features in multivariate logistic regression model, the predicted rate of small bowel MH was calculated as Logit (P) = −2.5576–0.0093 × ESR (mm/h) + 0.0658 × ALB (g/L) + 0.0687 × AST (U/L) − 0.0132 × CRP (mg/L) − 0.0062 × PLT (109/L) + 0.0115 × Lymphocyte (%). For easier clinical application, we built a nomogram to predict the rate of small bowel MH (Figure 2). The total points were calculated by adding the score in each row of variables. The AUC of this predictive nomogram model was 0.855 (95% confidence interval, 0.783–0.926) (Figure 3), and confirmed to be 0.821 through 1,000 bootstrap resamples, indicating good accuracy. The calibration plot was presented to illustrate the agreement between the observed outcome and the predicted outcome (Figure 4). The calibration curve in this study showed notable agreement between the predicted small bowel MH probability and observed MH rate as both the bias-corrected curve and the apparent curve deviated only slightly from the reference line.
FIGURE 2
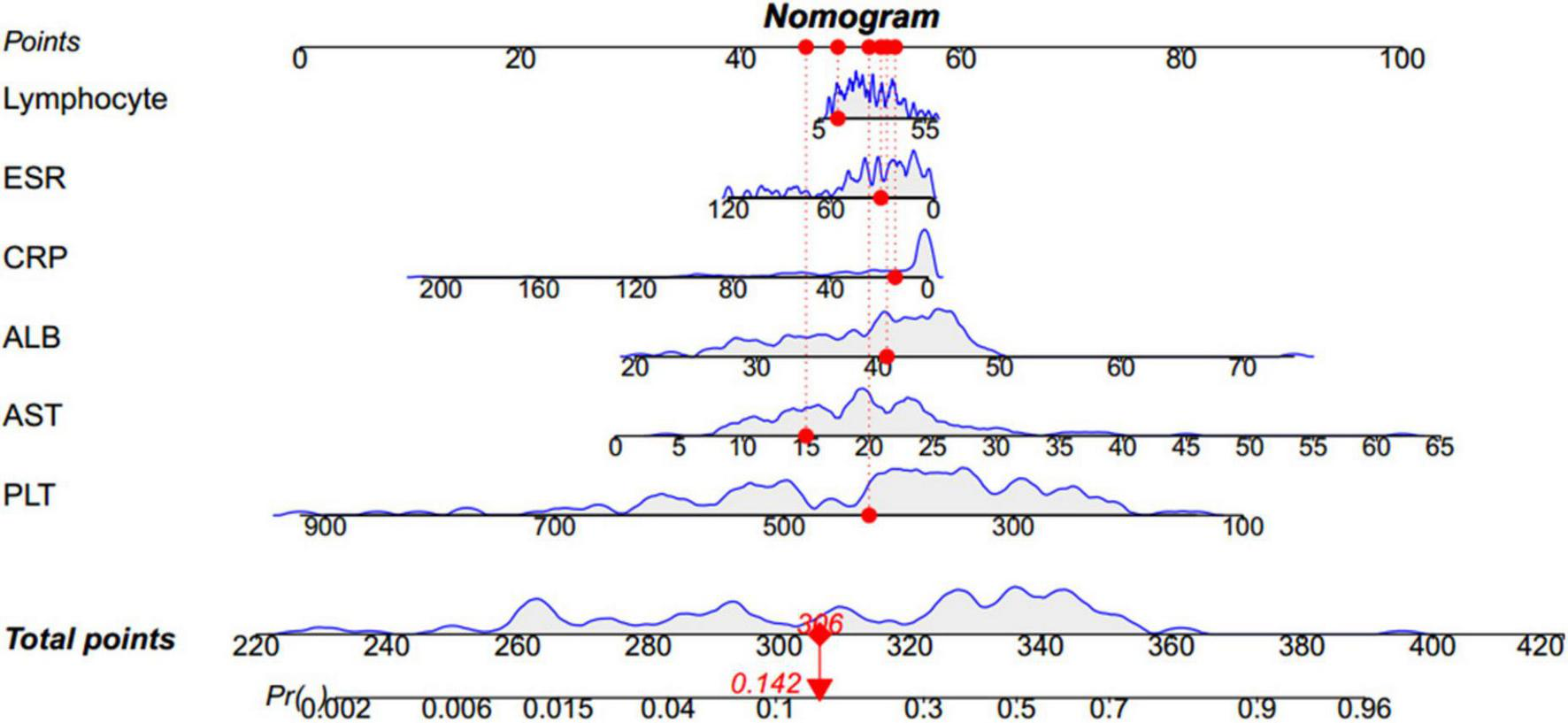
Nomogram to predict the rate of small bowel MH. For instance, for a child whose conditions are the following: 14% lymphocyte, 31 mm/h ESR, 13.43 mg/L CRP, 40.7 g/L ALB, 15 U/L AST, 426 × 109/L PLT, the nomogram provides a total score of 306 points and the probability of small bowel MH is 0.142, as shown in this figure. MH, mucosal healing; ESR, erythrocyte sedimentation rate; CRP, C-reactive protein; ALB, albumin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; PLT, platelet.
FIGURE 3
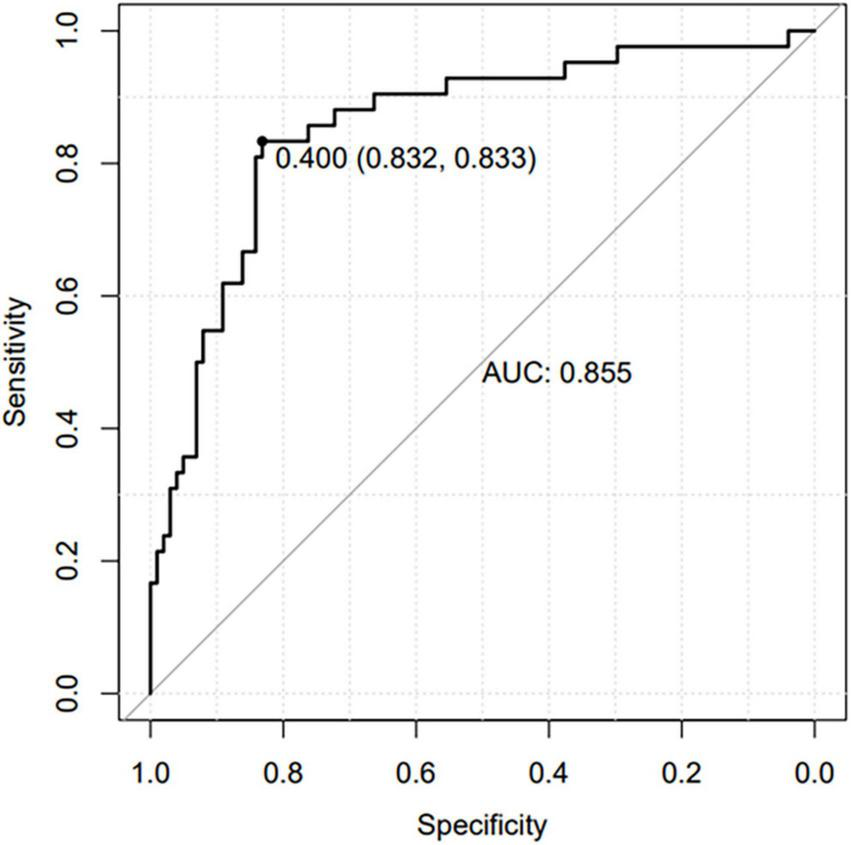
Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve of the nomogram prediction model.
FIGURE 4
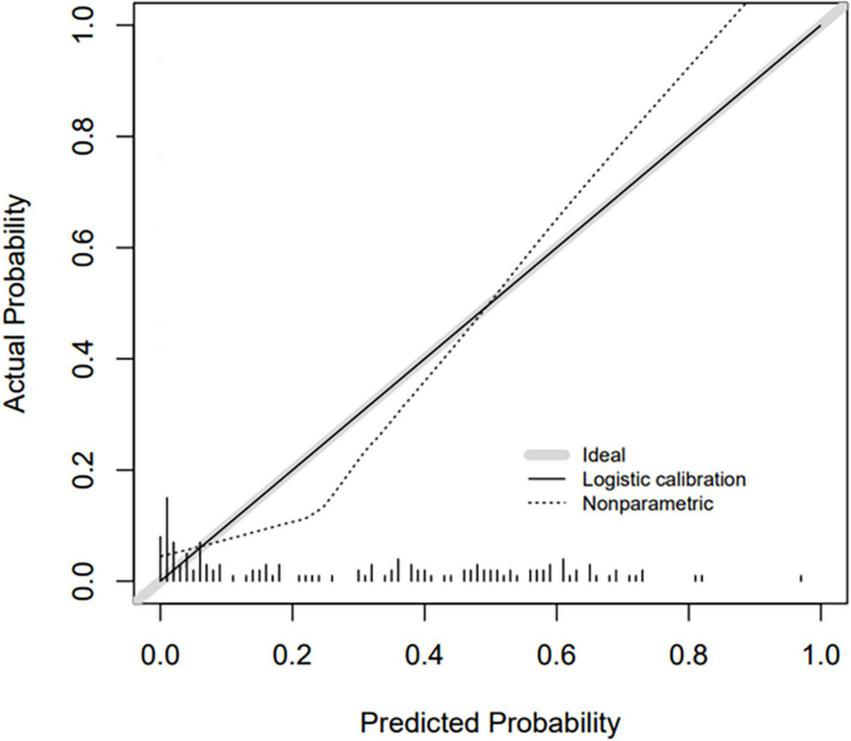
Calibration curve for nomogram prediction model.
Discussion
In this study, we identified ESR, ALB, AST, CRP, PLT, and lymphocyte percentage as the most significant predictors for small bowel mucosal inflammation and used these variables to construct a nomogram to predict small bowel MH in pediatric CD patients.
Simple serological parameters and clinical characteristics correlated with endoscopic findings are highly anticipated surrogates for monitoring disease activity. Some clinical and serological parameters, including Crohn’s Disease Activity Index (CDAI), CRP levels, ESR, ALB levels, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR), platelet to lymphocyte ratio (PLR), and CRP to ALB ratio (CAR), are reported associated with MH in patients with CD (25–27). The most widely recognized serological inflammation marker for monitoring disease activity in patients with CD is CRP (25, 26, 28). As an acute phase protein, serum CRP testing is widely available and relatively inexpensive to obtain. Increased CRP levels indicate mucosal inflammation and a probability of clinical relapse (29). However, elevated CRP levels might be related to other inflammatory disorders like infectious diseases. ESR testing is helpful to evaluate chronic and subacute inflammation and used as an aid to CRP. Hu et al. (25) found that the CD patients in endoscopic remission had significantly lower CRP, neutrophils, PLT, and higher hemoglobin (HB), lymphocytes, ALB than those with endoscopic activity. Huang et al. (30) reported agreement between the Simple Endoscopic Score for CD (SES-CD) scores and hs-CRP (r = 0.313, P < 0.001), ESR (r = 0.298, P = 0.001), white blood cells (WBCs) (r = 0.258, P = 0.005), fibrinogen (FIB) (r = 0.234, P = 0.013), plateletcrit (PCT) (r = 0.357, P < 0.001), and PLT (r = 0.303, P = 0.001). PLT is derived from bone marrow megakaryocytes and participates in wound repair and tissue regeneration. An increased PLT indicates an inflammatory activation state since PLTs release various bioactive inflammatory particles and express various inflammatory receptors under chronic inflammatory conditions (31, 32). Lymphocyte level was reported to decrease during the active period in pediatric patients with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) due to an increase in whole-blood lymphocyte apoptosis (33). On the other hand, a relative increase of neutrophil percentage contributed to the relative decrease of lymphocyte percentage. A retrospective study reported that the severity of endoscopic activity had a positive correlation with PLT (r = 0.458, P < 0.001) and a negative correlation with lymphocyte percentage (34). ALB, a negative acute phase reactant, decreased during intestinal inflammation, attributing to malnutrition and malabsorption (35). AST is a liver function biomarker and no study has explored the relationship between AST level and CD activity.
Numerous studies have investigated predictive models using non-invasive biomarkers for the assessment of MH in CD. In 2015, Minderhoud et al. (36) reported an index predicting endoscopic disease activity in patients with CD based on clinical and laboratory parameters. Recently, D’Haens (37) proposed a novel serum-based assay for mucosal inflammation in CD, the endoscopic healing index (EHI), which identified patients with resolved endoscopic disease activity with good overall accuracy. Nevertheless, most of them used ileocolonoscopy to determine the MH in CD, which cannot evaluate the entire small intestinal mucosa.
Mucosal healing in the small bowel and colon are not always synchronous. Takenaka et al. (38) evaluated the endoscopic healing of different site involvement among patients who received anti-TNF-α treatment in a post hoc analysis. They reported that small bowel and colonic endoscopic healing was achieved in 36% (41/114) and 79% (33/42) cases during maintenance therapy, with a significant difference (38). Studies comparing CD patients with and without small bowel involvement have reported CD patients with small bowel involvement were more serious than those with colonic involvement and needed more aggressive treatment (39–41). The incorporation of CE to assess MH in treat-to-target algorithms for CD when the small bowel is involved has been proposed, considering the higher incidence of intestinal complications in small bowel CD (15, 16).
A few studies have explored the relationship between simple biomarkers and small bowel MH evaluated by CE. Yang et al. (42) showed that the correlation between Lewis scores and CRP levels was moderate (r = 0.58, P < 0.01). He et al. (43) analyzed 150 patients with CD (including 30 children and adolescents) who underwent CE and reported weak correlations between the Lewis scores and CRP levels in pediatric patients (r = 0.379, P = 0.044). Mitselos et al. (44) reported that CDAI and CRP levels correlated with Lewis scores and the AUC toward endoscopic activity prediction was 0.70 and 0.69, respectively. However, most of the studies focused on adult CD. In our study, ESR, ALB, AST, CRP, PLT, and lymphocyte percentage were identified as important variables and utilized to construct a nomogram for predicting small bowel MH in pediatric CD, which may monitor response to the therapy and provide early warnings of relapse.
As far as we know, this is the first study to investigate the nomogram using serological parameters and clinical characteristics to distinguish between small bowel MH and non-MH in pediatric CD patients. The predictive model demonstrated superior performance, suggesting its high value in aiding clinical decision-making.
Notably, this study has a few limitations. Firstly, due to the retrospective approach, selection bias and missing data were inevitable. It is frustrating that not all patients had fecal calprotectin test and radiological imaging (computed tomography enterography and magnetic resonance enterography) at the time of CE examination because these tests were costly and inconvenient; therefore, the evaluation of these factors as predictors in our model was limited. Secondly, the amount of data used in this study was small and it is necessary to expand the amount of data used in order to improve the model’s learning ability and reduce its bias. Thirdly, we lacked external validation. In the future, prospective, multicenter validation using large-scale studies are needed to confirm these results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the model described in this study is feasible for differentiating between pediatric CD patients with small bowel MH and those with active lesions. Using readily available parameters, the model can provide early warnings for actionable feedback, which may improve the outcome of pediatric patients with CD in clinical settings.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethic committee of Guangzhou Women and Children’s Medical Center. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
BC: Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. HW: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. LR: Data curation, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. LX: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. YC: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. RL: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. MC: Data curation, Resources, Writing – review & editing. ZZ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. SG: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. PC: Methodology, Resources, Writing – review & editing. LG: Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This research work was supported by Guangzhou Science and Technology Project (Nos. 2023A04J1212 and 2023A03J0867).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Dolinger M Torres J Vermeire S . Crohn’s disease.Lancet. (2024) 403:1177–91. 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02586-2
2.
Dulai P Singh S Vande C Boland B Rivera-Nieves J Ernst P et al Should we divide crohn’s disease into ileum-dominant and isolated colonic diseases? Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 17:2634–43. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.04.040
3.
Yasukawa S Matsui T Yano Y Sato Y Takada Y Kishi M et al Crohn’s disease-specific mortality: A 30-year cohort study at a tertiary referral center in Japan. J Gastroenterol. (2019) 54:42–52. 10.1007/s00535-018-1482-y
4.
Benevento G Avellini C Terrosu G Geraci M Lodolo I Sorrentino D . Diagnosis and assessment of Crohn’s disease: The present and the future.Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2010) 4:757–66. 10.1586/egh.10.70
5.
Oliva S Thomson M de Ridder L Martin-de-Carpi J Van Biervliet S Braegger C et al Endoscopy in pediatric inflammatory bowel disease: A position paper on behalf of the porto IBD group of the European society for pediatric gastroenterology, hepatology and nutrition. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2018) 67:414–30. 10.1097/MPG.0000000000002092
6.
Cosnes J Gower-Rousseau C Seksik P Cortot A . Epidemiology and natural history of inflammatory bowel diseases.Gastroenterology. (2011) 140:1785–94. 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.055
7.
Oliva S Veraldi S Cucchiara S Russo G Spagnoli A Cohen S . Assessment of a new score for capsule endoscopy in pediatric Crohn’s disease (CE-CD).Endosc Int Open. (2021) 9:E1480–90. 10.1055/a-1522-8723
8.
Peyrin-Biroulet L Sandborn W Sands B Reinisch W Bemelman W Bryant R et al Selecting therapeutic targets in inflammatory Bowel disease (STRIDE): Determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target. Am J Gastroenterol. (2015) 110:1324–38. 10.1038/ajg.2015.233
9.
Turner D Ricciuto A Lewis A D’Amico F Dhaliwal J Griffiths A et al STRIDE-II: An update on the selecting therapeutic targets in inflammatory bowel disease (stride) initiative of the international organization for the study of IBD (IOIBD): Determining therapeutic goals for treat-to-target strategies in IBD. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:1570–83. 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.031
10.
Oliva S Aloi M Viola F Mallardo S Civitelli F Maccioni F et al A treat to target strategy using panenteric capsule endoscopy in pediatric patients with crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 17:2060–2067.e1. 10.1016/j.cgh.2018.10.015
11.
Baert F Moortgat L Van Assche G Caenepeel P Vergauwe P De Vos M et al Mucosal healing predicts sustained clinical remission in patients with early-stage Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterology. (2010) 138:e10–1. 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.09.056
12.
Neurath M Travis S . Mucosal healing in inflammatory bowel diseases: A systematic review.Gut. (2012) 61:1619–35. 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302830
13.
Oliva S Cohen S Di Nardo G Gualdi G Cucchiara S Casciani E . Capsule endoscopy in pediatrics: A 10-years journey.World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:16603–8. 10.3748/wjg.v20.i44.16603
14.
Levartovsky A Eliakim R . Video capsule endoscopy plays an important role in the management of Crohn’s disease.Diagnostics (Basel). (2023) 13:1507. 10.3390/diagnostics13081507
15.
Ben-Horin S Lahat A Amitai M Klang E Yablecovitch D Neuman S et al Assessment of small bowel mucosal healing by video capsule endoscopy for the prediction of short-term and long-term risk of Crohn’s disease flare: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 4:519–28. 10.1016/S2468-1253(19)30088-3
16.
Niv Y . Small-bowel mucosal healing assessment by capsule endoscopy as a predictor of long-term clinical remission in patients with Crohn’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2017) 29:844–8. 10.1097/MEG.0000000000000881
17.
Nishikawa T Nakamura M Yamamura T Maeda K Sawada T Mizutani Y et al Lewis score on capsule endoscopy can predict the prognosis in patients with small bowel lesions of Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 36:1851–8. 10.1111/jgh.15366
18.
Calabrese C Dussias N Impellizzeri G Lauro A Pagano N . CEing more-assessing small bowel Crohn’s with capsule endoscopy (CE).Dig Dis Sci. (2021) 66:2173–6. 10.1007/s10620-021-06966-8
19.
Pasha S Pennazio M Rondonotti E Wolf D Buras M Albert J et al Capsule retention in Crohn’s disease: A meta-analysis. Inflamm bowel dis. (2020) 26:33–42. 10.1093/ibd/izz083
20.
Sakurai T Omori T Tanaka H Ito T Ando K Yamamura T et al Multicenter prospective registration study of efficacy and safety of capsule endoscopy in Crohn’s disease in Japan (SPREAD-J study). J Gastroenterol. (2023) 58:1003–14. 10.1007/s00535-023-02017-3
21.
Levine A Koletzko S Turner D Escher J Cucchiara S de Ridder L et al ESPGHAN revised porto criteria for the diagnosis of inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. (2014) 58:795–806. 10.1097/MPG.0000000000000239
22.
Levine A Griffiths A Markowitz J Wilson D Turner D Russell R et al Pediatric modification of the Montreal classification for inflammatory bowel disease: The Paris classification. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2011) 17:1314–21. 10.1002/ibd.21493
23.
Turner D Griffiths A Walters T Seah T Markowitz J Pfefferkorn M et al Mathematical weighting of the pediatric Crohn’s disease activity index (PCDAI) and comparison with its other short versions. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2012) 18:55–62. 10.1002/ibd.21649
24.
Gralnek I Defranchis R Seidman E Leighton J Legnani P Lewis B . Development of a capsule endoscopy scoring index for small bowel mucosal inflammatory change.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2008) 27:146–54. 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2007.03556.x
25.
Hu X Li J Sun Y Wu D Zhao T Ma M et al Combined use of CDAI and blood indices for assessing endoscopic activity in ileocolic Crohn’s disease. BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:337. 10.1186/s12876-023-02968-0
26.
Tang N Chen H Chen R Tang W Zhang H . Combination of serological biomarkers and clinical features to predict mucosal healing in Crohn’s disease: A multicenter cohort study.BMC Gastroenterol. (2022) 22:229. 10.1186/s12876-022-02304-y
27.
Zhou F Gao N Sun X Jiang X Chen J Mao Q et al reactive protein/abumin ratio is a useful biomarker for predicting the mucosal healing in the Crohn disease: A retrospective study. Medicine (Baltimore). (2021) 100:e24925. 10.1097/MD.0000000000024925
28.
Mak L Tong T Cheung K Chen L Lui K Lau K et al Combined use of common fecal and blood markers for detection of endoscopically active inflammatory Bowel disease. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. (2020) 11:e00138. 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000138
29.
Jurgens M Mahachie J Cleynen I Schnitzler F Fidder H van Moerkercke W et al Levels of C-reactive protein are associated with response to infliximab therapy in patients with Crohn’s disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2011) 9:421–7.e1. 10.1016/j.cgh.2011.02.008
30.
Huang J Lu J Jiang F Song T . Platelet/Albumin ratio and plateletcrit levels are potential new biomarkers for assessing endoscopic inflammatory bowel disease severity.BMC Gastroenterol. (2023) 23:393. 10.1186/s12876-023-03043-4
31.
Voudoukis E Karmiris K Koutroubakis I . Multipotent role of platelets in inflammatory bowel diseases: A clinical approach.World J Gastroenterol. (2014) 20:3180–90. 10.3748/wjg.v20.i12.3180
32.
Danese S Motte C Fiocchi C . Platelets in inflammatory bowel disease: Clinical, pathogenic, and therapeutic implications.Am J Gastroenterol. (2004) 99:938–45. 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.04129.x
33.
El-Hodhod M Aly R Youssef S Mohamed S . Enhanced blood lymphocytes apoptosis in children with inflammatory bowel disease.ISRN Gastroenterol. (2013) 2013:415417. 10.1155/2013/415417
34.
Chen R Li L Chao K Hong M Cao Q Ye L et al Platelet-to-lymphocyte percentage ratio index: A simple non-invasive index to monitor the endoscopic activity in Crohn’s disease. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. (2020) 13:1756284820979442. 10.1177/1756284820979442
35.
Vermeire S Van Assche G Rutgeerts P . Laboratory markers in IBD: Useful, magic, or unnecessary toys?Gut. (2006) 55:426–31. 10.1136/gut.2005.069476
36.
Minderhoud I Steyerberg E van Bodegraven A van der Woude C Hommes D Dijkstra G et al Predicting endoscopic disease activity in crohn’s disease: A new and validated noninvasive disease activity index (The Utrecht Activity Index). Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2015) 21:2453–9. 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000507
37.
D’Haens G Kelly O Battat R Silverberg M Laharie D Louis E et al Development and validation of a test to monitor endoscopic activity in patients with crohn’s disease based on serum levels of proteins. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:515–526.e10. 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.034
38.
Takenaka K Fujii T Suzuki K Shimizu H Motobayashi M Hibiya S et al Small Bowel healing detected by endoscopy in patients with Crohn’s disease after treatment with antibodies against tumor necrosis factor. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 18:1545–52. 10.1016/j.cgh.2019.08.024
39.
Attard T Horton K DeVito K Darbari A Oliva-Hemker M Thompson R et al Pediatric jejunoileitis: A severe Crohn’s disease phenotype that requires intensive nutritional management. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2004) 10:357–60. 10.1097/00054725-200407000-00006
40.
Higuero T Merle C Thiefin G Coussinet S Jolly D Diebold M et al Jejunoileal Crohn’s disease: A case-control study. Gastroenterol Clin Biol. (2004) 28:160–6. 10.1016/s0399-8320(04)94871-3
41.
Du J Du H Chen H Shen L Zhang B Xu W et al Characteristics and prognosis of isolated small-bowel Crohn’s disease. Int J Colorectal Dis. (2020) 35:69–75. 10.1007/s00384-019-03432-w
42.
Yang L Ge Z Gao Y Li X Dai J Zhang Y et al Assessment of capsule endoscopy scoring index, clinical disease activity, and C-reactive protein in small bowel Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2013) 28:829–33. 10.1111/jgh.12146
43.
He C Zhang J Chen Z Feng X Luo Z Wan T et al Relationships of capsule endoscopy Lewis score with clinical disease activity indices, C-reactive protein, and small bowel transit time in pediatric and adult patients with small bowel Crohn’s disease. Medicine (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e7780. 10.1097/MD.0000000000007780
44.
Mitselos I Katsanos K Tatsioni A Skamnelos A Eliakim R Tsianos E et al Association of clinical and inflammatory markers with small bowel capsule endoscopy findings in Crohn’s disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2018) 30:861–7. 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001146
Summary
Keywords
Crohn’s disease, capsule endoscopy, mucosal healing, nomogram, prediction model
Citation
Chen B, Li H, Wang H, Ren L, Xiong L, Cheng Y, Li R, Cao M, Zeng Z, Gong S, Chen P and Geng L (2025) A nomogram for predicting small bowel mucosal healing in pediatric Crohn’s disease. Front. Med. 12:1582238. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1582238
Received
24 February 2025
Accepted
22 May 2025
Published
24 June 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Jan De Laffolie, University of Giessen, Germany
Reviewed by
Stefan Schumann, University Hospital Giessen, Germany
Shaoling Zheng, Guangdong Second Provincial General Hospital, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Chen, Li, Wang, Ren, Xiong, Cheng, Li, Cao, Zeng, Gong, Chen and Geng.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Bingxia Chen, 2589935838@qq.comPeiyu Chen, 2012690027@gzhmu.edu.cnLanlan Geng, genglan_2001@hotmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.