Abstract
Objective:
To investigate the relationship between the implantation position of dexamethasone intravitreal implant (DEX-I) and post-injection intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation.
Methods:
This retrospective study included 324 patients (332 eyes) who received at least one DEX-I injection between June 2020 and June 2024, with a follow-up period of at least 3 months. Patient demographics, diagnoses, and DEX-I implantation positions were recorded. The correlation between implantation position and post-injection IOP elevation was analyzed. IOP elevation was defined as an IOP greater than 25 mmHg and/or an increase of 10 mmHg from baseline. DEX-I implantation positions were defined as follows: P1: implant located in the vitreous near the ciliary body, anterior to the ora serrata (with or without ciliary body contact); P2: implant located in the vitreous from the ora serrata to the pre-equatorial region; P3: implant located in the post-equatorial vitreous. The equator was defined by the vortex veins.
Results:
During the follow-up period, 68 eyes (20.48%) experienced IOP elevation. Compared to P2 and P3, the P1 implantation position was significantly associated with a higher incidence of IOP elevation (p < 0.001) and was positively correlated with early IOP elevation (within 15 days post-injection) (r = 0.761; p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
The P1 implantation is positively correlated with IOP elevation, particularly with early IOP elevation.
1 Introduction
Intravitreal injection has emerged as a significant milestone in ophthalmic treatment over the past two decades, widely used for various retinal diseases. Dexamethasone intravitreal implant (DEX-I, trade name: Ozurdex; Allergan, Inc., Irvine, CA, United States) serves as an important therapeutic agent for diabetic macular edema (DME), macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion (RVO), and non-infectious uveitis. Its efficacy and safety have been validated by numerous clinical trials (1–4). However, DEX-I has been reported to increase the risk of intraocular pressure (IOP) elevation in both randomized controlled trials and real-world studies. The primary mechanism of corticosteroid-induced IOP elevation is the increased resistance to aqueous outflow through the trabecular meshwork. The reported incidence of IOP elevation following DEX-I injection ranges from 20 to 70% (2, 3, 5), with variability attributed to several factors, including the position of the implant.
Previous studies have suggested that implants in contact with the ciliary body are associated with a higher rate of glaucoma surgery compared to those positioned in the posterior segment (6–8). At present, there are very few studies on the relationship between DEX-I different positions and IOP in the world, especially the data of Chinese patients is still in a blank stage. This study further explores the relationship between DEX-I implantation position and IOP through retrospective analysis of large samples, helping clinicians to understand the key of increased intraocular pressure that may be caused by DEX-I position, so as to optimize surgical operations and improve the safety of patient treatment.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study population
This retrospective study included 324 patients (332 eyes) who received at least one DEX-I injection between June 2020 and June 2024, with a follow-up period of at least 3 months.
Inclusion Criteria: Patients who received at least one DEX-I injection, with a minimum of 3 months of follow-up records, and where the DEX-I implant remained in the same position for the duration of 3 months.
Exclusion Criteria: Aphakic eyes; eyes with incomplete posterior capsules or zonular fibers; a history of glaucoma or a family history of glaucoma; other causes of abnormal IOP; abnormal trabecular meshwork morphology or function; a history of steroid-induced IOP elevation or a family history; concurrent use of other ocular steroids; vitrectomized eyes; and high myopia (defined as spherical equivalent refraction >−6.00 D).
2.2 Methods
Data collected included complete medical history, age, gender, diagnosis, baseline and post-injection visual acuity, intraocular pressure (IOP: non-contact tonometer TOPCON CT-800), results from anterior and posterior segment examinations, and Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy (SLO: Optos P200DTX) combined with indirect ophthalmoscopy (Windsor SL4 4AA and/or Ocular Maxlight 90D) to confirm the position of the DEX-I implant. Follow-up records documented visits at 15 days, 1 month, 2 months, and 3 months post-injection.
DEX-I implantation positions were defined as follows: Position 1 (P1): implant located in the vitreous near the ciliary body, anterior to the ora serrata (with or without ciliary body contact). Position 2 (P2): implant located in the vitreous from the ora serrata to the pre-equatorial region.
Position 3 (P3): implant located in the post-equatorial vitreous. The equator is defined by the location of the vortex veins (Figure 1).
Figure 1

Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy (SLO) images showing different implantation positions. (P1) The white drug rod of DEX-I is situated in the anterior portion of the vitreous, adjacent to the ciliary body region. Due to its anterior location, the drug rod appears relatively large. (P2) The white drug rod ofDEX-I located in the vitreous from the ora serrata to the pre-equatorial region. (P3) The white drug rod of DEX-I is situated in the posterior vitreous of the inferotemporal region, appearing smaller due to its proximity to the retina.
Post-treatment IOP elevation was defined as an IOP ≥ 25 mmHg and/or an increase of ≥ 10 mmHg from baseline (9). Extensive research indicates that an IOP ≥ 25 mmHg and/or an increase of ≥ 10 mmHg is deemed a critical risk factor for rapid progression, necessitating aggressive management (9–13). IOP elevation was graded as mild (increase < 6 mmHg), moderate (increase of 6–15 mmHg), or severe (increase > 15 mmHg) (14). Early IOP elevation was defined as IOP elevation occurring within 15 days post-injection.
2.3 Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS version 25.0. Descriptive statistics included means, percentages, and variances. Parameter estimates were based on regression analysis, which provided model parameter estimates, standard errors, p-values, and 95% confidence intervals.
Univariate logistic regression analysis was employed to preliminarily screen factors potentially associated with IOP elevation, including gender, age, lens status, diagnosis, and implantation position. Subsequently, multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted to identify independent risk factors while controlling for confounding variables, thereby providing a more accurate assessment of the impact of implantation position on IOP elevation. Correlation coefficients (r) were calculated to determine the strength of associations between variables. Fisher’s exact test was utilized to compare differences between diagnostic groups, with a p-value < 0.05 considered statistically significant.
3 Results
3.1 Demographics
A total of 332 eyes (324 patients) met the inclusion criteria, with a mean age of 65.32 ± 7.87 years. The primary diagnoses included DME (185 eyes, 55.72%), RVO (117 eyes, 35.24%), uveitis (20 eyes, 6.02%), and other conditions, such as Irvine-Gass syndrome (10 eyes, 3.01%). The distribution of implantation positions was as follows: P1 (67 eyes, 20.18%), P2 (148 eyes, 44.58%), and P3 (117 eyes, 35.24%) (Table 1).
Table 1
| Baseline | DEX-I 0.7 mg (n = 332) |
|---|---|
| Age (years) | |
| Average age | 65.32 ± 7.87 |
| Gender | |
| Male | 191(57.53%) |
| Female | 141(42.47%) |
| Diabetes | 264(79.52%) |
| Hypertension | 251(75.6%) |
| Baseline IOP (mmHg) | 14.26 ± 2.85 |
| Clinical diagnosis | |
| DME | 185(55.72%) |
| RVO | 117(35.24%) |
| Uveitis | 20(6.02%) |
| Others | 10(3.01%) |
| Implantation position | |
| P1 | 67(20.18%) |
| P2 | 148(55.58%) |
| P3 | 117(35.24%) |
| Lens | |
| Pseudophakic | 191(57.53%) |
| Phakic | 141(42.47%) |
Baseline characteristics.
3.2 IOP elevation
The mean baseline IOP was 14.26 ± 2.85 mmHg. During the follow-up period, 68 eyes (20.48%) experienced IOP elevation, with a mean age of 64.63 ± 7.93 years. Among these, 51 eyes (75%) exhibited mild elevation, 11 eyes (16.18%) demonstrated moderate elevation, and 6 eyes (8.82%) presented with severe elevation. The most common time for IOP elevation occurred 2 months post-injection (60.41%). Of the eyes with IOP elevation, 50 (73.53%) required one IOP-lowering medication, 13 (19.12%) required two medications, 4 (5.88%) required three medications, and 1 (1.47%) required three medications in addition to selective laser trabeculoplasty (SLT). No cases required surgical intervention. All five cases that required three medications or SLT were in the P1 group.
Among the eyes with IOP elevation, 40 were in the P1 group (31 mild[77.5%], 4 moderate[10%], 5 severe[12.5%]), 10 in the P2 group (6 mild[60%], 4 moderate[40%]), and 18 in the P3 group (14 mild[77.78%], 3 moderate[16.67%], 1 severe[5.56%]) (Figure 2). Chi-square analysis showed no significant difference in the degree of IOP elevation among the different implantation positions (p = 0.495) (Table 2).
Figure 2
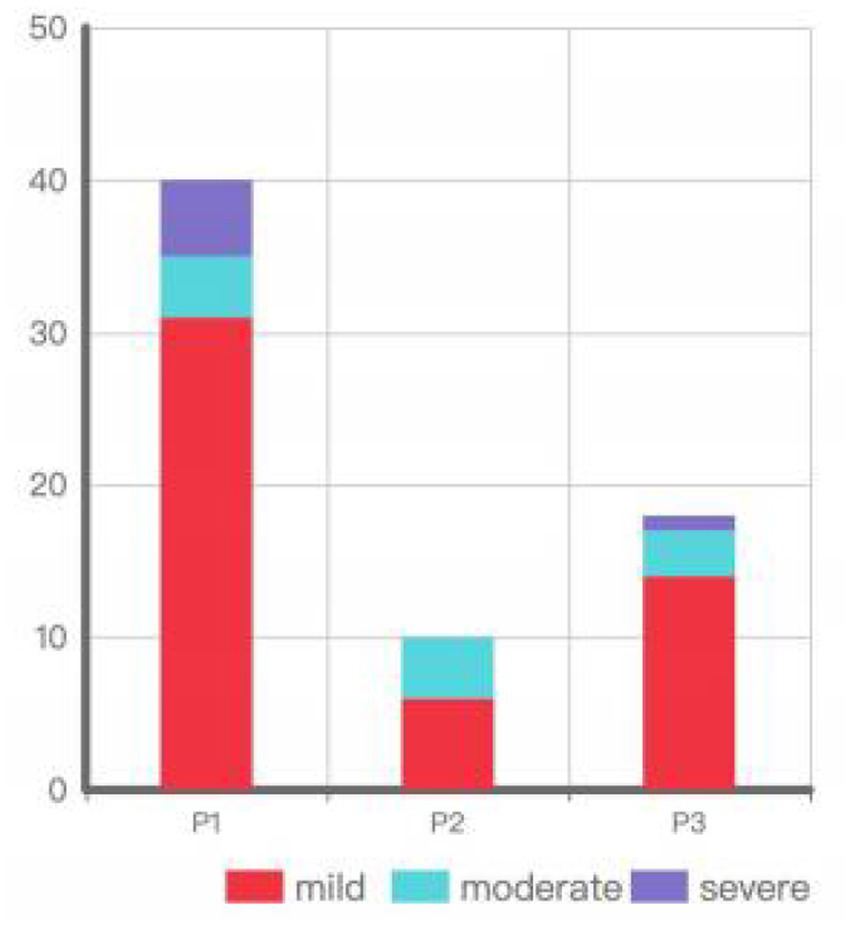
Degree of IOP elevation by implantation position.
Table 2
| Characteristics | P1 (n = 67) | P2 (n = 148) | P3 (n = 117) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Average age (years) | 63.76 ± 8.42 | 65.53 ± 7.95 | 65.94 ± 7.38 | 0.285 |
| Baseline IOP (mmHg) | 15.75 ± 3.36 | 13.97 ± 2.62 | 13.78 ± 2.53 | <0.001 |
| Gender | ||||
| Male (%) | 35 (52.24) | 60 (40.54) | 46 (39.32) | |
| Female (%) | 32 (47.76) | 88 (59.46) | 71 (60.68) | 0.123 |
| Diabetes (%) | 45 (67.16) | 143 (96.62) | 76 (64.96) | <0.001 |
| Hypertension (%) | 51 (76.12) | 108(72.97) | 92 (78.63) | 0.564 |
| Clinical diagnosis | <0.001 | |||
| DME | 32 (47.76) | 130 (87.84) | 23 (19.66) | |
| RVO | 31 (46.27) | 14 (9.46) | 72 (61.54) | |
| Uveitis | 4 (5.97) | 4 (2.70) | 12 (10.26) | |
| Others | 0 (0.00) | 0 (0.00) | 10 (8.55) | |
| Lens | 0.32 | |||
| Phakic | 30 (44.78) | 57 (38.51) | 54 (46.15) | |
| Pseudophakic | 37 (55.22) | 91 (61.49) | 63 (53.85) | |
Baseline characteristics by implantation position.
Statistical analysis revealed that male gender, the diagnosis of retinal vein occlusion (RVO), and P1 implantation were associated with IOP elevation (Table 3). Fisher’s exact test demonstrated that P1 implantation was significantly associated with IOP elevation compared to P2 and P3 (p < 0.001) (Table 4). Furthermore, early IOP elevation (within 15 days post-injection) was positively correlated with P1 implantation (r = 0.761; p < 0.001) (Table 5).
Table 3
| Variable | Correlation | P |
|---|---|---|
| Gender (male) | 0.213** | <0.001 |
| Uveit is | −0.003 | 0.956 |
| RVO | 0.235** | <0.001 |
| DME | −0.209** | <0.001 |
| P1 | 0.489** | <0.001 |
| P2 | −0.290** | <0.001 |
| P3 | −0.128 | 0.20 |
Correlation of different variables with IOP elevation.
**Indicates significant correlation.
Table 4
| Characteristics | Baseline characteristic | Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OR | 95% CI | P | Adjusted OR | 95% CI | P | |
| Age | ||||||
| >60 years | Ref | |||||
| < 60 years | 0.67 | 0.38 ~ 1.19 | 0.173 | 0.82 | 0.41 ~ 1.63 | 0.571 |
| Gender | ||||||
| Female | Ref | |||||
| Male | 2.91 | 1.68 ~ 5.06 | <0.001 | 3.28 | 1.69 ~ 6.36 | <0.001 |
| Lens | ||||||
| Phakic | Ref | |||||
| Pseudophakic | 0.68 | 0.4 ~ 1.16 | 0.16 | 0.67 | 0.35 ~ 1.29 | 0.66 |
| Clinical diagnosis | ||||||
| DME | Ref | |||||
| RVO | 3.35 | 1.89 ~ 5.97 | <0.001 | 3.97 | 2.11 ~ 7.47 | <0.001 |
| Uveitis | 1.68 | 0.52 ~ 5.44 | 0.389 | |||
| Others | 0.75 | 0.09 ~ 6.15 | 0.785 | |||
| Implantation position | ||||||
| P3 | Ref | |||||
| P1 | 8.71 | 4.29 ~ 17.71 | <0.001 | 7.46 | 3.96 ~ 14.05 | <0.001 |
| P2 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 1.05 | 0.066 | ||
Univariate and multivariate analysis of factors associated with IOP elevation.
Table 5
| Variable | Correlation coefficient | P |
|---|---|---|
| P1 | 0.761** | <0.001 |
| P2 | −0.193 | 0.115 |
| P3 | −0.525** | <0.001 |
Correlation of different positions with early IOP elevation.
**Indicates significant correlation.
4 Discussion
IOP elevation following DEX-I injection has been a major concern for clinicians. In this study, 68 eyes (20.48%) experienced IOP elevation during the follow-up period. The GENEVA study (13) reported a 15.4% incidence of IOP > 25 mmHg, peaking at 60 days post-injection, while the SAFODEX study (15) reported a 20% incidence of IOP elevation, consistent with our findings. Zarranz-Ventura et al. (16) (n = 82) and Mayer et al. (17) (n = 64) reported a higher incidence of IOP elevation (approximately 40%), possibly due to their smaller sample sizes, which could be more susceptible to extreme values or specific cases, potentially leading to an overestimation of IOP elevation rates. On the post hoc analyses of the global phase III clinical trials for DEX-I (2, 13), we observed that the incidence of IOP elevation during patient follow-up did not increase with the number of injections administered, suggesting that DEX-I does not exert a cumulative effect on IOP elevation, and the impact of each injection on IOP can be regarded as a relatively independent event. Our study, which includes a larger sample size and encompasses various retinal diseases, provides more representative data, offering a more accurate reflection of the true incidence of IOP elevation following DEX-I implantation.
The primary mechanism of DEX-I-induced IOP elevation involves alterations in the ultrastructure of the trabecular meshwork. Dexamethasone inhibits protease activity and cellular phagocytosis, upregulates glucocorticoid receptors in the trabecular meshwork, and induces structural changes in trabecular meshwork cells. These changes lead to increased extracellular matrix deposition and resistance to aqueous outflow (18–20). Previous studies have reported a higher incidence of glaucoma surgery in cases where steroids were implanted in the ciliary body region compared to the posterior segment (6–8). Aditya Sudhalkar et al. (21) also noted that DEX-I implantation in contact with the ciliary body region is more likely to result in IOP elevation. Our study found that P1 implantation (located in the vitreous near the ciliary body, anterior to the ora serrata, with or without ciliary body contact) was significantly associated with IOP elevation, particularly early IOP elevation, compared to P2 and P3. This association may be attributed to the higher concentration of steroids in the anterior segment and the specific area of the trabecular meshwork affected by the steroids. Although our study did not reveal a statistically significant difference in the degree of IOP elevation among the different implantation positions (p = 0.495), five of the six cases with severe IOP elevation were in the P1 group, suggesting that P1 implantation may increase the risk of severe IOP elevation. However, due to the limited sample size of cases with severe IOP elevation, the statistical power was insufficient to fully and accurately reflect the relationship between P1 implantation and severe IOP elevation.
In this study, male gender and the diagnosis of retinal vein occlusion (RVO) were associated with IOP elevation. RVO is a significant risk factor for open-angle glaucoma, and increasing evidence suggests a reciprocal relationship between the two conditions. Muhtaseb et al. (22) reported a notable incidence of open-angle glaucoma following RVO, potentially linked to factors such as optic disc characteristics, retinal nerve fiber layer thickness, and microvascular perfusion. Previous studies have identified type 1 diabetes as a risk factor for steroid-induced IOP elevation; however, due to the limited number of type 1 diabetes patients in our DME cohort (only 2 cases), we did not conduct a separate analysis of the relationship between diabetes type and IOP elevation.
This study has several limitations due to its retrospective design. Among the 148 cases of P2 implantation, 130 were DME. Most RVO implantation were distributed in P1 and P3, with very few in P2 implantation. To the best of our knowledge, no prior studies have reported an association between the positional distribution of DEX-I and specific ocular diseases. As this is a retrospective study, we cannot definitively determine whether the observed distribution is coincidental or statistically significant. The absence of a standardized treatment and follow-up protocol may have resulted in inconsistencies in data collection. Additionally, the limited documentation of IOP elevation timing prevented a comprehensive understanding of the dynamic processes involved in IOP changes, complicating the analysis of the relationship between implantation position and IOP fluctuations. Nevertheless, the large sample size strongly suggests that the position of DEX-I implantation is an independent risk factor for IOP elevation, with P1 implantation showing a positive correlation with IOP elevation, particularly in the early stages. These findings have significant implications for clinical practice. Ophthalmologists should take the patient’s ocular condition into account when administering DEX-I injections, and whenever possible, avoid P1 implantation. For patients who do receive P1 implantation, close monitoring of IOP—especially during the early post-injection period—is essential to promptly detect and manage any elevation in IOP, thereby preventing potential damage to visual function and enhancing treatment safety.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Dalian Third People’s Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because this study is a retrospective research. The research objectives are clear, and the waiver of informed consent will not have an adverse impact on the rights and health of the research participants. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
DL: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. XF: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. YZ: Methodology, Writing – original draft. LJ: Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YQ: Resources, Writing – review & editing. SL: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Lei S Lam W-C . Efficacy and safety of dexamethasone intravitreal implant for refractory macular edema in children. Can J Ophthalmol. (2015) 50:236–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2015.01.007
2.
Boyer DS Yoon YH Belfort R Bandello F Maturi RK Augustin AJ et al . Three-year,randomized, sham-controlled trial of dexamethasone intravitreal implant in patients with diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. (2014) 121:1904–14. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2014.04.024
3.
Blanc J Kodjikian L Bron A Creuzot-Garcher C . Response to safety and long-term efficacy of repeated dexamethasone intravitreal implant for the treatment of cystoid macular edema secondary to retinal vein occlusion with and without a switch to anti-VEGF agents: a 3-year experience. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. (2018) 256:2271. doi: 10.1007/s00417-018-4095-5
4.
Meyer LM Schonfeld C-L . Secondary glaucoma after intravitreal dexamethasone 0.7 Mg implant in patients with retinal vein occlusion: a one-year follow-up. J Ocul Pharmacol Ther. (2013) 29:560–5. doi: 10.1089/jop.2012.0253
5.
Rajesh B Zarranz-Ventura J Fung AT Busch C Sahoo NK Rodriguez-Valdes PJ et al . Safety of 6000 intravitreal dexamethasone implants. Br J Ophthalmol. (2020) 104:39–46. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2019-313991
6.
Yang Y Bailey C Loewenstein A Massin P . Intravitreal corticosteroids in diabetic macular edema: pharmacokinetic considerations. Retina. (2015) 35:2440–9. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000000726
7.
Campochiaro PA Brown DM Pearson A Ciulla T Boyer D Holz FG et al . Long-term benefit of sustained-delivery fluocinolone acetonide vitreous inserts for diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology. (2011) 118:626.e2–35.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2010.12.028
8.
Pearson PA Comstock TL Ip M Callanan D Morse LS Ashton P et al . Fluocinolone acetonide intravitreal implant for diabetic macular edema: a 3-year multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Ophthalmology. (2011) 118:1580–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.02.048
9.
Kiddee W Trope GE Sheng L Beltran-Agullo L Smith M Strungaru MH et al . Intraocular pressure monitoring post intravitreal steroids: a systematic review. Surv Ophthalmol. (2013) 58:291–310. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2012.08.003
10.
Chawla H Singh MD Vohra V . Clinical implications of energy used in neodymium: yttrium aluminum garnet posterior capsulotomy on intraocular pressure. Indian J Ophthalmol. (2021) 69:2717–20. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_3479_20
11.
Chin EK Almeida DRP Velez G Xu K Peraire M Corbella M et al . Ocular hypertension after intravitreal dexamethasone (OZURDEX) sustained-release implant. Retina. (2017) 37:1345–51. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001364
12.
Haller JA Kuppermann BD Blumenkranz MS Williams GA Weinberg DV Chou C et al . Randomized controlled trial of an intravitreous dexamethasone drug delivery system in patients with diabetic macular edema. Arch Ophthalmol. (2010) 128:289–96. doi: 10.1001/archophthalmol.2010.21
13.
Haller JA Bandello F Belfort R Blumenkranz MS Gillies M Heier J et al . Dexamethasone intravitreal implant in patients with macular edema related to branch or central retinal vein occlusion twelve-month study results. Ophthalmology. (2011) 118:2453–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2011.05.014
14.
Patel PD Kodati B Clark AF . Role of glucocorticoids and glucocorticoid receptors in Glaucoma pathogenesis. Cells. (2023) 12:2452. doi: 10.3390/cells12202452
15.
Malclès A Dot C Voirin N Vié A-L Agard É Bellocq D et al . Safety of intravitreal dexamethasone implant (Ozurdex): the SAFODEX study. Incidence and risk factors of ocular hypertension. Retina. (2017) 37:1352–9. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001369
16.
Zarranz-Ventura J Carreno E Johnston RL Mohammed Q Ross AH Barker C et al . Multicenter study of intravitreal dexamethasone implant in noninfectious uveitis: indications, outcomes, and reinjection frequency. Am J Ophthalmol. (2014) 158:1136–1145.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2014.09.003
17.
Mayer WJ Wolf A Kernt M Kook D Kampik A Ulbig M et al . Twelve-month experience with Ozurdex for the treatment of macular edema associated with retinal vein occlusion. Eye. (2013) 27:816–22. doi: 10.1038/eye.2013.79
18.
Zhang X Clark AF Yorio T . FK 506-binding protein 51 regulates nuclear transport of the glucocorticoid receptor beta and glucocorticoid responsiveness. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. (2008) 49:1037–47. doi: 10.1167/iovs.07-1279
19.
Wordinger RJ Clark AF . Effects of glucocorticoids on the trabecular meshwork: towards a better understanding of glaucoma. Prog Retin Eye Res. (1999) 18:629–67. doi: 10.1016/S1350-9462(98)00035-4
20.
Johnson D Gottanka J Flügel C Hoffmann F Futa R Lütjen-Drecoll E . Ultrastructural changes in the trabecular meshwork of human eyes treated with corticosteroids. Arch Ophthalmol. (1997) 115:375–83.
21.
Sudhalkar A Kodjikian L Chhablani J Bhojwani D Vasavada A . Intraocular dexamethasone implant position in situ and ocular hypertension. Retina. (2018) 38:2343–9. doi: 10.1097/IAE.0000000000001883
22.
Muhtaseb RE Huther A Alwreikat AM Ramsey DJ . Optimizing open-angle glaucoma risk assessment in patients with retinal vein occlusions. Eye. (2024) 38:2985–91. doi: 10.1038/s41433-024-03205-y
Summary
Keywords
dexamethasone intravitreal implant, implantation position, intraocular pressure elevation, DEX-i, IOP
Citation
Liu D, Chen Y, Fu X, Zhao Y, Ji L, Qiu Y and Li S (2025) The relationship between the intraocular position of dexamethasone intravitreal implant and post-injection intraocular pressure elevation. Front. Med. 12:1582422. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1582422
Received
24 February 2025
Accepted
28 August 2025
Published
08 September 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Poemen P. Chan, The Chinese University of Hong Kong, China
Reviewed by
Aharon Wegner, Technical University of Munich, Germany
Livio Vitiello, "Luigi Curto" Hospital, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Liu, Chen, Fu, Zhao, Ji, Qiu and Li.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Sheng Li, leoonnet@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.