Abstract
Background:
To establish a noninvasive mortality risk prediction model for sepsis secondary to pneumonia (SSP) and validate the model in the prediction of mortality risk in SSP patients at hospital admission.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort of SSP patients were recruited from January 2017 to December 2020 at the Henan Provincial People’s Hospital. Clinical data were collected at admission. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator and logistic regression were used to construct a prognosis prediction model. The predictive performance of the model was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Another retrospective cohort with SSP was recruited from January 2021 to July 2022 at the same hospital to validate the model.
Results:
A total of 1,337 patients were screened, including 941 patients in the derivation cohort and 396 patients in the validation cohort. The model included age, white blood cell count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, lactate dehydrogenase, arterial oxygen pressure / fraction inspired oxygen, D-dimer and vasoactive drug use. The area under ROC curve of derivation model was better than sequential organ failure assessment score and APACHE II score (0.777 vs. 0.600 vs. 0.625, p < 0.05). Besides, the proposed model had a significantly higher prediction performance than SOFA and APACHE II scores in the validation cohort (0.803 vs. 0.655 vs. 0.688, p < 0.05). The prediction model was publicly released as an online calculator.
Conclusion:
A prognosis model based on variables of SSP patients at hospital admission was developed.
Introduction
Pneumonia is responsible for great mortality and high costs. The World Health Organization reports around 2.5 million population died of lower respiratory infection mainly caused by pneumonia, making it the fourth cause of death globally and also the most deadly infectious disease (1). According to the China Public Health Statistical Yearbook 2019, the prevalence rate of pneumonia is 1.1‰ in 2008 and 0.6‰ in 2013, while the mortality rate is 17.46 and 15.09 per 100 thousand in 2012 and 2018, respectively (2). Sepsis is the organ dysfunction with a high mortality rate due to dysregulated inflammatory response in the host (3). In 2017, there were roughly 4.89 million sepsis patients around the globe, 1.10 million of whom died of sepsis, accounting for 19.7% of global death (4). In China, one fifth sepsis patients are admitted into ICU with a 90-day mortality rate of 35.5%, and the leading cause of sepsis is pneumonia (5). Sepsis secondary to pneumonia (SSP) is characterized by the lack of specific clinical manifestations during the early stage, but it progresses rapidly with poor prognosis. Therefore, early prediction of SSP mortality risk helps to correctly identify high-risk patients and timely adjust treatments, which may be crucial for improving the patients’ outcomes and survival rate.
Sepsis has complex pathogenetic mechanisms involving multiple systems including systemic inflammatory response, oxidative stress, coagulation system and immune system (6). Thus combined detection may be useful for improving the predictive accuracy. Several scoring systems have been proposed for prognosis assessment of pneumonia and sepsis, but the sensitivity and specificity are not consistent in published studies (7–11). Sequential organ failure assessment (SOFA) was proposed by European Society of Intensive Care Medicine in 1994 (12). According to the publication of Sepsis 3, organ dysfunction can be represented by an increase in the SOFA score of 2 points or more, which is associated with an in-hospital mortality. Pawar et al. (13) found that the predict mortality of SOFA score is different substantially based on infection type location. Besides, the SOFA score, taking no account comorbidities, age and physiologic status, performed lower than the other score (14). The score of CURB-65 including confusion, urea, respiratory rate, blood pressure, age ≥ 65 years is not effective for hospitalized patients mortality predication (15). Kolditz et al. (16) found that CURB-65 score is poor for identifying severe community acquired pneumonia (CAP) patients. It might because that the CURB-65 does not incorporate hypoxaemia and bilateral pneumonia in their scores (17). Similarly limitation also exists in APACHEII score that it consists of 20 variables, which are usually unavailable within 24 h after admission to hospital. So Ferrer reported that PSI, CURB-65 or acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II (APACHE II) score does not identify the severe CAP patients with a relatively high mortality risk (18). This study aims to identify the risk factors related to 28-day mortality in SSP patients and to develop and validate a multi-parameter combined prediction model.
Methods
Data collection and management
In this retrospective, single-center study, we collected data from 1,337 SSP patients admitted into respiratory ICU between January 2017 and June 2022. The patients were divided into model derivation cohort (January 2017 to December 2020) and validation cohort (January 2021 to June 2022). In this study, we defined study outcome as 28-day death and divided the patients into either survival group or death group. This study was approved by the Henan Provincial People’s Hospital Ethics Committee. Written informed consent was waived due to the retrospective use of patients’ data.
CAP and hospital acquired pneumonia (HAP) were diagnosed according to the guidelines jointly published by Infectious Diseases society of America and America Thoracic Society in 2019 and in 2016, respectively (19, 20). CAP was diagnosed if the patient had pulmonary infiltrates on chest imaging examination and presented one of the following clinical presentations: (1) cough, expectoration, (2) fever, (3) white blood cell count > 10 × 109/L or < 4 × 109/L, or (4) physical examination indicating pulmonary consolidation signs. HAP was diagnosed if the patient had new or progressive pulmonary infiltrates 48 h after admission and one of the following infectious manifestations: (1) fever, (2) purulent sputum, or (3) elevated white blood cell count. Sepsis was diagnosed if infection and sepsis-related SOFA score ≥ 2 according to The Third International Consensus Definitions for Sepsis and Septic Shock (Sepsis-3) published in 2016 (3).
All data were evaluated, extracted and cross-validated by a group of experienced respiratory physicians. Each recording was independently checked by two physicians. We included all the patients with the required clinical data (laboratory tests, clinical symptoms and signs, severity assessment and discharge information) during hospitalization. The patients were followed up for 28 days.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) age ≥ 18 years, (2) the patient was diagnosed with both pneumonia and sepsis, and (3) the patient had all the required clinical data.
Exclusion criteria: (1) age < 18 years, (2) history of malignant tumor in the past 5 years, (3) human immunodeficiency virus infection, (4) any connective tissue disease such as rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus or vasculitis, (5) drug therapy with hormone, immunosuppressor or immunoregulation drug in the past 3 months, (6) organ transplantation, (7) in-hospital death within 24 h of admission; and (8) the patient having incomplete clinical data.
Potential predictive variables
The following characteristics at hospital admission were included as potential predictive variables: demographic data, medical history, physical signs and laboratory tests. Demographic data included age, sex, history of smoking, and history of drinking. Medical history included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes mellitus, hypertension, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease and so on. Physical signs and symptoms included body temperature, respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure and state of consciousness. Laboratory tests included white blood cell count, neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, platelet count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), hemoglobin, C-reactive protein (CRP), procalcitonin (PCT), lactic dehydrogenase, aspartate transaminase, alanine transaminase, total bilirubin, creatine kinase, creatinine, urea, total protein, albumin, blood sodium, blood potassium, D-dimer, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastin time, fibrinogen, fasting blood-glucose level, lactic acid and arterial blood gas test.
Variable selection
The SSP patients in derivation cohort were used for variable selection and risk prediction model derivation. If the amount of missing values was less than 20%, the missing continuous values were replaced with median imputation technique. A total of 44 variables were finally selected. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression was utilized to minimize the potential collinearity and overfitting of variables within a patient via the glmnet package in R software. Then, the variables selected from the LASSO regression were included in a logistic regression model, after which the statistically significant variables were used for constructing a mortality risk prediction model and for building a web-based risk calculator.
Model derivation, external validation and evaluation of different models
The predictive performance of the proposed model was evaluated with ROC curve and calibration curve, and internally validated with reinforced bootstrap method. To evaluate the generalizability of the SSP risk prediction model, the patients admitted between January 2021 and June 2022 were used for external validation. The predictive performance of the proposed model in validation cohort was evaluated using discrimination and calibration.
The area under ROC curve (AUC) was utilized to compare the accuracy of our proposed model with those of SOFA and APACHE II.
Statistical analysis
Categorical variables were shown as number and percentage (%) and compared using chi-squared test between groups. Normally distributed data were shown as mean ± standard and compared using t test between groups. Non-normally distributed data were shown as median (interquartile range) and compared using Mann–Whitney U test between groups. All statistical analyses were performed using R 3.6.2 (R Foundation) and SPSS 23.0 software (IBM). Statistical significance was defined as a p value < 0.05.
Results
Study population characteristics
A total of 941 patients were included in the derivation cohort after excluding 1,138 pneumonia patients, with age younger than 16 years, complicated by tumor or connective tissue disease and lost to follow-up (Figure 1). The eligible patients had a median age of 71 years and were mainly male (n = 676, 71.8%). Mortality occurred in 461 (49.0%) patients. Most patients (89.0%) had at least one comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease (n = 651, 69.2%), cerebrovascular disease (n = 381, 40.5%) and diabetes (n = 231, 24.5%) (Table 1).
Figure 1

Patient flowchart of derivation and validation cohorts.
Table 1
| Variables | Derivation cohort (n = 941) | Validation cohort (n = 396) |
|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 71 (60–81) | 70 (59–79) |
| Sex, n (%) | ||
| Male | 676 (71.8%) | 292 (73.7%) |
| Female | 265 (28.2%) | 104 (26.3%) |
| Smoke | 443 (47.1%) | 178 (44.9%) |
| Drink | 316 (33.6%) | 125 (31.6) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 651 (69.2%) | 225 (56.8%) |
| Cerebrovascular disease | 381 (40.5%) | 173 (43.7%) |
| Diabetes | 231 (24.5%) | 117 (29.5%) |
| SOFA score | 6 (4, 8) | 6 (4, 8) |
| APACHE II score | 18 (13, 22) | 17 (12, 23) |
| Respiratory rate, cycles/min | 23 (20, 29) | 22 (20, 28.8) |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 122 (103.5, 142) | 120 (103, 145) |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 70 (60, 81) | 68 (60, 78) |
| P/F, mm Hg | 187.8 (131, 247.2) | 203.0 (141.1, 272.6) |
| WBC count, ×109/L | 11.2 (7.5, 15.3) | 11.5 (8.3, 16.5) |
| LYM count, ×109/L | 0.8 (0.5, 1.3) | 0.7 (0.5, 1.1) |
| N/L | 10.1 (6.1, 19.8) | 13.7 (7.7, 24.0) |
| HgB, g/L | 104 (87, 123) | 106 (90, 120) |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 188 (125.5, 267) | 186 (123.2, 272.8) |
| TP, g/l | 56.2 (51, 61.1) | 56 (51.3, 60.1) |
| ALB, g/l | 29.2 (26.2, 32.2) | 30.2 (27.4, 33.6) |
| LDH, U/L | 341 (245, 515.5) | 321 (241.5, 466.2) |
| CRE, μmol/L | 61 (45, 93) | 63.5 (42, 108) |
| BUN, mmol/L | 9 (6, 14.2) | 10.0 (6.3, 15.1) |
| CRP, mg/L | 98.8 (46.1, 163.2) | 92.0 (42.3, 147.8) |
| PCT | 0.8 (0.2, 3.4) | 0.8 (0.2, 3.2) |
| Glu, mmol/L | 7.1 (5,5, 9.7) | 7.7 (6.3, 9.7) |
| D-dimmer, μg/mL | 2.8 (1.5, 5.4) | 3.1 (3.5, 6.5) |
| Lac, mmol/L | 1.6 (1.2, 2.1) | 1.6 (1.2, 2.2) |
| VD | 403 (42.8%) | 166 (42.0%) |
Baseline characteristics of the two cohort.
P/F, PaO2/FiO2; WBC, white blood cell; LYM, lymphocyte; N/L, Neutrophils/lymphocyte; HgB, hemoglobin; TP, total protein; ALB, albumin; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; CRE, creatinine; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Glu, glucose,; Lac, lactate; VD, vasoactive drug.
Validation cohort included 396 patients (Figure 1). The eligible patients had a median age of 70 years and were mainly male (n = 292, 73.7%). Mortality occurred in 179 (45.2%) patients. Over half of the patients (57.1%) had at least one comorbidities, including cardiovascular disease (n = 225, 56.8%), cerebrovascular disease (n = 173, 43.7%) and diabetes (n = 117, 29.5%). The death group had a higher occurrence of septic shock (death group vs. survival group: 64.1% vs. 22.8%, p < 0.001) and a lower arterial oxygen pressure / fraction inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) death group vs. survival group: 173.7 mm Hg (116.4–235.1) vs. 207 mm Hg (155.7–267.3), p < 0.001 (Table 2). Pathogens were detected in 651 patients, with gram-negative bacilli accounting for 49.43%, gram-positive cocci accounting for 11.49%, and fungi accounting for 13.79%.
Table 2
| Variables | Death | p value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| No (n = 697) | Yes (n = 640) | ||
| Age, years | 68 (56, 78) | 74 (64, 82) | < 0.0001 |
| Sex, n (%) | |||
| Male | 504 (72.3%) | 464 (72.5%) | 0.006 |
| Female | 193 (27.7%) | 176 (27.5%) | |
| Smoke | 307 (44.0%) | 314 (49.1%) | 0.066 |
| Drink | 234 (33.6%) | 207 (32.3) | 0.633 |
| SOFA score | 5 (3, 7) | 7 (4, 9) | < 0.0001 |
| APACHE II score | 16 (11, 21) | 19 (15, 24) | < 0.0001 |
| Respiratory rate, cycles/min | 23 (20, 29) | 23 (20, 28) | 0.302 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 118 (100, 148.5) | 123 (107, 138.7) | 0.086 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mm Hg | 69 (58, 80.5) | 70 (61, 80) | 0.169 |
| P/F, mm Hg | 207 (155.7, 267.3) | 173.7 (116.4, 235.1) | < 0.0001 |
| WBC count, ×109/L | 10.2 (7.0, 13.8) | 12.6 (8.8, 17.4) | < 0.0001 |
| LYM count, ×109/L | 0.83 (0.6, 1.2) | 0.7 (0.4, 1.1) | < 0.0001 |
| N/L | 9.3 (5.6–17.2) | 14.3 (7.6–24.6) | < 0.0001 |
| HgB, g/L | 105 (88, 121.5) | 105 (89, 123) | 0.492 |
| Platelet count, ×109/L | 201 (136.5, 287) | 177 (113, 251.8) | < 0.0001 |
| TP, g/L | 56.3 (51.8, 61.0) | 56.0 (50.2, 60.6) | 0.111 |
| ALB, g/L | 29.9 (27.2, 33.1) | 28.8 (25.8, 32.2) | < 0.0001 |
| LDH, U/L | 298.5 (234, 424.8) | 387 (268, 573) | < 0.0001 |
| CRE, μmol/L | 56 (41, 82.5) | 67 (48, 114) | < 0.0001 |
| BUN, mmol/L | 8.2 (5.5, 12.6) | 10.9 (7.0, 17.9) | < 0.0001 |
| CRP, mg/L | 84.9 (40.9, 140.1) | 107.1 (48.0, 172.8) | < 0.0001 |
| PCT | 0.6 (0.2, 2.1) | 1.2 (0.3, 4.9) | < 0.0001 |
| Glu, mmol/L | 7.1 (5.8, 9.5) | 7.3 (5.7, 9.8) | 0.685 |
| D-dimmer, μg/mL | 2.4 (1.3, 4.8) | 3.4 (1.7, 7.1) | < 0.0001 |
| Lac, mmol/L | 1.4 (1.1, 1.9) | 1.8 (1.4, 2.4) | < 0.0001 |
| VD | 159 (22.8%) | 410 (64.1%) | < 0.0001 |
Clinical characteristics according to prognosis in the two cohorts.
Selection of predictive variables
The LASSO regression indicated 7 variables independently related to the SSP prognosis, including age, white blood cell count, NLR, lactic dehydrogenase, PaO2/FiO2, D-dimer and vasoactive drug use (Table 3). The prediction model was publicly available as an online calculator1 (Figure 2).
Table 3
| Characteristic | OR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | |||
| 1 (≤ 45) | 1 (ref) | – | |
| 2 (46–54) | 0.79 | 0.39, 1.61 | 0.5 |
| 3 (55–64) | 1.11 | 0.58, 2.13 | 0.8 |
| 4 (≥ 65) | 1.75 | 1.01, 3.10 | 0.048 |
| WBC (× 109 / L) | |||
| 1 (3.5–9.5) | 1 (ref) | – | |
| 2 (≤ 3.5) | 1.71 | 0.76, 3.87 | 0.2 |
| 3 (≥ 9.5) | 1.50 | 1.08, 2.07 | 0.015 |
| NLR | 1.01 | 1.00, 1.02 | 0.006 |
| LDH | 1.77 | 1.25, 2.53 | 0.002 |
| P/F (mmHg) | |||
| 1 (≤ 400) | 1 (ref) | – | |
| 2 (≤ 300) | 0.97 | 0.59, 1.59 | 0.9 |
| 3 (≤ 200) | 1.32 | 0.82, 2.15 | 0.3 |
| 4 (≤ 100) | 2.15 | 1.21, 3.86 | 0.010 |
| D-dimmer | 1.03 | 1.01, 1.06 | 0.008 |
| VD (yes or no) | 4.64 | 3.45, 6.26 | < 0.001 |
Lasso regression analysis of 28-day mortality in the derivation cohort.
Figure 2

The web-based calculator of the prediction model. The doctors are asked to put integers to the web-based calculator as following: the patient’s age (1: < 45 years; 2: 45–54 years; 3: 55–64 years; 4: > 65 years), PaO2/FiO2 (mmHg 1: < 400; 2: < 300; 3 < 200; 4: < 100), white blood cell count (1: 3.5–9.5 × 109 / L; 2: < 3.5 × 109 / L; 3: ≥ 9.5 × 109 / L) and lactic dehydrogenase level (0; < 250 U / L; 1: > 250 U / L).
Performance evaluation of the proposed model
The prediction model showed an AUC of 0.777 and 0.803 in the derivation cohort and validation cohort, respectively, indicating a good discrimination power of the model (Figure 3).
Figure 3

ROC curves for the prediction model. (A) The area under the curve of the prediction model in the derivation cohort is 0.777. (B) The area under the curve of the prediction model in the validation cohort is 0.803. The Bier score of the model was 0.197 in internal validation and 0.179 in external validation.
The Bier score of the model was 0.197 in internal validation and 0.179 in external validation. Moreover, the prediction model showed a high overlap between calibration curve and ideal curve in internal validation and external validation, indicating the high calibration of the proposed model (Figure 4).
Figure 4

Calibration plot of the prediction model. (A) derivation population, (B) internal validation, (C) external validation populations. In panels A and C, the solid diagonal line represents the ideal calibration and the dotted line is the calibration line of the prediction model. In panel B, dashed diagonal line represents the ideal calibration, straight line represents the bias-corrected calibration line of the prediction model, and dotted line represents the apparent calibration line of the prediction model.
Comparison of accuracies between models
The median SOFA score was not significantly different between death group and survival group in the derivation cohort (6 (4, 9) vs. 5 (3, 7)) or the validation cohort (5 (5, 10) vs. 5 (3, 7)). The APACHE II score in the death group vs. survival group was 19 (15, 24) vs. 17 (11, 21) in the derivation cohort and 20 (15, 25) vs. 14 (10, 20) in the validation cohort. The proposed model had a significantly higher prediction performance than SOFA and APACHE II scores in the derivation cohort (AUCs: 0.777 vs. 0.600 vs. 0.625, p < 0.05). Besides, the proposed model had a significantly higher prediction performance than SOFA and APACHE II scores in the validation cohort (AUCs: 0.803 vs. 0.655 vs. 0.688, p < 0.05) (Figure 5, Table 4).
Figure 5
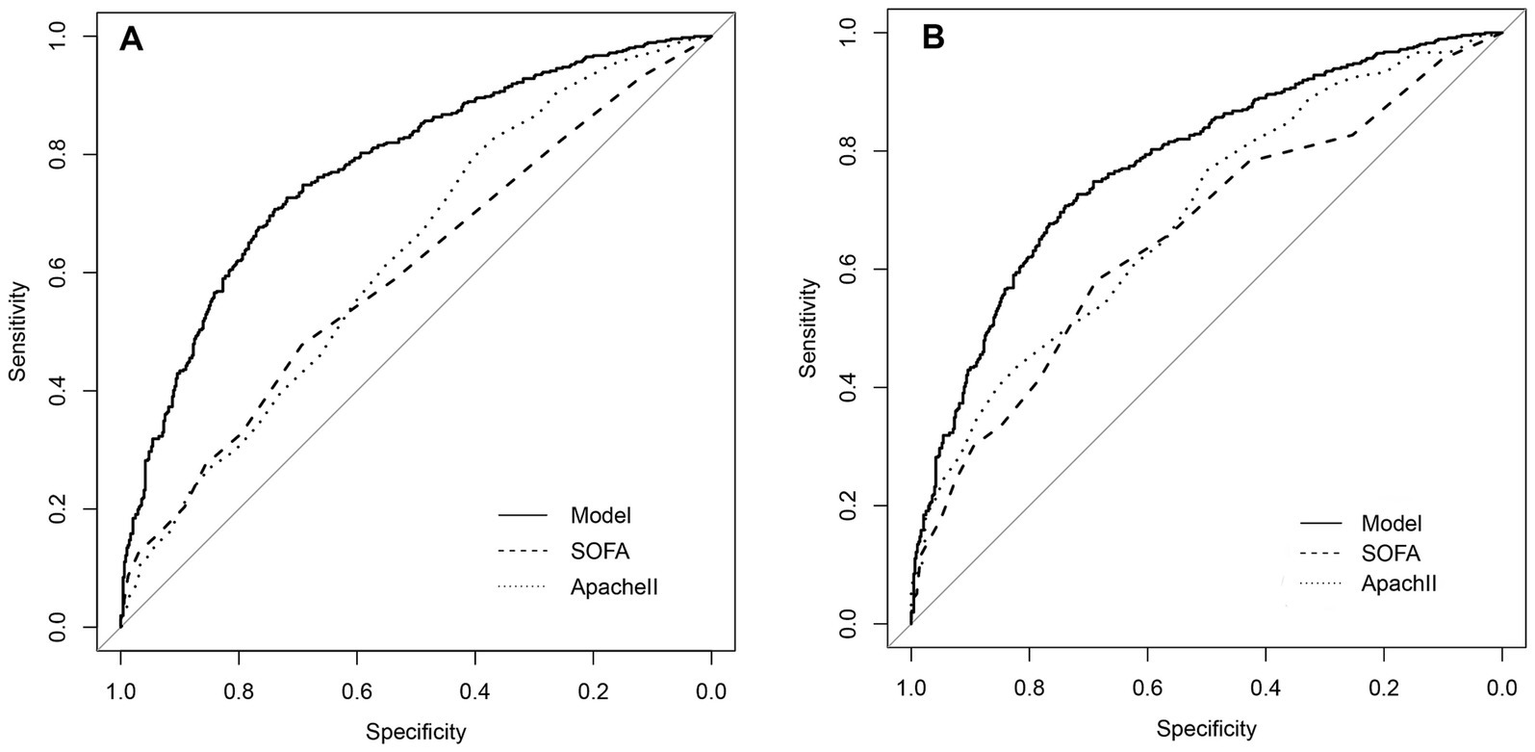
Comparison of discrimination function of the proposed model, SOFA and Apache II in the SSP patients. (A) The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the proposed model, SOFA and Apache II in the derivation cohort is 0.777, 0.600, 0.625, respectively (p < 0.05). (B) The area under the ROC curve (AUC) of the proposed model, SOFA and Apache II in the validation cohort, is 0.803, 0.655, 0.688, respectively.
Table 4
| Score system | AUC | 95%CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Derivation cohort | |||
| SOFA | 0.600 | 0.564–0.6356 | p < 0.001 |
| Apache II | 0.625 | 0.589–0.660 | p < 0.001 |
| Proposed model | 0.777 | 0.743–0.802 | p < 0.001 |
| Validation cohort | |||
| SOFA | 0.655 | 0.601–0.710 | p < 0.001 |
| Apache II | 0.688 | 0.634–0.740 | p < 0.001 |
| Proposed model | 0.803 | 0.759–0.846 | p < 0.001 |
The prognostic predictive value of three scoring systems.
Discussion
In this single-center retrospective cohort study, we evaluated the clinical and laboratory characteristics in SSP patients, developed a mortality risk prediction model for SSP patients, and built a web-based calculator of mortality prediction. The model included age, white blood cell count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, lactate dehydrogenase, PaO2/FiO2, D-dimer and vasoactive drug use. The proposed model had an AUC of 0.777, indicating a better prediction performance than SOFA score and APACHE II score.
The SOFA score and APCHE II score have been widely utilized for prognosis assessment in pneumonia and sepsis, but study results are discrepancy. In January 2014, the Sepsis-3 working group of Society of Critical Care Medicine and European Society of Intensive Care Medicine recommended a SOFA score ≥ 2 for sepsis diagnosis. However, the SOFA score does not include age or comorbidities and therefore has limited applications in clinical practice. The APACHE II score proposed by Knaus mainly includes age, comorbidities and Glasgow Coma Scale score, leading to the underestimation of disease severity in young patients who are healthy before hospital admission (21). In this study, the AUC of SOFA score and APCHE II score is 0.600 and 0.625, respectively, showing their limited predictive values in the 28-day mortality in SSP patients.
Age is a widely recognized independent predictive factor of mortality in SSP patients. Aging patients, especially those over 65 years, have a weak immune system, poor nutritional status and chronic comorbidities, thus the occurrence and mortality of sepsis are higher following pneumonia onset (22–24). Holter et al. (25) observed a 83% increase of pneumonia mortality risk per 10 years of age during 5-year follow-up. Montull et al. (26) and Kolditz et al. (27) reported age as an independent mortality risk in pneumonia patients. In a multi-center, retrospective study in China, Han also identified age as a risk factor of in-hospital death in pneumonia patients (odds ratio: 1.01, 95% confidence interval: 1.01–21.03), and the mortality rate significantly increases with age (28). Our findings support these studies by showing a significantly higher mean age in death group than survival group. Furthermore, the Logistic regression analysis also confirmed age as an independent risk factor of death in SSP patients and indicated an increasing SSP mortality rate with age.
NLR is an indicator for the severity assessment of systemic infection and inflammatory response by calculating the ratio of neutrophil count over lymphocyte count. In healthy adults, the NLR is between 0.78–3.53 (29). The systemic inflammation caused by pneumonia is mainly characterized by increasing neutrophils and decreasing lymphocytes. Hence, a high NLR indicates a severe inflammatory response. Liu and Hwang reported NLR as a risk factor of poor prognosis in sepsis patients (30, 31). Pantzaris et al. (32) found a close relation between NLR and SSP death. In our study, NLR was significantly higher in death group than survival group in both derivation cohort (12.9 (7.1, 23.6) vs. 8.3 (5.4, 15.8), p < 0.001) and validation cohort (16.6 (9.6, 29.2) vs. 12.1 (6.5, 18.8), p < 0.001) in our study. Moreover, the higher is the NLR, the poorer the patients’ prognosis will be. NLR shows the relative change between neutrophil and lymphocyte and has a high predictive value for SSP. Thus, the NLR instead of neutrophil count or lymphocyte count alone should be evaluated clinically.
Vasoactive drugs are required to maintain a mean arterial pressure above 65 mmHg to ensure sufficient tissue perfusion once septic shock is identified in SSP patients (33). The patients complicated by septic shock showed a significantly higher mortality rate (3). In our study, vasoactive drugs were more frequently used in death group than survival group (64.1% vs. 22.8%, p < 0.05). PaO2/FiO2 ratio was also reported to decrease with the severity of respiratory failure and mortality rate (34–36). In our study, the PaO2/FiO2 ratio was significantly lower in death group than survival group in both derivation cohort (169.8 (109.6, 231.5) mmHg vs. 203.3 (154.9, 259.4) mmHg, p < 0.05) and validation cohort (181.7 (122.0, 242.3) mmHg vs. 223.0 (164.5, 287.2) mmHg, p < 0.05). D-dimer elevation has been reported to relate to the outcomes in both pneumonia and sepsis patients, which is also confirmed in this study (37–39).
Our study has several advantages. Firstly, the 7 variables included in our proposed model can be easily acquired in hospital since they are commonly tested at the patients’ admission. The prediction model is also usable for primary hospitals with its noninvasiveness, simplicity and accuracy. Secondly, our proposed model is publicly available as a web-based calculator which can be freely accessible by global doctors for further validation. The clinicians can evaluate the patients’ mortality risk at their hospital admission by using the clinical data so as to tailor the monitoring and treatment plans for the patients to improve their prognosis. Thirdly, our proposed model has been internally and externally validated, and the discrimination and calibration analyses have shown the good predictive performance of the model. These findings provide evidence to support the generalizability of our proposed model.
Some limitations are worthy of consideration in interpreting our study results. Firstly, the study was single-center and retrospective, so some potentially relevant immune indicators such as interleukin – 6 and T cell subpopulations were not included and their relations to SSP severity were not investigated. Secondly, the study had a small sample size, and we did not explore the impacts of different pathogenic microorganisms, antibiotics and lactic acid on prognosis. Thirdly, our study was performed in a tertiary hospital which admits mostly severe patients, thus selection bias might exist in choosing the study population. Lastly, the findings of this retrospective study have not been confirmed in a prospective study, but the study provides some bases for future study design. Overall, a large-sample-size, multi-center prospective study may be needed to further validate our results.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the web-based mortality risk prediction model is likely to help the clinical decision makers to identify the high-risk SSP patients at an early stage so as to optimize the treatments, improve the patients’ prognosis and reduce the mortality rate.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Henan Provincial People’s Hospital Medical ethics Committee. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
XLi: Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XLei: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. LK: Methodology, Writing – original draft. JW: Data curation, Writing – original draft. ZY: Conceptualization, Methodology, Writing – review & editing, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1.
GBD 2017 Causes of Death Collaborators . Global, regional, and national age-sex-specific mortality for 282 causes of death in 195 countries and territories, 1980–2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1736–88. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32203-7
2.
National Health and Family Planning Commission . China public health statistical yearbook. Beijing: Peking Union Medical College Press (2019).
3.
Singer M Deutschman CS Seymour CW Shankar-Hari M Annane D Bauer M et al . The third international consensus definitions for sepsis and septic shock (Sepsis-3). JAMA. (2016) 315:801–10. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.0287
4.
Rudd KE Johnson SC Agesa KM Shackelford KA Tsoi D Kievlan DR et al . Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and mortality, 1990–2017: analysis for the global burden of disease study. Lancet. (2020) 395:200–11. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32989-7
5.
Xie JF Wang HL Kang Y Zhou LX Liu ZM Qin BY et al . The epidemiology of sepsis in Chinese ICUs: a National Cross-Sectional Survey. Crit Care Med. (2020) 48:e209–18. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004155
6.
Poll T Veerdonk FL Scicluna BP Netea MG . The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. (2017) 17:407–20. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.36
7.
Kirby TM Iris W Henrik E Tjebbe H Christian R Diederik G et al . Predicting mortality in adult patients with sepsis in the emergency department by using combinations of biomarkers and clinical scoring systems: a systematic review. BMC Emerg Med. (2021) 21:70. doi: 10.1186/s12873-021-00461-z
8.
Pereira JM Paiva JA Rello J . Severe sepsis in community-acquired pneumonia early recognition and treatment. Eur J Intern Med. (2012) 23:412–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2012.04.016
9.
Carmo TA Ferreira IB Menezes RC Telles GP Otero ML Arriaga MB et al . Derivation and validation of a novel severity scoring system for pneumonia at intensive care unit admission. Clin Infect Dis. (2021) 72:942–9. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa183
10.
Shankar T Kaeley N Nagasubramanyam V Bahurupi Y Bairwa A Infimate DJ et al . Evaluation of the predictive value of sepsis patient evaluation in the emergency department (SPEED) score in estimating 28-day mortality among patients with sepsis presenting to the emergency department: a prospective observational study. Cureus. (2022) 14:e22598. doi: 10.7759/cureus.22598
11.
Lv CX Chen Y Shi W Pan T Deng JH Xu JY . Comparison of different scoring Systems for Prediction of mortality and ICU admission in elderly CAP population. Clin Interv Aging. (2021) 16:1917–29. doi: 10.2147/CIA.S335315
12.
Vincent JL Moreno R Takala J Willatts S Mendonça AD Bruining H et al . The SOFA (sepsis-related organ failure assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the working group on sepsis-related problems of the European society of intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med. (1996) 22:707–10. doi: 10.1007/BF01709751
13.
Pawar RD Shih JA Balaji L Grossestreuer AV Patel PV Hansen CK et al . Variation in SOFA (sequential organ failure assessment) score performance in different infectious states. J Intensive Care Med. (2021) 36:1217–22. doi: 10.1177/0885066620944879
14.
Macdonald SPJ Arendts G Fatovich DM Brown SGA . Comparison of PIRO, SOFA, and MEDS scores for predicting mortality in emergency department patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Acad Emerg Med. (2014) 21:1257–63. doi: 10.1111/acem.12515
15.
Sharp AL Jones JP Wu I Huynh D Kocher KE Shah NR et al . CURB-65 performance among admitted and discharged emergency department patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Acad Emerg Med. (2016) 23:400–5. doi: 10.1111/acem.12929
16.
Kolditz M Ewig S Höffken G . Management-based risk prediction in community-acquired pneumonia by scores and biomarkers. Eur Respir J. (2013) 41:974–84. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00104412
17.
Loke YK Kwok CS Niruban A Myint PK . Value of severity scales in predicting mortality from community acquired pneumonia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax. (2010) 65:884–90. doi: 10.1136/thx.2009.134072
18.
Ferrer M Travierso C Cilloniz C Gabarrus A Ranzani OT Polverino E et al . Severe community-acquired pneumonia: characteristics and prognostic factors in ventilated and non-ventilated patients. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0191721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0191721
19.
Metlay JP Waterer GM Long AC Anzueto A Brozek J Crothers K et al . Diagnosis and treatment of adults with community-acquired pneumonia. An official clinical practice guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2019) 200:e45–67. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201908-1581ST
20.
Kalil AC Metersky ML Klompas M Muscedere J Sweeney DA Palmer LB et al . Management of Adults with Hospital acquired and ventilator-associated pneumonia: 2016 clinical practice guidelines by the Infectious Diseases Society of America and the American Thoracic Society. Clin Infect Dis. (2016) 63:e61–e111. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw353
21.
Knaus WA Draper EA Wagner DP Zimmerman JE . APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. (1985) 13:818–29. doi: 10.1097/00003246-198510000-00009
22.
Cillóniz C Rodríguez-Hurtado D Torres A . Characteristics and Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia in the era of global aging. Med Sci (Basel). (2018) 6:35. doi: 10.3390/medsci6020035
23.
Simonetti AF Viasus D Garcia VC Carratalà J . Management of community-acquired pneumonia in older adults. Adv Infect Dis. (2014) 2:3–16. doi: 10.1177/2049936113518041
24.
Cillóniz C Dominedò C Ielpo A Ferrer M Gabarrús A Battaglini D et al . Risk and prognostic factors in very old patients with sepsis secondary to community-acquired pneumonia. J Clin Med. (2019) 8:961. doi: 10.3390/jcm8070961
25.
Holter JC Ueland T Jenum PA Müller F Brunborg C Frøland SS et al . Risk factors for Long-term mortality after hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia: a 5-year prospective follow-up study. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0148741. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148741
26.
Montull B Menéndez R Torres A Reyes S Méndez R Zalacaín R et al . Predictors of severe sepsis among patients hospitalized for community-acquired pneumonia. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0145929. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145929
27.
Kolditz M Tesch F Mocke L Höffken G Ewig S Schmitt J . Burden and risk factors of ambulatory or hospitalized CAP: a population based cohort study. Respir Med. (2016) 121:32–8. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2016.10.015
28.
Han XD Zhou F Li H Xing XQ Chen L Wang YM et al . Effects of age, comorbidity and adherence to current antimicrobial guidelines on mortality in hospitalized elderly patients with community-acquired pneumonia. BMC Infect Dis. (2018) 18:192. doi: 10.1186/s12879-018-3098-5
29.
Forget P Khalifa C Defour JP Latinne D Pel MCV Kock MD . What is the normal value of the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio?BMC Res Notes. (2017) 10:12. doi: 10.1186/s13104-016-2335-5
30.
Liu X Shen Y Wang H Ge Q Fei A Pan S . Prognostic significance of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio in patients with sepsis: a prospective observational study. Mediat Inflamm. (2016) 2016:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2016/8191254
31.
Hwang SY Shin TG Jo IJ Jeon K Suh GY Lee TR et al . Neutrophil-to lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic marker in critically-ill septic patients. Am J Emerg Med. (2017) 35:234–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2016.10.055
32.
Pantzaris ND Platanaki C Pierrakos C Karamouzos V Velissaris D . Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio relation to sepsis severity scores and inflammatory biomarkers in patients with community-acquired pneumonia: a case series. J Transl Intern Med. (2018) 6:43–6. doi: 10.2478/jtim-2018-0009
33.
Priebe HJ . Early, goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. N Engl J Med. (2015) 373:576–8. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1506514
34.
Guo L Wei D Zhang X Wu Y Li Q Zhou M et al . Clinical features predicting mortality risk in patients with viral pneumonia: the MuLBSTA score. Front Microbiol. (2019) 10:27522019. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02752
35.
He YJ Li MG Mai CY Chen LJ Zhang XM Zhou JY et al . Anemia and low albumin levels are associated with severe community-acquired pneumonia in pregnancy: a case-control study. Tohoku J Exp Med. (2019) 248:297–305. doi: 10.1620/tjem.248.297
36.
Ayuso B Lalueza A Arrieta E Romay EM Marchán-López A García-País MJ et al . Derivation and external validation of a simple prediction rule for the derivation of respiratory failure in hospitalized patients with influenza. Respir Res. (2022) 23:323. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02245-w
37.
Cerda-Mancillas MC Santiago-Germán D Andrade-Bravo B Pedraza-Olivares F Valenzo-Hernández F Leaños-Miranda A et al . D-dimer as a biomarker of severity and adverse outcomes in patients with community acquired pneumonia. Arch Med Res. (2020) 51:429–35. doi: 10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.04.014
38.
Ge YL Liu CH Wang N Xu J Zhu XY Su CS et al . Elevated plasma D-dimer in adult community-acquired pneumonia patients is associated with an increased inflammatory reaction and lower survival. Clin Lab. (2019) 65:65. doi: 10.7754/Clin.Lab.2018.180720
39.
Rodelo JR De la Rosa G Valencia ML Ospina S Arango CM Gómez CI et al . D-dimer is a significant prognostic factor in patients with suspected infection and sepsis. Am J Emerg Med. (2012) 30:1991–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2012.04.033
Summary
Keywords
sepsis, pneumonia, SOFA score, APACHE II score, mortality
Citation
Li X, Lei X, Kou L, Wang J and Yang Z (2025) Development and validation of mortality risk prediction model for sepsis secondary to pneumonia at intensive care unit admission: a retrospective case-cohort study. Front. Med. 12:1592325. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1592325
Received
18 March 2025
Accepted
28 July 2025
Published
12 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Shisan (Bob) Bao, The University of Sydney, Australia
Reviewed by
Xiaogang Xiang, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
Youssif M. Ali, University of Cambridge, United Kingdom
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Li, Lei, Kou, Wang and Yang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Zhigang Yang, 18203679389@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.