- 1College of Nursing, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, China
- 2Laboratory of Geriatric Nursing and Health, Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei, China
Background: Studies have confirmed that obesity is an antecedent of chronic diarrhoea, and new evidence suggests that visceral fat accumulation may play a more critical role than total body fat in intestinal dysfunction and the development of chronic diarrhoea. Traditional body mass index (BMI) does not accurately reflect fat distribution, limiting the depth of relevant research. Body shape index (ABSI) and body rounding index (BRI), as emerging measurements that more accurately assess abdominal and visceral adiposity, have shown superior predictive value to BMI in cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. However, the use of these metrics in the prediction of chronic diarrhoea has not been explored. This study is the first to investigate the relationship between ABSI and BRI and chronic diarrhoea, aiming to provide a new clinical tool for risk assessment of obesity-related diarrhoea.
Methods: This study used data from the Bowel Health Questionnaire (BHQ) of the U.S. National Health Examination Survey (NHANES) database (2005–2010), and chronic diarrhoea was defined as “chronic diarrhoea” by the Bristol Stool Scale (BSFS) types 6 andI7(4). Weighted logistic regression and trend analyses were performed to examine the association between ABSI/BRI and chronic diarrhoea. Flexible restricted cubic spline (RCS) models showed dynamic associations. Stratified analyses examined associations between age, gender, race, and clinical characteristics (e.g., cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hypertension). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves assessed the predictive performance of ABSI/BRI for risk of chronic diarrhoea.
Results: Multivariate regression models with time-trend analyses indicated a dose–response relationship between higher BRI percentiles and the incidence of chronic diarrhoea. 13% per unit increase in BRI (OR = 1.13, 95% CI = 1.08–1.19, p < 0.001). Similarly, there was a 35% increase in risk for each 0.01 unit increase in ABSI (OR = 1.35, 95% CI = 1.01–1.80, p = 0.045), suggesting that those with higher ABSI were at higher risk. Subgroup analyses showed no significant interaction effect between BRI and chronic diarrhoea across age, sex, race, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension (p > 0.050). The ROC confirmed the nonlinear association between ABSI/BRI and chronic diarrhoea.
Conclusion: The objective of this study was to investigate the association between two novel abdominal fat indicators (ABSI and BRI) and chronic diarrhoea using nationally representative NHANES data (2005–2010). For the first time, we have identified ABSI and BRI as potentially useful clinical predictors of chronic diarrhoea.
1 Introduction
Chronic diarrhoea was defined as predominantly loose stools lasting more than 4 weeks (1). Chronic diarrhoea affects 17–30% of the global population (2), with significantly higher prevalence (21–30%) observed in obese individuals (3). Christopher Ma et al. found that chronic diarrhoea results in approximately 700,000 U.S. outpatient visits per year, costing $690 million annually (4). Chronic diarrhoea therefore not only poses a threat to patients’ health, but also creates a huge financial burden and reduces their quality of life. Obesity is a global public health problem, and regarding the causal relationship between obesity and chronic diarrhoea, current research suggests that obesity may be an antecedent to chronic diarrhoea (2, 5–7). It has been shown that bile acid malabsorption diarrhoea and secretory diarrhoea predominate in obese patients (6, 8). Firstly, obesity alters the composition of the intestinal bacterial flora and increases intestinal permeability, allowing bacterial endotoxins (e.g., lipopolysaccharides, LPS) to enter the bloodstream, which promotes intestinal permeability specialists to trigger diarrhoea (8). Secondly, obesity may accelerate the transit time in the large intestine, which leads to a shorter retention time of food and waste in the intestines, which can trigger diarrhoea (5, 8–11).
Research suggests that visceral fat accumulation may play a more critical role than total body fat in the development of intestinal dysfunction and chronic diarrhoea (12), and that the inability of body mass index (BMI) to accurately reflect fat distribution limits the depth of relevant studies (13–16). The ABSI is a new anthropometric tool that combines waist circumference, weight and height (17). It can provide an improved ability to quantify visceral and abdominal fat, which are key contributors to metabolic risk. The index was originally developed by Krakauer et al. in 2012 based on the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) database (18, 19), correlation with visceral adiposity and metabolic risk has been validated in multiple population-based cohorts in the United States, Europe, and Asia (18–20). Developed by Thomas and colleagues in 2013, the BRI is a geometric metric based on the human ellipse approximation (21), the BRI recognizes individuals with the same BMI but different body fat distributions, and its validity has been verified in a database and imaging MRI technique at the University of Kiel, Germany, and in large cohort studies in several countries (22–25). Although not yet routinely used in clinical practice, these two indices have significant practical advantages: they can be quickly calculated from standardized formulas using only three parameters, namely waist circumference, height and weight, obtained during a routine physical examination, without the need for additional equipment or complex tests. This non-invasive feature makes it particularly suitable for large-scale epidemiological studies and risk screening in primary care settings, compared to fat quantification methods that require expensive imaging.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Study design and participant selection from NHANES 2005–2010
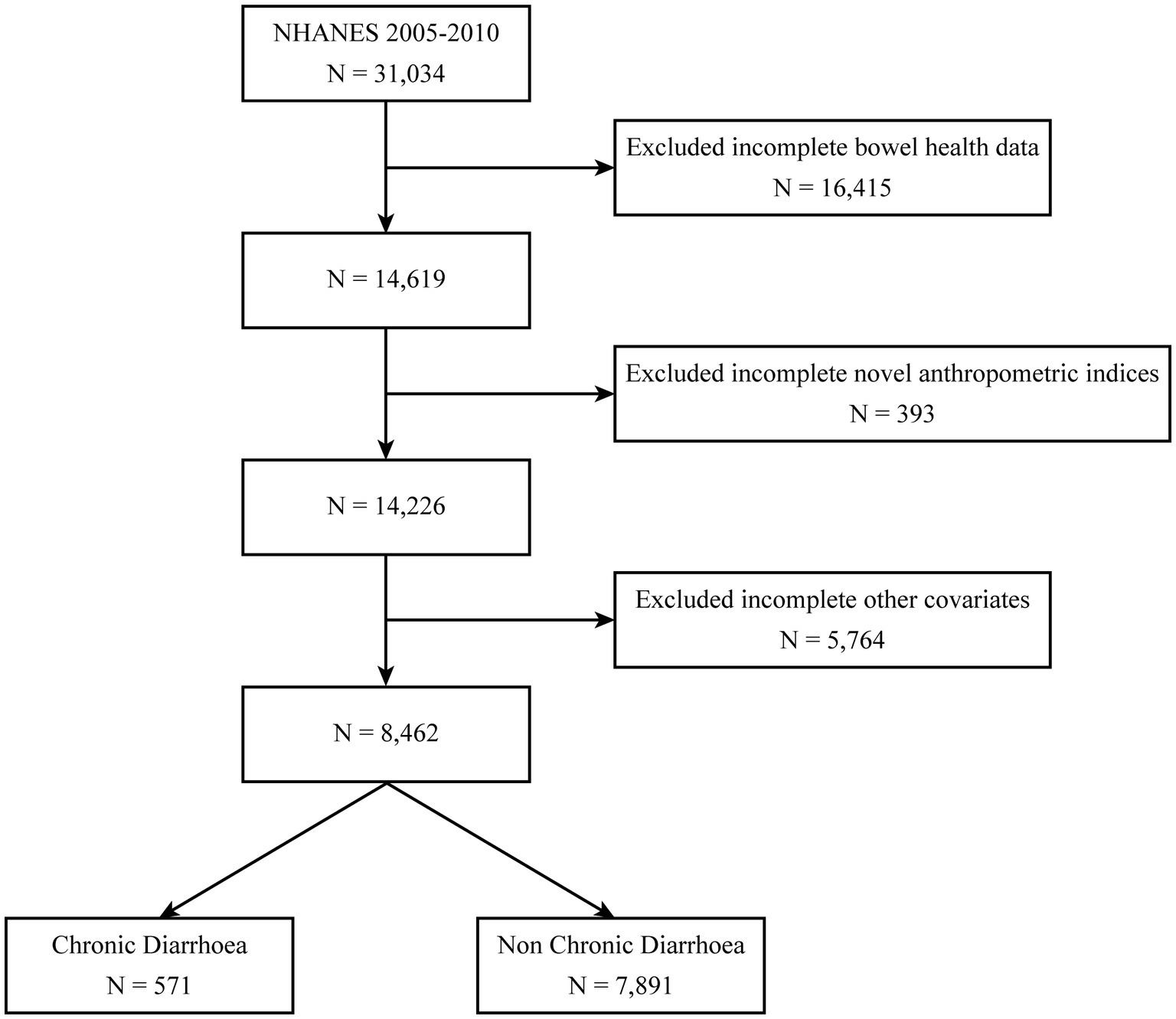
NHANES is a cross-sectional study that provides a nationally representative snapshot of the health status of the non-institutionalized population in the United States. From 2005 through 2010, the nationally representative NHANES dataset served as the epidemiological foundation for this cross-sectional investigation, initially comprising 31,034 participants. After excluding 16,415 individuals with incomplete bowel health questionnaire responses, 14,619 participants remained. Subsequent removal of 393 cases lacking novel anthropometric indices (ABSI/BRI) yielded 14,226 eligible subjects. After excluding 5,764 participants with missing covariate data, the final cohort consisted of 8,462 individuals, stratified into two groups: chronic diarrhoea (n = 571) and non-chronic diarrhoea (n = 7,891) (Figure 1). Ethical clearance for the research protocol was formally granted through the institutional review mechanisms of the National Center for Health Statistics Ethics Review Board (13). The NHANES website1 (23) offers comprehensive details on survey design, methodologies, population demographics, and dataset access. RetryClaude does not have internet access. Links provided may not be accurate or up to date. Claude can make mistakes. Please double-check responses.
2.2 Bowel health questionnaire
The bowel health questionnaire captured self-reported stool characteristics based on standardized classifications. Stool consistency was categorized into Types 1–7 following the Bristol Stool Form Scale (BSFS), a clinically validated diagnostic tool for fecal consistency assessment and morphological characterization. This scale operationally defines stool characteristics along a continuum: Type 1 (separate hard lumps, nut-like) to Type 7 (watery stools without solid fragments). Chronic diarrhoea was defined as persistent passage of Types 6 or 7 stools, while Types 1–2 indicated chronic constipation. Types 3–5 represented normal bowel patterns (26).
2.3 Covariate definitions and measurement protocols
Analyses adjusted for: age; sex (male ref); race/ethnicity (Mexican American, non-Hispanic Black, non-Hispanic White, other); education (<high school, high school, ≥college); marital status (married/cohabiting, single); alcohol use (heavy, low/moderate, non-drinker); smoking (current, former, never); PIR (<1.30, 1.30–3.49, ≥3.50); diabetes (defined by ≥1 of: FPG ≥ 7.0 mmol/L, OGTT>11.1 mmol/L, random glucose>11.1 mmol/L, HbA1c > 6.5%, diabetes medication use, or self-reported diagnosis); hypertension; CVD: Diagnosis ofCVD was determined by self-reported physician diagnoses obtained during individual interviews using a standardized medical condition questionnaire. Participants were asked: “Has a doctor or other health professional ever told you that you have congestive heart failure/coronary heart disease/angina/myocardial infarction/stroke?” A person was considered to have CVD if they answered “yes” to any of the above questions. Congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, and coronary artery disease were also defined according to the questions for the respective diseases listed above (27). Hypertension: The blood pressure measurement protocol follows the procedures established by the American Heart Association. After 3 measurements of blood pressure at rest, the average of systolic blood pressure (SBP) and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) was calculated. The 2017 American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology (AHA/ACC) guidelines recommend that individuals with an SBP ≥ 130 mmHg and/or a DBP ≥ 80 mmHg should be defined as hypertensive. In addition, participants who answered “yes” to the question “Have ou ever been told you have hypertension?” were categorized as hypertensive (28).
2.4 Calculation of body shape index (ABSI) and body roundness index (BRI)
Standardized anthropometric protocols were implemented to obtain iliac crest-level waist circumference measurements, along with standing height and body weight recordings. The following formulas were used to calculate BRI and ABSI:
BRI = 364.2-365.5 × √ 1-[(WC (cm)/2π)/(0.5 ×height (cm))]2 (21)
ABSI = WC (cm)/(BMI (kg/m2)2/3 × height (cm)1/2 (19)
2.5 Statistical analysis
Several statistical approaches were applied to examine the relationships between ABSI/BRI and chronic diarrhoea. For descriptive statistics, Continuous variables following a normal distribution were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, whereas categorical variables were reported as percentages. Differences between groups were evaluated using independent tests for continuous variables and chi-square tests for categorical variables. Appropriate sampling weights were applied to ensure national representativenes. ABSI and BRI were categorized into quartiles to better characterize population subgroups. We conducted weighted logistic regression analyses to evaluate ABSI/BRI-diarrhoea associations across progressive covariate adjustment levels: Model 1 (unadjusted), Model 2 (partially adjusted with demographics: age, sex, race, poverty-income ratio, and marital status), and Model 3 (fully adjusted for age, sex, race, poverty-income ratio, marital status, education, smoking, alcohol consumption, hypertension, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, total cholesterol, triglycerides, hemoglobin, and HbA1c) (29). Restricted cubic spline (RCS) curves with four knots were used to capture potential nonlinear relationships between anthropometric indices and chronic diarrhoea. Additionally, we performed stratified analyses by age, sex, race, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension to assess effect heterogeneity across different subgroups. Multiplicative interaction terms were included in regression models to determine statistical significance (p < 0.05) for differences between subgroups (30). R4.3.12 was used to perform all data analyses. A two-sided p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
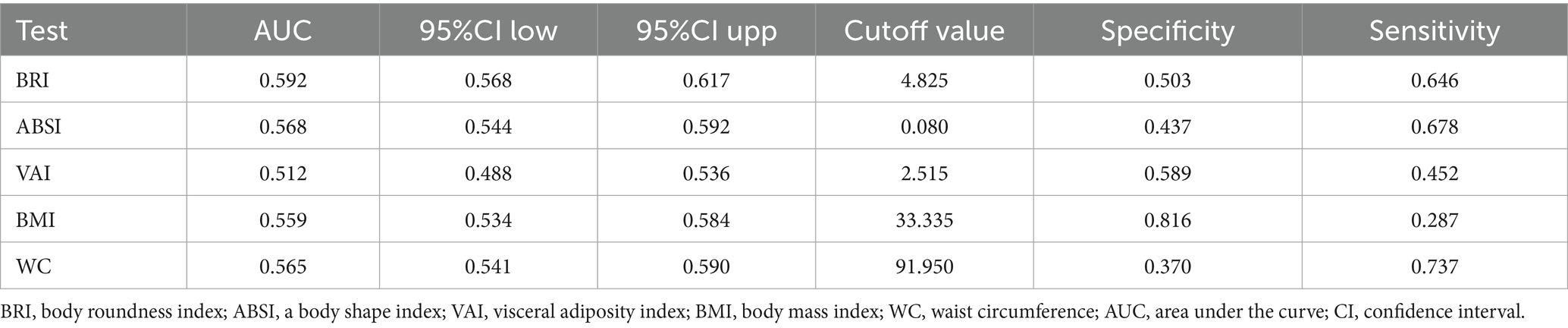
The ROC curves were generated to evaluate the predictive performance of BRI, ABSI and traditional indices (body mass index, waist circumference, visceral adiposity index). Area under the curve (AUC) was used to quantify overall accuracy. Sensitivity and specificity were derived from the ROC curves at the optimal cutoff point determined by the Youden index (J = sensitivity + specificity − 1) (31).
3 Result
3.1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of study participants
A total of 8,462 participants were recruited for this study, of which 6.7% (571) were categorized in the chronic diarrhoea group and the remaining 93.3% (7891) in the non-chronic diarrhoea group. The chronic diarrhoea group was older (49.74 years vs. 46.11 years). The proportion of females was higher in the chronic diarrhoea group (51.3% versus 45.8%), p = 0.029. When examining BRI quartiles, a higher proportion of chronic diarrhoea patients were found in Q4 (36. 1%) compared to Q1 (17.3%), <0.05. Similarly, for ABSI quartiles, a higher proportion of chronic diarrhoea patients were observed in Q4 (33.8%) compared to Q (25.6%), p = 0.002. In terms of marital status, high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease (CVD), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), and PIR (poverty-to-income ratio), p ≥ 0.050 (Table 1).
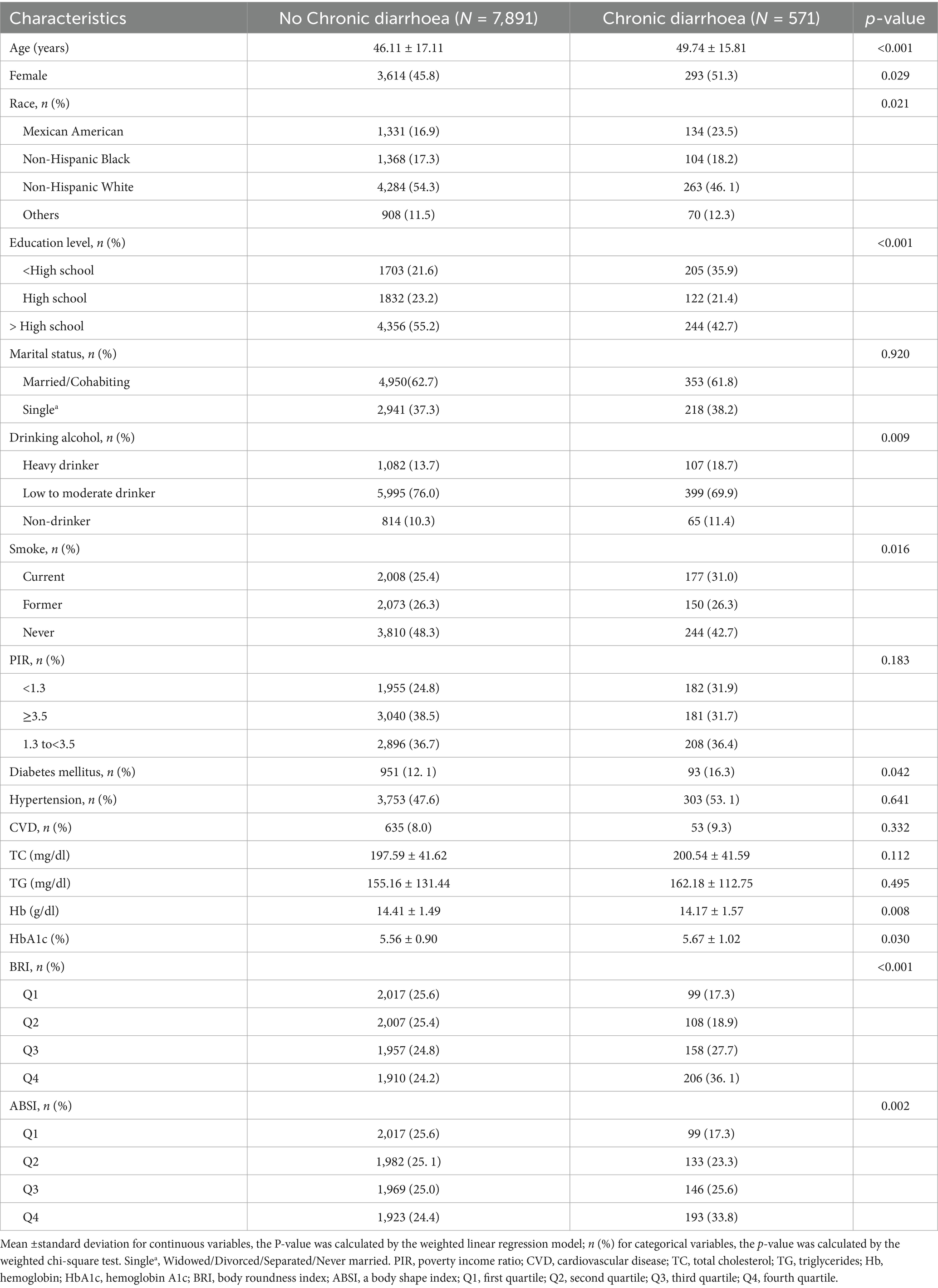
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the study population analyzed based on chronic diarrhoea status.
3.2 BRI and ABSI and the risk of chronic diarrhoea
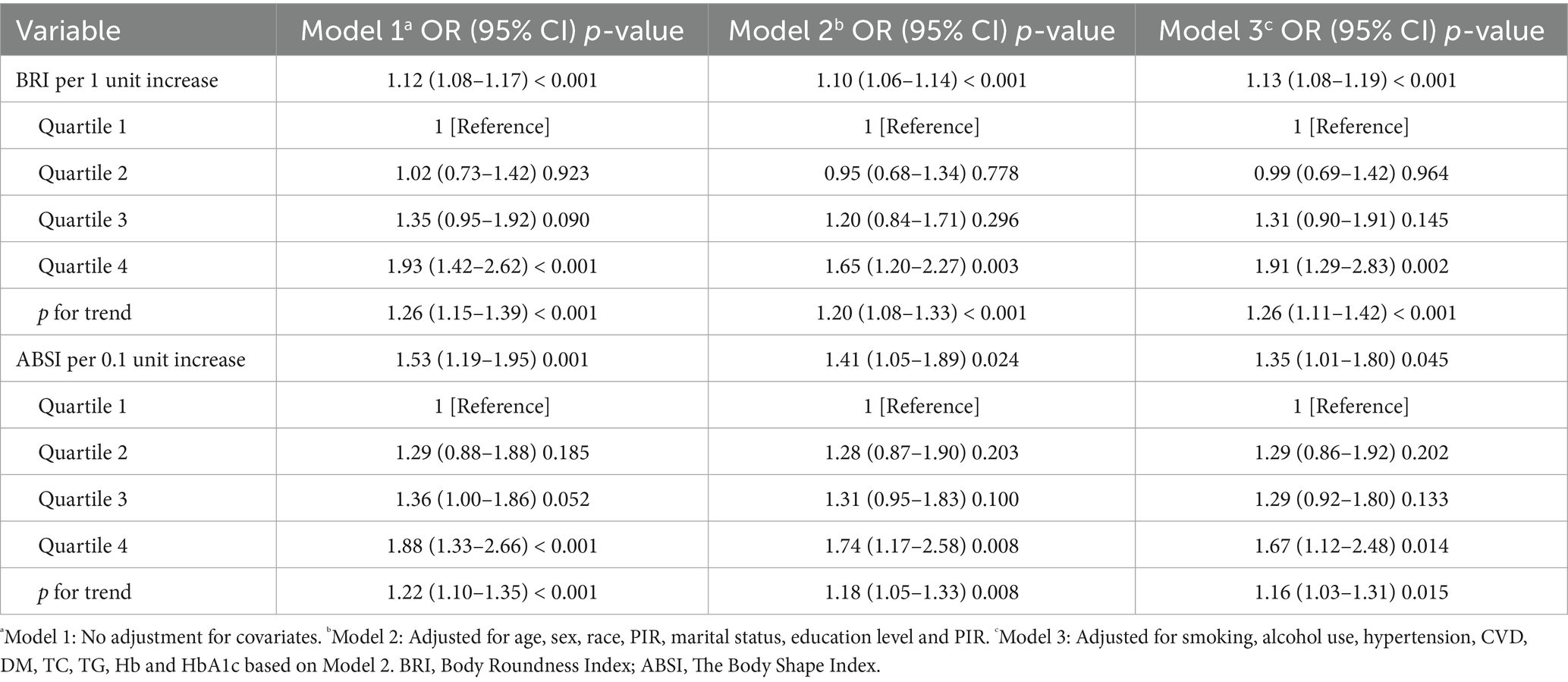
According to Table 2, Higher BRI and ABSI were significantly linked to an increased risk of chronic diarrhoea. In the unadjusted model (Model 1), each 1-unit increase in BRI corresponded to a 12% higher risk of chronic diarrhoea (OR = 1.12, 95% CI: 1.08–1.17, p < 0.001). This association persisted in the fully adjusted model (Model 3), with a 13% risk increase per BRI unit (OR = 1.13, 95% CI 1.08–1.19, p < 0.001). Quartile analysis further revealed that participants in the highest BRI quartile (Q4) had 1.91-fold greater odds of chronic diarrhoea compared to the lowest quartile (Q1) (OR = 1.91, 95% CI: 1.29–2.83, p = 0.002). Similarly, every 0.01-unit increment in ABSI demonstrated a statistically significant correlation with increased risk of chronic diarrhoea. In the unadjusted model (Model 1), ABSI demonstrated a strong positive association (OR = 1.53, 95% CI: 1.19–1.95, p = 0.001). This association remained significant after full covariate adjustment in Model 3 (OR = 1.35, 95% CI: 1.01–1.80, p = 0.045). Participants in the highest ABSI quartile (Q4) exhibited a 1.67-fold increased risk compared to the lowest quartile (Q1) (OR = 1.67, 95% CI: 1.12–2.48, p = 0.014). These results collectively indicate that both BRI and ABSI are independently associated with chronic diarrhoea risk.
In the analysis of BRI (Figure 2A), the R-squared value of 0.308 (p < 0.001) indicated a significant relationship between BRI and the risk of chronic diarrhoea, with risk escalating progressively as BRI increased. For ABSI (Figure 2B), the R-squared value of 0.210 (p < 0.001) suggested a modest yet significant positive correlation with chronic diarrhoea. Although ABSI exhibited weaker predictive capacity compared to BRI, it still demonstrated clinical utility by identifying high-risk individuals, particularly males (OR = 2.76, 95% CI: 1.70–4.47), and showed consistent associations across different patient subgroups, making it a valuable complementary tool for risk assessment in clinical practice. Thus, BRI demonstrated superior predictive utility and explanatory power for chronic diarrhoea risk, whereas ABSI, despite its lower correlation, retained diagnostic relevance in risk stratification.
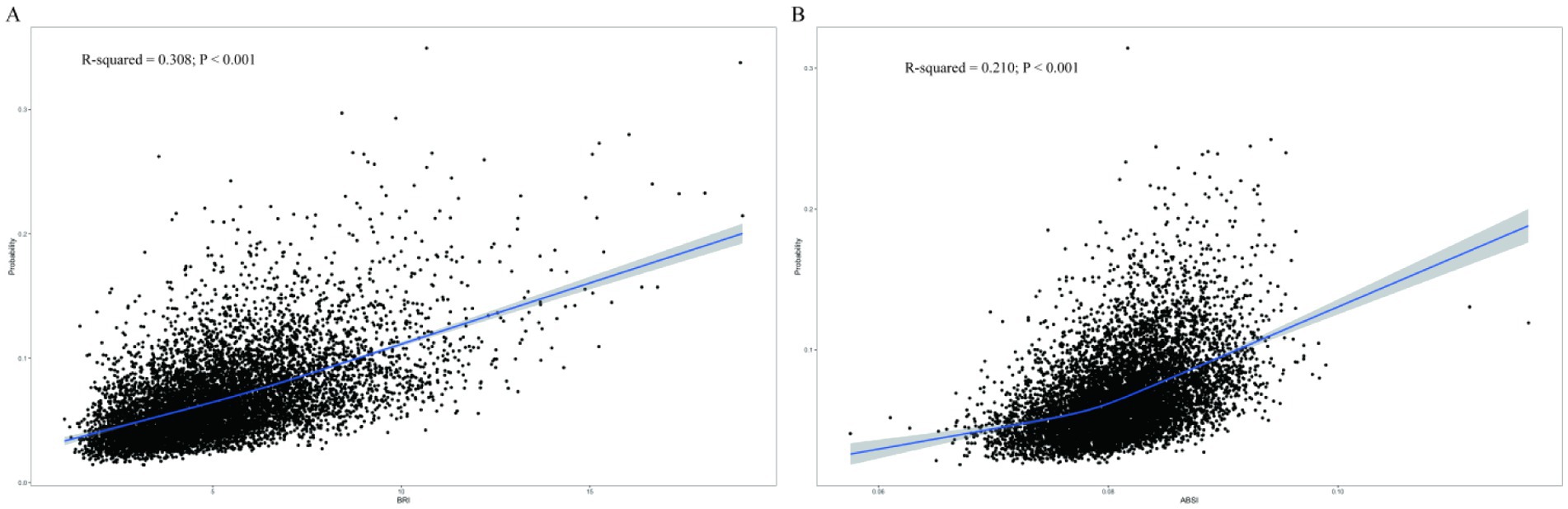
Figure 2. Restricted cubic spline curves for the relationship between the new anthropometric index and chronic diarrhoea. (A) BRI and (B) ABSI.
3.3 Subgroup analysis between BRI and ABSI and chronic diarrhoea
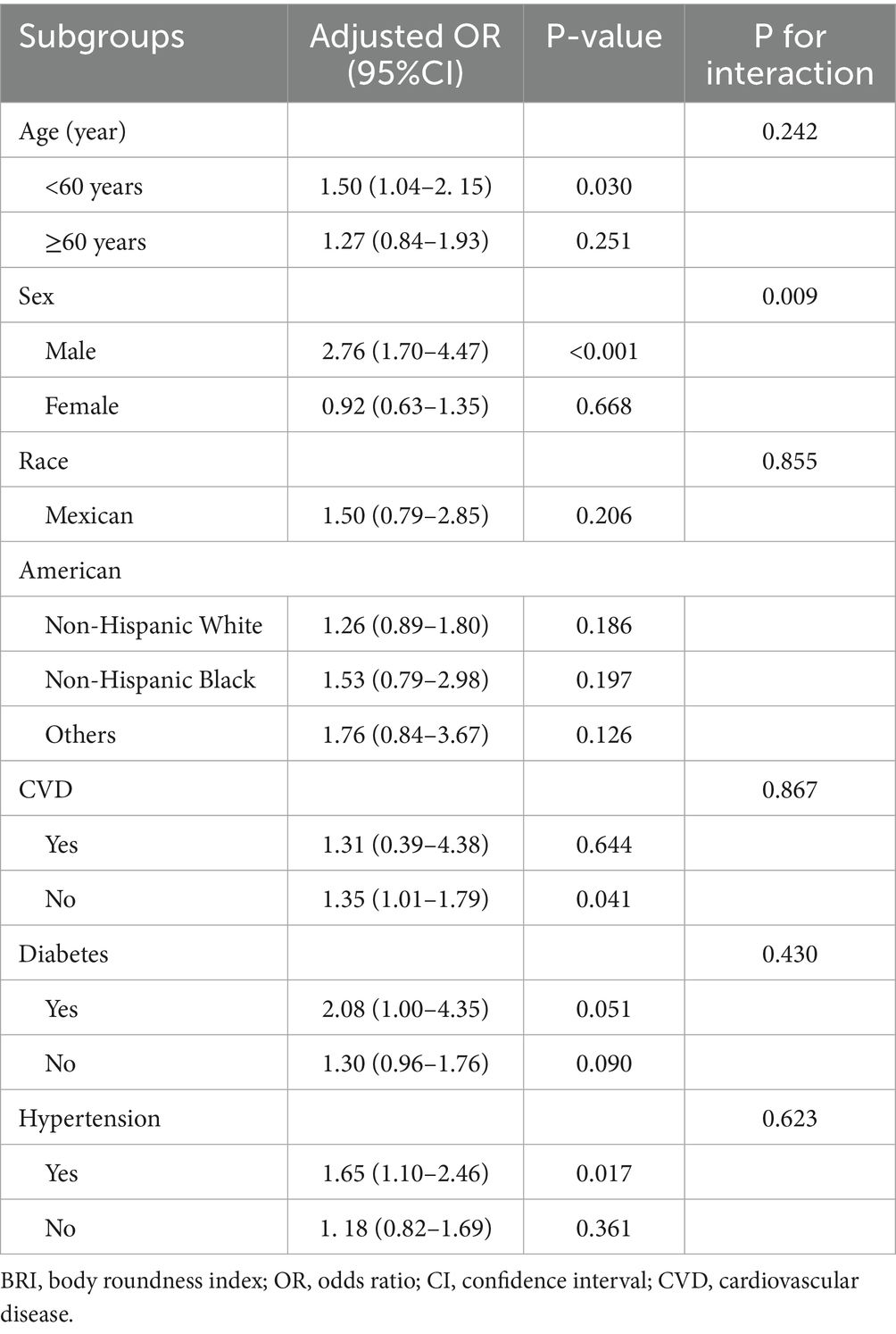
Analyses across subgroups of age, sex, race, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension showed no statistically significant interaction effects (all p for interaction>0.05), demonstrating homogeneity in the BRI-chronic diarrhoea association across these stratified subgroups (Table 3). Stratified analyses showed significant ABSI-chronic diarrhoea associations in males (OR = 2.76, 95% CI:1.70–4.47, p < 0.001), indicating aged<60 years (OR = 1.50, 95% CI:1.04–2.15, p = 0.030), non-CVD (OR = 1.35, 95% CI:1.01–1.79, p = 0.041), and the hypertensive groups (OR = 1.65, 95% CI:1.10–2.46, p = 0.017), with a significant sex interaction (p-interaction = 0.009). The ABSI-diarrhoea link demonstrated stability across demographics, modified only by sex (Table 4).
3.4 BRI is stronger than ABSI, VAI, BMI and WC in predicting chronic diarrhoea
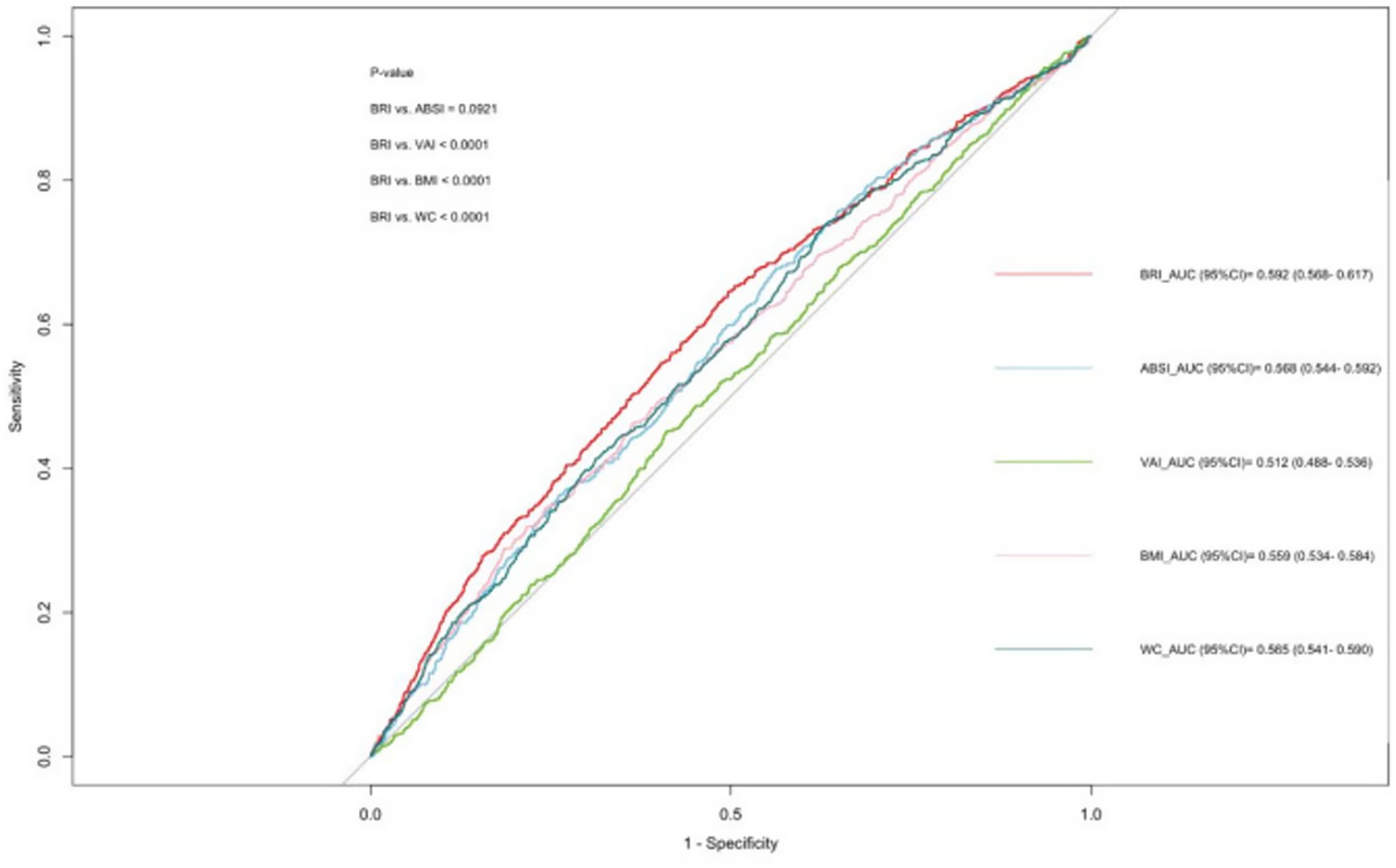
The ROC curve analysis showed that BRI and ABSI outperformed VAI, BMI, and WC in predicting chronic diarrhoea (Figure 3). The area under the curve (AUC) for BRI was 0.592, significantly higher than ABSI (0.568), BMI (0.559), WC (0.565), and VAI (0.512), indicating BRI’s enhanced classification accuracy in distinguishing chronic diarrhoea cases from non-cases. Although ABSI exhibited a lower AUC than BRI, it demonstrated higher sensitivity (0.678 vs. 0.646 for BRI), suggesting greater capability in identifying true positive cases. Conversely, BRI showed better specificity (0.503 vs. 0.437 for ABSI), supporting its utility in ruling out non-cases. Collectively, both BRI and ABSI outperformed traditional anthropometric indices (VAI/BMI/WC) in diagnostic efficacy, with BRI achieving marginally superior overall performance (AUC/specificity) and ABSI excelling in sensitivity (Table 5).
The area under the curve (AUC) values demonstrate the diagnostic accuracy of each indicator: BRI (Body Roundness Index, dark blue line, AUC = 0.592, 95% CI: 0.568–0.617), ABSI (A Body Shape Index, red line, AUC = 0.568, 95% CI: 0.544–0.592), VAI (Visceral Adiposity Index, orange line, AUC = 0.512, 95% CI: 0.488–0.536), BMI (Body Mass Index, green line, AUC = 0.559, 95% CI: 0.534–0.584), and WC (Waist Circumference, purple line, AUC = 0.565, 95% CI: 0.541–0.590). Higher AUC values indicate better discriminatory ability. The diagonal reference line represents random chance (AUC = 0.5). Statistical significance between curves was assessed using the DeLong test (p < 0.010).
4 Discussion
This study elucidated the association between visceral adiposity index (BRI/ABSI) and chronic diarrhoea disease by population level analysis method. The results showed that both indices were significantly and positively associated with chronic diarrhoea. After stratified multivariate logistic regression analysis and adjustment for all relevant covariates, a 1-unit increase in BRI was associated with a 13% increase in the risk of chronic diarrhoea (OR = 1.13, 95% CI: 1.08–1. 19), whereas a 0.01-unit increase in ABSI corresponded to a 35% increase in the risk of chronic diarrhoea (OR = 1.35, 95% CI: 1.01–1.80). These findings suggest that BRI and ABSI are significant independent predictors of chronic diarrhoea. The most striking finding in our study was that there was a significant gender difference in the association of ABSI with chronic diarrhoea (male OR = 2.76 vs. female OR = 0.92, p interaction = 0.009), whereas the association of BRI with chronic diarrhoea did not differ significantly between genders (p interaction = 0.737). This gender-specific difference reflects the originality of this study. From the perspective of physiological mechanisms, males secrete 5–10% more bile acids than females, and androgens promote CYP27A1 gene expression through the JNK signaling pathway (32, 33), significantly increases bile acid synthesis (34–36). Bile acids activate TGR5 receptors on intestinal smooth muscle (37, 38), enhance peristalsis strength and frequency, promote peristalsis acceleration and thus diarrhoea (39–43). Men tend to accumulate visceral adiposity (VAT), which is associated with increased metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk (44–47), expressed as elevated serum lipopolysaccharide (LPS) levels and decreased expression of tight junction proteins (ZO-1, Occludin and Claudin-3) (48, 49), and widening of cell gaps. These changes lead to increased permeability of the intestinal barrier, which in turn triggers diarrhoea (50–54). In contrast, estrogen in women can increase Nrf2-associated signaling pathways by inhibiting pathways such as NF-κB inflammation (55), increases beneficial bacteria and thus provides a protective effect on the intestinal tract (56–58). Consistent with previous studies we found a strong association of ABSI with chronic diarrhoea in men (OR = 2.76) reflecting the tendency for men to have a higher proportion of visceral fat distribution.
Another noteworthy result was the complementary value of BRI and ABSI in the diagnosis of chronic diarrhoea. BRI outperformed ABSI in overall predictive accuracy (AUC: 0.592 vs. 0.568), but ABSI performed better in sensitivity (0.678 vs. 0.646), while BRI was stronger in specificity (0.503 vs. 0.437). This finding suggests that the ABSI may be more valuable and the BRI may be more useful in clinical screening of high-risk populations when excluding non-cases. This complementarity further confirms that the two indices measure different aspects of abdominal fat distribution: the BRI focuses more on overall body fat distribution, whereas the ABSI emphasizes the geometric properties of body shape.
In the present study, it was found that high BRI and ABSI values represent accumulation of abdominal fat, and excessive abdominal fat secretes inflammatory factors such as alpha (TNF-α), interleukin 6 (IL-6), leptin, and others (59). TNF-α, IL-6 and leptin through common signaling pathways such as JAK–STAT (60–62), NF-κB and MAPK pathways (63–67), all three signaling pathways work together to trigger immune responses and inflammatory cascades, and this “leaky gut” phenomenon may be directly involved in the development of functional diarrhoea (68–70). Secondly, pro-inflammatory factors such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-1β stimulate degranulation of intestinal mast cells, releasing biologically active substances such as histamine and 5-hydroxytryptophan, which are potent stimulants of intestinal motility and promote peristalsis (71, 72). Finally, at the base of the brain-gut axis, excess fatty acids in obese individuals cause chronic inflammation of the hypothalamus (73–78), impairment of its ability to regulate the fine balance of intestinal motility, along with an abnormal increase in neurotransmitters such as intestinal 5-hydroxytryptamine and the formation of abnormal signaling loops through the vagus nerve, leading to over-excitement and disordered high-frequency contraction of the intestinal nervous system, which is ultimately manifested as recurrent diarrhoea (79, 80).
Our findings suggest that high ABSI and BRI values are mainly associated with several specific types of chronic diarrhoea. First, functional diarrhoea (FDr) and diarrhoeal irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) may be closely associated with visceral fat accumulation, which is mainly mediated through visceral fat-triggered low-grade inflammation and gut microbiome dysbiosis (15, 16). Secondly, high ABSI and BRI values were significantly associated with bile acid diarrhoea, which may be due to increased bile acid synthesis and abnormal bile acid metabolism in obese individuals. Third, diarrhoea due to small intestinal bacterial overgrowth syndrome (SIBO) is more common in people with a high visceral adiposity index, which is associated with altered obesity-associated bacterial communities (81–83). Notably, the association of diarrhoea with visceral fat found in the present study was predominantly in the form of altered fecal character (Bristol scale type 6–7) rather than inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-associated diarrhoea, which was particularly evident in males (OR = 2.76), suggesting that the distribution of abdominal fat has an important influence on functional bowel disease.
The present study has several methodological strengths: the use of the NHANES population-level dataset ensured the robustness of the analysis; nationally representative sampling enhanced the validity of epidemiologic inferences; and a rigorous multivariate confounding control scheme enhanced the validity of causal inferences. However, limitations remain (8): self-reported bowel habits may be subject to recall bias (3); categorization based on the “usual or most common” stool type in the Bowel Health Questionnaire may not be fully consistent with the Rome IV criteria for functional diarrhoea (84); the cross-sectional design did not allow for the establishment of a causal relationship between bowel patterns and ABSI/BRI; and (27) the 2005–2010 data collection period may have been time-limited. May have been time-limited.
In conclusion, our investigation pioneers the use of nationally representative NHANES data to establish BRI and ABSI as crucial predictors of chronic diarrhoea. Our findings revealed that every one-unit elevation in BRI corresponded to a 13% increased likelihood of developing chronic diarrhoea, whereas each 0.01-unit rise in ABSI was linked to a 35% greater risk. Notably, BRI outperformed conventional anthropometric indicators in predictive accuracy, while ABSI exhibited pronounced sex-specific effects, particularly among male participants. These results underscore the pivotal influence of visceral adiposity on gastrointestinal dysfunction and chronic diarrhoeal disorders.
5 Conclusion
The objective of this study was to investigate the association between two novel abdominal fat indicators (ABSI and BRI) and chronic diarrhoea using nationally representative NHANES data (2005–2010). For the first time, we have identified ABSI and BRI as potentially useful clinical predictors of chronic diarrhoea.
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: the data sets used in this study were all publicly available from NHANES (https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/index.htm).
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) Research Ethics Review Board. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
SC: Writing – original draft, Project administration, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Investigation, Software, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Resources, Investigation, Data curation, Software, Validation, Project administration, Formal analysis, Methodology, Writing – original draft, Supervision, Conceptualization. YN: Project administration, Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Supervision, Conceptualization, Methodology. YL: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Data curation, Supervision, Formal analysis, Methodology, Conceptualization, Software.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The manuscript uses GPT4 to embellish the language but not the scientific content.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Burgers, K, Lindberg, B, and Bevis, ZJ. Chronic diarrhea in adults: evaluation and differential diagnosis. Am Fam Physician. (2020) 101:472–80.
2. Linghu, E. Obesity and chronic diarrhea: a new syndrome? Chin Med J. (2022) 135:1806–7. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002147
3. Gudzune, KA, and Kushner, RF. Medications for obesity: a review. JAMA. (2024) 332:571. doi: 10.1001/jama.2024.10816
4. Ma, C, Congly, SE, Novak, KL, Belletrutti, PJ, Raman, M, Woo, M, et al. Epidemiologic burden and treatment of chronic symptomatic functional bowel disorders in the United States: a Nationwide analysis. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:88–98.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.09.041
5. Everard, A, Geurts, L, Van Roye, M, Delzenne, NM, and Cani, PD. Tetrahydro iso-alpha acids from hops improve glucose homeostasis and reduce body weight gain and metabolic endotoxemia in high-fat diet-fed mice. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e33858. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0033858
6. Ballou, S, Singh, P, Rangan, V, Iturrino, J, Nee, J, and Lembo, A. Obesity is associated with significantly increased risk for diarrhoea after controlling for demographic, dietary and medical factors: a cross-sectional analysis of the 2009-2010 National Health and nutrition examination survey. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. (2019) 50:1019–24. doi: 10.1111/apt.15500
7. Delgado-Aros, S, Camilleri, M, Garcia, MA, Burton, D, and Busciglio, I. High body mass alters colonic sensory-motor function and transit in humans. Am J Physiol-Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2008) 295:G382–8. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.90286.2008
8. Camilleri, M, Malhi, H, and Acosta, A. Gastrointestinal complications of obesity. Gastroenterology. (2017) 152:1656–70. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.12.052
9. Acciarino, A, Diwakarla, S, Handreck, J, Bergola, C, Sahakian, L, and McQuade, RM. The role of the gastrointestinal barrier in obesity-associated systemic inflammation. Obes Rev. (2024) 25:e13673. doi: 10.1111/obr.13673
10. Peng, Y, Liu, F, Qiao, Y, Wang, P, Ma, B, Li, L, et al. Association of abnormal bowel health with major chronic diseases and risk of mortality. Ann Epidemiol. (2022) 75:39–46. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2022.09.002
11. Cheru, L, Saylor, CF, and Lo, J. Gastrointestinal barrier breakdown and adipose tissue inflammation. Curr Obes Rep. (2019) 8:165–74. doi: 10.1007/s13679-019-00332-6
12. Gao, W, Jin, L, Li, D, Zhang, Y, Zhao, W, Zhao, Y, et al. The association between the body roundness index and the risk of colorectal cancer: a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis. (2023) 22:53. doi: 10.1186/s12944-023-01814-2
13. Ding, L, Duan, J, Yang, T, Jin, C, Lv, S, Ma, A, et al. Association between circadian syndrome and chronic diarrhea: a cross-sectional study of NHANES 2005-2010 data. Front Physiol. (2024) 15:1301450. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1301450
14. Chen, R, Fu, Z, Feng, Z, Xiao, F, and Wang, G. Association between atherogenic index of plasma and chronic diarrhea: a cross-sectional study of the NHANES 2005–2010. BMC Gastroenterol. (2025) 25. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03784-4
15. Yang, X, and Sun, Z. Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and bowel habits. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:17658. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66869-2
16. Yang, X, Wang, M, Ren, L, Shon, K, Cui, G, Cheng, Y, et al. Association between visceral adiposity index and bowel habits and inflammatory bowel disease: a cross-sectional study. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:23923. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73864-0
17. Gu, X, Luo, S, Sun, J, Jin, F, Chen, Z, and Song, J. Association between “a body shape index” (ABSI) with periodontitis in a hypertension population from the NHANES 2009-2014. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:23378. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-73998-1
18. Christakoudi, S, Tsilidis, KK, Muller, DC, Freisling, H, Weiderpass, E, Overvad, K, et al. A body shape index (ABSI) achieves better mortality risk stratification than alternative indices of abdominal obesity: results from a large European cohort. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:14541. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71302-5
19. Krakauer, NY, and Krakauer, JC. A new body shape index predicts mortality hazard independently of body mass index. PLoS One. (2012) 7:e39504. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039504
20. Wei, S, Jiang, W, Zheng, H, Zhang, J, Yang, J, Wang, Y, et al. The combined impact of BMI and ABSI on all-cause mortality among American adults with diabetes. Diabetol Metab Syndr. (2025) 17:48. doi: 10.1186/s13098-025-01614-x
21. Thomas, DM, Bredlau, C, Bosy-Westphal, A, Mueller, M, Shen, W, Gallagher, D, et al. Relationships between body roundness with body fat and visceral adipose tissue emerging from a new geometrical model. Obesity. (2013) 21:2264–71. doi: 10.1002/oby.20408
22. Bai, G, Peng, Y, Liu, Q, Shao, X, Zhan, Y, Chen, A, et al. Association between body roundness index and psoriasis among US adults: a nationwide population-based study. Lipids Health Dis. (2024) 23:373. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02365-w
23. Wu, M, Yu, X, Xu, L, Wu, S, and Tian, Y. Associations of longitudinal trajectories in body roundness index with mortality and cardiovascular outcomes: a cohort study. Am J Clin Nutr. (2022) 115:671–8. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqab412
24. Zhang, X, Ma, N, Lin, Q, Chen, K, Zheng, F, Wu, J, et al. Body roundness index and all-cause mortality among US adults. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e2415051. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.15051
25. Chen, Y, Wang, Y, Zheng, X, Liu, T, Liu, C, Lin, S, et al. Body roundness index trajectories and the risk of Cancer: a cohort study. Cancer Med. (2024) 13:e70447. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70447
26. Hu, J, Zou, H, Qiao, X, Wang, Y, Lv, M, Zhang, K, et al. The relationship between oxidative balance scores and chronic diarrhea and constipation: a population-based study. BMC Public Health. (2024) 24:1366. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-18683-8
27. Zhu, JY, Liu, MY, and Sun, C. Assessment of the triglyceride glucose index in adult patients with chronic diarrhea and constipation. World J Clin Cases. (2024) 12:1094, 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i6.1094–103.
28. Yuan, M, He, J, Hu, X, Yao, L, Chen, P, Wang, Z, et al. Hypertension and NAFLD risk: insights from the NHANES 2017-2018 and Mendelian randomization analyses. Chin Med J. (2024) 137:457–64. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002753
29. Liu, H, Kang, J, Liu, W, and Shen, Y. Association between a body shape index and colorectal cancer in US population: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1535655. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1535655
30. Marrie, RA, Dawson, NV, and Garland, A. Quantile regression and restricted cubic splines are useful for exploring relationships between continuous variables. J Clin Epidemiol. (2009) 62:511–517.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2008.05.015
31. Zhou, X, Tao, XL, Zhang, L, Yang, QK, Li, ZJ, Dai, L, et al. Association between cardiometabolic index and depression: National Health and nutrition examination survey (NHANES) 2011-2014. J Affect Disord. (2024) 351:939–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.02.024
32. Liu, P, Lin, S, Sheu, JJ, Lin, C, Lin, P, Chou, Y, et al. Regulation of androgen receptor expression by Z-isochaihulactone mediated by the JNK signaling pathway and might be related to cytotoxicity in prostate cancer. Prostate. (2013) 73:531–41. doi: 10.1002/pros.22593
33. Allam, EA, Ibrahim, HF, Abdulmalek, SA, Abdelmeniem, IM, and Basta, M. Coenzyme Q(10) alleviates testicular endocrine and spermatogenic dysfunction induced by high-fat diet in male Wistar rats: role of adipokines, oxidative stress and MAPK/ERK/JNK pathway. Andrologia. (2022) 54:e14544. doi: 10.1111/and.14544
34. Phelps, T, Snyder, E, Rodriguez, E, Child, H, and Harvey, P. The influence of biological sex and sex hormones on bile acid synthesis and cholesterol homeostasis. Biol Sex Differ. (2019) 10:52. doi: 10.1186/s13293-019-0265-3
35. Wang, L, Tu, Y, Chen, L, Zhang, Y, Pan, X, Yang, S, et al. Male-biased gut microbiome and metabolites aggravate colorectal cancer development. Adv Sci. (2023) 10:2206238. doi: 10.1002/advs.202206238
36. Aldini, R, Roda, A, Festi, D, Sama, C, Mazzella, G, Bazzoli, F, et al. Bile acid malabsorption and bile acid diarrhea in intestinal resection. Dig Dis Sci. (1982) 27:495–502. doi: 10.1007/BF01296727
37. Sorrentino, G, Perino, A, Yildiz, E, El Alam, G, Bou Sleiman, M, Gioiello, A, et al. Bile acids signal via TGR5 to activate intestinal stem cells and epithelial regeneration. Gastroenterology. (2020) 159:956–968.e8. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.067
38. Chávez-Talavera, O, Tailleux, A, Lefebvre, P, and Staels, B. Bile acid control of metabolism and inflammation in obesity, type 2 diabetes, dyslipidemia, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. (2017) 152:1679–1694.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.01.055
39. Camilleri, M. Dissecting molecular mechanisms in bile acid diarrhea. Am J Gastroenterol. (2016) 111:433–5. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2016.23
40. Lee, JM, Ong, JR, Vergnes, L, De Aguiar Vallim, TQ, Nolan, J, Cantor, RM, et al. Diet1, bile acid diarrhea, and FGF15/19: mouse model and human genetic variants. J Lipid Res. (2018) 59:429–38. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M078279
41. Fromm, H, and Malavolti, M. Bile acid-induced diarrhoea. Clin Gastroenterol. (1986) 15:567–82. doi: 10.1016/S0300-5089(21)00739-2
42. Di Ciaula, A, Khalil, M, Baffy, G, and Portincasa, P. Advances in the pathophysiology, diagnosis and management of chronic diarrhoea from bile acid malabsorption: a systematic review. Eur J Intern Med. (2024) 128:10–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2024.07.008
43. Mena Bares, LM, Carmona Asenjo, E, García Sánchez, MV, Moreno Ortega, E, Maza Muret, FR, Guiote Moreno, MV, et al. SeHCAT scan in bile acid malabsorption in chronic diarrhoea. Rev Esp Med Nucl E Imagen Mol. (2017) 36:37–47. doi: 10.1016/j.remn.2016.08.005
44. Moran, C, Herson, J, Than, S, Collyer, T, Beare, R, Syed, S, et al. Interactions between age, sex and visceral adipose tissue on brain ageing. Diabetes Obes Metab. (2024) 26:3821–9. doi: 10.1111/dom.15727
45. Gu, X, Zhu, F, Gao, P, Shen, Y, and Lu, L. Association between visceral adipose tissue and total testosterone among the United States male adults: a cross-sectional study. Int J Impot Res. (2025) 37:163–9. doi: 10.1038/s41443-024-00856-z
46. Lee, J, Busler, JN, Millett, CE, Principe, JL, Levin, LL, Corrigan, A, et al. Association between visceral adipose tissue and major depressive disorder across the lifespan: a scoping review. Bipolar Disord. (2022) 24:375–91. doi: 10.1111/bdi.13130
47. Yu, B, Sun, Y, Du, X, Zhang, H, Chen, C, Tan, X, et al. Age-specific and sex-specific associations of visceral adipose tissue mass and fat-to-muscle mass ratio with risk of mortality. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. (2023) 14:406–17. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13142
48. Li, W, and Hakkak, R. Soy protein concentrate diets inversely affect LPS-binding protein expression in Colon and Liver, reduce Liver inflammation, and increase fecal LPS excretion in obese Zucker rats. Nutrients. (2024) 16:982. doi: 10.3390/nu16070982
49. Hersoug, LG, Møller, P, and Loft, S. Role of microbiota-derived lipopolysaccharide in adipose tissue inflammation, adipocyte size and pyroptosis during obesity. Nutr Res Rev. (2018) 31:153–63. doi: 10.1017/S0954422417000269
50. Sehgal, P, Su, S, Zech, J, Nobel, Y, Luk, L, Economou, I, et al. Visceral adiposity independently predicts time to flare in inflammatory bowel disease but body mass index does not. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2024) 30:594–601. doi: 10.1093/ibd/izad111
51. Lee, CG, Lee, JK, Kang, YS, Shin, S, Kim, JH, Lim, YJ, et al. Visceral abdominal obesity is associated with an increased risk of irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. (2015) 110:310–9. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2014.422
52. Eder, P, Adler, M, Dobrowolska, A, Kamhieh-Milz, J, and Witowski, J. The role of adipose tissue in the pathogenesis and therapeutic outcomes of inflammatory Bowel disease. Cells. (2019) 8. doi: 10.3390/cells8060628
53. Karmiris, K, Koutroubakis, IE, and Kouroumalis, EA. The emerging role of adipocytokines as inflammatory mediators in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2005) 11:847–55. doi: 10.1097/01.mib.0000178915.54264.8f
54. Theocharidou, E, Balaska, A, Vogiatzis, K, Tellis, CC, Gossios, TD, Athyros, VG, et al. Hypertrophic mesenteric adipose tissue May play a role in Atherogenesis in inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2016) 22:2206–12. doi: 10.1097/MIB.0000000000000873
55. Kalaitzidis, D, and Gilmore, TD. Transcription factor cross-talk: the estrogen receptor and NF-kappaB. Trends Endocrinol Metab. (2005) 16:46–52. doi: 10.1016/j.tem.2005.01.004
56. Heo, JW, Kim, SE, and Sung, MK. Sex differences in the incidence of obesity-related gastrointestinal Cancer. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:1253. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031253
57. Wu, Z, Huang, Y, Zhang, R, Zheng, C, You, F, Wang, M, et al. Sex differences in colorectal cancer: with a focus on sex hormone-gut microbiome axis. Cell Commun Signal. (2024) 22:167. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01549-2
58. Santos-Marcos, JA, Mora-Ortiz, M, Tena-Sempere, M, Lopez-Miranda, J, and Camargo, A. Interaction between gut microbiota and sex hormones and their relation to sexual dimorphism in metabolic diseases. Biol Sex Differ. (2023) 14:4. doi: 10.1186/s13293-023-00490-2
59. Ayeser, T, Basak, M, Arslan, K, and Sayan, I. Investigating the correlation of the number of diagnostic criteria to serum adiponectin, leptin, resistin, TNF-alpha, EGFR levels and abdominal adipose tissue. Diabetes Metab Syndr Clin Res Rev. (2016) 10:S165–9. doi: 10.1016/j.dsx.2016.03.010
60. Guo, M, and Wang, X. Pathological mechanism and targeted drugs of ulcerative colitis: a review. Medicine (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e35020. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000035020
61. Wang, Y, Lai, W, Zheng, X, Li, K, Zhang, Y, Pang, X, et al. Linderae Radix extract attenuates ulcerative colitis by inhibiting the JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Phytomedicine. (2024) 132:155868. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2024.155868
62. Inoue, S, Ikai, M, Nambu, R, Moriya, K, Kojima, R, Tagami, Y, et al. JAK inhibitor ameliorates inflammatory bowel disease in a patient with IKZF1 haploinsufficiency. Clin Immunol. (2025) 274:110470. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2025.110470
63. Wang, K, Yin, J, Chen, J, Ma, J, Si, H, and Xia, D. Inhibition of inflammation by berberine: molecular mechanism and network pharmacology analysis. Phytomedicine. (2024) 128. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.155258
64. Xi, M, Hao, G, Yao, Q, Duan, X, and Ge, W. Galactooligosaccharide mediates NF-κB pathway to improve intestinal barrier function and intestinal microbiota. Molecules. (2023) 28:7611. doi: 10.3390/molecules28227611
65. Hassanin, TM, Fouad, Y, Mohamed, FE, Abdel-Hafeez, EH, and Hassnine, A. Colonic mucosal eosinophilia and immunohistochemical expression of COX-2 and NF-kB in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 34:512–7. doi: 10.1097/MEG.0000000000002363
66. Zhang, S, Tian, D, Xia, Z, Yang, F, Chen, Y, Yao, Z, et al. Chang-Kang-Fang alleviates diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) through inhibiting TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 pathway. J Ethnopharmacol. (2024) 330:118236. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.118236
67. Dong, N, Li, X, Xue, C, Zhang, L, Wang, C, Xu, X, et al. Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates LPS-induced inflammation via the NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. (2020) 235:5525–40. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29452
68. Mahurkar-Joshi, S, Rankin, CR, Videlock, EJ, Soroosh, A, Verma, A, Khandadash, A, et al. The colonic mucosal MicroRNAs, MicroRNA-219a-5p, and MicroRNA-338-3p are downregulated in irritable bowel syndrome and are associated with barrier function and MAPK signaling. Gastroenterology. (2021) 160:2409–2422.e19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.02.040
69. Mao, N, Yu, Y, Lu, X, Yang, Y, Liu, Z, and Wang, D. Preventive effects of matrine on LPS-induced inflammation in RAW 264.7 cells and intestinal damage in mice through the TLR4/NF-κB/MAPK pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 143:113432. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113432
70. Qian, W, Li, W, Chen, X, Cui, L, Liu, X, Yao, J, et al. Exploring the mechanism of Xingpi capsule in diarrhea predominant-irritable bowel syndrome treatment based on multiomics technology. Phytomedicine. (2023) 111:154653. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154653
71. Liu, N, Sun, S, Wang, P, Sun, Y, Hu, Q, and Wang, X. The mechanism of secretion and metabolism of gut-derived 5-Hydroxytryptamine. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:7931. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157931
72. Hao, Y, Jiang, L, Han, D, Si, D, Sun, Z, Wu, Z, et al. Limosilactobacillus mucosae and Lactobacillus amylovorus protect against experimental colitis via upregulation of colonic 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor 4 and transforming growth factor-β2. J Nutr. (2023) 153:2512–22. doi: 10.1016/j.tjnut.2023.06.031
73. Liu, R, Luo, Y, Ma, J, Zhang, Q, Sheng, Y, Li, J, et al. Traditional Chinese medicine for functional gastrointestinal disorders and inflammatory bowel disease: narrative review of the evidence and potential mechanisms involving the brain-gut axis. Front Pharmacol. (2024) 15:1444922. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1444922
74. Petracco, G, Faimann, I, and Reichmann, F. Inflammatory bowel disease and neuropsychiatric disorders: mechanisms and emerging therapeutics targeting the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Pharmacol Ther. (2025) 269:108831. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2025.108831
75. Piskorz, MM, Stefanolo, JP, Ibañez, A, Eugenia, H, Bravo Velez, G, Tevez, A, et al. Gut-brain axis and irritable bowel syndrome during the lockdown due to the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: a survey-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol. (2024) 2024:2123. doi: 10.1097/MCG.0000000000002123
76. Settanni, CR, Bibbò, S, Ianiro, G, Rinninella, E, Cintoni, M, Mele, MC, et al. Gastrointestinal involvement of autism spectrum disorder: focus on gut microbiota. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 15:599–622. doi: 10.1080/17474124.2021.1869938
77. Singh, R, Zogg, H, Ghoshal, UC, and Ro, S. Current treatment options and therapeutic insights for gastrointestinal Dysmotility and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:808195. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.808195
78. Dahiya, D, and Nigam, PS. Antibiotic-therapy-induced gut dysbiosis affecting gut microbiota-brain axis and cognition: restoration by intake of probiotics and synbiotics. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3074. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043074
79. Wu, H, Zhan, K, Rao, K, Zheng, H, Qin, S, Tang, X, et al. Comparison of five diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-D) rat models in the brain-gut-microbiota axis. Biomed Pharmacother. (2022) 149:112811. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.112811
80. Daulatzai, MA. Chronic functional bowel syndrome enhances gut-brain axis dysfunction, neuroinflammation, cognitive impairment, and vulnerability to dementia. Neurochem Res. (2014) 39:624–44. doi: 10.1007/s11064-014-1266-6
81. Yao, Q, Yu, Z, Meng, Q, Chen, J, Liu, Y, Song, W, et al. The role of small intestinal bacterial overgrowth in obesity and its related diseases. Biochem Pharmacol. (2023) 212:115546. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115546
82. Wijarnpreecha, K, Werlang, ME, Watthanasuntorn, K, Panjawatanan, P, Cheungpasitporn, W, Gomez, V, et al. Obesity and risk of small intestine bacterial overgrowth: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig Dis Sci. (2020) 65:1414–22. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05887-x
83. Banaszak, M, Górna, I, Woźniak, D, Przysławski, J, and Drzymała-Czyż, S. Association between gut dysbiosis and the occurrence of SIBO, LIBO, SIFO and IMO. Microorganisms. (2023) 11:573. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030573
84. Wang, L, Tian, M, Sun, H, Gao, J, Qi, W, Xu, J, et al. Association between bowel movement disorders and depressive symptoms: a cross-sectional study. Front Psychol. (2024) 15:1449948. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1449948
85. Alberto, J, Moreno-Castañeda, L, Uribe, M, and Carlos Chávez-Tapia, N. The role of bile acids in glucose metabolism and their relation with diabetes. Ann Hepatol. (2017) 16:S15–20. doi: 10.5604/01.3001.0010.5494
86. Gong, J, Zhang, Q, Hu, R, Yang, X, Fang, C, Yao, L, et al. Effects of Prevotella copri on insulin, gut microbiota and bile acids. Gut Microbes. (2024) 16:2340487. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2024.2340487
87. McLeod, A, Wolf, P, Chapkin, RS, Davidson, LA, Ivanov, I, Berbaum, M, et al. Design of the Building Research in CRC prevention (BRIDGE-CRC) trial: a 6-month, parallel group Mediterranean diet and weight loss randomized controlled lifestyle intervention targeting the bile acid-gut microbiome axis to reduce colorectal cancer risk among African American/black adults with obesity. Trials. (2023) 24:113. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07115-4
Glossary
ABSI - A body shape index
AUC - Area under the curve
BHQ - Bowel health questionnaire
BMI - Body mass index
BRI - Body roundness index
BSFS - Bristol stool form scale
CI - Confidence interval
CVD - Cardiovascular disease
DBP - Diastolic blood pressure
FDr - Functional diarrhoea
FPG - Fasting plasma glucose
Hb - Hemoglobin
HbA1c - Hemoglobin A1c
IBS-D - diarrhoeal irritable bowel syndrome
IBD - Inflammatory bowel disease
IL-6 - Interleukin-6
LPS - Lipopolysaccharide
MAPK - Mitogen-activated protein kinase
NCHS - National Center for Health Statistics
NF-κB - Nuclear Factor kappa B
NHANES - National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
OGTT - Oral glucose tolerance test
OR - Odds ratio
PIR - Poverty income ratio
Q1 - First quartile
Q2 - Second Quartile
Q3 - Third Quartile
Q4 - Fourth Quartile
RCS - Restricted cubic spline
ROC - Receiver operating characteristic
SBP - Systolic blood pressure
SIBO - Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth
TC - Total cholesterol
TG - Triglycerides
TNF-α - Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
VAI - Visceral Adiposity Index
VAT - Visceral Adipose Tissue
WC - Waist Circumference
Keywords: body shape index, body roundness index, chronic diarrhoea, NHANES, cross-sectionaI study
Citation: Chen S, Zhang J, Niu Y and Li Y (2025) Independent role of two novel abdominal fat indicators in chronic diarrhoea. Front. Med. 12:1593571. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1593571
Edited by:
Jianbin Zhang, Dalian Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Zehra Jamil, Aga Khan University, PakistanSabyasachi Mohanty, University of Nebraska-Lincoln, United States
Viridiana M. Mendoza-Martinez, General Hospital of Mexico, Mexico
Tania Rivera-Carranza, Universidad Autónoma Metropolitana, Mexico
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Zhang, Niu and Li. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yifang Li, bHlmMjAxMTA4MDFAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Shiming Chen
Shiming Chen Jingxia Zhang1,2
Jingxia Zhang1,2 Yifang Li
Yifang Li