- 1Department of Nuclear Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
- 2Department of Oncology, The First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University, Dalian, China
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is a rare chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by eosinophilic infiltration of the gastrointestinal tract. We report the case of a 42-year-old previously healthy man who presented with gradually worsening abdominal pain and bloating for approximately 1 month. Initial laboratory tests showed elevated eosinophil counts, increased immunoglobulin E levels, and raised C-reactive protein. Enhanced CT revealed diffuse edema of the gastric wall, thickening of the gastric and duodenal walls, enlargement of the abdominal lymph nodes, and thickening of the peritoneum, which was suspected to be caused by malignant tumors. However, gastroscopic pathological examination and multiple ascites examinations showed no obvious malignant cells. To investigate the underlying cause, the combined 18F-AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 (18F-FAPI) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) and 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) PET/CT were performed. The pattern of increased radionuclide uptake in these mentioned lesions differs from that of malignant neoplasms. Then, EGE was confirmed by diagnostic peritoneal biopsy. This case highlights that PET/CT imaging combined with 18F-FAPI and 18F-FDG demonstrates potential utility in diagnosing EGE, particularly in distinguishing inflammatory processes from malignancies.
1 Introduction
Eosinophilic gastroenteritis (EGE) is a rare gastrointestinal disorder, most commonly affecting the stomach and duodenum (1). The prevalence of EGE is approximately 1.7/100,000, which is more common in young and middle-aged people aged 30–50 years (2, 3). The clinical symptoms of EGE vary according to the site and depth of involvement (4). Mucosal EGE is the most common type, characterized by nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and decreased weight. The muscular type presents with thickening of the gastrointestinal wall, rigidity of the intestinal lumen, and potential obstruction. The serosal type is characterized by large amounts of ascites and abdominal distension, accompanied by marked eosinophilic infiltration (5, 6).
Studies have shown that up to 60–70% of patients exhibit peripheral eosinophilia and elevated immunoglobulin E levels (6), but both lack specificity. In one-third of EGE patients, barium contrast studies appear normal, with mucosal fold thickening being the most notable imaging feature (7). CT and MRI findings in EGE correlate with the location and depth of eosinophil infiltration in the gastrointestinal wall, such as the characteristic “target sign” and “tram-track sign” in small intestinal EGE, which aid in diagnosis (1, 8). Endoscopic findings in EGE patients commonly include mucosal congestion and edema, followed by erosion (5). However, these imaging and endoscopic features lack specificity. Endoscopic tissue biopsy is a crucial diagnostic tool for EGE (9). Definitive diagnosis requires a histopathological demonstration of >20 eosinophils/HPF. However, the heterogeneity of eosinophilic infiltration at different sites poses a challenge, particularly for lesions confined to the muscular or subserosal layers, where the mucosal layer may appear normal (10, 11), which brings great distress to the clinical diagnosis of EGE. While multiple biopsies (including duodenum) of endoscopy were recommended (10, 12), missed or misdiagnosed cases remain unavoidable, as demonstrated in this case.
To date, 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (18F-FDG) positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET/CT) imaging of EGE has only been reported in a few cases (13–16), while 18F-AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 (18F-FAPI) PET/CT imaging remains poorly understood (17). In this study, we present a case of EGE evaluated with both 18F-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT and review relevant literature to enhance the understanding of this condition. We emphasize the role of dual-tracer PET/CT in the diagnostic workup of EGE, particularly in excluding gastrointestinal malignancies.
2 Case presentation
A timeline of the onset, diagnosis, and therapy is shown in Figure 1. We present the case of a 42-year-old man who was admitted to our hospital on 7 December 2024, presenting with a 1-month history of abdominal distension, epigastric discomfort, and bilateral hypochondrial pain, accompanied by anorexia, mild fatigue, and 5 kg weight loss. Symptoms persisted despite self-administered gastric acid suppression and mucosal protectants. Physical examination showed abdominal distension with shifting dullness but no tenderness or masses. Laboratory tests revealed elevated blood eosinophil count (0.67 × 109/L, reference range 0.02–0.52 × 109/L), tumor marker CA125 (111.47 U/mL, reference range 0–35 U/mL), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (31.00 mm/h, reference range 0–15 mm/h), C-reactive protein (275.8 mg/L, reference range 0–5.0 mg/L), and immunoglobulin E (273 IU/mL, reference range 0–100 IU/mL). His tuberculosis screening, rheumatoid factor, amylase, and lipase were normal. Additionally, the patient had no history of past medical issues.
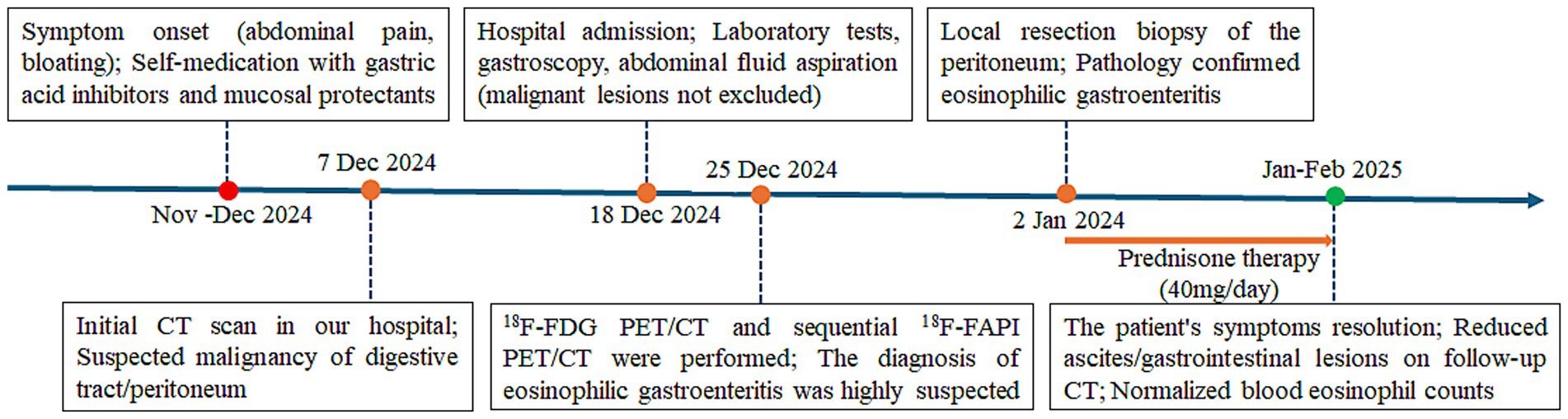
Figure 1. Timeline of the clinical course and treatment of the patient with eosinophilic gastroenteritis.
A three-phase enhanced scan of the entire abdomen was performed by Discovery HD CT (GE Healthcare, Chicago, USA). The images showed thickening of the gastric antrum and body walls, with the maximum thickness part reaching 2.3 cm. The CT value was approximately 22 Hu, and moderate heterogeneous enhancement was observed, with three-phase CT values of 41 Hu, 77 Hu, and 47 Hu, respectively. Contours were poorly defined, with blurred surrounding fat spaces and enlarged lymph nodes along the lesser curvature of the stomach. The proximal duodenal wall appeared irregular, and the pancreatic contour was coarse, but the density and enhancement were homogeneous. The amount of fluid density was observed in the abdominal cavity (Figure 2).
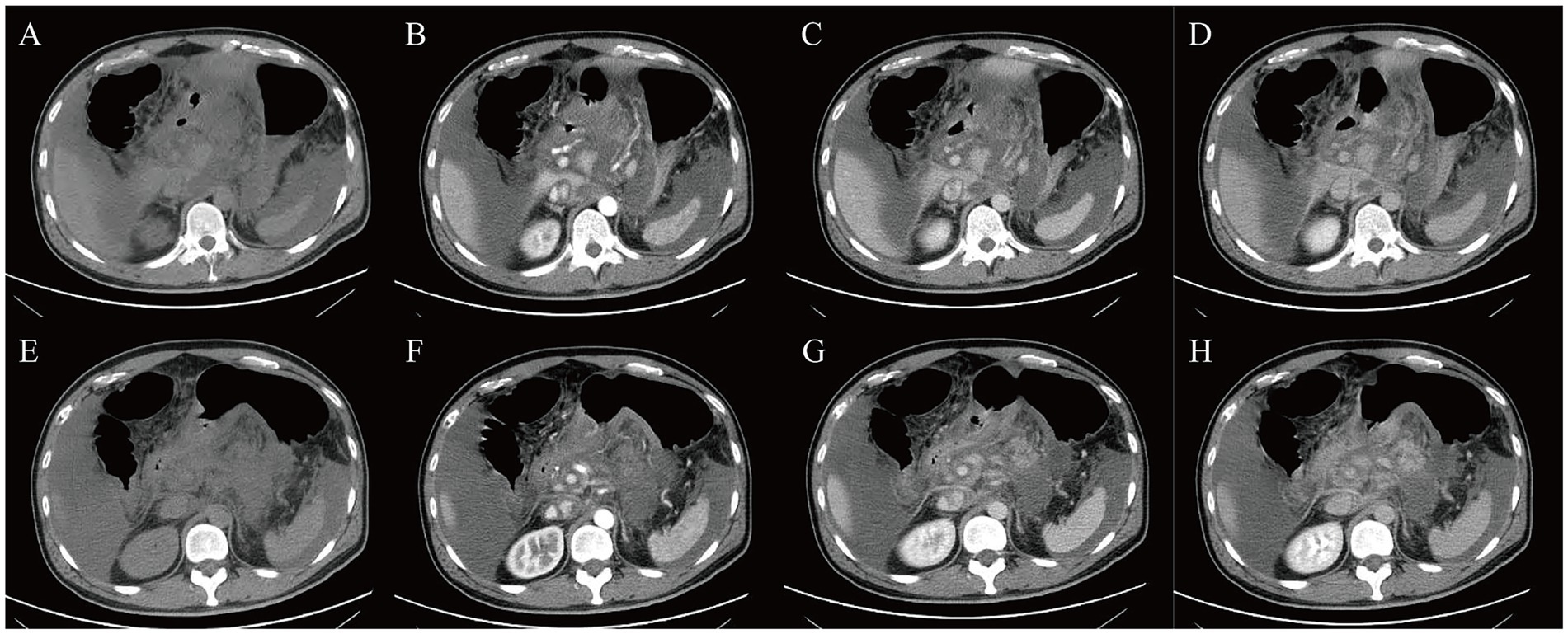
Figure 2. Contrast-enhanced CT scans. (A,E) plain CT, (B,F) enhanced CT arterial phase, (C,G) enhanced CT venous phase, (D,H) enhanced CT delayed phase.
Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (Figures 3A,B) revealed extensive congestive blood spots on the gastric fundus and body wall, with attached white exudates, stiff and coarse folds, poor extension after inflation, and rough and edematous mucosa in the gastric sinus. The lumen of the descending part of the duodenum was slightly narrowed, but no mucosal abnormality was observed. Multi-point mucosal sampling and biopsy were performed; pathology revealed chronic active inflammation with intestinal metaplasia. Multiple aspirations of ascites were performed, which appeared yellowish and turbid, with a specific gravity of 1.032, protein positivity (+), total cell counts of 2,200/μL, nucleated cell counts of 1,241/μL, eosinophil proportion in ascites of 14–20%, protein quantification of 48.7 g/L, adenosine deaminase (ADA) of 10.5 U/L, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) 197 U/L. Cytopathological examination of ascites showed no atypical cells.
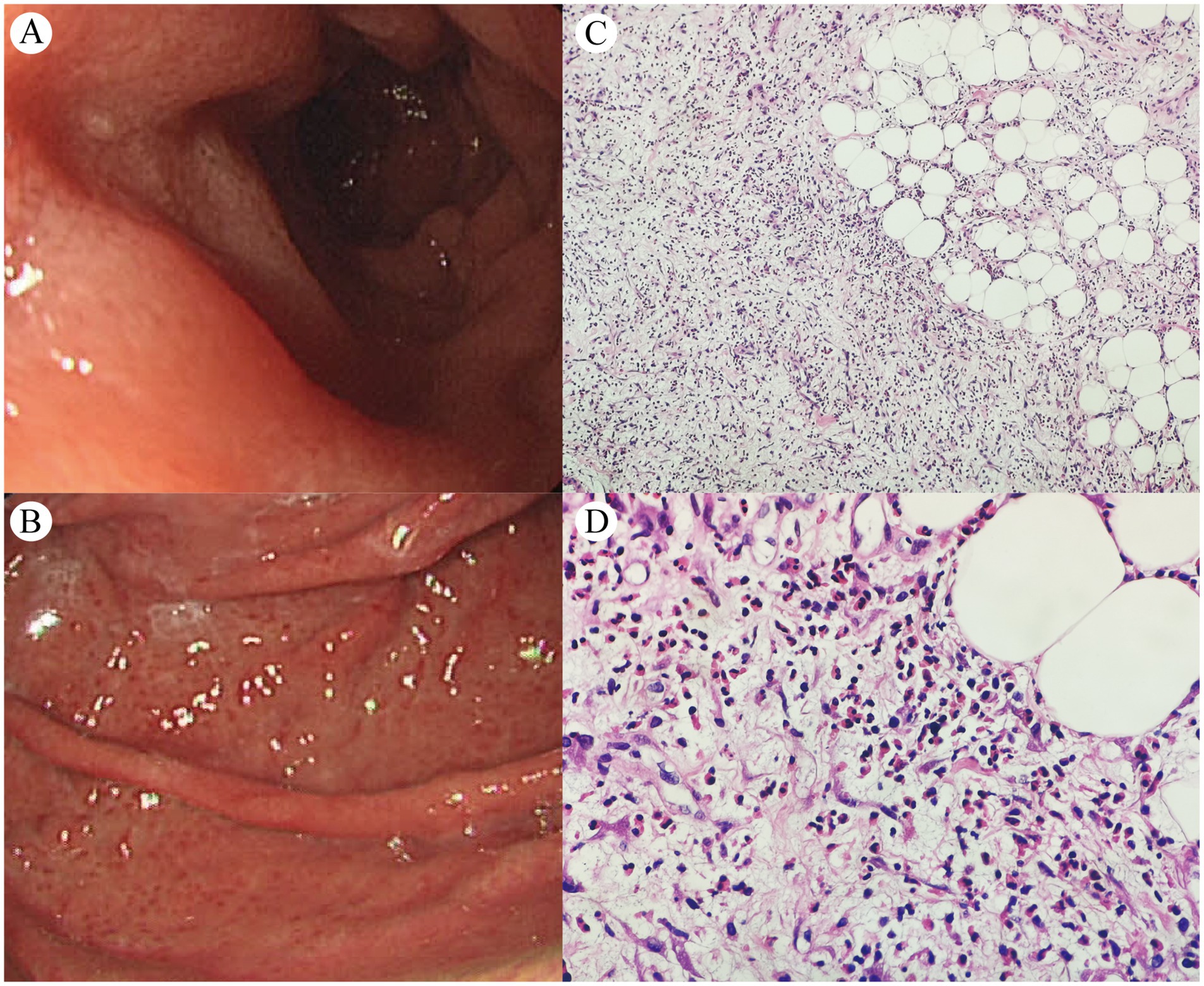
Figure 3. Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (A,B) and peritoneal histopathology of the biopsy specimen [C (×100) and D (×400)].
Subsequently, a Biograph True-Point Row 64 PET/CT (Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany) was performed for differentiating diagnosis (Figure 4), 18F was produced using a Siemens Eclipse cyclotron, 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI radiochemical synthesis was performed using the All in One® (Tarsias, Ans, Belgium) and Explora FDG4 (Siemens Medical Solutions, Erlangen, Germany) Synthesis Module. The radiochemical purities were both greater than 95%. Yellow arrows: Diffuse heterogeneous peritoneal thickening (hepatogastric ligament, lesser omental bursa, greater omentum, pancreatic anterior, left renal fascia) with mildly increased 18F-FDG uptake (SUVmax 3.9–5.5; Figures 4F–H) and markedly elevated 18F-FAPI uptake (SUVmax 6.7–12.9; Figures 4L–N), the latter revealing a larger lesion extent. White arrows: Thickening and edema of the gastric lesser curvature, antrum, duodenal bulb, and descending intestinal wall, with luminal narrowing and rough serosal surfaces. PET showed mild 18F-FDG (SUVmax 2.8; Figure 4H) and 18F-FAPI uptake (SUVmax 5.7; Figure 4N). Blue arrows: Slightly enlarged lesser-curvature lymph nodes (1.7 cm) with mild 18F-FDG (SUVmax 3.6; Figure 4G) and 18F-FAPI uptake (SUVmax 8.7; Figure 4M), accompanied by ascites.
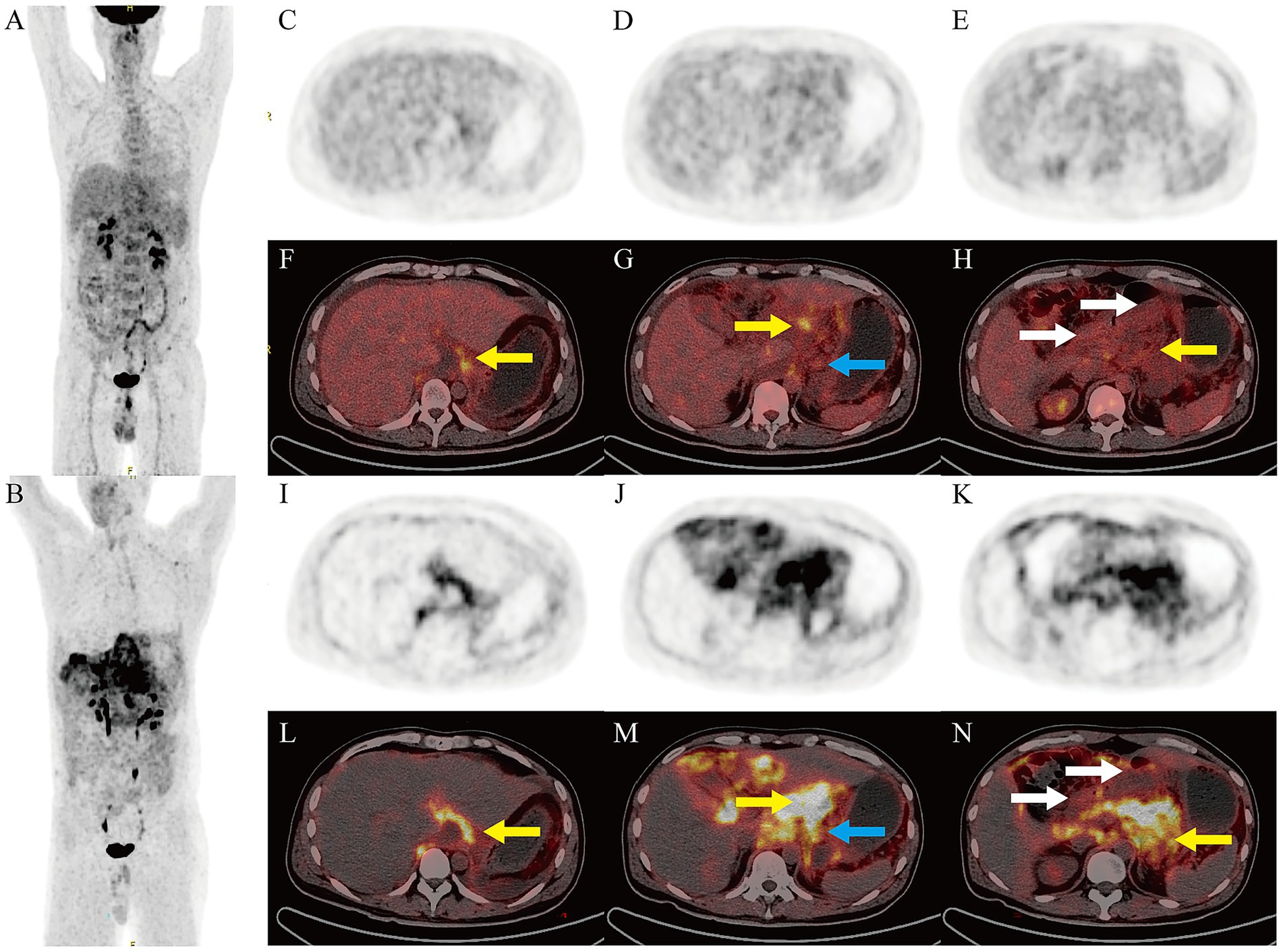
Figure 4. PET/CT Imaging. Maximum intensity projection of 18F-FDG (A) and 18F-FAPI (B) PET. Axial 18F-FDG PET (C–E) and PET/CT fusion scans (F–H), axial 18F-FAPI PET (I–K), and PET/CT fusion scans (L–N).
Taken together, the patient’s ascites test indicated low cell count but elevated specific gravity and protein levels, suggesting exudative ascites; the patient had no underlying liver, kidney, or heart disease. Tuberculosis, as a granulomatous lesion, often shows significant uptake of 18F-FDG on PET scans (18), while 18F-FAPI only shows slightly higher metabolism around the granuloma, and the patient’s tuberculosis test was negative, thereby ruling out these causes (19). In this patient, the denial distribution of peritoneal thickening lesions was more significant at the diaphragmatic dome and organ ligament sites, which was different from the common implantation metastasis pattern of carcinomatous peritonitis. Notably, 18F-FAPI is a positive imaging modality presenting advantages for signet ring cell carcinoma (SRCC), which did not show significantly high uptake in gastrointestinal lesions in this patient (20). Thus, we also questioned carcinomatous peritonitis, and in combination with other clinical test results, non-specific gastrointestinal inflammation, such as EGE, was considered.
Finally, diagnostic laparoscopy with omental biopsy (Figures 3C,D) revealed mesothelial hyperplasia, fibrous tissue proliferation with fibrinoid necrosis, and marked eosinophilic infiltration (90–120/HPF) with focal fat necrosis. Following diagnosis, the patient initiated oral prednisone therapy at 40 mg/day, with no significant adverse effects observed. After over 2 weeks of treatment, abdominal discomfort symptoms were alleviated, with a follow-up complete blood count showing normalization of eosinophil levels. A follow-up CT scan performed at another hospital on February 2025 showed resolution of ascites and reduced gastric antral/peritoneal thickening; continued follow-up and treatment were recommended. The patient declined repeat gastroscopy and PET/CT surveillance due to procedural anxiety and financial constraints, remaining under clinical monitoring.
3 Discussion
EGE is a rare condition characterized by eosinophilic infiltration of the gastrointestinal tract and can involve anywhere from the esophagus to the rectum (1). Its clinical manifestations, often non-specific digestive symptoms, are closely related to the location and depth of eosinophil infiltration (2). Due to its non-specific clinical manifestations, EGE is often misdiagnosed or overlooked, particularly when symptoms overlap with other abdominal pathologies. In this case report, we describe for the first time an EGE with extensive peritoneal involvement who underwent combined 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI PET/CT imaging, and this case report details the clinical course, diagnostic work-up, and follow-up of patients with EGE in order to deepen the understanding of this disease.
18F-FDG PET/CT, as a well-established imaging modality for visualizing glucose metabolism, is widely recognized in clinical practice (21). Previous data suggest that 18F-FDG PET, as a non-invasive imaging modality, holds potential for detecting gastrointestinal inflammatory conditions (22). FAP, a type II transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the dipeptidyl peptidase family, is highly expressed in cancer-associated fibroblasts within the tumor microenvironment. In recent years, FAPIs have emerged as a novel class of radiotracers for PET imaging (23–25). Compared to conventional imaging agents such as 18F-FDG, FAPI tracers offer unique advantages in tumors with low glucose metabolism or high stromal content. The combination of the two effectively improves the disease spectrum of PET/CT for tumor diagnosis, such as well-differentiated carcinoma, signet ring cell carcinoma, and soft tissue sarcoma (23–27). However, their uptake is not exclusive to malignant lesions. It is widely known that the false-positive uptake of 18F-FDG can be caused by inflammation, infection, or other benign lesions. FAPI PET imaging may produce false-positive results for non-malignant tumors, which are mainly related to inflammation and fibroblasts. Recent studies have revealed that FAP is often expressed in wound healing, tissue remodeling, and chronic inflammation, leading to growing interest in the application of 18F-AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 (18F-FAPI) PET in these areas (28–31). These non-specific uptakes present both challenges and opportunities for PET/CT imaging.
Here, we report a case of EGE that mimicked signet ring cell carcinoma with extensive peritoneal metastasis. In this case, the peritoneal lesions exhibited intense 18F-FAPI uptake, with more extensive detection than 18F-FDG PET. In contrast, gastrointestinal lesions and lymph nodes demonstrated only slightly increased 18F-FDG and 18F-FAPI uptake, distinct from gastrointestinal signet ring cell carcinoma with peritoneal metastases, underscoring its potential integration into clinical practice. There was heterogeneity in the levels of 18F-FDG uptake between the present case and previously reported gastrointestinal EGE (13–16), with SUVmax ranging from 2.8 ~ 7.1, and we speculate that this may be related to the different periods of the disease. The degree of 18F-FAPI uptake was similar to that of the only other case (17) of small bowel EGE (SUVmax 5.7 ~ 7.3), while the unique sign in the present case was that the peritoneum was involved and its extent was more extensive on FAPI than FDG, combined with massive ascites and lymph node enlargement. These findings emphasize that combined 18F-FAPI and 18F-FDG PET/CT can be used as a potential non-invasive method for evaluating eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases, which opens new avenues for its application in the field of non-oncology.
However, this is merely an exclusionary empirical diagnosis; this study is a case-by-case analysis, which limits its wider applicability. These findings cannot be used as a basis for diagnosing benign lesions, and further research is warranted to elucidate the underlying mechanisms of radionuclide uptake under these conditions and optimize its diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
4 Conclusion
The combined application of 18F-FAPI PET/CT and 18F-FDG PET/CT offers significant diagnostic value for EGE. However, the rarity of EGE limits large-scale studies, necessitating further evidence to validate PET/CT’s role. Biopsy remains the diagnostic gold standard.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
BC: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing, Visualization. TW: Writing – original draft, Formal analysis, Visualization. JX: Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Visualization, Writing – original draft.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The study was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province, China (No. 2024-BS-164).
Acknowledgments
We are especially grateful for the support of physicians from the Department of Pathology and the Gastroenterology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Dalian Medical University.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Chehade, M, Wright, BL, Walsh, S, Bailey, DD, Muir, AB, Klion, AD, et al. Challenging assumptions about the demographics of eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases: a systematic review. J Allergy Clin Immunol Glob. (2024) 3:100260. doi: 10.1016/j.jacig.2024.100260
2. Li, K, Ruan, G, Liu, S, Xu, T, Guan, K, Li, J, et al. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Chin Med J. (2023) 136:899–909. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002511
3. Kinoshita, Y, and Ishihara, S. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: epidemiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. (2020) 20:311–5. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000635
4. Leru, PM, Anton, VF, Muntean, IA, Neagoe, CD, and Matei, D. Follow-up of a rare case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis associated with persistent blood eosinophilia and multiple food allergies. Diagnostics (Basel). (2022) 12:1381. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12061381
5. Pineton de Chambrun, G, Desreumaux, P, and Cortot, A. Eosinophilic enteritis. Dig Dis. (2015) 33:183–9. doi: 10.1159/000369540
6. Galere, P, and Gilbert, A. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with ascites: an enigmatic diagnosis. Lancet. (2022) 400:126. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(22)01056-X
7. Ma, L, Li, W, Xiao, M, Liu, W, Liu, J, Zhou, W, et al. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis: imaging spectrum on intestinal ultrasonography and CT enterography. Eur J Radiol. (2024) 181:111820. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2024.111820
8. Yalon, M, Tahboub Amawi, AD, Kelm, ZS, Wells, ML, Teo, LLS, Heiken, JP, et al. Eosinophilic disorders of the gastrointestinal tract and associated abdominal viscera: imaging findings and diagnosis. Radiographics. (2022) 42:1081–102. doi: 10.1148/rg.220004
9. Koutri, E, and Papadopoulou, A. Eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases in childhood. Ann Nutr Metab. (2018) 73:18–28. doi: 10.1159/000493668
10. Collins, MH. Histopathologic features of eosinophilic esophagitis and eosinophilic gastrointestinal diseases. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. (2014) 43:257–68. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2014.02.007
11. Kuźmiński, A, Rosada, T, Przybyszewska, J, Ukleja-Sokołowska, N, and Bartuzi, Z. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis - a manifestation of an allergic disease in the gastrointestinal tract? Part 1 EPIDEMIOLOGY and diagnosis. Prz Gastroenterol. (2023) 18:43–6. doi: 10.5114/pg.2022.118634
12. Wang, WQ, Sun, H, Shen, D, Lin, L, and Yan, WC. Eosinophilic gastroenteritis with hemorrhagic ascites: a case report. Am J Transl Res. (2024) 16:6841–5. doi: 10.62347/TCOH9399
13. Çağlar, E, Karişmaz, K, and Dobrucali, A. A case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis mimicking gastric lymphoma associated with pancreatitis due to duodenal involvement. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2012) 23:585–9. doi: 10.4318/tjg.2012.0436
14. Manabe, N, Todo, E, Haruma, K, Ayaki, M, Nakamura, J, Fujita, M, et al. A case of eosinophilic gastroenteritis with high PET-CT accumulation treated by P-CAB. Radiol Case Rep. (2021) 16:2174–8. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2021.05.039
15. Zhou, J, Zhao, M, Wang, J, Tian, R, and Zhao, M. Role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in the detection of eosinophilic esophagitis. Hell J Nucl Med. (2023) 26:207–9. doi: 10.1967/s002449912605
16. Dong, A, Wang, Y, and Zuo, C. FDG PET/CT in eosinophilic esophagitis. Clin Nucl Med. (2014) 39:540–3. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e318286c025
17. Dong, Y, and Zhou, W. Superiority of 18F-FAPI-42 PET/CT in eosinophilic gastrointestinal disorders. Clin Nucl Med. (2024) 50:e440–2. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000005658
18. Alçın, G, Tatar, G, Şahin, R, Baloğlu, MC, and Çermik, TF. Peritoneal tuberculosis mimicking peritoneal Carcinomatosis on 68 Ga-FAPI-04 and 18 F-FDG PET/CT. Clin Nucl Med. (2022) 47:e557–8. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000004174
19. Bentestuen, M, Al-Obaydi, N, and Zacho, HD. FAPI-avid nonmalignant PET/CT findings: an expedited systematic review. Semin Nucl Med. (2023) 53:694–705. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2023.02.001
20. Sun, Y, Xu, J, Qiao, Y, Zhang, J, Pan, H, Xu, X, et al. Assessing the value of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT in gastric mucinous adenocarcinoma or signet ring cell carcinoma. Radiol Imaging Cancer. (2024) 6:e230195. doi: 10.1148/rycan.230195
21. Ng, QK, Triumbari, EKA, Omidvari, N, Cherry, SR, Badawi, RD, and Nardo, L. Total-body PET/CT - first clinical experiences and future perspectives. Semin Nucl Med. (2022) 52:330–9. doi: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2022.01.002
22. Louis, E, Ancion, G, and Colard, A. Noninvasive assessment of Crohn’s disease intestinal lesions with 18F-FDG PET/CT. J Nucl Med. (2007) 48:1053–9. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.107.040436
23. Yang, T, Ma, L, Hou, H, Gao, F, and Tao, W. FAPI PET/CT in the diagnosis of abdominal and pelvic tumors. Front Oncol. (2022) 11:797960. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.797960
24. Li, T, Zhang, J, Yan, Y, Tan, M, and Chen, Y. Applications of FAPI PET/CT in the diagnosis and treatment of breast and the most common gynecologic malignancies: a literature review. Front Oncol. (2024) 14:1358070. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1358070
25. Kessler, L. Fibroblast activation protein inhibitor (FAPI)-PET imaging in sarcoma. PET Clin. (2023) 18:353–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cpet.2023.03.001
26. Kratochwil, C, Flechsig, P, Lindner, T, Abderrahim, L, Altmann, A, Mier, W, et al. 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT: tracer uptake in 28 different kinds of Cancer. J Nucl Med. (2019) 60:801–5. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.119.227967
27. Elboga, U, Sahin, E, Kus, T, Cayirli, YB, Aktas, G, Okuyan, M, et al. Comparison of 68Ga-FAPI PET/CT and 18FDG PET/CT modalities in gastrointestinal system malignancies with peritoneal involvement. Mol Imaging Biol. (2022) 24:789–97. doi: 10.1007/s11307-022-01729-x
28. Hotta, M, Rieger, AC, Jafarvand, MG, Menon, N, Farolfi, A, Benz, MR, et al. Non-oncologic incidental uptake on FAPI PET/CT imaging. Br J Radiol. (2023) 96:20220463. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20220463
29. Mori, Y, Kramer, V, Novruzov, E, Mamlins, E, Röhrich, M, Fernández, R, et al. Initial results with [18F]FAPI-74 PET/CT in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2024) 51:1605–11. doi: 10.1007/s00259-023-06564-y
30. Song, Y, Qin, C, Chen, Y, Ruan, W, Gai, Y, Song, W, et al. Non-invasive visualization of liver fibrosis with [68Ga]Ga-DOTA-FAPI-04 PET from preclinical insights to clinical translation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2024) 51:3572–84. doi: 10.1007/s00259-024-06773-z
Keywords: FDG, FAPI, PET/CT, eosinophilic gastroenteritis, peritoneal
Citation: Chen B, Wu T and Xie J (2025) Combined 18F-AlF-NOTA-FAPI-04 and 18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT in patients with eosinophilic gastroenteritis: a case report and literature review. Front. Med. 12:1602306. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1602306
Edited by:
Sunyoung Jang, The Pennsylvania State University, United StatesReviewed by:
Khadija Hafidh, Dubai Health Authority, United Arab EmiratesJaiprakash Suresh Gurav, Armed Forces Medical College, Pune, India
Sheng Dai, Weifang Traditional Chinese Hospital, China
Polliana Leru, Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Romania
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Wu and Xie. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jinghui Xie, eGllamluZ2h1aTE2M21haWxAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Bo Chen1
Bo Chen1 Jinghui Xie
Jinghui Xie