Abstract
Background:
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive respiratory disorder characterized by persistent airflow limitation and chronic airway inflammation. Life’s Crucial 9 (LC9) is a comprehensive tool for evaluating cardiovascular and metabolic health. The neutrophil-to-albumin ratio (NPAR) has been proposed as a novel inflammation-nutrition biomarker. This study aimed to elucidate the association between LC9 scores and the prevalence of COPD while also assessing the potential mediating role of NPAR.
Methods:
A cross-sectional analysis was conducted using data from 25,634 U.S. participants in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) from 2005 to 2018. Multivariable logistic regression, stratified subgroup analyses, and restricted cubic spline (RCS) models were employed to evaluate the association between LC9 and COPD.
Results:
Among the 25,634 participants, 1,248 reported a history of COPD. After adjusting for multiple covariates, each 10-unit increase in the LC9 score was associated with a 28% lower odds of COPD (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.67–0.77), whereas each one-unit increase in NPAR was associated with a 6% higher odds of COPD (OR = 1.06, 95% CI: 1.03–1.10). Similar trends were observed when LC9 and NPAR were categorized into different levels (P for trend < 0.05). RCS analysis revealed a linear inverse relationship between LC9 scores and COPD prevalence. Mediation analysis indicated that NPAR accounted for 4.84% of the association between LC9 and COPD (p < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Higher LC9 scores were associated with a reduced risk of COPD, with NPAR acting as a significant mediator in this relationship. These findings highlight the potential value of optimizing cardiovascular health in COPD prevention strategies and underscore the importance of controlling inflammation and improving nutritional status. Further prospective studies are warranted to validate these preliminary findings.
Introduction
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a progressive respiratory disorder characterized by persistent airflow limitation, chronic inflammation, and irreversible damage to lung tissue (1, 2). Globally, COPD represents the third leading cause of death, accounting for 3.3 million deaths in 2019 (3), with its prevalence and disease burden continuing to rise, particularly in low- and middle-income countries (4). In addition to its high mortality rate, COPD imposes a substantial socioeconomic burden due to frequent hospitalizations, long-term treatment requirements, and reduced quality of life. Given its chronic and irreversible nature, identifying modifiable risk factors is essential for early prevention and slowing disease progression, ultimately reducing its societal and public health impact.
In recent years, increasing evidence has highlighted a strong link between COPD and cardiovascular health (5, 6). Studies have demonstrated that individuals with poor cardiovascular health are at a significantly elevated risk of developing COPD (7), with systemic inflammation and oxidative stress potentially serving as shared pathogenic mechanisms (8–10). In this context, the American Heart Association (AHA) introduced Life’s Essential 8 (LE8) (11), along with an expanded version, Life’s Crucial 9 (LC9) (12), as comprehensive tools for assessing individual cardiovascular and metabolic health. The LC9 builds upon the LE8 by incorporating psychological well-being, providing a more holistic and scientifically robust framework. LC9 has been applied in studies related to overactive bladder syndrome (13, 14) and infertility (15). Although some studies have preliminarily investigated the direct relationship between LC9 and COPD risk, the potential biological pathways underlying this association remain unclear (16, 17).
Notably, both inflammation and nutritional status are critical determinants of cardiovascular health (18) and key contributors to the pathogenesis of COPD (19). Unhealthy dietary patterns, physical inactivity, and metabolic dysfunction may exacerbate systemic inflammation and accelerate pulmonary function decline. Previous studies have suggested that several inflammation- and nutrition-related biomarkers are closely associated with both cardiovascular and respiratory diseases (19, 20). Among these markers, the neutrophil-to-albumin ratio (NPAR) has recently emerged as a novel indicator of systemic inflammation and nutritional status (21), attracting growing attention. NPAR has been shown to predict adverse outcomes in various cardiopulmonary conditions (22, 23), and elevated NPAR levels have been shown to predict COPD mortality risk (24). Neutrophils indicate systemic inflammation, which contributes to atherosclerosis, endothelial dysfunction, and plays a central role in airway inflammation and lung tissue damage seen in COPD. Albumin, on the other hand, reflects nutritional status and decreases during inflammation. Low albumin levels are linked to poor outcomes in both cardiovascular conditions and COPD (25). By combining these two indicators, NPAR serves as a comprehensive measure of inflammatory and nutritional status. This makes it a biologically plausible mediator between LC9, which reflects cardiovascular health, and the development of COPD. Therefore, exploring NPAR as a potential link can help clarify how systemic processes connect cardiovascular and pulmonary health.
Despite evidence supporting the individual associations of LC9 and NPAR with COPD, no prior study has elucidated whether LC9 may influence COPD risk via modulation of NPAR levels. Conceptually, individuals with better cardiovascular and metabolic health (as captured by higher LC9 scores) are more likely to maintain lower systemic inflammation and better nutritional status—factors directly reflected by a reduced NPAR. In turn, a lower NPAR may attenuate inflammatory-driven lung tissue damage and functional decline, thereby reducing COPD risk. This potential mediating pathway offers a biologically plausible mechanism linking cardiovascular health to pulmonary disease development but has not yet been empirically tested. Therefore, building upon prior research, this study aims to investigate the potential mediating effect of NPAR in the association between LC9 and COPD using data from the 2005–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). Through mediation analysis, we seek to uncover whether improved cardiovascular health may reduce COPD prevalence partly by lowering systemic inflammation and improving nutritional status, as captured by NPAR. This novel analytical approach may provide new mechanistic insights into the complex interplay among cardiovascular health, inflammation, nutrition, and respiratory disease.
Methods
Study participants
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) is a complex, multistage probability sampling program conducted by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS). It collects comprehensive data on demographic characteristics, health indicators, and dietary patterns of the U.S. population. The primary aim of NHANES is to assess and monitor the nutritional and health status of individuals across all age groups in the United States. All NHANES protocols were approved by the NCHS Research Ethics Review Board, and written informed consent was obtained from all participants. The present study utilized publicly available data and adhered to the STROBE guidelines for cross-sectional studies (26), thus exempting it from further institutional ethical review. Detailed documentation on the NHANES sampling design, methodology, and ethical considerations is available from the official CDC and NCHS websites.1
A rigorous participant selection process was applied to ensure data integrity and the reliability of the findings. Data from NHANES 2005–2018 were utilized. The participant flow is illustrated in Figure 1. Initially, 70,190 individuals were considered. Participants aged under 20 years and pregnant women (N = 31,152) were excluded, leaving 39,038 eligible individuals. Subsequently, 13,215 participants with incomplete LC9 data were removed, resulting in a sample of 25,823 individuals. Finally, 189 participants with missing data on NPAR or COPD-related variables were excluded, yielding a final analytical sample of 25,634 participants. This careful screening ensured the completeness and representativeness of the study population.
Figure 1

A flow diagram of eligible participant selection in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. LC9, Life’s Crucial 9; NPAR, neutrophil-to-albumin ratio; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
COPD assessment
Consistent with previous research (27), COPD was defined using one or more of the following criteria: (1) post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC ≤ 0.70; (2) the presence of emphysema or self-reported COPD; or (3) participants aged ≥ 40 years with a history of chronic bronchitis or smoking and currently using COPD-related medications, including mast cell stabilizers, inhaled corticosteroids, selective phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors, or leukotriene modifiers.
Definition of neutrophil-to-albumin ratio (NPAR)
Data used to calculate the NPAR were obtained from the complete blood count (CBC) panel in the NHANES database. CBC parameters were measured using the Beckman Coulter method (28). Detailed information regarding laboratory methods, quality control, and data handling procedures can be accessed via the NHANES website: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/Nchs/Data/Nhanes/Public/2017/DataFiles/CBC_J.htm. Albumin levels were assessed using standard NHANES biochemical protocols, specifically via a digital endpoint method with dual-wavelength detection (29). The NPAR was calculated using the following formula: NPAR = (Neutrophil percentage [%] × 100) / Albumin (g/dL) (28).
Definition of Life’s Crucial 9 (LC9)
LC9 integrates nine key health metrics, categorized into behavioral components (diet quality, physical activity, smoking avoidance, and sleep health) and physiological components (weight management, blood lipids, glucose control, blood pressure regulation, and mental health) (13, 14). The specific NHANES-based scoring methodology is detailed in Supplementary Table S1. Each component was assigned a score ranging from 0 to 100, and the overall LC9 score was calculated as the average of the nine components. Diet quality was assessed using the 2015 Healthy Eating Index (HEI-2015) (15), with detailed scoring components presented in Supplementary Table S2. Behavioral health data were collected through standardized questionnaires, whereas clinical measurements, including anthropometry, cardiovascular parameters, and metabolic markers, were obtained by trained personnel from the NHANES database (see text footnote 1).
Covariables
Covariates included in this study were age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital status, education level, poverty income ratio (PIR), hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. Detailed descriptions of these covariates are provided in Supplementary Table S3.
Statistical analysis
The R software environment was used for statistical processing (version 4.3.1). We used suitable sampling weights in all analyses to guarantee population-level inference and take into consideration the intricate sampling design of NHANES. Using weighted t-tests for between-group comparisons, descriptive statistics displayed continuous variables as weighted averages with standard deviations. Weighted frequencies with percentages were used to express categorical variables, and weighted chi-square techniques were used to evaluate differences between groups.
The multivariable logistic regression models (1) unadjusted, (2) demographically adjusted (adjusting for age, sex, education, marital status, poverty ratio, and race/ethnicity), and (3) fully adjusted (adding clinical covariates such as hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia) were used to investigate LC9-COPD and NPAR-COPD relationships. To assess possible non-linear relationships between variables and outcomes, we used restricted cubic spline modeling. The consistency of identified relationships across population strata was investigated by thorough subgroup analyses.
To assess NPAR’s potential mediating function in the LC9-COPD relationship, formal mediation analysis was performed to quantify direct effects, indirect effects, and total effects of LC9 on COPD development through NPAR pathways. The mediation proportion was mathematically derived as (indirect effect / [indirect effect + direct effect]) × 100% (27). All mediation effect evaluations were executed utilizing the specialized “mediation” package within the R statistical environment (27). Statistical significance was established at a two-sided probability threshold of p < 0.05.
Result
Baseline characteristics
Table 1 presents the baseline characteristics of 25,634 participants, including 1,248 individuals with COPD and 24,386 without COPD. After applying sample weights, the findings were extrapolated to represent approximately 120,660,843 U.S. adults, among whom an estimated 5,809,388 had COPD, corresponding to a national prevalence of 4.8%.
Table 1
| Characteristic | Overall, N = 120,660,843 (100%) | Non-COPD, N = 114,851,454 (95.2%) | COPD, N = 5,809,388 (4.8%) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of participants in the sample | 25,634 | 24,386 | 1,248 | - |
| Age (%) | <0.001 | |||
| 20–40 | 42,175,998 (35%) | 41,859,837 (36%) | 316,161 (5.4%) | |
| 41–60 | 45,482,817 (38%) | 43,152,400 (38%) | 2,330,417 (40%) | |
| >60 | 33,002,028 (27%) | 29,839,218 (26%) | 3,162,810 (54%) | |
| Sex (%) | 0.276 | |||
| Female | 62,042,783 (51%) | 59,195,517 (52%) | 2,847,266 (49%) | |
| Male | 58,618,060 (49%) | 55,655,938 (48%) | 2,962,122 (51%) | |
| Race (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Non-Hispanic White | 85,637,276 (71%) | 80,764,126 (70%) | 4,873,151 (84%) | |
| Non-Hispanic Black | 12,273,589 (10%) | 11,919,916 (10%) | 353,674 (6.1%) | |
| Other | 13,871,985 (11%) | 13,385,965 (12%) | 486,020 (8.4%) | |
| Mexican American | 8,877,992 (7.4%) | 8,781,448 (7.6%) | 96,544 (1.7%) | |
| Married/live with partner (%) | 0.570 | |||
| No | 42,987,128 (36%) | 40,973,888 (36%) | 2,013,240 (35%) | |
| Yes | 77,641,283 (64%) | 73,845,135 (64%) | 3,796,148 (65%) | |
| Education level (%) | 0.001 | |||
| Below high school | 16,821,258 (14%) | 15,741,070 (14%) | 1,080,188 (19%) | |
| High School or above | 103,802,597 (86%) | 99,073,397 (86%) | 4,729,200 (81%) | |
| PIR (%) | 0.004 | |||
| Poor | 21,961,758 (19%) | 20,685,929 (19%) | 1,275,830 (24%) | |
| Not poor | 91,404,896 (81%) | 87,268,735 (81%) | 4,136,161 (76%) | |
| Hypertension (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No | 73,643,152 (61%) | 71,157,478 (62%) | 2,485,674 (43%) | |
| Yes | 47,017,690 (39%) | 43,693,976 (38%) | 3,323,714 (57%) | |
| Diabetes (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No | 105,337,328 (87%) | 100,827,270 (88%) | 4,510,058 (78%) | |
| Yes | 15,323,515 (13%) | 14,024,184 (12%) | 1,299,330 (22%) | |
| Hyperlipidemia (%) | <0.001 | |||
| No | 34,172,193 (28%) | 33,192,788 (29%) | 979,406 (17%) | |
| Yes | 86,488,649 (72%) | 81,658,667 (71%) | 4,829,982 (83%) | |
| Mean LC9 score [mean (SE)] | 70.44 (13.61) | 70.82 (13.49) | 62.92 (13.74) | <0.001 |
| LC9, Tertile (%) | <0.001 | |||
| T1 | 39,075,080 (32%) | 36,032,687 (31%) | 3,042,393 (52%) | |
| T2 | 40,813,205 (34%) | 39,048,862 (34%) | 1,764,344 (30%) | |
| T3 | 40,772,557 (34%) | 39,769,906 (35%) | 1,002,651 (17%) | |
| Mean psychological health score [mean (SE)] | 89.26 (23.27) | 89.52 (22.96) | 84.10 (28.33) | <0.001 |
| Mean HEI-2015 diet score [mean (SE)] | 39.52 (31.43) | 39.55 (31.48) | 38.82 (30.36) | 0.625 |
| Mean physical activity score [mean (SE)] | 71.71 (41.06) | 72.24 (40.74) | 61.20 (45.64) | <0.001 |
| Mean tobacco exposure score [mean (SE)] | 71.32 (38.60) | 72.38 (38.27) | 50.36 (39.20) | <0.001 |
| Mean sleep health score [mean (SE)] | 83.45 (24.21) | 83.66 (24.00) | 79.23 (27.64) | <0.001 |
| Mean body mass index score (mean (SE)) | 60.55 (33.51) | 60.68 (33.49) | 58.10 (33.68) | 0.052 |
| Mean blood lipid score[mean (SE)] | 63.92 (30.32) | 64.21 (30.33) | 58.32 (29.61) | <0.001 |
| Mean blood glucose score [mean (SE)] | 85.61 (24.20) | 86.08 (23.93) | 76.23 (27.49) | <0.001 |
| Mean blood pressure score [mean (SE)] | 68.61 (31.13) | 69.05 (31.09) | 59.97 (30.57) | <0.001 |
| NPAR [mean (SE)] | 13.75 (2.46) | 13.71 (2.44) | 14.47 (2.70) | <0.001 |
| NPAR, Tertile (%) | <0.001 | |||
| T1 | 40,253,840 (33%) | 38,805,903 (34%) | 1,447,937 (25%) | |
| T2 | 40,167,876 (33%) | 38,492,849 (34%) | 1,675,026 (29%) | |
| T3 | 40,239,127 (33%) | 37,552,702 (33%) | 2,686,425 (46%) |
Baseline characteristics of all participants were stratified by COPD, weighted.
Mean (SE) for continuous variables: the P value was calculated by the weighted Students T-test. Percentages (weighted N, %) for categorical variables: the P value was calculated by the weighted chi-square test. Abbreviation: LC9, Life’s Crucial 9; NPAR, neutrophil-to-albumin ratio; PIR, poverty income ratio; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The bold values are less than 0.05.
Significant differences were observed between the COPD and non-COPD groups in terms of age distribution, race/ethnicity, educational level, family income, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia (all p < 0.05). Participants with COPD were generally older, more likely to be White, and had higher rates of hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. Moreover, the LC9 scores were significantly lower in the COPD group compared to the non-COPD group (p < 0.001), while NPAR values were significantly higher (p < 0.001). A comprehensive summary of the characteristics is shown in Table 1.
Association between LC9, NPAR, and COPD
As shown in Table 2, we constructed three progressively adjusted multivariable models to examine the association between LC9 and COPD. Across all models, LC9 was consistently and significantly inversely associated with COPD (all p < 0.05). In the fully adjusted model, controlling for all potential confounders, every 10-unit increase in LC9 was associated with a 28% lower likelihood of having COPD (OR = 0.72, 95% CI: 0.67–0.77, p < 0.001). In the sensitivity analysis using LC9 tertiles, individuals in the highest tertile (T3) had a 56% lower prevalence of COPD compared to those in the lowest tertile (OR = 0.44, 95% CI: 0.34–0.58, p < 0.001).
Table 2
| Characteristics | Model 1 [OR (95% CI)] | p-value | Model 2 [OR (95% CI)] | p-value | Model 3 [OR (95% CI)] | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC9 - COPD | ||||||
| Continuous (per 10 scores) | 0.67(0.63,0.71) | <0.001 | 0.74(0.69, 0.78) | <0.001 | 0.72(0.67, 0.77) | <0.001 |
| Tertile | ||||||
| T1 | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | |||
| T2 | 0.54(0.44,0.65) | <0.001 | 0.65(0.54, 0.79) | <0.001 | 0.65(0.54, 0.80) | <0.001 |
| T3 | 0.30(0.24,0.37) | <0.001 | 0.45(0.35, 0.57) | <0.001 | 0.44(0.34, 0.58) | <0.001 |
| P for trend | <0.001 | <0.001 | 0.004 | |||
| NPAR - COPD | ||||||
| Continuous | 1.13(1.10,1.16) | <0.001 | 1.07(1.03, 1.10) | <0.001 | 1.06(1.03, 1.10) | <0.001 |
| Tertile | ||||||
| T1 | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | 1 (ref.) | |||
| T2 | 1.17(0.95,1.43) | 0.140 | 0.99(0.79, 1.23) | 0.900 | 0.98(0.78, 1.22) | 0.840 |
| T3 | 1.92(1.57,2.34) | <0.001 | 1.38(1.11, 1.70) | 0.004 | 1.35(1.09, 1.66) | 0.010 |
| P for trend | <0.001 | 0.002 | 0.004 | |||
Association between LC9, NPAR, and COPD, NHANES 2005–2018.
Model 1: no covariates were adjusted. Model 2: age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, and race were adjusted. Model 3: age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia were adjusted. LC9, Life’s Crucial 9; NPAR, neutrophil-to-albumin ratio; PIR, poverty income ratio; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
Regarding NPAR, higher levels were positively associated with COPD risk. Specifically, each unit increase in NPAR was associated with a 6% increase in COPD prevalence (OR = 1.06, 95% CI: 1.03–1.10, p < 0.001).
Restricted cubic spline models (Figure 2) confirmed a linear inverse relationship between LC9 and COPD risk after adjusting for all covariates (overall p < 0.001; nonlinearity p > 0.05). In contrast, the association between NPAR and COPD was nonlinear, with an inflection point at 14.17. Threshold effect analysis (Table 3) revealed that NPAR was not significantly associated with COPD when levels were below 14.17 (OR = 1.01, 95% CI: 0.97–1.06) but showed a significant positive association when levels exceeded 14.17 (OR = 1.13, 95% CI: 1.09–1.17).
Figure 2
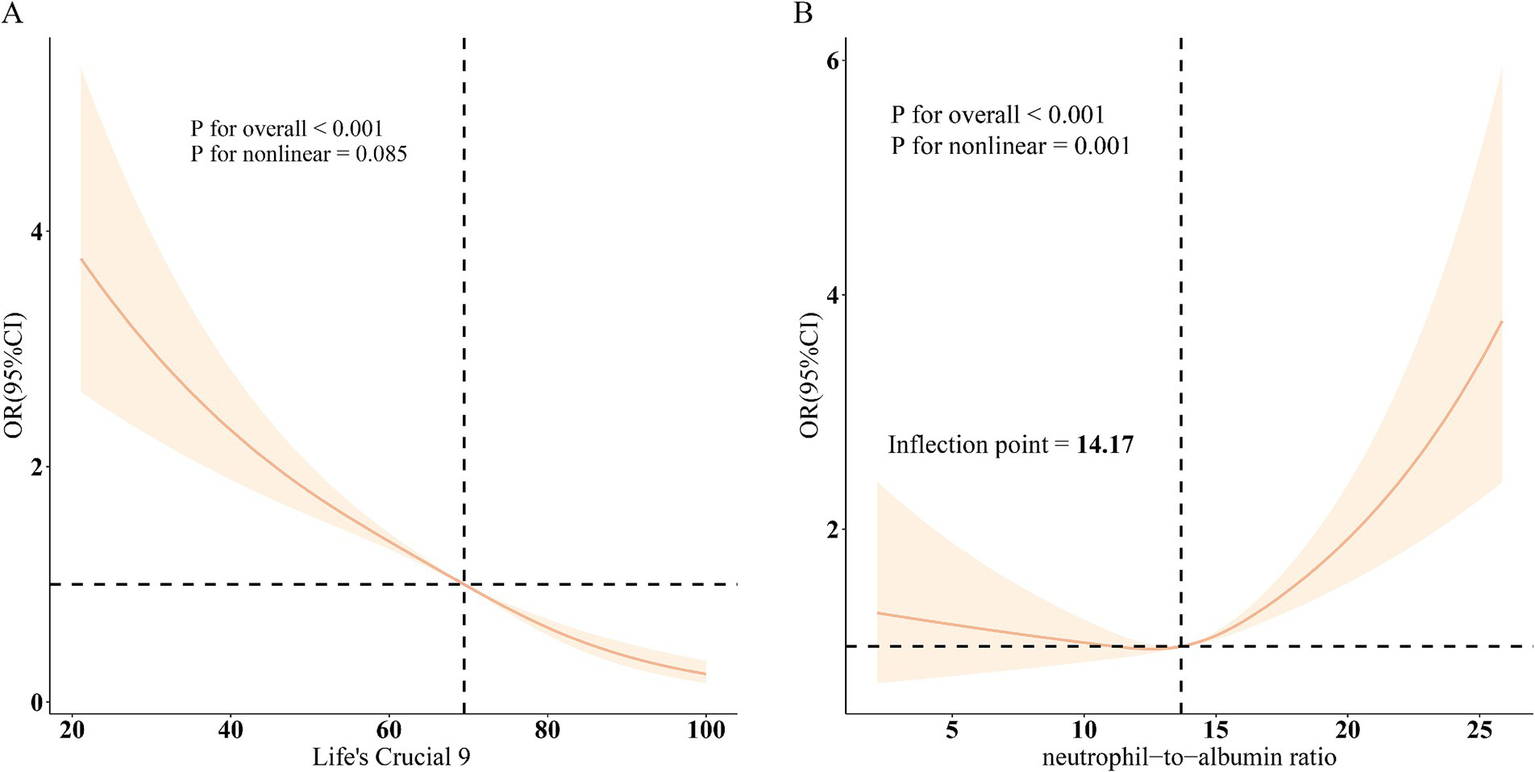
Dose–response relationships between LC9, NPAR, and COPD. (A), LC9 - COPD; (B), NPAR - COPD. OR (solid lines) and 95% confidence levels (shaded areas) were adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
Table 3
| Adjusted | OR (95%CI), p value |
|---|---|
| Inflection point | 14.17 |
| NPAR<14.17 | 1.01 (0.97, 1.06), 0.588 |
| NPAR≥14.17 | 1.13 (1.09, 1.17), <0.001 |
| P for likelihood ratio test | 0.002 |
Threshold effect analysis of the relationship between NPAR and COPD.
Adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
Subgroup analyses stratified by age, sex, race/ethnicity, marital status, educational level, PIR, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia (Figure 3) showed that the inverse association between LC9 and COPD, as well as the positive association between NPAR and COPD, remained consistent across all subgroups. No significant interactions were observed (all p for interaction > 0.05).
Figure 3
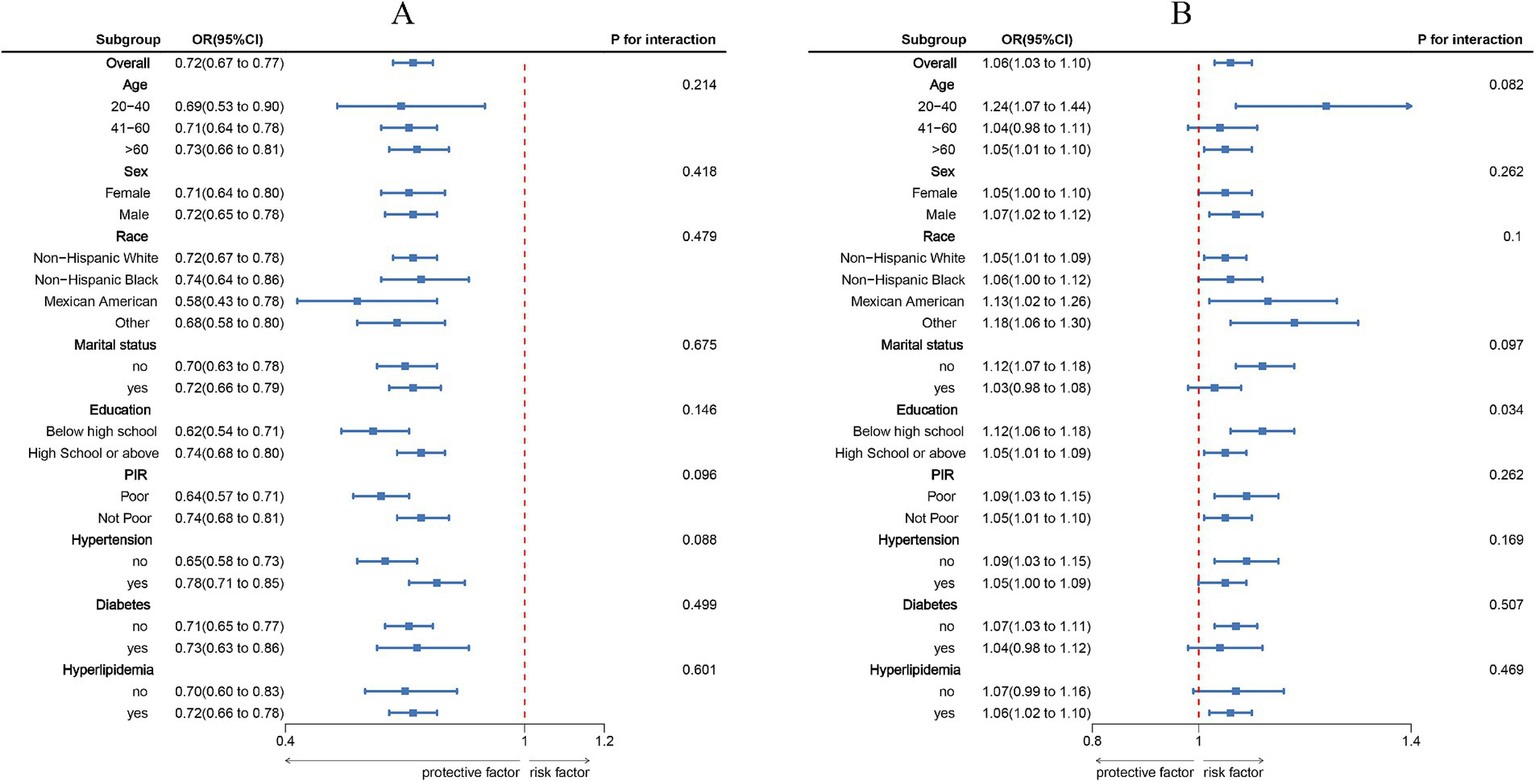
Subgroup analysis between LC9, NPAR, and COPD. (A), LC9 - COPD; (B), NPAR - COPD. ORs were calculated per 10-unit increase in LC9, and each standard deviation increased in NPAR. Analyses were adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
Mediation effect
As illustrated in Figure 4, a mediation analysis was conducted with LC9 as the independent variable, COPD as the dependent variable, and NPAR as the mediator. After adjusting for all covariates, Table 4 indicates a significant negative association between LC9 and NPAR (β = −0.27, 95% CI: −0.31 to −0.24). Further analysis confirmed the mediation role of NPAR (indirect effect = −3.00 × 10−3, p < 0.001; direct effect = −5.90 × 10−2, p < 0.001). The proportion of the effect of LC9 on COPD mediated by NPAR was 4.84% (p < 0.001). These results suggest that NPAR partially mediates the relationship between LC9 and COPD.
Figure 4
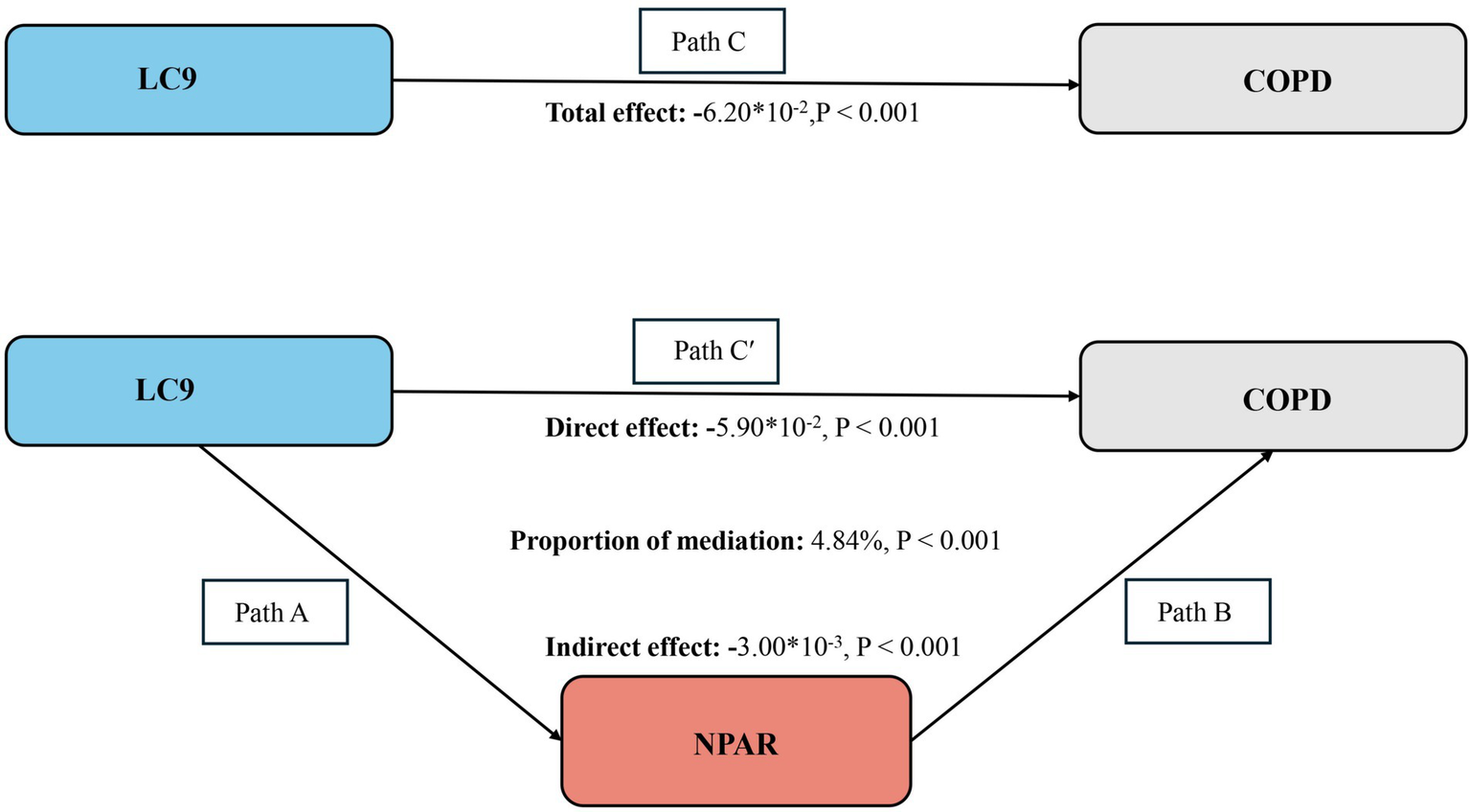
Schematic diagram of the mediation effect analysis. Path C indicates the total effect; path C′ indicates the direct effect. The indirect effect is estimated as the multiplication of paths A and B (path A*B). The mediated proportion is calculated as indirect effect/ (indirect effect + direct effect) × 100%. Abbreviation: LC9, Life’s Crucial 9; NPAR, neutrophil-to-albumin ratio; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Analyses were adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
Table 4
| β | 95%CI | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LC9 - NPAR | −0.27 | (−0.31, −0.24) | <0.001 |
Multivariate linear regression of LC9 and NPAR.
Adjusted for age, sex, education level, marital, PIR, race, hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia.
Discussion
In this nationally representative study of U.S. adults, a significant association was observed between Life’s Crucial 9 (LC9), the neutrophil-to-albumin ratio (NPAR), and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). After full adjustment for potential confounders, each 10-point increase in LC9 score was associated with a 28% reduction in COPD prevalence. Conversely, each 1-unit increase in NPAR was associated with a 1.06-fold increase in COPD prevalence. Mediation analysis further revealed that NPAR partially mediated the relationship between LC9 and COPD, suggesting that LC9 may influence COPD risk in part by improving systemic inflammation, as reflected by NPAR levels.
By capturing multiple dimensions of cardiovascular health, LC9 offers a comprehensive evaluation of overall health status, potentially enabling a more accurate assessment of COPD risk. These findings provide a theoretical foundation for further exploration of cardiopulmonary interactions and underscore the importance of cardiovascular health management in the prevention of chronic respiratory diseases. Moreover, the results may inform public health policy, supporting the implementation of integrative interventions aimed at reducing COPD prevalence and improving quality of life. Future research is warranted to investigate the broader applicability of LC9 in the early detection and management of other chronic diseases, thereby advancing the paradigm of holistic health management.
The favorable cardiovascular health behaviors and factors reflected in higher LC9 scores may mitigate the development and progression of COPD through various biological pathways. One hallmark of COPD is chronic and localized hypoxia, which promotes the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β (30, 31), thereby triggering systemic inflammation and an “inflammatory storm.” Several LC9 components—such as a healthy diet and optimal glycemic and lipid control—may reduce systemic inflammation by inhibiting oxidative stress and suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokine production (32). Furthermore, individuals with higher LC9 scores often exhibit improved vascular function and tissue perfusion, which may enhance pulmonary oxygenation, thus alleviating hypoxia-induced tissue damage and immune activation. A healthy lifestyle may also influence the secretory functions of alveolar epithelial and immune cells (33), reducing the excessive release of extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes and mucins, thereby slowing airway remodeling and obstruction.
Additionally, the inverse association between LC9 and COPD may be mediated through the regulation of both programmed and non-programmed cell death pathways. Recent studies have identified significant dysregulation of ferroptosis (34), pyroptosis (35), apoptosis (36), and cuproptosis (37) in the lung tissues of COPD patients. These forms of cell death are closely related to oxidative stress, metal ion imbalance, and chronic inflammation. Beneficial health behaviors encompassed in LC9, such as antioxidant-rich diets and physical activity, may help maintain redox homeostasis and mitochondrial function, thereby suppressing lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis (38, 39).
In the present study, NPAR was found to partially mediate the association between LC9 and COPD, suggesting that systemic inflammation may serve as a key biological pathway linking cardiovascular health and pulmonary outcomes. LC9, as a multidimensional index of cardiovascular health, incorporates both behavioral and physiological factors—including smoking status, physical activity, diet quality, body weight, blood pressure, blood lipids, blood glucose, sleep, and mental health—all of which are closely linked to systemic inflammation. NPAR, an easily obtainable biomarker, reflects systemic inflammatory and nutritional status (40, 41). In the pathogenesis of COPD, inflammation plays a central role in airway remodeling, lung tissue destruction, and functional decline (42, 43). Lower LC9 scores may reflect unhealthy lifestyle patterns and metabolic disturbances, contributing to elevated NPAR levels and the amplification of both airway and systemic inflammation, thereby promoting COPD onset and progression. These findings support a mediating role of inflammation in the LC9-COPD association and suggest that optimizing LC9 components and reducing systemic inflammation may be effective strategies for COPD prevention and management.
This study is the first to systematically explore the interrelationships and mediating role of LC9, NPAR, and COPD, contributing to the theoretical foundation for LC9 application in respiratory disease research and offering new evidence for the involvement of NPAR in COPD pathogenesis. The study leveraged data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), which features a large, nationally representative sample, thereby enhancing the generalizability and scientific robustness of the findings. Comprehensive statistical adjustments were made for a range of potential confounders, including age, sex, race/ethnicity, and socioeconomic status, using multivariable regression models to improve the reliability and validity of the results. Furthermore, subgroup analyses were conducted to verify the consistency and stability of the observed associations across various population strata, strengthening the credibility and translational value of the findings.
Several limitations of this study warrant consideration. First, the cross-sectional design of NHANES precludes the establishment of causal relationships among LC9, NPAR, and COPD. Although multiple sociodemographic, lifestyle, and health-related covariates were adjusted for, the influence of unmeasured or residual confounding—such as environmental exposures and genetic susceptibility—cannot be entirely ruled out. Second, reliance on self-reported data in NHANES may introduce information bias. Additionally, NPAR was only measured during specific survey cycles, potentially limiting sample size and representativeness. Furthermore, the diagnosis of COPD was based on a combination of self-reported physician diagnosis, post-bronchodilator spirometry results (FEV1/FVC ≤ 0.70), a history of chronic bronchitis or emphysema, smoking history, and the use of COPD-related medications. Due to the constraints of the NHANES database, objective confirmation of COPD for all participants—such as universal availability of spirometry data—was not feasible. As a result, some individuals may have been classified as having COPD solely based on self-reported information without corroboration by objective diagnostic measures. This may have led to misclassification bias and impacted the specificity of COPD case identification. Second, medication use, and medical history were self-reported, which could have introduced recall bias. Despite these limitations, our definition of COPD aligns with criteria commonly used in previous NHANES-based studies and allows for comparability of findings. Future research with access to more robust and objective diagnostic indicators is warranted to further validate these associations.
Finally, due to the inherent constraints of the NHANES database, we were unable to obtain detailed information regarding participants’ recent or chronic infections, hematological diseases, serious liver diseases, recent major trauma, or major surgery. These conditions may significantly affect neutrophil and albumin levels, potentially confounding the association between the neutrophil-to-albumin ratio and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. As a result, we could not exclude such individuals from our analysis. Future studies with more comprehensive clinical data collection are warranted to address and minimize these potential confounding factors.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our study demonstrates a significant inverse association between LC9 and COPD, with NPAR playing a partial mediating role. These findings highlight the potential link between cardiovascular health and COPD, underscoring the critical role of inflammation regulation and nutritional management in this relationship. This study offers a novel perspective for the prevention and management of COPD, suggesting that improving cardiovascular health and adopting comprehensive strategies to control inflammation and optimize nutritional status may help reduce the risk of COPD.
Statements
Data availability statement
Publicly available datasets were analyzed in this study. This data can be found here: https://wwwn.cdc.gov/nchs/nhanes/.
Author contributions
JF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. HG: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely appreciate the NHANES database for all the data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1610945/full#supplementary-material
Footnotes
References
1.
Barnes PJ Burney PGJ Silverman EK Celli BR Vestbo J Wedzicha JA et al . Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers. (2015) 1:1–21. doi: 10.1038/nrdp.2015.76
2.
Xu J Zeng Q Li S Su Q Fan H . Inflammation mechanism and research progress of COPD. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1404615. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1404615
3.
Chen S Kuhn M Prettner K Yu F Yang T Bärnighausen T et al . The global economic burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease for 204 countries and territories in 2020-50: a health-augmented macroeconomic modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. (2023) 11:e1183–93. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(23)00217-6
4.
Wang Z Lin J Liang L Huang F Yao X Peng K et al . Global, regional, and national burden of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2021: an analysis for the global burden of disease study 2021. Respir Res. (2025) 26:2. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03051-2
5.
Chen H Luo X Du Y He C Lu Y Shi Z et al . Association between chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cardiovascular disease in adults aged 40 years and above: data from NHANES 2013–2018. BMC Pulm Med. (2023) 23:318. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02606-1
6.
Singh D Han MK Hawkins NM Hurst JR Kocks JWH Skolnik N et al . Implications of cardiopulmonary risk for the management of COPD: a narrative review. Adv Ther. (2024) 41:2151–67. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02855-4
7.
Polman R Hurst JR Uysal OF Mandal S Linz D Simons S . Cardiovascular disease and risk in COPD: a state of the art review. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. (2024) 22:177–91. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2024.2333786
8.
Maeda T Dransfield MT . COPD and cardiovascular disease: mechanistic links and implications for practice. Curr Opin Pulm Med. (2023) 30:141–9. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000001040
9.
Zhang L Fang B Wang H Zeng H Wang N Wang M et al . The role of systemic inflammation and oxidative stress in the association of particulate air pollution metal content and early cardiovascular damage: A panel study in healthy college students. Environ Pollut. (2023) 323:121345. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2023.121345
10.
Tkacova R Kluchova Z Joppa P Petrasova D Molcanyiova A . Systemic inflammation and systemic oxidative stress in patients with acute exacerbations of COPD. Respir Med. (2007) 101:1670–6. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2007.03.005
11.
Lloyd-Jones DM Allen NB Anderson CAM Black T Brewer LC Foraker RE et al . Life’s essential 8: updating and enhancing the American Heart Association’s construct of cardiovascular health: a presidential advisory from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2022) 146:e18–43. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000001078
12.
Gaffey AE Rollman BL Burg MM . Strengthening the pillars of cardiovascular health: psychological health is a crucial component. Circulation. (2024) 149:641–3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.123.066132
13.
Gong H Duan S Huang S . Association between life’s crucial 9 and overactive bladder: the mediating role of weight-adjusted-waist index. Front Nutr. (2025) 11:1508062. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1508062
14.
Gong H Lin X Huang S . Atherogenic index of plasma mediates the association between life’s crucial 9 with overactive bladder: a secondary data analysis from NHANES. Front Endocrinol. (2025) 16:1505712. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1505712
15.
Huang S Duan S Choi S Gong H . Higher life’s crucial 9 protects against infertility among U.S. women aged 18–45 years. Front Endocrinol. (2025) 16:1465022. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1465022
16.
Shi H Ma X . Association between life’s crucial 9 and lung health: a population-based study. BMC Pulm Med. (2025) 25:213. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03684-z
17.
Gou R Chang X Dou D Meng X Hou L Zhu L et al . Association of cardiovascular health with COPD (NHANES 2007-2020): mediating potential of lean body mass. Front Endocrinol. (2025) 16:1539550. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2025.1539550
18.
Nakagomi A Kohashi K Morisawa T Kosugi M Endoh I Kusama Y et al . Nutritional status is associated with inflammation and predicts a poor outcome in patients with chronic heart failure. J Atheroscler Thromb. (2016) 23:713–27. doi: 10.5551/jat.31526
19.
Yao J Wu P Li Z Zhao L Fu Z Shi P et al . Nutritional status and systemic inflammation in COPD: prognostic value of the advanced lung Cancer inflammation index. Front Nutr. (2025) 12:1550490. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1550490
20.
Hou C Huang X Wang J Chen C Liu C Liu S et al . Inflammation and nutritional status in relation to mortality risk from cardio-cerebrovascular events: evidence from NHANES. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1504946. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1504946
21.
Bai J Lv T Yu H Ji Z Gu X Gao Y et al . The combined impact of neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio and depressive symptoms on mortality in US arthritis patients: insights from NHANES (2005–2018). Front Public Health. (2025) 13:1545250. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1545250
22.
Zhang X Bai F Ni H Chen S Fu D Ren H et al . Correlation of neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio with lung function in American adults: a population study. BMC Pulm Med. (2025) 25:86. doi: 10.1186/s12890-025-03537-9
23.
Li Y Yu C . Correlation between neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio and all-cause and cerebrovascular mortality among hypertension patients. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:2989. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-87253-8
24.
Shi Y Shi Y Liu Y Wang C Qi M Li C . Association between neutrophil percentage to serum albumin ratio and in-hospital mortality of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in intensive care unit: A retrospective cohort study. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2025) 20:1227–37. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S508964
25.
Qu J Tang X Tang W Pan L . Association of red cell distribution width/albumin ratio and 28-day mortality in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with atrial fibrillation: a medical information mart for intensive care IV study. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. (2025) 25:146. doi: 10.1186/s12872-025-04537-7
26.
von Elm E Altman DG Egger M Pocock SJ Gøtzsche PC Vandenbroucke JP et al . The strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE) statement: guidelines for reporting observational studies. BMJ. (2007) 61:335. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39335.541782.AD
27.
Wu R Gong H . The association between non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: the mediating role of dietary inflammatory index. Front Nutr. (2024) 11:1427586. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1427586
28.
Shen G Liu Y Zhou C Luo W Yang Y Guo S et al . Associations between neutrophil-percentage-to-albumin ratio level and all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease-cause mortality in diabetes population. BMC Public Health. (2025) 25:401. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20924-9
29.
Zhou H Li Y Chen X Miao D Zhang L Cao R et al . Association between neutrophil percentage-to-albumin ratio and periodontitis: A cross-sectional study. Int Dent J. (2025) 75:660–7. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2024.10.022
30.
Barnes PJ . The cytokine network in asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Clin Invest. (2008) 118:3546–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI36130
31.
Singh S Verma SK Kumar S Ahmad MK Nischal A Singh SK et al . Correlation of severity of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease with potential biomarkers. Immunol Lett. (2018) 196:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.01.004
32.
Aleksandrova K Koelman L Rodrigues CE . Dietary patterns and biomarkers of oxidative stress and inflammation: A systematic review of observational and intervention studies. Redox Biol. (2021) 42:101869. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2021.101869
33.
Kayongo A Robertson NM Siddharthan T Ntayi ML Ndawula JC Sande OJ et al . Airway microbiome-immune crosstalk in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front Immunol. (2023) 13:1085551. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1085551
34.
Meng D Zhu C Jia R Li Z Wang W Song S . The molecular mechanism of ferroptosis and its role in COPD. Front Med. (2023) 9:1052540. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1052540
35.
Zhang M-Y Jiang Y-X Yang Y-C Liu J-Y Huo C Ji X-L et al . Cigarette smoke extract induces pyroptosis in human bronchial epithelial cells through the ROS/NLRP3/caspase-1 pathway. Life Sci. (2021) 269:119090. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119090
36.
Demedts IK Demoor T Bracke KR Joos GF Brusselle GG . Role of apoptosis in the pathogenesis of COPD and pulmonary emphysema. Respir Res. (2006) 7:53. doi: 10.1186/1465-9921-7-53
37.
Qi W Liu L Zeng Q Zhou Z Chen D He B et al . Contribution of cuproptosis and cu metabolism-associated genes to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Cell Mol Med. (2023) 27:4034–44. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17985
38.
Feng S Tang D Wang Y Li X Bao H Tang C et al . The mechanism of ferroptosis and its related diseases. Mol Biomed. (2023) 4:33. doi: 10.1186/s43556-023-00142-2
39.
Thirupathi A Marqueze LF Outeiro TF Radak Z Pinho RA . Physical exercise-induced activation of NRF2 and BDNF as a promising strategy for Ferroptosis regulation in Parkinson’s disease. Neurochem Res. (2024) 49:1643–54. doi: 10.1007/s11064-024-04152-6
40.
Serhatlioglu F Yilmaz Y Baran O Yilmaz H Kelesoglu S . Inflammatory markers and postoperative new-onset atrial fibrillation: prognostic predictions of neutrophil percent to albumin ratio in patients with CABG. Diagnostics. (2025) 15:741. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060741
41.
He M Du X Liu Y . Association between neutrophil-albumin ratio and ultrasound-defined metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease in U.S. adults: evidence from NHANES 2017–2018. BMC Gastroenterol. (2025) 25:20. doi: 10.1186/s12876-025-03612-9
42.
Wang Y Xu J Meng Y Adcock IM Yao X . Role of inflammatory cells in airway remodeling in COPD. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. (2018) 13:3341–8. doi: 10.2147/COPD.S176122
43.
Rovina N Koutsoukou A Koulouris NG . Inflammation and immune response in COPD: where do we stand?Mediat Inflamm. (2013) 2013:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2013/413735
Summary
Keywords
Life’s Crucial 9, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, neutrophil-to-albumin ratio, NHANES, mediation analysis
Citation
Feng J and Gong H (2025) Neutrophil-to-albumin ratio mediates the association between Life’s Crucial 9 and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Front. Med. 12:1610945. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1610945
Received
14 April 2025
Accepted
11 June 2025
Published
23 June 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Vikrant Rai, Western University of Health Sciences, United States
Reviewed by
Yunhuan Liu, Tongji University, China
Fahrettin Katkat, University of Health Sciences, Türkiye
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Feng and Gong.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Hongyang Gong, hygong@chosun.ac.kr
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.