Abstract
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion requires stripping the multifidus muscle, destroying a large amount of cancellous bone and damaging the posterior spinal venous plexus. Typically, surgical trauma is extensive, the surgical duration is long, and the degree of bleeding is substantial. Excessive blood loss can compromise a patient's hemodynamic stability, elevate surgical risks, and cause damage to vital organs, potentially becoming life-threatening in severe cases. Tranexamic acid (TXA) is a lysine derivative that can inhibit fibrinolysis, reduce D-dimer production, and reduce inflammation. In this review, we discuss the application of and research progress on TXA regarding its mechanism of action, mode of administration, timing, dose, safety, and economic benefits. The primary purpose of this review is to provide an essential reference for the administration of TXA during posterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery as well as a reference for future research.
1 Introduction
Perioperative blood management refers to the use of multiple techniques for blood protection at various stages of the perioperative period (1). The primary purposes of blood management are to reduce blood loss, blood transfusion rates, and complication rates as well as to improve surgical safety and increase patient satisfaction (2). In the field of spinal surgery, lumbar degenerative diseases account for the majority of diseases requiring posterior lumbar interbody fusion (3, 4). In the past, lumbar degenerative diseases were reported to occur mainly among middle-aged and elderly individuals. In recent years, with the aging of the population and changes in people's lifestyles, the incidence of lumbar degenerative diseases has increased annually, and the age at onset has shown a decreasing trend. Minimally invasive spine surgery can expose the surgical field of vision and can reduce local tissue damage as well as vascular and nerve damage. Furthermore, minimally invasive spine surgery does not require the extensive stripping of muscles, and this technique can retain most of the bone structure and ligament structure (5). According, minimally invasive spine surgery has many advantages. For example, it is beneficial for maintaining the stability of the spine and the nutrition of blood vessels and nerves to the muscles. After minimally invasive spine surgery, postoperative lumbar function recovery is fast. Furthermore, degree of bleeding is low, the low back pain symptoms are mild, and the hospitalization time is short (3, 6, 7). Due to these advantages, minimally invasive spinal surgery is favored by both doctors and patients (8, 9). However, there are many limitations associated with the surgical indications for minimally invasive spine surgery (10). Therefore, posterior lumbar interbody fusion is still the mainstream surgical method for treating lumbar degenerative diseases (9, 11).
The amount of perioperative blood loss among patients requiring posterior lumbar interbody fusion ranges from 670 to 2570 ml (12), and hidden blood loss accounts for ~42%−47% of the total blood loss (12, 13). When no blood loss prevention measures are implemented, the blood transfusion rate ranges from 50 to 81% (12). This large amount of blood loss increases not only the blood transfusion rate but also the infection and complication rates. Moreover, a large amount of blood loss causes changes in patient hemodynamics, thereby affecting the supply of blood to essential organs (14). If substantial blood loss is not treated in time or is improperly controlled, adverse symptoms (such as anemia) may occur, thus affecting the patient's postoperative rehabilitation, quality of life, and prognosis; increasing medical costs; and prolonging hospital stays. In severe cases of blood loss, haemorrhagic shock or even death may occur (15). In addition, blood transfusion may present many risks, such as transfusion reactions, haemolytic reactions, fever, infection, postoperative spinal epidural haematoma formation, acute lung injury, and transfusion-related infectious diseases (16). Furthermore, many previous studies have shown that allogeneic blood transfusion increases the risk of postoperative infection (17), and the lack of blood management resources and high medical expenses have become considerable social burdens. Therefore, optimizing blood management strategies, effectively controlling perioperative bleeding, and reducing blood transfusions have become clinical problems that spinal surgeons urgently need to solve.
To this end, some studies have evaluated the role of patient blood management strategies in intraoperative bleeding and postoperative blood loss during posterior lumbar interbody fusion, including avoiding abdominal compression, controlling hypotension, bipolar coagulation haemostasis, local anesthesia, autologous blood transfusion, haemodilution, intraoperative blood recovery, and the use of iron and erythropoietin (15, 18, 19). These measures are only sometimes effective solutions to the problem of perioperative bleeding in posterior lumbar interbody fusion (20). In addition, tranexamic acid (TXA) is a lysine derivative that can stabilize the structure of fibrin and reduce the incidence of bleeding secondary to hyperfibrinolysis (21). Furthermore, TXA can also reduce the formation of D-dimers (19, 22), and reduce inflammatory responses (23–25). Therefore, TXA is also widely used as a blood management strategy in spinal surgery (21, 26). In this review, the mechanism of action, optimal mode of administration, optimal timing of administration, optimal dose of administration, safety, complications, and economic benefits of TXA during posterior lumbar interbody fusion were discussed.
2 Posterior lumbar interbody fusion results in increased blood loss
Posterior lumbar interbody fusion is considered one of the ten significant operations requiring blood transfusion due to the incidence of considerable perioperative blood loss (27). Among these operation, lumbar spinal stenosis and lumbar spondylolisthesis are the most common procedures for posterior lumbar interbody fusion in patients with lumbar degenerative diseases. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion is different from spinal orthopedic surgery. In spinal orthopedic surgery, the primary source of blood loss is only exposed bone surface blood loss. However, in posterior lumbar interbody fusion, the source of blood loss is multifaceted and multifactorial. For example, the complex anatomy of the spine and its rich blood supply, well-fed cancellous bone, and enhanced fibrinolytic activity resulting from surgery may lead to blood loss (28). In addition, patients with lumbar spinal stenosis and/or lumbar spondylolisthesis have a more abundant posterior spinal venous plexus (19). Posterior lumbar interbody fusion makes it difficult to avoid injury to the venous plexus, and the fragile venous plexus cannot contract after damage. An injured venous plexus often leads to difficulty in haemostasis and increased blood loss (29). Moreover, the fibrinolytic response induced by surgical trauma tends to intensify with prolonged operation duration, resulting in increased fibrinolytic hyperfunction. The results of Xie et al. (30) and Blanié et al. (31) indicated that the fibrinolytic effect triggered by surgical trauma peaks at 6 h after surgery and persists for a minimum of 24 h. In conclusion, increased fibrinolytic activity, extensive destruction of cancellous bone, and injury to the posterior spinal venous plexus during posterior lumbar interbody fusion are the primary contributors to perioperative bleeding.
3 The mechanism of action of TXA
TXA is a synthetic lysine derivative that was first described in the 1970s. TXA can reversibly and competitively adsorb the lysine binding site (LBS) of the fibrin affinity site on plasmin and plasminogen and form a reversible complex with it. TXA can reduce the conversion of plasminogen to active plasmin, thereby stabilizing the structure of fibrin, reducing the breakdown rate of fibrinogen, and reducing the degree of bleeding secondary to hyperfibrinolysis (21, 32) (Figure 1). In addition, abnormally hyperactive fibrinolytic enzymes inhibit platelet aggregation and decompose coagulation factors; therefore, TXA also has a protective effect on platelets and coagulation factors (19). In addition, TXA can also achieve antiallergic and anti-inflammatory effects by inhibiting vascular permeability, allergic reactions, and the production of kinin as well as other active peptides in inflammatory lesions (23–25). TXA is similar to the antifibrinolytic drug ε-aminocaproic acid (EACA); however, TXA exhibits more efficient and long-lasting antifibrinolytic activity in tissues than EACA. The effect of TXA is 6–10 times stronger than that of EACA and 4–6 times stronger than that of amino-toluic acid (33). In a study by Li et al. (34), the efficacy of TXA was compared with that of aprotinin and EACA among 943 patients who underwent spinal surgery. The findings revealed that all antifibrinolytic drugs can reduce perioperative blood loss and reduce the need for blood transfusions. However, TXA was more effective than aprotinin or EACA. In addition, Li et al. (34) also reported that TXA can reduce intraoperative blood loss by 53%, reduce postoperative blood loss by 20%, and reduce transfusion volume by 62%.
Figure 1
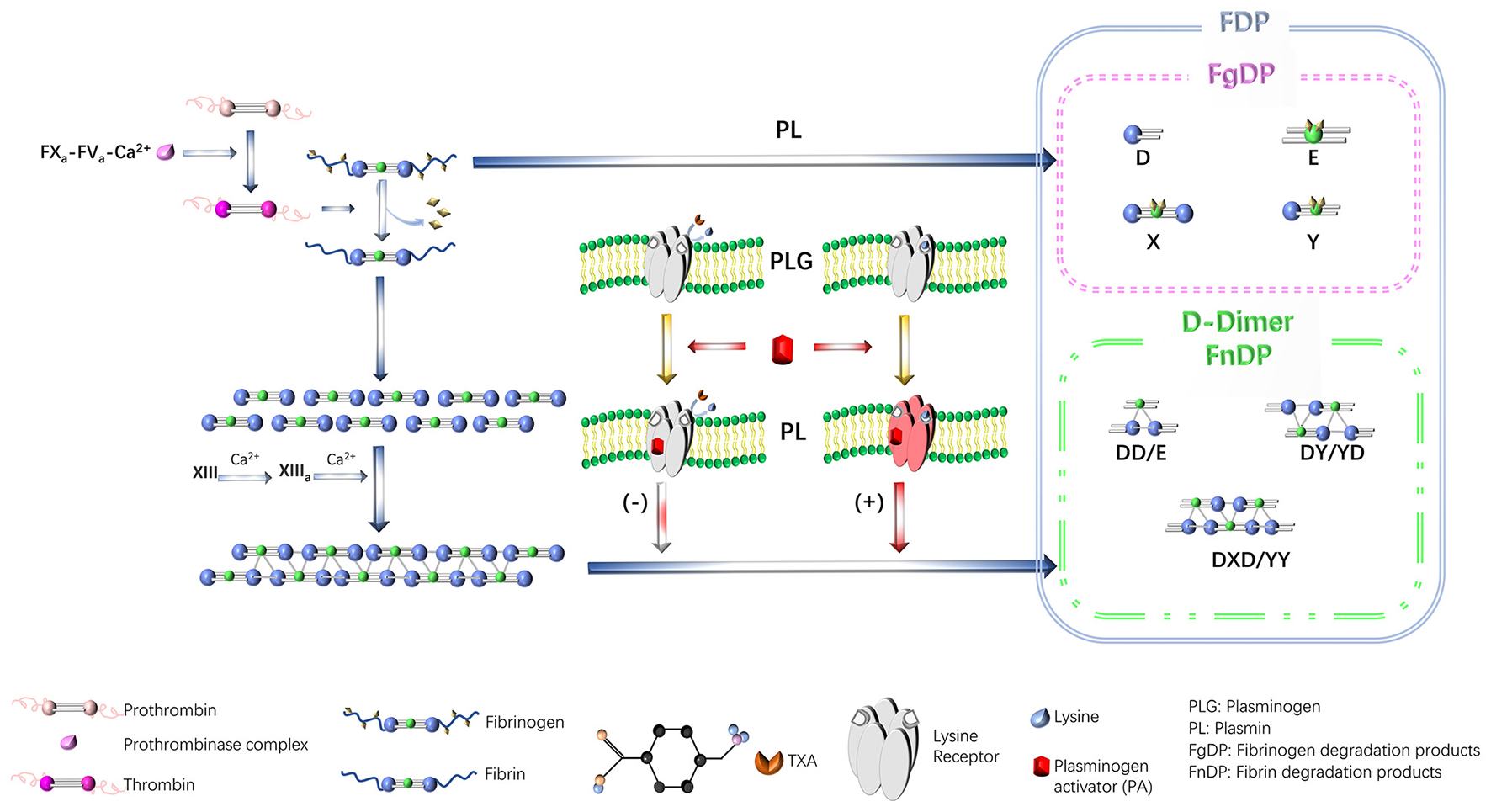
The mechanism of TXA action. TXA, tranexamic acid. Reproduced from ref. (21) with permission from the Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc, copyright 2024.
TXA is metabolized by the kidney and has a half-life of ~80–120 min, reaching a peak plasma concentration after 60 min of intravenous infusion. Approximately 30%−55% of TXA is excreted through the kidney 1–3 h after administration, and ~76%−90% of TXA is excreted through the kidneys in its original form through the urine within 24 h of administration (35). Therefore, for patients with renal insufficiency, the dose of TXA must be appropriately adjusted. Moreover, an in vitro study revealed that the minimum effective plasma concentration of TXA was 5–10 mg/L, and a plasma concentration of 10 mg/L could inhibited fibrinolysis by 80% (35). This critical finding provides a fundamental theoretical basis for future studies of the optimal timing and dosage of TXA.
4 The clinical application of TXA
TXA, a haemostatic agent, has gained widespread approval and clinical use after the ongoing controversy related to aprotinin, which was initially discontinued in 2007 (36). TXA was also approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and included in the World Health Organization's list of essential drugs in 2011 (36). TXA has been shown to reduce bleeding in a variety of surgeries, including heart surgeries, trauma surgeries, joint replacement surgeries, craniocerebral injury surgeries, and gynecological and urological surgeries (37–45). Moreover, TXA has also been used in nonsurgical applications, such as for the treatment of leukemia-related bleeding, eye-related bleeding, nose-related bleeding, repeated haemoptysis, gastrointestinal bleeding, menorrhagia, melasma, and other problems (46–49).
4.1 The mode of TXA administration
The application of TXA in total knee arthroplasty has been very mature, including intravenous administration (41), local administration (42), oral administration (40, 43, 44), and combination therapy (45). However, compared with total knee arthroplasty, posterior lumbar interbody fusion often requires the exposure of the spinal cord. When the spinal cord is immersed in TXA, the concentration of TXA in the cerebrospinal fluid increases, which can lead to epilepsy or neurotoxicity (36, 50, 51). Therefore, intravenous administration of TXA is preferred for posterior lumbar interbody fusion.
Some previous studies have shown that (52), local or intravenous administration of TXA can reduce perioperative blood loss. Furthermore, TXA does not increase the risk of thrombosis. Moreover, some researchers believe that local administration of TXA can provide the maximum drug concentration at the bleeding site, thereby minimizing systemic absorption. However, the fibrinolytic system caused by surgical trauma is usually activated at the beginning of surgery, and it releases a large amount of fibrinolytic enzyme to decompose fibrin. Compared with local administration after the activation of the fibrinolytic system, intravenous injection of TXA before the beginning of surgery can stabilize the structure of fibrin by inhibiting the activation of the fibrinolytic system in advance, improving the speed of haemostasis and enhaninge haemostasis (53, 54). Therefore, TXA should be intravenously administered before the start of posterior lumbar interbody fusion.
4.2 Timing and dosage of TXA administration
TXA is considered to be effective in terms of reducing perioperative blood loss. However, it remains unclear whether TXA is routinely used in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Furthermore, the optimal timing and dosage of TXA administration remain unclear. The fibrinolytic system is activated by surgical trauma. Fibrinolytic activation is a cascade reaction process. Therefore, choosing the appropriate timing for TXA administration is important. Most scholars believe that TXA should be used before fibrinolytic activation (41, 53).
Related studies have shown that the half-life of TXA is ~2 h, and the effective plasma concentration is 1 μg/ml. After an intravenous infusion of 15 mg/kg, TXA exerts the strongest effects within the first 16 h after administration (55). In addition, Abdou et al. (15) reported that a single intravenous infusion of TXA (10 mg/kg) did not significantly reduce the amount of blood loss or blood transfusion during spinal fusion surgery. However, Tsutsumimoto et al. (55) found that intravenous infusion of TXA (15 mg/kg) before skin incision significantly reduced the amount of bleeding in the first 16 h after surgery (~37%).
To better determine the optimal dose of TXA, Brown et al. (56) analyzed 11 articles related to the clinical application of TXA in spinal fusion surgery. Data from 411 patients revealed that the most common route of administration was intravenous administration, the most common timing of administration was preoperative administration, and the most common dosage was 15 mg/kg. By data from 2,042 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty, Wilde et al. (57) concluded that intravenous infusion of 1 g TXA has the same haemostatic effect as a dose of 2 g, indicating that higher doses have no additional benefits. Although the study by Wilde et al. was focused on total knee arthroplasty, the basic mechanism of action of TXA is similar in different surgeries, which is to reduce bleeding by inhibiting the fibrinolytic system. Moreover, some studies related to spinal surgery have shown that intravenous administration of 1 g of TXA also has a certain effect in reducing bleeding during spinal surgery, which is somewhat similar to its effect in total knee arthroplasty (58). Therefore, it is reasonable to refer to this dosage in spinal surgery to a certain extent. Although TXA has a similar mechanism of action in reducing surgical bleeding, the optimal dosage used in total knee arthroplasty cannot be directly applied to lumbar surgery due to potential differences in the surgical anatomy between posterior lumbar interbody fusion and total knee arthroplasty. The feasibility of this approach requires further validation. In addition, Lin and Xiaoyi (59) analyzed data from 26,079 patients who used TXA and 7,395 patients who did not use TXA. The found that the prevalence of TXA induced epilepsy was 2.7%, and this prevalence increased with increasing TXA dose. Thus, low-dose TXA (10–15 mg/kg or 1 g) is considered a relatively safe and effective dose in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Compared with high-dose TXA, it has a lower risk of causing epilepsy. However, due to factors such as individual differences, the possibility of low-dose TXA triggering epilepsy still cannot be completely ruled out. Clinicians still need to closely monitor the patient's condition when using it. Some studies have shown that high-dose TXA (10–100 mg/kg) is superior to low-dose TXA (< 10 mg/kg) in significantly reducing intraoperative blood loss (60). Currently, the commonly accepted intravenous dose of TXA is 10–15 mg/kg or 1 g. This is mainly because this dose is relatively common in clinical applications and is relatively safe. It can not only reduce bleeding to a certain extent but also control the risk of complications such as epilepsy (61). Nevertheless, there is still a lack of sufficient evidence regarding the optimal and safe dosage, and more high-quality studies are needed for further determination. In addition, hyperfibrinolysis caused by surgical trauma often lasts for at least 24 h after surgery (30, 31). Moreover, hidden blood loss accounts for a large proportion of postoperative blood loss (12, 13). Although a single preoperative dose or a single preoperative dose combined with an intraoperative maintenance dose can reduce bleeding to a certain extent, they may not completely inhibit the entire hyperfibrinolysis process. Therefore, it is necessary to further study the effect of continuous postoperative use of different doses of TXA on reducing blood loss in the future, in order to determine a more effective dosing regimen.
5 Safety and complications of TXA
The application of TXA during spinal surgery has been extensively studied. However, up to now, TXA is not routinely used in China. Because of the lack of high-quality, large-sample, multicenter clinical research articles and the lack of statistical analyses of previously reported studies, there are safety concerns with respect to TXA. These safety concerns include an increased incidence of thromboembolic events [such as pulmonary embolism (PE), deep vein thrombosis (DVT), and myocardial infarction (MI)] as well as increased incidence of epilepsy that can occur due to a single moderate or high dose of TXA (15, 61).
To confirm the safety of TXA, Yuan et al. (62) conducted a meta-analysis of 685 patients who underwent scoliosis surgery; none of these patients experienced thromboembolic events. Brown et al. (56) analyzed date from 411 patients who underwent spinal fusion surgery and concluded that TXA significantly reduced perioperative blood loss and did not increase the risk of related complications. Furthermore, in a meta-analysis by Neilipovitz et al. (63), only 1 case of deep vein thrombosis was observed in the control group. A meta-analysis by Chornenki et al. (64) revealed that there was no increased risk of venous or arterial thrombosis in nonsurgical patients receiving systemic TXA treatment (illustrated in Table 1). These studies indicated that intravenous application of TXA in spinal surgery is safe and does not increase the risk of thromboembolic events. The safety of TXA may be related to the fact that the inhibitory effect of TXA on fibrinolysis is mainly limited to surgical wounds rather than the circulatory system; therefore, TXA does not affect the venous wall (65). In addition, TXA does not increase the formation of epidural blood clots, which would increase the risk of nerve injury (28).
Table 1
| Complication | Number of trials (n) | Weighted event rates | RR (95% CI) | I 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TXA | No TXA | ||||
| DVT | 8 (46,630) | 0.28% | 0.29% | 0.97 (0.69–1.37) | 0% |
| PE | 6 (43,161) | 0.52% | 0.54% | 0.97 (0.75–1.26) | 0% |
| MI | 3 (42,470) | 0.27% | 0.30% | 0.88 (0.43–1.84) | 46% |
| Stroke | 5 (42,815) | 0.45% | 0.41% | 1.10 (0.68–1.78) | 31% |
Systematic review of 22 RCTs (including CRASH-2 and WOMAN).
DVT, Deep vein thrombosis; PE, Pulmonary embolism; MI, Myocardial infarction.
However, when it is administered via intravenous injection, TXA can penetrate the blood-brain barrier and affect the central nervous system (CNS) and the eyes. The concentration of TXA in cerebrospinal fluid and aqueous humor is ~10% of its concentration in plasma (51). During cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) surgery, administering a large dose of TXA (≥100 mg/kg) intravenously can lead to epilepsy and postoperative convulsions in some susceptible patients (66). Similar experimental studies have shown that when TXA is administered locally in central nervous system tissues, it may exert neurotoxic effects by interfering with central GABA-A and glycine receptors (36, 51). According to relevant studies, TXA also has some rare but severe side effects, such as visual impairment and acute renal cortical necrosis (67).
Larger doses of TXA can also cause non-ischemic seizures. When glycine (Gly) binds to the Gly receptor, it does not induce seizures (Figure 2A). TXA competitively binds to glycine receptors and inhibits their activation, thereby increasing muscle excitability and leading to non-ischemic seizures (36) (Figure 2B). When the concentration of TXA is low, glycine and GABA-A receptor agonists compete for the binding site of the glycine receptor, which does not cause seizures. In addition, anesthetics (such as propofol, sevoflurane, and desflurane) are positive allosteric modulators of the glycine receptor, which can enhance the function of the glycine receptor and reverse the inhibitory effect of TXA after binding to the glycine receptor, thereby preventing seizures (68) (Figure 2C). Typically, 5–8 h after surgery, the level of anesthesia in the central nervous system drops rapidly, while the level of TXA either remains at its peak or gradually decreases slowly. Therefore, seizures often occur during this period. Based on the above mechanism, we speculate that the use of TXA in posterior lumbar interbody fusion may lead to the possibility of epilepsy, and spinal surgeon must be aware of risk. When epilepsy occurs, the inhibitory effect of TXA binding to glycine receptors can be reversed by intravenous injection of propofol or midazolam. As there are currently few detailed clinical studies on the association between TXA use and epileptic seizures, future research is expected to focus on the risk stratification of TXA-induced epilepsy. This will involve identifying high-risk individuals (such as patients with renal insufficiency, pre-existing epilepsy, or those undergoing specific neurosurgical procedures) and suggest actionable monitoring protocols to mitigate this adverse effect.
Figure 2
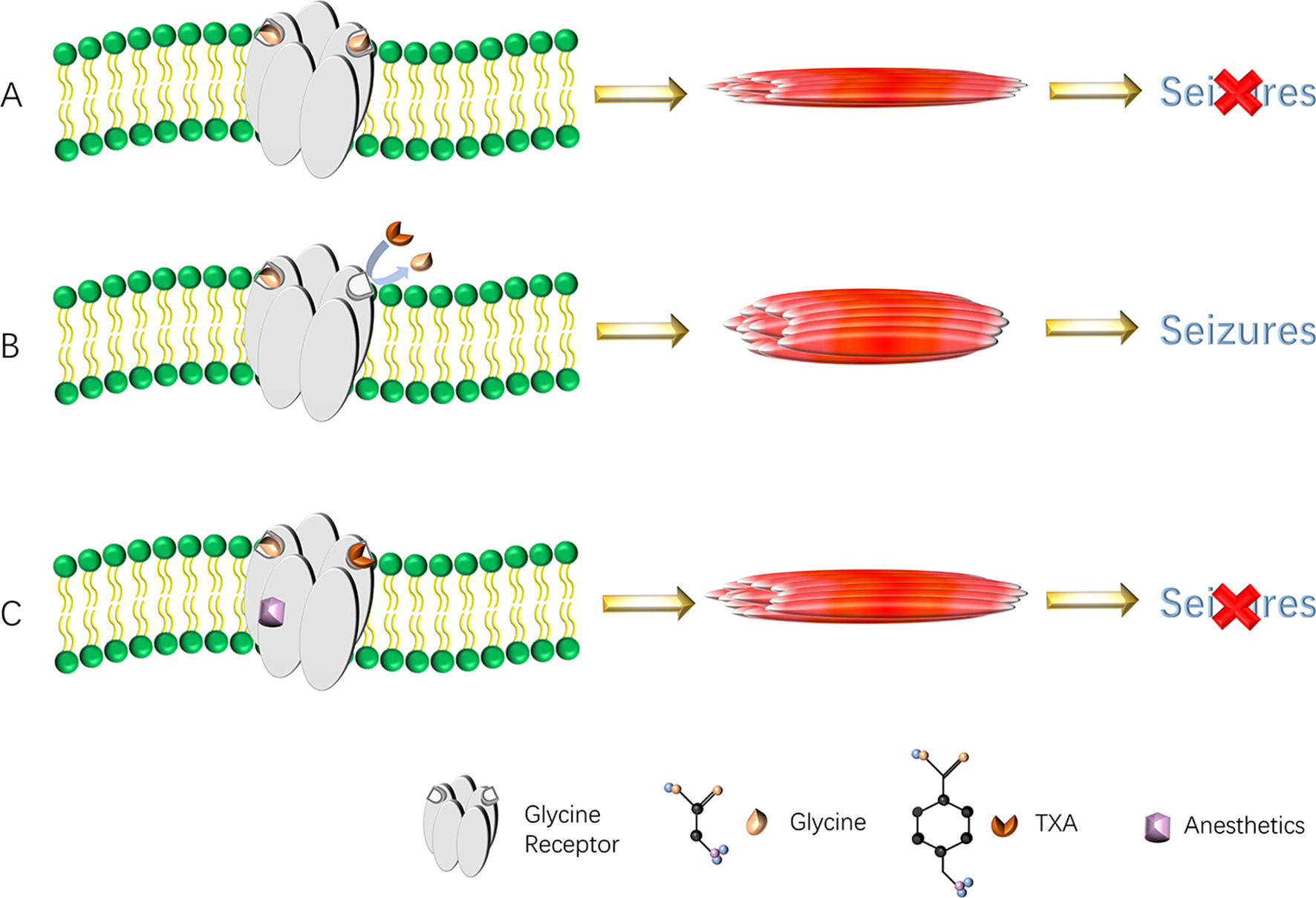
(A–C) Diagram of TXA causing seizures. TXA binds to the glycine receptors, resulting in a decrease in inhibitory current. This reduction in anion conduction increases excitability, which gives rise to seizures. Anesthetics reverse the effect of TXA by increasing glycine receptor function and thereby prevent or reverse TXA-induced seizures. TXA, tranexamic acid.
6 The economic benefits of TXA
To better clarify the economic benefits of TXA, a previous study conducted a statistical analysis of patients who underwent total hip arthroplasty. TXA was found to result to savings of at least $128 per patient and up to ~$600 among patients undergoing revision surgery (69). Similarly, Ehresman et al. (70) analyzed data from 1,353 patients who underwent lumbar fusion surgery and reported that TXA led to savings of ~$328.69 per patient and resulted in fewer allogeneic blood transfusions during hospitalization. Due to the considerable blood loss that occurs after posterior lumbar interbody fusion, patients often need blood products (12), which increases the economic burden of the surgery. Therefore, if TXA is used, it is expected to reduce patients' hospitalization expenses and alleviate the shortage of blood resources.
7 Conclusion and future prospects
During the perioperative period of posterior lumbar interbody fusion, doctors usually need to consider blood conservation strategies for patients. Intravenous use of TXA during perioperative period can reduce blood loss in patients without increasing the incidence of thromboembolic events (15, 53, 54). Therefore, the administration of TXA during posterior lumbar interbody fusion is very promising. However, to date, the administration details of TXA in posterior lumbar interbody fusion remains controversial. These controversies mainly revolve around the use, timing, and dose of TXA. In this manuscript, the application of TXA during spinal surgery was deeply explored, and new insights were put forward regarding the existing controversial issues (illustrated in Table 2). The findings were as follows. (1) The haemostatic effect of preoperative, intravenous administration of TXA was better than that of local administration. (2) The first dose of TXA should be administered before the activation of the fibrinolytic system. (3) The recommended dose of TXA is 10 to 15 mg/kg or 1 g; higher doses have no additional effects on increasing haemostasis. (4) The hyperfibrinolysis process caused by surgical trauma lasts for at least 24 h after the operation. The directions for further improvement of current research are as follows: (1) Clinical research validation: More high-quality, multicenter, and large-sample prospective clinical studies are needed to confirm the reliability of existing research findings. (2) Optimization of administration protocols: A randomized controlled clinical trial design combined with a long-term efficacy follow-up system was used to systematically explore the optimized administration regimen of TXA in posterior lumbar interbody fusion. This specifically covered the precise control of medication timing (such as different time points before, during, or after surgery), the scientific setting of dose gradients (including the reasonable ratio of loading dose to maintenance dose), and the comparative analysis of administration routes (intravenous infusion, local application, or combined administration). (3) Establishment of predictive models: Construct clinical predictive models for such surgeries to identify key influencing factors of TXA in reducing perioperative blood loss. (4) Expansion of application scope: Conduct in-depth studies on the efficacy of TXA in various spinal surgeries (such as cervical and thoracic surgeries) to verify its universality. (5) Analysis of risk factors: Analyze the risk factors of perioperative blood loss after posterior lumbar interbody fusion to achieve individualized and rational use of TXA.
Table 2
| Study | Research object | Groups | Conclusion |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hui et al., 2021 (52) | Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spinal surgery patients | Topical use of TXA vs. Control group | Topical use of TXA in spinal surgery can reduce blood loss |
| Mu et al., 2018 (53) | Double-segment posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) | Intravenous administration group vs. topical administration group vs. placebo group | TXA can reduce blood loss, extubation time, and the length of hospital stay. In addition, intravenous administration can minimize blood loss more efficiently |
| Cao et al., 2022 (54) | Patients undergoing spinal surgery | Intravenous plus topical administration of TXA vs. topical administration vs. placebo group | Effect of reducing blood loss: intravenous plus topical administration > topical administration > Placebo group |
| Abdou et al., 2022 (15) | interbody fusion (PLIF) | Intravenous infusion of 10 mg/kg for 20 min after induction of anesthesia + the maintenance dose of 1 mg/kg/h vs. no receive TXA | Low-dose TXA has no effect on the reduction of intraoperative blood loss volume or blood transfusion requirements. However, it can significantly reduce the need for postoperative blood transfusion requirements |
| Tsutsumimoto et al., 2011 (55) | “French-door” cervical laminoplasty from C3 to C6 was performed | Patients received 15 mg/kg body weight of TXA before the skin incision was made vs. placebo group | Intravenous infusion of TXA can significantly reduce the amount of bleeding in the first 16 h after surgery (~37% reduction) |
| Hui et al., 2018 (60) | Spinal surgeries: A meta-analysis | High-dose TXA (10–100 mg/kg) vs. low-dose TXA (<10 mg/kg) | High-dose TXA significantly reduces intraoperative-perioperative allogeneic transfusion rates and operative time |
| Brown et al., 2022 (56) | Cervical, thoracic, and lumbar laminectomy and fusion | A total of 411 patients from 11 relevant clinical studies were analyzed | The most common route of administration, timing, and dose of TXA was preoperative intravenous injection at a dose of 15 mg/kg |
| Lin et al., 2016 (59) | TXA associated seizures | 26,079 patients with TXA exposure vs. 7,395 patients without TXA exposure | The prevalence of TXA-induced epilepsy was 2.7%, and this rate increased as the TXA dose increased |
| Cheriyan et al., 2015 (61) | Efficacy of TXA on surgical bleeding in spine surgery | Intravenous TXA vs. placebo group | Intravenous injection of TXA at a dose of 10–15 mg/kg or 1 g is sufficient, and a higher dose does not yield additional haemostatic benefits but does increase the risk of epilepsy |
Major studies on the mode of administration, timing, and dosage of TXA.
Statements
Author contributions
WD: Conceptualization, Writing – original draft. YT: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization. YZ: Writing – original draft, Visualization. JL: Writing – original draft, Visualization. CW: Writing – original draft, Visualization. YL: Visualization, Writing – original draft. YY: Writing – original draft, Visualization. ZP: Supervision, Writing – review & editing. JZ: Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Yuzhong District (No. 20240137).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Ghadimi K Levy JH Welsby IJ . Perioperative management of the bleeding patient. Br J Anaesth. (2016) 117(suppl 3):iii18–30. 10.1093/bja/aew358
2.
Shander A Hardy J-F Ozawa S Farmer SL Hofmann A Frank SM et al . A global definition of patient blood management. Anesth Analg. (2022) 135:476–88. 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005873
3.
Hermansen E Austevoll IM Hellum C Storheim K Myklebust TÅ Aaen J et al . Comparison of 3 different minimally invasive surgical techniques for lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Netw Open. (2022) 5:e224291. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.4291
4.
Deyo RA Mirza SK Martin BI Kreuter W Goodman DC Jarvik JG . Trends, major medical complications, and charges associated with surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis in older adults. JAMA. (2010) 303:1259–65. 10.1001/jama.2010.338
5.
Choi J-Y Park S-M Kim H-J Yeom JS . Recent updates on minimally invasive spine surgery: techniques, technologies, and indications. Asian Spine J. (2022) 16:1013–21. 10.31616/asj.2022.0436
6.
Sharma A Shakya A Singh V Deepak P Mangale N Jaiswal A et al . Incidence of dural tears in open versus minimally invasive spine surgery: a single-center prospective study. Asian Spine J. (2022) 16:463–70. 10.31616/asj.2021.0140
7.
Droeghaag R Hermans SMM Caelers IJMH Evers SMAA van Hemert WLW van Santbrink H . Cost-effectiveness of open transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (OTLIF) versus minimally invasive transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (MITLIF): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. (2021) 21:945–54. 10.1016/j.spinee.2021.01.018
8.
White CA Patel AV Butler LR Amakiri UO Yeshoua BJ Steinberger JM et al . Comparison of patient preference, understanding, and sentiment for minimally invasive versus open spine surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). (2022) 47:309-16. 10.1097/BRS.0000000000004134
9.
Hagedorn JM Yadav A D'Souza RS DeTemple N Wolff JS Parmele JB et al . The incidence of lumbar spine surgery following Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression and Superion Indirect Decompression System for treatment of lumbar spinal stenosis: a retrospective review. Pain Pract. (2022) 22:516–21. 10.1111/papr.13111
10.
Park J Ham D-W Kwon B-T Park S-M Kim H-J Yeom JS . Minimally invasive spine surgery: techniques, technologies, and indications. Asian Spine J. (2020) 14:694–701. 10.31616/asj.2020.0384
11.
Wang S-K Wang Q-J Wang P Li X-Y Cui P Wang D-F et al . The impact of frailty on clinical outcomes of older patients undergoing enhanced recovery after lumbar fusion surgery: a prospective cohort study. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:4785–95. 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001594
12.
Smorgick Y Baker KC Bachison CC Herkowitz HN Montgomery DM Fischgrund JS . Hidden blood loss during posterior spine fusion surgery. Spine J. (2013) 13:877–81. 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.02.008
13.
Xu D Ren Z Chen X Zhuang Q Hui S Sheng L et al . The further exploration of hidden blood loss in posterior lumbar fusion surgery. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. (2017) 103:527–30. 10.1016/j.otsr.2017.01.011
14.
Yang C Meng Q Wang H Wang Y Su Z Liu L et al . Anemia and kidney function decline among the middle-aged and elderly in China: a population-based national longitudinal study. Biomed Res Int. (2020) 2020:2303541. 10.1155/2020/2303541
15.
Abdou M Kwon J-W Kim HJ Lee B Choi YS Moon S-H et al . Tranexamic acid and intraoperative and postoperative accumulative bleeding in elective degenerative spine surgery. Yonsei Med J. (2022) 63:927–32. 10.3349/ymj.2022.0163
16.
Zheng B Zheng B Niu H Wang X Lv G Li J et al . Effect analysis of preoperative intravenous tranexamic acid combined with intraoperative immersion in reducing perioperative blood loss of one stage posterior thoracolumbar tuberculosis. Front Surg. (2022) 9:852589. 10.3389/fsurg.2022.852589
17.
Falsetto A Roffey DM Jabri H Kingwell SP Stratton A Phan P et al . Allogeneic blood transfusions and infection risk in lumbar spine surgery: an American College of Surgeons National Surgery Quality Improvement Program Study. Transfusion. (2022) 62:1027–33. 10.1111/trf.16864
18.
Jericó C Osorio J García-Erce JA Pera M . Patient blood management strategies for iron deficiency anemia management in gastric cancer. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2019) 31:547–8. 10.1097/MEG.0000000000001383
19.
Li Y Zhang Y Fang X . Acute normovolemic hemodilution in combination with tranexamic acid is an effective strategy for blood management in lumbar spinal fusion surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. (2022) 17:71. 10.1186/s13018-022-02950-8
20.
Nagabhushan RM Shetty AP Dumpa SR Subramanian B Kanna RM Shanmuganathan R . Effectiveness and safety of batroxobin, tranexamic acid and a combination in reduction of blood loss in lumbar spinal fusion surgery. Spine. (2018) 43:E267–73. 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002315
21.
Dong W Tang Y Lei M Ma Z Zhang X Shen J et al . The effect of perioperative sequential application of multiple doses of tranexamic acid on postoperative blood loss after PLIF: a prospective randomized controlled trial. Int J Surg. (2024) 110:2122–33. 10.1097/JS9.0000000000001083
22.
Zhang Z Wang LN Yang X Liu LM Xiu P Zhou ZJ et al . The effect of multiple-dose oral versus intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing postoperative blood loss and transfusion rate after adolescent scoliosis surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Spine J. (2021) 21:312–20. 10.1016/j.spinee.2020.10.011
23.
Draxler DF Yep K Hanafi G Winton A Daglas M Ho H et al . Tranexamic acid modulates the immune response and reduces postsurgical infection rates. Blood Adv. (2019) 3:1598–609. 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019000092
24.
Zhang S Xu H Xie J Cao G Lei Y Pei F . Tranexamic acid attenuates inflammatory effect and modulates immune response in primary total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, placebo-controlled, pilot trial. Inflammopharmacology. (2020) 28:839–49. 10.1007/s10787-020-00695-6
25.
Lei Y Xie J Huang Q Huang W Pei F . Additional benefits of multiple-dose tranexamic acid to anti-fibrinolysis and anti-inflammation in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. (2020) 140:1087–95. 10.1007/s00402-020-03442-2
26.
Chou S-H Lin S-Y Wu M-H Tien Y-C Jong Y-J Liang W-C et al . Intravenous tranexamic acid reduces blood loss and transfusion volume in scoliosis surgery for spinal muscular atrophy: results of a 20-year retrospective analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2021) 18:9959. 10.3390/ijerph18199959
27.
Yoshihara H Yoneoka D . Predictors of allogeneic blood transfusion in spinal fusion in the United States, 2004-2009. Spine. (2014) 39:304–10. 10.1097/BRS.0000000000000123
28.
Gong M Liu G Chen L Chen R Xiang Z . The efficacy and safety of intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing surgical blood loss in posterior lumbar interbody fusion for the adult: a systematic review and a meta-analysis. World Neurosurg. (2019) 122:559–68. 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.09.115
29.
Shi H Ou Y Jiang D Quan Z Zhao Z Zhu Y . Tranexamic acid reduces perioperative blood loss of posterior lumbar surgery for stenosis or spondylolisthesis: a randomized trial. Medicine. (2017) 96:e5718. 10.1097/MD.0000000000005718
30.
Xie J Ma J Yao H Yue C Pei F . Multiple boluses of intravenous tranexamic acid to reduce hidden blood loss after primary total knee arthroplasty without tourniquet: a randomized clinical trial. J Arthroplasty. (2016) 31:2458–64. 10.1016/j.arth.2016.04.034
31.
Blanié A Bellamy L Rhayem Y Flaujac C Samama CM Fontenay M et al . Duration of postoperative fibrinolysis after total hip or knee replacement: a laboratory follow-up study. Thromb Res. (2013) 131:e6–11. 10.1016/j.thromres.2012.11.006
32.
Golz AG Yee HK Davis BJ Adams WH Brown NM . One dose versus two doses of intravenous tranexamic acid in total joint arthroplasty. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. (2021) 29:e555–62. 10.5435/JAAOS-D-20-00658
33.
Li ZJ Fu X Xing D Zhang HF Zang JC Ma XL . Is tranexamic acid effective and safe in spinal surgery? A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur Spine J. (2013) 22:1950–7. 10.1007/s00586-013-2774-9
34.
Li G Sun T-W Luo G Zhang C . Efficacy of antifibrinolytic agents on surgical bleeding and transfusion requirements in spine surgery: a meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. (2017) 26:140–54. 10.1007/s00586-016-4792-x
35.
Lanoiselee J Zufferey PJ Ollier E Hodin S Delavenne X PeriOpeRative tranexamic acid in hip arthrOplasty study I . Is tranexamic acid exposure related to blood loss in hip arthroplasty? A pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic study. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2018) 84:310–9. 10.1111/bcp.13460
36.
Aboul-Fotouh S Habib MZ Magdy SM Hassan BE-DE . Tranexamic acid-associated fatal status epilepticus in a paediatric non-cardiac surgery: a case report and literature review. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2022) 88:4211–6. 10.1111/bcp.15296
37.
Sentilhes L Sénat MV Le Lous M Winer N Rozenberg P Kayem G et al . Tranexamic acid for the prevention of blood loss after cesarean delivery. N Engl J Med. (2021) 384:1623–34. 10.1056/NEJMoa2028788
38.
Roberts I Shakur-Still H Aeron-Thomas A Beaumont D Belli A Brenner A et al . Tranexamic acid to reduce head injury death in people with traumatic brain injury: the CRASH-3 international RCT. Health Technol Assess. (2021) 25:1–76. 10.3310/hta25260
39.
Heyns M Knight P Steve AK Yeung JK . A single preoperative dose of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative blood loss: a meta-analysis. Ann Surg. (2021) 273:75–81. 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003793
40.
Zhang S Wang F Wang C Chu P Shi L . Xue Q. Are the applications of tranexamic acid in reverse hybrid total knee arthroplasty (TKA) the same as those in fully cemented TKA?: a randomized controlled trial. Adv Ther. (2021) 38:2542–57. 10.1007/s12325-021-01719-5
41.
Wilde JM Copp SN Ezzet KA Rosen AS Walker RH McCauley JC et al . No difference in blood loss and risk of transfusion between patients treated with one or two doses of intravenous tranexamic acid after simultaneous bilateral TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2022) 480:702–11. 10.1097/CORR.0000000000002037
42.
Hishimura R Onodera T Ohkoshi Y Okada K Matsuoka M Matsubara S et al . The effect of local injection of tranexamic acid into peri-articular tissue versus drain clamping in total knee arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2022) 23:111. 10.1186/s12891-022-05058-6
43.
Yuenyongviwat V Dissaneewate K Iamthanaporn K Tuntarattanapong P Hongnaparak T . Efficacy of extended oral tranexamic acid on blood loss in primary total knee arthroplasty. Acta Ortop Bras. (2022) 30(spe1):e247197. 10.1590/1413-785220223001e247197
44.
Electricwala AJ Dasgupta R Kulkarni S Electricwala JT . A comparison of oral vs intravenous tranexamic acid in patients undergoing staggered bilateral total knee arthroplasty. Arch Bone Jt Surg. (2022) 10:261–6. 10.22038/ABJS.2021.49561.2459
45.
Yi Z Yan L Haibo S Yuangang W Mingyang L Yuan L et al . Effects of tourniquet use on clinical outcomes and cement penetration in TKA when tranexamic acid administrated: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2021) 22:126. 10.1186/s12891-021-03968-5
46.
Collaborators H-IT . Effects of a high-dose 24-h infusion of tranexamic acid on death and thromboembolic events in patients with acute gastrointestinal bleeding (HALT-IT): an international randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. (2020) 395:1927–36. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30848-5
47.
Lee P-L Yang K-S Tsai H-W Hou S-K Kang Y-N Chang C-C . Tranexamic acid for gastrointestinal bleeding: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am J Emerg Med. (2021) 45:269–79. 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.08.062
48.
Joseph J Martinez-Devesa P Bellorini J Burton MJ . Tranexamic acid for patients with nasal haemorrhage (epistaxis). Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2018) 12:CD004328. 10.1002/14651858.CD004328.pub3
49.
Wang W-J Wu T-Y Tu Y-K Kuo K-L Tsai C-Y Chie W-C . The optimal dose of oral tranexamic acid in melasma: A network meta-analysis. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. (2023) 89:189–94. 10.25259/IJDVL_530_2021
50.
Lecker I Wang D-S Romaschin AD Peterson M Mazer CD Orser BA . Tranexamic acid concentrations associated with human seizures inhibit glycine receptors. J Clin Invest. (2012) 122:4654–66. 10.1172/JCI63375
51.
McCormack PL . Tranexamic acid: a review of its use in the treatment of hyperfibrinolysis. Drugs. (2012) 72:585–617. 10.2165/11209070-000000000-00000
52.
Hui S Peng Y Tao L Wang S Yang Y Du Y et al . Tranexamic acid given into wound reduces postoperative drainage, blood loss, and hospital stay in spinal surgeries: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2021) 16:401. 10.1186/s13018-021-02548-6
53.
Mu X Wei J Wang C Ou Y Yin D Liang B et al . Intravenous administration of tranexamic acid significantly reduces visible and hidden blood loss compared with its topical administration for double-segment posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a single-center, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. World Neurosurg. (2019) 122:e821–e7. 10.1016/j.wneu.2018.10.154
54.
Cao Z Li Q Guo J Li Y Wu J . Optimal administration strategies of tranexamic acid to minimize blood loss during spinal surgery: results of a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Ann Med. (2022) 54:2053–63. 10.1080/07853890.2022.2101687
55.
Tsutsumimoto T Shimogata M Ohta H Yui M Yoda I Misawa H . Tranexamic acid reduces perioperative blood loss in cervical laminoplasty: a prospective randomized study. Spine. (2011) 36:1913-8. 10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181fb3a42
56.
Brown NJ Choi EH Gendreau JL Ong V Himstead A Lien BV et al . Association of tranexamic acid with decreased blood loss in patients undergoing laminectomy and fusion with posterior instrumentation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Spine. (2022) 36:686–93. 10.3171/2021.7.SPINE202217
57.
Wilde JM Copp SN McCauley JC Bugbee WD . One dose of intravenous tranexamic acid is equivalent to two doses in total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2018) 100:1104–9. 10.2106/JBJS.17.00641
58.
Dong W Liang Y Li D Ma Z Cheng M Zhang X et al . The effect of sequential perioperative intravenous tranexamic acid in reducing postoperative blood loss and hidden blood loss after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: a randomized controlled trial. Front Med. (2023) 10:1192971. 10.3389/fmed.2023.1192971
59.
Lin Z Xiaoyi Z . Tranexamic acid-associated seizures: a meta-analysis. Seizure. (2016) 36:70–3. 10.1016/j.seizure.2016.02.011
60.
Hui S Xu D Ren Z Chen X Sheng L Zhuang Q et al . Can tranexamic acid conserve blood and save operative time in spinal surgeries?A meta-analysis Spine J. (2018) 18:1325–37. 10.1016/j.spinee.2017.11.017
61.
Cheriyan T Maier SP Bianco K Slobodyanyuk K Rattenni RN Lafage V et al . Efficacy of tranexamic acid on surgical bleeding in spine surgery: a meta-analysis. Spine J. (2015) 15:752–61. 10.1016/j.spinee.2015.01.013
62.
Yuan Q-M Zhao Z-H Xu B-S . Efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in reducing blood loss in scoliosis surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Spine J. (2017) 26:131–9. 10.1007/s00586-016-4899-0
63.
Neilipovitz DT . Tranexamic acid for major spinal surgery. Eur Spine J. (2004) 13(Suppl. 1):S62–5. 10.1007/s00586-004-0716-2
64.
Chornenki NLJ Um KJ Mendoza PA Samienezhad A Swarup V Chai-Adisaksopha C et al . Risk of venous and arterial thrombosis in non-surgical patients receiving systemic tranexamic acid: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Res. (2019) 179:81–6. 10.1016/j.thromres.2019.05.003
65.
Sharaby MMF El-Deeb YM . Is intravenous tranexamic acid effective in reduction of blood loss during pelvic and acetabular surgery?Int Orthop. (2022) 46:1721–9. 10.1007/s00264-022-05416-y
66.
Shi J Zhou C Pan W Sun H Liu S Feng W et al . Effect of high- vs low-dose tranexamic acid infusion on need for red blood cell transfusion and adverse events in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: the OPTIMAL randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2022) 328:336–47. 10.1001/jama.2022.10725
67.
Yoo JS Ahn J Karmarkar SS Lamoutte EH Singh K . The use of tranexamic acid in spine surgery. Ann Transl Med. (2019) 7:S172. 10.21037/atm.2019.05.36
68.
Lecker I Wang D-S Whissell PD Avramescu S Mazer CD Orser BA . Tranexamic acid-associated seizures: causes and treatment. Ann Neurol. (2016) 79:18–26. 10.1002/ana.24558
69.
Demos HA Lin ZX Barfield WR Wilson SH Robertson DC Pellegrini VD . Process improvement project using tranexamic acid is cost-effective in reducing blood loss and transfusions after total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. (2017) 32:2375–80. 10.1016/j.arth.2017.02.068
70.
Ehresman J Pennington Z Schilling A Medikonda R Huq S Merkel KR et al . Cost-benefit analysis of tranexamic acid and blood transfusion in elective lumbar spine surgery for degenerative pathologies. J Neurosurg Spine. (2020) 33:177–85. 10.3171/2020.1.SPINE191464
Summary
Keywords
tranexamic acid, posterior lumbar interbody fusion, mode of administration, timing and dose of administration, research progress
Citation
Dong W, Tang Y, Zhou Y, Li J, Wu C, Liu Y, Yan Y, Peng Z and Zhao J (2025) Application and research progress of tranexamic acid in the perioperative period of posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Front. Med. 12:1612281. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1612281
Received
15 April 2025
Accepted
21 July 2025
Published
08 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Xin Li, National Cancer Institute at Frederick (NIH), United States
Reviewed by
Germano Emílio Conceição-Souza, Hospital Alemão Oswaldo Cruz, Brazil
Lu Zhang, Affiliated Hospital of Jining Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Dong, Tang, Zhou, Li, Wu, Liu, Yan, Peng and Zhao.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jun Zhao 13678428203@163.comZhenggang Peng spinemedicine@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
‡These authors have contributed equally to this work and share last authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.