- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Shandong University Qilu Hospital, Jinan, Shandong, China
- 2Shandong Provincial Clinical Research Center for Digestive Diseases, Jinan, Shandong, China
Background: Balloon-assisted enteroscopy (BAE) plays an important role in the diagnosis and therapy of small bowel diseases. Complete enteroscopy is considered an objective quality indicator of enteroscopy. However, there are limited studies on the factors associated with complete BAE. This study aimed to determine the factors affecting complete BAE.
Methods: All adult patients with indications for BAE were investigated at a tertiary medical center from January 2019 to December 2022. Their medical records and BAE procedure-associated data were reviewed and analyzed. Risk factors of incomplete enteroscopy were investigated using univariate analysis and multivariable logistic regression analysis.
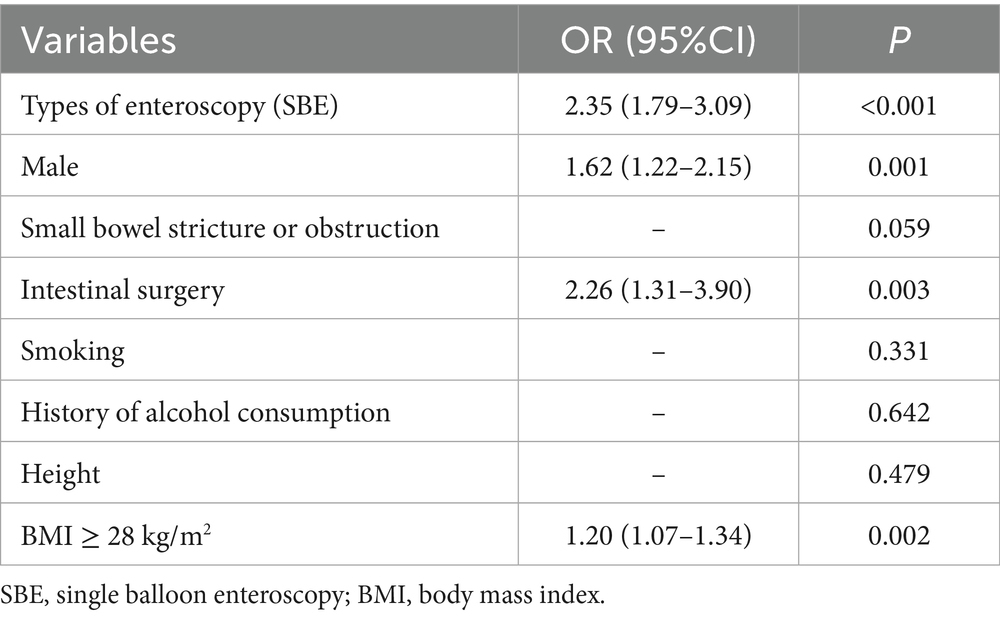
Results: A total of 943 patients meeting the eligibility criteria were analyzed. Among these, 558 patients achieved complete enteroscopy. In multivariable logistic regression analysis, single-balloon enteroscopy (SBE) [odds ratio (OR) = 2.35, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.79–3.09, p < 0.001], male sex (OR = 1.62, 95% CI: 1.22–2.15, p = 0.001), intestinal surgery (OR = 2.26, 95% CI: 1.79–3.09, p = 0.003), and body mass index (BMI) ≥ 28 kg/m2 (OR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.07–1.34, p = 0.002) were independent predictors of incomplete enteroscopy.
Conclusion: This retrospective study identified SBE, male sex, intestinal surgery, and BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2 as independent risk factors for incomplete enteroscopy.
1 Introduction
Balloon-assisted enteroscopy (BAE) is an effective endoscopic technique used for diagnosing and treating small bowel diseases. Two types of BAE, double-balloon enteroscopy (DBE) and single-balloon enteroscopy (SBE), are commercially available. BAE is not available in many endoscopy units, as it is time-consuming and requires specialized training.
The length of the adult small bowel averages around 600 cm (1), and the diagnostic and therapeutic yields of BAE depend on the depth of small bowel insertion and complete vision of the entire gastrointestinal tract for many patients (2–4). Complete enteroscopy is considered an objective quality indicator of enteroscopy and the most comprehensive method for the visualization of the small bowel (5). A higher rate of complete enteroscopy is associated with a greater chance of detecting meaningful gastrointestinal lesions. Complete enteroscopy ensures confirmation of the presence, variety, number, and distribution of lesions throughout the small intestine, which have a positive influence on further management and surveillance of the small bowel (3, 6–8). Patients with obscure gastrointestinal bleeding (OGIB) who achieved complete endoscopy had a lower chance of rebleeding than those without complete examination (9). However, limited data exists on the factors associated with the completion or insertion depth of BAE.
This study aimed to investigate the risk factors associated with incomplete enteroscopy. Identifying these factors may help to achieve hierarchical patient management and endoscopic procedure planning.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 Patients
This retrospective study was conducted at a tertiary medical center (Qilu Hospital of Shandong University, Jinan, China). Consecutive adult patients who underwent BAE from January 2019 to December 2022 were reviewed. Patients who met any of the following criteria were excluded: (1) cases terminated upon the target lesion (strictures, masses, hemorrhagic or other lesions) where further insertion was clinically unnecessary; (2) need for therapeutic intervention, including hemostasis, polypectomy, removal of foreign body in the small bowel, lithotripsy, enteroscopy-assisted endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography, and enteroscopy-assisted jejunostomy tube placement, making further insertion unnecessary; (3) risk of bleeding due to fragile gastrointestinal mucosa, gastrointestinal varices, and Mallory–Weiss syndrome; (4) poor bowel preparation; (5) patients with an insertion route of intestinal stoma; and (6) incomplete clinical data and endoscopic information.
The decision for complete enteroscopy as an examination endpoint was made by the endoscopist after understanding the patient’s clinical data, the purpose of the enteroscopy, and endoscopic findings. This study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University (No. KYLL-202401-030-1).
2.2 BAE
BAE was performed with DBE (EN-580 T enteroscopy, Fujifilm, Japan) or SBE (SIF-Q260 enteroscopy, Olympus Optical, Japan), both using a sliding overtube (ST-SB1, Olympus, Tokyo, Japan) and PB-10 pressure controlled pump system (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). All patients were instructed to fast for 12 h before the procedures, and bowel preparation (polyethylene glycol electrolyte solution mixed with 2 L water) was administered 4–5 h before enteroscopy. General anesthesia (intravenous propofol, 2–3 mg/kg/h) was administered by anesthesiologists monitoring cardiorespiratory parameters. All patients had intubation and mechanical ventilation. CO2 insufflation was used during all enteroscopic procedures. X-ray fluoroscopy guidance was used in some patients who had difficulty with endoscope insertion. To explore the influence of enteroscopy operators’ experience, we tried our best to collect the learning curves of each operator for DBE and SBE.
All patients were scheduled for both antegrade and retrograde procedures. The initial insertion path of the enteroscopy was determined based on clinical information, previous findings, or preference of the endoscopist. If scope advancement was unsuccessful despite applying abdominal pressure or changing the patient’s position, the procedure was terminated. Endoscopic tattooing was performed at the furthest insertion point as a landmark. The opposite route was subsequently carried out. Complete enteroscopy was confirmed if the cecum was reached via the oral route, the duodenal papilla was reached via the anal route, or the tattoo mark made by the initial procedure was reached via the opposite route.
2.3 Data collection
We retrospectively reviewed and analyzed the following variables: patients’ sex, age, height and body mass index (BMI); history of abdominal and pelvic surgery; history of diabetes, smoking and alcohol consumption; indications for enteroscopy (OGIB, small bowel stricture or obstruction, diagnosed or suspected polyposis/tumor, diagnosed or suspected Crohn’s disease, abdominal pain, diarrhea, and other reasons); types of enteroscopy (DBE or SBE); and the initial and subsequent insertion routes.
2.4 Statistical analysis
Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and compared using Student’s t-test. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages and compared using the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test. Factors with p < 0.10 in univariate analysis were included in the multivariable logistic regression analysis. Odds ratios (ORs) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were reported. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States).
3 Results
3.1 Patient characteristics
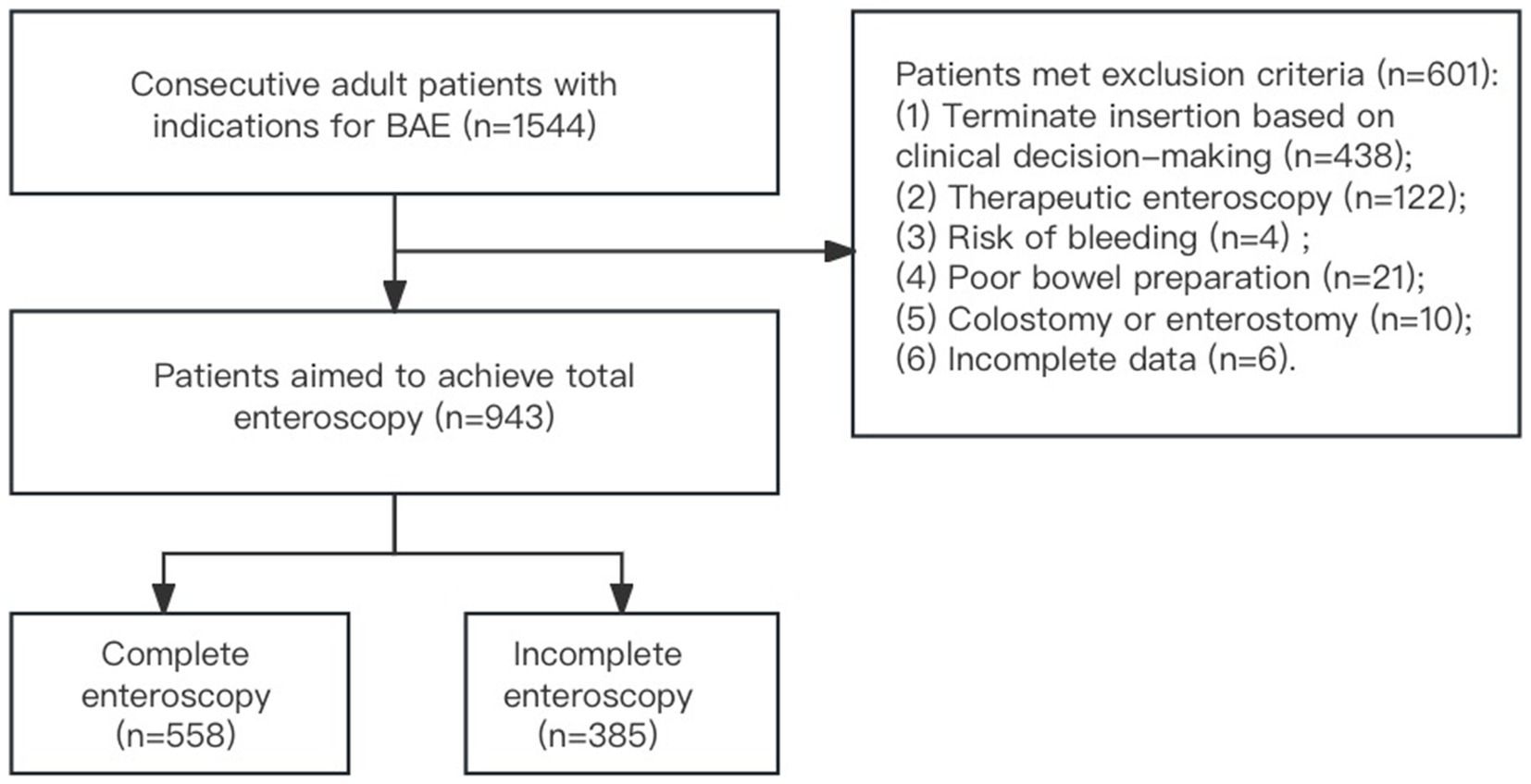
From January 2019 to December 2022, BAE was performed on 1,544 patients with suspected small bowel diseases at Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. Among these patients, 438 were excluded for terminating further insertion based on clinical decision-making, 122 for therapeutic intervention, 21 for poor bowel preparation, 10 for previous colostomy or enterostomy surgery, six for incomplete clinical data and endoscopic information, and four for risk of bleeding. A total of 943 patients were ultimately included in the analysis. Among these, 558 patients achieved complete enteroscopy, while 385 did not (Figure 1).
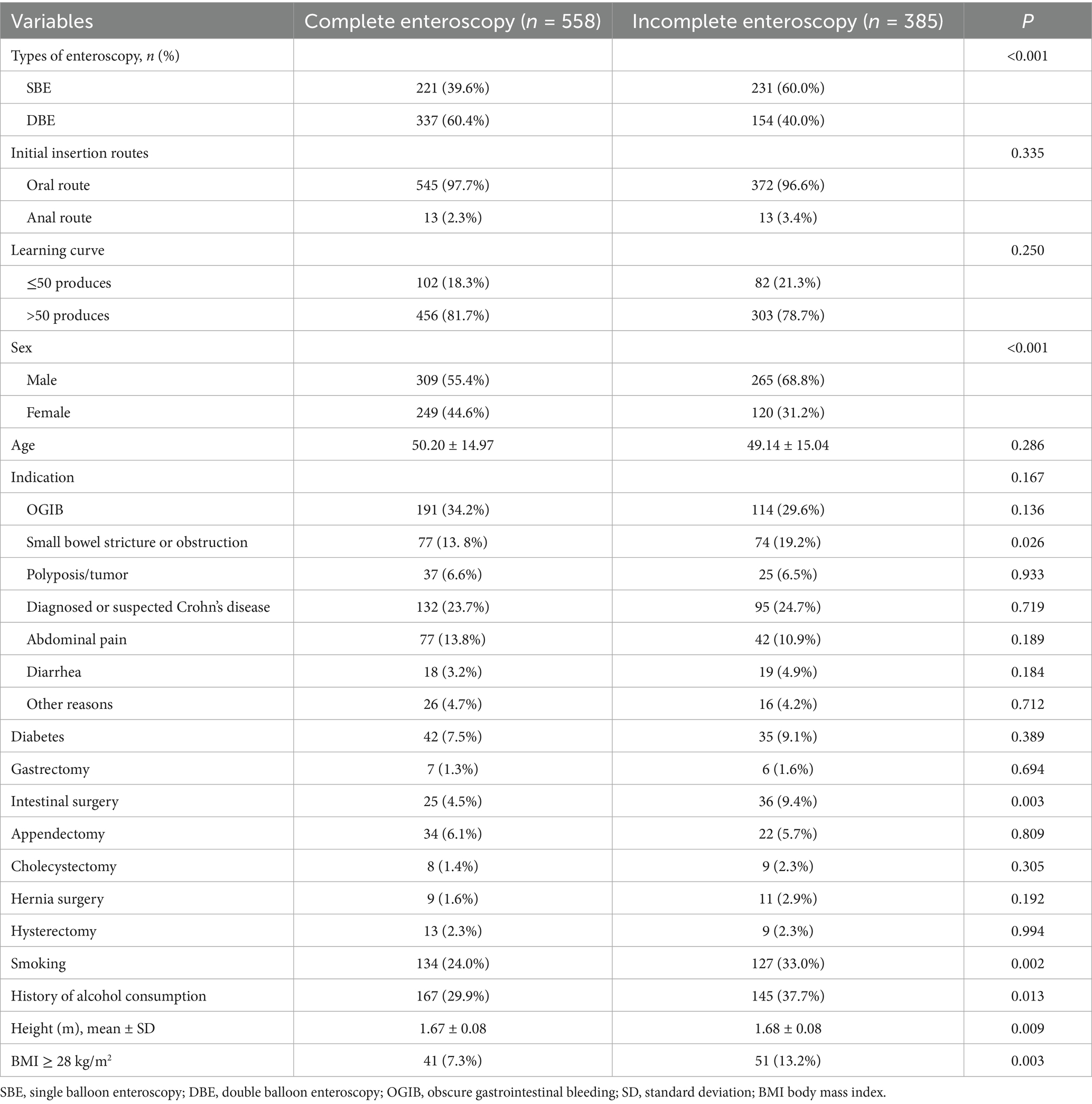
The baseline characteristics of the patients are summarized in Table 1. The mean age was 49.78 ± 15.0 years, and 60.9% were male. Indications for enteroscopy were OGIB (32.3%, 305/943), small bowel stricture or obstruction (16.0%, 151/943), diagnosed or suspected polyposis/tumor (6.6%, 62/943), diagnosed or suspected Crohn’s disease (24.1%, 227/943), abdominal pain (12.6%, 119/943), diarrhea (3.9%, 37/943), and other reasons (4.5%, 42/943). About 8.2% (77/943) of patients had diabetes.
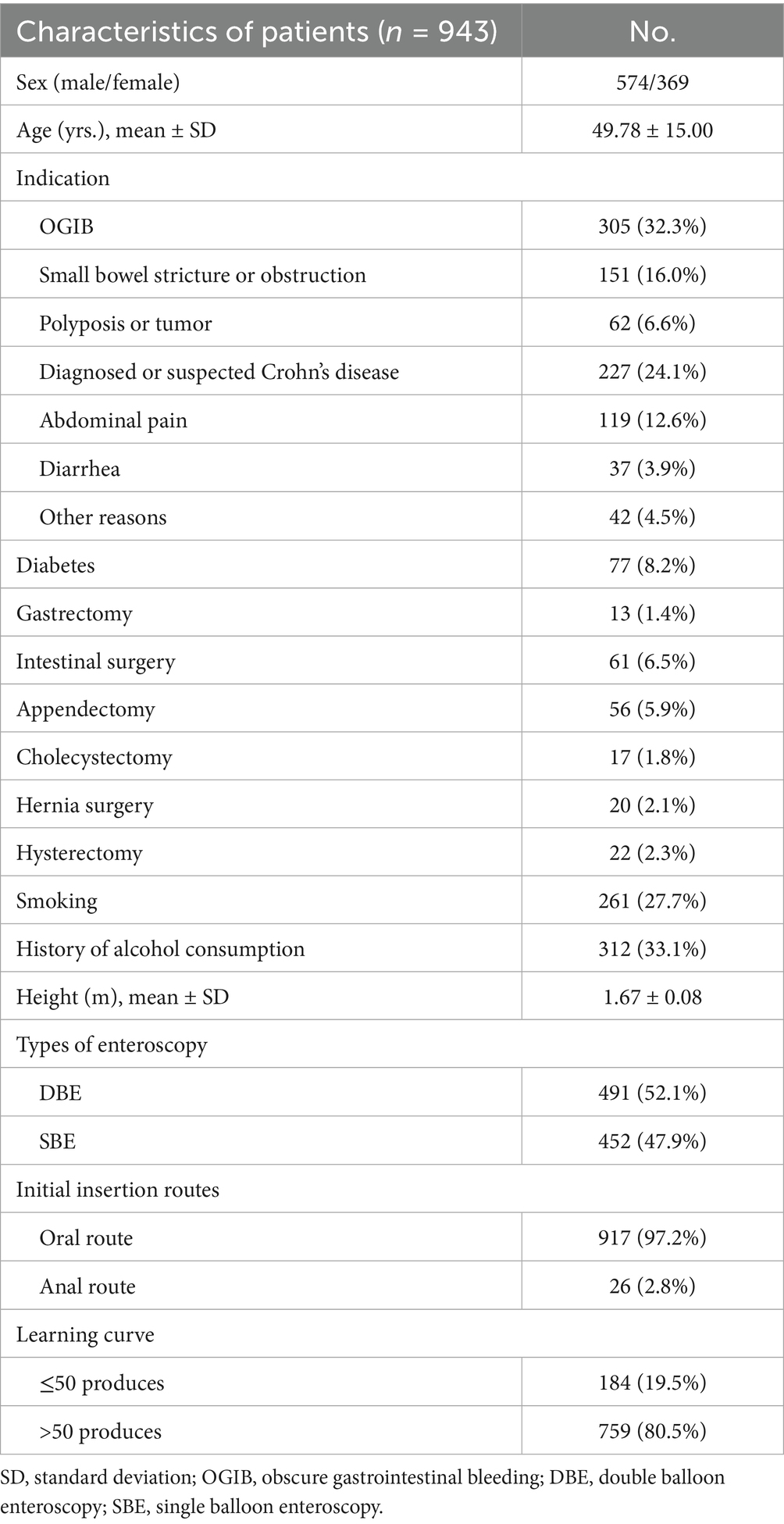
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of patients with suspected small bowel diseases aiming at complete enteroscopy by BAE.
The rates of different abdominal and pelvic surgical history were as follows: gastrectomy (1.4%, 13/943), intestinal surgery (61/943, 6.5%), appendectomy (5.9%, 56/943), cholecystectomy (1.8%, 17/943), hernia surgery (2.1%, 20/943), and hysterectomy (2.3%, 22/943). The rate of smoking was 27.7% (261/943), and 33.1% (312/943) had a history of alcohol consumption. SBE accounted for 47.9% (452/943), while DBE accounted for 52.1% (491/943). The oral route was used as the initial insertion route in 97.2% (917/943), and the anal route in 2.8% (26/943). A total of 184 (19.5%) patients were from the operators’ first 50 cases, and 759 (80.5%) patients were from the operators’ subsequent cases.
3.2 Univariate analysis
Among the 943 patients, 558 (59.2%) achieved complete enteroscopy. Potential predictive factors were assessed by univariate analysis (Table 2). Eight of them had p-values less than 0.10, including SBE (p < 0.001), male sex (p < 0.001), small bowel stricture or obstruction (p = 0.026), intestinal surgery (p = 0.003), smoking (p = 0.002), alcohol consumption (p = 0.013), greater height (p = 0.002), and BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2 (p = 0.003). The learning curve of operators (≤50 vs. >50 cases) did not significantly affect the completion rates of enteroscopy (p = 0.250) (Table 2).
3.3 Logistic multivariable analysis
Logistic multivariable regression analysis identified the following as independent predictors of incomplete enteroscopy: SBE (OR = 2.35, 95% CI: 1.79–3.09, p < 0.001), male sex (OR = 1.62, 95% CI: 1.22–2.15, p = 0.001), intestinal surgery (OR = 2.26, 95% CI: 1.79–3.09, p = 0.003), and BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2 (OR = 1.20, 95% CI: 1.07–1.34, p = 0.002) (Table 3).
4 Discussion
The introduction of BAE has improved the diagnosis and treatment of small bowel diseases. More lesions are being detected as the depth of insertion into the small bowel has increased (3). However, achieving complete enteroscopy is challenging due to the deep position and tortuous anatomy of the small bowel loops, and incomplete visualization of small bowel mucosa may partially account for missed pathologic lesions during BAE (10, 11). Prospective studies have reported a high heterogeneity in the percentage of complete enteroscopy during BAE, ranging from 0 to 92% (12–17). Thus, identifying the risk factors of incomplete enteroscopy is important in evaluating the diagnostic and therapeutic yield, as well as the time and risks associated with individual patients (18).
OGIB is the most common indication for small bowel visualization, and performing complete enteroscopy becomes essential in these cases (2). Similar to previous studies, the present study found that OGIB was the major indication. Uncertainties persist regarding the predictors of complete enteroscopy during BAE. Nevertheless, several factors have been implicated in previous studies, including a history of abdominal surgery, indications for enteroscopy, BMI, CO2 insufflation, and types of BAE (SBE or DBE) (19, 20). The present study demonstrated that SBE, male sex, intestinal surgery, and BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2 were independent predictors of incomplete BAE. The identification of these risk factors may aid with clinical procedure planning and a definite diagnosis, reduce the burden of the endoscopist, and decrease the procedure time of enteroscopy.
In a randomized controlled trial published in 2011, complete enteroscopy was more easily performed with DBE than with SBE, although the study was limited by a small sample size (13). In a more recent study, the complete enteroscopy rate of SBE was reported to be lower than that for DBE. However, the difference was not significant (21). Similarly, our findings, based on a large sample size (452 with SBE, 491 with DBE), also demonstrated DBE with a higher complete enteroscopy rate.
Sex was previously reported as a significant predictor of complete enteroscopy (22). This is consistent with our findings, indicating that male sex is an independent predictive factor for incomplete enteroscopy. It is well known that there is sexual dimorphism in body fat distribution. Men generally have more abdominal visceral adipose tissue than women (23), which may partially explain this result. Previous literature has shown that women are less likely to achieve complete colonoscopy (24), a finding that contrasts with findings in enteroscopy and should be noted by endoscopists.
A history of previous abdominal surgery can affect the depth of maximal insertion (DMI) during DBE, and there is a strong association between the number of abdominal surgeries and the DMI for both anterograde and retrograde approaches (20). The present study investigated the influence of abdominal and pelvic surgery in detail by categorizing procedures into gastrectomy, intestinal surgery, appendectomy, cholecystectomy, hernia surgery, and hysterectomy. Intestinal surgery was an independent negative factor for incomplete enteroscopy, while other abdominal and pelvic surgeries showed no significant difference. This may be explained by mesenteric adhesions limiting the mobility of the small bowel and creating areas of fixed angulations, which are difficult to negotiate even using flexible BAE.
Obesity has been postulated as a negative predictive factor for DMI by limiting the length of bowel that can be pleated on the overtube of BAE. However, the definite influence of BMI has not been rigorously studied (25). One study indicated a significant linear relationship between small bowel length and height, while the relationship between small bowel length and BMI, although also linear, was not significant (1). In the current study, obesity (BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2) was identified as an independent risk factor for incomplete BAE. Greater height was also identified as a risk factor for incomplete enteroscopy; however, it did not remain significant in multivariable logistic analysis.
Prior studies on the DMI or complete DBE did not identify age as an influencing factor, which was consistent with our findings (20, 26). In our study, an indication of small bowel stricture or obstruction was not an independent risk factor for incomplete enteroscopy in multivariable logistic analysis. This may be explained by our exclusion criteria regarding terminating examinations for patients with luminal stricture or huge mass, which may increase the complete enteroscopy rate of patients with small bowel stricture or obstruction indication. Previous studies have rarely reported the influence of smoking and alcohol consumption on complete enteroscopy. To our knowledge, our study is the first to investigate the relationship of these two factors with complete enteroscopy. While univariate analysis showed a trend toward higher incomplete enteroscopy rates in patients with a history of smoking and alcohol consumption, these associations were not statistically significant on multivariable logistic analysis. Most patients with smoking and alcohol consumption were male, which may have been a confounding factor in the univariate analysis.
Previous studies on the learning curve of enteroscopy were inconsistent. Gross et al. showed that the complete enteroscopy rose from 8% in the first 50 DBEs, to 63% in the last 50 of 200 DBEs (18). Whereas Tee et al. found that there was no learning curve for transoral DBE (27). Dutta et al. reported a learning curve for transoral SBE, but not for the transanal approach (28). In our endoscopy center, operators are required to have performed over 10,000 gastroscopies and colonoscopies before being permitted to independently perform enteroscopy procedures. We speculate that this rigorous pre-training may have partially mitigated the conventional learning curve of enteroscopy.
This study has some limitations. First, it was a single-center retrospective study. Second, the oral route was the initial insertion route in 97.2% of cases, which was primarily due to the habits and preferences of the endoscopists at our institution. This may partly explain the difference between the findings of the present study and those of previous studies, which demonstrated a higher complete enteroscopy rate by the retrograde approach (6).
5 Conclusion
The present retrospective study identified SBE, male sex, intestinal surgery, and BMI ≥ 28 kg/m2 as independent risk factors for incomplete enteroscopy. Identification of these predictive risk factors may contribute to the implementation of additional measures to reduce the rate of incomplete BAE, thereby improving the diagnostic efficiency and therapeutic yield of BAE.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Medical Ethics Committee of Qilu Hospital of Shandong University. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent for participation was not required from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin in accordance with the national legislation and institutional requirements.
Author contributions
JL: Writing – original draft, Data curation. MW: Resources, Writing – review & editing. PW: Resources, Writing – review & editing. JG: Resources, Writing – review & editing. Y-BY: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Conceptualization. X-LZ: Visualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Funding acquisition, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82070551).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Raines, D, Arbour, A, Thompson, HW, Figueroa-Bodine, J, and Joseph, S. Variation in small bowel length: factor in achieving total enteroscopy? Dig Endosc. (2015) 27:67–72. doi: 10.1111/den.12309
2. Xin, L, Liao, Z, Jiang, YP, and Li, ZS. Indications, detectability, positive findings, total enteroscopy, and complications of diagnostic double-balloon endoscopy: a systematic review of data over the first decade of use. Gastrointest Endosc. (2011) 74:563–70. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2011.03.1239
3. Zhao, L, Yin, A, Liao, F, Ding, Y, and Yu, H. Inspecting the total gastrointestinal tract by consecutive bidirectional double-balloon enteroscopy in patients wit suspected small bowel bleeding. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2020) 31:688–94. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2020.19387
4. Nehme, F, Goyal, H, Perisetti, A, Tharian, B, Sharma, N, Tham, TC, et al. The evolution of device-assisted enteroscopy: from sonde enteroscopy to motorized spiral enteroscopy. Front Med (Lausanne). (2021) 8:792668. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.792668
5. Rondonotti, E, Spada, C, Adler, S, May, A, Despott, EJ, Koulaouzidis, A, et al. Small-bowel capsule endoscopy and device-assisted enteroscopy for diagnosis and treatment of small-bowel disorders: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) technical review. Endoscopy. (2018) 50:423–46. doi: 10.1055/a-0576-0566
6. Zhao, L, Yin, AN, Liao, F, Ding, YJ, and Yu, HG. Achieving Total Enteroscopy by consecutive bidirectional double balloon Enteroscopy procedures. Curr Med Sci. (2022) 42:144–9. doi: 10.1007/s11596-022-2523-6
7. Mönkemüller, K, Weigt, J, Treiber, G, Kolfenbach, S, Kahl, S, Röcken, C, et al. Diagnostic and therapeutic impact of double-balloon enteroscopy. Endoscopy. (2006) 38:67–72. doi: 10.1055/s-2005-921190
8. Zhang, FB, Zhang, JP, Bai, YQ, Zhang, DJ, Cao, XG, and Guo, CQ. Effect of abdominal compression on Total single-balloon Enteroscopy rate: a randomized controlled trial. Mayo Clin Proc. (2023) 98:1660–9. doi: 10.1016/j.mayocp.2023.02.031
9. Shishido, T, Oka, S, Tanaka, S, Imagawa, H, Takemura, Y, Yoshida, S, et al. Outcome of patients who have undergone total enteroscopy for obscure gastrointestinal bleeding. World J Gastroenterol. (2012) 18:666–72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v18.i7.666
10. Gao, Y, Xin, L, Zhang, YT, Guo, XR, Meng, QQ, Li, ZS, et al. Technical and clinical aspects of diagnostic single-balloon enteroscopy in the first decade of use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Gut Liver. (2020) 15:262–72. doi: 10.5009/gnl19345
11. Hasak, S, Lang, G, Early, D, Mullady, D, Das, K, Chen, C, et al. Use of a transparent cap increases the diagnostic yield in Antegrade single-balloon Enteroscopy for obscure GI bleed. Dig Dis Sci. (2019) 64:2256–64. doi: 10.1007/s10620-019-05532-7
12. May, A, Färber, M, Aschmoneit, I, Pohl, J, Manner, H, Lotterer, E, et al. Prospective multicenter trial comparing push-and-pull Enteroscopy with the single- and double-balloon techniques in patients with small-bowel disorders. Am J Gastroenterol. (2010) 105:575–81. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2009.712
13. Takano, N, Yamada, A, Watabe, H, Togo, G, Yamaji, Y, Yoshida, H, et al. Single-balloon versus double-balloon endoscopy for achieving total enteroscopy: a randomized, controlled trial. Gastrointest Endosc. (2011) 73:734–9. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2010.10.047
14. Domagk, D, Mensink, P, Aktas, H, Lenz, P, Meister, T, Luegering, A, et al. Single- vs. double-balloon enteroscopy in small-bowel diagnostics: a randomized multicenter trial. Endoscopy. (2011) 43:472–6. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1256247
15. Efthymiou, M, Desmond, PV, Brown, G, La Nauze, R, Kaffes, A, Chua, TJ, et al. SINGLE-01: a randomized, controlled trial comparing the efficacy and depth of insertion of single- and double-balloon enteroscopy by using a novel method to determine insertion depth. Gastrointest Endosc. (2012) 76:972–80. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.06.033
16. Messer, I, May, A, Manner, H, and Ell, C. Prospective, randomized, singlecenter trial comparing double-balloon enteroscopy and spiral enteroscopy in patients with suspected small-bowel disorders. Gastrointest Endosc. (2013) 77:241–9. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2012.08.020
17. Liu, S, Dong, T, Shi, Y, Luo, H, Xue, X, Zhu, Y, et al. Water exchange-assisted vs. carbon dioxide-insufflated single-balloon enteroscopy: randomized controlled trial. Endoscopy. (2022) 54:281–9. doi: 10.1055/a-1459-4571
18. Gross, SA, and Stark, ME. Initial experience with double-balloon enteroscopy at a U.S. center. Gastrointest Endosc. (2008) 67:890–7. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.07.047
19. Domagk, D, Bretthauer, M, Lenz, P, Aabakken, L, Ullerich, H, Maaser, C, et al. Carbon dioxide insufflation improves intubation depth in double−balloon enteroscopy: a randomized, controlled, double−blind trial. Endoscopy. (2007) 39:1064–7. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-966990
20. Khashab, M, Helper, DJ, Johnson, CS, and Chiorean, MV. Predictors of depth of maximal insertion at double-balloon Enteroscopy. Dig Dis Sci. (2010) 55:1391–5. doi: 10.1007/s10620-009-0849-6
21. Winder, O, Fliss-Isakov, N, Winder, G, Scapa, E, Yanai, H, Barnes, S, et al. Clinical outcomes of endoscopic balloon dilatation of intestinal strictures in patients with Crohn’s disease. Medicine (Baltimore). (2019) 98:e16864. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016864
22. Saunders, H, Ghoz, H, Cortes, P, Alsafi, W, Mzaik, O, Ciofoaia, V, et al. Factors that influence the speed and completion of double balloon Enteroscopy in patients with arteriovenous malformations. Dig Dis Sci. (2023) 68:173–80. doi: 10.1007/s10620-022-07528-2
23. Zeng, Q, Wang, L, Dong, S, Zha, X, Ran, L, Li, Y, et al. CT-derived abdominal adiposity: distributions and better predictive ability than BMI in a nationwide study of 59,429 adults in China. Metabolism. (2021) 115:154456. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154456
24. Anderson, JC, Gonzalez, JD, Messina, CR, and Pollack, BJ. Factors that predict incomplete colonoscopy: thinner is not always better. Am J Gastroenterol. (2000) 95:2784–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03186.x
25. Kamal, A. Double-balloon enteroscopy: ready for prime time? Gastrointest Endosc. (2008) 67:898–901. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2007.10.033
26. Mehdizadeh, S, Han, NJ, Cheng, DW, Chen, GC, and Lo, SK. Success rate of retrograde double-balloon enteroscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. (2007) 65:633–9. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2006.12.038
27. Tee, HP, How, SH, and Kaffes, AJ. Learning curve for double-balloon enteroscopy: findings from an analysis of 282 procedures. World J Gastrointest Endosc. (2012) 4:368–72. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v4.i8.368
Keywords: complete enteroscopy, risk factors, balloon-assisted enteroscopy, double-balloon enteroscopy, single-balloon enteroscopy
Citation: Liu J, Wan M, Wang P, Guo J, Yu Y-B and Zuo X-L (2025) Risk factors of incomplete balloon-assisted enteroscopy with an analysis of 943 patients: a retrospective study. Front. Med. 12:1612974. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1612974
Edited by:
Ruixin Zhu, Tongji University, ChinaReviewed by:
Weiguo Dong, Renmin Hospital of Wuhan University, ChinaYingxuan Chen, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Wan, Wang, Guo, Yu and Zuo. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiu-Li Zuo, enVveGl1bGlAc2R1LmVkdS5jbg==
 Jun Liu
Jun Liu Meng Wan1,2
Meng Wan1,2 Yan-Bo Yu
Yan-Bo Yu Xiu-Li Zuo
Xiu-Li Zuo