Abstract
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a group of diseases characterized by chronic intestinal inflammation including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC). In recent years, probiotics have attracted more and more attention as a potential adjuvant therapy. Probiotics can improve the symptoms and quality of life of IBD patients mainly by regulating intestinal microflora, regulating immune response, enhancing intestinal barrier function and exerting anti-inflammatory effect. However, although a large number of studies have explored the role of probiotics, there are still individual differences and uncertainties in clinical application. This paper reviews the mechanism, clinical effect and future prospect of probiotics in the treatment of IBD, and analyzes the existing clinical research and experimental data to provide reference for further research. Finally, this paper looks forward to the research direction of probiotics in the treatment of IBD, aiming at providing evidence for clinical practice.
1 Introduction
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a complex and challenging chronic inflammatory disease, which is characterized by repeated intestinal inflammation, including Crohn’s disease (CD), ulcerative colitis (UC) and unclassified inflammatory bowel disease (IBD-U) (1). These diseases will not only significantly affect the digestive function of patients, but also often accompany a series of disturbing symptoms, such as abdominal pain and diarrhea (2, 3), as well as weight loss, it may also lead to a series of parenteral manifestations, such as peripheral arthritis, oral ulcer, scleritis or erythema nodosum, which seriously affects the quality of life and daily activities of patients (4–6). The pathogenesis of IBD is extremely complicated, involving the interaction of many factors, including genetic factors (genes related to immune response and intestinal barrier integrity) (7–10), environmental factors (such as smoking, eating habits, drug use, social pressure and psychological factors) (11–16), and immune factors (including the functions of innate and adaptive immune pathways) (17–19). Epidemiological studies show that the prevalence of IBD is significantly different in different regions. The prevalence rate in North America and Europe is high and has stabilized in recent years, while the incidence rate in some East Asian countries is on the rise (20). At present, the treatment of IBD mainly includes drug therapy, nutritional intervention and surgical treatment. Commonly used drugs include aminosalicylic acid preparation, glucocorticoid, immunomodulator and biological preparation (21–24). However, these treatments are often accompanied by various side effects, and some patients do not respond well to these treatments, leading to the recurrence or aggravation of the disease (25–27). Therefore, it is very important to identify new treatment schemes for improving the prognosis of patients with IBD.
In recent years, with the in-depth study of intestinal microbiota, people have gradually found that microbiota plays an important role in the occurrence, development and rehabilitation of IBD. Probiotics, as a new treatment method, show broad application prospects (28, 29). Probiotics can help alleviate inflammation in many ways, such as regulating intestinal microflora, enhancing intestinal barrier function and regulating immune response, thus becoming an important supplement to the treatment of IBD (26, 30). Therefore, probiotics, as a new treatment strategy, may bring hope to patients with IBD, which deserves further research and clinical application exploration in order to improve the quality of life and overall health status of patients.
2 Probiotics: conceptual definition and systematic categorization
2.1 What are probiotics?
Probiotics are living microorganisms that can change the intestinal flora and bring health benefits to the host when ingested in sufficient quantities (31). The viability of probiotics confers a spectrum of health benefits to the host, chiefly manifested in their pivotal roles in sustaining gut homeostasis and promoting overall wellbeing. These effects are mediated through mechanisms that include modulation of the intestinal microbiota equilibrium, enhancement of host immune function, suppression of pathogen growth, and facilitation of efficient nutrient absorption (32–34).
In addition, the application of probiotics has been extended to many health fields, from the most basic improvement of intestinal health to enhancing the immune function of the body, showing positive research prospects (35–37). However, although the potential of probiotics in the health field has been widely recognized, misunderstandings among the public still need to be clarified. A common misunderstanding stem from oversimplified commercial propaganda that all probiotics are the same. In fact, the efficacy of probiotics has a high degree of strain specificity and host individual differences (38). Although probiotics and prebiotics have a good safety record, they still need to be cautious in specific health conditions or specific patient groups (39, 40).
2.2 Main types of probiotics and functions
The probiotic types listed in Table 1 are diverse and primarily encompass the following major categories: Lactobacillus, Bifidobacterium, and Saccharomyces (41).
Table 1
| Strain | Function | References | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lactobacillus | |||
| L. rhamnosus GG | LGG | Inhibit inflammatory responses, anti-cancer effects and promote skin wound healing. | (45–47) |
| L. acidophilus | CICC 6092, NCFM | Improve obesity and related diseases; its surface proteins can improve the tissue pathological damage caused by colitis. | (48, 49) |
| L. casei | LTL1361 | Reducing the damage of pathogens to the intestines; its combination with DFC has anti-aging effects. | (50, 51) |
| Bifidobacterium | |||
| B. longum | BB536 | Improve chronic constipation in the elderly and inhibit obesity. | (52, 53) |
| B. breve | M-16v | Improve cognitive function, inhibit brain atrophy and suppress obesity. | (52, 54) |
| B. bifidum | ATCC29521 | Affect intestinal inflammatory cells, downregulate the expression of GDNF, TLR-2, and TNF-α, and exert anti-inflammatory effects. | (55) |
| Saccharomyces | |||
| S. cerevisiae | CNCM I-3856 | Alleviate abdominal pain in IBS-C patients primarily suffering from constipation, and improve the quality of life for these patients. | (56) |
| S. boulardii | CNCM I-745 | Quickly treat dysbiosis, reduce chloride secretion and treat diarrhea. | (57, 58) |
The main types and functions of probiotics.
Lactobacillus, as an important representative of probiotics (such as Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG (LGG), Lactobacillus acidophilus and Lactobacillus casei), have functional characteristics that exceed the traditional understanding of acid-producing and antibacterial effects. The latest research shows that Lactobacillus has multiple physiological functions, such as regulating the intestinal microecology, protecting the digestive system, and regulating the immune system (42–44). LGG can regulate immune responses, improve inflammatory responses, and prevent damage to colonic tissues (45). The extracellular vesicles released by Lactobacillus enhance the proliferation and migration abilities of epithelial and endothelial cells and promote the formation of endothelial tubes, showing therapeutic potential in skin wound healing (46). Besides, it can also improve cancer cell responses to anti-PD-1, thereby exerting anti-cancer effects (47). L. acidophilus can alleviate obesity and related diseases by improving endothelial dysfunction and gut microbiota imbalance through its anti-inflammatory properties (48). Chandhni et al. also indicated that the surface proteins in the Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM strain can reverse the histopathological damage caused by colitis (49). The surface layer protein of Lactobacillus casei FB05 can reduce the harmful effects of Escherichia coli and Salmonella on the intestine by decreasing pathogen adhesion and inhibiting pathogen-induced apoptosis (50). Additionally, Ren et al. showed that Lactobacillus casei LTL1361 and dietary fiber complexes (DFC) alleviated age-related cognitive impairment and protected brain and gut functions. L. casei LTL1361 and DFC may serve as novel and promising human anti-aging agents (51).
Bifidobacterium (such as Bifidobacterium longum, Bifidobacterium breve, and Bifidobacterium bifidum) possesses beneficial homeostatic and anti-inflammatory immune regulatory characteristics. Bifidobacterium longum BB536 and Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 may also reduce visceral fat and total body fat levels in healthy normal-weight and overweight adults, thereby helping to prevent obesity (52). In addition, Takeda et al. reported that B. longum BB536 can improve bowel movements and has a positive effect on chronic constipation in the elderly (53). B. breve MCC1274 can improve cognitive function and helps inhibit brain atrophy (54). B. bifidum exhibits anti-inflammatory effects. Yang et al. found that exogenous stimulation with lipopolysaccharide plus Interferon-γ (IFN-γ) induced increased expression of major histocompatibility complex class II (MHC-II) and CD86 in enteric glial cells (EGC), and further treatment with B. bifidum supernatant downregulated MHC-II expression. Additionally, B. bifidum downregulated the expression of glialcell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR-2), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) in stimulated EGC (55).
Saccharomyces, such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces boulardii, are also important probiotics and should not be ignored. They not only help to maintain the balance of intestinal microflora, but also show the characteristics of resisting pathogenic microorganisms in some cases. Mourey et al. studied the effect of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CNCM I-3856 on constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome (IBS-C), and found that the response rate of patients receiving probiotic supplementation in relieving abdominal pain was significantly higher than that of placebo group (45.1% vs. 33.9%, p = 0.017). In addition, after 8 weeks of supplementary treatment, the overall quality of life score of the probiotic group was significantly higher than that of the placebo group (p = 0.047), indicating that probiotic I-3856 is helpful to improve abdominal pain and quality of life of IBS-C patients (56). Oral administration of Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745 has no effect on the intestinal microflora of healthy subjects. However, under some conditions of intestinal flora imbalance, the application of S. boulardii CNCM I-745 can help to restore intestinal flora more quickly (57). In addition, S. boulardii CNCM I-745 can reduce chloride ion secretion, so it has a certain effect in treating diarrhea (58).
With the deepening of scientific research, the multiple functions of probiotics are gradually recognized. A large number of studies show that probiotics may have a positive effect on improving metabolic syndrome, diabetes, allergic diseases and intestinal infections (59–61). These results highlight the potential value of probiotics as an adjuvant therapy. These research results provide an important scientific basis for the application of probiotics in clinical treatment and show its great potential in modern medicine (Table 1).
2.3 Mechanisms of probiotics in IBD
The application potential of probiotics in the treatment of IBD has been paid more and more attention, which involves several key mechanisms. Its core mechanism involves many interrelated levels, far more than simple flora regulation. These key mechanisms together constitute the theoretical basis for probiotics to alleviate the pathological state of IBD, as shown in Figure 1 (62, 63).
Figure 1

Probiotics play several important roles in maintaining health. (1) Probiotics inhibit the reproduction of pathogenic bacteria and maintain microbial diversity. (2) Probiotics regulate immune cell activity and cytokine secretion to help maintain immune balance. (3) Probiotics enhance the integrity of tight junctions between cells to strengthen intestinal barrier function. (4) Their metabolites can reduce intestinal inflammation. SCFAs, short–chain fatty acids; EPS, exopolysaccharide; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; ZO-1, zonula occludens-1; ZO-2, zonula occludens-2; MPO, myeloperoxidase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR, toll-like receptor; M1, macrophage type 1; M2, macrophage type 2; BMDC, bone marrow-derived dendritic cell; MLCK, myosin light chain kinase.
2.3.1 Regulation of gut microbiota
Healthy intestinal microflora not only has diversity, but also has good stability, and cooperates in many ways to jointly safeguard the health of the host (64). For example, intestinal microflora plays a vital role in food digestion and absorption, vitamin synthesis, immune system regulation and intestinal barrier protection (65, 66). A large number of studies show that probiotics can effectively restore the balance of intestinal microflora through various mechanisms, such as inhibiting the growth of pathogenic microorganisms, thus reducing the risk of infection (67). Probiotics can also enhance the diversity and stability of intestinal microflora by producing antibacterial substances and promoting the proliferation of beneficial bacteria (68). Microbial diversity is an important factor to maintain intestinal health. This diversity not only helps to improve digestive function, but also reduces the risk of intestinal inflammation (69, 70).
For patients with IBD, the composition of intestinal microflora often changes significantly, which usually shows a decrease in microbial diversity and the number of some beneficial bacteria (71). For example, in the intestinal flora of patients with CD, the abundance of Christensenellaceae, Coriobacteria and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii decreased, while the abundance of Actinobacteria, Veillonella and Enterobacteriaceae increased. As for patients with UC, the abundance of Eubacterium rectale and Akkermansia decreased, while the abundance of Enterobacteriaceae increased (72). Some studies have found that patients with CD have a higher degree of flora imbalance than patients with UC (73). The root cause of IBD is not clear, but the imbalance of intestinal microflora, especially the decrease of abundance and diversity of specific genera, is considered as the inducement of IBD (74). Probiotics are widely regarded as a potential adjuvant therapy for IBD. They can effectively relieve inflammation by improving the composition of intestinal microflora, promoting the proliferation of beneficial bacteria and inhibiting the attachment of pathogenic microorganisms (75, 76). Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 (ECN-pE) can inhibit the growth of Salmonella and other pathogens. Its H1 flagella enables the probiotic to compete with pathogens for binding sites on host tissues effectively, thus inhibiting the adhesion and invasion of pathogens to intestinal epithelial cells. It can also directly stimulate intestinal epithelial cells to produce defensins and has anti-inflammatory effects. In addition, the gene encoding F1C fimbriae plays a key role in the continuous colonization of bacteria and its adhesion to intestinal epithelial cells (77). Bifidobacterium longum BBMN68 has a new surface adhesion protein called FimM (Fimbrial m protein), which is the main fimbrial protein subunit of B. longum BBMN68, which may be used as a surface adhesion monomer but cannot form a fimbrial-like structure, mucoprotein, fibronectin and fibrinogen are its adhesion receptors, mucoprotein is the main structural component of the mucus layer and provides a physical barrier to the intestinal epithelial surface, and normally FimM binds to mucin to prevent pathogens from entering the mucus layer. During pathogen invasion, FimM interacts with fibronectin and fibrinogen to inhibit pathogen adhesion (78), and FimM can produce various substances such as bacteriocin and biosurfactants for specific probiotic strains, which are harmful to pathogenic microorganisms (79, 80). Bacteriocins can also enhance immune function and inhibit the growth of pathogenic bacteria, and bacteriocin in Bacillus subtilis can induce interleukin-1β (IL-1β), IL-6, TNF-α, and nitric oxide release modulate innate immunity, enhance phagocytosis in mouse peritoneal macrophages, and induce phosphorylation of three mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) (p38 MAPK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK)) in macrophages. Aberrant activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway plays a key role in the molecular pathological mechanism of IBD, and studies have shown that sublancin-stimulated nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) p65 and κB inhibitor (IκB-α) can enhance the phosphorylation of NF-κB p65 and degrade IκB-α (81). The two most important bacterial phylum in gastrointestinal tract, Firmicutes and Bacteroides, showed that the ratio of Firmicutes/Bacteroides (F/B) related to IBD decreased. Firmicutes have anti-inflammatory effect, which can slow down the progress of IBD, while Bacteroides can produce endotoxin, which shows pro-inflammatory characteristics and affects the production of cytokines, thus leading to IBD. Some bacteria from Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, such as Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938, Lactobacillus plantarum AN1 and fermented milk containing Bifidobacterium, can affect the F/B ratio, thus relieving IBD (82–84). It is worth noting that the form of probiotic preparation also affects its curative effect. Compared with a single strain, multi-strain probiotic preparation can regulate the intestinal flora more effectively, generally regulate the intestinal flora structure more comprehensively, restore its diversity and balance, and may produce superposition or synergistic effect through multiple mechanisms, thus further enhancing the therapeutic effect on IBD (85). Therefore, probiotics show great potential and value in the management of IBD by precisely regulating key inflammatory pathways such as NF-κB, reshaping disordered intestinal flora (especially correcting the imbalance of F/B ratio) and strengthening the intestinal barrier (Figure 2).
Figure 2
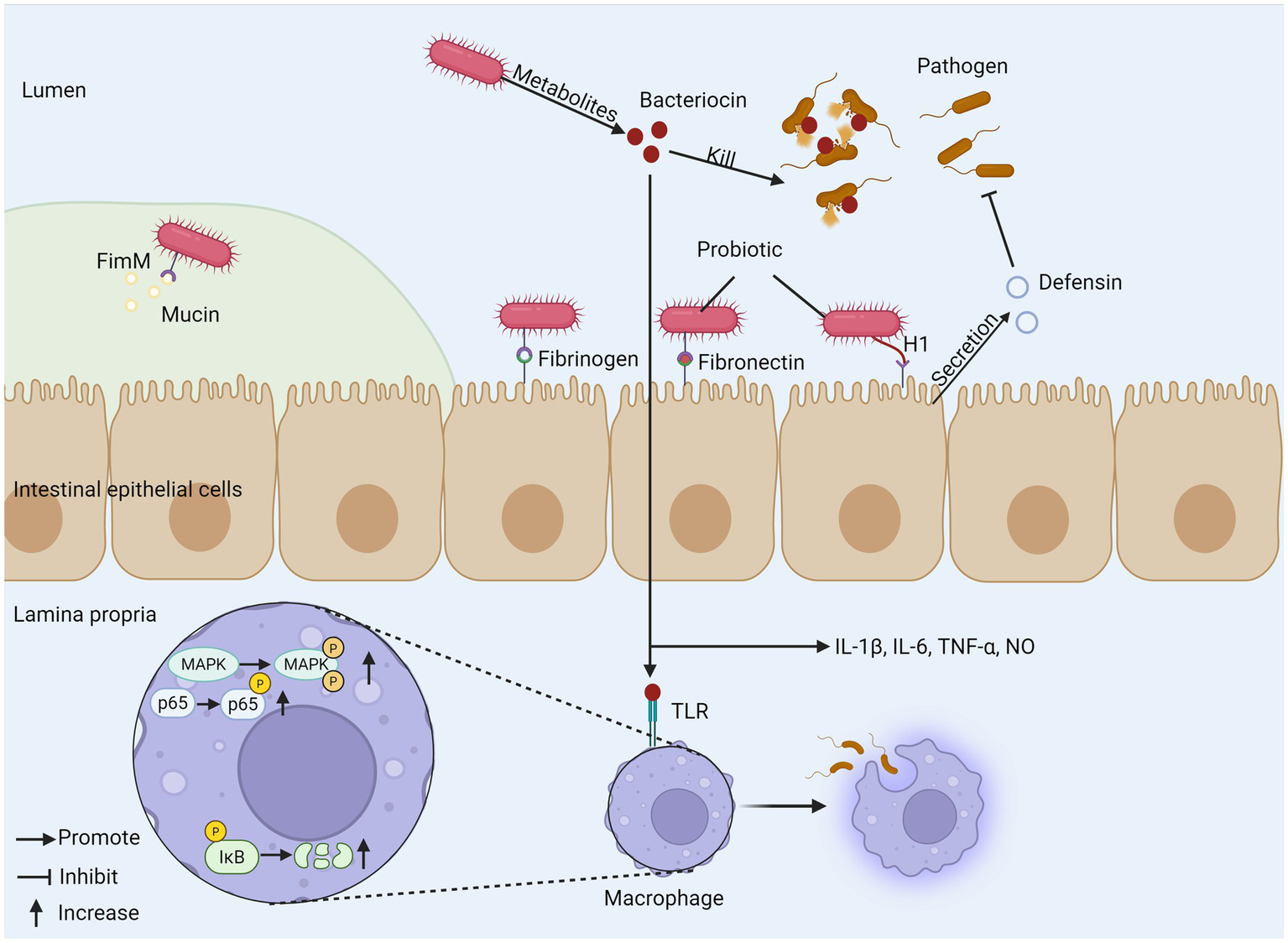
The mechanism of probiotics regulating gut microbiota. (1) Probiotics produce bacteriocins to kill pathogens and promote phagocytosis of macrophages, inducing cytokine release. (2) Probiotic FimM binds to mucin, fibronectin, and fibrinogen to inhibit pathogen invasion. (3) H1 flagellum compete with pathogens for binding sites and can stimulate epithelial cells to produce defensin. FimM, fimbrial m protein; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TLR, toll-like receptor; IκB, inhibitor of Kappa B.
2.3.2 Immune regulation
Probiotics exert their protective effects by modulating host immune responses, primarily reflected in promoting T cell differentiation, regulating cytokine levels, and increasing immunoglobulin A (IgA) levels (86–88). Probiotics may promote the interaction between co-stimulatory molecules CD80/86 on dendritic cells (DCs) and cytotoxic t-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4), thereby leading to a weakened T cell response (89). Experimental evidence has shown that the administration of probiotics enhances the production of interleukin (IL)-10 and increases the proportion of regulatory CD4+ T cells expressing surface transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) in the form of latency-associated peptide (LAP), also known as LAP+ regulatory T cells (Treg), whose presence depends on IL-10 production (90). Probiotics also increase the number of CD4+CD25+Foxp3+Treg cells, which can secrete inhibitory factors such as IL-2, IL-10, and TGF-β to regulate the balance of Th1/Th2 cells and maintain intestinal mucosal immunity (91). Additionally, it has been shown that LGG and B. breve may reduce the activity of IL-17 and IL-23, both of which play important roles in the formation and activation of Th17 cells. Different strains of Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium produce TNF-α and IFN-γ, which can inhibit the proliferation of Th17 inflammatory cells (92).
Probiotics have the capacity to influence macrophage polarization, facilitating the transition from M1 to M2 macrophages, thereby contributing to the amelioration of colitis (93, 94), Furthermore, elements of the probiotic cell wall are implicated in the immunomodulation of DCs. Specifically, the interaction of capsular polysaccharides with TLR2 receptors on DCs induces T helper cells to secrete IL-10, consequently mitigating inflammation linked to colitis (94).
Probiotics modulate a variety of immune signaling pathways, such as JAK/STAT and NF-κB, thereby reducing the production of inflammatory cytokines (95, 96). For example, Bifidobacterium has been shown in vitro experiments to downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and IL-1β (97), promote the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-10 and TGF-β by regulating T cell differentiation. Lactobacillus plantarum HNU082 (Lp082) inhibits the NF-κB pathway by downregulating the mRNA expression of NF-κB2, NF-κB1, cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2), RelA, Toll4, and iNOS, while inflammation is also regulated by NF-κB by regulating cytokine production. Additionally, UC can be alleviated by Lp082 by reducing neutrophil infiltration and myeloperoxidase (MPO) secretion (98). Probiotics can increase IL-6 secretion in a TLR2-dependent manner, induce clonal expansion of all IgA-producing B cells, promote IgA circulation, and stimulate humoral immune maturation (18, 99), and the secretion of large amounts of IgA into the intestinal lumen prevents pathogenic bacteria from reaching the intestinal epithelium and limits their colonization of the intestine (100).
Probiotics play an important role in regulating intestinal immune homeostasis through their close interaction with intestinal epithelial cells (IECs). For example, by stimulating the activation of immune cells in the intestine and regulating the production of cytokines, the immune balance in the intestinal environment can be promoted. Probiotics finely regulate immune cell function and cytokine network, which is the key molecular and cellular basis for realizing intestinal immune homeostasis reconstruction, thus exerting its anti-inflammatory and relieving IBD symptoms. This process plays a key role in inhibiting inflammatory reaction and is of great significance for relieving the symptoms of patients with IBD (Figure 3).
Figure 3
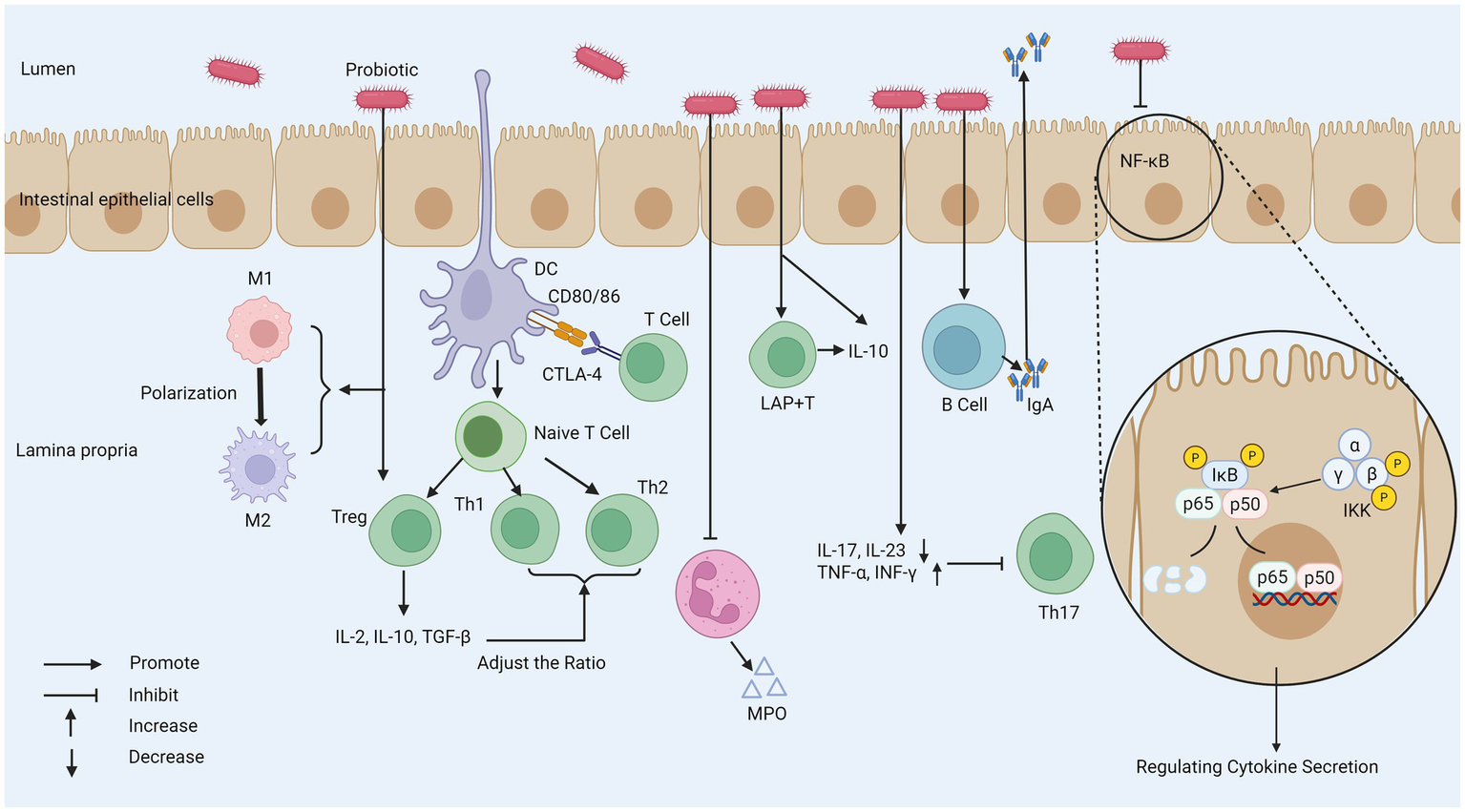
The mechanism of probiotics regulating intestinal immune response. (1) Probiotics weaken T cell response, increases the number of Tregs, and regulates the function of DC to affect the Th1/Th2 ratio. (2) Probiotics can reduce the secretion of MPO by neutrophils. (3) Probiotics promote the polarization of macrophages from the M1 phenotype to the M2 phenotype to regulate the inflammatory response. (4) Probiotics stimulate the production of IgA by B cells, and promote the IgA cycle. (5) Probiotics decrease IL-17 and IL-23 activity to inhibit Th17 activity. (6) Probiotics can inhibit the NF-κB pathway and regulate cytokine secretion. MPO, myeloperoxidase; M1, macrophage type 1; M2, macrophage type 2; CTLA-4, cytotoxic t-lymphocyte-associated protein 4; IκB, inhibitor of Kappa B; IKK, IκB kinase; LAP+T, latency-associated peptide-positive regulatory T cell; TGF-β, transforming growth factor beta; DC, dendritic cell.
2.3.3 Enhancement of intestinal barrier function
The enhancement of intestinal barrier function is crucial to the maintenance of overall health (Figure 4). Studies in patients with IBD show that the truncated expression of O-glycans is related to the existence of the disease and the increased activity of the disease. The variation of glycan composition may destroy the mucosal layer and immune function, and eventually lead to IBD (101). Intestinal barrier consists of mechanical barrier and chemical barrier mainly composed of mucus layer, and intestinal epithelial cells and their close connection constitute intestinal mechanical barrier (102), which can effectively prevent harmful substances and pathogens from invading. Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) not only induce intestinal mucosal damage, but also increase intestinal mucosal permeability (103) and the mRNA expression of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 decreases after probiotic intake.
Figure 4
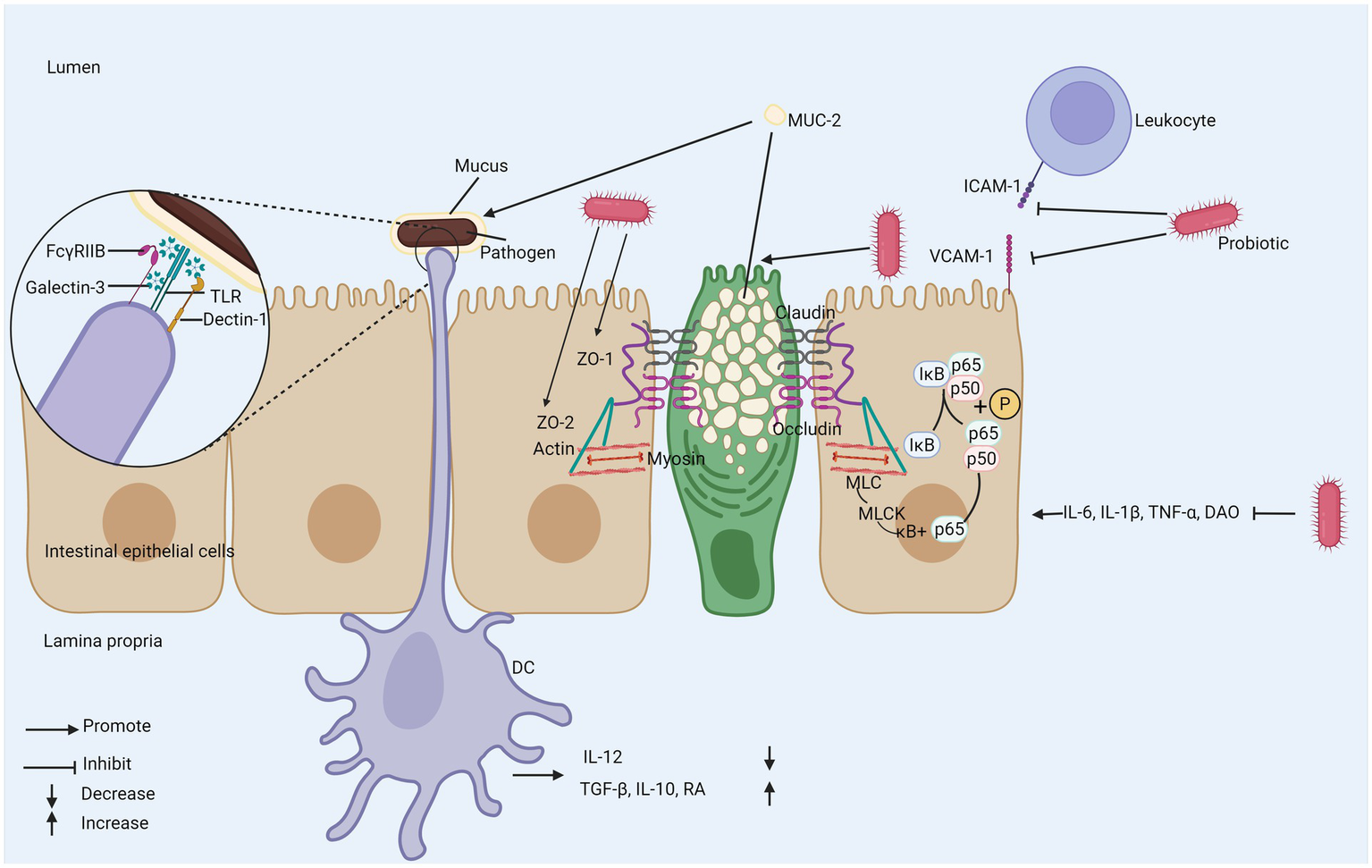
The mechanism of probiotics regulating intestinal mechanical and chemical barriers. (1) Probiotics inhibit the expression of adhesion molecules ICAM-1 and VCAM-2 to reduce damage to intestinal mucosa. (2) Probiotics promote the secretion of MUC-2 by goblet cells. (3) Probiotics promote the expression of tight junction proteins and inhibit NF-κB/MLCK to enhance intestinal barrier function. (4) DC recognizes bacteria wrapped in mucus to promote anti-inflammatory gene expression program. ZO-1; zonula occludens-1; ZO-2; zonula occludens-2; TLR; toll-like receptor; IκB; inhibitor of Kappa B; MLCK; myosin light chain kinase; MLC; myosin light chain; MUC-2; mucin-2; Dectin-1; dendritic cell-associated C-type lectin-1; galectin-3; galactose-binding lectin-3; FcγRIIB; Fc gamma receptor II B; RA; retinoic acid; DAO; diamine oxidase; TGF-β; transforming growth factor beta; DC; dendritic cell.
Abnormal tight junction (TJ) proteins between intestinal epithelial cells can damage the mechanical barrier of the intestine. Studies have shown that probiotics can enhance the function of the intestinal barrier by promoting the expression of TJ proteins such as zonula occludens-1 and zonula occludens-2 (ZO-1 and ZO-2). ZO-1 and ZO-2 play important roles in the repair of the intestinal barrier (104, 105). The absence of ZO-1 and ZO-2 prevents the recruitment of occludin to tight junctions and impairs barrier function (106). Lactobacillus paracasei downregulates pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, diamine oxidase (DAO), and NF-κB p65, myosin light chain 2 (MLC2), myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK), inhibiting NF-κB/MLCK and thereby promoting barrier function (107). The chemical barrier refers to the gel-like mucin layer covering the surface of intestinal epithelial cells, with mucin-2 (MUC-2) as its main component. MUC-2 is the primary glycoprotein in intestinal mucus and is mainly secreted by goblet cells. Probiotics can stimulate the expression of MUC-2 in intestinal goblet cells (108). The mucus layer protects the host from the invasion of pathogenic microbial communities; when MUC-2 expression is reduced, the mucus loses its barrier function, which can lead to worsening of the disease (109, 110). Mucus can encapsulate bacteria and, through the action of galactose-binding lectin-3 (Galectin-3), facilitate the binding of TLRs, Fc gamma receptor II B (FcγRIIB), and Dendritic cell-associated C-type lectin-1 (Dectin-1) on DCs. This promotes the expression of anti-inflammatory gene programs, leading to decreased IL-12 expression and increased expression of TGF-β, IL-10, and RA (111). Furthermore, probiotics can increase mucus production, enhance secretion capacity, improve tissue repair ability, and inhibit apoptosis of epithelial cells, significantly improving the integrity of intestinal epithelial cells and further enhancing the function of the intestinal barrier (112, 113).
2.3.4 Anti-inflammatory effects and bacterial metabolites
The anti-inflammatory properties of probiotics are not only derived from their inherent biological activity but are also closely related to the various metabolites produced during their metabolic processes shown in Figure 5 (114). During fermentation, probiotics generate a series of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), such as acetate, propionate, and butyrate, which promote the integrity and permeability of the intestinal barrier in different ways (115). SCFAs can directly act on neutrophils, reducing their production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and MPO. Butyrate increases the concentration of tight junctions by upregulating the genes encoding these proteins, such as claudin-1, ZO-1, and occludin (116). SCFAs regulate the integrity of the intestinal barrier by inducing intestinal epithelial cells to secrete interleukin 18 (IL-18) and express antimicrobial peptides; butyrate can also strengthen the mucus layer of the intestinal epithelium by increasing the expression of mucin 2 (117, 118). Additionally, SCFAs can inhibit the development of colon cancer (119). Various probiotics can metabolize to produce conjugated linoleic acid (CLA), which has been shown to have effective anti-inflammatory, immune-regulating, anti-obesity, and anti-cancer activities (120, 121). The imbalance of tryptophan (Trp) metabolism is closely related to the occurrence and development of IBD. After Trp is metabolized by bacteria into biologically active indole, it can activate the aromatic hydrocarbon receptor (AhR), thereby inhibiting IL-1β and IL-6 expression (122). A test of over 500 serum samples from IBD patients suggests that a continuous decline in Trp levels may not only promote disease progression but also further exacerbate active inflammation (123). Bone marrow-derived dendritic cells (BMDC), stimulated by the extracellular polysaccharides (EPS) of B. subtilis, first upregulate the immunosuppressive enzyme IDO through both classical and non-classical NF-κB dual pathways. Subsequently, signals are transmitted along the IDO-kynine-AhR axis, ultimately inhibiting T cell activation and exerting anti-inflammatory effects (124). Probiotics significantly alleviate IBD-related symptoms by improving the intestinal metabolic environment and maintaining intestinal health. Studies have shown that some probiotics can convert primary bile acids into secondary bile acids by activating the bile acid-FXR axis, and thereby exert their effects by inhibiting the NF-κB pathway in macrophages. This process can significantly reduce the expression levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, IL-18 and TNF-α, thereby effectively alleviating the intestinal inflammatory response (125–127).
Figure 5
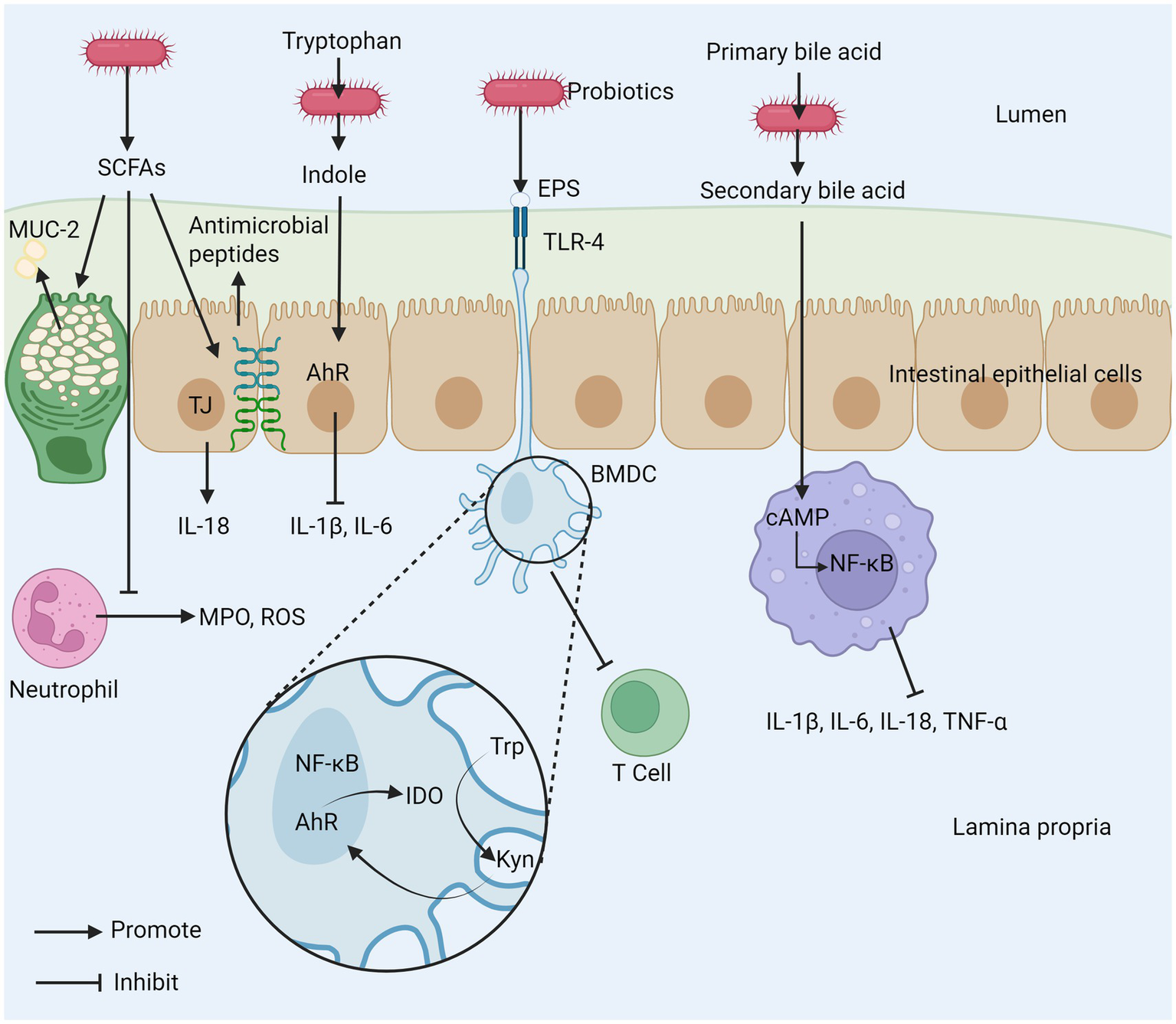
The mechanism of intestinal inflammation inhibited by probiotic metabolites. (1) SCFAs produced by probiotics can promote the secretion of MUC-2, inhibit the release of MPO and ROS from neutrophils, and promote tight junctions between cells. (2) Probiotics can metabolize tryptophan (Trp) to indole to inhibit the production of inflammatory cytokines. (3) EPS produced by probiotics can inhibit T cell activation. (4) Probiotics inhibit macrophages by metabolizing primary bile acids into secondary bile acids. SCFAs, short–chain fatty acids; EPS, exopolysaccharide; AhR, aryl hydrocarbon receptor; MPO, myeloperoxidase; ROS, reactive oxygen species; TLR-4, toll-like receptor 4; TJ, tight junction; Trp, tryptophan; Kyn, kynurenine; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; BMDC, bone marrow-derived dendritic cell; IDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase; MUC-2, mucin-2.
In summary, probiotics have many functions in IBD, such as regulating intestinal microflora, immunomodulating, enhancing intestinal barrier function and anti-inflammatory properties of its metabolites, which have laid a solid theoretical foundation for the use of probiotics as adjuvant therapy for IBD and pointed out the future research direction.
2.4 Clinical research and effect evaluation
2.4.1 Application of probiotics in CD
CD is a chronic IBD, which is complicated and difficult to treat. The lesions may involve all parts from the mouth to the anus, and may also cause parenteral complications (128). Because of the complex pathogenesis, alternating aggravation and remission of this disease is its important feature, and the drug treatment effect is limited. In recent years, surgical intervention has played a very important role in the management and control of CD (129, 130). The imbalance of intestinal microflora in patients with CD is obvious, which will aggravate intestinal inflammation (131, 132). Probiotics may reduce this inflammation by restoring the balance of intestinal microflora (133, 134). Probiotics such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium can reduce clinical activity and biomarker indicators (135).
Patients with CD often experience damage to intestinal barrier function, leading to increased intestinal permeability and exacerbating disease progression (136, 137). Studies have shown that in cells treated with probiotic mixtures, epithelial permeability measured by transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER) significantly decreases, showing that the epithelial barrier remains intact. Various probiotic mixtures protect the integrity of intestinal barrier function by boosting tight junctions and reducing the inflammatory response of intestinal cells (138, 139).
A study involving 96 patients with mildly active CD showed that mesalazine combined with a capsule containing Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and Enterococcus was more effective in treating mild active CD (140). Additionally, a review by Chen et al. of four studies involving 289 subjects reported no statistically significant difference in CD recurrence, with a p-value of 0.52. During the remission phase, probiotics demonstrated some efficacy (141). Bjarnason et al. studied Symprove (which contains Lactobacillus rhamnosus NCIMB 30173, 30174, 30175, and 30176) and found no significant changes between the placebo and probiotic groups in CD patients (142). Another experiment indicated that S. boulardii seems to improve CD activity index (CDAI), body mass index (BMI), serum Hb, and total cholesterol levels in CD patients during the remission phase, without safety issues (143). Bourreille et al. also studied S. boulardii finding that this strain is safe and well-tolerated, but it appears to have no beneficial effects on CD patients who achieved remission after steroid or salicylate treatment (144). Yılmaz et al. investigated the impact of kefir (Lactobacillus and Lactobacillus kefiri) intake on the fecal microbiota and symptoms of CD patients, discovering that regular kefir consumption may improve symptoms and quality of life in CD patients in the short term and positively affect biochemical parameters (Hemoglobin [Hgb], Erythrocyte sedimentation rate [ESR], and C-reactive protein [CPR]), significantly reducing bloating severity and increasing wellbeing index (145). In earlier experiments, Marteau et al. studied the therapeutic effects of Lactobacillus johnsonii LA1, concluding that this strain was well-tolerated in the study but did not significantly reduce the risk of endoscopic recurrence within 6 months after CD surgery (146). Another study on the LGG strain, conducted in pediatric subjects, showed that LGG was well tolerated and had side effects comparable to those of the placebo. When used as an adjunct to standard therapy, LGG did not prolong the time to relapse in children with CD (147).
Systematic reviews indicate that Bifidobacterium seems to be the only probiotic strain that is helpful, well-tolerated, and without significant side effects for CD (135). Although some studies have reported positive effects of probiotics, using probiotics for CD is still a bit controversial (148), especially since different probiotic strains exhibit varying effects, and clinical trial design and sample size are also important factors influencing research outcomes. More high-quality randomized controlled trials (RCTs) are urgently needed to further validate the efficacy and safety of probiotics in the treatment of CD (Table 2).
Table 2
| Probiotics | Placebo or other drugs | Number of people | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Symprove (L. rhamnosus NCIMB 30173, 30174, 30,175 and 30176) | Placebo | 61 patients | The same analysis in the CD group showed no statistically significant changes. | (142) |
| Bifidobacteria, Lactobacillus and Enterococcus | Mesalazine | 96 patients | Mesalazine combined with bifidobacteria, lactobacilli, and enterococci capsules is more effective for the treatment of mild active CD. | (140) |
| S. boulardii | / | Analysis of 92 patients among 154 cases. | S. boulardii can improve CDAI, BMI, serum Hb, and total cholesterol levels, safely and effectively. | (143) |
| Kefir (Lactobacillus and L. kefiri) | / | 45 patients included with 3 voluntarily withdrew. | The experimental group showed a significant decrease in ESR and CRP. The bloating severity significantly decreased, and the wellbeing index increased. | (145) |
| L. johnsonii LA1 | Placebo | 98 patients | L. johnsonii LA1 has a poor effect on preventing the recurrence of CD. | (146) |
| S. boulardii | Placebo | 165 patients | Probiotics as an adjunct treatment after standard therapy are not beneficial for maintaining remission. | (144) |
| LGG | Placebo | 75 patients | Probiotics, as an adjunct therapy in routine treatment, are not beneficial for prolonging the time to recurrence. | (147) |
Results of different probiotics in clinical trial for CD.
2.4.2 Application of probiotics in UC
A common IBD is UC, which affects the rectum and colon in different ways, mainly manifested by persistent inflammation of the colon lining, and patients usually have bloody diarrhea symptoms (149, 150). The first-line drug for mild to moderate diseases is 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA). If the drug does not respond well, it may be necessary to upgrade the treatment and adopt immunosuppressive drugs, biological agents and even surgical treatment (151). Probiotics have a good prospect in the treatment of UC. Several RCTs have confirmed that specific probiotics can effectively improve the clinical symptoms and biochemical indicators of UC patients. A systematic evaluation and analysis of 33 clinical studies found that probiotics were effective in 21 studies, with strains from Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus were regarded as the most effective choices, especially the clinical remission rate was significantly higher than that of placebo groups (135). There are great differences in the efficacy of different types of probiotics in the treatment of UC, and some studies show that the abundance of Ligilactobacillus ruminis in UC patients is obviously increased, which is very important for the diagnosis of the disease (152).
Most studies have shown that non-pathogenic ECN-pE are similar in efficacy and safety as mesalazine in the maintenance treatment of patients with mild to moderate UC (32). Recent studies have shown that short-term treatment with E. coli Nissle (ECN) is associated with reduced fecal calprotectin (FC) levels, suggesting its potential in maintaining remission in patients with UC (153).
Lactobacillus studies have found that Lp082 can synergistically optimize the biological, chemical, mechanical and immune barriers to improve the intestinal mucosal barrier to alleviate UC (98). In addition to strengthening the mucosal barrier, regulating the inflammatory pathway and regulating neutrophil infiltration are also potential mechanisms, Wu et al. compared the therapeutic effect of Lp082 and sulfonazioprine (SASP) on dextran sodium sulfate (DSS)-induced UC model, The results showed that Lp082 was more efficacious than SASP (98) and that UC could be alleviated by Lp082 by inhibiting NF-κB signaling molecules (154). Another study in mice showed that two strains, Lactobacillus fermentum GLF-217 and Lactiplantibacillus plantarum FLP-215, could enhance barrier function, regulate immune response, regulate intestinal microbiota composition, promote short-chain fatty acid production, and play a preventive role in DSS-induced colitis (155).
The combination of bifid triple viable capsule (B. longum, L. acidophilus, and Enterococcus faecalis) and mesalazine has been shown to improve the gut microbiota composition and reduce levels of inflammatory cytokines in IBD, with significant reductions observed in ulcerative colitis activity index (UCAI) scores and relapse rates (156). Another study divided 130 patients with UC into a treatment group (mesalazine combined with somatostatin and bifid triple viable capsule) and a control group (mesalazine combined with somatostatin). The results indicated that adjunctive therapy with bifid triple viable capsule could effectively enhance the therapeutic efficacy in UC patients, reduce plasma inflammatory factors, and modulate T cell frequencies (157). Experiments conducted by Jiang et al. also demonstrated that the combination of mesalazine and bifid triple viable capsule could enhance the treatment effect for UC, improve gut microbiota composition, attenuate immune responses, and lower levels of calprotectin (Cal) and matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) in the intestine (158).
S. boulardii has attracted much attention in the fields of food and medicine due to its anti-inflammatory properties and its promoting effect on intestinal health (159). The latest research has found that heat-killed S. boulardii shows better efficacy in the treatment of intestinal diseases compared with live S. boulardii and their β-glucan components. Heat-killed S. boulardii can effectively repair intestinal barrier function, inhibit inflammatory responses, and regulate the balance of intestinal flora, significantly alleviating DSS-induced UC in mice (160). Furthermore, animal studies have shown that S. boulardii and its postbiotics can effectively alleviate the symptoms of DSS-induced colitis by regulating the host immune response and maintaining intestinal homeostasis (161).
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) can effectively increase the diversity of intestinal flora in UC patients (162). Studies have shown that the combined use of FMT with probiotics rich in Clostridium butyricum can significantly prolong the disease remission period, and its mechanism of action may be related to the regulatory effect of butyrate. In addition, the increase in butyric acid levels in feces may serve as a potential biomarker for evaluating the therapeutic effect of FMT (163).
Probiotics are widely regarded as an intervention strategy suitable for long-term application due to their good safety and low risk of side effects (164). However, the mechanism of action and clinical efficacy of different probiotic strains in the treatment of UC still need to be verified through more high-quality clinical studies (Table 3).
Table 3
| Probiotics | Placebo or other drugs | Number of people or experimental animals | Results | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ECN-pE | / | 49 patients | After ECN-pE treatment, the FC values of patients significantly decreased, especially in UC patients, and the reduction was associated with the maintenance of clinical remission. | (153) |
| Lp082 | DSS, SASP | Mouse | Lp082 has therapeutic effects on mouse colitis through various pathways. | (154) |
| L. fermentum GLF-217 and L. plantarum FLP-215 | DSS | Mouse | The two strains can prevent DSS-induced colitis through various mechanisms. | (155) |
| Bifid triple viable capsule (B. longum, L. acidophilus and E. faecalis) | Mesalazine | 40 patients | The combination of probiotics and mesalazine can improve the composition of the microbiota in IBD patients and reduce the levels of inflammatory cytokines. | (156) |
| Mesalazine, somatostatin | 130 patients | The supplementation of Bifidobacterium triple live bacteria capsules can enhance the efficacy against UC. | (157) | |
| Mesalazine | 180 patients | Mesalazine combined with a Bifidobacterium triple therapy can enhance the efficacy of UC. | (158) | |
| S. boulardii | DSS | Mouse | Heat-inactivated S. boulardii alleviates DSS-induced UC in mice. | (160, 161) |
Results of different probiotics in clinical trial for UC.
2.4.3 Results and analysis of existing clinical trials
At present, the results of clinical trials are encouraging. Probiotics have a good potential in the treatment of IBD. Systematic evaluation shows that probiotics are effective in relieving UC. Some studies even suggest that probiotic supplements can replace conventional drug therapies (165–167). However, the research on CD is not only relatively few, but also controversial. Some studies have not shown significant clinical improvement (135, 148, 165, 168), but probiotics still have therapeutic potential in this field.
Studies have shown that the efficacy of probiotics is usually strain-specific, and the therapeutic effect may be significantly different when different strains treat different diseases (169, 170). In the future, more attention should be paid to specific strains, the optimal dosage and the combination with other therapies to determine more effective treatment strategies.
At present, the number of related clinical trials is limited and the sample size of many existing studies is small, which limits the universality of research results. In the future, we need to be stricter in clinical trial design to comprehensively assess the actual efficacy and safety of probiotics, providing patients with more reliable treatment options.
2.5 Future prospects of probiotic treatment for IBD
After in-depth exploration of the role of probiotics in the treatment of IBD, the future of probiotics looks bright and exciting. Probiotics can effectively improve gut microbiota dysbiosis and modulate immune responses to alleviate inflammation, offering IBD patients a novel and potentially effective treatment strategy (171).
The key directions of future research are personalized probiotic treatment regimens, the development of new probiotics, and its combination with other therapeutic approaches, which require extensive attention and discussion from the scientific community and clinical medicine (172, 173).
2.5.1 Personalized probiotic treatment
The increasing importance of personalized probiotic therapy for IBD, which may be more effective due to significant differences in gut microbiota and immune responses in different patients (174).
Selecting the right probiotic strain based on the specific characteristics of the patient’s gut microbiota can significantly improve the efficacy of treatment, and one study involving 24 adults showed that receiving B. longum BB536 was demonstrated (175). Dietary habits and the types and quantities of gut microbiota vary greatly among populations in different regions, which may lead to different outcomes from the same probiotic treatment. One study involving 66 patients with an average age of 46.2 years, of whom 53% were female and 89.4% were white, observed a trend between probiotic use and brain fog (p = 0.080), but it did not reach statistical significance. However, in white patients, the association between probiotic use and brain fog reached statistical significance (p = 0.044), and the study found a significant statistical association between probiotic use and brain fog symptoms in male patients (p = 0.004), with the duration of probiotic use also related to the occurrence of brain fog (p = 0.038). These results suggest that probiotic use may be significantly associated with brain fog symptoms in specific populations, such as white and male patients, and that the duration of use may also influence this relationship (176). Multiple studies have also shown that the efficacy of probiotic treatment varies among different age groups. An analysis of nine trials showed no significant effect of probiotics on CD (p = 0.07), but three trials involving children with IBD demonstrated significant advantages (p < 0.01) (177).
Research indicates that IBD severity is closely linked to specific bacterial biomarkers in fecal microbiota. Quantitative polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) is an effective method for detecting these biomarkers, aiding in monitoring IBD progression (178). Studies show that using probiotics derived from an individual’s own gut microbiota, rather than commercial options, can better treat DSS-induced colitis by reducing disease susceptibility and enhancing immune response (179). Future integration of genomics and metabolomics is expected to advance personalized probiotic therapies, improving treatment outcomes and patient quality of life.
2.5.2 Research directions for new probiotics
With the continuous development of probiotics, new probiotics have opened up a new direction for the treatment of IBD and shown us unprecedented potential. In the future, with the continuous progress of genetic engineering technology, the emergence of engineered probiotics will also provide new hope for the treatment of IBD (180, 181).
Genetically engineered probiotics are a leading field in the treatment of IBD, on the one hand, they can regulate intestinal dysbiosis, and on the other hand, they can also release therapeutic active molecules directly into the intestine, which can effectively avoid the side effects caused by systemic administration (182). Due to the high genetic stability and non-transferability of small recessive plasmid mutant 1 (pMUT1) and mutant 2 (pMUT2), E. coli is commonly used as genetically engineered bacteria, particularly ECN (183). For example, genetically engineered ECN-pE can eliminate harmful reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the gut, show significant anti-inflammatory effects in mouse IBD models, and successfully repair the intestinal epithelial barrier, significantly increasing the abundance of probiotics (184). Liu and colleagues engineered Bifidobacterium expressing the PEP-1-hMnSOD fusion protein, which can successfully express rhMnSOD in the colon, to treat DSS-induced UC in mice.
Results indicate that engineered Bifidobacterium effectively reduces DSS-induced UC, as evidenced by the levels of inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-8 in colonic tissue and histological damage (185). A strain of Lactobacillus paracasei F19 (pNAPE-LP) expressing N-acyl phosphatidylethanolamine-specific phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD) was developed by Esposito G et al. And under the promotion of ultra-low palmitate supply, the strain can produce palmitoyl ethanolamine (PEA), and when pNAPE-LP is co-administered with palmitate, PEA will be released over time, thus significantly improving the clinical and histological injury score in UC mouse model, and significantly reducing neutrophil infiltration, reducing the expression and release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and oxidative stress markers, and enhancing the integrity of epithelial barrier. PNAPE-LP is a new therapy to control intestinal inflammation in IBD (186). These genetically engineered probiotics can not only release therapeutic molecules in the intestine to enhance the anti-inflammatory effect, but also provide new ideas for future treatment strategies.
Recent studies have shown that the application of nanocoating of probiotics has attracted widespread attention. Due to the harsh intestinal environment, the feasibility and effectiveness of probiotic therapy may be affected, and modifying probiotics with nanocoating can enhance their resistance to the gastrointestinal environment (187, 188). A study encapsulated probiotic Bacillus coagulans spores with rosmarinic acid (RA) and silk fibroin protein (SF), among them, RA can clear ROS to alleviate oxidative damage and inhibit inflammatory response, while SF can assist in the colonization of probiotics. This probiotic alleviates a series of inflammatory symptoms and restores the balance of gut microbiota (189). In summary, such research may open up new avenues for probiotic treatment of IBD in the future.
2.5.3 Combined application of probiotics with other treatment methods
The use of probiotics alongside other treatments shows a lot of promise in providing more comprehensive and personalized treatment options for IBD patients (190).
Currently, traditional treatment methods such as immunosuppressants and biologics, while effective, often come with significant side effects (191), causing inconvenience and distress for patients. Therefore, incorporating probiotics into adjunctive treatment plans could help lower the doses of these medications and effectively reduce the incidence of their adverse reactions. Combining probiotics with other treatment methods can really boost treatment results and play an important role in improving patients’ quality of life (192). Additionally, synbiotics are emerging as a promising new approach with potential in treating IBD. Synbiotics are a combination of probiotics and prebiotics, with prebiotics being indigestible food components that selectively stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria or promote the activity of a limited number of health-promoting bacteria (30, 193). For example, research by Xue et al. found that Lp90 and soluble dietary fiber (SDF) obtained from mushroom byproducts, as synbiotics, can upregulate butyrate production and increase gut microbiota diversity to alleviate colitis (194). Other studies combined Lactobacillus plantarum SC-5 (SC-5) and tyrosol (TY), with this synbiotic alleviating and improving colitis in a gut microbiota-dependent manner (195). Relevant systematic reviews indicate that synbiotics significantly improved patients’ colonoscopy and histological scores, clinical activity index, serum CPR levels, gut microbiota index, and levels of messenger RNA, TNF-α, IL-1α, IL-10, and MPO (196). In summary, synbiotics can help in treating IBD in different ways (197, 198). Future research should investigate how probiotics can be combined with other treatments to improve IBD management and enhance patient health outcomes.
3 Conclusion
The medical community is increasingly recognizing and engaging in discourse regarding the significant role and potential application of probiotics in the management of IBD. Recent studies have demonstrated that probiotics can modulate intestinal microbiota, enhance the integrity of the intestinal barrier, regulate immune responses, and exert anti-inflammatory effects, thereby ameliorating symptoms and enhancing the quality of life for patients with IBD.
Although the application prospects of probiotics in IBD treatment are broad, we still need to pay close attention to the differences in research results. On one hand, some studies indicate that specific probiotic formulations can significantly improve patients’ clinical symptoms and quality of life; on the other hand, other studies have failed to find significant therapeutic effects. This variation might be due to several factors, including differences in study design, individual participant differences, types of probiotics, and their dosages. Therefore, future research should focus more on standardization and personalization in order to more accurately assess the actual effects and application value of probiotics in IBD treatment.
The research direction of probiotics in the treatment of IBD is expected to develop in the direction of personalized treatment, the development of new probiotics and the combined application of other treatment methods in the future, to improve the treatment effect, personalized treatment may have to be adjusted according to the characteristics of the patient’s intestinal flora to determine the best combination of probiotics, and the research of genetically engineered probiotics and synbiotics also brings new ideas to the management of IBD, and the application prospects and research value of probiotics in the adjuvant treatment of IBD are broad, and it is estimated that they will play a more important role in the treatment of IBD. This provides patients with better treatment options and improves their quality of life.
Statements
Author contributions
JZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Methodology, Project administration. XiZ: Investigation, Writing – original draft, Methodology. XC: Writing – review & editing, Methodology. SW: Writing – original draft, Data curation, Software. YL: Software, Writing – original draft. XuZ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Supervision, Funding acquisition. GW: Writing – review & editing, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Conceptualization.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by funding from Youth Talent Cultivation Fund Project of Dalian Medical University, the Liaoning Provincial Department of Education (numbers JYTMS20230577) and the Dalian Life and Health field Guidance Plan (2024ZDJH01PT068).
Acknowledgments
Figures were created with BioRender.com.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. The authors thank AI for polishing the language. DeepSeek R1 was used to translate and polish the language in sections 2.3.2, 2.3.4, and 2.4.1.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- AhR
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- BMDC
Bone marrow-derived dendritic cell
- BMI
Body mass index
- CD
Crohn’s disease
- CDAI
Crohn’s disease activity index
- CPR
C-reactive protein
- CTLA-4
Cytotoxic t-lymphocyte-associated protein 4
- DAO
Diamine oxidase
- Dectin-1
Dendritic cell-associated C-type lectin-1
- DFC
Dietary fiber complexes
- DSS
Dextran sulfate sodium
- ECN
E. coli Nissle
- EGC
Enteric glial cells
- EPS
Exopolysaccharide
- ESR
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- FC
Fecal calprotectin
- FcγRIIB
Fc gamma receptor II B
- FimM
Fimbrial m protein
- FMT
Fecal microbiota transplantation
- Galectin-3
Galactose-binding lectin-3
- GDNF
Glialcell-derived neurotrophic factor
- Hgb
Hemoglobin
- IBD
Inflammatory bowel disease
- IBS-C
Irritable bowel syndrome with constipation
- ICAM-1
Intercellular cell adhesion molecule 1
- IDO
Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- IgA
Immunoglobulin A
- IκB
Inhibitor of kappa B
- IL-1β
Interleukin 1β
- IL-10
Interleukin 10
- IL-17
Interleukin 17
- IL-18
Interleukin 18
- IL-23
Interleukin 23
- Kyn
Kynurenine
- LAP+T
Latency-associated peptide-positive regulatory T cell
- Lp082
Lactobacillus plantarum 082
- MAPK
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MHC-II
Major histocompatibility complex class II
- MLC
Myosin light chain
- MLCK
Myosin light chain kinase
- MPO
Myeloperoxidase
- MUC-2
Mucin-2
- NCFM
Matrix metallopeptidase 9
- NF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa B
- PEA
Palmitoyl ethanol amide
- RCT
Randomized controlled trial
- ROS
Reactive oxygen species
- SASP
Sulfasalazine
- SCFAs
Short-chain fatty acids
- SF
Silk fibroin protein
- TGF-β
Transforming growth factor-β
- TLR
Toll-like receptor
- TLR-2
Toll-like receptor 2
- Th17
T helper cell 17
- TJ
Tight junction
- TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- Trp
Tryptophan
- UC
Ulcerative colitis
- VCAM-1
Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1
- ZO-1
Zonula occludens-1
- ZO-2
Zonula occludens-2
Glossary
References
1.
Fabián O Kamaradová K . Morphology of inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD). Ceskoslovenska patologie. (2022) 58:27–37. PMID:
2.
Bruner LP White AM Proksell S . Inflammatory bowel disease. Prim Care. (2023) 50:411–27. doi: 10.1016/j.pop.2023.03.009
3.
Ranasinghe IR Tian C Hsu R . Crohn disease In. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing (2025)
4.
Rogler G Singh A Kavanaugh A Rubin DT . Extraintestinal manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease: current concepts, treatment, and implications for disease management. Gastroenterology. (2021) 161:1118–32. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.07.042
5.
He R Zhao S Cui M Chen Y Ma J Li J et al . Cutaneous manifestations of inflammatory bowel disease: basic characteristics, therapy, and potential pathophysiological associations. Front Immunol. (2023) 14:1234535. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1234535
6.
Faggiani I Fanizza J D'Amico F Allocca M Zilli A Parigi TL et al . Extraintestinal manifestations in inflammatory bowel disease: from pathophysiology to treatment. Biomedicine. (2024) 12:1839. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12081839
7.
Yao Y Kim G Shafer S Chen Z Kubo S Ji Y et al . Mucus sialylation determines intestinal host-commensal homeostasis. Cell. (2022) 185:1172–88.e28. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.02.013
8.
Jarmakiewicz-Czaja S Zielińska M Sokal A Filip R . Genetic and epigenetic etiology of inflammatory bowel disease: an update. Genes. (2022) 13:2388. doi: 10.3390/genes13122388
9.
Seyed Tabib NS Madgwick M Sudhakar P Verstockt B Korcsmaros T Vermeire S . Big data in IBD: big progress for clinical practice. Gut. (2020) 69:1520–32. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2019-320065
10.
Nambu R Warner N Mulder DJ Kotlarz D McGovern DPB Cho J et al . A systematic review of monogenic inflammatory bowel disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 20:e653–63. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2021.03.021
11.
Singh N Bernstein CN . Environmental risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease. United European Gastroenterol J. (2022) 10:1047–53. doi: 10.1002/ueg2.12319
12.
Mentella MC Scaldaferri F Pizzoferrato M Gasbarrini A Miggiano GAD . Nutrition, IBD and gut microbiota: a review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:944. doi: 10.3390/nu12040944
13.
Gevers D Kugathasan S Denson LA Vázquez-Baeza Y Van Treuren W Ren B et al . The treatment-naive microbiome in new-onset Crohn's disease. Cell Host Microbe. (2014) 15:382–92. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2014.02.005
14.
Ananthakrishnan AN Kaplan GG Bernstein CN Burke KE Lochhead PJ Sasson AN et al . Lifestyle, behaviour, and environmental modification for the management of patients with inflammatory bowel diseases: an international organization for study of inflammatory bowel diseases consensus. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 7:666–78. doi: 10.1016/S2468-1253(22)00021-8
15.
Marrie RA Walld R Bolton JM Sareen J Walker JR Patten SB et al . Rising incidence of psychiatric disorders before diagnosis of immune-mediated inflammatory disease. Epidemiol Psychiatr Sci. (2019) 28:333–42. doi: 10.1017/S2045796017000579
16.
Radziszewska M Smarkusz-Zarzecka J Ostrowska L Pogodziński D . Nutrition and supplementation in ulcerative colitis. Nutrients. (2022) 14:2469. doi: 10.3390/nu14122469
17.
Qiu P Ishimoto T Fu L Zhang J Zhang Z Liu Y . The gut microbiota in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2022) 12:733992. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2022.733992
18.
Mazziotta C Tognon M Martini F Torreggiani E Rotondo JC . Probiotics mechanism of action on immune cells and beneficial effects on human health. Cells. (2023) 12:184. doi: 10.3390/cells12010184
19.
Saez A Herrero-Fernandez B Gomez-Bris R Sánchez-Martinez H Gonzalez-Granado JM . Pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease: innate immune system. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:1526. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021526
20.
Mak JWY Ho AHY Ng SC . IBD barriers across the continents - East Asia. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. (2023) 16:17562848231212089. doi: 10.1177/17562848231212089
21.
Cai Z Wang S Li J . Treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: a comprehensive review. Front Med. (2021) 8:765474. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.765474
22.
Chao YS Loshak H . CADTH rapid response reports. Biologics versus Immunomodulators for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: a review of comparative clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness. Ottawa (ON): Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (2019).
23.
Bruscoli S Febo M Riccardi C Migliorati G . Glucocorticoid therapy in inflammatory bowel disease: mechanisms and clinical practice. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:691480. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.691480
24.
Triantafillidis JK Zografos CG Konstadoulakis MM Papalois AE . Combination treatment of inflammatory bowel disease: present status and future perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:2068–80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i15.2068
25.
Higashiyama M Hokari R . New and emerging treatments for inflammatory bowel disease. Digestion. (2023) 104:74–81. doi: 10.1159/000527422
26.
Yao S Zhao Z Wang W Liu X . Bifidobacterium Longum: protection against inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol Res. (2021) 2021:1–11. doi: 10.1155/2021/8030297
27.
Stallmach A Atreya R Grunert PC Stallhofer J de Laffolie J Schmidt C . Treatment strategies in inflammatory bowel diseases. Deutsches Arzteblatt Int. (2023) 120:768–78. doi: 10.3238/arztebl.m2023.0142
28.
Kotla NG Rochev Y . IBD disease-modifying therapies: insights from emerging therapeutics. Trends Mol Med. (2023) 29:241–53. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2023.01.001
29.
Zhang XF Guan XX Tang YJ Sun JF Wang XK Wang WD et al . Clinical effects and gut microbiota changes of using probiotics, prebiotics or synbiotics in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Nutr. (2021) 60:2855–75. doi: 10.1007/s00394-021-02503-5
30.
Roy S Dhaneshwar S . Role of prebiotics, probiotics, and synbiotics in management of inflammatory bowel disease: current perspectives. World J Gastroenterol. (2023) 29:2078–100. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i14.2078
31.
Salminen S Collado MC Endo A Hill C Lebeer S Quigley EMM et al . The international scientific association of probiotics and prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of postbiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2021) 18:649–67. doi: 10.1038/s41575-021-00440-6
32.
Akutko K Stawarski A . Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics in inflammatory bowel diseases. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:2466. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112466
33.
Rodrigues VF Elias-Oliveira J Pereira ÍS Pereira JA Barbosa SC Machado MSG et al . Akkermansia muciniphila and gut immune system: a good friendship that attenuates inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and diabetes. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:934695. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.934695
34.
Marasco G Cirota GG Rossini B Lungaro L Di Biase AR Colecchia A et al . Probiotics, prebiotics and other dietary supplements for gut microbiota modulation in celiac disease patients. Nutrients. (2020) 12:2674. doi: 10.3390/nu12092674
35.
Lee CG Cha KH Kim GC Im SH Kwon HK . Exploring probiotic effector molecules and their mode of action in gut-immune interactions. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (2023) 47:fuad046. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuad046
36.
Gao T Wang X Li Y Ren F . The role of probiotics in skin health and related gut-skin axis: a review. Nutrients. (2023) 15:3123. doi: 10.3390/nu15143123
37.
Gorreja F Walker WA . The potential role of adherence factors in probiotic function in the gastrointestinal tract of adults and pediatrics: a narrative review of experimental and human studies. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2149214. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2149214
38.
Abraham BP Quigley EMM . Probiotics in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. (2017) 46:769–82. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2017.08.003
39.
Jakubczyk D Leszczyńska K Górska S . The effectiveness of probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)-a critical review. Nutrients. (2020) 12:1973. doi: 10.3390/nu12071973
40.
Zawistowska-Rojek A Tyski S . Are probiotic really safe for humans?Pol J Microbiol. (2018) 67:251–8. doi: 10.21307/pjm-2018-044
41.
Kumar R Sood U Gupta V Singh M Scaria J Lal R . Recent advancements in the development of modern probiotics for restoring human gut microbiome dysbiosis. Indian J Microbiol. (2020) 60:12–25. doi: 10.1007/s12088-019-00808-y
42.
Yadav MK Kumari I Singh B Sharma KK Tiwari SK . Probiotics, prebiotics and synbiotics: safe options for next-generation therapeutics. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. (2022) 106:505–21. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11646-8
43.
Latif A Shehzad A Niazi S Zahid A Ashraf W Iqbal MW et al . Probiotics: mechanism of action, health benefits and their application in food industries. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1216674. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1216674
44.
Long B Gottlieb M . Probiotics for preventing antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Am Family Phys. (2021) 104Online
45.
Tong L Zhang X Hao H Liu Q Zhou Z Liang X et al . Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG derived extracellular vesicles modulate gut microbiota and attenuate inflammatory in DSS-induced colitis mice. Nutrients. (2021) 13:3319. doi: 10.3390/nu13103319
46.
Wang J Li X Zhao X Yuan S Dou H Cheng T et al . Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-derived extracellular vesicles promote wound healing via miR-21-5p-mediated re-epithelization and angiogenesis. J Nanobiotechnol. (2024) 22:644. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02893-8
47.
Si W Liang H Bugno J Xu Q Ding X Yang K et al . Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG induces cGAS/STING- dependent type I interferon and improves response to immune checkpoint blockade. Gut. (2022) 71:521–33. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2020-323426
48.
Kang Y Kang X Yang H Liu H Yang X Liu Q et al . Lactobacillus acidophilus ameliorates obesity in mice through modulation of gut microbiota dysbiosis and intestinal permeability. Pharmacol Res. (2022) 175:106020. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.106020
49.
Chandhni PR Pradhan D Sowmya K Gupta S Kadyan S Choudhary R et al . Ameliorative effect of surface proteins of probiotic lactobacilli in colitis mouse models. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:679773. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.679773
50.
Meng J Wang YY Hao YP . Protective function of surface layer protein from Lactobacillus casei fb05 against intestinal pathogens in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2021) 546:15–20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2021.01.101
51.
Ren M Li H Fu Z Li Q . Centenarian-sourced Lactobacillus casei combined with dietary Fiber complex ameliorates brain and gut function in aged mice. Nutrients. (2022) 14:324. doi: 10.3390/nu14020324
52.
Sato S Arai S Kato K Yoshida K Iwabuchi N Sagami T et al . Effects of Bifidobacterium longum BB536 and Bifidobacterium breve MCC1274 on body composition in Normal and overweight adults in randomized placebo-controlled study. Nutrients. (2024) 16:815. doi: 10.3390/nu16060815
53.
Takeda T Asaoka D Nojiri S Yanagisawa N Nishizaki Y Osada T et al . Usefulness of Bifidobacterium longum BB536 in elderly individuals with chronic constipation: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol. (2023) 118:561–8. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002028
54.
Asaoka D Xiao J Takeda T Yanagisawa N Yamazaki T Matsubara Y et al . Effect of probiotic Bifidobacterium breve in improving cognitive function and preventing brain atrophy in older patients with suspected mild cognitive impairment: results of a 24-week randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J Alzheimer's Dis. (2022) 88:75–95. doi: 10.3233/JAD-220148
55.
Yang YH Qian W Hou XH Dai CB . Bifidobacterium bifidum and Bacteroides fragilis induced differential immune regulation of enteric glial cells subjected to exogenous inflammatory stimulation. Inflammation. (2022) 45:2388–405. doi: 10.1007/s10753-022-01700-6
56.
Mourey F Decherf A Jeanne JF Clément-Ziza M Grisoni ML Machuron F et al . Saccharomyces cerevisiae I-3856 in irritable bowel syndrome with predominant constipation. World J Gastroenterol. (2022) 28:2509–22. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i22.2509
57.
Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka K Ruszkowski J Fic M Folwarski M Makarewicz W . Saccharomyces boulardii CNCM I-745: a non-bacterial microorganism used as probiotic agent in supporting treatment of selected diseases. Curr Microbiol. (2020) 77:1987–96. doi: 10.1007/s00284-020-02053-9
58.
Buccigrossi V Laudiero G Russo C Miele E Sofia M Monini M et al . Chloride secretion induced by rotavirus is oxidative stress-dependent and inhibited by Saccharomyces boulardii in human enterocytes. PLoS One. (2014) 9:e99830. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099830
59.
Iatcu CO Steen A Covasa M . Gut microbiota and complications of type-2 diabetes. Nutrients. (2021) 14:166. doi: 10.3390/nu14010166
60.
Cukrowska B Ceregra A Maciorkowska E Surowska B Zegadło-Mylik MA Konopka E et al . The effectiveness of probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus casei strains in children with atopic dermatitis and cow's Milk protein allergy: a multicenter, randomized, double blind, placebo controlled study. Nutrients. (2021) 13:1169. doi: 10.3390/nu13041169
61.
Green M Arora K Prakash S . Microbial medicine: prebiotic and probiotic functional foods to target obesity and metabolic syndrome. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:2890. doi: 10.3390/ijms21082890
62.
Wong WY Chan BD Sham TT Lee MM Chan CO Chau CT et al . Lactobacillus casei strain Shirota ameliorates dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice by increasing taurine-conjugated bile acids and inhibiting NF-κB signaling via stabilization of IκBα. Front Nutr. (2022) 9:816836. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.816836
63.
Peng C Li J Miao Z Wang Y Wu S Wang Y et al . Early life administration of Bifidobacterium bifidum BD-1 alleviates long-term colitis by remodeling the gut microbiota and promoting intestinal barrier development. Front Microbiol. (2022) 13:916824. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.916824
64.
Mills S Stanton C Lane JA Smith GJ Ross RP . Precision nutrition and the microbiome, part I: current state of the science. Nutrients. (2019) 11:923. doi: 10.3390/nu11040923
65.
Mohr AE Jäger R Carpenter KC Kerksick CM Purpura M Townsend JR et al . The athletic gut microbiota. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. (2020) 17:24. doi: 10.1186/s12970-020-00353-w
66.
Liu Q Yu Z Tian F Zhao J Zhang H Zhai Q et al . Surface components and metabolites of probiotics for regulation of intestinal epithelial barrier. Microb Cell Factories. (2020) 19:23. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-1289-4
67.
Zhou B Yuan Y Zhang S Guo C Li X Li G et al . Intestinal Flora and Disease mutually shape the regional immune system in the intestinal tract. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:575. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00575
68.
Chandrasekaran P Weiskirchen S Weiskirchen R . Effects of probiotics on gut microbiota: an overview. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:6022. doi: 10.3390/ijms25116022
69.
Wang J Ji H . Influence of probiotics on dietary protein digestion and utilization in the gastrointestinal tract. Curr Protein Pept Sci. (2019) 20:125–31. doi: 10.2174/1389203719666180517100339
70.
Zhao Y Yang H Wu P Yang S Xue W Xu B et al . Akkermansia muciniphila: a promising probiotic against inflammation and metabolic disorders. Virulence. (2024) 15:2375555. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2024.2375555
71.
Zakerska-Banaszak O Tomczak H Gabryel M Baturo A Wolko L Michalak M et al . Dysbiosis of gut microbiota in polish patients with ulcerative colitis: a pilot study. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:2166. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-81628-3
72.
Pittayanon R Lau JT Leontiadis GI Tse F Yuan Y Surette M et al . Differences in gut microbiota in patients with vs without inflammatory bowel diseases: a systematic review. Gastroenterology. (2020) 158:930–46.e1. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.294
73.
Kriss M Hazleton KZ Nusbacher NM Martin CG Lozupone CA . Low diversity gut microbiota dysbiosis: drivers, functional implications and recovery. Curr Opin Microbiol. (2018) 44:34–40. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2018.07.003
74.
Haneishi Y Furuya Y Hasegawa M Picarelli A Rossi M Miyamoto J . Inflammatory bowel diseases and gut microbiota. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:3817. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043817
75.
Niu W Yang F Fu Z Dong Y Zhang Z Ju J . The role of enteric dysbacteriosis and modulation of gut microbiota in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Microb Pathog. (2022) 165:105381. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105381
76.
Ma L Shen Q Lyu W Lv L Wang W Yu M et al . Clostridium butyricum and its derived extracellular vesicles modulate gut homeostasis and ameliorate acute experimental colitis. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0136822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01368-22
77.
Scaldaferri F Gerardi V Mangiola F Lopetuso LR Pizzoferrato M Petito V et al . Role and mechanisms of action of Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 in the maintenance of remission in ulcerative colitis patients: an update. World J Gastroenterol. (2016) 22:5505–11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i24.5505
78.
Xiong Y Zhai Z Lei Y Xiao B Hao Y . A novel major pilin subunit protein FimM is involved in adhesion of Bifidobacterium longum BBMN68 to intestinal epithelial cells. Front Microbiol. (2020) 11:590435. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.590435
79.
Wang Y Wu Y Wang Y Xu H Mei X Yu D et al . Antioxidant properties of probiotic Bacteria. Nutrients. (2017) 9:5. doi: 10.3390/nu9050521
80.
Kanmani P Satish Kumar R Yuvaraj N Paari KA Pattukumar V Arul V . Probiotics and its functionally valuable products-a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. (2013) 53:641–58. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2011.553752
81.
Wang S Ye Q Wang K Zeng X Huang S Yu H et al . Enhancement of macrophage function by the antimicrobial peptide Sublancin protects mice from methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Immunol Res. (2019) 2019:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2019/3979352
82.
Stojanov S Berlec A Štrukelj B . The influence of probiotics on the Firmicutes/Bacteroidetes ratio in the treatment of obesity and inflammatory bowel disease. Microorganisms. (2020) 8:1715. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8111715
83.
Liu Y Tian X He B Hoang TK Taylor CM Blanchard E et al . Lactobacillus reuteri DSM 17938 feeding of healthy newborn mice regulates immune responses while modulating gut microbiota and boosting beneficial metabolites. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. (2019) 317:G824–38. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00107.2019
84.
Salimi A Sepehr A Hejazifar N Talebi M Rohani M Pourshafie MR . The anti-inflammatory effect of a probiotic cocktail in human feces induced-mouse model. Inflammation. (2023) 46:2178–92. doi: 10.1007/s10753-023-01870-x
85.
Chapman CM Gibson GR Rowland I . Health benefits of probiotics: are mixtures more effective than single strains?Eur J Nutr. (2011) 50:1–17. doi: 10.1007/s00394-010-0166-z
86.
Laguna JG Freitas ADS Barroso FAL De Jesus LCL De Vasconcelos O Quaresma LS et al . Recombinant probiotic Lactococcus lactis delivering P62 mitigates moderate colitis in mice. Front Microbiol. (2024) 15:1309160. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1309160
87.
Fan L Qi Y Qu S Chen X Li A Hendi M et al . B. adolescentis ameliorates chronic colitis by regulating Treg/Th2 response and gut microbiota remodeling. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1–17. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1826746
88.
Nie K Ma K Luo W Shen Z Yang Z Xiao M et al . Roseburia intestinalis: a beneficial gut organism from the discoveries in genus and species. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:757718. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.757718
89.
Ghavami SB Yadegar A Aghdaei HA Sorrentino D Farmani M Mir AS et al . Immunomodulation and generation of Tolerogenic dendritic cells by probiotic Bacteria in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:6266. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176266
90.
Di Giacinto C Marinaro M Sanchez M Strober W Boirivant M . Probiotics ameliorate recurrent Th1-mediated murine colitis by inducing IL-10 and IL-10-dependent TGF-beta-bearing regulatory cells. J Immunol. (2005) 174:3237–46. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.6.3237
91.
Zhao HM Huang XY Zuo ZQ Pan QH Ao MY Zhou F et al . Probiotics increase T regulatory cells and reduce severity of experimental colitis in mice. World J Gastroenterol. (2013) 19:742–9. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i5.742
92.
Wong CB Odamaki T Xiao J-z . Beneficial effects of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum BB536 on human health: modulation of gut microbiome as the principal action. J Funct Foods. (2019) 54:506–19. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.02.002
93.
Jang SE Min SW . Amelioration of colitis in mice by Leuconostoc lactis EJ-1 by M1 to M2 macrophage polarization. Microbiol Immunol. (2020) 64:133–42. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12752
94.
Guo N Lv LL . Mechanistic insights into the role of probiotics in modulating immune cells in ulcerative colitis. Immunity Inflamm Dis. (2023) 11:e1045. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1045
95.
Aghamohammad S Sepehr A Miri ST Najafi S Rohani M Pourshafiea MR . The effects of the probiotic cocktail on modulation of the NF-kB and JAK/STAT signaling pathways involved in the inflammatory response in bowel disease model. BMC Immunol. (2022) 23:8. doi: 10.1186/s12865-022-00484-6
96.
Aghamohammad S Sepehr A Miri ST Najafi S Pourshafie MR Rohani M . The role of combining probiotics in preventing and controlling inflammation: a focus on the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in an in vitro model of IBD. Can J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 2022:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/2045572
97.
Aghamohammad S Sepehr A Miri ST Najafi S Pourshafie MR Rohani M . The potential role of Bifidobacterium spp. as a preventive and therapeutic agent in controlling inflammation via affecting inflammatory signalling pathways. Lett Appl Microbiol. (2022) 75:1254–63. doi: 10.1111/lam.13793
98.
Wu Y Jha R Li A Liu H Zhang Z Zhang C et al . Probiotics (Lactobacillus plantarum HNU082) supplementation relieves ulcerative colitis by affecting intestinal barrier functions, immunity-related gene expression, gut microbiota, and metabolic pathways in mice. Microbiol Spectr. (2022) 10:e0165122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01651-22
99.
Maldonado Galdeano C Cazorla SI Lemme Dumit JM Vélez E Perdigón G . Beneficial effects of probiotic consumption on the immune system. Ann Nutr Metab. (2019) 74:115–24. doi: 10.1159/000496426
100.
Cristofori F Dargenio VN Dargenio C Miniello VL Barone M Francavilla R . Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects of probiotics in gut inflammation: a door to the body. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:578386. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.578386
101.
Kudelka MR Stowell SR Cummings RD Neish AS . Intestinal epithelial glycosylation in homeostasis and gut microbiota interactions in IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2020) 17:597–617. doi: 10.1038/s41575-020-0331-7
102.
Chen Y Cui W Li X Yang H . Interaction between commensal bacteria, immune response and the intestinal barrier in inflammatory bowel disease. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:761981. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761981
103.
Mitselou A Grammeniatis V Varouktsi A Papadatos SS Klaroudas A Katsanos K et al . Immunohistochemical study of adhesion molecules in irritable bowel syndrome: a comparison to inflammatory bowel diseases. Adv Biomed Res. (2021) 10:21. doi: 10.4103/abr.abr_2_20
104.
Liu L Li Y He Y Wang Z Zhao H Jin X et al . Enterococcus faecium HDRsEf1 inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced downregulation of zona occludens −1 expression via toll-like receptor 2/4-mediated c-Jun N-terminal kinase/activator protein-1 signalling pathways. J Appl Microbiol. (2022) 132:605–17. doi: 10.1111/jam.15167
105.
Anderson RC Cookson AL McNabb WC Park Z McCann MJ Kelly WJ et al . Lactobacillus plantarum MB452 enhances the function of the intestinal barrier by increasing the expression levels of genes involved in tight junction formation. BMC Microbiol. (2010) 10:316. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-316
106.
Kuo WT Odenwald MA Turner JR Zuo L . Tight junction proteins occludin and ZO-1 as regulators of epithelial proliferation and survival. Ann N Y Acad Sci. (2022) 1514:21–33. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14798
107.
Ren S Wang C Chen A Lv W Gao R . The probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei ameliorates diarrhea cause by Escherichia coli O(8) via gut microbiota modulation(1). Front Nutr. (2022) 9:878808. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.878808
108.
Ma S Yeom J Lim YH . Dairy Propionibacterium freudenreichii ameliorates acute colitis by stimulating MUC2 expression in intestinal goblet cell in a DSS-induced colitis rat model. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:5523. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62497-8
109.
Kang Y Park H Choe BH Kang B . The role and function of mucins and its relationship to inflammatory bowel disease. Front Med. (2022) 9:848344. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.848344
110.
Van der Sluis M De Koning BA De Bruijn AC Velcich A Meijerink JP Van Goudoever JB et al . Muc2-deficient mice spontaneously develop colitis, indicating that MUC2 is critical for colonic protection. Gastroenterology. (2006) 131:117–29. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2006.04.020
111.
Bergstrom K Xia L . The barrier and beyond: roles of intestinal mucus and mucin-type O-glycosylation in resistance and tolerance defense strategies guiding host-microbe symbiosis. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2052699. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2052699
112.
Wang L Cao H Liu L Wang B Walker WA Acra SA et al . Activation of epidermal growth factor receptor mediates mucin production stimulated by p40, a Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG-derived protein. J Biol Chem. (2014) 289:20234–44. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.553800
113.
Ding X Tang R Zhao J Xu Y Fu A Zhan X . Lactobacillus reuteri alleviates LPS-induced intestinal mucosal damage by stimulating the expansion of intestinal stem cells via activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in broilers. Poult Sci. (2024) 103:104072. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2024.104072
114.
Hu Y Chen Z Xu C Kan S Chen D . Disturbances of the gut microbiota and microbiota-derived metabolites in inflammatory bowel disease. Nutrients. (2022) 14:5140. doi: 10.3390/nu14235140
115.
Fusco W Lorenzo MB Cintoni M Porcari S Rinninella E Kaitsas F et al . Short-chain fatty-acid-producing Bacteria: key components of the human gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2023) 15:2211. doi: 10.3390/nu15092211
116.
Chen G Ran X Li B Li Y He D Huang B et al . Sodium butyrate inhibits inflammation and maintains epithelium barrier integrity in a TNBS-induced inflammatory bowel disease mice model. EBioMedicine. (2018) 30:317–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2018.03.030
117.
Liang L Liu L Zhou W Yang C Mai G Li H et al . Gut microbiota-derived butyrate regulates gut mucus barrier repair by activating the macrophage/WNT/ERK signaling pathway. Clin Sci (Lond). (2022) 136:291–307. doi: 10.1042/CS20210778
118.
Sun M Wu W Liu Z Cong Y . Microbiota metabolite short chain fatty acids, GPCR, and inflammatory bowel diseases. J Gastroenterol. (2017) 52:1–8. doi: 10.1007/s00535-016-1242-9
119.
Liu P Wang Y Yang G Zhang Q Meng L Xin Y et al . The role of short-chain fatty acids in intestinal barrier function, inflammation, oxidative stress, and colonic carcinogenesis. Pharmacol Res. (2021) 165:105420. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105420
120.
Peng M Lee SH Rahaman SO Biswas D . Dietary probiotic and metabolites improve intestinal homeostasis and prevent colorectal cancer. Food Funct. (2020) 11:10724–35. doi: 10.1039/D0FO02652B
121.
Badawy S Liu Y Guo M Liu Z Xie C Marawan MA et al . Conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) as a functional food: is it beneficial or not?Food Res Int (Ottawa, Ont). (2023) 172:113158. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2023.113158
122.
Langan D Perkins DJ Vogel SN Moudgil KD . Microbiota-derived metabolites, Indole-3-aldehyde and Indole-3-acetic acid, differentially modulate innate cytokines and stromal remodeling processes associated with autoimmune arthritis. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:2017. doi: 10.3390/ijms22042017
123.
Nikolaus S Schulte B Al-Massad N Thieme F Schulte DM Bethge J et al . Increased tryptophan metabolism is associated with activity of inflammatory bowel diseases. Gastroenterology. (2017) 153:1504–16.e2. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.08.028
124.
Zamora-Pineda J Kalinina O Sperling AI Knight KL . Mechanism of TLR4-mediated anti-inflammatory response induced by exopolysaccharide from the probiotic Bacillus subtilis. J Immunol. (2023) 211:1232–9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2200855
125.
Liao Y Wu S Zhou G Mei S Ou B Wen M et al . Probiotic Bacillus cereus regulates metabolic disorders and activates the cholic acid-FXR axis to alleviate DSS-induced colitis. J Proteome. (2025) 312:105360. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2024.105360
126.
Wu W Kaicen W Bian X Yang L Ding S Li Y et al . Akkermansia muciniphila alleviates high-fat-diet-related metabolic-associated fatty liver disease by modulating gut microbiota and bile acids. Microb Biotechnol. (2023) 16:1924–39. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14293
127.
Nabavi-Rad A Sadeghi A Asadzadeh Aghdaei H Yadegar A Smith SM Zali MR . The double-edged sword of probiotic supplementation on gut microbiota structure in Helicobacter pylori management. Gut Microbes. (2022) 14:2108655. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2022.2108655
128.
Veauthier B Hornecker JR . Crohn's disease: diagnosis and management. Am Fam Physician. (2018) 98:661–9. PMID:
129.
Petagna L Antonelli A Ganini C Bellato V Campanelli M Divizia A et al . Pathophysiology of Crohn's disease inflammation and recurrence. Biol Direct. (2020) 15:23. doi: 10.1186/s13062-020-00280-5
130.
Meima-van Praag EM Buskens CJ Hompes R Bemelman WA . Surgical management of Crohn's disease: a state of the art review. Int J Color Dis. (2021) 36:1133–45. doi: 10.1007/s00384-021-03857-2
131.
Bi GW Wu ZG Li Y Wang JB Yao ZW Yang XY et al . Intestinal flora and inflammatory bowel disease: causal relationships and predictive models. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e38101. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38101
132.
Caparrós E Wiest R Scharl M Rogler G Gutiérrez Casbas A Yilmaz B et al . Dysbiotic microbiota interactions in Crohn's disease. Gut Microbes. (2021) 13:1949096. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2021.1949096
133.
Pavel FM Vesa CM Gheorghe G Diaconu CC Stoicescu M Munteanu MA et al . Highlighting the relevance of gut microbiota manipulation in inflammatory bowel disease. Diagnostics (Basel, Switzerland). (2021) 11:1090. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics11061090
134.
Gowen R Gamal A Di Martino L McCormick TS Ghannoum MA . Modulating the microbiome for Crohn's disease treatment. Gastroenterology. (2023) 164:828–40. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2023.01.017
135.
Vakadaris G Stefanis C Giorgi E Brouvalis M Voidarou CC Kourkoutas Y et al . The role of probiotics in inducing and maintaining remission in Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis: a systematic review of the literature. Biomedicine. (2023) 11:494. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11020494
136.
Dolinger M Torres J Vermeire S . Crohn's disease. Lancet (London, England). (2024) 403:1177–91. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)02586-2
137.
Huang S Xie Z Han J Wang H Yang G Li M et al . Protocadherin 20 maintains intestinal barrier function to protect against Crohn's disease by targeting ATF6. Genome Biol. (2023) 24:159. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-02991-0
138.
Han H You Y Cha S Kim TR Sohn M Park J . Multi-species probiotic strain mixture enhances intestinal barrier function by regulating inflammation and tight junctions in lipopolysaccharides stimulated Caco-2 cells. Microorganisms. (2023) 11:656. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms11030656
139.
di Vito R Conte C Traina G . A multi-strain probiotic formulation improves intestinal barrier function by the modulation of tight and adherent junction proteins. Cells. (2022) 11:2617. doi: 10.3390/cells11162617
140.
Shen M Shi Y Ge Z Qian J . Effects of Mesalamine combined with live combined Bifidobacterium, Lactobacillus and Enterococcus capsules on intestinal mucosa barrier function and intestinal microbiota in mildly active Crohn's disease patients. J Invest Surg. (2024) 37:2297565. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2023.2297565
141.
Chen M Feng Y Liu W . Efficacy and safety of probiotics in the induction and maintenance of inflammatory bowel disease remission: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Palliat Med. (2021) 10:11821–9. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-2996
142.
Bjarnason I Sission G Hayee B . A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of a multi-strain probiotic in patients with asymptomatic ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease. Inflammopharmacology. (2019) 27:465–73. doi: 10.1007/s10787-019-00595-4
143.
Oh GM Moon W Seo KI Jung K Kim JH Kim SE et al . Changes in the Crohn's disease activity index and safety of administering Saccharomyces Boulardii in patients with Crohn's disease in clinical remission: a single hospital-based retrospective cohort study. Korean J Gastroenterol. (2020) 76:314–21. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.115
144.
Bourreille A Cadiot G Le Dreau G Laharie D Beaugerie L Dupas JL et al . Saccharomyces boulardii does not prevent relapse of Crohn's disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2013) 11:982–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2013.02.021
145.
Yılmaz İ Dolar ME Özpınar H . Effect of administering kefir on the changes in fecal microbiota and symptoms of inflammatory bowel disease: a randomized controlled trial. Turkish J Gastroenterol. (2019) 30:242–53. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2018.18227
146.
Marteau P Lémann M Seksik P Laharie D Colombel JF Bouhnik Y et al . Ineffectiveness of Lactobacillus johnsonii LA1 for prophylaxis of postoperative recurrence in Crohn's disease: a randomised, double blind, placebo controlled GETAID trial. Gut. (2006) 55:842–7. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.076604
147.
Bousvaros A Guandalini S Baldassano RN Botelho C Evans J Ferry GD et al . A randomized, double-blind trial of Lactobacillus GG versus placebo in addition to standard maintenance therapy for children with Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. (2005) 11:833–9. doi: 10.1097/01.MIB.0000175905.00212.2c
148.
Limketkai BN Akobeng AK Gordon M Adepoju AA . Probiotics for induction of remission in Crohn's disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2020) 2020:CD006634. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006634.pub3
149.
Le Berre C Honap S Peyrin-Biroulet L . Ulcerative colitis. Lancet (London, England). (2023) 402:571–84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00966-2
150.
Ungaro R Mehandru S Allen PB Peyrin-Biroulet L Colombel JF . Ulcerative colitis. Lancet (London, England). (2017) 389:1756–70. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)32126-2
151.
Segal JP LeBlanc JF Hart AL . Ulcerative colitis: an update. Clin Med (Lond). (2021) 21:135–9. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.2021-0080
152.
Dahal RH Kim S Kim YK Kim ES Kim J . Insight into gut dysbiosis of patients with inflammatory bowel disease and ischemic colitis. Front Microbiol. (2023) 14:1174832. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1174832
153.
Bodini G Ghezzi A Pasta A Marabotto E Calabrese F Facchini C et al . Reduction of fecal calprotectin levels induced by a short course of Escherichia Coli Nissle is associated with a lower likelihood of disease flares in patients with ulcerative colitis in clinical remission. J Gastroint Liver Dis. (2023) 32:438–43. doi: 10.15403/jgld-4932
154.
Wu Y Li A Liu H Zhang Z Zhang C Ma C et al . Lactobacillus plantarum HNU082 alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis in mice through regulating gut microbiome. Food Funct. (2022) 13:10171–85. doi: 10.1039/D2FO02303B
155.
Li A Liu A Wang J Song H Luo P Zhan M et al . The prophylaxis functions of Lactobacillus fermentum GLF-217 and Lactobacillus plantarum FLP-215 on ulcerative colitis via modulating gut microbiota of mice. J Sci Food Agric. (2024) 104:5816–25. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.13410
156.
Fan H Du J Liu X Zheng WW Zhuang ZH Wang CD et al . Effects of pentasa-combined probiotics on the microflora structure and prognosis of patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Turkish J Gastroenterol. (2019) 30:680–5. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2019.18426
157.
Li S Yin Y Xiao D Zou Y . Supplemental bifid triple viable capsule treatment improves inflammatory response and T cell frequency in ulcerative colitis patients. BMC Gastroenterol. (2021) 21:314. doi: 10.1186/s12876-021-01887-2
158.
Jiang XE Yang SM Zhou XJ Zhang Y . Effects of mesalazine combined with bifid triple viable on intestinal flora, immunoglobulin and levels of cal, MMP-9, and MPO in feces of patients with ulcerative colitis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:935–42. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202001_20079
159.
Ahmad Zhang C Wang Y Ullah H Rahman AU Wei J et al . Saccharomyces boulardii (CNCM I-745) alleviates collagen-induced arthritis by partially maintaining intestinal mucosal integrity through TLR2/MYD88/NF-κB pathway inhibition. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 139:112738. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112738
160.
Jin Y Wu J Huang K Liang Z . Heat-killed Saccharomyces boulardii alleviates dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis by restoring the intestinal barrier, reducing inflammation, and modulating the gut microbiota. Nutrients. (2024) 16:702. doi: 10.3390/nu16050702
161.
Xu X Wu J Jin Y Huang K Zhang Y Liang Z . Both Saccharomyces boulardii and its Postbiotics alleviate dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice, association with modulating inflammation and intestinal microbiota. Nutrients. (2023) 15:1484. doi: 10.3390/nu15061484
162.
Březina J Bajer L Wohl P Ďuricová D Hrabák P Novotný A et al . Fecal microbial transplantation versus Mesalamine Enema for treatment of active left-sided ulcerative colitis-results of a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:2753. doi: 10.3390/jcm10132753
163.
Xu HM Huang HL Xu J He J Zhao C Peng Y et al . Cross-talk between butyric acid and gut microbiota in ulcerative colitis following fecal microbiota transplantation. Front Microbiol. (2021) 12:658292. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.658292
164.
Ma Y Yang D Huang J Liu K Liu H Wu H et al . Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease: is there sufficient evidence?Open Life Sci. (2024) 19:20220821. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0821
165.
Coqueiro AY Raizel R Bonvini A Tirapegui J Rogero MM . Probiotics for inflammatory bowel diseases: a promising adjuvant treatment. Int J Food Sci Nutr. (2019) 70:20–9. doi: 10.1080/09637486.2018.1477123
166.
Guandalini S . Probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel diseases. Adv Exp Med Biol. (2024) 1449:135–42. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-58572-2_8
167.
Hassan WNM Al-Kaabi MM Akram NN Kassim MAK Pantazi AC . Probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease; a deep dive into their impact on disease course and associated health risks. Curr Med Chem. (2024) 31:4807–25. doi: 10.2174/0109298673314861240429072352
168.
Lorentz A Müller L . Probiotics in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease in adulthood: a systematic review. J Gastroint Liver Dis. (2022) 31:74–84. doi: 10.15403/jgld-3936
169.
McFarland LV Evans CT Goldstein EJC . Strain-specificity and disease-specificity of probiotic efficacy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Med. (2018) 5:124. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2018.00124
170.
Sniffen JC McFarland LV Evans CT Goldstein EJC . Choosing an appropriate probiotic product for your patient: an evidence-based practical guide. PLoS One. (2018) 13:e0209205. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209205
171.
Deng Q Zhang L Liu X Kang L Yi J Ren J et al . COF-based artificial probiotic for modulation of gut microbiota and immune microenvironment in inflammatory bowel disease. Chem Sci. (2023) 14:1598–605. doi: 10.1039/D2SC04984H
172.
Subramanian S Xavier RJ . Tuning in to inflammation: a path forward for precise and efficacious microbiome medicines?Med (New York, NY). (2021) 2:892–4. doi: 10.1016/j.medj.2021.07.006
173.
Foppa C Rizkala T Repici A Hassan C Spinelli A . Microbiota and IBD: current knowledge and future perspectives. Digest Liver Dis. (2024) 56:911–22. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2023.11.015
174.
Das A Behera RN Kapoor A Ambatipudi K . The potential of Meta-proteomics and artificial intelligence to establish the next generation of probiotics for personalized healthcare. J Agric Food Chem. (2023) 71:17528–42. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c03834
175.
Nakamura Y Suzuki S Murakami S Nishimoto Y Higashi K Watarai N et al . Integrated gut microbiome and metabolome analyses identified fecal biomarkers for bowel movement regulation by Bifidobacterium longum BB536 supplementation: a RCT. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2022) 20:5847–58. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.10.026
176.
Dadlani A Gala K Rai J Rai S Dryden G . P027brain fog in patients with inflammatory bowel disease, and association with use of probiotics. Am J Gastroenterol. (2021) 116:S7. doi: 10.14309/01.ajg.0000798708.22025.c0
177.
Ganji-Arjenaki M Rafieian-Kopaei M . Probiotics are a good choice in remission of inflammatory bowel diseases: a meta analysis and systematic review. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:2091–103. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25911
178.
Sezgin E Terlemez G Bozkurt B Bengi G Akpinar H Büyüktorun İ . Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of bacterial biomarkers enable fast and accurate monitoring in inflammatory bowel disease. PeerJ. (2022) 10:e14217. doi: 10.7717/peerj.14217
179.
Celiberto LS Pinto RA Rossi EA Vallance BA Cavallini DCU . Isolation and characterization of potentially probiotic bacterial strains from mice: proof of concept for personalized probiotics. Nutrients. (2018) 10:1684. doi: 10.3390/nu10111684
180.
Murali SK Mansell TJ . Next generation probiotics: engineering live biotherapeutics. Biotechnol Adv. (2024) 72:108336. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2024.108336
181.
Ma J Lyu Y Liu X Jia X Cui F Wu X et al . Engineered probiotics. Microb Cell Factories. (2022) 21:72. doi: 10.1186/s12934-022-01799-0
182.
Pesce M Seguella L Del Re A Lu J Palenca I Corpetti C et al . Next-generation probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:5466. doi: 10.3390/ijms23105466
183.
Blum-Oehler G Oswald S Eiteljörge K Sonnenborn U Schulze J Kruis W et al . Development of strain-specific PCR reactions for the detection of the probiotic Escherichia coli strain Nissle 1917 in fecal samples. Res Microbiol. (2003) 154:59–66. doi: 10.1016/S0923-2508(02)00007-4
184.
Zhou J Li M Chen Q Li X Chen L Dong Z et al . Programmable probiotics modulate inflammation and gut microbiota for inflammatory bowel disease treatment after effective oral delivery. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:3432. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31171-0
185.
Liu M Li S Zhang Q Xu Z Wang J Sun H . Oral engineered Bifidobacterium longum expressing rhMnSOD to suppress experimental colitis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2018) 57:25–32. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2018.02.004
186.
Esposito G Pesce M Seguella L Lu J Corpetti C Del Re A et al . Engineered Lactobacillus paracasei producing Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) prevents colitis in mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:2945. doi: 10.3390/ijms22062945
187.
Peng P Feng T Yang X Ding R Wang J Chen P et al . Bioorthogonal conjugation and responsive nanocoating of probiotics for inflammatory bowel disease. J Control Rel. (2024) 374:538–49. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2024.08.036
188.
Su Z Li W Li S Wang R Sheng D Zhao GP et al . Harnessing Akkermansia muciniphila membrane coating for probiotic therapy in inflammatory bowel disease. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. (2025) 17:11653–66. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c18134
189.
Huang Y Cai H Liu H Wang L Feng G Ding Z et al . Probiotic nanocomposite materials with excellent resistance, inflammatory targeting, and multiple efficacies for enhanced treatment of colitis in mice. J Nanobiotechnol. (2025) 23:188. doi: 10.1186/s12951-025-03240-1
190.
Zhou S Wang M Li W Zhang Y Zhao T Song Q et al . Comparative efficacy and tolerability of probiotic, prebiotic, and synbiotic formulations for adult patients with mild-moderate ulcerative colitis in an adjunctive therapy: a network meta-analysis. Clin Nutr (Edinburgh, Scotland). (2024) 43:20–30. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2023.11.010
191.
Auletta S Bonfiglio R Wunder A Varani M Galli F Borri F et al . Animal models for the study of inflammatory bowel diseases: a meta-analysis on modalities for imaging inflammatory lesions. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. (2018) 62:78–100. doi: 10.23736/S1824-4785.17.03050-3
192.
Lei P Yu H Ma J Du J Fang Y Yang Q et al . Cell membrane nanomaterials composed of phospholipids and glycoproteins for drug delivery in inflammatory bowel disease: a review. Int J Biol Macromol. (2023) 249:126000. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.126000
193.
Oniszczuk A Oniszczuk T Gancarz M Szymańska J . Role of gut microbiota, probiotics and prebiotics in the cardiovascular diseases. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland). (2021) 26:1172. doi: 10.3390/molecules26041172
194.
Xue Z Li R Liu J Zhou J Zhang X Zhang T et al . Preventive and synbiotic effects of the soluble dietary fiber obtained from Lentinula edodes byproducts and Lactobacillus plantarum LP90 against dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis in mice. J Sci Food Agric. (2023) 103:616–26. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.12173
195.
Yu F Hu X Ren H Wang X Shi R Guo J et al . Protective effect of synbiotic combination of Lactobacillus plantarum SC-5 and olive oil extract tyrosol in a murine model of ulcerative colitis. J Transl Med. (2024) 22:308. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05026-9
196.
Rufino MN da Costa AL Jorge EN Paiano VF Camparoto ML Keller R et al . Synbiotics improve clinical indicators of ulcerative colitis: systematic review with meta-analysis. Nutr Rev. (2022) 80:157–64. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuab017
197.
Farah A Paul P Khan AS Sarkar A Laws S Chaari A . Targeting gut microbiota dysbiosis in inflammatory bowel disease: a systematic review of current evidence. Front Med. (2025) 12:1435030. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1435030
198.
Selvamani S Mehta V Ali El Enshasy H Thevarajoo S El Adawi H Zeini I et al . Efficacy of probiotics-based interventions as therapy for inflammatory bowel disease: a recent update. Saudi J Biol Sci. (2022) 29:3546–67. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.02.044
Summary
Keywords
probiotics, inflammatory bowel disease, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, gut microbiota
Citation
Zhang J, Zhang X, Cheng X, Wang S, Lv Y, Zheng X and Wu G (2025) Probiotics in inflammatory bowel diseases: emphasis on mechanisms and clinical application. Front. Med. 12:1620079. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1620079
Received
29 April 2025
Accepted
21 July 2025
Published
01 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Honghua Hu, Macquarie University, Australia
Reviewed by
Fang Liu, University of New South Wales, Australia
Wei Xu, State Oceanic Administration, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Zhang, Cheng, Wang, Lv, Zheng and Wu.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xu Zheng, zhengxu@dmu.edu.cn; Guangzhen Wu, wuguang0613@hotmail.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.