- 1Department of Surgical Sciences, University of Turin, Turin, Italy
- 2Department of Anesthesia, Intensive Care and Emergency, Anestesia e Rianimazione 1U, Città della Salute e della Scienza Hospital, Turin, Italy
- 3SSCVD Trapianto Cellule Staminali, Città della Salute e della Scienza Hospital, Turin, Italy
Background: Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a rare life-threatening syndrome characterized by hyperinflammation caused by abnormally activated macrophages and cytotoxic T cells overlapping with sepsis and multi-organ disfunction (MOD). Its frequency is probably underestimated.
Methods: Patients’ data were extracted from a literature search performed on PubMed (MEDLINE) and EMBASE using the following search terms: “Hemophagocyitic Lymphohistiocytosis” OR “HLH” OR “MACROPHAGE ACTIVATING SYNDROME” OR “MAS” AND “Intensive Care Unit” OR “Critical Care” OR “ICU.” Search was limited to articles published after 2014, when HScore was proposed.
Results: We found 126 case reports and case series for a total of 148 patients with an overall mortality of 47.5%. Main triggers were infections (111 patients; 88.1%) followed by dysimmune disorders (29 patients; 19.7%) and hematological malignancies (20 patients; 13.6%). The following factors were associated with increased ICU mortality: viral infection (76 patients; 52.8%) p = 0.0071 and p = 0.0086 at multivariate analysis for SARS-CoV-2, hematological malignancies (p = 0.0035 at univariate analysis; p = 0.0083 at multivariate analysis), invasive mechanical ventilation (116 patients; 83.3%) p = 0.0060 at univariate analysis not confirmed in multivariate analysis (p = 0.0599). Corticosteroids were associated with reduced ICU mortality at univariate analysis (86 patients; 59.7% p = 0.0250) not confirmed at multivariate analysis (p = 0.7196).
Conclusion: Evidence from our analysis confirms the severity and rapid evolution of HLH, suggesting the importance of prompt clinical suspicion. Since HLH can be found in different hospital settings, including ICU, we believe that this syndrome should be considered in differential diagnosis for all patients presenting with MOD with unclear etiology. Development of specific diagnostic and therapeutic schemes should be considered a priority.
Background
Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) is a syndromic disorder characterized by severe hyperinflammation and immune dysfunction with concomitant immune system activation (1).
Although rare, the exact frequency of HLH within the general and critical care population is unknown. However, HLH often requires supportive care management in ICUs (>60% in pediatric HLH cases) with high mortality rates (36–40% of pediatric cases and 41–68% of adult cases) (1).
Classically, HLH is categorized as primary (pHLH) and secondary (sHLH), although significant overlap exists (2). pHLH is caused by genetic mutations inherited in homozygous or compound heterozygous pattern, resulting in disruptive mutations that fully eliminate the function of cytotoxic T cells and NK cells. pHLH is also associated with various immunodeficiency disorders. Anyway, the diagnosis of pHLH cannot be excluded in patients older than 1 year.
Secondary or acquired HLH (sHLH) is induced by triggers such as infection, malignancy, rheumatologic disease, allogenic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), CAR-T therapy (3), drug hypersensitivity or other underlying causes. The immune dysfunction in sHLH is characterized by reversible natural killer (NK) or CD8 + T cell dysfunction, which occurs in some viral infections or rheumatologic disorders, or by NK-cell deficiency, which can occur after chemotherapy or during sepsis.
The diagnosis of HLH in the ICU may be challenging due to lack of specific laboratory, radiologic and histopathologic findings [bone marrow hemophagocytosis may be observed in the absence of proven hemophagocytic syndrome, in particular after blood transfusion or in sepsis (4)], and above all, due to the overlap of its clinical features with the Multi-Organ Disfunction syndrome (MOD) that characterizes the majority of ICU admission.
Scores considering clinical and laboratory finding have been developed for HLH diagnosis and their use is suggested in the ICU setting (4, 5).
Suggested treatment strategies are based on HLH-2004 protocols including high dose corticosteroids, etoposide and cyclosporine, followed by adjunctive/rescue therapy such as intravenous immunoglobulin, plasmapheresis and tocilizumab (1, 5). However, these therapeutic protocols are borrowed from pediatric and hematology guidelines and only scattered studies with data regarding ICU treatment have been reported. A growing interest and novel awareness about this syndrome are spreading among ICU physicians.
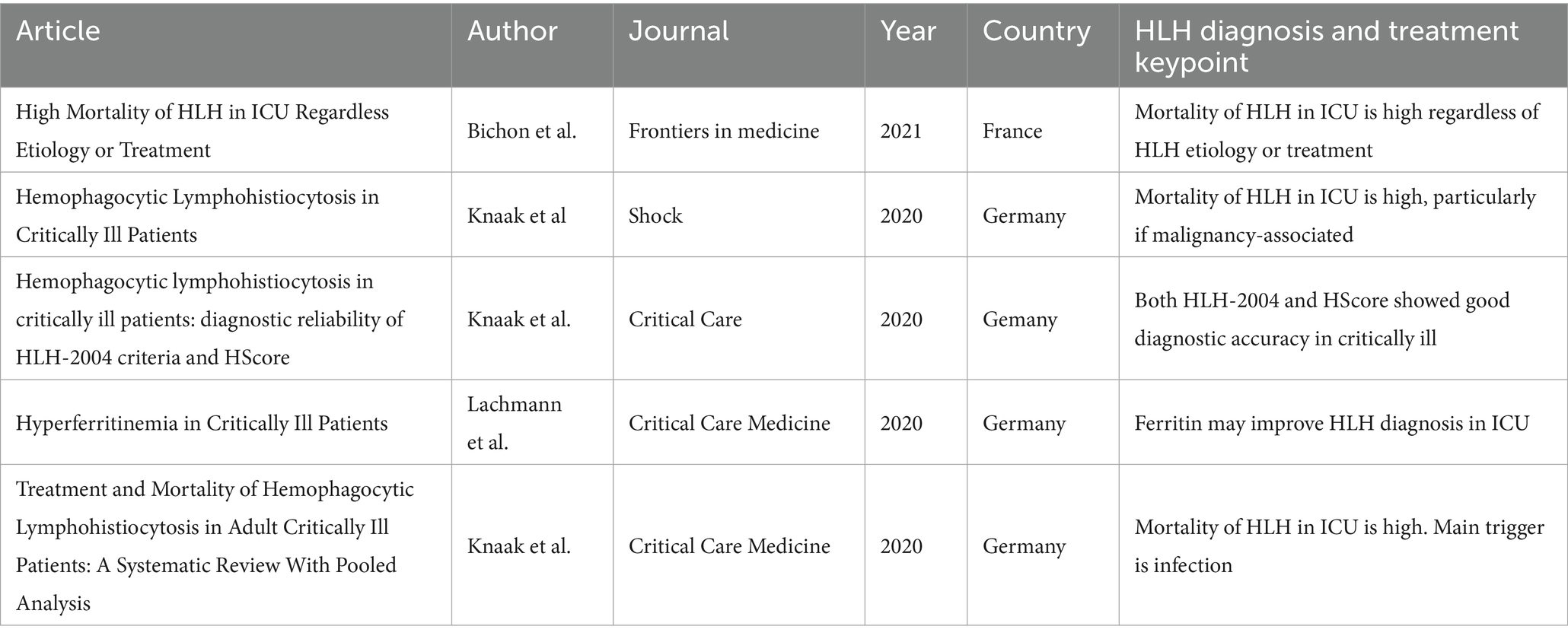
Previous observational studies and reviews have been realized in ICU patients in recent years. Table 1 provides an overview of major studies conducted in ICU settings with large cohorts of HLH patients, which offer important perspectives. However, case series and case reports were excluded from the considered literature, although they might have a complementary role in identifying knowledge gaps and generating hypotheses that can inform both clinical practice and future prospective research.
For this reason, here we present results from a literature search on case series and case reports, aimed at describing epidemiology, risk factors, diagnostics test, triggers, treatment modalities and outcomes of HLH patients treated in the ICU. Specifically, our narrative review highlights rare or atypical presentations, diagnostic delays, and treatment challenges that may not be fully captured in large databases or registry-based analyses.
Methods
Review search algorithm
Literature search in PubMed (MEDLINE) and EMBASE databases has been performed on June 22, 2024, using the following search terms: (“Hemophagocyitic Lymphohistiocytosis” OR “HLH” OR “Macrophaghe Activation Syndrome” or “MAS”) AND (“Intensive Care Unit” OR “Critical Care” OR “ICU”). Only articles published after 2014—the year of publication of HScore (4), suggested by the Society of Critical Care Medicine for the diagnosis of HLH in intensive care—were taken into consideration.
Given the narrative nature of our work, protocol registration was not undertaken.
Review study selection
All case reports and case series on patients ≥ 16 years old admitted to ICU for HLH published in English were evaluated (Figure 1). Eligible studies were those including patients with a positive diagnostic score, such as HScore or HLH-2004, for HLH or if HLH diagnosis was reported by paper’s author. In all cases where data regarding clinical course, treatment or outcome were not fully described, corresponding authors were contacted to obtain missing data. Screening of suitable articles was performed manually by two authors who independently reviewed titles and abstracts, with disagreements regarding inclusion in the review was resolved by discussion.
HLH triggers were assigned to predefined categories: viral, bacterial or fungal infection, dysimmune disease, hematologic or solid malignancy, pregnancy related. Data regarding infectious triggers were then divided into sub-categories when the trigger was reported in more than five patients. Specific pharmacological and non-pharmacological treatment was grouped if such treatment was reported in more than five patients. Mortality was categorized into 7-day, 14-day and overall ICU mortality.
Statistical analysis
Values are presented as means and standard deviation or frequency and proportion. Comparison between groups was made using the t-test or Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney for and Chi square or Fisher exact test was applied as appropriate. Possible independent risk factors of ICU mortality were tested performing a multivariable logistic model estimating the ODDS RATIO (OR) and the 95% confidence interval (CI 95%). All statistical tests were two-sided and p values of 0.05 or less were considered statistically significant. Statistical analyses were conducted using the SAS software package (SAS Institute, Cary, NC; version 9.4).
Results
Review and pooled analysis results
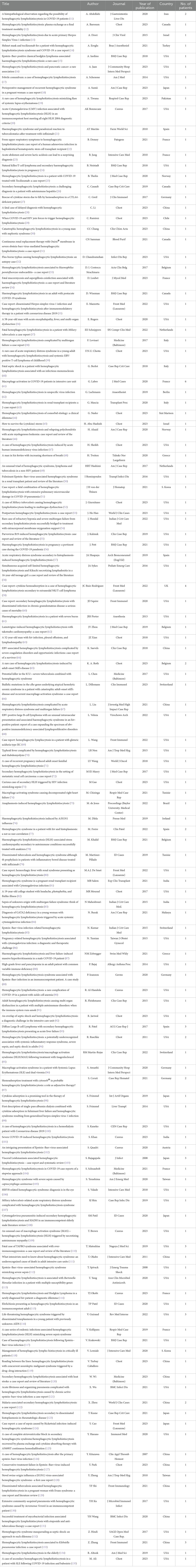
Literature search identified 391 papers: 260 were excluded not being conducted in ICU or including pediatric population, 2 not being written in English, 1 being withdrawn and 2 not reporting enough data, even after the investigation with Authors. Fifty-five articles came from North America (43.6%), 35 from Europe (27.8%), 27 from Asia (21.6%), 3 from South America (2.4%), 3 from Middle East (2.4%) and 2 from Africa (1.6%) (Table 2).
Overall, data on suspected triggers, diagnostic workup, treatment and mortality were available for 146 patients with a mean age of 45 [±17] years.
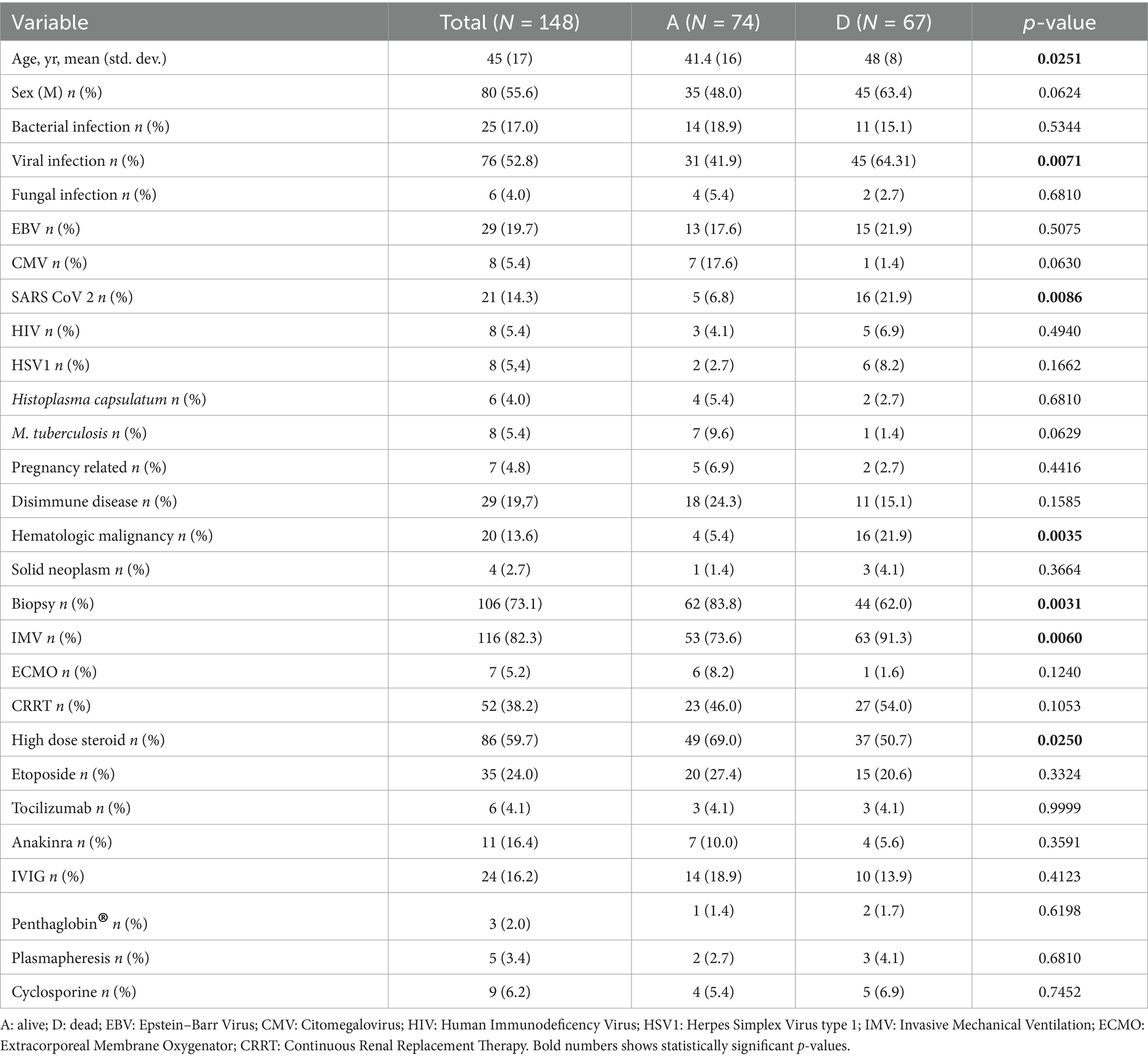
Overall mortality was 47.5%: 25 (19.2%) and 30 (23.8%) patients died before 7 and 14 days from ICU admission, respectively. Age was significantly higher in non-survivors (p = 0.0251) at univariate analysis (Table 3) but not at multivariate analysis (Table 4).
Diagnosis was performed using the composite score (HLH-2004, HScore) in 78 (52.70%) patients; clinical suspicion or direct hematology referral in 62 (41.9%) cases and was only autoptic in 6 (4.05%) cases.
Bone marrow biopsy (BMB) was performed on 108 (74.0%) patients and this subgroup was found to have a lower ICU mortality (p = 0.003).
Triggers
The most frequent suspected triggers were infections (106), followed by dysimmune disorders (30), malignancies (24), HIV (8) and pregnancy (7). Seventy-six patients had viral infection, 24 had bacterial infection and 6 fungal infections.
The most represented pathogens were Epstein–Barr virus (EBV, 29; 19.7%), SARS-CoV-2 (21; 14.3%) and Citomegalovirus (CMV, 8; 5.4%).
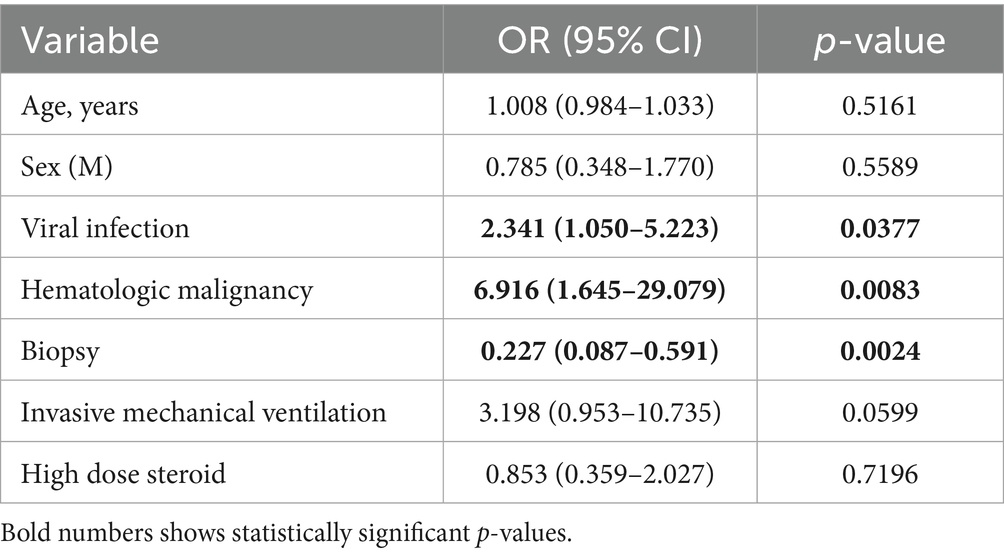
Viral infection was found to have a significant correlation with ICU mortality (p = 0.0377) at multivariate analysis.
The trigger factor was found to be hematologic malignancy in 20 (13.6%) patients and malignancy overall in 24 (16.3%).
All patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (8; 5.4%) had clinical and/or laboratory criteria defining acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS).
ICU mortality was found to be significantly correlated with viral infection (p = 0.0071) and SARS-CoV-2 (p = 0.0086) at univariate analysis. Hematologic malignancy was also statistically correlated with mortality at both univariate (p = 0.0035) and multivariate (p = 0.0083) analysis.
Treatment
One hundred and sixteen patients (82.3%) were treated with invasive mechanical ventilation, 52 required continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT) (38.2%), 7 (5.2%) extracorporeal membrane oxygenator (ECMO) namely veno-venous ECMO in 6 patients and veno-arterial ECMO for cardiogenic shock in 1 patient.
Invasive mechanical ventilation was statistically associated with ICU mortality at univariate analysis (p = 0.0060) but not at multivariate analysis (p = 0.0599).
The most used pharmacological treatment were corticosteroids (86 cases; 59.7%), etoposide (35; 23.6%), intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) (24; 16.2%). Only corticosteroids use was associated with a reduction in ICU mortality (p = 0.0250) at univariate analysis but not at multivariate analysis (p = 0.7196).
Discussion
HLH is an under-recognized, life-threatening syndrome requiring prompt but challenging diagnosis and treatment, especially in the ICU context. Although limited data exist on critically ill adult with HLH, in recent years there has been a growing interest in understanding the epidemiology and outcomes of this condition (1, 6). A large retrospective study conducted in a French ICU and a German pooled analysis already showed clinical relevance of HLH in intensive care setting, highlighting most relevant triggers and clinical features of critically ill patients with HLH.
In this paper we reviewed the evidence from 126 case reports and case series that analyzed cases of HLH in the ICU.
Most of the articles included in our analysis come from North America and Europe and this geographical distribution could be explained by the poor availability of clinical and laboratory resources in low-and middle-income countries.
Included patients were mainly male, in line with data reported in the literature (1, 7).
The mortality we observed in this analysis is also in line with the values reported in other studies on severe patients with HLH without any significant differences being observed between the genders.
Although age at the univariate analysis seems to be correlated with mortality, the limited sample size probably did not allow us to confirm the data at the multivariate analysis. On the other hand, viral infections appear to explain a significant increase in mortality and among viral infections those induced by SARS-CoV-2 seem to be particularly important, probably due to the intense inflammatory pattern brought about by COVID-19. It should also be considered that the growing interest in HLH in recent years coincides with the pandemic period and the growing research activity related.
Viral infection, and particularly that induced by EBV, appears to have a more significant impact than reported by other works conducted both in ICU and outside (6, 7). However, it was not possible to identify a statistically higher mortality in the EBV group.
We observed a frequency of autoimmune disease in line with data reported in the literature. Hematologic malignancy accounted for a small share of triggers (12,2%) even in comparison with other studies on ICU and non-ICU population (6, 7), but strongly correlated with higher mortality. Hematologic patients requiring ICU admission are burdened with a constant increase in mortality regardless of diagnosis (8). In this context HLH in patients with hematologic malignancy can be seen as the progression of patients characterized by massive immunological dysregulation to multi-organ failure.
Almost two-third of patients underwent BMB or biopsy of other immune tissues and this cohort showed a significantly lower mortality. It can be assumed that this confirms the role of histopathology as a fundamental criterion used by clinicians to establish diagnosis and start a specific treatment for HLH. However, it should be noted that also composite scores (especially HScore) proved to be able to correctly guide clinical decision with sufficiently good sensitivity and specificity.
No treatment, except for high dose corticosteroids, has been shown to significantly reduce mortality and even this efficacy has not been confirmed by multivariate analysis or found in other studies.
This could be explained by at least two reasons: first, HLH treatments – both pharmacological and non-pharmacological – lack of standardization and the choice of their use is left to single centers expertise, second, all these therapies draw their efficacy from hematology setting and may not be as effective for critically ill patients. Aside from standard treatments suggested by available guidelines based on corticosteroids and etoposide as first-line therapy, Ruxolitinib, a Janus Kinase pathways inhibitor, represents a valid etoposide-sparing drug that showed association with favourable outcomes in association with steroids.
Although a previous review (9) highlighted the importance of this syndrome in critical area, specific and updated evidence supporting personalized diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for ICU is still lacking (1). For these reasons, we consider the results of the present work of particular interest in the context of intensive care, since HLH is a condition classically treated and studied by hematologist who developed a strong diagnostic awareness and standardized treatment protocols. Furthermore, the differential diagnosis of this condition in the critical care context is typically septic shock and/or MOD that accounts for a vast majority of ICU population.
Considering the overall review, our analysis appears to highlight a decidedly significant incidence of HLH, which is progressively increasing over time, in step with the diagnostic awareness of the treating physicians. Diagnostic score, such as HScore, can rapidly lead to HLH diagnosis with a more than acceptable level of certainty even in critically ill patients making HLH rule out easy and feasible when assessing most critical ICU patients.
The growing relevance of laboratory tests—triglycerides, ferritin, etc.—in new diagnostic protocols represents another great clinical clue. In fact, although invasive diagnostic methods are certainly difficult, particularly in critical patients, and require more time for reporting, the combination of clinical and laboratory diagnosis scores represents a feasible option that should be highlighted. Soluble IL2 receptor (CD25) is a simple and under-utilized biomarker for T cell activation in HLH and its use should be encouraged in HLH diagnostic work up. CD25 is also useful for differentiating catastrophic Still’s disease from HLH, as both condition could possibly need intensive care support. However, in our review, we found that these laboratory tests were explicitly reported only in a minority of cases, possibly suggesting how they still need to be implemented in clinical practice.
Data from this literature review show how diagnostic score, such as HScore, can rapidly lead to HLH diagnosis with a more than acceptable level of certainty even in critically ill patients (4, 10). A possible diagnostic and treatment approach for HLH, applicable in the ICU setting, is suggested in Figure 2.
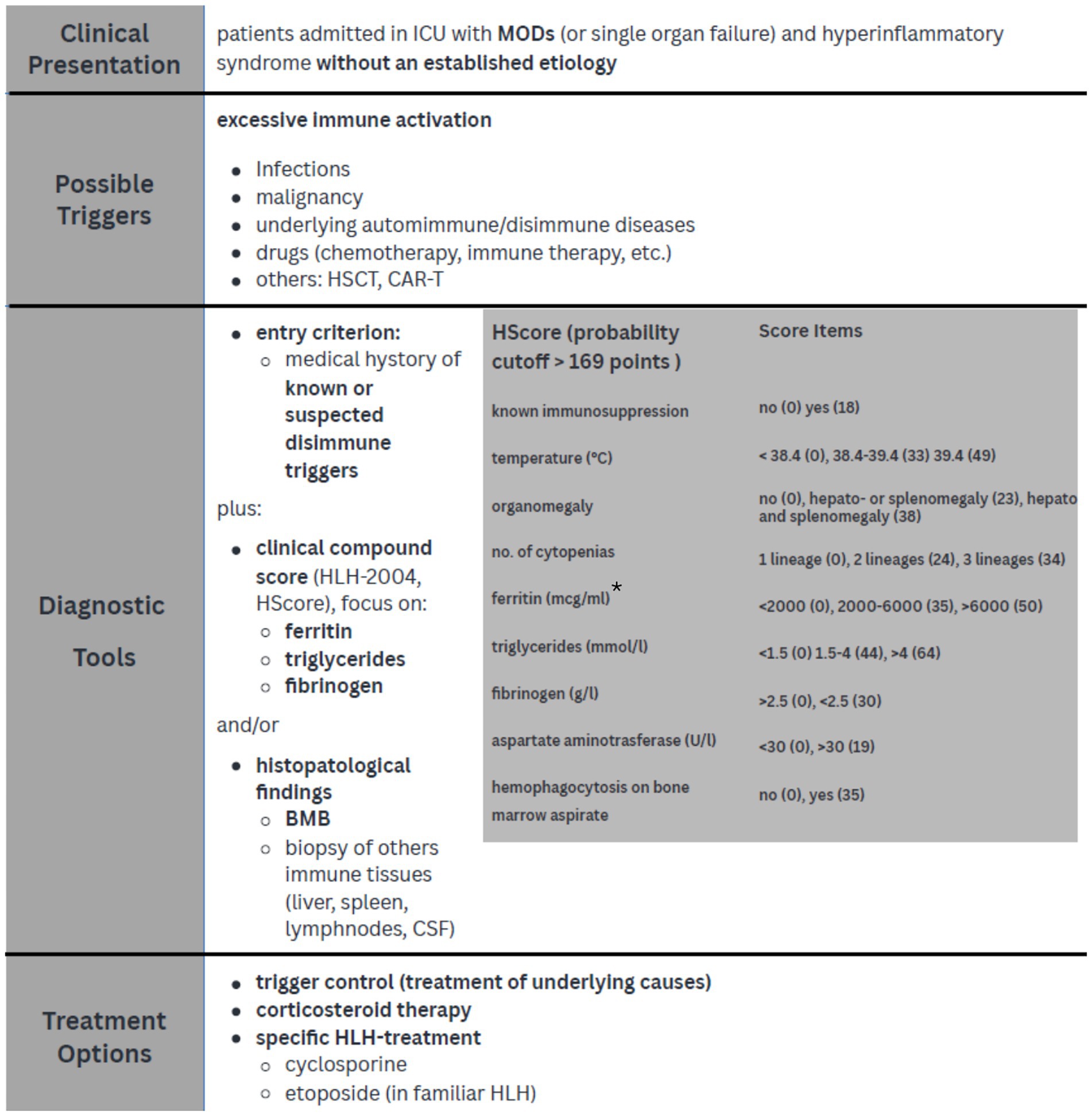
Figure 2. Diagnostic approach and treatment strategies in critically ill patients with HLH. *Knaak et al. demonstrated that a ferritin level > 3,000 μg/L improved diagnostic power when associated with HLH-2004 score; Lachmann et al. suggest that a threshold of 9,000 μg/L is very sensible and specific for HLH diagnosis in ICU SIRS sistemic inflammatory response syndrome; MODs multi organ dysfunction; HSCT hematopoietic stem cell transplantation, CAR-T chimeric antigen receptor T-cell, BMB bone marrow biopsy, CSF cerebrospinal fluid.
Limitations
Our study has several limitations. First, the narrative (non-systematic) approach to data selection, the absence of formal bias assessment, and the inherent limitations of using uncontrolled observational data. In fact, all papers included in our analysis are case report or case series, with risk of survival bias even if overall ICU mortality is in line with other studies about HLH in critical care population.
Given the nature of the included studies, we did not apply formal risk of bias tools, which are typically designed for comparative or interventional studies.
Furthermore, we decided to include in this analysis only articles published after 2014 when HScore has been proposed for HLH diagnosis, to underline the importance of the proposed score and the impact on clinical diagnosis. However, this decision might limit the number of the included articles.
Finally, due to lack of standardized medical treatment for HLH in critical care population, we found strong differences in treatment strategies among different reports, for example in steroid use with different molecules and different regimens, limiting the strength of the treatment indications.
Conclusion
HLH is a syndrome characterized by immune dysregulation and hyperinflammation that can present with multi-organ disfunction. Prompt diagnosis in ICU is particularly challenging due to critical presentation, limited diagnostic options and clinical awareness.
Given that several HLH trigger are extremely frequent in critical patients, HLH should always be considered in patients with MOD or sepsis/septic shock-like clinical presentation without an established etiology and predisposing risk factors for HLH.
This narrative review is deliberately based on case reports and case series, with the aim of evaluating the available ICU-specific literature, limited, but of growing relevance. Despite the underlined limitations, some aspects of great clinical relevance emerge, in particular the association of SARS-CoV-2 and hematologic malignancies with mortality. Diagnostic scores such as HScore or HLH-2004 can help clinicians in identifying HLH especially with the combination of non-invasive laboratory tests, but the relevance of the role of bone marrow biopsy, remain pivotal. In the absence of effective treatment strategies, which continue to be mutuated from hematologic populations, further studies are needed to develop treatment protocols tailored on critical care population.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
GM: Writing – original draft, Supervision, Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Methodology. RT: Writing – review & editing, Investigation, Data curation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. GA: Investigation, Writing – review & editing, Data curation. CB: Writing – review & editing, Data curation. GS: Writing – review & editing. AB: Data curation, Writing – review & editing. VF: Writing – review & editing. CF: Writing – review & editing, Formal analysis. LB: Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Abbreviations
HLH, Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis; ICU, Intensive Care Unit; MOD, Multiorgan Disfunction; MOF, Multiorgan Failure; IMV, Invasive Mechanical Ventilation; CRRT, Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy; IVIG, Intravenous Immunoglobulin; BMB, Bone Marrow Biopsy; AKI, Acute Kidney Injury; ALF, Acute Liver Failure; ARF, Acute Respiratory Failure; URTI, Upper Respiratory Tract Syndrome; AIDS, Acquired Immunodeficency Syndrome; ECMO, Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenator; CAR-T, Chimeric Antigen Receptor – T cell; CSF, Cerebrospinal Fluid.
References
1. Hines, MR, Von Bahr Greenwood, T, Beutel, G, Beutel, K, Hays, JA, Horne, A, et al. Consensus-based guidelines for the recognition, diagnosis, and management of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill children and adults. Crit Care Med. (2022) 50:860–72. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000005361
2. Hines, MR, Knight, TE, Mcnerney, KO, Leick, MB, Jain, T, Ahmed, S, et al. Transplantation and cellular therapy immune effector cell-associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis-like syndrome. Transplant Cell Ther. (2023) 29:438.e1–438.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.jtct.2023.03.006
3. Sandler, RD, Tattersall, RS, Schoemans, H, Greco, R, Badoglio, M, Labopin, M, et al. Diagnosis and management of secondary HLH/MAS following HSCT and CAR-T cell therapy in adults; a review of the literature and a survey of practice within EBMT centres on behalf of the autoimmune diseases working party (ADWP) and transplant complications w. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00524
4. Fardet, L, Galicier, L, Lambotte, O, Marzac, C, Aumont, C, Chahwan, D, et al. Development and validation of the hscore, a score for the diagnosis of reactive hemophagocytic syndrome. Arthritis Rheumatol. (2014) 66:2613–20. doi: 10.1002/art.38690
5. Egeler, RM, Webb, D, Winiarski, J, and Janka, G. HLH-2004: diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatric Blood and Cancer. (2007) 48:124–31. doi: 10.1002/pbc.21039
6. Abdelhay, A, Mahmoud, AA, Al Ali, O, Hashem, A, Orakzai, A, and Jamshed, S. Epidemiology, characteristics, and outcomes of adult haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the USA, 2006–19: a national, retrospective cohort study. eClinicalMed. (2023) 62:102143. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2023.102143
7. Knaak, C, Schuster, FS, Nyvlt, P, Spies, C, Feinkohl, I, Beutel, G, et al. Treatment and mortality of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in adult critically ill patients: a systematic review with pooled analysis. Crit Care Med. (2020) 48:1137–46. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000004581
8. Lafarge, A, Chean, D, Whiting, L, Jehl, RC, and Recherche, D. Management of hematological patients requiring emergency chemotherapy in the intensive care unit. Intensive Care Med. (2024) 50:849–60. doi: 10.1007/s00134-024-07454-z
9. Knaak, C, Schuster, FS, Spies, C, Vorderwülbecke, G, Nyvlt, P, Schenk, T, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in critically ill patients. Shock. (2020) 53:701–9. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000001454
10. Bichon, A, Bourenne, J, Allardet-Servent, J, Papazian, L, Hraiech, S, Guervilly, C, et al. High mortality of HLH in ICU regardless etiology or treatment. Frontiers in medicine. (2021) 8:735796. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.735796
11. Abdollahi, A, Beigmohammadi, MT, Safaei, M, Mehrtash, V, and Jafarzadeh, B. A histopathological observation regarding the possibility of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in COVID-19 patients. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. (2020) 29:475–6. doi: 10.15403/jgld-2934
12. Barsoum, A, Lam, J, Saleh, M, and Mohamed, H. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: plasma exchange as a final treatment modality. Chest. (2023) 164:A2724–5. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1801
13. Drori, A, Ribak, Y, van Heerden, PV, Meir, K, Wolf, D, and Safadi, R. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis due to acute primary herpes simplex virus 1 infection. J Clin Virol. (2015) 68:6–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2015.04.013
14. Eroglu, A, Kartal, S, and Saral, OB. Helmet mask and tocilizumab for a patient with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis syndrome and COVID-19: a case report. Braz J Anesthesiol. (2021) 71:79–83. doi: 10.1016/j.bjane.2020.10.009
15. Iardino, A, Amar, Z, and Ahmed, Y. Epstein-Barr-positive classical Hodgkin lymphoma-associated haemophagocytic lymphohistocytiosis: a rare case. BMJ Case Rep Published online August 14. (2018):bcr-2018-225262. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-225262
16. Jaan, A, Khalid, F, Ahmed, AMF, Salman, A, Meghal, T, and Du, D. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and pancreatic cancer: a rare association. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. (2023) 13:68–71. doi: 10.55729/2000-9666.1225
17. Schenone, A, Bandyopadhyay, D, Panchabhai, TS, Mireles-Cabodevilla, E, Duggal, A, and Krishnan, S. Febrile conundrum: a case of Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Am J Med. (2014) 127:1164–6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2014.09.006
18. Sumii, A, Miyoshi, H, Kato, T, Otsuki, S, Horikawa, YT, Satomi, S, et al. Perioperative Management of Recurrent Hemophagocytic Syndrome in a pregnant woman: a case report. Am J Case Rep. (2023) 24:e939369. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.939369
19. Tiwana, A, Tiwana, M, Wang, J, and Khawar, MU. A rare case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis mimicking flare of systemic lupus erythematosus. Respirol Case Rep. (2023) 11:e01140. doi: 10.1002/rcr2.1140
20. Bonnecaze, A, Willeford, WG, Lichstein, P, and Ohar, J. Acute cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection associated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) in an immunocompetent host meeting all eight HLH 2004 diagnostic criteria. Cureus. (2017) 9:e1070. doi: 10.7759/cureus.1070
21. Mariño, AT, Sánchez, EC, Castro, NML, and Bobo, MTI. Haemophagocytic syndrome and paradoxical reaction to tuberculostatics after treatment with infliximab. Pharm World Sci. (2010) 32:117–9. doi: 10.1007/s11096-010-9369-x
22. Demey, B, Brault, C, Maizel, J, and Francois, C. From upper respiratory symptoms to Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: case report of a human adenovirus infection in Haploidentical hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipient. Pathogens. (2021) 10:340. doi: 10.3390/pathogens10030340
23. Jung, B, Zoric, L, Chanques, G, Konate, A, Nocca, D, and Jaber, S. Acute abdomen and severe lactic acidosis can lead to a surprising diagnosis. Intensive Care Med. (2010) 36:169–70. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1631-0
24. Neistadt, B, Carrubba, A, and Zaretksy, MV. Natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and secondary haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in pregnancy. BMJ Case Rep Published online September 15. (2018):bcr2018224832:2018. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224832
25. Tholin, B, Hauge, MT, Aukrust, P, Fehrle, L, and Tvedt, TH. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with COVID-19 treated with tocilizumab: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2020) 14:187. doi: 10.1186/s13256-020-02503-9
26. Casault, C, and Posadas-Calleja, JG. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a challenging diagnosis in a patient with autoimmune hepatitis. Case Rep Crit Care. (2019) 2019:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2019/3580796
27. Greil, C, Roether, F, La Rosée, P, Grimbacher, B, Duerschmied, D, and Warnatz, K. Rescue of Cytokine Storm due to HLH by Hemoadsorption in a CTLA4-deficient patient. J Clin Immunol. (2017) 37:273–6. doi: 10.1007/s10875-017-0377-7
28. Li, C. A fatal case of delayed diagnosis with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Chest. (2023) 164:A1977. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1357
29. Ramirez, C, Gonzalez, P, Sanekommu, H, Angelova, EVGENIYA, Patel, PURVI, Abu Homoud, AHMAD, et al. When COVID-19 and HIV join forces to trigger hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Chest. (2023) 164:A2647–A 2648. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1756
30. Chang, C-C, Hsiao, P-J, Chiu, C-C, Chen, YC, Lin, SH, Wu, CC, et al. Catastrophic hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a young man with nephrotic syndrome. Clin Chim Acta. (2015) 439:168–71. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2014.10.025
31. Samman, KN, Baalbaki, H, Bouchard, J, and Albert, M. Continuous renal replacement therapy with oXiris® membrane in severe Ebstein-Barr virus-mediated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: a case report. Blood Purif. (2021) 50:578–81. doi: 10.1159/000511724
32. Chandramohan, D, Awobajo, M, Fisher, O, Dayton, CL, and Anstead, GM. Flea-borne typhus causing Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis: An autopsy case. Infect Dis Rep. (2023) 15:132–41. doi: 10.3390/idr15010014
33. Costescu Strachinaru, DI, Chaumont, M, Gobin, D, Sattar, L, Strachinaru, M, Karakike, E, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated to Haemophilus parainfluenzae endocarditis– a case report. Acta Clin Belg. (2018) 73:220–3. doi: 10.1080/17843286.2017.1341691
34. Loubet, D, Sarton, B, Lelièvre, L, Grouteau, G, Iriart, X, Chauvin, P, et al. Fatal mucormycosis and aspergillosis coinfection associated with haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report and literature review. J Med Mycol. (2023) 33:101325. doi: 10.1016/j.mycmed.2022.101325
35. Mazzotta, E, Fiorda Diaz, J, Echeverria-Villalobos, M, Eisinger, G, Sprauer, S, Singha, A, et al. Case report: disseminated herpes simplex virus 1 infection and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis after immunomodulatory therapy in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019. Front Med. (2022) 9:9. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1053012
36. Rogers, E, Moffet, EW, Huang, S, Ouni, A, Patel, D, Kay, D, et al. A 58-year-old man with acute encephalopathy, fever, and multi-organ dysfunction. Chest. (2020) 158:e187–90. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2020.06.003
37. Schippers, EE, Creemers, SG, Paltansing, S, van Zaanen, HCT, and Heijneman, JAM. Fatal Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with Miliary tuberculosis: a case report. SN Compr Clin Med. (2022) 4:152. doi: 10.1007/s42399-022-01232-y
38. Lovisari, F, Terzi, V, Lippi, MG, Brioschi, PR, and Fumagalli, R. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis complicated by multiorgan failure. Medicine (Baltimore). (2017) 96:e9198. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000009198
39. Chesta, F, and Matsuda, BJ. A rare case of acute respiratory distress syndrome in a young adult with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and systemic EBV-positive T-cell lymphoma of childhood. Chest. (2023) 164:A2824. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1858
40. Berlot, G, Tomasini, A, Zandonà, L, Leonardo, E, Bussani, R, and Zarrillo, N. Fatal septic shock in a patient with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with an infectious mononucleosis. Case Rep Crit Care. (2018) 2018:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2018/9756050
41. Labro, G, Jandeaux, LM, Rusu, A, Virot, E, Pointurier, V, Pinto, L, et al. Macrophage activation in COVID-19 patients in intensive care unit. J Med Cases. (2020) 11:211–4. doi: 10.14740/jmc3520
42. Lachmann, G, Knaak, C, La Rosée, P, Spies, C, Nyvlt, P, Oberender, C, et al. Hämophagozytische Lymphohistiozytose bei unspezifischer Virusinfektion. Anaesthesist. (2019) 68:626–32. doi: 10.1007/s00101-019-00634-3
43. Mascia, G, Argiolas, D, Carta, E, Ibba, S, and Piredda, GB. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in renal transplant recipients: a 2-case report. Transplant Proc. (2020) 52:1566–9. doi: 10.1016/j.transproceed.2020.02.047
44. Nader, G, Al-Deen Alattal, S, Ghnaima, H, Chennupati, S, Shaban, D, and Ely, JR. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis of comorbid etiology: a clinical dilemma. Chest. (2023) 164:A2780–A 2781. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1832
45. Abu-Hashish, H, Ang, G, Abuhashish, H, and Jung, G. How to survive the (cytokine) storm. Chest. (2023) 164:A2213–A 2214. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1497
46. Alsaid, HM, Wahdan, AAM, Tahboub, IN, and Almakadma, NM. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and relapsing Polychondritis with acute Myelogenous leukemia: case report and review of the literature. Am J Case Rep. (2020) 21:e925287. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.925287
47. Sheikh, H, Lim, S, and Davidovich, AE. A case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis induced by acute human immunodeficiency virus infection. Chest. (2023) 164:A2912–3. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1909
48. Tveiten, H, Lehne, G, Aukrust, P, Rodriguez, JR, and Skjønsberg, OH. En mann i 40-årene med økende pustevansker. Tidsskr Den Nor Legeforen. (2020) 140. doi: 10.4045/tidsskr.19.0692
49. Hashmi, HRT, Mishra, R, Niazi, M, Venkatram, S, and Diaz-Fuentes, G. An unusual triad of Hemophagocytic syndrome, lymphoma and tuberculosis in a Non-HIV patient. Am J Case Rep. (2017) 18:739–45. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.903990
50. Romiopoulos, I, Pyrpasopoulou, A, Onoufriadis, I, Massa, E, Mouloudi, E, Kydona, C, et al. Fulminant Epstein–Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome in a renal transplant patient and review of the literature. Transpl Infect Dis. (2016) 18:795–800. doi: 10.1111/tid.12586
51. von der Thüsen, JH, van Bommel, J, Kros, JM, Verdijk, RM, Lopuhaä, B, Lam, KH, et al. Case report: a fatal combination of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with extensive pulmonary microvascular damage in COVID-19 pneumonia. J Hematop. (2021) 14:79–83. doi: 10.1007/s12308-020-00423-7
52. Giurintano, J, Koger, T, Sohmer, J, and Neupane, A. A case of miliary tuberculosis causing hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis leading to multiorgan dysfunction. Chest. (2023) 164:A2902–3. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1904
53. An, JH, and Ahn, JH. Postpartum hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report. World J Clin Cases. (2023) 11:6183–8. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i26.6183
54. Jaiswal, A, Hundal, J, Bowers, D, and Gadela, NV. Rare case of refractory hypoxia and severe multiorgan failure from secondary Lymphohistiocytosis successfully bridged to treatment with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2022) 26:970–3. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-24284
55. Kalmuk, J, Matar, S, Feng, G, Kilb, E, and Lim, MY. Parvovirus B19-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: case report and review of the literature. Clin Case Reports. (2019) 7:2076–81. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.2401
56. Potts, J, Gaudet, B, Durie, D, and Quinones, J. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in pregnancy: a pertinent case during the COVID-19 pandemic. BMJ Case Rep. (2021) 14:e244716. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-244716
57. Huapaya, JA, Yogiaveetil, E, Qamer, S, Sidawy, M, and Anderson, E. Acute respiratory distress syndrome secondary to histoplasmosis-induced Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Arch Bronconeumol. (2019) 55:446–7. doi: 10.1016/j.arbres.2018.12.011
58. Sykes, JA, Badizadegan, K, Gordon, P, Sokol, D, Escoto, M, ten, I, et al. Simultaneous acquired self-limited Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis and Kikuchi necrotizing lymphadenitis in a 16-year-old teenage girl. Pediatr Emerg Care. (2016) 32:792–8. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000000560
59. Ruiz-Rodríguez, JC, Chiscano-Camón, L, Ruiz-Sanmartin, A, Palmada, C, Bajaña, I, Iacoboni, G, et al. Case report: cytokine hemoadsorption in a case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Front Med. (2022) 9:9. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.925751
60. Squire, JD, Vazquez, SN, Chan, A, Smith, ME, Chellapandian, D, Vose, L, et al. Case report: secondary Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis with disseminated infection in chronic granulomatous disease—a serious cause of mortality. Front Immunol. (2020) 11:11. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.581475
61. Porter, JRS, Handy, J, Yarranton, H, and Gurney, S. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a patient with severe burns. Anaesthesia. (2013) 68:413–6. doi: 10.1111/anae.12062
62. Zhou, JY, Martinez, JA, and Shen, JP. Lamotrigine-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2019) 13:345. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-2295-1
63. Xian, JZ, Cherian, SV, Golardi, N, and Estrada-Y-Martin, RM. A 32-year-old man with HIV infection, pleural effusions, and lymphadenopathy. Chest. (2018) 154:e147–51. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.05.013
64. Saevels, K, Robert, D, Van den Broeck, S, Malfait, R, Gadisseur, A, Jorens, P, et al. EBV−associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis complicated by severe coagulation disorders and opportunistic infections: case report of a survivor. Clin Case Reports. (2018) 6:115–8. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.1301
65. Roth, KA, and Mousbah Al-Tabbaa, M. A rare case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-induced by adult-onset stills disease. Chest. (2023) 164:A1888–A 1889. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1302
66. Dillemans, L, Bekhuis, Y, Betrains, A, Yu, K, van Hemelen, M, Pörtner, N, et al. Biallelic mutations in the CFHR genes underlying atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome in a patient with catastrophic adult-onset still’s disease and recurrent macrophage activation syndrome: a case report. Clin Immunol. (2023) 257:109815. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2023.109815
67. Liu, L, Bashir, H, Awada, H, Alzubi, J, and Lane, J. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis complicated by acute respiratory distress syndrome and multiorgan failure. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. (2021) 9:1–5. doi: 10.1177/23247096211052180
68. Veloza, L, Tsai, C-Y, Bisig, B, Pantet, O, Alberio, L, Sempoux, C, et al. EBV-positive large B-cell lymphoma with an unusual intravascular presentation and associated haemophagocytic syndrome in an HIV-positive patient: report of a case expanding the spectrum of EBV-positive immunodeficiency-associated lymphoproliferative disorders. Virchows Arch. (2022) 480:699–705. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03142-1
69. Huang, L, Wu, W, Zhu, Y, Yu, H, Tang, L, and Fang, X. Case report: Hemophagocytic lymphocytosis in a patient with Glutaric aciduria type IIC. Front Immunol. (2022) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.810677
70. Non, LR, Patel, R, Esmaeeli, A, and Despotovic, V. Typhoid fever complicated by hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and rhabdomyolysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. (2015) 93:1068–9. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0385
71. Wang, LY, Hu, J, Ramsingh, G, Theodory, B, Yaghmour, B, Vergara-Lluri, M, et al. A case of recurrent pregnancy-induced adult onset familial Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. World J Oncol. (2018) 9:123–7. doi: 10.14740/wjon1145w
72. El-Masry, M, Eisenbud, L, and Tran, M-H. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in the setting of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a case report. J Med Case Rep. (2017) 11:56. doi: 10.1186/s13256-016-1196-9
73. Gao, M, Wong, A, Vo, C, Alkoutami, SS, Astua, AJ, and Policar, M. Curious case of secondary HLH triggered by HIV infection mimicking sepsis. Chest. (2023) 164:A2265–6. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1527
74. Chizinga, M, Kalra, SS, Innabi, A, Rackauskas, M, Ataya, A, and Emtiazjoo, A. Macrophage activating syndrome causing decompensated right heart failure. Respir Med Case Rep. (2021) 33:101409. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2021.101409
75. de Jesus, M, Lopez, A, Yabut, J, Vu, S, Manne, M, Ibrahim, L, et al. Anaplasmosis-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Baylor Univ Med Cent Proc. (2022) 35:379–81. doi: 10.1080/08998280.2022.2039046
76. Dlela, M, Turki, O, Bahloul, M, Kallel, H, Jedidi, I, and Bouaziz, M. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis induced by a/H1N1 influenza. Presse Med. (2019) 48:576–8. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2019.02.034
77. Freire, M, Carvalho, V, Spener, R, da Silva, CR, da Silva Neto, JR, Carlos Ferreira, L, et al. Hemophagocytic syndrome in a patient with HIV and histoplasmosis: a not so rare correlation. Clin Pathol. (2022) 15:15. doi: 10.1177/2632010X221118059
78. Khalid, M, Abdalla, A, McCarthy, G, and Stack, J. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)-associated stress cardiomyopathy secondary to autoimmune conditions successfully treated with anakinra. BMJ Case Rep. (2021) 14:e246416. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2021-246416
79. Martínez-Pillado, M, Varela-Durán, M, Said-Criado, I, Díaz-Parada, P, Rodríguez-Losada, M, and Mendoza-Pintos, M. Disseminated tuberculosis and hemophagocytic syndrome although TB prophylaxis in patients with inflammatory bowel disease treated with infliximab. IDCases. (2019) 16:e00518. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2019.e00518
80. De Smet, MAJ, Bogaert, S, Schauwvlieghe, A, Dendooven, A, Depuydt, P, and Druwé, P. Case report: hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome presenting as hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Front Med. (2022) 9:9. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.1096900
81. Ben Salem, M, Bchir, S, Taieb, SK, Hamouda, M, Mezrigui, R, Ben Saleh, M, et al. Hemophagocytic syndrome in a pregnant renal transplant recipient associated with cytomegalovirus infection. Exp Clin Transplant. (2021) 19:739–43. doi: 10.6002/ect.2021.0041
82. Mourad, MR, Siwoski, OM, and Brownback, KR. A 19-year-old college student with headache, photophobia, and flulike illness. Chest. (2017) 151:e95–8. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2016.10.047
83. Mandal, AK, and Maheshwari, N. Sepsis of unknown origin with multiorgan failure syndrome: think of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2015) 19:419–21. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.160291
84. Burak, N, Jan, N, Kessler, J, Oei, E, Patel, P, and Feldman, S. Diagnosis of GATA2 deficiency in a young woman with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis triggered by acute systemic cytomegalovirus infection. Am J Case Rep. (2021) 22:e927087. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.927087
85. Singh, S, Mehta, C, Kumar, N, and Sarma, S. Epstein-Barr virus infection-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Indian J Crit Care Med. (2015) 19:416–8. doi: 10.4103/0972-5229.160290
86. Tumian, NR, and Wong, CL. Pregnancy-related hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with cytomegalovirus infection: a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. (2015) 54:432–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2014.11.023
87. Zellweger, NM, Huber, J, Tsakiris, DA, Tzankov, A, Gebhard, CE, and Siegemund, M. Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and liver failure-induced massive hyperferritinaemia in a male COVID-19 patient. Swiss Med Wkly. (2021) 151:w20420. doi: 10.4414/smw.2021.20420
88. Bajaj, P, Clement, J, Bayerl, MG, Kalra, N, Craig, TJ, and Ishmael, FT. High-grade fever and pancytopenia in an adult patient with common variable immune deficiency. Allergy Asthma Proc. (2014) 35:78–82. doi: 10.2500/aap.2014.35.3704
89. Ioannou, P, Akoumianaki, E, Alexakis, K, Proklou, A, Psyllaki, M, Stamatopoulos, E, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis syndrome associated with Epstein-Barr infection in an omnicompetent patient. A case study. Germs. (2020) 10:266–71. doi: 10.18683/germs.2020.1216
90. Al-Handola, R, Abdelkader, K, Karrar, A, Chinnappan, J, and Rode, G. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a rare complication of COVID-19 in a patient with sickle cell anemia. Cureus. (2023) 15:e47631. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47631
91. Fleischmann, R, Böhmerle, W, von Laffert, M, Jöhrens, K, Mengel, A, Hotter, B, et al. Adult hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis causing multi organ dysfunction in a patient with multiple autoimmune disorders: when the immune system runs amok. Clin Case Reports. (2016) 4:165–70. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.467
92. Jariwal, R, Thomas, J, Reihani, AR, Mehta, A, and Medani, A. An overlap of septic shock and hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a diagnostic challenge in the intensive care unit. Chest. (2023) 164:A2006–7. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1376
93. Patel, R, Patel, H, Mulvoy, W, and Kapoor, S. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis presenting as acute liver failure. ACG Case Rep J. (2017) 4:e68. doi: 10.14309/crj.2017.68
94. Raschke, RA, and Garcia-Orr, R. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis. Chest. (2011) 140:933–8. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-0619
95. Martín-Rojas, RM, Gómez-Centurión, I, Bailén, R, Bastos, M, Diaz-Crespo, F, Carbonell, D, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis/macrophage activation syndrome (HLH/MAS) following treatment with tisagenlecleucel. Clin Case Reports. (2022) 10:e05209. doi: 10.1002/ccr3.5209
96. Awasthi, S, and Upreti, S. Macrophage activation syndrome in a patient with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and dual viremia. J Community Hosp Intern Med Perspect. (2020) 10:470–4. doi: 10.1080/20009666.2020.1787811
97. Ceruti, S, Glotta, A, Adamson, H, Mauri, R, and Molnar, Z. Hemoadsorption treatment with Cyto sorb® in probable hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a role as adjunctive therapy? Case Rep Hematol. (2021) 2021:1–5. doi: 10.1155/2021/5539126
98. Frimmel, S, Hinz, M, Schipper, J, Bogdanow, S, Mitzner, S, and Koball, S. Cytokine adsorption is a promising tool in the therapy of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Int J Artif Organs. (2019) 42:658–64. doi: 10.1177/0391398819857444
99. Frimmel, S, Schipper, J, Henschel, J, Yu, TT, Mitzner, SR, and Koball, S. First description of single-pass albumin dialysis combined with cytokine adsorption in fulminant liver failure and hemophagocytic syndrome resulting from generalized herpes simplex virus 1 infection. Liver Transpl. (2014) 20:1523–4. doi: 10.1002/lt.24005
100. Kaneko, S, Inoue, T, Tarumoto, N, Haga, Y, Yokota, K, Yamaguchi, H, et al. A case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in a hemodialysis patient with coronavirus disease 2019. CEN Case Rep. (2023) 12:390–6. doi: 10.1007/s13730-023-00776-9
101. Khan, S, Rizvi, TA, Sadiq, W, Sattar, SBA, and Maroun, R. Severe COVID-19-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cureus. (2023) 15:e34022. doi: 10.7759/cureus.34022
102. Quadri, SP, Jain, NK, Brandon, BL, Modi, H, and Bawaadam, H. An intriguing presentation of Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Cureus. (2020) 12:e9561. doi: 10.7759/cureus.9561
103. Rajagopala, S, Dutta, U, Chandra, KSP, Bhatia, P, Varma, N, and Kochhar, R. Visceral leishmaniasis associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis – case report and systematic review. J Infect. (2008) 56:381–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2008.02.013
104. Schnaubelt, S, Tihanyi, D, Strassl, R, Schmidt, R, Anders, S, Laggner, AN, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis in COVID-19. Medicine (Baltimore). (2021) 100:e25170. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025170
105. Terashima, S, Hayakawa, K, Saito, F, Wada, D, Iwamura, H, Kuro, A, et al. Hemophagocytic syndrome with severe sepsis caused by Capnocytophaga canimorsus. Am J Emerg Med. (2020) 38:1540.e5–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.03.017
106. Valade, S, Fadlallah, J, Martin, JE, and Galicier, L. HHV8-related hemophagocytic syndrome: diagnosis is in the eye. Intensive Care Med. (2019) 45:697–7. doi: 10.1007/s00134-018-5336-0
107. Shiu, S-J, Li, T-T, Lee, B-J, Fu, P-K, Wang, C-Y, and Shiu, S-I. Miliary tuberculosis-related acute respiratory distress syndrome complicated with Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis syndrome. Case Rep Infect Dis. (2019) 2019:1–4. doi: 10.1155/2019/9501610
108. Patil, SM, Beck, PP, Patel, TP, Hunter, MP, Johnson, J, Acevedo, BA, et al. Cytomegalovirus pneumonitis-induced secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and SIADH in an immunocompetent elderly male literature review. IDCases. (2020) 22:e00972. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00972
109. Brown, TS, Vo, G, and Charoenpong, P. An unusual case of macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)- hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) triggered by necrotizing autoimmune myopathy. Cureus. (2023) 15:e38501. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38501
110. Matsuhisa, T, Takahashi, N, Nakaguro, M, Sato, M, Inoue, E, Teshigawara, S, et al. Fatal case of TAFRO syndrome associated with over-immunosuppression: a case report and review of the literature. Nagoya J Med Sci. (2019) 81:519–28. doi: 10.18999/nagjms.81.3.519
111. Okabe, T, Shah, G, Mendoza, V, Hirani, A, Baram, M, and Marik, P. What intensivists need to know about Hemophagocytic syndrome. J Intensive Care Med. (2012) 27:58–64. doi: 10.1177/0885066610393462
112. Spivack, T, Chawla, R, and Marik, P. Epstein-Barr virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome mimicking severe sepsis. J Emerg Trauma Shock. (2008) 1:119–22. doi: 10.4103/0974-2700.43198
113. Yang, T, Mei, Q, Zhang, L, Chen, Z, Zhu, C, Fang, X, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis is associated with Bartonella henselae infection in a patient with multiple susceptibility genes. Ann Clin Microbiol Antimicrob. (2020) 19:28. doi: 10.1186/s12941-020-00370-2
114. Okobi, TJ, Cautha, S, Bhatt, T, Atogwe, ID, Schmidt, P, Patel, D, et al. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis and Hodgkin lymphoma in a newly diagnosed HIV patient: a diagnostic dilemma. Cureus. (2023) 15:e41127. doi: 10.7759/cureus.41127
115. Patel, TP, Beck, P, Chairman, D, and Regunath, H. Ehrlichiosis presenting as Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in an immunocompetent adult. IDCases. (2020) 20:e00813. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00813
116. Guiraud, V, Verney, C, Tetelboum, N, Argy, N, Debus, J, Herbel, S, et al. Life-threatening hemophagocytic syndrome triggered by disseminated toxoplasmosis in a young patient with previously unknown AIDS. Rev Med Interne. (2022) 43:622–5. doi: 10.1016/j.revmed.2022.07.016
117. Kraskovsky, V, Harhay, J, and Mador, MJ. Case of haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis following Epstein-Barr virus infection. BMJ Case Rep. (2021) 14:e241222. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2020-241222
118. Lemiale, V, Valade, S, Calvet, L, and Mariotte, E. Management of Hemophagocytic Lympho-Histiocytosis in critically ill patients. J Intensive Care Med. (2020) 35:118–27. doi: 10.1177/0885066618810403
119. Turbay Caballero, V, Eash, C, Sacoto, H, Sweis, RT, Pandya, M, Boly, F, et al. Reading between the lines: hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with concurrent neuroleptic malignant syndrome triggered by a drug-drug interaction. Chest. (2023) 164:A2698–A 2699. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1786
120. Wi, W, Yoon, KW, and Kim, HJ. Secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis associated with heat stroke: a case report and review of literature. Medicine (Baltimore). (2023) 102:e33842. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000033842
121. Wu, X, Wang, K, Gao, Y, Cai, Y, Wang, W, Zhong, D, et al. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia complicated with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis caused by chronic active Epstein-Barr virus infection: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. (2021) 21:1207. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06868-0
122. Zhou, X, and Duan, M-L. Malaria-associated secondary hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis: a case report. World J Clin Cases. (2021) 9:6403–9. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i22.6403
123. Kusne, Y, Christiansen, M, Conley, C, Gea-Banacloche, J, and Sen, A. Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis secondary to disseminated histoplasmosis in rheumatologic disease. Case Rep Crit Care. (2021) 2021:1–6. doi: 10.1155/2021/6612710
124. Cao, Y, Liu, P, Song, Q, and Wang, J. Case report: a case of sepsis caused by rickettsial infection-induced hemophagocytic syndrome. Front Med. (2023) 10:10. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1209174
125. Harano, Y, Ishikawa, Y, Hattori, K, Ichinose, M, Tomofuji, Y, Okano, H, et al. A case of complete atrioventricular block in secondary hemophagocytic syndrome/hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis recovered by plasma exchange and cytokine absorbing therapy with AN69ST continuous hemodiafiltration. Immunol Med. (2020) 43:171–8. doi: 10.1080/25785826.2020.1761145
126. Kitazawa, Y, Saito, F, Nomura, S, Ishii, K, and Kadota, E. A case of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis after the primary Epstein-Barr virus infection. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. (2007) 13:323–8. doi: 10.1177/1076029607302570
127. Park, Y, O’Reilly, M, Deleveaux, S, Kaltman, D, Coughlin, C, Gonzalez Vazquez, C, et al. Conservative treatment failure in Epstein-Barr virus-induced hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Chest. (2023) 164:A2808–9. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2023.07.1849
128. Zheng, Y, Yang, Y, Zhao, W, and Wang, H. Novel swine-origin influenza a (H1N1) virus-associated hemophagocytic syndrome—a first case report. Am Soc Trop Med Hyg. (2010) 82:743–5. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0666
129. Shi, Y-F, Shi, X-H, Zhang, Y, Chen, JX, Lai, WX, Luo, JM, et al. Disseminated tuberculosis associated Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in a pregnant woman with Evans syndrome: a case report and literature review. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676132
130. Ku, Y-H, and Yu, W-L. Extensive community-acquired pneumonia with hemophagocytic syndrome caused by Aeromonas veronii in an immunocompetent patient. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. (2017) 50:555–6. doi: 10.1016/j.jmii.2015.06.007
131. Wang, Y-H, Ba, J-H, Shi, X-W, and Wu, B-Q. Successful treatment of mycobacterial infection associated hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis with etoposide and anti-tuberculous therapy: a case report. BMC Infect Dis. (2020) 20:321. doi: 10.1186/s12879-020-05016-4
132. Hindi, Z, Khaled, AA, and Abushahin, A. Hemophagocytic syndrome masquerading as septic shock: an approach to such dilemma. SAGE Open Med Case Rep. (2017) 5:2050313X17746309. doi: 10.1177/2050313X17746309
133. Zhang, Z, Liu, J, Wang, J, and Wang, Y. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis associated to Klebsiella pneumoniae infection: a case report. Front Immunol. (2021) 12:12. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.684805
134. Altook, R, Ruzieh, M, Singh, A, Alamoudi, W, Moussa, Z, Alim, H, et al. Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in the elderly. Am J Med Sci. (2019) 357:67–74. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2018.07.004
Keywords: septic shock, immune dysregulation, hematology critical care, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH), hemophagocytic syndromes (HPS), HLH-2004 criteria, HScore
Citation: Montrucchio G, Traversi R, Arrigo G, Bonetto C, Sales G, Busca A, Fanelli V, Filippini C and Brazzi L (2025) Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in the adult critically ill: a narrative review of case reports and case series. Front. Med. 12:1622770. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1622770
Edited by:
Eizo Watanabe, Aichi Medical University, JapanReviewed by:
Luke Chen, University of British Columbia, CanadaKasumi Satoh, Akita University Hospital, Japan
Abhimanyu Chand, National Academy of Medical Sciences, Nepal
Copyright © 2025 Montrucchio, Traversi, Arrigo, Bonetto, Sales, Busca, Fanelli, Filippini and Brazzi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Riccardo Traversi, cmljY2FyZG8udHJhdmVyc2lAdW5pdG8uaXQ=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Giorgia Montrucchio1,2†
Giorgia Montrucchio1,2† Riccardo Traversi
Riccardo Traversi Alessandro Busca
Alessandro Busca Vito Fanelli
Vito Fanelli Claudia Filippini
Claudia Filippini Luca Brazzi
Luca Brazzi