Abstract
Purpose:
Although arthroscopic shoulder surgery confers clear advantages for recovery, it is often complicated by intraoperative hemodynamic instability and prolonged postoperative pain. This study investigates the clinical utility of stellate ganglion block (SGB) combined with general anesthesia (GA) to address these issues.
Methods:
In this retrospective analysis, 60 patients undergoing elective shoulder arthroscopy were categorized into SGB+GA (n = 30) and GA-only (n = 30) cohorts. Outcomes included intraoperative hemodynamic parameters (MAP, HR), postoperative pain (VAS scores), opioid-related complications, and hospitalization duration. Statistical analyses utilized t-tests and non-parametric tests.
Results:
The SGB+GA group demonstrated superior hemodynamic stability (P < 0.001) and markedly lower pain scores postoperatively (P < 0.001). Opioid-induced complications such as nausea (P = 0.028) were significantly reduced. Median hospital stay was shorter with SGB+GA (P < 0.001).
Conclusion:
Integrating SGB with GA optimizes perioperative management by stabilizing hemodynamics, enhancing analgesia, and minimizing opioid reliance, thereby expediting recovery. These findings support SGB as a valuable adjunct, though prospective validation is needed.
1 Introduction
Arthroscopic shoulder surgery, recognized as the gold standard for managing shoulder pathologies, offers numerous advantages due to its minimally invasive approach and favorable recovery profile (1). Optimizing regional anesthesia for these procedures is crucial to ensure adequate analgesia while minimizing side effects associated with general anesthesia, such as sedation and postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV), thereby enhancing postoperative recovery. However, significant challenges persist, including intraoperative hemodynamic instability and persistent postoperative pain linked to sympathetic hyperactivity and neuroinflammation (2, 3). Traditional peripheral nerve block techniques, notably interscalene brachial plexus block (ISB) (4) and suprascapular nerve block (SNB) (5), have limitations such as rebound pain upon block resolution,1 diaphragmatic paralysis, and inadequate control of sympathetically mediated pain. These limitations underscore the need for the development and implementation of more advanced or multifaceted analgesic strategies.
SGB provides a dual mechanism of action (6, 7): it stabilizes hemodynamics by suppressing sympathetic overactivity and reduces inflammatory mediators, thereby targeting both nociceptive and neuropathic pain pathways (8). Although SGB has been proven effective in thoracic and vascular surgeries, its synergistic effects with general anesthesia in shoulder arthroscopy remain underexplored. Notably, while interscalene brachial plexus block (ISB) is the current gold standard for perioperative analgesia in shoulder arthroscopy (4, 9), its implementation may be limited by resource constraints or contraindications [e.g., coagulopathy, pre-existing neuropathy, severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and obesity]. Thus, exploring SGB as an alternative remains clinically relevant. its synergistic effects with general anesthesia in shoulder arthroscopy remain underexplored, which limits evidence-based integration.
This trial evaluates the use of SGB in conjunction with general anesthesia during arthroscopic shoulder surgery. Our findings aim to refine perioperative protocols and improve clinical efficiency.
2 Materials and methods
2.1 General information
Ethical approval for this study was obtained from the Institutional Review Board of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Approval No. LW2024092201). This program ensured the scientific, ethical, and compliant nature of the study and safeguarded the rights and safety of the participants. Initial screening identified 48 eligible patients. After comprehensive evaluation, 18 were excluded:
-
Preoperative exclusions (n = 12): ASA > II: uncontrolled hypertension (n = 3), diabetic nephropathy (n = 2), Chronic opioid use (> 30 MME/day, n = 3), Contraindications to local anesthetics: coagulopathy (INR > 1.5, n = 2), Prior ipsilateral shoulder surgery (n = 1), Cervical pathology affecting SGB (n = 1),
-
Intraoperative exclusions (n = 4): SGB failure (absence of Horner’s syndrome, n = 2), Vasoactive drug requirement (norepinephrine infusion, n = 2),
-
Postoperative data exclusions (n = 2): incomplete outcome records (> 20% missing VAS/PCA data, n = 2).
Thirty patients receiving SGB+GA, matched 1:1 based on anesthesia records from December 2020 to August 2023 to GA-only controls using criteria including age (±5 years), ASA status, and surgery duration (±15 min). Cohort assignment was based on documented anesthesia protocols. Rationale for GA-only control: this design was selected to (a) reflect real-world practice in settings lacking regional anesthesia expertise, and (b) establish baseline efficacy of SGB+GA before comparative studies with ISB. According to institutional records, 35% of shoulder arthroscopies during 2020–2023 received GA-only due to contraindications to regional techniques or anesthesiologist availability. Patients receiving SGB+GA were classified as the intervention cohort (SGB+GA, n = 30), while those receiving GA-only comprised the control cohort (GA-only, n = 30). As a retrospective analysis of existing data, this study did not require prospective trial registration.
The baseline characteristics, including age, gender, ASA classification, and operative duration, exhibited no significant intergroup differences (P > 0.05), thereby ensuring comparability.
2.2 Intervention protocols
2.2.1 Group SGB+GA
SGB procedure: SGB was performed under real-time ultrasound guidance with color Doppler, using a high-frequency linear probe in a transverse short-axis view of the neck. The target injection site was identified anterior to the longus colli muscle and posterior to the carotid sheath at the level of the C6 transverse process. A paracarotid lateral approach was selected, and the needle trajectory was planned under Doppler guidance to avoid aberrant vessels such as the inferior thyroid artery and vertebral artery. The needle was advanced using an in-plane technique until the tip reached the target location. After confirming negative aspiration for blood or cerebrospinal fluid, 10 mL of 0.25% ropivacaine was injected (7). Successful blockade was confirmed by the development of ipsilateral Horner’s syndrome (miosis, ptosis, and anhidrosis) (10).
2.2.1.1 General anesthesia
Induction: Administer midazolam (0.05 mg/kg), propofol (1.5–2.0 mg/kg), sufentanil (0.4–0.5 μg/kg), and cisatracurium (0.15–0.20 mg/kg), followed by tracheal intubation.
Maintenance: Administer propofol (4–8 mg/kg/h) and remifentanil (0.1–0.2 μg/kg/min), adjusting dosages to maintain a Bispectral Index (BIS) of 40–60 and stable hemodynamics. As needed, sevoflurane, propofol, remifentanil, and rocuronium may be administered to ensure adequate depth of anesthesia.
2.2.2 Group GA-only
Identical induction and maintenance protocols were implemented, excluding SGB.
Postoperative Pain Management (Both Groups):
All patients were given intravenous patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) following this protocol:
Sufentanil at a concentration of 2 μg/mL in a total volume of 100 mL.
Continuous infusion: 2 mL per hour.
Bolus dose: 2 mL per dose, with a lockout period of 5 min. For additional pain relief, intramuscular tramadol 50 mg was provided if the resting VAS score was 6 or higher.
Inclusion criteria:
-
Type: Patients undergoing elective arthroscopic shoulder surgery.
-
Age: 20 to 65 years.
-
Health status: ASA physical status I–II.
-
Anesthesia contraindication: No contraindications to local anesthetics.
-
Data completeness: Complete hemodynamic records, postoperative pain scores, and opioid consumption data.
Exclusion criteria:
-
Intraoperative exclusions:
-
SGB failure (absence of Horner’s syndrome).
-
Use of vasoactive drugs (e.g., norepinephrine).
-
-
Clinical factors:
-
Severe cardiopulmonary/hepatic/renal dysfunction or coagulopathy.
-
History of psychiatric/cognitive disorders.
-
Prior ipsilateral shoulder surgery/trauma.
-
Cervical spine pathology affecting SGB efficacy.
-
-
Data missingness: ≥ 20% missing key outcomes (MAP, HR, VAS).
-
Special populations: Pregnancy or lactation.
2.3 Outcome measures
2.3.1 Primary outcomes
2.3.1.1 Pain assessment
(1) Postoperative pain was quantified utilizing Visual Analog Scale (VAS) scores collected at 2, 6, 12, and 24 h following surgery.
(2) The overall usage of remifentanil during surgery and the total amount of tramadol used within 24 h after the operation.
2.3.2 Secondary outcomes
(1) Intraoperative hemodynamics were evaluated through the measurement of blood pressure and heart rate at five designated time points: baseline (T0), post-induction (T1), during incision (T2), 30 min into surgery (T3), and at the procedure’s conclusion (T4).
(2) Potential adverse effects encompass nausea, vomiting, dizziness, drowsiness, and respiratory depression.
(3) The duration of hospital stay.
2.4 Statistical methods
Outcome assessors for VAS and complications were blinded to group allocation using anonymized patient identifiers. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 22.0. Continuous variables (MAP, HR, and VAS) are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD) and compared with independent t-tests. Categorical variables (e.g., complications) were analyzed using chi-square tests or Fisher’s exact tests, the latter applied when expected cell frequencies were < 5. A two-tailed P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Multivariate regression controlled for age/ASA status.
3 Results
3.1 General conditions
There were no significant differences between the two groups in terms of gender, age, ASA classification, operation duration, and intraoperative fluid after comparison (P > 0.05; see Table 1).
TABLE 1
| Characteristic | Group | p-value | |
| GA-only, N = 301 | SGB+GA, N = 301 | ||
| Age (years) | 42 ± 7 | 43 ± 8 | 0.6432 |
| Surgery duration (min) | 117 (110, 125) | 116 (103, 127) | 0.5843 |
| Intraoperative fluid (ml) | 2,125 ± 165 | 2,136 ± 146 | 0.7892 |
| Sex (M/F) | 0.7964 | ||
| F | 16 (53.3%) | 15 (50.0%) | |
| M | 14 (46.7%) | 15 (50.0%) | |
| ASA I/II | 0.4174 | ||
| I | 21 (70.0%) | 18 (60.0%) | |
| II | 9 (30.0%) | 12 (40.0%) | |
Comparison of general condition of patients in 2 groups (n = 30).
1Mean ± SD; median (IQR); n (%).
2Welch two sample t-test.
3Wilcoxon rank sum test.
4Pearson’s chi-squared test.
3.2 Intraoperative hemodynamic indicators
At T0, there was no statistically significant difference in MAP and HR between the two groups (P > 0.05). The fluctuation amplitudes of MAP and HR in SGB+GA group from T1 to T4 were smaller than those in the control group (see Figure 1), and this difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05; see Table 2).
FIGURE 1

Vital signs at different time points.
TABLE 2
| Characteristic | Group | p-value | Effect size | |
| GA-only, N = 301 | SGB+GA, N = 301 | |||
| T0MAP | 85 ± 10 | 85 ± 10 | 0.7892 | 0.044 |
| T0HR | 79 ± 10 | 79 ± 10 | 0.7952 | 0.164 |
| T1MAP | 70 (64, 76) | 79 (72, 88) | 0.0013 | 1.09 4 |
| T1HR | 64 (59, 73) | 78 (61, 78) | < 0.0013 | 0.814 |
| T2MAP | 73 ± 7 | 80 ± 9 | < 0.0012 | 0.91 4 |
| T2HR | 69 ± 7 | 75 ± 8 | < 0.0012 | 0.97 4 |
| T3MAP | 77 (71, 79) | 87 (76, 88) | < 0.0013 | 0.754 |
| T3HR | 69 (66, 74) | 80 (73, 81) | < 0.0013 | 0.814 |
| T4MAP | 79 ± 8 | 84 ± 8 | 0.0172 | 0.694 |
| T4HR | 73 ± 6 | 78 ± 7 | 0.0062 | 0.554 |
Comparison of intraoperative hemodynamic indexes in 2 groups (n = 30).
1Mean ± SD; median (IQR).
2Welch two sample t-test.
3Wilcoxon rank sum test.
4Cohen’s d. Bolded values indicate statistically significant differences (i.e., P < 0.05).
3.3 Postoperative pain scores
The VAS scores of patients in SGB+GA group at 2, 6, 12, and 24 h post-surgery were consistently lower than those in the control group (see Figure 2), with the differences being statistically significant (P < 0.05) (see Table 3).
FIGURE 2
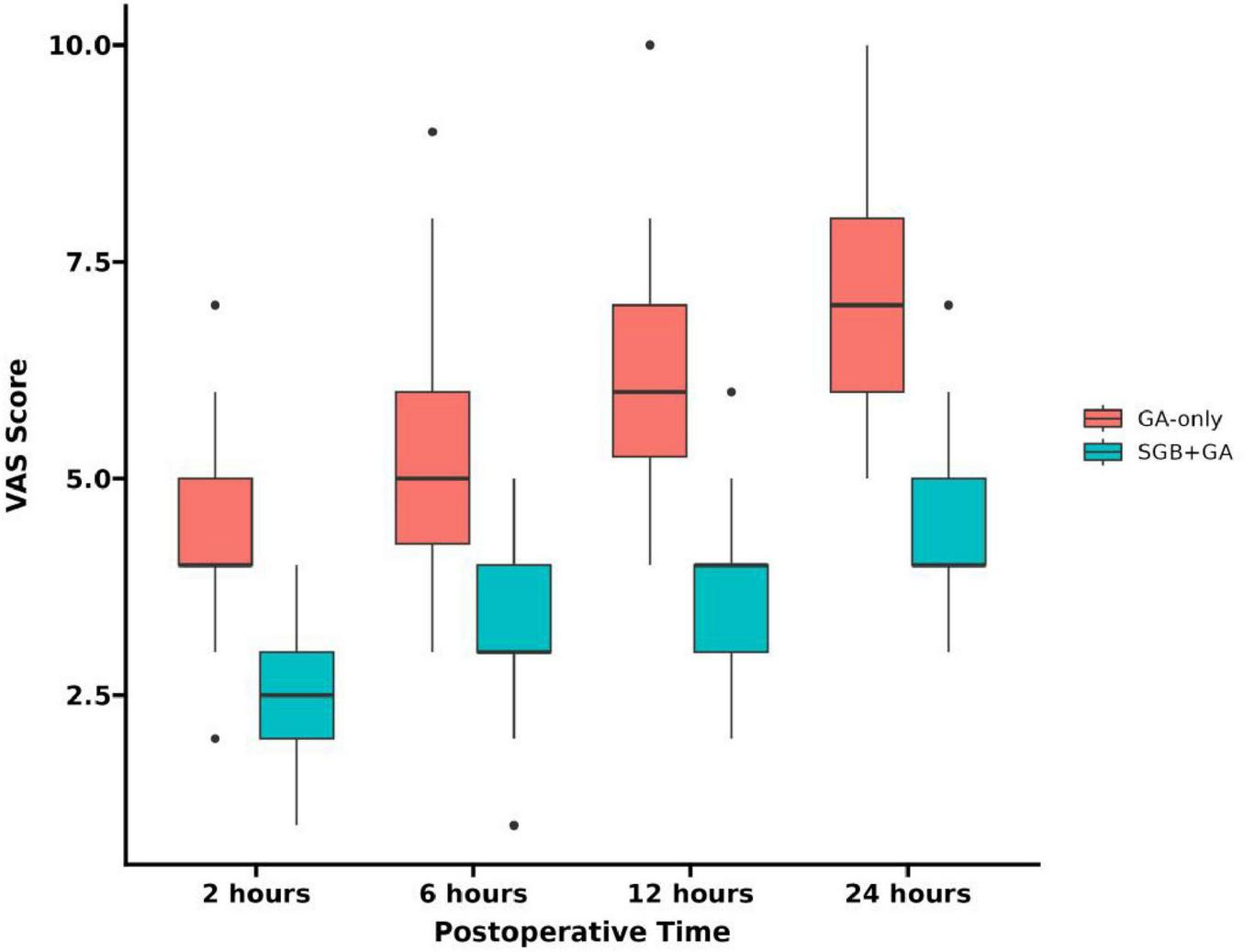
VAS scores at different time points.
TABLE 3
| Characteristic | Group | p-value | Effect size | |
| GA-only, N = 301 | SGB+GA, N = 301 | |||
| 2 h postop | 4.00 (3.00, 5.00) | 2.50 (2.00, 3.00) | < 0.0012 | −0.8023 |
| 6 h postop | 6.00 (4.25, 6.00) | 3.00 (3.00, 4.00) | < 0.0012 | −0.8923 |
| 12 h postop | 6.00 (5.00, 7.75) | 4.00 (3.00, 4.00) | < 0.0012 | −0.6893 |
| 24 h postop | 8.00 (6.00, 9.00) | 4.00 (4.00, 5.00) | < 0.0012 | −0.9223 |
Comparison of postoperative pain scores between the 2 groups (n = 30).
1Median (IQR).
2Wilcoxon rank sum test.
3Cliff’s delta. Bolded value indicates statistically significant differences (i.e., P < 0.05).
3.4 Comparison of analgesic drug usage
The analysis of opioid consumption revealed significant intergroup differences (P < 0.001 for all comparisons). Patients receiving SGB+GA required 24.1% less intraoperative remifentanil compared to GA-only controls. Postoperatively, the SGB+GA group demonstrated a 75% reduction in median tramadol consumption. Notably, 40% of patients in the SGB+GA group required no tramadol rescue analgesia during the first 24 h, whereas all patients in the GA-only group (100%) needed supplemental doses (χ2 = 15.43) (see Table 4).
TABLE 4
| Parameter | GA-only group (n = 30) | SGB+GA group (n = 30) | Statistic | P-value | Effect size |
| Total intraoperative remifentanil consumption (μg) | 1,053.4 ± 210.8 | 789.2 ± 158.3 | *t* = 5.67 | < 0.001 | 1.421 |
| Postoperative 24-h tramadol consumption (mg) | 200.0 (150.0, 250.0) | 50.0 (0.0, 100.0) | Z = 4.35 | < 0.001 | 0.652 |
| Patients requiring no tramadol rescue (%) | 0.0 (0/30) | 40.0 (12/30) | χ2 = 15.43 | < 0.001 | 1.123 |
Comparison of opioid consumption between groups.
1Cohen’s d.
2Cliff’s Delta.
3Cohen’s h. The symbol “*t*” denotes the result of the t-test, which, together with the corresponding p-value (<0.001), demonstrates a highly significant statistical difference in the “total intraoperative remifentanil consumption” metric between the two groups.
3.5 Occurrence of postoperative complications
The incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting, dizziness, and drowsiness in SGB+GA group was lower than that in GA-only group, and the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05). However, there was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of respiratory depression between the two groups (P > 0.05) (see Table 5).
TABLE 5
| Characteristic | Group | p-value | Effect size | |
| GA-only, N = 301 | SGB+GA, N = 301 | |||
| Nausea and vomiting | 0.0282 | −0.534 | ||
| N | 20 (66.7%) | 27 (90.0%) | ||
| Y | 10 (33.3%) | 3 (10.0%) | ||
| Dizziness | 0.0382 | −0.494 | ||
| N | 22 (73.3%) | 28 (93.3%) | ||
| Y | 8 (26.7%) | 2 (6.7%) | ||
| Somnolence | 0.1033 | −0.484 | ||
| N | 24 (80.0%) | 29 (96.7%) | ||
| Y | 6 (20.0%) | 1 (3.3%) | ||
| Respiratory depression | > 0.9993 | −0.36* | ||
| N | 29 (96.7%) | 30 (100.0%) | ||
| Y | 1 (3.3%) | 0 (0.0%) | ||
Comparison of postoperative complications between the 2 groups (n = 30).
1n (%).
2Pearson’s chi-squared test.
3Fisher’s exact test.
4Cohen’s d.
*Haldane correction used for respiratory depression.
3.6 Hospital stay
Patients in SGB+GA Group had a significantly shorter hospital stay compared to the control group (see Table 6).
TABLE 6
| Characteristic | Group | p-value | Effect size | |
| GA-only, N = 301 | SGB+GA, N = 301 | |||
| Length of hospitalization | 7.00 (7.00, 9.00) | 5.00 (4.00, 6.00) | < 0.0012 | −1.353 |
Comparison of length of hospitalization between the 2 groups.
1Median (IQR).
2Wilcoxon rank sum test.
3Robust Cohen.
1Rebound pain: Severe acute pain occurring after resolution of peripheral nerve blockade; Horner’s syndrome: transient triad of miosis, ptosis, and facial anhidrosis indicating successful sympathetic blockade.
4 Discussion
Shoulder arthroscopic surgery, known for its minimally invasive approach, rapid recovery, and low complication rate, has become the preferred surgical method for treating shoulder disorders (11). However, hemodynamic instability frequently occurs during these procedures due to surgical stimulation and pain (12). Our findings demonstrate that supplementing general anesthesia with a stellate ganglion block significantly attenuated fluctuations in mean arterial pressure and heart rate. This stabilizing effect can be attributed to the ability of SGB to suppress sympathetic nerve overactivity, promote vasodilation, and reduce peripheral vascular resistance, thereby promoting a more balanced cerebral oxygen supply and demand (13). This suggests that the integration of SGB effectively mitigates the surgical stress response and fosters superior hemodynamic maintenance throughout the operation.
Beyond stabilizing intraoperative hemodynamics, SGB exerted a profound impact on the quality of postoperative recovery, primarily through enhanced analgesia. Postoperative pain following shoulder arthroscopy is often dominated by a dull, movement-evoked character, arising from persistent sympathetic hyperactivity and neuroinflammation—elements that are notoriously poorly controlled by conventional peripheral nerve blocks (14). While techniques like the interscalene block provide excellent transient sensory blockade, their resolution can be accompanied by significant rebound pain driven by unresolved inflammatory cascades. Our findings are consistent with those of Uppal et al. (15), who also reported a substantial reduction in postoperative pain scores (approximately 3 points on the VAS at 24 h) following the implementation of a similar analgesic strategy. SGB circumvents this limitation via a multimodal, dual-pathway mechanism. Its selective sympathetic inhibition reduces norepinephrine release, dilates arterioles, and improves microcirculation (16), which in turn attenuates ischemic pain and accelerates the clearance of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6 and TNF-α (13, 16). These effects collectively blunt central sensitization and suppress pain amplification, which is particularly crucial during shoulder mobilization when tissue tension exacerbates neuroinflammatory signaling (17). Consequently, SGB delivered sustained analgesia that extended beyond 24 h without the characteristic rebound pain, thereby lowering immediate opioid requirements and permitting earlier and less painful engagement in rehabilitation—a key determinant of functional recovery. This aligns with clinical evidence underscoring the mechanistic advantages of sympathetic blockade (18, 19). The magnitude of pain reduction observed in our SGB+GA group not only confirms its efficacy against general anesthesia alone but also suggests a potential advantage over historical reports for brachial plexus blocks (20, 21), indicating that SGB offers a superior, multi-target strategy for managing complex postoperative pain by simultaneously inhibiting sympathetic activity and modulating inflammatory pathways.
The superior analgesia provided by SGB had direct and favorable downstream consequences. The significantly lower consumption of both intraoperative remifentanil and postoperative tramadol in the SGB+GA group provides a clear pharmacological basis for the observed reduction in opioid-induced complications. As nausea, vomiting, and dizziness are frequently driven by opioid use (22), the opioid-sparing effect of SGB—achieved through its dual inhibition of nociceptive transmission and inflammatory cascades (13, 16)—directly translated into a significantly lower incidence of these adverse events.
Ultimately, the synergistic benefits of improved hemodynamic stability, superior analgesia, and fewer complications converged to significantly shorten the hospital stay. Dull pain is a major impediment to active participation in physiotherapy, such as passive range-of-motion exercises. By effectively alleviating this type of pain, SGB enables patients to engage in rehabilitation sooner, accelerating key milestones like independent ambulation and self-care. This accelerated functional recovery is further potentiated by SGB’s opioid-sparing effects, as reduced opioid exposure minimizes sedation and gastrointestinal dysfunction, thereby facilitating earlier mobilization (23). Furthermore, enhanced microcirculation secondary to sympatholysis may also contribute to improved wound healing and a reduced risk of secondary complications like adhesive capsulitis, further expediting the overall recovery timeline.
From a healthcare economics perspective, a reduced length of stay (LOS) decreases direct medical costs and indirect burdens. Our data indicate that SGB could enhance bed turnover rates, a metric with significant implications for resource-constrained environments.
This study has several limitations. Its single-center retrospective design and relatively small sample size may limit the generalizability of the findings. Potential unmeasured confounding factors might also persist. Furthermore, the absence of a direct comparison with brachial plexus blocks, along with the reliance on subjective pain measures rather than objective biomarkers (e.g., IL-6) or multidimensional assessments, restricts a deeper mechanistic understanding of SGB’s therapeutic effects. The optimal dosage and concentration of local anesthetics for SGB also require further investigation. Future research should prioritize multicenter, prospective, three-arm trials incorporating dynamic monitoring of inflammatory biomarkers, standardization of procedural and follow-up protocols, and inclusion of 3-month functional outcomes to comprehensively evaluate the efficacy and recovery impact of SGB.
5 Conclusion
In shoulder arthroscopic surgery, the combination of SGB with general anesthesia offers numerous benefits. It stabilizes intraoperative hemodynamics, substantially reduces opioid requirements, lowers postoperative pain, minimizes complications, and shortens hospital stays. This combination makes it a valuable option for anesthesia and analgesia, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and satisfaction. However, the application of SGB should be tailored to each individual patient. A thorough assessment of the patient’s condition is essential to ensure its safe and effective use.
Future research should involve large-sample studies to confirm these results, long-term follow-up to evaluate enduring effects, and multidisciplinary collaboration. This approach will help optimize the use of SGB and enhance patient care.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by the Ethics Committee of the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University (Approval No. LW2024092201). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee because the study involved secondary analysis of anonymized patient data extracted from electronic health records, with no direct patient contact, additional interventions, or risks to participants. All data were de-identified prior to analysis to ensure confidentiality, adhering to national regulations and the Declaration of Helsinki guidelines for retrospective research.
Author contributions
ZP: Data curation, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. JL: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft. YX: Data curation, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft. YY: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Project administration, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The authors declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Bureau of Science and Technology of Shuimogou District, Urumqi City, which provided funding for the research.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Bureau of Science and Technology, Shuimogou, Urumqi, Xinjiang. We thank the Second Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University and the Shuimogou Science and Technology Bureau of Xinjiang Urumqi for their support. Additionally, we sincerely appreciate the contributions of the two departments involved in the implementation of this investigation.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Rupp M Chang P Horan M Hussain Z Godin J Pogorzelski J et al Arthroscopic rotator cuff repair in active patients younger than 45 Years: a prospective analysis with a mean 5-year follow-up. JSES Int. (2024) 8:798–805. 10.1016/j.jseint.2024.03.002
2.
Kuechly H Kurkowski S Johnson B Shah N Grawe B . Postoperative negative pain thoughts and their correlation with patient-reported outcomes after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: an observational cohort study.Am J Sports Med. (2024) 52:1700–6. 10.1177/03635465241247289
3.
Huang Y Ng Y Chiu C Chuang C Sheu H Yang C et al Addition of preoperative ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block and axillary nerve block to parecoxib is more effective in early postoperative pain control after arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a prospective randomized controlled study. Arthroscopy. (2024) 40:2532–9. 10.1016/j.arthro.2024.02.031
4.
Luo Q Zheng J Yang C Wei W Wang K Xiang X et al Effects of the costoclavicular block versus interscalene block in patients undergoing arthroscopic shoulder surgery under monitored anesthesia care: a randomized, prospective, non-inferiority study. Korean J Anesthesiol. (2023) 76:413–23. 10.4097/kja.22638
5.
Kalthoff A Sanda M Tate P Evanson K Pederson J Paranjape G et al Peripheral nerve blocks outperform general anesthesia for pain control in arthroscopic rotator cuff repair: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthroscopy. (2022) 38:1627–41. 10.1016/j.arthro.2021.11.054
6.
Kirkpatrick K Khan M Deng Y Shah KB . A review of stellate ganglion block as an adjunctive treatment modality.Cureus. (2023) 15:e35174. 10.7759/cureus.35174
7.
Piraccini E Munakomi S Chang K. Stellate Ganglion Blocks. (2023). Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing
8.
Ren Y Zhang Z Li H Zhang P Duo J Kong HA . Comprehensive Overview of the stellate ganglion block throughout the past three decades: a bibliometric analysis.Pain Physician. (2024) 27:E597–610. 10.36076/ppj.2024.7.E597
9.
Goel V Patwardhan A Ibrahim M Howe C Schultz D Shankar H . Complications associated with stellate ganglion nerve block: a systematic review.Reg Anesth Pain Med. (2019): 10.1136/rapm-2018-100127Online ahead of print.
10.
Zhao Y Xiao X . Efficacy of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block in relieving acute postoperative pain: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Int Med Res. (2024) 52:3000605241252237. 10.1177/03000605241252237
11.
Lin S Chen L Tang Y Zheng C Ke P Chen M et al Establishment of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block in rats. Front Neurosci. (2023) 16:1061767. 10.3389/fnins.2022.1061767
12.
Zhang C Wu J Li X Wang Z Lu W Wong T . Current biological strategies to enhance surgical treatment for rotator cuff repair.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. (2021) 9:657584. 10.3389/fbioe.2021.657584
13.
Qian M Yuan C Jiang W Zhao L Yang F Xie Y . Effects of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block on the balance of the supply and demand of cerebral oxygen during permissive hypercapnia in patients undergoing shoulder arthroscopy in beach chair position.Am J Transl Res. (2022) 14:6678–88. 10.15674/0030-59872024138-42
14.
Gan Y Chen J Xian L Shi Y . Objective evaluation of stellate ganglion block effects using ultrasound wave intensity technology: a study on hemodynamics.J Pain Res. (2024) 17:2063–70. 10.2147/JPR.S451952
15.
Uppal V Barry G Ke J Kwofie M Trenholm A Khan M et al Reducing rebound pain severity after arthroscopic shoulder surgery under general anesthesia and interscalene block: a two-centre randomized controlled trial of pre-emptive opioid treatment compared with placebo. Can J Anaesth. (2024) 71:773–83. 10.1007/s12630-023-02594-0
16.
Li M Huang W Shi Y Zeng Y Liu G . Continuous SGB inhibits occurrence and maintenance of mechanical hyperalgesia via reducing inflammatory cytokines in striatum and PAG of PD nociception rat models.Turk Neurosurg. (2023) 33:568–75. 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.38254-22.2
17.
Singh H Rajarathinam M . Stellate ganglion block beyond chronic pain: a literature review on its application in painful and non-painful conditions.J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. (2024) 40:185–91. 10.4103/joacp.joacp_304_22
18.
Nobre L Ferraro L Júnior J Winkeler V Muniz L Braga H et al Efficacy of dexamethasone or clonidine as adjuvants in interscalene brachial plexus block for preventing rebound pain after shoulder surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Braz J Anesthesiol. (2025) 75:844575. 10.1016/j.bjane.2024.844575
19.
Yuan Z Luo J Cheng Q Zhang Q . Clinical efficacy of ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block combined with extracorporeal shock wave therapy on limb spasticity in patients with ischemic stroke.BMC Neurol. (2023) 23:349. 10.1186/s12883-023-03391-4
20.
Rajagopalan V Chouhan R Pandia M Lamsal R Bithal P Rath G . Effect of stellate ganglion block on intraoperative propofol and Fentanyl consumption in patients with complex regional pain syndrome undergoing surgical repair of brachial plexus injury: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial.Neurol India. (2020) 68:617–23. 10.4103/0028-3886.288992
21.
Jiangping W Xiaolin Q Han S Zhou X Mao N Zhibo D et al Network meta-analysis of perioperative analgesic effects of different interventions on postoperative pain after arthroscopic shoulder surgery based on randomized controlled trials. Front Med. (2022) 9:921016. 10.3389/fmed.2022.921016
22.
Cho D Li J Nazarian A . Ultrasound-guided stellate ganglion block with preserved motor function for upper extremity surgery.Cureus. (2021) 13:e18537. 10.7759/cureus.18537
23.
Updegrove GF Stauch CM Ponnuru P Kunselman AR Armstrong AD . Efficacy of local infiltration anesthesia versus interscalene nerve blockade for total shoulder arthroplasty.JSES Int. (2020) 4:357–61. 10.1016/j.jseint.2019.12.007
Summary
Keywords
stellate ganglion block, shoulder arthroscopy, perioperative stability, analgesia, recovery efficiency
Citation
Pan Z, Li J, Xu Y and Yuan Y (2025) Retrospective efficacy analysis of stellate ganglion block combined with general anesthesia in arthroscopic shoulder surgery: a cohort study. Front. Med. 12:1625121. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1625121
Received
08 May 2025
Accepted
01 September 2025
Published
15 September 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Christian Bohringer, UC Davis Medical Center, United States
Reviewed by
Mohanchandra Mandal, Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education & Research, Kolkata, India
Dipasri Bhattacharya, Government of West Bengal, India
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Pan, Li, Xu and Yuan.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yingchuan Yuan, yyc84_315@163.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.