Abstract
Brucellosis remains one of the most impactful zoonotic diseases worldwide, posing major socioeconomic and public health challenges, particularly in low- and middle-income countries. This review presents recent progress in understanding the pathogenesis of Brucella species, emphasizing the role of key adhesins—SP29, SP41, BigA, BigB, BamA, BmaB, BmaC, Bp26, BtaF, and BtaE—in host-pathogen interactions that drive adhesion, invasion, and immune evasion. We also critically assess current diagnostic approaches, including conventional culture techniques, serological assays, and emerging molecular platforms, which offer improved sensitivity and specificity. Current treatment regimens involve extended antibiotic combinations—typically doxycycline with rifampin or streptomycin—and may include surgical intervention in complicated cases. Additionally, the integration of nanotechnology-based drug delivery and traditional Chinese medicine offers promising adjunctive therapies. Although several animal vaccines exist, no approved vaccine is currently available for human use. Novel vaccine platforms, including live vectors, DNA subunits, and nanoparticle-based formulations, are under development. Finally, we address the disease's broad socioeconomic impact—ranging from livestock losses to healthcare burdens—and highlight ongoing challenges, such as diagnostic limitations, antimicrobial resistance, underreporting, and barriers to vaccine development. A One Health approach, alongside translational research and integrated surveillance, is vital to advancing prevention and control strategies for this neglected zoonosis.
1 Introduction
Brucellosis is a globally significant zoonotic disease that continues to pose serious public health, veterinary, and socioeconomic challenges. It is caused by gram-negative, facultative intracellular coccobacilli of the genus Brucella, which infect a wide range of domestic and wild animals and can be transmitted to humans through direct contact with infected animals or the consumption of contaminated animal products, especially unpasteurized dairy products (1, 2). In many developing regions, brucellosis remains endemic, placing considerable burdens on public health systems and agricultural economies due to decreased productivity, increased abortion rates in livestock, and chronic illness in humans (3).
The genus Brucella includes several species with varying host preferences and pathogenic potential. Among these, Brucella melitensis (B. melitensis), Brucella abortus (B. abortus), Brucella suis (B. suis), and Brucella canis (B. canis) are of particular concern to human health. B. melitensis is considered the most virulent and is most frequently associated with human brucellosis, particularly in endemic regions such as the Middle East, the Mediterranean basin, parts of Asia, and Latin America (4, 5). The genus includes three highly pathogenic species—B. abortus, B. melitensis, and B. suis—which primarily infect livestock. Among these, B. melitensis is the most virulent in humans and is responsible for the majority of severe brucellosis cases worldwide (3, 6). Most cases occur in the Mediterranean, Central Asia, the Middle East, South Asia, North Africa, and Latin America (7, 8).
Brucella relies on cyclic glucans, the VirB type IV secretion system, and modified lipopolysaccharides (LPSs) for invasion and replication, as it lacks conventional virulence factors (9, 10). Compared with other gram-negative bacteria, its LPS elicits a limited immune response (6, 11). Additionally, genomic islands and outer membrane proteins (e.g., BacA, SagA, BmaC, BetB, BtaE, MucR) play pivotal roles in pathogenicity (1).
The clinical manifestations of brucellosis range from asymptomatic to severe and include prolonged fever, night sweats, joint pain, fatigue, weight loss, abdominal discomfort, and hepatosplenomegaly, with complications such as endocarditis and neurological disorders (12–14). Neurobrucellosis is a rare but severe complication of human brucellosis that presents significant diagnostic and therapeutic challenges. Its clinical spectrum includes neurological and psychiatric manifestations such as meningitis, meningoencephalitis, myelitis, psychosis, personality changes, and persistent fatigue-like syndromes. These symptoms often mimic other infectious or autoimmune disorders, leading to frequent misdiagnosis or delayed treatment (15, 16). Effective treatment typically requires prolonged, multi-agent therapy—commonly combining ceftriaxone, doxycycline, and rifampin—with durations of several months (17, 18). Relapse remains a concern even after extended courses, highlighting the necessity for sustained clinical vigilance and follow-up (19). Given the condition's varied presentations and potential for chronic morbidity, clinicians—especially in endemic or high-risk occupational settings—must maintain a high index of suspicion.
Various Brucella species infect animals such as cattle, sheep, goats, and dogs (20, 21), with human infections commonly arising from contact with infected livestock or the consumption of unpasteurized dairy products (7, 22). Transmission occurs primarily through the ingestion of raw dairy products, contact with infected tissues, or inhalation of airborne particles (14), whereas human-to-human transmission is rare (23).
Conjunctival exposure also represents an important transmission route, particularly when infectious particles contaminate the eyes of individuals assisting with animal parturition. Several studies have documented that mucosal exposure during birthing practices and veterinary procedures significantly increases the risk of human infection (24, 25). In addition, nosocomial transmission has been reported, placing healthcare and laboratory workers at elevated risk of accidental infection through handling of clinical specimens or cultures. Hospital-based outbreaks have highlighted that even limited exposure can result in secondary transmission if biosafety protocols are not maintained (26, 27). Such exposures, especially in laboratory environments, can lead to serious outbreaks if biosafety protocols are not strictly followed. For this reason, culture handling and diagnostic procedures involving Brucella should be performed under Biosafety Level 3 (BSL-3) conditions, with the use of biological safety cabinets and appropriate personal protective equipment to minimize occupational hazards (28, 29).
Brucellosis pathogenesis involves complex interactions between bacteria and the host immune system (30). Brucella species are highly adaptable to evade immune responses, facilitating persistent infections (30). Once inside the host, Brucella survives and proliferates within macrophages, enabling widespread dissemination (31, 32). Its ability to manipulate host processes such as autophagy and apoptosis is central to persistence and replication (32, 33), making the intracellular environment a significant barrier to effective vaccine and therapeutic development.
Brucellosis diagnosis has traditionally relied on serological tests and culture methods; however, these methods can be limited by atypical clinical presentations and irregular bacterial distributions (34, 35). Advances in molecular diagnostics, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and whole-genome sequencing (WGS), offer more rapid and accurate detection, thereby facilitating earlier treatment and improving patient outcomes (36, 37).
Although several therapeutic options exist, the emergence of antibiotic-resistant Brucella strains has become a growing concern (38, 39). Reducing disease transmission by eliminating potential animal carriers, especially cattle, may help control disease spread (40). Current treatment regimens typically involve multiple antibiotics, but treatment failure and relapse are still common, highlighting the need for novel therapeutic strategies (41). For optimal clinical outcomes, careful selection of effective antibacterial agents and appropriate treatment protocols is essential (42).
Despite advances in diagnosis and management, brucellosis continues to present substantial public health challenges. This review aims to explore disease pathogenesis, diagnostic methods, and therapeutic approaches, with a particular focus on transmission routes. Strengthened collaboration among public health authorities, clinicians, and veterinary professionals is essential to enhance prevention and control strategies and better understand the global impact of brucellosis.
2 Pathogenesis and adhesins of Brucella spp.
Brucella spp. can overcome various host defense mechanisms during the early stages of infection, during which the bacterial survival rate is approximately 10% (43). These pathogens have evolved sophisticated strategies to evade immune responses and can infect a range of cell types, including phagocytic cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, as well as non-phagocytic cells such as epithelial cells and placental trophoblasts. Red and white blood cells (RBCs and WBCs), although not sites of replication, contribute to bacterial dissemination (31). A hallmark of Brucella pathogenicity is its ability to survive and replicate within macrophages, leading to chronic infections (44).
In animals, particularly cattle, sheep, and goats, Brucella infection is strongly associated with reproductive disorders such as abortion, retained placenta, orchitis, and infertility, which represent major veterinary and economic concerns (22, 45, 46). By contrast, in humans, spontaneous abortion is relatively uncommon; instead, brucellosis more frequently results in systemic and focal complications such as osteoarticular disease, endocarditis, and neurobrucellosis (47–50). This contrast underscores the divergent pathogenic outcomes and host-pathogen interactions between animal and human infections.
The internalization of Brucella into macrophages involves a zipper-like mechanism. Virulent strains preferentially enter through lipid rafts, whereas avirulent strains undergo phagocytosis, resulting in lysosomal fusion and degradation. This finding underscores the importance of lipid raft-mediated entry for intracellular survival during early infection (51, 52). Once inside the host cell, Brucella resides in membrane-bound vesicles known as Brucella-containing vacuoles (BCVs) (9, 43). These phagosomes evolve through stages, initially fusing with early endosomes to form early BCVs (eBCVs), which express markers such as early endosome antigen 1 (EEA1), Rab5, and transferrin receptor (TfR). Subsequently, fusion with late endosomes produces late BCVs containing lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1), Rab7, and Rab-interacting lysosomal protein (RILP) (Figure 1A) (53).
Figure 1
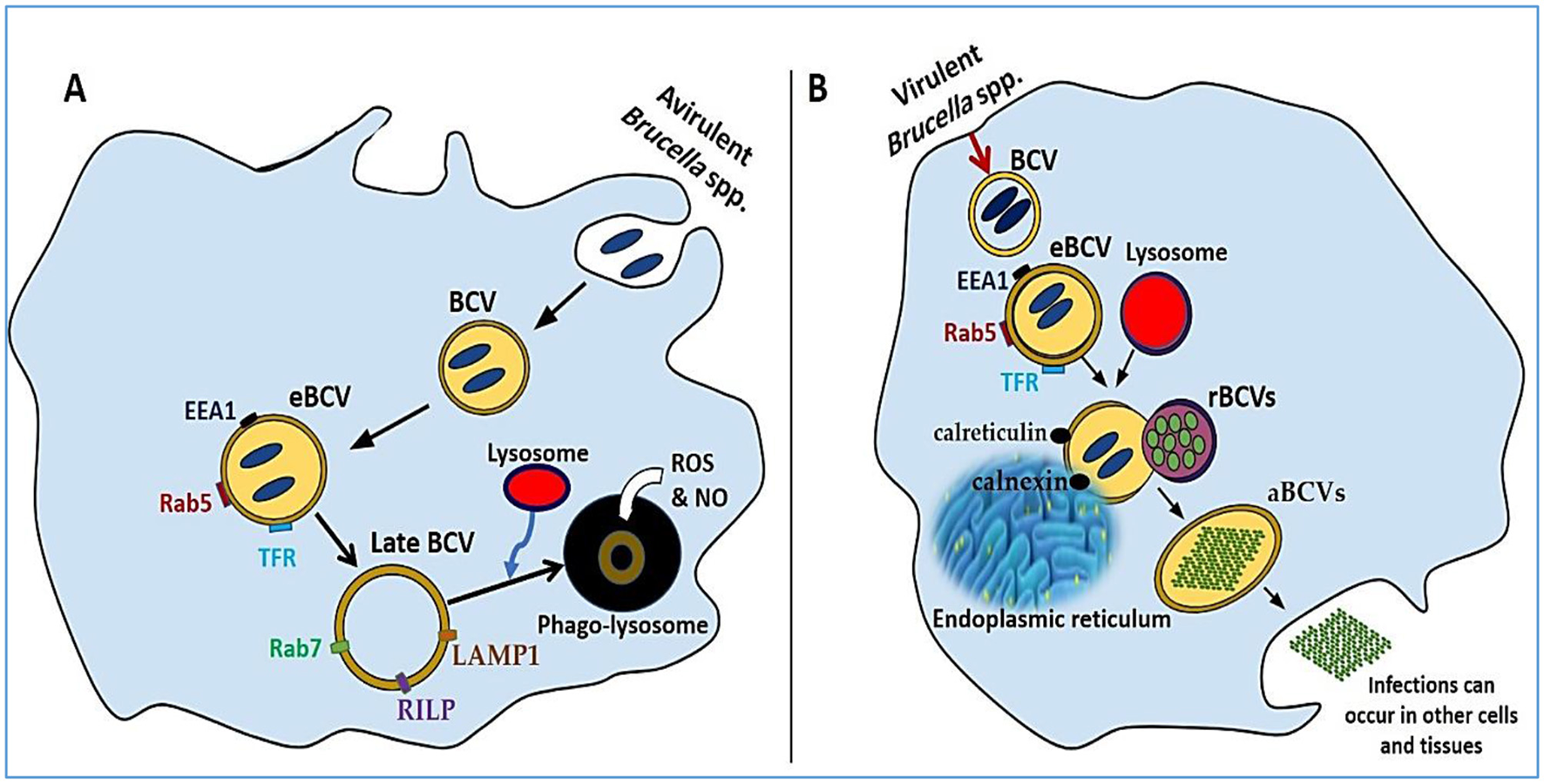
A comparative analysis of phagocytosis and exocytosis. (A) The intracellular development of an avirulent Brucella strain, highlighting the formation of eBCVs and late BCVs that eventually merge with lysosomes for bacterial degradation. (B) The progression of a virulent Brucella strain, showing evasion of lysosomal fusion and replication within the ER, followed by host cell lysis and dissemination to other tissues.
In avirulent strains, these BCVs typically merge with lysosomes, where they are exposed to reactive oxygen species (ROS), nitric oxide (NO), and lysosomal antimicrobial peptides, ultimately leading to bacterial degradation (9, 54, 55). Conversely, smooth LPS Brucella strains evade lysosomal fusion. They achieve this by secreting muramidase and expressing SegA, a protein that blocks the maturation of eBCVs into degradative compartments (56). The type IV secretion system (T4SS) is also key to avoiding immune detection and enabling intracellular survival. Replicative BCVs (rBCVs) emerge through fusion with the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), where they acquire ER markers such as calnexin and calreticulin, where Brucella replicates and evades immune responses (Figure 1B) (52). Further adaptation leads to the formation of autophagic BCVs (aBCVs), which are marked by the expression of autophagy-related proteins such as ULK1, Beclin 1, and ATG14L, allowing long-term intracellular persistence (57). Once macrophages fail to control infection, they undergo lysis, releasing Brucella into adjacent tissues and facilitating systemic spread (58).
Brucellar adhesins play pivotal roles in host cell invasion. Although Brucella spp. lack fimbrial adhesin loci and do not form pilus-like structures under electron microscopy, several non-fimbrial adhesins that mediate adherence to host cells have been identified (59). A graphical overview of these adhesins and their receptor interactions is presented in Figure 2. The diagram highlights how distinct adhesins mediate attachment to a variety of host cell types, including epithelial cells, erythrocytes, osteoblasts, and placental trophoblasts. By exploiting host receptors such as sialic acid-containing proteins, fibronectin, vitronectin, hyaluronic acid, and type I collagen, Brucella ensures successful adhesion and invasion, which are critical for intracellular survival and dissemination.
Figure 2
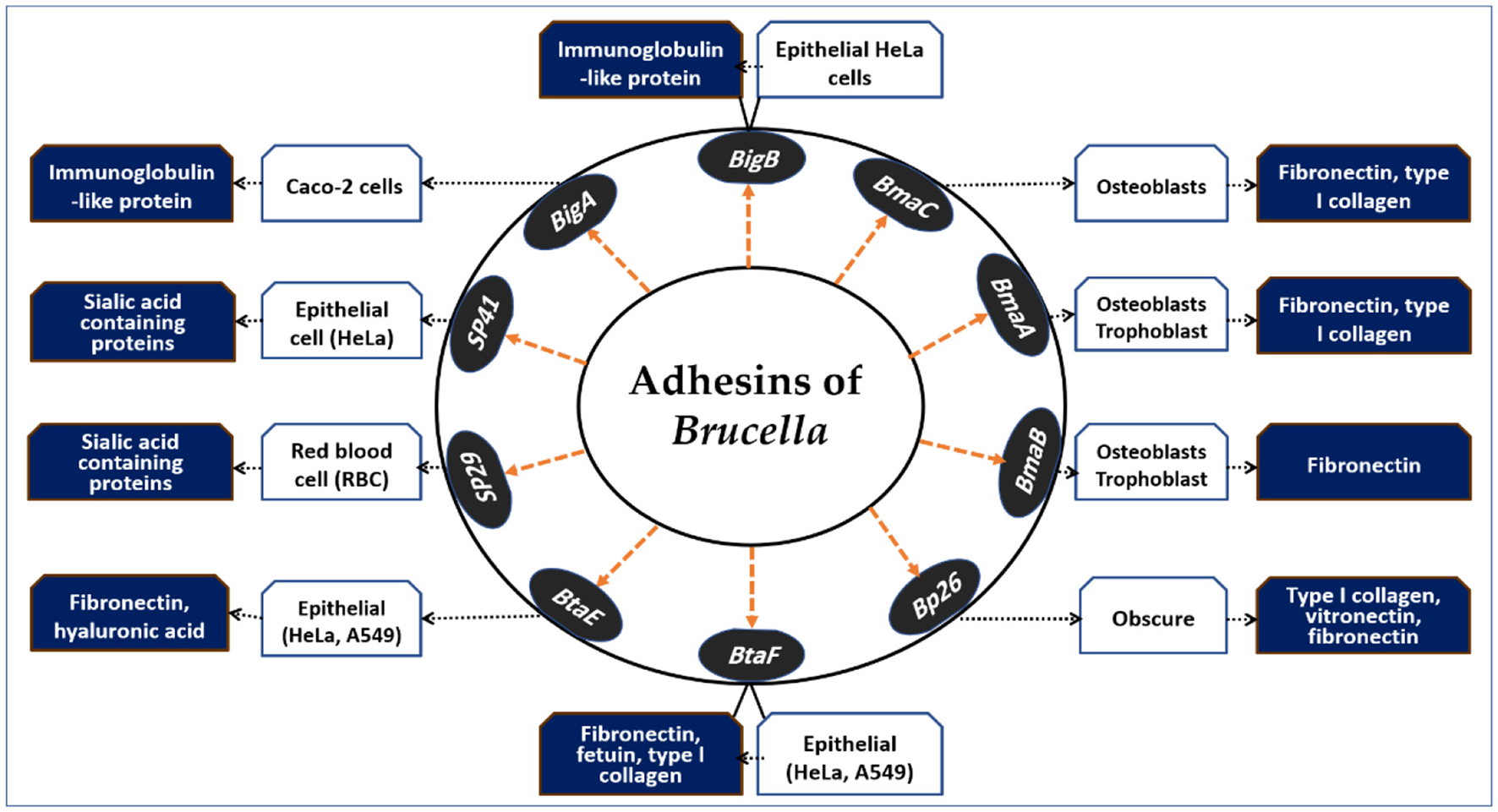
Adhesins of Brucella spp. and their host cell interactions. This schematic illustrates the major Brucella adhesins (SP29, SP41, BigA, BigB, BmaA, BmaB, BmaC, Bp26, BtaE, and BtaF) and their interactions with host cell types and receptors. Adhesins facilitate binding to epithelial cells, red blood cells, osteoblasts, and placental trophoblasts via host molecules such as sialic acid–containing proteins, fibronectin, vitronectin, hyaluronic acid, fetuin, and type I collagen. These adhesion mechanisms contribute to tissue tropism, colonization, and the intracellular persistence of Brucella, representing key steps in pathogenesis.
Hemagglutination assays using RBCs have identified lectin-like adhesins. Rocha-Gracia et al. (60) reported that B. abortus and B. melitensis agglutinate erythrocytes from various species via a 29 kDa surface protein (SP29). Neuraminidase treatment reduced SP29 binding to rabbit RBCs, suggesting that it interacts with sialic acid receptors. In B. melitensis, SP29 likely functions as a D-ribose-binding periplasmic protein precursor. While this species can infect erythrocytes in murine models (61), further work is needed to define the in vivo role of SP29.
SP41 was the first Brucella adhesin characterized in vitro (62). Antibodies against SP41 reduced B. suis adhesion to HeLa cells, and deletion of the ugpB gene—which is implicated in SP41 function—also diminished adhesion. Binding was inhibited by neuraminidase, highlighting a role for sialic acid residues. However, in B. ovis, ugpB deletion has no effect on adhesion or survival in macrophages or HeLa cells (63). Notably, the ugpB gene is functional in B. ovis but differs slightly from its homolog in B. suis. The lack of O-polysaccharide chains in B. ovis may indicate that alternative adhesins predominate.
The bigA gene, located on chromosome 1 of B. abortus (54), facilitates adherence to MDCK and Caco-2 cells. Czibener et al. (64) reported that this outer membrane adhesin, which contains an immunoglobulin-like domain, is essential for adherence. Deleting the pathogenic island BAB1_2009–2012 reduced adherence to HeLa cells. The BAB1_2009 gene encodes BigA, which has a BIg-like domain found in invasin/intimin family adhesins (65). Preincubating bacteria with antibodies against this domain significantly decreased the number of intracellular bacteria in HeLa cells (64). Overexpression of BigA enhanced adhesion and invasion in polarized epithelial cell lines by promoting contact with cell–cell junctions and inducing cytoskeletal rearrangements. The same locus also expresses BigB (BAB1_2012) (66), and the ΔbigB mutation significantly reduced the number of intracellular bacteria in HeLa and polarized MDCK cells during early infection stages. Recombinant BigB, like BigA, alters the cytoskeleton and affects focal adhesion locations. The BAB1_2011 gene encodes PalA, which is necessary for BigA and BigB expression, highlighting the role of the genomic island in Brucella adherence.
One study investigated Brucella Bp26 as an in vitro adhesin and reported that it elicits significant antibody responses in infected individuals (67). Bp26, which is approximately 250 amino acids long and contains a poorly understood motif (DUF541), interacts with type I collagen, soluble vitronectin, and soluble fibronectin but not with laminin. Its role in Brucella cell attachment and in vivo infection effects remains unclear. B. suis 1330 contains the monomeric autotransporter proteins BmaA and BmaB, encoded by BR0173 and BR2013, which are smaller than BmaC. Compared with wild-type strains, mutants lacking BmaB are removed more quickly from the spleen of BALB/c mice, suggesting that BmaB plays a role in chronic infection (68). A recent study by Bialer et al. (69) indicated that the bmaB locus in B. abortus and the bmaA and bmaC loci in B. melitensis may be pseudogenes, although some reports suggest that Bma proteins may have functional roles in certain B. suis strains. BmaA, BmaB, and BmaC likely contribute to bacterial attachment to various cell types, indicating diversity in Brucella spp. adhesins and potential host preferences. The discovery of BmaB also suggests its involvement in cell division, generating a new pole (69).
The autotransporter adhesin (AT) is essential for bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells (70). Brucella possesses five AT adhesins: type I monomeric ATs OmaA and BmaC (71), type II trimeric ATs BtaE and BtaF (72, 73), and the inverted AT adhesin BigA (64). BmaC specifically binds fibronectin (71), whereas BtaE and BtaF bind hyaluronic acid (72, 74). Mutants lacking these adhesins exhibit reduced adhesion to epithelial cells but maintain wild-type macrophage replication. In mice, these mutations are reversed when AT adhesins are administered intragastrically or nasally, indicating their role in mucosal adhesion. Some pathogens, such as BigA, exploit eukaryotic cell junctions to breach mucosal barriers (75). A double mutant of B. suis btaE btaF is more attenuated than a single mutant, suggesting complementary virulence roles (76). BtaF also shields B. suis from serum bactericidal action (72). BmaC, BtaE, and BtaF are localized near the cell pole (71, 74) and form a binding pole with G1 phase Brucella cells (77). In planktonic cultures, Brucella produces these adhesins in limited amounts, resulting in effective gene transcription during interactions with human cells. Several AT-encoding genes are regulated by VjbR (78) and MucR (79, 80), whereas btaE expression in B. abortus is controlled by a complex regulatory network (81, 82). Brucella AT-type adhesins may have multiple functions (82), necessitating cross-species and strain studies using mutants with gene disruptions to clarify their role in pathogenicity.
3 Diagnosis of brucellosis
Timely and accurate diagnosis is critical for the effective treatment and control of brucellosis. Current diagnostic tools include a range of serological, culture-based, and molecular methods. Serological assays, such as the Rose Bengal test and ELISA, offer rapid screening capabilities but can be limited in both sensitivity and specificity. Blood culture remains the gold standard for definitive diagnosis; however, it is time-consuming and may yield false negatives, particularly in patients who have already begun antibiotic therapy. Molecular approaches, including PCR and WGS, offer faster detection of Brucella DNA and are particularly valuable when traditional methods fall short. These complementary techniques collectively increase diagnostic accuracy, guide treatment decisions and improve patient outcomes. The following section outlines both current and emerging diagnostic approaches for brucellosis in humans and animals.
Recent advances in proteomics are reshaping brucellosis research and its applications in diagnosis, prevention, and control. In clinical microbiology, MALDI-TOF MS has emerged as a powerful tool for rapid, species-level discrimination of Brucella (e.g., B. abortus vs. B. melitensis) based on whole-cell proteomic fingerprints. The continuous expansion of spectral databases for highly pathogenic bacteria is closing gaps that previously limited diagnostic coverage, while machine-learning approaches applied to spectral data are further improving the classification of closely related species (83–85). Large-scale LC–MS/MS proteomic analyses are also generating serum biomarker panels capable of distinguishing acute from chronic brucellosis, with network-based and machine-learning methods offering promising candidates for future clinical assays (86, 87). In addition, immuno-proteomics has identified type IV secretion system components and outer-membrane proteins with high diagnostic sensitivity and specificity, and the design of multi-epitope fusion proteins from proteome-mined antigens is advancing serological testing while reducing the problem of LPS cross-reactivity (88, 89).
On the prevention and control side, proteomic prioritization of conserved outer-membrane proteins (e.g., Omp16, Omp25/BP26) supports the development of next-generation vaccines, including mRNA and outer-membrane vesicle (OMV)-based platforms, with OMV proteomes revealing multiple protective antigens (90, 91). Finally, pan-proteomic studies of reference and field isolates using label-free quantitation are identifying conserved stress-responsive proteins as potential biomarkers for surveillance and intervention, while innovations such as magnetics-assisted MALDI workflows point toward future culture-independent detection strategies for high-risk pathogens including Brucella (92, 93). These advances in proteomics complement conventional diagnostic modalities and highlight the ongoing evolution of brucellosis diagnostics; the following subsections detail the established culture-, serology-, and molecular-based methods that remain central to routine practice.
3.1 Culture methods
Accurate identification of Brucella species—the causative agents of zoonotic brucellosis—relies on isolation of the pathogen from blood, bone marrow, or other tissues (37). The success of culture-based detection varies according to disease stage, sample type, prior antimicrobial exposure, and culture technique used (94). Despite its limited sensitivity, culture remains the most definitive method of diagnosis (95). Innovations such as advanced incubators and the Ruiz-Castañeda biphasic culture system have improved biosafety and fostered more reliable bacterial growth. When performed promptly upon clinical suspicion, peripheral blood cultures are crucial for confirming the diagnosis, with reported sensitivities ranging from 10% to 90% (14, 96). These cultures are especially valuable when serological results are inconclusive (97). The techniques used include manual culture, lysis-based systems (98), clot cultures, and automated platforms—each contributing to increased sensitivity and faster detection (99).
During early infection, the bacterial load in the bloodstream is typically low and may be missed if the sample size is insufficient. To maximize diagnostic yield, it is recommended that two or three separate peripheral blood cultures be obtained (100). As brucellosis progresses, the bacterial burden often decreases, complicating pathogen isolation (101). Given the slow growth rate of Brucella, culture protocols must be extended to accommodate delayed detection (102). In severe cases, traditional culture methods may require incubation for up to 7 days, whereas automated systems may detect growth within 5 days (103). The American Society for Microbiology and the World Health Organization advocate for a 1-month incubation period for blood culture bottles, although this recommendation can pose logistical and financial challenges (104).
Within 24 h of infection, an estimated 25%−35% of patients may exhibit dissemination of Brucella beyond the bloodstream. Cultures may also be performed from bone marrow, urine, liver biopsies, lymph nodes, and cerebrospinal fluid and incubated at 35 °C in 5% CO2 for up to 2 weeks (105). Confirming the identity of Brucella species is essential for mitigating biosafety risks. Classic identification methods include phage lysis testing, oxidative metabolism assays, and agglutination with monospecific antisera (37). Owing to the limitations of conventional culture, serological testing can be employed to increase sensitivity. In recent years, matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) has emerged as a rapid, non-phenotypic identification method (106, 107). However, prior genomic validation is needed to ensure accuracy (39). Many laboratories now apply MALDI-TOF MS by directly introducing broth from positive cultures into the matrix (108, 109). Brucella organisms are safely inactivated via 100% ethanol prior to protein extraction, minimizing the risk of laboratory exposure (110).
MALDI-TOF MS has been used to identify Brucella reference strains from synthetic blood cultures (111). A refined Vitek MS database—including 590 protein spectra from 84 Brucella isolates—facilitates discrimination between Brucella and Ochrobactrum species, as well as accurate identification of B. abortus, B. melitensis, and B. suis. Further validation using wild-type isolates from diverse geographic and host sources is necessary. While the cost per sample with MALDI-TOF MS is relatively low, the initial investment and operational expenses can restrict access in endemic regions with limited resources (110).
Brucella species are among the most common causes of laboratory-acquired infections and are capable of causing outbreaks if proper containment measures are not enforced (112). Laboratory workers face significant risk due to the aerosolized particles generated during specimen handling. The routes of infection include inhalation, mucosal exposure, ingestion, and percutaneous entry. Reported infection rates among clinical laboratory staff range from 10% to 100%, influenced by pathogen load and laboratory safety standards (113, 114). Early-phase blood cultures, if misinterpreted by Gram staining, can lead to diagnostic errors due to Brucella's subtle morphology (115).
Inadequate biosafety protocols, particularly in resource-limited settings, increase the risk of laboratory-acquired infections (116). For example, one Turkish laboratory reported an 18% infection rate among staff, with an annual risk of 8% (116). Effective communication between clinicians and microbiologists is essential to ensure proper identification and handling of suspected Brucella samples. Until a diagnosis is confirmed or ruled out, all potentially hazardous samples should be managed with heightened containment and stored appropriately to prevent accidental exposure (117).
3.2 Serological methods
The primary diagnostic tools for brucellosis include culture, serological assays, and molecular techniques (3, 104). Given the nonspecific clinical presentation of brucellosis, laboratory confirmation is essential (118). Although serological methods are widely employed for identifying Brucella infections, their accuracy can be affected by limited sensitivity, cross-reactivity with other pathogens, and the need for well-equipped laboratories (3). In low-resource settings or in areas with lower disease prevalence, serological testing remains the cornerstone of diagnosis because of its relative simplicity, affordability, and high negative predictive value (104). Nonetheless, interpreting serological results can be challenging and sometimes inconclusive (118).
Common serological assays for diagnosing human brucellosis include the serum agglutination test (SAT), Rose Bengal test (RBT), Coombs test, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), which are generally ranked in the following order: ELISA > RBT > SAT > Coombs test (119). Compared with SAT or RBT, ELISA offers greater sensitivity (120–122). The performance of ELISA depends on the specific immunoglobulin detected. For example, Araj et al. (122) reported 91% sensitivity for IgG and 100% sensitivity for IgM, both with 100% specificity. In contrast, Memish et al. (123) reported lower IgG sensitivity (45.5%) but similarly high specificity (97.1%); IgM showed 79% sensitivity and 100% specificity. Overall, the combined ELISA results had a sensitivity of 94.1% and a specificity of 97.1%. Xu et al. (124) reported a sensitivity of 88.37% for IgG and 74.42% for IgM, matching the sensitivity of SAT. When the IgG and IgM data were combined, the sensitivity increased to 98.84%, whereas the specificity decreased to 84.13% (121, 125). These results suggest that while ELISA has excellent sensitivity (119), its reduced specificity may limit its standalone diagnostic utility (126).
As the disease progresses, IgG antibodies may become non-agglutinating (127). The Coombs test helps detect blocking antibodies in such cases, although it is infrequently used owing to its technical demands and the requirement for trained personnel. Alternatively, the Brucellacapt test detects both agglutinating and non-agglutinating antibodies (120) and may serve as a practical replacement for the Coombs test (120, 128). Xu et al. (124) demonstrated the increased specificity of Brucellacapt for diagnosing human brucellosis. Ardic et al. (129) reported a sensitivity of 97.3%, specificity of 55.6%, positive predictive value of 90%, and negative predictive value of 83.3% at a 1:160 titer. The test performance varied depending on the disease stage. A titer of 1:160 was considered optimal by Xu et al. (124), while increasing the threshold to 1:320 reduced the sensitivity. Although Brucellacapt can help detect chronic brucellosis (120), it may yield negative results in some chronic cases (124). An effective serological diagnostic strategy requires a highly sensitive test followed by a confirmatory assay (130). Xu et al. (124) reported that ELISA, with a sensitivity of 98.84% and a negative predictive value of 98.15%, is effective for rapid screening, especially in endemic regions. Brucellacapt offers excellent specificity and positive predictive value, making the combination of ELISA and Brucellacapt highly beneficial for diagnosing brucellosis in resource-limited and high-burden settings.
The RBT is a rapid, card-based agglutination assay that detects both agglutinating and non-agglutinating antibodies, yielding qualitative results (104). Performing RBT with serum dilutions can improve the specificity for samples initially testing positive (131, 132). However, false-positive results may occur due to factors such as hemolyzed serum, prior exposure, non-specific antibody binding, or cross-reactivity. This is particularly problematic in low-endemic areas, where the reduced positive predictive value of serological testing may lead to unnecessary follow-up, increased healthcare costs, and patient anxiety (133). Test accuracy can also be influenced by the disease stage, immune status of the host, and specific Brucella species involved. Laboratory-related errors further highlight the need for proper training and stringent quality assurance practices (104).
Because of the complexity of Brucella antigenic structures, various immunological approaches are employed for diagnosis (37). Whole-cell antigens are used in indirect fluorescent antibody tests (134). Most serological assays target antibodies against smooth LPS or cytosolic proteins. The immune response to smooth LPS—common to smooth Brucella species—results in sequential production of IgM (first week) and IgG1 (second week), followed by IgG2 and IgA (third week) (104). Misdiagnosis may occur with species such as B. canis, which lack O-polysaccharides, complicating detection in human infections (135). To address these diagnostic limitations, Loubet et al. (133) conducted a retrospective study at the French National Reference Center for Brucella, analyzing 3,587 serum samples from June 2012 to June 2023. Among these cases, 148 were confirmed brucellosis cases. Although individual tests exhibited high sensitivity and specificity, the diagnostic accuracy improved significantly when the assays were combined. The best-performing algorithm—using RBT, Brucellacapt, and ELISA for IgM and IgG—achieved a sensitivity of 90.5% and specificity of 99.7%. These findings underscore the importance of integrated diagnostic strategies and the need for continued innovation in testing methods.
In animals, brucellosis is primarily diagnosed via serological assays such as RBT, complement fixation tests (CFTs), and ELISA (136). Although these tests effectively detect Brucella-specific antibodies, their reliability diminishes in chronic infections, when antibody titers often fall below detectable levels (137). Furthermore, Brucella's ability to survive intracellularly enables the pathogen to evade immune detection, complicating serological diagnosis (138). As a result, seronegative carriers—infected animals that do not produce detectable antibodies—pose a serious challenge for disease control, as they can still transmit the infection to other animals and humans (139). To address these diagnostic gaps, molecular techniques such as PCR should be used alongside serological methods to detect and manage brucellosis accurately in both humans and animals.
3.3 Molecular methods
Molecular diagnostic technologies, particularly PCR, have gained significant prominence in the detection and identification of Brucella species (138). PCR offers high sensitivity and specificity, enabling the detection of Brucella DNA in various biological samples, including blood, milk, tissues, and semen (136). Unlike serological tests, which detect host antibody responses, PCR directly targets Brucella DNA, making it particularly valuable for identifying infections in seronegative individuals and animals. Among the molecular targets, the insertion sequence IS711 is widely utilized because of its specificity for the Brucella genus (140). PCR assays based on this gene have demonstrated high diagnostic utility, especially in cases where culture fails or serological tests yield negative results. For example, Hinić et al. (141) demonstrated that IS711-based PCR could detect Brucella DNA in wild boars even when traditional isolation methods were unsuccessful and serological tests were negative. The ability of PCR to amplify DNA from a variety of sample types underscores its importance in endemic regions where rapid and accurate diagnosis is critical. This is particularly relevant in scenarios where serological tests are limited by low sensitivity or delayed antibody responses (133).
Several outer membrane protein (OMP) genes, including omp2, omp31, and omp28 (Bp26), which serve as additional targets for PCR-based detection, have also been identified through molecular diagnostics (142, 143). Although 16S rRNA and IS711 remain widely used for Brucella identification, some studies have raised concerns regarding IS711′s variability and occasional deletions in certain strains, which may affect assay sensitivity. Another widely used marker is the bcsp31 gene, which encodes a highly immunogenic membrane protein and has been validated for reliable species identification (142, 144, 145). Multiple PCR-based techniques, including conventional PCR, real-time PCR, multiplex PCR, nested PCR, and PCR-enzyme immunoassays in microplate formats, have been developed to increase diagnostic performance (104). Multiplex PCR is particularly advantageous, as it allows for simultaneous detection and differentiation of field strains and vaccine strains such as S19, RB51, and Rev.1 in a single assay (146, 147).
In recent years, loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) has emerged as a promising alternative to PCR. LAMP offers several advantages, including rapid amplification, visual detection of results, and minimal equipment requirements—typically only a constant-temperature heat source such as a 63 °C water bath. This method eliminates the need for gel electrophoresis and produces results in under 1 h, making it highly suitable for field diagnostics and use in low-resource settings (148). Its affordability and ease of use make it an attractive option for point-of-care testing in brucellosis-endemic regions.
Sequencing-based technologies also contribute to an improved understanding of Brucella epidemiology. Whole-genome sequencing and other genetic analyses have elucidated the mechanisms underlying strain variation, virulence, and evolutionary relationships (149, 150). Such data are critical for advancing vaccine development and refining diagnostic targets (151). However, the high cost and technological demands of next-generation sequencing limit its widespread application, especially in low-income countries where brucellosis is often endemic (150, 152, 153).
Emerging molecular innovations aim to overcome these barriers. Magnetic nanoparticle-based DNA biosensors have shown potential for rapid and highly specific detection of Brucella DNA. These biosensors employ frequency-mixing magnetic detection and DNA hybridization, enabling the identification of low DNA concentrations within minutes—even in field conditions (138, 154). Additionally, immuno-surface plasmon resonance biosensors have been developed to detect Brucella without the need for DNA amplification. These portable, cost-effective devices offer a detection threshold as low as 2.8 bacteria/ml, presenting a promising solution for decentralized testing (155).
Despite the increasing availability of molecular tools, traditional culture and serological methods remain the standard diagnostic approaches for brucellosis in many settings. However, the diagnosis remains challenging because of the disease's non-specific symptoms, which often resemble those of other febrile illnesses and can result in delayed or missed diagnoses (156). The lack of pathognomonic clinical signs, combined with the risk of false-negative serological results in early or atypical presentations, highlights the need for improved diagnostic awareness (95, 157). Education of clinicians and health workers, especially in endemic areas and among at-risk populations, is critical for enhancing early recognition and response to brucellosis (158).
4 Pathways of brucellosis transmission
In addition to implementing accurate diagnostic strategies, identifying and disrupting the transmission pathways of brucellosis to effectively control and prevent the disease is imperative (159). Brucellosis is primarily a zoonotic disease transmitted from animals to humans, although human-to-human transmission—while rare—has also been documented (160). Although the latter route is less common, both pathways contribute to the persistence and potential expansion of brucellosis, emphasizing the need for comprehensive preventive measures (Figure 3).
Figure 3
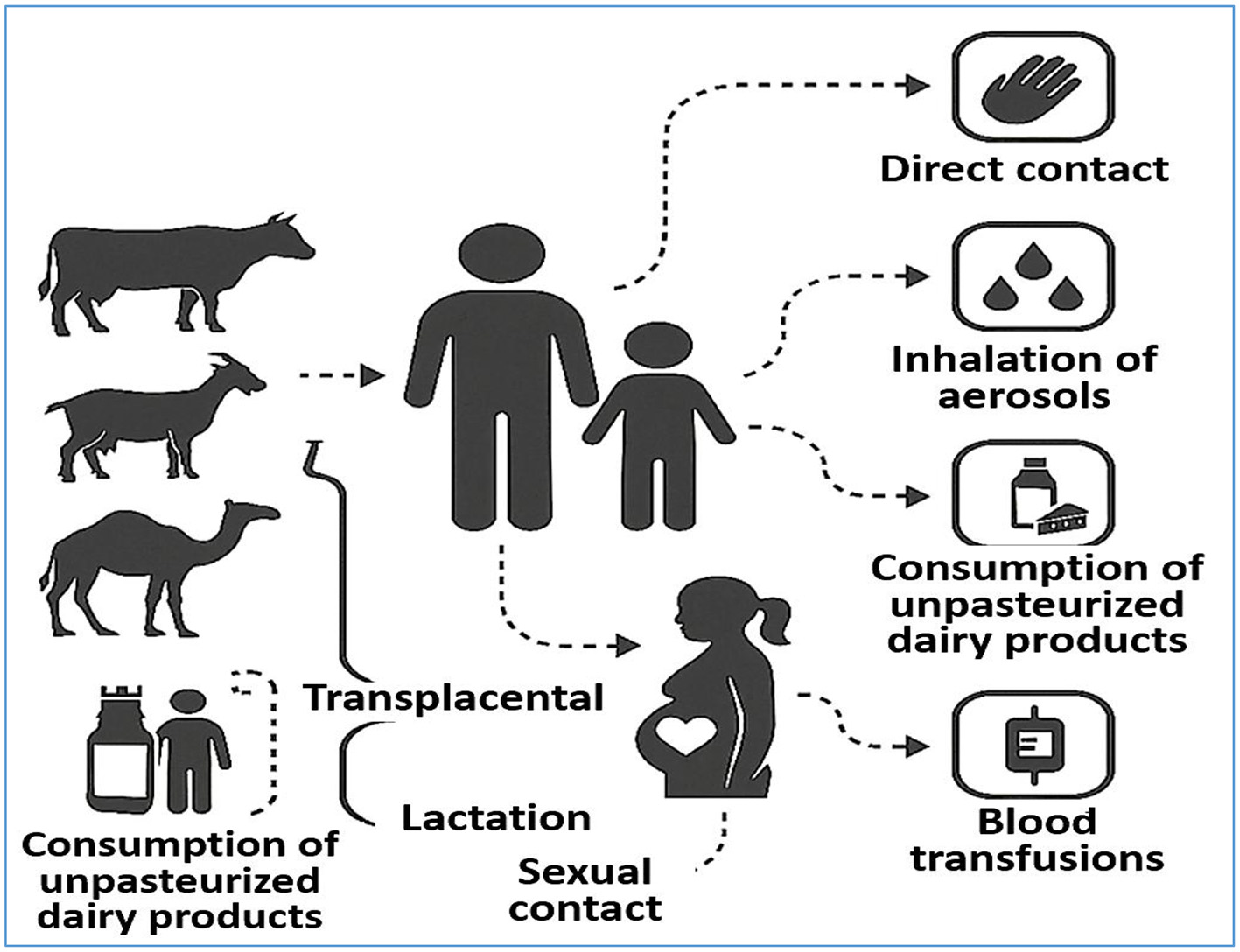
Transmission Pathways of Brucellosis. The diagram illustrates the major transmission routes of Brucella spp. from animals to humans, including direct contact with infected animals, ingestion of unpasteurized dairy products, inhalation of contaminated aerosols, and exposure through mucous membranes or broken skin. It also highlights less common human-to-human transmission pathways such as transplacental transfer, breastfeeding, sexual contact, blood transfusion, and organ transplantation. Understanding these routes is critical for developing effective prevention and control strategies.
Zoonotic transmission typically occurs through direct contact with infected animals or their secretions, especially during the handling of aborted fetuses, placental tissues, or birth fluids. Occupational exposure is a significant risk factor, particularly for farmers, veterinarians, abattoir workers, and laboratory personnel. Inhalation of infectious aerosols—especially in confined environments such as laboratories and livestock facilities—is another important mode of transmission (161, 162). Moreover, the ingestion of unpasteurized milk, cheese, and other dairy products derived from infected animals remains a major source of human brucellosis, particularly in endemic regions where food safety regulations are inadequately enforced (162).
Although infrequent, human-to-human transmission via several mechanisms has been reported. These include vertical transmission across the placenta, breastfeeding, sexual contact, and iatrogenic exposure through contaminated blood transfusions or bone marrow transplantation (160). Aerosol transmission has also been implicated in clinical and laboratory settings under specific conditions (96). Although such cases are uncommon, the wide array of possible transmission routes expands the pool of susceptible individuals and necessitates vigilance across multiple sectors of public health and clinical care.
A diverse range of animals serve as reservoirs for Brucella species, including cattle (B. abortus), goats and sheep (B. melitensis), swine (B. suis), camels, dogs (B. canis), poultry, and numerous wildlife species (163). These hosts play crucial roles in maintaining the endemicity of brucellosis and facilitating its transmission to humans. Human infection is not restricted by age or sex; however, young and middle-aged adults are most frequently affected by increased occupational and environmental exposure (164). Pregnant women and newborns also remain vulnerable, given the potential for transplacental transmission and perinatal complications (165, 166).
5 Brucellosis treatment regimens
Brucellosis treatment has evolved significantly since the mid-19th century. Early therapeutic attempts—dating back to 1855—included quinine, colchicine, and ampicillin, followed by the use of salicylates, ichthyol, iodine, immune sera, and early vaccines. However, these treatments often lack efficacy and are associated with considerable toxicity (162). Sulfonamide drugs were introduced in 1936, marking the beginning of antimicrobial therapy for brucellosis, although the results have been inconsistent (9). The addition of streptomycin in the late 1940s, used alone or combined with oral sulfadiazine, also failed to achieve consistently successful outcomes (161).
Subsequent studies demonstrated that combination antibiotic therapy produced significantly better results than monotherapy, reducing relapse rates and improving overall efficacy (161). In 1971, the World Health Organization (WHO) recommended a 3-week treatment course comprising tetracycline and streptomycin. This protocol was revised in 1986 to recommend a 6-week regimen of doxycycline and rifampicin or a 2 to 3-week course of tetracycline plus streptomycin, which has become the standard treatment approach for human brucellosis (167). Today, the cornerstone of brucellosis treatment remains antimicrobial therapy, particularly the use of dual antibiotics such as doxycycline (100 mg twice daily for 6 weeks) in combination with either streptomycin (1 g intramuscularly daily for 2–3 weeks) or rifampicin (600–900 mg daily for 6 weeks) (167, 168). The choice of regimen depends on the disease severity, patient comorbidities, and the presence of focal complications such as osteoarticular involvement or neurobrucellosis, which may require extended or adjusted courses of therapy.
Effective treatment is critical not only for resolving infection but also for minimizing the risks of chronic disease, relapse, complications, and transmission (Figure 4). Prompt therapy can reduce the incubation period, accelerate symptom relief, and lower both morbidity and mortality rates (169, 170). In addition to standard antibiotic regimens, adjunctive approaches—such as surgical intervention for severe cases, traditional Chinese and integrative medicines to enhance the immune response, and nanotechnology-based therapies for targeted drug delivery—are increasingly explored. These strategies underscore the importance of individualized treatment plans tailored to disease severity, comorbidities, and available resources. This section reviews each modality, outlining its key benefits and limitations.
Figure 4
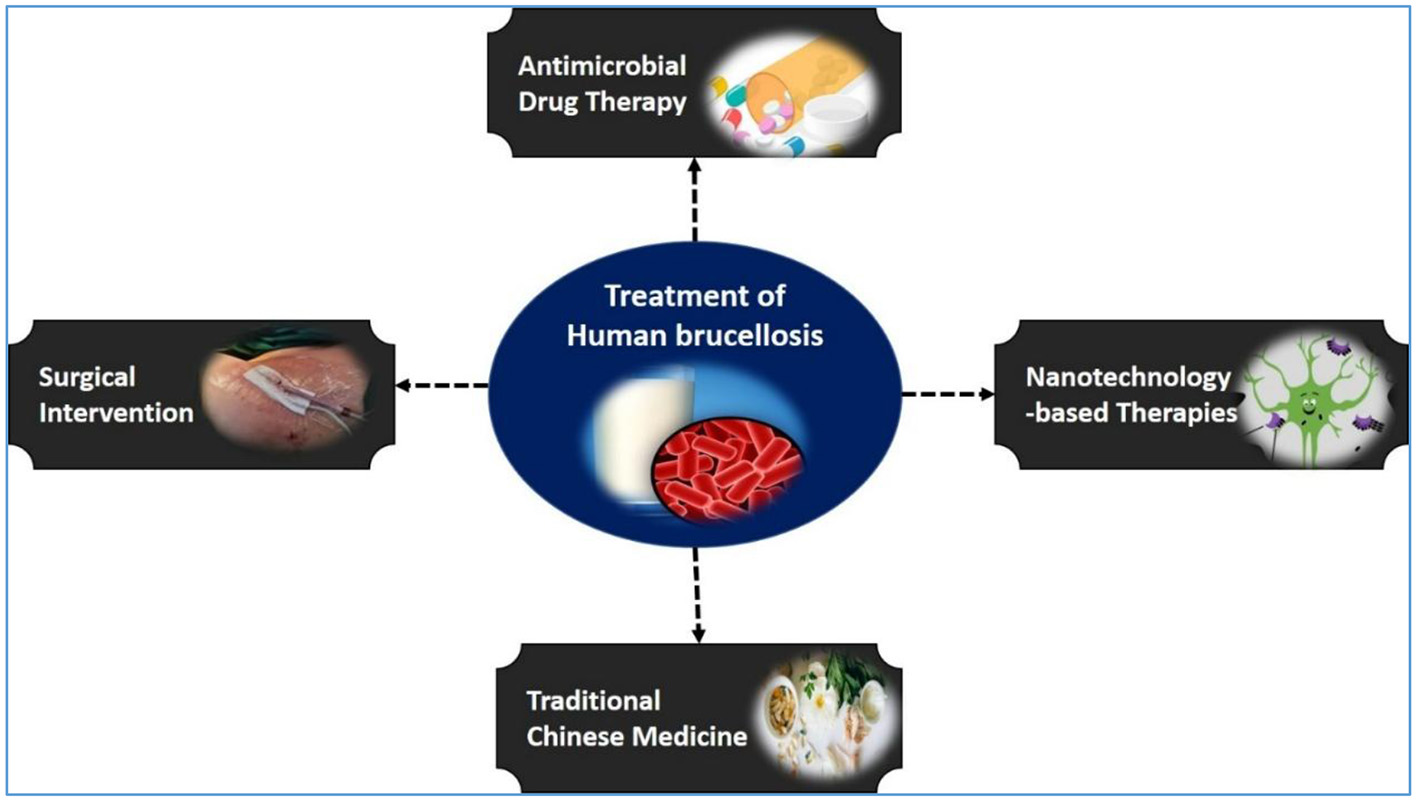
Treatment strategies for human brucellosis. A schematic overview showing the main therapeutic approaches for human brucellosis, including antimicrobial drug therapy, surgical intervention, traditional Chinese medicine, and emerging nanotechnology-based therapies.
5.1 Antimicrobial drug therapy
As no licensed vaccine exists for human brucellosis, antibiotic therapy remains the cornerstone of treatment (171). The intracellular nature of Brucella, particularly its residence within reticuloendothelial cells and bone, poses significant challenges for effective antibiotic penetration (172). Consequently, combination antimicrobial regimens that can penetrate macrophages and maintain efficacy in acidic environments are standard practices (173–175). Earlier monotherapies, including tetracycline, rifampin, and quinolones, had limited success, with high relapse rates; for example, ciprofloxacin alone was associated with an 83% recurrence rate (176). The WHO first recommended combination therapy in 1976, advocating for a 6-week course of rifampin and doxycycline (177), with other common regimens, including doxycycline plus streptomycin, rifampin, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (176). While 6-week treatments are generally recommended to reduce relapse (171), recent evidence suggests comparable outcomes with 4-week regimens using doxycycline, streptomycin, and hydroxychloroquine (178), potentially offering shorter, safer treatment options.
The current WHO and CDC guidelines endorse dual or triple antibiotic regimens (41). Triple therapy can reduce Brucella DNA levels more significantly (179). It is associated with higher rates of adverse effects, lower adherence, and increased risk of resistance (180). Injectable aminoglycosides such as gentamicin or streptomycin, often part of triple therapy, require parenteral administration and can limit feasibility in outpatient settings. Recent studies, including one conducted in Saudi Arabia, reported no significant differences in cure rates between dual and triple therapies (181). A 2025 study by Alsowaida et al. (41) further confirmed that dual therapy is equally effective but better tolerated, making it more cost-effective and preferable for most patients.
Despite these advances, several challenges remain. Routine antibiotic susceptibility testing is often bypassed due to safety risks to laboratory personnel and a lack of standardized testing protocols (182). Some antibiotics lack approval or defined breakpoints by the EUCAST or CLSI, complicating treatment decisions. High rifampicin resistance in regions with endemic tuberculosis, along with 5%−16% relapse rates, further complicates management (183–185). Severe cases involving osteoarticular infections, neurobrucellosis, or endocarditis require intensive therapy (186). Tetracyclines are contraindicated in young children and lactating women (187), and fluoroquinolones should not be used as monotherapy due to high relapse rates (188–190). While doxycycline remains the preferred agent, resource-limited settings may require alternative tetracyclines. Distinguishing relapse from reinfection remains a diagnostic challenge, emphasizing the need for timely and appropriate therapy (191). Antimicrobial therapy offers high cure rates and structured protocols but must be balanced against recurrence risk, side effects, and the emergence of resistance (175–178).
5.2 Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is an important adjunct to antimicrobial therapy in cases where medical management alone is insufficient or when complications arise. In Brucella endocarditis, early antibiotic treatment combined with valve surgery significantly improves prognosis, reduces mortality, and enhances quality of life (192, 193). A study by Keshtkar-Jahromi et al. (194) involving 308 patients revealed that combining surgery with medical therapy lowered mortality from 32.7% to 6.7%. Surgery is indicated in cases of advanced heart failure, hemodynamic instability, prosthetic valve endocarditis, persistent bacteremia, valve dysfunction, local abscess formation, sinus tracts, and vegetation ≥30 mm—or >10 mm if highly mobile—despite adequate antimicrobial therapy (195, 196). For example, Hong et al. (197) reported a case where antibiotic therapy initially managed a small vegetation (<10 mm), but progression to mitral valve dysfunction required delayed surgical intervention. Postoperative antibiotic therapy was continued for 6 weeks, followed by lifelong prophylaxis.
In Brucella spondylodiscitis, long-term antibiotic therapy is the primary treatment, although surgery may be necessary in 3%−29% of cases (198, 199). Indications for surgical intervention include neurological deficits, large paravertebral or epidural abscesses unresponsive to medical therapy, spinal instability, or deformity (200, 201). While limited data exist on the surgical management of Brucella spondylitis, studies suggest that spinal instrumentation can be safely employed in infected patients without impeding bacterial eradication (201–203). Jiang et al. (204) suggested the combination of surgery with antibiotics such as rifampin and doxycycline. However, Katonis et al. (201). noted that chemotherapy alone is often effective and that surgery should be reserved for refractory or complicated cases. Surgical management is particularly beneficial for patients with extensive intervertebral disc damage, vertebral collapse, neurological deterioration, or spinal deformities. Postsurgical care necessitates extended antibiotic courses, typically exceeding 6 months, to prevent relapse and ensure full recovery.
5.3 Nanotechnology-based therapies
Despite the efficacy of conventional antimicrobial regimens, brucellosis frequently relapses owing to the ability of Brucella spp. to persist intracellularly within macrophages. This persistence impedes immune clearance and restricts antibiotic penetration (205). Nanotechnology offers a promising approach to overcome these limitations by enhancing drug delivery, reducing recurrence, and addressing antimicrobial resistance (206). NPs possess unique physicochemical properties that facilitate membrane penetration and enable targeted disruption of bacterial metabolic pathways (207, 208). NPs may function as intrinsic antimicrobials or act as delivery vehicles—referred to as nanobiotics or nanoantibiotics—for traditional antibiotics (207). Inorganic NPs with antimicrobial activity are termed nanobacteriocides, while those used to transport drugs are known as nanocarriers (207). These systems can bypass common resistance mechanisms, such as poor intracellular access and bacterial efflux pumps, which limits the effectiveness of standard antimicrobial agents (207, 209).
Several nanocarrier systems—such as solid lipid NPs, liposomes, chitosan-based NPs, niosomes, and their combinations with sodium alginate—have demonstrated potential for improving treatment outcomes in patients with brucellosis (210). For example, hydroxychloroquine and doxycycline delivered via solid lipid NPs combined with cadmium telluride quantum dots exhibited enhanced efficacy and may reduce relapse rates (211). In a study by Hosseini et al. (205), compared with free doxycycline, doxycycline-loaded solid lipid NPs reduced the intracellular burden of B. melitensis in macrophages by 3.5 logs, supporting their potential for preventing recurrence.
Codelivery strategies further improve outcomes. Curcumin, which has pH-sensitive antimicrobial activity, can potentiate doxycycline under acidic conditions (212). El-Essa et al. (213) assessed pH-responsive chitosan-sodium alginate NPs loaded with doxycycline and a curcumin-loaded niosome hydrogel in guinea pigs infected with B. melitensis biovar 3. This dual nanoformulation reduced the splenic bacterial load to 19 ± 3.0 log CFU, whereas it was 640.66 ± 4.3 log CFU in the untreated controls. Polyanhydride-based NPs encapsulating doxycycline and rifampicin have also shown promise. Lueth et al. (206) reported that these NPs, ranging from 162.8 to 326.8 nm in size, with polydispersity indices of 0.1–0.13 and zeta potentials of −1.56 to −21.2 mV, provided extended-release delivery. Over 5 days, they eradicated B. melitensis from infected macrophages and significantly reduced liver bacterial counts in BALB/c mice. Notably, no significant difference was observed between animals treated with daily free drugs and those treated weekly with nanoformulations, suggesting similar efficacy with a reduced dosing frequency.
The use of gentamicin, a potent but nephrotoxic antibiotic, can be enhanced via the use of nanocarriers (214, 215). Poly(lactic–coglycolic acid) (PLGA) microparticles and NPs (~1 μm and ~299 nm, respectively), which are coencapsulated with gentamicin and bis(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate sodium salt, reduce splenic infection by 3.23 logs and achieve 50% eradication in mice without renal toxicity (216). Poly(amidoamine) (PAMAM) dendrimers—water-soluble, hyperbranched polymers (1–15 nm, 30–200 kDa)—are another promising platform (217, 218). These nanocarriers (generations G0–G5) can deliver drugs or genetic material (219). Gentamicin-loaded G4 dendrimers modified with polyethylene glycol produced NPs with a diameter of 51.23 nm, a zeta potential of −8.8 mV, and a 0.2 polydispersity index. Enhanced intracellular drug release can be achieved via glutathione-mediated mechanisms and efflux pump inhibition (220).
Overall, nanoblass-based strategies—including microspheres, dendrimers, chitosan particles, and PEGylated formulations—offer targeted delivery, reduce toxicity, and improve efficacy for treating brucellosis. These advancements could revolutionize brucellosis therapy in both human and veterinary medicine by overcoming current limitations in antibiotic delivery and persistence (212).
5.4 Traditional Chinese medicine
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has long been utilized for the treatment of infectious diseases in China and is increasingly gaining recognition for its potential role in managing brucellosis (159, 221). One of the most well-documented examples of TCM's therapeutic potential is artemisinin, derived from Artemisia annua, which has been adopted globally as a first-line treatment for malaria (221). Moreover, herbal formulations have demonstrated efficacy in alleviating symptoms and reducing hospital stays in patients with viral infections such as SARS and COVID-19 owing to their immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory effects (222–224).
In the context of brucellosis, TCM is often employed as an adjunct to antibiotic therapy to enhance treatment outcomes, minimize side effects, and reduce the risk of antimicrobial resistance (225, 226). Zhang et al. (227) identified ten medicinal herbs that are frequently used to treat brucellosis: Gan Cao (GC), Dang Gui (DG), Fu Ling (FL), Chen Pi (CP), Bai Shao (BS), Chuan Xiong (CX), Bai Zhu (BZ), Huang Qi (HQ), Dang Shen (DS), and Di Huang (DH). These herbs exhibit a range of pharmacological activities, including analgesic, antioxidant, antibacterial, antiviral, immunoregulatory, and hepatoprotective effects. Notable examples include the antiarthritic activity of GC (228), the antifibrotic action of DG (229), the antidiabetic effects of FL (230), and the antiatherosclerotic and anticancer potential of CX (231). BZ enhances spleen function (232), HQ and DS are known for their nephroprotective effects (233, 234), and DH has demonstrated antitumor properties (235).
The therapeutic effects of TCM are attributed to bioactive compounds within the plants, some of which may have direct activity against Brucella spp. (236). Wen et al. (237) evaluated the antibacterial properties of ten ethanol extracts from herbs used in Malaysian Chinese medicine against B. melitensis. Using disc diffusion assays, four extracts—Coptis chinensis, Radix paeoniae rubra, Galla chinensis, and Cortex phellodendrin—showed inhibitory activity, with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) ranging from 3.75 to 30 mg/ml. These findings suggest the potential utility of these herbs as prophylactic or therapeutic agents against brucellosis.
Coptis chinensis (Huanglian) is particularly noteworthy for its antimicrobial potency. Kim et al. (238) demonstrated that ethanol extracts of C. chinensis and its major constituents—berberine and palmatine—exhibited inhibitory activity against B. abortus at concentrations of 1,000 μg/ml and 100 μg/ml, respectively. However, the extracts and isolated compounds had limited effects on the intracellular survival and replication of Brucella within RAW 264.7 macrophages, indicating that while they are bacteriostatic, their intracellular efficacy may be restricted. Further exploration by Xuan et al. (239) highlighted the antiadhesive potential of emodin, an anthraquinone compound derived from traditional herbs. Emodin significantly reduced B. abortus entry into macrophages and decreased bacterial adhesion at the highest non-cytotoxic dose. These effects were associated with reduced ERK1/2 phosphorylation and F-actin polymerization, suggesting disruption of host-pathogen interactions. Although emodin does not inhibit Brucella growth directly, its ability to modulate host cell signaling implies a promising adjunctive role.
The therapeutic potential of Caryopteris mongolica root extract, which is used in traditional Mongolian medicine, was evaluated in vivo by Tsevelmaa et al. (240) BALB/c mice were treated for 21 days with doxycycline (2 mg/day), a combination of doxycycline (1 mg/day) and C. mongolica extract (20 mg/day), or the extract alone. Compared with the controls, all the treatment groups presented significant reductions in splenic bacterial loads, with the combination therapy providing enhanced efficacy. The extract alone reduced the splenic bacterial burden by 1.47 log units, supporting its synergistic potential in brucellosis therapy and the possibility of lowering antibiotic doses to mitigate resistance.
Collectively, Chinese herbal medicines, including compound formulations and monomeric constituents, display diverse antibacterial mechanisms (241). These include limiting bacterial gene expression, modulating immune responses, and reducing the release of proinflammatory mediators. Ongoing research into TCM-derived compounds is driving the development of novel therapeutics, particularly those against antibiotic-resistant pathogens (242). By elucidating the molecular interactions between herbal bioactives and bacterial or host targets, TCM offers a complementary strategy to conventional antibiotic therapy—one that may help curtail resistance, enhance treatment efficacy, and provide alternative or adjunctive options in brucellosis management.
6 Vaccination
Vaccination remains a cornerstone in the control and prevention of animal brucellosis, with significant implications for public health (243–246). Live attenuated vaccines such as B. abortus S19 and RB51 for cattle and B. melitensis Rev.1 for small ruminants are widely employed in various countries. However, these vaccines pose notable challenges, including the risk of accidental human infection and adverse effects in animals, particularly abortion in pregnant livestock (245, 247–249). Furthermore, standard serological tests used to detect Brucella infections cannot reliably differentiate between vaccine and field strains or detect antibodies specific to RB51 (250). In contrast, molecular methods such as PCR provide higher specificity and can distinguish between vaccine and wild-type strains (147).
At present, no vaccines are approved for human use. The potential for severe side effects makes current animal vaccines unsuitable for human application (251). This has spurred research into safer and more effective human vaccine candidates. Despite their importance in reducing zoonotic transmission, current animal vaccines have limitations, including short-term efficacy, hypersensitivity reactions, and interference with serodiagnosis (252). For example, while the S19 vaccine offers temporary protection, it requires frequent boosters and may elicit hypersensitivity. Other experimental vaccines, such as B. abortus 84-C and M-104, are generally safe but can cause severe side effects in some individuals (37, 40).
An emerging strategy for vaccine development involves the use of genetically engineered live vectors derived from nonpathogenic bacteria or viruses that express immunogenic Brucella antigens (253). Examples include Lactococcus lactis (254), Escherichia coli (255), Salmonella enterica (256), and Semliki Forest virus (257). These vectors have been shown to infect a variety of cell types and express antigens intracellularly, promoting robust immune responses (253). One such example is the Flu-BA vaccine, which employs recombinant influenza viruses (H5N1 as the prime and H1N1 as the booster) to deliver OMP 16 and ribosomal protein L7/L12, with the aim of protecting cattle against B. abortus (258, 259).
Subunit vaccines, which are composed of purified antigens such as Omp31, BP26, and L7/L12 or outer membrane vesicles, offer a safer alternative to live vaccines. These compounds have shown immunogenicity in murine models but often require strong adjuvants and multiple doses to achieve protective immunity (175). Among the subunit approaches, DNA vaccines have garnered significant interest. These vaccines encode antigenic components of Brucella and stimulate both humoral and cellular responses. They are inherently safe, contain CpG motifs for immune stimulation, and do not require complex storage conditions (76, 260).
DNA vaccines for brucellosis frequently target genes essential for Brucella's intracellular survival and virulence, including bvrR/bvrS (261), Cu-Zn superoxide dismutase (262), ribosomal L7/L12, Brucella lumazine synthase (BLS) (76), Omp31 and Omp25 (263), BCSP31 (264), SP41 (265), and ribosomal protein L9 (266). These antigens have been shown to elicit protective immune responses in animal models challenged with virulent strains such as B. abortus S19 and 2308 and B. melitensis 16 M and Rev.1 (264, 265). DNA vaccine development holds promise for overcoming limitations associated with current live attenuated vaccines (261, 264, 267). However, despite their potential, DNA vaccines generally elicit weaker immune responses in humans than in animal models—particularly in mice—underscoring the need for improved delivery systems and optimized codon usage to increase their efficacy (252).
NP-based vaccine delivery has shown promise in enhancing immune responses. In animal models, NPs containing Brucella antigens effectively elicit IgM, IgA, and IgG responses and promote T-helper 1 (Th1) and T-helper 17 (Th17) cell-mediated immunity (3, 268). However, NP-based vaccines are not yet recommended for human use because of concerns about antigen loading efficiency, immune activation capacity, and potential toxicity or disease transmission risks (269, 270). Strategies that integrate LPS and oligosaccharide antigens into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) NPs have demonstrated enhanced antibody production, offering significant protective benefits in animal models (271).
The use of recombinant peptides in vaccine design represents another innovative approach to brucellosis prevention. These peptides provide a safer and more targeted alternative to traditional vaccines, avoiding the risks of abortion and diagnostic interference associated with live attenuated vaccines such as Rev.1 (272). One promising candidate, rBtuB-Hia-FlgK, has demonstrated the capacity to enhance CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell responses to Brucella antigens (273). Compared with attenuated vaccines, recombinant peptide vaccines could achieve protective efficacy while offering improved safety profiles for use in both livestock and humans.
The successful development of a human brucellosis vaccine necessitates a comprehensive understanding of Brucella pathogenicity and host immune interactions. Although DNA vaccines are particularly suited for inducing cell-mediated immunity, they must overcome limitations related to immunogenicity in humans (274). Innovative strategies such as codon optimization, advanced delivery systems, and adjuvant formulations are being explored to improve their efficacy (275). Additional techniques—including transposon mutagenesis, the creation of green fluorescent protein-tagged strains, gene knockouts, and high-throughput bacterial imaging—are being employed to identify and evaluate novel vaccine targets (276).
Ultimately, vaccine candidates must demonstrate efficacy in preclinical models (e.g., mice and non-human primates) and undergo rigorous safety and immunogenicity testing before they can be approved for human use. Although clinical trials in humans remain challenging, the integration of genomics, immunology, and nanotechnology is paving the way for next-generation brucellosis vaccines that could be safer, more effective, and more broadly applicable (251).
7 Socioeconomic burden associated with brucellosis
Brucellosis imposes a significant socioeconomic burden worldwide, particularly in regions where livestock farming is a primary source of income. In animals, the disease leads to direct economic losses through decreased productivity, reproductive failure, abortion, and reductions in milk and meat yields (277). These losses are further compounded by expenses related to control strategies, including diagnostic testing, veterinary care, vaccination programs, culling of infected animals, and the implementation of stringent biosecurity measures (278, 279). In addition to animal health, brucellosis represents a major public health concern. Infected individuals often experience non-specific but debilitating symptoms such as fever, fatigue, arthralgia, and prolonged illness (280), which can significantly impair work capacity and reduce economic productivity. The associated costs of medical diagnostics, long-term antibiotic therapy, and follow-up care place financial strain on both affected individuals and healthcare systems (281).
The economic impact extends to international trade and food security. The presence of brucellosis in livestock populations limits market access for animals and animal-derived products (282). Several countries, including Australia, the United States, and New Zealand, have enacted strict regulations regarding the import and export of livestock to prevent the spread of infectious diseases (283). Consequently, brucellosis outbreaks can result in trade restrictions, disrupting the global market for cattle and related commodities (284, 285). Preventive measures are critical to curbing transmission, especially given the zoonotic potential of brucellosis through the consumption of unpasteurized dairy products and undercooked meat. Ensuring food safety through proper hygiene practices, including pasteurization and effective disease surveillance systems, is essential (286). Compliance with international food safety standards not only mitigates the spread of brucellosis but also helps maintain public confidence in food production systems (287).
In addition to affecting humans and domestic animals, brucellosis poses ecological risks by impacting wildlife populations, particularly in regions where wild and domesticated animals share habitats. Wildlife species such as elk and bison can act as reservoirs for the disease, perpetuating transmission cycles and complicating eradication efforts (288). These infections can alter wildlife population dynamics by reducing reproductive success and increasing mortality rates (289). In summary, brucellosis is a multifaceted disease with profound socioeconomic consequences. Addressing these challenges requires a holistic, One Health approach involving coordinated efforts across veterinary, medical, environmental, and regulatory sectors to effectively control and mitigate its widespread impact.
8 Challenges and future directions
Brucellosis remains a critical public health and veterinary concern globally, particularly in regions where animal husbandry is intensive and healthcare infrastructure is limited. The disease is notoriously difficult to diagnose owing to its non-specific clinical presentation, which often mimics other febrile or inflammatory illnesses, leading to delayed or misdiagnosed cases. Such diagnostic ambiguity contributes to prolonged illness, increased morbidity, and the potential for ongoing transmission (290). The zoonotic nature of brucellosis further complicates control efforts, as transmission can occur through the consumption of unpasteurized dairy products, direct contact with infected animals, or inhalation of contaminated aerosols—placing high-risk groups such as farmers, veterinarians, abattoir workers, and consumers at continual risk (277, 291, 292).
In endemic regions, disease control is hindered by inadequate healthcare infrastructure, insufficient veterinary coverage, a lack of public awareness, and poor surveillance systems (293, 294). The growing issue of antibiotic resistance in Brucella spp. adds another layer of complexity, threatening the efficacy of current therapeutic regimens and highlighting the urgent need for new antimicrobial strategies (42, 295). Addressing these multifaceted challenges necessitates a comprehensive and collaborative One Health approach that integrates human, animal, and environmental health. Priorities should include improved disease surveillance, public health education, and expanded access to healthcare and veterinary services, particularly in resource-limited settings.
Historic eradication programs offer valuable insights for guiding future brucellosis control strategies. In the European Union, coordinated efforts that combined mass vaccination, test-and-slaughter protocols, strict animal movement controls, and mandatory dairy pasteurization enabled many member states to secure official brucellosis-free status (296). In the United States, the longstanding National Brucellosis Eradication Program has virtually eliminated bovine brucellosis, with occasional spillover cases persisting only in wildlife reservoirs such as in the Greater Yellowstone Area (297, 298). New Zealand offers another exemplar: a national campaign initiated in the 1970s, featuring compulsory herd testing, slaughter of reactors, movement restrictions, and farmer compensation, culminated in the country being officially declared brucellosis-free (299–301). These programs demonstrate that elimination is attainable when surveillance and vaccination are coupled with compensation frameworks, rigorous enforcement, and sustained political engagement. Embedding these successful models within a modern One Health framework is key to adapting eradication strategies to the socioeconomic and infrastructural challenges of endemic regions.
Future research must delve deeper into the molecular mechanisms underlying Brucella pathogenesis, particularly Brucella's ability to evade host immune responses by modulating key cellular processes such as autophagy and apoptosis (302). Omics technologies, including genomics and proteomics, hold promise for identifying novel virulence factors and vaccine candidates that could inform next-generation immunization strategies (303, 304). The emergence of antimicrobial resistance underscores the need for innovative therapeutics, including the use of monoclonal antibodies, host-directed therapies, and repurposed drugs with enhanced activity against Brucella (305). Moreover, combining conventional antibiotics with emerging modalities such as bacteriophage therapy may provide synergistic effects and improve clinical outcomes (306).
Public health and veterinary professionals play vital roles in advancing brucellosis control through education, early detection, and disease reporting. The application of the One Health concept is pivotal for successful management, encompassing livestock immunization, animal hygiene, wildlife monitoring, and intersectoral collaboration (307, 308). During outbreaks, rapid interventions such as livestock quarantine and movement restrictions are essential to limit disease spread. In healthcare settings, clinicians must maintain a high index of suspicion for brucellosis in patients with compatible symptoms and relevant exposure histories (309–311). Enhanced food safety practices—including pasteurization, safe processing of dairy and meat products, and rigorous monitoring systems—are indispensable for reducing transmission risk. Historical accounts, such as the restriction of unpasteurized milk during wartime to prevent brucellosis among British soldiers, underscore the importance of stringent food safety regulations (312). Laboratory and veterinary personnel working with Brucella cultures should receive adequate biosafety training and utilize personal protective equipment to minimize occupational risk.
Although no vaccine is currently approved for human use, significant progress has been made in the development of novel animal vaccines, including vector-based, recombinant, DNA, and subunit vaccines. These strategies aim to reduce disease incidence in animal reservoirs and indirectly curb zoonotic transmission. Continued research and investment are needed to optimize these candidates for broader application and eventual translation into human use.
9 Conclusions
Brucellosis remains a persistent global health threat at the crossroads of human, animal, and environmental health. Its chronic nature, diagnostic ambiguity, and intracellular persistence—driven by immune-evasive mechanisms such as low-immunogenic LPS and specialized adhesins—complicate detection and treatment, particularly in resource-limited settings. While molecular diagnostics and novel biosensors show promise, conventional serology still dominates in endemic areas despite its limitations. Prolonged antibiotic regimens face challenges such as high relapse rates and increasing resistance. Emerging therapies, including nanotechnology-based delivery systems, host-targeted approaches, and traditional phytomedicines, offer promising alternatives. Preventive efforts have largely focused on animal vaccination, yet the lack of a human vaccine remains a significant gap. Advances in DNA, subunit, and vector-based vaccines show potential but require further development and validation. Tackling brucellosis demands a One Health approach—integrating medical, veterinary, and environmental strategies. Strengthening diagnostics, expanding access to care, and fostering cross-sector collaboration are essential for reducing the global burden. Continued innovation and coordinated policy efforts are critical to transforming scientific progress into sustainable public health solutions.
Statements
Author contributions
AA: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Resources, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. AE: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article. The researchers would like to thank the Deanship of Graduate Studies and Scientific Research at Qassim University for financial support (QU-APC-2025).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Dadar M Tiwari R Sharun K Dhama K . Importance of brucellosis control programs of livestock on the improvement of one health. Vet Q. 41:137–51. 10.1080/01652176.2021.1894501
2.
Moriyón I Blasco JM Letesson JJ De Massis F Moreno E . Brucellosis and one health: inherited and future challenges. Microorganisms. (2023) 11:2070. 10.3390/microorganisms11082070
3.
Qureshi KA Parvez A Fahmy NA Abdel Hady BH Kumar S Ganguly A et al . Brucellosis: epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment–a comprehensive review. Ann Med. (2023) 55:2295398. 10.1080/07853890.2023.2295398
4.
Jennings GJ Hajjeh RA Girgis FY Fadeel MA Maksoud MA Wasfy MO et al . Brucellosis as a cause of acute febrile illness in Egypt. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. (2007) 101:707–13. 10.1016/j.trstmh.2007.02.027
5.
Laine CG Johnson VE Scott HM Arenas-Gamboa AM . Global estimate of human brucellosis incidence. Emerg Infect Dis. (2023) 29:1789. 10.3201/eid2909.230052
6.
Shin IS Roh SG Gill BC Kim YS Hwang KW . Assessment of brucellosis-causing pathogens with an emphasis on the prevalence of Brucella melitensis in the Republic of Korea: insights from a decade of pathogen surveillance (2014–2023), a retrospective study. Osong Public Health Res Perspect. (2024) 15:489–96. 10.24171/j.phrp.2024.0134
7.
Pappas G Papadimitriou P Akritidis N Christou L Tsianos EV . The new global map of human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. (2006) 6:91–9. 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70382-6
8.
Khoshnood S Pakzad R Koupaei M Shirani M Araghi A Irani GM et al . Prevalence, diagnosis, and manifestations of brucellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:976215. 10.3389/fvets.2022.976215
9.
Głowacka P Żakowska D Naylor K Niemcewicz M Bielawska-Drozd A . Brucella–virulence factors, pathogenesis and treatment. Pol J Microbiol. (2018) 67:151. 10.21307/pjm-2018-029
10.
He Y . Analyses of Brucella pathogenesis, host immunity, and vaccine targets using systems biology and bioinformatics. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2012) 2:2. 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00002
11.
Roop RM Gaines JM Anderson ES Caswell CC Martin DW . Survival of the fittest: how Brucella strains adapt to their intracellular niche in the host. Med Microbiol Immunol. (2009) 198:221–38. 10.1007/s00430-009-0123-8
12.
Morovati S Bozorgomid A Mohammadi A Ahmadi F Arghand L Khosravi Shadmani F et al . Brucellar arthritis and sacroiliitis: an 8-year retrospective comparative analysis of demographic, clinical, and paraclinical features. Ther Adv Infect Dis. (2024) 11:20499361241246937. 10.1177/20499361241246937
13.
Atluri VL Xavier MN de Jong MF den Hartigh AB Tsolis RM . Interactions of the human pathogenic Brucella species with their hosts. Annu Rev Microbiol. (2011) 65:523–41. 10.1146/annurev-micro-090110-102905
14.
Pappas G Akritidis N Bosilkovski M Tsianos E . The B. melitens is genome. N Engl J Med. (2005) 352:2325–36. 10.1056/NEJMra050570
15.
Soares CN Angelim AIM Brandão CO Santos RQ Mehta R Silva MTTd . Neurobrucellosis: the great mimicker. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. (2022) 55:e0567–2021. 10.1590/0037-8682-0567-2021
16.
Arazi F Haddad M Sheybani F Farzadfard MT Rezaeian MK . Neurobrucellosis: a retrospective cohort of 106 patients. Trop Med Health. (2025) 53:9. 10.1186/s41182-025-00680-1
17.
Yang L Pan W Cai Q An M Wang C Pan X . The research trend on neurobrucellosis over the past 30 years (1993–2023): a bibliometric and visualization analysis. Front Neurol. (2024) 15:1349530. 10.3389/fneur.2024.1349530
18.
Zhang Y Zou X-Y Liu L . Case report of neurobrucellosis: a rare complication and neuroimaging findings of a common disease. Front Immunol. (2025) 15:1449909. 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1449909
19.
Fusetti C Petri F Murad MH Merli S Giorgi R Rizzardini G et al . Neurobrucellosis presenting with motor damage or hearing loss, and use of steroids are associated with a higher risk of sequelae or relapse: a systematic review of individual participant data. Neurol Sci. (2024) 45:5441–8. 10.1007/s10072-024-07621-6
20.
Shoukat S Wani H Ali U Para PA Ara S Ganguly S . Brucellosis: a current review update on zoonosis. J Immunol Immunopathol. (2017) 19:61–9. 10.5958/0973-9149.2017.00009.0
21.
Megid J Mathias LA Robles C . Clinical manifestations of brucellosis in domestic animals and humans. Open Vet Sci J. (2010) 4:119–26. 10.2174/1874318801004010119
22.
Godfroid J Scholz H Barbier T Nicolas C Wattiau P Fretin D et al . Brucellosis at the animal/ecosystem/human interface at the beginning of the 21st century. Prev Vet Med. (2011) 102:118–31. 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2011.04.007
23.
Vigeant P Mendelson J Miller MA . Human to human transmission of Brucella melitensis. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. (1995) 6:153–5. 10.1155/1995/909404
24.
Bosilkovski M Dimzova M Grozdanovski K . Natural history of brucellosis in an endemic region in different time periods. Acta Clin Croat. (2009) 48:41–6.
25.
Pereira CR Cotrim de Almeida JVF Cardoso de Oliveira IR Faria de Oliveira L Pereira LJ Zangeronimo MG et al . Occupational exposure to Brucella spp: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2020) 14:e0008164. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008164
26.
Lowe CF Showler AJ Perera S McIntyre S Qureshi R Patel SN et al . Hospital-associated transmission of Brucella melitensis outside the laboratory. Emerg Infect Dis. (2015) 21:150. 10.3201/eid2101.141247
27.
Dadar M Tabibi R Alamian S Caraballo-Arias Y Mrema EJ Mlimbila J et al . Safety concerns and potential hazards of occupational brucellosis in developing countries: a review. J Public Health. (2023) 31:1681–90. 10.1007/s10389-022-01732-0
28.
Corbel MJ . Brucellosis in Humans and Animals. Geneva: World Health Organization (2006).
29.
CDC . Laboratory Risks for Brucellosis (2024). Available online at: https://www.cdc.gov/brucellosis/hcp/laboratory-risks/index.html (Accessed March 12, 2025).
30.
Pellegrini JM Gorvel J-P Mémet S . Immunosuppressive mechanisms in brucellosis in light of chronic bacterial diseases. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:1260. 10.3390/microorganisms10071260
31.
González-Espinoza G Arce-Gorvel V Mémet S Gorvel J-P . Brucella: reservoirs and niches in animals and humans. Pathogens. (2021) 10:186. 10.3390/pathogens10020186
32.
Guo X Zeng H Li M Xiao Y Gu G Song Z et al . The mechanism of chronic intracellular infection with Brucella spp. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1129172. 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1129172
33.
Celli J . The intracellular life cycle of Brucella spp. Microbiol Spectr. (2019) 7:10.1128/microbiolspec. bai-0006-2019. 10.1128/microbiolspec.BAI-0006-2019
34.
Artuk H Gul H . Complications and treatment of brucellosis: 11-year results. Acta Med Mediterr. (2019) 35:1131. 10.19193/0393-6384_2019_3_201
35.
Franco MP Mulder M Gilman RH Smits HL . Human brucellosis. Lancet Infect Dis. (2007) 7:775–86. 10.1016/S1473-3099(07)70286-4
36.
Khurana SK Sehrawat A Tiwari R Prasad M Gulati B Shabbir MZ et al . Bovine brucellosis–a comprehensive review. Vet Q. (2021) 41:61–88. 10.1080/01652176.2020.1868616
37.
Elbehiry A Aldubaib M Marzouk E Abalkhail A Almuzaini AM Rawway M et al . The development of diagnostic and vaccine strategies for early detection and control of human brucellosis, particularly in endemic areas. Vaccines. (2023) 11:654. 10.3390/vaccines11030654
38.
Ariza J Bosilkovski M Cascio A Colmenero JD Corbel MJ Falagas ME et al . Perspectives for the treatment of brucellosis in the 21st century: the Ioannina recommendations. PLoS Med. (2007) 4:e317. 10.1371/journal.pmed.0040317
39.
Elbehiry A Aldubaib M Al Rugaie O Marzouk E Abaalkhail M Moussa I et al . Proteomics-based screening and antibiotic resistance assessment of clinical and sub-clinical Brucella species: an evolution of brucellosis infection control. PLoS ONE. (2022) 17:e0262551. 10.1371/journal.pone.0262551
40.
Schurig GG Sriranganathan N Corbel MJ . Brucellosis vaccines: past, present and future. Vet Microbiol. (2002) 90:479–96. 10.1016/S0378-1135(02)00255-9
41.
Alsowaida YS Alowais SA Aldugiem RA Albahlal HN Bin Saleh K Alshoumr B et al . Effectiveness and safety of dual versus triple antibiotic therapy for treating brucellosis infection: a retrospective cohort study. Antibiotics. (2025) 14:265. 10.3390/antibiotics14030265
42.
Wareth G Dadar M Ali H Hamdy ME Al-Talhy AM Elkharsawi AR et al . The perspective of antibiotic therapeutic challenges of brucellosis in the Middle East and North African countries: current situation and therapeutic management. Transbound Emerg Dis. (2022) 69:e1253–e68. 10.1111/tbed.14502
43.
de Figueiredo P Ficht TA Rice-Ficht A Rossetti CA Adams LG . Pathogenesis and immunobiology of brucellosis: review of Brucella–host interactions. Am J Pathol. (2015) 185:1505–17. 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.003
44.
Arellano-Reynoso B Lapaque N Salcedo S Briones G Ciocchini AE Ugalde R et al . Cyclic β-1, 2-glucan is a Brucella virulence factor required for intracellular survival. Nat Immunol. (2005) 6:618–25. 10.1038/ni1202
45.
Rehman S Ullah S Kholik K Munawaroh M Sukri A Malik MIU et al . A detailed review of bovine brucellosis. Open Vet J. (2025) 15:1520. 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i4.2
46.
Sibhat B Adamu H Benti T Tuli G Asmare K Lindahl JF et al . Brucella Seropositivity and associated risk factors in pastoral livestock system in Northeastern Ethiopia. Vet Sci. (2024) 11:620. 10.3390/vetsci11120620
47.
Mahmoud E Alaman A Alsayari R Hakeem A Bosaeed M Ibrahim A et al . Outcome of complicated osteoarticular brucellosis in a tertiary care center in Saudi Arabia. PLoS ONE. (2024) 19:e0299878. 10.1371/journal.pone.0299878
48.
Zhuang W He T Tuerheng J He G Wang B-L Yang Y-H et al . Neurobrucellosis: laboratory features, clinical characteristics, antibiotic treatment, and clinical outcomes of 21 patients. BMC Infect Dis. (2024) 24:485. 10.1186/s12879-024-09308-x
49.
Alfakeeh S Alghanem RF Bin Obaid S Alsuwayhib A Al Kawabah G Abanamy R et al . Clinical characteristics and outcome of Brucella endocarditis: a case series. Infect Drug Resist. (2024):4733–40. 10.2147/IDR.S485537
50.
Başaran S Simşek-Yavuz S Saricaoglu ME Aydin M Aygün G Azap A et al . A systematic review and analysis of Brucella endocarditis cases. Anatol J Cardiol. (2025) 29:111. 10.14744/AnatolJCardiol.2025.4259
51.
Haag AF Myka KK Arnold MF Caro-Hernández P Ferguson GP . Importance of lipopolysaccharide and cyclic β-1, 2-glucans in Brucella-mammalian infections. Int J Microbiol. (2010) 2010:124509. 10.1155/2010/124509
52.
Jiao H Zhou Z Li B Xiao Y Li M Zeng H et al . The mechanism of facultative intracellular parasitism of Brucella. Int J Mol Sci. (2021) 22:3673. 10.3390/ijms22073673
53.
Celli J . The changing nature of the Brucella-containing vacuole. Cell Microbiol. (2015) 17:951–8. 10.1111/cmi.12452
54.
Huy TX Nguyen TT Kim H Reyes AW Kim S . Brucella phagocytosis mediated by pathogen-host interactions and their intracellular survival. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:2003. 10.3390/microorganisms10102003
55.
Celli J de Chastellier C Franchini D-M Pizarro-Cerda J Moreno E Gorvel J-P . Brucella evades macrophage killing via VirB-dependent sustained interactions with the endoplasmic reticulum. J Exp Med. (2003) 198:545–56. 10.1084/jem.20030088
56.
Del Giudice MG Ugalde JE Czibener C . A lysozyme-like protein in Brucella abortus is involved in the early stages of intracellular replication. Infect Immun. (2013) 81:956–64. 10.1128/IAI.01158-12
57.
Brumell JH . Brucella “hitches a ride” with autophagy. Cell Host Microbe. (2012) 11:2–4. 10.1016/j.chom.2012.01.003
58.
Christopher S . Brucellosis: review on the recent trends in pathogenicity and laboratory diagnosis. J Lab Physicians. (2010) 2:055–60. 10.4103/0974-2727.72149
59.
Bialer MG Sycz G Muñoz González F Ferrero MC Baldi PC Zorreguieta A . Adhesins of Brucella: their roles in the interaction with the host. Pathogens. (2020) 9:942. 10.3390/pathogens9110942
60.
Rocha-Gracia RdC Castañeda-Roldán EI Giono-Cerezo S Girón JA . Brucella sp. bind to sialic acid residues on human and animal red blood cells. FEMS Microbiol Lett. (2002) 213:219–24. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11309.x
61.
Vitry M-A Hanot Mambres D Deghelt M Hack K Machelart A Lhomme F et al . Brucella melitensis invades murine erythrocytes during infection. Infect Immun. (2014) 82:3927–38. 10.1128/IAI.01779-14
62.
Rendon M . Characterization of SP41, a surface protein of Brucella associated with adherence and invasion of host epithelial cells characterization of SP41, a surface protein of Brucella associated with adherence and invasion of host epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. (2007) 8:1877–87. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00754.x
63.
Sidhu-Muñoz RS Sancho P Vizcaíno N . Brucella ovis PA mutants for outer membrane proteins Omp10, Omp19, SP41, and BepC are not altered in their virulence and outer membrane properties. Vet Microbiol. (2016) 186:59–66. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2016.02.010
64.
Czibener C Merwaiss F Guaimas F Del Giudice MG Serantes DAR Spera JM et al . BigA is a novel adhesin of Brucella that mediates adhesion to epithelial cells. Cell Microbiol. (2016) 18:500–13. 10.1111/cmi.12526
65.
Bodelón G Palomino C Fernández LÁ . Immunoglobulin domains in Escherichia coli and other enterobacteria: from pathogenesis to applications in antibody technologies. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (2013) 37:204–50. 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2012.00347.x
66.
Lopez P Guaimas F Czibener C Ugalde JE . A genomic island in Brucella involved in the adhesion to host cells: identification of a new adhesin and a translocation factor. Cell Microbiol. (2020) 22:e13245. 10.1111/cmi.13245
67.
Seco-Mediavilla P Verger J-M Grayon M Cloeckaert A Marín CM Zygmunt MS et al . Epitope mapping of the Brucella melitensis BP26 immunogenic protein: usefulness for diagnosis of sheep brucellosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2003) 10:647–51. 10.1128/CDLI.10.4.647-651.2003
68.
Bandara AB Sriranganathan N Schurig GG Boyle SM . Putative outer membrane autotransporter protein influences survival of Brucella suis in BALB/c mice. Vet Microbiol. (2005) 109:95–104. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.05.012
69.
Bialer MG Ferrero MC Delpino MV Ruiz-Ranwez V Posadas DM Baldi PC et al . Adhesive functions or pseudogenization of type Va autotransporters in Brucella species. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11:607610. 10.3389/fcimb.2021.607610
70.
Henderson IR Navarro-Garcia F Desvaux M Fernandez RC Ala'Aldeen D . Type V protein secretion pathway: the autotransporter story microbiology and molecular biology reviews. (2004) 68:692–744. 10.1128/MMBR.68.4.692-744.2004
71.
Posadas DM Ruiz-Ranwez V Bonomi HR Martín FA Zorreguieta A . BmaC, a novel autotransporter of Brucella suis, is involved in bacterial adhesion to host cells. Cell Microbiol. (2012) 14:965–82. 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01771.x
72.
Ruiz-Ranwez V Posadas DM Estein SM Abdian PL Martin FA Zorreguieta A . The BtaF trimeric autotransporter of Brucella suis is involved in attachment to various surfaces, resistance to serum and virulence. PLoS ONE. (2013) 8:e79770. 10.1371/journal.pone.0079770
73.
Muñoz González F Sycz G Alonso Paiva IM Linke D Zorreguieta A Baldi PC et al . The BtaF adhesin is necessary for full virulence during respiratory infection by Brucella suis and is a novel immunogen for nasal vaccination against Brucella infection. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:1775. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01775
74.
Ruiz-Ranwez V Posadas DM Van der Henst C Estein SM Arocena GM Abdian PL et al . BtaE, an adhesin that belongs to the trimeric autotransporter family, is required for full virulence and defines a specific adhesive pole of Brucella suis. Infect Immun. (2013) 81:996–1007. 10.1128/IAI.01241-12
75.
Ruch TR Engel JN . Targeting the mucosal barrier: how pathogens modulate the cellular polarity network. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. (2017) 9:a027953. 10.1101/cshperspect.a027953
76.
Hu X-D Yu D-H Chen S-T Li S-X Cai H . A combined DNA vaccine provides protective immunity against Mycobacterium bovis and Brucella abortus in cattle. DNA Cell Biol. (2009) 28:191–9. 10.1089/dna.2008.0790
77.
Deghelt M Mullier C Sternon J-F Francis N Laloux G Dotreppe D et al . G1-arrested newborn cells are the predominant infectious form of the pathogen Brucella abortus. Nat Commun. (2014) 5:4366. 10.1038/ncomms5366
78.
Uzureau S Lemaire J Delaive E Dieu M Gaigneaux A Raes M et al . Global analysis of quorum sensing targets in the intracellular pathogen Brucella melitensis 16 M. J Proteome Res. (2010) 9:3200–17. 10.1021/pr100068p
79.
Pirone L Pitzer JE D'Abrosca G Fattorusso R Malgieri G Pedone EM et al . Identifying the region responsible for Brucella abortus MucR higher-order oligomer formation and examining its role in gene regulation. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:17238. 10.1038/s41598-018-35432-1
80.
Caswell CC Elhassanny AE Planchin EE Roux CM Weeks-Gorospe JN Ficht TA et al . Diverse genetic regulon of the virulence-associated transcriptional regulator MucR in Brucella abortus 2308. Infect Immun. (2013) 81:1040–51. 10.1128/IAI.01097-12
81.
Kleinman CL Sycz G Bonomi HR Rodríguez RM Zorreguieta A Sieira R . ChIP-seq analysis of the LuxR-type regulator VjbR reveals novel insights into the Brucella virulence gene expression network. Nucleic Acids Res. (2017) 45:5757–69. 10.1093/nar/gkx165
82.
Sieira R Bialer MG Roset MS Ruiz-Ranwez V Langer T Arocena GM et al . Combinatorial control of adhesion of Brucella abortus 2308 to host cells by transcriptional rewiring of the trimeric autotransporter bta E gene. Mol Microbiol. (2017) 103:553–65. 10.1111/mmi.13576
83.
Hamidi H Bagheri Nejad R Es-Haghi A Ghassempour A . A combination of MALDI-TOF MS proteomics and species-unique biomarkers' discovery for rapid screening of brucellosis. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. (2022) 33:1530–40. 10.1021/jasms.2c00110
84.
Lasch P Beyer W Bosch A Borriss R Drevinek M Dupke S et al . A MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry database for identification and classification of highly pathogenic bacteria. Sci Data. (2025) 12:187. 10.1038/s41597-025-04504-z
85.
Dematheis F Walter MC Lang D Antwerpen M Scholz HC Pfalzgraf M-T et al . Machine learning algorithms for classification of MALDI-TOF MS spectra from phylogenetically closely related species Brucella melitensis, Brucella abortus and Brucella suis. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:1658. 10.3390/microorganisms10081658
86.
Li X Wang B Li X He J Shi Y Wang R et al . Analysis and validation of serum biomarkers in brucellosis patients through proteomics and bioinformatics. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2025) 14:1446339. 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1446339
87.
Yang Y Qiao K Yu Y Zong Y Liu C Li Y . Unravelling potential biomarkers for acute and chronic brucellosis through proteomic and bioinformatic approaches. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2023) 13:1216176. 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1216176
88.
Wu Q Sun C Guo L Xie Y Zhang J Yin D . Preparation and evaluation of Brucella T4SS recombinant proteins in serodiagnosis of human brucellosis based on TMT-based proteomics technology. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2025) 14:1514046. 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1514046
89.
Wang G Qi X Zhao S Pei Q Chen Y Yin D et al . Preparation of a Brucella multiepitope fusion protein based on bioinformatics and its application in serological diagnosis of human brucellosis. Sci Rep. (2025) 15:19106. 10.1038/s41598-025-04244-5
90.
Zhang L Bai J Li L Jia Y Qiu X Luo Y et al . The role of outer membrane protein 16 in Brucella pathogenesis, vaccine development, and diagnostic applications. Vet Sci. (2025) 12:605. 10.3390/vetsci12070605
91.
Liu X Xiu C He L Zhao Y Li B . Strong immune response and protection against Brucella abortus by Omp25 and BP26 mRNA vaccine candidates. Int Immunopharmacol. (2025) 158:114765. 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114765
92.
Murugaiyan J Eravci M Weise C Roesler U Sprague LD Neubauer H et al . Pan-proteomic analysis and elucidation of protein abundance among the closely related Brucella species, Brucella abortus and Brucella melitensis. Biomolecules. (2020) 10:836. 10.3390/biom10060836
93.
Sharif A Nejad RB Ghassempour A . Immunoassay–mass spectrometry to identify Brucella melitensis. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2025) 15:1531018. 10.3389/fcimb.2025.1531018
94.
Al Dahouk S Tomaso H Nöckler K Neubauer H Frangoulidis D . Laboratory-based diagnosis of brucellosis–a review of the literature. Part II: serological tests for brucellosis. Clin Lab. (2003) 49:577–89.
95.
Moreno E Blasco J-M Moriyón I . Facing the human and animal brucellosis conundrums: the forgotten lessons. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:942. 10.3390/microorganisms10050942
96.
Di Bonaventura G Angeletti S Ianni A Petitti T Gherardi G . Microbiological laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis: an overview. Pathogens. (2021) 10:1623. 10.3390/pathogens10121623
97.
Tang L Liu J Wang Y Zhang H Chen C . Evaluation of a hypervariable octameric oligonucleotide fingerprints assay for identification of and discrimination between wild-type and vaccine strains of Brucella melitensis. Am J Vet Res. (2017) 78:495–9. 10.2460/ajvr.78.4.495
98.
Fatollahzadeh B Maleknejad P Hejazi M Pyri H . Development and evaluation of TUMS medium, a novel biphasic culture medium for isolation of Brucella spp. from patients. Iran J Microbiol. (2009) 1:21–5.
99.
Sagi M Nesher L Yagupsky P . The Bactec FX blood culture system detects Brucella melitensis bacteremia in adult patients within the routine 1-week incubation period. J Clin Microbiol. (2017) 55:942–6. 10.1128/JCM.02320-16
100.
Baron E Weinstein M Dunne W Yagupsky P Welch D Wilson D . Cumitech 1C, blood cultures IV. Cumitech C. (2005) 1:1–34.
101.
Pappas G Papadimitriou P . Challenges in Brucella bacteraemia. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2007) 30:29–31. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2007.06.011
102.
Yagupsky P Peled N Press J Abramson O Abu-Rashid M . Comparison of BACTEC 9240 Peds Plus medium and isolator 1.5 microbial tube for detection of Brucella melitensis from blood cultures. J Clin Microbiol. (1997) 35:1382–4. 10.1128/jcm.35.6.1382-1384.1997
103.
Raj A Gautam V Gupta PK Sethi S Rana S Ray P . Rapid detection of Brucella by an automated blood culture system at a tertiary care hospital of north India. Indian J Med Res. (2014) 139:776–8.
104.
Yagupsky P Morata P Colmenero JD . Laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2019) 33:10.1128/cmr.00073-19. 10.1128/CMR.00073-19
105.
Wang X Yan Y Wu F Su G Li S Yuan X et al . Sixteen Chinese pediatric brucellosis patients onset of fever in non-epidemic areas and 8 developed with osteoarticular involvement. Clin Rheumatol. (2018) 37:145–9. 10.1007/s10067-017-3819-y
106.
Mesureur J Arend S Cellière B Courault P Cotte-Pattat P-J Totty H et al . A MALDI-TOF MS database with broad genus coverage for species-level identification of Brucella. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2018) 12:e0006874. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006874
107.
Poonawala H Marrs Conner T Peaper DR . The Brief Case: Misidentification of Brucella melitensis as Ochrobactrum Anthropi by Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption Ionization–Time of Flight Mass Spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS). Washington: American Society for Microbiology (2018). 10.1128/JCM.00914-17
108.
Ferreira L Vega Castaño S Sánchez-Juanes F González-Cabrero S Menegotto F Orduña-Domingo A et al . Identification of Brucella by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Fast and reliable identification from agar plates and blood cultures. PLoS ONE. (2010) 5:e14235. 10.1371/journal.pone.0014235
109.
Elbehiry A Aldubaib M Abalkhail A Marzouk E ALbeloushi A Moussa I et al . How MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry technology contributes to microbial infection control in healthcare settings. Vaccines. (2022) 10:1881. 10.3390/vaccines10111881
110.
Sali M De Maio F Tarantino M Garofolo G Tittarelli M Sacchini L et al . Rapid and safe one-step extraction method for the identification of Brucella strains at genus and species level by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. PLoS ONE. (2018) 13:e0197864. 10.1371/journal.pone.0197864
111.
Karger A Melzer F Timke M Bettin B Kostrzewa M Nöckler K et al . Interlaboratory comparison of intact-cell matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization–time of flight mass spectrometry results for identification and differentiation of Brucella spp. J Clin Microbiol. (2013) 51:3123–6. 10.1128/JCM.01720-13
112.
Yagupsky P . Preventing laboratory-acquired brucellosis in the era of MALDI-TOF technology and molecular tests: a narrative review. Zoonotic Dis. (2022) 2:172–82. 10.3390/zoonoticdis2040016
113.
Noviello S Gallo R Kelly M Limberger RJ DeAngelis K Cain L et al . Laboratory-acquired brucellosis. Emerg Infect Dis. (2004) 10:1848. 10.3201/eid1010.040076
114.
Sophie R Michael L Marcel B Earl R . Prevention of laboratory-acquired brucellosis. Clin Infect Dis. (2004) 38:e119–e22. 10.1086/421024
115.
Batchelor B Brindle R Gilks G Selkon J . Biochemical mis-identification of Brucella melitensis and subsequent laboratory-acquired infections. J Hosp Infect. (1992) 22:159–62. 10.1016/0195-6701(92)90100-Z
116.
Ergönül Ö Celikbaş A Tezeren D Güvener E Dokuzoguz B . Analysis of risk factors for laboratory-acquired brucella infections. J Hosp Infect. (2004) 56:223–7. 10.1016/j.jhin.2003.12.020
117.
Miller J Astles R Baszler T Chapin K Carey R Garcia L et al . Guidelines for safe work practices in human and animal medical diagnostic laboratories recommendations of a CDC-convened, biosafety blue ribbon panel. MMWR Suppl. (2012) 61:1–102.
118.
Whatmore AM Koylass MS Muchowski J Edwards-Smallbone J Gopaul KK Perrett LL . Extended multilocus sequence analysis to describe the global population structure of the genus Brucella: phylogeography and relationship to biovars. Front Microbiol. (2016) 7:2049. 10.3389/fmicb.2016.02049
119.
Al Dahouk S Nöckler K . Implications of laboratory diagnosis on brucellosis therapy. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. (2011) 9:833–45. 10.1586/eri.11.55
120.
Orduña A Almaraz A Prado A Gutierrez MPn Garcia-Pascual A Dueñas A et al . Evaluation of an immunocapture-agglutination test (Brucellacapt) for serodiagnosis of human brucellosis. J Clin Microbiol. (2000) 38:4000–5. 10.1128/JCM.38.11.4000-4005.2000
121.
Xu N Wang W Chen F Li W Wang G . ELISA is superior to bacterial culture and agglutination test in the diagnosis of brucellosis in an endemic area in China. BMC Infect Dis. (2020) 20:1–7. 10.1186/s12879-019-4729-1
122.
Araj GF Kattar MM Fattouh LG Bajakian KO Kobeissi SA . Evaluation of the PANBIO Brucella immunoglobulin G (IgG) and IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for diagnosis of human brucellosis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol. (2005) 12:1334–5. 10.1128/CDLI.12.11.1334-1335.2005
123.
Memish Z Almuneef M Mah M Qassem L Osoba A . Comparison of the Brucella standard Agglutination test with the ELISA IgG and IgM in patients with Brucella bacteremia. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. (2002) 44:129–32. 10.1016/S0732-8893(02)00426-1
124.
Xu N Qu C Sai L Wen S Yang L Wang S et al . Evaluating the efficacy of serological testing of clinical specimens collected from patients with suspected brucellosis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2023) 17:e0011131. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011131
125.
Özdemir M Feyzioglu B Kurtoglu MG Dogan M Dagi HT Yüksekkaya S et al . A comparison of immuncapture agglutination and ELISA methods in serological diagnosis of brucellosis. Int J Med Sci. (2011) 8:428. 10.7150/ijms.8.428
126.
Gómez MC Nieto JA Rosa C Geijo P Escribano MA Munoz A et al . Evaluation of seven tests for diagnosis of human brucellosis in an area where the disease is endemic. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2008) 15:1031–3. 10.1128/CVI.00424-07
127.
Solís García del Pozo J Lorente Ortuño S Navarro E Solera J . Detection of IgM antibrucella antibody in the absence of IgGs: a challenge for the clinical interpretation of Brucella serology. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2014) 8:e3390. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003390
128.
Casanova A Ariza J Rubio M Masuet C Díaz R . BrucellaCapt versus classical tests in the serological diagnosis and management of human brucellosis. Clin Vaccine Immunol. (2009) 16:844–51. 10.1128/CVI.00348-08
129.
Ardic N Ozyurt M Ogun S Ali E Haznedaroglu T . Comparison of Coombs' and immunocapture-agglutination tests in the diagnosis of brucellosis. Chin Med J. (2005) 118:252–4.
130.
Monaghan TF Rahman SN Agudelo CW Wein AJ Lazar JM Everaert K et al . Foundational statistical principles in medical research: sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value. Medicina. (2021) 57:503. 10.3390/medicina57050503
131.
World Health Organization, Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations . Vitamin and Mineral Requirements in Human Nutrition.Vol. 2. Geneva: World Health Organization (2004). p. 17–299.
132.
Díaz R Casanova A Ariza J Moriyon I . The rose Bengal test in human brucellosis: a neglected test for the diagnosis of a neglected disease. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2011) 5:e950. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000950
133.
Loubet P Magnan C Salipante F Pastre T Keriel A O'Callaghan D et al . Diagnosis of brucellosis: combining tests to improve performance. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2024) 18:e0012442. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012442
134.
Araj GF . Update on laboratory diagnosis of human brucellosis. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2010) 36:S12–S7. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.06.014
135.
Riezu-Boj JI Moriyón I Blasco J Gamazo C Díaz R . Antibody response to Brucella ovis outer membrane proteins in ovine brucellosis. Infect Immun. (1990) 58:489–94. 10.1128/iai.58.2.489-494.1990
136.
Legesse A Mekuriaw A Gelaye E Abayneh T Getachew B Weldemedhin W et al . Comparative evaluation of RBPT, I-ELISA, and CFT for the diagnosis of brucellosis and PCR detection of Brucella species from Ethiopian sheep, goats, and cattle sera. BMC Microbiol. (2023) 23:216. 10.1186/s12866-023-02962-2
137.
Islam MS Islam MA Khatun MM Saha S Basir MS Hasan M-M . Molecular detection of Brucella spp. from milk of seronegative cows from some selected area in Bangladesh. J Pathog. (2018) 2018:9378976. 10.1155/2018/9378976
138.
Islam MS Habib MA Tonu NS Haque MS Rahman MM . Beyond serology: a meta-analysis of advancements in molecular detection of Brucella spp. in seronegative animals and biological samples. Vet Med Sci. (2025) 11:e70200. 10.1002/vms3.70200
139.
Freire ML Machado de Assis TS Silva SN Cota G . Diagnosis of human brucellosis: systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2024) 18:e0012030. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012030
140.
Ntivuguruzwa JB Kolo FB Gashururu R Uwibambe E Musanayire V Ingabire A et al . Molecular characterization of Brucella spp. from seropositive herds of cattle farmed at the wildlife–livestock–human interface in Rwanda. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:1017851. 10.3389/fvets.2022.1017851
141.
Hinić V Brodard I Thomann A Holub M Miserez R Abril C et al . 711-based real-time PCR assay as a tool for detection of Brucella spp. in wild boars and comparison with bacterial isolation and serology. BMC Vet Res. (2009) 5:1–8. 10.1186/1746-6148-5-22
142.
Becker GN Tuon FF . Comparative study of IS711 and bcsp31-based polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for the diagnosis of human brucellosis in whole blood and serum samples. J Microbiol Methods. (2021) 183:106182. 10.1016/j.mimet.2021.106182
143.
Kattar MM Zalloua PA Araj GF Samaha-Kfoury J Shbaklo H Kanj SS et al . Development and evaluation of real-time polymerase chain reaction assays on whole blood and paraffin-embedded tissues for rapid diagnosis of human brucellosis. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis. (2007) 59:23–32. 10.1016/j.diagmicrobio.2007.04.002
144.
Baddour MM Alkhalifa DH . Evaluation of three polymerase chain reaction techniques for detection of Brucella DNA in peripheral human blood. Can J Microbiol. (2008) 54:352–7. 10.1139/W08-017
145.
Bounaadja L Albert D Chénais B Hénault S Zygmunt MS Poliak S . Garin-Bastuji B. Real-time PCR for identification of Brucella spp: a comparative study of IS711, bcsp31 and per target genes. Vet Microbiol. (2009) 137:156–64. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2008.12.023
146.
López-Goñi I García-Yoldi D Marín CM de Miguel MJ Barquero-Calvo E Guzman-Verri C et al . New Bruce-ladder multiplex PCR assay for the biovar typing of Brucella suis and the discrimination of Brucella suis and Brucella canis. Vet Microbiol. (2011) 154:152–5. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2011.06.035
147.
Lopez-Goñi I Garcia-Yoldi D Marín C De Miguel M Muñoz P Blasco J et al . Evaluation of a multiplex PCR assay (Bruce-ladder) for molecular typing of all Brucella species, including the vaccine strains. J Clin Microbiol. (2008) 46:3484–7. 10.1128/JCM.00837-08
148.
Soroka M Wasowicz B Rymaszewska A . Loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP): the better sibling of PCR?Cells. (2021) 10:1931. 10.3390/cells10081931
149.
Halling SM Peterson-Burch BD Bricker BJ Zuerner RL Qing Z Li L-L et al . Completion of the genome sequence of Brucella abortus and comparison to the highly similar genomes of Brucella melitensis and Brucella suis. J Bacteriol. (2005) 187:2715–26. 10.1128/JB.187.8.2715-2726.2005
150.
Eko SM Esemu SN Nota AD Ndip LM . A review on brucellosis in Cameroon: diagnostic approaches, epidemiology and risk factors for infection. Adv Microbiol. (2022) 12:415–42. 10.4236/aim.2022.127030
151.
Islam MS El Zowalaty ME Van Vliet AH Thakur S Khatun MM Saha S et al . First genome sequence of Brucella abortus biovar 3 strain BAU21/S4023, isolated from a dairy cow in Bangladesh. Microbiol Resour Announc. (2019) 8:10.1128/mra.00446-19. 10.1128/MRA.00779-19
152.
Etemadi A Moniri R Neubauer H Goli YD Alamian S . Laboratory diagnostic procedures for human brucellosis: an overview of existing approaches. Jundishapur J Microbiol. (2019) 12:1–9. 10.5812/jjm.91200
153.
Liu Z Wang M Tian Y Li Z Gao L Li Z et al . Systematic analysis of and recommendations for public health events involving brucellosis from 2006 to 2019 in China. Ann Med. (2022) 54:1859–66. 10.1080/07853890.2022.2092894
154.
Abuawad A Ashhab Y Offenhäusser A Krause H-J . DNA sensor for the detection of Brucella spp. based on magnetic nanoparticle markers. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:17272. 10.3390/ijms242417272
155.
Pasquardini L Cennamo N Arcadio F Perri C Chiodi A D'agostino G et al . Immuno-SPR biosensor for the detection of Brucella abortus. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:22832. 10.1038/s41598-023-50344-5
156.
Bosilkovski M Arapović J Keramat F . Human brucellosis in pregnancy–an overview. Bosn J Basic Med Sci. (2020) 20:415. 10.17305/bjbms.2019.4499
157.
Al Dahouk S Sprague L Neubauer H . New developments in the diagnostic procedures for zoonotic brucellosis in humans. Rev Sci Tech. (2013) 32:177–88. 10.20506/rst.32.1.2204
158.
Zhang N Zhou H Huang D-S Guan P . Brucellosis awareness and knowledge in communities worldwide: a systematic review and meta-analysis of 79 observational studies. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2019) 13:e0007366. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007366
159.
Li C Wang Y Peng Q . Research progress in the therapy of brucellosis. Anim Res One Health. (2023) 1:127–36. 10.1002/aro2.5
160.
Tuon FF Gondolfo RB Cerchiari N . Human-to-human transmission of Brucella–a systematic review. Trop Med IntHealth. (2017) 22:539–46. 10.1111/tmi.12856
161.
Zheng R Xie S Lu X Sun L Zhou Y Zhang Y et al . Systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiology and clinical manifestations of human brucellosis in China. Biomed Res Int. (2018) 2018:5712920. 10.1155/2018/5712920
162.
Solera J Solis Garcia del Pozo J . Treatment of pulmonary brucellosis: a systematic review. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther. (2017) 15:33–42. 10.1080/14787210.2017.1254042
163.
Adel M . Brucella transmission from domestic and wild animals to dromedary camel: diagnostic methods and zoonotic threats–a review. Open Vet Sci. (2022) 3:1–12. 10.1515/ovs-2022-0113
164.
Al-Amr M Abasi L Khasawneh R Almharat S Al-Smadi R Abbasi N et al . Epidemiology of human brucellosis in military hospitals in Jordan: a five-year study. J Infect Dev Ctries. (2022) 16:1870–6. 10.3855/jidc.16861
165.
Alsaif M Dabelah K Featherstone R Robinson JL . Consequences of brucellosis infection during pregnancy: a systematic review of the literature. Int J Infect Dis. (2018) 73:18–26. 10.1016/j.ijid.2018.05.023
166.
Huy TXN . Exploring the impact of brucellosis on maternal and child health: transmission mechanisms, patient effects, and current trends in drug use and resistance: a scoping review. Beni-Suef Univ J Basic Appl Sci. (2024) 13:108. 10.1186/s43088-024-00569-8
167.
Wiggins GS . Joint Fao who expert committee on brucellosis - who. J R Soc Health. (1987) 107:114. Available online at: https://iris.who.int/handle/10665/40202
168.
Hou H Liu X Peng Q . The advances in brucellosis vaccines. Vaccine. (2019) 37:3981–8. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2019.05.084
169.
Solera J . Update on brucellosis: therapeutic challenges. Int J Antimicrob Agents. (2010) 36:S18–20. 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2010.06.015
170.
Alavi SM Alavi L . Treatment of brucellosis: a systematic review of studies in recent twenty years. Caspian J Intern Med. (2013) 4:636.
171.
Bosilkovski M Keramat F Arapović J . The current therapeutical strategies in human brucellosis. Infection. (2021) 49:823–32. 10.1007/s15010-021-01586-w
172.
Moreno E Barquero-Calvo E . The role of neutrophils in brucellosis. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. (2020) 84:10–128. 10.1128/MMBR.00048-20
173.
Huang S Wang H Li F Du L Fan W Zhao M et al . Better efficacy of triple antibiotics therapy for human brucellosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2023) 17:e0011590. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011590
174.
Pizarro-Cerdá J Moreno E Gorvel J-P . Invasion and intracellular trafficking of Brucella abortus in nonphagocytic cells. Microbes Infect. (2000) 2:829–35. 10.1016/S1286-4579(00)90368-X
175.
Celli J . Surviving inside a macrophage: the many ways of Brucella. Res Microbiol. (2006) 157:93–8. 10.1016/j.resmic.2005.10.002
176.
Rossetti CA Arenas-Gamboa AM Maurizio E . Caprine brucellosis: a historically neglected disease with significant impact on public health. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2017) 11:e0005692. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0005692
177.
Olsen SC Stoffregen W . Essential role of vaccines in brucellosis control and eradication programs for livestock. Expert Rev Vaccines. (2005) 4:915–28. 10.1586/14760584.4.6.915
178.
Majzoobi MM Hashmi SH Emami K Soltanian AR . Combination of doxycycline, streptomycin and hydroxychloroquine for short-course treatment of brucellosis: a single-blind randomized clinical trial. Infection. (2022) 50:1267–71. 10.1007/s15010-022-01806-x
179.
Vrioni G Bourdakis A Pappas G Pitiriga V Mavrouli M Pournaras S et al . Administration of a triple versus a standard double antimicrobial regimen for human brucellosis more efficiently eliminates bacterial DNA load. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. (2014) 58:7541–4. 10.1128/AAC.03841-14
180.
Lagarde M Blaauw D . Levels and determinants of overprescribing of antibiotics in the public and private primary care sectors in South Africa. BMJ Global Health. (2023) 8:e012374. 10.1136/bmjgh-2023-012374
181.
Al-Madfaa RO Alalawi MA Basudan LO Alhejaili SF Eljaaly K Madani TA et al . Dual versus triple therapy for uncomplicated brucellosis: a retrospective cohort study. J Infect Dev Ctries. (2020) 14:1380–6. 10.3855/jidc.12741
182.
Lonsway DR Jevitt LA Uhl JR Cockerill FR III Anderson ME Sullivan MM et al . Effect of carbon dioxide on broth microdilution susceptibility testing of Brucella spp. J Clin Microbiol. (2010) 48:952–6. 10.1128/JCM.01860-09
183.
Ariza J Gudiol F Pallares R Viladrich PF Rufi G Corredoira J et al . Treatment of human brucellosis with doxycycline plus rifampin or doxycycline plus streptomycin: a randomized, double-blind study. Ann Intern Med. (1992) 117:25–30. 10.7326/0003-4819-117-1-25
184.
Solís García del Pozo J Solera J . Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials in the treatment of human brucellosis. PloS ONE. (2012) 7:e32090. 10.1371/journal.pone.0032090
185.
Pappas G Memish Z . Brucellosis in the Middle East: a persistent medical, socioeconomic and political issue. J Chemother. (2007) 19:243–8. 10.1179/joc.2007.19.3.243
186.
Ma L Ma J Chen X Dong L . A 10-year retrospective comparative analysis of the clinical features of brucellosis in children and adults. J Infect Dev Ctries. (2021) 15:1147–54. 10.3855/jidc.13962
187.
Vojtová V Urbánek K . Pharmacokinetics of tetracyclines and glycylcyclines. Klin Mikrobiol Infekc Lek. (2009) 15:17–21.
188.
Acocella G Bertrand A Beytout J Durrande JB Rodriguez J-AG Kosmidis J et al . Comparison of three different regimens in the treatment of acute brucellosis: a multicenter multinational study. J Antimicrob Chemother. (1989) 23:433–9. 10.1093/jac/23.3.433
189.
Castillo C Marquez H Iglesias R Franquelo C Diaz R Alonso A . Comparative trial of doxycycline plus streptomycin versus doxycycline plus rifampin for the therapy of human brucellosis. Chemotherapy. (1989) 35:146–52. 10.1159/000238662
190.
Falagas ME Bliziotis IA . Quinolones for treatment of human brucellosis: critical review of the evidence from microbiological and clinical studies. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2006) 50:22–33. 10.1128/AAC.50.1.22-33.2006
191.
Madkour MM . Brucellosis: Overview. Madkour's brucellosis: Springer (2001). p. 1–14. 10.1007/978-3-642-59533-2_1
192.
Sasmazel A Baysal A Fedakar A Bugra O Özkokeli M Büyükbayrak F et al . Treatment of Brucella endocarditis: 15 years of clinical and surgical experience. Ann Thorac Surg. (2010) 89:1432–6. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2010.01.048
193.
Cohen N Golik A Alon I Zaidenstein R Dishi V Modai D et al . Conservative treatment for Brucella endocarditis. Clin Cardiol. (1997) 20:291–4. 10.1002/clc.4960200319
194.
Keshtkar-Jahromi M Razavi S-M Gholamin S Keshtkar-Jahromi M Hossain M Sajadi MM . Medical versus medical and surgical treatment for Brucella endocarditis. Ann Thorac Surg. (2012) 94:2141–6. 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2012.07.006
195.
Lu D Zhou Y Jing Z . Epidemiology of Brucellosis and why should we strengthen the awareness of Brucella endocarditis: clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and outcome. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. (2020) 48:901–5. 10.3760/cma.j.cn112148-20200514-00396
196.
Mert A Kocak F Ozaras R Tabak F Bilir M Kucukuglu S et al . The role of antibiotic treatment alone for the management of Brucella endocarditis in adults: a case report and literature review. Ann Thoracic Cardiovasc Surg. (2002) 8:381–5.
197.
Hong J Xu B Qian X He F . Successful surgical treatment of mitral valve endocarditis caused by Brucella: a case report. Heart Surg Forum. (2023) 26:E322–E5. 10.59958/hsf.5857
198.
Koubaa M Maaloul I Marrakchi C Lahiani D Hammami B Mnif Z et al . Spinal brucellosis in South of Tunisia: review of 32 cases. Spine J. (2014) 14:1538–44. 10.1016/j.spinee.2013.09.027
199.
Spernovasilis N Karantanas A Markaki I Konsoula A Ntontis Z Koutserimpas C et al . Brucella spondylitis: current knowledge and recent advances. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:595. 10.3390/jcm13020595
200.
Solera J Lozano E Martínez-Alfaro E Espinosa A Castillejos ML Abad L . Brucellar spondylitis: review of 35 cases and literature survey. Clin Infect Dis. (1999) 29:1440–9. 10.1086/313524
201.
Katonis P Tzermiadianos M Gikas A Papagelopoulos P Hadjipavlou A . Surgical treatment of spinal brucellosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2006) 444:66–72. 10.1097/01.blo.0000203455.59393.9a
202.
Wang X Long Y Li Y Guo Y Mansuerjiang M Tian Z et al . Biportal endoscopic decompression, debridement, and interbody fusion, combined with percutaneous screw fixation for lumbar brucellosis spondylitis. Front Surg. (2023) 9:1024510. 10.3389/fsurg.2022.1024510
203.
Faraj A Webb J . Spinal instrumentation for primary pyogenic infection, Report of 31 patients. Acta Orthop Belg. (2000) 66:242–7.
204.
Jiang D Ma L Wang X Xu Z Sun G Jia R et al . Comparison of two surgical interventions for lumbar brucella spondylitis in adults: a retrospective analysis. Sci Rep. (2023) 13:16684. 10.1038/s41598-023-43812-5
205.
Hosseini SM Abbasalipourkabir R Jalilian FA Asl SS Farmany A Roshanaei G et al . Doxycycline-encapsulated solid lipid nanoparticles as promising tool against Brucella melitensis enclosed in macrophage: a pharmacodynamics study on J774A.1 cell line. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. (2019) 8:1–12. 10.1186/s13756-019-0504-8
206.
Lueth P Haughney SL Binnebose AM Mullis AS Peroutka-Bigus N Narasimhan B et al . Nanotherapeutic provides dose sparing and improved antimicrobial activity against Brucella melitensis infections. J Control Release. (2019) 294:288–97. 10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.12.024
207.
Vassallo A Silletti MF Faraone I Milella L . Nanoparticulate antibiotic systems as antibacterial agents and antibiotic delivery platforms to fight infections. J Nanomater. (2020) 2020:6905631. 10.1155/2020/6905631
208.
Chatzimitakos TG Stalikas CD . Qualitative alterations of bacterial metabolome after exposure to metal nanoparticles with bactericidal properties: a comprehensive workflow based on 1H NMR, UHPLC-HRMS, and metabolic databases. J Proteome Res. (2016) 15:3322–30. 10.1021/acs.jproteome.6b00489
209.
Darby EM Trampari E Siasat P Gaya MS Alav I Webber MA et al . Molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance revisited. Nat Rev Microbiol. (2023) 21:280–95. 10.1038/s41579-022-00820-y
210.
Razei A Javanbakht M Hajizade A Heiat M Zhao S Aghamollaei H et al . Nano and microparticle drug delivery systems for the treatment of Brucella infections. Biomed Pharmacother. (2023) 169:115875. 10.1016/j.biopha.2023.115875
211.
Hosseini SM Farmany A Alikhani MY Taheri M Asl SS Alamian S et al . Co-delivery of doxycycline and hydroxychloroquine using CdTe-labeled solid lipid nanoparticles for treatment of acute and chronic Brucellosis. Front Chem. (2022) 10:890252. 10.3389/fchem.2022.890252
212.
Alavi M Nokhodchi A . Micro-and nanoformulations of antibiotics against Brucella. Drug Discov Today. (2023) 28:103809. 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103809
213.
El-Ela FIA Hussein KH El-Banna HA Gamal A Rouby S Menshawy AM et al . Correction to: treatment of brucellosis in guinea pigs via a combination of engineered novel pH-responsive curcumin niosome hydrogel and doxycycline-loaded chitosan-sodium alginate nanoparticles: an in vitro and in vivo study. AAPS PharmSciTech. (2020) 22:12. 10.1208/s12249-020-01899-3
214.
Sukhorukova I Sheveyko A Manakhov A Zhitnyak I Gloushankova N Denisenko E et al . Synergistic and long-lasting antibacterial effect of antibiotic-loaded TiCaPCON-Ag films against pathogenic bacteria and fungi. Mater Sci Eng C. (2018) 90:289–99. 10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.068
215.
Jackson J Lo J Hsu E Burt HM Shademani A Lange D . The combined use of gentamicin and silver nitrate in bone cement for a synergistic and extended antibiotic action against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Materials. (2021) 14:3413. 10.3390/ma14123413
216.
Imbuluzqueta E Gamazo C Lana H Campanero MÁ Salas D Gil AG et al . Hydrophobic gentamicin-loaded nanoparticles are effective against Brucella melitensis infection in mice. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. (2013) 57:3326–33. 10.1128/AAC.00378-13
217.
Kaminskas LM Boyd BJ Porter CJ . Dendrimer pharmacokinetics: the effect of size, structure and surface characteristics on ADME properties. Nanomedicine. (2011) 6:1063–84. 10.2217/nnm.11.67
218.
Mittal P Saharan A Verma R Altalbawy FM Alfaidi MA Batiha GE-S et al . Dendrimers: a new race of pharmaceutical nanocarriers. Biomed Res Int. (2021) 2021:8844030. 10.1155/2021/8844030
219.
Ficker M Paolucci V Christensen JB . Improved large-scale synthesis and characterization of small and medium generation PAMAM dendrimers. Can J Chem. (2017) 95:954–64. 10.1139/cjc-2017-0108
220.
Sheykhloo H Milani M Najafi F Bani F Zarebkohan A . Conjugation of gentamicin to polyamidoamine dendrimers improved anti-bacterial properties against Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Adv Pharm Bull. (2020) 11:675. 10.34172/apb.2021.076
221.
Zhao T Zhang Y Liu L Deng X Guo J Cao S et al . Systemic pharmacology reveals the potential targets and signaling mechanisms in the adjuvant treatment of brucellosis with traditional Chinese Medicine. ACS Omega. (2023) 8:28797–812. 10.1021/acsomega.3c03716
222.
Ma N Zhang Z Liao F Jiang T Tu Y . The birth of artemisinin. Pharmacol Ther. (2020) 216:107658. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107658
223.
Lau T Leung P Wong E Fong C Cheng K Zhang S et al . Using herbal medicine as a means of prevention experience during the SARS crisis. Am J Chin Med. (2005) 33:345–56. 10.1142/S0192415X05002965
224.
Huang K Zhang P Zhang Z Youn JY Wang C Zhang H et al . Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) in the treatment of COVID-19 and other viral infections: efficacies and mechanisms. Pharmacol Ther. (2021) 225:107843. 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2021.107843
225.
Sheng Y . Treatment of chronic Brucellosis with combined traditional Chinese medicine and Western medicine therapy. Zhongguo Zhong xi yi jie he za zhi Zhongguo Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. (1993) 13:88–90, 68.
226.
Miao J Wang L Cui H Guo L Wang J Lei J et al . Study on the effect of integrated traditional Chinese and western medicine in the treatment of brucellosis. Zhonghua lao Dong wei Sheng zhi ye Bing za zhi. (2021) 39:253–7. 10.3760/cma.j.cn121094-20200817-00468
227.
Zhang P Wang Y Liu J Gao H Zhou W . Rule of prescription and mechanism of TCM in the treatment of brucellosis. Shandong Med J. (2021) 20:30–5.
228.
Pastorino G Cornara L Soares S Rodrigues F Oliveira MBP . Liquorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra): a phytochemical and pharmacological review. Phytother Res. (2018) 32:2323–39. 10.1002/ptr.6178
229.
Wei W-L Zeng R Gu C-M Qu Y Huang L-F . Angelica sinensis in China-a review of botanical profile, ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and chemical analysis. J Ethnopharmacol. (2016) 190:116–41. 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.023
230.
Sun Y . Biological activities and potential health benefits of polysaccharides from Poria cocos and their derivatives. Int J Biol Macromol. (2014) 68:131–4. 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.04.010
231.
Chen Z Zhang C Gao F Fu Q Fu C He Y Zhang J . A systematic review on the rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort (Chuanxiong). Food Chem Toxicol. (2018) 119:309–25. 10.1016/j.fct.2018.02.050
232.
Ruqiao L Yueli C Xuelan Z Huifen L Xin Z Danjie Z et al . Rhizoma Atractylodis macrocephalae: a review of photochemistry, pharmacokinetics and pharmacology. Pharmazie. (2020) 75:42–55. 10.1691/ph.2020.9738
233.
Shahzad M Shabbir A Wojcikowski K Wohlmuth H Gobe GC . The antioxidant effects of Radix Astragali (Astragalus membranaceus and related species) in protecting tissues from injury and disease. Curr Drug Targets. (2016) 17:1331–40. 10.2174/1389450116666150907104742
234.
Luan F Ji Y Peng L Liu Q Cao H Yang Y et al . Extraction, purification, structural characteristics and biological properties of the polysaccharides from Codonopsis pilosula: a review. Carbohydr Polym. (2021) 261:117863. 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117863
235.
Zhang R-X Li M-X Jia Z-P . Rehmannia glutinosa: review of botany, chemistry and pharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol. (2008) 117:199–214. 10.1016/j.jep.2008.02.018
236.
Li F-S Weng J-K . Demystifying traditional herbal medicine with modern approach. Nat Plants. (2017) 3:1–7. 10.1038/nplants.2017.109
237.
Wen KW Bejo S editors . Screening of Chinese medicinal herbs for the inhibition of Brucella melitensis. In: 5th Proceedings of the Seminar in Veterinary Sciences. Serdang: Penerbit Universiti Putra Malaysia (aka UPM Press) (2010).
238.
Kim D Simborio H Reyes A Min W Lee HJ Lee J et al . Antibacterial effects of Coptis chinensis Franch against Brucella abortus. J Agric Life Sci. (2014) 48:107–14. 10.14397/jals.2014.48.1.107
239.
Huy TXN Reyes AWB Hop HT Arayan LT Son VH Min W et al . Emodin successfully inhibited invasion of Brucella abortus via modulting adherence, microtubule dynamics and ERK signaling pathway in RAW 2647 cells. J Microbiol Biotechnol. (2018) 28:1723–9. 10.4014/jmb.1804.04040
240.
Tsevelmaa N Narangerel B Odgerel O Dariimaa D Batkhuu J . Anti-Brucella activity of Caryopteris mongolica Bunge root extract against Brucella melitensis infection in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med. (2018) 18:144. 10.1186/s12906-018-2220-y
241.
Jia L-y Deng D Sun L-h BU J-h Chen Z-y YE M-q et al . Mechanism of traditional Chinese medicine in treating drug-resistant. Chin J Exp Tradit Med Formulae. (2020):228–34.
242.
Siebra ALA Oliveira LR Martins AO Siebra DC Albuquerque RS Lemos ICS et al . Potentiation of antibiotic activity by Passiflora cincinnata Mast. front of strains Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Saudi J Biol Sci. (2018) 25:37–43. 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.01.019
243.
Vives-Soto M Puerta-García A Rodríguez-Sánchez E Pereira J-L Solera J . What risk do Brucella vaccines pose to humans? A systematic review of the scientific literature on occupational exposure. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2024) 18:e0011889. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0011889
244.
Lalsiamthara J Lee JH . Development and trial of vaccines against Brucella. J Vet Sci. (2017) 18:281–90. 10.4142/jvs.2017.18.S1.281
245.
Heidary M Dashtbin S Ghanavati R Mahdizade Ari M Bostanghadiri N Darbandi A et al . Evaluation of brucellosis vaccines: a comprehensive review. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:925773. 10.3389/fvets.2022.925773
246.
Zhu L Feng Y Zhang G Jiang H Zhang Z Wang N et al . Brucella suis strain 2 vaccine is safe and protective against heterologous Brucella spp. infections. Vaccine. (2016) 34:395–400. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.09.116
247.
Olsen S Palmer M . Advancement of knowledge of Brucella over the past 50 years. Vet Pathol. (2014) 51:1076–89. 10.1177/0300985814540545
248.
Carvalho TF Haddad JPA Paixao TA Santos RL . Meta-analysis and advancement of brucellosis vaccinology. PLoS ONE. (2016) 11:e0166582. 10.1371/journal.pone.0166582
249.
Spink WW Hall JW III Finstad J Mallet E . Immunization with viable Brucella organisms: results of a safety test in humans. Bull World Health Organ. (1962) 26:409.
250.
Kahler S . Brucella abortus strain RB51 vaccine: its advantages and risks. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (1998) 213:12, 22.
251.
Perkins SD Smither SJ Atkins HS . Towards a Brucella vaccine for humans. FEMS Microbiol Rev. (2010) 34:379–94. 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00211.x
252.
Darbandi A Alamdary SZ Koupaei M Ghanavati R Heidary M Talebi M . Evaluation of immune responses to Brucella vaccines in mouse models: a systematic review. Front Vet Sci. (2022) 9:903890. 10.3389/fvets.2022.903890
253.
Piri-Gharaghie T Ghajari G Rezaeizadeh G Adil M Mahdi MH . A novel vaccine strategy against brucellosis using Brucella abortus multi-epitope OMPs vaccine based on Lactococcus lactis live bacterial vectors. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 134:112204. 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112204
254.
Miyoshi A Bermúdez-Humarán LG Ribeiro LA Le Loir Y Oliveira SC Langella P et al . Heterologous expression of Brucella abortus GroEL heat-shock protein in Lactococcus lactis. Microb Cell Fact. (2006) 5:1–8. 10.1186/1475-2859-5-14
255.
Gupta V Radhakrishnan G Harms J Splitter G . Invasive Escherichia coli vaccines expressing Brucella melitensis outer membrane proteins 31 or 16 or periplasmic protein BP26 confer protection in mice challenged with B.melitensis. Vaccine. (2012) 30:4017–22. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.04.036
256.
Zhao Z Li M Luo D Xing L Wu S Duan Y et al . Protection of mice from Brucella infection by immunization with attenuated Salmonellaenterica serovar typhimurium expressing A L7/L12 and BLS fusion antigen of Brucella. Vaccine. (2009) 27:5214–9. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2009.06.075
257.
Onate AA Donoso G Moraga-Cid G Folch H Céspedes S Andrews E . An RNA vaccine based on recombinant Semliki Forest virus particles expressing the Cu, Zn superoxide dismutase protein of Brucella abortus induces protective immunity in BALB/c mice. Infect Immun. (2005) 73:3294–300. 10.1128/IAI.73.6.3294-3300.2005
258.
Tabynov K . Influenza viral vector based Brucella abortus vaccine: a novel vaccine candidate for veterinary practice. Expert Rev Vaccines. (2016) 15:1237–9. 10.1080/14760584.2016.1208089
259.
Tabynov K Kydyrbayev Z Ryskeldinova S Yespembetov B Zinina N Assanzhanova N et al . Novel influenza virus vectors expressing Brucella L7/L12 or Omp16 proteins in cattle induced a strong T-cell immune response, as well as high protectiveness against B. abortus infection. Vaccine. (2014) 32:2034–41. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.02.058
260.
Gheibi A Khanahmad H Kashfi K Sarmadi M Khorramizadeh MR . Development of new generation of vaccines for Brucella abortus. Heliyon. (2018) 4:e01079. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2018.e01079
261.
Chen B Liu B Zhao Z Wang G . Evaluation of a DNA vaccine encoding Brucella BvrR in BALB/c mice. Mol Med Rep. (2019) 19:1302–8. 10.3892/mmr.2018.9735
262.
Escalona E Sáez D Oñate A . Immunogenicity of a multi-epitope dna vaccine encoding epitopes from Cu–Zn superoxide dismutase and open reading Frames of Brucella abortus in mice. Front Immunol. (2017) 8:125. 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00125
263.
Shojaei M Tahmoorespur M Soltani M Sekhavati MH . Immunogenicity evaluation of plasmids encoding Brucella melitensis Omp25 and Omp31 antigens in BALB/c mice. Iran J Basic Med Sci. (2018) 21:957. 10.22038/IJBMS.2018.27540.6722
264.
Imtiaz W Khan A Gul ST Saqib M Saleemi MK Shahzad A et al . Evaluation of DNA vaccine encoding BCSP31 surface protein of Brucella abortus for protective immunity. Microb Pathog. (2018) 125:514–20. 10.1016/j.micpath.2018.10.016
265.
Al-Mariri A Abbady AQ . Evaluation of the immunogenicity and the protective efficacy in mice of a DNA vaccine encoding SP41 from Brucella melitensis. J Infect Dev Ctries. (2013) 7:329–37. 10.3855/jidc.2296
266.
Jain S Afley P Dohre SK Saxena N Kumar S . Evaluation of immunogenicity and protective efficacy of a plasmid DNA vaccine encoding ribosomal protein L9 of Brucella abortus in BALB/c mice. Vaccine. (2014) 32:4537–42. 10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.06.012
267.
González-Smith A Vemulapalli R Andrews E Oñate A . Evaluation of Brucella abortus DNA vaccine by expression of Cu–Zn superoxide dismutase antigen fused to IL-2. Immunobiology. (2006) 211:65–74. 10.1016/j.imbio.2005.09.004
268.
Abkar M Fasihi-Ramandi M Kooshki H Sahebghadam Lotfi A . Oral immunization of mice with Omp31-loaded N-trimethyl chitosan nanoparticles induces high protection against Brucella melitensis infection. International journal of nanomedicine. (2017):8769-78. 10.2147/IJN.S149774
269.
Maleki M Salouti M Shafiee Ardestani M Talebzadeh A . Preparation of a nanovaccine against Brucella melitensis M16 based on PLGA nanoparticles and oligopolysaccharide antigen. Artif cells Nanomed Biotechnol. (2019) 47:4248–56. 10.1080/21691401.2019.1687490
270.
Al-Halifa S Gauthier L Arpin D Bourgault S Archambault D . Nanoparticle-based vaccines against respiratory viruses. Front Immunol. (2019) 10:22. 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00022
271.
Afshari H Maleki M Salouti M . Immunological effects of two new nanovaccines against Brucella based on OPS and LPS antigens conjugated with PLGA nanoparticles. Eur Polym J. (2020) 139:110021. 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.110021
272.
Cassataro J Estein SM Pasquevich KA Velikovsky CA de la Barrera S Bowden R et al . Vaccination with the recombinant Brucella outer membrane protein 31 or a derived 27-amino-acid synthetic peptide elicits a CD4+ T helper 1 response that protects against Brucella melitensis infection. Infect Immun. (2005) 73:8079–88. 10.1128/IAI.73.12.8079-8088.2005
273.
Miguel A Arellano-Reynoso B Hernández-Badillo E Guerra-Infante FM Mancilla-Herrera I Chaki S et al . Evaluation of the goat cellular immune response to rBtuB-Hia-FlgK peptides from Brucella melitensis. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. (2023) 94:101944. 10.1016/j.cimid.2023.101944
274.
Gurunathan S Wu C-Y Freidag BL Seder RA . DNA vaccines: a key for inducing long-term cellular immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. (2000) 12:442–7. 10.1016/S0952-7915(00)00118-7
275.
Ingolotti M Kawalekar O Shedlock DJ Muthumani K Weiner DB . DNA vaccines for targeting bacterial infections. Expert Rev Vaccines. (2010) 9:747–63. 10.1586/erv.10.57
276.
Ko J Splitter GA . Molecular host-pathogen interaction in brucellosis: current understanding and future approaches to vaccine development for mice and humans. Clin Microbiol Rev. (2003) 16:65–78. 10.1128/CMR.16.1.65-78.2003
277.
Aslam M Mehnaz S Fatima T Ather A Tehreem A Haq S et al . Brucellosis: a global challenge. In: Zoonosis. Vol. 4. Faisalabad: Unique Scientific Publishers. (2023). p. 432–42. 10.47278/book.zoon/2023.167
278.
Mengele IJ Shirima GM Bronsvoort BM Hernandez-Castro LE Cook EA . Diagnostic challenges of brucellosis in humans and livestock in Tanzania: a thematic review. CABI One Health. (2023) ohcs20230001. 10.1079/cabionehealth.2023.0001
279.
Baroncelli S Tarantino M Galluzzo CM Liotta G Orlando S Sagno JB et al . Seroprevalence of Brucella infection in a cohort of HIV-positive Malawian pregnant women living in urban areas. Vector-Borne Zoonotic Dis. (2022) 22:263–6. 10.1089/vbz.2021.0088
280.
Uzunović S Skomorac M Bašić F Kamberović F Ibrahimagić A Dizdarević J . Human brucellosis as an epidemic zoonosis in Zenica-Doboj Canton (Bosnia and Herzegovina) during 2008-2018. Open Infect Dis J. (2020) 12:1–6. 10.2174/1874279302012010001
281.
Hussain A Jamil T Tareen AM Melzer F Hussain MH Khan I et al . Serological and molecular investigation of brucellosis in breeding equids in Pakistani Punjab. Pathogens. (2020) 9:673. 10.3390/pathogens9090673
282.
Erkyihun GA Gari FR Kassa GM . Bovine brucellosis and its public health significance in Ethiopia. Zoonoses. (2022) 2:985. 10.15212/ZOONOSES-2022-0005
283.
About F Pastre T Boutrou M Martinez AY Melzani A Peugny S et al . Novel species of Brucella causing human brucellosis, French Guiana. Emerg Infect Dis. (2023) 29:333. 10.3201/eid2902.220725
284.
Troupin C Ellis I Doukouré B Camara A Keita M Kagbadouno M et al . Seroprevalence of brucellosis, Q fever and Rift Valley fever in domestic ruminants in Guinea in 2017–2019. BMC Vet Res. (2022) 18:64. 10.1186/s12917-022-03159-x
285.
Bodenham RF Lukambagire AS Ashford RT Buza JJ Cash-Goldwasser S Crump JA et al . Prevalence and speciation of brucellosis in febrile patients from a pastoralist community of Tanzania. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:7081. 10.1038/s41598-020-62849-4
286.
Mol JP Guedes AC Eckstein C Quintal AP Souza TD Mathias LA et al . Diagnosis of canine brucellosis: comparison of various serologic tests and PCR. J Vet Diagn Invest. (2020) 32:77–86. 10.1177/1040638719891083
287.
Pinn-Woodcock T Frye E Guarino C Franklin-Guild R Newman AP Bennett J et al . One-health review on brucellosis in the United States. J Am Vet Med Assoc. (2023) 261:451–62. 10.2460/javma.23.01.0033
288.
Kucuk GO Gorgun S Kucuk GO . Brucellosis mimicking COVID-19: a point of view on differential diagnosis in patients with fever, dry cough, arthralgia, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cureus. (2021) 13:e15848. 10.7759/cureus.15848
289.
Grützke J Gwida M Deneke C Brendebach H Projahn M Schattschneider A et al . Direct identification and molecular characterization of zoonotic hazards in raw milk by metagenomics using Brucella as a model pathogen. Microb Genom. (2021) 7:000552. 10.1099/mgen.0.000552
290.
Zhang S Hu J An S Li M Li F Zhang P et al . Prevalence and relevant factors of positive RF in brucellosis patients with arthralgia. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2021) 15:e0009749. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009749
291.
Berhanu G Pal M . Brucellosis: a highly infectious zoonosis of public health and economic importance. J Emerg Environ Technol Health Protection. (2020) 3:5–9.
292.
Lozano-López E Austreberta-Nazar-Beutelspacher D Nahed-Toral J . Bovine and human brucellosis in southern Mexico: a neglected zoonosis. Rev Chilena Infect. (2022) 39:157–65. 10.4067/S0716-10182022000200157
293.
Jamil T Khan AU Saqib M Hussain MH Melzer F Rehman A et al . Animal and human brucellosis in Pakistan. Front Publ Health. (2021) 9:660508. 10.3389/fpubh.2021.660508
294.
Jamil T Kasi KK Melzer F Saqib M Ullah Q Khan MR et al . Revisiting brucellosis in small ruminants of western border areas in Pakistan. Pathogens. (2020) 9:929. 10.3390/pathogens9110929
295.
Pritam M Kumar R . Pathophysiology, current therapeutic options, vaccine candidates, and drug targets for human brucellosis. Curr Mol Pharmacol. (2024) 17:e130723218680. 10.2174/1874467217666230713093802
296.
Jamil T Akar K Erdenlig S Murugaiyan J Sandalakis V Boukouvala E et al . Spatio-temporal distribution of brucellosis in European terrestrial and marine wildlife species and its regional implications. Microorganisms. (2022) 10:1970. 10.3390/microorganisms10101970
297.
National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine; Division on Earth and Life Studies, Board on Agriculture and Natural Resources; Committee on Revisiting Brucellosis in the Greater Yellowstone Area . Revisiting Brucellosis in the Greater Yellowstone Area. Washington, DC: National Academies Press (2021).
298.
Olsen S Boggiatto PM Putz EJ . Comparison of bison and elk susceptibility to experimental challenge with Brucella abortus strain 2308. Front Vet Sci. (2025) 11:1519453. 10.3389/fvets.2024.1519453
299.
Tattersfield JG Rogers G Blunt M . Progress of the Brucellosis Eradication scheme 1970 to 1977. N Z Vet J. (1978) 26:79–84. 10.1080/00480169.1978.34501
300.
Davidson R . Field operations in the Brucellosis Eradication Scheme. N Z Vet J. (1978) 26:44–5. 10.1080/00480169.1978.34493
301.
McDermott J Grace D Zinsstag J . Economics of brucellosis impact and control in low-income countries. Rev Sci Tech. (2013) 32:249–61. 10.20506/rst.32.1.2197
302.
Qin Y Zhou G Jiao F Cheng C Meng C Wang L et al . Brucella mediates autophagy, inflammation, and apoptosis to escape host killing. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2024) 14:1408407. 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1408407
303.
Poetsch A Marchesini MI . Proteomics of Brucella. Proteomes. (2020) 8:8. 10.3390/proteomes8020008
304.
González FM Bialer MG Cerruti ML Estein SM Ramis LY Baldi PC et al . Brucella suis Δ mapB outer membrane vesicles as an acellular vaccine against systemic and mucosal B. suis infection. Front Immunol. (2025) 15:1501791. 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1501791
305.
La Guidara C Adamo R Sala C Micoli F . Vaccines and monoclonal antibodies as alternative strategies to antibiotics to fight antimicrobial resistance. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:5487. 10.3390/ijms25105487
306.
Knezevic P Aleksic Sabo V . Combining bacteriophages with other antibacterial agents to combat bacteria. In: Phage Therapy: A Practical Approach. Cham: Springer (2019). p. 257–93. 10.1007/978-3-030-26736-0_10
307.
Bagheri Nejad R Krecek RC Khalaf OH Hailat N Arenas-Gamboa AM . Brucellosis in the Middle East: current situation and a pathway forward. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2020) 14:e0008071. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008071
308.
Addis M . Public health and economic importance of brucellosis: a review. Public Health. (2015) 5:68–84.
309.
Islam MA Khatun MM Werre SR Sriranganathan N Boyle SM . A review of Brucella seroprevalence among humans and animals in Bangladesh with special emphasis on epidemiology, risk factors and control opportunities. Vet Microbiol. (2013) 166:317–26. 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.06.014
310.
Di Bari C Venkateswaran N Bruce M Fastl C Huntington B Patterson GT et al . Methodological choices in brucellosis burden of disease assessments: a systematic review. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. (2022) 16:e0010468. 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010468
311.
Herrera JAR Thomsen ST Jakobsen LS Fagt S Banasik K Izarzugaza JM et al . The burden of disease of three food-associated heavy metals in clusters in the Danish population – towards targeted public health strategies. Food Chem Toxicol. (2021) 150:112072. 10.1016/j.fct.2021.112072
312.
Golshani M Buozari S . A review of brucellosis in Iran: epidemiology, risk factors, diagnosis, control, and prevention. Iran Biomed J. (2017) 21:349. 10.18869/acadpub.ibj.21.6.349
Summary
Keywords
brucellosis, pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment regimens, public health
Citation
Almuzaini AM and Elbehiry A (2025) Unraveling brucellosis: advances in pathogenesis, diagnostic strategies, therapeutic innovations, and public health perspectives. Front. Med. 12:1629008. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1629008
Received
15 May 2025
Accepted
22 September 2025
Published
08 October 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Mahmoud A. Ebada, Zagazig University, Egypt
Reviewed by
Nazan Tuna, Namik Kemal University, Türkiye
Samah Attia Algharib, Benha University, Egypt
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Almuzaini and Elbehiry.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Ayman Elbehiry ar.elbehiry@qu.edu.sa
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.