- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Civil Aviation General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, The First Medical Center, Chinese PLA General Hospital, Beijing, China
- 3Department of Pharmacy, Civil Aviation General Hospital, Beijing, China
Objective: The identification of novel and effective treatments for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection remains a critical need. Treatment is indicated for peptic ulcer disease, gastric MALT lymphoma, and gastric cancer prevention, following diagnosis via non-invasive testing or endoscopy. This study aimed to investigate the efficacy and safety of tegoprazan-based regimens compared to bismuth-containing quadruple therapy in H. pylori eradication.
Patients and methods: In a randomized, controlled, treatment-naïve adult patients with confirmed H. pylori infection were assigned in a 1:1:1 ratio to one of the following 14-day open-label therapies: BQT (rabeprazole 10 mg twice daily, compound bismuth aluminate granules 2.6 g thrice daily, amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily), tegoprazan-based therapies (TAD, tegoprazan 50 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1 g thrice daily; TBQT, tegoprazan 50 mg twice daily, compound bismuth aluminate granules 2.6 g thrice daily, amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily). The primary outcome was the eradication rate of H. pylori. Secondary outcomes included the assessment of adverse events and treatment compliance.
Results: A total of 468 patients were enrolled. The eradication rates for TBQT, TAD and BQT were 86.3, 85.5 and 77.2%, respectively, by intention-to-treat analysis (p = 0.059), and 87.3, 87.2 and 77.7%, respectively, by per-protocol analysis (p = 0.029). The incidence of adverse events was comparable between the BQT and tegoprazan-based therapies (p > 0.05). Treatment compliance was similar across all three groups.
Conclusion: Tegoprazan-based therapies achieved acceptable H. pylori eradication rates exceeding 85%, outperforming the BQT. Additionally, tegoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy may serve as an alternative H. pylori eradication regimen in regions with high clarithromycin resistance.
Clinical trial registration: http://clinicaltrials.gov, Identifier ChiCTR2300077088.
Introduction
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection remains one of the most prevalent chronic bacterial infections globally, affecting approximately 50% of the population (1, 2). Although the incidence has been declining in developed regions, H. pylori continues to be a major contributor to morbidity and mortality worldwide (3). This pathogen is identified in nearly half of all adults and is strongly linked to a range of upper gastrointestinal disorders, including chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastric mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma, and gastric carcinoma (4). Consequently, the development of effective eradication therapies for H. pylori is essential for the management and mitigation of H. pylori-related diseases.
A multitude of therapeutic regimens have been advocated for the eradication of H. pylori, including triple, quadruple, and sequential therapies (5). In light of the rising incidence of antimicrobial resistance, bismuth-containing quadruple therapy (BQT), which comprising a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), clarithromycin, amoxicillin, and bismuth, has emerged as the preferred first-line treatment (6). This regimen has demonstrated high efficacy in eliminating H. pylori, including strains resistant to antibiotics. Nevertheless, despite the global recommendation of a 14-day BQT as both first-line and rescue therapy, failures of PPI-based treatments persist in approximately 10–30% of patients, predominantly due to antibiotic resistance (7). In China, the management of H. pylori is further complicated by exceptionally high infection rates, frequent adverse effects, disruptions to intestinal microbiota, and elevated recurrence rates (8). These challenges underscore the necessity for the development of modified therapeutic strategies.
Tegoprazan (TPZ) and vonoprazan (VPZ) represent novel, orally administered potassium-competitive acid blockers (P-CABs) that exhibit competitive and reversible binding to the potassium-binding site of the gastric proton pump (9). In contrast to PPIs, which necessitate activation under highly acidic conditions, P-CABs effectively inhibit the proton pump independent of acid activation (10). Furthermore, P-CABs demonstrate the capability to bind both active and inactive conformations of the proton pump (11). This dual-binding mechanism enables P-CABs to achieve maximal acid suppression more rapidly, maintains efficacy irrespective of food intake, prolongs the duration of action, and circumvents the variability introduced by CYP2C19 polymorphisms (12). Emerging evidence from recent studies indicates that P-CAB-based regimens surpass PPI-based regimens in H. pylori eradication rates (13). Notably, P-CAB-based regimens characterized by shorter durations and simplified drug administration protocols have achieved eradication rates that are both clinically acceptable and comparable to more complex regimens. Studies have revealed that high-dose amoxicillin-vonoprazan dual therapy attained pooled eradication rates of 85.0% in intention-to-treat (ITT) analyses and 90.0% in per-protocol (PP) analyses (14, 15). Despite these promising findings, the application of tegoprazan-based therapies for H. pylori eradication remains underexplored, with limited studies available to date. Future research should focus on elucidating the efficacy and optimization of tegoprazan-containing regimens to fully establish their role in H. pylori management.
Consequently, we initiated a prospective, single-center clinical study to assess the efficacy and safety of 14-day tegoprazan-based therapies in comparison with the 14-day BQT as first-line treatments for H. pylori infection. The results of this investigation indicate that tegoprazan-based therapies may provide a safer and more effective treatment alternative for patients diagnosed with H. pylori infection.
Materials and methods
Ethical approval
This study adhered to the recommendations outlined in the Consolidated Standards of Reporting Trials (CONSORT) statement for randomized controlled trials. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants prior to enrollment. The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Ethics Board of the Civil Aviation General Hospital, Beijing, China (Approval No. 2023-L-K-44). The trial was registered with the Chinese Clinical Trials Registry1 under registration number ChiCTR2300077088.
Study design and participants
This study was a single-center, prospective, open-label, randomized controlled trial conducted from November 2023 to August 2024. A total of 468 eligible participants were recruited from outpatient clinics. Inclusion criteria: (1) male or female aged ≥18 years; (2) H. pylori infection confirmed by a positive 13C-urea breath test (UBT); (3) upper gastrointestinal symptoms, including epigastric pain, acid reflux, heartburn, epigastric distention, or nausea; (4) signed informed consent form. Exclusion Criteria: (1) prior receipt of standard H. pylori eradication therapy; (2) use of antibiotics, bismuth, or PPIs within 4 weeks prior to treatment initiation; (3) recurrent or long-term use of macrolides; (4) allergy or contraindication to study-related medications; (5) serious primary diseases; (6) hepatic or renal insufficiency; (7) alcohol abuse. Participants meeting the inclusion criteria and none of the exclusion criteria were randomized to receive the study intervention.
Treatment regiments
Eligible patients were randomized to one of three treatment groups: (1) BQT (rabeprazole 10 mg twice daily, compound bismuth aluminate granules 2.6 g thrice daily, amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily), (2) tegoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy (TAD, tegoprazan 50 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1 g thrice daily), (3) tegoprazan-based quadruple therapy (TBQT, tegoprazan 50 mg twice daily, compound bismuth aluminate granules 2.6 g thrice daily, amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily) for 14 days. Tegoprazan, compound bismuth aluminate granules and rabeprazole were taken orally 30 min before breakfast, lunch, and dinner, while amoxicillin and clarithromycin were taken 30 min after breakfast and dinner. Administration timing was standardized to optimize treatment adherence and efficacy.
Study outcomes
The primary endpoint was the H. pylori eradication rate in the three groups. Eradication was evaluated using the 13C-UBT conducted 4 weeks after the completion of the treatment period. The primary analysis was performed using both ITT and PP analyses. The ITT analysis included all randomized patients, with those lost to follow-up or not undergoing the 13C-UBT classified as treatment failures. The PP analysis included patients who achieved at least 85% drug compliance and completed the 13C-UBT. Drug compliance was documented through a questionnaire completed by patients.
The secondary endpoints were the adverse events (AEs) and compliance. AEs related to the study drugs were recorded daily for 14 days using a patient-completed questionnaire. When patients reported any adverse event in the questionnaire form, investigators inquired them and assessed the severity using a grading system (1–5) based on the National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI-CTCAE) Version 5.0. The severity of the adverse events was classified into three levels: mild (transient and well-tolerated), moderate (causing discomfort and partially interfering with daily activities), or severe (causing considerable interference with daily activities). Compliance was assessed by standardized interview at the end of treatment, as well as by pill count in the medication boxes returned at the interview. Low compliance was defined as consumption of < 85% of dispensed pills.
Randomization and blinding
Eligible participants were randomly assigned to one of three treatment groups in a 1:1:1 ratio using block randomization with blocks of six, employing the sequentially numbered, opaque sealed envelope method (16). Allocation was managed through opaque, sealed envelopes handled by designated personnel unaffiliated with the trial. Upon enrollment, participants were sequentially provided with an envelope to determine their group assignment. To minimize selection bias and preserve the study’s integrity, outcome assessments were conducted by researchers blinded to the treatment allocations. These blinded assessors were instructed to refrain from discussing treatment specifics with participants or other investigators, ensuring that blinding was maintained throughout the duration of the study.
Sample size calculation and statistical analysis
Based on prior studies, the eradication rates of 14-day BQT for first-line H. pylori treatment ranged from 70 to 85% (17, 18). As a result, this study assumed that the eradication rate was 90% in both tegoprazan-amoxicillin and tegoprazan-bismuth quadruple therapy groups. Assuming a power of 80% and an alpha of 0.025 (one-sided), and a noninferiority margin of 10%. Accounting for a 10% dropout rate, a minimum of 145 participants per group was required, resulting in a total sample size of 435 participants.
All statistical analyses were conducted utilizing the SPSS version 22.0 or R V.3.5.2 software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria). Categorical variables are delineated by the number of patients along with their corresponding percentages, whereas continuous variables are reported as mean values accompanied by their standard deviations (SD). For the assessment of categorical data, the Chi-square test was employed, while the paired t-test was applied to evaluate continuous data. The non-inferiority of the two groups was assessed using the derivation of a two-sided 95% CI and one-sided μ-test. A p-value of less than 0.05 was deemed indicative of statistical significance.
Results
Patient enrolment and baseline characteristics
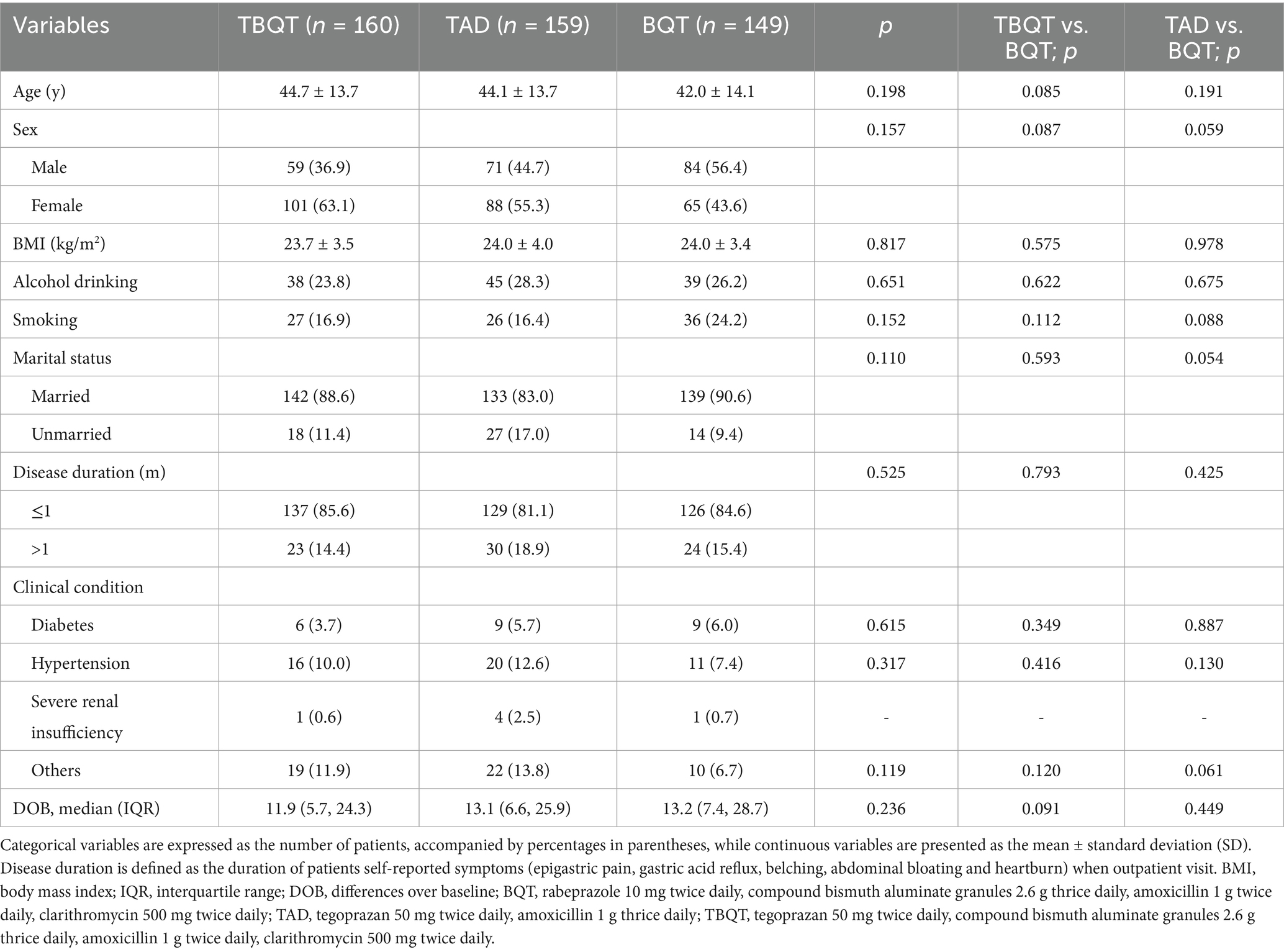
Figure 1 delineates the patient enrollment process. Initially, 552 individuals were screened for eligibility, and finally 468 participants for the study. These participants were subsequently randomized into three distinct groups: TBQT (n = 160), TAD (n = 159), and BQT (n = 149). There were no significant differences in baseline characteristics across the three groups, except for a slight differences observed in the distribution of sex, with a higher proportion of males and smokers in the BQT group (Table 1). Throughout the study period, two participants from the TBQT group, three from the TAD group, and one from the BQT group lost to follow-up and consequently did not undergo the 13C-UBT. In the ITT analysis, these individuals were categorized as treatment failures.
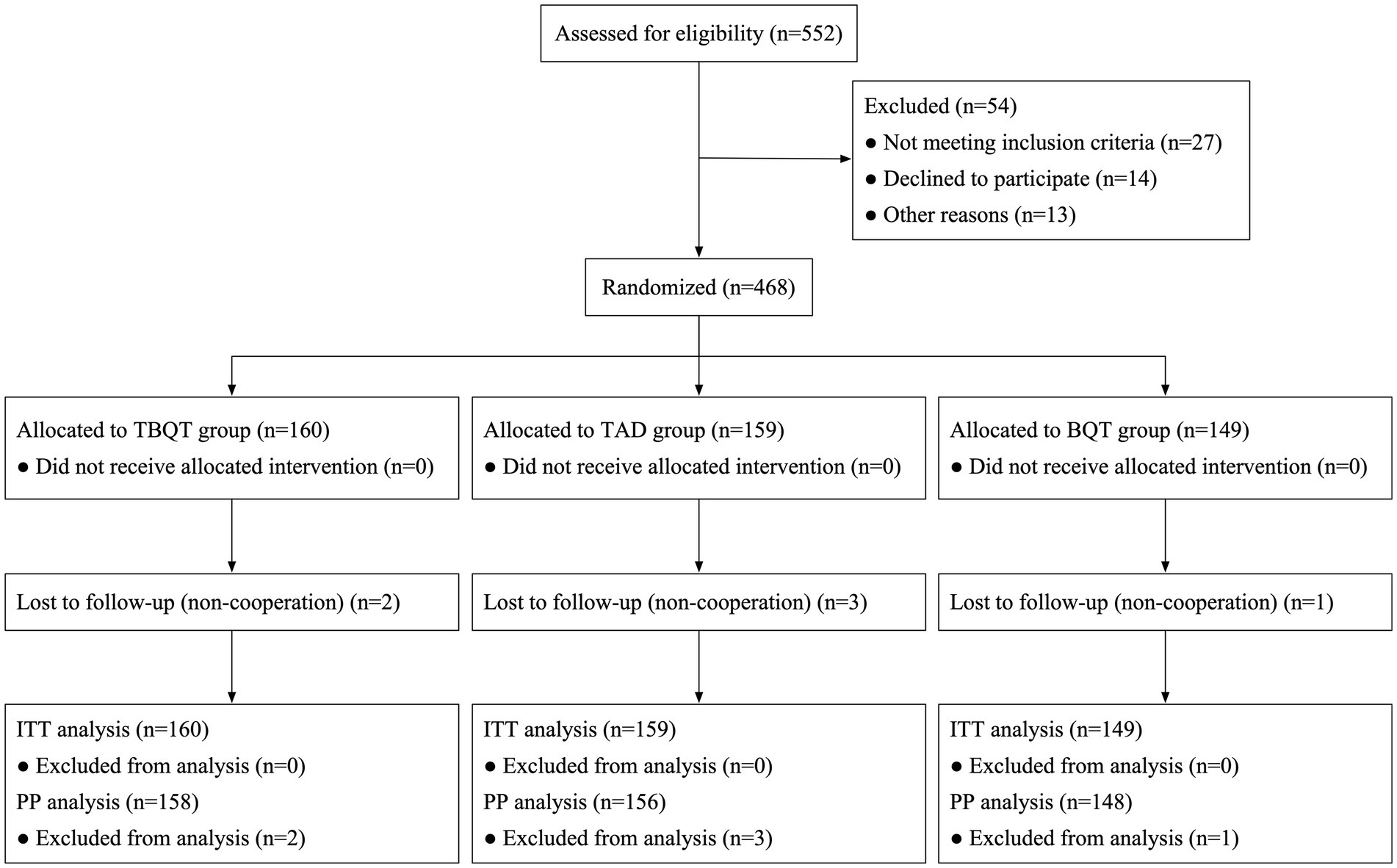
Figure 1. Flow chart of patient enrolment and study design. ITT, intention-to-treat; PP, per-protocol; BQT, rabeprazole 10 mg twice daily, compound bismuth aluminate granules 2.6 g thrice daily, amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily; TAD, tegoprazan 50 mg twice daily, amoxicillin 1 g thrice daily; TBQT, tegoprazan 50 mg twice daily, compound bismuth aluminate granules 2.6 g thrice daily, amoxicillin 1 g twice daily, clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily.
Helicobacter pylori eradication rates
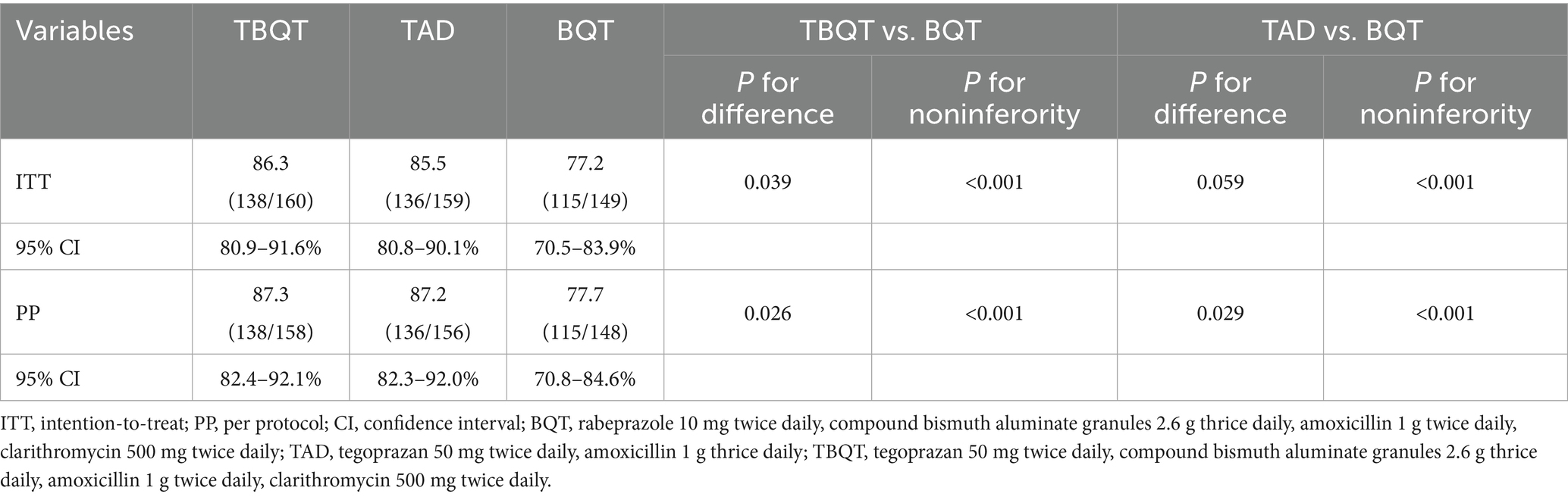
Eradication rates for the three treatment groups are detailed in Table 2. In the ITT analysis, the eradication rates for TBQT, TAD, and BQT were 86.3% (138/160), 85.5% (136/159), and 77.2% (115/149), respectively. Statistical comparisons revealed that TBQT significantly outperformed BQT (p = 0.039), while TAD approached significance compared to BQT (p = 0.059). Conversely, the PP analysis demonstrated eradication rates of 87.3% (138/158) for TBQT, 87.2% (136/156) for TAD, and 77.7% (115/148) for BQT. Both TBQT and TAD showed statistically significant improvements over BQT (TBQT vs. BQT, p = 0.026; TAD vs. BQT, p = 0.029; noninferiority p < 0.001). These findings indicate that both TBQT and TAD regimens significantly enhance the eradication rates of H. pylori.
Rates of AEs and compliance
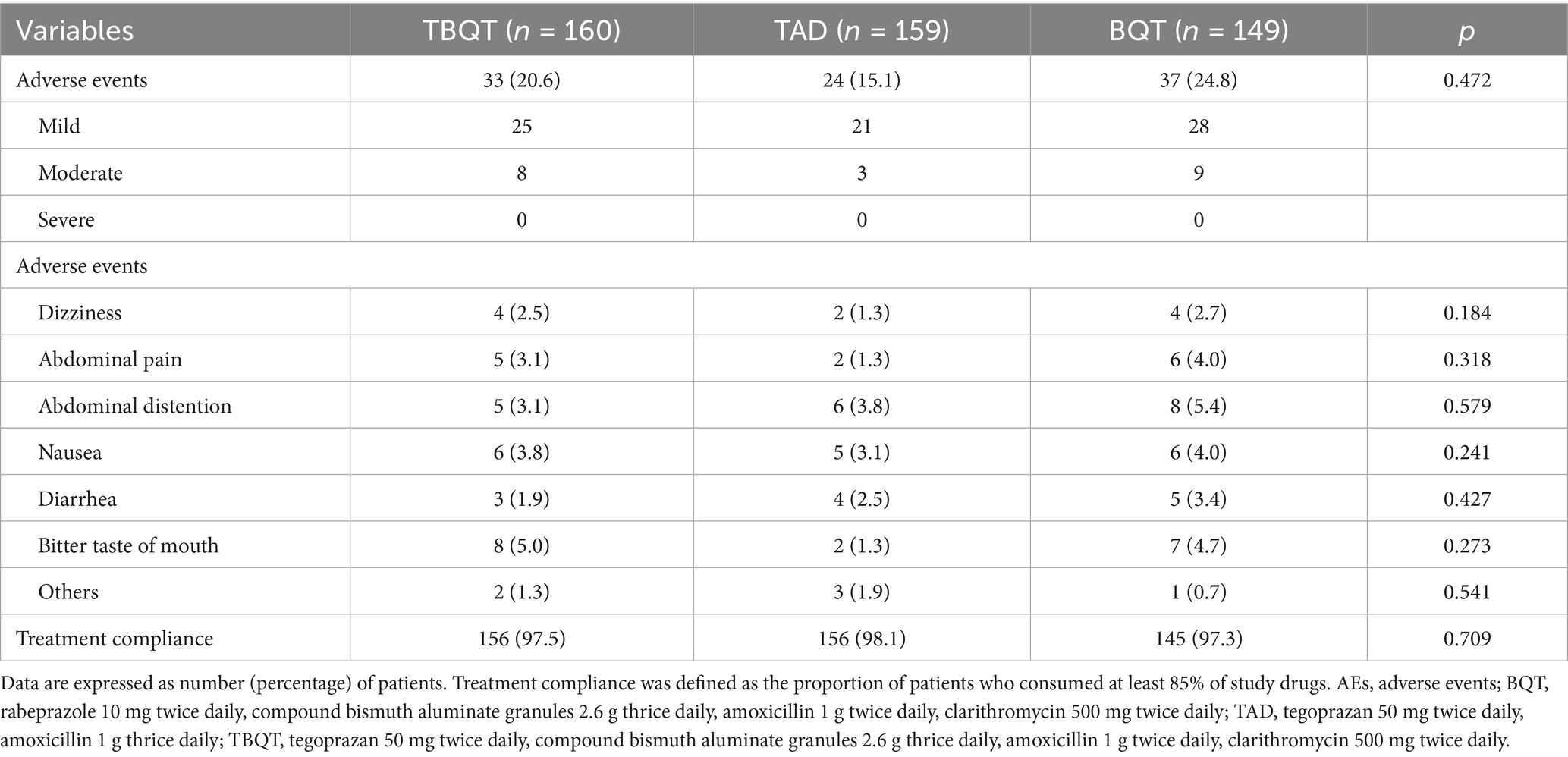
Table 3 delineates the incidence rates of AEs across TBQT, TAD, and BQT groups, which were observed to be 20.6% (33/160), 15.1% (24/159), and 24.8% (37/149), respectively. Predominant AEs encompassed dizziness, abdominal pain, abdominal distention, nausea, diarrhea, and bitter taste of mouth. Importantly, no serious AEs were reported, and all other adverse events were classified as either mild or moderate in severity. Moreover, treatment adherence was notably high and did not significantly differ among the three groups, with compliance rates recorded at 97.5% (156/160) for TBQT, 98.1% (156/159) for TAD, and 97.3% (145/149) for BQT (p > 0.05). These findings suggest a favorable safety and compliance profile across the treatment regimens evaluated.
Discussion
This study represents the assessment of the efficacy and safety profiles associated with 14-day tegoprazan-based therapeutic regimens in comparison to BQT for the eradication of H. pylori. In the PP analysis, both the TBQT and TAD demonstrated eradication rates of 87.3 and 87.2%, respectively. These rates were statistically superior to those observed with BQT, which achieved a 77.2% eradication rate (p < 0.01). Furthermore, tegoprazan-based therapies maintained high levels of patient compliance, with no significant differences noted between the regimens. Collectively, these outcomes endorse the consideration of tegoprazan-based therapies, particularly the tegoprazan-amoxicillin therapy, as viable options for the management of H. pylori infections.
Triple therapy, which includes a PPI alongside two antimicrobial agents, typically clarithromycin combined with amoxicillin or metronidazole, has served as the standard first-line eradication regimen for H. pylori infection (19). However, owing to antibiotic resistance, particularly to clarithromycin alone or in combination with metronidazole, constitutes a significant barrier to the global success of H. pylori eradication (20). In regions characterized by high antibiotic resistance, the efficacy of standard triple therapy has markedly declined, with eradication rates now ranging between 50 and 70% (21). The persistent failure to eradicate H. pylori is strongly associated with elevated gastric acidity and antibiotic resistance. Antibiotic activity is substantially enhanced when gastric acidity is neutralized; therefore, maintaining a gastric pH above 5 is recommended to optimize the effectiveness of antibiotics in eradicating H. pylori (22). Despite this, currently available PPIs generally do not achieve the necessary level of acid suppression consistently over a 24-h period to maintain the targeted pH level (23). P-CABs have emerged as viable alternatives to conventional PPIs. Currently, the principal P-CABs utilized in H. pylori eradication therapy are VPZ and TPZ (24). Compared to PPIs, P-CABs demonstrate superior and sustained gastric acid suppression, with the additional advantage of efficacy independent of cytochrome P450 2C19 (CYP2C19) polymorphism (25). Clinical evidence indicates that both VPZ- and TPZ-based regimens achieve significantly higher eradication rates than PPI-based quadruple therapy, while maintaining comparable safety profiles (26, 27). However, large-scale randomized controlled trials are warranted to conclusively establish the superior efficacy of P-CAB-based regimens relative to BQT.
The superior eradication rates observed in this study with tegoprazan dual and quadruple therapies may be ascribed to the robust gastric acid suppression of tegoprazan and its capacity to sustain elevated gastric pH levels (28). In comparative analyses (21), tegoprazan-containing quadruple therapy demonstrated eradication rates of 90.3% (modified ITT) and 90.2% (PP). In contrast, quadruple therapies based on PPIs achieved eradication rates of 84.5% (modified ITT) and 82.4% (PP). These findings indicate that tegoprazan-based quadruple therapy significantly outperforms PPI-based regimens in H. pylori eradication, underscoring the acid-suppressive superiority of P-CABs in therapeutic interventions against this pathogen (28). Although existing studies indicate TPZ offers faster onset and sustained acid suppression versus VPZ, its shorter mean elimination half-life (3.7–5.4 h) contrasts with VPZ’s longer terminal half-life (mean 7.7 h) (12). This pharmacokinetic profile of VPZ may contribute to its superior H. pylori eradication rates relative to TPZ. Given the current lack of direct comparative evidence, large-scale randomized controlled trials are warranted to assess the efficacy and safety of TPZ versus VPZ for H. pylori eradication. This study demonstrated a marginally higher eradication rate with tegoprazan-based quadruple therapy compared to tegoprazan-based dual therapy (ITT: 86.3% vs. 85.5%; PP: 87.3% vs. 87.2%). This observed difference may be potentially attributable to the inclusion of bismuth within the quadruple regimen. Bismuth, a gastric mucosa protector, is another crucial component of the quadruple therapy for H. pylori eradication. Its advantages include non-resistance and high safety in short-term applications, and its ability to improve the eradication rate of antibiotic-resistant bacteria (29, 30). Currently, BQT is recommended as the primary empirical treatment for H. pylori eradication by the fifth Chinese national consensus report on H. pylori infection management (31).
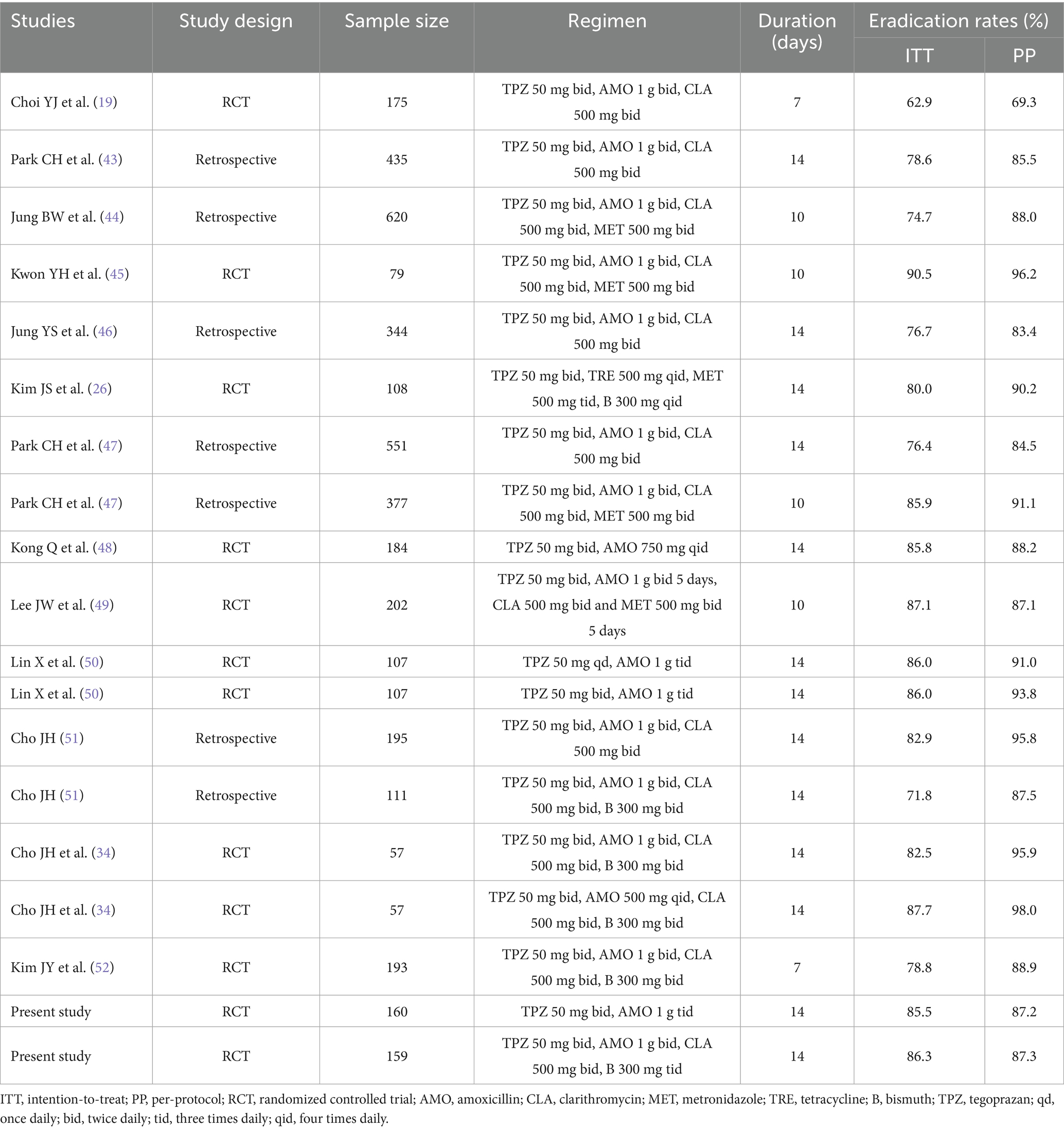
Another plausible explanation for the high eradication rates observed with tegoprazan-dual and tegoprazan-quadruple therapies pertains to the susceptibility of the H. pylori strains involved, which exhibited no resistance to amoxicillin. Notably, the resistance rate of H. pylori to amoxicillin remains significantly lower compared to other antibiotics, a factor that is often underemphasized in the development of H. pylori treatment regimens (32). In China, amoxicillin resistance is particularly minimal, consistently reported to be maintained at approximately 5% (33). Tegoprazan plays a crucial role in reducing the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of amoxicillin by ensuring sustained acid suppression, thereby maintaining the gastric pH above 6 for the majority of the treatment period (34). This maintenance of elevated gastric pH enhances the stability of amoxicillin, allowing the antibiotic to exert its full therapeutic efficacy. The effectiveness of tegoprazan is further evidenced by its ability to enhance the sensitivity of antimicrobials, such as amoxicillin, against H. pylori. The pharmacodynamic properties of amoxicillin are significantly influenced by both temporal factors and pH levels (35). For instance, achieving sustained and effective blood concentrations above the MIC typically requires dosing regimens of 500 mg four times daily or 750 mg three times daily (36). However, in the present study, the tegoprazan-dual regimen, which included the administration of amoxicillin at a dosage of 1,000 mg tid, successfully prolonged maintenance facilitated the bactericidal effects of amoxicillin, enhancing its overall efficacy against H. pylori. Tegoprazan-based therapies as first-line treatments for H. pylori infection were initially reported in the early 2020s and are comprehensively summarized in Table 4.
The eradication failures documented in this study likely stem from the escalating prevalence of antimicrobial resistance, a factor not directly assessed herein. The surge in antibiotic resistance, alongside the heterogeneous virulence profiles of H. pylori strains, has profoundly undermined the effectiveness of conventional eradication protocols. In Beijing, primary resistance rates to commonly employed antibiotics, amoxicillin, clarithromycin, metronidazole, levofloxacin, and moxifloxacin, were reported at 0.7, 55.2, 68.0, 49.7, and 64.5%, respectively, with secondary resistance rates escalating to 3.2, 96.7, 90.7, 93.1, and 80.0% (37). Clarithromycin, a fundamental component of first-line eradication therapy, exhibits notably high primary resistance in Beijing, presenting a substantial obstacle (38). Clarithromycin resistance has been associated with a 40–50% reduction in eradication success rates (39). Additionally, our study revealed no statistically significant differences (p > 0.05) in sex distribution, with the BQT group demonstrating higher proportions of male and smoking. Our prior research demonstrated a significant association between smoking and reduced H. pylori eradication rates (40). However, some studies have reported no association between H. pylori infection and smoking. A meta-analysis found no evidence supporting an association between smoking and H. pylori seropositivity (41). Wu et al. (42) indicated no significant difference in smoking between H. pylori when analyzing combined male and female participants.
This study is subject to several limitations that warrant consideration. Firstly, the antibiotic resistance profile of H. pylori was not assessed, which may have influenced the evaluation of eradication rates, given that antibiotic resistance is a pivotal factor affecting treatment efficacy. Secondly, three of the treatment regimens included amoxicillin, thereby excluding individuals who are either resistant to amoxicillin or possess a penicillin allergy, which limits the applicability of these regimens to the broader patient population. Additionally, the research was conducted at a single center with a relatively small sample size, potentially restricting the generalizability of the findings. Moreover, the single-center design introduces the possibility of selection bias, which cannot be entirely ruled out and may affect the study’s overall validity.
Conclusion
A 14-day dual therapy regimen comprising tegoprazan and amoxicillin achieved acceptable eradication rates for H. pylori, demonstrating efficacy comparable to tegoprazan-based quadruple therapy as a first-line eradication strategy in Beijing, China, a region characterized by high clarithromycin resistance. Notably, tegoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy offers several advantages, including the use of a single antibiotic and reduced antibiotic consumption, thereby positioning it as a promising alternative regimen for patients with H. pylori infection.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by The Institutional Ethics Board of the Civil Aviation General Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
JC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XlZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Software, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. CF: Conceptualization, Data curation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing. KH: Conceptualization, Software, Writing – review & editing. YC: Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. ZL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. DX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. LZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Project administration, Resources, Writing – review & editing. XmZ: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Resources, Writing – review & editing. HD: Conceptualization, Data curation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the China Zhongguancun Precision Medicine science and technology foundation (320.6799.2022.09. 24).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Footnotes
References
1. Zhong, Z, Zhan, B, Xu, B, and Gao, H. Achieving Helicobacter Pylori eradication in the primary treatment requires a deep integration of personalization and standardization. Helicobacter. (2022) 27:e12916. doi: 10.1111/hel.12916
2. Graham, DY, and Megraud, F. Classification system for Helicobacter Pylori therapies: compared and contrasted to traditional infectious disease therapy. Helicobacter. (2021) 26:e12773. doi: 10.1111/hel.12773
3. FitzGerald, R, and Smith, SM. An overview of Helicobacter Pylori infection. Methods Mol Biol. (2021) 2283:1–14. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1302-3_1
4. Cho, J, Prashar, A, Jones, NL, and Moss, SF. Helicobacter Pylori infection. Gastroenterol Clin N Am. (2021) 50:261–82. doi: 10.1016/j.gtc.2021.02.001
5. Malfertheiner, P, Megraud, F, Rokkas, T, Gisbert, JP, Liou, JM, Schulz, C, et al. Management of Helicobacter Pylori Infection: the Maastricht vi/Florence consensus report. Gut. (2022) 71:1724–62. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327745
6. Qian, HS, Li, WJ, Dang, YN, Li, LR, Xu, XB, Yuan, L, et al. Ten-day Vonoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy as a first-line treatment of Helicobacter Pylori infection compared with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy. Am J Gastroenterol. (2023) 118:627–34. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000002086
7. Ding, YM, Duan, M, Han, ZX, Song, XH, Zhang, FL, Wang, Z, et al. Bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for Helicobacter Pylori eradication: a randomized clinical trial of 10 and 14 days. Dig Dis Sci. (2024) 69:2540–7. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08460-3
8. Liu, DN, Wang, QY, Li, PY, Wu, DH, Pan, J, Chen, ZY, et al. Comparing high-dose dual therapy with bismuth-containing quadruple therapy for the initial eradication of Helicobacter Pylori infection on Hainan Island: a randomized, multicenter clinical trial. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. (2023) 47:102125. doi: 10.1016/j.clinre.2023.102125
9. Yang, E, Kim, S, Kim, B, Kim, B, Kim, Y, Park, SS, et al. Night-time gastric acid suppression by Tegoprazan compared to Vonoprazan or esomeprazole. Br J Clin Pharmacol. (2022) 88:3288–96. doi: 10.1111/bcp.15268
10. Yang, E, Ji, SC, Jang, IJ, and Lee, S. Evaluation of Cyp2c19-mediated pharmacokinetic drug interaction of Tegoprazan, compared with Vonoprazan or esomeprazole. Clin Pharmacokinet. (2023) 62:599–608. doi: 10.1007/s40262-023-01228-4
11. Scarpignato, C, and Hunt, RH. Potassium-competitive acid blockers: current clinical use and future developments. Curr Gastroenterol Rep. (2024) 26:273–93. doi: 10.1007/s11894-024-00939-3
12. Jiang, Y, Zhang, R, Fang, Y, Zhao, R, Fu, Y, Ren, P, et al. P-cab versus Ppi in the eradication of Helicobacter Pylori: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. (2024) 17:17562848241241223. doi: 10.1177/17562848241241223
13. Ouyang, M, Zou, S, Cheng, Q, Shi, X, Zhao, Y, and Sun, M. Comparative efficacy and safety of potassium-competitive acid blockers vs. proton pump inhibitors for peptic ulcer with or without Helicobacter Pylori infection: a systematic review and network Meta-analysis. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). (2024) 17:698. doi: 10.3390/ph17060698
14. Chey, WD, Mégraud, F, Laine, L, López, LJ, Hunt, BJ, and Howden, CW. Vonoprazan triple and dual therapy for Helicobacter Pylori infection in the United States and Europe: randomized clinical trial. Gastroenterology. (2022) 163:608–19. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2022.05.055
15. Kiyotoki, S, Nishikawa, J, and Sakaida, I. Efficacy of Vonoprazan for Helicobacter Pylori eradication. Intern Med. (2020) 59:153–61. doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.2521-18
16. Paavola, M, Kanto, K, Ranstam, J, Malmivaara, A, Inkinen, J, Kalske, J, et al. Subacromial decompression versus diagnostic arthroscopy for shoulder impingement: a 5-year follow-up of a randomised, placebo surgery controlled clinical trial. Br J Sports Med. (2021) 55:99–107. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2020-102216
17. Bang, CS, Lim, H, Jeong, HM, Shin, WG, Choi, JH, Soh, JS, et al. Amoxicillin or tetracycline in bismuth-containing quadruple therapy as first-line treatment for Helicobacter Pylori infection. Gut Microbes. (2020) 11:1314–23. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1754118
18. Xie, Y, Hu, Y, Zhu, Y, Wang, H, Wang, QZ, Li, YQ, et al. Colloidal bismuth pectin-containing quadruple therapy as the first-line treatment of Helicobacter Pylori infection: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, non-inferiority clinical trial. Helicobacter. (2023) 28:e12978. doi: 10.1111/hel.12978
19. Choi, YJ, Lee, YC, Kim, JM, Kim, JI, Moon, JS, Lim, YJ, et al. Triple therapy-based on Tegoprazan, a new potassium-competitive acid blocker, for first-line treatment of Helicobacter Pylori infection: a randomized, double-blind, phase iii, clinical trial. Gut Liver. (2022) 16:535–46. doi: 10.5009/gnl220055
20. Chen, J, Guo, Y, Huang, Y, Ding, Z, Wang, J, Liang, X, et al. Rifabutin-containing triple therapy versus bismuth quadruple therapy for Helicobacter Pylori rescue treatment: a multicenter, randomized controlled trial. J Infect Dis. (2023) 228:511–8. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiad114
21. Kanu, JE, and Soldera, J. Treatment of Helicobacter Pylori with potassium competitive acid blockers: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. World J Gastroenterol. (2024) 30:1213–23. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v30.i9.1213
22. Medakina, I, Tsapkova, L, Polyakova, V, Nikolaev, S, Yanova, T, Dekhnich, N, et al. Helicobacter Pylori antibiotic resistance: molecular basis and diagnostic methods. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:9433. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119433
23. Sawaid, IO, and Samson, AO. Proton pump inhibitors and Cancer risk: a comprehensive review of epidemiological and mechanistic evidence. J Clin Med. (2024) 13:1970. doi: 10.3390/jcm13071970
24. Jin, T, Wu, W, Zhang, L, Xuan, H, Zhang, H, and Zhong, L. The efficacy and safety of Vonoprazan and Tegoprazan in Helicobacter Pylori eradication: a comprehensive systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. (2025) 18:17562848251314801. doi: 10.1177/17562848251314801
25. Oshima, T, and Miwa, H. Potent potassium-competitive acid blockers: a new era for the treatment of acid-related diseases. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. (2018) 24:334–44. doi: 10.5056/jnm18029
26. Kim, JS, Ko, W, Chung, JW, and Kim, TH. Efficacy of Tegoprazan-based bismuth quadruple therapy compared with bismuth quadruple therapy for Helicobacter Pylori infection: a randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study. Helicobacter. (2023) 28:e12977. doi: 10.1111/hel.12977
27. Huang, J, and Lin, Y. Vonoprazan on the eradication of Helicobacter Pylori infection. Turk J Gastroenterol. (2023) 34:221–6. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2022.211041
28. Jung, YS, Kim, S, Kim, HY, Noh, SJ, Park, JH, and Park, CH. 7-day versus 14-day Tegoprazan-based triple therapy to treat Helicobacter Pylori infection: real-world evidence. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2022) 37:1911–8. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15939
29. Wang, R, Lai, TP, Gao, P, Zhang, H, Ho, PL, Woo, PC, et al. Bismuth antimicrobial drugs serve as broad-Spectrum Metallo-Β-lactamase inhibitors. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:439. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-02828-6
30. Han, B, Zhang, Z, Xie, Y, Hu, X, Wang, H, Xia, W, et al. Multi-omics and temporal dynamics profiling reveal disruption of central metabolism in Helicobacter Pylori on bismuth treatment. Chem Sci. (2018) 9:7488–97. doi: 10.1039/c8sc01668b
31. Liu, WZ, Xie, Y, Lu, H, Cheng, H, Zeng, ZR, Zhou, LY, et al. Fifth Chinese National Consensus Report on the Management of Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Helicobacter. (2018) 23:e12475. doi: 10.1111/hel.12475
32. Peng, X, Chen, HW, Wan, Y, Su, PZ, Yu, J, Liu, JJ, et al. Combination of Vonoprazan and amoxicillin as the first-line Helicobacter Pylori eradication therapy: a multicenter, prospective, randomized, parallel-controlled study. Clin Exp Med. (2023) 23:4011–9. doi: 10.1007/s10238-023-01074-5
33. Hong, TC, El-Omar, EM, Kuo, YT, Wu, JY, Chen, MJ, Chen, CC, et al. Primary antibiotic resistance of Helicobacter Pylori in the Asia-Pacific region between 1990 and 2022: an updated systematic review and Meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 9:56–67. doi: 10.1016/s2468-1253(23)00281-9
34. Cho, JH, and Jin, SY. Comparison of amoxicillin administered twice versus four times a day in first-line Helicobacter Pylori eradication using Tegoprazan, clarithromycin, and bismuth: a propensity score matching analysis. Microorganisms. (2024) 12:1952. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12101952
35. Hwong-Ruey Leow, A, Chang, JV, and Goh, KL. Searching for an optimal therapy for H pylori eradication: high-dose proton-pump inhibitor dual therapy with amoxicillin vs. standard triple therapy for 14 days. Helicobacter. (2020) 25:e12723. doi: 10.1111/hel.12723
36. Liu, HN, Wang, R, Cao, Y, Xian, F, Bi, XJ, Wu, DJ, et al. Comparison of the efficacy between the dual therapy of Tegoprazan and the quadruple therapy of Tegoprazan: a randomized controlled multicenter study. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. (2024) 15:e1. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000699
37. Hu, J, Qi, D, Chen, Q, and Sun, W. Comparison and prioritization of antibiotics in a reservoir and its inflow Rivers of Beijing, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2022) 29:25209–21. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17723-9
38. Lok, CH, Zhu, D, Wang, J, Ren, YT, Jiang, X, Li, SJ, et al. Phenotype and molecular detection of clarithromycin and levofloxacin resistance in Helicobacter Pylori clinical isolates in Beijing. Infect Drug Resist. (2020) 13:2145–53. doi: 10.2147/idr.S249370
39. Chen, Y, Li, S, Li, W, Wang, Y, Shi, J, Xu, X, et al. Role of mic levels and 23s Rrna mutation sites to clarithromycin in 14-day clarithromycin bismuth quadruple therapy for Helicobacter Pylori eradication: a prospective trial in Beijing. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e29774. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29774
40. Cheng, J, Fan, C, Li, Z, Dong, Z, Zhao, X, Cai, Y, et al. Real-world situation of eradication regimens and risk factors for Helicobacter Pylori treatment in China: a retrospective single-center study. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. (2024) 17:191–200. doi: 10.2147/ceg.S466975
41. Ferro, A, Morais, S, Pelucchi, C, Aragonés, N, Kogevinas, M, López-Carrillo, L, et al. Smoking and Helicobacter Pylori infection: an individual participant pooled analysis (stomach Cancer pooling- stop project). Eur J Cancer Prev. (2019) 28:390–6. doi: 10.1097/cej.0000000000000471
42. Wu, W, Leja, M, Tsukanov, V, Basharat, Z, Hua, D, and Hong, W. Sex differences in the relationship among alcohol, smoking, and Helicobacter Pylori infection in asymptomatic individuals. J Int Med Res. (2020) 48:300060520926036. doi: 10.1177/0300060520926036
43. Park, CH, Park, JH, and Jung, YS. Comparative efficacy of Tegoprazan vs esomeprazole/sodium bicarbonate for the treatment of Helicobacter Pylori infection. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. (2023) 14:e00632. doi: 10.14309/ctg.0000000000000632
44. Jung, BW, Park, CH, and Jung, YS. Efficacy and safety of Tegoprazan- and rabeprazole-based concomitant therapies for Helicobacter Pylori infection: real-world evidence. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. (2024) 39:2409–16. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16719
45. Kwon, YH, Jeon, SW, Nam, SY, Lee, DW, Park, JH, and Bae, HJ. Ten-day Tegoprazan-based concomitant therapy as a first-line treatment for Helicobacter Pylori eradication. Korean J Intern Med. (2023) 38:493–503. doi: 10.3904/kjim.2022.345
46. Jung, YS, Kim, S, Kim, HY, Noh, SJ, Park, JH, Sohn, CI, et al. Efficacy and tolerability of 14-day Tegoprazan- versus rabeprazole-based triple therapy for eradication of Helicobacter Pylori: a real-world evidence study. Gut Liver. (2023) 17:711–21. doi: 10.5009/gnl220218
47. Park, CH, Song, MJ, Jung, BW, Park, JH, and Jung, YS. Comparative efficacy of 14-day Tegoprazan-based triple vs. 10-day Tegoprazan-based concomitant therapy for Helicobacter Pylori eradication. J Pers Med. (2022) 12:1918. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111918
48. Kong, Q, Mirza, IA, Zhang, X, Song, X, Li, X, Zhang, Q, et al. Fourteen-day Tegoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy as the first-line treatment of Helicobacter Pylori infection (Share2301): a multicenter, noninferiority, randomized clinical trial. Helicobacter. (2024) 29:e13098. doi: 10.1111/hel.13098
49. Lee, JW, Kim, N, Lee, J, Jo, SY, and Lee, DH. Efficacy of Tegoprazan-containing sequential eradication treatment compared to esomeprazole-containing sequential eradication of Helicobacter Pylori in South Korea, a region with high antimicrobial resistance: a prospective, randomized, single tertiary center study. Helicobacter. (2024) 29:e13143. doi: 10.1111/hel.13143
50. Lin, X, Huang, H, Liu, Y, Zeng, Y, Lu, S, Xu, X, et al. Tegoprazan-amoxicillin dual therapy for Helicobacter Pylori eradication: a prospective, randomized, multicenter study in Fujian, China. Helicobacter. (2024) 29:e13151. doi: 10.1111/hel.13151
51. Cho, JH. Bismuth add-on improves the efficacy of 2-week Tegoprazan-based triple therapy for first-line Helicobacter Pylori eradication: a real-world evidence study. Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther. (2024) 22:793–9. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2024.2329251
Keywords: Helicobacter pylori , tegoprazan, bismuth, dual therapy, quadruple therapy, eradication rate
Citation: Cheng J, Zhao X, Fan C, Huang K, Cai Y, Li Z, Xie D, Zhai L, Zhang X and Ding H (2025) Tegoprazan dual and quadruple therapy for Helicobacter pylori eradication: a prospective, randomized controlled trial in Beijing, China. Front. Med. 12:1629567. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1629567
Edited by:
Amit Kumar Dutta, Christian Medical College and Hospital, IndiaReviewed by:
Ben-Gang Zhou, Dalian Medical University, ChinaReuben Thomas Kurien, Christian Medical College and Hospital, India
Copyright © 2025 Cheng, Zhao, Fan, Huang, Cai, Li, Xie, Zhai, Zhang and Ding. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Jianping Cheng, Y2pwY3p5MjAwNEAxNjMuY29t
 Jianping Cheng
Jianping Cheng Xiaolin Zhao1
Xiaolin Zhao1 Kun Huang
Kun Huang Xiaomei Zhang
Xiaomei Zhang