Abstract
Background:
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) represent a unique population characterized by poorer prognoses, which may be further exacerbated by mechanical complications. This study aims to develop a predictive model to identify high-risk individuals within this populations.
Methods:
This study enrolled AMI patients with T2DM and categorized them into complication and control groups. The mechanical complications were defined as papillary muscle rupture (with or without acute mitral regurgitation), ventricular septal defect, left ventricular pseudoaneurysm or aneurysm (with or without thrombus) and free wall rupture. Characteristics were selected using relaxed least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression, multivariate logistic regression and random forest model. Selected variables were utilized to construct a nomogram to predict the possibility of mechanical complications.
Results:
A total of 2,816 patients were enrolled, with 191 individuals classified into the complication group. Baseline analysis identified 31 factors exhibiting potential differences, which were subsequently employed for LASSO-logistic regression, multivariate logistic regression and random forest model. After comprehensive evaluation, nine variables emerged as predictive factors for mechanical complications, including gender, pulmonary hypertension, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, body mass index, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide, creatine kinase, left ventricle ejection fraction and hemoglobin A1c, which were used to construct a reliable nomogram. The complication group also showed higher in-hospital mortality rates compared to controls, alerting the worse prognosis of these populations.
Conclusion:
This study identified nine factors upon admission that may be associated with mechanical complications during the hospitalization. A nomogram was developed based on these factors for clinical application. T2DM patients should emphasize glucose control, which may offer benefits following the onset of AMI.
1 Introduction
Acute myocardial infarction (AMI) is a disease characterized by the rupture of atherosclerotic plaques, resulting in coronary artery occlusion and subsequent myocardial ischemia and infarction (1). Currently, direct percutaneous coronary intervention has emerged as the standard treatment for AMI, effectively reducing infarct size and significantly improving early survival rates among AMI patients (2). Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is recognized as a risk factor for AMI (3). The incidence of cardiovascular diseases in adults with T2DM is two to three times higher than that in their non-diabetic counterparts. Furthermore, studies indicate that the mortality rate within 5 years post-AMI for T2DM patients is twice that of other individuals, potentially reaching as high as 50% (4). Consequently, AMI patients with a history of T2DM represent a distinct population at elevated risk, necessitating heightened attention to enhance prognosis.
The overall incidence of mechanical complications following AMI ranges from approximately 0.1 to 0.3%, mainly including papillary muscle rupture (with or without acute mitral regurgitation), ventricular septal defect, pseudoaneurysm, among others (5, 6). Despite advancements in reperfusion therapies, continue to serve as critical determinants of clinical results in AMI patients (7, 8). Researches indicated that the risks associated with in-hospital death, cardiogenic shock, acute kidney injury and respiratory complications are all markedly higher among patients who experience mechanical complications compared to those who do not (5, 9). Identifying high-risk AMI patients is essential for the early prevention and management of these mechanical complications.
Given the lack of literature addressing the prediction of mechanical complications, this study aims to construct a model to predict the possibility of mechanical complications during the hospitalization in AMI patients with T2DM at admission. This study may assist clinicians in distinguishing high-risk individuals more effectively, helping hierarchical management of patients and early interventions.
2 Methods
2.1 Patient enrollment
Patients who were hospitalized at the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University from January 2020 to December 2024 due to AMI combined with T2DM were included in this study. The diagnosis of AMI was established according to the guidelines set forth by European Society of Cardiology. The exclusion criteria mainly consisted of: (1) patients with a history of severe comorbidities that may affect the occurrence of the outcomes, such as hepatic dysfunction; (2) other subtypes of diabetes or unclassifiable diabetes (e.g., type 1 diabetes mellitus, gestational diabetes mellitus); (3) patients with incomplete clinical data that could not be addressed through statistical methods.
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU1AF2025LSYY-505; date: 9 May 2025), in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. The Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University granted a waiver for informed consent to this study due to its retrospective design.
2.2 Data collection and grouping
The basic demographic information, biochemical test results, imaging data and in-hospital outcomes were obtained from the Biobank of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University. Enrolled patients were categorized into complication and control groups based on the occurrence of in-hospital mechanical complications. To enhance the selection of high-risk patients, the definition of mechanical complications was broadened to encompass papillary muscle rupture (with or without acute mitral regurgitation), ventricular septal defect, left ventricular pseudoaneurysm or aneurysm (with or without thrombus) and free wall rupture. These definitions included both traditional acute complications and chronic conditions associated with mechanical complications (5, 10).
2.3 Statistical analysis
Baseline variables with more than 20% missing values were excluded from further analysis, such as platelet counts (30.0%), left ventricular end-diastolic and end-systolic diameter (44.5% and 44.5%), and cardiac output (53.8%). The remaining variables were missing at random and were addressed using multiple interpolation by chained equations techniques with 5 iterations. A total of five imputed datasets generated, and the fifth dataset without missing values was used for following analysis. Continuous variables, following normal distribution, were presented as mean ± standard deviation and compared using Student’s t-tests. Other continuous variables were represented as median with interquartile range and were analyzed using Mann–Whitney U tests. Categorical variables were reported as absolute counts with relative frequencies. Chi-square tests and Fisher’s exact tests were employed for comparisons. The relaxed least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) logistic regression model was used for preliminary screening of variables which had a p value less than 0.10 in the baseline characteristics. Screened variables underwent further examination through multivariate logistic regression and random forest model. Random forest modeling included 500 trees, with variable importance ranked by the arithmetic means of the accuracy and Gini index values. Factors demonstrating significant differences in either the multivariate or random forest models were included to construct a nomogram. The receiver operating characteristic curve, calibration curve and decision curve were employed to evaluate the performance of nomogram. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS software (version 27.0) and R software (version 4.1.1). P-value less than 0.05 was identified as having statistical difference.
3 Results
3.1 Baseline characteristics and clinical outcomes
A total of 2,816 patients with AMI complicated by T2DM were enrolled in this study, among whom 191 (6.78%) developed in-hospital mechanical complications. The baseline characteristics of both groups were summarized in Table 1. In comparison to the control group, the complication group exhibited higher proportions of female gender, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), and Killip class III/IV classification. Additionally, this group demonstrated elevated levels of age, body mass index (BMI), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), neutrophil count, lymphocyte count, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, aminotransferase, globulin, albumin/globulin ratio, lipoprotein (a), N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-ProBNP), high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T, lactate dehydrogenase, fibrinogen, D-dimer, and fibrin degradation products. Conversely, this group displayed lower levels of left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) and triglycerides when compared to the control group. Furthermore, correlation analysis of the incidence of mechanical complications and parameters which might relate to mechanical complications (p < 0.10) in baseline was illustrated in Figure 1.
Table 1
| Items | Total | Complication group | Control group | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n = 2,816) | (n = 191) | (n = 2,625) | ||
| Age (years) | 62.50 (54.00, 70.00) | 64.00 (55.00, 71.00) | 62.00 (54.00, 70.00) | 0.043 |
| Gender (male, %) | 2,141 (76.0) | 129 (67.5) | 2012 (76.6) | 0.004 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 24.74 (22.57, 26.89) | 23.94 (21.38, 26.12) | 24.48 (22.65, 26.91) | 0.001 |
| Body temperature (°C) | 36.30 (36.00, 36.50) | 36.30 (36.00, 36.50) | 36.30 (36.00, 36.50) | 0.887 |
| Smoking (%) | 887 (31.5) | 56 (29.3) | 831 (31.7) | 0.502 |
| Drinking (%) | 408 (14.5) | 21 (11.0) | 387 (14.7) | 0.155 |
| STEMI (%) | 1,557 (55.3) | 140 (73.3) | 1,417 (54.0) | <0.001 |
| Killip III/IV (%) | 171 (6.1) | 20 (10.5) | 151 (5.8) | 0.008 |
| Comorbidities (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 976 (34.7) | 62 (32.5) | 914 (34.8) | 0.508 |
| Diabetic complications | 164 (5.8) | 13 (6.8) | 151 (5.8) | 0.548 |
| Hyperlipidemia | 228 (8.1) | 12 (6.3) | 216 (8.2) | 0.341 |
| CKD | 121 (4.3) | 6 (3.1) | 115 (4.4) | 0.415 |
| Biochemical results | ||||
| Hb (g/L) | 139.00 (125.00, 151.00) | 137.00 (124.50, 151.00) | 139.00 (125.00, 151.00) | 0.555 |
| HbA1c (%) | 7.80 (6.90, 9.20) | 8.20 (7.10, 9.70) | 7.80 (6.90, 9.20) | 0.003 |
| WBC (109/L) | 8.72 (6.82, 11.08) | 9.10 (6.84, 12.15) | 8.69 (6.82, 11.00) | 0.099 |
| NEU (109/L) | 6.39 (4.67, 8.80) | 6.95 (4.90, 10.09) | 6.34 (4.65, 8.74) | 0.012 |
| NEU% (%) | 75.00 (67.90, 82.10) | 77.40 (70.63, 83.80) | 74.90 (67.5, 81.99) | 0.001 |
| LYMPH (109/L) | 1.46 (1.08, 1.92) | 1.35 (1.00, 1.69) | 1.47 (1.08, 1.94) | 0.005 |
| LYMPH% (%) | 17.67 (11.97, 23.82) | 15.11 (10.06, 21.54) | 17.76 (12.13, 23.98) | <0.001 |
| NLR | 4.28 (2.83, 6.89) | 5.24 (3.32, 8.40) | 4.21 (2.81, 6.76) | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 61.14 (31.09, 97.15) | 62.75 (31.80, 100.82) | 61.10 (30.97, 97.00) | 0.851 |
| hs-CRP (mg/L) | 2.42 (1.13,4.70) | 2.31 (1.21, 3.82) | 2.42 (1.13, 4.72) | 0.976 |
| PCT (ng/mL) | 1.44 (0.11, 3.85) | 0.88 (0.10, 3.36) | 1.48 (0.11, 3.92) | 0.074 |
| ALT (U/L) | 30.00 (20.00, 46.00) | 30.00 (20.00,46.00) | 32.00 (21.00, 48.00) | 0.224 |
| AST (U/L) | 41.00 (24.00,93.00) | 50.00 (25.00, 127.00) | 40.29 (24.00, 91.00) | 0.015 |
| Total protein (g/L) | 63.70 (59.10, 68.20) | 63.10 (57.20, 69.40) | 63.70 (59.20, 68.10) | 0.322 |
| Albumin (g/L) | 37.70 (34.50, 41.10) | 37.10 (32.15, 41.48) | 37.80 (34.60, 41.10) | 0.570 |
| Globulin (g/L) | 25.80 (23.40, 28.50) | 26.20 (23.90, 29.10) | 25.80 (23.33, 28.50) | 0.136 |
| A/G | 1.46 (1.29, 1.64) | 1.41 (1.21, 1.61) | 1.46 (1.29, 1.65) | 0.019 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2) | 94.25 (72.81, 104.61) | 91.94 (65.11,103.61) | 94.51 (73.32, 104.65) | 0.149 |
| Cr (umol/L) | 65.00 (53.00, 82.00) | 65.00 (53.00, 84.75) | 65.00 (53.00, 82.00) | 0.764 |
| BUN (mmol/L) | 6.07 (4.80, 7.74) | 6.32 (5.07, 8.01) | 6.06 (4.79, 7.72) | 0.085 |
| LDL (mmol/L) | 2.25 (1.70, 2.88) | 2.25 (1.67, 2.92) | 2.25 (1.70, 2.87) | 0.876 |
| HDL (mmol/L) | 0.88 (0.76, 1.02) | 0.94 (0.75, 1.08) | 0.88 (0.76, 1.02) | 0.034 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 1.43 (1.01, 2.11) | 1.29 (0.95, 1.86) | 1.44 (1.02, 2.13) | 0.011 |
| TC (mmol/L) | 3.96 (3.26, 4.81) | 4.05 (3.20, 4.85) | 3.96 (3.27, 4.81) | 0.931 |
| Lipoprotein (a) (mg/L) | 220.50 (118.25, 414.26) | 277.57 (140.00, 488.00) | 217.00 (117.79, 412.00) | 0.005 |
| ApoE (mg/L) | 34.40 (27.10, 44.55) | 34.60 (27.20, 44.00) | 34.40 (27.08, 44.63) | 0.928 |
| ApoB (g/L) | 0.80 (0.65, 0.97) | 0.81 (0.66, 0.98) | 0.80 (0.65, 0.97) | 0.698 |
| ApoA (g/L) | 1.03 (0.92, 1.16) | 1.04 (0.91, 1.18) | 1.03 (0.92, 1.15) | 0.530 |
| NT-ProBNP (pg/mL) | 930.00 (295.13, 2709.00) | 2452.00 (873.50, 4888.00) | 870.00 (279.00, 2555.51) | <0.001 |
| hs-cTnT (ng/mL) | 0.49 (0.11, 1.62) | 1.03 (0.31, 2.29) | 0.47 (0.11, 1.53) | <0.001 |
| CK-MB (U/L) | 26.20 (15.00, 77.00) | 15.00 (11.30, 29.80) | 15.00 (10.00, 26.00) | 0.080 |
| CK (U/L) | 232.00 (93.25, 722.95) | 95.00 (62.00, 299.00) | 93.00 (60.00, 227.00) | 0.076 |
| LDH (U/L) | 277.50 (219.00, 419.71) | 346.00 (239.00, 545.00) | 276.00 (217.00, 408.00) | <0.001 |
| APTT (s) | 31.40 (26.70, 37.20) | 29.92 (26.20, 36.57) | 31.40 (26.70, 37.30) | 0.141 |
| PT (s) | 13.10 (12.10, 13.90) | 13.10 (12.05, 14.00) | 13.10 (12.10, 13.80) | 0.924 |
| PTA (%) | 97.00 (85.20, 108.00) | 95.00 (84.00, 108.00) | 97.00 (85.50, 108.00) | 0.575 |
| INR | 1.02 (0.97, 1.09) | 1.03 (0.98, 1.10) | 1.02 (0.97, 1.08) | 0.152 |
| APTR | 1.02 (0.93, 1.15) | 1.00 (0.93, 1.12) | 1.02 (0.93, 1.16) | 0.158 |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | 3.55 (2.87, 4.52) | 3.81 (3.01, 4.99) | 3.53 (2.86, 4.47) | 0.001 |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | 0.56 (0.31, 1.10) | 0.80 (0.44, 1.80) | 0.54 (0.30, 1.07) | <0.001 |
| FDP (mg/L) | 1.99 (1.22, 4.60) | 2.79 (1.54, 9.49) | 1.93 (1.20, 4.31) | <0.001 |
| Echocardiology | ||||
| LVEF (%) | 52.00 (44.00, 60.00) | 43.50 (39.70, 48.00) | 52.50 (45.00, 60.00) | <0.001 |
| PH (%) | 121 (4.3) | 24 (12.6) | 97 (3.7) | <0.001 |
| Pericardial effusion (%) | 181 (6.4) | 37 (19.4) | 144 (5.5) | <0.001 |
| ECG (%) | ||||
| Ventricular arrhythmia | 119 (4.2) | 13 (6.8) | 106 (4.0) | 0.066 |
| Atrioventricular block | 118 (4.2) | 5 (2.6) | 113 (4.3) | 0.261 |
| In-hospital outcomes | ||||
| IABP (%) | 124 (4.4) | 23 (12.0) | 101 (3.8) | <0.001 |
| ECMO (%) | 32 (1.1) | 6 (3.1) | 26 (1.0) | 0.007 |
| PCI (%) | 2,422 (86.0) | 161 (84.3) | 2,261 (86.1) | 0.479 |
| CABG (%) | 24 (0.9) | 2 (1.0) | 22 (0.8) | 0.762 |
| Temporary pacemaker (%) | 42 (1.5) | 2 (1.0) | 40 (1.5) | 0.600 |
| CRRT (%) | 57 (2.0) | 5 (2.6) | 52 (2.0) | 0.546 |
| Length of hospital stay (days) | 5.00 (3.00, 7.00) | 5.00 (3.00, 8.00) | 5.00 (3.00, 7.00) | 0.159 |
| In-hospital mortality (%) | 31 (1.1) | 5 (2.6) | 26 (1.0) | 0.037 |
Baseline characteristics and in-hospital clinical outcomes between the two groups.
BMI, body mass index; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; CKD, chronic kidney disease; Hb, hemoglobin; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; WBC, white blood cell; NEU, neutrophil count; LYMPH, lymphocyte count; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; CRP, C-reactive protein; hs-CRP, high-sensitivity C-reactive protein; PCT, procalcitonin; ALT: alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; A/G, albumin/globulin ratio; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; Cr, creatinine; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; LDL, low-density lipoprotein; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; TG, triglycerides; TC, total cholesterol; ApoE, apolipoprotein E; ApoB, apolipoprotein B; ApoA, apolipoprotein A; NT-ProBNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; hs-cTnT, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; CK-MB, creatine kinase isoenzymes MB; CK, creatine kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; APTT, activated partial thromboplastin time; PT, prothrombin time; PTA, prothrombin activity; INR, international normalized ratio; APTR, activated partial thromboplastin ratio; FDP, fibrin degradation products; LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; PH, pulmonary hypertension; ECG, electrocardiogram; IABP, intra-aortic balloon pump; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; PCI, percutaneous coronary intervention; CABG, coronary artery bypass grafting; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy.
Figure 1
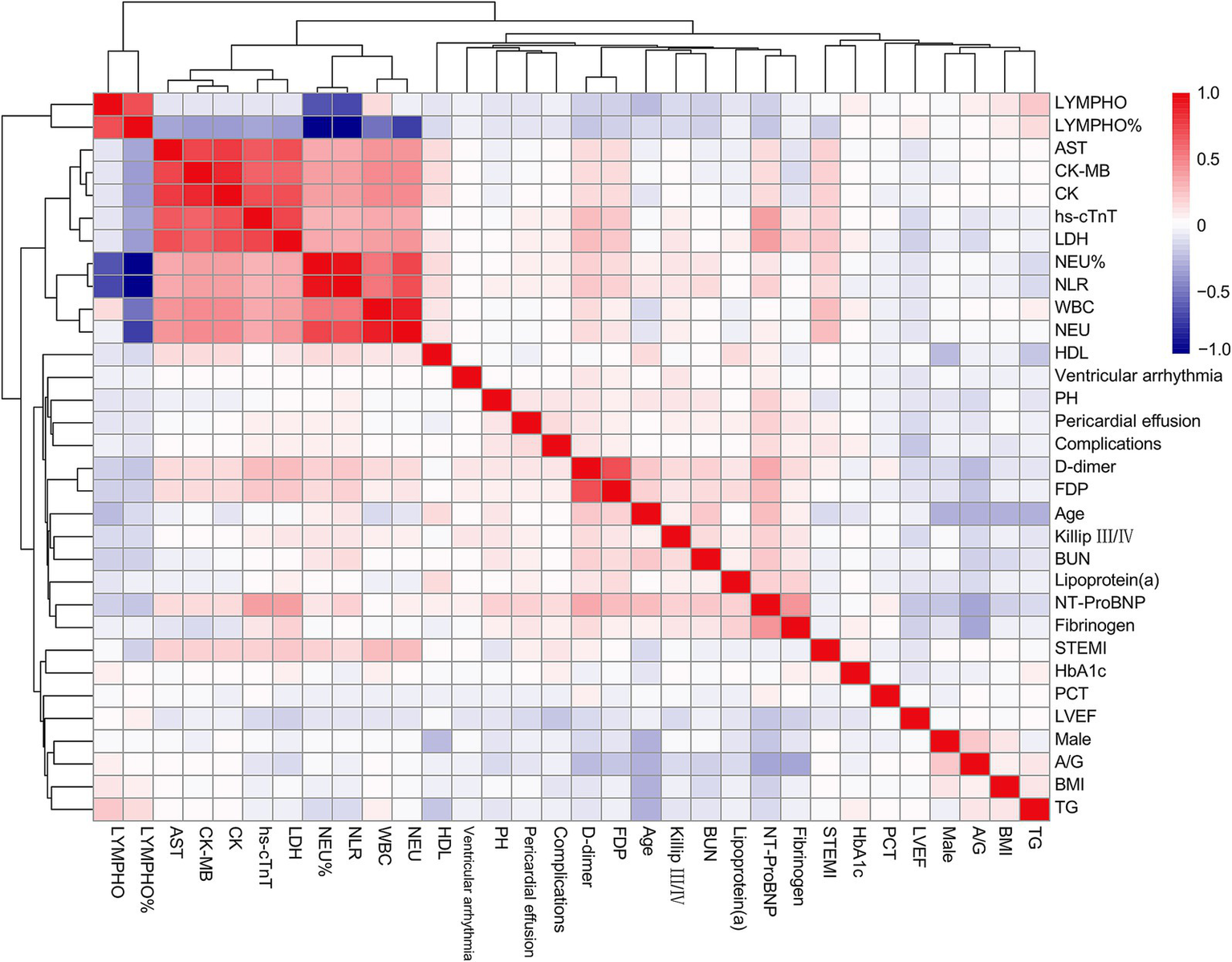
Correlation heatmap between selected variables and the incidence of complications. LYMPH, lymphocyte count; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; CK-MB, creatine kinase isoenzymes MB; CK, creatine kinase; hs-cTnT, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; NEU, neutrophil count; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; WBC, white blood cell; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; PH, pulmonary hypertension; FDP, fibrin degradation products; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; NT-ProBNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; PCT, procalcitonin; LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; A/G, albumin/globulin ratio; BMI, body mass index; TG, triglycerides.
Additionally, the complication group exhibited a higher proportion of intra-aortic balloon pump [23 (12.0) vs. 101 (3.8), p < 0.001] and extracorporeal membrane oxygenation [6 (3.1) vs. 26 (1.0), p = 0.007] utilization, along with an elevated levels of in-hospital mortality [5 (2.6) vs. 26 (1.0), p = 0.037] (Table 1). Cardiac rupture was confirmed or suspected in all fatal cases in complication group. One patient developed ventricular septal rupture complicated by ventricular aneurysm and was supported with intra-aortic balloon pump. During the discussion regarding surgical intervention of the family, the patient experienced sudden ventricular fibrillation followed by cardiogenic shock and eventually died. Another patient presented with ventricular aneurysm and developed acute cardiogenic shock. Despite combined support with extracorporeal membrane oxygenation and intra-aortic balloon pump, the patient did not survive. Three additional patients were diagnosed with ventricular aneurysm, one of whom received extracorporeal membrane oxygenation support. However, all three patients suddenly lost consciousness during hospitalization, with concomitant hypotension. Echocardiography revealed large pericardial effusion, and cardiac rupture was suspected as the cause of death.
3.2 LASSO-logistic regression results
Considering the correlation among potential variables, characteristics demonstrating statistical differences were incorporated into the LASSO-logistic regression analysis. When lambda.min = 0.0045 and log (lambda.min) = −5.3468, 13 variables were preliminary selected for further evaluation (Figure 2; Table 2).
Figure 2
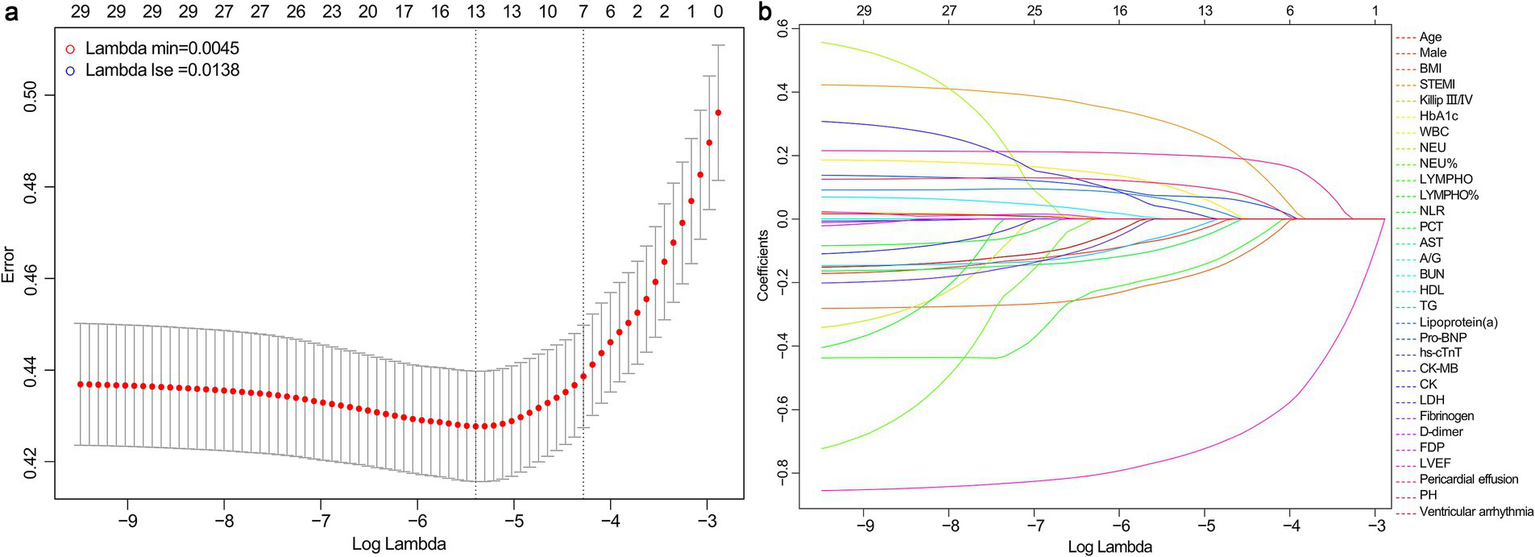
Results of LASSO-logistic regression. (a) Cross-validation plot of LASSO-logistic regression. (b) Selection process of LASSO-logistic regression model by cross-validation method. BMI, body mass index; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; WBC, white blood cell; NEU, neutrophil count; LYMPH, lymphocyte count; NLR, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio; PCT, procalcitonin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; A/G, albumin/globulin ratio; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; TG, triglycerides; NT-ProBNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; hs-cTnT, high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T; CK-MB, creatine kinase isoenzymes MB; CK, creatine kinase; LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; FDP, fibrin degradation products; LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; PH, pulmonary hypertension.
Table 2
| Items | LASSO-logistic regression | |
|---|---|---|
| Assignment | Coefficient | |
| Age (years) | Continuous variable | |
| Gender (male, %) | Male = 1, Female = 0 | −0.1245 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | Continuous variable | −0.2571 |
| STEMI (%) | Yes = 1, No = 0 | 0.3920 |
| Killip III/IV (%) | Yes = 1, No = 0 | |
| HbA1c (%) | Continuous variable | 0.1797 |
| WBC (10^9/L) | Continuous variable | |
| NEUT (10^9/L) | Continuous variable | |
| NEUT% (%) | Continuous variable | |
| LYMPH (10^9/L) | Continuous variable | −0.2476 |
| LYMPH% (%) | Continuous variable | |
| NLR | Continuous variable | |
| PCT (ng/ml) | Continuous variable | −0.1671 |
| AST (U/L) | Continuous variable | |
| Globulin (g/L) | Continuous variable | |
| A/G | Continuous variable | |
| BUN (mmol/L) | Continuous variable | |
| HDL (mmol/L) | Continuous variable | |
| TG (mmol/L) | Continuous variable | −0.1389 |
| Lipoprotein (a) (mg/L) | Continuous variable | 0.1096 |
| NT-ProBNP (pg/mL) | Continuous variable | 0.0800 |
| hs-cTnT (ng/mL) | Continuous variable | |
| CK-MB (U/L) | Continuous variable | |
| CK (U/L) | Continuous variable | 0.0825 |
| LDH (U/L) | Continuous variable | |
| Fibrinogen (g/L) | Continuous variable | |
| D-dimer (mg/L) | Continuous variable | |
| FDP (mg/L) | Continuous variable | |
| LVEF (%) | Continuous variable | −0.8338 |
| PH (%) | Yes = 1, No = 0 | 0.1335 |
| Pericardial effusion (%) | Yes = 1, No = 0 | 0.2133 |
| Ventricular arrhythmia (%) | Yes = 1, No = 0 | |
Results pf LASSO-logistic regression model.
LASSO, least absolute shrinkage and selection operator; other abbreviations as in Table 1.
3.3 Multivariate logistic regression and random forest model
After the LASSO-logistic regression analysis, multivariate logistic regression analysis was conducted (Table 3). The results indicated that male gender (OR = 0.66, 95%CI: 0.47–0.94; p = 0.020); BMI (OR = 0.93, 95%CI: 0.89–0.98; p = 0.004); STEMI (OR = 2.23, 95%CI: 1.55–3.20; p < 0.001); HbA1c (OR = 1.11, 95%CI: 1.03–1.21; p = 0.010); LVEF (OR = 0.92, 95%CI: 0.91–0.94; p < 0.001); pulmonary hypertension (PH) (OR = 2.36, 95%CI: 1.36–4.09; p = 0.002); pericardial effusion (OR = 2.23, 95%CI: 1.43–3.47; p < 0.001) were independent risk factors for prediction.
Table 3
| Items | Multivariate logistic regression | |
|---|---|---|
| OR (95% CI) | p value | |
| Gender (male, %) | 0.66 (0.47, 0.94) | 0.020 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.93 (0.89, 0.98) | 0.004 |
| STEMI (%) | 2.23 (1.55, 3.20) | <0.001 |
| HbA1c (%) | 1.11 (1.03, 1.21) | 0.010 |
| LYMPH (10^9/L) | 0.81 (0.63, 1.04) | 0.103 |
| PCT (ng/dL) | 0.97 (0.92, 1.03) | 0.387 |
| TG (mmol/L) | 0.90 (0.77, 1.06) | 0.210 |
| Lipoprotein (a) (mg/L) | 1.00 (0.99, 1.00) | 0.162 |
| NT-ProBNP (pg/mL) | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | 0.348 |
| CK (U/L) | 1.00 (1.00, 1.00) | 0.205 |
| LVEF (%) | 0.92 (0.91, 0.94) | <0.001 |
| PH (%) | 2.36 (1.36, 4.09) | 0.002 |
| Pericardial effusion (%) | 2.23 (1.43, 3.47) | <0.001 |
Results of multivariate logistic regression model.
OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; other abbreviations as in Table 1.
Furthermore, a random forest model analysis was performed following the LASSO-logistic regression (Figure 3). The mean accuracy and Gini index for each variable were calculated and subsequently ranked based on the arithmetic means of the accuracy and Gini index values. Given the numerical character of the arithmetic mean, the top four variables were included in subsequent analyses, which encompassed LVEF, NT-ProBNP, CK and BMI.
Figure 3
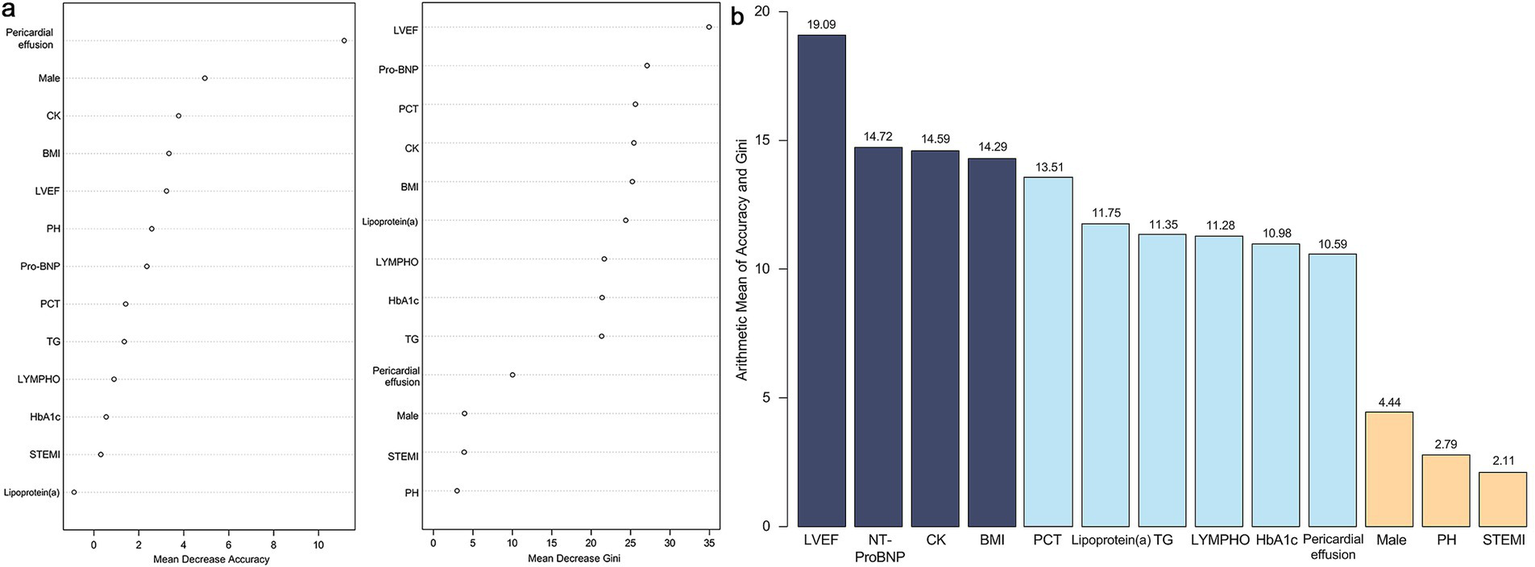
Results of random forest model. (a) Mean decrease accuracy and mean decrease Gini index of all variables. (b) Arithmetic mean value between mean decrease accuracy and mean decrease Gini index of all variables. LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction; NT-ProBNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide; CK, creatine kinase; BMI, body mass index; PCT, procalcitonin; TG, triglycerides; LYMPH, lymphocyte count; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; PH, pulmonary hypertension; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
3.4 Construction of nomogram and its evaluation
Based on variable selection by multivariate logistic regression and random forest modeling, nine variables were used to construct a nomogram, including gender, pulmonary hypertension (PH), STEMI, pericardial effusion, BMI, NT-ProBNP, creatine kinase (CK), LVEF and HbA1c (Figure 4). For continuous variables, the shaded areas under the curve visually represent the distribution of individuals across different ranges, whereas for categorical variables, color blocks illustrate the relative proportions within each category. According to biochemical results and characteristics of patients, each variable was assigned specific points. The total score, calculated by summing all nine component scores, corresponded to the probability of experiencing in-hospital mechanical complications. The receiver operating characteristic curve indicated an area under the curve of 0.817 (95% CI: 0.787–0.847). Both the decision curve and calibration curve confirmed that the nomogram possessed good accuracy and consistency for clinical assessment (Figure 5).
Figure 4
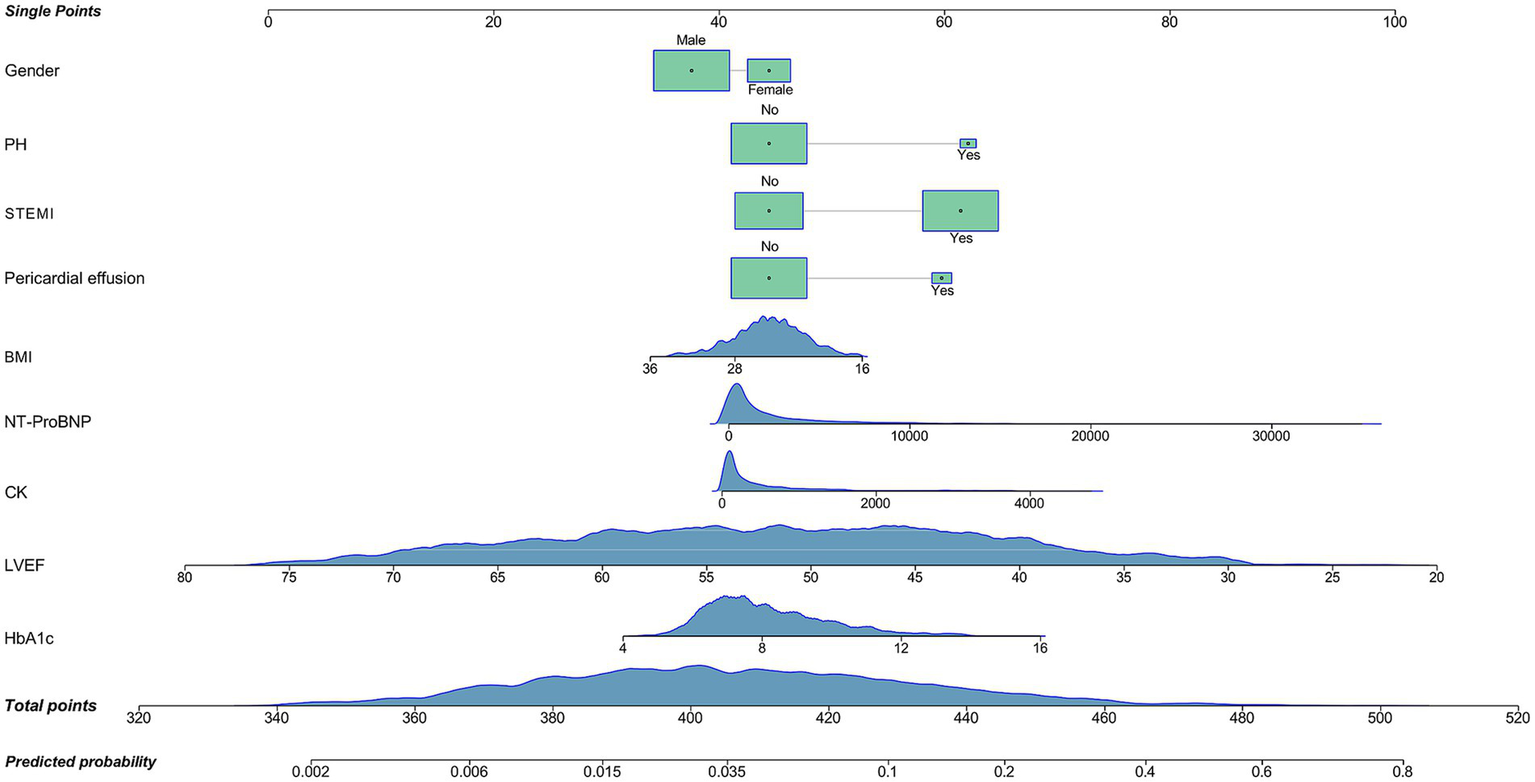
Nomogram for the prediction of mechanical complications in acute myocardial infarction patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. PH, pulmonary hypertension; STEMI, ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; BMI, body mass index; NT-ProBNP, N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (reference range for healthy populations: 0–125 ng/mL; diagnosis range for acute heart failure in people less than 50 years old: >450 ng/mL; diagnosis range for chronic heart failure: >2,000 ng/mL; upper detection limit: 35,000 pg/mL); CK, creatine kinase (reference range: 40–200 U/L); LVEF, left ventricle ejection fraction (reference range: 52–75%); HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c (reference range: 4.0–6.0%).
Figure 5
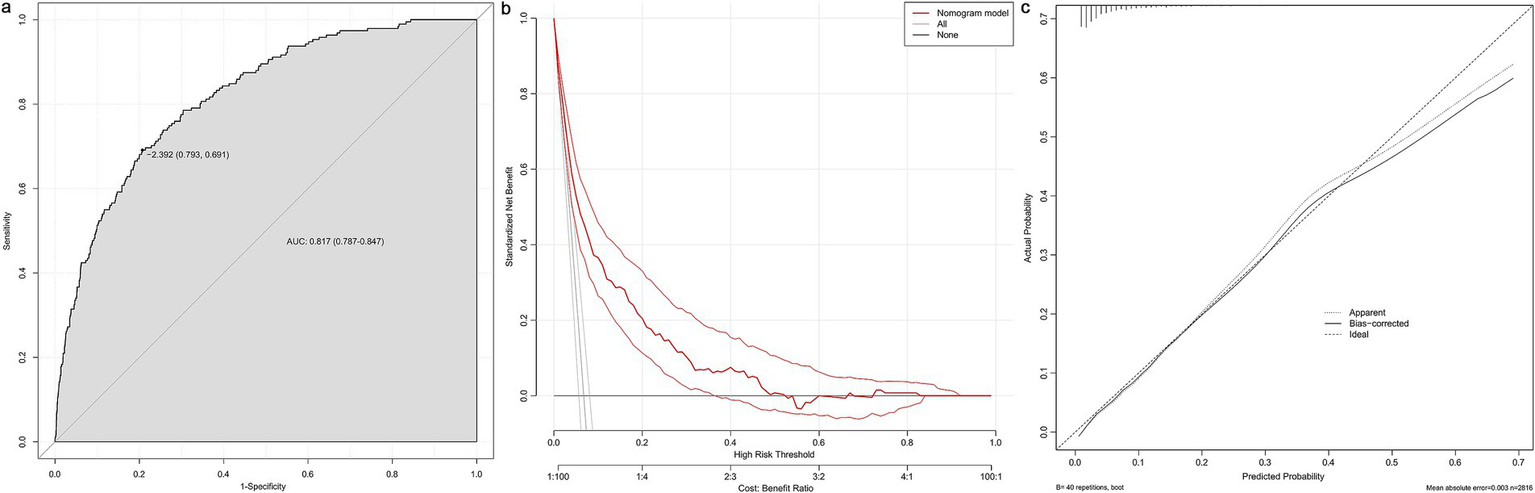
Evaluation of the nomogram. The receiver operating characteristic curve (a), decision curve (b) and calibration curve (c) of the nomogram. AUC, area under curve.
4 Discussion
Although the reperfusion therapies have significantly improved outcomes for AMI patients, mechanical complications continue to pose challenges regarding both short-and long-term prognosis, particularly in patients with concurrent T2DM. This study focused on AMI patients with T2DM, dividing them into complication and control groups. Following the analysis of their baseline characteristics upon admission, nine risk factors for in-hospital mechanical complications were identified. The complication group also exhibited a higher proportion of in-hospital mortality and extracorporeal life support device usage, indicating a poorer prognosis for this population.
T2DM is increasingly prevalent among AMI patients, with an incidence rate of approximately 25% (11). This trend may be attributed to the prolonged hyperglycemia experienced in T2DM patients, which can lead to platelet and endothelial dysfunction, thereby accelerating the atherosclerosis of coronary arteries. From a treatment perspective, somehow, it has been observed that the receiving rates of coronary angiography and percutaneous coronary intervention are lower in T2DM patients compared to their non-diabetic counterparts, which may contribute to worse outcomes, including mechanical complications (12). Furthermore, T2DM patients demonstrate limited left ventricular remodeling following AMI, which also elevates the risk of complications. A study indicated that even patients with transient hyperglycemia are more likely to develop in hospital complications (11). However, this study found that the long-term blood glucose control could benefit patients even after the onset of AMI, and elevated HbA1c levels could potentially serve as a predictor for mechanical complications, highlighting the importance of intensive glycemic management. Notably, the use of metformin post-AMI is also associated with reduced mortality rates (13). Emerging evidence also suggests that in T2DM patients, early and intensive glycemic control, along with the use of glucose-lowering medications, can help reduce the future risk of major adverse cardiovascular events, including stroke, AMI, and all-cause mortality (14). The implementation of timely and rapidly blood glucose control within 24 h of hospital admission may be advantageous in reducing the risk of 30-day mortality (15). Additionally, the triglyceride glucose index, calculated from triglycerides and fasting blood glucose, may serve as a predictor for major adverse cardiac and cerebral events over a median follow-up period of approximately 2 years (16).
There are also several studies focusing on the prediction of mechanical complications. A study found that the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, as an inflammatory marker, serves as an independent predictor for the occurrence of mechanical complications and left ventricular dysfunction in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (17). In this study, although the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio was included in the analysis, it did not demonstrate a significant difference. It is speculated that the influence of blood glucose may be more pronounced than inflammation in AMI patients combined with T2DM, further underscoring the importance of glucose control. Another study indicated that AMI patients experiencing mechanical complications might have fewer comorbidities such as hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. However, mechanical complications are more likely to be associated with patients who do not have malignancies or a history of AMI (18). These results contrast with our findings, as our patient cohort exhibited higher levels of blood lipids. Meanwhile, one study indicated that females have higher risk of mechanical complications and associated mortality, as females are less likely to receive necessary operations compared to males, which is consistent with results of this study (19). Overall, further research is needed to better elucidate the risk factors associated with mechanical complications.
After the onset of mechanical complications, prompt surgical interventions combined with preoperative or postoperative extracorporeal life support devices are essential. These may include intra-aortic balloon pumps, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, implantation of ventricular assist devices, and even heart transplantation, as shown in this study (7, 20). However, due to limited ECMO cases (n = 6) in this study, its impact on survival could not be reliably quantified, warranting further investigation. It has been suggested that achieving hemodynamic stabilization prior to surgery may enhance survival rates postoperatively, particularly in patients with ventricular septal defects (20). However, despite receiving necessary therapies, the in-hospital mortality rate for AMI patients with mechanical complications remains around 50%, especially among older individuals, those with heart failure, cardiogenic shock or renal dysfunction (6, 21, 22). Furthermore, the literature assessing outcomes of surgical interventions presents considerable differences. Among all mechanical complications, ventricular septal defect repair appears to yield the most favorable results (23). Some studies have indicated that long-term survival rates for patients undergoing surgical procedures are promising. The 5-year and 10-year survival rates are approximately 48.1 and 41.0%, respectively (24). However, another study indicated that concomitant coronary artery bypass grafting may not necessarily result in lower early or late mortality, rendering the benefits of revascularization controversial (25). Meanwhile, a study found that the extracorporeal life support devices may only improve the clinical outcomes in patients with pseudoaneurysm and papillary muscle rupture, but do not significantly affect the overall survival (18). Overall, the management of AMI patients with mechanical complications requires further improvement, which includes the selection of appropriate life support devices and determination of optimal timing for surgical intervention.
This study also has certain limitations. Firstly, the conditions experienced during hospitalization were not included in the analysis, which may also influence the occurrence of mechanical complications. Furthermore, as this is a retrospective study, some relevant factors may be unable to obtain. Additionally, prospective analyses with long-term follow-up are necessary to more comprehensively evaluate the effectiveness of the nomogram.
5 Conclusion
This study found that gender, PH, STEMI, pericardial effusion, BMI, NT-ProBNP, CK, LVEF and HbA1c upon admission were associated with in-hospital mechanical complications among AMI patients who have a history of T2DM. A nomogram was constructed based on these risk factors to facilitate earlier identification and intervention of high-risk patients. It is imperative for individuals with T2DM to manage their blood glucose levels effectively since this may provide advantages even after experiencing an episode of AMI.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU1AF2025LSYY-505). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because of the retrospective design of this study.
Author contributions
CZ: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. HW: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing. WY: Writing – review & editing, Conceptualization. YY: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This study was supported by the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2024SF-YBXM-011) and the Clinical Research Award of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU1AF2021CRF-005 and XJTU1AFCRF2023-XK006).
Acknowledgments
We thank all participants of this study, and are grateful to the Biobank of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University for providing clinical data.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Taggart C Wereski R Mills NL Chapman AR . Diagnosis, investigation and Management of Patients with acute and chronic myocardial injury. J Clin Med. (2021) 10:2331. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112331
2.
Peet C Ivetic A Bromage DI Shah AM . Cardiac monocytes and macrophages after myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res. (2020) 116:1101–12. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvz336
3.
Wang H Xie X Zu Q Lu M Chen R Yang Z et al . Treatment of the new era: Long-term Ticagrelor monotherapy for the treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus following percutaneous coronary intervention: a Meta-analysis. Diabetes Ther. (2023) 14:47–61. doi: 10.1007/s13300-022-01350-9
4.
Henning RJ . Type-2 diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Futur Cardiol. (2018) 14:491–509. doi: 10.2217/fca-2018-0045
5.
Gong FF Vaitenas I Malaisrie SC Maganti K . Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction: a review. JAMA Cardiol. (2021) 6:341–9. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2020.3690
6.
Sanmartín-Fernández M Raposeiras-Roubin S Anguita-Sánchez M Marín F Garcia-Marquez M Fernández-Pérez C et al . In-hospital outcomes of mechanical complications in acute myocardial infarction: analysis from a nationwide Spanish database. Cardiol J. (2021) 28:589–97. doi: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0181
7.
Sánchez-Luna JP Amat-Santos IJ . Interventional management of mechanical complications in acute myocardial infarction. Rev Esp Cardiol. (2023) 76:362–9. doi: 10.1016/j.recesp.2022.11.014
8.
Montrief T Davis WT Koyfman A Long B . Mechanical, inflammatory, and embolic complications of myocardial infarction: an emergency medicine review. Am J Emerg Med. (2019) 37:1175–83. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2019.04.003
9.
Elbadawi A Elgendy IY Mahmoud K Barakat AF Mentias A Mohamed AH et al . Temporal trends and outcomes of mechanical complications in patients with acute myocardial infarction. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. (2019) 12:1825–36. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2019.04.039
10.
Damluji AA van Diepen S Katz JN Menon V Tamis-Holland JE Bakitas M et al . Mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. (2021) 144:e16–35. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000985
11.
Fojt A Kowalik R Gierlotka M Gąsior M Smeding C Opolski G . Three-year mortality after acute myocardial infarction in patients with different diabetic status. Pol Arch Intern Med. (2021) 131:6095. doi: 10.20452/pamw.16095
12.
Sethupathi P Matetić A Bang V Myint PK Rendon I Bagur R et al . Association of Diabetes Mellitus and its Types with in-hospital management and outcomes of patients with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. (2023) 52:16–22. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2023.02.008
13.
Bromage DI Godec TR Pujades-Rodriguez M Gonzalez-Izquierdo A Denaxas S Hemingway H et al . Metformin use and cardiovascular outcomes after acute myocardial infarction in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cohort study. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2019) 18:168. doi: 10.1186/s12933-019-0972-4
14.
Hsu H Kocis PT Pichardo-Lowden A Hwang W . Major adverse cardiovascular events' reduction and their association with glucose-lowering medications and glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study using electronic health records. J Diabetes. (2024) 16:e13604. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13604
15.
Deng B Liu Q Qiao L Lv S . Longitudinal trajectories of blood glucose and 30-day mortality in patients with diabetes mellitus combined with acute myocardial infarction: a retrospective cohort analysis of the MIMIC database. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0307905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0307905
16.
Zhang Y Ding X Hua B Liu Q Gao H Chen H et al . Predictive effect of triglyceride-glucose index on clinical events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and acute myocardial infarction: results from an observational cohort study in China. Cardiovasc Diabetol. (2021) 20:43. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01236-3
17.
Yoon GS Choi SH Woo SI Baek YS Park SD Shin SH et al . Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio at emergency room predicts mechanical complications of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction. J Korean Med Sci. (2021) 36:e131. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e131
18.
Sanchez-Jimenez E Fanne RA Levi Y Saada M Kobo O Roguin A . Predictors, outcomes and impact of mechanical circulatory support of patients with mechanical complications after acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. (2023) 52:23–9. doi: 10.1016/j.carrev.2023.02.004
19.
Rivera FB Salva F Gonzales JS Cha SW Tang S Lumbang GNO et al . Sex differences in trends and outcomes of acute myocardial infarction with mechanical complications in the United States. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther. (2024) 22:111–20. doi: 10.1080/14779072.2024.2311707
20.
Bhardwaj A Kumar S Salas de Armas IA Nascimbene A Nathan S Kar B et al . Pre-and post-operative mechanical circulatory support in surgical repair of post-acute myocardial infarction mechanical complications. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. (2022) 11:304–9. doi: 10.21037/acs-2021-ami-206
21.
Younes AM Mahmoud AK Kamel I Williams L Maraey A Khalil M et al . Outcomes of mechanical circulatory support devices among patients with mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. (2025) 14:288–94. doi: 10.1093/ehjacc/zuaf039
22.
Koeda Y Itoh T Ishikawa Y Morino Y Mizutani T Ako J et al . A multicenter study on the clinical characteristics and risk factors of in-hospital mortality in patients with mechanical complications following acute myocardial infarction. Heart Vessel. (2020) 35:1060–9. doi: 10.1007/s00380-020-01586-0
23.
Yousef S Sultan I VonVille HM Kahru K Arnaoutakis GJ . Surgical management for mechanical complications of acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review of long-term outcomes. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. (2022) 11:239–51. doi: 10.21037/acs-2021-ami-20
24.
Matteucci M Ronco D Kowalewski M Massimi G De Bonis M Formica F et al . Long-term survival after surgical treatment for post-infarction mechanical complications: results from the caution study. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes. (2024) 10:737–49. doi: 10.1093/ehjqcco/qcae010
25.
Ronco D Corazzari C Matteucci M Massimi G Di Mauro M Ravaux JM et al . Effects of concomitant coronary artery bypass grafting on early and late mortality in the treatment of post-infarction mechanical complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. (2022) 11:210–25. doi: 10.21037/acs-2021-ami-19
Summary
Keywords
acute myocardial infarction, type 2 diabetes mellitus, mechanical complications, prediction model, hemoglobin A1c
Citation
Zhao C, Wang H, Yuan W and Yan Y (2025) Prediction of mechanical complications post-acute myocardial infarction in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Front. Med. 12:1635357. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1635357
Received
26 May 2025
Accepted
18 July 2025
Published
01 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Guo-wei Tu, Fudan University, China
Reviewed by
Haixia Xu, Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University, China
Lishui Shen, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences and Peking Union Medical College, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhao, Wang, Yuan and Yan.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Yang Yan, yangyan3@xjtu.edu.cn
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.