Abstract
Background:
The impact of fracture reduction quality on clinical outcomes in hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures remains insufficiently characterized. This study aimed to establish a standardized postoperative radiographic evaluation system for reduction quality and assess its correlation with postoperative function and complications.
Methods:
A retrospective cohort study included 237 patients undergoing hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures (2012–2024). Reduction quality was classified as optimal, acceptable, or poor based on four criteria: (1) greater trochanter alignment, (2) lesser trochanter reduction, (3) femoral stem stability, and (4) postoperative femoral anteversion (optimal: 13 ± 3°; acceptable: 6–10° or 16–20°; poor: <6° or >20°). Outcomes included Harris Hip Scores, Engh's scores, delayed healing, and complications. Statistical analyses were adjusted for AO/OTA fracture classification.
Results:
Optimal reduction (Grade A, n = 107) correlated with superior Harris Hip Scores (92.57 ± 4.27 vs. 82.46 ± 7.05, P < 0.001), lower delayed healing (3.74% vs. 14.29%, P = 0.031), and reduced abductor weakness (1.87% vs. 14.29%, P = 0.014). Acceptable reductions (Grade B, n = 74) showed intermediate outcomes. Poor reductions (Grade C, n = 56) exhibited the highest complication rates. Engh's scores were significantly higher in Grade A (97.20% vs. 73.21%, P = 0.002). Dislocation and heterotopic ossification rates did not differ significantly (P > 0.05).
Conclusion:
This study introduced and validated a standardized radiographic evaluation system to assess reduction quality in arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures, emphasizing the prognostic importance of anatomic trochanteric alignment and cortical continuity. High-quality reduction is critical for optimizing functional recovery and minimizing complications in arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures. Future research should explore long-term outcomes and advanced fixation techniques to enhance reduction precision.
Introduction
Osteoporotic hip fractures, prevalent in aging populations, are associated with high mortality and socioeconomic burdens (1–4). Intertrochanteric fractures are about half as common as osteoporotic hip fractures (5, 6). Although internal fixation is the current treatment of choice for intertrochanteric fractures, a risk of failure persists, particularly in cases of unstable fracture or severe osteoporosis (7–10). Furthermore, patients with pre-existing hip pathologies, such as hip osteoarthritis or osteonecrosis of the femoral head, may face an increased likelihood of requiring subsequent surgical intervention following internal fixation for intertrochanteric femoral fractures (11).
Numerous studies have compared treatment approaches for intertrochanteric fractures. Intramedullary fixation, exemplified by the Gamma nail and Intertan double nail system, and extramedullary fixation using dynamic hip screws, demonstrated advantages over arthroplasty. These fixation techniques require shorter operative times, reduce intraoperative blood loss, decrease transfusion requirements, and preserve the native hip joint, ultimately yielding improved patient outcomes (6, 12–14). However, in certain situations such as unstable fractures, severe osteoporosis, or hip diseases such as femoral head necrosis and hip osteoarthritis, the failure rate of internal fixation devices will significantly increase (15, 16). Such failure carries catastrophic consequences, potentially resulting in severe hip joint function decline and complications including fixation loosening, cut-out, nonunion, and coxa vara subsequent to treatment (17–21). Therefore, increasing studies have shown that hip arthroplasty is superior to internal fixation in cases of unstable intertrochanteric fractures, or hip joint diseases such as severe osteoporosis, femoral head necrosis, and hip osteoarthritis (6, 22–26). Therefore, in select cases of intertrochanteric fractures, hip arthroplasty can be considered as the primary treatment strategy to avoid reoperation and enhance patient outcomes (27, 28).
The reduction of intertrochanteric fractures during arthroplasty procedures is a critical aspect of surgical technique. Disruption in the anatomical reduction of the greater trochanter, particularly in cases of comminuted fractures, can lead to compromised abductor muscle function. This dysfunction manifests clinically as pain and the characteristic Trendelenburg gait pattern, significantly affecting patients' quality of life (16, 21, 29). Recognizing this, surgeons often prioritize stable fixation of the greater trochanter fragment during hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures (30). Patients with lesser trochanter fractures often experienced prolonged impairment in hip flexion, as indicated by reduced iliopsoas muscle function on the Ludloff's test. This deficit may lead to difficulties in activities requiring hip flexion, such as standing from a seated position or ascending stairs (31). Although overall hip function scores may not show significant differences, the presence of a displaced lesser trochanter was associated with increased fatty infiltration of the iliopsoas muscle, which could contribute to long-term functional decline (32). However, no studies have investigated how to assess reduction quality during arthroplasty procedures for intertrochanteric fractures or its impact on hip function and postoperative complications.
Against this background, this retrospective cohort study pursued two primary objectives. First, it endeavored to establish a robust radiographic assessment criterion to assess reduction quality based on postoperative radiographs. Second, it sought to determine the necessity of achieving stable fracture reduction quality during hip arthroplasty for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. By analyzing the relationship between fracture reduction quality and clinical outcomes, this study aimed to optimize surgical techniques and improve prognoses for this challenging patient population.
Materials and methods
Study design and patient selection
Of 275 patients diagnosed with intertrochanteric fractures and treated with arthroplasty between March 2012 and January 2024, 237 patients were followed-up for at least 1 year, with a sufficient number of radiographs taken with an image intensifier during surgery, and were included in this retrospective research. Indications for hip arthroplasty included unstable fractures (AO/OTA 31–A2.3, A3.1–A3.3) with posteromedial comminution, pre-existing ipsilateral hip osteoarthritis (Kellgren-Lawrence grade ≥3), femoral head avascular necrosis, or severe osteoporosis (T-score ≤ −3.0) (22–25). Exclusion criteria included: (1) Incomplete imaging data; (2) Under 55 years old or over 90 years old; (3) Follow up time <1 year; (4) Postoperative periprosthetic joint infection (patients with functional impairments caused by other postoperative complications were excluded); (5) Pathological fracture; (6) Complicating other fracture; (7) Uncompleted clinical records; (8) Other accompanying diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or dysplasia of the hip joint; (9) The greater trochanter of the femur has been removed during the operation.
Surgical procedure and postoperative management
All patients suffered fractures due to low-energy injuries caused by falling while walking, falling from a height of <2 m, or falling while riding a bicycle. According to the AO/OTA classification, patients were classified based on pelvic anterior-posterior radiographs before surgery. All patients underwent posterior approach incisions for hip arthroplasty, and received fracture reduction and internal fixation treatment during the operation according to the situation. The weight-bearing time after surgery was determined based on the specific circumstances of the patient.
Follow-up procedures
All patients received standardized outpatient follow-up at 1, 3, 6, and 12 months postoperatively. All clinical outcomes were evaluated by an independent surgeon who was not involved in the surgery and was unaware of the grouping. At 1-month follow-up, clinical assessments included wound healing status, pain evaluation using a visual analog scale, and initial ambulation ability. The anteroposterior and axial hip radiographs were obtained to assess early fracture alignment and prosthesis position. At 3-month follow-up, clinical evaluations focused on fracture healing progress assessed via tenderness mobility of fracture site, and abductor flexor muscle strength. The anteroposterior and axial hip radiographs were also obtained. Engh's score was calculated based on these images defined as low if <0 and high if ≥0. At 6-month follow-up, clinical assessments included continued fracture healing monitoring, range of motion of the hip joint, and complications such as heterotopic ossification and dislocation. The anteroposterior and axial hip radiographs were obtained to evaluate stem stability and bone integration. At 12-month final follow-up, comprehensive evaluations were performed, including confirmation of fracture healing, functional recovery assessment via Harris Hip Score, and final complications check. The anteroposterior and axial hip radiographs were reviewed to document long-term prosthesis position and bone ingrowth.
Each patient underwent a total of 8 anteroposterior and axial hip radiographs at each of the 4 follow-up time points. Engh's score was specifically obtained at 3 months while Harris Hip Scores were measured at the 12-month follow-up. The Harris Hip Score was exclusively measured at the 12-month because functional recovery after hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures typically requires sufficient time for fracture healing, soft tissue adaptation, and prosthesis stabilization. By 12-month postoperatively, fracture union is generally achieved, and the hip joint function reaches a relatively stable state, allowing for a reliable assessment of long-term functional outcomes. Earlier follow-up time points focus more on acute recovery processes such as wound healing, early fracture alignment, and initial complication screening, during which functional status remains dynamic and less representative of the final therapeutic effect. Thus, measuring the Harris Hip Score at 12 months ensures a valid and meaningful evaluation of the ultimate functional recovery.
Radiographic evaluation protocol
The anteroposterior and axial radiographs of hip joints of these patients were collected after surgery. Yoon et al. (33) evaluated the reduction quality of open reduction and internal fixation for intertrochanteric fractures. Therefore, the reduction quality evaluation plan for hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures was based on their research reference. The quality of fracture reduction is evaluated by the following four criteria: (1) Greater trochanter alignment, defined as the apex positioning within the middle third of the prosthetic femoral head (optimal), upper/lower third without abductor laxity (acceptable), or displacement >5 mm (poor); (2) Lesser trochanter reduction, categorized by anatomic continuity with the medial cortex (optimal), ≤ 5 mm displacement (acceptable), or >5 mm avulsion (poor); (3) Femoral stem stability, evaluated by stem-canal fit (≥80% cortical contact, no radiolucency for optimal; 50%−80% contact with <5° angulation for acceptable; <50% contact or ≥5° malalignment for poor); and (4) Postoperative femoral anteversion angles were categorized as optimal (13 ± 3°), acceptable (6–10° or 16–20°), or poor (<6° or >20°) to optimize joint stability and reduce dislocation risk (Table 1). Compared to computed tomography, measuring femoral anteversion angle using axial femoral radiographs is a simpler, more economical method that reduces postoperative discomfort for patients. Its reliability has been validated by multiple studies (34–37). The specific measurement technique involved the following steps: on axial hip radiographs, the longitudinal axes of the femoral shaft and femoral neck were drawn, and the angle formed by the intersection of these two lines was defined as the femoral anteversion angle. These criteria prioritized biomechanical stability over anatomic perfection, reflecting the unique demands of arthroplasty in fracture management (Figures 1–3).
Table 1
| Reduction quality | Optimal reduction | Acceptable reduction | Poor reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Greater trochanter reduction | The apex of the greater trochanter aligns with the center of the prosthetic femoral head (middle third on anteroposterior view) | The apex lies within the upper or lower third of the prosthetic head | Displacement exceeding the upper/lower third of the prosthetic head or comminution |
| Lesser trochanter reduction | Anatomic alignment with the medial femoral cortex (no posterior displacement on lateral view) | Mild displacement (≤ 5 mm) without compromising iliopsoas attachment | Displacement >5 mm or complete avulsion, leading to iliopsoas dysfunction |
| Femoral stem stability | Optimal stem-canal fit with no radiolucent lines and cortical contact ≥80% on both views | Minor stem malalignment (<5° angulation) with 50%−80% cortical contact | Significant malalignment (≥5° angulation), subsidence, or cortical contact <50% |
| Femoral anteversion restoration | Femoral anteversion angle 13 ± 3° | Femoral anteversion angle 6–10°or 16–20° | Femoral anteversion angle <6°or >20° |
Quality assessment of reduction of intertrochanteric fractures.
Figure 1

(a) Preoperative radiographs of a patient with intertrochanteric fracture. (b, c) Postoperative radiographs of a patient fulfilling all four predefined criteria for optimal alignment were classified as “Optimal Reduction.” Solid red lines A and C divided the prosthetic femoral head into three equal parts. Red dashed line B passed through the apex of the greater trochanter and between lines A and C. Blue arrows indicated no significant displacement of the lesser trochanter on the lateral view. Yellow arrows denoted optimal stem-canal fit with no radiolucent lines and cortical contact ≥80% on both views. The angle formed by two black lines, representing the intersection of the longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft and the longitudinal axis of the prosthetic femoral neck, was the femoral anteversion angle, measuring ~14°.
Figure 2

(a) Preoperative radiographs of a patient with intertrochanteric fracture. (b, c) Postoperative radiographs demonstrating acceptable alignment in two criteria, with none rated as poor, were categorized as “Acceptable Reduction.” Red dashed line B lied outside the area between lines A and C but remained within the superior and inferior margins of the prosthetic femoral head. Blue arrows indicated the lesser trochanter was well-positioned. Yellow arrows denoted optimal stem-canal fit with no radiolucent lines and cortical contact ≥80% on both views. Black lines represented the femoral anteversion angle, measuring ~17°.
Figure 3

(a) Preoperative radiographs of a patient with intertrochanteric fracture. (b, c) Postoperative radiographs exhibiting at least one criterion of poor alignment were designated as “Poor Reduction”. Red dashed line B had extended beyond the inferior margin of the prosthetic femoral head. Blue arrows indicated poor reduction of the lesser trochanter. Yellow arrows denoted optimal stem-canal fit with no radiolucent lines and cortical contact ≥80% on both views. Black lines represented the femoral anteversion angle, measuring~24°.
To ensure evaluation accuracy, these radiographs were independently reviewed in a blinded manner by two orthopedic surgeons who were unaware of patient group assignments and the study objectives; any discrepancies were resolved by a third orthopedic surgeon. To minimize measurement error and assess reliability, all radiographic measurements were repeated by one of the researchers after a 6-week interval. Intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were calculated to evaluate both intra-observer and inter-observer reliability. An ICC value ≥ 0.8 was considered indicative of good reliability, and ≥ 0.9 indicated excellent reliability.
Reduction quality grading system
The reduction quality was stratified into three grades based on integrated radiographic criteria: (1) Optimal reduction (Grade A): all radiographic parameters achieved optimal status (Figure 1). (2) Acceptable reduction (Grade B): up to two radiographic parameters were classified as acceptable (Figure 2). (3) Poor reduction (Grade C): any radiographic parameter categorized as poor (Figure 3). Fracture reduction quality grade of each case was determined according to the criteria. Based on the quality grade of fracture reduction, the follow-up information of cases in three grades was statistically analyzed. In order to prevent the impact of fracture classification, we calculated adjusted P-values based on fracture classification (AO/OTA).
Ethical approval
This retrospective study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hebei Medical University Third Hospital. Informed consent was waived due to the anonymized and retrospective nature of the data. All procedures complied with the ethical standards of the Declaration of Helsinki and relevant national regulations to ensure patient privacy and data security.
Statistical analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using SPSS 26.0 software. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation, and categorical variables were presented as frequencies. For comparisons of continuous variables among the three groups, one-way analysis of variance was applied. Post-hoc pairwise comparisons were conducted using Tukey's honestly significant difference test to control for Type I error associated with multiple comparisons. For categorical variables, chi-square test was used, or Fisher's exact test was employed when expected cell counts were <5. To eliminate potential confounding by fracture complexity, all statistical results were adjusted for AO/OTA fracture classification using analysis of covariance for continuous outcomes and logistic regression for categorical outcomes. The adjusted P-values were reported to reflect these corrections. An a priori power analysis using G-Power software version 3.1.9.7 (Heinrich-Heine-Universitat Dusseldorf, Dusseldorf, Germany) showed that 53 patients in each group could detect significant difference at 80% power.
Results
Patient demographics and baseline characteristic
In the end, 99 male (41.77%) and 138 female (58.23%) patients were included in this study. Their demographic characteristics were shown in Table 2. According to the quality of reduction, patients were divided into three groups: perfect reduction (n = 107, 45.15%), acceptable reduction (n = 74, 31.22%) and poor reduction (n = 56, 23.63%; Figure 4). The average follow-up time for the three groups was 4.65 ± 2.39 years, 4.95 ± 2.37 years, and 4.96 ± 2.11 year, respectively. There were no significant differences in age, gender, body mass index, and bone mineral density among the three groups of patients (P > 0.05).
Table 2
| Baseline characteristics | Perfect reduction (n = 107) | Acceptable reduction (n = 74) | Poor reduction (n = 56) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 70.41 ± 10.28 | 71.50 ± 9.70 | 70.46 ± 8.46 | 0.733 |
| Sex (Male/Female) | 41/66 | 33/41 | 25/31 | 0.623 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 24.22 ± 3.26 | 24.03 ± 3.11 | 23.87 ± 2.71 | 0.782 |
| Comorbidity | ||||
| Hypertension | 43 | 24 | 16 | 0.290 |
| Diabetes | 22 | 13 | 11 | 0.882 |
| Cardiovascular disorders | 17 | 13 | 13 | 0.512 |
| Neurological disorders | 24 | 15 | 10 | 0.789 |
| Classification of intertrochanteric fracture | <0.001 | |||
| 31–A1 | 61 | 20 | 10 | |
| 31–A2 | 34 | 45 | 38 | |
| 31–A3 | 12 | 9 | 8 | |
| Bone mineral density (g/cm3) | −2.28 ± 1.15 | −2.38 ± 1.22 | −2.26 ± 1.17 | 0.802 |
| Follow-up time (years) | 4.65 ± 2.39 | 4.95 ± 2.37 | 4.96 ± 2.11 | 0.595 |
Baseline characteristics of patients with intertrochanteric fractures undergoing hip arthroplasty.
Figure 4
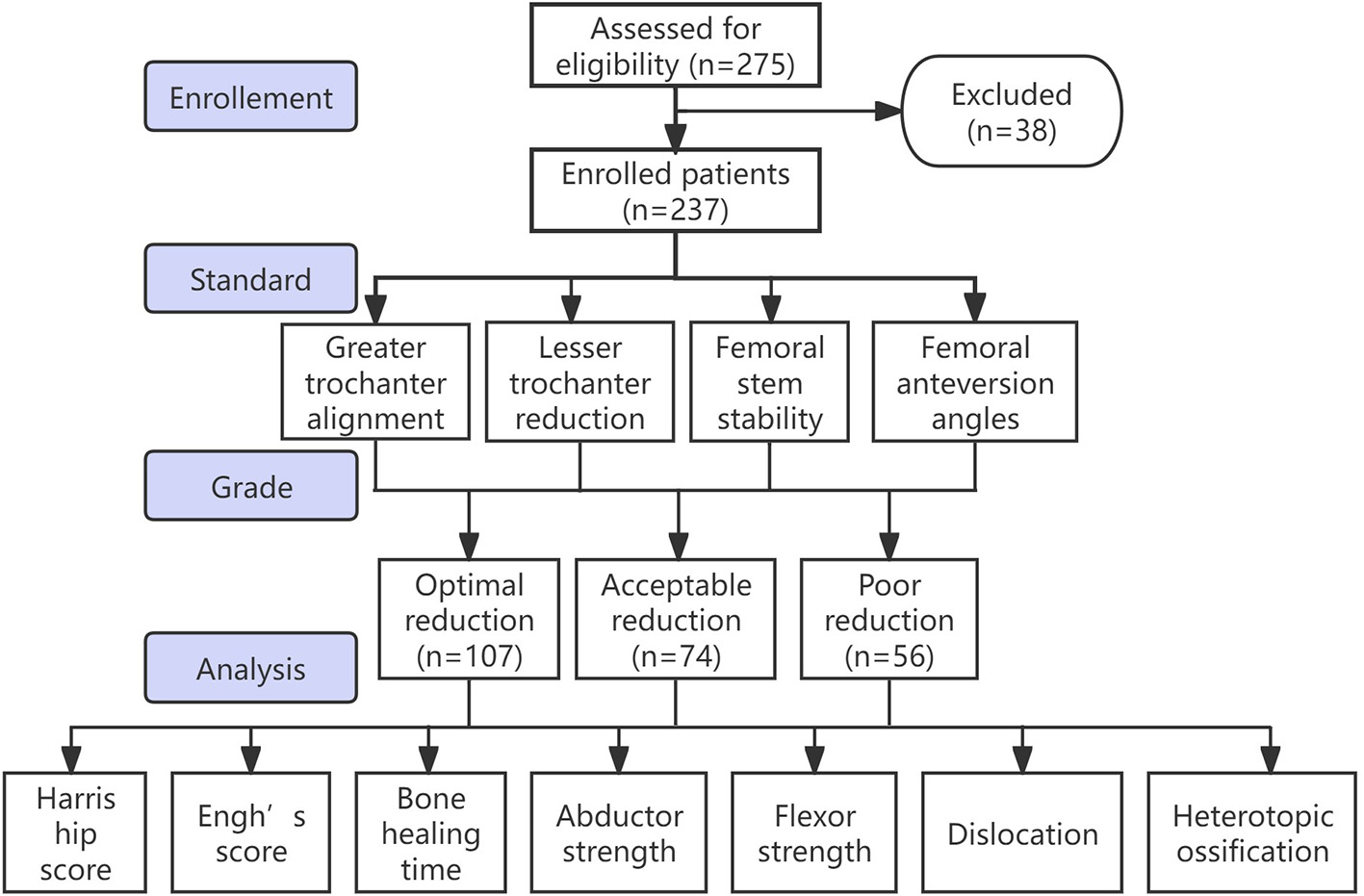
Flow diagram of the research. According to the quality of reduction, patients were divided into three groups: perfect reduction, acceptable reduction, and poor reduction.
Surgical procedural details
There was no statistically significant difference in surgical time and intraoperative bleeding among the three groups of patients. In the selection of femoral stems during surgery, the group with perfect reduction mostly used type IV femoral stems, with a small number of type V femoral stems and a very small number of type III femoral stems (79 vs. 23 vs. 5). The acceptable reduction group consisted mainly of type IV and V femoral stems, with a small amount of type III femoral stems (46 vs. 25 vs. 3). The poor reduction group was mainly composed of type IV femoral stems (39 vs. 15 vs. 2). In the selection of intraoperative internal fixation devices, both cable and tension were the most commonly used internal fixation devices in the three groups (Table 3).
Table 3
| Characteristics | Perfect reduction (n = 107) | Acceptable reduction (n = 74) | Poor reduction (n = 56) | P |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operative time (min) | 128.74 ± 32.54 | 125.14 ± 36.78 | 130.09 ± 22.53 | 0.641 |
| Bleeding volume (ml) | 434.11.21 ± 166.77 | 378.38 ± 134.24 | 409.82 ± 141.56 | 0.053 |
| Femoral stem type | 0.422 | |||
| Type III | 5 | 3 | 2 | |
| Type IV | 79 | 46 | 39 | |
| Type V | 23 | 25 | 15 | |
| Internal fixation | 0.316 | |||
| Nothing | 11 | 7 | 8 | |
| Cable only | 51 | 37 | 30 | |
| Tension band | 27 | 17 | 9 | |
| Plate with screws or cables | 3 | 9 | 0 | |
| Others | 15 | 11 | 9 | |
| Postoperative weight-bearing time | <0.001 | |||
| Immediately | 80 | 56 | 39 | |
| ≤ 4-week non-weight-bearing time | 26 | 15 | 14 | |
| > 4-week non-weight-bearing time | 1 | 3 | 3 |
Characteristics of surgical process of patients with intertrochanteric fractures undergoing hip arthroplasty.
Fracture healing and radiographic integration
The ICC values indicated good to excellent intra-observer and inter-observer reliability for all measurements, with the intra-observer ICC values ranging from 0.878 to 0.941 and inter-observer ICC values ranging from 0.861 to 0.929. In the perfect reduction group, 4 patients (3.74%) were diagnosed with delayed fracture healing, while in the acceptable reduction group, there were 8 patients (10.81%). In the group with poor reduction quality, 8 patients (14.29%) were diagnosed with delayed fracture healing (P = 0.031). Among the three groups, the proportion of high Engh's scores was 97.20%, 82.43%, and 73.21%, respectively (P = 0.002).
Functional outcomes
The average Harris score of the hip joint in the perfect reduction group was 92.57 ± 4.27 (77–99). The Harris score of the hip joint in the group with acceptable reduction quality was relatively low, which is 84.35 ± 4.89 (78–93). The Harris score of the hip joint in the group with poor reduction quality was 82.46 ± 7.05 (52–91), which was the lowest among the three groups (Table 4).
Table 4
| Clinical outcomes | Perfect reduction (n = 107) | Acceptable reduction (n = 74) | Poor reduction (n = 56) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harris hip score | 92.57 ± 4.27 | 84.35 ± 4.89 | 82.46 ± 7.05 | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Harris hip score excellent/poor ratio | <0.001 | <0.001 | |||
| Excellent (80–100) | 105 | 61 | 39 | ||
| Poor (<80) | 2 | 13 | 17 | ||
| Engh's score | <0.001 | 0.002 | |||
| Unstable (<−10) | 0 | 0 | 3 | ||
| Suboptimum, but Stable (−10 to 0) | 3 | 13 | 12 | ||
| Ingrowth suspected (0–10) | 46 | 29 | 20 | ||
| Bone Ingrown (>10) | 58 | 32 | 21 |
Clinical outcomes of hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures.
*P1 represented unadjusted statistical significance values from initial analyses.
#P2 represented adjusted P-values after correcting for AO/OTA fracture classification, with the correction based on this classification. For continuous outcomes, analysis of covariance was applied; for categorical outcomes, logistic regression with AO/OTA classification as a covariate was used.
Muscle strength assessment
After evaluation, a total of 2 patients were diagnosed with abductor weakness in the perfect reduction group (1.87%). In the acceptable reduction group, 7 patients were diagnosed with abductor weakness (9.46%). In the group with poor reduction quality, 8 patients diagnosed with abductor weakness increased this proportion to 14.29% (P = 0.014). Meanwhile, the patient's hip flexor muscle strength was measured. When the flexor muscle strength was between 4–5 levels, it is considered normal flexor strength, while flexor weakness is considered muscle strength less than or equal to 3 levels. Only one patient was diagnosed with flexor weakness in the perfect reduction group (0.93%). However, in the acceptable reduction group and the poor reduction group, this number increased to 5 cases (6.78%) and 6 cases (10.71%), respectively (P = 0.020; Table 5).
Table 5
| Postoperative complications | Perfect reduction (n = 107) | Acceptable reduction (n = 74) | Poor reduction (n = 56) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bone healing time | 0.048 | 0.031 | |||
| ≤ 3 months | 103 | 66 | 48 | ||
| >3 months | 4 | 8 | 8 | ||
| Abductor strength | 0.009 | 0.014 | |||
| ≤ 3 | 2 | 7 | 8 | ||
| 4–5 | 105 | 67 | 48 | ||
| Flexor strength | 0.018 | 0.020 | |||
| ≤ 3 | 1 | 5 | 6 | ||
| 4–5 | 106 | 69 | 50 | ||
| Dislocation | 0.195 | 0.278 | |||
| Yes | 2 | 2 | 4 | ||
| No | 105 | 72 | 52 | ||
| Heterotopic ossification | 0.833 | 0.897 | |||
| Yes | 5 | 3 | 3 | ||
| No | 102 | 71 | 53 |
Postoperative complications of hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures.
*P1 represented unadjusted statistical significance values from initial analyses.
#P2 represented adjusted P-values after correcting for AO/OTA fracture classification, with the correction based on this classification. For continuous outcomes, analysis of covariance was applied; for categorical outcomes, logistic regression with AO/OTA classification as a covariate was used.
Complications
The number of cases of hip dislocation in the three groups of patients is 2, 4, and 4, respectively (1.87% vs. 2.70% vs. 7.14%), but there was no statistical significance (P = 0.278). The number of cases of heterotopic ossification in the three groups was 5, 3, and 3, respectively (4.67% vs. 4.05% vs. 5.36%), and there was no statistical significance (P = 0.897; Table 5).
Discussion
Our findings further validated the rationale for hip arthroplasty as a preferred treatment for unstable intertrochanteric fractures, particularly in elderly patients with osteoporosis or hip joint diseases such as osteoarthritis or femoral head necrosis. Hip arthroplasty addresses these limitations by providing immediate structural stability and reducing the risks associated with fixation failure. However, the success of arthroplasty hinges significantly on the quality of fracture reduction and fixation, as demonstrated in our study. This underscores the need for refinement in surgical techniques and evaluation standards to further bridge the gap between the advantages of arthroplasty and its dependence on reduction quality.
There has been controversy over how to reduce fracture fragments and evaluate the quality of reduction during hip arthroplasty. Lee et al. (30) used the Ethibond Suture technique to firmly fix the greater trochanter of the fracture during hip arthroplasty, and found that good fixation of the greater trochanter can lead to better prognosis for patients. However, unlike previous studies, we quantified the impact of lesser trochanter reduction on hip flexion strength, highlighting its biomechanical role in load distribution. Zhang et al. (38) found through 2–11 years of follow-up that the use of Kirschner wires and tension band in hip arthroplasty can achieve good therapeutic effects for intertrochanteric fractures. Grimsrud et al. (39) treated unstable intertrochanteric fractures using a novel cerclage cable technique during surgery. There have been lots of studies (40–42) on the quality of fracture reduction in intertrochanteric fractures, but most of these studies have focused on internal fixation rather than hip arthroplasty.
The fracture reduction quality was divided into three levels and the differences in therapeutic effects caused by different reduction qualities were evaluated. The results demonstrated that better reduction quality significantly correlated with improved clinical outcomes, as evidenced by higher Harris hip scores and Engh's scores, faster fracture healing, and lower rates of complications such as abductor and flexor muscle weakness. These findings aligned with existing literature emphasizing the critical role of anatomical reduction in promoting optimal load distribution, mechanical stability, and effective osseointegration of the prosthesis. Optimal reduction directly correlated with restored hip biomechanics. Grade A patients demonstrated near-normal abductor strength and flexion capacity, whereas Grade C reductions were associated with functional deficits. This aligned with biomechanical models highlighting the dependence of hip kinematics on trochanteric integrity and stem stability. Notably, even minor malreductions (Grade B) led to measurable functional declines, underscoring the need for stringent reduction criteria.
Reduction and fixation of the greater and lesser trochanters were particularly significant for postoperative function. Proper fixation of the greater trochanter supported better abductor muscle recovery, reducing the risk of gait abnormalities and weakness. Similarly, the fixation of the lesser trochanter proved essential for preserving hip flexion strength. These findings corroborated earlier studies on the biomechanical relevance of trochanteric stabilization in hip arthroplasty (43). Similarly, the lesser trochanter, essential for hip flexion, and external rotation, must be adequately reduced and stabilized to prevent postoperative flexor weakness. Inadequate fixation of these regions, as seen in patients with poor reduction quality, led to weaker hip flexor and abductor muscle strength in our study. Patients with Grade A reductions exhibited superior Harris Hip Scores and lower rates of delayed union, emphasizing the biomechanical advantages of precise reduction in arthroplasty. Dislocation rates, though statistically insignificant across groups, trended higher in Grade C, likely due to abductor insufficiency and altered joint mechanics. These results advocated for prioritizing greater trochanter fixation to mitigate instability. These findings suggested that meticulous intraoperative reduction is not merely a technical preference but a prognostic imperative, particularly in osteoporotic patients prone to instability. Our findings aligned with earlier studies, such as those by Lee et al. (30) and Zhang et al. (38), which reported that techniques like Ethibond suture fixation or Kirschner wire application significantly improved postoperative outcomes by enhancing trochanteric stability.
The anatomical reduction of the posteromedial cortex is the most important component in the reduction of intertrochanteric fractures (33). However, these elderly patients often suffer from osteoporosis or comminuted fractures, greatly increasing the difficulty of reducing the posteromedial cortex (42, 44). Patients with cortical contact <50% (Grade C) exhibited higher instability rate evaluated by Engh's score, reflecting poor osseointegration. This corroborated the study of Haidukewych et al. (41) emphasizing the cortical support for load distribution, suggesting that even imperfect reductions must prioritize cortical continuity to prevent stem subsidence. Our study emphasizes that the anterior medial cortex, although less challenging to visualize and align, plays a crucial role in supporting the femoral prosthesis stem, as its integrity significantly impacts femoral stem stability and bone ingrowth. Prior research supported this focus on achieving cortical continuity and stability (43).
Haidukewych et al. (41) reported that hip inversion or hip eversion can be evaluated by the positional relationship between the greater trochanter and the femoral head, and the best effect can be achieved when the horizontal line where the apex of the greater trochanter is located passes through the center of the femoral head. Considering that the recovery of femoral anteversion and neck-shaft angle is extremely important in both hip arthroplasty and reduction of intertrochanteric fractures, we applied the research of Haidukewych et al. to hip arthroplasty and achieved good results (41).
Beyond functional scores, our study observed a notable correlation between reduction quality and fracture healing. Delayed healing was significantly more common in patients with poor reduction quality, emphasizing the importance of anatomical alignment for promoting osteogenesis and reducing complications. Delayed union rates escalated with poorer reductions, likely due to disrupted vascularity and mechanical instability. Notably, delayed healing itself exacerbated functional deficits, as seen in lower Harris scores. These findings mirrored Huang et al.'s (15) meta-analysis linking anatomic reduction to accelerated union, highlighting a bidirectional relationship: reduction quality drives healing, while healing underpins functional recovery.
Prosthesis selection in hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures is critical, with options varying by design, fixation, and indication. Cemented calcar-replacement and long-stem cemented hemiarthroplasty showed similar clinical outcomes in octogenarians with unstable fractures (45). Bipolar hemiarthroplasty is preferable over total hip arthroplasty in elderly osteoporotic patients due to shorter operative time, less blood loss, and lower dislocation rates (46). Cementless long stems with double cross binding technique achieved good mid-term results in octogenarians, with stable fixation and successful trochanteric healing (47). For failed fixation, cementless revision stems were safer in early failures to reduce reoperations, while primary stems worked in late failures (48), and primary cementless stems yielded comparable outcomes to revision stems in conversion arthroplasty with shorter hospital stays (49). However, for the independence of implant type selection from reduction quality, due to the small sample size and large variety of prostheses, we were unable to accurately assess this relationship, which should be further studied in the large-scale research.
This study's findings validated the reduction quality evaluation method adapted from Yoon et al. (33), demonstrating its utility in postoperative assessments. While intramedullary nailing remains first-line for most intertrochanteric fractures, hip arthroplasty offers immediate stability in select cases where anatomical reduction is unachievable or pre-existing joint degeneration warrants definitive management (17, 25). Our findings support hip arthroplasty as a viable option for elderly patients with complex fractures or osteoporosis, prioritizing early mobilization to mitigate systemic risk. Further research should explore the long-term durability of outcomes across varying reduction qualities and examine potential advancements in fixation techniques, especially for complex fracture patterns. In conclusion, achieving high-quality reduction during hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures is paramount for optimizing functional recovery and minimizing complications. Our findings advocate for meticulous preoperative planning and intraoperative strategies to enhance reduction quality, thereby improving patient prognosis and quality of life postoperatively.
This study has several limitations that should be considered when interpreting the results. First, while postoperative radiographs were reviewed independently by two orthopedic surgeons in a blinded manner, we did not explicitly address masking protocols for outcome assessors, quantify inter-rater reliability for reduction quality grading, or systematically document the independence of outcome assessors, which may introduce potential biases and uncertainties in the consistency and objectivity of assessments. Second, as a single-center retrospective study with a sample restricted to patients aged 55–90 years meeting specific arthroplasty indications, the findings lack sufficient discussion of external validity and generalizability, limiting their applicability to other populations or institutions with varying surgical practices. Third, the measurement of femoral anteversion relied on axial radiographs, which, though validated, are less precise than computed tomography, potentially introducing minor inaccuracies in anteversion classification and affecting reduction quality stratification. Additionally, due to the relatively small sample size and the wide variety of hip prostheses used, we were unable to analyze the relationship between prosthesis type and reduction quality, leaving unresolved questions about potential interactions between implant selection and reduction outcomes.
Conclusion
This study introduced and validated a standardized radiographic evaluation system to assess reduction quality in arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures, emphasizing the prognostic importance of anatomic trochanteric alignment and cortical continuity. High-quality reduction is critical for optimizing functional recovery and minimizing complications in arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures. Future research should explore long-term outcomes and advanced fixation techniques to enhance reduction precision.
Statements
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Hebei Medical University Third Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
BZ: Writing – original draft, Methodology, Formal analysis, Investigation. JH: Writing – review & editing, Validation, Supervision. HL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. The work was financially supported by Central Government Guided Local Science and Technology Development Fund Project, China (No. 236Z7720G).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Bhandari M Swiontkowski M . Management of acute hip fracture. N Engl J Med. (2017) 377:2053–62. 10.1056/NEJMcp1611090
2.
Tsuboi M Hasegawa Y Suzuki S Wingstrand H Thorngren KG . Mortality and mobility after hip fracture in Japan: a ten-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Br. (2007) 89:461–6. 10.1302/0301-620X.89B4.18552
3.
Abrahamsen B van Staa T Ariely R Olson M Cooper C . Excess mortality following hip fracture: a systematic epidemiological review. Osteoporos Int. (2009) 20:1633–50. 10.1007/s00198-009-0920-3
4.
Wang CB Lin CF Liang WM Cheng CF Chang YJ Wu HC et al . Excess mortality after hip fracture among the elderly in Taiwan: a nationwide population-based cohort study. Bone. (2013) 56:147–53. 10.1016/j.bone.2013.05.015
5.
Koval KJ Aharonoff GB Rokito AS Lyon T Zuckerman JD . Patients with femoral neck and intertrochanteric fractures. Are they the same. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (1996) 166–72. 10.1097/00003086-199609000-00020
6.
Sniderman J Vivekanantha P Shah A Safir O Wolfstadt J Kuzyk P . Hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures: a matched cohort study. J Arthroplasty. (2023) 38:1522–7. 10.1016/j.arth.2023.01.057
7.
Zhang B Chiu KY Wang M . Hip arthroplasty for failed internal fixation of intertrochanteric fractures. J Arthroplasty. (2004) 19:329–33. 10.1016/j.arth.2003.10.010
8.
Hsu CJ Chou WY Chiou CP Chang WN Wong CY . Hemi-arthroplasty with supplemental fixation of greater trochanter to treat failed hip screws of femoral intertrochanteric fracture. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. (2008) 128:841–5. 10.1007/s00402-007-0483-8
9.
Haidukewych GJ Berry DJ . Hip arthroplasty for salvage of failed treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2003) 85:899–904. 10.2106/00004623-200305000-00019
10.
Kashigar A Vincent A Gunton MJ Backstein D Safir O Kuzyk PR . Predictors of failure for cephalomedullary nailing of proximal femoral fractures, Bone Joint J. (2014) 96-B:1029–34. 10.1302/0301-620X.96B8.33644
11.
Liu XZ Yang W Yang SH Xu WH Ye SN . Total hip arthroplasty for treatment of elderly patients with comminuted intertrochanteric fracture accompanied by femoral head necrosis. Chin J Traumatol. (2008) 11:359–63. 10.1016/S1008-1275(08)60072-3
12.
Nie B Wu D Yang Z Liu Q . Comparison of intramedullary fixation and arthroplasty for the treatment of intertrochanteric hip fractures in the elderly: a meta-analysis. Medicine. (2017) 96:e7446. 10.1097/MD.0000000000007446
13.
Chowdhury AK Townsend O Edwards MR . A comparison of hemiarthroplasty versus dynamic hip screw fixation for intertrochanteric femoral fractures: a systematic review. Hip Int. (2023) 33:752–61. 10.1177/11207000221112579
14.
Kumar P Rajnish RK Sharma S Dhillon MS . Proximal femoral nailing is superior to hemiarthroplasty in AO/OTA A2 and A3 intertrochanteric femur fractures in the elderly: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis. Int Orthop. (2020) 44:623–33. 10.1007/s00264-019-04351-9
15.
Huang G Zhang M Qu Z Zhang Y Wang X Kang W et al . Fixation options for reconstruction of the greater trochanter in unstable intertrochanteric fracture with arthroplasty. Medicine. (2021) 100:e26395. 10.1097/MD.0000000000026395
16.
Martinho T Stoffel K . Treatment of intertrochanteric femur fractures with hip arthroplasty in older patients: a narrative review of indications and outcomes. Medicina. (2021) 57:763. 10.3390/medicina57080763
17.
Gashi YN Elhadi AS Elbushra IM . Outcome of primary cemented bipolar hemiarthroplasty compared with dynamic hip screw in elderly patients with unstable intertrochanteric fracture. Malays Orthop J. (2018) 12:36–41. 10.5704/MOJ.1803.007
18.
Haynes RC Pöll RG Miles AW Weston RB . Failure of femoral head fixation: a cadaveric analysis of lag screw cut-out with the gamma locking nail and AO dynamic hip screw. Injury. (1997) 28:337–41. 10.1016/S0020-1383(97)00035-1
19.
Wolfgang GL Bryant MH O'Neill JP . Treatment of intertrochanteric fracture of the femur using sliding screw plate fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (1982) 148–58. 10.1097/00003086-198203000-00022
20.
Liu L Sun Y Wang L Gao Q Li A Wang J et al . Total hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fracture fixation failure. Eur J Med Res. (2019) 24:39. 10.1186/s40001-019-0398-1
21.
Shi T Fang X Huang C Li W You R Wang X et al . Conversion hip arthroplasty using standard and long stems after failed internal fixation of intertrochanteric fractures. Orthop Surg. (2023) 15:124–32. 10.1111/os.13574
22.
Tang P Hu F Shen J Zhang L Zhang L . Proximal femoral nail antirotation versus hemiarthroplasty: a study for the treatment of intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. (2012) 43:876–81. 10.1016/j.injury.2011.11.008
23.
Kim SY Kim YG Hwang JK . Cementless calcar-replacement hemiarthroplasty compared with intramedullary fixation of unstable intertrochanteric fractures. A prospective, randomized study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2005) 87:2186–92. 10.2106/00004623-200510000-00005
24.
Bonnevialle P Saragaglia D Ehlinger M Tonetti J Maisse N Adam P et al . Trochanteric locking nail versus arthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric fracture in patients aged over 75 years. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. (2011) 97:S95–100. 10.1016/j.otsr.2011.06.009
25.
Cho SH Cho HL Cho H . Primary cementless hip arthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric femur fracture in elderlys: short-term results. Hip Pelvis. (2014) 26:157–65. 10.5371/hp.2014.26.3.157
26.
Chen W Ma Y Ma H Nie M . Total hip arthroplasty for Crowe type IV developmental dysplasia of the hip combined with intertrochanteric fracture: a case report and literature review. BMC Surg. (2020) 20:278. 10.1186/s12893-020-00941-2
27.
Mäkinen TJ Gunton M Fichman SG Kashigar A Safir O Kuzyk PR . Arthroplasty for pertrochanteric hip fractures. Orthop Clin North Am. (2015) 46:433–44. 10.1016/j.ocl.2015.06.001
28.
Xie Y Zhou H . Primary cemented hemiarthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly severe osteoporotic patients. Injury. (2020) 51:670–3. 10.1016/j.injury.2020.01.010
29.
Nutton RW Checketts RG . The effects of trochanteric osteotomy on abductor power. J Bone Joint Surg Br. (1984) 66:180–3. 10.1302/0301-620X.66B2.6707052
30.
Lee KH Lee DH Noh JH Kim YV . Is rigid fixation of the greater trochanter necessary for arthroplasty of intertrochanteric fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. (2019) 105:41–5. 10.1016/j.otsr.2018.09.015
31.
van der Sijp M Moonen L Schipper IB Krijnen P du Pré KJ Niggebrugge A . The functional effect of lesser trochanter involvement in hip fractures: a prospective cohort study. Injury. (2020) 51:2634–9. 10.1016/j.injury.2020.09.002
32.
Schenkel M Kaniewska M Bühler T Anderson S Eid K . No difference in flexion power despite iliopsoas fatty degeneration in healed hip fractures with large lesser trochanter displacement. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. (2018) 28:1313–9. 10.1007/s00590-018-2200-4
33.
Yoon YC Oh CW Sim JA Oh JK . Intraoperative assessment of reduction quality during nail fixation of intertrochanteric fractures. Injury. (2020) 51:400–6. 10.1016/j.injury.2019.10.087
34.
Brunner A Eichinger M Hengg C Hoermann R Brenner E Kralinger F . A Simple method for measurement of femoral anteversion-validation and assessment of reproducibility. J Orthop Trauma. (2016) 30:e273–8. 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000595
35.
Chung CY Lee KM Park MS Lee SH Choi IH Cho TJ . Validity and reliability of measuring femoral anteversion and neck-shaft angle in patients with cerebral palsy. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2010) 92:1195–205. 10.2106/JBJS.I.00688
36.
Lee JW Oh M Choi MN Lee SY . Reliability and validity of a mobile application for femoral anteversion measurement in adult patients. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:372. 10.1186/s13018-023-03853-y
37.
Chimhundu C Sivarasu S Steiner S Smit J Douglas TS . Femoral neck anteversion measurement using linear slot scanning radiography. Med Eng Phys. (2016) 38:187–91. 10.1016/j.medengphy.2015.11.017
38.
Zhang H Xu Z Zhou A Yan W Zhao P Huang X et al . Efficacy of Kirschner-wires and tension band in hip arthroplasty for aged patients with unstable intertrochanteric osteoporotic fracture: a 2-to-11-year follow-up. Medicine. (2017) 96:e5614. 10.1097/MD.0000000000005614
39.
Grimsrud C Monzon RJ Richman J Ries MD . Cemented hip arthroplasty with a novel cerclage cable technique for unstable intertrochanteric hip fractures. J Arthroplasty. (2005) 20:337–43. 10.1016/j.arth.2004.04.017
40.
Anglen JO Weinstein JN American American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Research Committee . Nail or plate fixation of intertrochanteric hip fractures: changing pattern of practice. A review of the American board of orthopaedic surgery database. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2008) 90:700–7. 10.2106/JBJS.G.00517
41.
Haidukewych GJ . Intertrochanteric fractures: ten tips to improve results. J Bone Joint Surg Am. (2009) 91:712–9.
42.
Tan BY Lau AC Kwek EB . Morphology and fixation pitfalls of a highly unstable intertrochanteric fracture variant. J Orthop Surg. (2015) 23:142–5. 10.1177/230949901502300204
43.
Khair MM Salem EA Mohamed SA . Hip arthroplasty for failed internal fixation of intertrochanteric fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. QJM. (2021) 114:hcab104.013. 10.1093/qjmed/hcab104.013
44.
Lichtblau S . The unstable intertrochanteric hip fracture. Orthopedics. (2008) 31:792–7. 10.3928/01477447-20080801-15
45.
Khatri K Banga RK Malhotra N Bansal D . Cemented calcar replacement versus long stem cemented hemiarthroplasty in unstable intertrochanteric fractures in octogenarians. Rev Bras Ortop. (2022) 57:511–20. 10.1055/s-0041-1732392
46.
Fan L Dang X Wang K . Comparison between bipolar hemiarthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty for unstable intertrochanteric fractures in elderly osteoporotic patients. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e39531. 10.1371/journal.pone.0039531
47.
Mao Q Zhang Y Hua J He B . Mid-term follow-up results after hemiarthroplasty using long femoral stem prosthesis (Peerless-160) for intertrochanteric fractures in octogenarians. Geriatr Orthop Surg Rehabil. (2023) 14:21514593231184314. 10.1177/21514593231184314
48.
Ma HH Chou TA Tsai SW Chen CF Wu PK Chen WM . Is there a role for cementless primary stem in hip arthroplasty for early or late fixation failures of intertrochanteric fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2022) 23:266. 10.1186/s12891-022-05223-x
49.
Thalody HS Post ZD Lutz RW Czymek M Ong AC Ponzio DY . Primary cementless femoral stems in conversion hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of intertrochanteric fractures. Orthopedics. (2024) 47:e6–6e12. 10.3928/01477447-20230517-04
Summary
Keywords
reduction, fracture, hip, arthroplasty, radiographic
Citation
Zhang B, Huo J and Li H (2025) Impact of fracture reduction quality on clinical outcomes in hip arthroplasty for intertrochanteric fractures based on a novel radiographic evaluation system: a retrospective study. Front. Med. 12:1637763. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1637763
Received
29 May 2025
Accepted
26 July 2025
Published
14 August 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Michela Saracco, University of Naples Federico II, Italy
Reviewed by
Cesare Di Bona, Federico II University Hospital, Italy
Roberta Pagano, Federico II University Hospital, Italy
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Zhang, Huo and Li.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Huijie Li lihuijie@hebmu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.