- 1Clinical Medical College, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 2Department of Respiratory Medicine, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 3School of Basic Medicine, Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chengdu, Sichuan, China
- 4Sichuan College of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Mianyang, Sichuan, China
Traditional studies of pulmonary fibrosis (PF) have focused on alveolar epithelial cells injury and abnormal myofibroblast aggregation, but recent studies have revealed that imbalances in pulmonary capillary homeostasis also play pivotal roles in this disease. The pulmonary microvasculature, composed of aerocyte capillary (aCap) and general capillary (gCap) endothelial cells, forms the core structure of the alveolar-capillary membrane. It performs key roles in gas exchange and nutrient/metabolite transport, while modulating the trafficking of inflammatory factors and immune cells and regulating alveolar damage repair. Abnormal activation of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis, reprogramming of cellular metabolism, secretion of proinflammatory and profibrotic factors, and disruption of pulmonary capillary homeostasis, lead to abnormal remodeling of the pulmonary microvasculature and other pathological changes, promoting the deterioration of PF. Notably, maintaining and restoring normal pulmonary capillary homeostasis is beneficial for improving the local microenvironment of fibrotic lesions and attenuating pathological changes such as hypoxia. In this review, the pathological changes associated with pulmonary capillary homeostasis imbalance in PF are described. Therapeutic directions for restoring pulmonary capillary homeostasis are also proposed with the expectation that they will provide assistance in the treatment of PF.
1 Introduction
Interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are characterized by inflammation or fibrosis of the lung parenchyma. ILD with fibrosis as the predominant pathological manifestation may be classified as secondary or idiopathic. Common causes of secondary ILD include connective tissue disease-associated ILD (e.g., rheumatoid arthritis, scleroderma), environmental/occupational exposure-related ILD (e.g., silicosis, asbestosis), and drug-induced ILD (e.g., amiodarone, bleomycin), among others (1). Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most important subtype of ILD, and accounts for approximately one-third of ILD patients (2). The incidence of IPF varies according to region, with 7–1,650 IPF cases per 100,000 people worldwide, and the annual incidence of IPF is increasing (3–5). IPF has a high mortality rate, a life expectancy of 2–3 years (6), and a lack of effective treatments. Pirfenidone and nintedanib are approved antifibrotic drugs that can slow the decline in lung function in IPF but do not reverse pulmonary fibrosis (7, 8). And Long-term use of these drugs has a high incidence of adverse events, such as gastrointestinal events (dyspepsia, diarrhea, etc.), skin-related events (rash, photosensitivity reactions, etc.), and in severe cases, discontinuation is required due to intolerable adverse events (9–13). The cost of treating IPF is much greater than that of the general population because of the long treatment period, which imposes a significant financial burden on the families of IPF sufferers and poses a significant challenge to global public health (14–16). This is due to the complexity of the pathogenesis of IPF, which hinders the development of effective therapeutic options.
Previous studies have suggested that dysregulation of alveolar epithelial cells (AECs) injury and repair, and overproduction of myofibroblasts are the central mechanisms underlying the emergence of pulmonary fibrosis (PF) (17). However, this does not explain the pathological changes in PF lesions, where the density of pulmonary capillaries decreases or disappears. Furthermore, 16% of myofibroblasts in PF lesions are derived from vascular endothelial cells (VECs) (18). This evidence suggests that the role of VECs in PF has been overlooked (19, 20). An analysis of VECs in fibrosis revealed that abnormal activation of VECs stimulated by pathological factors leads to structural and functional alterations in the cells, disrupting pulmonary capillary homeostasis and leading to pathological alterations in the vasculature, such as increased permeability and vascular remodeling (21, 22). Moreover, an imbalance in pulmonary microvascular homeostasis disrupts alveolar–capillary gas exchange function (19). Therefore, this review summarizes the specific pathological mechanisms by which the abnormal activation of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVECs) disrupts pulmonary capillary homeostasis and promotes the progression of PF. And it proposes a therapeutic strategy to restore pulmonary capillary homeostasis for the treatment of PF, which provides ideas for the development of new therapeutic options.
2 The normal structure and function of PMVECs are fundamental to the maintenance of pulmonary capillary homeostasis
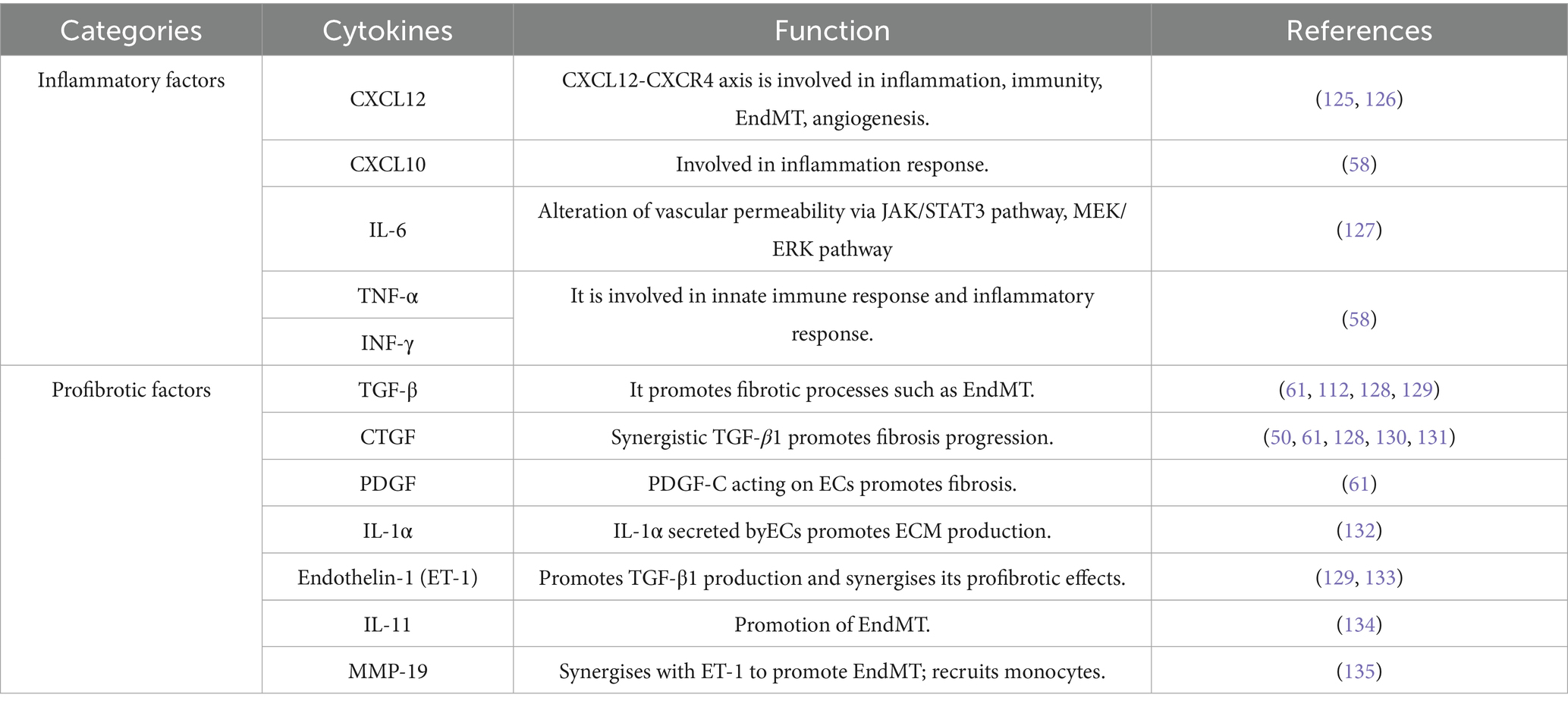
Pulmonary capillaries are vascular barriers formed by the interconnection of VECs, which control the entry and exit of nutrients, metabolic products, cells, etc. When lung tissue is damaged, the vascular barrier also allows cytokines and immune cells, among others, to enter the damaged area and participate in the inflammatory response, among others (23). Pulmonary capillaries are closely connected to alveoli, forming an alveolar–capillary membrane structure (Figure 1A), which facilitates gas exchange between the lungs and the external environment. Pulmonary capillaries are composed of two types of VECs (Figure 1B) (24–26). The first type is aerocyte capillary (aCaps) ECs, which are responsible for gas exchange and cellular transport within the lungs. The second type consists of general capillary (gCaps) ECs, which have a progenitor cell function and are involved in processes such as vascular repair, immunomodulation and maintenance of capillary homeostasis. Single-cell analysis revealed that in the healthy state, aCap and gCap ECs were stable, and only a very small number of gCap ECs intermittently differentiated into aCap ECs (26). This study also found that gCap ECs could differentiate into aCap ECs in the injured state, but the exact differentiation process was not explained. Subsequent single-cell transcriptome profiling revealed that after damage to the pulmonary capillary endothelium, gCap ECs appeared as a new population expressing apelin and the stem cell marker protein C receptor, and then continued to transform into proliferative endothelial progenitor-like cells expressing the apelin receptor and the pro-proliferative transcription factor Foxm1, which rapidly replenished depleted ECs, including the highly specialized aCap ECs (27).
Figure 1. (A) Cross-sectional view of the alveolar-capillary junction. AECs and PMVECs make up the alveolar-capillary membrane, an important structure for gas exchange in the lungs. (B) Schematic representation of the pulmonary capillary wall. The walls of healthy pulmonary capillaries are formed by two distinct endothelial cell types: aerocytes and general capillary endothelial cells.
3 Abnormal activation of PMVECs disrupts pulmonary capillary homeostasis and promotes the progression of PF
Normal VECs are usually in a homeostatic state and are transiently activated in response to stimulation by injurious factors, and return to the homeostatic state after the injury has been repaired (Figure 2A). Single-cell RNA sequencing further demonstrates that the activation of VECs is reversible; for example, in young mice, after bleomycin stimulation, activated VECs return to a resting state after completion of repair (28). However, in pathological conditions, such as persistent fibrosis, this leads to sustained aberrant activation of VECs. PMVECs showed persistent activation in response to stimulation by pathogenic factors (Table 1). Moreover, single-cell RNA sequencing showed that PMVECs are activated to undergo pro-fibrotic changes at an early stage of PF (21, 29).
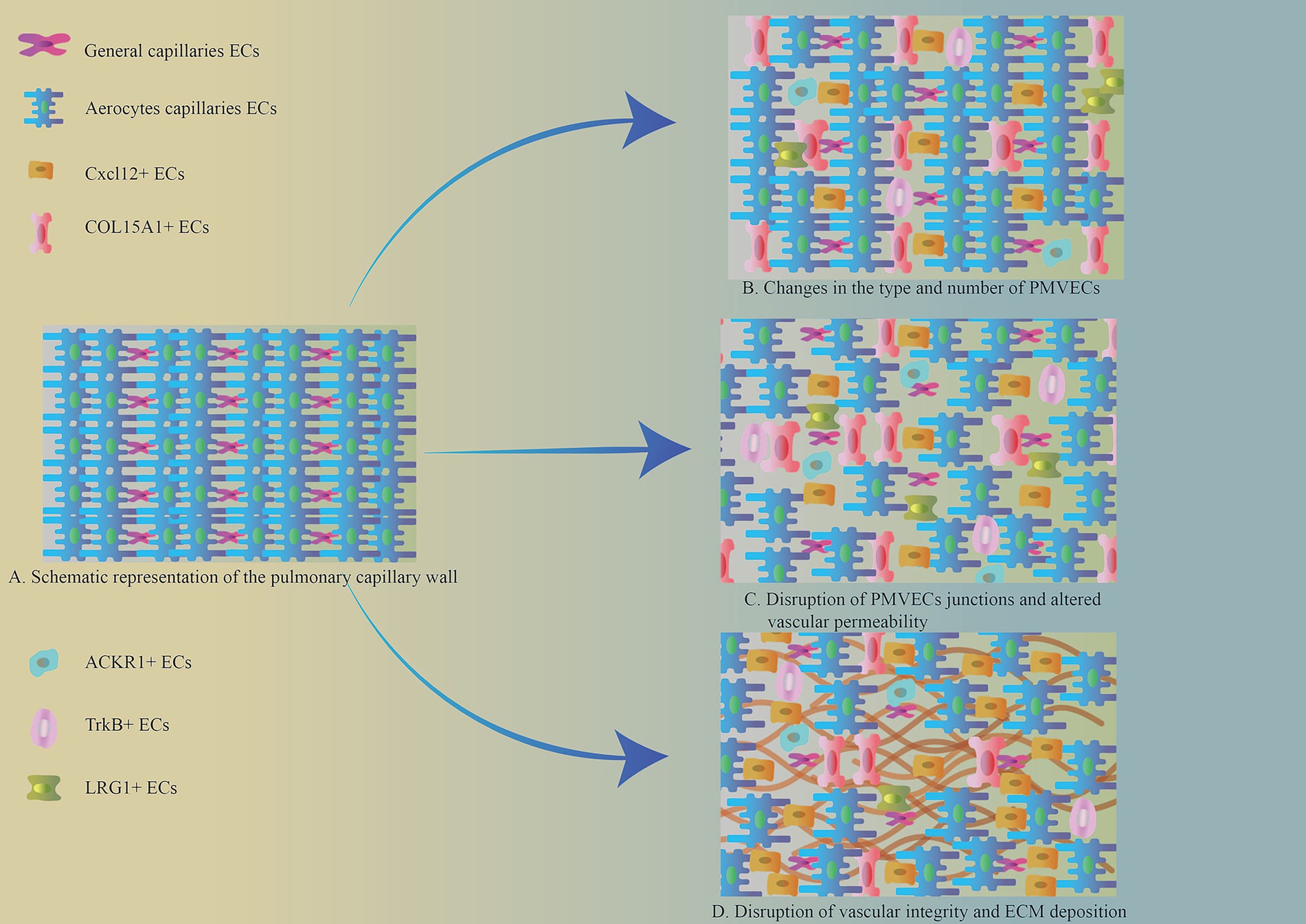
Figure 2. (A) Schematic representation of the pulmonary capillary wall. (B) Changes in the type and number of PMVECs. The number of pulmonary microvascular gCap ECs was significantly reduced in the area of PF. And new VEC phenotypes appeared, including Cxcl12+, ACKR1+, TrkB+, LRG1+, and COL15A1+ phenotypes. (C) Intercellular junctions of PMVECs in the region of pulmonary fibrosis lesions were disrupted, vascular permeability was increased, and the barrier function of blood vessels suffered disruption. (D) Disruption of vascular integrity and ECM deposition. Pulmonary capillary permeability is altered in the area of pulmonary fibrosis lesions, and some VECs produce large amounts of ECM via EndMT, which promotes lung fibrosis progression.
3.1 Aberrant activation of PMVECs in PF lesions alters their cytoarchitecture and disrupts vascular homeostasis
The cytoarchitectural alterations of PMVECs in PF are mainly reflected in the altered number and abnormal distribution of VECs subpopulations, disruption of the connective structures between VECs, and endothelial mesenchymal transition (EndMT). These pathological changes lead to an imbalance in pulmonary capillary homeostasis, increasing vascular permeability and driving abnormal vascular remodeling in PF.
3.1.1 Altered subpopulation numbers and abnormal distribution of PMVECs
PMVEC subpopulations and numbers were different in healthy and fibrotic lung tissues (Figure 2B). Typical gCap capillary endothelial cell numbers were significantly reduced in lung fibrotic tissues (19, 30, 31). Phenotypic changes in activated pulmonary capillary endothelial cells occur under the influence of the fibrotic environment of the lung. Single-cell RNA sequencing of different phenotypes of PMVECs differentiated them, and typical phenotypes included Cxcl12+, ACKR1+, TrkB+, LRG1+, and COL15A1+. The Cxcl12+ subpopulation was associated with various pro-fibrotic activities, including inflammation, vascular remodeling, and ECM deposition (21). The ACKR1+ subpopulation is distributed within the veins and is involved in the regulation of inflammatory pathways, pulmonary vein remodeling and angiogenesis-related pathways, and is closely associated with αSMA+ mesenchymal cells (28, 32, 33). The presence of TrkB+ subpopulation marks the activation of capillary ECs, is predominantly located in areas where fibroblasts accumulate after lung tissue injury, and correlates with the severity of PF (28). LRG1+ subpopulation interacts with lung fibroblasts through the TGFβ/Smad2 pathway, and promotes ECM deposition (34). COL15A1+ VECs are located in the blood vessels surrounding the proximal fine bronchioles in healthy lung tissue. However, in IPF, a large number of COL15A+ VECs were abnormally distributed in fine bronchioles and fibrotic areas (35, 36).
3.1.2 Disruption of VECs junctions and increased vascular permeability in PF lesions
Normal VECs make up the vascular barrier by means of tight junctions, adherent junctions, and gap junctions (Figure 1B) (37). This gives the vasculature the ability to selectively pass metabolic substances and cells. In PF lesions, the connective structure between PMVECs is disrupted (Figure 2C) (38), the barrier function of the vasculature is impaired, and vascular permeability within the lesion is increased, leading to local inflammation. Sphingosine-1 phosphate (S1P) in phospholipid membranes plays an important role in maintaining the connections between PMVECs. Under normal conditions, S1P maintains the connectivity between lung capillaries (39). When vascular endothelial junctions are disrupted, the overexpression of S1P restores endothelial cell junctions and strengthens the endothelial barrier function (40–42). Decreased expression of S1P was observed in PF, along with increased levels of ceramide, which has a disruptive effect on intercellular junctions and disrupts the integrity of the vascular endothelium (43).
3.1.3 EndMT disrupts vascular integrity and promotes perivascular extracellular matrix protein deposition
PMVECs can be activated into mesenchymal cells with ECM secretion after lung tissue injury, a process known as EndMT (36, 44), which is one of the key pathological changes that promote the exacerbation of PF (Figure 2D). Persistent endothelial cell activation is prevalent in pulmonary fibrosis lesions (28, 45). Recently, it has been found that there is a transient acquisition of mesenchymal characteristics after Plvap+ gCap endothelial cell activation in PF, while still maintaining endothelial properties (46). As fibrosis worsened, endothelial cell activation became more frequent. This better explains the course of pathological changes of PMVECs in PF. With the accumulation of inflammation (IL-1β, TNF-α, etc.), pro-fibrotic factor (TGF-β1) and other cytokines in fibrotic lungs, the microenvironment around PMVECs is altered (47–49). This leads to an increased susceptibility of PMVECs to fibrosis, and transient EndMT promotes vascular repair. However, as fibrosis progresses, processes such as iron death, glycolysis, and lipid metabolism are altered in PMVECs (50, 51), promoting increased expression of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) (a key protein for cholesterol homeostasis), the transcription factors Sox9 and Snail, and ultimately leading to persistent endothelial cell activation (47, 52, 53). And it induces EndMT in the ECs of neighboring lung microvessels, leading to over-repair of lung capillaries, disruption of their integrity, increased vascular permeability, and the appearance of a distinct honeycomb structure (54–56).
3.2 Abnormal activation of VECs in PF alters their cellular function and promotes the formation of a local inflammatory environment and fibrotic lesions
PMVECs in the physiological state are associated with the intrinsic immune response, intercellular adhesion and endothelial regeneration (21, 57). In contrast, in PF, activated PMVECs are involved in the inflammatory response and fibrosis, and are also involved in coagulation processes. Some activated PMVECs exhibit reduced endothelial-specific gene expression and increased expression of inflammation-related genes (58, 59), secrete large amounts of inflammatory factors (Table 2) and form a local inflammatory microenvironment.
Peripheral immune cells, including macrophages and monocytes, are also recruited to amplify the inflammatory response (60). In addition to the increased expression of inflammatory genes, this fraction of cells also overexpresses profibrotic genes, promoting the deterioration of pulmonary fibrotic lesions (61), as shown in Table 2. Microvascular thrombus formation has also been observed in damaged pulmonary capillaries and is associated with VEC injury, leading to the release of anticoagulant molecules and increased levels of procoagulant factors on the vascular surface (50, 62). Microthrombi also slow local blood flow, exacerbate local thrombus formation, lead to a localized hypoxic state in the lesion, promote the expression of inflammatory and fibrotic genes in the pulmonary capillary endothelium, and recruit immune cells, among other types of cells (63).
4 Imbalances in pulmonary capillary homeostasis promote pulmonary capillary remodeling and ECM protein deposition and attenuate lung tissue repair
Metabolic reprogramming occurs in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells in pulmonary fibrotic lesions, which disrupts the balance between damage to and repair of the pulmonary capillaries and changes vascular permeability within the lesion, leading to pathological changes such as hypoxia, inflammatory infiltrates, and ECM protein deposition in the lesion. Pulmonary capillaries, in turn, undergo vascular remodeling (Figure 3) (20, 30). In the early stages of pulmonary fibrosis, pulmonary capillaries exhibit reduced integrity and increased permeability (64, 65). With the abnormal repair of pulmonary fibrosis lesions, the distribution of blood vessels within the lesion area decreases, whereas the density of blood vessels increases in the area surrounding the lesion (66–68). In the end stage of pulmonary fibrosis, because of the expansion of fibrotic lesions, the cross-sectional area of pulmonary capillaries within the lesions decreases or even disappears, leading to an increase in pulmonary circulatory resistance and even pulmonary hypertension (69, 70).
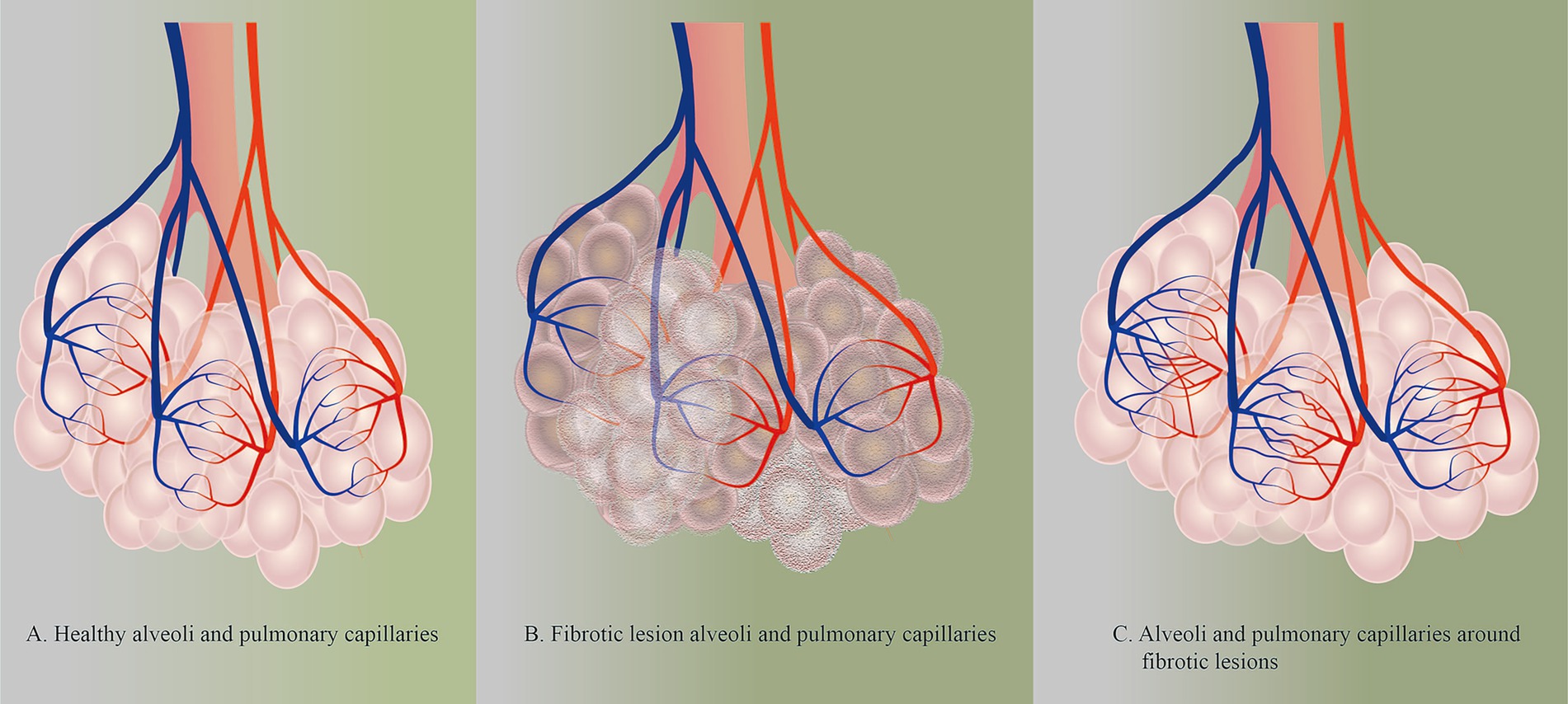
Figure 3. (A) Healthy alveoli and pulmonary capillaries. (B) Fibrotic lesion alveoli and pulmonary capillaries. ECM protein deposition and reduced density of PMVECs within fibrotic lesions in lung tissue with PF. (C) Alveoli and pulmonary capillaries around fibrotic lesions.
4.1 Vascular homeostatic imbalance in PF results in the disappearance of pulmonary capillaries within the lesion and an increase in the density of pulmonary capillaries around the lesion
Vascular injury and regenerative imbalance in PF are central to pulmonary capillary remodeling. Pulmonary capillaries show different pathological manifestations at different stages of PF. As PF progresses, there is a gradual decrease in capillary density within the lesion and a lack of vascular structures within the mature fibrotic lesion (Figure 3B) (30). This phenomenon is associated with increased expression of vascular inhibitory factors (e.g., PEDG) and decreased expression of angiogenic factors (e.g., VEGF) and vasculoprotective factors (e.g., BMPR2) in lesions (67). PEDG inhibits the expression of VEGF in lesions and induces apoptosis in VECs, which results in undetectable low levels of VEGF in lesions (66, 67, 71). Moreover, in the microenvironment of fibrosis, the expression of BMPR2, which is protective for endothelial cells, is reduced, increasing the susceptibility of the vascular endothelium to fibrosis (72).
In PF, in contrast to the situation within fibrotic lesions, VEGF proteins were detected in the vascular endothelium within nonfibrotic lesions (67, 71). These VEGFs are mainly due to the activation of the HIF-α pathway by hypoxic vascular endothelial cells, which initiates VEGF transcription and expression (73, 74). This process is a compensatory manifestation of the pathology. In addition, the reduced vascular density within the lesion leads to an increase in fluid shear stress in the blood around the lesion, which stimulates endothelial cells to produce miR-143-3p and promotes capillary regeneration in healthy lung tissue (75). In addition to the role of VECs in angiogenesis, the upregulation of proangiogenic genes was also observed in the gene expression profile of airway epithelial cells (76). Furthermore, recent studies have shown that a subpopulation of myofibroblasts characterized by the expression of collagen triple helix repeat containing 1 (CTHRC1) exists in PF (77–81). These cells are derived from alveolar fibroblasts and can express high levels of ECM (82–86). In tumor-related studies, CTHRC1 protein promotes vascular remodeling and angiogenesis by enhancing glycolytic processes in VECs (87, 88). This suggests a potential mechanism whereby CTHRC1+ fibroblasts may contribute to the increased capillary density around fibrotic lesions, representing a promising future research direction. Together, these factors contribute to the emergence of newborn pulmonary capillaries around the lesion and the increased percentage of VECs in the PF (Figure 3C) (89). Thus, protection of pulmonary capillaries in the lesion helps delay the onset of pulmonary vascular remodeling and increases the time needed for the repair of damaged lung tissue.
4.2 Imbalances in vascular homeostasis within pulmonary fibrosis lesions reduce alveolar repair capacity and increase ECM protein deposition
The essence of PF is the deposition of ECM proteins due to excessive repair. More studies have suggested that PF begins with dysregulated damage and repair of AECs. Under normal conditions, PMVECs can secrete S1P or perform paracrine delivery of miR-200c-3p, which promotes the differentiation of AT2 cells into AT1 cells to repair damaged alveoli (60, 90). It can also secrete MMP-14 to promote the repair of AECs (91). However, in pulmonary fibrosis lesions, MMP-14 and miR-200c-3p expression was reduced in damaged PMVECs, which attenuated the repair capacity of damaged alveoli (92). In addition, pulmonary capillaries suffer damage in the early stage of fibrosis, resulting in increased vascular permeability, plasma exudation into the interalveolar stroma and alveolar lumen, and ultimately, the formation of hyaline membranes covering the surface of the alveolar epithelium, which affects the gas exchange capacity of alveolar capillaries (93). Thus imbalances in pulmonary capillary homeostasis can attenuate the repair capacity of damaged alveoli.
In PF, damaged PMVECs can activate the proliferation and differentiation of fibroblasts through multiple pathways. Changes in the content of proteins secreted by damaged PMVECs influence lung fibroblasts to develop a fibrotic response, such as decreased expression of ERG and BMPR2 or increased expression of CTGF in endothelial cells, which can lead to fibroblasts expressing a fibrotic phenotype (58, 72, 94). Some PMVECs with reduced expression of the chemokine receptor CXCR7 were recruited toward perivascular macrophages. This resulted in sustained upregulation of Jagged1 (ligand for Notch) on PMVECs, activating the Notch signaling pathway in perivascular fibroblasts (60). At the same time, Galectin-3 (Gal3) secreted by senescent PMVECs can initiate fibroblast-myofibroblast differentiation by binding to TGFBR1 on the cell membrane of lung fibroblasts (95). In addition, Gas6, secreted by PMVECs with a PANoptosis phenotype, binds to Axl in fibroblasts and activates fibroblasts (96). These molecular pathways demonstrate how aberrant PMVECs signaling directly promotes pathogenic fibroblast transitions and ECM deposition.
5 Therapeutic strategies to restore pulmonary capillary homeostasis in PF
The maintenance of pulmonary capillary homeostasis is the basis for the exchange of gasses, nutrients and metabolites between the blood and alveoli. In PF lesions, the structure and function of VECs are highly abnormal. Maintaining and restoring normal pulmonary capillary homeostasis is conducive to attenuating pathological changes such as hypoxia in fibrotic lesions, as well as increasing the efficiency of drug delivery and ameliorating PF (65, 97). Therefore, to restore pulmonary capillary homeostasis, damaged PMVECs can be repaired by improving the inflammatory and fibrotic microenvironments around PMVECs and increasing the resistance of endothelial cells to fibrotic alterations.
The first step is to improve the microenvironment. Structural and functional changes in PMVECs during fibrosis are strongly linked to the surrounding inflammatory and fibrotic environment. Because it is not possible to isolate the communication between endothelial cells and the surrounding environment, the microenvironment can be improved by inhibiting the secretion of factors with damaging effects or by increasing beneficial factors in the microenvironment. Myofibroblasts, the core cells involved in the development of pulmonary fibrosis, can secrete large amounts of profibrotic cytokines. A team developed an engineered mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) called MSC-MM@LPHN to target myofibroblasts in lung tissues by modifying the surface of MSCs to encapsulate ROS-responsive paper polymer hybrid nanoparticles of metformin and macitentan, which induced their dedifferentiation, reduced endothelial damage factor secretion and restored vascular homeostasis (98). Thrombopoietin mimetic (TPOm), which acts on the TPOm receptor, inhibits ICAM-1 expression in primary mouse PMVECs, reducing endothelial cell–neutrophil adhesion and decreasing immune cell recruitment (99). Another study inhibited iron death and fibrotic alterations in endothelial cells by increasing dopamine in the periendothelial environment and balancing lipid/glucose metabolism in endothelial cells (51).
The next step is to repair damaged PMVECs. Maintaining the normal differentiation of gCaps repaired damaged lung capillaries and restored vascular homeostasis. Matrix Gla protein (MGP), an antagonist of bone morphogenic protein (BMP), is highly expressed in lung cells (100, 101), and MGP supports the normal differentiation of progenitor cells and inhibits the abnormal differentiation of endothelial cells (102, 103). However, the mechanism by which MGP promotes the differentiation of gCaps ECs to repair damaged pulmonary capillaries in PF needs to be further investigated. Moreover, MGP binds to BMP-1 and reduces the production of mature TGFβ1, thereby inhibiting EndMT (100). Treamid may be a promising antifibrotic drug that can stimulate regeneration of the lung endothelium in patients with IPF (104).
Finally, the resistance of PMVECs to fibrotic alterations is enhanced. In the lung fibrosis environment, PMVECs are susceptible to fibrotic stimuli. This is related to the fact that the stimulation of PMVECs in the fibrotic microenvironment leads to intracellular metabolic reprogramming, with alterations such as increased glycolysis and reduced expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and the stromal cell proteins CCN3 and S1PR1 (45, 105–108). Therefore, maintaining normal intracellular metabolic processes in PMVECs enhances their resistance to fibrotic alterations. For example, inhibition of CD38 gene expression can significantly affect fibrotic lesions during EndMT (45). The overexpression of S1PR1 can also increase the stability of connections between PMVECs and improve vascular permeability (105, 107). In PMVECs that have undergone fibrotic changes, the EndMT process can be inhibited by miR-218 in exosomes secreted from MSCs, which inhibits the MeCP2/BMP2 pathway (109). Therefore, enhancing the resistance of PMVECs to fibrotic alterations could inhibit pathological changes in the vasculature within pulmonary fibrotic lesions and protect the integrity of the vascular endothelium.
6 Conclusion
Abnormal activation of PMVECs disrupts pulmonary capillary homeostasis one of the core pathological mechanisms underlying the progression of PF. Abnormal activation of PMVECs disrupts the structure and function of normal cells, leading to disruption of intercellular junctions, altered vascular permeability, and imbalance of pulmonary capillary homeostasis. These pathological changes cause impaired substance exchange function, inflammatory response, abnormal ECM deposition and other pathological changes within the fibrotic lesions. This ultimately leads to abnormal vascular remodeling. Therefore maintaining or restoring pulmonary capillary homeostasis is conducive to ameliorating the above pathological changes, and improving the efficiency of drug delivery to fibrotic lesions, thereby inhibiting or reversing the progression of PF.
Author contributions
JZ: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XX: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. XA: Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. DL: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZS: Funding acquisition, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. WL: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing. QH: Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the joint innovation fund of the Chengdu Municipal Health Commission and Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. WXLH202403229). The funders were not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication. All authors declare no other competing interests.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Wijsenbeek, M, Suzuki, A, and Maher, TM. Interstitial lung diseases. Lancet. (2022) 400:769–86. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(22)01052-2
2. Gagliardi, M, Berg, DV, Heylen, CE, Koenig, S, Hoton, D, Tamirou, F, et al. Real-life prevalence of progressive Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:23988. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-03481-8
3. Koudstaal, T, and Wijsenbeek, MS. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Presse Med. (2023) 52:104166. doi: 10.1016/j.lpm.2023.104166
4. Shah Gupta, R, Koteci, A, Morgan, A, George, PM, and Quint, JK. Incidence and prevalence of interstitial lung diseases worldwide: a systematic literature review. BMJ Open Respir Res. (2023) 10:e001291. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2022-001291
5. Podolanczuk, AJ, Thomson, CC, Remy-Jardin, M, Richeldi, L, Martinez, FJ, Kolb, M, et al. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: state of the art for 2023. Eur Respir J. (2023) 61:2200957. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00957-2022
6. Wijsenbeek, M, and Cottin, V. Spectrum of fibrotic lung diseases. N Engl J Med. (2020) 383:958–68. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra2005230
7. Galli, JA, Pandya, A, Vega-Olivo, M, Dass, C, Zhao, H, and Criner, GJ. Pirfenidone and Nintedanib for pulmonary fibrosis in clinical practice: tolerability and adverse drug reactions. Respirology. (2017) 22:1171–8. doi: 10.1111/resp.13024
8. Raghu, G, Rochwerg, B, Zhang, Y, Garcia, CA, Azuma, A, Behr, J, et al. An official Ats/Ers/Jrs/Alat clinical practice guideline: treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. An update of the 2011 clinical practice guideline. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2015) 192:e3–e19. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201506-1063ST
9. Maher, TM, and Strek, ME. Antifibrotic therapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: time to treat. Respir Res. (2019) 20:205. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1161-4
10. Inoue, Y, Wells, AU, Song, JW, Xu, Z, Kitamura, H, Suda, T, et al. Nintedanib in Asian patients with progressive Fibrosing interstitial lung diseases: results from the Inbuild trial. Respirology. (2023) 28:465–74. doi: 10.1111/resp.14452
11. Maher, TM, Corte, TJ, Fischer, A, Kreuter, M, Lederer, DJ, Molina-Molina, M, et al. Pirfenidone in patients with unclassifiable progressive Fibrosing interstitial lung disease: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial. Lancet Respir Med. (2020) 8:147–57. doi: 10.1016/s2213-2600(19)30341-8
12. Thong, L, McElduff, EJ, and Henry, MT. Trials and treatments: an update on pharmacotherapy for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Life (Basel). (2023) 13:486. doi: 10.3390/life13020486
13. Flaherty, KR, Fell, CD, Huggins, JT, Nunes, H, Sussman, R, Valenzuela, C, et al. Safety of Nintedanib added to Pirfenidone treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. (2018) 52:1800230. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00230-2018
14. Kreuter, M, Picker, N, Schwarzkopf, L, Baumann, S, Cerani, A, Postema, R, et al. Epidemiology, healthcare utilization, and related costs among patients with Ipf: results from a German claims database analysis. Respir Res. (2022) 23:62. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-01976-0
15. Hilberg, O, Bendstrup, E, Ibsen, R, Løkke, A, and Hyldgaard, C. Economic consequences of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Denmark. ERJ Open Res. (2018) 4:00045–2017. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00045-2017
16. Cox, IA, de Graaff, B, Ahmed, H, Campbell, J, Otahal, P, Corte, TJ, et al. The economic burden of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in Australia: a cost of illness study. Eur J Health Econ. (2023) 24:1121–39. doi: 10.1007/s10198-022-01538-7
17. Blokland, KEC, Waters, DW, Schuliga, M, Read, J, Pouwels, SD, Grainge, CL, et al. Senescence of Ipf lung fibroblasts disrupt alveolar epithelial cell proliferation and promote migration in wound healing. Pharmaceutics. (2020) 12:389. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics12040389
18. Hashimoto, N, Phan, SH, Imaizumi, K, Matsuo, M, Nakashima, H, Kawabe, T, et al. Endothelial-mesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2010) 43:161–72. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2009-0031OC
19. May, J, Mitchell, JA, and Jenkins, RG. Beyond epithelial damage: vascular and endothelial contributions to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. (2023) 133:133 (18). doi: 10.1172/jci172058
20. Bian, F, Lan, YW, Zhao, S, Deng, Z, Shukla, S, Acharya, A, et al. Lung endothelial cells regulate pulmonary fibrosis through Foxf 1/R-Ras signaling. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:2560. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38177-2
21. Liu, X, Qin, X, Qin, H, Jia, C, Yuan, Y, Sun, T, et al. Characterization of the heterogeneity of endothelial cells in bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis using single-cell Rna sequencing. Angiogenesis. (2021) 24:809–21. doi: 10.1007/s10456-021-09795-5
22. Fließer, E, Lins, T, Berg, JL, Kolb, M, and Kwapiszewska, G. The endothelium in lung fibrosis: a Core signaling hub in disease pathogenesis? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2023) 325:C2–c16. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00097.2023
23. Cook-Mills, JM, and Deem, TL. Active participation of endothelial cells in inflammation. J Leukoc Biol. (2005) 77:487–95. doi: 10.1189/jlb.0904554
24. Zepp, JA, and Morrisey, EE. Cellular crosstalk in the development and regeneration of the respiratory system. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. (2019) 20:551–66. doi: 10.1038/s41580-019-0141-3
25. Sauler, M, McDonough, JE, Adams, TS, Kothapalli, N, Barnthaler, T, Werder, RB, et al. Characterization of the COPD alveolar niche using single-cell RNA sequencing. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:494. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28062-9
26. Gillich, A, Zhang, F, Farmer, CG, Travaglini, KJ, Tan, SY, Gu, M, et al. Capillary cell-type specialization in the alveolus. Nature. (2020) 586:785–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2822-7
27. Godoy, RS, Cober, ND, Cook, DP, McCourt, E, Deng, Y, Wang, L, et al. Single-cell transcriptomic atlas of lung microvascular regeneration after targeted endothelial cell ablation. eLife. (2023) 12:e80900. doi: 10.7554/eLife.80900
28. Raslan, AA, Pham, TX, Lee, J, Kontodimas, K, Tilston-Lunel, A, Schmottlach, J, et al. Lung injury-induced activated endothelial cell states persist in aging-associated progressive fibrosis. Nat Commun. (2024) 15:5449. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49545-x
29. Zhao, W, Wang, L, Wang, Y, Yuan, H, Zhao, M, Lian, H, et al. Injured endothelial cell: a risk factor for pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2023) 24:8749. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108749
30. Hanumegowda, C, Farkas, L, and Kolb, M. Angiogenesis in pulmonary fibrosis: too much or not enough? Chest. (2012) 142:200–7. doi: 10.1378/chest.11-1962
31. Barratt, S, and Millar, A. Vascular remodelling in the pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. QJM. (2014) 107:515–9. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcu012
32. Bonecchi, R, and Graham, GJ. Atypical chemokine receptors and their roles in the resolution of the inflammatory response. Front Immunol. (2016) 7:224. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2016.00224
33. Thiriot, A, Perdomo, C, Cheng, G, Novitzky-Basso, I, McArdle, S, Kishimoto, JK, et al. Differential Darc/Ackr 1 expression distinguishes Venular from non-Venular endothelial cells in murine tissues. BMC Biol. (2017) 15:45. doi: 10.1186/s12915-017-0381-7
34. Honda, H, Fujimoto, M, Serada, S, Urushima, H, Mishima, T, Lee, H, et al. Leucine-rich Α-2 glycoprotein promotes lung fibrosis by modulating Tgf-Β signaling in fibroblasts. Physiol Rep. (2017) 5:e13556. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13556
35. Adams, TS, Schupp, JC, Poli, S, Ayaub, EA, Neumark, N, Ahangari, F, et al. Single-cell rna-seq reveals ectopic and aberrant lung-resident cell populations in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Adv. (2020) 6:eaba1983. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aba1983
36. Lang, NJ, Gote-Schniering, J, Porras-Gonzalez, D, Yang, L, De Sadeleer, LJ, Jentzsch, RC, et al. Ex vivo tissue perturbations coupled to single-cell Rna-Seq reveal multilineage cell circuit dynamics in human lung Fibrogenesis. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15:eadh0908. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adh0908
37. Bazzoni, G, and Dejana, E. Endothelial cell-to-cell junctions: molecular organization and role in vascular homeostasis. Physiol Rev. (2004) 84:869–901. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00035.2003
38. Santos-Ribeiro, D, Lecocq, M, de Beukelaer, M, Verleden, S, Bouzin, C, Ambroise, J, et al. Disruption of Gcn 2 pathway aggravates vascular and parenchymal remodeling during pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2023) 68:326–38. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0541OC
39. Brown, MB, Hunt, WR, Noe, JE, Rush, NI, Schweitzer, KS, Leece, TC, et al. Loss of cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator impairs lung endothelial cell barrier function and increases susceptibility to microvascular damage from cigarette smoke. Pulm Circ. (2014) 4:260–8. doi: 10.1086/675989
40. Dudek, SM, and Garcia, JG. Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability. J Appl Physiol (1985). (2001) 91:1487–500. doi: 10.1152/jappl.2001.91.4.1487
41. Garcia, JG, Liu, F, Verin, AD, Birukova, A, Dechert, MA, Gerthoffer, WT, et al. Sphingosine 1-phosphate promotes endothelial cell barrier integrity by Edg-dependent cytoskeletal rearrangement. J Clin Invest. (2001) 108:689–701. doi: 10.1172/jci12450
42. Schaphorst, KL, Chiang, E, Jacobs, KN, Zaiman, A, Natarajan, V, Wigley, F, et al. Role of Sphingosine-1 phosphate in the enhancement of endothelial barrier integrity by platelet-released products. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2003) 285:L258–67. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00311.2002
43. Ghidoni, R, Caretti, A, and Signorelli, P. Role of sphingolipids in the pathobiology of lung inflammation. Mediat Inflamm. (2015) 2015:487508. doi: 10.1155/2015/487508
44. Zeisberg, EM, Tarnavski, O, Zeisberg, M, Dorfman, AL, McMullen, JR, Gustafsson, E, et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition contributes to cardiac fibrosis. Nat Med. (2007) 13:952–61. doi: 10.1038/nm1613
45. Hu, M, Guan, XH, Wang, LF, Xu, HM, Ke, SF, Yuan, QY, et al. Endothelial Cd38-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition is a pivotal driver in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. (2024) 82:30. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05548-x
46. Li, H, Zhang, S, Huang, X, Zhang, Z, Liu, K, Wang, QD, et al. Genetic recording of transient endothelial activation in distinct alveolar capillary cells during pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Discov. (2024) 10:119. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00745-1
47. Xiong, W, Chen, S, Xiang, H, Zhao, S, Xiao, J, Li, J, et al. S1pr1 attenuates pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting Endmt and improving endothelial barrier function. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. (2023) 81:102228. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2023.102228
48. Pérez, L, Muñoz-Durango, N, Riedel, CA, Echeverría, C, Kalergis, AM, Cabello-Verrugio, C, et al. Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition: cytokine-mediated pathways that determine endothelial fibrosis under inflammatory conditions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. (2017) 33:41–54. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2016.09.002
49. Suzuki, HI, Horie, M, Mihira, H, and Saito, A. Molecular analysis of endothelial-mesenchymal transition induced by transforming growth factor-Β signaling. J Vis Exp. (2018) 138:57577. doi: 10.3791/57577
50. Akahori, D, Inui, N, Inoue, Y, Yasui, H, Hozumi, H, Suzuki, Y, et al. Effect of hypoxia on pulmonary endothelial cells from bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis model mice. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23:8996. doi: 10.3390/ijms23168996
51. Mo, C, Li, H, Yan, M, Xu, S, Wu, J, Li, J, et al. Dopaminylation of endothelial Tpi 1 suppresses Ferroptotic Angiocrine signals to promote lung regeneration over fibrosis. Cell Metab. (2024) 36:1839–57.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2024.07.008
52. Martin, M, Zhang, J, Miao, Y, He, M, Kang, J, Huang, HY, et al. Role of endothelial cells in pulmonary fibrosis via Srebp2 activation. JCI Insight. (2021) 6:e125635. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125635
53. Trogisch, FA, Abouissa, A, Keles, M, Birke, A, Fuhrmann, M, Dittrich, GM, et al. Endothelial cells drive organ fibrosis in mice by inducing expression of the transcription factor Sox9. Sci Transl Med. (2024) 16:eabq4581. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abq4581
54. Mahmoud, MM, Serbanovic-Canic, J, Feng, S, Souilhol, C, Xing, R, Hsiao, S, et al. Author correction: shear stress induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition via the transcription factor snail. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:3870. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-60955-x
55. Good, RB, Gilbane, AJ, Trinder, SL, Denton, CP, Coghlan, G, Abraham, DJ, et al. Endothelial to mesenchymal transition contributes to endothelial dysfunction in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Pathol. (2015) 185:1850–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.03.019
56. Yan, Z, Wang, ZG, Segev, N, Hu, S, Minshall, RD, Dull, RO, et al. Rab 11a mediates vascular endothelial-cadherin recycling and controls endothelial barrier function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2016) 36:339–49. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.115.306549
57. Zhang, L, Gao, S, White, Z, Dai, Y, Malik, AB, and Rehman, J. Single-cell transcriptomic profiling of lung endothelial cells identifies dynamic inflammatory and regenerative subpopulations. JCI Insight. (2022) 7:e158079. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.158079
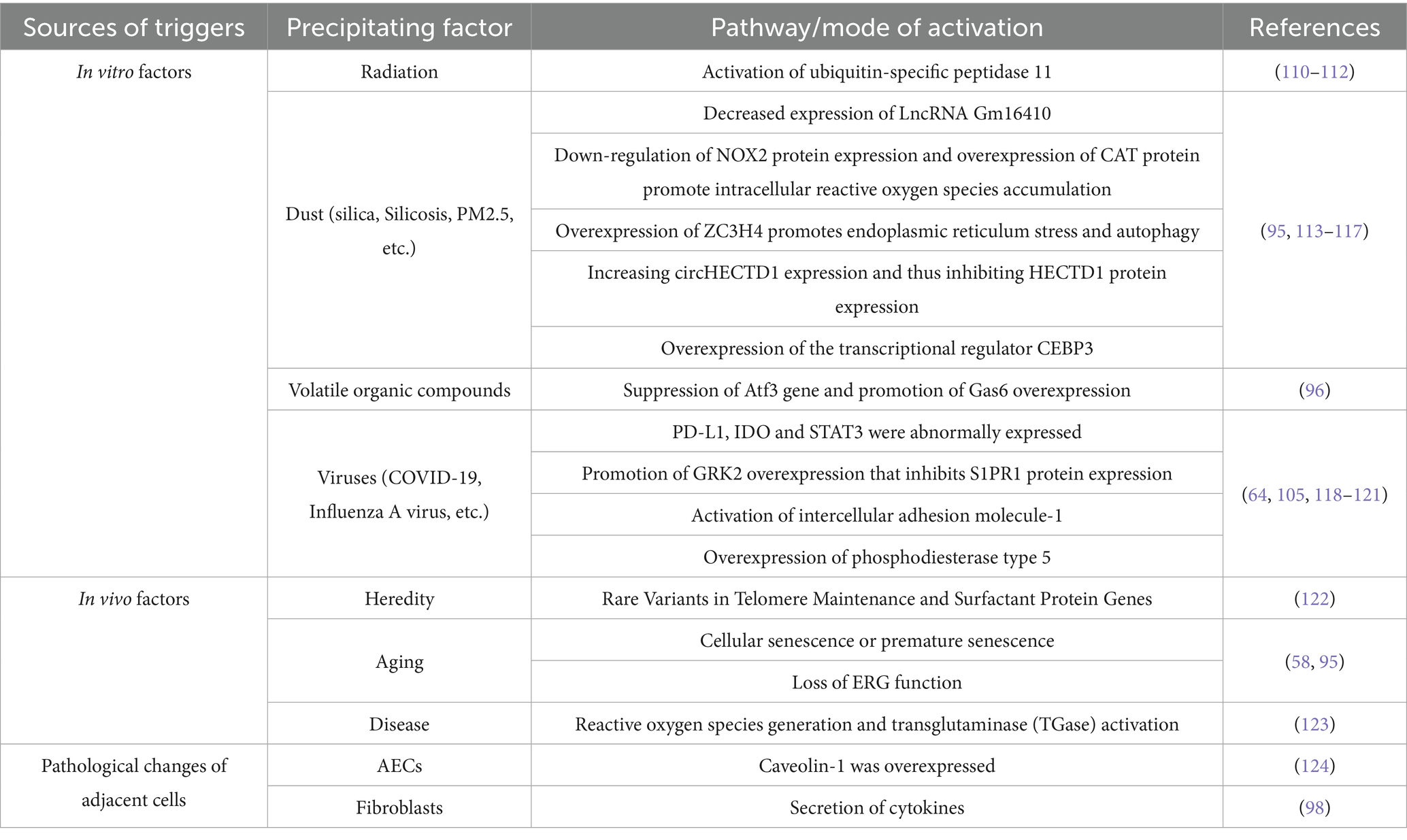
58. Caporarello, N, Lee, J, Pham, TX, Jones, DL, Guan, J, Link, PA, et al. Dysfunctional erg signaling drives pulmonary vascular aging and persistent fibrosis. Nat Commun. (2022) 13:4170. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31890-4
59. Caporarello, N, Meridew, JA, Aravamudhan, A, Jones, DL, Austin, SA, Pham, TX, et al. Vascular dysfunction in aged mice contributes to persistent lung fibrosis. Aging Cell. (2020) 19:e13196. doi: 10.1111/acel.13196
60. Cao, Z, Lis, R, Ginsberg, M, Chavez, D, Shido, K, Rabbany, SY, et al. Targeting of the pulmonary capillary vascular niche promotes lung alveolar repair and ameliorates fibrosis. Nat Med. (2016) 22:154–62. doi: 10.1038/nm.4035
61. Kato, S, Inui, N, Hakamata, A, Suzuki, Y, Enomoto, N, Fujisawa, T, et al. Changes in pulmonary endothelial cell properties during bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. (2018) 19:127. doi: 10.1186/s12931-018-0831-y
62. Livingstone, SA, Wildi, KS, Dalton, HJ, Usman, A, Ki, KK, Passmore, MR, et al. Coagulation dysfunction in acute respiratory distress syndrome and its potential impact in inflammatory subphenotypes. Front Med. (2021) 8:723217. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.723217
63. Spagnolo, P, and Cottin, V. Genetics of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: from mechanistic pathways to personalised medicine. J Med Genet. (2017) 54:93–9. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2016-103973
64. de Rooij, L, Becker, LM, Teuwen, LA, Boeckx, B, Jansen, S, Feys, S, et al. The pulmonary vasculature in lethal Covid-19 and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis at single-cell resolution. Cardiovasc Res. (2023) 119:520–35. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvac139
65. Fließer, E, Jandl, K, Lins, T, Birnhuber, A, Valzano, F, Kolb, D, et al. Lung fibrosis is linked to increased endothelial cell activation and dysfunctional vascular barrier integrity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2024) 71:318–31. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2024-0046OC
66. Cosgrove, GP, Brown, KK, Schiemann, WP, Serls, AE, Parr, JE, Geraci, MW, et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a role in aberrant angiogenesis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2004) 170:242–51. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200308-1151OC
67. Ebina, M, Shimizukawa, M, Shibata, N, Kimura, Y, Suzuki, T, Endo, M, et al. Heterogeneous increase in Cd34-positive alveolar capillaries in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2004) 169:1203–8. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200308-1111OC
68. Farkas, L, Gauldie, J, Voelkel, NF, and Kolb, M. Pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a tale of angiogenesis, apoptosis, and growth factors. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2011) 45:1–15. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0365TR
69. Hamada, K, Nagai, S, Tanaka, S, Handa, T, Shigematsu, M, Nagao, T, et al. Significance of pulmonary arterial pressure and diffusion capacity of the lung as prognosticator in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. (2007) 131:650–6. doi: 10.1378/chest.06-1466
70. Smith, JS, Gorbett, D, Mueller, J, Perez, R, and Daniels, CJ. Pulmonary hypertension and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a dastardly duo. Am J Med Sci. (2013) 346:221–5. doi: 10.1097/MAJ.0b013e31827871dc
71. Barratt, SL, Blythe, T, Jarrett, C, Ourradi, K, Shelley-Fraser, G, Day, MJ, et al. Differential expression of Vegf-a(xxx) isoforms is critical for development of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2017) 196:479–93. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201603-0568OC
72. Yanagihara, T, Tsubouchi, K, Zhou, Q, Chong, M, Otsubo, K, Isshiki, T, et al. Vascular-parenchymal cross-talk promotes lung fibrosis through Bmpr2 signaling. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2023) 207:1498–514. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202109-2174OC
73. Krenn, K, Klepetko, W, Taghavi, S, Paulus, P, and Aharinejad, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor increases pulmonary vascular permeability in cystic fibrosis patients undergoing lung transplantation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. (2007) 32:35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcts.2007.04.006
74. Lucitti, JL, Mackey, JK, Morrison, JC, Haigh, JJ, Adams, RH, and Faber, JE. Formation of the collateral circulation is regulated by vascular endothelial growth factor-a and a Disintegrin and metalloprotease family members 10 and 17. Circ Res. (2012) 111:1539–50. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.112.279109
75. Troidl, K, Hammerschick, T, Albarran-Juarez, J, Jung, G, Schierling, W, Tonack, S, et al. Shear stress-induced Mir-143-3p in collateral arteries contributes to outward vessel growth by targeting collagen V-Α2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2020) 40:e126–37. doi: 10.1161/atvbaha.120.313316
76. Verhaeghe, C, Tabruyn, SP, Oury, C, Bours, V, and Griffioen, AW. Intrinsic pro-Angiogenic status of cystic fibrosis airway epithelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. (2007) 356:745–9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.02.166
77. Tsukui, T, Sun, KH, Wetter, JB, Wilson-Kanamori, JR, Hazelwood, LA, Henderson, NC, et al. Collagen-producing lung cell atlas identifies multiple subsets with distinct localization and relevance to fibrosis. Nat Commun. (2020) 11:1920. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15647-5
78. Mayr, CH, Sengupta, A, Asgharpour, S, Ansari, M, Pestoni, JC, Ogar, P, et al. Sfrp1 inhibits lung fibroblast invasion during transition to injury-induced Myofibroblasts. Eur Respir J. (2024) 63:2301326. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01326-2023
79. Melms, JC, Biermann, J, Huang, H, Wang, Y, Nair, A, Tagore, S, et al. A molecular single-cell lung atlas of lethal Covid-19. Nature. (2021) 595:114–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03569-1
80. Freeberg, MAT, Camus, SV, Robila, V, Perelas, A, Thatcher, TH, and Sime, PJ. Piezo2 is a key mechanoreceptor in lung fibrosis that drives Myofibroblast differentiation. Am J Pathol. (2025) 195:626–38. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2024.12.015
81. Jyothula, SSK, Peters, A, Liang, Y, Bi, W, Shivshankar, P, Yau, S, et al. Fulminant lung fibrosis in non-resolvable Covid-19 requiring transplantation. EBioMedicine. (2022) 86:104351. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104351
82. Fang, Y, Chung, SSW, Xu, L, Xue, C, Liu, X, Jiang, D, et al. Runx2 promotes fibrosis via an alveolar-to-pathological fibroblast transition. Nature. (2025) 640:221–30. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-08542-2
83. Kathiriya, JJ, Wang, C, Zhou, M, Brumwell, A, Cassandras, M, Le Saux, CJ, et al. Human alveolar type 2 epithelium transdifferentiates into metaplastic Krt5(+) basal cells. Nat Cell Biol. (2022) 24:10–23. doi: 10.1038/s41556-021-00809-4
84. Jin, C, Chen, Y, Wang, Y, Li, J, Liang, J, Zheng, S, et al. Single-cell Rna sequencing reveals special basal cells and fibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep. (2024) 14:15778. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-66947-5
85. Lingampally, A, Truchi, M, Mauduit, O, Delcroix, V, Vasquez-Pacheco, E, Gautier-Isola, M, et al. Evidence for a Lipofibroblast-to-Cthrc1 (+) Myofibroblast reversible switch during the development and resolution of lung fibrosis in young mice. Eur Respir J. (2025) 65:2300482. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00482-2023
86. Mukhatayev, Z, Adilbayeva, A, and Kunz, J. Cthrc1: an emerging Hallmark of pathogenic fibroblasts in lung fibrosis. Cells. (2024) 13:946. doi: 10.3390/cells13110946
87. Toomey, BH, Mitrovic, SA, Lindner-Liaw, M, Leon Vazquez, RG, Kacer, D, Ryzhov, S, et al. Activated Cthrc1 promotes glycolysis in endothelial cells: implications for metabolism and angiogenesis. Vasc Pharmacol. (2023) 153:107246. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2023.107246
88. Vaupel, P, and Multhoff, G. Revisiting the Warburg effect: historical dogma versus current understanding. J Physiol. (2021) 599:1745–57. doi: 10.1113/jp278810
89. Zhang, T, Hou, Z, Ding, Z, Wang, P, Pan, X, and Li, X. Single cell Rna-Seq identifies cell subpopulations contributing to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in humans. J Cell Mol Med. (2025) 29:e70402. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70402
90. Chen, Q, Rehman, J, Chan, M, Fu, P, Dudek, SM, Natarajan, V, et al. Angiocrine Sphingosine-1-phosphate activation of S1pr2-yap signaling Axis in alveolar type ii cells is essential for lung repair. Cell Rep. (2020) 31:107828. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2020.107828
91. Ding, BS, Nolan, DJ, Guo, P, Babazadeh, AO, Cao, Z, Rosenwaks, Z, et al. Endothelial-derived Angiocrine signals induce and sustain regenerative lung Alveolarization. Cell. (2011) 147:539–53. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.10.003
92. Volpe, MC, Ciucci, G, Zandomenego, G, Vuerich, R, Ring, NAR, Vodret, S, et al. Flt1 produced by lung endothelial cells impairs Atii cell Transdifferentiation and repair in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Death Dis. (2023) 14:437. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05962-2
93. Bos, LDJ, and Ware, LB. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: causes, pathophysiology, and phenotypes. Lancet. (2022) 400:1145–56. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(22)01485-4
94. Bacha, NC, Blandinieres, A, Rossi, E, Gendron, N, Nevo, N, Lecourt, S, et al. Endothelial microparticles are associated to pathogenesis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Stem Cell Rev Rep. (2018) 14:223–35. doi: 10.1007/s12015-017-9778-5
95. Cheng, D, Lian, W, Jia, X, Wang, T, Sun, W, Jia, Z, et al. Senescent endothelial cell-derived galectin 3 promotes silicosis through endothelial-fibroblast and endothelial-macrophage crosstalk. J Hazard Mater. (2025) 489:137605. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.137605
96. Liu, Q, Niu, Y, Pei, Z, Yang, Y, Xie, Y, Wang, M, et al. Gas 6-Axl signal promotes indoor vocs exposure-induced pulmonary fibrosis via pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells-fibroblasts cross-talk. J Hazard Mater. (2024) 474:134786. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2024.134786
97. Martin, JD, Seano, G, and Jain, RK. Normalizing function of tumor vessels: Progress, opportunities, and challenges. Annu Rev Physiol. (2019) 81:505–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020518-114700
98. Fang, YF, Zhang, C, Han, MM, Wang, Y, Zhou, TJ, Xing, L, et al. Engineered Mscs break endothelial-Myofibroblast crosstalk in pulmonary fibrosis: reconstructing the vascular niche. Adv Mater. (2025) 37:e2414601. doi: 10.1002/adma.202414601
99. English, J, Dhanikonda, S, Tanaka, KE, Koba, W, Eichenbaum, G, Yang, WL, et al. Thrombopoietin mimetic reduces mouse lung inflammation and fibrosis after radiation by attenuating activated endothelial phenotypes. JCI Insight. (2024) 9:e181330. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.181330
100. Wu, X, Zhang, D, Qiao, X, Zhang, L, Cai, X, Ji, J, et al. Regulating the cell shift of endothelial cell-like Myofibroblasts in pulmonary fibrosis. Eur Respir J. (2023) 61:2201799. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01799-2022
101. Yao, Y, Jumabay, M, Wang, A, and Boström, KI. Matrix Gla protein deficiency causes arteriovenous malformations in mice. J Clin Invest. (2011) 121:2993–3004. doi: 10.1172/jci57567
102. Yao, J, Guihard, PJ, Blazquez-Medela, AM, Guo, Y, Liu, T, Boström, KI, et al. Matrix Gla protein regulates differentiation of endothelial cells derived from mouse embryonic stem cells. Angiogenesis. (2016) 19:1–7. doi: 10.1007/s10456-015-9484-3
103. Yao, J, Guihard, PJ, Blazquez-Medela, AM, Guo, Y, Moon, JH, Jumabay, M, et al. Serine protease activation essential for endothelial-mesenchymal transition in vascular calcification. Circ Res. (2015) 117:758–69. doi: 10.1161/circresaha.115.306751
104. Skurikhin, E, Nebolsin, V, Widera, D, Ermakova, N, Pershina, O, Pakhomova, A, et al. Antifibrotic and regenerative effects of Treamid in pulmonary fibrosis. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:21 (21). doi: 10.3390/ijms21218380
105. Brazee, PL, Cartier, A, Kuo, A, Haring, AM, Nguyen, T, Hariri, LP, et al. Augmentation of endothelial S1pr1 attenuates Postviral pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2024) 70:119–28. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2023-0286OC
106. Lee, JY, Stevens, RP, Kash, M, Zhou, C, Koloteva, A, Renema, P, et al. Kd025 shifts pulmonary endothelial cell bioenergetics and decreases baseline lung permeability. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2020) 63:519–30. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2019-0435OC
107. Knipe, RS, Spinney, JJ, Abe, EA, Probst, CK, Franklin, A, Logue, A, et al. Endothelial-specific loss of Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 increases vascular permeability and exacerbates bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2022) 66:38–52. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0408OC
108. Betageri, KR, Link, PA, Haak, AJ, Ligresti, G, Tschumperlin, DJ, and Caporarello, N. The Matricellular protein Ccn3 supports lung endothelial homeostasis and function. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2023) 324:L154–68. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00248.2022
109. Zhao, Y, Du, L, Sun, J, Wang, X, Cong, Z, Chen, S, et al. Exosomal Mir-218 derived from mesenchymal stem cells inhibits endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by epigenetically modulating of Bmp2 in pulmonary fibrosis. Cell Biol Toxicol. (2023) 39:2919–36. doi: 10.1007/s10565-023-09810-z
110. Wang, Y, Zhang, J, and Shao, C. Cytological changes in radiation-induced lung injury. Life Sci. (2024) 358:123188. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2024.123188
111. Tang, Y, Yuan, Q, Zhao, C, Xu, Y, Zhang, Q, Wang, L, et al. Targeting Usp 11 May alleviate radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis by regulating endothelium tight junction. Int J Radiat Biol. (2022) 98:30–40. doi: 10.1080/09553002.2022.1998711
112. Ying, H, Zhou, C, Hang, Q, and Fang, M. The preventive effect of Endostar on radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Mol Med. (2024) 24:610–9. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230406134640
113. Ma, K, Li, C, Xu, J, Ren, F, Xu, X, Liu, C, et al. Lncrna Gm16410 regulates pm (2.5)-induced lung endothelial-mesenchymal transition via the Tgf-Β1/Smad 3/P-Smad 3 pathway. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2020) 205:111327. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111327
114. Li, N, Chang, M, Zhou, Q, Zhang, L, Wang, Y, Guan, Y, et al. Activation of Ampk Signalling by metformin: implication an important molecular mechanism for protecting against mice silicosis via inhibited endothelial cell-to-mesenchymal transition by regulating oxidative stress and apoptosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2023) 120:110321. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110321
115. Jiang, R, Han, L, Gao, Q, and Chao, J. Zc3h4 mediates silica-induced Endomt via Er stress and autophagy. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. (2021) 84:103605. doi: 10.1016/j.etap.2021.103605
116. Fang, S, Guo, H, Cheng, Y, Zhou, Z, Zhang, W, Han, B, et al. Circhectd 1 promotes the silica-induced pulmonary endothelial-mesenchymal transition via Hectd 1. Cell Death Dis. (2018) 9:396. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0432-1
117. Zhou, X, Zhang, C, Yang, S, Yang, L, Luo, W, Zhang, W, et al. Macrophage-derived Mmp 12 promotes fibrosis through sustained damage to endothelial cells. J Hazard Mater. (2024) 461:132733. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.132733
118. Ravaglia, C, Doglioni, C, Chilosi, M, Piciucchi, S, Dubini, A, Rossi, G, et al. Clinical, radiological and pathological findings in patients with persistent lung disease following Sars-Cov-2 infection. Eur Respir J. (2022) 60:2102411. doi: 10.1183/13993003.02411-2021
119. Zhang, L, Tang, C, Zhang, M, Tong, X, Xie, Y, Yan, R, et al. Single cell Meta-analysis of Endmt and Emt state in Covid-19. Front Immunol. (2022) 13:976512. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.976512
120. Das, A, Meng, W, Liu, Z, Hasib, MM, Galloway, H, Ramos da Silva, S, et al. Molecular and immune signatures, and pathological trajectories of fatal Covid-19 lungs defined by in situ spatial single-cell transcriptome analysis. J Med Virol. (2023) 95:e29009. doi: 10.1002/jmv.29009
121. Isidori, AM, Giannetta, E, Pofi, R, Venneri, MA, Gianfrilli, D, Campolo, F, et al. Targeting the no-Cgmp-Pde 5 pathway in Covid-19 infection. The Dedalo project. Andrology. (2021) 9:33–8. doi: 10.1111/andr.12837
122. Liu, Q, Zhou, Y, Cogan, JD, Mitchell, DB, Sheng, Q, Zhao, S, et al. The genetic landscape of familial pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. (2023) 207:1345–57. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202204-0781OC
123. Jeon, HY, Lee, AJ, Kim, EB, Kim, M, Park, WS, and Ha, KS. C-peptide attenuates hyperglycemia-induced pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting transglutaminase 2. J Mol Endocrinol. (2022) 68:209–23. doi: 10.1530/jme-21-0271
124. Kulshrestha, R, Singh, H, Pandey, A, Soundarya, D, Jaggi, AS, and Ravi, K. Differential expression of Caveolin-1 during pathogenesis of combined pulmonary fibrosis and emphysema: effect of Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol basis Dis. (2020) 1866:165802. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165802
125. Jin, C, Li, J, Li, Q, Zhang, L, Zheng, S, Feng, Q, et al. Contribution of Cuproptosis and immune-related genes to idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis disease. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1458341. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1458341
126. Wu, X, Qian, L, Zhao, H, Lei, W, Liu, Y, Xu, X, et al. Cxcl 12/Cxcr4: an amazing challenge and opportunity in the fight against fibrosis. Ageing Res Rev. (2023) 83:101809. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2022.101809
127. Alsaffar, H, Martino, N, Garrett, JP, and Adam, AP. Interleukin-6 promotes a sustained loss of endothelial barrier function via Janus kinase-mediated Stat3 phosphorylation and De novo protein synthesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. (2018) 314:C589–c602. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00235.2017
128. Yanagihara, T, Tsubouchi, K, Gholiof, M, Chong, SG, Lipson, KE, Zhou, Q, et al. Connective-tissue growth factor contributes to Tgf-Β1-induced lung fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. (2022) 66:260–70. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0504OC
129. Wermuth, PJ, Li, Z, Mendoza, FA, and Jimenez, SA. Stimulation of transforming growth factor-Β1-induced endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tissue fibrosis by Endothelin-1 (Et-1): a novel Profibrotic effect of Et-1. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0161988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0161988
130. Bryant, AJ, Carrick, RP, McConaha, ME, Jones, BR, Shay, SD, Moore, CS, et al. Endothelial Hif signaling regulates pulmonary fibrosis-associated pulmonary hypertension. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2016) 310:L249–62. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00258.2015
131. Bickelhaupt, S, Erbel, C, Timke, C, Wirkner, U, Dadrich, M, Flechsig, P, et al. Effects of Ctgf blockade on attenuation and reversal of radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2017) 109:djw339. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djw339
132. Zhang, C, Ma, J, Zhang, X, Zhou, D, Cao, Z, Qiao, L, et al. Processing of angiocrine alarmin Il-1α in endothelial cells promotes lung and liver fibrosis. Int Immunopharmacol. (2024) 134:112176. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112176
133. Hartopo, AB, Arfian, N, Nakayama, K, Suzuki, Y, Yagi, K, and Emoto, N. Endothelial-derived Endothelin-1 promotes pulmonary vascular remodeling in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Physiol Res. (2018) 67:S185–97. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.933812
134. Milara, J, Roger, I, Montero, P, Artigues, E, Escrivá, J, and Cortijo, J. Il-11 system participates in pulmonary artery remodeling and hypertension in pulmonary fibrosis. Respir Res. (2022) 23:313. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-02241-0
Keywords: vascular endothelial cells, pulmonary capillary homeostasis, vascular remodeling, therapeutic strategies, pulmonary fibrosis
Citation: Zhou J, Xia X, An X, Liu D, Zhao H, Sun Z, Li W and Huang Q (2025) New perspectives on the progression of pulmonary fibrosis: the cascade from aberrant microvascular endothelial cell activation to fibrosis. Front. Med. 12:1639043. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1639043
Edited by:
Nunzia Caporarello, Mayo Clinic, United StatesReviewed by:
Bisheng Zhou, University of Illinois Chicago, United StatesAhmed A. Raslan, Boston University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Zhou, Xia, An, Liu, Zhao, Sun, Li and Huang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Qingsong Huang, aHVhbmdxaW5nc29uZ0BjZHV0Y20uZWR1LmNu; Weihong Li, bHdoQGNkdXRjbS5lZHUuY24=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Jie Zhou
Jie Zhou Xiuwen Xia
Xiuwen Xia Xing An1†
Xing An1† Danping Liu
Danping Liu Hongyi Zhao
Hongyi Zhao Weihong Li
Weihong Li