- 1Shenzhen Hospital (Fu Tian) of Guangzhou University of Chinese Medicine, Shenzhen, China
- 2Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Shenzhen, China
Introduction and objectives: Statins may effectively treat PH-COPD, but current guidelines do not endorse their use. This study aims to assess the comparative effectiveness and safety of Statins in adult patients with pulmonary hypertension associated with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (PH-COPD) through a systematic review and network meta-analysis.
Materials and methods: We searched 8 databases for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving Statins in individuals with PH-COPD from inception to July 1, 2024. We assessed bias using the ROB 2.0 tool and evaluated evidence quality with the CINeMA framework. We employed a Bayesian network meta-analysis approach to assess outcomes including pulmonary artery pressure, exercise tolerance, lung function, oxygenation parameters, inflammatory markers, and vasoactive substances. Using RStudio and other software, we generated forest plots, league tables, and SUCRA curves to evaluate both direct and indirect comparisons.
Results: We analyzed data from 41 RCTs involving 3,606 participants. Our analysis revealed that all 5 statins were effective in reducing Systolic Pulmonary Artery Pressure (sPAP) compared to standard treatment (ST). Rosuvastatin was the most effective, significantly lowering sPAP [MD = –8.8; (95%CI –11.68, −5.85)] and IL-6 (MD = -16.41; 95%Cl − 29.64, −3.04) and improving the 6-Minute Walk Distance (6MWD) (MD = 67.03; 95%Cl 2.77, 130.86). Atorvastatin 20 mg was the most effective in improving lung function, increasing PO2, reducing inflammatory markers such as TNF-α and hs-CRP, and lowering ET-1. Finally, Simvastatin 20 mg + ST was identified as the most effective regimen for reducing PCO2 and increasing NO levels.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that statins are more effective than standard treatment for adults with PH-COPD. Rosuvastatin is the most effective at reducing sPAP. It also improves the 6MWD and lowers IL-6 levels. Additionally, statins have significantly enhanced lung function, oxygenation parameters, and inflammatory markers in PH-COPD patients, with Atorvastatin showing the best performance in these areas.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/view/CRD42024573849, identifier CRD42024573849.
Introduction
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the third leading cause of death globally, following cardiovascular diseases and stroke, posing a significant public health challenge (1, 2). Over the past five decades, the prevalence of COPD has risen markedly, now affecting over 400 million people worldwide (1, 2). According to the World Economic Forum, by 2030, the global cost of COPD treatment will reach $50 trillion annually, surpassing the expenses associated with cardiovascular diseases (2, 3). Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is diagnosed in COPD patients (PH-COPD) when the mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP) is ≥25 mmHg. Severe PH-COPD is identified when mPAP is ≥35 mmHg or the cardiac index is below 2.0 L/min/m2.
Approximately half of COPD patients develop PH, which is associated with a poor prognosis. Without timely treatment, the average survival time for these patients is less than 5 years (4, 5). The 2021 Chinese guidelines for diagnosing and treating pulmonary hypertension classify PH-COPD as Group 3 PH (6). Recent studies have focused on targeted therapies for PH, with long-term oxygen therapy currently recommended for Group 3 PH. The 2021 COPD guidelines (7) suggest that treatment for mild to moderate pulmonary hypertension should focus on managing acute COPD exacerbations and improving hypoxemia and hypercapnia rather than using vasodilators or targeted drugs. Long-term oxygen therapy, administered for over 6 months, has improved survival rates in COPD patients and reduced mPAP, likely due to the reduction of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. However, it has not proven beneficial for patients with a baseline oxygen saturation above 89% (8). Currently, the standard clinical approach for PH-COPD patients involves routine supportive care. This includes maintaining clear airways, facilitating expectoration, using bronchodilators, managing infections, and improving microcirculation. However, searching for safe and effective treatments for these patients remains a critical challenge.
Statins are widely used in clinical settings to lower plasma cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Recent studies have revealed that statins also offer benefits beyond lipid reduction, such as reducing inflammation, stabilizing endothelial cells, preventing pulmonary vascular remodeling, and reducing lipid oxidation (9–16). Additionally, studies have suggested that statins may effectively treat PH-COPD, opening up new treatment possibilities (17). However, current guidelines do not endorse their use for this condition due to small sample sizes and a lack of direct comparisons among different statins. Furthermore, there is no comprehensive analysis comparing the efficacy of various statins. Therefore, further research and network meta-analyses are necessary to assess their potential benefits fully.
Materials and methods
This study follows the PRISMA 2020 guidelines and the PRISMA-NMA extension for network meta-analyses (18, 19). It has been registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024573849), as outlined in Appendix 1.
Search strategy
We conducted a comprehensive search across multiple databases, including CKNI, Wanfang, Weipu, CBM, PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and CENTRAL, to find randomized controlled trials (RCTs) on statins for PH-COPD patients, covering each database from inception to July 1, 2024. We also manually searched ClinicalTrials.gov and reviewed references from selected articles and related systematic reviews. Two reviewers independently selected the studies, resolving discrepancies with a third reviewer. The full search strategy is detailed in Appendix 2.
Eligibility criteria
Eligible RCTs focused on PH-COPD, including cases with cor pulmonale. Trials assessed any commercially available statin against a placebo, standard treatment (STs), or both in the control group. Control groups could include consistent additional medications, typically oxygen therapy, bronchodilators, expectorants, and antibiotics. Statin interventions had to last more than 4 weeks. Only RCTs published in peer-reviewed journals were included, excluding conference abstracts, duplicates, crossover designs, and non-English or non-Chinese publications.
Screening process
We imported the retrieved items from the databases into EndNote 20, eliminated duplicates, and integrated them with results from additional sources. The screening process comprised three stages. Initially, two reviewers independently assessed the articles based on their titles, including those with uncertain relevance. The selected articles were summarized in the second stage, and any disagreements were addressed through discussion and consultation with a third reviewer. In the final stage, articles with appropriate titles and abstracts were meticulously reviewed against the established inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Data extraction
For each eligible study, we systematically collected data using a pre-designed template, including the title, first author, publication date, study location, and methodology (randomization, blinding, allocation concealment, outcome data completeness, selective reporting). We also gathered demographic details (age, sample sizes, sex ratios, inclusion/exclusion criteria, COPD stages, baseline sPAP and intervention specifics; type of statin, dosage, treatment duration, control group interventions).
Our evaluation focused on six outcomes: pulmonary artery pressure, exercise tolerance, lung function, oxygenation parameters, inflammatory markers, and vasoactive substances. Pulmonary artery pressure (sPAP, mPAP), exercise tolerance (6-Minute Walk Distance (6MWD)), lung function (FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC), and Oxygenation Parameters (PO2, PCO2) were treated as primary outcomes, while inflammatory markers (TNF-a, hs-CRP, IL-6) and vasoactive substances (NO, ET-1) were secondary outcomes. We assessed the safety of interventions by reviewing the incidence of adverse events. Two reviewers conducted Data extraction independently, with any discrepancies resolved through consultation with a third reviewer.
Quality assessment of evidence
We assessed the risk of bias in the included trials using the Cochrane Risk of Bias tool (RoB 2.0) (20). This tool evaluates five key areas: randomization process, adherence to intended interventions, management of missing data, consistency of outcome measurements, and reporting of pre-specified outcomes. Proper procedures in these domains indicate a low risk of bias, while issues suggest a high risk. Two reviewers independently conducted the bias assessment, resolving discrepancies by consensus. We used the CINeMA (Confidence in Network Meta-Analysis) framework to evaluate the quality of evidence from our network meta-analysis. CINeMA examines the certainty of evidence across six domains: within-study bias, reporting bias, indirectness, imprecision, heterogeneity, and inconsistency. Each domain was meticulously assessed to ensure a thorough evaluation of the evidence (21, 23).
Methods for evidence synthesis
This network meta-analysis was conducted in RStudio using a Bayesian framework to integrate direct and indirect evidence, thereby enabling a comprehensive comparison and ranking of multiple treatments. We assessed transitivity by comparing clinical and methodological variables between studies providing direct and indirect evidence (24). Consistency within closed loops and the entire network was evaluated using node-splitting and design treatment interaction models (24–26). For both continuous and dichotomous outcomes, we employed random-effects models to calculate mean differences (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). We assessed heterogeneity using the I2 statistic, with values above 50% indicating significant heterogeneit (27). Indirect comparisons employed Bayesian network meta-analysis with Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) methods, involving 20,000 burn-ins and 50,000 iterations with a thinning interval of 10. Summary estimates for pairwise comparisons were derived, and treatment effects were ranked using Surface Under the Cumulative Ranking Curve (SUCRA) values based on posterior probabilities (28).
Results
Literature selection and study characteristics
We began with 449 records from our database search. After removing 191 duplicates, we reviewed 258 titles and abstracts, discarding 194 records. This left us with 64 full-text articles for a detailed assessment. Following our inclusion criteria, we identified 41 RCTs involving 3,606 patients as suitable for our study (see Figure 1). These trials were conducted in three countries, with sample sizes ranging from 16 to 80 participants and intervention durations between 1 and 12 months (see Table 1). From the publications reviewed, we identified five statin medications. Our network analysis then compared these five statins, all approved by regulatory authorities (see Appendix 3: Table S3.1).
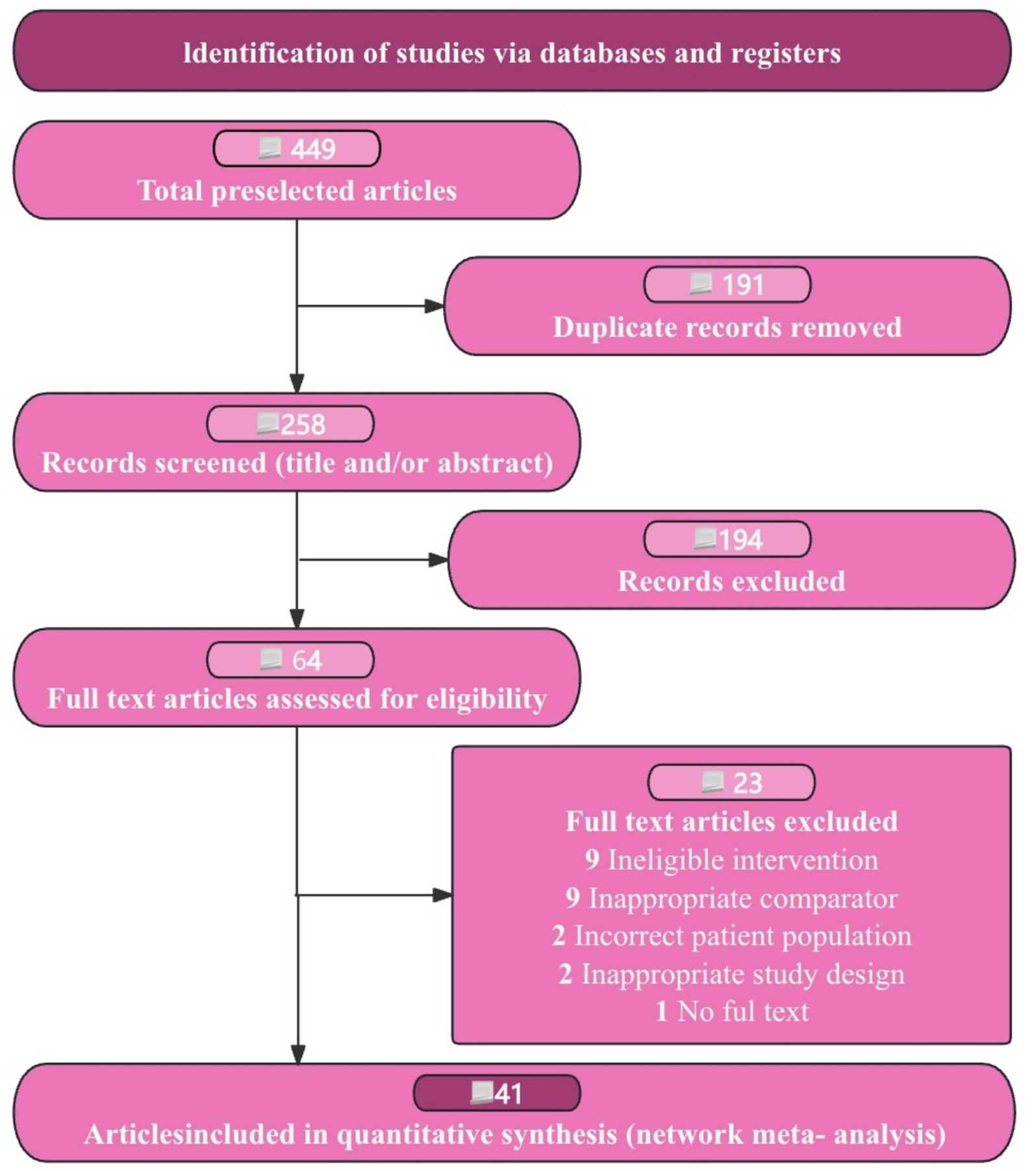
Figure 1. Flow diagram of preferred reporting items identified, included, and excluded for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA).
Risk of bias, certainty of evidence, and consistency
Appendix 4 provides an overview of the risk of bias for each trial. A major issue was the insufficient details regarding blinding methods for participants, researchers, and assessors, as well as the absence of data loss reports. Of the 41 trials reviewed, the summaries of those with a low risk of bias are: 37 studies (90.2%) for randomization, 35 studies (85.3%) for adherence to interventions, 38 studies (92.6%) for missing outcome data, 40 studies (97.5%) for outcome measurement, and 38 studies (92.6%) for reporting results. Overall, 5 studies (12.1%) exhibited a high risk of bias, and 2 (4.8%) raised concerns about potential bias.
Our evaluation of the consistency between direct and indirect evidence shows high agreement across all comparisons, illustrated in density and convergence plots (Appendices 6, 7). The I2 results indicate no significant heterogeneity within the network, with most comparisons showing low heterogeneity (Appendix 5). Using CINeMA, we found most pairwise comparisons had low confidence levels, with a few showing moderate to high confidence (Appendix 8). All networks complied with the transitivity principle, ensuring the validity of indirect comparisons (Appendix 8: Table S8.1). Additionally, the funnel plots showed no asymmetry (Appendix 9). This comprehensive analysis underscores the robustness and reliability of our findings.
Pulmonary artery pressure
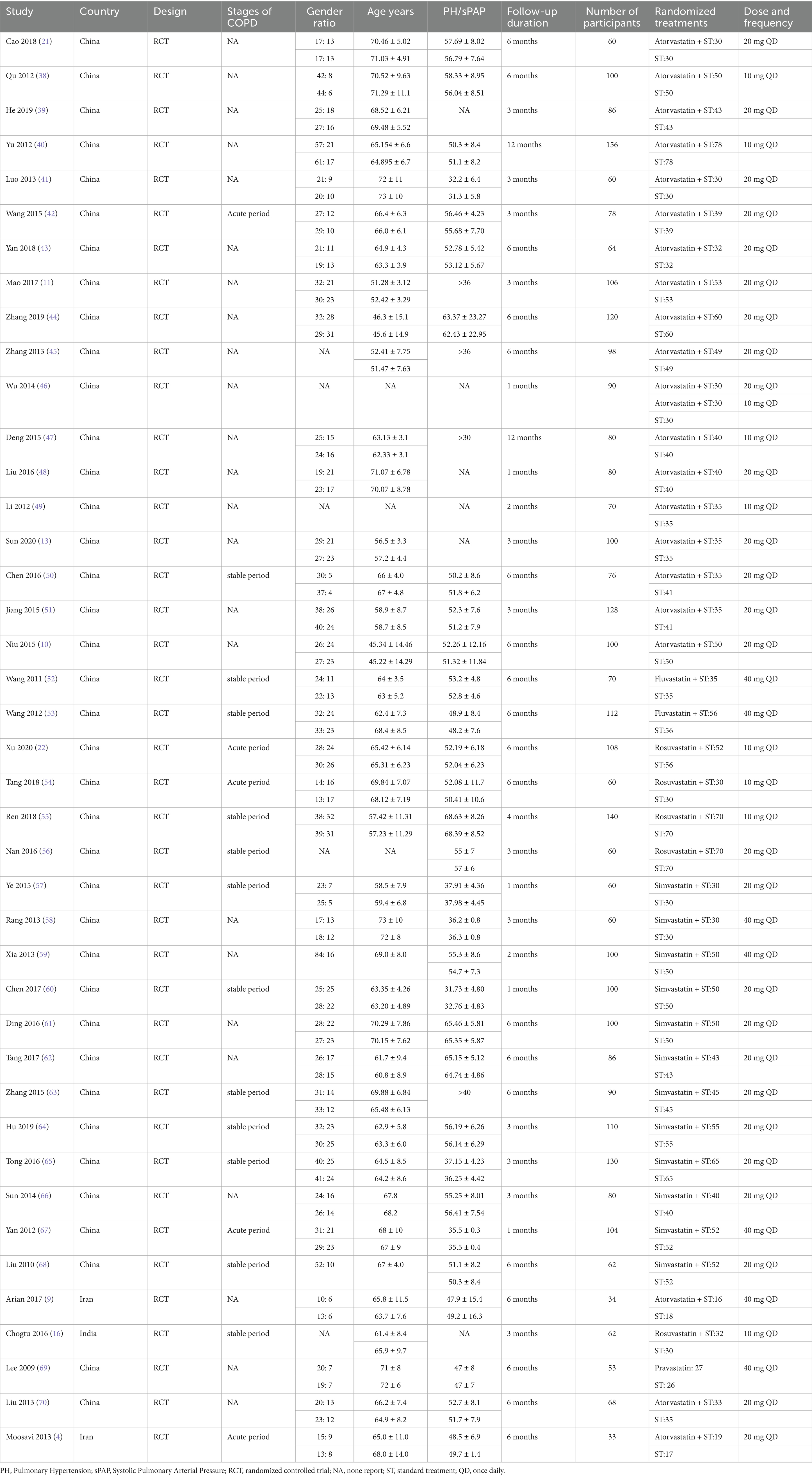
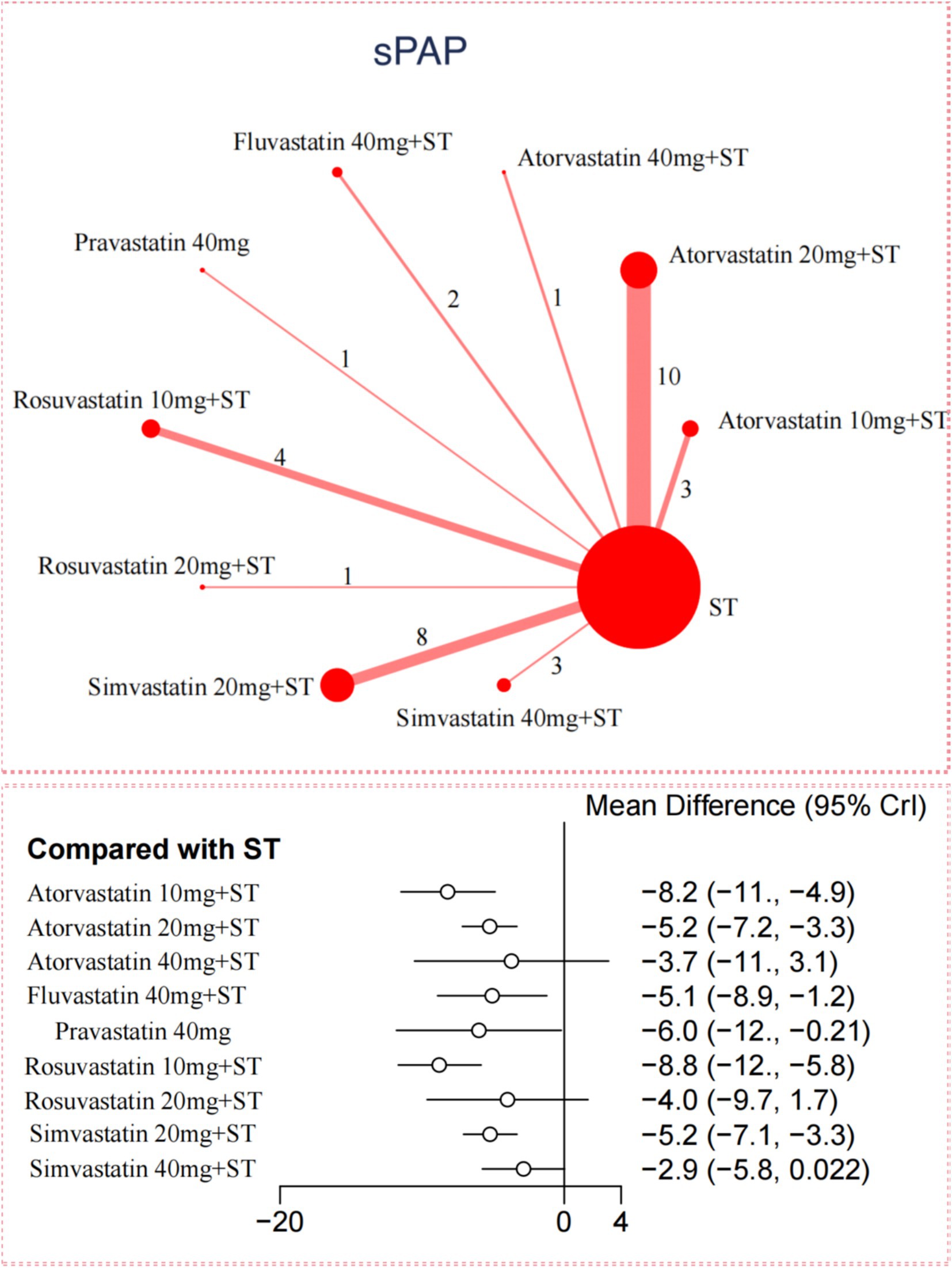
For sPAP reduction, the network meta-analysis included 33 trials with 2,816 participants. Compared to ST, all 5 statins significantly reduced sPAP levels in adults with PH-COPD (Figure 2). Rosuvastatin 10 mg combined with ST showed the most substantial reduction in sPAP [MD = –8.8; (95%CI –11.68 to −5.85); SUCRA 91.5%; high-confidence evidence], followed by Atorvastatin 10 mg with ST [MD = –8.21; (95%CI –11.49 to −4.87); SUCRA 85.8%; high-confidence evidence], and Pravastatin 40 mg [MD = –6.01; (95%CI –11.81 to −0.21); SUCRA 61%; low-confidence evidence]. Among the different statins, Rosuvastatin 10 mg combined with ST resulted in a significantly more significant reduction in sPAP compared to Atorvastatin 20 mg with ST, Simvastatin 20 mg with ST, and Simvastatin 40 mg with ST (Appendix 12: Table S12.1). According to CINeMA, the overall quality of evidence for sPAP was mainly moderate to high (Appendix 8: Table S8.2).
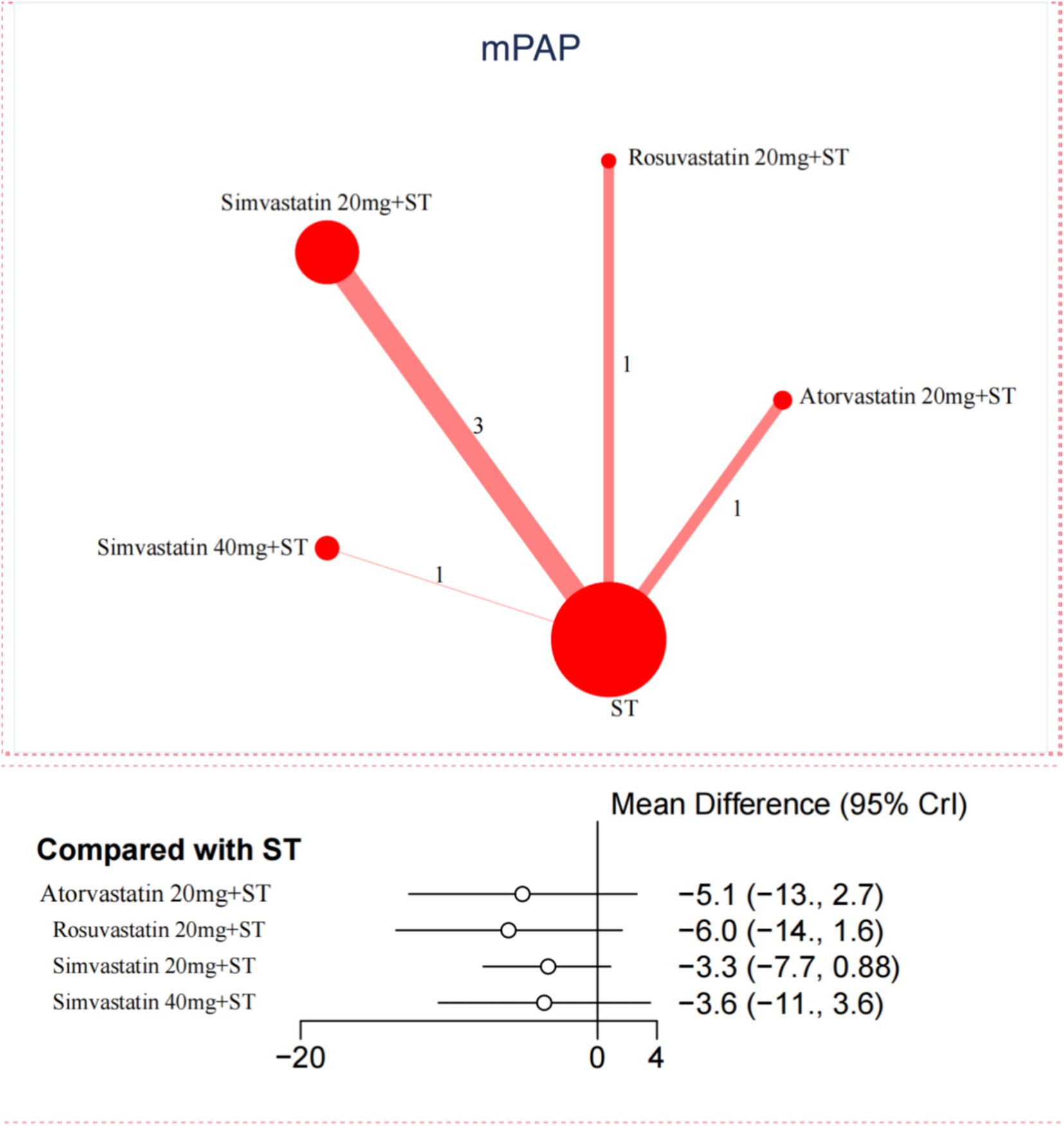
In contrast, for the reduction of mPAP, only 6 trials were included in the network meta-analysis. No significant differences were observed between statins and ST in reducing mPAP (Figure 3). Further details are provided in Appendix Figures S11.1, S11.2 and Appendix Tables S12.1, S12.2.
Exercise tolerance
Based on the 6MWD assessment, a network meta-analysis was conducted, incorporating 12 RCTs with 1,119 participants. This analysis confirmed the effectiveness of all 5 different doses of statins in comparing ST (Appendix 10: Supplementary Figure S10.1). Among these, Rosuvastatin 20 mg combined with ST was the most effective in enhancing 6MWD, with a MD of 67.03 (95%Cl 2.77 to 130.86) and a SUCRA of 87.9%. A detailed comparison of 6MWD results is provided in Appendix 11: Table S11.3 and Appendix 12: Table S12.3.
Lung function
The network meta-analysis examined the effects of statins on lung function through 21 studies each for FVC and FEV1. FVC studies involved 1,976 participants, while FEV1 studies included 1,868 participants. Eleven studies with 1,038 participants were also analyzed for the FEV1/FVC ratio.
Atorvastatin 20 mg combined with ST was found to be the most effective statin for improving FVC [MD = 0.4; (95%Cl 0.21 to 0.58); SUCRA 82.2%] (Appendix 10: Figure S10.2). Rosuvastatin 10 mg + ST and Simvastatin 20 mg + ST also significantly improved FVC compared to ST alone. In terms of enhancing FEV1, all 4 different doses of statins were effective. Pravastatin 40 mg led to the most substantial increase in FEV1 (MD = 0.56 (95%CI 0.27 to 0.85); SUCRA 98.7%). This was followed by Rosuvastatin 10 mg + ST (MD = 0.33; (95% CI 0.16 to 0.5); SUCRA 79.5%) and Atorvastatin 20 mg + ST (MD = 0.17; (95% CI 0.06 to 0.3); SUCRA 50.9%). For improving the FEV1/FVC ratio, Atorvastatin 20 mg + ST, Rosuvastatin 10 mg + ST, and Simvastatin 20 mg + ST all showed significant benefits over ST alone. The SUCRA data (Appendix 11: Tables S11.4–S11.6) and additional tables (Appendix 12: Table S12.4–S12.6) provide detailed comparisons of these outcomes.
Oxygenation parameters
The effect of statins on oxygenation parameters was assessed through measurements of PO2 and PCO2. The network meta-analysis revealed that Atorvastatin 20 mg + ST (MD = 11.81; 95%Cl 2.93 to 20.78), Atorvastatin 10 mg + ST (MD = 11.6; 95%Cl 2.78 to 20.43), and Simvastatin 20 mg + ST (MD = 7.51; 95%Cl 3.71 to 11.49) all led to significant increases in PO2 levels compared to ST alone. Only Simvastatin 20 mg + ST was significantly lower PCO2, with a MD of −9.59 (95%Cl − 16.65 to −2.5) (see Appendix Figures S10.5, S10.6, S11.7, S11.8 and Appendix Tables S11.7, S11.8, S12.7, S12.8).
Inflammatory markers
The effect of statins on inflammation was evaluated by measuring TNF-α, hs-CRP, and IL-6 levels. The network meta-analysis demonstrated that Atorvastatin 20 mg + ST and Simvastatin 20 mg + ST were effective in significantly reducing TNF-α, hs-CRP, and IL-6 compared to ST alone. Among the statins studied, Rosuvastatin 10 mg + ST was found to be the most effective in lowering IL-6, with a MD of −16.41 (95%Cl − 29.64 to −3.04) (refer to Supplementary Figures S10.7–S10.9 and Supplementary Tables S11.9–S11.11, S12.9–S12.11.
Vasoactive substances
The network meta-analysis assessed the effects of 5 different doses of statins on NO and ET-1 levels. The findings showed that Simvastatin 20 mg + ST, Atorvastatin 10 mg + ST, and Atorvastatin 20 mg + ST were significantly more effective than ST alone in increasing NO and decreasing ET-1. Specifically, Simvastatin 20 mg + ST was the most effective in raising NO levels, with a MD of 8.42 (95%Cl 3.66 to 12.86). Meanwhile, Atorvastatin 20 mg + ST was the most effective in lowering ET-1, with a MD of −9.82 (95%Cl − 13.03 to −6.6) (refer to Supplementary Figures S10.10, S10.11 and Supplementary Tables S11.12, S11.13, S12.12, S12.13).
Adverse events
Fourteen studies involving 947 patients monitored for adverse reactions during treatment. Of these, 7 studies reported no adverse effects, and 1 study noted that a few patients experienced nausea and vomiting. The remaining 6 studies detailed specific adverse reactions. All reported adverse events occurred in the Atorvastatin treatment groups. These included 4 cases of elevated liver enzymes, all at a dosage of 20 mg, which returned to normal after dose reduction. Additionally, 3 cases of upper abdominal discomfort did not affect the continuation of treatment, 4 cases of muscle pain, and 3 cases of gastrointestinal issues. Specific management measures for these reactions were not provided. Due to the limited data, a network meta-analysis could not be conducted for these adverse effects.
Sensitivity analyses and meta-regressions
To test the robustness of our results, we performed a sensitivity analysis by excluding one study at a time from each group. No single study was found to affect the outcomes significantly. As shown in Appendix 13, the sensitivity analysis results were consistent with the primary findings, confirming their robustness. We also conducted a meta-regression analysis to evaluate the impact of potential baseline effect modifiers on the primary outcomes. Factors such as the baseline sPAP, gender, and age were assessed. None of these factors significantly influenced the primary outcomes (Appendix 14).
Discussion
Principal findings
This network meta-analysis thoroughly assesses the efficacy and safety of 9 different statin doses for treating adults with PH-COPD. The statins evaluated include Atorvastatin, Fluvastatin, Pravastatin, Rosuvastatin, and Simvastatin. We analyzed data from 41 RCTs involving 3,606 participants, focusing on key outcomes such as pulmonary artery pressure, exercise tolerance, lung function, oxygenation parameters, inflammatory markers, and vasoactive substances. Our analysis revealed that all 5 statins were effective in reducing sPAP compared to ST. Rosuvastatin was the most effective, significantly lowering sPAP and IL-6 and improving the 6MWD. Rosuvastatin was particularly effective at 10 mg for the first two outcomes and at 20 mg for enhancing 6MWD. Atorvastatin at 20 mg was the most effective in improving lung function, increasing PO2, reducing inflammatory markers such as TNF-α and hs-CRP, and lowering ET-1. Although Pravastatin at 40 mg had the highest SUCRA score for improving FEV1, its findings were based on a single study, which limits its reliability. Finally, Simvastatin 20 mg + ST was identified as the most effective regimen for reducing PCO2 and increasing NO levels. A comprehensive summary of effect estimates for key outcomes, along with their corresponding CINeMA confidence ratings, is presented in Appendix 15 to facilitate interpretation and support clinical decision-making.
Comparisons with other studies
Earlier pairwise meta-analyses in COPD, sometimes including mixed study designs, suggested a modest reduction in pulmonary arterial pressure (PAP) with statins but without drug–dose differentiation. For example, Lu et al. (29) reported that statins reduced PH in COPD (SMD ≈ −0.71) without robust head-to-head ranking, while Wang et al. found sPAP decreased by ~4–5 mmHg versus placebo. Our NMA corroborates a class effect on sPAP and further ranks rosuvastatin as the most effective, with supportive RCT signals in PH-COPD cohorts (30). For exercise tolerance, prior meta-analyses in pulmonary vascular disease showed inconsistent 6MWD gains, particularly null in PAH-focused analyses (31, 32), whereas COPD-focused reviews suggested potential improvement (33). Our NMA aligns with the COPD signal and indicates rosuvastatin 20 mg confers the greatest 6MWD improvement, consistent with small RCTs/series reporting class-wide benefits in COPD-PH. By integrating more COPD-PH RCTs and modeling dose, we likely captured efficacy diluted in disease-agnostic analyses.
Beyond hemodynamics and exercise capacity, our NMA identifies drug–dose patterns across lung function, oxygenation, and inflammatory/vasoactive biomarkers. Atorvastatin 20 mg ranked highest for FEV₁, PO₂, PCO₂ reduction, TNF-α, hs-CRP, and ET-1 improvement; rosuvastatin 10 mg was optimal for IL-6 reduction and sPAP lowering, while 20 mg was needed for maximal 6MWD gain. Simvastatin 20 mg plus ST ranked best for NO increase. These findings expand on prior syntheses (33, 34) by separating drug–dose nodes and are biologically plausible given statins’ pleiotropy (35). The pravastatin 40 mg FEV₁ signal carried wide uncertainty (single study), consistent with the limited direct evidence base. Our dose–response modeling suggests rosuvastatin 10 mg is sufficient for sPAP and IL-6, whereas 20 mg may be required for exercise capacity; atorvastatin 20 mg appears optimal for composite pulmonary/inflammatory endpoints. These results complement mechanistic and observational studies supporting a protective association of statins against PH in COPD, while CINeMA ratings contextualize confidence across nodes (36, 37).
By focusing on PH-COPD and disentangling dose-specific effects, our work addresses limitations of earlier reviews that mixed etiologies, lacked dose resolution, or were underpowered for ranking. Compared with Lu et al.’s COPD-focused NMA (29), we incorporated more PH-COPD RCTs, modeled drug–dose networks across hemodynamic, functional, gas-exchange, inflammatory, and vasoactive outcomes, and applied CINeMA to guide clinical selection (e.g., rosuvastatin for hemodynamics/6MWD; atorvastatin for lung function/inflammation/ET-1). Clinically, our rankings suggest: rosuvastatin (10 mg for hemodynamics/IL-6; 20 mg for 6MWD) when prioritizing vascular and performance outcomes; atorvastatin 20 mg when lung function, oxygenation, and systemic inflammation are key targets; and simvastatin 20 mg when aiming to reduce PCO₂ and augment NO. The absence of new safety signals is consistent with prior COPD meta-analyses (34), though higher-dose nodes warrant future monitoring for myalgias and transaminase elevations.
Policy implications
This study evaluates the effectiveness of statins in treating adult patients with PH-COPD. Among the statins, Rosuvastatin was the most effective in reducing sPAP and improving 6MWD, especially at higher doses. Atorvastatin showed the greatest improvement in lung function. Statins also demonstrated anti-inflammatory effects, with notable efficacy from Atorvastatin 20 mg and Rosuvastatin 10 mg. Additionally, combining statins with standard treatments significantly improved PO2 and PCO2 levels compared to standard treatments alone. Unlike some targeted therapies, statins effectively reduce pulmonary artery pressure without compromising oxygen saturation, offering a promising approach for managing COPD. The potential benefits of statins in PH may be attributed to their pleiotropic effects beyond lipid-lowering. Statins can improve endothelial function by enhancing NO bioavailability, reducing oxidative stress, and inhibiting the expression of ET-1, a potent vasoconstrictor. They also exert anti-inflammatory effects by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6, which are implicated in pulmonary vascular remodeling. These mechanisms may collectively contribute to reduced pulmonary artery pressure and improved exercise capacity in PH-COPD patients.
While these pleiotropic mechanisms provide a biologically plausible explanation for the observed clinical benefits, they remain incompletely understood in the context of PH-COPD. Much of the mechanistic evidence is derived from preclinical studies or extrapolated from other disease models, such as atherosclerosis or left heart failure. It is still unclear to what extent individual statins differ in their endothelial, anti-inflammatory, or vasomodulatory effects, especially in patients with coexisting pulmonary and systemic vascular disease. Moreover, the relative contributions of lipid-independent versus lipid-lowering pathways remain debated. A more precise understanding of these mechanisms will require mechanistic studies directly targeting the pulmonary vasculature in COPD-related PH, ideally in human subjects.
However, given that most of the included studies were conducted in Chinese populations, caution is needed when applying these findings to other ethnic and geographic groups. Differences in genetic background, comorbidities, environmental exposures, and healthcare systems may influence treatment response. Future studies in more diverse populations are warranted to validate the generalizability and optimize the clinical application of statins in PH-COPD globally.
Strengths and limitations of this study
This study is the most comprehensive and current systematic review and network meta-analysis of statins for patients with PH-COPD. It compares the effectiveness of nearly all available statins in reducing pulmonary artery pressure and evaluates their impact on exercise tolerance, lung function, and blood gas levels (PO2, PCO2). The study also examines effects on inflammatory markers (TNF-α, hs-CRP, IL-6) and vasoactive substances (NO, ET-1), using the CINeMA quality assessment method to ensure result reliability.
Despite its strengths, this study has several limitations. Most included trials were conducted in China and published in Chinese, which may limit the generalizability of the findings to other populations and ethnic groups. Although five statins were analyzed, some (e.g., pravastatin and fluvastatin) were supported by only a small number of studies, reducing the reliability of efficacy estimates for these agents. Safety reporting was also inconsistent, with adverse events described in only 14 studies, mostly involving atorvastatin, making it difficult to draw firm conclusions regarding tolerability. Furthermore, some outcomes—especially secondary ones—were associated with wide confidence intervals and low certainty ratings according to the CINeMA assessment. Several studies carried a moderate risk of bias due to insufficient reporting of randomization or blinding procedures. Most trials relied on echocardiographic measurements rather than right heart catheterization, which may have compromised the precision of pulmonary pressure estimates.
These limitations highlight the need for future high-quality, multicenter trials conducted in diverse geographic and ethnic populations, with standardized outcome reporting, rigorous methodology, and adequate safety monitoring. Greater emphasis on underrepresented statins and the use of gold-standard diagnostic tools such as RHC will also be essential for strengthening the evidence base and informing clinical decision-making in PH-COPD management.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates that statins are more effective than standard treatment for adults with PH-COPD. Among the statins, Rosuvastatin is the most effective at reducing sPAP. It also improves the 6MWD and lowers IL-6 levels. Additionally, statins have significantly enhanced lung function, oxygenation parameters, and inflammatory markers in PH-COPD patients, with Atorvastatin showing the best performance in these areas. Further research with larger sample sizes and higher quality is needed to confirm these findings and evaluate the safety of different statins.
Data availability statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors, without undue reservation.
Author contributions
GX: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. RZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WH: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Software, Writing – review & editing. XD: Methodology, Writing – review & editing. WX: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was financially supported by Sanming Project of Medicine in Shenzhen (No. SZZYSM202211006).
Acknowledgments
We thank all authors of previous studies who kindly provided additional information and data of their studies for this meta-analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1640270/full#supplementary-material
References
1. GBD Chronic Respiratory Disease Collaborators. Prevalence and attributable health burden of chronic respiratory diseases, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet Respir Med. (2020) 8:585–96. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30105-3
2. Barnes, PJ. COPD 2020: new directions needed. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. (2020) 319:L884–6. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00473.2020
3. Bloom, DE, Cafiero, E, Jané-Llopiss, E, Abrahams-Gessel, S, Bloom, LR, Fathima, S, et al. The global economic burden of noncommunicable diseases. PGDA working papers (2012) 8712.
4. Moosavi, SA, Raji, H, Faghankhani, M, Yazdani, R, and Esmaeili, M. Evaluation of the effects of atorvastatin on the treatment of secondary pulmonary hypertension due to chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases: a randomized controlled trial. Iran Red Crescent Med J. (2013) 15:649–54. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.8267
5. Fan, CH, Li, MX, Li, M, Luo, GP, and Luo, ZC. Changes and clinical significance of serum CRP, IL-1β, and IL-17 levels in COPD patients. Chin J Clin Pulm Med. (2014) 19:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2014.05.009
6. Chinese Thoracic Society Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Vascular Disease Group; Chinese Association of Chest Physicians Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Vascular Disease Committee; National Cooperation Group on Prevention and Treatment of Pulmonary Embolism and Pulmonary Vascular Disease; National Pulmonary Hypertension Standardization Construction Project Expert Group. Chin Med J. (2021) 101:11–51. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20201008-02778
7. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (2021 revised edition). Chin J Tuberc Respir Dis. (2021) 44:170–205. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20210109-00031
8. Cassady, SJ, and Reed, RM. Pulmonary hypertension in COPD: a case study and review of the literature. Medicina (Kaunas). (2019) 55:432. doi: 10.3390/medicina55080432
9. Arian, A, Moghadam, SG, Kazemi, T, and Hajihosseini, M. The effects of statins on pulmonary artery pressure in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a randomized controlled trial. J Res Pharm Pract. (2017) 6:27–30. doi: 10.4103/2279-042X.200985
10. Niu, LN, Guo, SJ, Niu, LX, and Xiao, SX. Clinical observation of atorvastatin in treating COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Chin J Clin Pulm Med. (2015) 2114–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6663.2015.11.057
11. Mao, LJ, Li, Y, and Qiang, H. Effects of atorvastatin on serum inflammatory factors, pulmonary function, and right ventricular remodeling in COPD patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Drug Eval Res. (2017) 40:1323–6. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2017.09.026
12. He, J, Yan, L, Yang, Y, Jia, J, and Zhang, YM. Effects of atorvastatin on pulmonary function, endothelial function, and inflammatory factors in elderly COPD patients with secondary pulmonary arterial hypertension. Adv Biomed. (2020) 20:4.
13. Sun, Q. Application value of atorvastatin in the treatment of COPD with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Henan Med Res. (2020) 29:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-437X.2020.06.062
14. Zheng, SZ, Wang, C, and Xu, ZB. Efficacy of atorvastatin in the treatment of COPD with pulmonary arterial hypertension. North Pharm. (2016) 13:2.
15. Hu, ZW, Zhu, JJ, Lu, HG, Zheng, JH, and Qian, YL. Clinical observation of simvastatin in the treatment of COPD complicated with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Zhejiang Pract Med. (2019) 24:4.
16. Chogtu, B, Kuriachan, S, Magazine, R, Shetty, KR, Kamath, A, George, MM, et al. A prospective, randomized study: evaluation of the effect of rosuvastatin in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary hypertension. Indian J Pharmacol. (2016) 48:503–8. doi: 10.4103/0253-7613.190721
17. Cao, XL. Effect of atorvastatin on chronic inflammatory response in COPD with PH. Chin J Contin Educ. (2020) 12:3.
18. Page, MJ, McKenzie, JE, Bossuyt, PM, Boutron, I, Hoffmann, TC, Mulrow, CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
19. Hutton, B, Salanti, G, Caldwell, DM, Chaimani, A, Schmid, CH, Cameron, C, et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann Intern Med. (2015) 162:777–84. doi: 10.7326/M14-2385
20. Sterne, JAC, Savović, J, Page, MJ, Elbers, RG, Blencowe, NS, Boutron, I, et al. RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
21. Nikolakopoulou, A, Higgins, JPT, Papakonstantinou, T, Chaimani, A, del Giovane, C, Egger, M, et al. CINeMA: an approach for assessing confidence in the results of a network meta-analysis. PLoS Med. (2020) 17:e1003082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003082
22. Xu, WW. Efficacy observation of rosuvastatin calcium in treating acute exacerbation of COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Chin Mod Drug App. (2020) 14:2.
23. Papakonstantinou, T, Nikolakopoulou, A, Higgins, JPT, Egger, M, and Salanti, G. CINeMA: software for semiautomated assessment of the confidence in the results of network meta-analysis. Campbell Syst Rev. (2020) 16:e1080. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1080
24. Furukawa, TA, Salanti, G, Atkinson, LZ, Leucht, S, Ruhe, HG, Turner, EH, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of first-generation and second-generation antidepressants in the acute treatment of major depression: protocol for a network meta-analysis. BMJ Open. (2016) 6:e010919. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010919
25. Dias, S, Welton, NJ, Sutton, AJ, Caldwell, DM, Lu, G, and Ades, AE. Evidence synthesis for decision making 4: inconsistency in networks of evidence based on randomized controlled trials. Med Decis Mak. (2013) 33:641–56. doi: 10.1177/0272989X12455847
26. Higgins, JP, Jackson, D, Barrett, JK, Lu, G, Ades, AE, and White, IR. Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies. Res Synth Methods. (2012) 3:98–110. doi: 10.1002/jrsm.1044
27. Higgins, JP, Thompson, SG, Deeks, JJ, and Altman, DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ. (2003) 327:557–60. doi: 10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
28. Salanti, G, Ades, AE, and Ioannidis, JP. Graphical methods and numerical summaries for presenting results from multiple-treatment meta-analysis: an overview and tutorial. J Clin Epidemiol. (2011) 64:163–71. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2010.03.016
29. Lu, Y, Chang, R, Yao, J, Xu, X, Teng, Y, and Cheng, N. Effectiveness of long-term using statins in COPD - a network meta-analysis. Respir Res. (2019) 20:17. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0984-3
30. Wang, G, Shang, W, Ren, Y, Liu, S, Ren, X, Wei, S, et al. Benefits of statins in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with pulmonary hypertension: a meta-analysis. Eur J Intern Med. (2019) 70:39–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ejim.2019.09.009
31. Wang, L, Qu, M, Chen, Y, Zhou, Y, and Wan, Z. Statins have no additional benefit for pulmonary hypertension: a Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. PLoS One. (2016) 11:e0168101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0168101
32. Rysz-Górzynska, M, Gluba-Brzózka, A, Sahebkar, A, Serban, MC, Mikhailidis, DP, Ursoniu, S, et al. Efficacy of statin therapy in pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review and Meta-analysis. Sci Rep. (2016) 6:30060. doi: 10.1038/srep30060
33. Chen, X, Hu, F, Chai, F, and Chen, X. Effect of statins on pulmonary function in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Thorac Dis. (2023) 15:3944–52. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1042
34. Walsh, A, Perrem, L, Khashan, AS, Henry, MT, and Ni Chroinin, M. Statins versus placebo for people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2019) 7:CD011959. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011959.pub2
35. Neukamm, A, Høiseth, AD, Einvik, G, Lehmann, S, Hagve, TA, Søyseth, V, et al. Rosuvastatin treatment in stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (RODEO): a randomized controlled trial. J Intern Med. (2015) 278:59–67. doi: 10.1111/joim.12337
36. Young, RP, Hopkins, R, and Eaton, TE. Pharmacological actions of statins: potential utility in COPD. Eur Respir Rev. (2009) 18:222–32. doi: 10.1183/09059180.00005309
37. Wu, WT, and Chen, CY. Protective effect of statins on pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients: a Nationwide retrospective, matched cohort study. Sci Rep. (2020) 10:3104. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-59828-0
38. Qu, CH, Yu, FX, Yang, HY, Fan, MZ, and Kang, LJ. Effect of atorvastatin on hypoxic pulmonary artery pressure. Southeast Def Med. (2012) 14:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-271X.2012.02.009
39. He, J, Yan, L, Yang, Y, Jia, J, and Zhang, YM. Impact of atorvastatin on lung function, endothelial function, and inflammatory markers in elderly COPD patients with secondary pulmonary hypertension. Adv Biomed Prog. (2020) 20:4.
40. Yu, FX, Yang, HY, Fan, MZ, Kang, LJ, Qu, CH, Wang, SJ, et al. Clinical study of atorvastatin in patients with COPD and pulmonary hypertension. Chin J Clin Pract: Electron Ed. (2012) 6:6. doi: 10.3877/cma.j.issn.1674-0785.2012.05.084
41. Luo, XB, Zou, HL, Xie, CD, Peng, WP, and Li, XL. Effect of atorvastatin on peripheral ROCK2 kinase activity and pulmonary artery pressure in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Adv Biomed Prog. (2013) 13:6113–6115.
42. Wang, JD, and Han, M. Impact of atorvastatin on chronic inflammatory response in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Intern Med. (2015) 1:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9057.2015.01.007
43. Yan, J. Study on the effect of atorvastatin on serum C-reactive protein levels and pulmonary artery systolic pressure in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. J Pract Cardio Cerebrovasc Dis. (2018) 38:90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2018.z1.090
44. Zhang, J, and Tian, Y. Observational study on the effect of atorvastatin in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Rational Drug Use J. (2019) 4:2
45. Zhang, YP, and Zhong, HD. Efficacy of atorvastatin calcium in patients with COPD and pulmonary hypertension induced right ventricular remodeling. Shanghai Pharm. (2015) 36:4.
46. Wu, LP, Liang, FB, Wang, HQ, Zhang, HW, and Zhang, JY. Effect of atorvastatin calcium on endothelial factors in COPD patients with secondary pulmonary hypertension. Clin Rational Drug Use J. (2014) 7:2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3296.2014.31.030
47. Deng, XF. Clinical efficacy observation of atorvastatin calcium in treating COPD with secondary pulmonary hypertension. Mod Diagn Treat. (2015) 26:2.
48. Liu, YJ, Zhang, YZ, Xia, RR, and Ye, F. Effect of atorvastatin combined with conventional therapy on VEGF levels and lung function in elderly COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension. J Pract Pharm Clin. (2016) 19:3. doi: 10.14053/j.cnki.ppcr.201609013
49. Li, YK. Clinical application and mechanism of atorvastatin in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Chin Comm Med: Med Spec. (2012) 14:1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-614x.2012.25.045
50. Chen, D, Wang, BY, and Chen, D. Clinical effect observation of atorvastatin in treating COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Rational Drug Use J. (2016) 9:1–2. doi: 10.15887/j.cnki.13-1389/r.2016.05.001
51. Jiang, WS, Xu, JW, and Chen, L. Efficacy observation of atorvastatin in treating COPD-induced pulmonary hypertension. J Pract Cardio Cerebrovasc Dis. (2015) 23:151–152.
52. Wang, LL, Lei, MJ, Tu, YP, and Wu, S. Therapeutic effect of Fluvastatin on COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension. Chin J Geriatr. (2011) 31:2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2011.09.083
53. Wang, W, and Lin, JQ. Fluvastatin as adjuvant therapy in 56 cases of COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Med Herald. (2012) 31:3. doi: 10.3870/yydb.2012.09.019
54. Tang, C, Xi, WW, and Li, S. Rosuvastatin calcium in the treatment of acute exacerbation of COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Chin Clin Res. (2018) 31:4.
55. Ren, RH, Wang, J, Liang, J, Lei, JH, and Liu, ZZ. Clinical effectiveness and safety of rosuvastatin in treating COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Int J Resp. (2018) 38:4. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-436X.2018.22.010
56. Nan, JL, He, WS, Han, XF, Fan, Y, and Wang, CP. Clinical observation and mechanism study of rosuvastatin in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Chin Geriatr Health Med. (2016) 14:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4860.2016.01.022
57. Ye, Q, and Kuang, J. Effect of low-dose simvastatin on COPD with pulmonary hypertension. J Med Res. (2015) 44:4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-548X.2015.01.031
58. Ran, QC, and Xia, BH. Effect of simvastatin on endothelial function and pulmonary artery pressure in COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Rational Drug Use J. (2013) 6:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-3296.2013.04.004
59. Xia, XQ, Yuan, XL, Luo, HZ, Miao, JY, Lin, YP, and Guo, WH. Observational study on the therapeutic effect of simvastatin in COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension. J Pract Cardio Cerebrovasc Dis. (2013) 21:2. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5971.2013.04.040
60. Chen, DG, and Du, F. Impact of simvastatin on serum inflammatory factors, pulmonary hypertension, and lung function in COPD patients during acute exacerbation. Chin J Geriatr. (2017). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2017.14.064
61. Ding, Y. Observational study on the efficacy of simvastatin in treating COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Today Pharm. (2016):3.
62. Tang, C. Effect of simvastatin treatment on cardio-pulmonary function and inflammatory cytokines in COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension. Mod Chin-West Med. (2017) 26:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-8849.2017.08.018
63. Zhang, RH, Lin, Q, and Wang, XY. Effect of simvastatin on cytokine levels and lung function in elderly COPD patients with pulmonary hypertension. Chin J Geriatr. (2015) 35:7105–6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2015.24.063
64. Hu, ZW, Zhu, JJ, Lu, HG, Zheng, JH, and Qian, YL. Clinical observation of simvastatin in treating COPD complicated with pulmonary hypertension. Zhejiang Pract Med. (2019) 24:4.
65. Tong, XY. Study on the efficacy of simvastatin in treating COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Clin Med Res Pract. (2016) 1:2.
66. Sun, J, and Ding, YP. Efficacy observation of simvastatin in treating COPD with pulmonary hypertension. Hainan Med. (2014) 25:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2014.02.0063
67. Yan, XY, and Yu, CL. Clinical research on simvastatin in treating COPD. Hebei Med. (2010) 32:3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2010.21.024
68. Liu, RL, Yang, XP, Li, F, and Liu, WX. Observation on simvastatin in treating obstructive lung disease with pulmonary hypertension. Chin Ethnic Med. (2011) 20:1. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-8517.2011.04.061
69. Lee, TM, Chen, CC, Shen, HN, and Chang, NC. Effects of pravastatin on functional capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and pulmonary hypertension. Clin Sci (Lond). (2009) 116:497–505. doi: 10.1042/CS20080241
Keywords: statins, pulmonary hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, network meta-analysis, systematic review
Citation: Xu G, Zhang R, Huang W, Du X and Xu W (2025) Comparative effectiveness of statins for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with pulmonary hypertension: systematic review and network meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1640270. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1640270
Edited by:
Mohan Giri, First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University, ChinaReviewed by:
Natalia Eduarda Furlan, São Paulo State University, BrazilSmitesh Padte, WellSpan Health, United States
Copyright © 2025 Xu, Zhang, Huang, Du and Xu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xuelian Du, am5keGxAaG90bWFpbC5jb20=; Weifang Xu, MjQ4NzMxNzAwNkBxcS5jb20=
†These authors have contributed equally to this work and share first authorship
 Guobo Xu1†
Guobo Xu1† Rui Zhang
Rui Zhang Wenrui Huang
Wenrui Huang Xuelian Du
Xuelian Du Weifang Xu
Weifang Xu