- Department of Radiology, Xiamen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Xiamen, China
Objective: To explore the relationship between sarcopenia and bone mineral density (BMD) in middle-aged and elderly male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), construct a prediction model for sarcopenia based on dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), and evaluate its clinical value.
Methods: A total of 523 middle-aged and elderly male patients with T2DM in the hospital from January 2021 to December 2024 were selected and divided into the training set (366 cases) and the validation set (157 cases) at a ratio of 7:3. The BMD T-value was measured by DXA, and clinical data were collected. A prediction model was constructed using multivariate logistic regression in the training set, and the model efficacy was evaluated by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration curve, and decision curve analysis (DCA).
Results: The incidence of sarcopenia was 27.05% (99/366) in the training set and 28.02% (44/157) in the validation set. Multivariate analysis showed that age, HbA1c, and HOMA-IR were independent risk factors for sarcopenia, while the lumbar L1–L4 T-value, and femoral neck T-value were independent protective factors for sarcopenia (p < 0.05). The C-index of the nomogram model were 0.773 (in the training set) and 0.750 (in the validation set) respectively. The calibration curve showed good agreement between predicted and actual values, and the Hosmer–Lemeshow test were significant (all p > 0.05). The ROC curve showed the area under the curve (AUC) of the nomogram model for predicting the risk of sarcopenia was 0.773 (95% CI: 0.652–0.895) and 0.750 (95% CI, 0.686–0.814) in the training set and the validation set, respectively. The sensitivity and specificity were 0.714, 0.887 and 0.688, 0.796, respectively.
Conclusion: The prediction model constructed based on DXA can effectively predict the risk of sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly male patients with T2DM, providing a basis for clinical early screening and intervention.
Introduction
With the intensification of population aging, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) has become a significant global public health issue (1). Epidemiological studies have shown that the prevalence of T2DM in the middle-aged and elderly population reaches 15–20%. It is often accompanied by sarcopenia and a decrease in bone mineral density (BMD), which seriously affects the quality of life (2). Sarcopenia is characterized by a reduction in muscle mass, a decline in strength, and a decrease in function, while a decrease in BMD is the core marker of osteoporosis. These two conditions often co-exist in middle-aged and elderly T2DM patients, resulting in an “imbalance in muscle-bone interaction” (3). Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), as the gold standard for evaluating muscle mass and BMD, can accurately measure the appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) and the BMD of the lumbar spine, femoral neck, and other parts.
Studies have indicated that sarcopenia and a decrease in BMD in T2DM patients may share pathological mechanisms such as insulin resistance, chronic inflammation, and oxidative stress: insulin resistance inhibits muscle protein synthesis and interferes with the function of osteoblasts; hyperglycemia induces the accumulation of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), which damages the microstructures of muscle and bone; persistent low-grade inflammation [such as an increase in interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α)] accelerates muscle breakdown and bone resorption (4, 5). However, current studies on middle-aged and elderly male T2DM patients have limitations: the quantitative association between sarcopenia and BMD lacks large-sample support, and a prediction model for sarcopenia based on DXA indicators has not been established (6). As a clinical decision-making tool, a prediction model can integrate multi-dimensional indicators to achieve early quantitative assessment of the risk of sarcopenia. However, the application of previous prediction models that combine muscle mass, BMD, and metabolic indicators in T2DM patients is still in the exploratory stage.
In this study, DXA was used to measure the musculoskeletal indicators of middle-aged and elderly male T2DM patients. The correlation between them was analyzed, and a nomogram prediction model was constructed to provide a basis for early clinical screening and personalized intervention.
Methods
Study subjects
A total of 523 middle-aged and elderly male patients with T2DM in Xiamen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine from January 2021 to December 2024 were selected as the research subjects. Patients were randomly allocated to the training set (70%, n = 366) and validation set (30%, n = 157) using computer-generated random numbers (SPSS 26.0, IBM Corporation, United States). The randomization ensured comparable baseline characteristics between the two sets. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Xiamen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine (No. TCM10-1053). This study adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Inclusion criteria: (1) meeting the diagnostic criteria for type 2 diabetes (7), (2) age ≥45 years, (3) both the patients and their families signed the informed consent forms.
Exclusion criteria: (1) complicated with other endocrine diseases, (2) having severe heart, lung, liver, or kidney function disorders, (3) recently using drugs that affect bone metabolism or muscle mass, (4) having a history of malignant tumors.
Collection of baseline data
The patients’ basic information was recorded, including age, height, and weight, and the body mass index (BMI) was calculated. Smoking history and drinking history were also recorded. The detection of diabetes-related indicators included the duration of diabetes, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), 2-h postprandial glucose (2hPG), hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), and the homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR). For the diagnosis of sarcopenia, the appendicular skeletal muscle (ASM) was measured using a dual-energy X-ray absorptiometer, and the appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI) was calculated. Grip strength was measured using a dynamometer, and gait speed was evaluated through a 4-meter walking test. The diagnosis of sarcopenia was based on the 2019 criteria of the Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia (AWGS) (8). BMD T-values of the lumbar spine (L1–L4) and the femoral neck were measured by DXA. In addition, total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and serum creatinine (SCr) were detected, and the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was estimated.
Grouping method
Patients’ BMD and skeletal muscle mass (SMM) were measured using dual-energy DXA. BMD was expressed in g/cm2, and SMM was expressed in kg. Sarcopenia diagnosis strictly followed AWGS 2019 criteria requiring: (1) Low muscle mass (ASMI <7.0 kg/m2 by DXA) AND (2) Either low muscle strength (grip strength <28 kg) OR low physical performance (gait speed <1.0 m/s) (8). All measurements were performed by trained staff using standardized protocols with daily quality control checks.
Statistical analysis
Data were analyzed using SPSS 26.0 (IBM Corporation, United States) and R4.5.1 (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Austria). Continuous variables conforming to the normal distribution were expressed as x̄ ± s; otherwise, they were expressed as M (Q₁, Q₃). Categorical variables were expressed as n (%). Patients were divided into the training set and the validation set at a ratio of 7:3. Univariate analysis was performed using the t-test, Mann–Whitney U test, or χ2 test, and indicators with p < 0.05 were selected and included in the multivariate logistic regression. Multivariate analysis excluded diagnostic components of sarcopenia (ASM/ASMMI), grip strength and gait speed to avoid tautological prediction and collinearity. The nomogram model was constructed using the “rms” package in R language. The model efficacy was evaluated through the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve (area under the curve, AUC), calibration curve, C-index, and decision curve analysis (DCA). p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Comparison of baseline data between the training set and the validation set
The incidence of sarcopenia in the training set was 27.05% (99/366), and that in the validation set was 28.02% (44/157). There were no statistically significant differences in baseline data such as age, gender, smoking history, and BMI between the training set and the validation set (p > 0.05), indicating that the two groups had good balance and could be used for subsequent analysis (Table 1).
Univariate analysis of influencing factors for sarcopenia
Univariate analysis revealed that among the patients in the training set, there were statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) in age, HbA1c, HOMA-IR, lumbar L1–L4 T-value, ASM, ASMI, and disease duration between the sarcopenia group and the non-sarcopenia group (Table 2).
Multivariate logistic regression analysis of influencing factors for sarcopenia
Sarcopenia was used as the dependent variable, and the factors with statistical significance in the univariate analysis were used as independent variables for multivariate logistic regression analysis (the variable assignments were shown in Table 3). Multivariate analysis excluded diagnostic components of sarcopenia (ASM/ASMMI), grip strength and gait speed to avoid tautological prediction and collinearity. The results showed that age, HbA1c, and HOMA-IR were independent risk factors influencing sarcopenia (p < 0.05), while the lumbar spine L1–L4 T-value, and femoral neck T-value were independent protective factors influencing sarcopenia (p < 0.05) (Table 4).
Establishment of a prediction model for sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes mellitus
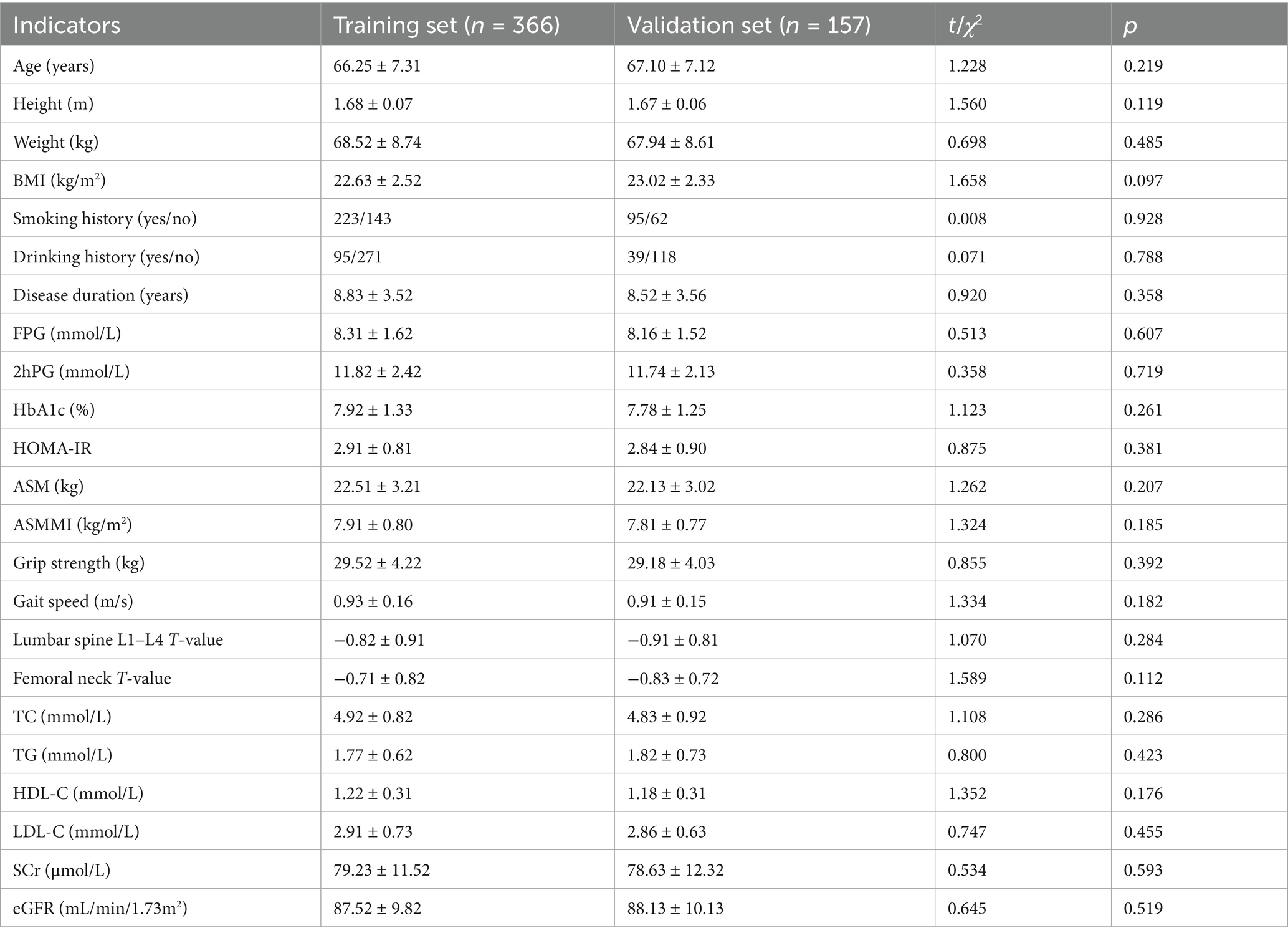
Based on the influencing factors determined by multivariate logistic regression analysis, a nomogram model for predicting sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly men with T2DM was constructed. In this model, scores were assigned to each independent influencing factor, and the probability of sarcopenia was predicted by calculating the total score. The higher the total score, the higher the probability of predicting sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes mellitus (Figure 1).
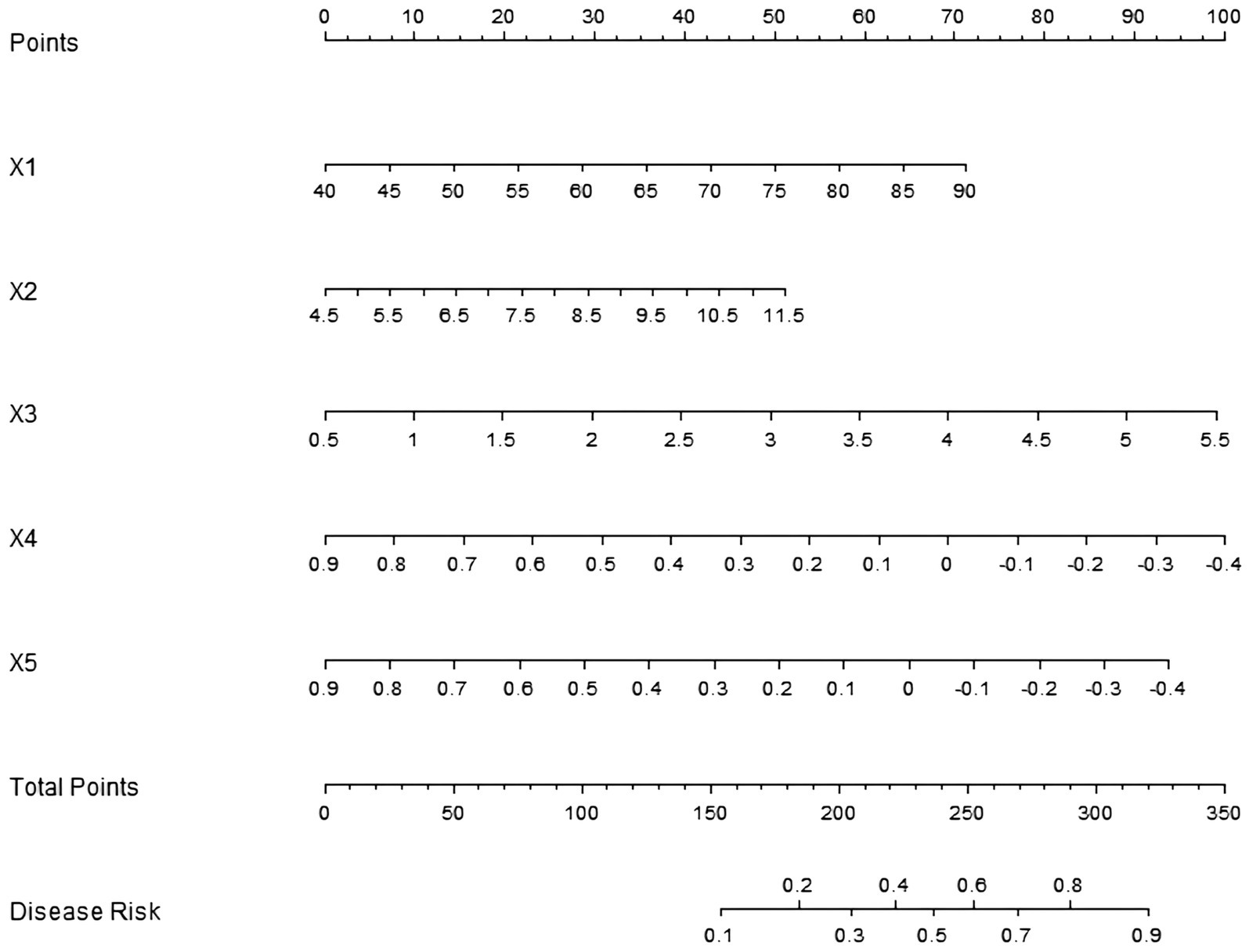
Figure 1. Establishment of a prediction model for sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly male patients with T2DM. X1: age; X2: HbA1c; X3: HOMA-IR; X4: lumbar spine L1–L4 T-value; X5: femoral neck T-value.
Evaluation and validation of the prediction model for sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly male patients with T2DM
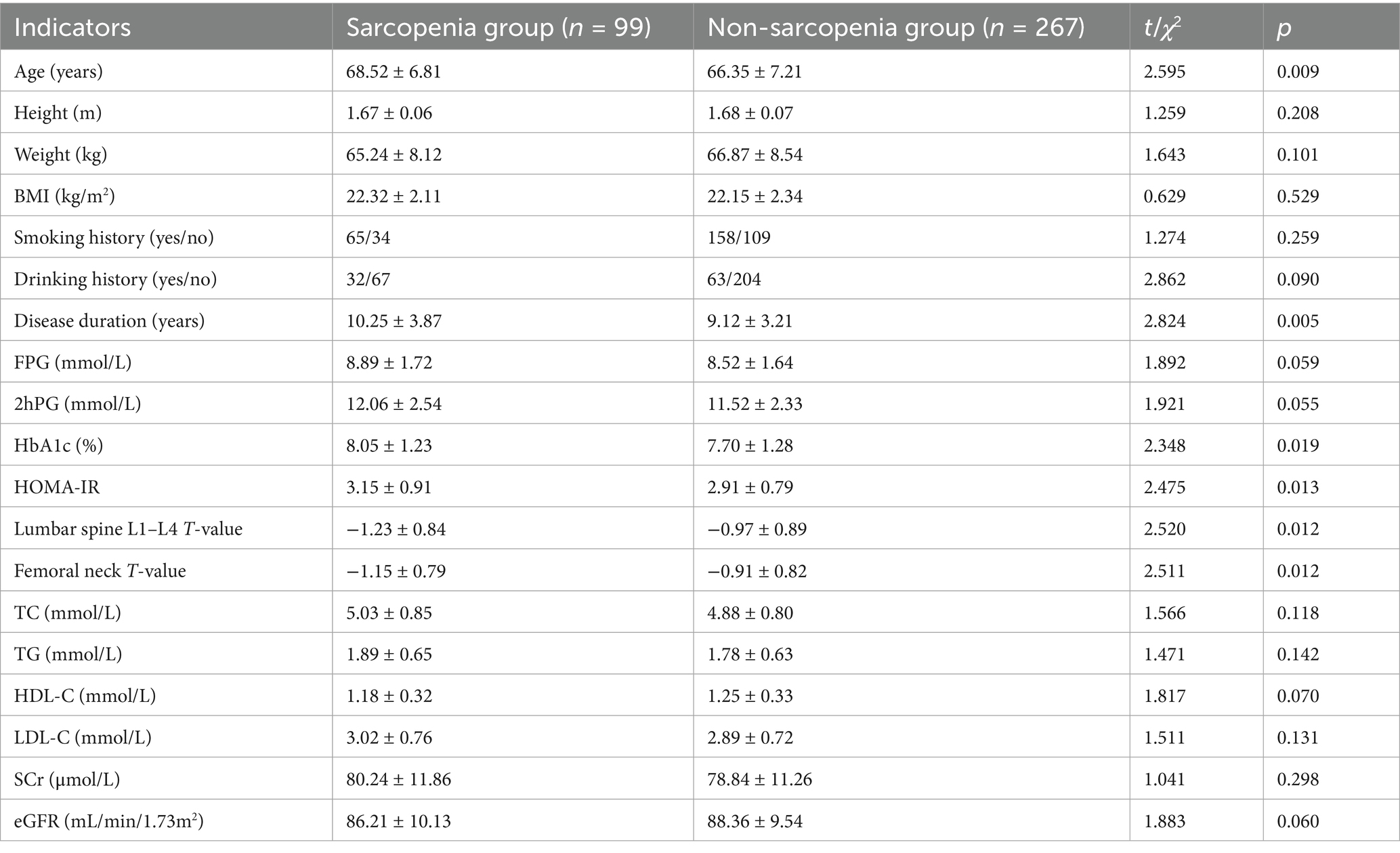
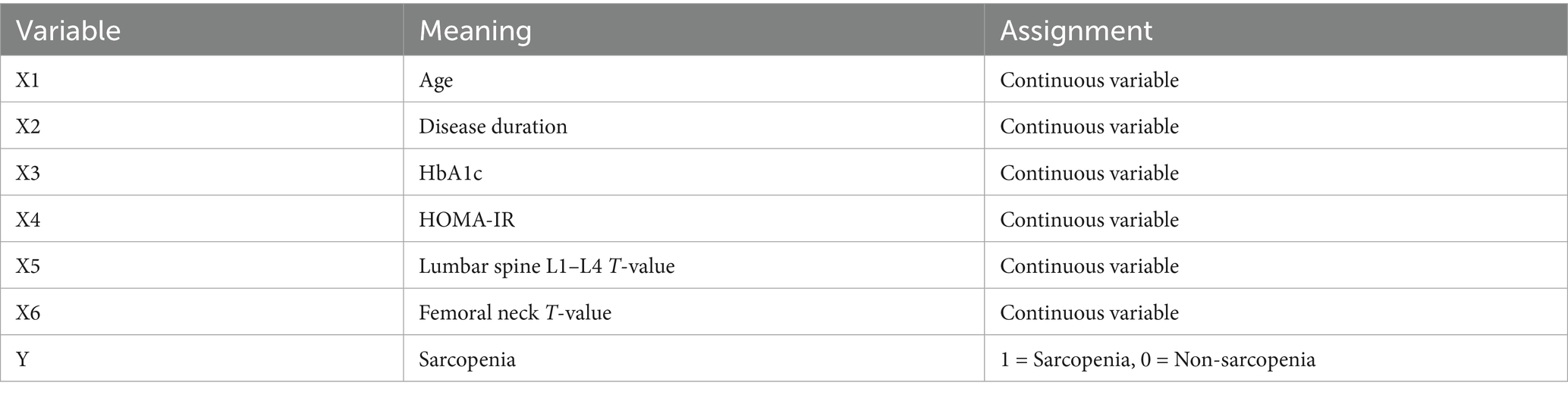
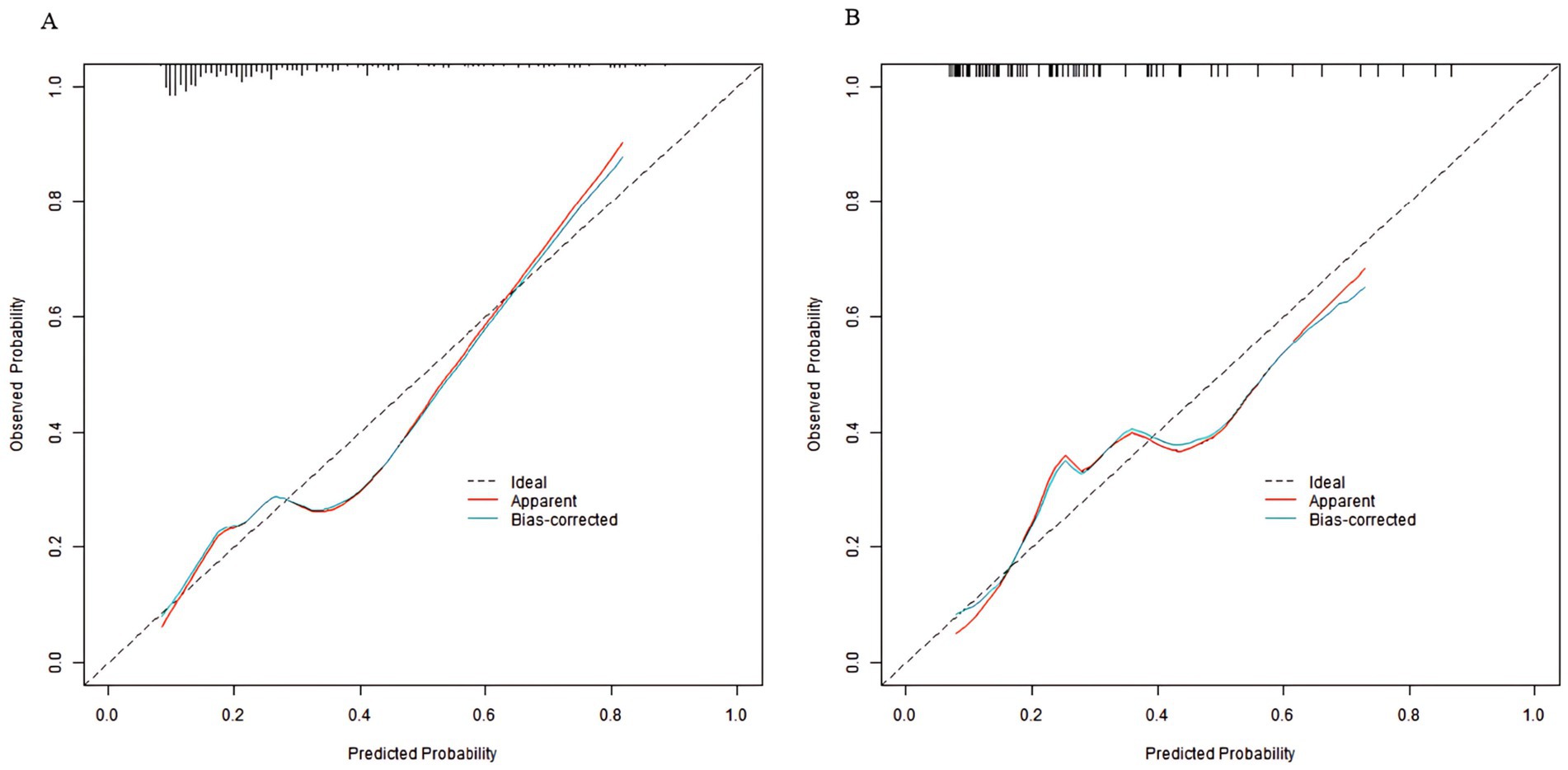
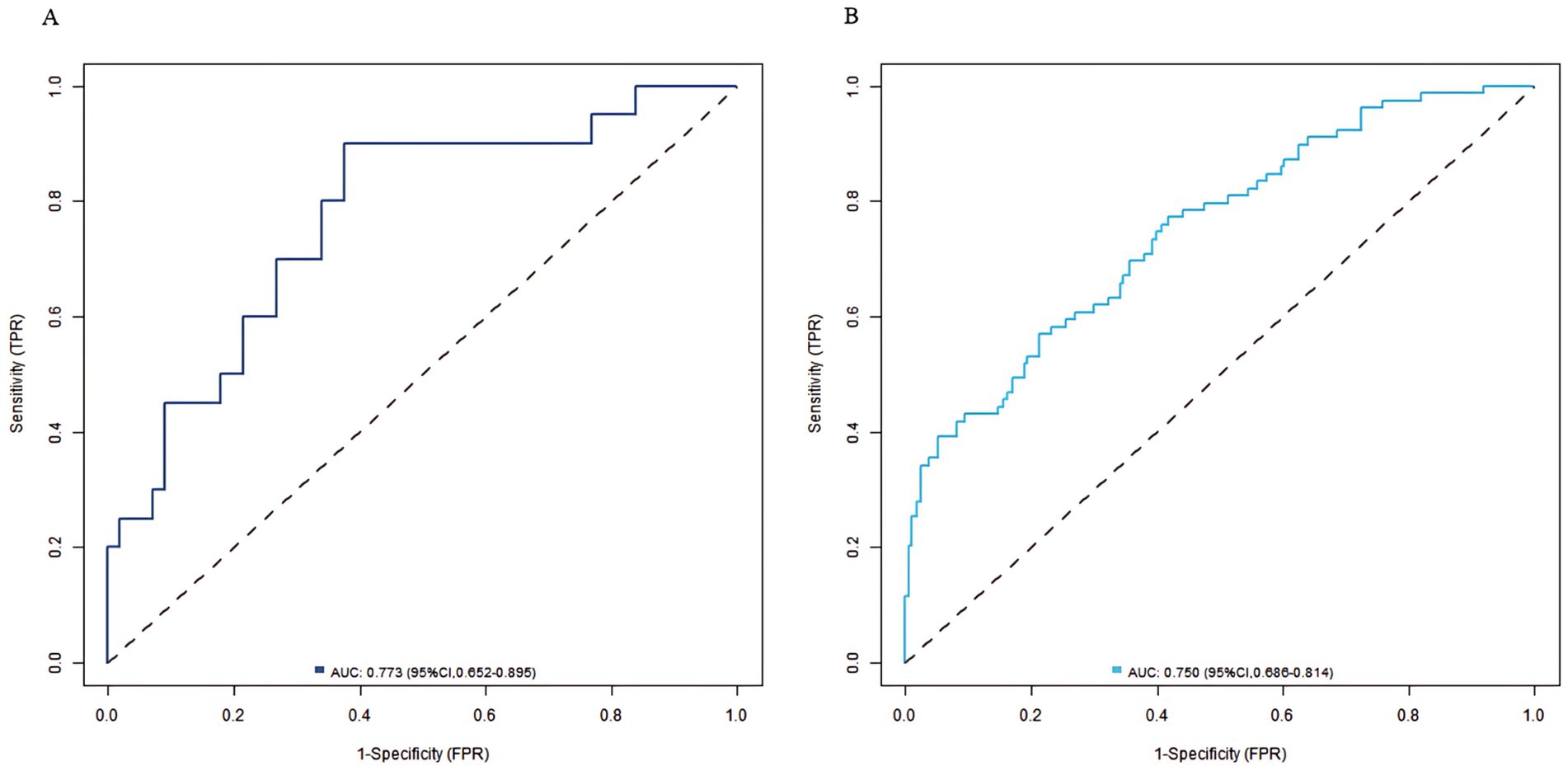
In the training set and validation set, the C-index of the nomogram model was 0.773 and 0.750, respectively. The calibration curve showed a good agreement between the predicted values and the actual values. The results of the Hosmer–Lemeshow test were χ2 = 10.955 (p = 0.204) and χ2 = 8.139 (p = 0.420), respectively. The ROC curves showed that in the training set and validation set, the AUCs of the nomogram model were 0.773 (95% CI: 0.652–0.895) and 0.750 (95% CI: 0.686–0.814), respectively. The sensitivity and specificity were 0.714, 0.887 and 0.688, 0.796, respectively. The calibration curves were shown in Figure 2, and the ROC curves were shown in Figure 3.
Decision curve analysis of the prediction model for sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes mellitus
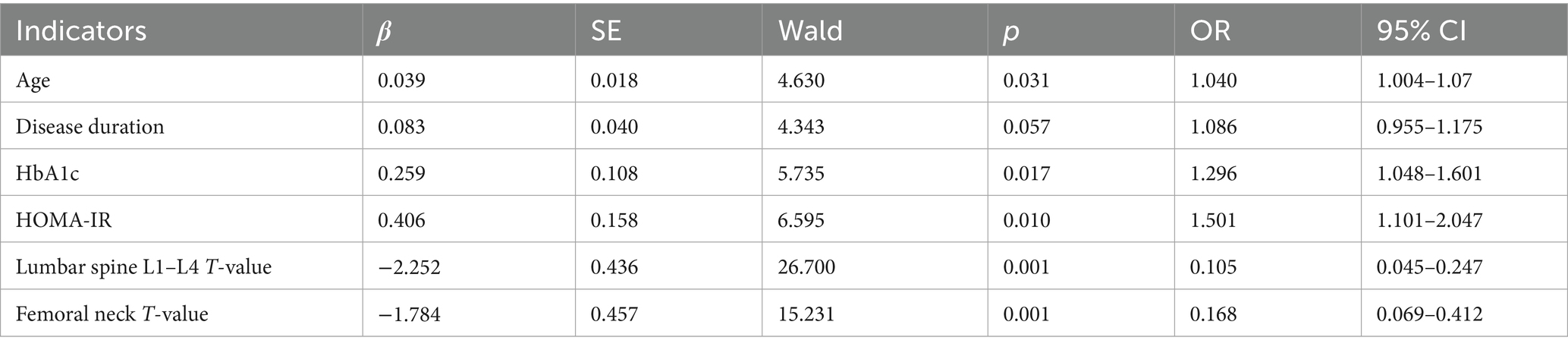
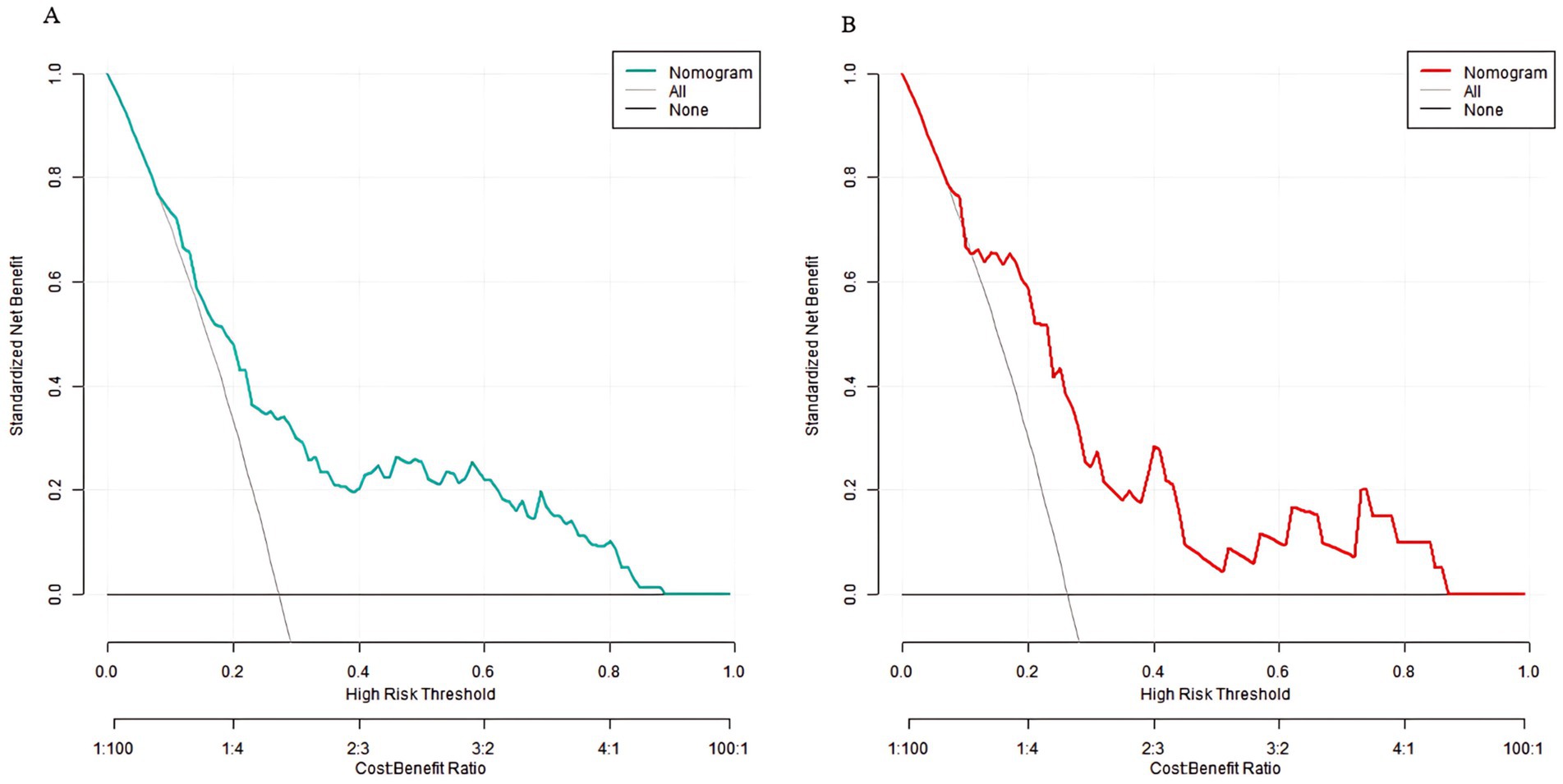
Decision curve analysis showed that when the threshold probability was between 0.06 and 0.92, the decision of applying the nomogram model constructed in this study to predict sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes mellitus had more clinical benefits compared with the decisions of pre-operatively assuming that all patients had sarcopenia or none of them had sarcopenia (Figure 4).
Discussion
In this study, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) was employed to analyze the relationship between sarcopenia and BMD in middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and a risk prediction model for sarcopenia based on multivariate logistic regression was constructed. The results indicated that age, HbA1c, and HOMA-IR were independent risk factors for sarcopenia, while the T-scores of lumbar vertebrae L1–L4, the T-score of the femoral neck, appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM), and appendicular skeletal muscle mass index (ASMI) were independent protective factors. The C-indexes of the nomogram model were 0.773 and 0.750, and the AUCs of the ROC curves were 0.773 and 0.750. Decision curve analysis (DCA) showed that it had clinical application value, providing a basis for early clinical screening and intervention.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that age was an important independent risk factor for sarcopenia. With the increase of age, various physiological functions of the human body gradually decline, and muscle tissue is no exception (9). During the aging process, the balance between muscle protein synthesis and decomposition is disrupted, with a decrease in synthesis and an increase in decomposition, leading to a gradual reduction in muscle mass. This phenomenon may be more obvious in diabetic patients. Diabetes itself accelerates the aging process and affects muscle metabolism through multiple mechanisms such as insulin resistance and oxidative stress, making elderly diabetic patients more prone to sarcopenia (10, 11). In this study, for every 1-year increase in age, the risk of sarcopenia increased by 4.4%, which was consistent with the results of many previous studies, further verifying the important role of age in the occurrence and development of sarcopenia (12).
An elevated HbA1c level was also an independent risk factor for sarcopenia (13). HbA1c reflects the average blood glucose level of patients in the past 2–3 months, and its increase indicates poor blood glucose control (14). Hyperglycemia can damage muscle health through multiple pathways. Persistent hyperglycemia induces the production of advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), which can bind to proteins in muscle tissue, altering their structure and function, leading to muscle fibrosis and functional decline. In this study, for every 1% increase in HbA1c, the risk of sarcopenia increased by 30.1%, suggesting that good blood glucose control is crucial for the prevention of sarcopenia. HOMA-IR, as an important indicator for evaluating insulin resistance, was also closely associated with an increased risk of sarcopenia when elevated (15). In the state of insulin resistance, the effect of insulin in promoting muscle protein synthesis is weakened, and it also interferes with the transport and utilization of amino acids, resulting in a decrease in muscle mass (16). In addition, insulin resistance can further inhibit muscle growth by affecting the function of the growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor-1 (GH-IGF-1) axis (17). The results of this study showed that for every 1-unit increase in HOMA-IR, the risk of sarcopenia increased by 52.1%, highlighting the importance of improving insulin resistance in the prevention of sarcopenia. Although our study did not measure inflammatory biomarkers directly, the observed association between elevated HbA1c/HOMA-IR and sarcopenia aligns with prior evidence linking hyperglycemia and insulin resistance to muscle deterioration (18). Specifically, our multivariate analysis identified HbA1c and HOMA-IR as independent risk factors for sarcopenia (p < 0.05), which may indirectly support the involvement of metabolic dysregulation in muscle loss. Future studies incorporating inflammatory markers (e.g., IL-6, CRP) are needed to validate these mechanistic pathways in T2DM patients.
There was a significant negative correlation between the T-scores of BMD of lumbar vertebrae L1–L4 and the femoral neck and sarcopenia, indicating that higher BMD was a protective factor for sarcopenia (19). There is a close “muscle-bone interaction” relationship between bone and muscle. The mechanical load generated by muscle contraction is an important factor in maintaining BMD, and bones also provide attachment points and support for muscles. When muscle mass decreases, the mechanical stimulation to bones weakens, which can lead to a decrease in BMD. Conversely, higher BMD may reflect better muscle function and load status of the body (20, 21). In this study, for every 1-unit increase in the T-score of lumbar vertebrae L1–L4, the risk of sarcopenia decreased by 88.8%, and for every 1-unit increase in the T-score of the femoral neck, the risk decreased by 83.8%. This result further confirmed the interdependent relationship between the musculoskeletal system and provided a theoretical basis for predicting the risk of sarcopenia by assessing BMD (22).
ASM and ASMI, as important indicators for measuring muscle mass, significantly reduced the risk of sarcopenia when elevated (23, 24). Maintaining muscle mass is the core of sarcopenia prevention. The higher the ASM and ASMI, the more sufficient the muscle reserve, and the lower the possibility of sarcopenia. For patients with T2DM, especially middle-aged and elderly men, while controlling blood glucose, attention should be paid to maintaining and increasing muscle mass, which can be achieved through resistance training, reasonable nutrition, etc. (25). The revised model demonstrates that sarcopenia risk can be predicted using routinely available clinical parameters without incorporating diagnostic muscle mass criteria, strength and performance. This reflects a more clinically realistic scenario where sarcopenia must be identified before DXA assessment.
In this study, a nomogram model for predicting sarcopenia was constructed based on independent influencing factors. By assigning scores to each factor, the probability of a patient’s illness can be calculated, providing a visual tool for clinical decision-making. The C-indexes of the model in the training set and the validation set were 0.773 and 0.750, respectively. The calibration curve showed a good fit between the predicted values and the true values, and the Hosmer–Lemeshow test were significant (all p > 0.05). The AUC of the ROC curves were 0.773 and 0.750 respectively, while these metrics alone are insufficient to confirm its clinical utility. The present study represents an essential first step in model development, but prospective impact studies are now needed to evaluate whether application of this model in clinical practice actually improves patient outcomes (e.g., through earlier sarcopenia detection or more targeted interventions). Future work should: (1) implement the model in electronic health records for real-time risk stratification, (2) assess its impact on clinical decision-making through randomized trials, and (3) evaluate long-term outcomes in patients managed using the model versus standard care. Until such studies are conducted, clinicians should interpret model predictions with appropriate caution. The sensitivity and specificity were 0.714 and 0.887 in the training set, and 0.688 and 0.796 in the validation set, indicating that the model had good discrimination, calibration, and prediction accuracy, which could balance the detection ability and specificity. The DCA demonstrated clinical utility across a wide threshold probability range (0.06–0.92), reflecting varying clinical tolerance for false-positive and false-negative predictions. The lower bound (0.06) represents scenarios where early intervention is prioritized, while the upper bound (0.92) aligns with conservative settings where overtreatment must be minimized. This range was selected to encompass diverse clinical decision-making preferences, as sarcopenia screening strategies may differ based on patient profiles and resource availability. This means that in most clinical scenarios, using this model for sarcopenia risk assessment can bring actual clinical benefits to patients and help guide clinicians to develop personalized prevention and intervention strategies. For example, for high-risk patients, measures such as intensive blood glucose management and resistance training can be taken in time to reduce the risk of sarcopenia; for low-risk patients, the monitoring frequency can be appropriately reduced to avoid waste of medical resources (26, 27).
This study has several advantages. DXA, the gold standard for evaluating muscle mass and BMD, was used to accurately measure the whole-body and local muscle and bone components, ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data and providing high-quality data support for studying the relationship between sarcopenia and BMD. The study focused on middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes, conducting research on a specific gender and disease group, filling the gap in gender-specific research in this field. The results were more targeted and had clinical guiding significance. Not only was the relationship between sarcopenia and BMD analyzed, but also a prediction model containing multiple clinical indicators was constructed, providing a practical tool for clinical practice.
The study also had certain limitations (28, 29). First, the sample was from a single center, so its representativeness was limited. The differences in the clinical characteristics of patients from hospitals in different regions and with different medical levels may affect the external applicability of the model. Second, external validation was not carried out in this study, mainly due to time and resource limitations. Building a perfect prediction model usually requires external validation in different populations and centers to ensure its general applicability. However, due to the tight time requirements of this study and the need for more resources and cooperation to obtain external data, external validation could not be carried out. In future research, multi-center cooperation should be actively sought to further externally validate and optimize the model. Finally, the study only evaluated the indicators at a specific time point, lacking long-term follow-up data, and was unable to explore the dynamic relationship between sarcopenia and changes in BMD.
In conclusion, through DXA technology, this study found that there was a close relationship between sarcopenia and BMD in middle-aged and elderly men with type 2 diabetes. Age, HbA1c, and HOMA-IR were identified as independent risk factors, while the T-scores of lumbar vertebrae L1–L4 and the femoral neck were independent protective factors. The constructed nomogram model had good prediction efficacy. In the future, the sample size should be expanded, multi-center external validation should be carried out, more influencing factors should be included, and long-term follow-up should be conducted.
Conclusion
The prediction model constructed based on DXA can effectively predict the risk of sarcopenia in middle-aged and elderly male patients with T2DM, providing a basis for clinical early screening and intervention.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of Xiamen Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study.
Author contributions
GZ: Software, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Formal analysis, Validation, Data curation, Conceptualization, Methodology. LH: Data curation, Validation, Investigation, Methodology, Resources, Writing – original draft, Visualization, Software. LL: Data curation, Conceptualization, Writing – review & editing, Methodology, Validation, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Yan, Y, Wu, T, Zhang, M, Li, C, Liu, Q, and Li, F. Prevalence, awareness and control of type 2 diabetes mellitus and risk factors in Chinese elderly population. BMC Public Health. (2022) 22:1382. doi: 10.1186/s12889-022-13759-9
2. Chen, DQ, Wu, YX, Zhang, YX, Yang, HL, Huang, HH, Lv, JY, et al. Sarcopenia-associated factors and their bone mineral density levels in middle-aged and elderly male type 2 diabetes patients. World J Diabetes. (2024) 15:2285–92. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v15.i12.2285
3. Dai, H, and Xu, J. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio as a marker of sarcopenia for identifying osteoporosis in male patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2022) 23:672. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05636-8
4. Hashimoto, Y, Takahashi, F, Okamura, T, Hamaguchi, M, and Fukui, M. Diet, exercise, and pharmacotherapy for sarcopenia in people with diabetes. Metabolism. (2023) 144:155585. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2023.155585
5. Chen, H, Huang, X, Dong, M, Wen, S, Zhou, L, and Yuan, X. The association between sarcopenia and diabetes: from pathophysiology mechanism to therapeutic strategy. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. (2023) 16:1541–54. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S410834
6. da Rocha, DS, Tessari, JA, Mainardi, NB, Hax, V, Gasparin, AA, de Oliveira, CAV, et al. Assessment of muscle mass using chest computed tomography-based quantitative and qualitative measurements in patients with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective study with cross-sectional and longitudinal analyses. Semin Arthritis Rheum. (2023) 59:152168. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2023.152168
7. Harreiter, J, and Roden, M. Diabetes mellitus: definition, classification, diagnosis, screening and prevention (update 2023). Wien Klin Wochenschr. (2023) 135:7–17. doi: 10.1007/s00508-022-02122-y
8. Chen, LK, Woo, J, Assantachai, P, Auyeung, TW, Chou, MY, Iijima, K, et al. Asian Working Group for Sarcopenia: 2019 consensus update on sarcopenia diagnosis and treatment. J Am Med Dir Assoc. (2020) 21:300–307.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jamda.2019.12.012
9. Marzetti, E, Calvani, R, Coelho-Júnior, HJ, Landi, F, and Picca, A. Mitochondrial quantity and quality in age-related sarcopenia. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:2052. doi: 10.3390/ijms25042052
10. Lima, TI, Laurila, PP, Wohlwend, M, Morel, JD, Goeminne, LJE, Li, H, et al. Inhibiting de novo ceramide synthesis restores mitochondrial and protein homeostasis in muscle aging. Sci Transl Med. (2023) 15:eade6509. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.ade6509
11. Song, L, Xue, J, Xu, L, Cheng, L, Zhang, Y, and Wang, X. Muscle-specific PGC-1α modulates mitochondrial oxidative stress in aged sarcopenia through regulating Nrf2. Exp Gerontol. (2024) 193:112468. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2024.112468
12. Benz, E, Pinel, A, Guillet, C, Capel, F, Pereira, B, de Antonio, M, et al. Sarcopenia and sarcopenic obesity and mortality among older people. JAMA Netw Open. (2024) 7:e243604. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.3604
13. Chen, Y, Liao, J, Zeng, Y, Ma, H, Jiang, C, Yu, S, et al. The combined effect of diabetes mellitus and sarcopenia on depression and cognitive function: insights from the CHARLS cohort, 2011–2020. Eur Geriatr Med. (2024) 15:1881–90. doi: 10.1007/s41999-024-01039-1
14. Zhang, Y, Gong, M, Feng, XM, and Yan, YX. Bidirectional association between sarcopenia and diabetes: a prospective cohort study in middle-aged and elderly adults. Clin Nutr ESPEN. (2025) 66:556–63. doi: 10.1016/j.clnesp.2025.02.026
15. Booranasuksakul, U, Macdonald, IA, Stephan, BCM, and Siervo, M. Body composition, sarcopenic obesity, and cognitive function in older adults: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2002 and 2011–2014. J Am Nutr Assoc. (2024) 43:539–52. doi: 10.1080/27697061.2024.2333310
16. Ren, Q, Chen, S, Chen, X, Niu, S, Yue, L, Pan, X, et al. An effective glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists, semaglutide, improves sarcopenic obesity in obese mice by modulating skeletal muscle metabolism. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2022) 16:3723–35. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S381546
17. Kaur, P, Verma, N, Wadhawan, A, Garg, P, Ralmilay, S, Kalra, N, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 levels reflect muscle and bone health and determine complications and mortality in decompensated cirrhosis. J Clin Exp Hepatol. (2025) 15:102402. doi: 10.1016/j.jceh.2024.102402
18. Qiao, YS, Chai, YH, Gong, HJ, Zhuldyz, Z, Stehouwer, CDA, Zhou, JB, et al. The association between diabetes mellitus and risk of sarcopenia: accumulated evidences from observational studies. Front Endocrinol. (2021) 12:782391. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.782391
19. Evans, WJ, Guralnik, J, Cawthon, P, Appleby, J, Landi, F, Clarke, L, et al. Sarcopenia: no consensus, no diagnostic criteria, and no approved indication-how did we get here? Geroscience. (2024) 46:183–90. doi: 10.1007/s11357-023-01016-9
20. Kai, K, Fujiwara, T, Nagao, Y, Oki, E, Yoshizumi, T, Eto, M, et al. Evaluation of bone density and skeletal muscle mass after sleeve gastrectomy using computed tomography method. Bone Rep. (2023) 18:101661. doi: 10.1016/j.bonr.2023.101661
21. Chen, L, Wu, J, Ren, W, Li, X, Luo, M, and Hu, Y. The relationship between skeletal muscle mass and bone mass at different sites in older adults. Ann Nutr Metab. (2023) 79:256–62. doi: 10.1159/000528585
22. Maeda, K, Imatani, J, Narazaki, S, and Ozaki, T. Bone mineral density, limb muscle mass, muscle strength, and exercise capacity are reduced in female patients with distal radius fractures when the unaffected side grip strength is less than 18 kg. J Orthop Sci. (2023) 28:1279–84. doi: 10.1016/j.jos.2022.09.001
23. Du, H, Yu, M, Xue, H, Lu, X, Chang, Y, and Li, Z. Association between sarcopenia and cognitive function in older Chinese adults: evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:1078304. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1078304
24. de Luis, D, Primo, D, Izaola, O, and López Gómez, JJ. Lack of association between serum apelin levels and sarcopenia in elderly malnourished subjects. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2024) 28:3841–8. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202406_36461
25. Kobayashi, Y, Long, J, Dan, S, Johannsen, NM, Talamoa, R, Raghuram, S, et al. Strength training is more effective than aerobic exercise for improving glycaemic control and body composition in people with normal-weight type 2 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. (2023) 66:1897–907. doi: 10.1007/s00125-023-05958-9
26. Argyropoulou, D, Nomikos, T, Terzis, G, Tataki, S, Geladas, ND, and Paschalis, V. The effects of dietary protein on physical performance and body composition in middle age and older people having type II diabetes mellitus: a randomized pilot study. Eur J Nutr. (2025) 64:63. doi: 10.1007/s00394-024-03575-9
27. Taskent, I, Ece, B, and Aydin, S. Assessment of psoas muscle index in middle-aged type 2 diabetes patients: impact of insulin therapy on sarcopenia. Tomography. (2024) 10:1054–63. doi: 10.3390/tomography10070079
28. Laohajaroensombat, O, Limpaarayakul, T, Sathavarodom, N, Boonyavarakul, A, and Samakkarnthai, P. A comparative analysis of sarcopenia screening methods in Thai people with type 2 diabetes mellitus in an outpatient setting. BMC Geriatr. (2025) 25:346. doi: 10.1186/s12877-025-06020-6
Keywords: type 2 diabetes mellitus, sarcopenia, bone mineral density, dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, prediction model
Citation: Zhang G, Huang L and Liao L (2025) Constructing the prediction model based on DXA between sarcopenia and BMD in middle-aged and elderly men with T2DM. Front. Med. 12:1655263. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1655263
Edited by:
Yun Shen, Pennington Biomedical Research Center, United StatesReviewed by:
Ruichao Shi, Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, United StatesManrong Xu, University of Toronto, Canada
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Huang and Liao. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Liangzhong Liao, dHloMTYzNzg5NzRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
 Guoyang Zhang†
Guoyang Zhang† Liangzhong Liao
Liangzhong Liao