Abstract
Lymphedema is a chronic disorder of impaired lymphatic transport that leads to fluid accumulation, fibrosis, and adipose expansion. It presents as primary disease, caused by genetic defects in lymphatic development, or as secondary disease after surgery, radiotherapy, infection, trauma, or malignancy. Recent studies have broadened the genetic basis of primary forms and clarified host and treatment-related risks for secondary forms. Mechanistic insights show that lymphatic stasis drives inflammation, fibrosis, and hypoxia, which remodel the microenvironment and reinforce lymphatic failure. Advances in imaging, including lymphoscintigraphy, indocyanine green lymphography, and magnetic resonance lymphangiography, enable earlier and more accurate diagnosis. Conservative treatment with complete decongestive therapy remains standard, while microsurgical techniques such as lymphaticovenous anastomosis and vascularized lymph node transfer expand options. Emerging pharmacologic strategies that target immune and fibrotic pathways show promise. This review summarizes current progress and highlights opportunities for precision interventions to improve outcomes.
Graphical Abstract
1 Introduction
The lymphatic system is unique to vertebrates and functions as a drainage of excess interstitial fluid, fat absorption and immune surveillance. It consists of lymphatic vessels, lymphatic tissues, and lymphatic organs. Unlike blood vessels, lymphatic vessels do not form a closed circulation but operate as a unidirectional system, with lymph flowing centripetally toward the heart. The system begins with initial lymphatic vessels, followed by precollectors, collectors, and trunks. These vessels are composed of a single layer of lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) connected by anchoring filaments, which open lymphatic junctions when tissue pressure increases, facilitating the absorption of macromolecules, cells, and interstitial fluid. Lymph, absorbed from the interstitial spaces, contains proteins, water, fatty acids, salts, white blood cells, microorganisms, and cellular debris. It enters the lymphatic vessels, where it is transported through collectors and trunks before being filtered through lymph nodes. Ultimately, the lymph reenters the venous circulation. There are two distinct systems of lymphatic drainage: the superficial system, responsible for draining the skin and subcutaneous tissues, and the deep system, which drains the tissues located beneath the fascia. The interconnection between these two systems is facilitated by perforating vessels penetrating the fascia.
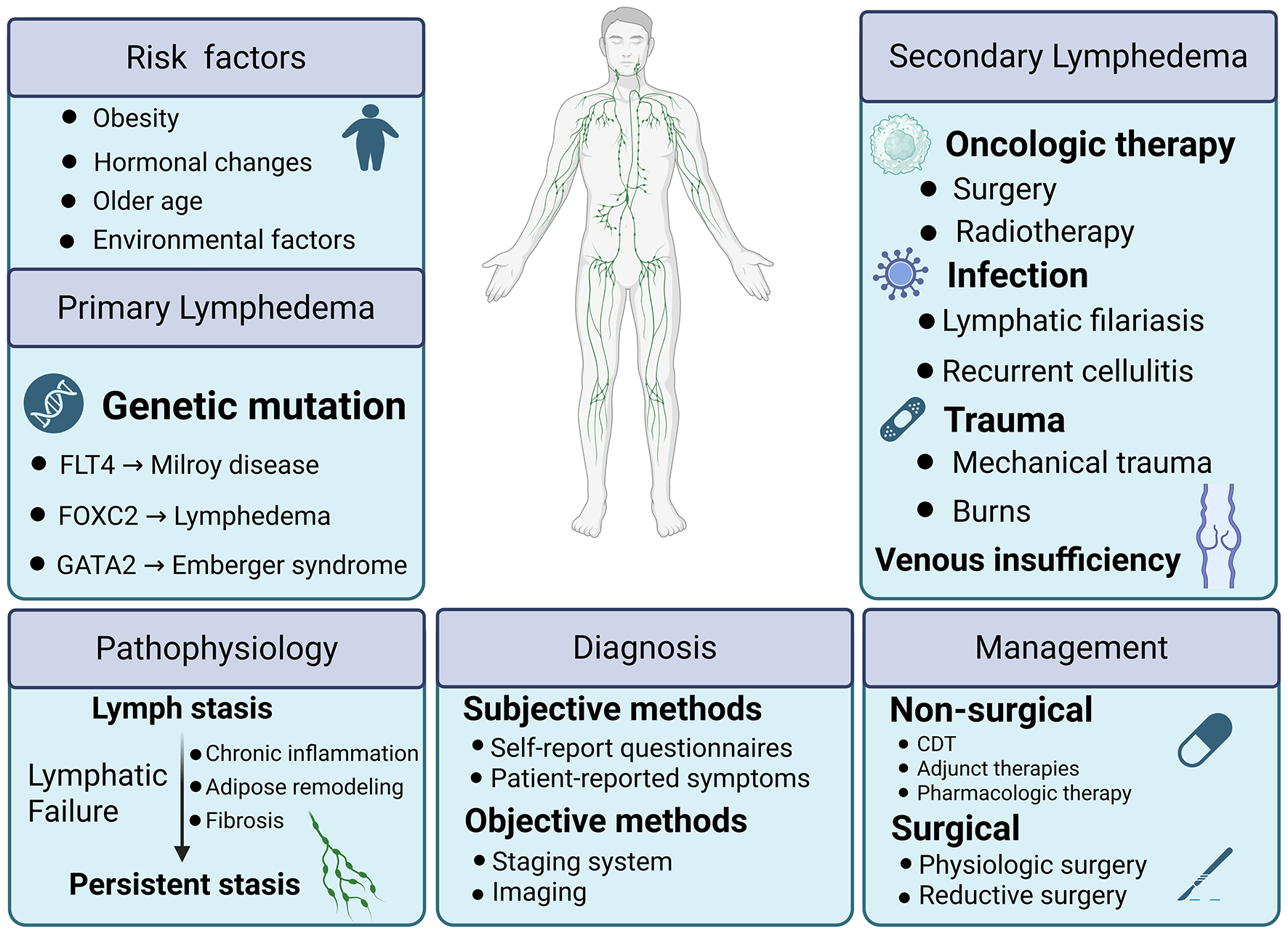
Lymphedema arises when there is an imbalance between the microvascular filtration rate of the capillaries and venules, and the capacity of the lymphatic drainage system to remove the excess interstitial fluid. This results in the accumulation of interstitial fluid in the tissue spaces, particularly in the subcutaneous tissue, leading to the manifestation of swelling. The primary symptom of lymphedema is swelling of the affected area, which can sometimes be severe and deforming, causing significant discomfort and impacting mobility. Depending on the cause, lymphedema can be divided into primary and secondary lymphedema.
Primary lymphedema results from an intrinsic fault in the lymphatic vessels such as Milroy's disease and Meige's disease, characterized by the underdevelopment or absence of the lymphatic system, resulting in a diminished ability to absorb interstitial fluid.
Secondary lymphedema, also known as acquired lymphedema, results from damage to the lymphatic vessels or nodes due to factors such as surgery, radiation, trauma, or infection caused by lymphatic filariasis. In addition to these causes, secondary lymphedema can also arise from chronic venous insufficiency, obesity, environmental factors (e.g., podoconiosis), and even self-harm. Chronic venous insufficiency leads to impaired venous return, which negatively affects lymphatic drainage. Obesity, through excess adipose tissue, can exert pressure on lymphatic vessels, hindering their function. Podoconiosis, caused by prolonged exposure to certain soils, can also disrupt the lymphatic system. Lymphatic gene dysfunction can also affect immune function leading to infection which can influence cancer development. Secondary lymphedema is a prevalent kind of lymphedema that impacts a substantial number of individuals globally. It is commonly associated with various tumors, especially in gynecologic oncologic surgery, where the incidence of lymphedema is as high as 20% (1). Given the profound impact on patients' quality of life and the complexity of its mechanisms, lymphedema has become an important focus of both basic and clinical research. This review aims to summarize recent advances in etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management, while highlighting translational opportunities for improved care.
2 Etiology of lymphedema
Lymphedema arises either from primary defects in lymphatic formation or from secondary injury to lymphatic vessels and nodes (2). The underlying etiology dictates the downstream pathophysiologic cascade. Persistent lymph stasis leads to chronic inflammation, progressive fibrosis, and adipose tissue remodeling (3). These processes provide the foundation for prevention, risk stratification, and management strategies. Recent advances have broadened the genetic spectrum of primary lymphedema and refined the quantification of both treatment-related and host-related risks for secondary disease, although a substantial proportion of primary cases remain genetically unexplained (4).
2.1 Primary lymphedema
Primary lymphedema results from congenital or hereditary defects of the lymphatic system. To date, more than 30 genes have been associated with abnormal lymphangiogenesis, defective lymphatic valve formation, or impaired lymphatic vessel contractility (5). The monogenic causes and phenotypes of lymphedema, including inheritance patterns and clinical features, are summarized in Table 1, whereas biomarkers and molecular pathways are presented in Table 2. These discoveries have been driven by next-generation sequencing, which has revealed both coding and regulatory variants.
Table 1
| Genes | Function |
|---|---|
| Fms related receptor tyrosine kinase 4 (FLT4/VEGFR3) | High-affinity receptor for VEGFC (157); essential for lymphatic endothelial cell survival, proliferation, and lymphangiogenesis (158). |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) | Primary lymphangiogenic growth factor (159); binds and activates VEGFR3 to stimulate lymphatic vessel sprouting and growth (160). |
| Forkhead box C2 (FOXC2) | Transcription factor regulating lymphatic valve formation, patterning, and inhibition of pericyte coverage on lymphatic vessels (161). |
| GATA binding protein 2 (GATA2) | Transcription factor necessary for lymphatic valve maintenance and the expression of cell junction molecules (162, 163). |
| Collagen and calcium binding EGF domains 1 (CCBE1) | Enhances the bioactivity and signaling of VEGFC (164); critical for lymphatic endothelial cell budding and migration (165, 166). |
| A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 3 (ADAMTS3) | Protease that processes and activates VEGFC (167); expressed in pro-lymphangiogenic stromal cells (168). |
| EPH receptor B4 (EPHB4) | Receptor involved in cell repulsion (169); interacts with EFNB2 to regulate lymphatic valve formation by spatially inhibiting Erk signaling (170). |
| Piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 (PIEZO1) | Mechanosensitive ion channel (171); dysfunction can lead to lymphatic vascular defects and lymphedema (172, 173). |
| Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 14 (PTPN14) | Involved in cell growth and differentiation (174); associated with lymphatic development and lymphedema (175). |
| Gap junction protein gamma 2 (GJC2) | Genetic variations associated with secondary lymphedema risk (176). |
| FAT atypical cadherin 4 (FAT4) | Regulates planar cell polarity and collective cell migration during lymphatic vessel development (177). |
| Kinesin family member 11 (KIF11) | Motor protein; mutations cause syndromes featuring microcephaly and lymphedema (178–180); role in lymphatic function is indirect (178). |
| Gap junction protein alpha 1 (GJA1) | Forms connexin 43 gap junctions; implicated in cell communication within the lymphatic vasculature (research ongoing). |
| SRY-box transcription factor 18 (SOX18) | Master transcription factor initiating lymphatic endothelial cell differentiation and development (181, 182). |
| Protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 14 (PTPN14) | Regulates cell adhesion and growth (175). |
| Dachsous cadherin-related 1 (DCHS1) | Interacts with FAT4; involved in planar cell polarity signaling for lymphatic valve morphogenesis (183). |
| Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGFC) | Primary ligand for VEGFR3; master stimulator of lymphatic vessel growth (lymphangiogenesis) (184). |
| Forkhead box C2 (FOXC2) | Transcription factor critical for lymphatic valve formation and vessel maturation (161). |
| Gap junction protein gamma 2 (GJC2) | Forms connexin 47 gap junctions; mutations linked to hereditary lymphedema (185, 186). |
Monogenic causes and phenotypes of lymphedema.
Table 2
| Biomarkers | Function summary |
|---|---|
| Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF)/c-MET pathway | Promotes lymphatic endothelial cell growth, migration, and protects against radiation-induced lymphatic injury (187, 188). |
| Angiopoietin 2 (ANG2)/TIE2 signaling | Regulates lymphatic vessel maturation, stability, and permeability. Imbalance leads to vascular leakage (189, 190). |
| Transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGF-β1) | Key driver of tissue fibrosis and chronic inflammation in secondary lymphedema (26). |
| Interleukin 6 (IL-6) | Pro-inflammatory cytokine; elevated in lymphedema tissue, contributing to chronic inflammation and fibrosis (30). |
| C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2) | Recruits monocytes/macrophages to the lymphedematous limb, promoting inflammation and tissue changes (191). |
| Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1) | Receptor for hyaluronic acid (192); a specific marker for lymphatic endothelial cells (192). |
| Podoplanin (PDPN) | Transmembrane glycoprotein critical for lymphatic development, separation from blood vasculature, and function (193, 194). |
| Proximal homeobox protein 1 (PROX1) | Master control transcription factor for lymphatic endothelial cell fate and maintenance (195). |
Biomarkers or pathways of lymphedema.
Canonical clinical entities include Milroy disease, caused by mutations in FLT4/VEGFR3, and lymphedema–distichiasis syndrome, associated with FOXC2 mutations. Emberger syndrome, caused by GATA2 haploinsufficiency, links primary lymphedema with hematological malignancies (6, 7). More recently, novel variants in PROX1 and HGF have been reported, expanding the genetic landscape (8, 9).
Despite progress, most patients with primary lymphedema remain variant-negative with current testing, suggesting further undiscovered genes or complex regulatory mechanisms (10). Phenotypic variability is also striking: onset may occur at birth, adolescence, or adulthood, and severity is strongly modified by age, hormonal status (puberty, pregnancy), and body mass index (BMI) (11). High BMI in particular has emerged as a consistent risk factor for earlier onset and worse outcomes, highlighting the interplay between genetic predisposition and lifestyle and environmental modifiers (12, 13).
2.2 Secondary lymphedema
Secondary lymphedema is an acquired condition, most commonly occurring after oncologic therapies. Infections such as lymphatic filariasis remain a leading cause worldwide (14). In cancer survivors, both surgery and radiotherapy constitute the principal risk factors (15). The extent of lymph node dissection, particularly in the axillary or pelvic basins, is directly associated with lymphedema risk, with higher nodal counts predicting increased incidence and severity (16, 17). Radiotherapy contributes by inducing fibrosis and obliteration of lymphatic pathways; when combined with surgery, risk is synergistically elevated (18).
Host factors further modify risk. Obesity independently increases both incidence and severity, while older age and recurrent cellulitis are additional contributors. Recognizing these modifiers, validated risk prediction models have emerged: for example, a five-factor model (age, BMI, breast density, nodal burden, and axillary dissection) accurately stratifies 2-year lymphedema-free survival in breast cancer cohorts (19). Prospective data in gynecologic oncology confirm similar long-term predictors (20).
Beyond oncology, lymphatic filariasis (LF) remains a significant global health problem. Recent estimates suggest that tens of millions of individuals suffer from lymphedema as a chronic sequela of filarial infection, with global figures ranging up to 40 million affected cases (21). This highlights the persistent burden of infection-related secondary lymphedema, particularly in endemic regions.
3 Pathophysiology of lymphedema
The pathogenesis of lymphedema is increasingly recognized as a self-perpetuating cascade. Lymphatic stasis triggers a CD4? T-cell–driven inflammatory response that promotes extracellular matrix fibrosis and progressive tissue stiffening. In parallel, adipose tissue undergoes metabolic reprogramming, marked by dysregulated lipid metabolism and altered immune signaling. These events unfold within a hostile microenvironment characterized by hypoxia, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and tissue injury secondary to surgery or radiotherapy. The interplay of these factors drives lymphatic pump failure and the progressive rarefaction of lymphatic vessels (2, 22, 23). Foundational human and murine studies have shown that CD4? T cells become activated in regional lymph nodes and subsequently home to the skin after lymphatic injury. Depletion or functional blockade of these cells prevents lymphedema and improves lymphatic transport, establishing adaptive immunity as a causal driver rather than a bystander. Mechanistically, Th2 polarization with interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 suppresses lymphangiogenesis and promotes extracellular matrix deposition (24). Translationally, topical calcineurin inhibition with tacrolimus attenuates pathogenic T-cell signaling, reduces edema and fibrosis, and promotes collateral lymphangiogenesis in preclinical models, supporting immune modulation as a disease-modifying rather than purely symptomatic approach (25). Converging evidence identifies transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) as a central profibrotic hub that links inflammation to myofibroblast activation, collagen and elastin deposition, and extracellular matrix cross-linking. Pharmacologic or genetic inhibition of TGF-β1 signaling attenuates fibrosis and lymphatic dysfunction in experimental lymphedema (26). Hypoxia pathways intersect this axis: in both human and murine tissues, lymphatic HIF-2α expression is reduced while HIF-1α is elevated. Restoration of HIF-2α/TIE2 activity stabilizes lymphatic endothelium and mitigates pathological remodeling, implicating oxygen sensing as an upstream regulator of matrix–vessel crosstalk (22, 27). A defining late feature of lymphedema is adipose expansion, termed lymphedema-associated adipose tissue, characterized by up-regulation of inflammatory cytokines and lipid-handling genes such as PPARγ and C/EBPα. Multi-omic and clinical studies indicate that inflammation precedes and drives fat deposition, with interleukin-6 emerging as a key immunometabolic node that modulates adipose homeostasis in lymphedematous limbs (28–30). These biological processes are determined by the local tissue microenvironment. Surgical or radiotherapy-induced injury, together with persistent cytokine signaling, establishes an adverse niche characterized by fibrosis, pathological adipose accumulation, hypoxia, and increased extracellular matrix stiffness. This remodeled microenvironment reduces lymphatic vessel compliance and intrinsic contractile function, impairs lymphangiogenesis, and perpetuates lymph stasis. The resulting feed-forward interaction between stasis, chronic inflammation, and fibroadipose remodeling closes a pathogenic loop that helps explain the clinical refractoriness observed once fibroadipose changes predominate (31–33). Contemporary expert reviews have synthesized these mechanistic insights into an integrated framework that supports multi-pronged therapeutic strategies. Such approaches include modulation of immune and cytokine pathways, targeting of fibrotic remodeling and extracellular matrix dynamics, and interventions aimed at the microenvironment and oxygen-sensing mechanisms. When combined with early detection, these strategies hold the potential to disrupt the pathogenic cycle before irreversible fibroadipose remodeling becomes established (31, 34).
4 Diagnosis: objective methods and subjective methods
The risk of lymphedema peaked at 12–30 months after surgery (35). The lymphatic function is regulated by a variety of factors, including chronic inflammation, tumors, external stimuli (eg., radiation), age, obesity, and metabolic dysfunction. These factors will affect the occurrence and development of lymphedema. The primary presentation of lymphedema involves the buildup of interstitial fluid rich in proteins within the subcutaneous and subfascial tissues which triggers the initiation of an inflammatory response. The retended fluid exacerbates tissue fibrosis, deposition of fat, and formation of scars (36). This fibrotic development is mediated by the synthesis of pro-fibrotic cytokines by Th2 cells (such as IL-4, IL-13, and TGF-β1). These cytokines can affect the survival, proliferation, and migration of lymphatic endothelial cells (37). Lymphedema is known to elicit systemic alterations beyond the confines of the affected limb. Research has shown that collagen accumulation and the presence of CD4+ cells can be observed in tissues unaffected in the patients of lymphedema (38). Patients with the acute phase of lymphedema are susceptible to the development of cellulitis (erysipelas) and there may be a further decline in physical function. Psychological effects may also occur, leading to a lower quality of life (QOL) (39). One study analyzed the association between breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) and cellulitis incidence and mortality in the National Health Insurance database in Taiwan. The results showed that the incidence and mortality rates of cellulitis were significantly higher in patients with BCRL than in patients without BCRL, and there was a significant correlation between the three (40). Therefore, early diagnosis and treatment play an important role in delaying disease progression and improving prognosis.
The diagnosis of lymphedema is based on the patient's pathography, physical examination, and ancillary tests such as lymphography and tissue biopsy (41). Associated risk factors such as previous surgery with nodal dissection, radiation therapy, infection, malignancy, family history of congenital lymphedema, and trauma should be taken into consideration during the diagnostic process (42). Depending on the etiology, further tests may be carried out to assess the severity and cause of the lymphedema. Imaging techniques for visualization of the lymphatic system are less well developed than those for imaging of blood vessels for the reason that the lymphatic system is more difficult to be visible (43). Technological advances in biomedical imaging have opened new possibilities in the diagnosis of lymphedema (44). Effective diagnostic measures play a crucial role in the identification and prevention of this disease, as well as aiding in the process of treatment and rehabilitation (45). The precise identification of a patient's health status together with the prompt detection and intervention at an early stage are essential ways of rehabilitation and preventing potential complications and optimization of therapy intervention can be achieved through the diagnosis of early-onset lymphedema. Multiple methods are available for the quantification of physiological alterations that manifest in lymphedema (46). Different diagnostic procedures include inherent limitations which often entail the use of many approaches in combination. A reasonable staging system plays an important role in the diagnostic process of lymphedema which promotes consistency and comparability in the diagnosis. Though imaging techniques for visualization of the lymphatic system are objective and standardized, subjective methods are implemented at the same time due to their convenience, low cost, and supplementary function. Subjective ways like self-report questionnaires can promote rapid diagnosis and facilitate the evaluation of treatment outcomes. Patients often report symptoms such as pain, heaviness, and discomfort when having or in the developing process of lymphedema. Combining subjective symptomatic and quality-of-life self-reports with objective measures is of great help in defining the level of lymphedema (47).
4.1 Objective methods for lymphedema
4.1.1 Staging systems of lymphedema contribute to the uniform diagnosis
The staging system is a crucial component in the management of lymphedema and assists with the standardization of diagnostic procedures and treatment protocols. The implementation of standardized staging criteria for lymphedema in clinical practice serves several important purposes. A universal staging system promotes consistency and comparability in the diagnosis process across different medical professionals and institutions, minimizing regional variations, and thereby ensuring uniformity and reliability in the obtained results. The utilization of a uniform staging system helps to mitigate diagnostic discrepancies that may arise due to subjective factors, enhancing the accuracy and objectivity of the diagnostic process. Additionally, the adoption of standardized criteria facilitates physicians' comprehension of the condition, enabling effective communication with patients, formulation of appropriate treatment plans, and ultimately enhancing the credibility and reliability of medical outcomes (45, 48–50).
An ideal staging system should be comprehensive, reproducible, and correlate with imaging and clinical manifestations. While there exist many staging methods in use, the most often utilized one is recommended by the International Society of Lymphedema (ISL), which classifies lymphedema into four levels of severity, namely stage 0 to stage III. The corresponding clinical manifestations and sorting criteria are shown in Table 3, which has been adapted from ISL (2023) (51).
Table 3
| Stage | Clinical manifestation |
|---|---|
| 0 | Latent or subclinical condition, subtle swelling, impaired lymph transport, having subjective symptoms |
| I | Protein-rich fluid accumulation; pitting edema may occur |
| II | Fibrotic changes; persistent swelling; poor response to limb elevation |
| III | Severe lymphedema with marked skin thickening, fat deposition, and fibrosis |
Clinical manifestations and sorting criteria.
While the staging approach proposed by ISL demonstrates reproducibility, it lacks adequate inclusion of the physiological characteristics associated with lymphedema (49). It solely refers to the physical state of the extremities and lacks the ability for spatial distribution. Thus, a more detailed and inclusive classification is needed when special circumstances arise (45).
When it comes to the description of trunk lymphedema linked with breast cancer, the Pittsburgh Trunk Lymphedema Staging System (PTLSS) is proved to be a validated staging system which is a reliable method for assessing the extent of lymphedema in the whole trunk (52). Other staging systems and their corresponding methods used to assess the existence and severity of lymphedema are listed in Table 4. Various staging methods own their own set of pros and limitations. The advent of novel technology necessitates and propels the development of fresh staging systems.
Table 4
| Staging system | Key features | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISL staging (51) | Four stages (0–III) based on clinical severity; Severity classification: In each period, according to the degree of volume exceeding the standard, it is divided into mild (>5%−20%), moderate (20%−40%) and severe (>40%) | Simple, widely used, reproducible | Relies mainly on physical signs; lacks physiological detail; Dysfunction, quality of life or lymphedema in the head, torso and other parts were not evaluated |
| Lymphoscintigraphy staging (196) | Classification based on lymphatic flow obstruction | High accuracy; validated | Radiation exposure; poor spatial/temporal resolution (197) |
| ICG lymphography (198, 199) | Visualizes superficial lymphatic flow patterns (200) | Non-ionizing, real-time, high temporal resolution (201) | limited tissue penetration (202), potential off-label status of intradermal injection depending on jurisdiction |
Staging systems.
4.1.2 Lymphedema imaging: major technologies
Among various diagnostic technologies, lymphoscintigraphy is widely recognized as the benchmark imaging modality utilized in the diagnosis of lymphedema (53). Lymphoscintigraphy can accurately visualize and delineate the lymphatic system, as well as identify the precise location of sentinel nodes. This technology offers comprehensive and precise data about the diagnosis and classification of lymphedema affecting the extremities, as well as its corresponding severity assessment (54). During the process, lymphoscintigraphy entails the administration of a tracer dye into the distal extremity, where it is afterward absorbed by the lymphatic vasculature (55). It allows for the examination of lymph-node uptake in the groin and axillary regions, as well as the identification of potential dermal backflow, collateral pathways, and delayed nodal uptake, with visualization of the popliteal or epitrochlear lymph nodes (39). Lymphoscintigraphy serves as a valuable indicator for BCRL (56) and is an efficacious approach for diagnosing and confirming cases of primary lymphedema (39). The utilization of this diagnosis modality has proven to be beneficial in managing limb edema cases where etiology is not well understood or in patients who are suspected to have lymphedema (57). The procedure is characterized by low levels of radiation. However, it is contraindicated for individuals who are pregnant or breastfeeding. Indocyanine green (ICG) lymphography is a valuable lymphatic imaging technique that can visualize superficial lymph flow in real time without exposing the patient to radiation (58). It has established itself as a cornerstone technique in many clinical settings, with its principal applications encompassing pattern classification and surgical planning (59–62). The procedure is simple and convenient to execute, rendering it valuable for real-time comprehension of the lymphatic system's state (63). ICG dye was administered at three distinct sites in the distal arm or leg: two interdigital injections and one injection at the volar wrist or posterior to the medial malleolus. An immediate scan was conducted to assess lymphatic pump velocity and function. A follow-up scan, performed 6 h later, visualized the dermal backflow (DB) pattern, which is diagnostic for lymphedema and indicative of disease severity (64). It shows the DB pattern on both the thigh and lower leg regions demonstrating a high level of sensitivity and specificity in the identification of aberrant lymph circulation. According to the visibility of lymphatics and DB extension, the ICG lymphography pattern was categorized as linear, low enhancement (LE), distal DB, or extended DB in bilateral lymphedema. Each has different patient characteristics (65). ICG is conventionally injected in the distal leg or arm. In cases when lymphatic activity is insufficient in the distal limb, the precise location of lymphatic vessels cannot be ascertained. This is true even if lymphatic vessel function is satisfactory in the proximal limb. Consequently, injecting the dermal leg may prove to be futile (66). Except for the distal part of the limbs, the first web space of the foot, the lateral ankle, and the lateral thigh are chosen to be the injection site (67). The aforementioned study revealed that Multi-lymphosome ICG lymphography demonstrates superior performance in the given scenario. The use of this method facilitates enhanced identification of functioning lymphatic vessels during lymphatic venous anastomosis (LVA), thus leading to improved surgical results (66–68). However, ICG lymphography is limited by its shallow detection depth and low spatiotemporal resolution. In contrast, Protein@Cyanine-based NIR-II lymphography overcomes these limitations, enabling the highly sensitive visualization of lymphedema and tumor lymphatic metastasis, thereby presenting a promising strategy (69).
Magnetic resonance lymphangiography (MRL) has become a new non-invasive method capable of delivering high-resolution three-dimensional images of an entire limb, with enough detail to identify individual lymphatic channels and regions of dermal backflow (70). MRL is neither sensitive nor specific for lymphedema but it is capable of visualizing preclinical alterations in lymphatic flow thus contributing to the early diagnosis of lymphedema and can evaluate other causes of limb swelling (71–73). MRL has demonstrated satisfactory outcomes in differential diagnosis, quantitative classification of disease severity, and optimal treatment planning (74). Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR lymphangiography is increasingly used for 3D deep anatomy (75). Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging via intranodal, intrahepatic, and intramesenteric routes enables the direct visualization of the central lymphatic system from the inguinal region to the venous angle (76). Dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance lymphangiography serves as the reference standard for diagnosing a range of thoracic lymphatic diseases, such as traumatic chylothorax and plastic bronchitis (77).
CT is an objective method to assess patients undergoing lymphadenectomy (78). CT-based quantitative assessments can offer objective volume measurements and detailed information about the structural characteristics of subcutaneous tissue (79). During CT scanning, patients were instructed to keep an anatomically neutral position with both arms fully extended. The CT scanned both limbs simultaneously, from the point where the legs separate to 5 cm above the lateral malleolus, or from the distal ends of the clavicles to the wrist crease (80). The study found that assessment of subcutaneous fat thickness using CT lymphangiography is useful for screening lymphedema at an early stage (81) and is beneficial for planning microsurgical therapies (82).
Ultrasound is a readily accessible bedside technique for evaluating dermal thickness, echogenicity, and tissue stiffness in patients with lymphedema. Nevertheless, its diagnostic performance is generally inferior to that of lymphoscintigraphy, indocyanine green lymphography, or magnetic resonance imaging. Owing to nonspecific B-mode findings and operator dependence, ultrasound is best regarded as a complementary rather than a stand-alone modality for lymphedema diagnosis (44, 83). Besides conventional B-mode ultrasound, advanced techniques such as strain (compression) elastography have also been applied in recent years to provide additional contrast in tissue stiffness. For example, Demirci et al. (84) used strain elastography to demonstrate significant differences in strain parameters between affected and unaffected limbs. Also, Yang et al. (85) developed a 2D registration-based strain imaging method for arm lymphedema and showed higher strain values in affected arms vs. contralateral arms. Furthermore, in a recent integrative study from Jeon et al. (86) strain elastography combined with multi-frequency bioimpedance was used to classify tissue stiffness phenotypes in lymphedema limbs and correlated with clinical severity. In lymphedema, strain elastography may help detect early microstructural changes such as incipient fibrosis or stiffening and monitor response to therapy by quantifying subtle changes in tissue elasticity over time.
Different approaches possess unique qualities. ICG lymphography is limited to visualizing superficial lymphatic flows up to a depth of 1.5 cm. In contrast, lymphoscintigraphy and magnetic resonance lymphography are better suited for evaluating deep lymphatic flows (65). However, Lymphoscintigraphy exposes patients to ionizing radiation and has poor spatial and temporal resolution. Each examination has merits and demerits, and we should combine several examinations to evaluate the lymphatic conditions accurately (67, 87). For instance, MRL can serve as a complementary method to be used alongside ICG-L in preoperative evaluations for LVA. This is because it is less effective at identifying lymphatic vessels in the initial stages of lymphedema when lymph stasis or lymphangiectasia are not present (88). Ultrasonography provides a noninvasive and non-ionizing diagnostic technique for patients with lymphedema by assessing the shear wave speed of subcutaneous tissue and visible dermal structure (89, 90). Other objective evaluations of lower extremity lymphedema including dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) (91), and imaging biomarkers (92), serve the diagnostic procedure of lymphedema in different ways. The advantages and limitations of some of the technologies are summarized in Table 5.
Table 5
| Imaging technique | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| X-ray lymphography | Provides deep tissue penetration and direct visualization of lymphatic channels | Invasive; rarely used in current practice |
| Lymphoscintigraphy | Considered the gold standard; high accuracy for detecting lymphatic obstruction; useful for staging | Involves ionizing radiation; poor spatial and temporal resolution |
| Ultrasonography | Non-invasive; no radiation; reliable for assessing soft tissue changes and dermal structure | Limited to superficial tissues; operator dependent |
| Magnetic resonance lymphangiography (MRL) | Non-invasive; high-resolution 3D imaging; allows visualization of lymphatic channels and dermal backflow | Expensive; variable sensitivity and specificity; limited availability |
| Computed tomography (CT)/CT lymphangiography | Provides detailed anatomical localization and quantification of subcutaneous tissue changes | Radiation exposure; limited temporal resolution |
| Near-infrared fluorescence lymphography (NIRF-LI/ICG lymphography) | Clinically approved (203, 204); Real-time (201), dynamic visualization (63); no radiation (205); high sensitivity for superficial lymph flow (200) | Limited penetration depth ( ≤ 1.5 cm); requires dye injection |
| Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) | Objective and quantitative assessment of limb volume and composition | Limited application; less specific for lymphatic dysfunction |
| Optical/molecular imaging and biomarkers | Provide functional and molecular-level insights into lymphatic health; potential for early detection | Mostly experimental; not yet standardized for routine clinical use |
Imaging technologies.
4.2 Subjective methods for lymphedema diagnosis
Compared with the objective methods, the subjective method bears its advantages. It is convenient and cost-effective to perform. Patients who need a long-term rehabilitation process, and higher frequency diagnosis require simpler diagnostic methods since the objective methods can be expensive and complicated if employed frequently. Some patients with limited time are in favor of the subjective assessments compared to the more time-consuming objective measures, enabling more time to be dedicated to treatment. Moreover, since lymphedema is complicated and differs among patients, objective methods alone may not be performed smoothly which requires subjective methods to play a crucial role in the diagnosis process.
Generally, patients suspected of lymphedema complain about subjective symptoms such as a feeling of heaviness, numbness, or tingling. To get insights into these symptoms, self-report tools such as lymphedema-specific questionnaires consistent with symptoms of lymphedema can promote rapid diagnosis and facilitate evaluation of treatment outcomes (93). Lymphedema Symptom Intensity and Distress Survey Arm (LSIDS-A) is a reliable and valid instrument to assess arm lymphedema and its multidimensional symptoms which provides valuable information that can be used to inform clinicians and enhance patient care (94). When involved lymphedema occurs in lower limbs, the Lymphedema Symptom Intensity and Distress Survey-Lower Limb (LSIDS-L) is a valid tool for detecting and quantifying symptoms of patients with lymphedema (95). A similar tool can be used to evaluate symptoms related to the head and neck (96). Subjective clinical measures are often based on medical history and physical examinations (85). During subjective measures, the unaffected side provided a baseline for comparison, comparing changes over time (97) and assessing patients' subjective symptoms (98).
In clinical practice, the selection of appropriate diagnostic methods for lymphedema depends on a variety of factors, including risk factors and physical examination findings. To illustrate the diagnostic decision-making process, Figure 1 provides a flowchart that integrates risk factors and objective limb measurements. This diagram outlines how clinicians can select the most appropriate diagnostic tests and interventions based on the patient's specific condition and presentation.
Figure 1
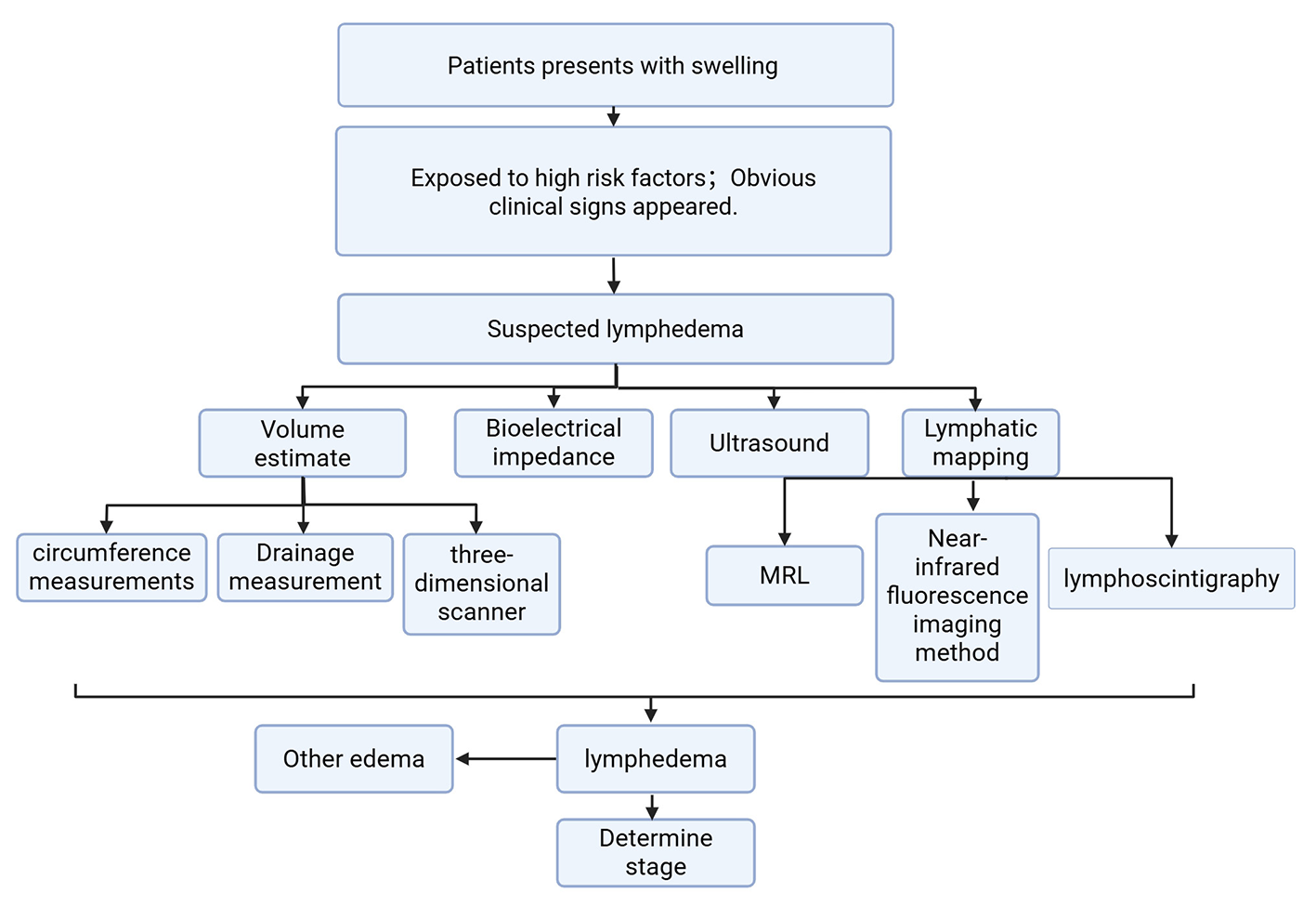
Diagnostic decision making flow chart for lymphedema.
5 Clinical research and standard of care
Treatment of lymphedema aims to relieve symptoms, reduce swelling, and improve quality of life. Common treatment methods, including manual lymphatic drainage, total decongestive physiotherapy, compression sleeve therapy, exercise, and weight reduction, are all non-surgical approaches that require prolonged persistence. However, patient adherence to these treatments tends to decline over time. Surgical interventions such as lymphovenous anastomosis/bypass or vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT), are applicable in early postoperative interventions and are ineffective for fibrosis caused by late lymphedema or fat deposition (99). Currently, no approved pharmacological standard therapy exists for lymphedema. However, early clinical data, such as the 2023 pilot study on topical tacrolimus, show promising results in reducing volume and symptoms (100). Additionally, translational research focusing on immune modulation (e.g., targeting the TGF-β axis and CD4+T cells) and fibrosis is emerging as a potential therapeutic approach (101). The mechanism of lymphedema is an important area of research to understand how lymphatic damage and interstitial fluid accumulation impair lymphocyte function and lead to a range of complications, which may help to identify appropriate targeted treatments for prevention and diagnosis. The establishment of collateral circulation pathways and the resolution of lymphatic circulation abnormalities are the core of the lymphedema treatment. Studies indicate that lymphatic side branches are present in both affected and absent limbs and are more frequent in primary lymphedema compared to secondary lymphedema (71). This is important for early diagnosis and treatment planning of lymphedema.
5.1 Non-surgical method: multiple methods are often used in combination
5.1.1 Rehabilitation
The primary aim of non-surgical methods is to relieve the symptoms associated with swelling, rather than to cure the underlying disease. Complete decongestive therapy (CDT) is currently considered the standard treatment for lymphedema, including skin care, manual lymph drainage, compression and exercise. The duration of lymphedema is a predictor of treatment effectiveness (102). CDT can effectively reduce lymphedema, but the contribution of each component of complete decongestive therapy has not been determined. As one of the methods, Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) may be beneficial in mild lymphedema and prevention, but its role in reducing tissue edema and extracellular fluid or skin thickness and improving fibrosis needs to be further explored. Long-term self-management is a challenge for patients with lymphedema, and CDT is not suitable for patients who have difficulty controlling blood pressure, paralysis, diabetes, bronchial asthma, acute infection, heart failure, and deep vein thrombosis (103). The majority of patients with primary lymphedema are controlled by compression therapy (compression bandages and compression garments) (104), exercise, and maintaining normal weight (105). For patients with secondary lymphedema, other modalities are usually more effective in combination with CDT. For example, the integration of electrotherapy modalities, specifically faradic current or ultrasound, in conjunction with CDT, has the potential to provide more substantial decreases in lymphedema volume, discomfort, and functional handicap (106).
In addition, there are many ways to further control the progression of lymphedema and reduce the impact of complications. In particular, electric stimulation (ES) has an influence on lymphedema's critical stages from onset to ulcer formation, inhibiting lymphedema progression and managing complications (107). The effectiveness of photobiomodulation (PBM) in treating head and neck lymphedema (108) and its anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic effects (109). Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) therapy and low-level laser therapy (LLLT) have been identified as efficacious interventions for the management of postmastectomy upper limb lymphedema (PML). When used together, these therapies have been shown to have slightly better long-term effects on pain compared to using pneumatic compression therapy alone (110).
5.1.2 Pharmacotherapy
Inflammation preceded lipogenesis in the mouse tail lymphedema model, and inflammatory markers MCP-1 and nitric oxide may be potential targets for lymphedema management (111). Lymphedema and lymphatic stasis also led to CD4+ cell inflammation and mature T helper cell infiltration. CD4+ cell depletion significantly reduced lymphedema, inflammation, fibrosis, and fat deposition increased lymphangiogenesis, and reduced the pathological changes with lymphedema (112). Similarly, transcription of the type III collagen gene is also upregulated in fibrotic skin nodules of lower-extremity lymphedema (113). Therefore, inflammation-related pathological changes will provide a reliable treatment thought for lymphedema. Numerous studies have employed the migration and accumulation of CD4+ T lymphocytes in edematous regions as an innovative therapeutic target for addressing lymphedema (25, 112). Moreover, pharmacological therapies (Tacrolimus, Anti-IL-4/IL-13 antibodies, Leukotriene B4 antagonists) and cellular therapies have been demonstrated in animal models to treat lymphedema by promoting lymphangiogenesis, improving lymphatic function and inhibiting fibrosis and inflammatory responses (114, 115).
5.1.3 Other treatments
Many cytokines also have potential in the treatment of lymphedema. T-cell-derived cytokines such as IL-4, IL-13, interferon-gamma (IFN-γ), and TGF-β1 are important negative regulators of lymphangiogenesis, which reduce collateral lymphatic vessel formation by inhibiting lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC) proliferation and lymphatic vessel formation, migration and function (26, 116). Inhibiting anti-lymphangiogenic cytokines to promote collateral lymphatic vessel formation is an important area of research. Compared to approaches that use pro-lymphangiogenic cytokines like VEGF-C or other methods, this approach reduces inflammatory responses without increasing cancer metastasis or tumor growth (117), which is a breakthrough in the direction of disease research. Transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1) is an important regulator of extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition in secondary lymphedema, which is significantly increased in the skin of lymphedema patients. Inhibition of TGF-β1 in the mouse model of lymphedema can reduce extracellular matrix deposition, increase the formation of collateral lymphatic vessels, and inhibit the infiltration of T cells, which may play a role in the treatment of lymphedema (26). In recent years, cell therapy has also had a significant effect on lymphedema. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are believed to be progenitors of lymphatic endothelial cells with anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic, antioxidant stress, and immunomodulatory effects, which may be useful in promoting lymphangiogenesis to improve lymphedema (114). In addition, Toyserkani et al. (118) treated lymphedema for the first time using freshly isolated adipose-derived stromal cells and fat grafting, and patients had significant improvement in their daily symptoms after 4 months, reduced need for compression therapy, reduced volume of the affected arm, and no adverse events.
5.2 Surgical method: significantly improve symptoms
Surgical intervention utilizing reductive techniques is considered the preferred course of action for patients with lymphedema who have not experienced successful outcomes with conservative treatment methods. Suction-assisted liposuction effectively removes excess subcutaneous fibro-adipose tissue and may improve underlying lymphatic function (4) for the treatment of cancer-associated lower extremity lymphedema (119). However, it is important to emphasize that patients undergoing this procedure must wear compression garments for life to maintain the results and prevent recurrence. Additionally, factors such as gender, staging, and a previous history of recurrent dengue may impact the progression and outcomes of liposuction procedures (120).
Further innovations in microsurgical techniques, based on the use of indocyanine green to map lymphatic vessels during surgery, have improved the efficacy of lymphedema. Physiosurgical procedures are widely used, including LVA to divert lymphatic drainage into the veins, and VLNT to transfer healthy lymph nodes from unaffected areas of the body to lymphedematous limbs (74). LVA is a safe and effective method of reducing the severity of lymphedema, which correlates positively with the degree of lymphosclerosis and imaging stage, with lower extremity lymphedema being more severe and higher body mass index (BMI) and older age also leading to more severe lymphosclerosis (121). Hence, while LVA is most effective in managing early-stage upper extremity lymphedema, it can also benefit selected later-stage cases (122, 123). VLNT is believed to enhance the spontaneous regeneration of lymphatic vessel regeneration by stimulating the growth of new vessels from pre-existing capillary lymph vessels and lymphatic endothelial progenitor cells, which aids in the restoration of the regional lymphatic network, hence facilitating physiological recovery (124). VLNT is effective even in advanced cases and has been shown to reduce cellulitis incidence, as well as improve the impaired immunity associated with lymphedema (125, 126). Additionally, VLNT effectively reduces limb volume in both upper and lower limb lymphedema after cancer treatment (127). Nevertheless, the two approaches have little efficacy in addressing fat accumulation and lymphatic solidification and a firm and inflexible swelling during the advanced phase of the disease, therefore prompting the consideration of suction-assisted protein lipectomy (SAPL) as a potential alternative (128). However, it is important to note that patients who undergo SAPL are required to wear compression garments for life to maintain the results and prevent recurrence (129).
When faced with some complex situations, multiple methods are often used in combination. LVA combined with physiotherapy can reduce swollen volume, prevent cellulitis, and improve patients' quality of life (130). The utilization of a combined approach involving LVA and physiotherapy in conjunction with Lymphaticovenous anastomosis with node transfer (LVAN) is a highly efficacious treatment for both initial and advanced stages of lymphedema (126). Therefore, combination therapy should be used for advanced lymphedema (123).
5.3 Lymphedema prevention: a necessary way for this uncurable disease
Since lymphedema is hard to cure, and there will be many complications, it has a significant impact on the quality of life and morbidity of patients. Along with the substantial effort required to control it once it appears, the concept of lymphedema prevention is naturally attractive. Prognosis and preventive measures depend on the etiology and severity of the disease. For primary lymphedema, preventive measures mainly include regular self-management (lymphatic drainage massage, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and avoiding injury or infection). For secondary lymphedema, it is mainly before and after surgery or radiotherapy to avoid the occurrence of lymphatic tissue damage or secondary infection. Radiotherapy can have an adverse effect on the outcomes of anastomosis by causing lymphatic fibrosis and impairing the regeneration of lymphatic vessels (131). At the same time, the update of technology also provides new possibilities for the prevention of lymphedema.
The timely identification of lymphedema, particularly among populations at high risk, is essential for effective preventative strategies. Comprehensively identifying and illustrating the potential risk factors predicting the occurrence of lymphedema are essential for the effective prevention and management of lymphedema (132). Near-infrared fluorescence lymphatic imaging (NIRF-LI) monitoring can characterize the early onset of peripheral lymphatic dysfunction as a predictor of breast cancer-associated lymphedema (133). Newer technologies such as bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) have shown the ability to detect subclinical lymphedema, allowing for early intervention and lower incidence of long-term lymphedema. Notably, the PREVENT trial demonstrated that BIS-triggered intervention significantly reduced the progression to chronic lymphedema compared to traditional tape measurement techniques (134).
Self-management is a viable strategy for the prevention of many issues (135). For instance, the use of self-management practices has a critical role in the prevention and management of lymphedema associated with breast cancer. Nevertheless, it is worth noting that breast cancer survivors exhibited inadequate lymphedema self-management practices. This deficiency can be attributed to their limited understanding of lymphedema, low levels of self-confidence, distorted perceptions of their condition, and insufficient social support. These factors should be taken into account when designing comprehensive intervention programmes (136). Multiple randomized clinical trials have provided evidence of the preventive efficacy of physiotherapy in the immediate postoperative period (137–139). While MLD has been shown to have a positive preventive impact on lymphedema (140, 141), its long-term efficacy in preventing the development of lymphedema may be limited (142). Thus, additional prophylactic strategies may be necessary.
Lymphedema Prevention Surgery (LPS) like axillary reverse mapping (ARM), immediate lymphatic reconstruction (ILR) Simplified Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventing Healing Approach (SLYMPHA) to preserve and restore lymphatic flow through lymphatic venous bypass (LVB), and has been shown to have the potential to reduce the risk of lymphedema in breast cancer patients requiring axillary lymph node dissection (143–145). Recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) data published in 2023 have demonstrated that ILR significantly reduces the incidence of BCRL following axillary lymph node dissection (ALND). This preliminary evidence highlights the promising role of ILR in preventing the development of lymphedema in these patients. However, the study's limitations include a relatively small sample size and short follow-up duration, which may affect the long-term applicability of the results (146). Lymphedema is observed in around 30% of breast cancer patients who have undergone axillary lymph node dissection. The implementation of ILR has been found to significantly decrease the risk of developing lymphedema. This is achieved through the construction of prophylactic lymphovenous anastomosis, which involves connecting disrupted lymphatic channels in the arm to nearby axillary venous tributaries after ALND (147), thereby providing a route for the restoration of lymphatic drainage (148). Based on the present findings, the utilization of ILR demonstrates considerable potential as a secure strategy for the prevention of lymphedema among patients at high risk (149, 150). Also, in the face of BCRL, axillary reverse mapping (ARM) was developed to map and preserve arm lymphatic drainage during ALND (151), which is a simple and effective technique that appears to have reduced lymphedema rates after axillary surgery (152, 153). SLYMPHA can be regarded as an adjunct procedure to ALND for all patients during breast surgery. It is a simplified version of LYMPHA. The study showed that the lymphedema rate of patients who underwent SLYMPHA was significantly lower in comparison to those without SLYMPHA (154).
The immune functions exhibit a notable decrease in individuals with secondary lymphedema, accompanied by an upregulation of many T-cell-associated networks in such circumstances. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that lymphatic dysfunction plays a role in promoting secondary bacterial and fungal infections, as well as initiating inflammation in the skin and subcutaneous tissue, contributing to the advancement of lymphedema. Therefore, CD8+T-cell exhaustion patterns should be taken into consideration for the prevention of lymphedema (155). The study found that CD4+T cells contribute to lymphangiogenesis are activated in regional lymph nodes and migrate to the skin to initiate lymphedema which demonstrates that the CD4+T cell is a potential therapeutic target for the prevention of lymphedema (112, 116, 156). As shown in Table 6, the clinical evidence for the main treatment methods in lymphedema management is summarized.
Table 6
| Intervention | Patient selection criteria/indications | Primary endpoints/outcomes | Follow-up duration | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete decongestive therapy (CDT) (206–210) | Head and neck lymphedema; early to moderate lymphedema; compliant patients | Volume reduction, symptom relief, improved QoL; questionnaire for lower limb lymphoedema | 5–18 months | Requires lifelong adherence; not suitable for patients with comorbidities (e.g., DVT, heart failure); supplemented with advanced treatments like liposuction or enhanced compression techniques in later stage; psychological support |
| Manual lymphatic drainage (MLD) (138, 211) | Mild lymphedema or prophylaxis | Subjective symptom improvement, reduced swelling; volumetric changes, adverse events, function, subjective sensations, QoL, cost of care | 4–6 months | Limited evidence for long-term efficacy; operator-dependent |
| Lymphaticovenous anastomosis (LVA) (212–215) | Early-stage lymphedema; functional lymphatic vessels | Volume reduction, limb/subfascial volume, decreased cellulitis episodes | 1–5 years | Less effective in late-stage fibrosis; requires microsurgical expertise |
| Vascularized lymph node transfer (VLNT) (216, 217) | Moderate to advanced lymphedema; failed conservative therapy | Volume reduction, improved lymphatic function, reduced infections; improved circumferential reduction rates and lymphedema-specific quality-of-life questionnaire scores | 2–5 years | Donor-site morbidity; variable graft survival |
| Liposuction (SAPL) (119, 218, 219) | Non-pitting edema; fibrofatty deposition; advanced lymphedema | Volume reduction, improved contour | 3–24 months | Requires lifelong compression; not addressing lymphatic function; sex, stage, and recurrent erysipelas history influence effect |
| Topical tacrolimus (100, 220, 221) | Early inflammatory lymphedema; women with stage I or II BCRL | Volume reduction, skin softening, improved arm volume, L-Dex, and HRQoL | 3–12 months | Limited clinical data; not yet standard therapy |
| Exercise + weight control (222–225) | All stages, especially obese patients | Volume stabilization, improved mobility | 3–12 months | Adherence challenging |
Clinical evidence table of main treatment methods.
6 Conclusion
Lymphedema reflects the convergence of genetic susceptibility, lymphatic injury, chronic inflammation, and tissue remodeling. Early detection and timely intervention are critical, as delayed treatment permits irreversible fibroadipose changes that diminish therapeutic efficacy. Current management combines careful risk assessment, advanced imaging, and multimodal therapy incorporating conservative, surgical, and emerging pharmacologic strategies. Future priorities include comprehensive genomic profiling of primary lymphedema, refinement of imaging biomarkers for preclinical disease, and development of targeted immunomodulatory and antifibrotic agents. Progress will depend on close integration of basic, translational, and clinical research to disrupt the pathogenic cycle, personalize therapy, and reduce the global burden of this disabling condition.
Statements
Author contributions
TW: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JP: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. QY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SChe: Conceptualization, Data curation, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. YY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. SCha: Conceptualization, Data curation, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. RY: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing. JS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National College Students Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program (202510304053), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82101455), Nantong 14th Five-Year Plan for Science, Education and Health Project (NTCXTD48), Nantong Civic Science, Technology Project of China(MS2023045), Jiangsu Provincial Medical Innovation Center (CXZX202212), Jiangsu Provincial Research Hospital (YJXYY202204).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The author(s) declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1.
Rofstad EK Tunheim SH Mathiesen B Graff BA Halsør EF Nilsen K et al . Pulmonary and lymph node metastasis is associated with primary tumor interstitial fluid pressure in human melanoma xenografts. Cancer Res. (2002) 62:661–4.
2.
Lee S-O Kim IK . Molecular pathophysiology of secondary lymphedema. Front Cell Dev Biol. (2024) 12 1363811. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1363811
3.
Bowman C Rockson SG . The role of inflammation in lymphedema: a narrative review of pathogenesis and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25 3907. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073907
4.
Sudduth C Greene AK . Primary lymphedema: update on genetic basis and management. Adv Wound Care. (2022) 11 374–81. doi: 10.1089/wound.2020.1338
5.
Aspelund A Robciuc MR Karaman S Makinen T Alitalo K . Lymphatic system in cardiovascular medicine. Circ Res. (2016) 118 515–30. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306544
6.
Ostergaard P Simpson MA Connell FC Steward CG Brice G Woollard WJ et al . Mutations in GATA2 cause primary lymphedema associated with a predisposition to acute myeloid leukemia (Emberger syndrome). Nat Genet. (2011) 43 929–31. doi: 10.1038/ng.923
7.
Calvo KR Hickstein DD . The spectrum of GATA2 deficiency syndrome. Blood. (2023) 141 1524–32. doi: 10.1182/blood.2022017764
8.
Chen J Wang L Wu X Wu B Li H Xiao S et al . Case report: surgical management of primary lymphedema with a novel PR OX1 mutation involving upper and lower limbs. Front Genet. (2025) 16 1560471. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1560471
9.
Mantovani F Kitsou K Magiorkinis G . HERVs: expression control mechanisms and interactions in diseases and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Genes. (2024) 15 192. doi: 10.3390/genes15020192
10.
Bonetti G Paolacci S Samaja M Maltese PE Michelini S Michelini S et al . Low efficacy of genetic tests for the diagnosis of primary lymphedema prompts novel insights into the underlying molecular pathways. Int J Mol Sci. (2022) 23. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137414
11.
Greene AK Zurakowski D Goss JA . Body mass index and lymphedema morbidity: comparison of obese versus normal-weight patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2020) 146 402–7. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007021
12.
Burian EA Rungby J Karlsmark T Nørregaard S Cestari M Franks PJ et al . The impact of obesity on chronic oedema/lymphoedema of the leg - an international multicenter cross-sectional study (LIMPRINT). Int J Obes. (2024) 48 1238–47. doi: 10.1038/s41366-024-01544-0
13.
Scalise A Aggarwal A Sangwan N Hamer A Guntupalli S Park HE et al . A divergent platelet transcriptome in patients with lipedema and lymph edema. Genes. (2024) 15 737. doi: 10.3390/genes15060737
14.
Mantilla B Shapiro SC . Acute urinary retention in systemic lupus erythematosus: UR-INE for disaster. Am J Med. (2021) 134 332–4. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2020.09.032
15.
DiSipio T Rye S Newman B Hayes S . Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. (2013) 14 500–15. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70076-7
16.
Coleman-Belin JC Rubin J Boe LA Diwan R Monge JJL Dinh D-D et al . Protective factors associated with normal lymphatic function after axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer treatment. Ann Surg Oncol. (2025) 32:3260–7. doi: 10.1245/s10434-025-16918-5
17.
Jakub JW Boughey JC Hieken TJ Piltin M Forte AJ Vijayasekaran A et al . Lymphedema rates following axillary lymph node dissection with and without immediate lymphatic reconstruction: a prospective trial. Ann Surg Oncol. (2024) 31:7349–59. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15715-w
18.
Pillay V Shukla L Herle P Maciburko S Bandara N Reid I et al . Radiation therapy attenuates lymphatic vessel repair by reducing VEGFR−3 signalling. Front Pharmacol. (2023) 14:1152314. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1152314
19.
Lin C Su J Wu AJ Lin N Hossack M-S Shi W et al . External validation of a 5-factor risk model for breast cancer-related lymphedema. JAMA Netw Open. (2025) 8 e2455383. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.55383
20.
Decorte T Cerckel M Kheir GB Monten C Vandecasteele K Vanden Bossche L et al . Risk factors for lower limb lymphedema after gynecological cancer treatment: a systematic review. Front Oncol. (2025) 15 1561836. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1561836
21.
Couteaux C Demaneuf T Bien L Munoz M Worms B Chésimar S et al . Postelimination cluster of lymphatic filariasis, futuna, 2024. Emerg Infect Dis. (2025) 31:488–96. doi: 10.3201/eid3103.241317
22.
Jiang X Tian W Granucci EJ Tu AB Kim D Dahms P et al . Decreased lymphatic HIF-2α accentuates lymphatic remodeling in lymphedema. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:5562–75. doi: 10.1172/JCI136164
23.
Jiang X Tian W Kim D McQuiston AS Vinh R Rockson SG et al . Hypoxia and hypoxia-inducible factors in lymphedema. Front Pharmacol. (2022) 13:851057. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.851057
24.
Savetsky IL Ghanta S Gardenier JC Torrisi JS García Nores GD Hespe GE et al . Th2 cytokines inhibit lymphangiogenesis. PLoS ONE. (2015) 10 e0126908. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0126908
25.
Gardenier JC Kataru RP Hespe GE Savetsky IL Torrisi JS Nores GDG et al . Topical tacrolimus for the treatment of secondary lymphedema. Nat Commun. (2017) 8 14345. doi: 10.1038/ncomms14345
26.
Baik JE Park HJ Kataru RP Savetsky IL Ly CL Shin J et al . TGF-β1 mediates pathologic changes of secondary lymphedema by promoting fibrosis and inflammation. Clin Transl Med. (2022) 12 e758. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.758
27.
Chen Z Ghavimi SAA Wu M McNamara J Barreiro O Maridas D et al . PPARγ agonist treatment reduces fibroadipose tissue in secondary lymph edema by exhausting fibroadipogenic PDGFRα+ mesenchymal cells. JCI Insight. (2023) 8:e165324. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.165324
28.
Karaman S Lehti S Zhang C Taskinen M-R Käkelä R Mardinoglu A et al . Multi-omics characterization of lymphedema-induced adipose tissue resulting from breast cancer-related surgery. FASEB J. (2024) 38:e70097. doi: 10.1096/fj.202400498RR
29.
Koc M Wald M Varaliová Z Ondrujová B CíŽková T Brychta M et al . Lymphedema alters lipolytic, lipogenic, immune and angiogenic properties of adipose tissue: a hypothesis-generating study in breast cancer survivors. Sci Rep. (2021) 11 8171. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-87494-3
30.
Cuzzone DA Weitman ES Albano NJ Ghanta S Savetsky IL Gardenier JC et al . IL-6 regulates adipose deposition and homeostasis in lymphedema. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. (2014) 306:H1426–34. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.01019.2013
31.
Rockson SG . Advances in lymphedema. Circ Res. (2021) 128:2003–16. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.318307
32.
Brown S Dayan JH Kataru RP Mehrara BJ . The vicious circle of stasis, inflammation, and fibrosis in lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2023) 151:330e−41e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009866
33.
Hu Z Zhao X Wu Z Qu B Yuan M Xing Y et al . Lymphatic vessel: origin, heterogeneity, biological functions, and therapeutic targets. Signal Transduct Target Ther. (2024) 9:9. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01723-x
34.
Fu A Liu C . The function of T cell immunity in lymphedema: a comprehensive review. Lymphat Res Biol. (2023) 21:556–64. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2023.0002
35.
McDuff SGR Mina AI Brunelle CL Salama L Warren LEG Abouegylah M et al . Timing of lymphedema after treatment for breast cancer: when are patients most at risk?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2019) 103:62–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.08.036
36.
Maruccia M Elia R Ciudad P Nacchiero E Nicoli F Vestita M et al . Postmastectomy upper limb lymphedema: combined vascularized lymph node transfer and scar release with fat graft expedites surgical and patients' related outcomes. A retrospective comparative study. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2019) 72:892–901. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2019.01.029
37.
Wynn TA . Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol. (2008) 214:199–210. doi: 10.1002/path.2277
38.
Wolf S von Atzigen J Kaiser B Grünherz L Kim BS Giovanoli P et al . Is lymphedema a systemic disease? A paired molecular and histological analysis of the affected and unaffected tissue in lymphedema patients. Biomolecules. (2022) 12:62–70. doi: 10.3390/biom12111667
39.
Vignes S Albuisson J Champion L Constans J Tauveron V Malloizel J et al . Primary lymphedema French national diagnosis and care protocol (PNDS; Protocole National de Diagnostic et de Soins). Orphanet J Rare Dis. (2021) 16:18. doi: 10.1186/s13023-020-01652-w
40.
Cheng MH Ho OA Tsai TJ Lin YL Kuo CF . Breast cancer-related lymphedema correlated with incidence of cellulitis and mortality. J Surg Oncol. (2022) 126:1162–8. doi: 10.1002/jso.27054
41.
Vargo M Aldrich M Donahue P Iker E Koelmeyer L Crescenzi R et al . Current diagnostic and quantitative techniques in the field of lymphedema management: a critical review. Med Oncol. (2024) 41:241. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02472-9
42.
Gillespie TC Sayegh HE Brunelle CL Daniell KM Taghian AG . Breast cancer-related lymphedema: risk factors, precautionary measures, and treatments. Gland Surg. (2018) 7:379–403. doi: 10.21037/gs.2017.11.04
43.
Aron A Zavaleta C . Current and developing lymphatic imaging approaches for elucidation of functional mechanisms and disease progression. Mol Imaging Biol. (2024) 26:1–16. doi: 10.1007/s11307-023-01827-4
44.
Nagy BI Mohos B Tzou CJ . Imaging modalities for evaluating lymphedema. Medicina. (2023) 59:241. doi: 10.3390/medicina59112016
45.
Executive Committee of the International Society of Lymphology . The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2020 consensus document of the international society of lymphology. Lymphology. (2020) 53:3–19. doi: 10.2458/lymph.4649
46.
Coriddi M Dayan J Sobti N Nash D Goldberg J Klassen A et al . Systematic review of patient-reported outcomes following surgical treatment of lymphedema. Cancers. (2020) 12:1–16. doi: 10.3390/cancers12030565
47.
Thomas M Gabe-Walters M Humphreys I Watkins A . A new validated lymphoedema-specific patient reported outcome measure (LYMPROM) for adults with Lymphoedema. PLoS ONE. (2025) 20:e0315314. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0315314
48.
Togawa K Ma H Smith AW Neuhouser ML George SM Baumgartner KB et al . Self-reported symptoms of arm lymphedema and health-related quality of life among female breast cancer survivors. Sci Rep. (2021) 11 10701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-89055-0
49.
Garza RM Ooi ASH Falk J Chang DW . The relationship between clinical and indocyanine green staging in lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. (2019) 17:329–33. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2018.0014
50.
Douglass J Kelly-Hope L . Comparison of staging systems to assess lymphedema caused by cancer therapies, lymphatic filariasis, and podoconiosis. Lymphat Res Biol. (2019) 17:550–6. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2018.0063
51.
Executive Committee of the International Society of Lymphology . The diagnosis and treatment of peripheral lymphedema: 2023 consensus document of the international society of lymphology. Lymphology. (2023) 56:133–51. doi: 10.2458/lymph.6372
52.
Fishman JE Moroni EA Cruz C . The Pittsburgh trunk lymphedema staging system (PTLSS) - a validated staging system for the description of breast cancer-associated trunk lymphedema. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2022) 75:3122–8. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2022.02.041
53.
Campisi CC Ryan M Villa G Di Summa P Cherubino M Boccardo F et al . Rationale for study of the deep subfascial lymphatic vessels during lymphoscintigraphy for the diagnosis of peripheral lymphedema. Clin Nucl Med. (2019) 44:91–8. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0000000000002400
54.
Pappalardo M Lin C Ho OA Kuo CF Lin CY Cheng MH . Staging and clinical correlations of lymphoscintigraphy for unilateral gynecological cancer-related lymphedema. J Surg Oncol. (2020) 121:422–34. doi: 10.1002/jso.25817
55.
Kim JB Lee DG . Findings of lymphoscintigraphy and the severity of lymphedema according to the extent of axillary lymph node dissection. Asian J Surg. (2020) 43:95–101. doi: 10.1016/j.asjsur.2019.02.003
56.
Oh SH Kim JH Seong ST Park JY Lee JH Kim GC et al . Lymphoscintigraphy in patients with breast cancer-related lymphedema after sentinel lymph node dissection and axillary radiation therapy. Medicine. (2022) 101:e31985. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031985
57.
Donohoe KJ Carroll BJ Chung DKV Dibble EH Diego E Giammarile F et al . Summary: appropriate use criteria for lymphoscintigraphy in sentinel node mapping and lymphedema/lipedema. J Nucl Med. (2023) 64:525–8. doi: 10.2967/jnumed.123.265560
58.
Yoshida S Koshima I Imai H Sasaki A Fujioka Y Nagamatsu S et al . Indocyanine green lymphography findings in older patients with lower limb lymphedema. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2020) 8:251–8. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2019.03.021
59.
Osterkamp J Strandby R Nerup N Svendsen MB Svendsen LB Achiam M . Intraoperative near-infrared lymphography with indocyanine green may aid lymph node dissection during robot-assisted resection of gastroesophageal junction cancer. Surg Endosc. (2023) 37:1985–93. doi: 10.1007/s00464-022-09684-y
60.
Roh CK Choi S Seo WJ Cho M Son T Kim HI et al . Indocyanine green fluorescence lymphography during gastrectomy after initial endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Br J Surg. (2020) 107:712–9. doi: 10.1002/bjs.11438
61.
Sevick-Muraca EM Fife CE Rasmussen JC . Imaging peripheral lymphatic dysfunction in chronic conditions. Front Physiol. (2023) 14:1132097. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1132097
62.
Trevethan M Bennett S Doig E Patterson F Pigott A . Navigating the application of new innovations: establishing an indocyanine green lymphography clinic in Australia. Health Soc Care Community. (2022) 30:e5549–59. doi: 10.1111/hsc.13979
63.
Matsumoto K Shinaoka A Yamada K Kimata Y . Exercise-loaded indocyanine green fluorescence lymphangiography for diagnosing lymphedema. J Reconstr Microsurg. (2019) 35:138–44. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1667366
64.
Qin ES Bowen MJ James SL Chen WF . Multi-segment bioimpedance can assess patients with bilateral lymphedema. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2020) 73:328–36. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2019.06.041
65.
Yamamoto T Yoshimatsu H Narushima M Yamamoto N Hayashi A Koshima I . Indocyanine green lymphography findings in primary leg lymphedema. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. (2015) 49:95–102. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2014.10.023
66.
Hara H Mihara M . Multilymphosome injection indocyanine green lymphography can detect more lymphatic vessels than lymphoscintigraphy in lymphedematous limbs. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2020) 73:1025–30. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2020.01.021
67.
Hara H Mihara M . Lymphaticovenous anastomosis for advanced-stage lower limb lymphedema. Microsurgery. (2021) 41:140–5. doi: 10.1002/micr.30689
68.
Hara H Mihara M . Multi-area lymphaticovenous anastomosis with multi-lymphosome injection in indocyanine green lymphography: a prospective study. Microsurgery. (2019) 39:167–73. doi: 10.1002/micr.30398
69.
Xu J Du Y Han T Zhu N Zhu S . Protein@Cyanine-based NIR-II lymphography enables the supersensitive visualization of lymphedema and tumor lymphatic metastasis. Adv Healthc Mater. (2023) 12:e2301051. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202301051
70.
Abdelfattah U Jaimez PM Clavero JA Bellantonio V Pons G Masia J . Correlation between superficial and deep lymphatic systems using magnetic resonance lymphangiography in breast cancer-related lymphedema: clinical implications. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2020) 73:1018–24. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2019.11.053
71.
Soga S Onishi F Jinzaki M Mikoshi A Minabe T Shinmoto H . Analysis of collateral lymphatic circulation in patients with lower limb lymphedema using magnetic resonance lymphangiography. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2021) 9:471–81.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.04.029
72.
Miseré RML Wolfs J Lobbes MBI van der Hulst R Qiu SS . A systematic review of magnetic resonance lymphography for the evaluation of peripheral lymphedema. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2020) 8:882–92.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.03.007
73.
Wang L Wu X Wu M Zhao Z Tang H Li S et al . Edema areas of calves measured with magnetic resonance imaging as a novel indicator for early staging of lower extremity lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. (2018) 16:240–7. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2016.0052
74.
Bianchi LMG Irmici G Cè M D'Ascoli E Della Pepa G Di Vita F et al . Diagnosis and treatment of post-prostatectomy lymphedema: what's new?Curr Oncol. (2023) 30:4512–26. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30050341
75.
Rabinowitz D Dysart K Itkin M . Neonatal lymphatic flow disorders: central lymphatic flow disorder and isolated chylothorax, diagnosis and treatment using novel lymphatic imaging and interventions technique. Curr Opin Pediatr. (2022) 34:191–6. doi: 10.1097/MOP.0000000000001109
76.
Yekeler E Krishnamurthy G Smith CL Escobar FA Pinto E Rapp JB et al . Dynamic contrast-enhanced MR lymphangiography: feasibility of using ferumoxytol in patients with chronic kidney disease. Eur Radiol. (2022) 32:2564–71. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-08448-x
77.
Patel S Hur S Khaddash T Simpson S Itkin M . Intranodal CT lymphangiography with water-soluble iodinated contrast medium for imaging of the central lymphatic system. Radiology. (2022) 302:228–33. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021210294
78.
Kim M Suh DH Yang EJ Lim MC Choi JY Kim K et al . Identifying risk factors for occult lower extremity lymphedema using computed tomography in patients undergoing lymphadenectomy for gynecologic cancers. Gynecol Oncol. (2017) 144:153–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.10.037
79.
Yoo JS Chung SH Lim MC Kim YJ Kim KG Hwang JH et al . Computed tomography-based quantitative assessment of lower extremity lymphedema following treatment for gynecologic cancer. J Gynecol Oncol. (2017) 28:e18. doi: 10.3802/jgo.2017.28.e18
80.
Koo KI Ko MH Lee Y Son HW Lee S Hwang CH . Comparison of a novel algorithm quantitatively estimating epifascial fibrosis in three-dimensional computed tomography images to other clinical lymphedema grading methods. PLoS ONE. (2019) 14:e0224457. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0224457
81.
Akita S Ogata F Manabe I Mitsuhashi A Nakamura R Yamaji Y et al . Noninvasive screening test for detecting early stage lymphedema using follow-up computed tomography imaging after cancer treatment and results of treatment with lymphaticovenular anastomosis. Microsurgery. (2017) 37:910–6. doi: 10.1002/micr.30188
82.
Weiss M Baumeister RG Frick A Wallmichrath J Bartenstein P Rominger A . Primary lymphedema of the lower limb: the clinical utility of single photon emission computed tomography/CT. Korean J Radiol. (2015) 16:188–95. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2015.16.1.188
83.
Pirri C Ferraretto C Pirri N Bonaldo L De Caro R Masiero S et al . Ultrasound examination of skin, fasciae and subcutaneous tissue: optimizing rehabilitation for secondary upper limb lymphedema. Diagnostics. (2024) 14:2824. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14242824
84.
Demirci M Sanal C Yagci I Akyuz G . Evaluation of elastographic parameters in patients with breast cancer- related lymphedema and examination of their relationship with clinical data. Lymphat Res Biol. (2025) 23:263–71. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2024.0088
85.
Yang X Torres M Kirkpatrick S Curran WJ Liu T . Ultrasound 2D strain measurement for arm lymphedema using deformable registration: a feasibility study. PLoS ONE. (2017) 12:e0181250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0181250
86.
Jeon H Kim DY Park S-W Lee B-S Kim D Han H-W et al . Biomarkers in lymphedema assessment: integrating elastography and muti-frequency bioimpedance analysis. Biomark Med. (2024) 18:983–93. doi: 10.1080/17520363.2024.2415283
87.
Polomska AK Proulx ST . Imaging technology of the lymphatic system. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. (2021) 170:294–311. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2020.08.013
88.
Yasunaga Y Nakajima Y Mimura S Yuzuriha S Kondoh S . Magnetic resonance lymphography as three-dimensional navigation for lymphaticovenular anastomosis in patients with leg lymphedema. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2021) 74:1253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2020.10.099
89.
Bustos SS Zhou B Huang TCT Shao J Ciudad P Forte AJ et al . Ultrasound vibroelastography for evaluation of secondary extremity lymphedema: a clinical pilot study. Ann Plast Surg. (2020) 85:S92–6. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002448
90.
Dai M Sato A Maeba H Iuchi T Matsumoto M Okuwa M et al . Dermal structure in lymphedema patients with history of acute dermatolymphangioadenitis evaluated by histogram analysis of ultrasonography findings: a case-control study. Lymphat Res Biol. (2016) 14:2–7. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2015.0020
91.
Tassenoy A De Strijcker D Adriaenssens N Lievens P . The use of noninvasive imaging techniques in the assessment of secondary lymphedema tissue changes as part of staging lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. (2016) 14:127–33. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2016.0011
92.
Maita K Garcia JP Torres RA Avila FR Kaplan JL Lu X et al . Imaging biomarkers for diagnosis and treatment response in patients with lymphedema. Biomark Med. (2022) 16:303–16. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2021-0487
93.
Hidding JT Viehoff PB Beurskens CHG van Laarhoven HWM Nijhuis-van der Sanden MWG van der Wees PJ . Measurement properties of instruments for measuring of lymphedema: systematic review. Phys Ther. (2016) 96:1965–81. doi: 10.2522/ptj.20150412
94.
Ridner SH Dietrich MS . Development and validation of the lymphedema symptom and intensity survey-arm. Support Care Cancer. (2015) 23:3103–12. doi: 10.1007/s00520-015-2684-y
95.
Ridner SH Doersam JK Stolldorf DP Dietrich MS . Development and validation of the lymphedema symptom intensity and distress survey-lower limb. Lymphat Res Biol. (2018) 16:538–46. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2017.0069
96.
Ridner SH Deng J Doersam JK Dietrich MS . Lymphedema symptom intensity and distress surveys-truncal and head and neck, version 20. Lymphat Res Biol. (2021) 19:240–8. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0071
97.
Sierla R Dylke ES Shaw T Poon S Kilbreath SL . Assessment of upper limb lymphedema: a qualitative study exploring clinicians' clinical reasoning. Lymphat Res Biol. (2021) 19:151–8. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0006
98.
Mihara M Hara H Tange S Zhou HP Kawahara M Shimizu Y et al . Multisite lymphaticovenular bypass using supermicrosurgery technique f or lymphedema management in lower lymphedema cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2016) 138:262–72. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000002254
99.
Drobot A Bez M Abu Shakra I Merei F Khatib K Bickel A et al . Microsurgery for management of primary and secondary lymphedema. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2021) 9:226–33.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.04.025
100.
Gulmark Hansen FC Jørgensen MG Sørensen JA . Treatment of breast cancer-related lymphedema with topical tacrolimus: a prospective, open-label, single-arm, phase II pilot trial. J Breast Cancer. (2023) 26:46–59. doi: 10.4048/jbc.2023.26.e2
101.
Campbell AC Stull-Lane AR Baik JE Sarker A Shin J Ashokan G et al . Lymphedema pathogenesis involves antigen-driven expansion of CD4+ T cells in skin. Front Immunol. (2025) 16:1620571. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1620571
102.
Michopoulos E Papathanasiou G Krousaniotaki K Vathiotis I Troupis T Dimakakos E . Lymphedema duration as a predictive factor of efficacy of complete decongestive therapy. Lymphology. (2021) 54:140–53. doi: 10.2458/lymph.4788
103.
Godette K Mondry TE Johnstone PA . Can manual treatment of lymphedema promote metastasis?J Soc Integr Oncol. (2006) 4:8–12. doi: 10.1177/15347354241226625
104.
McNeely ML Dolgoy ND Rafn BS Ghosh S Ospina PA Al Onazi MM et al . Nighttime compression supports improved self-management of breast cancer-related lymphedema: a multicenter randomized controlled trial. Cancer. (2022) 128:587–96. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33943
105.
Kwan ML Cohn JC Armer JM Stewart BR Cormier JN . Exercise in patients with lymphedema: a systematic review of the contemporary literature. J Cancer Surviv. (2011) 5:320–36. doi: 10.1007/s11764-011-0203-9
106.
Hemmati M Rojhani-Shirazi Z Zakeri ZS Akrami M Salehi Dehno N . The effect of the combined use of complex decongestive therapy with electrotherapy modalities for the treatment of breast cancer-related lymphedema: a randomized clinical trial. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. (2022) 23:837. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05780-1
107.
Baglivo M Martelli F Paolacci S Manara E Michelini S Bertelli M . Electrical stimulation in the treatment of lymphedema and associated skin ulcers. Lymphat Res Biol. (2020) 18:270–6. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2019.0052
108.
Deng J Lukens JN Swisher-McClure S Cohn JC Spinelli BA Quinn RJ et al . Photobiomodulation therapy in head and neck cancer-related lymphedema: a pilot feasibility study. Integr Cancer Ther. (2021) 20:15347354211037938. doi: 10.1177/15347354211037938
109.
Assis L Moretti AI Abrahão TB de Souza HP Hamblin MR Parizotto NA . Low-level laser therapy (808 nm) contributes to muscle regeneration and prevents fibrosis in rat tibialis anterior muscle after cryolesion. Lasers Med Sci. (2013) 28:947–55. doi: 10.1007/s10103-012-1183-3
110.
Kozanoglu E Gokcen N Basaran S Paydas S . Long-term effectiveness of combined intermittent pneumatic compression plus low-level laser therapy in patients with postmastectomy lymphedema: a randomized controlled trial. Lymphat Res Biol. (2022) 20:175–84. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0132
111.
Cuadrado GA de Andrade MFC Ariga SK de Lima TM Souza HP . Inflammation precedes fat deposition in an experimental model of lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. (2021) 19:116–25. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0061
112.
Zampell JC Yan A Elhadad S Avraham T Weitman E Mehrara BJ . CD4(+) cells regulate fibrosis and lymphangiogenesis in response to lymphatic fluid stasis. PLoS ONE. (2012) 7:e49940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049940
113.
Karayi AK Basavaraj V Narahari SR Aggithaya MG Ryan TJ Pilankatta R . Human skin fibrosis: up-regulation of collagen type III gene transcription in the fibrotic skin nodules of lower limb lymphoedema. Trop Med Int Health. (2020) 25:319–27. doi: 10.1111/tmi.13359
114.
Conrad C Niess H Huss R Huber S von Luettichau I Nelson PJ et al . Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells acquire a lymphendothelial phenotype and enhance lymphatic regeneration in vivo. Circulation. (2009) 119:281–9. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.793208
115.
Meshram GG Kaur N Hura KS . Unilateral primary congenital lymphedema of the upper limb in an 11-month-old infant: a clinical and pharmacological perspective. Open Access Maced J Med Sci. (2018) 6:1682–4. doi: 10.3889/oamjms.2018.261
116.
García Nores GD Ly CL Cuzzone DA Kataru RP Hespe GE Torrisi JS et al . CD4(+) T cells are activated in regional lymph nodes and migrate to skin to initiate lymphedema. Nat Commun. (2018) 9:1970. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04418-y
117.
Korhonen EA Murtomäki A Jha SK Anisimov A Pink A Zhang Y et al . Lymphangiogenesis requires Ang2/Tie/PI3K signaling for VEGFR3 cell-surface expression. J Clin Invest. (2022) 132:14345. doi: 10.1172/JCI155478
118.
Toyserkani NM Jensen CH Sheikh SP Sørensen JA . Cell-assisted lipotransfer using autologous adipose-derived stromal cells for alleviation of breast cancer-related lymphedema. Stem Cells Transl Med. (2016) 5:857–9. doi: 10.5966/sctm.2015-0357
119.
Xin J Sun Y Xia S Chang K Dong C Liu Z et al . Liposuction in cancer-related lower extremity lymphedema: an investigative study on clinical applications. World J Surg Oncol. (2022) 20:6. doi: 10.1186/s12957-021-02472-3
120.
Willet JW Alvaro AI Ibrahim AK Javed MU . A systematic review of efficacy and complications of high-definition liposuction. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2023) 152:57–63. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010203
121.
Lin YS Liu CJ . Predictors of severity of lymphosclerosis in extremity lymphedema. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2022) 10:721–7.e2. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2021.07.019
122.
Campisi CC Scarabosio A Campisi C . Lymphatic microsurgical preventive healing approach for the primary prevention of lymphedema: a 4-year follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg. 153:490e−1e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000010764
123.
Onoda S Nishimon K . The utility of surgical and conservative combination therapy for advanced stage lymphedema. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2021) 9:234–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2020.05.007
124.
Aschen SZ Farias-Eisner G Cuzzone DA Albano NJ Ghanta S Weitman ES et al . Lymph node transplantation results in spontaneous lymphatic reconnection and restoration of lymphatic flow. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2014) 133:301–10. doi: 10.1097/01.prs.0000436840.69752.7e
125.
Sakarya AH Huang CW Yang CY Hsiao HY Chang FC Huang JJ . Vascularized lymph node transplantation successfully reverses lymphedema and maintains immunity in a rat lymphedema model. Bioeng Transl Med. (2022) 7:e10301. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10301
126.
Garza RM Beederman M Chang DW . Physical and functional outcomes of simultaneous vascularized lymph node transplant and lymphovenous bypass in the treatment of lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2022) 150 169–80. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009247
127.
Ward J King I Monroy-Iglesias M Russell B van Hemelrijck M Ramsey K et al . A meta-analysis of the efficacy of vascularised lymph node transfer in reducing limb volume and cellulitis episodes in patients with cancer treatment-related lymphoedema. Eur J Cancer. (2021) 151:233–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.02.043
128.
Granzow JW . Lymphedema surgery: the current state of the art. Clin Exp Metastasis. (2018) 35:553–8. doi: 10.1007/s10585-018-9897-7
129.
Brorson H Ohlin K Olsson G Långström G Wiklund I Svensson H . Quality of life following liposuction and conservative treatment of arm lymphedema. Lymphology. (2006) 39:8–25.
130.
Darrach H Yesantharao PS Persing S Kokosis G Carl HM Bridgham K et al . Surgical versus nonsurgical management of postmastectomy lymphedema: a prospective quality of life investigation. J Reconstr Microsurg. (2020) 36:606–15. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1713667
131.
Spiegel DY Willcox J Friedman R Kinney J Singhal D Recht A et al . Prospective study of radiation therapy after immediate lymphatic reconstruction: analysis of the dosimetric implications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2023) 117:446–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2023.04.027
132.
Shen A Lu Q Zhang L Bian J Zhu F Zhang Z et al . Risk factors of breast cancer-related lymphoedema: protocol of an umbrella review. BMJ Open. (2023) 13:e070907. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-070907
133.
Aldrich MB Rasmussen JC DeSnyder SM Woodward WA Chan W Sevick-Muraca EM et al . Prediction of breast cancer-related lymphedema by dermal backflow detected with near-infrared fluorescence lymphatic imaging. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2022) 195:33–41. doi: 10.1007/s10549-022-06667-4
134.
Shah C Boyages J Koelmeyer L Chen SL Vicini F . Timing of breast cancer related lymphedema development over 3 years: observations from a large, prospective randomized screening trial comparing bioimpedance spectroscopy (BIS) versus tape measure. Ann Surg Oncol. (202) 31:7487–95. doi: 10.1245/s10434-024-15706-x
135.
Temur K Kapucu S . The effectiveness of lymphedema self-management in the prevention of breast cancer-related lymphedema and quality of life: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Oncol Nurs. (2019) 40:22–35. doi: 10.1016/j.ejon.2019.02.006
136.
Shen A Wu P Qiang W Fu X Zhu F Pang L et al . Factors associated with lymphedema self-management behaviours among breast cancer survivors: a cross-sectional study. J Clin Nurs. (2023) 32:7330–45. doi: 10.1111/jocn.16833
137.
Torres Lacomba M Yuste Sánchez MJ Zapico Goñi A Prieto Merino D Mayoral del Moral O Cerezo Téllez E et al . Effectiveness of early physiotherapy to prevent lymphoedema after surgery for breast cancer: randomised, single blinded, clinical trial. BMJ. (2010) 340:b5396. doi: 10.1136/bmj.b5396
138.
Cho Y Do J Jung S Kwon O Jeon JY . Effects of a physical therapy program combined with manual lymphatic drainage on shoulder function, quality of life, lymphedema incidence, and pain in breast cancer patients with axillary web syndrome following axillary dissection. Support Care Cancer. (2016) 24:2047–57. doi: 10.1007/s00520-015-3005-1
139.
Lin Y Wu C He C Yan J Chen Y Gao L et al . Effectiveness of three exercise programs and intensive follow-up in improving quality of life, pain, and lymphedema among breast cancer survivors: a randomized, controlled 6-month trial. Support Care Cancer. (2022) 31:9. doi: 10.1007/s00520-022-07494-5
140.
Liang M Chen Q Peng K Deng L He L Hou Y et al . Manual lymphatic drainage for lymphedema in patients after breast cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine. (2020) 99:e23192. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023192
141.
Lin Y Yang Y Zhang X Li W Li H Mu D . Manual lymphatic drainage for breast cancer-related lymphedema: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Breast Cancer. (2022) 22:e664–73. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2022.01.013
142.
Devoogdt N Geraerts I Van Kampen M De Vrieze T Vos L Neven P et al . Manual lymph drainage may not have a preventive effect on the development of breast cancer-related lymphoedema in the long term: a randomised trial. J Physiother. (2018) 64:245–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2018.08.007
143.
Abdelhamid MI Bari AA Farid MI Nour H . Evaluation of axillary reverse mapping (ARM) in clinically axillary node negative breast cancer patients - randomised controlled trial. Int J Surg. (2020) 75:174–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2020.01.152
144.
Levy AS Murphy AI Ishtihar S Peysakhovich A Taback B Grant RT et al . Lymphatic microsurgical preventive healing approach for the primary prevention of lymphedema: a 4-year follow-up. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2023) 151:413–20. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009857
145.
Shaffer K Cakmakoglu C Schwarz GS ElSherif A Al-Hilli Z Djohan R et al . Lymphedema prevention surgery: improved operating efficiency over time. Ann Surg Oncol. (2020) 27:4695–701. doi: 10.1245/s10434-020-08890-z
146.
Coriddi M Dayan J Bloomfield E McGrath L Diwan R Monge J et al . Efficacy of immediate lymphatic reconstruction to decrease incidence of breast cancer-related lymphedema: preliminary results of randomized controlled trial. Ann Surg. (2023) 278:630–7. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000005952
147.
Cook JA Sinha M Lester M Fisher CS Sen CK Hassanein AH . Immediate lymphatic reconstruction to prevent breast cancer-related lymphedema: a systematic review. Adv Wound Care. (2022) 11:382–91. doi: 10.1089/wound.2021.0056
148.
Friedman R Spiegel DY Kinney J Willcox J Recht A Singhal D . Quantifying radiation in the axillary bed at the site of lymphedema surgical prevention. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2023) 201:299–305. doi: 10.1007/s10549-023-06988-y
149.
Abdelfattah U Pons G Masià J . Evaluating the impact of immediate lymphatic reconstruction for the surgical prevention of lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2023) 151:522e−3e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000009942
150.
Johnson AR Fleishman A Granoff MD Shillue K Houlihan MJ Sharma R et al . Evaluating the impact of immediate lymphatic reconstruction for the surgical prevention of lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2021) 147:373e−81e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007636
151.
Noguchi M Inokuchi M Noguchi M Morioka E Kurita T . Axillary reverse mapping in patients undergoing axillary dissection -a short review of the literature. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2020) 46:2218–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2020.07.026
152.
Tummel E Ochoa D Korourian S Betzold R Adkins L McCarthy M et al . Does axillary reverse mapping prevent lymphedema after lymphadenectomy?Ann Surg. (2017) 265:987–92. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001778
153.
Faisal M Sayed MG Antonious K Abo Bakr A Farag SH . Prevention of lymphedema via axillary reverse mapping for arm lymph-node preservation following breast cancer surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Patient Saf Surg. (2019) 13:35. doi: 10.1186/s13037-019-0217-1
154.
Ozmen T Layton C Friedman-Eldar O Melnikau S Kesmodel S Moller MG et al . Evaluation of simplified lymphatic microsurgical preventing healing approach (SLYMPHA) for the prevention of breast cancer-related lymphedema after axillary lymph node dissection using bioimpedance spectroscopy. Eur J Surg Oncol. (2022) 48:1713–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2022.04.023
155.
Horn S Borrero-Wolff D Ritter M Arndts K Wiszniewsky A Debrah LB et al . Distinct immune profiles of exhausted effector and memory CD8+ T cells in individuals with filarial lymphedema. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. (2021) 11 680832. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.680832
156.
Ogata F Fujiu K Matsumoto S Nakayama Y Shibata M Oike Y et al . Excess lymphangiogenesis cooperatively induced by macrophages and CD4 (+) T cells drives the pathogenesis of lymphedema. J Invest Dermatol. (2016) 136:706–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2015.12.001
157.
Hou Y Shin YJ Han EJ Choi JS Park JM Cha JH et al . Distribution of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-3/Flt4 mRNA in adult rat central nervous system. J Chem Neuroanat. (2011) 42:56–64. doi: 10.1016/j.jchemneu.2011.06.001
158.
Kannan S Rutkowski JM . VEGFR-3 signaling in macrophages: friend or foe in disease?Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1349500. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1349500
159.
Duff SE Jeziorska M Kumar S Haboubi N Sherlock D O'Dwyer ST et al . Lymphatic vessel density, microvessel density and lymphangiogenic growth factor expression in colorectal cancer. Colorectal Dis. (2007) 9:793–800. doi: 10.1111/j.1463-1318.2006.01199.x
160.
Banerjee K Kerzel T Bekkhus T de Souza Ferreira S Wallmann T Wallerius M et al . VEGF-C-expressing TAMs rewire the metastatic fate of breast cancer cells. Cell Rep. (2023) 42:113507. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113507
161.
Tan C Ge ZD Kurup S Dyakiv Y Liu T Muller WA et al . FOXC1 and FOXC2 ablation causes abnormal valvular endothelial cell junctions and lymphatic vessel formation in myxomatous mitral valve degeneration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2024) 44:1944–59. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.124.320316
162.
Kazenwadel J Betterman KL Chong CE Stokes PH Lee YK Secker GA et al . GATA2 is required for lymphatic vessel valve development and maintenance. J Clin Invest. (2015) 125:2979–94. doi: 10.1172/JCI78888
163.
Mahamud MR Geng X Ho YC Cha B Kim Y Ma J et al . GATA2 controls lymphatic endothelial cell junctional integrity and lymphovenous valve morphogenesis through miR-126. Development. (2019) 146:680832. doi: 10.1101/660068
164.
Ding W Tang W Zhi J . The lymphangiogenic factor CCBE1 promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth in colorectal cancer. Curr Mol Med. (2022) 22:819–25. doi: 10.2174/1566524021666211124092804
165.
Marchiò S Astanina E Bussolino F . Emerging lymphae for the fountain of life. EMBO J. (2013) 32:609–11. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.13
166.
Bos FL Caunt M Peterson-Maduro J Planas-Paz L Kowalski J Karpanen T et al . CCBE1 is essential for mammalian lymphatic vascular development and enhances the lymphangiogenic effect of vascular endothelial growth factor-C in vivo. Circ Res. (2011) 109:486–91. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.111.250738
167.
Dupont L Joannes L Morfoisse F Blacher S Monseur C Deroanne CR et al . ADAMTS2 and ADAMTS14 can substitute for ADAMTS3 in adults for pro-VEGFC activation and lymphatic homeostasis. JCI Insight. (2022) 7:56–64. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.151509
168.
Westcott GP Emont MP Gulko A Zhou Z Kim C Varma G et al . Single-nuclear transcriptomics of lymphedema-associated adipose reveals a pro-lymphangiogenic stromal cell population. bioRxiv. (2025). doi: 10.1101/2025.02.18.638907
169.
Kawano H Katayama Y Minagawa K Shimoyama M Henkemeyer M Matsui T et al . novel feedback mechanism by Ephrin-B1/B2 in T-cell activation involves a concentration-dependent switch from costimulation to inhibition. Eur J Immunol. (2012) 42:1562–72. doi: 10.1002/eji.201142175
170.
Héroult M Schaffner F Pfaff D Prahst C Kirmse R Kutschera S et al . EphB4 promotes site-specific metastatic tumor cell dissemination by interacting with endothelial cell-expressed ephrinB2. Mol Cancer Res. (2010) 8:1297–309. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-09-0453
171.
Tang H Zeng R He E Zhang I Ding C Zhang A . Piezo-type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 (Piezo1): a promising therapeutic target and its modulators. J Med Chem. (2022) 65:6441–53. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00085
172.
Choi D Park E Yu RP Cooper MN Cho IT Choi J et al . Piezo1-regulated mechanotransduction controls flow-activated lymphatic expansion. Circ Res. (2022) 131:e2–21. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.320565
173.
Mustacich DJ Lai LW Bernas MJ Jones JA Myles RJ Kuo PH et al . Digenic inheritance of a FOXC2 mutation and two PIEZO1 mutations underlies congenital lymphedema in a multigeneration family. Am J Med. (2022) 135:e31–41. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.09.007
174.
Li W Huang M Wu Z Zhang Y Cai Y Su J et al . mRNA-lipid nanoparticle-mediated restoration of PTPN14 exhibits antitumor effects by overcoming anoikis resistance in triple-negative breast cancer. Adv Sci. (2024) 11:e2309988. doi: 10.1002/advs.202309988
175.
Au AC Hernandez PA Lieber E Nadroo AM Shen YM Kelley KA et al . Protein tyrosine phosphatase PTPN14 is a regulator of lymphatic function and choanal development in humans. Am J Hum Genet. (2010) 87:436–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.08.008
176.
Visser J van Geel M Cornelissen AJM van der Hulst R Qiu SS . Breast cancer-related lymphedema and genetic predisposition: a systematic review of the literature. Lymphat Res Biol. (2019) 17:288–93. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2017.0083
177.
Betterman KL Sutton DL Secker GA Kazenwadel J Oszmiana A Lim L et al . Atypical cadherin FAT4 orchestrates lymphatic endothelial cell polarity in response to flow. J Clin Invest. (2020) 130:3315–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI99027
178.
Robitaille JM Gillett RM LeBlanc MA Gaston D Nightingale M Mackley MP et al . Phenotypic overlap between familial exudative vitreoretinopathy and microcephaly, lymphedema, and chorioretinal dysplasia caused by KIF11 mutations. JAMA Ophthalmol. (2014) 132:1393–9. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2014.2814
179.
Ostergaard P Simpson MA Mendola A Vasudevan P Connell FC van Impel A et al . Mutations in KIF11 cause autosomal-dominant microcephaly variably associated with congenital lymphedema and chorioretinopathy. Am J Hum Genet. (2012) 90:356–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.12.018
180.
Zhou Y Xu MF Chen J Zhang JL Wang XY Huang MH et al . Loss-of-function of kinesin-5 KIF11 causes microcephaly, chorioretinopathy, and developmental disorders through chromosome instability and cell cycle arrest. Exp Cell Res. (2024) 436:113975. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2024.113975
181.
Herpers R van de Kamp E Duckers HJ Schulte-Merker S . Redundant roles for sox7 and sox18 in arteriovenous specification in zebrafish. Circ Res. (2008) 102:12–5. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.107.166066
182.
Zhou X Li P Li C Dai Q Qi J Yang Y . SOX18 promotes lymphatic vessel regeneration to alleviate lymphedema by upregulating PROX1. Exp Cell Res. (2025) 452:114743. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2025.114743
183.
Pujol F Hodgson T Martinez-Corral I Prats AC Devenport D Takeichi M et al . Dachsous1-Fat4 signaling controls endothelial cell polarization during lymphatic valve morphogenesis-brief report. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2017) 37:1732–5. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.117.309818
184.
Szoke D Kovács G Kemecsei E Bálint L Szoták-Ajtay K Aradi P et al . Nucleoside-modified VEGFC mRNA induces organ-specific lymphatic growth and reverses experimental lymphedema. Nat Commun. (2021) 12:3460. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23546-6
185.
Castorena-Gonzalez JA Zawieja SD Li M Srinivasan RS Simon AM de Wit C et al . Mechanisms of connexin-related lymphedema. Circ Res. (2018) 123:964–85. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.312576
186.
Davis MJ Castorena-Gonzalez JA Li M Simon AM Srinivasan RS . Hierarchical requirement for endothelial cell connexins Cx37, Cx47, Cx43, and Cx45 in lymphatic valve function. Function. (2025) 6:288–93. doi: 10.1093/function/zqaf034
187.
Finegold DN Schacht V Kimak MA Lawrence EC Foeldi E Karlsson JM et al . HGF and MET mutations in primary and secondary lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. (2008) 6:65–8. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2008.1524
188.
Kozacikova R Veselenyiova D Gelanova V Belanova I Bonetti G Kaftalli J et al . Genetic study of HGF-MET signaling pathway in primary lymphedema patients: supporting evidence for loss of function variants in HGF. Lymphology. (2024) 57:198–210. doi: 10.2458/lymph.8461
189.
Leppänen VM Brouillard P Korhonen EA Sipilä T Jha SK Revencu N et al . Characterization of ANGPT2 mutations associated with primary lymphedema. Sci Transl Med. (2020) 12:356–62. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax8013
190.
Shen B Shang Z Wang B Zhang L Zhou F Li T et al . Genetic dissection of tie pathway in mouse lymphatic maturation and valve development. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. (2014) 34:1221–30. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.302923
191.
Sano M Hirakawa S Sasaki T Inuzuka K Katahashi K Kayama T et al . Role of subcutaneous adipose tissues in the pathophysiology of secondary lymphedema. Lymphat Res Biol. (2022) 20:593–9. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2021.0054
192.
Becker J Wilting J . Molecules that have rarely been studied in lymphatic endothelial cells. Int J Mol Sci. (2024) 25:114743. doi: 10.20944/preprints202409.2067.v1
193.
Chen Y Keskin D Sugimoto H Kanasaki K Phillips PE Bizarro L et al . Podoplanin+ tumor lymphatics are rate limiting for breast cancer metastasis. PLoS Biol. (2018) 16:e2005907. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2005907
194.
Schacht V Ramirez MI Hong YK Hirakawa S Feng D Harvey N et al . T1alpha/podoplanin deficiency disrupts normal lymphatic vasculature formation and causes lymphedema. EMBO J. (2003) 22:3546–56. doi: 10.1093/emboj/cdg342
195.
Ricci M Amato B Barati S Compagna R Veselenyiova D Kenanoglu S et al . Two rare PROX1 variants in patients with lymphedema. Mol Genet Genomic Med. (2020) 8:e1424. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1424
196.
Cheng MH Pappalardo M Lin C Kuo CF Lin CY Chung KC . Validity of the novel Taiwan lymphoscintigraphy staging and correlation of cheng lymphedema grading for unilateral extremity lymphedema. Ann Surg. (2018) 268:513–25. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002917
197.
Wolfs J Qiu SS Lobbes MBI Bijkerk E van der Hulst R Keuter XHA . Visualization of both the superficial and deep lymphatic system of the upper extremity using magnetic resonance lymphography. Lymphat Res Biol. (2022) 20:275–81. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2021.0012
198.
Aso K Tsukuura R . Universal ICG lymphography stage for reproducible severity evaluation of extremity lymphedema. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. (2021) 74:1633–701. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2020.12.106
199.
Jørgensen MG Hermann AP Madsen AR Christensen S Sørensen JA . Indocyanine green lymphangiography is superior to clinical staging in breast cancer-related lymphedema. Sci Rep. (2021) 11:21103. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-00396-2
200.
Yuan Y Li F Zhou Y Li S Cao Y Liu M et al . Lymphatic pathways on indocyanine green lymphography in patients with labia minora hypertrophy. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2024) 154:665–71. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000011027
201.
Johnson AR Granoff MD Suami H Lee BT Singhal D . Real-time visualization of the mascagni-sappey pathway utilizing ICG lymphography. Cancers. (2020) 12:563–99. doi: 10.3390/cancers12051195
202.
Mo YW Lee SJ Lee DW Lee WJ Im SH Suh YC . Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography as an adjunctive method to ICG lymphography for functional lymphaticovenous anastomosis. J Surg Oncol. (2024) 129:965–74. doi: 10.1002/jso.27576
203.
Kim S Lim YT Soltesz EG De Grand AM Lee J Nakayama A et al . Near-infrared fluorescent type II quantum dots for sentinel lymph node mapping. Nat Biotechnol. (2004) 22:93–7. doi: 10.1038/nbt920
204.
Soltesz EG Kim S Laurence RG DeGrand AM Parungo CP Dor DM et al . Intraoperative sentinel lymph node mapping of the lung using near-infrared fluorescent quantum dots. Ann Thorac Surg. (2005) 79:269–77; discussion 269–77. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.06.055
205.
Shinaoka A . A new lymphography protocol and interpretation principles based on functional lymphatic anatomy in lower limb lymphedema. Anat Sci Int. (2024) 99:153–8. doi: 10.1007/s12565-023-00754-2
206.
Smith BG Hutcheson KA Little LG Skoracki RJ Rosenthal DI Lai SY et al . Lymphedema outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. (2015) 152:284–91. doi: 10.1177/0194599814558402
207.
Dzupina A Yaluri N Singh J Jankajova M . Predictors of the efficacy of lymphedema decongestive therapy. Medicina. (2025) 61:513–25. doi: 10.3390/medicina61020231
208.
Yin Y Lin J Yang L Zhao Y Zhu L Pu L et al . Experiences of complete decongestive therapy for patients with lower limb lymphedema: a descriptive phenomenological study. J Psychosom Res. (2025) 197:112351. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2025.112351
209.
Zhou X Ma G Qi X Qin A Liu B . Application of complete decongestive therapy after lymphaticovenular anastomosis of the lower limb combined with liposuction-A retrospective study research. Phlebology. (2024) 39:49–57. doi: 10.1177/02683555231209056
210.
Hamner JB Fleming MD . Lymphedema therapy reduces the volume of edema and pain in patients with breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. (2007) 14:1904–8. doi: 10.1245/s10434-006-9332-1
211.
Ezzo J Manheimer E McNeely ML Howell DM Weiss R Johansson KI et al . Manual lymphatic drainage for lymphedema following breast cancer treatment. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. (2015) 2015:Cd003475. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003475.pub2
212.
Brahma B Yamamoto T Panigoro SS Haryono SJ Yusuf PA Priambodo PS et al . Supermicrosurgery lymphaticovenous and lymphaticolymphatic anastomosis: technical detail and short-term follow-up for immediate lymphatic reconstruction in breast cancer treatment-related lymphedema prevention. J Vasc Surg Venous Lymphat Disord. (2024) 12:101863. doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2024.101863
213.
Forte AJ Khan N Huayllani MT Boczar D Saleem HY Lu X et al . Lymphaticovenous anastomosis for lower extremity lymphedema: a systematic review. Indian J Plast Surg. (2020) 53:17–24. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1709372
214.
Yang JC Wu SC Wang YM Luo SD Kuo SC Chien PC et al . Effect of lymphaticovenous anastomosis on muscle edema, limb, and subfascial volume in lower limb lymphedema: MRI studies. J Am Coll Surg. (2022) 235:227–39. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000236
215.
Alshomer F Cho J Noh H Pak CJ Suh HP Hong JP . Lymphaticovenous and lymph node-to-vein anastomosis to improve milroy disease-related chylothorax and lymphedema. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2025) 155:610e−7e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000011635
216.
Roka-Palkovits J Lin MC Tzou CJ Tinhofer I Cheng MH . Retrograde manual lymphatic drainage following vascularized lymph node transfer to distal recipient sites for extremity lymphedema: a retrospective study and literature review. Plast Reconstr Surg. (2021) 148:425e−36e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000008252
217.
De Vrieze T Gebruers N Nevelsteen I Fieuws S Thomis S De Groef A et al . Manual lymphatic drainage with or without fluoroscopy guidance did not substantially improve the effect of decongestive lymphatic therapy in people with breast cancer-related lymphoedema (EFforT-BCRL trial): a multicentre randomised trial. J Physiother. (2022) 68:110–22. doi: 10.1016/j.jphys.2022.03.010
218.
Karlsson T Karlsson M Ohlin K Olsson G Brorson H . Liposuction of breast cancer-related arm lymphedema reduces fat and muscle hypertrophy. Lymphat Res Biol. (2022) 20:53–63. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0120
219.
Boyages J Kastanias K Koelmeyer LA Winch CJ Lam TC Sherman KA et al . Liposuction for advanced lymphedema: a multidisciplinary approach for complete reduction of arm and leg swelling. Ann Surg Oncol. (2015) 22 Suppl 3:S1263–70. doi: 10.1245/s10434-015-4700-3
220.
Hansen FG Jørgensen MG Thomsen JB Sørensen JA . Topical tacrolimus for the amelioration of breast cancer-related lymphedema (TACLE Trial): a study protocol for a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II/III trial. Trials. (2025) 26:127. doi: 10.1186/s13063-025-08829-3
221.
Forte AJ Boczar D Huayllani MT Lu X McLaughlin SA . Pharmacotherapy agents in lymphedema treatment: a systematic review. Cureus. (2019) 11:e6300. doi: 10.7759/cureus.6300
222.
Atan T Bahar-Özdemir Y . The effects of complete decongestive therapy or intermittent pneumatic compression therapy or exercise only in the treatment of severe lipedema: a randomized controlled trial. Lymphat Res Biol. (2021) 19:86–95. doi: 10.1089/lrb.2020.0019
223.
Schmitz KH Troxel AB Dean LT DeMichele A Brown JC Sturgeon K et al . Effect of home-based exercise and weight loss programs on breast cancer-related lymphedema outcomes among overweight breast cancer survivors: the WISER survivor randomized clinical trial. JAMA Oncol. (2019) 5:1605–13. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2109
224.
Tsai CL Chih-Yang H Chang WW Yen-Nung L . Effects of weight reduction on the breast cancer-related lymphedema: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Breast. (2020) 52:116–21. doi: 10.1016/j.breast.2020.05.007
225.
Ruiz-Molina Y Padial M Martín-Bravo MDM García-Olivares M Porras N Chicharro A et al . Targeting lymphedema in overweight breast cancer survivors: a pilot randomized controlled trial of diet and exercise intervention. Nutrients. (2025) 17:227–39. doi: 10.3390/nu17172768
Summary
Keywords
lymphedema, primary lymphedema, breast cancer-related lymphedema, lymphoscintigraphy, indocyanine green lymphography, magnetic resonance lymphangiography, lymphaticovenous anastomosis, liposuction
Citation
Wu T, Pu J, Yao Q, Chen S, Yao Y, Chang S, Yang R and Shen J (2025) Advances in etiology, pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of lymphedema: a comprehensive review. Front. Med. 12:1666522. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1666522
Received
15 July 2025
Accepted
13 October 2025
Published
06 November 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Stav Brown, Yale University, United States
Reviewed by
Hwayeong Cheon, University of Ulsan, Republic of Korea
Siba Haykal, Yale University, United States
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Wu, Pu, Yao, Chen, Yao, Chang, Yang and Shen.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Riyun Yang, yangriyunyx@126.com; Jianhong Shen, tysjh@163.com
†These authors have contributed equally to this work
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.