Abstract
Purpose:
This study compared the role of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) followed by surgery vs. upfront surgery for avoiding axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) in patients with cT1-2N0M0 breast cancer and clinically negative axillary lymph nodes (LNs) at diagnosis.
Patients and methods:
Medical records of a sample of 1,695 patients with a primary diagnosis of axillary LN-negative early-stage breast cancer who underwent surgical treatment for breast cancer at the First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University between June 2019 and December 2022 were retrospectively reviewed. The positive rate of sentinel lymph nodes (PRSLN) and the positive rate of total axillary lymph nodes (PRTLN) were compared between patients who received 4–8 cycles of NAC followed by surgery (n = 135) and patients who underwent upfront surgery (n = 1,560).
Results:
15 patients who received NAC followed by surgery and 79 patients who underwent upfront surgery had positive SLNs. Four patients who received NAC followed by surgery and 1 patient who underwent upfront surgery had other positive LNs. Overall, NAC followed by surgery significantly lowered PRSLN and PRTLN compared to upfront surgery in patients with cT1-2N0M0 breast cancer. In subgroup analyses, PRSLN and PRTLN were significantly lower for NAC followed by surgery compared to upfront surgery in patients aged 40–60 years, with cT2 stage disease, and HER2+ breast cancer. At a median follow-up of 23.15 months, invasive disease-free survival was similar for all patients.
Conclusion:
NAC may reduce the rate of axillary LN positivity and the likelihood of ALND in patients aged 40–60 years with cT2N0M0 HER2+ breast cancer and clinically negative axillary LNs at diagnosis.
Introduction
As of 2020, female breast cancer surpassed lung cancer as the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide, with an estimated 2.3 million new cases in 2020, accounting for 11.7% of all cancer cases (1). Breast cancer is a major public health concern. It is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality in most countries and is responsible for one quarter of all cancer cases and one sixth of cancer deaths among women (1).
Diagnostic staging and molecular subtype are critical factors associated with survival in patients with breast cancer. In China, 76.8% of women with breast cancer are diagnosed at Stages I and II (2). The pathological phase of breast cancer is determined by lymph node (LN) involvement and the number and location of positive LNs (3). Patients with localized breast cancer at diagnosis have a 5-year survival rate of 98.8%, whereas patients with a diagnosis of regional breast cancer have a 5-year survival rate of only 85.8% (4).
Currently, breast cancer treatment is focused on de-escalation. Most patients with early-stage breast cancer (cT1 ~ 2N0M0) undergo surgery, with sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) for staging (5). Since 2014, with the publication of results from several clinical trials, including ACOSOG Z0011 (6–8), IBCSG 23-01 (9, 10), AATRM (11), Sinodar One (12), and EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS (13), SLNB is gradually replacing ALND as the standard surgical procedure for early breast cancer. Neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC) and complementary radiotherapy can also minimize the use of ALND; however, only a small proportion of patients with triple-negative (TNBC) or HER2+ breast cancer (tumor >2 cm), or those who have opted for breast-conserving surgery but are contraindicated due to their tumor-to-breast volume ratio, are offered NAC (9). Remarkably, axillary lymph node metastasis remains a possibility in patients with tumor diameters ≤2 cm, with a prevalence ranging from 6 to 31% (14–16); therefore, ALND without radiotherapy is often considered in these cases.
This study investigated the potential role of NAC followed by surgery in patients with cT1-2N0M0 breast cancer and clinically negative axillary LNs at diagnosis. NAC may be beneficial for downstaging disease and improving prognosis, avoiding ALND, and reducing postoperative morbidity, including upper limb edema and long-term shoulder dysfunction, in these patients (17, 18).
Methods
Patients
Patients with a primary diagnosis of axillary LN-negative early-stage breast cancer who underwent surgical treatment for breast cancer at the First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University between June 2019 and December 2022 were eligible for this study. Inclusion criteria were: (1) unilateral breast cancer; (2) tumor ≤5 cm in diameter; (3) pre-operative staging with ultrasound and mammography performed at the First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University; (4) pathology revealed invasive breast cancer; and (5) no missing clinical information. Exclusion criteria were: (1) pre-operative staging and/or postoperative pathology performed at a different institution; (2) preoperative diagnosis of axillary LN metastasis; (3) inflammatory breast cancer; (4) previous axillary surgery or radiation therapy to the breast or chest wall; (5) pregnancy or breastfeeding; (6) history of recurrent breast cancer, metastatic breast cancer, or breast cancer accompanied by localized infections; or (7) other malignancies. In this study, a subset of patients was selected for NAC, based on aggressive features (such as HER2+ or TNBC) to reduce recurrence risk and potentially facilitate breast-conserving surgery, as well as strong patient desire for breast conservation despite an initially unfavorable tumor-to-breast size ratio, with the goal of achieving downstaging. These treatment decisions were consistent with guideline. NAC regimens and postoperative therapies were determined according to CSCO guidelines and multidisciplinary team (MDT) discussions (Supplementary Table S5), although a subset of patients did not fully adhere to the recommended treatment. The final analyses included sample of 1,695 patients; of these, 135 patients received 4–8 cycles of NAC followed by surgery and 1,560 patients underwent upfront surgery.
Among all patients, surgical procedures included total mastectomy plus SLNB, total mastectomy plus SLNB and ALND, breast-conserving surgery (BCS) plus SLNB, BCS plus SLNB and ALND, and modified radical mastectomy (MRM). It was determined on clinical and imaging characteristics of the tumor, patient preference, and discussion within MDT. BCS was offered to patients with favorable tumor size and location who provided consent. MRM was performed in cases with multifocal/multicentric disease, tumors not amenable to resection through single incision, inability to achieve negative margins, or upon patient’s preference for mastectomy. For patients initially diagnosed as cN0, axillary management followed SLNB.
Preoperative axillary LN status was evaluated by ultrasonography. Sonographic criteria for determining axillary LN involvement included: cortical thickness (e.g., diffuse cortical thickening >3 mm or eccentric cortical thickening), abnormal morphologic characteristics (e.g., dysmorphic lymph nodes without normal structures, non-gated flow patterns), or lack of fatty hilum (19, 20). Assessment of LNs on ultrasound was performed by two physicians experienced in ultrasonography. If axillary ultrasonography was positive, patients underwent fine needle aspiration (FNA) for cytological examination or hollow needle biopsy followed by pathology to determine whether metastases were present. Patients were identified as cN0 if their axillary LNs showed no abnormalities on ultrasonography and/or if a US-guided biopsy gave negative results (21). To rule out distant metastases, all patients underwent baseline evaluations including chest computed tomography (CT) and abdominal ultrasonography. For those with high-risk factors (cT2 stage, TNBC or HER2+, or suggestive clinical symptoms), further imaging with breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), bone scintigraphy, or positron emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) was performed as clinically indicated.
As this was a retrospective study, informed consent to participate from individual patients was waived by the ethics committee of The First Hospital of Jilin University (2023-325), and all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
Data collection
Data were collected from the medical record system of our hospital. Information included: patient age at diagnosis, tumor size, histological grade, estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 (HER2) and Ki-67 status, management plan (treatment modality and cycle), surgical procedure, number of SLNs removed, number of positive SLNs, number of non-SLNs removed, and number of positive non-SLNs. Cancer was staged according to the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC), 7th ed. (22), assuming low Ki67 expression if ≤20% malignant cells exhibited Ki67 staining on immunohistochemistry and high PR expression if >20% malignant cells exhibited PR staining on immunohistochemistry.
SLNB and ALND procedure
SLNB used a dual-tracer method of 1% methylene blue combined with indocyanine green (ICG). First, 0.5 mL 1% methylene blue (2 mL/branch) was injected subcutaneously at 3, 6, 9, and 12 o’clock at the edge of the areola. Two minutes later, ICG (1 mL/branch) was injected in the same way. After the ICG injection, the mammary gland was massaged for approximately 30 s. Eight minutes later, luminous and blue-stained nodes were removed. For patients who required modified radical surgery or ALND, a skin flap of appropriate thickness was raised, the pectoralis minor and pectoralis major muscles were kept intact, and the skin was cut at the patient’s transverse axillary stripe, allowing removal of level I and II LNs in the ipsilateral axilla (n ≥ 10). A small number of patients received technetium 99 sulfur colloid + methylene blue or a combination of nanocarbon + methylene blue as a tracer, with intraoperative rapid frozen pathological examination performed on all blue-stained, fluorescent-appearing, nuclear high signal, and nanocarbon-black-stained LNs that were removed during surgery. Data for these patients were not analyzed separately as the sample size was small and all patients in this study were evaluated with dual tracers, such that type of tracer was not expected to impact outcomes.
Pathology
Biopsied LNs were embedded in paraffin, serially sectioned at 500 μm intervals, and stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). Patients were considered node-positive based on the presence of isolated tumor cell clusters (ITCs) (≤0.2 mm), micrometastases (>0.2 mm-≤2.0 mm), and macrometastases (>2.0 mm).
Follow-up
Follow-up ended in May 2023. In accordance with clinical guidelines, patients underwent clinical examination, annual mammography, and additional imaging in cases showing recurrence (21). The clinical endpoint was invasive disease-free survival (iDFS), defined as the time from treatment to first occurrence of one of the following events: ipsilateral invasive breast tumor recurrence, ipsilateral local or regional invasive breast cancer recurrence, distant recurrence, contralateral invasive breast cancer, or death from any cause.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed with SPSS v. 26.0. Normally distributed data were reported as mean ± standard deviation, and compared with the t-test. Non-normally distributed data were reported as median (25th–75th percentile) and compared with the Mann–Whitney U test. Qualitative data were reported as frequencies and compared with the χ2 test or Fisher’s exact test.
Baseline characteristics were compared between patients who received NAC followed by surgery and patients who underwent upfront surgery. Logistic regression-based propensity score matching (matching ratio: 1:3, caliper value 0.04) was used to control for confounding due to patient baseline characteristics that may influence decision-making regarding NAC (patient age at diagnosis, T-staging [T1 vs. T2], molecular subtype).
The positive rate of SLNs (PRSLN) and the positive rate of total axillary LNs (PRTLN) were calculated using the following formula and were compared between patients who received NAC followed by surgery and patients who underwent upfront surgery.
(where, number of LN positive cases = number of SLN positive cases + number of cases with ALND).
A two-tailed p value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Patient baseline characteristics
This study included 1,695 patients; of these, 135 patients received 4–8 cycles of NAC followed by surgery and 1,560 patients underwent upfront surgery. All patients had unilateral breast cancer with no previous history of tumor. Patients who received NAC followed by surgery were significantly younger, had significantly larger tumors and were significantly more likely to have HER2+ or TNBC compared to patients who underwent upfront surgery. As patient age, tumor stage (diameter), and molecular subtype may influence decisions regarding NAC, a logistic regression model was used to balance the baseline characteristics of the two groups of patients (p > 0.05). The demographic and clinicopathological characteristics of patients before and after propensity score matching are summarized in Table 1. The number of patients after propensity score matching was 123 who received NAC followed by surgery and 313 who underwent upfront surgery (Figure 1).
Table 1
| General clinical data | Before | After | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UpS (n = 1,560) | NAC (n = 135) | p | UpS (n = 313) | NAC (n = 123) | p | ||
| Average age (years) | 53.24 ± 10.29 | 51.02 ± 10.09 | 0.016 | 51.25 ± 10.94 | 51.56 ± 9.90 | 0.786 | |
| Tumor size (cm) | 21.19 ± 8.34 | 29.37 ± 9.81 | 0.000 | 26.49 ± 9.08 | 28.29 ± 9.51 | 0.068 | |
| Type | Luminal A | 474 (30.38%) | 11 (8.15%) | 0.000 | 47 (15.06%) | 11 (8.94%) | 0.424 |
| Luminal B | 610 (39.10%) | 39 (28.89%) | 97 (30.99%) | 39 (31.71%) | |||
| HER2+(HR+) | 157 (10.06%) | 21 (15.56%) | 50 (15.97%) | 21 (17.07%) | |||
| HER2+(HR−) | 129 (8.27%) | 29 (21.48%) | 41 (13.10%) | 26 (21.14%) | |||
| TNBC | 190 (12.18%) | 385 (25.93%) | 78 (24.92%) | 26 (21.14%) | |||
Patient baseline characteristics before and after propensity score matching.
Figure 1

Flow chart of patient selection and propensity score matching.
LN positivity
PRSLN and PRTLN are summarized in Table 2. NAC was associated with significantly lower rates of both PRSLN (12.9% vs. 25.4%, RR 0.503, 95% CI 0.302–0.836) and PRTLN (15.4% vs. 25.9%, RR 0.597, 95% CI 0.379–0.940) compared to upfront surgery (Figures 2, 3).
Table 2
| PR | Group | Total | ypN+ (%) | Difference and 95% CI | χ 2 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRSLN | B-pCR | 57 | 3 (5.3%) | 15.00 [3.28, 26.87] | 5.852 | 0.016 |
| B-nonpCR | 59 | 12 (20.3%) | ||||
| PRTLN | B-pCR | 58 | 3 (5.2%) | 19.40 [7.52, 31.37] | 8.871 | 0.003 |
| B-nonpCR | 65 | 16 (24.6%) |
Subgroup analysis of pCR status and lymph node positivity after NAC.
Figure 2
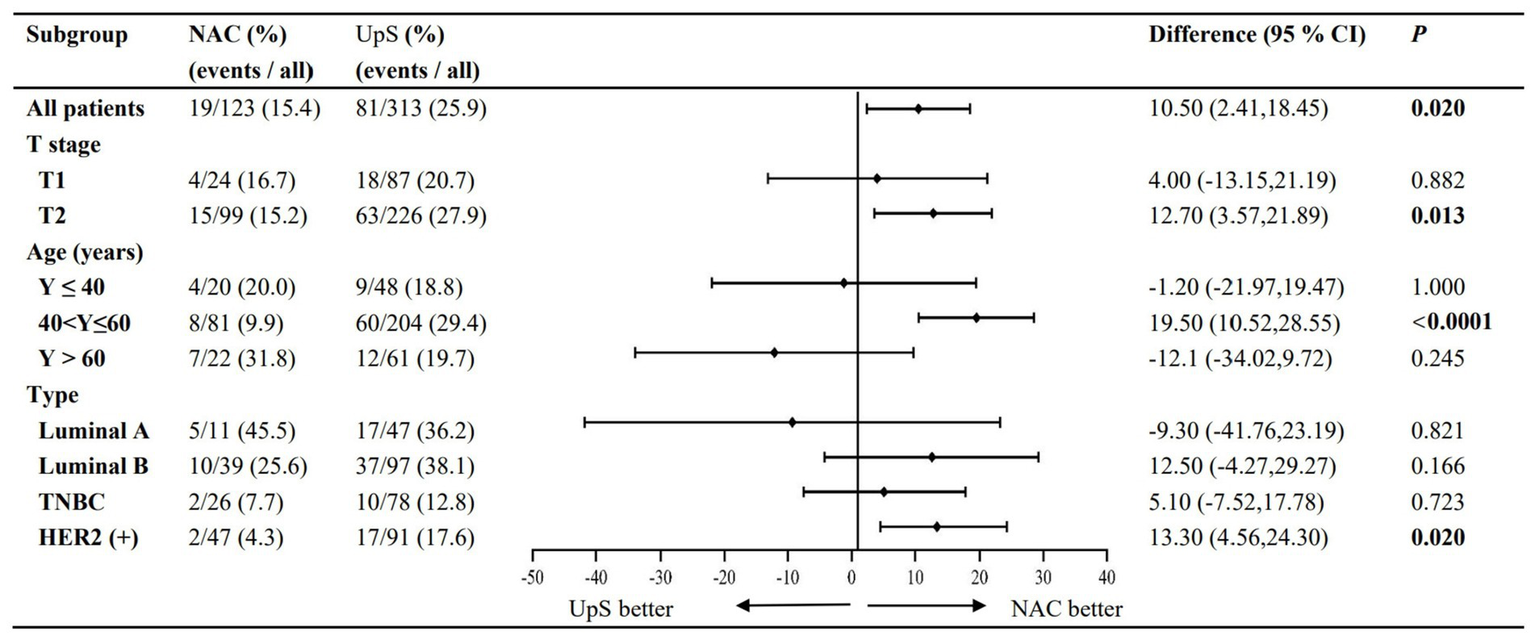
Subgroup analyses: PRTLN.
Figure 3

Subgroup analyses: PRSLN.
Subgroup analyses
Subgroup analyses of LN positivity stratified by patient age at diagnosis, cT stage, and molecular subtype were performed for the 436 patients that remained after propensity score matching.
Age
Patients were categorized into three groups based on age at diagnosis: ≤40 years (n = 48), >40 to ≤ 60 years (n = 204), and >60 years (n = 61). While NAC significantly reduced both PRSLN and PRTLN in patients aged 40–60 years, the differences were not statistically significant in the ≤40 or >60 age groups, despite a numerical trend toward higher rates with NAC (Figures 2, 3).
cT-staging
In accordance with the 7th edition of the AJCC guidelines, tumors were classified as cT1 (≤20 mm; n = 111) or cT2 (>20 mm-≤50 mm; n = 325) based on maximum tumor diameter before surgery. For cT2 tumors, NAC significantly lowered rates of PRSLN (13.8% vs. 27.7%) and PRSLN (15.2% vs. 27.9%) compared to upfront surgery. A similar, but non-significant, trend was seen in cT1 tumors (Figures 2, 3).
Molecular subtype
Tumors were classified as luminal A (n = 47), luminal B (n = 97), TNBC (n = 78), and HER2+ (n = 91). A significant reduction in both PRSLN and PRTLN with NAC was observed only in HER2+ breast cancer. For TNBC and Luminal B tumors, NAC showed a numerical reduction in rates, while Luminal A tumors showed a numerical increase; however, these trends were not statistically significant (Figures 2, 3).
Pathologic complete response in patients who received NAC
PRSLN and PRTLN in patients who received NAC followed by surgery were investigated further. Patients were stratified based on the presence or absence of breast pathologic complete response (pCR) after NAC, defined as the lack of invasive cancer (ductal carcinoma in situ may be present) in the initial breast lesion (Miller-Payne grade 5). PRSLN [5.3% vs. 20.3%, p = 0.016, RR = 0.259 (0.077, 0.869)] and PRTLN [5.2% vs. 24.6%, p = 0.003, RR = 0.210 (0.064, 0.685)] were statistically significantly lower in patients with breast pCR compared to residual disease after NAC (Table 2). These data imply that the pathological response of a patient’s primary breast lesion to NAC may directly influence axillary LN status.
Prognosis
Overall prognosis
Among all patients, median follow-up was 23.15 months and mean follow-up was 23.85 months. 13% of patients who received NAC followed by surgery and 19.2% of patients who received upfront surgery were lost to follow-up. Three patients who received NAC followed by surgery and seven patients who received upfront surgery developed metastases during follow-up; no other patients experienced recurrence or death (Table 3; Supplementary Table S1). There were no significant differences in the frequency of events determining iDFS for NAC followed by surgery compared to upfront surgery (both 2.8%). Kaplan–Meier estimates of iDFS were 94.09% for NAC followed by surgery and 93.32% for upfront surgery (Figure 4A).
Table 3
| Group | Age (year) | Type | Postoperative pathology | Practical treatment | Adverse events |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NAC 3 cases | 47 | TNBC | B: MP2 | Pre-o: 8AC-T | Ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node metastasis at 31.7 months |
| L: 0/4 | Post-o: none | ||||
| 60 | Luminal A | B: MP3 | Pre-o: 8AC-T | Ipsilateral supraclavicular lymph node metastases at 21.1 months | |
| L:0/3 | Post-o: Letrozole | ||||
| 58 | TNBC | B: MP2 | Pre-o: 3AC+TA+4TP | Brain metastases at 22.7 months | |
| L:0/5 | Post-o: none | ||||
| 47 | HR-Her-2+ | 0/2 | Failure to comply | Lung metastases, liver metastases, adrenal metastases, pleural metastases at 32.3 months | |
| PO 7 cases | 43 | Luminal A | 1/2 macro ALND 2/15 | Failure to comply | Brain metastases at 12.83 months |
| 72 | HR+Her-2+ | 1/6 macro ALND 0/12 | 4TCH+Letrozole +17H | Lung metastases at 12.7 months | |
| 35 | HR-Her-2+ | 0/2 | 8AC-THP+17HP | Breast recurrence at 26.8 months | |
| 48 | TNBC | 0/5 | 6TC | Brain metastases at 26.4 months | |
| 74 | Luminal B | 0/5 | Failure to comply | Lung metastases at 12.5 months | |
| 51 | Luminal A | 2/9 | 8AC-T | Chest wall recurrence at 31.6 months |
Clinicopathological characteristics of patients who experienced metastases during follow-up.
B, Breast response; L, Lymph node metastasis; MP, Miller & Payne; A, Anthracyclines; C, Cyclophosphamide; T, Paclitaxel/Paclitaxel-albumin; H, Trastuzumab; P, Perjeta/Platinum; Post-o, post-operative; Pre-o, preoperative.
Figure 4
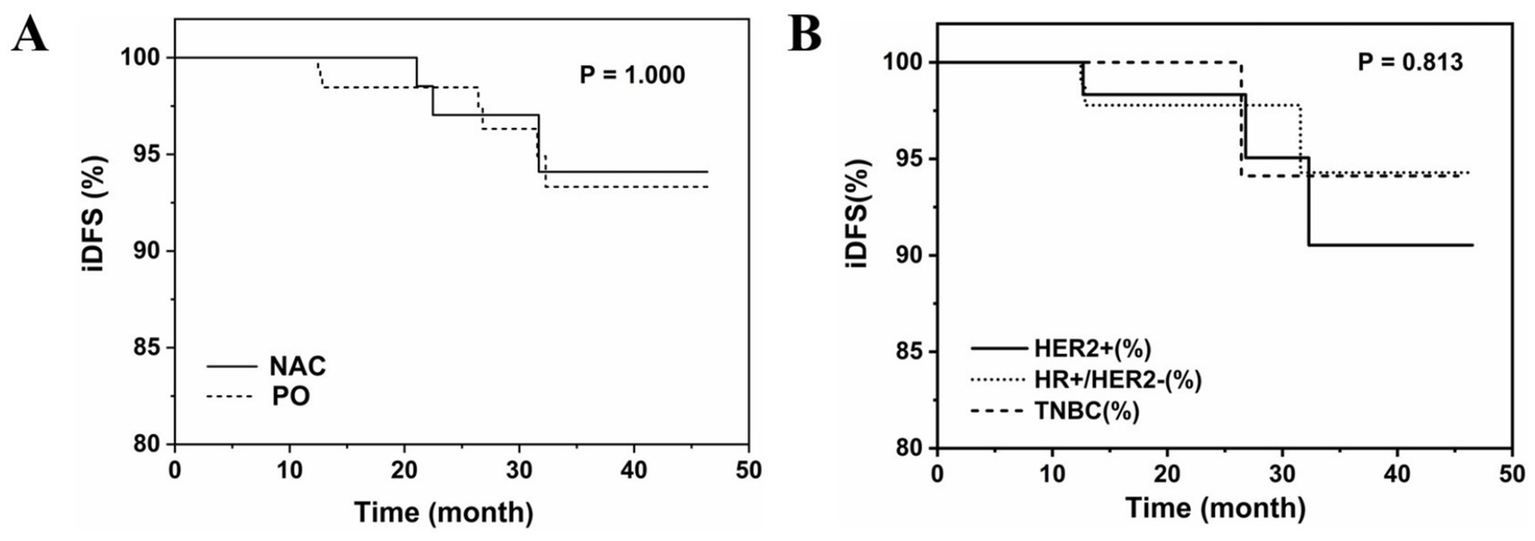
Kaplan–Meier curves (A) patients who received NAC followed by surgery or underwent upfront surgery; (B) Patients who underwent upfront surgery.
Subgroup analyses
Pathologic complete response in patients who received NAC
There was no significant difference in the frequency of events determining iDFS between patients with breast pCR (0.0%) compared to residual disease (5.1%) after NAC (Supplementary Table S2).
Molecular subtype in patients who received NAC
There were no significant differences in the frequency of events determining iDFS in patients stratified by molecular subtype of breast cancer with breast pCR compared to residual disease after NAC (luminal: 0.0% vs. 3.1%, p = 1.000; TNBC: 0.0% vs. 15.4%, p = 0.581; HER2+: 0.0% vs. 0.0%) (Supplementary Table S3).
Molecular subtype in patients who underwent upfront surgery
There were no significant differences in the frequency of events determining iDFS in patients stratified by molecular subtype of breast cancer who underwent upfront surgery (luminal: 2.54%; TNBC: 1.69%; HER2+: 3.95%) (Figure 4B; Supplementary Table S4).
Discussion
SLNB, which spares 60–75% of patients from ALND, has become the standard surgical procedure for early breast cancer due to advancements in medical technology and a growing understanding of the disease. Notably, recent large-scale clinical trials have revealed that ALND may not have clinical benefits for patients with early-stage breast cancer (7, 10, 23, 24). However, a considerable portion of patients with axillary LN metastasis still experience a range of post-ALND complications, including sensory abnormalities (25), lymphatic fistulae (26), lymphedema (27), infections (3–15%) (28, 29), hematoma (2–10%) (26) and restricted shoulder joint movement (30).
NAC is widely administered to patients with locally advanced and inoperable breast cancer. Its main purpose is to achieve a pCR (31). The use of NAC in less aggressive breast cancer is more controversial. The present study examined the clinical utility of NAC for patients with early-stage breast cancer (cT1-2N0M0) and clinically negative axillary LNs at diagnosis. Overall, NAC followed by surgery significantly lowered PRSLN and PRTLN compared to upfront surgery in this patient population. In subgroup analyses, PRSLN and PRTLN were significantly lower for NAC followed by surgery compared to upfront surgery in patients aged 40–60 years, with cT2 stage disease, and HER2+ breast cancer. In contrast, patients aged ≤40 years or >60 years or with luminal A cT1-2N0M0 breast cancer were unlikely to achieve axillary downstaging by NAC. Among patients who received NAC followed by surgery, those who achieved breast pCR had significantly lower PRSLN and PRTLN compared to patients with residual disease. Overall, these findings imply that patients with cT2N0M0 HER2+ breast cancer aged 40–60 years may benefit most from NAC followed by surgery through a reduction in the rate of axillary LN positivity and the likelihood of ALND. Our findings align with the current trend in CSCO and NCCN guidelines toward de-escalating axillary surgery in patients who respond favorably to NAC. The significant reduction in nodal positivity rates observed in our study, particularly in HER2+ and cT2 subgroups, contributes to the growing evidence supporting less invasive axillary management. While our data support the avoidance of ALND in initially node-positive patients who convert to ypN0 after NAC, the potential omission of SLNB in those achieving breast pCR remains exploratory. Larger trials (32) are currently investigating this approach, and our results help identify patient subgroups that may be most suitable for such de-escalated strategies in the future.
Previous studies have shown that HER2+ or TNBCs are most likely to be associated with high breast and axillary pCR rates and the possibility of axillary downstaging after NAC. A retrospective study revealed that patients with HR+/HER2+, HR−/HER2+, and TNBC achieved higher breast and axillary pCR rates after NAC than patients with HR+/HER2 breast cancer, and PRSLN was lower (3.6%) in patients with breast pCR (33). Others have reported that patients with cN0 HER2+ or TNBC achieving breast pCR may not need axillary surgery due to an extremely low LN positivity (34, 35).
In the present study, median follow-up was 23.15 months after definitive surgery for primary breast cancer. During follow-up, three patients who received NAC followed by surgery developed supraclavicular lymph node and brain metastases, with a recurrence rate of 2.80% and iDFS of 94.09%. Seven patients who underwent upfront surgery developed recurrent metastases, including bone metastases, lung metastases, in situ recurrence of breast cancer, brain metastases, and recurrence in the chest wall, with a recurrence rate of 2.80% and iDFS of 93.32%. Overall, NAC followed by surgery appeared to reduce the risk of tumor recurrence compared to upfront surgery, although the difference was not statistically significant (p > 0.05). The principal limitation of this study is its median follow-up of approximately 23.15 months, which is insufficient to draw definitive conclusions regarding long-term survival outcomes. Future studies with extended follow-up are warranted to confirm the oncological safety of this strategy.
In 2023, the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology (CSCO) updated its guidelines for postoperative intensive treatment in patients with breast cancer who have undergone neoadjuvant therapy (36). In the ExteNET (37) trial, intensive treatment of HER2+ breast cancer with neratinib for 1 year after trastuzumab-based adjuvant therapy led to a 2.5% increase in iDFS. BRCA-related genetic testing is recommended in TNBC with positive LNs and tumors >2 cm. In the absence of mutations, continuous treatment with capecitabine (level of evidence: 2A) for 1 year is recommended, and the five-year iDFS can be improved from 56.1 to 69.8%. If mutations are present, 1 year of continuous olaparib (level of evidence: 1B) can increase the 3-year iDFS from 77.1 to 85.9%. For patients with HR+ breast cancer, the MonarchE (38) study reaffirmed the place of abemaciclib in combination with tamoxifen or an aromatase inhibitor or in the adjuvant treatment of HR+/HER2−breast cancer, especially for adjuvant intensification in high-risk breast cancer (level of evidence: 1A). In the present study, only two patients underwent postoperative treatment intensification with oral capecitabine, one patient underwent postoperative treatment intensification with abemaciclib, and two patients received carilizumab immunotherapy, because of the high cost of CDK4/6 inhibitor or immunosuppressant therapy, among other reasons (Supplementary Table S5). As only a small number of patients underwent postoperative intensive treatment, the impact on iDFS was likely minimal. Beyond clinicopathological factors, genetic profiling—especially BRCA1/2 germline mutation status—plays an increasingly important role in personalized breast cancer treatment. Although genetic testing was not routinely performed for all patients in this study, BRCA status is known to affect surgical choices (risk-reducing mastectomy or oophorectomy) (39), systemic therapy selection (platinum-based chemo or PARP inhibitors) (40), and long-term risk management (41, 42). Future studies incorporating genetic data and NAC response could help optimize axillary management strategies. Larger cohorts and longer follow-up are still needed to better evaluate the effect of treatment intensification on iDFS and OS in early breast cancer.
In conclusion, NAC may reduce the rate of axillary LN positivity and the likelihood of ALND in patients aged 40–60 years with cT2N0M0 HER2+ breast cancer and clinically negative axillary LNs at diagnosis. Improvement in long-term prognosis, upper extremity function, and patient quality of life represent potential benefits of NAC. In the future, clinical trials in NAC should focus on patients with early-stage breast cancer, with findings informing the development of individualized treatment plans that optimize safety and efficacy and prevent overtreatment.
Statements
Data availability statement
The datasets presented in this article are not readily available because the datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to patient’s privacy, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Requests to access the datasets should be directed to wxzhen@jlu.edu.cn.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Ethics Committee of The First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University (2023-325). The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The ethics committee/institutional review board waived the requirement of written informed consent for participation from the participants or the participants’ legal guardians/next of kin because written informed consent was waived in accordance with Ethics Committee of The First Bethune Hospital of Jilin University regulations for retrospective studies using de-identified data.
Author contributions
JM: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Project administration, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft. ZF: Conceptualization, Supervision, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. ZJ: Methodology, Software, Supervision, Writing – review & editing. XD: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. JS: Data curation, Investigation, Writing – original draft. XW: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Resources, Supervision, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Youth Foundation (Grant number: 81602335), Wu Jieping Medical Foundation (320.6750.2023-03-35), and the Education Department of Jilin Province (JJKH20241325KJ).
Acknowledgments
We are very grateful to Professor Zhimin Fan for his guidance on the conceptualization of the article, and to Professor Zhifang Jia for her assistance with statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1672369/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Sung H Ferlay J Siegel RL Laversanne M Soerjomataram I Jemal A et al . Global Cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. (2021) 71:209–49. doi: 10.3322/caac.21660
2.
Benitez Fuentes JD Morgan E de Luna Aguilar A Mafra A Shah R Giusti F et al . Global stage distribution of breast cancer at diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Oncol. (2023) 10:71–8. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.4837
3.
Beenken SW Urist MM Zhang Y Desmond R Krontiras H Medina H et al . Axillary lymph node status, but not tumor size, predicts locoregional recurrence and overall survival after mastectomy for breast cancer. Ann Surg. (2003) 237:732–8; (discussion 738-9). doi: 10.1097/01.SLA.0000065289.06765.71
4.
Chang JM Leung JWT Moy L Ha SM Moon WK . Axillary nodal evaluation in breast cancer: state of the art. Radiology. (2020) 295:500–15. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020192534
5.
Krag DN Meijer SJ Weaver DL Loggie BW Harlow SP Tanabe KK et al . Minimal-access surgery for staging of malignant melanoma. Arch Surg. (1995) 130:654–8; (discussion 659–60). doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1995.01430060092018
6.
Lucci A LM MC Beitsch PD Whitworth PW Reintgen DS Blumencranz PW et al . Surgical complications associated with sentinel lymph node dissection (SLND) plus axillary lymph node dissection compared with SLND alone in the American College of Surgeons oncology group trial Z0011. J Clin Oncol. (2007) 25:3657–63. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2006.07.4062, (1527-7755 (Electronic))
7.
Giuliano AE Ballman KV McCall L Beitsch PD Brennan MB Kelemen PR et al . Effect of axillary dissection vs no axillary dissection on 10-year overall survival among women with invasive breast Cancer and sentinel node metastasis: the ACOSOG Z0011 (Alliance) randomized clinical trial. JAMA. (2017) 318:918–26. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.11470
8.
Giuliano AE McCall L Beitsch P Whitworth PW Blumencranz P Leitch AM et al . Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: the American College of Surgeons oncology group Z0011 randomized trial. Ann Surg. (2010) 252:426–32. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181f08f32, (discussion 432-3)
9.
Gradishar WJ Anderson BO Balassanian R Blair SL Burstein HJ Cyr A et al . NCCN guidelines insights: breast Cancer, version 1.2017. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. (2017) 15:433–51. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2017.0044
10.
Galimberti V Cole BF Zurrida S Viale G Luini A Veronesi P et al . Axillary dissection versus no axillary dissection in patients with sentinel-node micrometastases (IBCSG 23-01): a phase 3 randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. (2013) 14:297–305. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70035-4
11.
Solá M Alberro JA Fraile M Santesteban P Ramos M Fabregas R et al . Complete axillary lymph node dissection versus clinical follow-up in breast cancer patients with sentinel node micrometastasis: final results from the multicenter clinical trial AATRM 048/13/2000. Ann Surg Oncol. (2013) 20:120–7. doi: 10.1245/s10434-012-2569-y
12.
Tinterri C Gentile D Gatzemeier W Sagona A Barbieri E Testori A et al . Preservation of axillary lymph nodes compared with complete dissection in T1-2 breast cancer patients presenting one or two metastatic sentinel lymph nodes: the SINODAR-ONE multicenter randomized clinical trial. Ann Surg Oncol. (2022) 29:5732–44. doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11866-w
13.
Donker M van Tienhoven G Straver ME Meijnen P van de Velde CJ Mansel RE et al . Radiotherapy or surgery of the axilla after a positive sentinel node in breast cancer (EORTC 10981-22023 AMAROS): a randomised, multicentre, open-label, phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. (2014) 15:1303–10. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70460-7
14.
Carter CL Allen C Henson DE . Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. (1989) 63:181–7. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890101)63:1<>3.0.co;2-h
15.
Michaelson JS Silverstein M Sgroi D Cheongsiatmoy JA Taghian A Powell S et al . The effect of tumor size and lymph node status on breast carcinoma lethality. Cancer. (2003) 98:2133–43. doi: 10.1002/cncr.11765
16.
Barth A Craig PH Silverstein MJ . Predictors of axillary lymph node metastases in patients with T1 breast carcinoma. Cancer. (1997) 79:1918–22. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0142(19970515)79:10<1918::AID-CNCR12>3.0.CO;2-Y
17.
Nyayapathi N Xia J . Photoacoustic imaging of breast cancer: a mini review of system design and image features. J Biomed Opt. (2019) 24:1–13. doi: 10.1117/1.JBO.24.12.121911
18.
Jafari SH Saadatpour Z Salmaninejad A Momeni F Mokhtari M Nahand JS et al . Breast cancer diagnosis: imaging techniques and biochemical markers. J Cell Physiol. (2018) 233:5200–13. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26379
19.
Mainiero MB . Regional lymph node staging in breast cancer: the increasing role of imaging and ultrasound-guided axillary lymph node fine needle aspiration. Radiol Clin North Am. (2010) 48:989–97. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2010.06.010
20.
Li J Qin S Xu J Xiong J Wu C Bai Y et al . Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase III trial of Apatinib in patients with chemotherapy-refractory advanced or metastatic adenocarcinoma of the stomach or gastroesophageal junction. J Clin Oncol. (2016) 34:1448–54. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2015.63.5995
21.
Shigematsu H Nishina M Yasui D Hirata T Ozaki S . Minimal prognostic significance of sentinel lymph node metastasis in patients with cT1-2 and cN0 breast cancer. World J Surg Oncol. (2019) 17:41. doi: 10.1186/s12957-019-1585-9
22.
Edge SB Compton CC . The American joint committee on cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. (2010) 17:1471–4. doi: 10.1245/s10434-010-0985-4
23.
Kuru B . The adventure of axillary treatment in early stage breast cancer. Eur J Breast Health. (2020) 16:1–15. doi: 10.5152/ejbh.2019.5157
24.
Cserni G Maguire A Bianchi S Ryska A Kovács A . Sentinel lymph node assessment in breast cancer-an update on current recommendations. Virchows Arch. (2022) 480:95–107. doi: 10.1007/s00428-021-03128-z
25.
Abdullah TI Iddon J Barr L Baildam AD Bundred NJ . Prospective randomized controlled trial of preservation of the intercostobrachial nerve during axillary node clearance for breast cancer. Br J Surg. (1998) 85:1443–5. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2168.1998.00843.x
26.
Vitug A.F. Newman L.A. , Complications in breast surgery, Surg Clin North Am87 (2007) 431–451, x.
27.
Deutsch M Land S Begovic M Sharif S . The incidence of arm edema in women with breast cancer randomized on the national surgical adjuvant breast and bowel project study B-04 to radical mastectomy versus total mastectomy and radiotherapy versus total mastectomy alone. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. (2008) 70:1020–4. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.07.2376
28.
Crane-Okada R Wascher RA Elashoff D Giuliano AE . Long-term morbidity of sentinel node biopsy versus complete axillary dissection for unilateral breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. (2008) 15:1996–2005. doi: 10.1245/s10434-008-9909-y
29.
Langer I Guller U Berclaz G Koechli OR Schaer G Fehr MK et al . Morbidity of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLN) alone versus SLN and completion axillary lymph node dissection after breast cancer surgery: a prospective Swiss multicenter study on 659 patients. Ann Surg. (2007) 245:452–61. doi: 10.1097/01.sla.0000245472.47748.ec
30.
Winters-Stone KM Schwartz AL Hayes SC Fabian CJ Campbell KL . A prospective model of care for breast cancer rehabilitation: bone health and arthralgias. Cancer. (2012) 118:2288–99. doi: 10.1002/cncr.27465
31.
Aktas A Gunay-Gurleyik M Aker F Kaan-Akgok Y Atag E . Does neoadjuvant chemotherapy provide any benefit for surgical de-escalation in luminal B, HER2(−) breast cancers?Cir Cir. (2023) 91:186–94. doi: 10.24875/CIRU.22000277
32.
Reimer T Stachs A Veselinovic K Kühn T Heil J Polata S et al . Axillary surgery in breast cancer—primary results of the INSEMA trial. N Engl J Med. (2025) 392:1051–64. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2412063
33.
Choi HJ Ryu JM Kim I Nam SJ Kim SW Yu J et al . Prediction of axillary pathologic response with breast pathologic complete response after neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. (2019) 176:591–6. doi: 10.1007/s10549-019-05214-y
34.
Tadros AB Yang WT Krishnamurthy S Rauch GM Smith BD Valero V et al . Identification of patients with documented pathologic complete response in the breast after neoadjuvant chemotherapy for omission of axillary surgery. JAMA Surg. (2017) 152:665–70. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0562
35.
Ma L Gao P Liu Z Jiao D Ling R Xiao J et al . Association of a complete breast cancer pathologic response with axillary lymph node metastasis via neoadjuvant chemotherapy: results from the CSBrS-012 study. Chin Med J. (2023) 137:1369–71. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002849
36.
Wang Y Yin Y Jiang Z . Interpretation of updated key points of Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology(CSCO) breast cancer guidelines 2023. Chin J Surg Oncol. (2023) 15:209–13. doi: 10.21037/tbcr-24-31
37.
Martin M Holmes FA Ejlertsen B Delaloge S Moy B Iwata H et al . Neratinib after trastuzumab-based adjuvant therapy in HER2-positive breast cancer (ExteNET): 5-year analysis of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. (2017) 18:1688–700. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30717-9
38.
Martin M Hegg R Kim SB Schenker M Grecea D García-Sáenz JA et al . Abemaciclib combined with adjuvant endocrine therapy in patients with high risk early breast cancer who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). J Clin Oncol. (2021) 39:517. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.517
39.
Gaba F Goyal S Marks D Chandrasekaran D Evans O Robbani S et al . Surgical decision making in premenopausal BRCA carriers considering risk-reducing early salpingectomy or salpingo-oophorectomy: a qualitative study. J Med Genet. (2022) 59:122–32. doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2020-107501
40.
Zhou T Zhang J . Therapeutic advances and application of PARP inhibitors in breast cancer. Transl Oncol. (2025) 57:102410. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2025.102410
41.
Della Corte L Palumbo M Ascione M D'Angelo G La Verde M Ferrari F et al . Impact on global health status, quality-sexual life and chronic fatigue state of risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy in women who are BRCA1/2 mutation carriers: experience from a third-level Italian center. Gynecol Obstet Investig. (2025):1–10. doi: 10.1159/000543869
42.
de Jonge MM de Kroon CD Jenner DJ Oosting J de Hullu JA Mourits MJE et al . Endometrial cancer risk in women with germline BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations: multicenter cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. (2021) 113:1203–11. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab036
Summary
Keywords
breast cancer, neoadjuvant chemotherapy, sentinel lymph node biopsy, axillary lymph node dissection, invasive disease-free survival
Citation
Ma J, Fan Z, Jia Z, Dong X, Sun J and Wang X (2025) Neoadjuvant chemotherapy impacts axillary lymph node positivity in early breast cancer (cT1-2N0M0) with negative axillary lymph nodes at diagnosis. Front. Med. 12:1672369. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1672369
Received
24 July 2025
Accepted
25 September 2025
Published
10 October 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Ming Liu, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China
Reviewed by
Mario Palumbo, Federico II University Hospital, Italy
Remzi Can Çakır, Hatay Training and Research Hospital, Türkiye
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Ma, Fan, Jia, Dong, Sun and Wang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiaozhen Wang, wxzhen@jlu.edu.cn
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.