- College of Medicine and Health Sciences, Sultan Qaboos University, Muscat, Oman
Renal biopsies remain indispensable in the diagnosis and management of renal diseases, offering critical histopathological insights that guide clinical decisions. Recent advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and multi-omics technologies have begun to transform renal pathology by enabling deeper molecular profiling, enhanced diagnostic precision, and personalized treatment strategies. Despite these promising developments, challenges such as implementation complexity, cost, and limited integration into routine clinical workflows have slowed widespread adoption. Notably, a significant gap exists in the literature regarding how these modern technologies are applied to maximize the diagnostic and prognostic value of renal biopsies. This mini-review highlights emerging applications of AI and omics in renal biopsy interpretation, emphasizing their potential to transform diagnostic approaches in precision nephrology. It aims to inform nephrologists, renal pathologists, and researchers about the evolving landscape of renal diagnostics, while highlighting areas for further clinical integration and interdisciplinary collaboration.
Introduction
Renal biopsy remains an essential diagnostic modality in nephrology, offering crucial histopathological insights into various renal diseases such as focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, membranous nephropathy, IgA nephropathy, lupus nephritis, and diabetic nephropathy. It guides disease classification, severity assessment, and therapeutic decision-making, particularly in complex or unclear clinical scenarios (1, 2). While light microscopy, immunofluorescence, and electron microscopy remain the cornerstones of tissue evaluation, the increasing complexity of renal disorders has driven the need for more precise, mechanistic insights beyond histology alone.
Recent advancements in omics technologies, including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, and metabolomics, are transforming renal pathology by enabling molecular-level understanding of disease processes. These approaches offer opportunities to identify disease-specific biomarkers, stratify patients by risk, and personalize treatment strategies (3, 4). Similarly, artificial intelligence (AI) is emerging as a powerful tool in renal biopsy analysis, enhancing diagnostic consistency, automating pattern recognition, and integrating histological and molecular data for improved clinical decision-making (5, 6).
Despite these innovations, clinical adoption remains limited, and few studies comprehensively address how omics and AI can be integrated with renal biopsy to enhance diagnostic precision and therapeutic stratification. Current clinical workflows rarely incorporate these tools in a standardized manner, and limited research has addressed their combined utility in enhancing diagnostic precision, monitoring disease progression, or predicting treatment response (7, 8).
This mini-review highlights recent advances in AI and multi-omics integration in renal biopsy interpretation. It focuses on their clinical relevance, diagnostic potential, and translational challenges, aiming to guide nephrologists, renal pathologists, and researchers in adopting modern approaches to kidney disease diagnostics and personalized care.
Omics technologies
Omics technologies refer to advanced scientific techniques used to study the complete set of molecules within a cell, tissue, or organism. These technologies include genomics (study of genes and DNA), transcriptomics (study of RNA and gene expression), proteomics (study of proteins), and metabolomics (study of metabolites and metabolic pathways), lipidomics (study of lipids), and microbiomics (study of the structure, function, and dynamics of a microbial community) (9). According to the systemic review study, the proteomic approach was the most common ‘omics platform (43.1%), followed by metabolomics (24.4%), genomics (13.8%), epigenomics (8.1%), transcriptomics (4.1) (10). Proteomics techniques include mass spectrometry (MS) combined with ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and capillary electrophoresis (CE) (11). Genomics techniques include next generation sequencing (NGS) (12). Metabolomic techniques include high field nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and mass spectrometry (MS) coupled with capillary electrophoresis (CE-MS), liquid chromatography MS (LC-MS), or gas chromatography (GC-MS) (13). Transcriptomics techniques include DNA microarrays and RNA sequencing (14). Microbiomics techniques include targeted sequencing of the 16S rRNA gene, and whole metagenome shotgun sequencing (15). Lipidomics techniques include mass spectrometry, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, and matrix assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (16, 17).
Clinical applications of omics in renal diseases
Renal biopsy has been revolutionized by multi-omics technologies, which provide a molecular layer of interpretation beyond morphology. By integrating histopathologic features with transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic data, nephrologists can better understand the mechanisms of renal injury, identify early molecular signatures of disease, and discover novel therapeutic targets. Samples from biopsy tissue, urine, and blood can all be analyzed using omics platforms (18).
Omics approaches have enhanced renal biopsy interpretation by revealing how molecular changes correspond to classical histopathologic lesions. For example, transcriptomic studies have demonstrated that reduced intrarenal epidermal growth factor (EGF) expression correlates with tubular atrophy and interstitial fibrosis (TA/IF), refining prognostic assessment within the same morphologic class (19, 20). Urinary proteomic classifiers such as CKD273 detect extracellular matrix remodeling before fibrosis becomes apparent on light microscopy, providing an opportunity for early therapeutic intervention (21). Similarly, multi-omic studies in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis has shown that proteomic and transcriptomic signatures reflecting neutrophil activation and complement pathways distinguish active inflammation from chronic scarring, even when biopsies appear morphologically similar, improving treatment stratification (22).
Recent work demonstrated that the urinary peptide-based classifier CKD273 can detect early molecular changes preceding morphologic evidence of chronic kidney disease, allowing more precise staging and prognosis beyond what is seen in biopsy alone (23). Likewise, upregulation of retinol dehydrogenase 9 in podocytes was shown to mitigate structural damage, providing mechanistic insight into podocyte injury observed histologically (24). In diabetic kidney disease (DKD), urine metabolomics identified dysregulation of the pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis pathway, linking specific metabolic signatures with characteristic glomerular and tubular lesions (25). Complementing these omics-based insights, a machine-learning model integrating biochemical and clinical data accurately predicted acute kidney injury, demonstrating how computational and omics-driven approaches can refine biopsy interpretation, guide early intervention, and reclassify renal pathologies with greater precision (26).
In lupus nephritis (LN), proximity extension assay proteomics identified urinary ICAM-2, FABP4, FASLG, IGFBP-2, SELE, and TNFSF13B/BAFF as markers distinguishing active LN from inactive SLE, correlating with histologic activity indices (27). In large cohort studies such as the Chronic Renal Insufficiency and Joslin Kidney Studies, integration of proteomic and transcriptomic profiles identified proteins such as TNFRSF1A, FGF20, and ANGPT1 that better predict renal function decline than conventional mesangial-expansion or IFTA scores (28, 29). Another study identified an inflammatory signature of 17 TNF receptor superfamily proteins associated with 10-year end-stage renal disease risk, supporting their potential use as biomarkers and therapeutic targets (30).
Collectively, these examples illustrate that omics does not replace histopathology but rather augments it, transforming static microscopic patterns into dynamic molecular phenotypes that improve diagnostic precision, prognostic accuracy, and personalized patient management. The integration of omics data with renal biopsy thus represents a paradigm shift in nephrology, offering a comprehensive view that bridges morphology with molecular mechanisms. However, it remains important to recognize that these technologies are still evolving and require further validation before their routine clinical adoption.
Omics technologies: challenges and solutions
While omics technologies offer transformative potential in renal biopsy analysis, their clinical application faces several challenges. One major limitation is the high cost, complexity of omics techniques, and large sample size is required, which can limit their accessibility in resource-limited settings (31, 32). To address the challenges, solutions include reducing costs through improved technology and automation, focusing on targeted biomarker panels, using machine learning to analyze smaller datasets, fostering collaborations for shared data, developing portable and cost-effective platforms, and optimizing sample preparation and data analysis protocols (31). These approaches can make omics more accessible and applicable in clinical settings, even in resource-limited environments. In addition, the massive amount of data generated by omics analyses requires advanced bioinformatics tools and expertise for interpretation, which may not be readily available in all clinical laboratories (33, 34). To address these challenges, collaborative efforts between researchers, clinicians, and bioinformaticians are essential to develop cost-effective and user-friendly omics platforms (35). Another issue is the lack of standardized protocols for sample preparation, data analysis, and interpretation, which can lead to variability in results. Establishing standardized guidelines and quality control measures can help improve the reproducibility and reliability of omics-based diagnostics (36).
AI in renal biopsy
In recent years, the change from human systems to machine systems [artificial intelligence (AI)], has been a great progress in the field of medical imaging, including renal pathology (37). AI techniques are increasingly being integrated into renal biopsy analysis, significantly enhancing diagnostic accuracy and efficiency. Machine learning algorithms, particularly deep learning, can be trained to identify and classify various renal diseases by analyzing histopathological images with high precision. This prognostic study found better performance for quantifying percent global glomerulosclerosis from whole-slide images of frozen and of permanent hematoxylin-eosin–stained donor transplant kidney biopsy specimens by a deep learning model (94% accuracy) than by on-call board-certified pathologists (80%) (38). Similarly, Convolutional neural networks (CNNs)-based systems indicated that this technique is suitable for correct glomerulus detection in Whole Slide Images, showing robustness while reducing false positive and false negative detections (39). These findings underscore the importance of hybrid approaches combining AI with expert histopathological evaluation.
These AI models can detect subtle changes in tissue structure, cellular patterns, and disease markers that might be overlooked by human eyes, leading to earlier and more accurate diagnoses. AI can also assist in quantifying the extent of fibrosis, inflammation, and other pathological features, providing standardized and reproducible assessments (40). Moreover, AI-driven image analysis can streamline the workflow of pathologists, allowing them to focus on complex cases and improving overall diagnostic throughput (41).
Various AI techniques are used for the analysis of renal biopsy samples, enhancing the accuracy and efficiency for diagnoses. CNNs, a type of deep learning, are effective in analyzing histopathological images (42). CNN and its variants are the most common neural networks utilized for categorizing renal carcinoma pathology images (43). CNNs can automatically identify and classify different renal diseases by learning from large datasets of annotated biopsy images, detecting patterns and features that may be imperceptible to human pathologists (44, 45). Another AI technique, machine learning algorithms like support vector machines (SVMs) and random forests, can be employed to analyze quantitative features extracted from biopsy images, such as glomerular size, tubular atrophy, and interstitial fibrosis (46). These algorithms can classify disease severity and predict outcomes based on the extracted features. In addition, natural language processing (NLP) can be used to analyze pathology reports and integrate clinical data with histopathological findings, providing a comprehensive diagnostic approach (47). Joint learning, which combines multiple AI models to improve prediction accuracy, is also used to enhance the robustness of biopsy analysis. These AI techniques not only improve diagnostic accuracy and reproducibility but also facilitate personalized treatment plans and better patient management in nephrology (48).
Clinical applications of AI in renal diseases
AI has demonstrated significant potential in improving the diagnosis and management of kidney diseases. For example, in a clinical study involving 948 patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN), artificial neural networks (ANNs) successfully identified individuals at high risk of developing end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) and predicted the time-to-event endpoint, aiding in risk assessment and early intervention (49). Another study focused on predicting renal flare in 1,694 patients with biopsy-proven LN and stratifying risk to enhance clinical decision-making and personalized management. The XGBoost model and the simplified risk score prediction model (SRSPM) effectively predicted renal flare in LN, with SRSPM also enabling risk stratification, ultimately supporting improved kidney outcomes (50). Additionally, a study aiming to enhance kidney disease severity assessment beyond traditional semiquantitative scoring utilized image digitization and morphometric techniques on 300 biopsy samples. The results showed that six CNN models outperformed pathologists in estimating the percentage of interstitial fibrosis, demonstrating the potential for AI in histopathological evaluation (51).
Another study developed a deep learning model for continuous risk prediction of patient deterioration, using acute kidney injury as an example. Trained on electronic health records from 703,782 adult patients across diverse clinical settings, the model predicted 55.8% of all inpatient AKI cases and 90.2% of severe cases requiring dialysis, with a lead time of up to 48 h. It also provided confidence assessments, highlighted key clinical features, and predicted blood test trajectories, offering a valuable tool for early intervention and improved patient outcomes (52). Furthermore, an artificial neural network model was developed to predict ESKD in patients with primary IgAN using a retrospective cohort of 948 patients. The model included a classifier for ESKD prediction and a regression model for estimating time to onset. Performance improved over time, achieving an area under the curve of 0.82 at 5 years and 0.89 at 10 years. External validation in 167 patients showed successful predictions for 91%, with superior discrimination (Harrell C index: 81% at 5 years, 86% at 10 years) and calibration compared to other models. The tool demonstrated strong predictive accuracy over a 25-year follow-up period, effectively identifying high-risk patients and supporting early therapeutic strategies to enhance clinical outcomes (49). Figure 1 shows an integration of traditional renal biopsy assessment with omics technologies and artificial intelligence to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
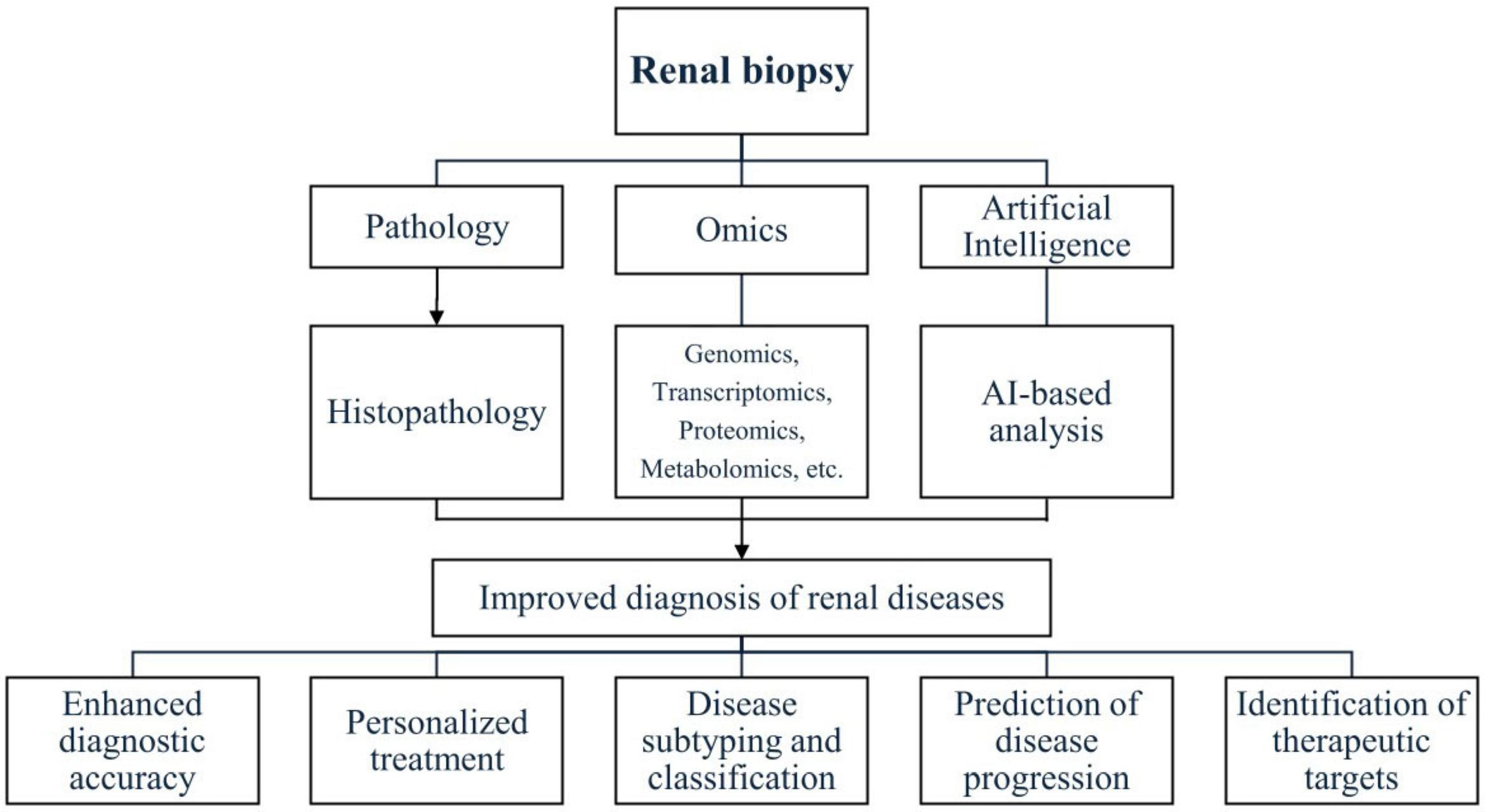
Figure 1. Integration of traditional renal biopsy assessment with omics technologies and artificial intelligence to enhance diagnostic accuracy.
AI in renal biopsy: challenges and solutions
The integration of AI into renal biopsy analysis also presents several challenges. One significant limitation is the need for large, high-quality datasets to train AI models effectively. Inadequate or biased datasets can lead to inaccurate predictions and reduced generalizability of AI algorithms (53). To overcome this, multicenter collaborations and data-sharing initiatives are critical to build strong and diverse datasets. Another challenge is the black box nature of some AI algorithms, where the decision-making process is not transparent, making it difficult for clinicians to trust and interpret AI-generated results (54, 55). Developing explainable AI models and providing training for pathologists on AI tools can help bridge this gap. In addition, the integration of AI into clinical workflows requires significant infrastructure and training, which may pose logistical and financial challenges for healthcare institutions (56). Gradually introducing AI technologies and continuously training healthcare providers can help make the transition easier. Another significant issue is related to ethical and safety concerns. Current laws and regulations are insufficient to address issues surrounding patient privacy, data security, and data ownership (57). To overcome these challenges, it is crucial to establish an international consensus on the ethical and safe use of AI in renal pathology, ensuring that these concerns are addressed and managed effectively by the global community (58).
Conclusion
The integration of advanced technologies such as omics and AI into renal biopsy interpretation represents a transformative shift in nephrology. These tools enable deeper molecular insights, enhance diagnostic accuracy, and support the development of personalized treatment strategies. Omics technologies provide a comprehensive understanding of the complex biological pathways underlying renal diseases, while AI offers automation, standardization, and predictive power in image and data analysis. Together, they hold the potential to improve patient outcomes and drive precision medicine in nephrology. Despite their promise, challenges remain in terms of clinical implementation, data interpretation, infrastructure, and ethical considerations. Addressing these issues through standardization, interdisciplinary collaboration, and robust validation studies is essential for successful clinical integration. As research continues to advance, the role of AI, alongside omics, in renal biopsy is expected to become increasingly crucial. Embracing these innovations will be key to enhancing diagnostic precision and improving patient care in the era of precision nephrology.
Author contributions
NA: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Supervision, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. MA: Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Nooran Al-Hamadani for her outstanding work in designing and illustrating Figure 1 featured in this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Generative AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Fiorentino M, Bolignano D, Tesar V, Pisano A, Biesen W, Tripepi G, et al. ERA-EDTA Immunonephrology Working Group. Renal biopsy in patients with diabetes: a pooled meta-analysis of 48 studies. Nephrol Dial Transplant. (2017) 32:97–110. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfw070
2. Walker P, Cavallo T, Bonsib S. Ad hoc committee on renal biopsy guidelines of the renal pathology society practice guidelines for the renal biopsy. Mod Pathol. (2004) 17:1555–63. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3800239
3. Hull K, Adenwalla S, Topham P, Graham-Brown M. Indications and considerations for kidney biopsy: an overview of clinical considerations for the non-specialist. Clin Med. (2022) 22:34–40. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.2021-0472
4. Pascual M, Vallhonrat H, Cosimi A, Tolkoff-Rubin N, Colvin R, Delmonico F, et al. The clinical usefulness of the renal allograft biopsy in the cyclosporine era: a prospective study. Transplantation. (1999) 67:737–41. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199903150-00016
5. Haas M, Spargo B, Wit E, Meehan S. Etiologies and outcome of acute renal insufficiency in older adults: a renal biopsy study of 259 cases. Am J Kidney Dis. (2000) 35:433–47. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(00)70196-x
6. Lipkowitz M, Freedman B, Langefeld C, Comeau M, Bowden D, Kao W, et al. Apolipoprotein L1 gene variants associate with hypertension-attributed nephropathy and the rate of kidney function decline in African Americans. Kidney Int. (2013) 83:114–20. doi: 10.1038/ki.2012.263
7. Working Group of the International IgA Nephropathy Network and the Renal Pathology Society, Cattran DC, Coppo R, Cook HT, Feehally J, Roberts IS, et al. The Oxford classification of IgA nephropathy: rationale, clinicopathological correlations, and classification. Kidney Int. (2009) 76:534–45. doi: 10.1038/ki.2009.243
8. Berden A, Ferrario F, Hagen E, Jayne D, Jennette J, Joh K, et al. Histopathologic classification of ANCA-associated glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2010) 21:1628–36. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2010050477
9. Horgan R, Kenny L. ‘Omic’ technologies: genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics and metabolomics. Obstetr Gynaecol. (2011) 13:189–95.
10. Govender M, Brandenburg J, Fabian J, Ramsay M. The use of ’Omics for diagnosing and predicting progression of chronic kidney disease: a scoping review. Front Genet. (2021) 12:682929. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.682929
11. Di Meo A, Pasic M, Yousef G. Proteomics and peptidomics: moving toward precision medicine in urological malignancies. Oncotarget. (2016) 7:52460–74. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8931
12. Groopman E, Marasa M, Cameron-Christie S, Petrovski S, Aggarwal V, Milo-Rasouly H, et al. Diagnostic utility of exome sequencing for kidney disease. N Engl J Med. (2019) 380:142–51. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1806891
15. Gryp T, Huys G, Joossens M, Van Biesen W, Glorieux G, Vaneechoutte M. Isolation and quantification of uremic toxin precursor-generating gut bacteria in chronic kidney disease patients. Int J Mol Sci. (2020) 21:1986. doi: 10.3390/ijms21061986
16. Cajka T, Fiehn O. Comprehensive analysis of lipids in biological systems by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Trends Analyt Chem. (2014) 61:192–206.
17. Dennis E, Deems R, Harkewicz R, Quehenberger O, Brown H, Milne S, et al. A mouse macrophage lipidome. J Biol Chem. (2010) 285:39976–85. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.182915
18. Rinschen M, Limbutara K, Knepper M, Payne D, Pisitkun T. From molecules to mechanisms: functional proteomics and its application to renal tubule physiology. Physiol Rev. (2018) 98:2571–606. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00057.2017
19. Eddy S, Mariani L, Kretzler M. Integrated multi-omics approaches to improve classification of chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. (2020) 16:657–68. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-0286-5
20. Ju W, Nair V, Smith S, Zhu L, Shedden K, Song P, et al. Tissue transcriptome-driven identification of epidermal growth factor as a chronic kidney disease biomarker. Sci Transl Med. (2015) 7:316ra193. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aac7071
21. Øvrehus M, Zürbig P, Vikse B, Hallan S. Urinary proteomics in chronic kidney disease: diagnosis and risk of progression beyond albuminuria. Clin Proteomics. (2015) 12:21. doi: 10.1186/s12014-015-9092-7
22. Haubitz M, Good D, Woywodt A, Haller H, Rupprecht H, Theodorescu D, et al. Identification and validation of urinary biomarkers for differential diagnosis and evaluation of therapeutic intervention in anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Mol Cell Proteomics. (2009) 8:2296–307. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M800529-MCP200
23. Pontillo C, Mischak H. Urinary peptide-based classifier CKD273: towards clinical application in chronic kidney disease. Clin Kidney J. (2017) 10:192–201. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfx002
24. Li X, Dai Y, Chuang P, He J. Induction of retinol dehydrogenase 9 expression in podocytes attenuates kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2014) 25:1933–41. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013111150
25. Ma T, Liu T, Xie P, Jiang S, Yi W, Dai P, et al. UPLC-MS-based urine nontargeted metabolic profiling identifies dysregulation of pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis pathway in diabetic kidney disease. Life Sci. (2020) 258:118160. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118160
26. Koyner J, Carey K, Edelson D, Churpek M. The development of a machine learning inpatient acute kidney injury prediction model. Crit Care Med. (2018) 46:1070–7. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003123
27. Li Y, Tang C, Vanarsa K, Thai N, Castillo J, Lea G, et al. Proximity extension assay proteomics and renal single cell transcriptomics uncover novel urinary biomarkers for active lupus nephritis. J Autoimmun. (2024) 143:103165. doi: 10.1016/j.jaut.2023.103165
28. Dubin R, Deo R, Ren Y, Wang J, Zheng Z, Shou H, et al. CRIC study investigators; CKD biomarkers consortium. Proteomics of CKD progression in the chronic renal insufficiency cohort. Nat Commun. (2023) 14:6340. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41642-7
29. Md Dom Z, Satake E, Skupien J, Krolewski B, O’Neil K, Willency J, et al. Circulating proteins protect against renal decline and progression to end-stage renal disease in patients with diabetes. Sci Transl Med. (2021) 13:eabd2699. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.abd2699
30. Niewczas M, Pavkov M, Skupien J, Smiles A, Md Dom Z, Wilson J, et al. A signature of circulating inflammatory proteins and development of end-stage renal disease in diabetes. Nat Med. (2019) 25:805–13. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0415-5
31. Mantione K, Kream R, Kuzelova H, Ptacek R, Raboch J, Samuel J, et al. Comparing bioinformatic gene expression profiling methods: microarray and RNA-Seq. Med Sci Monit Basic Res. (2014) 20:138–42. doi: 10.12659/MSMBR.892101
32. Hrdlickova R, Toloue M, Tian B. RNA-Seq methods for transcriptome analysis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. (2017) 8: doi: 10.1002/wrna.1364
33. Eberhardt K, Stiebing C, Matthaus C, Schmitt M, Popp J. Advantages and limitations of Raman spectroscopy for molecular diagnostics: an update. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. (2015) 15:773–87. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1036744
34. Jurowski K, Kochan K, Walczak J, Baranska M, Piekoszewski W, Buszewski B. Analytical techniques in lipidomics: state of the art. Crit Rev Anal Chem. (2017) 47:418–37. doi: 10.1080/10408347.2017.1310613
35. Zhang Z, Wu S, Stenoien D, Pasa-Tolic L. High-throughput proteomics. Annu Rev Anal Chem. (2014) 7:427–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev-anchem-071213-020216
36. Cambiaghi A, Ferrario M, Masseroli M. Analysis of metabolomic data: tools, current strategies and future challenges for omics data integration. Brief Bioinform. (2017) 18:498–510. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbw031
37. Alhussaini A, Steele J, Jawli A, Nabi G. Radiomics machine learning analysis of clear cell renal cell carcinoma for tumour grade prediction based on intra-tumoural sub-region heterogeneity. Cancers. (2024) 16:1454. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081454
38. Marsh J, Liu T, Wilson P, Swamidass S, Gaut J. Development and validation of a deep learning model to quantify glomerulosclerosis in kidney biopsy specimens. JAMA Netw Open. (2021) 4:e2030939. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.30939
39. Gallego J, Pedraza A, Lopez S, Steiner G, Gonzalez L, Laurinavicius A, et al. Glomerulus classification and detection based on convolutional neural networks. J Imaging. (2018) 4:20. doi: 10.3390/jimaging4010020
40. Ginley B, Lutnick B, Jen K, Fogo A, Jain S, Rosenberg A, et al. Computational segmentation and classification of diabetic glomerulosclerosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2019) 30:1953–67. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2018121259
41. Simon O, Yacoub R, Jain S, Tomaszewski J, Sarder P. Multi-radial LBP features as a tool for rapid glomerular detection and assessment in whole slide histopathology images. Sci Rep. (2018) 8:2032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20453-7
42. Komura D, Ishikawa S. Machine learning methods for histopathological image analysis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. (2018) 16:34–42. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2018.01.001
43. Hermsen M, de Bel T, den Boer M, Steenbergen E, Kers J, Florquin S, et al. Deep learning-based histopathologic assessment of kidney tissue. J Am Soc Nephrol. (2019) 30:1968–79. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2019020144
44. Jayapandian CP, Chen Y, Janowczyk AR, Palmer MB, Cassol CA, Sekulic M, et al. Development and evaluation of deep learning-based segmentation of histologic structures in the kidney cortex with multiple histologic stains. Kidney Int. (2021) 99:86–101. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.07.044
45. Naik D, Mohana R, Ramu G, Lalitha Y, SureshKumar M, Raghavender K. Analyzing histopathological images by using machine learning techniques. Appl Nanosci. (2023) 13:2507–13. doi: 10.1007/s13204-021-02217-4
46. Albahra S, Gorbett T, Robertson S, D’Aleo G, Kumar S, Ockunzzi S, et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning overview in pathology & laboratory medicine: a general review of data preprocessing and basic supervised concepts. Semin Diagn Pathol. (2023) 40:71–87. doi: 10.1053/j.semdp.2023.02.002
47. Sageshima J, Than P, Goussous N, Mineyev N, Perez R. Prediction of high-risk donors for kidney discard and nonrecovery using structured donor characteristics and unstructured donor narratives. JAMA Surg. (2024) 159:60–8. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2023.4679
48. Chaudhuri S, Long A, Zhang H, Monaghan C, Larkin J, Kotanko P, et al. Artificial intelligence enabled applications in kidney disease. Semin Dial. (2021) 34:5–16. doi: 10.1111/sdi.12915
49. Schena FP, Anelli VW, Trotta J, Di Noia T, Manno C, Tripepi G, et al. Development and testing of an artificial intelligence tool for predicting end-stage kidney disease in patients with immunoglobulin a nephropathy. Kidney Int. (2021) 99:1179–88. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.07.046
50. Chen Y, Huang S, Chen T, Liang D, Yang J, Zeng C, et al. Machine learning for prediction and risk stratification of lupus nephritis renal flare. Am J Nephrol. (2021) 52:152–60. doi: 10.1159/000513566
51. Kolachalama V, Singh P, Lin C, Mun D, Belghasem M, Henderson J, et al. Association of pathological fibrosis with renal survival using deep neural networks. Kidney Int Rep. (2018) 3:464–75. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2017.11.002
52. Tomašev N, Glorot X, Rae J, Zielinski M, Askham H, Saraiva A, et al. A clinically applicable approach to continuous prediction of future acute kidney injury. Nature. (2019) 572:116–9. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1390-1
53. Wellekens K, Koshy P, Naesens M. Challenges in standardizing preimplantation kidney biopsy assessments and the potential of AI-Driven solutions. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. (2025) 34:185–90. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000001064
54. Huo Y, Deng R, Liu Q, Fogo A, Yang H. AI applications in renal pathology. Kidney Int. (2021) 99:1309–20. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.01.015
55. Kadhim D, Mohammed M. A comprehensive review of artificial intelligence approaches in kidney cancer medical images diagnosis, datasets, challenges and issues and future directions. Int J Math Comput Sci. (2024) 2:199–243. doi: 10.59543/ijmscs.v2i.9747
56. Lay J, Liyanage R, Borgmann S, Wilkins C. Problems with the “omics”. TrAC Trends Analy Chem. (2006) 25:1046–56. doi: 10.1016/j.trac.2006.10.007
57. Becker J, Mayerich D, Padmanabhan M, Barratt J, Ernst A, Boor P, et al. Artificial intelligence and machine learning in nephropathology. Kidney Int. (2020) 98:65–75. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.02.027
Keywords: renal biopsy, omics techniques, artificial intelligence, deep learning, precision nephrology
Citation: Alwahaibi N and Alwahaibi M (2025) Revolutionizing renal biopsy: the emerging role of omics and artificial intelligence in nephrology. Front. Med. 12:1680813. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1680813
Received: 06 August 2025; Accepted: 20 October 2025;
Published: 04 November 2025.
Edited by:
Gregory Braden, University of Massachusetts Medical School, United StatesReviewed by:
Nadja Grobe, Renal Research Institute, United StatesCopyright © 2025 Alwahaibi and Alwahaibi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Nasar Alwahaibi, bmFzYXJAc3F1LmVkdS5vbQ==
 Nasar Alwahaibi
Nasar Alwahaibi Maryam Alwahaibi
Maryam Alwahaibi