- Department of Radiology, Faculty of Medicine, Universiti Kebangsaan Malaysia, Cheras, Malaysia
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a globally prevalent respiratory pathogen, primarily affecting young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. Typical airway-centric radiological findings like other viral infections are commonly reported. However, atypical findings in computed tomography (CT) have yet to be reported in literature. We present a case of hMPV infection in an immunocompetent adult with rare findings of cystic lesions in CT thorax. A 67-year-old female with underlying valvular heart disease and chronic heart failure presented to our centre with respiratory symptoms and reduced effort tolerance. Initial chest radiographs were suggestive of an active pulmonary infection superimposed on acute pulmonary edema, leading to empirical antibiotic treatment with the differentials of community-acquired pneumonia. Despite antibiotics and diuretics treatment, her condition worsened requiring oxygenation supplementation. High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) thorax was performed and demonstrated typical airway-centered findings including peribronchial wall thickening and ground-glass opacities. In addition, multiple cystic lung lesions of varying sizes in random distribution are seen scattered in both lung fields. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) confirmed an hMPV infection, with no evidence of bacterial or other viral co-infection. The patient improved with supportive care and was discharged after 5 days of admission. While there is no preceding literature on atypical lung changes during the course of hMPV infection, this case highlights the possibility of the broader imaging dynamics of this virus.
Introduction
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is a globally prevalent respiratory pathogen, primarily affecting young children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. Radiologically, hMPV infections typically present an airway-centric pattern that closely resembles other viral infections but also exhibits features overlapping with bacterial pneumonia. These include bronchial wall thickening, centrilobular nodules, peri-bronchial consolidation, ground-glass opacities (GGO), and nodular consolidation (1–4). However, the cystic changes in CT thorax have yet to be reported in literature. Here, we presented a case of a 67-year-old female with a background of valvular heart disease and chronic heart failure, who tested positive for hMPV infection. Radiological findings highlighted atypical findings of multiple cystic lung lesions with typical airway-centered findings of viral infection.
Case description
A 67-year-old female with a background of valvular heart disease and chronic heart failure presented to our facility with complaints of respiratory symptoms and reduced exercise tolerance over the preceding 2 days. Further history revealed close contact with a symptomatic spouse and non-compliance with her prescribed diuretics medications for the past week.
Upon arrival at the Emergency Department, she appeared breathless but was not using accessory muscles and remained alert. She was febrile (39.6 °C), tachypneic (respiratory rate of 24–26 breaths/min) and hypoxemic with peripheral oxygen saturation of 92% on room air. Her blood pressure and heart rate were unremarkable; BP 119/68 HR 90 bpm. On physical examination, lung auscultation revealed crepitations localized to the right lower lung zone. Arterial blood gas (ABG) analysis demonstrated type 1 respiratory failure, while inflammatory markers including PCT (0.04 ng/mL), CRP (2.52 mg/dL) white blood cell count (6.6 × 109/L) were within normal limits. She tested negative for COVID-19. A chest radiograph (Figure 1a) performed on presentation demonstrated features suggestive of pulmonary edema. In correlation with the clinical presentation and laboratory results, the initial working diagnosis was community-acquired pneumonia (CAP), and the patient was subsequently admitted for empirical antibiotic therapy (intravenous augmentin 1.2 g QID and oral azithromycin 500 mg OD) targeting both typical and atypical respiratory pathogens. Her previous diuretics medications were also on board, which were oral spironolactone 12.5 mg OD and furosemide 20 mg PRN.
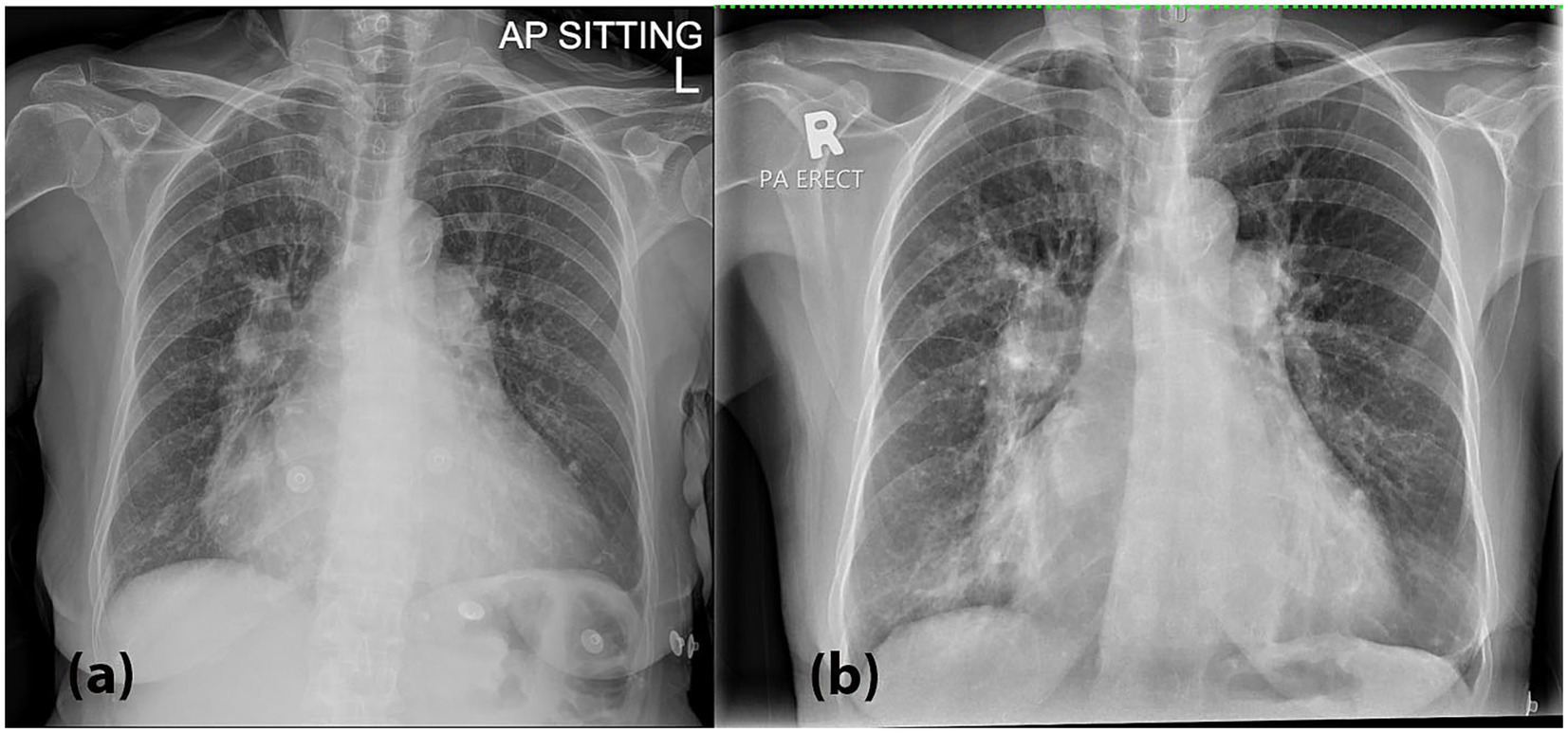
Figure 1. (a) A chest radiograph (CXR) performed on presentation demonstrated bilateral hilar opacities with peribronchial cuffing, along with radiographic features suggestive of pulmonary edema, including fluid in the right horizontal fissure and Kerley B lines, especially in the right lower zone. These findings are suggestive of an active pulmonary infection superimposed on acute pulmonary edema. (b) A repeat CXR on Day 3 showed worsening bilateral hilar and lower zone opacities, along with persistent peribronchial cuffing.
During hospitalization, the patient experienced recurrent fever spikes and oxygen desaturation, necessitating anti-pyretic and supplemental oxygen via nasal prong 3 L/min. A repeat chest radiograph on Day 3 (Figure 1b) showed worsening bilateral hilar and lower zone opacities, along with persistent peribronchial cuffing. Laboratory investigations at that point revealed thrombocytopenia and leucocytopenia, with infective screenings (blood and sputum bacterial and tuberculosis cultures, PCT, CRP, dengue serology, BFMP) yielded negative results.
Given the progression in radiographic findings, a high-resolution CT (HRCT) thorax was performed on Day 4. The HRCT (Figure 2) showed patchy ground-glass opacities in a peribronchovascular distribution, with diffuse peribronchial wall thickening and mucus plugging, most pronounced in the right lung. Multiple lung cysts of varying sizes were scattered throughout the lung fields, predominantly in the right lung. A large cystic lesion measuring 5.8 × 4.0 × 4.7 cm was seen in the inferior lingular segment of the left lower lobe, which could be of a pneumatocele or subpleural bullae. Additionally, a calcified pleural plaque was present at the posterior segment of the right lower lobe.
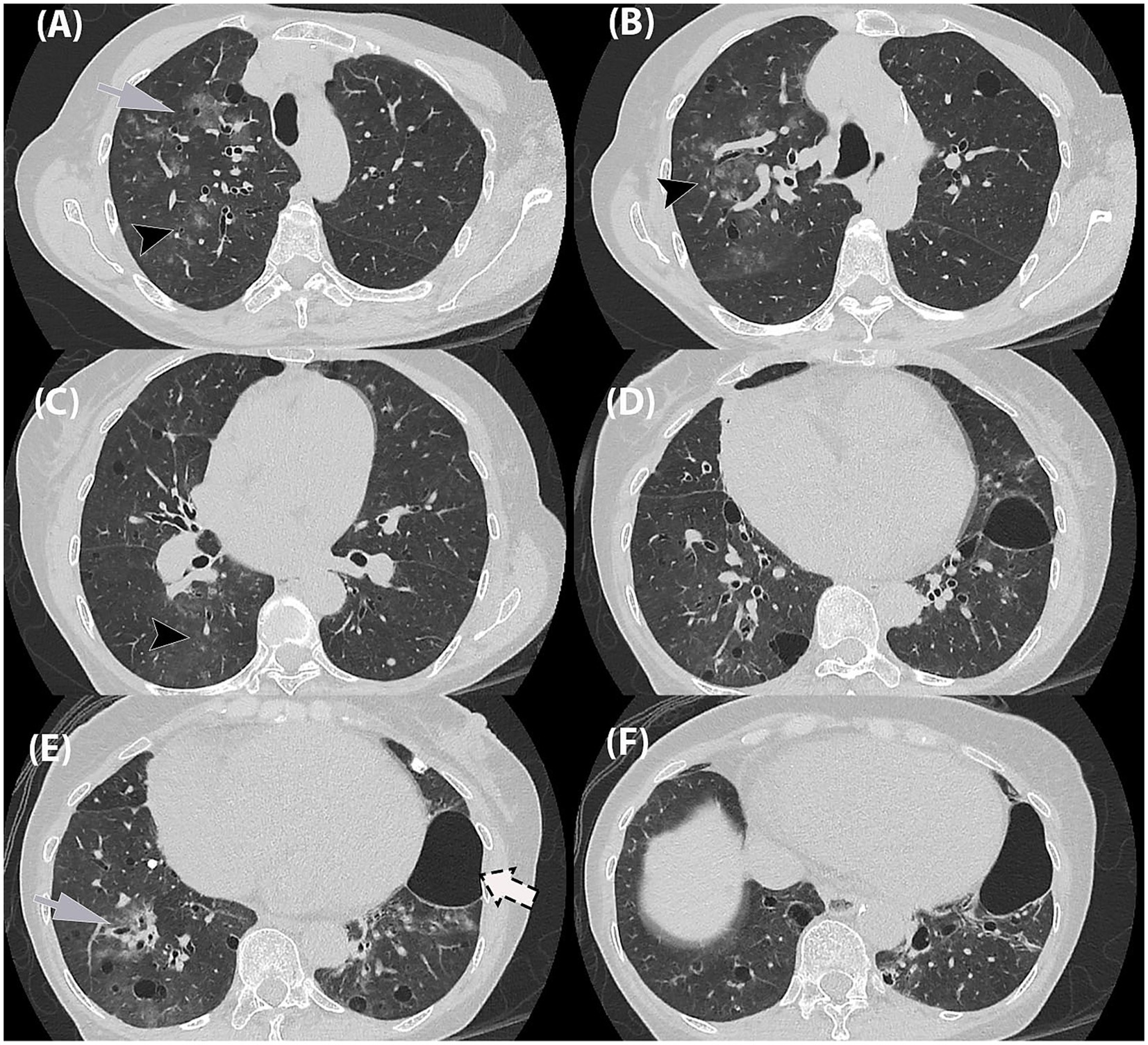
Figure 2. High-resolution chest tomography (HRCT) thorax in axial planes. (A,B) Ground-glass opacities in a bronchocentric distribution (grey arrow) as well as ground-glass centrilobular nodules in the right upper lobe (black arrowhead). (C,D) Similar ground-glass centrilobular nodules in right lower lobe (black arrowhead). (E,F) Ground-glass opacities in bronchocentric (grey arrow) distribution in bilateral lower lobes. (A–F) Randomly distributed thin-walled cysts of varying in bilateral lungs, (F) largest in left lower lobe (dashed-arrow).
At the time of imaging, routine serology and sputum cultures were negative, thereby leaving no microbiological evidence for the patient’s acute symptoms. High-resolution CT (HRCT) was therefore central in guiding the diagnostic workup. The scan revealed airway inflammation consistent with viral infection with no radiological feature of organizing pneumonia. This posed a diagnostic challenge as the HRCT findings led to several differential diagnoses. The lung nodules were indeterminate, while the cystic lesions raised the possibility of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP), lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP), or an underlying cystic lung disease. Although acute presentation and airway inflammation favored an infective etiology, alternative diagnoses could not be excluded. A post-treatment follow-up was recommended to monitor the cystic changes.
Subsequently, a QIAstat respiratory panel was conducted via nasopharyngeal swab sample, confirming the presence of hMPV (A and B) through RT-PCR, with Ct value for hMPV A/B of 33.9. Other viral and bacterial co-infections were not detected (e.g., adenovirus, influenza, Mycoplasma pneumoniae etc.). Patient received supportive care and completed her course of antibiotics for atypical organisms, while antibiotics for typical bacteria were discontinued based on the viral diagnosis. Her clinical condition improved, and she was discharged with appropriate outpatient follow-up. However, no post treatment imaging follow up was recorded.
Discussion
Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) is an enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA virus, belonging to the family Pneumoviridae within the order Mononegavirales and is phylogenetically closely related to respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and parainfluenza viruses. Molecular characterization has delineated two major genetic lineages, designated A and B, each comprising two distinct sublineages based on antigenic and genomic analyses (2, 5–8).
hMPV is a ubiquitous respiratory pathogen infecting all age groups, with primary infection typically occurring in early childhood; seroprevalence data indicate that most children are infected by 5 years of age. Due to the induction of incomplete and transient immunity, reinfections are common throughout life. Seasonal epidemiology reveals a marked winter and spring predominance, with clinical presentations overlapping significantly with other paramyxoviruses such as RSV and influenza viruses.
The clinical spectrum ranges from mild upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) to severe lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs), including bronchiolitis, pneumonia, and exacerbations of chronic pulmonary diseases such as asthma and COPD. Severe disease manifestations predominantly affect pediatric populations, elderly adults, immunocompromised individuals, and those with underlying comorbidities (2, 5–7). It is primarily transmitted via respiratory secretion. The ciliated epithelial cells in the respiratory system are primarily affected, impairing mucociliary clearance (9).
Conventional viral culture is suboptimal for isolating hMPV due to its fastidious growth characteristics. Currently, nucleic-acid-based techniques (NAAT), including polymerase chain reactions (PCRs), are one of the major diagnostic approaches (9). Radiologically, hMPV primarily leads to an airway-centric infection pattern, which includes bronchial wall thickening, centrilobular nodules, peribronchial consolidation, ground-glass opacities (GGO), and nodular consolidation, often with an asymmetric bilateral multilobar involvement (1–4). In our case, typical airway-centric findings were observed. Additionally, atypical findings of multiple pulmonary cystic lesions in random distributions were also seen. These cystic lesions were of various shapes and sizes and thin walled. There was no pneumothorax.
To date, the association between hMPV and cystic lung lesions has not been reported. Pulmonary cysts, however, have been described in COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 infections (10–12). Generally, pulmonary cyst formation occurs through various mechanisms, including check-valve airway obstruction leading to distal airspace dilation, ischemia and necrosis of airway walls, and destruction of lung parenchyma (13). Additionally, mechanical ventilation causing cystic changes in COVID-19 patients has also been documented (12).
Pertaining to our case, these cystic changes observed may be linked to alveolar damage, as hMPV increases perivascular and peribronchiolar infiltration, triggering inflammatory responses and causing alveolar damage. This is supported by histopathological findings of acute and organizing diffuse alveolar damage (DAD), with the virus localized in bronchial epithelial cells and pneumocytes through immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization (14). Other reported histopathological findings of intra-alveolar foamy macrophages, hemosiderin, and smudge cells, have also been reported, suggesting lung injury (15–17). Additionally, diffuse alveolar hemorrhage secondary to hMPV infection in adults has been documented (14, 18). However, since bronchoalveolar lavage and lung biopsy specimens are not available in this case report, the direct association between the radiologically observed pulmonary cysts and histopathological findings of DAD remains unclear. Another limitation is the availability of only a single set of CT thorax images, with no prior or follow-up images to assess the progression of the cystic lesions.
At present, there are no antivirals specifically approved for the treatment of hMPV infections. The mainstay treatment is supportive care which includes oxygen therapy and intravenous fluids. Although bronchodilators and corticosteroids are often administered as a standard practice, there is no clinical evidence confirming their effectiveness against hMPV. Ribavirin has also been explored but its clinical impact alone has yet to be ascertained. The combination of IV ribavirin and IV immunoglobulin (IVIG) has otherwise shown promising results especially in critically ill patients (9).
In conclusion, this case report underscores the possibility of hMPV infection potentially leading to the independent formation of pulmonary cysts, in addition to the typical airway-centric radiological patterns. However, the direct mechanism of multiple lung cysts during hMPV infection cannot be definitively determined. Further research is needed to fully understand the imaging dynamics associated with this virus.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
The studies involving humans were approved by Research Ethics Committee National University of Malaysia. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the individual(s) for the publication of any potentially identifiable images or data included in this article.
Author contributions
LJ: Investigation, Data curation, Writing – review & editing, Resources, Writing – original draft, Formal analysis. HY: Writing – review & editing, Resources, Formal analysis, Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Visualization, Investigation. MA: Writing – original draft, Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Visualization, Formal analysis, Writing – review & editing, Supervision.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the Faculty of Medicine, UKM, for providing funds for the publication of this paper.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
References
1. Philippot, Q, Rammaert, B, Dauriat, G, Daubin, C, Schlemmer, F, Costantini, A, et al. Human metapneumovirus infection is associated with a substantial morbidity and mortality burden in adult inpatients. Heliyon. (2024) 10:e33231. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33231
2. Marinari, LA, Danny, MA, Simpson, SA, Schmitt, JE, and Miller, WT. Lower respiratory tract infection with human metapneumovirus: chest CT imaging features and comparison with other viruses. Eur J Radiol. (2020) 128:108988. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2020.108988
3. Contes, KM, and Liu, BM. Epidemiology, clinical significance, and diagnosis of respiratory viruses and their co-infections in the post-COVID era. Pathogens. (2025) 14:262. doi: 10.3390/pathogens14030262
4. Al-Hamoud, A, Pansu, N, Brun, AL, Etienne, N, Farfour, E, Avettand-Fenoel, V, et al. Determinants of radiological patterns and severity in immunocompromised adults with metapneumovirus infection. Respir Med. (2024) 227:107604. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2024.107604
5. Falsey, AR. Human metapneumovirus infection in adults. Pediatr Infect Dis J. (2008) 27:S80–3. doi: 10.1097/INF.0b013e3181684dac
6. Costa-Filho, RC, Saddy, F, Costa, JLF, Tavares, LR, and Castro Faria Neto, HC. The silent threat of human metapneumovirus: clinical challenges and diagnostic insights from a severe pneumonia case. Microorganisms. (2025) 13:73. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13010073
7. Walsh, EE, Peterson, DR, and Falsey, AR. Human metapneumovirus infections in adults. Arch Intern Med. (2008) 168:2489–96. doi: 10.1001/archinte.168.22.2489
8. Krüger, N, Laufer, SA, and Pillaiyar, T. An overview of progress in human metapneumovirus (hMPV) research: structure, function, and therapeutic opportunities. Drug Discov Today. (2025) 30:104364. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2025.104364
9. Mohammadi, K, Faramarzi, S, Yaribash, S, Valizadeh, Z, Rajabi, E, Ghavam, M, et al. Human metapneumovirus (hMPV) in 2025: emerging trends and insights from community and hospital-based respiratory panel analyses—a comprehensive review. Virol J. (2025) 22:150. doi: 10.1186/s12985-025-02782-y
10. Itoh, M, Herai, Y, Nakamura, H, and Aoshiba, K. Multiple pulmonary cyst formation after COVID-19 pneumonia. IDCases. (2022) 27:e01389. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2022.e01389
11. Mariscal Aguilar, P, Zamarrón De Lucas, E, and Álvarez-Sala, WR. Lung cysts in a patient with SARS-CoV-2. Med Clín. (2020) 155:325. doi: 10.1016/j.medcle.2020.06.009
12. Liu, K, Zeng, Y, Xie, P, Ye, X, Xu, G, Liu, J, et al. COVID-19 with cystic features on computed tomography. Medicine. (2020) 99:e20175. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000020175
13. Lee, KC, Kang, EY, Yong, HS, Kim, C, Lee, KY, Hwang, SH, et al. A stepwise diagnostic approach to cystic lung diseases for radiologists. Korean J Radiol. (2019) 20:1368–80. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0057
14. Rodriguez-Nava, G, Shrestha, E, Upadhyay, B, Morante, A, Joseph, D, Suhail, A, et al. Bleeding pneumonia: diffuse alveolar hemorrhage due to human metapneumovirus. IDCases. (2020) 21:e00894. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2020.e00894
15. Sumino, KC, Agapov, E, Pierce, RA, Trulock, EP, Pfeifer, JD, Ritter, JH, et al. Detection of severe human metapneumovirus infection by real-time polymerase chain reaction and histopathological assessment. J Infect Dis. (2005) 192:1052–60. doi: 10.1086/432728
16. Vargas, SO, Kozakewich, HPW, Perez-Atayde, AR, and McAdam, AJ. Pathology of human metapneumovirus infection: insights into the pathogenesis of a newly identified respiratory virus. Pediatr Dev Pathol. (2004) 7:478–86. doi: 10.1007/s10024-004-1011-2
17. Mastrolia, M, and Esposito, S. Metapneumovirus infections and respiratory complications. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. (2016) 37:512–21. doi: 10.1055/s-0036-1584800
18. Anstett, S, Gravenstein, KS, Finn, A, and Salloum, I. Diffuse alveolar hemorrhage secondary to human metapneumovirus pulmonary infection. R I Med J. (2022) 105:31–3. Available at: http://rimed.org/rimedicaljournal/2022/11/2022-11-31-case-anstett.pdf
Keywords: CT, cystic lung disease, adult, human metapneumovirus (hMPV), imaging
Citation: Jiun LC, Yee HS and Azmi MI (2025) Case Report: Unusual radiological findings in adult human metapneumovirus infection. Front. Med. 12:1687321. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1687321
Edited by:
Karolina Henryka Czarnecka-Chrebelska, Medical University of Lodz, PolandReviewed by:
Benjamin M. Liu, George Washington University, United StatesW. Abdullah Brooks, Johns Hopkins University, United States
Copyright © 2025 Jiun, Yee and Azmi. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Mohd Imree Azmi, aW1yZWVAdWttLmVkdS5teQ==
 Ling Chieng Jiun
Ling Chieng Jiun Ho Shuang Yee
Ho Shuang Yee Mohd Imree Azmi
Mohd Imree Azmi