- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Xianju Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
- 2Emergency Department, Xianju Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Taizhou, Zhejiang, China
Background: This study aimed to explore risk factors for osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus by meta-analysis.
Methods: PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library were searched for case–control/cohort studies on the occurrence of osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus from the time the database was created until 1 December 2024. Data were analyzed using Stata 15.0, and the quality of the included studies was evaluated using the NOS score.
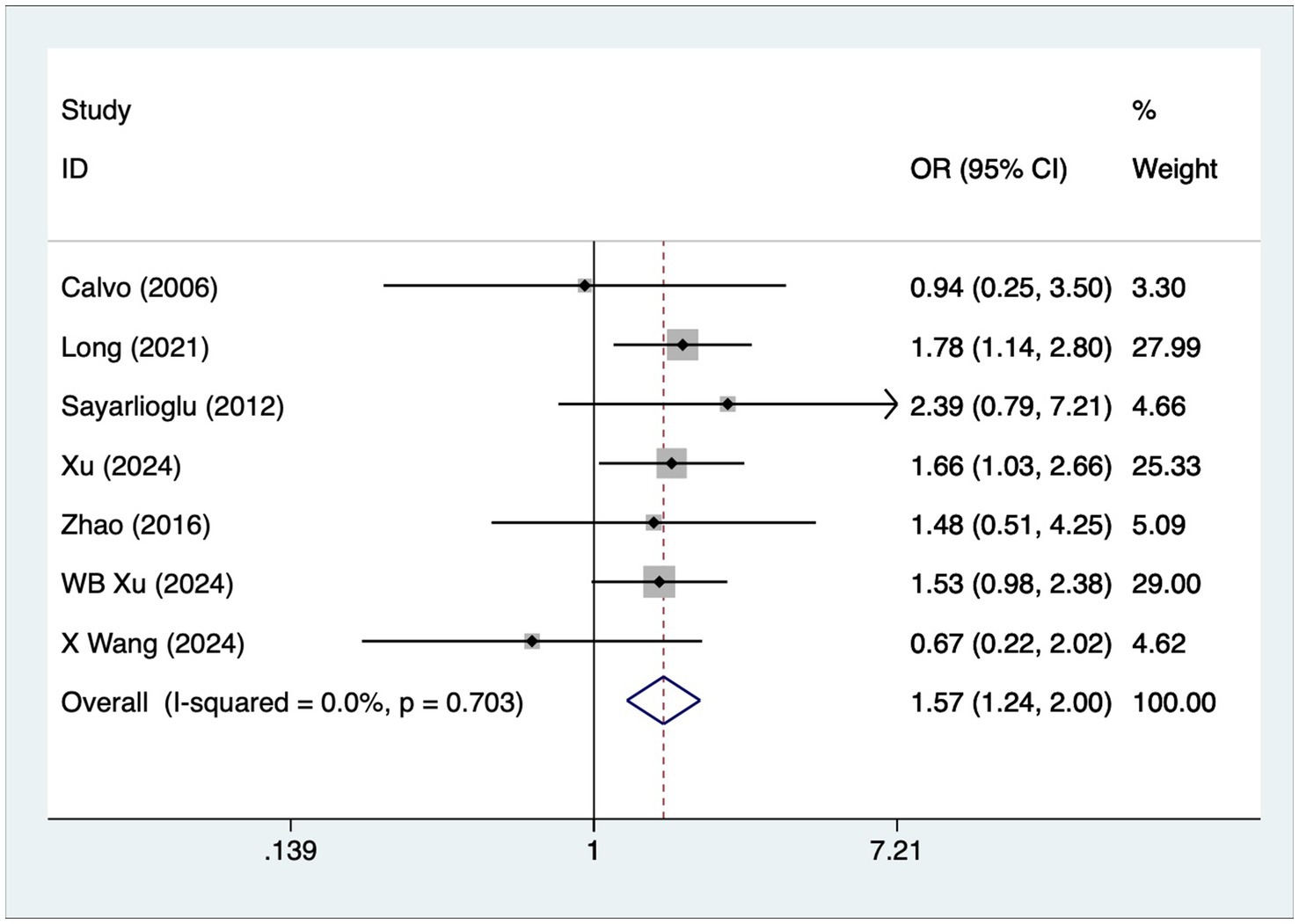
Result: A total of 14 articles, including 3,890 patients, were included in the study, and the meta-analysis indicates that younger age in SLE patients [SMD = −0.23, 95% CI (−0.39, −0.06)], diabetes mellitus [OR = 1.78, 95% CI (1.03, 3.09)], hypertension [OR = 1.33, 95% CI (1.03, 1.72)], arthritis [OR = 1.57, 95% CI (1.24, 2.00)], Raynaud’s phenomenon [OR = 1.76, 95% CI (1.35, 2.30)], and cyclophosphamide use [OR = 2.24, 95% CI (1.38, 3.63)] are risk factors for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE.
Conclusion: The current study found that younger age, hypertension, diabetes, arthritis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and cyclophosphamide use are independent risk factors for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE.
Introduction
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease that affects multiple organs and systems (1, 2). It is common in young women and usually develops between the ages of 15 and 45 years (3). The clinical manifestations of SLE are varied and include, but are not limited to, rash, arthritis, renal damage, neurological damage, and cardiovascular lesions (4). The inflammatory response and tissue damage result from an abnormal immune system response to autologous cells. Epidemiological studies have shown that the prevalence of SLE varies across regions and ethnicities, but it is generally on the rise (5). With advances in therapeutic approaches, the survival of patients has been significantly improved, and the use of immunosuppressive therapy and anti-inflammatory drugs has significantly enhanced clinical outcomes (6). However, these treatments may also lead to various complications, such as osteoporosis and osteonecrosis, which can seriously affect patients’ quality of life and even endanger their lives (7, 8).
Osteonecrosis is a type of ischemic necrosis of bone tissue caused by an interruption of the blood supply, usually affecting large joints such as the femoral head and hip (9). The incidence of osteonecrosis is higher in patients with SLE, especially in patients on long-term steroid medication. Steroid therapy is a common treatment option for patients with SLE; however, its long-term use is strongly associated with the development of osteonecrosis (10, 11). The combination of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE significantly increases the risk of joint dysfunction, leading to severe pain, mobility problems, and, in some cases, the need for joint replacement surgery (12). Epidemiological studies have shown that the incidence of osteonecrosis is significantly higher in SLE patients than in the general population and that its early diagnosis and treatment are important (13). Nevertheless, the exact pathogenesis of osteonecrosis is still not fully understood and may involve a combination of factors (14). In SLE patients, osteonecrosis most frequently involves large joints such as the hip and knee; however, rare and atypical presentations may also occur. For example, Gökten (15) recently reported two cases of Freiberg’s infraction in patients with SLE, highlighting the potential for unusual skeletal sites to be affected and the importance of maintaining clinical vigilance beyond the classical locations.
This study aimed to assess the major risk factors for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE through a systematic review and meta-analysis. Although there have been several individual studies (16, 17) examining the effects of factors such as steroid use, age, and gender on osteonecrosis in patients with SLE, no uniform conclusions have been reached due to conflicting findings and the small sample sizes of some studies. The present meta-analysis aims to pool high-quality existing studies to systematically assess various factors influencing the development of osteonecrosis in SLE patients, including treatment, genetics, immunity, and environment. Through this study, we aim to provide a more solid theoretical basis for the early prevention and treatment of osteonecrosis in SLE patients and to help clinicians in developing more effective, individualized treatment plans, thereby improving patients’ quality of life and long-term survival.
Methods
Literature search
The search was performed by searching PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane Library from database creation to 1 December 2024. The search terms were osteonecrosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, and risk factors, and the specific search strategy is described in Supplementary Table S1.
Literature screening
Inclusion Criteria: This study included adults diagnosed with SLE, with osteonecrosis as the exposure factor and controls without osteonecrosis. The primary outcome was the identification of risk factors associated with the development of osteonecrosis. Only case–control or cohort studies were included.
Exclusion criteria: Studies were excluded if they were conference abstracts, meta-analyses, protocols, letters, previously published articles, systematic reviews, animal experiments, or if the full text or relevant data could not be obtained.
Data extraction
Two independent evaluators screened the literature and extracted the data. Studies that could be readily accessed were directly screened by reviewing the title and abstract, followed by a full-text review when required. For studies that could be included with objections, we consulted relevant faculty members, directly downloaded and read the full texts, and strictly followed the inclusion and exclusion criteria during the screening process. We extracted the corresponding indicators from each study and performed cross-checks to ensure data consistency. The main data extracted included the first author’s name, publication year, study design, country, sample size, gender, age, and NOS scores. For studies where data were unavailable, we contacted the corresponding author, and if no data were received from them, such studies were excluded.
Quality evaluation
The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) (18) was used to evaluate the case–control study, including the selection of study population (4 points), comparability between groups (2 points), and measurement of exposure factors or results (3 points). The total score of the scale is 9, with ≤4 being low quality, 5–6 being medium quality, and ≥7 being high quality. If two researchers disagreed in the evaluation process, they discussed until a consensus was reached or a third party was asked to decide.
Statistical analysis
Stata 15.0 was used for statistical data analysis. The risk values from each study were expressed as odds ratios (ORs), and the corresponding 95% confidence intervals were calculated. According to the results of the heterogeneity test (Q test) and the I2 statistic, the appropriate model was selected to calculate the combined RR value. If I2 was greater than 50%, a random-effects model was adopted; if I2 was less than or equal to 50%, a fixed-effects model was adopted. For cases where I2 > 50%, sensitivity analysis was performed using the leave-one-out method. Publication bias was assessed using Egger’s test, with a significance level α = 0.05. A p-value of < 0.05 was statistically significant.
Results
Literature search results
A preliminary search identified 42 studies from PubMed, 46 from Embase, 3 from Cochrane Library, and 146 from Web of Science. After removing duplicates (n = 23), excluding studies based on title and abstract screening (n = 193), and full-text review (n = 6), a total of 14 articles (19–31) were finally included in the analysis (see Figure 1).
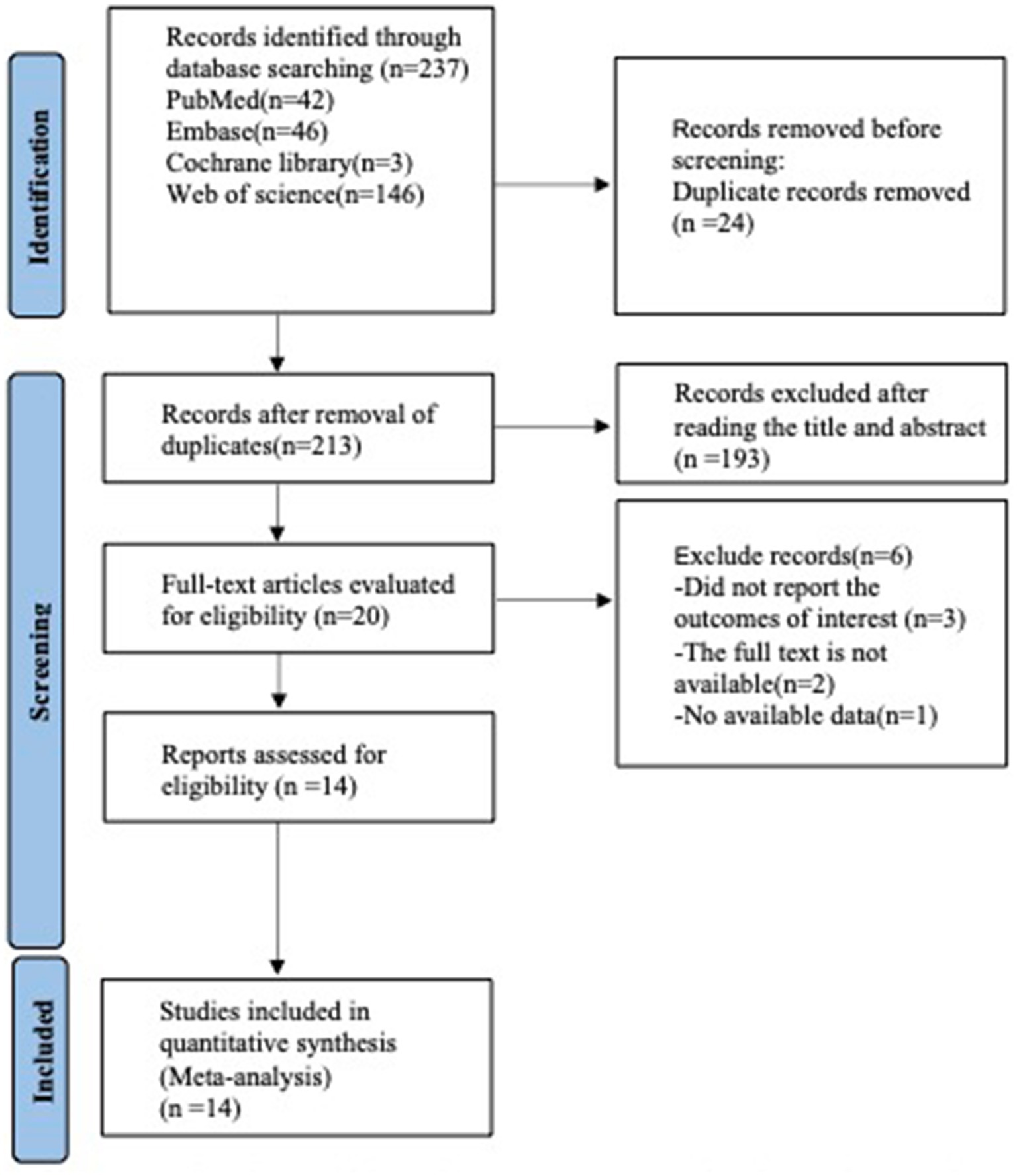
Figure 1. PRISMA flow diagram of the study process. PRISMA, preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis.
Basic characteristics of the included literature
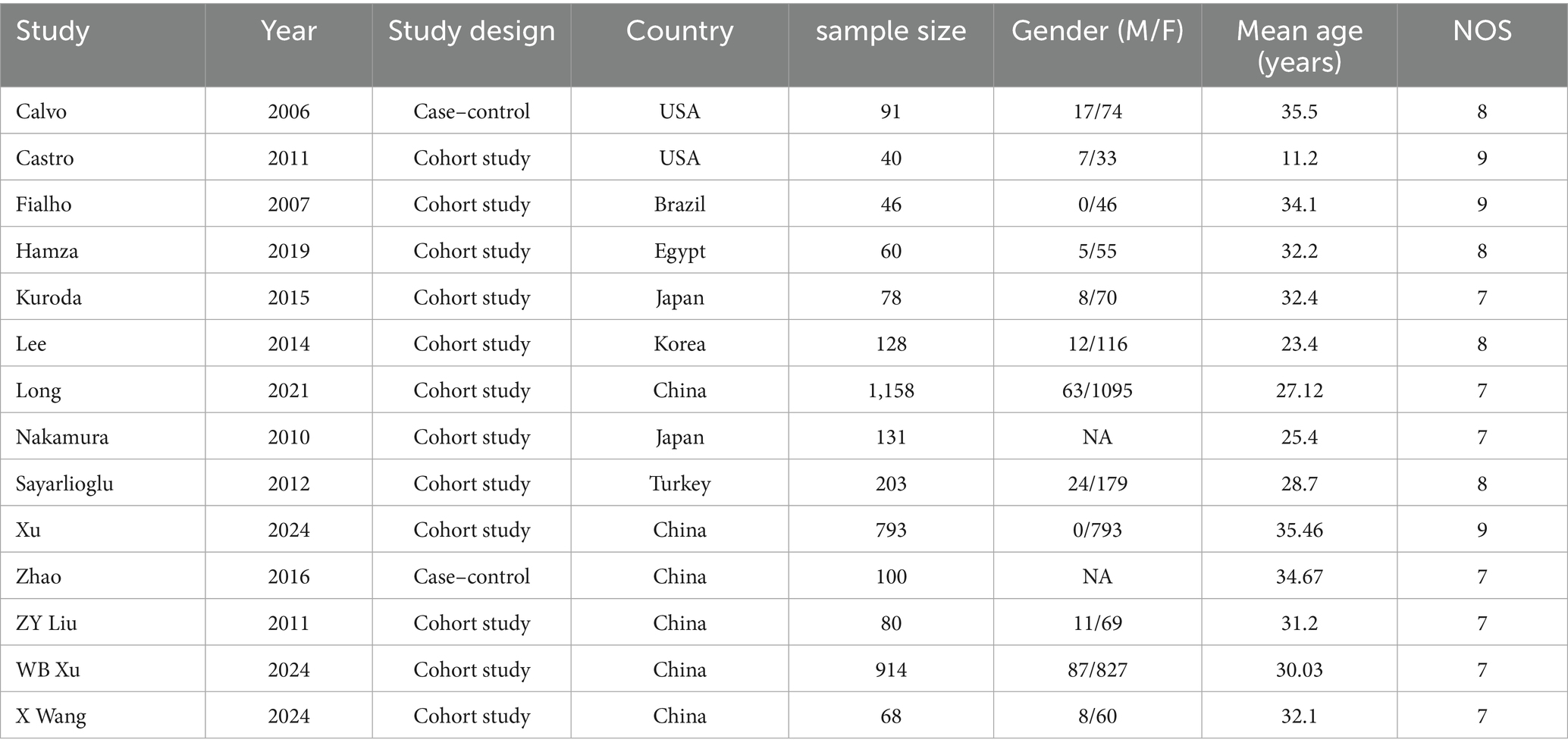
A total of 14 articles, including 3,890 patients, were included, of which 2 were case–control studies and 12 were cohort studies. This study was scored using the NOS score, and all studies received scores of 7 or more. The specific basic characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Results of meta-analysis
Age
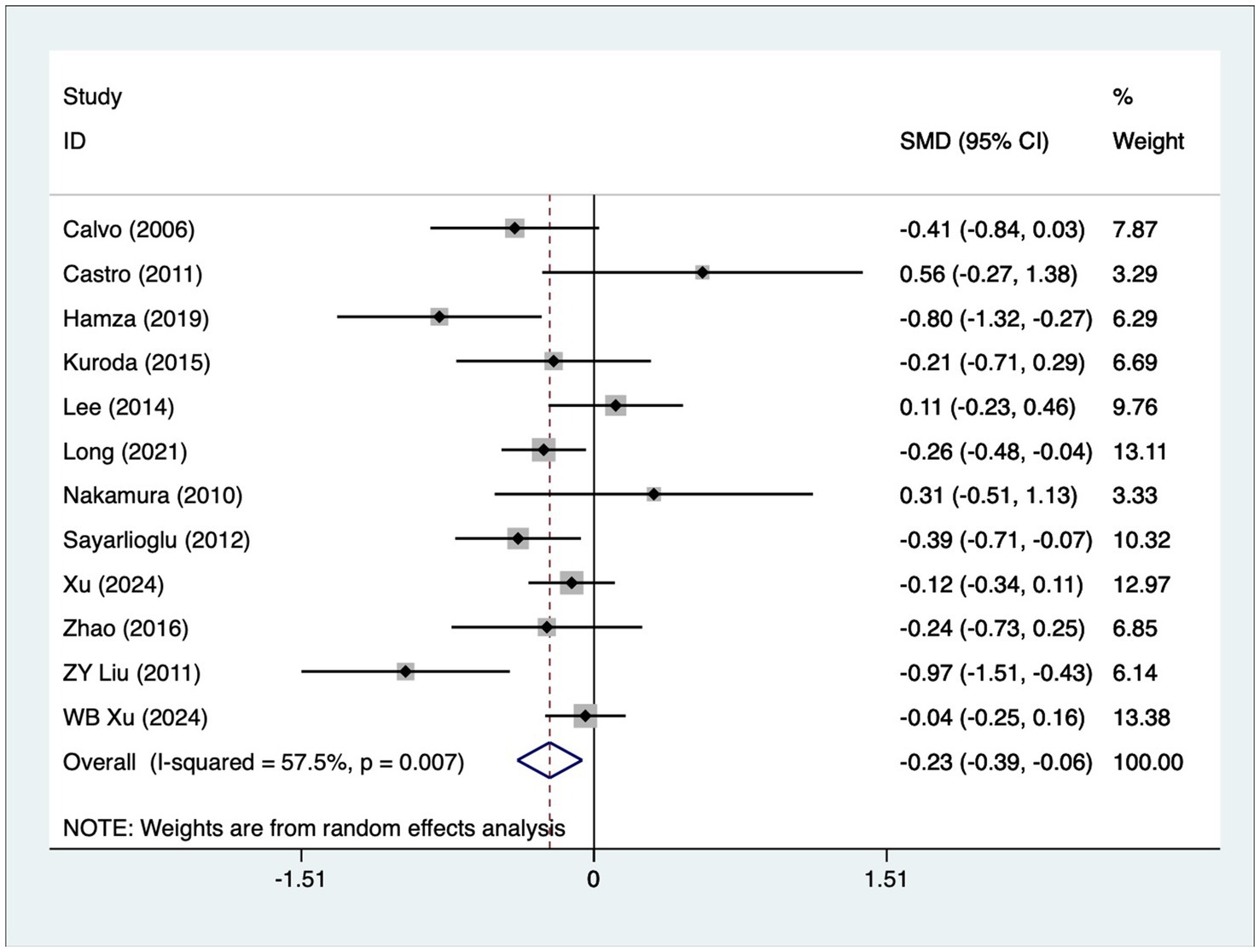
A total of 12 articles reported patient age. A heterogeneity test (I2 = 57.5%, p = 0.007) was performed, and a random-effects model was used for the analysis. The results (Figure 2) indicate that younger SLE patients are more likely to develop osteonecrosis [SMD = −0.23, 95% CI (−0.39, −0.06)]. Due to high heterogeneity, a sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially excluding each study. The results (Supplementary Figure S1) demonstrated low sensitivity and confirmed the stability of the analysis results.
Diabetes
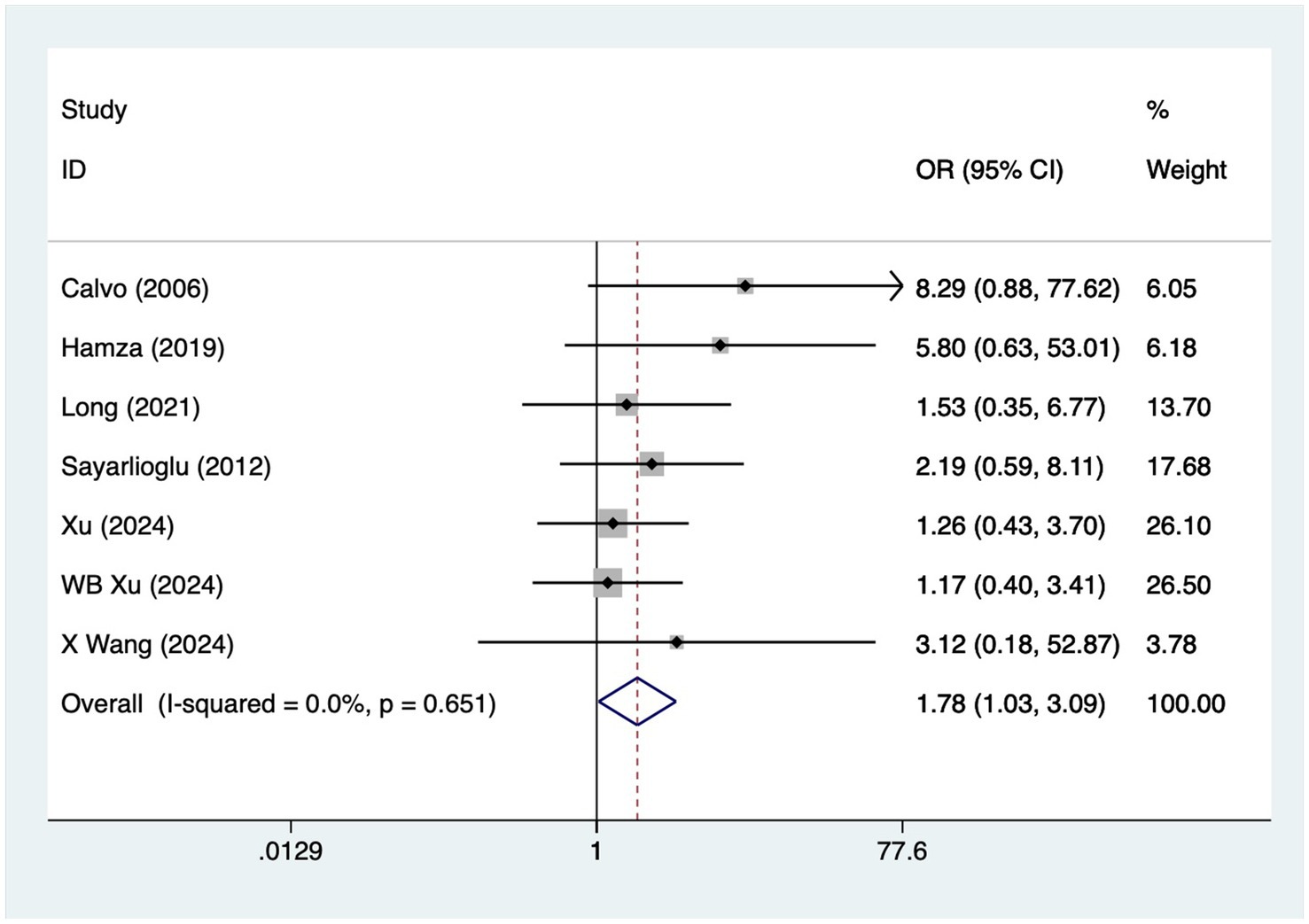
A total of seven articles reported on patients with diabetes mellitus. A heterogeneity test (I2 = 0%, p = 0.651) was performed using a fixed-effects model, and the analysis results (Figure 3) suggested that diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE [OR = 1.78, 95% CI (1.03, 3.09)].
Hypertension
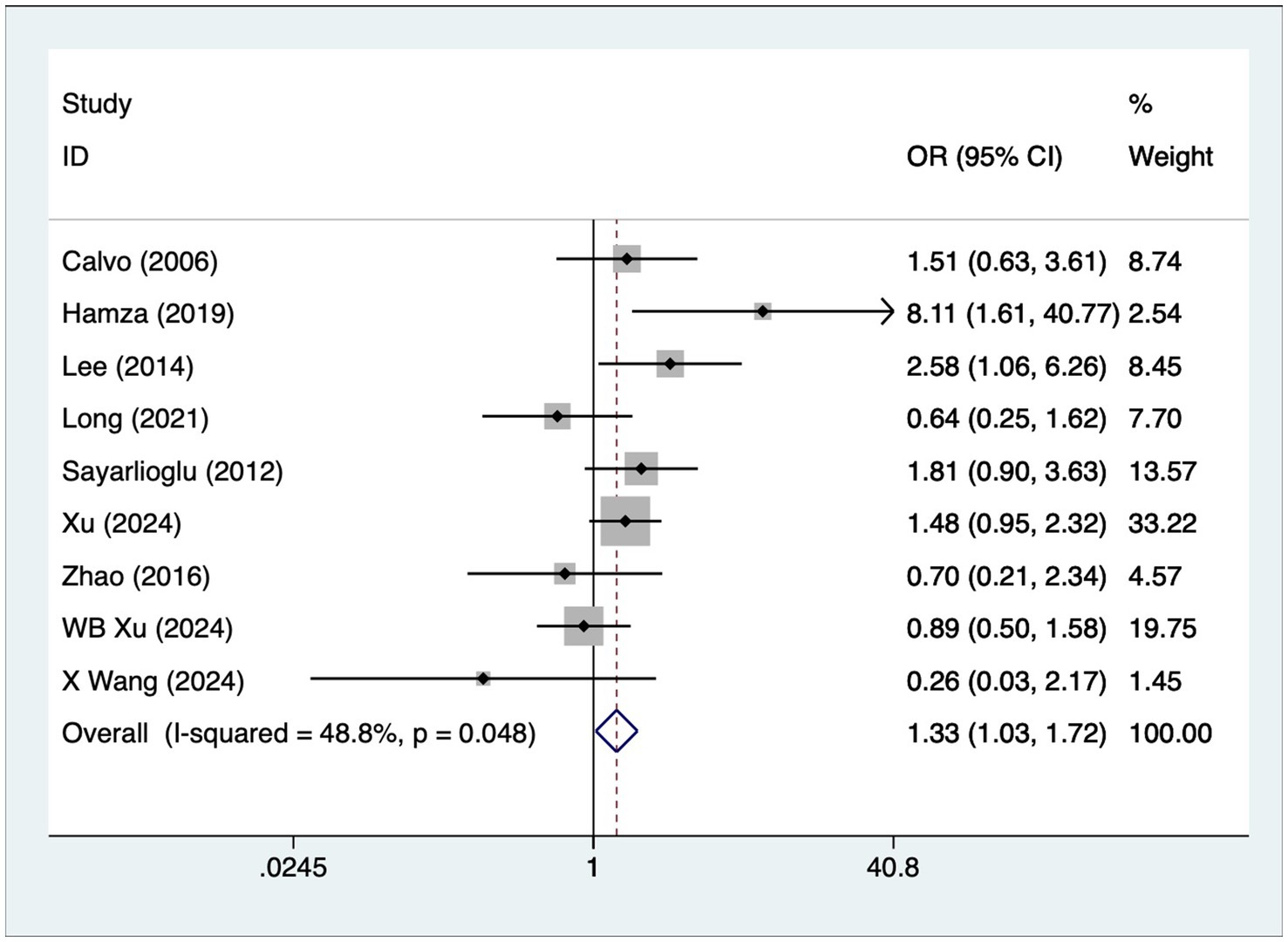
A total of nine articles reported on patients with hypertension. A heterogeneity test (I2 = 48.8%, p = 0.048) was performed using a fixed-effects model, and the analysis results (Figure 4) suggested that hypertension is a risk factor for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE [OR = 1.33, 95% CI (1.03, 1.72)].
Arthritis
A total of seven articles reported on patients with arthritis. A heterogeneity test (I2 = 0%, p = 0.703) was performed using a fixed-effects model, and the analysis results (Figure 5) suggested that arthritis is a risk factor for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE [OR = 1.57, 95% CI (1.24, 2.00)].
Raynaud’s phenomenon
A total of eight articles reported on patients with Raynaud’s phenomenon. A heterogeneity test (I2 = 11%, p = 0.345) was performed using a fixed-effects model, and the analysis results (Supplementary Figure S2) suggested that Raynaud’s phenomenon is a risk factor for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE [OR = 1.76, 95% CI (1.35, 2.30)].
Cyclophosphamide
A total of five articles reported on patients with cyclophosphamide. A heterogeneity test (I2 = 68.5%, p = 0.013) was performed using a random-effects model, and the analysis results (Supplementary Figure S3) suggested that cyclophosphamide is a risk factor for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE [OR = 2.24, 95% CI (1.38, 3.63)]. Due to high heterogeneity, sensitivity analysis was performed by sequentially excluding each study. The results (Supplementary Figure S4) suggest low sensitivity and stable analysis results.
Publication bias
The present study used Egger’s test to assess publication bias, and the results (Supplementary Figures S5–S10) for age (0.677), diabetes mellitus (0.15), hypertension (0.91), arthritis (0.278), and Raynaud’s phenomenon (0.416) suggested no publication bias.
Meta regression
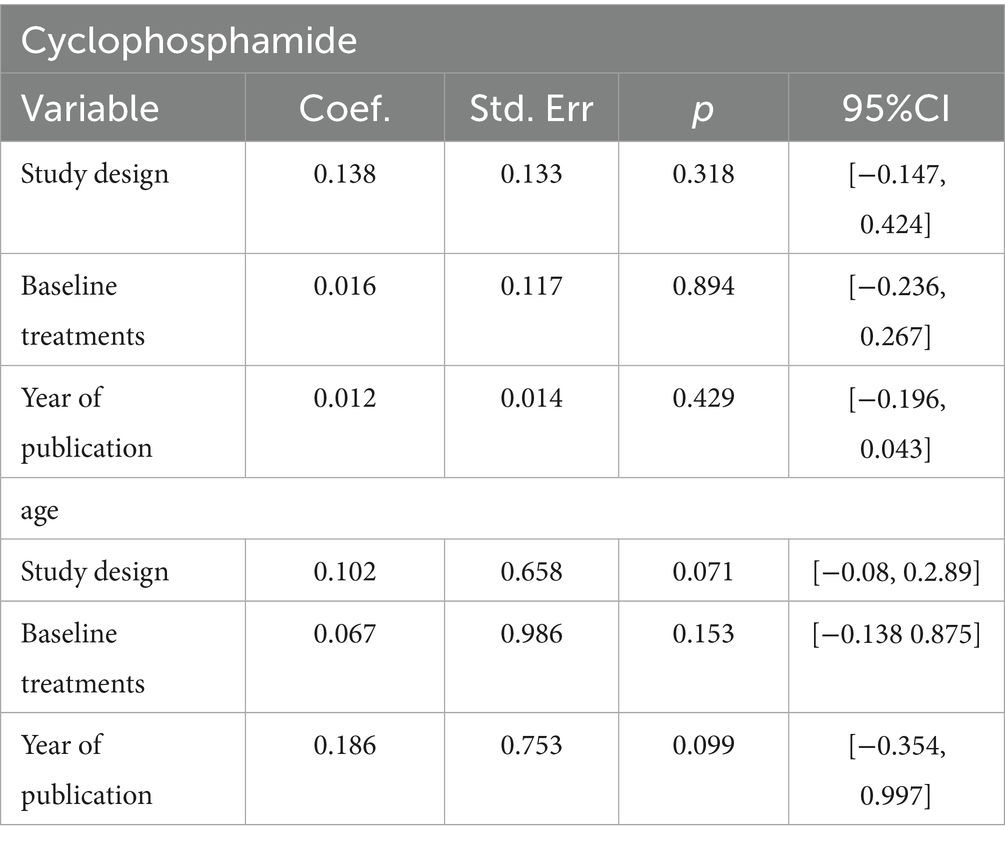
Given the substantial heterogeneity observed in cyclophosphamide and age across studies, a meta-regression analysis was used to identify sources of heterogeneity. The meta-regression results (Table 2) indicate that study design, baseline treatments, and year of publication were not sources of heterogeneity between cyclophosphamide and age.
Discussion
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first meta-analysis to explore the risk factors for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE, and the results of the study identified young age, diabetes, hypertension, arthritis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and cyclophosphamide as risk factors for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE.
Younger patients with SLE are more likely to develop osteonecrosis, a phenomenon that may be related to several mechanisms. First, young patients have active bone metabolism and relatively frequent bone remodeling processes, so when drugs such as glucocorticoids are used to treat SLE, the bone tissue in young patients is more susceptible to the effects of the drugs, leading to the disruption of the vascular supply to the bone, which in turn leads to osteonecrosis (32). In addition, young patients have a more active immune system, and immune complex deposition and vascular inflammation due to SLE may be more severe, further aggravating the risk of bone tissue damage and necrosis (33). Therefore, bone mineral density and bone metabolism indices should be monitored in young SLE patients, and effective interventions should be taken to reduce this complication and improve patients’ quality of life. The current study found that diabetes mellitus is a risk factor for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. Mechanisms may include vascular lesions and microcirculatory disturbances caused by diabetes, toxic effects of hyperglycemia on bone cells, chronic inflammation exacerbated by abnormalities in the immune system, and the occlusion of bone vessels due to lipid metabolism disorders (34). This conclusion is supported by similar studies showing a significantly higher incidence of osteonecrosis in diabetic patients than in non-diabetic patients (35). Preventive measures, including tight control of blood glucose levels and regular monitoring of blood glucose and glycated hemoglobin, may be effective in reducing the risk of diabetes-related osteonecrosis in patients with SLE (36). The current study suggests that hypertension is a risk factor for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. The mechanisms may include hypertension-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction and microcirculatory disorders, and these lesions lead to reduced blood supply to bone tissue, increasing the risk of osteonecrosis. In addition, patients with hypertension are often associated with atherosclerosis, which may also exacerbate the lack of blood flow and hypoxia to bone tissue (37, 38). For hypertensive SLE patients, special attention should be paid to avoiding high-dose and long-term use of glucocorticoids and taking calcium supplementation, which can effectively reduce the risk of hypertension-related osteonecrosis among SLE patients. Arthritis is a risk factor for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. The mechanisms may include inflammatory responses and immune system abnormalities due to arthritis, and these changes affect the blood supply and metabolic function of bone tissue, increasing the risk of osteonecrosis (39). Timely calcium and vitamin D supplementation, appropriate physical activity, and avoidance of smoking and excessive alcohol consumption are also important preventive tools (40). Through these comprehensive measures, the risk of arthritis-related osteonecrosis can be effectively reduced among SLE patients. Raynaud’s phenomenon is a risk factor for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. It causes vasospasm and microcirculatory disturbances that reduce the blood supply to bone tissue and increase the risk of osteonecrosis (41). Preventive measures, including the control of Raynaud’s phenomenon, regular monitoring of vascular health, and reduction of glucocorticoid use, can effectively reduce the risk of Raynaud’s phenomenon-related osteonecrosis in SLE patients. Cyclophosphamide is a risk factor for osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. Cyclophosphamide is a commonly used immunosuppressant, primarily for the treatment of SLE and other autoimmune diseases (42). However, its use may increase the risk of osteonecrosis by mechanisms that may include drug-induced vascular endothelial damage and bone marrow suppression, leading to reduced blood supply and decreased repair capacity of bone tissue (43). Minimizing the dose and duration of cyclophosphamide use, choosing other immunosuppressant alternatives, strengthening the monitoring of patients’ bone health, and performing regular bone density examinations are measures that may help to reduce the risk of cyclophosphamide-associated osteonecrosis in patients with SLE.
As a recognized risk factor for osteonecrosis in SLE, glucocorticoids have been confirmed in numerous studies. However, we could not quantitatively analyze it due to insufficient data on the associated steroid use in this study. Future studies should further collect and analyze relevant data to assess the specific effects of glucocorticoids on osteonecrosis in SLE. For age, heterogeneity may be partly explained by the lack of a standardized definition of “younger” patients, with some studies using a threshold of <30 years, while others used <40 years or alternative cut-offs. For cyclophosphamide, differences in treatment protocols—including cumulative dose, duration of exposure, and route of administration—likely contributed to variability in the results.
Clinical implications
Based on the results of this meta-analysis, clinicians can effectively prevent osteonecrosis in patients with SLE by identifying high-risk individuals and implementing early interventions. First, younger patients, particularly those with SLE at a younger age, are more susceptible to developing osteonecrosis. Therefore, regular imaging screenings—especially MRI or CT scans—are essential for early detection and treatment. Additionally, diabetes, hypertension, and arthritis represent significant risk factors. Clinicians should actively monitor these comorbidities, maintain optimal glycemic and blood pressure control, and promptly treat arthritis symptoms to reduce osteonecrosis incidence. For patients receiving cyclophosphamide, the necessity of its use should be carefully evaluated, and alternative immunosuppressive agents should be considered to mitigate osteonecrosis risk. Regular examinations, particularly in high-risk patients, enable the early detection of osteonecrosis. This allows for timely intervention, such as combined physical therapy and medication, thereby improving patient prognosis. Overall, comprehensive management of risk factors in SLE patients, combined with individualized treatment plans, is key to preventing osteonecrosis.
This meta-analysis has several limitations that should be acknowledged. First, although 14 studies were included overall, the number of studies contributing to some individual factors was relatively small (e.g., five for cyclophosphamide and seven for diabetes). This limited evidence base reduces the statistical power and increases the risk of type II error, and therefore, the corresponding findings should be interpreted with caution. Second, moderate-to-high heterogeneity was observed in certain analyses, particularly for age (I2 = 57.5%) and cyclophosphamide (I2 = 68.5%). Such heterogeneity may stem from differences in patient populations (e.g., ethnicity, baseline disease activity, and comorbidities) as well as variations in treatment regimens, including cumulative drug dose, administration route, and concomitant therapies. Although sensitivity analyses suggested that the results were relatively stable, the presence of heterogeneity indicates that these findings may not be uniformly applicable across all clinical settings. Third, most included studies only reported univariate data, and our analyses were therefore based on unadjusted odds ratios. This prevents adequate control for confounding factors such as disease severity, treatment history, and comorbid conditions. For instance, the observed association between cyclophosphamide use and osteonecrosis may be partly explained by confounding by indication, since the drug is more frequently administered to patients with severe systemic lupus erythematosus. Furthermore, unmeasured confounders are likely to have influenced our results, as most of the included studies were observational in nature. These confounding factors could include disease activity, cumulative steroid dose, and the use of concomitant immunosuppressants, all of which may have an independent effect on the development of osteonecrosis. The absence of these variables in the analyses limits the ability to draw definitive conclusions about the independent impact of the identified risk factors. Taken together, these limitations suggest that the results should be viewed as exploratory and hypothesis-generating rather than definitive. Further large-scale, high-quality prospective studies using multivariable analyses that can account for these confounders are needed to confirm whether the identified factors represent independent risk determinants.
Conclusion
The current study found that young age, hypertension, diabetes, arthritis, Raynaud’s phenomenon, and cyclophosphamide use were identified as independent risk factors for the development of osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. However, because of the heterogeneity of the studies, we need more high-quality, multicenter, large-sample studies to justify our conclusions.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
XZ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. YC: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that no financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that no Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1694721/full#supplementary-material
References
1. Hoi, A, Igel, T, Mok, CC, and Arnaud, L. Systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet. (2024) 403:2326–38. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(24)00398-2
2. Morand, EF, Fernandez-Ruiz, R, Blazer, A, and Niewold, TB. Advances in the management of systemic lupus erythematosus. BMJ. (2023) 383:e073980. doi: 10.1136/bmj-2022-073980
3. Barber, MRW, Falasinnu, T, Ramsey-Goldman, R, and Clarke, AE. The global epidemiology of SLE: narrowing the knowledge gaps. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2023) 62:i4–9. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keac610
4. Yaung, KN, Yeo, JG, Kumar, P, Wasser, M, Chew, M, Ravelli, A, et al. Artificial intelligence and high-dimensional technologies in the theragnosis of systemic lupus erythematosus. Lancet Rheumatol. (2023) 5:e151–65. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(23)00010-3
5. Eades, LE, Hoi, AY, Liddle, R, Sines, J, Kandane-Rathnayake, R, Khetan, S, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in aboriginal and Torres Strait islander peoples in Australia: addressing disparities and barriers to optimising patient care. Lancet Rheumatol. (2024) 6:e713–26. doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(24)00095-X
6. Crow, MK. Pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus: risks, mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Ann Rheum Dis. (2023) 82:999–1014. doi: 10.1136/ard-2022-223741
7. Lazar, S, and Kahlenberg, JM. Systemic lupus erythematosus: new diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Annu Rev Med. (2023) 74:339–52. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-043021-032611
8. Tsokos, GC. The immunology of systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Immunol. (2024) 25:1332–43. doi: 10.1038/s41590-024-01898-7
9. Zheng, Y, Zheng, Z, Zhang, K, and Zhu, P. Osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: systematic insight from the epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis and management. Autoimmun Rev. (2022) 21:102992. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2021.102992
10. Abu-Shakra, M, Buskila, D, and Shoenfeld, Y. Osteonecrosis in patients with SLE. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. (2003) 25:13–24. doi: 10.1385/CRIAI:25:1:13
11. Kaneko, K, Chen, H, Kaufman, M, Sverdlov, I, Stein, EM, and Park-Min, KH. Glucocorticoid-induced osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients. Clin Transl Med. (2021) 11:e526. doi: 10.1002/ctm2.526
12. Ehmke, TA, Cherian, JJ, Wu, ES, Jauregui, JJ, Banerjee, S, and Mont, MA. Treatment of osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: a review. Curr Rheumatol Rep. (2014) 16:441. doi: 10.1007/s11926-014-0441-8
13. Mont, MA, and Jones, LC. Management of osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheum Dis Clin N Am. (2000) 26:279–309. doi: 10.1016/s0889-857x(05)70139-3
14. Torrente-Segarra, V, and Bonet, M. Multifocal osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: two case reports and literature review. Eur J Rheumatol. (2021) 8:46–7. doi: 10.5152/eurjrheum.2020.20013
15. Gökten, DB, Gökten, M, Deniz, Ç, and Mercan, R. Rare combo: moyamoya and lupus in men. Clin Rheumatol. (2024) 43:2139–43. doi: 10.1007/s10067-024-06960-1
16. Fajardo-Hermosillo, LD, López-López, L, Nadal, A, and Vilá, LM. Multifocal osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: case report and review of the literature. BMJ Case Rep. (2013) 2013:bcr2013008980. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2013-008980
17. Mendoza-Alonzo, J, Zayas-Castro, J, and Soto-Sandoval, K. Osteonecrosis in individuals with systemic lupus erythematosus: a predictive model. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed). (2020) 16:161–4. doi: 10.1016/j.reuma.2018.05.002
18. Stang, A. Critical evaluation of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol. (2010) 25:603–5. doi: 10.1007/s10654-010-9491-z
19. Calvo-Alén, J, McGwin, G, Toloza, S, Fernández, M, Roseman, JM, Bastian, HM, et al. Systemic lupus erythematosus in a multiethnic US cohort (LUMINA):: XXIV.: cytotoxic treatment is an additional risk factor for the development of symptomatic osteonecrosis in lupus patients:: results of a nested matched case-control study. Ann Rheum Dis. (2006) 65:785–90. doi: 10.1136/ard.2005.040428
20. Castro, TCM, Lederman, H, Terreri, MTA, Caldana, WI, Kaste, SC, and Hilário, MO. The use of joint-specific and whole-body MRI in osteonecrosis: a study in patients with juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Br J Radiol. (2011) 84:621–8. doi: 10.1259/bjr/34972239
21. Fialho, S, Bonfá, E, Vitule, LF, D'Amico, E, Caparbo, V, Gualandro, S, et al. Disease activity as a major risk factor for osteonecrosis in early systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. (2007) 16:239–44. doi: 10.1177/0961203307076771
22. Hamza, SMH, Samy, N, Younes, TB, and Othman, AIA. Risk factors for osteonecrosis severity among Egyptian systemic lupus erythematosus patients: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) staging. Egypt Rheumatol. (2019) 41:295–301. doi: 10.1016/j.ejr.2018.12.007
23. Kuroda, T, Tanabe, N, Wakamatsu, A, Takai, C, Sato, H, Nakatsue, T, et al. High triglyceride is a risk factor for silent osteonecrosis of the femoral head in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Rheumatol. (2015) 34:2071–7. doi: 10.1007/s10067-015-3075-y
24. Lee, J, Kwok, SK, Jung, SM, Min, HK, Nam, HC, Seo, JH, et al. Osteonecrosis of the hip in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: risk factors and clinical outcome. Lupus. (2014) 23:39–45. doi: 10.1177/0961203313512880
25. Long, Y, Zhang, S, Zhao, J, You, H, Zhang, L, Li, J, et al. Risk of osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: an 11-year Chinese single-center cohort study. Lupus. (2021) 30:1459–68. doi: 10.1177/09612033211021166
26. Nakamura, J, Ohtori, S, Sakamoto, M, Chuma, A, Abe, I, and Shimizu, K. Development of new osteonecrosis in systemic lupus erythematosus patients in association with long-term corticosteroid therapy after disease recurrence. Clin Exp Rheumatol. (2010) 28:13–8.
27. Sayarlioglu, M, Yuzbasioglu, N, Inanc, M, Kamali, S, Cefle, A, Karaman, O, et al. Risk factors for avascular bone necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int. (2012) 32:177–82. doi: 10.1007/s00296-010-1597-9
28. Xu, W, Wang, L, Shi, P, Liu, L, and Zhang, W. Risk factors and prediction model for osteonecrosis of the femoral head in female systemic lupus erythematosus. Front Immunol. (2024) 15:1381035. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1381035
29. Zhaoyun, L, Cheng, Z, Cundong, M, Zhanrui, C, Ling, L, and Meixiang, T. Analysis of factors associated with ischemic necrosis of the femoral head in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Pract Med. (2011) 27:1226–8.
30. Wenbo, X, Lihé, W, Songwei, L, and Pengbo, S. Establishment and validation of a risk factor scoring model for predicting femoral head necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Chin J Tissue Eng Res. (2025) 29:3215–26.
31. Wang, X, Zhongli, G, Yinli, G, Qiongjie, C, and Zhuanrun, C. Clinical characteristics and risk factor analysis of femoral head necrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Arthritis. (2024) 13:14–9.
32. Haque, W, Kadikoy, H, Pacha, O, Maliakkal, J, Hoang, V, and Abdellatif, A. Osteonecrosis secondary to antiphospholipid syndrome: a case report, review of the literature, and treatment strategy. Rheumatol Int. (2010) 30:719–23. doi: 10.1007/s00296-009-1269-9
33. Shigemura, T, Nakamura, J, Kishida, S, Harada, Y, Ohtori, S, Kamikawa, K, et al. Incidence of osteonecrosis associated with corticosteroid therapy among different underlying diseases: prospective MRI study. Rheumatology (Oxford). (2011) 50:2023–8. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker277
34. Li, W, Chai, JL, Li, Z, Guo, CC, Wei, R, Sun, TF, et al. No evidence of genetic causality between diabetes and osteonecrosis: a bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. (2023) 18:970. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04428-7
35. Yu, W, Lyu, YP, Li, YY, Zhang, F, Geng, CX, Wang, CY, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of extensive osteonecrosis of maxilla caused by enterobacter cloacae infection in diabetes: a case report. Zhonghua Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. (2021) 56:1109–10. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20210112-00018
36. Konarski, W, Poboży, T, Kotela, A, Śliwczyński, A, Kotela, I, Hordowicz, M, et al. Does diabetes mellitus increase the risk of avascular osteonecrosis? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2022) 19:15219. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192215219
37. Xu, J, Qiu, X, Yu, G, Ly, M, Yang, J, Silva, RM, et al. Soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor can protect the femoral head against tobacco smoke exposure-induced osteonecrosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Toxicology. (2022) 465:153045. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2021.153045
38. Janke, LJ, Van Driest, SL, Portera, MV, Atreya, RV, Denny, JC, Pei, D, et al. Hypertension is a modifiable risk factor for osteonecrosis in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood. (2019) 134:983–6. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000006
39. de Molon, RS, Hsu, C, Bezouglaia, O, Dry, SM, Pirih, FQ, Soundia, A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis exacerbates the severity of osteonecrosis of the jaws (ONJ) in mice. A randomized, prospective, controlled animal study. J Bone Miner Res. (2016) 31:1596–607. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2827
40. Hernigou, P, Daltro, G, Flouzat-Lachaniette, CH, Roussignol, X, and Poignard, A. Septic arthritis in adults with sickle cell disease often is associated with osteomyelitis or osteonecrosis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (2010) 468:1676–81. doi: 10.1007/s11999-009-1149-3
41. Wang, DX, Li, GY, Ma, L, and Wang, GC. A clinical study of femoral head osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. (2009) 48:926–9.
42. Ruiz-Irastorza, G, Danza, A, Perales, I, Villar, I, Garcia, M, Delgado, S, et al. Prednisone in lupus nephritis: how much is enough? Autoimmun Rev. (2014) 13:206–14. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2013.10.013
43. Socié, G, Clift, RA, Blaise, D, Devergie, A, Ringden, O, Martin, PJ, et al. Busulfan plus cyclophosphamide compared with total-body irradiation plus cyclophosphamide before marrow transplantation for myeloid leukemia: long-term follow-up of 4 randomized studies. Blood. (2001) 98:3569–74. doi: 10.1182/blood.v98.13.3569
Keywords: systemic lupus erythematosus, osteonecrosis, risk factors, meta-analysis, systematic review
Citation: Zhou X and Chai Y (2025) Risk factors of osteonecrosis in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a meta-analysis. Front. Med. 12:1694721. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1694721
Edited by:
Rubén Queiro, Foundation for Biosanitary Research and Innovation of the Principality of Asturias (FINBA), SpainReviewed by:
Dilara Bulut Gökten, Namik Kemal University, TürkiyeNgan Van Nguyen, Hanoi Medical University, Vietnam
Copyright © 2025 Zhou and Chai. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Xiang Zhou, ZG9jemhvdTIwMjRAMTYzLmNvbQ==
 Xiang Zhou
Xiang Zhou Yijie Chai2
Yijie Chai2