Abstract
Background and Aim:
Hysteroscopy necessitates appropriate sedation to ensure patient comfort and operative success. The relative safety profile of remimazolam compared to propofol in this context is unclear. This study evaluates the safety of remimazolam in comparison to propofol for sedation during hysteroscopy and other gynecological procedures.
Methods:
We systematically searched MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, and Scopus from inception until September 2024. We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared remimazolam and propofol for sedation in hysteroscopy procedures. The analyses were conducted using a random-effects model by PRISMA guidelines. The main outcome was the incidence of total adverse events. Secondary outcomes comprised respiratory depression, hypotension, bradycardia, emergence time, and recovery time.
Results:
Thirteen RCTs comprising 1765 patients (remimazolam: n = 1,026; propofol: n = 739) met the inclusion criteria. The overall incidence of adverse events was significantly lower with remimazolam compared to propofol. Remimazolam was associated with lower risks of respiratory depression (OR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.17–0.39; p 0.00001) and hypotension (OR, 0.30; 95% CI: 0.21–0.42; p 0.00001). No significant difference was observed in bradycardia (OR, 0.53; 95% CI, 0.28–1.02; p = 0.06). Recovery time [mean difference (MD), 0.18 min; 95% CI, −0.3, 0.65] and operation time (MD, 0.02 min; 95% CI, −1.0, 1.03) were almost similar for both groups.
Conclusion:
In patients undergoing gynecological procedures, remimazolam demonstrated a superior safety profile compared to propofol, with significantly lower rates of overall adverse events, respiratory depression, and hypotension. More studies are required to confirm these results.
Systematic Review registration:
https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/, identifier CRD42024614416
Introduction
Gynecological procedures, particularly hysteroscopy, are commonly performed and require adequate sedation to ensure patient comfort and facilitate the successful completion of the procedure (1, 2). For many years, propofol has been the most commonly used sedative due to its rapid onset and quick recovery characteristics, making it exceptionally appropriate for brief procedures (3, 4). However, despite its prevalent application, propofol possesses considerable limitations, including a restricted therapeutic period and the risk of adverse effects such as respiratory depression and hemodynamic instability (5–7). The identified hazards have prompted the pursuit of safer and more dependable alternatives for procedural sedation in hysteroscopy (7).
In recent years, remimazolam, a novel ultra-short-acting benzodiazepine, has emerged as a promising candidate for procedural sedation. Its unique pharmacological properties distinguish it from traditional sedatives like propofol (8–11). Notably, remimazolam undergoes organ-independent metabolism, which reduces the risk of accumulation and prolonged sedation, particularly in patients with hepatic or renal impairment (11, 12). Additionally, the availability of flumazenil which is a specific antagonist, allows for rapid reversal of sedation in the event of complications, further enhancing its safety profile (13). These characteristics suggest that remimazolam may offer significant advantages over propofol, particularly in terms of reducing the incidence of adverse events (11).
Despite these potential benefits, there is a notable lack of comprehensive evidence comparing the safety profiles of remimazolam and propofol specifically in the context of hysteroscopy. While previous meta-analyses have explored the efficacy and safety of remimazolam in various procedural settings, none have focused exclusively on hysteroscopy or provided a detailed analysis of adverse events associated with its use in this specific procedure (5, 14, 15). This gap in the literature highlights the need for a targeted evaluation of the safety of remimazolam relative to propofol in gynecological procedures.
We conducted this systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the safety of remimazolam versus propofol during gynecological procedures.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis adhered to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (16) and is registered with PROSPERO (CRD42024614416).
Data sources and searches
We searched multiple databases, MEDLINE (Pubmed), Embase, Scopus, and Web of Science, to collect studies that were relevant. This search spanned from the inception of these databases up to 24th of September 2024. We developed a search strategy incorporating terms related to “remimazolam,” “propofol,” and “hysteroscopy,” using different combinations and words (Supple search strategy). Importantly, we did not impose any language restrictions during our searches to ensure a broad inclusion of studies.
Study selection
The selection of studies was performed independently by two investigators who screened titles, abstracts, and full texts. We established specific inclusion criteria to ensure that only relevant studies were considered. The inclusion criteria was as per PICOS framework.
P (Population): Studies focused on sedation during gynecological procedures.
I (Intervention): Studies comparing remimazolam to propofol.
C (Comparison): Studies comparing remimazolam to propofol.
O (Outcomes): Studies that included data on main outcomes, such as adverse events or other important outcomes of interest.
S (Study Design): Randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
Conversely, we excluded studies based on the following criteria:
-
Non-randomized studies.
-
Case reports or only abstract.
-
Duplicate publications.
-
Studies lacking sufficient data reporting, ie, not reporting adverse events or other important outcomes of interest.
Data extraction
Data extraction was carried out independently by two reviewers using standardized forms designed to capture essential information. The extracted data included study characteristics, patient demographics, details of the interventions, and relevant outcomes. In case disagreements arose, we resolved them through consulting a third reviewer.
Outcomes and definitions
The primary outcome of our meta-analysis was the overall incidence of adverse events (AEs) (defined as any type of adverse event or adverse effect that occurred during the procedure). We also evaluated several secondary outcomes, including specific adverse events such as respiratory depression (defined as an oxygen saturation level below 90% or a respiratory rate of fewer than eight breaths per minute), hypotension (defined as a systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg or a mean arterial pressure below 65 mmHg), and bradycardia (defined as a heart rate of fewer than 50 beats per minute), as well as recovery parameters like emergence time (defined as time needed for patient to wake up) and recovery time (defined as the total time needed for the patient to return to a normal state), which includes the time from the initial drug administration to discharge from the Post-Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU).
Statistical analysis
We conducted this meta-analysis using Review Manager 5.4, a tool provided by The Cochrane Collaboration. To analyze dichotomous outcomes, we calculated odd ratios (ORs) along with 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs) using the Mantel–Haenszel method. For continuous outcomes, we calculated mean differences (MDs) and their corresponding 95% CIs using the inverse variance method. Given the anticipated clinical heterogeneity among the included studies, we employed random-effects models. To evaluate the degree of statistical heterogeneity, we used I2 statistics, with thresholds of 25%–49%, 50%–74%, and over 75% indicating low, moderate, and high heterogeneity, respectively (17). A p-value of 0.05 or less was considered significant.
Risk of Bias assessment
To assess the quality of the RCTs in our analysis, we utilized the Cochrane Collaboration’s risk of bias assessment tool. Each study was rated for risk of bias as “low” (minimal risk), “high” (significant risk), or “some concerns” (uncertainty due to incomplete information). We examined factors such as the randomization of participant assignment to treatment groups, the potential impact of missing data on results, the evaluation of outcomes, and adherence to the original study plan (18).
Publication bias
To assess publication bias, we generated funnel plots and performed Egger’s test, applicable when 10 or more studies were available for analysis. Additionally, we conducted sensitivity analyses to evaluate the robustness of our results. We systematically removed each study from our analysis to observe its impact on the outcome. When a study that demonstrated a significant influence on the results was excluded, we conducted further analysis to assess the implications of this removal (19).
Results
Study selection and characteristics
The initial search identified 692 records. After removing duplicates, 149 studies were selected. After screening titles and abstracts, 130 studies were removed, and19 full-text articles were assessed for eligibility. Thirteen RCTs met inclusion criteria, comprising 1,765 patients (remimazolam: n = 1,026; propofol: n = 739) (6, 7, 20–30) (Figure 1). Study characteristics are summarized in Tables 1 and 2. Sample sizes ranged from 8 to 125 patients in each group. All studies were conducted in Asia [12 in China (6, 7, 20, 22–30) and one in Japan (21)] between 2021 and 2024. The participants’ mean age ranged between 30 and 71 years and mean BMI ranged from 20.7 to 24.7. Four studies were conducted as multiple-arm investigations (6, 20, 28, 29), comparing various doses of remimazolam to a propofol group independently. Six studies utilized remimazolam tosylate (6, 25, 26, 28–30), while seven studies utilized remimazolam besylate (7, 20–24, 29). Nine studies focused on the hysteroscopy procedure, while two investigated different gynecological surgical procedures, and one each included cervical conization and surgical abortion. One study was multi-center, and the other 12 studies were single-center. One study was conducted as a multicenter study, whereas the other 12 studies were conducted at a single center.
Figure 1

PRISMA flow diagram of study selection.
Table 1
| Study | Design | Patients | Age | BMI | Procedure | Dosage/Kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. (6) China | Single center | RB = 41 | 43.8 ± 8.0 | 24.7 ± 2.7 | Hysteroscopy | 0.2 mg |
| P = 41 | 45.2 ± 7.0 | 24.1 ± 2.8 | 1.5–2 mg | |||
| Zhang et al. (29) China | Single center | RT = 30 | 32.60 ± 5.06 | 23.58 ± 3.48 | Hysteroscopy | 0.48 mg/kg/h |
| RT = 30 | 31.13 ± 3.95 | 22.50 ± 2.64 | 0.6 mg/kg/h | |||
| P = 30 | 32.70 ± 5.25 | 23.70 ± 2.73 | 5 mg/kg/h | |||
| Zhang et al. (27) China | Single center | RT = 64 | 33.73 ± 6.27 | 21.54 ± 3.01 | Hysteroscopy | 0.2 mg |
| P = 64 | 34.58 ± 7.48 | 21.76 ± 3.03 | 1.5 mg | |||
| RT + P = 65 | 33.49 ± 6.26 | 22.29 ± 3.17 | 0.2 + 0.5 mg | |||
| Fan et al. (7) China | Single center | RB = 40 | 43.95 ± 7.51 | 22.93 ± 3.02 | Hysteroscopy | 0.25 mg |
| P = 43 | 42.05 ± 9.071 | 23.03 ± 2.96 | 2.5 mg | |||
| Matsumoto et al. (21) Japan | Multi-center | RB = 30 | 50.0 ± 15.7 | NA | Gynecological Surgery | 12 mg/kg/h |
| P = 30 | 46.5 ± 16.9 | 0.4–1 mg/kg/h | ||||
| Wang et al. (23) China | Single center | RB = 102 | 40.0 (8.8) | 21.9 (20.3, 23.8) | Cervical Conization | 0.2 mg |
| P = 102 | 40.6 (8.2) | 22.6 (20.8, 24.9) | 2 mg | |||
| Yue et al. (26) China | Single center | RT = 100 | 31 (19–41) | 20.7 (16.9–26.0) | Surgical abortion | 0.3 mg |
| P = 100 | 30 (20–53) | 20.8 (16.4–26.6) | 2 mg | |||
| Huang et al. (20) China | Single center | RB = 52 | 50.02 ± 10.82 | 23.32 ± 3.53 | Hysteroscopy | 0.2 mg |
| RB = 52 | 47.02 ± 10.61 | 23.33 ± 3.47 | 0.25 mg | |||
| RB = 52 | 47.98 ± 11.78 | 22.52 ± 2.77 | 0.3 mg | |||
| P = 52 | 47.73 ± 11.29 | 23.21 ± 3.29 | 2 mg | |||
| Tan et al. (22) China | Single center | RB + P = 125 | 35.0(29.5–39.0) | 20.7 (19.5–22.4) | Hysteroscopy | 0.125 + 2.5 mg |
| P = 125 | 34.0(31.5–39.0) | 21.0 (19.9–21.8) | 2.5 mg | |||
| Wang et al. (24) China | Single center | RB = 84 | 31.5 (7.3) | 21.6 (2.9) | Gynecological Surgery | 0.2–0.3 mg |
| P = 84 | 30.5 (6.8) | 21.8 (3.3) | 1.5-3 mg | |||
| Xie et al. (25) China | Single center | RT = 30 | 70.2 ± 6.3 | 22.6 ± 4.5 | Hysteroscopy | 0.2 mg |
| P = 30 | 71.8 ± 6.7 | 23.1 ± 6.2 | 2 mg | |||
| Yang et al. (30) China | Single center | RT = 9 | 18–40 overall | 20–28 overall | Hysteroscopy | 0.27 mg |
| P = 8 | 2.0 mg | |||||
| Zhou et al. (28) China | Single center | P = 30 | 34.1 ± 6.4 | 22.2 ± 3.0 | Hysteroscopy | 3.5 μg/mL |
| RT = 30 | 33.8 ± 8.2 | 21.2 ± 2.6 | 0.05 mg | |||
| RT = 30 | 36.0 ± 7.8 | 21.2 ± 2.4 | 0.1 mg | |||
| RT = 30 | 33.6 ± 6.8 | 21.3 ± 2.7 | 0.15 mg | |||
| RT = 30 | 33.5 ± 6.6 | 22.4 ± 2.5 | 0.2 mg |
Characteristics of included studies.
RB, remimazolam besylate; RT, remimazolam tosylate; P, Propofol; BMI, Body mass index.
Table 2
| Study | Overall AEs | Hypotension | Low SpO2 90% | Movement | Pain at the injection site | Recovery time; Awakening time (m) | Nausea and vomiting | Bradycardia | Operation time | Success rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. (6) | R = 6 | 1 | 4 | 15 | 1 | 3.31 ± 1.3 | NA | 0 | 13.2 ± 4.2 | NA |
| P = 60 | 5 | 21 | 20 | 33 | 1 ± 0.02 | 1 | 12.6 ± 4.7 | |||
| Zhang et al. (6) | Ra = 4 | NA | 1 | NA | 0 | NA | 1 | NA | 12.27 ± 5.94 | NA |
| Rb = 5 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 12.23 ± 3.66 | ||||||
| P = 12 | 4 | 7 | 1 | 11.27 ± 4.68 | ||||||
| Zhang et al. (27) | R = 34 | 6 | 2 | 24 | 0 | 4.46 ± 0.66 | 0 | 0 | 11.34 ± 4.62 | NA |
| P = 117 | 27 | 25 | 3 | 39 | 3.98 ± 0.83 | 0 | 2 | 13.27 ± 6.25 | ||
| R + P = 16 | 10 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 2.83 ± 0.75 | 0 | 1 | 12.91 ± 6.64 | ||
| Fan et al. (7) | R = 3 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 10.20 ± 0.34 | NA | NA | NA | 37 |
| P = 29 | 7.91 ± 0.47 | 43 | ||||||||
| Matsumoto et al. (21) | R = 13 | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | 9 | NA | 158 ± 55 | NA |
| P = 16 | 9 | 151 ± 46 | ||||||||
| Wang et al. (23) | R = 183 | 31 | 22 | 33 | 1 | 5.0 ± 3.3 | 6 | 4 | NA | NA |
| P = 329 | 51 | 43 | 36 | 36 | 3.00 ± 2 | 9 | 6 | |||
| Yue et al. (26) | R = 82 | 0 | 4 | 21 | 2 | 9.3 ± 8.27 | 1 | 0 | 6.3 ± 6. | 81 |
| P = 52 | 2 | 4 | 20 | 9 | 8.6 ± 9 | 0 | 6 | 5.6 ± 6 | 78 | |
| Huang et al. (20) | Ra = 44 | NA | 5 | 31 | 0 | 5.37 ± 1.47 | 0 | NA | 16.17 ± 4.13 | 46 |
| Rb = 47 | 6 | 26 | 0 | 6.88 ± 1.62 | 1 | 15.94 ± 4.92 | 49 | |||
| Rc = 57 | 11 | 16 | 0 | 8.06 ± 1.56 | 2 | 15.4 ± 4.46 | 51 | |||
| P = 76 | 20 | 26 | 16 | 8.71 ± 1.88 | 5 | 15.99 ± 4.65 | 50 | |||
| Tan et al. (22) | RP = 73 | NA | 2 | 25 | 0 | 3.0 ± 1.5 | 2 | 0 | 12.6 ± 5.25 | NA |
| P = 127 | 12 | 23 | 39 | 3.6 ± 2.25 | 0 | 2 | 12.3 ± 3.75 | |||
| Wang et al. (24) | R = 42 | 1 | NA | 7 | 3 | 6.3 ± 1.9 | NA | NA | 7.0 ± 3 | 82 |
| P = 89 | 7 | 8 | 38 | 6.0 ± 1.3 | 6.8 ± 3.0 | 84 | ||||
| Xie et al. (25) | R = 16 | NA | NA | 5 | 4 | 13.5 ± 4.9 | 2 | NA | NA | 29 |
| P = 41 | 1 | 21 | 11.6 ± 4.2 | 1 | 30 | |||||
| Yang et al. (30) | R = 13 | NA | NA | 6 | 0 | 5.2 ± 2.7 | NA | NA | 10 ± 4.1 | NA |
| P = 13 | 2 | 8 | 7.6 ± 2.9 | 9.9 ± 5.8 | ||||||
| Zhou et al. (28) | P = 24 | 10 | 8 | NA | NA | NA | NA | 3 | NA | NA |
| R = 15 | 7 | 2 | 4 | |||||||
| R = 11 | 4 | 4 | 2 | |||||||
| R = 13 | 3 | 6 | 1 | |||||||
| R = 11 | 3 | 5 | 2 |
Characteristics of included studies.
R, Remimazolam; P, Propofol; RP, Remimazolam+ Propofol, NA, Not available.
Risk of Bias assessment
Overall, the quality was moderate to high. Nine studies demonstrated low risk of bias across all domains. Four studies had some concerns regarding the blinding of outcome assessment. This risk of bias was mainly due to the randomization procedure, the allocation procedure, and other aspects. No studies were judged to have a high risk of bias in any domain (Risk of bias outcomes in Supplementary material).
Primary outcome
Adverse events
The total number of overall AEs in the propofol group was higher than the total number of patients, as some of the patients showed more than 1 AEs. So, we compared the two groups by the rate of AEs per patient in both groups. The AEs rate in the propofol group was 985/739 = 1.33, while in the remimazolam group, it was 688/1026 = 0.67. The relative rate of AEs between the two groups was (1.33/0.67 = 1.98), showing a significant difference between the two groups (almost two times) (p 0.0001).
Secondary outcomes
Respiratory depression (SpO2 90%)
Remimazolam was associated with significantly lower risk of respiratory depression (Low SpO2 90%) compared to propofol (OR, 0.25; 95% CI, 0.17–0.39; p 0.00001; I2 = 42%) with moderate heterogeneity in the results (Figure 2).
Figure 2
![Forest plot comparing Remimazolam and Propofol based on various studies. The plot lists individual studies, showing the number of events and total participants for both drugs, along with weight percentages. Odds ratio values with 95% confidence intervals are displayed, indicating variability and significance. A diamond at the bottom represents the overall effect size, with a value of 0.72 [0.41, 1.29]. Statistical heterogeneity is low, indicated by I² = 0%. The plot suggests no significant difference in effects.](https://www.frontiersin.org/files/Articles/1701785/xml-images/fmed-12-1701785-g002.webp)
Forest plot of respiratory depression (Low O2 90%).
Hypotension
The incidence of hypotension was significantly lower with remimazolam, yielding an OR of 0.30 (95% CI: 0.21–0.42; p 0.00001). The I2 statistic was 0%, indicating no heterogeneity in the results (Figure 3a).
Figure 3

(a) Forest plot of hypotension; (b) Forest plot of bradycardia.
Bradycardia
The OR for bradycardia between the two groups was 0.53 (95% CI: 0.28–1.02; p = 0.06), indicating no significant difference and showing no heterogeneity (I2 = 0%). However, the overall incidence of bradycardia was lower in the remimazolam group (Figure 3b).
Nausea and vomiting
The cases of nausea and vomiting were similar between the two groups, with an OR of 0.72 (95% CI: 0.41–1.29; p = 0.27). The I2 statistic was 0%, indicating no heterogeneity in the results (Figure 4a).
Figure 4
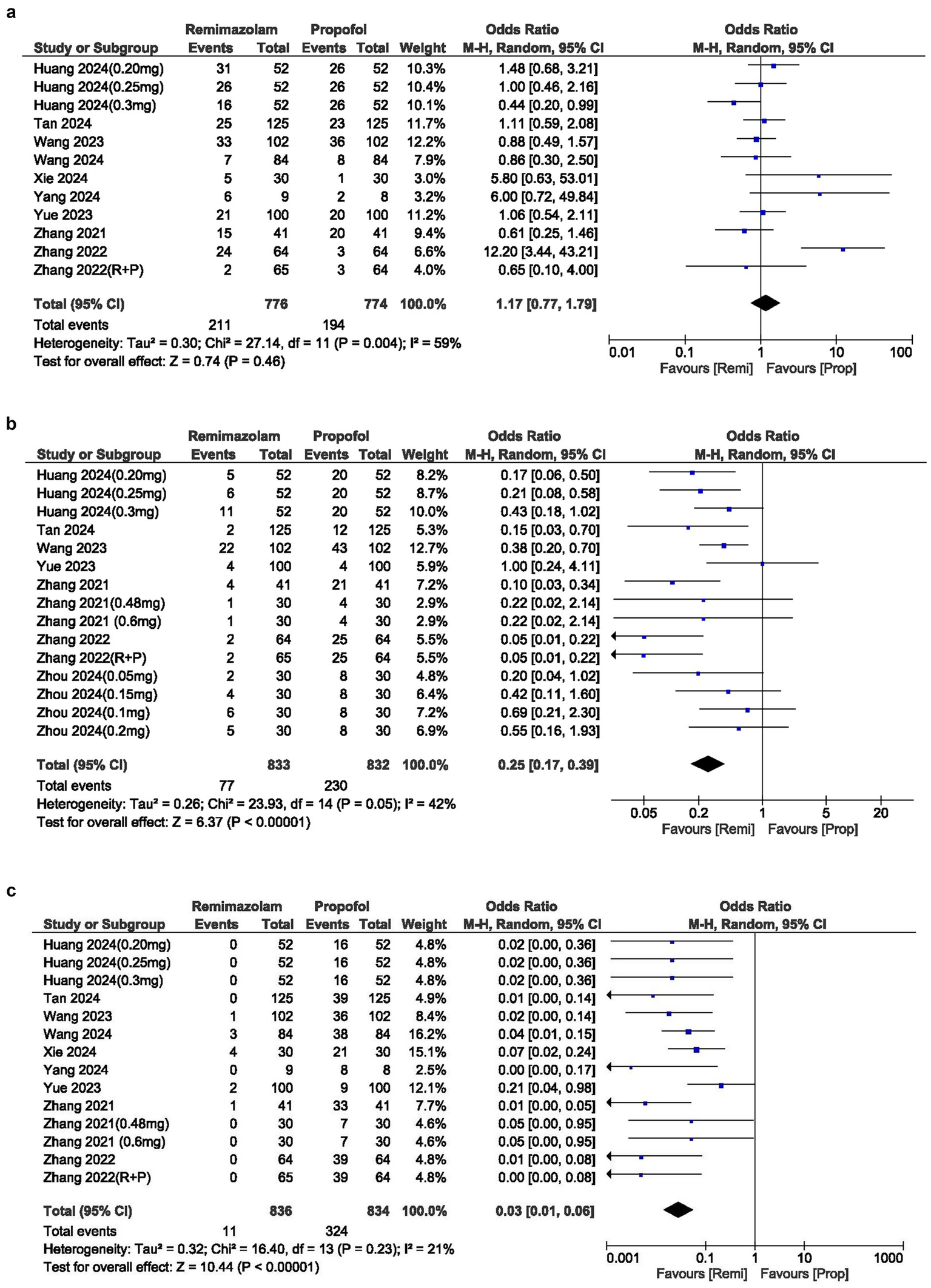
(a) Forest plot of hypotension; (b) Forest plot of bradycardia; (c) Forest plot of movement during procedure.
Pain
The incidence of injection site pain was significantly lower in the remimazolam group compared to the propofol group, with an OR of 0.03 (95% CI: 0.01–0.06; p 0.00001; I2 = 21%) (Figure 4b).
Movement during procedure
The cases of movement during the procedure were similar between the two groups, with an OR of 1.17 (95% CI: 0.77–1.79; p = 0.46). The I2 statistic was 59%, indicating moderate heterogeneity in the results (Figure 4c).
Sedation success
Only five studies reported sedation success with the injected sedative drugs. There was no significant difference in the sedation success rate between the two groups, with an OR of 0.84 (95% CI: 0.48–1.46; p = 0.54; I2 = 0%) (Supplementary Figure S1).
Recovery parameters
Emergence time was similar between the two groups (MD, 0.18 min; 95% CI, −0.3, 0.65; I2 = 0%) (Supplementary Figure S2).
Operation time
Operation time also showed no difference between the two groups (MD, 0.02 min; 95% CI, −1.0, 1.03; I2 = 99%) with higher heterogeneity (Supplementary Figure S3).
Sensitivity analyses
Sensitivity analyses that excluded each study one by one did not significantly alter the main findings, indicating the robustness of the results. Additionally, the findings remained consistent in analyses restricted to studies that utilized standardized sedation protocols.
Publication Bias
Visual inspection of funnel plots showed a little asymmetry, but this was not enough for us to we can conclude the presence of publication bias. Moreover, the Egger’s test also could not find any significant publication bias (p = 0.44) (Supplementary Figure S4).
Discussion
This meta-analysis aimed to evaluate the safety and efficacy of remimazolam compared to propofol in patients undergoing various gynecological procedures. Our findings suggest that remimazolam is associated with a significantly lower risk of overall AEs compared to propofol. Secondary outcomes further highlight the favorable safety profile of remimazolam, including markedly reduced risks of respiratory depression, hypotension, and injection site pain.
Remimazolam exhibits a significant safety advantage compared to propofol, as patients report significantly fewer adverse events, approximately half as many (0.67 versus 1.33 events per patient). This suggests an important 60% reduction in risk and suggests that patients are significantly less prone to experiencing complications. The improved safety profile of remimazolam is linked to its pharmacological characteristics (11). In contrast to propofol, remimazolam is metabolized by tissue esterases in an organ-independent manner, which may lead to more predictable pharmacokinetics. The availability of flumazenil as a specific antagonist offers an additional safety margin that propofol does not provide.
Remimazolam demonstrates significant safety advantages, particularly in two key domains: a 75% reduction in the risk of respiratory depression and a 70% reduction in the risk of hypotension. These complications are common during sedation and often require immediate clinical intervention; thus, their reduction indicates a significant improvement in patient safety. This results in reduced interruptions for clinicians in managing unstable blood pressure or respiratory issues, which improves the procedural process.
Remimazolam also significantly reduces injection site pain, an important negative effect associated with propofol. Patients administered remimazolam exhibited a 97% reduction in the risk of pain during drug administration, thereby converting a typically distressing experience into one of relative comfort. This improvement is particularly crucial for procedures involving active or lightly sedated patients, as pain during injection can increase anxiety and reduce trust in care. Addressing this long-standing issue, remimazolam enhances safety while prioritizing dignity and comfort, benefiting both clinical outcomes and patient-centered care. It was also found that there is no difference in safety outcomes between remimazolam tosylate and besylate formulations. This highlights the importance of essential pharmacologic properties of remimazolam rather than focusing on formulation modifications, which may enhance drug optimization approaches.
Remimazolam provides advantages not only in gynecological contexts but also in other clinical fields such as gastrointestinal endoscopy, surgery, and bronchoscopy (14, 15, 31–33). During procedures like colonoscopies and upper endoscopies, remimazolam showed superior outcomes relative to propofol (31). A significant advantage is its cardiorespiratory stability, which reduces the risk of hypotension and respiratory complications, particularly in elderly patients with comorbidities. Remimazolam’s less severe effect on respiration during bronchoscopy may facilitate smoother procedures and enhance the overall experience for patients undergoing outpatient procedures (34). Furthermore, remimazolam has demonstrated favorable outcomes in multiple surgical procedures, establishing it as a valuable option in clinical practice.
This meta-analysis has multiple strengths that strengthen its credibility. A comprehensive literature search was conducted to include every relevant research study, which reduced bias. The methodology adhered to established guidelines, highlighting significant clinical outcomes such as adverse events and respiratory depression. The majority of the studies included showed high quality and low bias, thereby enhancing the reliability of our findings. The results were consistent across multiple studies conducted in various Asian countries. The strengths identified offer important insights into the safety and efficacy of remimazolam compared to propofol, supporting its application as a preferred anesthetic choice in gynecological procedures.
We should acknowledge the limitations of this meta-analysis. First, all studies were performed in Asia (mostly in China because its commonly used in the East Asia but this is becoming more and more common in all over the world), which raises concerns regarding the generalizability to other populations. The significant heterogeneity observed in the primary outcome, despite being addressed through sensitivity analyses, indicates possible residual confounding due to clinical or methodological diversity, as only a few studies have reported all these (pretreatment, additional sedation, ASA status, BIS score, etc.) characteristics of the included patients. That’s why we were unable to perform subgroup analysis on this basis. Third, the limited sample sizes in specific trials (e.g., n = 8 per group) may restrict statistical power. The emphasis on gynecological procedures (e.g., 9/13 studies on hysteroscopy) limits the applicability of findings to wider surgical contexts. Finally, although Egger’s test showed no significant publication bias (p = 0.44), minor asymmetry in the funnel plot may suggest a misrepresentation of smaller negative studies.
Our findings suggest that remimazolam may be safer than propofol for sedation during hysteroscopy, especially for patients with a higher risk of respiratory or hemodynamic complications. Further studies should focus on cost-effectiveness, particular patient subgroups (including the elderly and individuals with comorbidities), and optimal dosing strategies. Furthermore, ongoing research investigating cognitive outcomes and patient satisfaction could offer significant findings.
Conclusion
Remimazolam is a safer alternative to propofol for gynecological sedation, with significantly fewer cases of adverse events, respiratory depression, and hypotension. More large-scale studies are required to verify these findings across various populations and procedural contexts.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Author contributions
OJ: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. WS: Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. JL: Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Visualization, Writing – review & editing. XY: Conceptualization, Investigation, Project administration, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Funding
The author(s) declare that financial support was received for the research and/or publication of this article. This work was supported by Jiaxing Science and Technology Project 2022 AD10009.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Generative AI statement
The authors declare that Gen AI was used in the creation of this manuscript. During the preparation of this work, the author(s) used AI-assisted technologies in order to improve language quality and grammar checking. The author(s) reviewed and edited the content as needed and take(s) full responsibility for the content of the publication.
Any alternative text (alt text) provided alongside figures in this article has been generated by Frontiers with the support of artificial intelligence and reasonable efforts have been made to ensure accuracy, including review by the authors wherever possible. If you identify any issues, please contact us.
Publisher’s note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmed.2025.1701785/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Farquhar C Ekeroma A Furness S Arroll B . A systematic review of transvaginal ultrasonography, sonohysterography and hysteroscopy for the investigation of abnormal uterine bleeding in premenopausal women. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. (2003) 82:493–504. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0412.2003.00191.x
2.
Centini G Troia L Lazzeri L Petraglia F Luisi S et al . Modern operative hysteroscopy. Minerva Ginecol. (2016) 68:126–32.
3.
Bryson HM Fulton BR Faulds D . Propofol an update of its use in anaesthesia and conscious sedation. Drugs. (1995) 50:513–59. doi: 10.2165/00003495-199550030-00008
4.
Zhang K Xu H Li HT . Safety and efficacy of propofol alone or in combination with other agents for sedation of patients undergoing colonoscopy: an updated meta-analysis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. (2020) 24:4506–18. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202004_21033
5.
Barbosa EC Espírito Santo PA Baraldo S Meine GC . Remimazolam versus propofol for sedation in gastrointestinal endoscopic procedures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth. (2024) 132:1219–29. doi: 10.1016/j.bja.2024.02.005
6.
Zhang X Li S Liu J . Efficacy and safety of remimazolam besylate versus propofol during hysteroscopy: single-Centre randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. (2021) 21:156. doi: 10.1186/s12871-021-01373-y
7.
Fan S Zhu Y Sui C Li Q Jiang W Zhang L . Remimazolam compared to Propofol during hysteroscopy: a safety and efficacy analysis. Pain Ther. (2023) 12:695–706. doi: 10.1007/s40122-023-00483-4
8.
Lee A Shirley M . Remimazolam: a review in procedural sedation. Drugs. (2021) 81:1193–201. doi: 10.1007/s40265-021-01544-8
9.
Elmati PR Nagaradona T Jagirdhar GSK Surani S . Remimazolam in intensive care unit: Potential applications and considerations. World J Crit Care Med. (2024) 13:96877. doi: 10.5492/wjccm.v13.i3.96877
10.
Zhang J Cairen Z Shi L Pang S Shao Y Wang Y et al . Remimazolam versus propofol for procedural sedation and anesthesia: a systemic review and meta-analysis. Minerva Anestesiol. (2022) 88:1035–42. doi: 10.23736/S0375-9393.22.16817-3
11.
Kim KM . Remimazolam: pharmacological characteristics and clinical applications in anesthesiology. Anesth Pain Med. (2022) 17:1–11. doi: 10.17085/apm.21115
12.
Wesolowski AM Zaccagnino MP Malapero RJ Kaye AD Urman RD . Remimazolam: pharmacologic considerations and clinical role in anesthesiology. Pharmacotherapy. (2016) 36:1021–7. doi: 10.1002/phar.1806
13.
Hu Q Liu X Wen C Li D Lei X . Remimazolam: an updated review of a new sedative and Anaesthetic. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2022) 16:3957–74. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S384155
14.
Zhao MJ Hu HF Li XL Li XM Wang DC Kuang MJ . The safety and efficacy between remimazolam and propofol in intravenous anesthesia of endoscopy operation: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. (2023) 109:3566–77. doi: 10.1097/JS9.0000000000000638
15.
Pastis NJ Yarmus LB Schippers F Ostroff R Chen A Akulian J et al . Safety and efficacy of remimazolam compared with placebo and midazolam for moderate sedation during bronchoscopy. Chest. (2019) 155:137–46. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.09.015
16.
Page MJ McKenzie JE Bossuyt PM Boutron I Hoffmann TC Mulrow CD et al . The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. (2021) 372:n71. doi: 10.1136/bmj.n71
17.
Higgins JP Thompson SG . Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat Med. (2002) 21:1539–58. doi: 10.1002/sim.1186
18.
Sterne JAC Savović J Page MJ Elbers RG Blencowe NS Boutron I et al . RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials. BMJ. (2019) 366:l4898. doi: 10.1136/bmj.l4898
19.
Lin L Chu H . Quantifying publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. (2018) 74:785–94. doi: 10.1111/biom.12817
20.
Huang B Li NP Tan GK Liang N . Effectiveness and safety of remimazolam combined with alfentanil in hysteroscopic examination: a prospective, randomized, single-blind trial. Medicine (Baltimore). (2024) 103:e37627. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000037627
21.
Matsumoto A Satomi S Kakuta N Narasaki S Toyota Y Miyoshi H et al . Remimazolam’s effects on postoperative nausea and vomiting are similar to those of Propofol after laparoscopic gynecological surgery: a randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med. (2023) 12:5402. doi: 10.3390/jcm12165402
22.
Tan H Lou A Wu J Chen X Qian X . Comparison of hypotension between propofol and remimazolam-propofol combinations sedation for day-surgery hysteroscopy: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol. (2024) 24:360. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02746-9
23.
Wang L Wang Y Ma L Wang Y Mu X Huang Z et al . Cardiopulmonary adverse events of Remimazolam versus Propofol during cervical Conization: a randomized controlled trial. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2023) 17:1233–43. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S405057
24.
Wang XL Dai LL Li YN Zhang JW Qu MC Zhou YY et al . Comparing Remimazolam and Propofol for postoperative anesthesia satisfaction in outpatient gynecological surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2024) 18:4615–27. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S483029
25.
Xie M Zeng F Tian Q Deng H Tao S . Clinical study on the safety and efficacy of remimazolam in hysteroscopic surgery under general anesthesia in elderly patients. Front Med. (2024) 11:1409233. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1409233
26.
Yue L Ma X Li N Chen J Wang J Wan Z et al . Remimazolam versus propofol in combination with esketamine for surgical abortion: a double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clin Transl Sci. (2023) 16:1606–16. doi: 10.1111/cts.13572
27.
Zhang F Chang H Qing W Yu R Liao Q Tong J . Remimazolam Tosylate combined with low-dose Propofol improves sedation and safety in hysteroscopy. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2022) 16:4101–8. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S390403
28.
Zhou YH Li SX Li L Deng CM Shen JJ Wang DX et al . Effect of remimazolam supplementation on propofol requirements during hysteroscopy: a double-blind, dose-response study. Anesth Analg. (2024) 139:1309–16. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000006921
29.
Zhang S Wang J Ran R Peng Y Xiao Y . Efficacy and safety of remimazolam tosylate in hysteroscopy: a randomized, single-blind, parallel controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther. (2022) 47:55–60. doi: 10.1111/jcpt.13525
30.
Yang C Jiao J Nie Y Shao W Zhang H Huang S . Comparison of the bispectral indices of patients receiving remimazolam and propofol for general anesthesia: a randomized crossover trial. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med. (2024) 43:101377. doi: 10.1016/j.accpm.2024.101377
31.
Ahmer W Imtiaz S Alam DM Ahmed K Sajid B Yousuf J et al . Remimazolam versus propofol for sedation in gastrointestinal endoscopy and colonoscopy within elderly patients: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. (2024) 80:493–503. doi: 10.1007/s00228-024-03624-6
32.
Yang JJ Lei L Qiu D Chen S Xing LK Zhao JW et al . Effect of Remimazolam on postoperative delirium in older adult patients undergoing orthopedic surgery: a prospective randomized controlled clinical trial. Drug Des Devel Ther. (2023) 17:143–53. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S392569
33.
Cai YH Zhong JW Ma HY Szmuk P Wang CY Wang Z et al . Effect of Remimazolam on emergence delirium in children undergoing laparoscopic surgery: a double-blinded randomized trial. Anesthesiology. (2024) 141:500–10. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000005077
34.
Pan Y Chen M Gu F Chen J Zhang W Huang Z et al . Comparison of remimazolam-flumazenil versus propofol for rigid bronchoscopy: a prospective randomized controlled trial. J Clin Med. (2022) 12:257. doi: 10.3390/jcm12010257
Summary
Keywords
sedation, hysteroscopy, remimazolam, propofol, gynecological surgery, anesthesia
Citation
Jin O, Shao W, Lai J and Yang X (2025) Safety and efficacy of remimazolam versus propofol sedation in gynecological procedures: a meta-analysis of East Asian randomized trials. Front. Med. 12:1701785. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1701785
Received
09 September 2025
Revised
16 October 2025
Accepted
06 November 2025
Published
26 November 2025
Volume
12 - 2025
Edited by
Mattia Dominoni, San Matteo Hospital Foundation (IRCCS), Italy
Reviewed by
Luis Laranjeira, Ordem dos Médicos, Portugal; Bin Yi, Army Medical University, China
Updates
Copyright
© 2025 Jin, Shao, Lai and Yang.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: XiaoMin Yang, yang_xiaomin@hotmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.